- DL manuals
- Magnetek
- Controller
- HPV 600
- Technical Manual
Magnetek HPV 600 Technical Manual
Summary of HPV 600
Page 1
Hpv 600 ac elevator drive technical manual.
Page 2
Warranty standard products manufactured by the company are warranted to be free from defects in workmanship and material for a period of one year from the date of shipment, and any products which are defective in workmanship or material will be repaired or replaced, at the company’s option, at no ch...
Page 3: Table of Contents
3 table of contents current ratings ............................................................................................. 4 drive specifications...................................................................................... 5 general start-up procedure....................................
Page 4: Current Ratings
Ratings 4 current ratings north american voltage class rated hp rated kw continuous output general purpose current rating continuous output elevator duty cycle current rating 150% output current for 60 sec 200% maximum output current for 5 sec cube size* model number** 10 7.5 18 a 20.8 a 27 a 36 a b...
Page 5: Drive Specifications
Specifications 5 drive specifications power ratings • 208/230 volt ac input: 7.5, 10, 15, and 20 hp (north american) • 460 volt ac input: 10, 15, 20, and 25 hp (north american) • 400 volt ac input: 4, 5.5, 7.5, 11, and 15 kw (european) • 150% of continuous current rating for 60 seconds • 200% of con...
Page 6
Specifications 6 drive derating altitude derating control ratings apply to 1000 meters (3300 feet) altitude without derating. For installations at higher altitudes, derate both the continuous and peak current levels 5% for each 300 m (1000 ft) above 1000 m (3300 ft). Derating for carrier frequency c...
Page 7: General Start-Up Procedure
General start-up 7 general start-up procedure the following is a recommended start-up procedure: 1. The hpv 600 is thoroughly tested at the factory. Verify the drive has been installed without shipping and installation damage. 2. Review the hpv 600 technical manual, shipped with the drive. 3. Verify...
Page 8
General start-up 8 separate conduits from power and motor wiring. 6. Verify that the input voltage matches the drive’s rating. 7. Verify that the motor is wired for the application voltage and amperage. 8. Tighten all of the three-phase power and ground connections. Check that all control and signal...
Page 9: Open-Loop Start-Up Procedure
Open-loop start-up 9 open-loop start-up procedure the following is a recommended open-loop start-up procedure: motor parameter set-up 1) select one of the four default motors (listed in table 1) for the motor id (a5) parameter (or select a valid motor id, if available). These typical v/f patterns ar...
Page 10
Open-loop start-up 10 verify parameters at default 5) verify the following a1 and a4 parameters are set at default. Parameter name default dc start level (a1) 50.0 dc stop level (a1) 50.0 dc stop freq (a1) 0.5 dc start time (a1) 1.00 dc stop time (a1) 1.00 slip comp time (a1) 1.50 slip comp gain (a1...
Page 11: Performance Adjustments
Open-loop start-up 11 performance adjustments stalling attempting to lift load if the motor stalls as it attempts to lift the load, then until resolved, try the following (in order): 1. Increase the torque boost gain parameter 2. Adjust the motor stator resistance parameter 3. Adjust the motor mid v...
Page 12
Open-loop start-up 12 rollback or bump at start if rollback is observed or a bump is felt at the start, then until resolved, try the following (in order): 1. Verify mechanical brake timing 2. Increase dc injection start level note: if no performance change is observed after any one step, set any cha...
Page 13
Open-loop start-up 13 decrease the s-curve parameters • decrease jerk rates via - accel jerk in x (a2), - accel jerk out x (a2) - decel jerk in x (a2) - decel jerk out x (a2) • decrease accel/decel rates via - accel x (a2), - decel x (a2) verify motor min/mid voltage parameters • motor mid volts (a5...
Page 14
Open-loop start-up 14 decrease the motor mid voltage parameter • motor mid volts (a5) and motor min volts (a5) parameters should usually be set at default, see table 1 on page 9. • these parameters would only be adjusted slightly with certain issues (see stalling attempting to lift load (page 11); s...
Page 15
Open-loop start-up 15 verify mechanical brake timing the mechanical brake should be dropped during the dc injection stop time (dc stop time (a1) parameter), see “mechanical brake timing at stop” on page 17. Decrease decel jerk out rate • decrease jerk rate via decel jerk out x (a2) parameter and obs...
Page 16
Open-loop start-up 16 overshooting floor only with regen load if the car overshoots the floor only with a regen load (i.E. Empty-up) then: • verify the car does not overshoot with balanced car and empty-down…if it does refer to overshooting floor section on page 15. • if only overshoots empty-up, in...
Page 17
Open-loop start-up 17 mechanical brake timing at start the mechanical brake should be picked during the dc injection start time (dc start time (a1) parameter). • but allow 0.5 seconds for the motor to build up flux before lifting the mechanical brake. • also, do not have the dc injection last more t...
Page 18
Closed-loop start-up 18 closed-loop start-up procedure the following is a recommended closed-loop start-up procedure: encoder set-up 1) verify the incremental encoder option card has been installed correctly. And the encoder has been selected and installed in accordance with the following: electrica...
Page 19
Closed-loop start-up 19 low speed inspection mode 5) run the drive in low speed inspection mode and… • start with default values for inertia (a1) and % no load curr (a5) parameters. • verify encoder polarity… the motor phasing should match the encoder phasing. Common failure mode: encoder fault with...
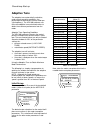
Page 20: Adaptive Tune
Closed-loop start-up 20 adaptive tune the adaptive tune automatically calculates, under certain operating conditions, the percentage no load current and the rated rpm (slip frequency). The hpv 600 software uses these two adaptive tune calculated values to obtain the maximum performance from the moto...
