- DL manuals
- Magnetek
- Elevators
- DSD 412
- Technical Manual
Magnetek DSD 412 Technical Manual
DSD 412
DSD 412 DC Elevator Drive
Technical Manual
To properly use the product, read this manual thoroughly and retain for easy reference, inspection,
and maintenance. Ensure that the end user receives this manual.
CS00407 rev 11
© Magnetek Elevator 2016
U39 / U40 97SA407x-0010 Rv16
U13 / U14 97SA404x-0008 Rv08
Summary of DSD 412
Page 1
Dsd 412 dsd 412 dc elevator drive technical manual to properly use the product, read this manual thoroughly and retain for easy reference, inspection, and maintenance. Ensure that the end user receives this manual. Cs00407 rev 11 © magnetek elevator 2016 u39 / u40 97sa407x-0010 rv16 u13 / u14 97sa40...
Page 2
Warranty standard products manufactured by the company are warranted to be free from defects in workmanship and material for a period of one year from the date of shipment, and any products, which are defective in workmanship or material, will be repaired or replaced, at the company’s option, at no ...
Page 3: Table of Contents
1 table of contents introduction ............................................................................................................. 11 drive description ............................................................................................................................. 11 the sta...
Page 4
2 self tune function .......................................................................................................................... 37 power conversion diagnostics ....................................................................................................... 39 drive setup & adj...
Page 5
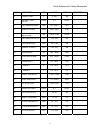
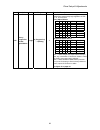
Quick reference for setup parameters 3 fnct. # description unit range default site setting 1 current limit. % 0 - 300 250 2 use self- tune values logic 0 - 1 0=off 3 rtd. Armature amps adc 2.0 - 1250.0 50.0 4 armature ohms ohms 0.001 - 5.000 0.100 6 armature inductance hny 0.0010 -1.000 0.0100 7 rtd...
Page 6
Quick reference for setup parameters 4 fnct. # description unit range default site setting 42 stiffness - 0.2 - 9.9 1.0 49 weak field current adc 0.20 - 40.00 40.00 50 full field current adc 0.20 - 40.00 1.90 51 motor field l/r sec 0.10 - 10.00 0.54 52 rtd. Field volts dc vdc 50 - 525 240 53 standby...
Page 7
Quick reference for setup parameters 5 fnct. # description unit range default site setting 92 brake auto stop on logic 0 - 1 0=off 93 analog out 0 bias - -1.00 - +1.00 0.00 94 analog out 1 bias - -1.00 - +1.00 0.00 95 analog out 0 select tb1(45) num 0 - 8 1 96 analog out 1 select tb1(46) num 0 - 8 3...
Page 8
Quick reference for setup parameters 6 fnct. # description unit range default site setting 120 speed error detect time sec 0.0 – 5.0 0.5 121 speed error threshold % 0.0 – 15.0 2.0 130 arb mode num 0 – 2 0 (off) 131 arb bandwidth rad 1.0 – 15.0 6.0 132 arb damping - 0.01 –20.00 2.00 133 arb spd thres...
Page 9
Quick reference for setup parameters 7 fnct. # description unit range default site setting 177 decel #2 % s % 0.1 – 100.0 25.0 178 accel #3 time sec 1.00 – 15.00 5.00 179 decel #3 time sec 1.00 – 15.00 5.00 180 accel #3 % s % 0.1 – 100.0 25.0 181 decel #3 % s % 0.1 – 100.0 25.0 182 invert alarm rela...
Page 10
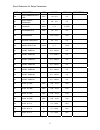
Read-out and control parameters 8 fnct. # description unit 600 car speed - 601 motor rpm rpm 602 speed ref - 603 pre-torq signl % 609 cemf volts vdc 610 motor arm v vdc 611 motor arm i adc 612 motor field i adc 613 measured r ohm 614 measured l hny 615 meas. Field l/r sec 616 measured speed error % ...
Page 11
Common fault references 9 fault # description 97 overspeed trip 98 tach/encoder loss 99 reverse tach/encoder 117/118 serial com fault 400 motor overload 401 excessive field current 402 contactor fault 403 5 min full field fault 404 open armature circuit fault 405 safety circuit fault 406 10% low lin...
Page 12
Common fault references 10 fault # description 923 rated arm. I. Setting error 924 rated field i. Setting error 925 field pcb sense fault 926 pcu watchdog 929 ifld fb cannot be reduced to zero during selftune. 930 ifld fb cannot get to rated 931 excess open circuit voltage during selftune. 932 armat...
