- DL manuals
- National Instruments
- Media Converter
- NI 6220
- User Manual
National Instruments NI 6220 User Manual - Usb-6229 Screw Terminal
Appendix A
Device-Specific Information
© National Instruments Corporation
A-51
USB-6229 Screw Terminal
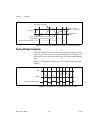
USB-6229 Screw Terminal Pinout
Figure A-18 shows the pinout of the USB-6229 Screw Terminal.
For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the
section of Chapter 3,
.
Summary of NI 6220
Page 1
Daq m series m series user manual ni 622x, ni 625x, and ni 628x devices m series user manual june 2007 371022h-01.
Page 2
Support worldwide technical support and product information ni.Com national instruments corporate headquarters 11500 north mopac expressway austin, texas 78759-3504 usa tel: 512 683 0100 worldwide offices australia 1800 300 800, austria 43 662 457990-0, belgium 32 (0) 2 757 0020, brazil 55 11 3262 3...
Page 3: Important Information
Important information warranty m series devices are warranted against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one year from the date of shipment, as evidenced by receipts or other documentation. National instruments will, at its option, repair or replace equipment that proves to be defe...
Page 4: Compliance
Compliance compliance with fcc/canada radio frequency interference regulations determining fcc class the federal communications commission (fcc) has rules to protect wireless communications from interference. The fcc places digital electronics into two classes. These classes are known as class a (fo...
Page 5: Contents
© national instruments corporation v m series user manual contents about this manual conventions ...................................................................................................................Xv related documentation...................................................................
Page 6: Chapter 4
Contents m series user manual vi ni.Com disk drive power connector......................................................................................... 3-8 when to use the disk drive power connector .............................................. 3-8 disk drive power connector installation .........
Page 7
Contents © national instruments corporation vii m series user manual connecting ground-referenced signal sources ...........................................................4-21 what are ground-referenced signal sources? ..............................................4-21 when to use differential conn...
Page 8: Chapter 5
Contents m series user manual viii ni.Com chapter 5 analog output ao offset and ao reference selection........................................................................ 5-2 minimizing glitches on the output signal.................................................................... 5-4 analog o...
Page 9: Chapter 7
Contents © national instruments corporation ix m series user manual i/o protection.................................................................................................................6-7 programmable power-up states ...........................................................................
Page 10
Contents m series user manual x ni.Com pulse train generation.................................................................................... 7-21 continuous pulse train generation.................................................. 7-21 frequency generation ..........................................
Page 11: Chapter 8
Contents © national instruments corporation xi m series user manual synchronization modes ...................................................................................7-38 80 mhz source mode .......................................................................7-39 other internal source mode....
Page 12: Chapter 11
Contents m series user manual xii ni.Com data transfer methods .................................................................................................. 10-4 changing data transfer methods ................................................................... 10-5 chapter 11 triggering trigger...
Page 13: Appendix D
Contents © national instruments corporation xiii m series user manual appendix d upgrading from e series to m series appendix e technical support and professional services glossary index device pinouts figure a-1. Pci/pxi-6220 pinout .....................................................................
Page 14: About This Manual
© national instruments corporation xv m series user manual about this manual the m series user manual contains information about using the national instruments m series data acquisition (daq) devices with ni-daq 8.6 and later. M series devices feature up to 80 analog input (ai) channels, and up to f...
Page 15: Related Documentation
About this manual m series user manual xvi ni.Com programs, subprograms, subroutines, device names, functions, operations, variables, filenames, and extensions. Platform text in this font denotes a specific platform and indicates that the text following it applies only to that platform. Related docu...
Page 16
About this manual © national instruments corporation xvii m series user manual the ni-daqmx for linux configuration guide provides configuration instructions, templates, and instructions for using test panels. Note all ni-daqmx documentation for linux is installed at /usr/local/natinst/nidaqmx/docs ...
Page 17: Labview
About this manual m series user manual xviii ni.Com labview if you are a new user, use the getting started with labview manual to familiarize yourself with the labview graphical programming environment and the basic labview features you use to build data acquisition and instrument control applicatio...
Page 18: Measurement Studio
About this manual © national instruments corporation xix m series user manual measurement studio if you program your ni-daqmx-supported device in measurement studio using visual c++, visual c#, or visual basic .Net, you can interactively create channels and tasks by launching the daq assistant from ...
Page 19
About this manual m series user manual xx ni.Com .Net languages without ni application software with the microsoft .Net framework version 1.1 or later, you can use ni-daqmx to create applications using visual c# and visual basic .Net without measurement studio. You need microsoft visual studio .Net ...
Page 20: Training Courses
About this manual © national instruments corporation xxi m series user manual training courses if you need more help getting started developing an application with ni products, ni offers training courses. To enroll in a course or obtain a detailed course outline, refer to ni.Com/training . Technical...
Page 21: Getting Started
© national instruments corporation 1-1 m series user manual 1 getting started m series devices feature up to 80 analog input (ai) channels, up to four analog output (ao) channels, up to 48 lines of digital input/output (dio), and two counters. If you have not already installed your device, refer to ...
Page 22: Device Specifications
Chapter 1 getting started m series user manual 1-2 ni.Com device specifications refer to the specifications for your device, the ni 622x specifications, the ni 625x specifications, or the ni 628x specifications, available on the ni-daq device document browser or ni.Com/manuals , for more detailed in...
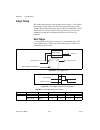
Page 23: Usb Cable Strain Relief
Chapter 1 getting started © national instruments corporation 1-3 m series user manual usb cable strain relief (usb-622x/625x screw terminal and usb-622x/625x mass termination devices) use the supplied strain relief hardware to provide strain relief for your usb cable. Adhere the cable tie mount to t...
Page 24
Chapter 1 getting started m series user manual 1-4 ni.Com (usb-622x/625x bnc devices) thread a zip tie through two of the strain relief holes on the end cap to provide strain relief for your usb cable as shown in figure 1-3. The strain relief holes can also be used as cable management for signal wir...
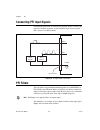
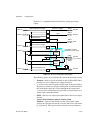
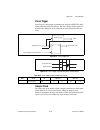
Page 25: Daq System Overview
© national instruments corporation 2-1 m series user manual 2 daq system overview figure 2-1 shows a typical daq system, which includes sensors, transducers, signal conditioning devices, cables that connect the various devices to the accessories, the m series device, programming software, and pc. Th...
Page 26: Daq-Stc2 and Daq-6202
Chapter 2 daq system overview m series user manual 2-2 ni.Com figure 2-2. General m series block diagram daq-stc2 and daq-6202 the daq-stc2 and daq-6202 implement a high-performance digital engine for m series data acquisition hardware. Some key features of this engine include the following: • flexi...
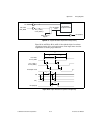
Page 27: Calibration Circuitry
Chapter 2 daq system overview © national instruments corporation 2-3 m series user manual calibration circuitry the m series analog inputs and outputs have calibration circuitry to correct gain and offset errors. You can calibrate the device to minimize ai and ao errors caused by time and temperatur...
Page 28: Signal Conditioning Options
Chapter 2 daq system overview m series user manual 2-4 ni.Com it. The manipulation of signals to prepare them for digitizing is called signal conditioning. For more information about sensors, refer to the following documents. • for general information about sensors, visit ni.Com/sensors . • if you a...
Page 29: Scc
Chapter 2 daq system overview © national instruments corporation 2-5 m series user manual scc scc is a front-end signal conditioning system for m series plug-in data acquisition devices. An scc system consists of a shielded carrier that holds up to 20 single- or dual-channel scc modules for conditio...
Page 30: Cables and Accessories
Chapter 2 daq system overview m series user manual 2-6 ni.Com note for more information about scxi, scc, and 5b series products, refer to ni.Com/signalconditioning . Cables and accessories ni offers a variety of products to use with m series devices, including cables, connector blocks, and other acc...
Page 31
Chapter 2 daq system overview © national instruments corporation 2-7 m series user manual board mating connectors, by going to ni.Com/info and entering the info code rdspmb . Programming devices in software national instruments measurement devices are packaged with ni-daq driver software, an extensi...
Page 32
© national instruments corporation 3-1 m series user manual 3 connector and led information the i/o connector signal descriptions , m series and e series pinout comparison , +5 v power source , disk drive power connector , and rtsi connector pinout sections contain information about m series connect...
Page 33
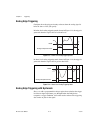
Chapter 3 connector and led information m series user manual 3-2 ni.Com i/o connector signal descriptions table 3-1 describes the signals found on the i/o connectors. Not all signals are available on all devices. Table 3-1. I/o connector signals signal name reference direction description ai gnd — —...
Page 34
Chapter 3 connector and led information © national instruments corporation 3-3 m series user manual ao ao gnd output analog output channels 0 to 3—these terminals supply the voltage output of ao channels 0 to 3. Ao gnd — — analog output ground—ao gnd is the reference for ao . All three ground refere...
Page 35
Chapter 3 connector and led information m series user manual 3-4 ni.Com chs gnd * — — chassis ground * —this terminal connects to the usb-62xx bnc device metal enclosure. You can connect your cable’s shield wire to chs gnd for a ground connection. Nc — — no connect—do not connect signals to these te...
Page 36
Chapter 3 connector and led information © national instruments corporation 3-5 m series user manual m series and e series pinout comparison the pinout of connector 0 of 68-pin m series devices is similar to the pinout of 68-pin e series devices. On m series devices, some terminals have enhanced func...
Page 37
Chapter 3 connector and led information m series user manual 3-6 ni.Com refer to appendix d, upgrading from e series to m series , for more information about the differences between these two device families. 11 pfi 0/ai start trig (trig1) pfi 0/p1.0 on e series devices, as an input, this terminal c...
Page 38: +5 V Power Source
Chapter 3 connector and led information © national instruments corporation 3-7 m series user manual +5 v power source the +5 v terminals on the i/o connector supply +5 v referenced to d gnd. Use these terminals to power external circuitry. A self-resetting fuse protects the supply from overcurrent c...
Page 39: Disk Drive Power Connector
Chapter 3 connector and led information m series user manual 3-8 ni.Com disk drive power connector (ni pcie-625x devices only) the disk drive power connector is a four-pin hard drive connector on pci express devices that, when connected, increases the current the device can supply on the +5 v termin...
Page 40: Usb Device Fuse Replacement
Chapter 3 connector and led information © national instruments corporation 3-9 m series user manual figure 3-1. Connecting to the disk drive power connector 4. Replace the computer cover, and plug in and power on the computer. 5. Self-calibrate the pci express daq device in max by following the inst...
Page 41
Chapter 3 connector and led information m series user manual 3-10 ni.Com 3. Replace the fuse while referring to figure 3-2 for the fuse location. Figure 3-2. Usb-62xx screw terminal fuse location 4. Replace the lid and screws. Fuse.
Page 42
Chapter 3 connector and led information © national instruments corporation 3-11 m series user manual (usb-62xx bnc devices) to remove the fuse from the usb-62xx bnc, complete the following steps. 1. Power down and unplug the device. Note take proper esd precautions when handling the device. Figure 3...
Page 43: Rtsi Connector Pinout
Chapter 3 connector and led information m series user manual 3-12 ni.Com (usb-62xx mass termination devices) to remove the fuse from the usb-62xx mass termination, complete the following steps. 1. Power down and unplug the device. 2. Loosen the four phillips screws that attach the lid to the enclosu...
Page 44: Led Patterns
Chapter 3 connector and led information © national instruments corporation 3-13 m series user manual led patterns (usb-62xx devices only) all variants of m series usb devices have leds labeled active and ready. The active led indicates activity over the bus. The ready led indicates whether or not th...