Page 21
Closed-loop start-up 21 tuning motor no-load current with a balanced car, run the car at 70% contract speed from top floor to the bottom floor then back to the top floor. During these runs verify under display menu - power data d2 that the motor torque is between ±15%. If the value is larger then ±1...
Page 22
Closed-loop start-up 22 enter this estimated value into the motor parameter. • continue iterating the above two steps until the two values are within 2%. If the values do not converge after two iterations, verify the information entered in the initial set-up is correct. • after the values converge, ...
Page 23
Closed-loop start-up 23 estimating system inertia the hpv 600 software can be used to calculate the inertia of the entire elevator, which is used for accurate tuning of the speed regulator. The following is a step-by-step procedure for using the hpv 600 to estimate the elevator system inertia. Using...
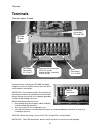
Page 24: Terminals
Terminals 24 remember when servicing the hpv 600: hazardous voltages may exist in the drive circuits even with drive circuit breaker in off position. Important: use extreme caution: do not touch any circuit board, the drive, or motor electrical connections without making sure that the unit is proper...
Page 25
Terminals 25 terminal layout b-cube remember when servicing the hpv 600: hazardous voltages may exist in the drive circuits even with drive circuit breaker in off position. Important: use extreme caution: do not touch any circuit board, the drive, or motor electrical connections without making sure ...
Page 26
Terminals 26 terminal layout c-cube remember when servicing the hpv 600: hazardous voltages may exist in the drive circuits even with drive circuit breaker in off position. Important: use extreme caution: do not touch any circuit board, the drive, or motor electrical connections without making sure ...
Page 27
Terminals 27 remember when servicing the hpv 600: hazardous voltages may exist in the drive circuits even with drive circuit breaker in off position. Important: use extreme caution: do not touch any circuit board, the drive, or motor electrical connections without making sure that the unit is proper...
Page 28
Terminals 28 remember when servicing the hpv 600: hazardous voltages may exist in the drive circuits even with drive circuit breaker in off position. Important: use extreme caution: do not touch any circuit board, the drive, or motor electrical connections without making sure that the unit is proper...
Page 29
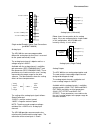
Interconnections 29 warning terminal layout for only control boards with part numbers 46s03740-xxxx note the differences in the logic output connections between boards since miswiring could result in drive functionality problems or damage 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 15 13 14 1 4 3 2 51 52 53 54 55 56...
Page 30
Interconnections 30 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 15 13 14 1 4 3 2 1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 14 1 51 52 53 54 55 56 tb2 tb1 tb1 logic input 1 logic input 2 logic input 3 logic input 4 logic input 5 logic input 6 logic input 7 logic input 8 logic input 9 logic input +24vdc or common +24vdc isolated shield an...
Page 31
Interconnections 31 details logic inputs the hpv 600’s nine programmable logic inputs are opto-isolated. The inputs become “true” by closing contacts or switches between the logic input terminal and voltage source common (or voltage source). The voltage supply for the logic inputs is 24vdc. Importan...
Page 32
Interconnections 32 below shows the connection for using the external voltage supply. Sinking logic inputs (external supply) sourcing logic inputs (external supply) the logic inputs have a current rating of 9ma. The switches or contacts used to operate the logic inputs may be replaced by logic outpu...
Page 33
Interconnections 33 logic outputs the hpv 600’s four programmable logic outputs are opto-isolated. The outputs are normally open and can withstand an applied maximum voltage of 50vdc. When the outputs become “true”, the output closes and are capable of sinking up to 150ma between the logic output te...
Page 34
Interconnections 34 close proximity to other conductors which carry current to heavy loads such as motors, motor starters, contactors, or solenoids. Doing so could result in electrical transients in the encoder cable, which can cause undesired signal pulses. Power leads are defined as the transforme...
Page 35
Interconnections 35 single-ended encoder option card connections (pn46s03710-0020) analog input the hpv 600 has one non-programmable differential analog input channel that is reserved for the speed command (if used). The analog input channel is bipolar and has a voltage range of ±10vdc. Available wi...
Page 36
Interconnections 36 the formula below shows the scaling effects of these two parameters. Voltage output channel analog bias offset creates software drive signal = × − the connection of these two inputs is shown below. Analog outputs (via option card) a1 a2 ac analog output 1 ana output common analog...
Page 37: Parameters
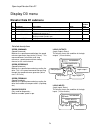
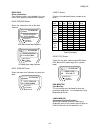
Parameters 37 parameters parameter introduction this section describes the parameter menu structure; how to navigate this menu structure via the hpv 600 digital operator; and a detailed description of each parameter. Parameters are grouped under six major menus: • adjust a0 • configure c0 • utility ...
Page 38
Parameters 38 menu navigation the digital operator keys operate on three levels, the menu level, the sub-menu level and the entry level. At the menu level, they function to navigate between menus or sub-menus. At the sub-menu level, they navigate between sub- menus or menu items. At the entry level,...
Page 39
Parameters 39 navigation at the entry level when in the entry level, the data ent led on the digital operator is lit. At the entry level, the function of keys are redefined. The “escape” key remains as the key used to move back to the higher level (in this case to the sub-menu level). The left and r...
Page 40
Parameters 40 display d0 adjust a0 → elevator data d1 • speed command • speed reference • speed feedback • encoder speed • logic outputs • logic inputs → drive a1 • contract car spd • contract mtr spd • contact flt time • cont dwell time • brake pick time • brake hold time • brake drop delay • dc st...
Page 41
Parameters 41 configure c0 utility u0 faults f0 → password u1 • enter password • new password • password lockout → hidden items u2 • hidden items enable → active faults f1 • display active faults • reset active faults → units u3 • units selection → user switches c1 • spd command src • run command sr...