Page 13: Introduction
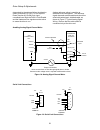
Introduction 11 introduction drive description the dsd 412 drive is a complete digital system drive that provides individual drive and system control in one compact package. It is of 12scr regenerative configuration. The drive uses two microprocessors, one for the power conversion unit (pcu) circuit...
Page 14
Introduction 12 software operating features the dsd 412 is configured by software to operate geared and gearless elevators and lifts. The sa407 drive control software contains desirable feature improvements from the previous version, sa274. Basic features include: user choice of operating speed refe...
Page 15
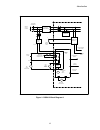
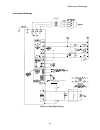
Introduction 13 figure 1: dsd 412 block diagram a isolation transformer 50/60 hz utility power customer disconnect f1 f2 f3 snubber pcb and components l1 l2 l3 lpr loop pick-up relay k1 contactor pilot relay motor & transformer thermostats e-stop sense k1 safety chain lpr me loop contactor control p...
Page 16
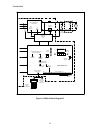
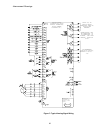
Introduction 14 scr power bridge 12 scr regen f4 current sensor ripple filter motor arm. Me scr gate signals rt1 armature interface pcb db resistor control signal wiring local cdu status leds +18888 un prot nv mem mem prot switch re- set power conversion unit microprocessor dual port memory ram & ep...
Page 17
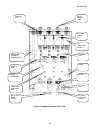
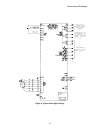
Introduction 15 figure 3: component layout front view q7, field scr scr's a2tb5 snubber pcb ac input for field supply dc output field supply armature current transducer dc armature fuse f4 ac lines fuses f1-3 input power lugs ground lug armature interface pcb bridge thermistor cube i.D. Pcb.
Page 18
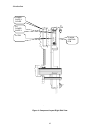
Introduction 16 figure 4: component layout right side view power supply cover a4 power supply a4 tb3 a1 main control pcb.
Page 19
Introduction 17 power conversion unit description the power conversion unit circuitry has three major functions: 1. It converts three phase ac input power to variable dc voltage for application to a motor armature. 2. It converts motor generated dc power to three-phase power to feed back to the line...
Page 20
Introduction 18 scr's the drive uses different selections of doubler packs or individual “hockey puck” scrs according to the horsepower ranges specified below: motor armature current scr type 25a - 195 a doubler 300 - 1285 a "hockey puck" field interface pcb (a3) provides the interface circuitry bet...
Page 21
Introduction 19 status leds located to the right of the reset button is a vertical strip of six light emitting diodes (leds): ready — indicates that the drive is ready to run. Run — dc loop contactor is closed and drive is controlling motor speed. I limit — drive operation is demanding current limit...
Page 22
Introduction 20 precautionary statements in addition to notes, the following types of precautionary statements appear in this manual. Important a statement of conditions that should be observed during drive setup or operation to ensure dependable service. Caution a statement of conditions that must ...
Page 23: Installation
Installation 21 installation pre-installation considerations receipt of shipment all equipment is tested against defect at the factory. Any damages or shortages evident when the equipment is received must be reported immediately to the commercial carrier who transported the equipment. Assistance, if...
Page 24
Installation 22 the magnetek recommendation for mounting the encoder used for motor speed feedback is to direct connect it to the motor shaft, usually to the end opposite the drive end. Normally a stub shaft is mounted in the end of the motor shaft. The stub shaft must be absolutely concentric (shar...
Page 25
Installation 23 step 3: compare the maximum operating speed as determined in step 2 above with the application requirements. To determine if the application exceeds the operating specification of the dsd412: calculate the maximum pulses per revolution (ppr) for this application (using the hpv 900 ...
Page 26
Installation 24 drive start up refer to the recommended connections shown in the connection diagrams. Attach a voltmeter across the 115vac source for the control power supply, at a4tb3-1 & a4tb3-7. Apply the control and three-phase power and verify that the control power is between 103 vac and 126va...
Page 27
Interconnect drawings 25 interconnect drawings 3-ph drive isolation transformer as req'd tb1(82) +24vdc tb1(78) k4 see table 5: rated motor field current range figure 6: power signal wiring.
Page 28
Interconnect drawings 26 figure 7: typical analog signal wiring j2 rj-12 connection rs232 (pcdu port) data flow alarm relay, may be energized or de-energized on alarms. See tech manual, function #182 input/output connections using analog interface, model number 53stxxxx-3x00. Drive ok/ no faults rel...