Page 45: Analog Input
© national instruments corporation 4-1 m series user manual 4 analog input figure 4-1 shows the analog input circuitry of m series devices. Figure 4-1. M series analog input circuitry the main blocks featured in the m series analog input circuitry are as follows: • i/o connector—you can connect anal...
Page 46: Analog Input Range
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-2 ni.Com ni-pgia can amplify or attenuate an ai signal to ensure that you use the maximum resolution of the adc. M series devices use the ni-pgia to deliver high accuracy even when sampling multiple channels with small input ranges at fast rates. M serie...
Page 47
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-3 m series user manual for more information about setting ranges, refer to the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Tables 4-1, 4-2, and 4-3 show the input ranges and resolutions supported by each m series device famil...
Page 48: Analog Input Lowpass Filter
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-4 ni.Com analog input lowpass filter a lowpass filter attenuates signals with frequencies above the cutoff frequency while passing, with minimal attenuation, signals below the cutoff frequency. The cutoff frequency is defined as the frequency at which th...
Page 49
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-5 m series user manual analog input ground-reference settings m series devices support the analog input ground-reference settings shown in table 4-4. The ai ground-reference setting determines how you should connect your ai signals to the m...
Page 50
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-6 ni.Com figure 4-2. Ni-pgia table 4-5 shows how signals are routed to the ni-pgia. Notice that some m series devices do not support the ai signals. For differential measurements, ai 0 and ai 8 are the positive and negative inputs of differential analog ...
Page 51
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-7 m series user manual ai ground-reference setting is sometimes referred to as ai terminal configuration. Configuring ai ground-reference settings in software you can program channels on an m series device to acquire with different ground r...
Page 52: Use Low Impedance Sources
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-8 ni.Com adc. The specifications document for your daq device lists its settling time. M series devices are designed to have fast settling times. However, several factors can increase the settling time which decreases the accuracy of your measurements. T...
Page 53
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-9 m series user manual carefully choose the channel scanning order avoid switching from a large to a small input range switching from a channel with a large input range to a channel with a small input range can greatly increase the settling...
Page 54: Example 1
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-10 ni.Com minimize voltage step between adjacent channels when scanning between channels that have the same input range, the settling time increases with the voltage step between the channels. If you know the expected input range of your signals, you can...
Page 55: Software-Timed Acquisitions
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-11 m series user manual switches between channels much less often and is affected much less by settling time. Analog input data acquisition methods when performing analog input measurements, you either can perform software-timed or hardware...
Page 56: Non-Buffered
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-12 ni.Com finite sample mode acquisition refers to the acquisition of a specific, predetermined number of data samples. Once the specified number of samples has been read in, the acquisition stops. If you use a reference trigger, you must use finite samp...
Page 57
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-13 m series user manual connecting analog input signals table 4-6 summarizes the recommended input configuration for both types of signal sources..
Page 58
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-14 ni.Com table 4-6. Analog input configuration ai ground-reference setting * floating signal sources (not connected to building ground) ground-referenced signal sources † examples: • ungrounded thermocouples • signal conditioning with isolated outputs •...
Page 59: Floating Signal Sources
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-15 m series user manual connecting floating signal sources what are floating signal sources? A floating signal source is not connected to the building ground system, but has an isolated ground-reference point. Some examples of floating sign...
Page 60: Signal Sources
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-16 ni.Com result of differences in the signal path. Magnetic coupling is proportional to the area between the two signal conductors. Electrical coupling is a function of how much the electric field differs between the two conductors. With this type of co...
Page 61
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-17 m series user manual out of the maximum working voltage range of the ni-pgia and the daq device returns erroneous data. The easiest way to reference the source to ai gnd is to connect the positive side of the signal to ai+ and connect th...
Page 62
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-18 ni.Com you can fully balance the signal path by connecting another resistor of the same value between the positive input and ai gnd, as shown in figure 4-6. This fully balanced configuration offers slightly better noise rejection, but has the disadvan...
Page 63: Signal Sources
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-19 m series user manual 1 m Ω). In this case, connect the negative input directly to ai gnd. If the source has high output impedance, balance the signal path as previously described using the same value resistor on both the positive and neg...
Page 64: Sources
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-20 ni.Com rejection of nrse mode is better than rse mode because the ai sense connection is made remotely near the source. However, the noise rejection of nrse mode is worse than diff mode because the ai sense connection is shared with all channels rathe...
Page 65: Sources
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-21 m series user manual connecting ground-referenced signal sources what are ground-referenced signal sources? A ground-referenced signal source is a signal source connected to the building system ground. It is already connected to a common...
Page 66
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-22 ni.Com when to use non-referenced single-ended (nrse) connections with ground-referenced signal sources only use non-referenced single-ended input connections if the input signal meets the following conditions. • the input signal is high-level (greate...
Page 67
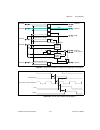
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-23 m series user manual using differential connections for ground-referenced signal sources figure 4-10 shows how to connect a ground-referenced signal source to the m series device configured in diff mode. Figure 4-10. Differential connect...
Page 68
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-24 ni.Com using non-referenced single-ended (nrse) connections for ground-referenced signal sources figure 4-11 shows how to connect ground-reference signal sources in nrse mode. Figure 4-11. Single-ended connections for ground-referenced signal sources ...
Page 69: Field Wiring Considerations
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-25 m series user manual using the daq assistant, you can configure the channels for rse or nrse input modes. Refer to the configuring ai ground-reference settings in software section for more information about the daq assistant. Field wirin...
Page 70
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-26 ni.Com figure 4-12. Analog input timing options m series devices use ai/sampleclock and ai/convertclock to perform interval sampling. As figure 4-13 shows, ai/sampleclock controls the sample period, which is determined by the following equation: 1/sam...
Page 71
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-27 m series user manual typically, this rate is the sampling rate for the task multiplied by the number of channels in the task. Note the sampling rate is the fastest you can acquire data on the device and still achieve accurate results. Fo...
Page 72: Ai Sample Clock Signal
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-28 ni.Com figure 4-15. Pretriggered data acquisition example if an ai/referencetrigger pulse occurs before the specified number of pretrigger samples are acquired, the trigger pulse is ignored. Otherwise, when the ai/referencetrigger pulse occurs, the sa...
Page 73: Using An Internal Source
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-29 m series user manual using an internal source one of the following internal signals can drive ai/sampleclock. • counter n internal output • ai sample clock timebase (divided down) • a pulse initiated by host software a programmable inter...
Page 74
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-30 ni.Com a counter on your device internally generates ai/sampleclock unless you select some external source. Ai/starttrigger starts this counter and either software or hardware can stop it once a finite acquisition completes. When using an internally g...
Page 75: Ai Convert Clock Signal
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-31 m series user manual ai/sampleclocktimebase is not available as an output on the i/o connector. Ai/sampleclocktimebase is divided down to provide one of the possible sources for ai/sampleclock. You can configure the polarity selection fo...
Page 76: Using An Internal Source
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-32 ni.Com using an internal source one of the following internal signals can drive ai/convertclock: • ai convert clock timebase (divided down) • counter n internal output a programmable internal counter divides down the ai convert clock timebase to gener...
Page 77: Other Timing Requirements
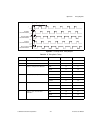
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-33 m series user manual figure 4-17 shows the relationship of ai/sampleclock to ai/convertclock. Figure 4-17. Ai/sampleclock and ai/convertclock other timing requirements the sample and conversion level timing of m series devices work such ...
Page 78
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-34 ni.Com figure 4-18. Ai/sampleclock too fast figure 4-19. Ai/convertclock too fast figure 4-20. Ai/sampleclock and ai/convertclock improperly matched • sample clock too fast for convert clock ai/sampleclock ai/convertclock sample #1 sample #2 sample #3...
Page 79
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-35 m series user manual figure 4-21. Ai/sampleclock and ai/convertclock properly matched it is also possible to use a single external signal to drive both ai/sampleclock and ai/convertclock at the same time. In this mode, each tick of the e...
Page 80: Ai Start Trigger Signal
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-36 ni.Com ai hold complete event signal the ai hold complete event (ai/holdcompleteevent) signal generates a pulse after each a/d conversion begins. You can route ai/holdcompleteevent out to any pfi or rtsi terminal. The polarity of ai/holdcompleteevent ...
Page 81: Using An Analog Source
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-37 m series user manual using an analog source when you use an analog trigger source, the acquisition begins on the first rising edge of the analog comparison event signal. Routing ai start trigger to an output terminal you can route ai/sta...
Page 82: Using A Digital Source
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-38 ni.Com when the reference trigger occurs, the daq device continues to write samples to the buffer until the buffer contains the number of posttrigger samples desired. Figure 4-23 shows the final buffer. Figure 4-23. Reference trigger final buffer usin...
Page 83: Ai Pause Trigger Signal
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-39 m series user manual ai pause trigger signal you can use the ai pause trigger (ai/pausetrigger) signal to pause and resume a measurement acquisition. The internal sample clock pauses while the external trigger signal is active and resume...
Page 84
Chapter 4 analog input m series user manual 4-40 ni.Com getting started with ai applications in software you can use the m series device in the following analog input applications. • single-point analog input • finite analog input • continuous analog input you can perform these applications through ...
Page 85: Analog Output
© national instruments corporation 5-1 m series user manual 5 analog output many m series devices have analog output functionality. M series devices that support analog output have either two or four ao channels that are controlled by a single clock and are capable of waveform generation. Refer to a...
Page 86
Chapter 5 analog output m series user manual 5-2 ni.Com • ao sample clock—the ao sample clock signal reads a sample from the dac fifo and generates the ao voltage. • ao offset and ao reference selection—ao offset and ao reference selection signals allow you to change the range of the analog outputs....
Page 87
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-3 m series user manual (ni 628x devices) on ni 628x devices, the ao offset of each analog output can be individually set to one of the following: • 0 v (ao gnd) • 5 v • apfi • ao you can connect an external signal to apfi to provide the ao...
Page 88: Software-Timed Generations
Chapter 5 analog output m series user manual 5-4 ni.Com minimizing glitches on the output signal when you use a dac to generate a waveform, you may observe glitches on the output signal. These glitches are normal; when a dac switches from one voltage to another, it produces glitches due to released ...
Page 89: Non-Buffered
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-5 m series user manual non-buffered in non-buffered acquisitions, data is written directly to the dacs on the device. Typically, hardware-timed, non-buffered operations are used to write single samples with good latency and known time incr...
Page 90: Analog Output Triggering
Chapter 5 analog output m series user manual 5-6 ni.Com with non-regeneration, old data will not be repeated. New data must be continually written to the buffer. If the program does not write new data to the buffer at a fast enough rate to keep up with the generation, the buffer will underflow and c...
Page 91: Analog Output Timing Signals
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-7 m series user manual analog output timing signals figure 5-3 summarizes all of the timing options provided by the analog output timing engine. Figure 5-3. Analog output timing options m series devices feature the following ao (waveform g...
Page 92: Using An Analog Source
Chapter 5 analog output m series user manual 5-8 ni.Com • ai/referencetrigger • ai/starttrigger • pxi_star the source also can be one of several internal signals on your daq device. Refer to device routing in max in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later for more information. ...
Page 93: Using A Digital Source
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-9 m series user manual figure 5-4. Ao/pausetrigger with the onboard clock source if you are using any signal other than the onboard clock as the source of your sample clock, the generation resumes as soon as the pause trigger is deasserted...
Page 94: Using An Analog Source
Chapter 5 analog output m series user manual 5-10 ni.Com using an analog source when you use an analog trigger source, the samples are paused when the analog comparison event signal is at a high level. Refer to the triggering with an analog source section of chapter 11, triggering , for more informa...
Page 95: Other Timing Requirements
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-11 m series user manual other timing requirements a counter on your device internally generates ao/sampleclock unless you select some external source. Ao/starttrigger starts the counter and either the software or hardware can stop it once ...