Page 42
Parameters 42 display d0 adjust a0 → elevator data d1 • speed command • speed reference • speed feedback • speed error • pre-torque ref • spd reg torq cmd • tach rate cmd • aux torque cmd • est inertia • rx com status • logic inputs • logic outputs → drive a1 • contract car spd • contract mtr spd • ...
Page 43
Parameters 43 configure c0 utility u0 faults f0 → password u1 • new password • enter password • password lockout → active faults f1 • display active faults • reset active faults → hidden items u2 • hidden items enable → fault history f2 • display fault history • clear fault history → units u3 • unit...
Page 44: Drive A1 Submenu
Open-loop drive a1 44 adjust a0 menu drive a1 submenu a1 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out contract car spd elevator contract speed 200.0 1.000 fpm or m/s 0.0 0.00 3000.0 16.00 n y contract mtr spd motor speed at elevator contract speed 1130.0 rpm 50.0 3000.0 n y c...
Page 45
Open-loop drive a1 45 a1 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out dc stop level the level of dc injection current at stop as a percent of motor rated current. 50.0 % rated motor current 0.0 150.0 n y dc stop freq the frequency level where the drive initiates output of dc ...
Page 46
Open-loop drive a1 46 a1 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out up/dwn threshold threshold for detection of up or down direction 1.00 % contract speed 0.00 9.99 n y mtr torque limit motoring current limit as a percent of the drive’s rated current 200.0 % rated torque 0....
Page 47
Open-loop drive a1 47 detailed descriptions contract car spd (contract car speed) this parameter programs the elevator contract speed in feet per minute (fpm) or meters per second (m/s). Contract mtr spd (contract motor speed) this parameter programs the motor speed at elevator contract speed in rev...
Page 48
Open-loop drive a1 48 dc start time (dc injection current start time) the time dc injection current is applied following valid run command until release of the speed command. After receiving a valid run command the drive will maintain dc start level current for dc start time seconds before releasing...
Page 49
Open-loop drive a1 49 torq boost time (torque boost time constant) this parameter is the torque boost filter time constant. Adjusted for torque compensation response and stability. Increasing the value of the parameter, decreases response. Reducing the parameter to a lower value increases response. ...
Page 50
Open-loop drive a1 50 mtr torque limit (motoring current limit) this parameter sets the motoring current limit as a percentage of the drive’s rated current. This parameter helps define the stall prevention (current limit) function. Stall prevention causes the drive to deviate from the commanded spee...
Page 51: S-Curves A2 Submenu
Open-loop s-curves a2 51 adjust a0 menu s-curves a2 submenu a2 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out accel rate 0 acceleration rate limit ft/s 2 or m/s 2 n y 2.60 0.800 n y decel rate 0 deceleration rate limit ft/s 2 or m/s 2 n y 2.60 0.800 n y accel jerk in 0 rate of ...
Page 52
Open-loop s-curves a2 52 a2 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out accel jerk in 2 rate of increase of acceleration, up to accel rate, when increasing elevator speed ft/s 3 or m/s 3 n y 2.0 n y accel jerk out 2 rate of decrease of acceleration to zero when approaching c...
Page 53
Open-loop s-curves a2 53 detailed descriptions the hpv 600 speed command is passed through an internal s-curve in order to produce the speed reference. In general, the s curve function takes an arbitrary speed command and generates a speed reference subject to the conditions that the maximum accel, ...
Page 54: Multistep Ref A3 Submenu
Open-loop multistep ref a3 54 adjust a0 menu multistep ref a3 submenu a3 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out speed command 1 multi-step speed command #1 0.0 0.000 ft/min or m/sec -3000 -16.00 3000 16.00 n y speed command 2 multi-step speed command #2 0.0 0.000 ft/min...
Page 55
Open-loop multistep ref a3 55 detailed descriptions the multi-step speed reference function is one possible way for the drive to accept speed command. To use this function, the user can enter up to fifteen speed commands (cmd1 – cmd15) and assign four logic inputs as speed command selections. Note: ...
Page 56: Power Convert A4 Submenu
Open-loop multistep ref a3 56 adjust a0 menu power convert a4 submenu a4 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out id reg diff gain flux current regulator differential gain 0.50 none 0.10 2.00 y n id reg prop gain flux current regulator proportional gain 0.30 none 0.10 1.0...
Page 57
Open-loop power convert a4 57 detailed descriptions id reg diff gain (current regulator differential gain for flux generation) the differential gain for the current regulator flux generation. This parameter is meant for advanced operation, therefore, the parameter will rarely need to be changed from...
Page 58
Open-loop power convert a4 58 hunt prev gain (hunt prevent gain) determines the response to changes in torque (torque slew rate gain). Increasing the gain slows drive torque response (more dampening). Be cautious not to set the parameter too high or the drive will become unstable. Note: it is usuall...
Page 59: Motor A5 Submenu
Open-loop motor a5 59 adjust a0 menu motor a5 submenu a5 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out motor id motor identification none n y rated mtr power rated motor output power per id hp or kw 1.0 500.0 n y rated mtr volts rated motor terminal rms voltage per id volts 19...
Page 60
Open-loop motor a5 60 detailed description motor id (motor identification) this parameter allows for the selection of specific sets of motor parameters. A listing of each motor ids with its corresponding set of motor parameters is shown below. Motor id motor parameter 4 pole 400 v 4 pole 200 v 6 pol...
Page 61
Open-loop motor a5 61 motor min freq (v/hz pattern minimum frequency) this parameter sets minimum frequency used to define the v/hz pattern. Note: a setup flt #9 will occur if the below formula is not meet. Freq excit rated freq mid motor freq min motor rated motor curr (rated motor amps) this param...
Page 62
Open-loop motor a5 62 ovld start level (motor overload start level) this parameter defines maximum current at which motor can run continuously. This parameter is also one of the two parameters that define the motor overload curve. The motor overload parameters can be adjusted by the user. The follow...
