- DL manuals
- National Instruments
- Network Card
- NI 6232
- User Manual
National Instruments NI 6232 User Manual - Rtsi Connector Pinout
Summary of NI 6232
Page 1
Daq m series ni 6232/6233 user manual ni 6232/6233 user manual july 2006 371995a-01.
Page 2
Support worldwide technical support and product information ni.Com national instruments corporate headquarters 11500 north mopac expressway austin, texas 78759-3504 usa tel: 512 683 0100 worldwide offices australia 1800 300 800, austria 43 0 662 45 79 90 0, belgium 32 0 2 757 00 20, brazil 55 11 326...
Page 3: Important Information
Important information warranty the ni 6232/6233 is warranted against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of three years from the date of shipment, as evidenced by receipts or other documentation. National instruments will, at its option, repair or replace equipment that proves to be de...
Page 4
National instruments products are incorporated in a system or application, including, without limitation, the appropriate design, process and safety level of such system or application..
Page 5: Compliance
Compliance compliance with fcc/canada radio frequency interference regulations determining fcc class the federal communications commission (fcc) has rules to protect wireless communications from interference. The fcc places digital electronics into two classes. These classes are known as class a (fo...
Page 6: Contents
© national instruments corporation vii ni 6232/6233 user manual contents about this manual conventions ...................................................................................................................Xv related documentation.............................................................
Page 7
Contents ni 6232/6233 user manual viii ni.Com chapter 3 connector information i/o connector signal descriptions................................................................................ 3-1 rtsi connector pinout .....................................................................................
Page 8
Contents © national instruments corporation ix ni 6232/6233 user manual using an external source..................................................................4-23 routing ai sample clock signal to an output terminal .................4-23 other timing requirements....................................
Page 9
Contents ni 6232/6233 user manual x ni.Com ao sample clock signal ................................................................................ 5-8 using an internal source .................................................................. 5-9 using an external source ...............................
Page 10
Contents © national instruments corporation xi ni 6232/6233 user manual position measurement .....................................................................................7-16 measurements using quadrature encoders ......................................7-16 measurements using two pulse encode...
Page 11
Contents ni 6232/6233 user manual xii ni.Com prescaling ........................................................................................................ 7-34 duplicate count prevention ............................................................................ 7-35 duplicate count preventio...
Page 12
Contents © national instruments corporation xiii ni 6232/6233 user manual using rtsi terminals as timing input signals .............................................10-6 rtsi filters .....................................................................................................10-6 pxi clock an...
Page 13: About This Manual
© national instruments corporation xv ni 6232/6233 user manual about this manual the ni 6232/6233 user manual contains information about using the national instruments 6232/6233 m series data acquisition (daq) devices with ni-daqmx 8.0 and later. Ni 6232/6233 devices feature eight analog input (ai) ...
Page 14: Related Documentation
About this manual ni 6232/6233 user manual xvi ni.Com monospace text in this font denotes text or characters that you should enter from the keyboard, sections of code, programming examples, and syntax examples. This font is also used for the proper names of disk drives, paths, directories, programs,...
Page 15
About this manual © national instruments corporation xvii ni 6232/6233 user manual the ni-daqmx for linux configuration guide provides configuration instructions, templates, and instructions for using test panels. Note all ni-daqmx documentation for linux is installed at /usr/local/ natinst/nidaqmx/...
Page 16
About this manual ni 6232/6233 user manual xviii ni.Com • getting started»getting started with daq —includes overview information and a tutorial to learn how to take an ni-daqmx measurement in labview using the daq assistant. • vi and function reference»measurement i/o vis and functions —describes t...
Page 17
About this manual © national instruments corporation xix ni 6232/6233 user manual .Net and visual c++ class libraries. This help collection is integrated into the visual studio .Net documentation. In visual studio .Net, select help»contents . Note you must have visual studio .Net installed to view t...
Page 18: Getting Started
© national instruments corporation 1-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 1 getting started m series ni 6232/6233 devices feature sixteen analog input (ai) channels, two analog output (ao) channels, two counters, six lines of digital input (di), and four lines of digital output (do). If you have not already i...
Page 19: Device Specifications
Chapter 1 getting started ni 6232/6233 user manual 1-2 ni.Com device specifications refer to the ni 6232/6233 specifications , available on the ni-daq device document browser or ni.Com/manuals , for more detailed information on the ni 6232/6233 device. Device accessories and cables ni offers a varie...