Page 29
Interconnect drawings 27 figure 8: typical serial signal wiring alarm relay, may be energized or de-energized on alarms. See tech manual, function #182 drive ok/ no faults relay energized when no faults are present. J1 db9 connection rs422 data flow programmable function outputs. Refer to f#183 - 18...
Page 30
Interconnect drawings 28 figure 9: power/signal wiring notes figure 10: run-up/run-down vs. Run w/ direction table 5: rated motor field current range notes: 1. Items not supplied by magnetek are indicated with an asterisk ( * ) or (**). 2. The dc motor connections shown is for ccw rotation facing th...
Page 31
Interconnect drawings 29 83 k6 82 +24 vdc k6x, 24vdc (lift & hold) r/c r/c 115 vac control power k3x k6x brake pick brake lift elevator brake coil r-hold brake pick brake vac supply source brake lift connections for elevator brake control rectifier as req'd brake lift relay coils 24vdc less than 100...
Page 32
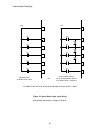
Interconnect drawings 30 figure 12: speed select logic input wiring see detailed descriptions on pages 51 and 69. 52 54 12 53 11 s4 s3 s2 s1 48 s0 +24v 52 54 12 53 11 s4 s3 s2 s1 48 s0 +24v alternate methods to achieve progressive speed select logic or progressively scanned relay logic using diodes ...
Page 33: Standard Control/display
Standard control/display operation 31 standard control/display unit operation general the standard control/display unit (scdu) is used to change and/or monitor various drive dependent operational set points and perform diagnostics for the magnetek dsd elevator drive. The scdu is located in the upper...
Page 34
Standard control/display operation 32 this ‘p-up’ display will remain on the scdu until a key is pressed or a fault occurs. After power-up after the drive has powered up and the scdu display is showing ‘p-up’ or a fault number, it can be used to enter new parameters, monitor drive operation, and/or ...
Page 35
Standard control/display operation 33 the scdu display will increment from ‘10.6’ to ‘11.0’ if the ▲ key is pressed 4 times: 4) press the enter key to transfer the value in the scdu display to the actual value used by the drive. Note that the green led will now light to indicate that this value is n...
Page 36
Standard control/display operation 34 powered down or reset. Whether or not the drive stops or continues to run is dependent on the way the particular fault is implemented. Most standard faults are set up so that the drive will stop if a fault occurs. Faults stored on the fault list will appear when...
Page 37
Standard control/display operation 35 pressing the ▼ key once more will change the display to: this is the desired status for the new disposition of the numeric underflow error, which is to not report it to either the fault or error list. 6) press the ent key when the new disposition code is in the ...
Page 38
Standard control/display operation 36 this list is held in battery-backed-up ram (nvram), so it is retained when power is lost. Each time an error condition occurs, and if its entry in the disposition list is set to allow recording in the error list, that new error is placed in the list. Function # ...
Page 39
Standard control/display operation 37 this display means that the nv ram protection switch is in the incorrect position preventing writes to the nvram. Move the switch to the "off" position, press the data/fctn key, and start over from step 2. If the save or restore operation was successful, the gre...
Page 40
Standard control/display operation 38 parameter’s 4, 6, and 51) are used if this item is set to “off”. Note: armature current is circulated through the armature circuit during parts of the pcu parameter measurement function. The pcu will reduce the field current to zero on motors with a shunt field ...
Page 41
Standard control/display operation 39 6) after completion of self-tune, enable function # 2. (unless using manual entry) power conversion diagnostics the drive has built-in diagnostic routines that can be performed via the scdu. The pcu diagnostic routines are able to test for four failure modes. Th...
Page 42
Standard control/display operation 40 press the data/fctn key to exit the pcu diagnostics routine and return to the "function" level. The scdu displays: if the pcu detects one or more open ac fuses , it displays the fault code for a blown fuse (f910): if the pcu detects one or more shorted scr/doubl...
Page 43: Drive Setup & Adjustments
Drive setup & adjustments 41 drive setup & adjustments motor field current control motor field current is held at stand-by amps function # 53 when the elevator is idle. When the drive enable command is given, field current will rise as fast as possible to the level programmed in function # 50. The d...
Page 44
Drive setup & adjustments 42 event of a severe drive fault, there will be no timed delay for current ramp-down. Electronic motor over-load an electronic motor over-load function is provided to take the place of heater type power components. Motor armature current is continuously monitored and the he...