Page 63
Open-loop motor a5 63 when the motor had exceeded the user defined motor overload curve, the drive will declare an motor overload alarm. The motor overload alarm can also be assigned to a logic output. Under the power data display sub-menu, the motor overload value displays the percentage of motor o...
Page 64: User Switches C1 Submenu
Open-loop user switches c1 64 configure c0 menu user switches c1 submenu c1 parameter description default choices hidden item run lock out spd command src speed command source multi-step analog input multi-step serial n y run command src run command source external tb1 external tb1 serial serial+ext...
Page 65
Open-loop user switches c1 65 c1 parameter description default choices hidden item run lock out stallp regen ena regeneration stall prevention function enable disable disable enable n y s-curve abort addresses handling of a speed command change before s- curve target speed disable disable enable n y...
Page 66
Open-loop user switches c1 66 cont confirm src (contactor confirm source) this switch selects if hardware confirmation of motor contactor closure is necessary before drive attempts to pass current through motor. If hardware confirmation is available set to external tb1 and select the contact cnfirm ...
Page 67
Open-loop user switches c1 67 stall test ena (stall test enable) when enabled, the function checks that motor current goes at or above a percentage (defined by stall test lvl(a1)) for defined amount of time (defined by stall fault time(a1)). If the motor current exceeds the defined parameters a stal...
Page 68
Open-loop user switches c1 68 torque calc sel (torque calculation select) this parameter select between one of two methods for calculating torque in the motor. The result is used to produce the proper voltage boost at low speed. This parameter is meant for advanced operation, therefore, the paramete...
Page 69: Logic Inputs C2 Submenu
Open-loop logic inputs c2 69 configure c0 menu logic inputs c2 submenu c2 parameter description default hidden item run lock out logic input 1 logic input #1 drive enable n y logic input 2 logic input #2 run n y logic input 3 logic input #3 fault reset n y logic input 4 logic input #4 up/dwn n y log...
Page 70
Open-loop logic inputs c2 70 choices contact cfirm (contact confirm signal) closure of the auxiliary contacts confirming closure of the motor contactor (normally open). Drive enable (drive enable) enables drive to run. This signal must be asserted to permit drive to run. This does not initiate run, ...
Page 71
Open-loop logic inputs c2 71 up/dwn (up/down signal) this signal is used to change the sign of the speed command. Default is false; therefore, positive commands are for the up direction and negative speed command are for the down direction. Making this input true reverses the car’s direction..
Page 72: Logic Outputs C3 Submenu
Open-loop logic outputs c3 72 configure c0 menu logic outputs c3 submenu c2 parameter description default hidden item run lock out logic output 1 logic output #1 ready to run n y logic output 2 logic output #2 run commanded n y logic output 3 logic output #3 mtr overload n y logic output 4 logic out...
Page 73
Open-loop logic outputs c3 73 detailed description logic output x (logic outputs 1-4) this parameter defines the function of the logic outputs. Note: the current setting of each parameter is displayed in all caps; all other choices in the list are displayed in lower case. Relay coil x (relay logic o...
Page 74
Open-loop logic outputs c3 74 ground fault (ground fault) the output is true when the sum of all phase current exceeds 50% of rated current of the drive. Motor trq lim (motor torque limit) the output is true when the torque limit has been reached while the drive is in the motoring mode. The motoring...
Page 75
Open-loop logic outputs c3 75 uv alarm (low voltage alarm) the output is true when the dc bus voltage drops below the user specified percent of the input line-to-line voltage. Zero speed (zero speed) the output is true when the motor speed is below the user specified speed for the user specified tim...
Page 76: Analog Outputs C4 Submenu
Open-loop logic outputs c3 76 configure c0 menu analog outputs c4 submenu c4 parameter description default hidden item run lock out analog output 1 analog output #1 n y analog output 2 analog output #2 n y choices bus voltage measured dc bus voltage current out percent motor current drv overload per...
Page 77
Open-loop logic outputs c3 77 choices bus voltage (dc bus voltage output) measured dc bus voltage. D/a units: % of peak bus current out (current output) percent motor current. D/a units: % rated current drv overload (drive overload) percent of drive overload trip level reached. D/a units: % of trip ...
Page 78: Elevator Data D1 Submenu
Open-loop elevator data d1 78 display d0 menu elevator data d1 submenu d1 parameter description units hidden item speed command speed command before speed reference generator ft/min or m/s n speed reference speed reference after speed reference generator ft/min or m/s n speed feedback speed referenc...
Page 79: Power Data D2 Submenu
Open-loop power data d2 79 display d0 menu power data d2 submenu d2 parameter description units hidden item motor current rms motor current amps n % motor current percent motor current %rated current n motor voltage rms motor terminal voltage volts n motor frequency electrical frequency output hz n ...
Page 80
Open-loop power data d2 80 flux current (flux current) displays the flux producing current of the motor. Torque current (torque current) displays the torque producing current of the motor. Flux voltage (flux voltage) displays the flux voltage reference. Torque voltage (torque voltage) displays the t...
Page 81: Drive A1 Submenu
Closed-loop drive a1 81 adjust a0 menu drive a1 submenu a1 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out contract car spd elevator contract speed 400.0 2.00 fpm or m/s 0.0 0.00 3000.0 16.00 n y contract mtr spd motor speed at elevator contract speed 1130.0 rpm 50.0 3000.0 n y ...
Page 82
Closed-loop drive a1 82 a1 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out overspeed time time before a overspeed fault is declared when above the defined overspeed level 1.00 seconds 0.00 9.99 y n overspeed mult multiplier for overspeed test 125.0 % 100.0 150.0 y n encoder puls...