Page 96
Chapter 5 analog output m series user manual 5-12 ni.Com you might use ao/sampleclocktimebase if you want to use an external sample clock signal, but need to divide the signal down. If you want to use an external sample clock signal, but do not need to divide the signal, then you should use ao/sampl...
Page 97: Digital I/o
© national instruments corporation 6-1 m series user manual 6 digital i/o m series devices contain up to 32 lines of bidirectional dio signals on port 0. In addition, m series devices have up to 16 pfi signals that can function as static dio signals. M series devices support the following dio featur...
Page 98: Static Dio
Chapter 6 digital i/o m series user manual 6-2 ni.Com figure 6-1. M series digital i/o circuitry the dio terminals are named p0. On the m series device i/o connector. The voltage input and output levels and the current drive levels of the dio lines are listed in the specifications of your device. St...
Page 99: Digital Waveform Triggering
Chapter 6 digital i/o © national instruments corporation 6-3 m series user manual digital waveform triggering m series devices do not have an independent di or do start trigger for digital waveform acquisition or generation. To trigger a di or do operation, first select a signal to be the source of ...
Page 100: Di Sample Clock Signal
Chapter 6 digital i/o m series user manual 6-4 ni.Com you can configure each dio line to be an output, a static input, or a digital waveform acquisition input. Di sample clock signal use the di sample clock (di/sampleclock) signal to sample the p0. Terminals and store the result in the di waveform a...
Page 101: Digital Waveform Generation
Chapter 6 digital i/o © national instruments corporation 6-5 m series user manual • pxi_star • analog comparison event (an analog trigger) you can sample data on the rising or falling edge of di/sampleclock. Routing di sample clock to an output terminal you can route di/sampleclock out to any pfi te...
Page 102: Using An Internal Source
Chapter 6 digital i/o m series user manual 6-6 ni.Com using an internal source to use do/sampleclock with an internal source, specify the signal source and the polarity of the signal. The source can be any of the following signals: • ai sample clock • ai convert clock • ao sample clock • counter n i...
Page 103: I/o Protection
Chapter 6 digital i/o © national instruments corporation 6-7 m series user manual i/o protection each dio and pfi signal is protected against overvoltage, undervoltage, and overcurrent conditions as well as esd events. However, you should avoid these fault conditions by following these guidelines. •...
Page 104: Di Change Detection
Chapter 6 digital i/o m series user manual 6-8 ni.Com di change detection you can configure the daq device to detect changes in the dio signals. Figure 6-3 shows a block diagram of the dio change detection circuitry. Figure 6-3. Di change detection note di change detection is supported by ni-daqmx 8...
Page 105: Applications
Chapter 6 digital i/o © national instruments corporation 6-9 m series user manual the change detection event signal can do the following: • drive any rtsi , pfi , or pxi_star signal • drive the do sample clock or di sample clock • generate an interrupt the change detection event signal also can be u...
Page 106
Chapter 6 digital i/o m series user manual 6-10 ni.Com figure 6-4. Digital i/o connections caution exceeding the maximum input voltage ratings, which are listed in the specifications document for each m series device, can damage the daq device and the computer. Ni is not liable for any damage result...
Page 107: Counters
© national instruments corporation 7-1 m series user manual 7 counters m series devices have two general-purpose 32-bit counter/timers and one frequency generator, as shown in figure 7-1. The general-purpose counter/timers can be used for many measurement and pulse generation applications. Figure 7-...
Page 108: Counter Input Applications
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-2 ni.Com the counters have seven input signals, although in most applications only a few inputs are used. For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the default counter/timer pinouts section. Counter input applications counting edges in edge ...
Page 109
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-3 m series user manual figure 7-3. Single point (on-demand) edge counting with pause trigger buffered (sample clock) edge counting with buffered edge counting (edge counting using a sample clock), the counter counts the number of edges on the s...
Page 110: Pulse-Width Measurement
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-4 ni.Com controlling the direction of counting in edge counting applications, the counter can count up or down. You can configure the counter to do the following: • always count up • always count down • count up when the counter n b input is high; count down...
Page 111
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-5 m series user manual figure 7-5 shows an example of a single pulse-width measurement. Figure 7-5. Single pulse-width measurement buffered pulse-width measurement buffered pulse-width measurement is similar to single pulse-width measurement, b...
Page 112: Period Measurement
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-6 ni.Com condition is not met, consider using duplicate count prevention, described in the duplicate count prevention section. For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the default counter/timer pinouts section. Period measurement in period ...
Page 113: Buffered Period Measurement
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-7 m series user manual buffered period measurement buffered period measurement is similar to single period measurement, but buffered period measurement measures multiple periods. The counter counts the number of rising (or falling) edges on the...
Page 114: Semi-Period Measurement
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-8 ni.Com semi-period measurement in semi-period measurements, the counter measures a semi-period on its gate input signal after the counter is armed. A semi-period is the time between any two consecutive edges on the gate input. You can route an internal or ...
Page 115: Frequency Measurement
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-9 m series user manual note that if you are using an external signal as the source, at least one source pulse should occur between each active edge of the gate signal. This condition ensures that correct values are returned by the counter. If t...
Page 116: One Counter (Averaged)
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-10 ni.Com method 1b—measure low frequency with one counter (averaged) in this method, you measure several periods of your signal using a known timebase. This method is good for low to medium frequency signals. You can route the signal to measure (f1) to the ...
Page 117: Two Counters
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-11 m series user manual method 2—measure high frequency with two counters in this method, you measure one pulse of a known width using your signal and derive the frequency of your signal from the result. This method is good for high frequency s...
Page 118: Using Two Counters
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-12 ni.Com method 3—measure large range of frequencies using two counters by using two counters, you can accurately measure a signal that might be high or low frequency. This technique is called reciprocal frequency measurement. In this method, you generate a...
Page 119
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-13 m series user manual from counter 0, the length of the pulse is n/f1. From counter 1, the length of the same pulse is j/f2. Therefore, the frequency of f1 is given by f1 = f2 * (n/j). Choosing a method for measuring frequency the best method...
Page 120: Position Measurement
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-14 ni.Com for your application. Another disadvantage of method 2 is that it requires two counters (if you cannot provide an external signal of known width). An advantage of method 2 is that the measurement completes in a known amount of time. • method 3 meas...
Page 121: X1 Encoding
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-15 m series user manual x1 encoding when channel a leads channel b in a quadrature cycle, the counter increments. When channel b leads channel a in a quadrature cycle, the counter decrements. The amount of increments and decrements per cycle de...
Page 122: Channel Z Behavior
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-16 ni.Com figure 7-16. X4 encoding channel z behavior some quadrature encoders have a third channel, channel z, which is also referred to as the index channel. A high level on channel z causes the counter to be reloaded with a specified value in a specified ...
Page 123
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-17 m series user manual measurements using two pulse encoders the counter supports two pulse encoders that have two channels—channels a and b. The counter increments on each rising edge of channel a. The counter decrements on each rising edge o...
Page 124
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-18 ni.Com single two-signal edge-separation measurement with single two-signal edge-separation measurement, the counter counts the number of rising (or falling) edges on the source input occurring between an active edge of the gate signal and an active edge ...
Page 125: Counter Output Applications
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-19 m series user manual figure 7-20 shows an example of a buffered two-signal edge-separation measurement. Figure 7-20. Buffered two-signal edge-separation measurement for information about connecting counter signals, refer to the default count...
Page 126
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-20 ni.Com figure 7-21 shows a generation of a pulse with a pulse delay of four and a pulse width of three (using the rising edge of source). Figure 7-21. Single pulse generation single pulse generation with start trigger the counter can output a single pulse...
Page 127: Pulse Train Generation
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-21 m series user manual retriggerable single pulse generation the counter can output a single pulse in response to each pulse on a hardware start trigger signal. The pulses appear on the counter n internal output signal of the counter. You can ...
Page 128: Frequency Generation
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-22 ni.Com input. You also can specify the active edge of the source input (rising or falling). The counter can begin the pulse train generation as soon as the counter is armed, or in response to a hardware start trigger. You can route the start trigger to th...
Page 129
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-23 m series user manual figure 7-25 shows a block diagram of the frequency generator. Figure 7-25. Frequency generator block diagram the frequency generator generates the frequency output signal. The frequency output signal is the frequency out...
Page 130: Frequency Division
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-24 ni.Com frequency division the counters can generate a signal with a frequency that is a fraction of an input signal. This function is equivalent to continuous pulse train generation. For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the default c...
Page 131: Counter Timing Signals
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-25 m series user manual figure 7-27. Pulse generation for ets for information about connecting counter signals, refer to the default counter/timer pinouts section. Counter timing signals m series devices feature the following counter timing sig...
Page 132: Counter N Source Signal
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-26 ni.Com counter n source signal the selected edge of the counter n source signal increments and decrements the counter value depending on the application the counter is performing. Table 7-3 lists how this terminal is used in various applications. Routing ...
Page 133: Counter N Gate Signal
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-27 m series user manual routing counter n source to an output terminal you can route counter n source out to any pfi or rtsi terminal. All pfis are set to high-impedance at startup. Counter n gate signal the counter n gate signal can perform ma...
Page 134: Counter N Aux Signal
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-28 ni.Com counter n aux signal the counter n aux signal indicates the first edge in a two-signal edge-separation measurement. Routing a signal to counter n aux each counter has independent input selectors for the counter n aux signal. Any of the following si...
Page 135: Counter N Up_Down Signal
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-29 m series user manual counter n up_down signal counter n up_down is another name for the counter n b signal. Counter n hw arm signal the counter n hw arm signal enables a counter to begin an input or output function. To begin any counter inpu...
Page 136: Terminal
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-30 ni.Com with pulse or pulse train generation tasks, the counter drives the pulse(s) on the counter n internal output signal. The counter n internal output signal can be internally routed to be a counter/timer input or an “external” source for ai, ao, di, o...
Page 137: Counter Triggering
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-31 m series user manual you can use these defaults or select other sources and destinations for the counter/timer signals in ni-daqmx. Refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later for more...
Page 138: Start Trigger
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-32 ni.Com trigger to have start trigger-like behavior. The arm start trigger can be used for synchronizing multiple counter input and output tasks. When using an arm start trigger, the arm start trigger source is routed to the counter n hw arm signal. Start ...
Page 139: Other Counter Features
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-33 m series user manual other counter features cascading counters you can internally route the counter n internal output and counter n tc signals of each counter to the gate inputs of the other counter. By cascading two counters together, you c...
Page 140: Prescaling
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-34 ni.Com the filter setting for each input can be configured independently. On power up, the filters are disabled. Figure 7-28 shows an example of a low to high transition on an input that has its filter set to 125 ns (n = 5). Figure 7-28. Filter example en...
Page 141: Duplicate Count Prevention
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-35 m series user manual prescaling is intended to be used for frequency measurement where the measurement is made on a continuous, repetitive signal. The prescaling counter cannot be read; therefore, you cannot determine how many edges have occ...
Page 142: (Duplicate Counting)
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-36 ni.Com the counter synchronizes or samples the gate signal with the source signal, so the counter does not detect a rising edge in the gate until the next source pulse. In this example, the counter stores the values in the buffer on the first rising sourc...
Page 143
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-37 m series user manual figure 7-32. Duplicate count prevention example even if the source pulses are long, the counter increments only once for each source pulse. Normally, the counter value and counter n internal output signals change synchro...
Page 144: Synchronization Modes
Chapter 7 counters m series user manual 7-38 ni.Com enabling duplicate count prevention in ni-daqmx you can enable duplicate count prevention in ni-daqmx by setting the enable duplicate count prevention attribute/property. For specific information about finding the enable duplicate count prevention ...
Page 145: 80 Mhz Source Mode
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-39 m series user manual 80 mhz source mode in 80 mhz source mode, the device synchronizes signals on the rising edge of the source, and counts on the following rising edge of the source, as shown in figure 7-33. Figure 7-33. 80 mhz source mode ...