Page 45
Drive setup & adjustments 43 speed regulator adjustment/e-reg the magnetek dsd 412 drive uses a proprietary velocity regulator called e-reg. This is a double speed loop encoder feedback regulator designed specifically for elevator / lift applications where the objective is to smoothly follow a repea...
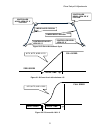
Page 46
Drive setup & adjustments 44 e-reg velocity tracking with per-unit inertia setting too low, velocity over-shoot figure 14: e-reg tracking profiles (2) e-reg velocity tracking with per-unit inertia setting too high, velocity under-shoot figure 15: e-reg tracking profiles (3) s p e e d 0 time accel ti...
Page 47
Drive setup & adjustments 45 field regulator set-up proper control of motor field current requires knowledge of the motor field resistance, the electrical time constant, and the line voltage available to control power to the motor field. Motor field resistance is calculated from the settings of rate...
Page 48
Drive setup & adjustments 46 (undershoot) – decrease the setting for per unit inertia. Repeat the above at higher set speeds until the car will accelerate up to rated top speed, or decelerate back down to zero speed, without over/under shoot. Ideally, the per unit inertia should be set with a balanc...
Page 49
Drive setup & adjustments 47 motor overload motor armature current is sensed and mathematically integrated over time to detect potential over heating caused by a dragging brake shoe or other repeated abuse beyond ratings of the equipment. The calculation formula used for the electronic motor overloa...
Page 50
Drive setup & adjustments 48 stop sequence 1. Select leveling or zero speed reference – will cause start of deceleration to new target speed. 2. When speed becomes less than the setting of #64, the low speed logic indicator will become active to indicate a door pre-opening speed. (output function ‘f...
Page 51
Drive setup & adjustments 49 figure 17: elevator start - stop timing ramp down accel decel field weakening if req'd set released elevator brake zero other elevator velocity zero other motor armature current full stand-by motor field current must remain valid during entire run zero speed speed direct...
Page 52
Drive setup & adjustments 50 stopping distance the internal s-curve velocity generator of the magnetek dsd 412 drive is digital in nature and is therefore very repeatable. The accel/decel time is fixed per the selected rate adjustment setting. The time setting represents the total acceleration time ...
Page 53
Drive setup & adjustments 51 example: (with #150=on) s2 s1 s0 pre-set # use 0 0 0 none zero speed select 0 0 1 1 leveling speed 0 1 1 3 1 floor run speed 1 1 1 7 multi-floor run speed 0 1 0 2 inspection speed (could also be speed 4, 5, or 6) note: always set all other unused pre-set speeds to zero. ...
Page 54
Drive setup & adjustments 52 determined by the status of either the direction select (function #115 =off) or run-up/run- down (function #115=on) logic input command lines. Both the drive & field enable and the hardware run signals must be active to cause the drive to run. Analog reference wiring is ...
Page 55
Drive setup & adjustments 53 serial communication specification see function #110 to enable this feature. The serial communication link between a host and the dsd 412 consists of two messages. There will be a demand velocity/pretorque command sent from the host to the dsd 412 every 15 ms. There will...
Page 56
Drive setup & adjustments 54 byte 8: this byte contains the calculated checksum of the data within this packet. It is the modulo- 256 sum of bytes 1 through byte 7 inclusive. Demand velocity response message from the dsd 412 is as follows: byte 1 byte 2 byte 3 byte 4 byte 5 byte 6 byte 7 byte 8 byte...
Page 57
Drive setup & adjustments 55 using anti-rollback (arb) elevator rollback occurs when an elevator motor drive is started and the brake is released but the hoist motor has not yet developed enough torque to prevent gravity from moving the car. The car may move up or down depending on the overall balan...
Page 58
Drive setup & adjustments 56 observed at #611 on the local display or a separate dc clamp-on ammeter, if available. D) set the brake and turn the drive off via normal commands. (in that order, to prevent the car from drifting away!) 4. Repeat #3 several times and..... A) increase the setting of #131...
Page 59
Drive setup & adjustments 57 before position settling is complete, the car will begin to accelerate toward the next landing from wherever it may be in the arb cycle. The position regulator to speed regulator change- over will be smooth, but the repeatability of velocity profile tracking during accel...
Page 60
Drive setup & adjustments 58 the dspr feature is programmable by selection of output option p on relay k4. See table 4.2.3. The time delay before power is turned off is adjusted at #88, dspr delay. This timer is held in reset whenever the drive is enabled, and timing for a delayed shutdown whenever ...