Page 83
Closed-loop drive a1 83 a1 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out flt resets / hour number of faults that is allowed to be automatically reset per hour 3 faults 0 10 y n up to spd. Level threshold for up to spd logic output 80.00 % contract speed 0.00 110.00 y n mains d...
Page 84
Closed-loop drive a1 84 a1 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out notch filt depth notch filter maximum attenuation 0 % 0 100 y y mspd delay 1-4 determines the recognition time delay for a defined multi- step speed command 0.000 seconds 0.000 10.000 y y detailed descrip...
Page 85
Closed-loop drive a1 85 the high / low gain switch can be controlled externally by either: • a logic input • the serial channel. The high / low gain switch can also be controlled internal by: • the gain change level parameter (gain chng level), which defines a percentage of contract speed. With the ...
Page 86
Closed-loop drive a1 86 a method of providing the ramp down enable would be with a logic signal (external tb1) that is dedicated to that function. The ramp down enable would be asserted while the run command is still present and remain there until the ramp is completed, after which the run command w...
Page 87
Closed-loop drive a1 87 spd dev time (speed deviation time) this parameter defines the time the speed feedback needs to be in the range around the speed reference defined by spd dev lo level (a1) before the speed deviation low logic output is true. Spd dev hi level (speed deviation high level) this ...
Page 88
Closed-loop drive a1 88 parameter may need adjustment to reduce the effects of field weakening. Regen torq limit (regenerating current limit) this parameter sets the maximum amount of regenerative torque the drive will see during regeneration. This parameter may need adjustment to reduce the effects...
Page 89
Closed-loop drive a1 89 ana 2 out offset (digital to analog #2 output offset) offset for scaling analog output channel #2. Voltage output channel analog gain out ana offset out ana creates software drive signal = × − ana 1 out gain (digital to analog #1 output gain) adjusts the scaling for the analo...
Page 90
Closed-loop drive a1 90 ab off delay (auto brake off delay) this parameter determines the time after zero speed is reached (level determined by the ab zero spd lev (a1) parameter) that the auto brake logic output goes false. The units are seconds and the parameter has a maximum value of 9.99 seconds...
Page 91
Closed-loop drive a1 91 notch filter frq (notch filter center frequency) this parameter determines the notch filter center frequency. Notch filter although originally created for gearless applications where elevator rope resonance is sometimes an issue, this filter affects the torque command output ...
Page 92: S-Curves A2 Submenu
Closed-loop s-curves a2 92 adjust a0 menu s-curves a2 submenu a2 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out accel rate 0 acceleration rate limit ft/s 2 or m/s 2 n y 2.60 0.800 n y decel rate 0 deceleration rate limit ft/s 2 or m/s 2 n y 2.60 0.800 n y accel jerk in 0 rate o...
Page 93
Closed-loop s-curves a2 93 a2 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out accel jerk in 2 rate of increase of acceleration, up to accel rate, when increasing elevator speed ft/s 3 or m/s 3 n y 2.0 n y accel jerk out 2 rate of decrease of acceleration to zero when approaching...
Page 94
Closed-loop s-curves a2 94 detailed descriptions the hpv 600 speed command is passed through an internal s-curve in order to produce the speed reference. In general, the s curve function takes an arbitrary speed command and generates a speed reference subject to the conditions that the maximum accel...
Page 95: Multistep Ref A3 Submenu
Closed-loop multistep ref a3 95 adjust a0 menu multistep ref a3 submenu a3 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out speed command 1 multi-step speed command #1 0.0 0.000 ft/min or m/sec -3000 -16.00 3000 16.00 n y speed command 2 multi-step speed command #2 0.0 0.000 ft/m...
Page 96
Closed-loop multistep ref a3 96 detailed descriptions the multi-step speed reference function is one possible way for the drive to accept speed command. To use this function, the user can enter up to fifteen speed commands (cmd1 – cmd15) and assign four logic inputs as speed command selections. Note...
Page 97: Power Convert A4 Submenu
Closed-loop power convert a4 97 adjust a0 menu power convert a4 submenu a4 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out id reg diff gain flux current regulator differential gain 1.00 none 0.80 1.20 y n id reg prop gain flux current regulator proportional gain 0.30 none 0.00 0...
Page 98
Closed-loop power convert a4 98 pwm frequency (pwm frequency) this parameter sets the pwm or ‘carrier’ frequency of the drive. The carrier is defaulted at 10.0 khz, which is well out of audible range. The drive does not derate when the pwm frequency is set to 10khz or below. Uv alarm level (undervol...
Page 99: Motor A5 Submenu
Closed-loop motor a5 99 adjust a0 menu motor a5 submenu a5 parameter description default units min max hidden item run lock out motor id motor identification none n y rated mtr power rated motor output power per id hp or kw 1.0 500.0 n y rated mtr volts rated motor terminal rms voltage per id volts ...
Page 100
Closed-loop motor a5 100 detailed description motor id (motor identification) this parameter allows for the selection of specific sets of motor parameters. A listing of each motor ids with its corresponding set of motor parameters is shown below. Motor parameter motor id 4 pole dflt 6 pole dflt rate...
Page 101
Closed-loop motor a5 101 rotor leakage x (rotor leakage reactance) this parameter sets the rotor reactance leakage, as a percent of the base impedance (d2), which appears in the power data display. Note: the base impedance is based on the rated mtr pwr (a5) and rated mtr volts (a5) parameters. Stato...
Page 102
Closed-loop motor a5 102 motor overload curve ovld time out (motor overload time out) this parameter defines the amount of time before a motor overload alarm occurs when the motor is running at the current level defined below: o v l d s t a r t l e v e l r a t e d m o t o r c u r r e n t : + 4 0 % t...