Page 146: Pfi
© national instruments corporation 8-1 m series user manual 8 pfi m series devices have up to 16 programmable function interface (pfi) signals. In addition, m series devices have up to 32 lines of bidirectional dio signals. Each pfi can be individually configured as the following. • a static digital...
Page 147
Chapter 8 pfi m series user manual 8-2 ni.Com when a terminal is used as a timing input or output signal, it is called pfi x (where x is an integer from 0 to 15). When a terminal is used as a static digital input or output, it is called p1.X or p2.X. On the i/o connector, each terminal is labeled pf...
Page 148
Chapter 8 pfi © national instruments corporation 8-3 m series user manual exporting timing output signals using pfi terminals you can route any of the following timing signals to any pfi terminal configured as an output. • ai convert clock* • ai hold complete event • ai reference trigger • ai sample...
Page 149: Connecting Pfi Input Signals
Chapter 8 pfi m series user manual 8-4 ni.Com connecting pfi input signals all pfi input connections are referenced to d gnd. Figure 8-2 shows this reference, and how to connect an external pfi 0 source and an external pfi 2 source to two pfi terminals. Figure 8-2. Pfi input signals connections pfi ...
Page 150
Chapter 8 pfi © national instruments corporation 8-5 m series user manual assume that an input terminal has been low for a long time. The input terminal then changes from low to high, but glitches several times. When the filter clock has sampled the signal high on n consecutive edges, the low to hig...
Page 151: I/o Protection
Chapter 8 pfi m series user manual 8-6 ni.Com i/o protection each dio and pfi signal is protected against overvoltage, undervoltage, and overcurrent conditions as well as esd events. However, you should avoid these fault conditions by following these guidelines. • if you configure a pfi or dio line ...
Page 152: Digital Routing and Clock
© national instruments corporation 9-1 m series user manual 9 digital routing and clock generation the digital routing circuitry has the following main functions. • manages the flow of data between the bus interface and the acquisition/generation sub-systems (analog input, analog output, digital i/o...
Page 153: 80 Mhz Timebase
Chapter 9 digital routing and clock generation m series user manual 9-2 ni.Com 80 mhz timebase the 80 mhz timebase can be used as the source input to the 32-bit general-purpose counter/timers. The 80 mhz timebase is generated from the following sources. • onboard oscillator • external signal (by usi...
Page 154: 10 Mhz Reference Clock
Chapter 9 digital routing and clock generation © national instruments corporation 9-3 m series user manual 10 mhz reference clock the 10 mhz reference clock can be used to synchronize other devices to your m series device. The 10 mhz reference clock can be routed to the rtsi terminals. Other devices...
Page 155: Rtsi Connector Pinout
Chapter 9 digital routing and clock generation m series user manual 9-4 ni.Com real-time system integration (rtsi) real-time system integration (rtsi) is a set of bused signals among devices that allows you to do the following: • use a common clock (or timebase) to drive the timing engine on multipl...
Page 156
Chapter 9 digital routing and clock generation © national instruments corporation 9-5 m series user manual figure 9-2. M series rtsi pinout table 9-1. Rtsi signals rtsi bus signal terminal rtsi 7 34 rtsi 6 32 rtsi 5 30 rtsi 4 28 rtsi 3 26 rtsi 2 24 rtsi 1 22 rtsi 0 20 not connected. Do not connect s...
Page 157: Using Rtsi As Outputs
Chapter 9 digital routing and clock generation m series user manual 9-6 ni.Com using rtsi as outputs rtsi are bidirectional terminals. As an output, you can drive any of the following signals to any rtsi terminal: • ai/starttrigger • ai/referencetrigger • ai/convertclock* • ai/sampleclock • ai/pause...
Page 158: Rtsi Filters
Chapter 9 digital routing and clock generation © national instruments corporation 9-7 m series user manual • counter input signals for either counter—source, gate, aux, hw_arm, a, b, or z • di sample clock • do sample clock most functions allow you to configure the polarity of pfi inputs and whether...
Page 159: Pxi_Clk10
Chapter 9 digital routing and clock generation m series user manual 9-8 ni.Com figure 9-3. Filter example enabling filters introduces jitter on the input signal. For the 125 ns and 6.425 µs filter settings, the jitter is up to 25 ns. On the 2.56 ms setting, the jitter is up to 10.025 µs. When a pfi ...
Page 160: Pxi_Star Trigger
Chapter 9 digital routing and clock generation © national instruments corporation 9-9 m series user manual note that in a pxi chassis with more than eight slots, the pxi trigger lines may be divided into multiple independent buses. Refer to the documentation for your chassis for details. Pxi_star tr...
Page 161
Chapter 9 digital routing and clock generation m series user manual 9-10 ni.Com the filter setting for each input can be configured independently. On power up, the filters are disabled. Figure 9-4 shows an example of a low to high transition on an input that has its filter set to 125 ns (n = 5). Fig...
Page 162: Bus Interface
© national instruments corporation 10-1 m series user manual 10 bus interface the bus interface circuitry of m series devices efficiently moves data between host memory and the measurement and acquisition circuits. M series devices are available for the following platforms: • pci • pci express • pxi...
Page 163: Pxi Considerations
Chapter 10 bus interface m series user manual 10-2 ni.Com transferred simultaneously between the ports. The dma controller supports burst transfers to and from the fifo. Each dma controller supports several features to optimize pci/pxi bus utilization. The dma controllers pack and unpack data throug...
Page 164: Using Pxi With Compactpci
Chapter 10 bus interface © national instruments corporation 10-3 m series user manual hybrid slot-compatible defines where the device can be installed. Pxi m series devices can be installed in the following chassis and slots: • pxi chassis—pxi m series devices can be installed in any peripheral slot...
Page 165: Data Transfer Methods
Chapter 10 bus interface m series user manual 10-4 ni.Com compatible as long as those terminals on the sub-bus are disabled by default and never enabled. Caution damage can result if these lines are driven by the sub-bus. Ni is not liable for any damage resulting from improper signal connections. Da...
Page 166
Chapter 10 bus interface © national instruments corporation 10-5 m series user manual operations. Refer to the software-timed generations section of chapter 5, analog output , for more information. Changing data transfer methods (ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie devices) on pci, pci express, pxi, and pxi expres...
Page 167: Triggering
© national instruments corporation 11-1 m series user manual 11 triggering a trigger is a signal that causes an action, such as starting or stopping the acquisition of data. When you configure a trigger, you must decide how you want to produce the trigger and the action you want the trigger to cause...
Page 168: Apfi Terminals
Chapter 11 triggering m series user manual 11-2 ni.Com you also can program your daq device to perform an action in response to a trigger from a digital source. The action can affect the following: • analog input acquisition • analog output generation • counter behavior • digital waveform acquisitio...
Page 169: Analog Input Channels
Chapter 11 triggering © national instruments corporation 11-3 m series user manual analog input channels select any analog input channel to drive the ni-pgia. The ni-pgia amplifies the signal as determined by the input ground-reference setting and the input range. The output of the ni-pgia then driv...
Page 170: Analog Edge Triggering
Chapter 11 triggering m series user manual 11-4 ni.Com analog edge triggering configure the analog trigger circuitry to detect when the analog signal is below or above a level you specify. In below-level analog triggering mode, shown in figure 11-3, the trigger is generated when the signal value is ...
Page 171
Chapter 11 triggering © national instruments corporation 11-5 m series user manual analog edge trigger with hysteresis (rising slope) when using hysteresis with a rising slope, you specify a trigger level and amount of hysteresis. The high threshold is the trigger level; the low threshold is the tri...
Page 172: Analog Window Triggering
Chapter 11 triggering m series user manual 11-6 ni.Com figure 11-6. Analog edge triggering with hysteresis falling slope example analog window triggering an analog window trigger occurs when an analog signal either passes into (enters) or passes out of (leaves) a window defined by two voltage levels...
Page 173: Analog Trigger Accuracy
Chapter 11 triggering © national instruments corporation 11-7 m series user manual analog trigger accuracy the analog trigger circuitry compares the voltage of the trigger source to the output of programmable trigger dacs. When you configure the level (or the high and low limits in window trigger mo...
Page 174: Device-Specific Information
© national instruments corporation a-1 m series user manual a device-specific information this appendix contains device pinouts, specifications, cable and accessory choices, and other information for the following m series devices. • ni 6220 • ni 6221 • ni 6224 • ni 6225 • ni 6229 • ni 6250 • ni 625...
Page 175: Ni 6220
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-2 ni.Com ni 6220 pci/pxi-6220 pinout figure a-1 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6220. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, connector and led information . Note m s...
Page 176
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-3 m series user manual figure a-1. Pci/pxi-6220 pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5...
Page 177: Pci/pxi-6220 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-4 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6220 specifications refer to the ni 622x specification...
Page 178: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-5 m series user manual scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter an...
Page 179: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-6 ni.Com screw terminal accessories national instruments offers several styles of screw terminal connector blocks. Use an shc68-68-epm shielded cable to connect an m series device to a connector block, such as the following: • cb-68lp and...
Page 180: Ni 6221
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-7 m series user manual ni 6221 the following sections contain information about the pci/pxi-6221 (68-pin), pci-6221 (37-pin), usb-6221 screw terminal, and usb-6221 bnc devices. Pci/pxi-6221 (68-pin) pci/pxi-6221 (68-pin) pin...
Page 181
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-8 ni.Com figure a-2. Pci/pxi-6221 (68-pin) pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5 p0.0 d gnd ao gnd ...
Page 182: Options
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-9 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6221 (68-pin) specificatio...
Page 183: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-10 ni.Com scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter and an shc68-68-epm cable. Yo...
Page 184: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-11 m series user manual screw terminal accessories national instruments offers several styles of screw terminal connector blocks. Use an shc68-68-epm shielded cable to connect an m series device to a connector block, such as...
Page 185: Pci-6221 (37-Pin)
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-12 ni.Com pci-6221 (37-pin) pci-6221 (37-pin) pinout figure a-3 shows the pinout of the pci-6221 (37-pin) device. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, connector an...
Page 186
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-13 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci-6221 (37-pin) specifications ...
Page 187: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-14 ni.Com screw terminal accessories national instruments offers several styles of screw terminal connector blocks. Use an sh37f-37m cable to connect a pci-6221 (37-pin) device to a connector block, such as the following: • cb-37fh—din-mo...
Page 188: Usb-6221 Screw Terminal
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-15 m series user manual usb-6221 screw terminal usb-6221 screw terminal pinout figure a-4 shows the pinout of the usb-6221 screw terminal. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descript...
Page 189
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-16 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6221 screw terminal specifications refer to the ni 622x s...
Page 190: Usb-6221 Bnc
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-17 m series user manual usb-6221 bnc usb-6221 bnc pinout figure a-5 shows the pinout of the usb-6221 bnc. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, connec...
Page 191
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-18 ni.Com figure a-5. Usb-6221 bnc top panel and pinout.
Page 192: Analog Input
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-19 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Connecting signals to the usb-622...
Page 193
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-20 ni.Com to measure a floating signal source, move the switch to the fs position. To measure a ground-referenced signal source, move the switch to the gs position. Figure a-6 shows the ai 0 bnc and corresponding fs/gs switch on the top p...
Page 194: Analog Output
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-21 m series user manual figure a-8. Single-ended channels when you set the source type to the gs position and software-configure the device for single-ended input, each bnc connector provides access to two single-ended chann...
Page 195: Digital I/o and Timing I/o
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-22 ni.Com digital i/o and timing i/o you can access digital i/o and timing i/o signals on the bnc connectors labeled pfi /p1...7>. Figure a-10 shows the dio/tio circuitry on the usb-6221 bnc. Figure a-10. Digital i/o and timing i/o circui...
