Summary of Soundhack tELHARMONIC
Page 1
V. 2. 2.
Page 2
This device complies with part 15 of the fcc rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. Changes / modifications ...
Page 3
Limited warranty: make noise warrants this product to be free of defects in materials or construction for a period of one year from the date of purchase (proof of purchase/invoice required). Malfunction resulting from wrong power supply voltages, backwards or reversed eurorack bus board cable connec...
Page 4
Electrocution hazard! Always turn the eurorack case off and unplug the power cord before plugging or un-plugging any eurorack bus board connection cable cable. Do not touch any electrical terminals when attaching any eurorack bus board cable. The make noise telharmonic is an electronic music module ...
Page 5
The telharmonic is a multi-voice, multi-algorithm synthesizer module coded by tom erbe and named for the music hall where the first telharmonium concerts were held. Telharmonic hall is considered by some to be the location of the first electronic music concerts. The telharmonium was an early, pionee...
Page 6
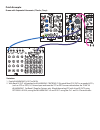
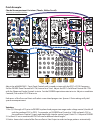
Telharmonic panel controls 1. Gate out: outputs gate signal at each change in degree. Dc-coupled, 10v gate. 2. Gate led: visual indication of activity at gate output. 3. Fm in: input for linear frequency modulation of the telharmonic core. Modulates all 3 algorithms (n, h, and p outputs). Ac-coupled...
Page 7
Telharmonic panel controls (cont’d) 7. Tonic panel control: adjusts the pitch of all voices across 6 octaves. 8. Tonic cv in: unity, 1v/ octave pitch control input. Not quantized. Range 0v to 6v. 9. Interval panel control: sets the pitch spacing of the three harmonic and phase mod voices to form tri...
Page 8
Telharmonic panel controls (cont’d) 17. Centroid panel control: centroid has a different effect on the n, h, and p outputs: -h out: modulates or selects harmonics for emphasis by flux and h-lock parameters. -p out: sets the phase modulation ratio. -n out: has no effect. 18. Centroid cv attenuator: b...
Page 9
Telharmonic panel controls (cont’d) 22. Flux combo pot: unipolar combo knob. With nothing patched to flux cv input, functions as a standard panel control. When a control signal is patched to the flux cv input, functions as an attenuator for that signal as it is applied to the flux paramater. Flux ha...
Page 10
Composing with telharmonic 101 the left side of the module allows for patch programming chord progressions, scales, and melodies. It consists of the tonic, interval, degree and d-gate parameters and the visual indication of the color staff. Although you will find great detail below about the inner w...
Page 11
Sculpting timbre with telharmonic: moving centroid w/ flux the telharmonic has 3 independent and simultaneously available algorithms, each with a unique timbre. Using two control voltages and a gate signal, full timbral animation of the telharmonic is possible. Because the noise, harmonic and phase ...
Page 12
Sculpting timbre with telharmonic: (cont’d) fm in : another method of exerting external influence upon the telharmonic, allowing for even more complex timbres by generating sidebands around all the harmonics created by each algorithm. Typically an analog sine or triangle waveform from a vco such as ...
Page 13
Color staff : toward the center of the telharmonic there is a visual indicator that will change color to indicate the states of interval and degree while pulsing to indicate the frequency of the tonic (often this frequency is high enough that the eye will not be able to discern). Warning: color staf...
Page 14
Composing with telharmonic: voltage-controlled music theory recall from the previous section that the left side of the module allows for patch programming chord progressions, scales, and melodies. It consists of the tonic, interval, degree, and d-gate parameters and the visual indication of the colo...
Page 15
Composing with telharmonic: degree (cont’d) here is what a partial sweep of degree looks like with interval set to root position and tonic set to d. Note that the resulting triads' sonorities always match their scale positions in the key of d major/b minor: when interval is not set to triad, degree ...
Page 16
Composing with telharmonic: (cont’d) chord progressions: with interval set to triad, degree is the easiest parameter to sequence for traditional diatonic chord progressions in which the sonority of the chord changes according to its scale position. Because of this, the telharmonic is quite a bit mor...
Page 17
Variation: 1. Patch telharmonic n out to fm in. 2. With rené cv out still patched to telharmonic centroid cv in, patch rené qcv out to an analog vco’s, (such as sto or dpo) 1v/ octave input and tune the sto or dpo to one octave below the tonic of telharmonic. Set rené q page for octaves only. Blend ...
Page 18
-set tonic and degree to taste. -set rené to cartesian mode on x-fun page, and engage “clock and mod. Press the pressure points touchplate to "write in" the four harmonics of the selected rené row. Each new press will clear the locked harmonics and write the new ones. Variation: 1. Use a slow clock ...
Page 19
Variations: 1. Patch a sequencer to telharmonic degree in 2. Set centroid panel control full cw and centroid cv attenuvertor full ccw patch example: interstellar drone (thanks, tony): if patched correctly, you should hear an ascending run. Setting the degree attenuvertor to 10 o'clock and degree pan...
Page 20
Variation: -instead of using the pressure points tuned voltage output, use a keyboard or sequencer’s cv output to control degree. Patch the keyboard/sequencer gate out to maths (or function) trigger input. Patch example: intelligent bass (thanks, tony): set interval to unison (~3:00, turquoise color...
Page 21
Variation: 1. Run qcv through a vca prior to degree to place chord progression range under voltage control (should still mult the unaltered qcv to dpo). For example, set degree panel control to 12:00, and patch qcv to the moddemix channel 1 input, modulated with a bipolar control signal. Patch ch.1 ...