Page 103: User Switches C1 Submenu
Closed-loop user switches c1 103 configure c0 menu user switches c1 submenu c1 parameter description default choices hidden item run lock out spd command src speed command source multi-step analog input multi-step serial ser mult step y y run command src run command source external tb external tb se...
Page 104
Closed-loop user switches c1 104 c1 parameter description default choices hidden item run lock out brake hold src determines the source of the brake hold command. (if drive controls mechanical brake) internal internal serial y y ramped stop sel chooses between normal stop and torque ramp down stop n...
Page 105
Closed-loop user switches c1 105 c1 parameter description default choices hidden item run lock out mlt-spd to dly1 assigns multi-step speed command to recognition delay timer 1 none y y mlt-spd to dly2 assigns multi-step speed command to recognition delay timer 2 none y y mlt-spd to dly3 assigns mul...
Page 106
Closed-loop user switches c1 106 by using the gain reduce multiplier, the user can specify a lower response (gain) for the speed regulator when the drive is at higher speeds. The gain reduce multiplier (gain reduce mult(a1)) tells the software how much lower, as a percentage, the speed regulator res...
Page 107
Closed-loop user switches c1 107 speed reg type (speed regulator type) this switch toggles between the elevator speed regulator (ereg) and the pi speed regulator. Magnetek recommends the use of the elevator speed regulator for better elevator performance. If set to external regulator, the drive will...
Page 108
Closed-loop user switches c1 108 because of this overshoot, the pi regulator is not recommended for elevator control pi speed regulator example the pi speed regulator is tuned by: • system inertia parameter (inertia(a1)), which is easy to obtain by using the drive software to estimate the system ine...
Page 109
Closed-loop user switches c1 109 the pre-torque latch clock controls when the pre-torque command is latched. The pre- torque latch clock parameter (ptorq latch clck) determines the source of this latch control. The two choices for latch control are the serial channel or a logic input (external tb1)....
Page 110
Closed-loop user switches c1 110 the ramp down enable source parameter (ramp down en src(c1)) is used to select one of the above options. A method of providing the ramp down enable would be with a logic signal (external tb1) that is dedicated to that function. The ramp down enable would be asserted ...
Page 111
Closed-loop user switches c1 111 • the s-curve abort function must be enabled (s-curve abort = enabled). Fast flux (fast flux enable) this parameter addresses the method the hpv 600 uses to build up flux in the motor. Enabling the fast flux function can decrease the motor fluxing time significantly....
Page 112
Closed-loop user switches c1 112 stopping mode (multi-step stopping mode selection) when the speed command source is set to multi-step (spd command src (c1)=multi- step), the parameter, stopping mode (c1), determines the stopping mode of the hpv 600. The two selectable methods for the stopping mode ...
Page 113
Closed-loop user switches c1 113 the first of the two following termination conditions are reached. O the hardware “drive enable” logic input is removed. O a timer set by parameter ser2 rs crp time (a1) has elapsed. Drv fast disable (drive fast disable function) this function determines how fast the...
Page 114: Logic Inputs C2 Submenu
Closed-loop logic inputs c2 114 configure c0 menu logic inputs c2 submenu c2 parameter description default hidden item run lock out logic input 1 logic input #1 drive enable y y logic input 2 logic input #2 run y y logic input 3 logic input #3 fault reset y y logic input 4 logic input #4 up/dwn y y ...
Page 115
Closed-loop logic inputs c2 115 detailed descriptions logic input x (logic inputs 1-9) this parameter defines the function of the logic inputs. Note: the user can assign particular functions to each input terminal. Only one function per terminal is allowed and multiple terminals cannot have the same...
Page 116
Closed-loop logic inputs c2 116 run up (run up) if drive is enabled through the drive enable logic input, this function will start drive operation with positive speed commands. Note: if both run up and run down are true then the run is not recognized. Note: if dir confirm (c1) is enabled, this input...
Page 117: Logic Outputs C3 Submenu
Closed-loop logic outputs c3 117 configure c0 menu logic outputs c3 submenu c2 parameter description default hidden item run lock out logic output 1 logic output #1 ready to run y y logic output 2 logic output #2 run commanded y y logic output 3 logic output #3 mtr overload y y logic output 4 logic ...
Page 118
Closed-loop logic outputs c3 118 c2 parameter description default hidden item run lock out undervolt flt dc bus voltage has dropped below a specified percent up to speed the motor speed is above a user defined level uv alarm dc bus voltage has dropped below a specified percent zero speed the motor s...
Page 119
Closed-loop logic outputs c3 119 curr reg flt (current regulator fault) the output is true when the actual current measurement does not match commanded current. Drv overload (drive overload) the output is true when the drive has exceeded the drive overload curve. Encoder flt (encoder fault) the outp...
Page 120
Closed-loop logic outputs c3 120 run confirm (run command confirm) the output is true after the software has initialized, no faults are present, the drive has been commanded to run, the contactor has closed and the igbts are firing. Speed dev (speed deviation) the output is true when the speed feedb...
Page 121: Analog Outputs C4 Submenu
Closed-loop analog outputs c4 121 configure c0 menu analog outputs c4 submenu c4 parameter description default hidden item run lock out analog output 1 analog output #1 torque ref n y analog output 2 analog output #2 speed feedbk n y choices aux torq cmd additional torque command from auxiliary sour...
Page 122
Closed-loop analog outputs c4 122 choices aux torq cmd (auxiliary torque command) additional torque command from auxiliary source, when used. D/a units: % rated torque bus voltage (dc bus voltage output) measured dc bus voltage. D/a units: % of peak in current out (current output) percent motor curr...
Page 123: Elevator Data D1 Submenu
Closed-loop elevator data d1 123 display d0 menu elevator data d1 submenu d1 parameter description units hidden item speed command speed command before speed reference generator ft/min or m/s n speed reference speed reference after speed reference generator ft/min or m/s n speed feedback encoder fee...