Page 196: Usb-6221 Bnc Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-23 m series user manual figure a-12 shows an example of how to use the user 1 and user 2 bncs. To access the pfi 8 signal from a bnc, connect user 1 on the screw terminal block to pfi 8 with a wire. Figure a-12. Connecting p...
Page 197: Ni 6224
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-24 ni.Com ni 6224 pci/pxi-6224 pinout figure a-13 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6224. The i/o signals appear on two 68-pin connectors. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of ...
Page 198
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-25 m series user manual figure a-13. Pci/pxi-6224 pinout d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5 p0.0 d gnd nc nc ai ...
Page 199: Pci/pxi-6224 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-26 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6224 specifications refer to the ni 622x specificatio...
Page 200: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-27 m series user manual scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter a...
Page 201: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-28 ni.Com • bnc-2120—similar to the bnc-2110, and also has a built-in function generator, quadrature encoder, temperature reference, and thermocouple connector • bnc-2090a—desktop/rack-mountable device with 22 bncs for connecting analog, ...
Page 202: Cables
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-29 m series user manual cables in most applications, you can use the following cables: • shc68-68-epm 1 —high-performance cable designed specifically for m series devices. It has individual bundles separating analog and digi...
Page 203: Ni 6225
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-30 ni.Com ni 6225 the following sections contain information about the pci/pxi-6225, usb-6225 screw terminal, and usb-6225 mass termination devices. Pci/pxi-6225 pci/pxi-6225 pinout figure a-14 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6225. For a ...
Page 204
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-31 m series user manual figure a-14. Pci/pxi-6225 pinout d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5 p0.0 d gnd ao gnd ao...
Page 205: Pci/pxi-6225 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-32 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6225 specifications refer to the ni 622x specificatio...
Page 206: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-33 m series user manual scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter a...
Page 207: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-34 ni.Com you can use the shc68-68-epm shielded cable, to connect connector 0 of your daq device to bnc accessories. Using a bnc accessory with connector 1 connector 1 of your device is compatible with bnc-2115. Bnc-2115 provides bnc conn...
Page 208: Cables
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-35 m series user manual cables the pci/pxi-6225 has two connectors that require different cables. Choosing a cable for connector 0 in most applications, you can use the following cables with connector 0: • shc68-68-epm 1 —hi...
Page 209: Usb-6225 Screw Terminal
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-36 ni.Com usb-6225 screw terminal usb-6225 screw terminal pinout figure a-15 shows the pinout of the usb-6225 screw terminal. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, ...
Page 210
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-37 m series user manual figure a-15. Usb-6225 screw terminal pinout 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 ai 8 ai 9 ai 10 ai 11 ai 12 ai gnd ai 13 ai 14 ai 15 ai 24 ai 25 ai 26 ai gnd nc ao gnd ao 1 ai 0 ai 1 ai 2 ...
Page 211
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-38 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6225 screw terminal specifications refer to the ni 622x s...
Page 212: Usb-6225 Mass Termination
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-39 m series user manual usb-6225 mass termination usb-6225 mass termination pinout figure a-16 shows the pinout of the usb-6225 mass termination device. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector s...
Page 213
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-40 ni.Com figure a-16. Usb-6225 mass termination pinout ai 71 ai 78 ai 69 ai 68 ai 75 ai 66 ai 65 ai 72 ai gnd ai 55 ai 54 ai 61 ai 52 ai 51 ai 58 ai 49 ai 48 ai 47 ai 38 ai 37 ai 44 ai gnd ai 35 ai 34 ai 41 ai 32 ai 23 ai 30 ai 21 ai 20 ...
Page 214: Options
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-41 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6225 mass termination specifi...
Page 215: Scc Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-42 ni.Com scc accessories scc provides portable, modular signal conditioning to your daq system. To connect your m series device to an scc module carrier, such as the sc-2345, sc-2350, or scc-68, use an sh68-68-ep shielded cable. Use conn...
Page 216: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-43 m series user manual screw terminal accessories national instruments offers several styles of screw terminal connector blocks. Use an sh68-68-ep shielded cable to connect an m series device to a connector block, such as t...
Page 217
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-44 ni.Com custom cabling and connectivity the ca-1000 is a configurable enclosure that gives user-defined connectivity and flexibility through customized panelettes. Visit ni.Com for more information about the ca-1000. Refer to the custom...
Page 218: Ni 6229
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-45 m series user manual ni 6229 the following sections contain information about the pci/pxi-6229, usb-6229 screw terminal, and usb-6229 bnc devices. Pci/pxi-6229 pci/pxi-6229 pinout figure a-17 shows the pinout of the pci/p...
Page 219
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-46 ni.Com figure a-17. Pci/pxi-6229 pinout d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5 p0.0 d gnd ao gnd ao gnd ai gnd ai 7 ai 14 ai gn...
Page 220: Pci/pxi-6229 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-47 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6229 specifications refer...
Page 221: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-48 ni.Com scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter and an shc68-68-epm cable. Us...
Page 222: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-49 m series user manual • bnc-2090a—desktop/rack-mountable device with 22 bncs for connecting analog, digital, and timing signals you can use one bnc accessory with the signals on either connector of your m series device. Yo...
Page 223: Cables
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-50 ni.Com cables in most applications, you can use the following cables: • shc68-68-epm 1 —high-performance cable designed specifically for m series devices. It has individual bundles separating analog and digital signals. Each differenti...
Page 224: Usb-6229 Screw Terminal
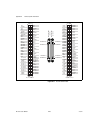
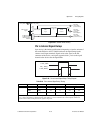
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-51 m series user manual usb-6229 screw terminal usb-6229 screw terminal pinout figure a-18 shows the pinout of the usb-6229 screw terminal. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descrip...
Page 225
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-52 ni.Com figure a-18. Usb-6229 screw terminal pinout 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 ai 4 ai 12 ai gnd ai 5 ai 13 ai gnd ai 6 ai 14 ai gnd ai 7 ai 15 ai gnd nc ai gnd ao 1 ao gnd ai 0 ai 8 ai gnd ai 1 ai 9 ai gnd ai 2 ai ...
Page 226
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-53 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6229 screw terminal specifica...
Page 227: Usb-6229 Bnc
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-54 ni.Com usb-6229 bnc usb-6229 bnc pinout figure a-19 shows the pinout of the usb-6229 bnc. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, connector and led information ..
Page 228
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-55 m series user manual figure a-19. Usb-6229 bnc top panel and pinout.
Page 229: Analog Input
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-56 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Connecting signals to the usb-6229 bnc analog input you can u...
Page 230
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-57 m series user manual to measure a floating signal source, move the switch to the fs position. To measure a ground-referenced signal source, move the switch to the gs position. Figure a-20 shows the ai 0 bnc and correspond...
Page 231: Analog Output
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-58 ni.Com figure a-22. Single-ended channels when you set the source type to the gs position and software-configure the device for single-ended input, each bnc connector provides access to two single-ended channels, ai x and ai x+8. For e...
Page 232: Digital I/o and Timing I/o
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-59 m series user manual digital i/o and timing i/o you can access digital i/o and timing i/o signals on the bnc connectors labeled pfi /p1...7>. Figure a-24 shows the dio/tio circuitry on the usb-6229 bnc. Figure a-24. Digit...
Page 233: Usb-6229 Bnc Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-60 ni.Com figure a-26 shows an example of how to use the user 1 and user 2 bncs. To access the pfi 8 signal from a bnc, connect user 1 on the screw terminal block to pfi 8 with a wire. Figure a-26. Connecting pfi 8 to user 1 bnc the desig...
Page 234: Ni 6250
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-61 m series user manual ni 6250 pci/pxi-6250 pinout figure a-27 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6250. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, connector ...
Page 235
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-62 ni.Com figure a-27. Pci/pxi-6250 pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5 p0.0 d gnd nc nc ai gnd a...
Page 236: Pci/pxi-6250 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-63 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6250 specifications refer...
Page 237: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-64 ni.Com scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter and an shc68-68-epm cable. Yo...
Page 238: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-65 m series user manual screw terminal accessories national instruments offers several styles of screw terminal connector blocks. Use an shc68-68-epm shielded cable to connect an m series device to a connector block, such as...
Page 239: Ni 6251
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-66 ni.Com ni 6251 the following sections contain information about the ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie-6251, usb-6251 screw terminal, usb-6251 bnc, and usb-6251 mass termination devices. Ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie-6251 ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie-6251 pinout fig...
Page 240
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-67 m series user manual figure a-28. Ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie-6251 pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 ...
Page 241: Options
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-68 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie-6251 specifications refer to the ni 625x...
Page 242: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-69 m series user manual scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter a...
Page 243: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-70 ni.Com screw terminal accessories national instruments offers several styles of screw terminal connector blocks. Use an shc68-68-epm shielded cable to connect an m series device to a connector block, such as the following: • cb-68lp an...
Page 244: Usb-6251 Screw Terminal
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-71 m series user manual usb-6251 screw terminal usb-6251 screw terminal pinout figure a-29 shows the pinout of the usb-6251 screw terminal. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descrip...
Page 245
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-72 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6251 screw terminal specifications refer to the ni 625x s...
Page 246: Usb-6251 Bnc
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-73 m series user manual usb-6251 bnc usb-6251 bnc pinout figure a-30 shows the pinout of the usb-6251 bnc. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, conne...
Page 247
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-74 ni.Com figure a-30. Usb-6251 bnc top panel and pinout.
Page 248: Analog Input
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-75 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Connecting signals to the usb-625...
Page 249
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-76 ni.Com to measure a floating signal source, move the switch to the fs position. To measure a ground-referenced signal source, move the switch to the gs position. Figure a-31 shows the ai 0 bnc and corresponding fs/gs switch on the top ...
Page 250: Analog Output
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-77 m series user manual figure a-33. Single-ended channels when you set the source type to the gs position and software-configure the device for single-ended input, each bnc connector provides access to two single-ended chan...
Page 251: Digital I/o and Timing I/o
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-78 ni.Com digital i/o and timing i/o you can access digital i/o and timing i/o signals on the bnc connectors labeled pfi /p1...7>. Figure a-35 shows the dio/tio circuitry on the usb-6251 bnc. Figure a-35. Digital i/o and timing i/o circui...
Page 252: User 1 and User 2
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-79 m series user manual user 1 and user 2 the user 1 and user 2 bnc connectors allow you to use a bnc connector for a digital or timing i/o signal of your choice. The user 1 and user 2 bnc connectors are routed (internal to ...
Page 253: Usb-6251 Bnc Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-80 ni.Com figure a-38 shows an example of how to use the user 1 and user 2 bncs. To access the pfi 8 signal from a bnc, connect user 1 on the screw terminal block to pfi 8 with a wire. Figure a-38. Connecting pfi 8 to user 1 bnc the desig...
Page 254: Usb-6251 Mass Termination
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-81 m series user manual usb-6251 mass termination usb-6251 mass termination pinout figure a-39 shows the pinout of the usb-6251 mass termination device. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector s...
Page 255
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-82 ni.Com figure a-39. Usb-6251 mass termination pinout pfi 14/p2.6 pfi 12/p2.4 pfi 9/p2.1 d gnd pfi 6/p1.6 pfi 5/p1.5 d gnd +5 v d gnd pfi 1/p1.1 pfi 0/p1.0 d gnd d gnd +5 v d gnd p0.6 p0.1 d gnd p0.4 apfi 0 ao 1 ao 0 ai 15 ai gnd ai 6 a...
Page 256: Options
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-83 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6251 mass termination specifi...
Page 257: Scc Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-84 ni.Com scc accessories scc provides portable, modular signal conditioning to your daq system. To connect your m series device to an scc module carrier, such as the sc-2345, sc-2350, or scc-68, use an sh68-68-ep shielded cable. Refer to...