Page 61
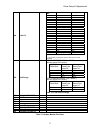
Drive setup & adjustments 59 adjustment function descriptions fnct # description units range default extended description 1 current limit % 0 - 300 250 sets the positive and negative current limit for the drive. Set as a percent of rated armature amps (function # 3). 2 use self- tune logic 0(off) – ...
Page 62
Drive setup & adjustments 60 fnct # description units range default extended description 11 motor rpm rpm 50.0 – 1999.0 1150 sets the motor speed at rated elevator contract speed. The motor rpm x encoder ppr x encoder/motor ratio is what will actually be speed regulated. May be used to compensate fo...
Page 63
Drive setup & adjustments 61 fnct # description units range default extended description 21 external acceleration limit - 2.00 –10.00 4.20 maximum acceleration rate for the elevator when an external analog or serial link speed reference is used. This function provides a slew rate limit in the event ...
Page 64
Drive setup & adjustments 62 fnct # description units range default extended description 42 stability - 0.2 – 9.9 1.0 this setting affects the proportional gain and phase margin of the regulator. Increasing this setting will make the regulator more responsive to correct mechanical load speed varianc...
Page 65
Drive setup & adjustments 63 fnct # description units range default extended description 64 low speed threshold % 0.1 – 100.0 2.0 sets the speed threshold where the at-low-speed indicator will turn on and off. This can be used to indicate when the elevator is moving below the door pre-opening speed....
Page 66
Drive setup & adjustments 64 fnct # description units range default extended description 87 pre-torque multiplier - 0.25 – 2.00 1.00 multiplies the available pre-torque reference signal for calibration adjustment. If this is set to 1.0, a +/- 10v analog signal or full-scale serial link signal will c...
Page 67
Drive setup & adjustments 65 fnct # description units range default extended description 96 analog output 1 logic 0 – 8 3 sets the specific analog output signal to be observed at tb1-46 and tp44. Selections are: 0 = calculated cemf 1 = raw speed command 2 = ramped speed command 3 = encoder feedback ...
Page 68
Drive setup & adjustments 66 fnct # description units range default extended description 104 serial gain switch logic 0(off) – 1(on) 1 (on) selects the source of the gain switch control to be from local or serial link commands. If an analog reference velocity or pre-set speed selects are used, set t...
Page 69
Drive setup & adjustments 67 fnct # description units range default extended description 112 encoder feedback enable logic 0(off) – 1(on) 1 (on) setting this value to 0, off, enables the armature voltage feedback mode to operate. This parameter must be set to 1 for normal operation of the drive. Whe...
Page 70
Drive setup & adjustments 68 fnct # description units range default extended description 120 speed error detect sec 0.0 – 5.0 0.5 sets the time sensitivity of the speed- error-is-low detector. This is a useful indicator to tell when/if the drive is following the velocity reference properly. Exceedin...
Page 71
Drive setup & adjustments 69 fnct # description units range default extended description 150 binary / progressive pre-set speed select logic 0 (progressive) – 1 (binary) 1 determines the method for selecting pre-set speeds from external relay logic applied to a1tb1- 11, 12, 52, 53 and 54 binary spee...
Page 72
Drive setup & adjustments 70 fnct # description units range default extended description 151 – 157 pre-set speeds 1 through 7 - 0.0 – 1900.0 0.0 these function values specify the elevator car speed for each individual pre-set speed setting. The units must agree with that set for rated car speed in f...
Page 73
Drive setup & adjustments 71 fnct # description units range default extended description 175 acceleration #2 %s % 0.1 – 100.0 25.0 the percent of time that will be spent in the controlled jerk or s-portion of the timed ramp curve during ramped acceleration #2. A percent s of 0.1% corresponds to almo...
Page 74
Drive setup & adjustments 72 fnct # description units range default extended description 182 invert alarm relay logic 0(off) – 1(on) 0 (off) alarms are classified as non-critical faults detected by the dsd 412 that pose no immediate need to stop operation. The alarm output relay k2 (on the drive con...
Page 75
Drive setup & adjustments 73 fnct # description units range default extended description setting desc. Extended description a excessive field current relay k3 is picked during normal operating conditions with n.O. Contact closed. Relay k3 drops and contact opens if measured motor field current ever ...
