Summary of MMG
Page 1
Mmg.
Page 2
Limited warranty: make noise warrants this product to be free of defects in materials or construction for a period of two years from the date of manufacture. Malfunction resulting from wrong power supply voltages, backwards power cable connection, abuse of the product or any other causes determined ...
Page 3
Installation: the make noise mmg is an electronic signal generator requiring 50ma of +/-12v of regulated power and properly formatted distribution receptacle to operate. It is designed to be used within the euro format modular synthesizer system. Go to http://www.Doepfer.De/a100_man/a100t_e.Htm for ...
Page 4
Overview: the mmg is a vactrol based voltage controlled filter and low pass gate using our qmmg core. The mmg bridges the far east and west coast synthesis styles by allowing for highly resonant acidic squelch and organic, percussive animations to be programmed simultaneously with a single module. T...
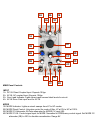
Page 5
Mmg panel controls input 1a dc in: direct coupled input. Expects 10vpp. 2a ac in: ac coupled input. Expects 10vpp. 3a over load indicator: lights when inputs exceed ideal levels for circuit. 4a ac in drive: sets input level for ac in. Mode 1b mode indicator: lights as circuit sweeps from lp to hp mo...
Page 6
Mmg panel controls (continued) frequency 1c strike input: briefly opens the filter circuit to 100%. Expects 8 to 10v gate or clock. 2c frequency panel control: uni-polar control setting the cut-off frequency of filter. 3c frequency cv in 2: unity gain control signal input for cut-off frequency. No a...
Page 7
Filter and low pass gate basics: there are many different types of filters. The most commonly used filters in synthesizers are low pass, high pass and band pass. In musical terms, a filter removes harmonic content from the signal making it sound different. A low pass filter lets frequencies below th...
Page 8
Understanding the mmg the mmg is no more complicated than other synthesizer filters, however it does have some features that are less typical. The input stage: there are two inputs which allows for mixing two signals at the input of the mmg. One input is marked ac in and the other is marked dc in. T...
Page 9
Understanding the mmg cont. The q-factor control this is where the amount of resonance is programmed in the filter. Almost all music synthesizer filters have a control for resonance or q-factor (aka q). The mmg offers voltage control over this behavior. The first half the q range generates clean res...
Page 10
Tips and tricks: -to achieve classic low pass gate sounds, use a complex audio signal source such as a frequency modulated sine wave and apply gate or clock signal to strike input. Set freq to full ccw (0%). -at lowest cut-off frequencies the high-pass filter setting will seem to pass the signal wit...
Page 11
Calibrating the mmg requires small flat head screw driver or trimmer tool, square wave reference signal, monitors. If available, an oscilloscope and dvm are useful. All trimmers are accessed from the left and right sides of the module. This will require the module to be lifted out of the system for ...
Page 12
Calibrating the mmg (continued) q (trimmer 3) 1. Apply square wave at around 220hz (a3) to ac in. Set freq to full cw. Q and mode to full ccw. Set attenuator so over load indicator is just about to light, but is not lighted. This is around 3.65vac rms. 2. Frequency panel control to around 2 or 3 o' ...