Page 124
Closed-loop elevator data d1 124 rx com status (serial communications status) serial communication status display. Bit severity name description/reason 0 info rx_invalid_setup_id invalid setup id on setup message 1 info rx_setup_in_run a setup message to write was received while the serial run bit w...
Page 125: Power Data D2 Submenu
Closed-loop power data d2 125 display d0 menu power data d2 submenu d2 parameter description units hidden item torque reference torque reference used by the drive control % rated torque n motor current rms motor current amps n % motor current percent motor current %rated current n motor voltage rms ...
Page 126
Closed-loop power data d2 126 flux reference (flux reference) flux reference used by the vector control of the drive. Flux output (flux output) measured value of the flux output. Slip frequency (slip frequency) displays the commanded slip frequency of the motor. Motor overload (motor overload) displ...
Page 127
Utility u0 127 utility u0 menu u0 parameter description default choices hidden item run lock out u1 password enter password allows the user to enter in a password 012345 n n new password used to change the established password n n password lockout used to enable and disable password lockout disabled...
Page 128
Utility u0 128 detailed description password (password function) the following three different screens are used by the password function: • enter password • new password • password lockout password function the password function allows the user to select a six-digit number for a password. The passwo...
Page 129
Utility u0 129 units (units selection function) when the units selection sub-menu is displayed, the user can choose either metric units or standard english measurements units for use by the drive’s parameters. Important the units selection must be made before entering any setting values into the par...
Page 130
Utility u0 130 restore dflts (restore parameter defaults) two different functions are included in this sub- menu. Restore drive defaults this function resets all parameters to there default values except the parameters in the motor a5 sub-menu. The following shows how to restore the drive defaults: ...
Page 131
Utility u0 131 drive info (drive information) four different screens are included in this sub- menu, each display an identification number. Drive version screen shows the software version of the drive software. Hpv 600 closed-loop software hpv 600 open-loop software boot version screen shows the low...
Page 132
Fault f0 132 fault f0 menu f0 parameter description hidden item run lock out f1 active faults display active faults? Contains a list of the active faults n n reset active faults? Allows for reset of active faults n n f2 fault history display fault history? Contains a list of up to the last sixteen f...
Page 133
Fault f0 133 press the enter key. The sub-menu led will turn on, and the digital operator will display: • press the enter key again to begin the fault reset procedure. The sub-menu led will go out and the data ent led will turn on. Fault history (fault history) this sub-menu contains a list of up to...
Page 134
Fault f0 134 the active faults must be cleared in order to clear the fault history. If not the following message will appear when trying to clear the fault history. The sub-menu led will go out and the data ent led will turn on. Run/fault sub menu data ent hpv operator rst faults first push any key ...
Page 135: Maintenance
Fault f0 135 maintenance maintenance overview preventive maintenance is primarily a matter of routine inspection and cleaning. The most important maintenance factors are the following: is their sufficient air flow to cool the drive? Has vibration loosened any connections? The hpv 600 needs to have s...
Page 136
Maintenance 136 parameters locked out the following three conditions would cause parameter changes to be locked out. The password protection is enabled. The drive is running and the parameter being changed is protected by run lockout. The hidden items are disabled and the parameter to be change is a...
Page 137: Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting 137 troubleshooting faults and alarms two classes of warnings are reported by the hpv 600; these are identified as faults and alarms. Faults and fault annunciation a fault a severe failure that will stop a drive if it has been running and prevent the drive from starting as long as it...
Page 138
Troubleshooting 138 below lists the hpv 600’s faults, alarms, and operator messages along with possible causes and corrective actions. Note: • fault - a severe failure that will stop a drive if it has been running and prevent the drive from starting as long as it is present. All faults require some ...
Page 139
Troubleshooting 139 name description possible causes & corrective action bridge fault the integrated power module is sensing an overcurrent or overtemperature condition (only b and c-cubes) overcurrent problem ➲ check for a possible short between the motor windings. ➲ verify dynamic brake resistor s...
Page 140
Troubleshooting 140 name description possible causes & corrective action contactor flt the command to close the contactor and the contactor feedback do not match for the time specified by the contact flt time parameter. Check parameter settings and contactor ➲ check contact flt time (a1) parameter f...
Page 141
Troubleshooting 141 name description possible causes & corrective action dcu data flt the dcu parameters checksum is invalid. Parameters corrupted ➲ check & re-enter parameters and power cycle the drive ➲ if re-occurs, replace drive control board dir conflict (alarm) declared when the speed command ...
Page 142
Troubleshooting 142 name description possible causes & corrective action encoder flt the drive is in a run condition and the encoder is: • not functioning or • not connected. Or • phasing is not proper with the motor. Encoder should match motor phasing ➲ usually drive’s “hit torque limit” alarm mess...
Page 143
Troubleshooting 143 name description possible causes & corrective action extrn fault 3 user defined external logic fault input ...Closure of this contact will cause the drive to declare the fault check parameter settings and external fault signal wiring ➲ check the correct logic input is configured ...
Page 144
Troubleshooting 144 name description possible causes & corrective action hw/sw mismatch software not compatible with hardware incorrect software ➲ hpv 900 software installed in a hpv 600 ➲ replace software with correct version motor id flt motor parameters checksum is invalid. Parameters corrupted m...
Page 145
Troubleshooting 145 name description possible causes & corrective action overcurr flt the phase current exceeded 250% of rated current. Motor problem ➲ possible motor lead short ➲ check for motor failure excessive load ➲ verify motor and drive sizing. May need a larger capacity hpv 600 accurate moto...
Page 146
Troubleshooting 146 name description possible causes & corrective action ready, waiting for drive (operator) the operator is waiting to establish communications with the drive’s control board. Normal, if displayed momentarily ➲ no action is required, if the message disappears shortly after power-up ...