Page 258: Cables
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-85 m series user manual cables in most applications, you can use the following cables: • sh68-68-ep—high-performance cable with individual bundles separating analog and digital signals. Each differential analog input channel...
Page 259: Ni 6254
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-86 ni.Com ni 6254 pci/pxi-6254 pinout figure a-40 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6254. The i/o signals appear on two 68-pin connectors. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of ...
Page 260
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-87 m series user manual figure a-40. Pci/pxi-6254 pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) connect or 1 (ai 16-31) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3...
Page 261: Pci/pxi-6254 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-88 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6254 specifications refer to the ni 625x specificatio...
Page 262: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-89 m series user manual scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter a...
Page 263: Bnc Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-90 ni.Com bnc accessories you can use the shc68-68-epm shielded cable, to connect your daq device to bnc accessories, such as the following: • bnc-2110—provides bnc connectivity to all analog signals, some digital signals, and spring term...
Page 264: Rtsi Cables
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-91 m series user manual rtsi cables use rtsi bus cables to connect timing and synchronization signals among pci devices, such as m series, e series, can, and other measurement, vision, and motion devices. Since pxi devices u...
Page 265: Ni 6255
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-92 ni.Com ni 6255 the following sections contain information about the pci/pxi-6255, usb-6255 screw terminal, and usb-6255 mass termination devices. Pci/pxi-6255 pci/pxi-6255 pinout figure a-41 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6255. For a ...
Page 266
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-93 m series user manual figure a-41. Pci/pxi-6255 pinout d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5 p0.0 d gnd ao gnd ao...
Page 267: Pci/pxi-6255 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-94 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6255 specifications refer to the ni 625x specificatio...
Page 268: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-95 m series user manual scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter a...
Page 269: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-96 ni.Com using a bnc accessory with connector 1 connector 1 of your device is compatible with bnc-2115. Bnc-2115 provides bnc connectivity to 24 of the differential (48 single ended) analog input signals on connector 1. You can use an sh...
Page 270
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-97 m series user manual choosing a cable for connector 0 in most applications, you can use the following cables with connector 0: • shc68-68-epm 1 —high-performance cable designed specifically for m series devices. It has in...
Page 271: Usb-6255 Screw Terminal
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-98 ni.Com usb-6255 screw terminal usb-6255 screw terminal pinout figure a-42 shows the pinout of the usb-6255 screw terminal. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, ...
Page 272
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-99 m series user manual figure a-42. Usb-6255 screw terminal pinout 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 ai 8 ai 9 ai 10 ai 11 ai 12 ai gnd ai 13 ai 14 ai 15 ai 24 ai 25 ai 26 ai gnd apfi 0 ao gnd ao 1 ai 0 ai 1 a...
Page 273
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-100 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6255 screw terminal specifications refer to the ni 625x ...
Page 274: Usb-6255 Mass Termination
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-101 m series user manual usb-6255 mass termination usb-6255 mass termination pinout figure a-43 shows the pinout of the usb-6255 mass termination device. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector ...
Page 275
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-102 ni.Com figure a-43. Usb-6255 mass termination pinout ai 71 ai 78 ai 69 ai 68 ai 75 ai 66 ai 65 ai 72 ai gnd ai 55 ai 54 ai 61 ai 52 ai 51 ai 58 ai 49 ai 48 ai 47 ai 38 ai 37 ai 44 ai gnd ai 35 ai 34 ai 41 ai 32 ai 23 ai 30 ai 21 ai 20...
Page 276: Options
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-103 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6255 mass termination specif...
Page 277: Scc Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-104 ni.Com scc accessories scc provides portable, modular signal conditioning to your daq system. To connect your m series device to an scc module carrier, such as the sc-2345, sc-2350, or scc-68, use an sh68-68-ep shielded cable. Use con...
Page 278: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-105 m series user manual screw terminal accessories national instruments offers several styles of screw terminal connector blocks. Use an sh68-68-ep shielded cable to connect an m series device to a connector block, such as ...
Page 279
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-106 ni.Com custom cabling and connectivity the ca-1000 is a configurable enclosure that gives user-defined connectivity and flexibility through customized panelettes. Visit ni.Com for more information about the ca-1000. Refer to the custo...
Page 280: Ni 6259
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-107 m series user manual ni 6259 the following sections contain information about the ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie-6259, usb-6259 screw terminal, usb-6259 bnc, and usb-6259 mass termination devices. Ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie-6259 ni pci/...
Page 281
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-108 ni.Com figure a-44. Ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie-6259 pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) connect or 1 (ai 16-31) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0....
Page 282: Options
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-109 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Ni pci/pcie/pxi/pxie-6259 specif...
Page 283: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-110 ni.Com scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter and an shc68-68-epm cable. U...
Page 284: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-111 m series user manual • bnc-2111—provides bnc connectivity to 16 single-ended analog input signals, two analog output signals, five dio/pfi signals, and the external reference voltage for analog output • bnc-2120—similar ...
Page 285: Cables
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-112 ni.Com cables in most applications, you can use the following cables: • shc68-68-epm 1 —high-performance cable designed specifically for m series devices. It has individual bundles separating analog and digital signals. Each different...
Page 286: Usb-6259 Screw Terminal
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-113 m series user manual usb-6259 screw terminal usb-6259 screw terminal pinout figure a-45 shows the pinout of the usb-6259 screw terminal. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descri...
Page 287
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-114 ni.Com figure a-45. Usb-6259 screw terminal pinout 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 ai 4 ai 12 ai gnd ai 5 ai 13 ai gnd ai 6 ai 14 ai gnd ai 7 ai 15 ai gnd apfi 0 ai gnd ao 1 ao gnd ai 0 ai 8 ai gnd ai 1 ai 9 ai gnd ai ...
Page 288
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-115 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6259 screw terminal specific...
Page 289: Usb-6259 Bnc
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-116 ni.Com usb-6259 bnc usb-6259 bnc pinout figure a-46 shows the pinout of the usb-6259 bnc. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, connector and led information ..
Page 290
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-117 m series user manual figure a-46. Usb-6259 bnc top panel and pinout.
Page 291: Analog Input
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-118 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Connecting signals to the usb-6259 bnc analog input you can ...
Page 292
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-119 m series user manual to measure a floating signal source, move the switch to the fs position. To measure a ground-referenced signal source, move the switch to the gs position. Figure a-47 shows the ai 0 bnc and correspon...
Page 293: Analog Output
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-120 ni.Com figure a-49. Single-ended channels when you set the source type to the gs position and software-configure the device for single-ended input, each bnc connector provides access to two single-ended channels, ai x and ai x+8. For ...
Page 294: Digital I/o and Timing I/o
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-121 m series user manual digital i/o and timing i/o you can access digital i/o and timing i/o signals on the bnc connectors labeled pfi /p1...7>. Figure a-51 shows the dio/tio circuitry on the usb-6259 bnc. Figure a-51. Digi...
Page 295: User 1 and User 2
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-122 ni.Com user 1 and user 2 the user 1 and user 2 bnc connectors allow you to use a bnc connector for a digital or timing i/o signal of your choice. The user 1 and user 2 bnc connectors are routed (internal to the usb-6259 bnc) to the us...
Page 296: Usb-6259 Bnc Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-123 m series user manual figure a-54. Connecting pfi 8 to user 1 bnc the designated space below each user bnc is for marking or labeling signal names. Usb-6259 bnc specifications refer to the ni 625x specifications for more ...
Page 297: Usb-6259 Mass Termination
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-124 ni.Com usb-6259 mass termination usb-6259 mass termination pinout figure a-55 shows the pinout of the usb-6259 mass termination device. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section ...
Page 298
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-125 m series user manual figure a-55. Usb-6259 mass termination pinout pfi 14/p2.6 pfi 12/p2.4 pfi 9/p2.1 d gnd pfi 6/p1.6 pfi 5/p1.5 d gnd +5 v d gnd pfi 1/p1.1 pfi 0/p1.0 d gnd d gnd +5 v d gnd p0.6 p0.1 d gnd p0.4 apfi 0 ...
Page 299: Options
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-126 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Usb-6259 mass termination specifications refer to the ni 625...
Page 300: Scc Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-127 m series user manual scc accessories scc provides portable, modular signal conditioning to your daq system. To connect your m series device to an scc module carrier, such as the sc-2345, sc-2350, or scc-68, use an sh68-6...
Page 301: Cables
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-128 ni.Com you can use one screw terminal accessory with the signals on either connector of your m series device. You can use two screw terminal accessories with one m series device by using both connectors. Cables in most applications, y...
Page 302: Ni 6280
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-129 m series user manual ni 6280 pci/pxi-6280 pinout figure a-56 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6280. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, connector...
Page 303
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-130 ni.Com figure a-56. Pci/pxi-6280 pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5 p0.0 d gnd nc nc ai gnd ...
Page 304: Pci/pxi-6280 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-131 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6280 specifications refe...
Page 305: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-132 ni.Com scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter and an shc68-68-epm cable. Y...
Page 306: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-133 m series user manual screw terminal accessories national instruments offers several styles of screw terminal connector blocks. Use an shc68-68-epm shielded cable to connect an m series device to a connector block, such a...
Page 307: Ni 6281
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-134 ni.Com ni 6281 pci/pxi-6281 pinout figure a-57 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6281. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector signal descriptions section of chapter 3, connector and led information . Note ...
Page 308
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-135 m series user manual figure a-57. Pci/pxi-6281 pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p...
Page 309: Pci/pxi-6281 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-136 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6281 specifications refer to the ni 628x specificati...
Page 310: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-137 m series user manual scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter ...
Page 311: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-138 ni.Com screw terminal accessories national instruments offers several styles of screw terminal connector blocks. Use an shc68-68-epm shielded cable to connect an m series device to a connector block, such as the following: • cb-68lp a...
Page 312: Ni 6284
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-139 m series user manual ni 6284 pci/pxi-6284 pinout figure a-58 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6284. The i/o signals appear on two 68-pin connectors. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector si...
Page 313
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-140 ni.Com figure a-58. Pci/pxi-6284 pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) connect or 1 (ai 16-31) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5 ...
Page 314: Pci/pxi-6284 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-141 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6284 specifications refe...
Page 315: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-142 ni.Com scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter and an shc68-68-epm cable. U...
Page 316: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-143 m series user manual • bnc-2120—similar to the bnc-2110, and also has a built-in function generator, quadrature encoder, temperature reference, and thermocouple connector • bnc-2090a—desktop/rack-mountable device with 22...
Page 317: Cables
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-144 ni.Com cables in most applications, you can use the following cables: • shc68-68-epm 1 —high-performance cable designed specifically for m series devices. It has individual bundles separating analog and digital signals. Each different...
Page 318: Ni 6289
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-145 m series user manual ni 6289 pci/pxi-6289 pinout figure a-59 shows the pinout of the pci/pxi-6289. The i/o signals appear on two 68-pin connectors. For a detailed description of each signal, refer to the i/o connector si...
Page 319
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-146 ni.Com figure a-59. Pci/pxi-6289 pinout connect or 0 (ai 0-15) connect or 1 (ai 16-31) d gnd d gnd pfi 8/p2.0 pfi 7/p1.7 pfi 15/p2.7 pfi 13/p2.5 pfi 4/p1.4 pfi 3/p1.3 pfi 2/p1.2 d gnd pfi 10/p2.2 pfi 11/p2.3 p0.3 p0.7 p0.2 d gnd p0.5 ...
Page 320: Pci/pxi-6289 Specifications
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-147 m series user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview help in version 8.0 or later. Pci/pxi-6289 specifications refe...
Page 321: Scxi Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-148 ni.Com scxi accessories scxi is a programmable signal conditioning system designed for measurement and automation applications. To connect your m series device to an scxi chassis, use the scxi-1349 adapter and an shc68-68-epm cable. U...