Page 76
Drive setup & adjustments 74 fnct # description units range default extended description 190 notch depth - 0 – 10 0 controls the depth of the notch filter used for a rope resonance counter-measure. When set to zero, the filter is not active. Increase the setting toward 10 as required to suppress sys...
Page 77
Drive setup & adjustments 75 figure 20: s-curve accel/decel cycle figure 21: s-curve accel with minimum %s figure 22: s-curve with 100% s linear accel region linear decel region controlled accel jerk or ‘s’ controlled decel jerk or ‘s’ controlled accel jerk or ‘s’ portion controlled decel jerk or ‘s...
Page 78
Drive setup & adjustments 76 display monitor functions fnct # description units extended description 600 car speed - measured velocity of the elevator. Units are as set in function 17. 601 motor speed rpm measured elevator motor rpm. 602 dictated speed reference - reference velocity after accel/dece...
Page 79
Drive setup & adjustments 77 688 cube i.D. - cube i.D. No. Hp 53st*** max input vac 1 002, 003 525 3 005, 007 525 6 010, 015 525 9 020, 025, 030 525 12 040, 050, 060 525 15 075, 100, 125 525 18 150 525 21 200 525 24 250 525 28 300 525 31 400 525 34 500 525 37 600 525 40 700 525 43 800 525 44 040, 05...
Page 80
Drive setup & adjustments 78 miscellaneous functions fnct. # description reference pages 22 clear errors list - 000 view fault list - 800 view error list - 801 fault/error actions see error reporting on page 33. 980 trace monitor - 981 verify i/o see input – output signal verification on page 89. 99...
Page 81: Drive Faults
Drive faults 79 drive faults the following faults are custom to the sa407 generation 2 dsd 412 software. Function error code listing *** dcu errors *** display # - description 13 = illegal instruction 14 = line 1010 emulator 15 = line 1111 emulator 16 = privelege violation 17 = divide by zero 21 = w...
Page 82
Drive faults 80 troubleshooting error/fault code probable cause/ — corrective action 400 motor overload fault --- indicates that the drive has delivered excess motor amps for a significant period of time. refer to #83 and #84 for proper set-up. check for dragging elevator brake or weakened motor...
Page 83
Drive faults 81 error/fault code probable cause/ — corrective action 408 pcu cemf fault - the cemf of the motor exceeded 118% of the rated vac input voltage to the drive. This fault causes a drive shut down to prevent fuse blowing. – causes: 3 phase input ac line voltage is low. Check and correct....
Page 84
Drive faults 82 error/fault code probable cause/ — corrective action 97 overspeed fault - the motor speed has exceeded the trip level set in function #12, as measured by the encoder. #12 is a percentage of the motor speed value set in #11. Possible cause incorrect setting of #10, #11 or #12. poo...
Page 85
Drive faults 83 error/fault code probable cause/ — corrective action 905 field loss fault this fault will shutdown the drive. The field current feedback has dropped below 80% of the expected current during the following conditions: #49 when drive is in field weakening mode (top speed). #50 when driv...
Page 86
Drive faults 84 error/fault code probable cause/ — corrective action 915 parameter setup fault (dsd power down is required.) one of the following parameters is not within the range of the chassis hardware. Rated volts #7 or #9 rated current #3 or #50 corrective action: enter correct parameter data, ...
Page 87
Drive faults 85 error/fault code probable cause/ — corrective action 926 pcu watchdog - (dsd power down is required.) this fault is declared when the pcu is reset via its own software watchdog timer. It is an indication of a pcb hardware problem more so than a dcu or pcu software problem. A likely c...
Page 88
Drive faults 86 error/fault code probable cause/ — corrective action 930 motor field current does not increase to near rated amperes within 6 seconds. Verify motor field current with an independent clamp-on dc ammeter. Probable causes: motor field not connected. not enough voltage available to a...
Page 89
Drive faults 87 error/fault code probable cause/ — corrective action 937 low read-back volts from motor armature circuit. Probable causes: missing or reversed wires to armature voltage feedback at a2tb5-1 & a2tb5-2. component problem – feedback voltage divider ratio does not match that identifie...
Page 90
Drive faults 88 other conditions probable cause / corrective action no led display with power on no power at tb3 or failed power supply. Verify 115 vac control voltage at tb3(1 & 7) verify that cable j11 is seated properly. Short circuit on external wiring dragging down the power supply. Verify by t...
Page 91
Input – output signal verification 89 input – output signal verification the control display unit (cdu) function #981 may be used to directly read and track the status of logic input and output signals at dsd 412 drive terminals. This is an easy way to verify the integrity of input and output logic ...