Page 147
Troubleshooting 147 name description possible causes & corrective action setup fault 6 this fault is declared if the multi-step speed references have exceeded a defined limit, which is defined in terms of a percentage of contract speed (contract car spd parameter). Check parameters settings: ➲ check...
Page 148
Troubleshooting 148 name description possible causes & corrective action stall test fault generated when the motor current goes at or above a percentage (defined by stall test lvl) for defined amount of time (defined by stall fault time). Check parameter settings ➲ check stall test lvl (a1) paramete...
Page 149
Troubleshooting 149 name description possible causes & corrective action uv alarm generated during a run condition when the dc bus voltage drops below the user specified percent of the input line-to-line voltage. The input line-to- line voltage is specified by the input l- l volts parameter and the ...
Page 150: Testpoint Layout
Troubleshooting 150 testpoint layout fault led cube id pcb tp1 common tp2 tp3 tp8 tp9 tp10 tp11 tp19 tp12 dc bus voltage 1 tp13 u phase current 2 tp15 w phase current 2 tp16 v phase current 2 tp14 common tp17 common tp6 encoder channel b tp7 encoder channel a tp4 +15v power tp5 -15v power tp18 +5v p...
Page 151: Testpoints
Troubleshooting 151 testpoints checking power supplies • tp4 +15v power • tp5 -15v power • tp18 +5v power • tb1-13 +24v isolated • tb1-14 +24v isolated common • tb1-66 encoder +12v supply • tb1-67 encoder +5v supply • tb1-61 encoder common other useful testpoints • tp6 encoder channel b • tp7 encode...
Page 152: Dimensions / Weights
Dimensions / weights 152 dimensions / weights north america dimensions rated input voltage rated hp rated kw model number cube size height width depth weight 10 7.5 -4018 b 15 11 -4024 b 15in (390mm) 10in (250mm) 8in (200mm) 22 lbs (10 kg) 20 15 -4034 c 380v to 480v 25 18 -4039 c 19in (460mm) 13in (...
Page 153
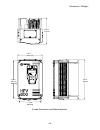
Dimensions / weights 153 7.87 in 199.9 mm 12.0 in 305 mm mounting 7.0 in 177 mm mounting 8.27 in 210 mm 12.6 in 320 mm a-cube dimensions and mounting holes.
Page 154
Dimensions / weights 154 7.95 in 202 mm 9.92 in 252 mm 9.29 in 236 mm mounting 15.20 in 386 mm 14.37 in 365 mm mounting b-cube dimensions and mounting holes.
Page 155
Dimensions / weights 155 c-cube dimensions and mounting holes 12.63 in 320.8 mm 10.91 in 275.59 mm mounting 10.91 in 277.11 mm 17.54 in 445.52 mm mounting 18.16 in 461.26 mm.
Page 156
Dynamic braking resistor selection 156 dynamic braking resistor selection north america rated input voltage rated hp rated kw model number cube size power dissipation kw (worm gear) resistor value range (worm gear) power dissipation kw (planetary gear) resistor value (planetary gear) 10 7.5 -4018 b ...
Page 157
Three-phase ac input reactor selection 157 three-phase ac input reactor selection north america rated input voltage rated hp rated kw model number cube size inductance (mh) amps 10 7.5 -4018 b 0.88 mh 25 a 15 11 -4024 b 0.63 mh 35 a 20 15 -4034 c n/a * n/a 380v to 480v 25 18 -4039 c n/a * n/a 7.5 5....
Page 158: Dc Choke Selection
Dc choke selection 158 dc choke selection north america rated input voltage rated hp rated kw model number cube size inductance (mh) amps 10 7.5 -4018 b 0.38 mh 36 a 15 11 -4024 b 0.38 mh 36 a 20 15 -4034 c n/a * n/a 380v to 480v 25 18 -4039 c n/a * n/a 7.5 5.5 -2028 a 0.38 mh 36 a 10 7.5 -2035 b 0....
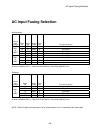
Page 159: Ac Input Fusing Selection
Ac input fusing selection 159 ac input fusing selection north america rated input voltage rated hp rated kw model number cube size fuse size (in amps) 10 7.5 -4018 b 25 to 45 a 15 11 -4024 b 35 to 45 a 20 15 -4034 c 45 to 100 a 380v to 480v 25 18 -4039 c 50 to 100 a 7.5 5.5 -2028 a 45 to 100 a 10 7....
Page 160
Dynamic braking resistor fusing selection 160 dynamic braking resistor fusing selection north america rated input voltage rated hp rated kw model number cube size fuse type (bussmann pn) fuse size (in amps) 10 7.5 -4018 b fwj-20a14f 20 a 15 11 -4024 b fwj-25a14f 25 a 20 15 -4034 c fwj-30a14f 30 a 25...
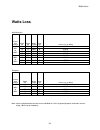
Page 161: Watts Loss
Watts loss 161 watts loss north america rated input voltage rated hp rated kw model number cube size power loss (in watts) 10 7.5 -4018 b 383 w 15 11 -4024 b 510 w 20 15 -4034 c 722 w 380v to 480v 25 18 -4039 c 826 w 7.5 5.5 -2028 a 286 w 10 7.5 -2035 b 354 w 15 11 -2047 b 477 w 200v to 240v 20 15 -...
Page 164: Hpv 600
Hpv 600 data subject to change without notice. Hpv 600 is a trademark of magnetek, inc. Magnetek elevator products n50 w13605 overview drive menomonee falls, wisconsin 53051 (800) 236-1705, (262) 252-6999, fax (262) 790-4143 http://www.Elevatordrives.Com magnetek elevator products - europe 20 drake ...