Summary of DPO
Page 1
Dpo.
Page 2
Limited warranty: make noise warrants this product to be free of defects in materials or construction for a period of one year from the date of purchase (proof of purchase/invoice required) . Malfunction resulting from wrong power supply voltages, backwards power cable connection, abuse of the produ...
Page 3
Installation: the make noise dpo is an electronic signal generator requiring 70ma of +/-12v of regulated power and properly formatted distribution receptacle to operate. It is designed to be used within the euro format modular synthesizer system. Go to http://www.Doepfer.De/a100_man/a100t_e.Htm for ...
Page 4
Overview: the dpo is a voltage controlled oscillator designed for generating complex waveforms and implementing fm synthesis within the analog domain. Expanding on the classic arrangement of primary and modulator oscillators, the dpo has both of the vcos operable as complex signal sources. It is in ...
Page 5
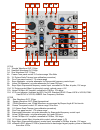
1a 2a 3a 1b 2b 3b 4b 5b 6b 7b 8b 12b 4a 5a 6a 7a 12a 8a 9a 10a 11a 9b 10b 11b vco a 1a triangle waveform out: 10vpp 2a sawtooth waveform out: 9vpp 3a sine waveform out: 10vpp 4a coarse tune panel control: 9.5 octave range 12hz-6khz 5a 1v/ octave scale trimmer (see calibration procedure) 6a fine tune...
Page 6
1 2 7 3 4 5 6 vco interaction 1. Beat frequency led: visual indication of phase difference between vcos a & b. 2. Follow cv input: unipolar control input. Range 0v to 5v. 3. Follow attenuator: determines how well vco a will follow vco b. With nothing patched to follow cv in works as standard panel c...
Page 7
1a 1b 2a 3a 2b 3b 1c 2c 3c 4c 3d 4d 5d 2d 1d vco b timbre controls and mod bus 1a. Shape panel control: unipolar control that determines the shape of the waveform feeding the folding circuit. Morphs from sine to spike to glitched triangle. 2a. Shape cv attenuator: unipolar attenuator for shape cv in...
Page 8
Complex waveforms through frequency modulation and sync: on the dpo both vcos are capable of generating complex and harmonically rich waveforms. This is accomplished through the use of fm and hard sync on vco a, and fm and timbre shaping on vco b. Fm bus the internal fm bus is hardwired for sine wav...
Page 9
Vco b core behavior there is one way to affect the behavior of the vco b core. The external lock input allows for an extremely weak, phase reversed synchronization of vco b to an external vco where as vco b approaches an inte- ger frequency of the applied external vco, vco b will reset to match the ...
Page 10
Mod bus and timbre shaping sections: mod bus the internal mod bus source is hardwired for vco a sine wave, with the power to use any external source by patching to the ext. Source input. The internal mod bus system makes use of the normaliza- tion switch found on the mini-jacks, so with nothing patc...
Page 11
The phase reversal and amplitude modulation that occurs around the 50% range of the shape parameter value is useful on it’s own (before folding occurs) for subtle and pleasing modulations via lfo. The shape circuit is slow and smooth with a unique response quite unlike the typical balanced modulator...
Page 12
The other waveform outputs in addition to the final out there are several wave shapes that are all tapped or derived from the oscillator cores. Except for the vco a saw and vco b square, these signals are all around 10v peak to peak and centered around 0v (bi-polar). The sine wave is derived from th...
Page 13
Patch ideas: animated lead: patch sequencer or keyboard cv to vco b 1v/ octave input. Monitor vco b final out. Set shape and angle panel controls and cv attenuators to noon. Set folds to 9 o' clock and set folds cv attenuator to noon. Set mod bus panel control to noon. Patch gate from sequencer or c...
Page 14
2b 3b 4b 6 1b 1a 2a 3a 4a 5 calibrating the dpo requires small flat head screw driver or trimmer tool, tuned reference signal, oscilloscope. Note: if you plan to use the dpo with another vco or synth in your system (even another dpo), it is a good idea to use that vco/ synth for your reference signa...
Page 15
2b 3b 4b 6 1b 1a 2a 3a 4a 5 7. To calibrate vco a 1v/ octave scale, use vco b (that is now tuned) as reference. 8. Monitor vco a and b sines. Patch or midi to cv to vco a 1v/ octave input (6), and follow (5) still at 0%. 9. Send note c6 to the dpo and adjust the vco a freq (2a) and fine tune (4a) pa...
Page 16
4b 6b 1a 4a 6a 2a 3a 1b 2b 3b vco sine shape and amplitude trims for sine shape (1a, 1b) and amplitude (3a, 3b) are accessed through the top side of the module. Take care in lifting the top half of the module out of case for calibration. 1.Monitor the sine (2a, 2b) from the vco to be calibrated. If ...
Page 17
4 1 2 3 5 calibrating the vco b final out trims for final out are shape balance (3) which is accessed through the top side of the module and fold gain (4) which is accessed through the right side of the module. Take care in lifting the module out of case for calibration. 1. Before this calibration m...