Page 322: Screw Terminal Accessories
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-149 m series user manual • bnc-2120—similar to the bnc-2110, and also has a built-in function generator, quadrature encoder, temperature reference, and thermocouple connector • bnc-2090a—desktop/rack-mountable device with 22...
Page 323: Cables
Appendix a device-specific information m series user manual a-150 ni.Com cables in most applications, you can use the following cables: • shc68-68-epm 1 —high-performance cable designed specifically for m series devices. It has individual bundles separating analog and digital signals. Each different...
Page 324: Timing Diagrams
© national instruments corporation b-1 m series user manual b timing diagrams analog input timing diagrams the following sections describe the timing specifications and timing of the triggers and clock signals related to the analog input timing engine: • input timing —input timing relates to any sig...
Page 325
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-2 ni.Com figure b-1 is a simplified model of the m series analog input timing engine. Figure b-1. M series analog input timing engine the following signals are used in figure b-1 and in the following sections: • terminal—refers to any device terminal...
Page 326
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-3 m series user manual that will be divided by the si2 counter, or can be an external convert clock signal. Sync convert clock timebase is a signal related to convert clock timebase that is used to synchronize external signals before th...
Page 327: Input Timing
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-4 ni.Com input timing input timing refers to the delays involved in importing external signals to be used as triggers or clocks in the ai timing engine. Figures b-2 and b-3 and table b-1 describe the insertion delays for external signals. Figure b-2....
Page 328: Internal Timing
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-5 m series user manual internal timing ai timing clocks the analog input timing engine has two levels of timing that control an ai acquisition. The first level is the convert level. This is the timing that controls when the analog to di...
Page 329
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-6 ni.Com the second level of timing is the sample level. Basically, converts are grouped in sets called samples, and the timing of the samples can be independent from the timing of the converts. The m series device can use a timebase to generate the ...
Page 330
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-7 m series user manual figure b-5. Ai timing clocks timing diagram table b-2. Ai timing clocks timing time description line min (ns) max (ns) t 2 minimum pulse width — 12.5 — t 3 minimum period — 50.0 — t 4 delay to sample clock timebas...
Page 331: Convert Clock
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-8 ni.Com convert clock convert clock is the signal that determines when an analog to digital conversion is started. The signal going to the adc is called p_ai_convert. Convert clock also can be routed to several external i/o terminals for external us...
Page 332
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-9 m series user manual figure b-7. Convert clock timing diagram figure b-8. Convert clock and any internal signal timing diagram table b-3. Convert clock timing time description line min (ns) max (ns) t 8 delay from _i to sync convert c...
Page 333: Start
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-10 ni.Com start start is the signal that starts an ai acquisition. This signal can come from an external source (through an external terminal) or from an internal source. One possible internal source is a software-generated pulse. A multiplexer selec...
Page 334
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-11 m series user manual figure b-9. Convert clock timebase timing and the analog input timing engine figure b-10. Convert clock timebase timing diagram start terminal selected reference trigger reference trigger terminal terminal select...
Page 335
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-12 ni.Com figure b-11. Sample clock timebase timing and the analog input timing engine table b-5. Convert clock timebase timing time description line min (ns) max (ns) t 13 delay to selected start pfi 3.4 8.8 rtsi 3.3 8.5 star 2.7 5.7 t 14 selected s...
Page 336: Reference Trigger
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-13 m series user manual figure b-12. Sample clock timebase timing diagram reference trigger use the reference trigger to stop the acquisition. It is normally used in pretrigger acquisitions; it is necessary to acquire data before and af...
Page 337
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-14 ni.Com figure b-13. Reference trigger and the analog input timing engine figure b-14. Reference trigger timing diagram start terminal selected reference trigger reference trigger terminal terminal selected sample clock terminal terminal terminal s...
Page 338: Sample Clock
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-15 m series user manual sample clock sample clock signals the start of a sample (which, in turn, is a set of converts). Sample clock is generated from external or internal sources. The main internal source is the terminal count (tc) of ...
Page 339
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-16 ni.Com figure b-15. Sample clock and the analog input timing engine figure b-16. Sample clock timing diagram si2_tc start terminal selected reference trigger reference trigger terminal terminal selected sample clock terminal terminal terminal sele...
Page 340
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-17 m series user manual the ai timing engine also can export a signal related to the sample clock called ai_sample_in_progress. This signal asserts with the sample clock and stays asserted until after the last convert of the sample. It ...
Page 341: Pause Trigger
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-18 ni.Com pause trigger the pause trigger signal can be used to pause the acquisition any time the signal deasserts. It is generated from internal or external sources. A multiplexer selects a signal from the _i bus; its output is called selected paus...
Page 342: Output Timing
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-19 m series user manual figure b-19. Pause trigger timing diagram output timing output timing refers to the delays involved in exporting internal signals to external terminals, so they can be used to trigger or time external devices. Th...
Page 343
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-20 ni.Com figure b-20. Output timing and the analog input timing engine figure b-21. Output timing diagram table b-11. Output timing edge line min (ns) max (ns) rising edge pfi 7.2 25.7 rtsi 5.6 14.0 falling edge pfi 7.5 25.9 rtsi 6.0 13.9 start term...
Page 344
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-21 m series user manual analog output timing diagrams the analog output timing can be broken into the following three sections: • input timing —the timing for external signals to enter the m series device and be available on the interna...
Page 345: Input Timing
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-22 ni.Com • sample clock timebase—this signal can be used to generate the sample clock. This signal acts as the clock for the ui counter, and a sample clock can be generated every n periods of the sample clock timebase by programming the ui counter a...
Page 346
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-23 m series user manual figure b-23. Input timing diagram internal analog output timing the analog output timer has two internal clocks that are referenced—sample clock timebase and sync sample clock timebase. How they are generated dep...
Page 347
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-24 ni.Com if the sample clock is being generated by dividing down the sample clock timebase, the analog output generation is timed from the output of the ui counter. The signal sample clock timebase can be an external signal. When the analog output t...
Page 348: Start Trigger
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-25 m series user manual start trigger as an output, the start trigger is routed as an asynchronous pulse. The actual signal that gets routed is the selected start signal, so there is no synchronous delay involved. Figure b-26. Start tri...
Page 349: Input Timing Verification
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-26 ni.Com figure b-28. Pause trigger input delay path figure b-29. Pause trigger timing diagram input timing verification consider an application that uses an external trigger and an external clock. The trigger and clock signals are routed to an inte...
Page 350
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-27 m series user manual • let dff setup and dff hold be the setup and hold time of the dff. • let external setup and external hold be the setup and hold time of the trigger to the clock at the terminals. Figure b-30 shows the external t...
Page 351: Output Timing
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-28 ni.Com output timing the analog output timer has three possible trigger outputs—start trigger, pause trigger, and sample clock. The delays presented in this section assume a 200 pf load on pfi lines and a 50 pf load on rtsi lines. Actual delays wi...
Page 352: Pause Trigger
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-29 m series user manual pause trigger pause trigger is only output asynchronously and only to rtsi. The actual signal being routed is selected pause. The pause trigger output timing can be derived by adding the delay in table b-20 to th...
Page 353: Digital I/o Timing Diagrams
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-30 ni.Com figure b-35. Sample clock path figure b-36. Sample clock delay timing diagram digital i/o timing diagrams this section describes the timing delays and requirements of digital waveform acquisitions and digital waveform generations. Digital w...
Page 354
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-31 m series user manual figure b-37. Digital waveform acquisition timing circuitry figure b-38 and tables b-22 and b-23 describe the digital waveform acquisition timing delays and requirements. Your inputs must meet the requirements to ...
Page 355
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-32 ni.Com table b-22. Di timing delays time from to min (ns) max (ns) t 3 * pfi pfi_i 5.2 6.2 18.2 22.0 rtsi rtsi_i 2.0 2.5 5.0 6.0 pxi_star pxi_star_i 1.5 3.5 t 4 pfi_i, rtsi_i, pxi_star_i, or other internal signal di sample clock 3.5 9 t 7 p0 p0_i ...
Page 356
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-33 m series user manual digital waveform generation timing to describe digital waveform generation timing delays and requirements, we model the circuitry as shown in figure b-39. In the figure, p0, pfi, rtsi, and pxi_star represent sign...
Page 357: Counters Timing Diagrams
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-34 ni.Com counters timing diagrams this section describes input delays, input requirements, output delays, gating modes, and quadrature and two pulse encoder timing. Input delays this section describes some of the timing delays of the counter/timer c...
Page 358
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-35 m series user manual figure b-41. Counter/timer circuitry pin to internal signal delays input timing is the timing specification for importing a signal to an internal bus on the m series device. Table b-26 shows the input timing for ...
Page 359
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-36 ni.Com selected gate and selected source delays tables b-27 and b-28 show the timing for the selected source and selected gate internal signals. Selected source is used to clock the 32-bit counter. Selected gate drives the gate logic, which genera...
Page 360: Count Enable Delay
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-37 m series user manual count enable delay table b-29 shows timing for the internal count enable signal, as shown in figure b-41. Count enable enables the 32-bit counter to count on the rising edge of the selected source signal. The del...
Page 361: Input Requirements
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-38 ni.Com input requirements refer to the figure b-41 for the m series counter/timer circuitry. Source period and pulse width figure b-46 and table b-30 show the timing requirements for counter n source. The requirements depend on the synchronization...
Page 362: Gate Pulse Width
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-39 m series user manual gate pulse width figure b-47 and table b-31 show the timing requirements for counter n gate. The requirements depend on the gating mode. Figure b-47. Counter n gate pulse width timing diagram gate to source setup...
Page 363: Example of The General Case
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-40 ni.Com figure b-49 and table b-33 show the setup and hold requirements of the internal block of the daq-stc2. Use the table to calculate the setup and hold times for your source and gate signals for the general case. In the general case, you can d...
Page 364: Setup
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-41 m series user manual setup to calculate the setup time, subtract the source delay from the gate delay. Use maximum delays. Hold to calculate the hold time, subtract the gate delay from the source delay. Use minimum delays. Gate delay...
Page 365: Output Delays
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-42 ni.Com output delays refer to the figure b-41 for the m series counter/timer circuitry. Figure b-50 and table b-34 show the output delays. Figure b-50. Output delays table b-34. Output delays timing time line min (ns) max (ns) t 10 — 1.0 4.0 t 11 ...
Page 366: Gating Modes
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-43 m series user manual gating modes gating mode refers to how the counter/timer uses the gate input. Some timing operations depend on the gating mode. Depending on the application, the counter/timers either level gating mode or edge ga...
Page 367
Appendix b timing diagrams m series user manual b-44 ni.Com clock generation timing diagrams table b-36 shows delays for generating different clocks, described in the clock routing section of chapter 9, digital routing and clock generation , from the onboard 80 mhz oscillator. Figure b-52. Generatin...
Page 368
Appendix b timing diagrams © national instruments corporation b-45 m series user manual table b-37 shows delays for generating different clocks using an external reference clock and the pll. Figure b-53. Generating different clocks using an external reference clock and the pll table b-36. Generating...
Page 369: Troubleshooting
© national instruments corporation c-1 m series user manual c troubleshooting this section contains common questions about m series devices. If your questions are not answered here, refer to the national instruments knowledgebase at ni.Com/kb . Analog input i am seeing crosstalk or ghost voltages wh...
Page 370
Appendix c troubleshooting m series user manual c-2 ni.Com are various methods of achieving this reference while maintaining a high common-mode rejection ratio (cmrr). These methods are outlined in the connecting analog input signals section of chapter 4, analog input . Ai gnd is an ai common signal...
Page 371: Analog Output
Appendix c troubleshooting © national instruments corporation c-3 m series user manual analog output i am seeing glitches on the output signal. How can i minimize it? When you use a dac to generate a waveform, you may observe glitches on the output signal. These glitches are normal; when a dac switc...