Page 92
Input – output signal verification 90 figure 24: i/o serial monitor function e-stop tb3(6) tb1(53) tb1(7) tb1(12) tb1(49) tb1(54) tb1(8) tb1(50) tb1(9) thrmst tb3(8) tb1(51) tb1(10) tb1(11) tb1(40,41,42) tb1(79) tb1(38-39) tb1(83) tb1(36-37) tb1(84) tb1(78) lpr tb3(5) i n p u t l o g i c d a t a b i...
Page 93: Maintenance
Maintenance 91 maintenance preventive maintenance warning hazardous voltages may exist in the drive circuits even with drive circuit breaker in off position. Never attempt preventive maintenance unless incoming three-phase and control power is disconnected and locked out. Preventive maintenance is p...
Page 94
Maintenance 92 connector type function j1 db-9 provides interface to connections for external rs422 serial link controls. J1 and j2 are mutually exclusive. J2 rj-12 phone jack plug 6-pin provides interface connection for external rs232 devices. The optional pcdu plugs into this connector. J1 and j2 ...
Page 95
Maintenance 93 figure 25: connector and e-prom locations u13 u14 j11 s3 nv ram protect switch u39 u40 u50 j12 j14 j13 j2 j1 only one present at a time.
Page 96
Maintenance 94 figure 26: test point locations tp1 +24v tp1 +24v tp1 +24v tp19-21 na tp1 +24v tp2 +15v tp3 -15v tp16 e scan tp7 low tp6 thst open tp5 sopen tp4 +5v tp15 f scan tp14 e/o tp13 lan tp8 common tp9-12 a-d scan tp23 wdog dis tp40 follow tp40 follow tp40 follow tp40 follow tp17 abcde scan t...
Page 97
Maintenance 95 test point function description tp1 +24v supply +24v supply tp2 +15v supply +15v supply tp3 -15v supply -15v supply tp4 +5v supply +5v supply tp5 emergency stop open hi = emergency stop is open tp6 thermostat open hi = thermostat is open tp7 low pwr supply warn hi = low 115vac to pwr ...
Page 98
Maintenance 96 test point function description tp35 -10v reference output -10v ref output at tb1-29 tp36 +10v reference output +10v ref output at tb1-28 tp37 armature current feedback 3v @ 1 pu (use shielded probe to avoid noise pick-up. Noise will cause erratic drive operation) see tp39. Tp38 analo...
Page 99
Maintenance 97 drive control pcb replacement 1. Release the front cover of the drive by pulling out the four corner fasteners, approximately 1/4 inch, until they snap; then remove the cover. 2. Mark each cable and wire to ensure proper reconnection; before disconnecting them. 3. Disconnect all cable...
Page 100
Maintenance 98 resistance readings are less than 100 k-ohms, suspect shorted or badly damaged scrs. Replace those faulty parts before attempting to power up again with fresh fuses. There is a small fuse inside the drive power supply, a4. This fuse may blow if 115 vac control power has surged above 1...
Page 101
Maintenance 99 repair of the 195amp assembly the layout of basic component parts of the 100-195adc dsd 412. Figure 3: component layout front view snubber circuit the snubber capacitor components are mounted on the snubber pcb. Power resistors are mounted on the heat sink. Snubber circuit repair is e...
Page 102
Maintenance 100 note: if scrs were indicated as bad, continue to disassemble for repair by... 1. Remove the armature interface pcb. 2. Remove the four power fuses. 3. Label and remove one end of the two wires that go between l1a, ac1 and l2a, ac2 on the field interface pcb. 4. On the 195adc chassis,...
Page 103
Maintenance 101 requires the aid of alignment jigs, proper tools and considerable patience for proper success. Whole drives or scr power bridge assemblies may be returned to the factory for repair. Snubber circuit snubber capacitors are mounted on a pcb attached to the underside of scr heat sinks. T...
Page 104
Maintenance 102 2. To reinstall a completely assembled scr power bridge, follow all of the above steps in reverse order...And: a. Use a thin coating of joint-al-z compound at all electrical bus bar to bus bar interfaces. B. Use the correct washers nuts and bolts as were removed for re- assembly. Sta...
Page 105
Maintenance 103 of the way for access to the upper bus bolt by the current transducer. F. Place the upper bus bar over the fuse mounting stud. G. Now tighten both bus bar bolts to 40 inch pounds. H. Replace the signal interface pcb. Plug in j31 and j15. I. Replace fuse f4. Be sure to use the same wa...
Page 106: Appendix
Appendix – drive ratings 104 appendix drive ratings for elevator applications rated input voltage rated input ac current rated output dc current model number 5 2 5 v 20 25 53st015-xxxx 41 50 53st030-xxxx 82 100 53st060-xxxx 160 195 53st125-xxxx 245 300 53st200-xxxx 359 440 53st300-xxxx 473 580 53st4...
Page 107: Appendix
Appendix – power loss 105 appendix power loss model number power loss (watts) power loss (btu/hour) 53st060-xxxx 400 1365 53st125-xxxx 645 2201 53st200-xxxx 1082 3693.
Page 108: Appendix
Appendix – wire terminal specs 106 appendix wire terminal specs power terminal wire sizes torque torque wire size* 275 in-lb 05p00204-0278 6awg – 350mcm table 23: wire specs for power terminals ground wire sizes torque wire size** 35 in lb 14 – 10 awg 40 in lb 8 awg 45 in lb 6 – 4 awg 50 in lb 3...
Page 109: Appendix
Appendix – spare parts 107 appendix spare parts description dsd 412 rating reference designator magnetek part or kit number quantity per drive fan 50a b1 la05p00016-0048 1 100a b1 la05p00016-0048 1 195a b1 la05p00016-0012 1 300a b1 la05p00016-0008 1 ac line fuse 25a f1-f3 la05p00017-0227 (50a,700v) ...
Page 110
Appendix – spare parts 108 description dsd 412 rating reference designator magnetek part or kit number quantity per drive cube id pcb 25a a2j28 46s03577-1015 1 50a a2j28 46s03577-1030 (note 2) 1 50a a2j28 46s03577-2030 (note 2) 1 100a a2j28 46s03577-1060 1 195a a2j28 46s03577-1125 1 300a a2j19 46s03...
Page 111
Appendix – spare parts 109 pcdu hand-held service / adjustment tool, use only with the 46s02975-0403 version control pcb. All easy parameter adjustments with 2-line numeric read- out with english labels, direct entry numeric keypad. 46s03281-0010 optional joint-al-z electric joint compound all 2-gra...
Page 112: Appendix
Appendix – packing instructions 110 appendix packing instructions when receiving a drive from magnetek: 1. Open carton and remove the osb panel located on top of the drive. 2. Remove foam from carton 3. Lift drive out of box, grip only sheet metal chassis. Do not lift using the door assembly or the ...
Page 113: Appendix
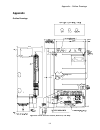
Appendix – outline drawings 111 appendix outline drawings figure 30: drive chassis outline, dsd 412, 100 amp.
Page 114
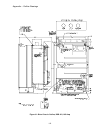
Appendix – outline drawings 112 figure 31: drive chassis outline, dsd 412, 195 amp.
Page 115
Appendix – outline drawings 113 figure 32: drive chassis outline, dsd 412, 300 amp.
Page 116
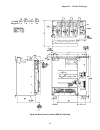
Appendix – layout drawings 114 figure 33: layout, dsd 412, 100 amp a3 a1 a2 a2 l1 neg gnd l2 l3 pos.
Page 117
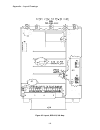
Appendix – layout drawings 115 figure 34: layout, dsd 412, 195 amp a3 a1 a2 a2.
Page 118
Appendix – layout drawings 116 figure 35: layout, dsd 412, 300 amp a3 a1 a2 a2.
Page 119: Index
117 index 3 3 second loop fault parameter .................... 65 a abnormal display conditions ........................ 24 ac input voltage requirement & adjustment ................................................................... 45 ac line frequency monitor function ............. 76 ac line vol...
Page 120
118 function error code listing ........................... 79 g gain reduce .................................................. 46 gain switch speed parameter ...................... 66 gain switch speed-setting ........................... 46 ground wire sizes ...................................... 1...
Page 121
119 scdu description ......................................... 31 scdu error display ....................................... 35 scdu error reporting ................................... 33 scdu fault display/clear ............................. 35 scdu monitor functions ..................................
Page 124: Dsd 412 Dc Elevator Drive
Dsd 412 dc elevator drive data subject to change without notice. Dsd is a trademark of magnetek, inc. Magnetek elevator products n50 w13775 overview drive menomonee falls, wisconsin 53051 (800) 236-1705, (262) 252-6999, fax (262) 790-4142 http://www.Elevatordrives.Com info@elevatordrives.Com magnete...