Page 372: Upgrading From E Series to
© national instruments corporation d-1 m series user manual d upgrading from e series to m series the following knowledgebase and developer zone documents will help you overcome typical hurdles in upgrading from e series to m series devices. • major differences between e series and m series daq devi...
Page 373: Technical Support and
© national instruments corporation e-1 m series user manual e technical support and professional services visit the following sections of the national instruments web site at ni.Com for technical support and professional services: • support—online technical support resources at ni.Com/support includ...
Page 374
Appendix e technical support and professional services m series user manual e-2 ni.Com • calibration certificate—if your product supports calibration, you can obtain the calibration certificate for your product at ni.Com/calibration . If you searched ni.Com and could not find the answers you need, c...
Page 375: Glossary
© national instruments corporation g-1 m series user manual glossary symbol prefix value p pico 10 –12 n nano 10 –9 μ micro 10 – 6 m milli 10 –3 k kilo 10 3 m mega 10 6 symbols % percent. + positive of, or plus. – negative of, or minus. ± plus or minus. Less than. > greater than. ≤ less than or equa...
Page 376
Glossary m series user manual g-2 ni.Com a a amperes—the unit of electric current. A/d analog-to-digital. Most often used as a/d converter. Ac alternating current. Accuracy a measure of the capability of an instrument or sensor to faithfully indicate the value of the measured signal. This term is no...
Page 377
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-3 m series user manual ao 0 analog channel 0 output signal. Ao 1 analog channel 1 output signal. Ao 2 analog channel 2 output signal. Ao 3 analog channel 3 output signal. Ao gnd analog output ground signal. Application a software program that creates an ...
Page 378
Glossary m series user manual g-4 ni.Com bus, buses the group of electrical conductors that interconnect individual circuitry in a computer. Typically, a bus is the expansion vehicle to which i/o or other devices are connected. Examples of pc buses are the pci, at(isa), and eisa bus. C c celsius. Ca...
Page 379
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-5 m series user manual common-mode signal 1. Any voltage present at the instrumentation amplifier inputs with respect to amplifier ground. 2. The signal, relative to the instrument chassis or computer’s ground, of the signals from a differential input. T...
Page 380
Glossary m series user manual g-6 ni.Com daq 1. Data acquisition—the process of collecting and measuring electrical signals from sensors, transducers, and test probes or fixtures and inputting them to a computer for processing. 2. Data acquisition—the process of collecting and measuring the same kin...
Page 381
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-7 m series user manual diff differential mode—an analog input mode consisting of two terminals, both of which are isolated from computer ground, whose difference is measured. Differential input an input circuit that actively responds to the difference be...
Page 382
Glossary m series user manual g-8 ni.Com encoder a device that converts linear or rotary displacement into digital or pulse signals. The most popular type of encoder is the optical encoder, which uses a rotating disk with alternating opaque areas, a light source, and a photodetector. Extclk external...
Page 383
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-9 m series user manual floating the condition where a common mode voltage exists, or may exist, between earth ground and the instrument or circuit of interest. Neither the high, nor the low side of a circuit is at earth potential. Floating signal sources...
Page 384
Glossary m series user manual g-10 ni.Com hz 1. Hertz—the si unit for measurement of frequency. One hertz (hz) equals one cycle per second. 2. The number of scans read or updates written per second. Hysteresis lag between making a change and the effect of the change. I i/o input/output—the transfer ...
Page 385
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-11 m series user manual i oh current, output high. I ol current, output low. Irq see interrupt, interrupt request line . K khz kilohertz—a unit of frequency; 1 khz = 10 3 = 1,000 hz. Ks 1,000 samples. L labview a graphical programming language. Led light...
Page 386
Glossary m series user manual g-12 ni.Com micro ( μ) the numerical prefix designating 10 –6 . Mio multifunction i/o—daq module. Designates a family of data acquisition products that have multiple analog input channels, digital i/o channels, timing, and optionally, analog output channels. An mio prod...
Page 387
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-13 m series user manual ni-daqmx the latest ni-daq driver with new vis, functions, and development tools for controlling measurement devices. The advantages of ni-daqmx over earlier versions of ni-daq include the daq assistant for configuring channels an...
Page 388
Glossary m series user manual g-14 ni.Com period the period of a signal, most often measured from one zero crossing to the next zero crossing of the same slope. The period of a signal is the reciprocal of its frequency (in hz). Period is designated by the symbol t. Periods the number of periods of a...
Page 389
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-15 m series user manual pxi_star a special set of trigger lines in the pxi backplane for high-accuracy device synchronization with minimal latencies on each pxi slot. Only devices in the pxi star controller slot 2 can set signal on this line. For additio...
Page 390
Glossary m series user manual g-16 ni.Com s s seconds. S samples. Sample counter the clock that counts the output of the channel clock, in other words, the number of samples taken. On devices with simultaneous sampling, this counter counts the output of the scan clock and hence the number of scans. ...
Page 391
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-17 m series user manual single trigger mode when the arbitrary waveform generator goes through the staging list only once. Single-buffered describes a device that acquires a specified number of samples from one or more channels and returns the data when ...
Page 392
Glossary m series user manual g-18 ni.Com terminal an object or region on a node through which data passes. Terminal count the highest value of a counter. T gh gate hold time. T gsu gate setup time. T gw gate pulse width. Timebase the reference signals for controlling the basic accuracy of time or f...
Page 393
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-19 m series user manual u usb universal serial bus—a 480 mbit/s serial bus with up to 12-mbps bandwidth for connecting computers to keyboards, printers, and other peripheral devices. Usb 2.0 retains compatibility with the original usb specification. V v ...
Page 394: Index
© national instruments corporation i-1 m series user manual index symbols +5 v power source, 3-7 numerics 10 mhz reference clock, 9-3 100 khz timebase, 9-2 20 mhz timebase, 9-2 5b series, 2-5 80 mhz source mode, 7-39 80 mhz timebase, 9-2 a a/d converter, 4-2 accessories, 2-6 choosing for your device...
Page 395
Index m series user manual i-2 ni.Com analog edge triggering with hysteresis, 11-4 analog input, 4-1 channels, 11-3 charge injection, c-1 circuitry, 4-1 connecting signals, 4-13 connecting through i/o connector, 4-1 crosstalk when sampling multiple channels, c-1 data acquisition methods, 4-11 differ...
Page 396
Index © national instruments corporation i-3 m series user manual applications counter input, 7-2 counter output, 7-19 edge counting, 7-2 arm start trigger, 7-31 avoiding scanning faster than necessary, 4-10 b bnc connecting signals, a-19, a-56, a-75, a-118 buffered edge counting, 7-3 hardware-timed...
Page 397
Index m series user manual i-4 ni.Com digital i/o signals, 6-9 floating signal sources, 4-15 ground-referenced signal sources, 4-21 pfi input signals, 8-4 connections for floating signal sources, 4-20 single-ended for floating signal sources, 4-20 single-ended, rse configuration, 4-20 connector info...
Page 398
Index © national instruments corporation i-5 m series user manual counters, 7-1 cascading, 7-33 connecting terminals, 7-30 duplicate count prevention, 7-35 edge counting, 7-2 filters, 7-33 generation, 7-19 input applications, 7-2 other features, 7-33 output applications, 7-19 prescaling, 7-34 pulse ...
Page 399
Index m series user manual i-6 ni.Com when to use with ground-referenced signal sources, 4-21 differential analog input, troubleshooting, c-1 differential connections using with floating signal sources, 4-16 using with ground-referenced signal sources, 4-23 when to use with floating signal sources, ...
Page 400
Index © national instruments corporation i-7 m series user manual encoding x1, 7-15 x2, 7-15 x4, 7-15 equivalent time sampling, 7-24 examples (ni resources), e-1 exporting timing output signals using pfi terminals, 8-3 external reference clock, 9-2 external source mode, 7-39 f features, counter, 7-3...
Page 401
Index m series user manual i-8 ni.Com ground-referenced signal sources connecting, 4-21 description, 4-21 using in differential mode, 4-23 using in nrse mode, 4-24 when to use in differential mode, 4-21 when to use in nrse mode, 4-22 when to use in rse mode, 4-22 h hardware, 1-1, 2-1 hardware-timed ...
Page 402
Index © national instruments corporation i-9 m series user manual l labview documentation, xviii labview pda 8.X, xvii labwindows/cvi documentation, xviii led patterns usb-6221 bnc, a-23 usb-6221 screw terminal, a-16 usb-6225 mass termination, a-44 usb-6225 screw terminal, a-38 usb-6229 bnc, a-60 us...
Page 403
Index m series user manual i-10 ni.Com ni 6224, a-24 accessory options, a-26 cabling options, a-26 pinout, a-24 specifications, a-26 ni 6225, a-30 specifications, a-41 ni 6229, a-45 ni 6250, a-61 accessory options, a-63 cabling options, a-63 pinout, a-61 specifications, a-63 ni 6251, a-66 specificat...
Page 404
Index © national instruments corporation i-11 m series user manual order of channels for scanning, 4-9 other internal source mode, 7-39 software, installing, 1-1 output signal glitches, c-3 minimizing, 5-4 terminal, routing analog comparison events, 11-3 outputs, using rtsi as, 9-6 overview, 2-1 p p...
Page 405
Index m series user manual i-12 ni.Com using terminals as timing input signals, 8-2 pfi terminals as static digital i/os, 8-3 pin assignments. See pinouts pinouts comparison, 3-5 counter default, 7-30 device, 1-1 ni 6220, a-2 ni 6224, a-24 ni 6250, a-61 ni 6254, a-86 ni 6280, a-129 ni 6281, a-134 ni...
Page 406
Index © national instruments corporation i-13 m series user manual pxi-6224, a-24 pxi-6225, a-30 pxi-6229, a-45 pxi-6250, a-61 pxi-6251, a-66 pxi-6254, a-86 pxi-6255, a-92 pxi-6259, a-107 pxi-6280, a-129 pxi-6281, a-134 pxi-6284, a-139 pxi-6289, a-145 pxie-6251, a-66 pxie-6259, a-107 q quadrature en...
Page 407
Index m series user manual i-14 ni.Com signal sources floating, 4-15 ground-referenced, 4-21 signal stream, usb, 10-1 signals ai convert clock, 4-31 ai convert clock timebase, 4-35 ai hold complete event, 4-36 ai pause trigger, 4-39 ai reference trigger, 4-37 ai sample clock, 4-28 ai sample clock ti...
Page 408
Index © national instruments corporation i-15 m series user manual pci-6221 (37-pin), a-13 usb-6221 bnc, a-23 usb-6221 screw terminal, a-16 usb-6225 mass termination, a-41 usb-6225 screw terminal, a-38 usb-6229 bnc, a-60 usb-6229 screw terminal, a-53 usb-6251 bnc, a-80 usb-6251 mass termination, a-8...
Page 409
Index m series user manual i-16 ni.Com quadrature encoder, b-43 selected gate to count enable delays, b-37 selected gate to selected source delays, b-36 source period input requirements, b-38 two pulse encoder, b-43 timing output signals, exporting using pfi terminals, 8-3 training, xxi training and...
Page 410
Index © national instruments corporation i-17 m series user manual usb-6225 screw terminal, a-30 fuse replacement, a-38 led patterns, a-38 pinout, a-36 signal label, 1-2 specifications, a-38 usb cable strain relief, 1-3 usb-6229 bnc cable management, 1-4 connecting signals, a-56 fuse replacement, a-...
Page 411
Index m series user manual i-18 ni.Com usb-6259 screw terminal fuse replacement, a-115 led patterns, a-115 pinout, a-113 signal label, 1-2 specifications, a-115 usb cable strain relief, 1-3 using low impedance sources, 4-8 pfi terminals as static digital i/os, 8-3 as timing input signals, 8-2 to exp...