Page 20: Daq System Overview
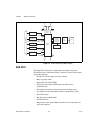
© national instruments corporation 2-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 2 daq system overview figure 2-1 shows a typical daq system, which includes sensors, transducers, cables that connect the various devices to the accessories, the m series device, programming software, and a pc. The following sections co...
Page 21
Chapter 2 daq system overview ni 6232/6233 user manual 2-2 ni.Com figure 2-2. General ni 6232/6233 block diagram daq-stc2 the daq-stc2 implements a high-performance digital engine for ni 6232/6233 data acquisition hardware. Some key features of this engine include the following: • flexible ai and ao...
Page 22: Sensors and Transducers
Chapter 2 daq system overview © national instruments corporation 2-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual calibration circuitry the m series analog inputs and outputs have calibration circuitry to correct gain and offset errors. You can calibrate the device to minimize ai and ao errors caused by time and temper...
Page 23: Cables and Accessories
Chapter 2 daq system overview ni 6232/6233 user manual 2-4 ni.Com cables and accessories ni offers a variety of products to use with ni 6232/6233 devices, including cables, connector blocks, and other accessories, as follows: • cables and cable assemblies – shielded – unshielded ribbon • screw termi...
Page 24
Chapter 2 daq system overview © national instruments corporation 2-5 ni 6232/6233 user manual programming devices in software national instruments measurement devices are packaged with ni-daq driver software, an extensive library of functions and vis you can call from your application software, such...
Page 25: Connector Information
© national instruments corporation 3-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 3 connector information the i/o connector signal descriptions and rtsi connector pinout sections contain information on m series connectors. Refer to appendix a, device-specific information , for device i/o connector pinouts. I/o connec...
Page 26
Chapter 3 connector information ni 6232/6233 user manual 3-2 ni.Com ao gnd — — analog output ground —ao gnd is the reference for ao . Ai gnd and ao gnd are connected on the device. Note: ai gnd and ao gnd are isolated from earth ground, chassis ground, p0.Gnd, and p1.Gnd. Pfi /p0. P0.Gnd input progr...
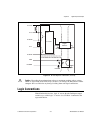
Page 27: Rtsi Connector Pinout
Chapter 3 connector information © national instruments corporation 3-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual rtsi connector pinout refer to the rtsi connector pinout section of chapter 10, digital routing and clock generation , for information on the rtsi connector..
Page 28: Analog Input
© national instruments corporation 4-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 4 analog input figure 4-1 shows the analog input circuitry of ni 6232/6233 devices. Figure 4-1. Ni 6232/6233 analog input circuitry analog input circuitry i/o connector you can connect analog input signals to the m series device through...
Page 29: Analog Input Range
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-2 ni.Com ground-reference settings the analog input ground-reference settings circuitry selects between differential and referenced single-ended modes. Each ai channel can use a different mode. Instrumentation amplifier (ni-pgia) the ni programmable ...
Page 30
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual 16-bit adc converts analog inputs into one of 65,536 (= 2 16 ) codes—that is, one of 65,536 possible digital values. These values are spread fairly evenly across the input range. So, for an input range of –10 v to...
Page 31
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-4 ni.Com the ai ground-reference setting determines how you should connect your ai signals to the ni 6232/6233 device. Refer to the connecting analog voltage input signals section for more information. Ground-reference settings are programmed on a pe...
Page 32
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-5 ni 6232/6233 user manual table 4-3 shows how signals are routed to the ni-pgia. For differential measurements, ai 0 and ai 8 are the positive and negative inputs of differential analog input channel 0. For a complete list of signal pairs ...
Page 33
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-6 ni.Com figure 4-3. Enabling multimode scanning in labview multichannel scanning considerations m series devices can scan multiple channels at high rates and digitize the signals accurately. However, you should consider several issues when designing...
Page 34
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-7 ni 6232/6233 user manual settling times increase when scanning high-impedance signals due to a phenomenon called charge injection. Multiplexers contain switches, usually made of switched capacitors. When one of the channels, for example c...
Page 35
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-8 ni.Com 1/50 lsb) of the ±10 v range. Some devices can take many microseconds for the circuitry to settle this much. To avoid this effect, you should arrange your channel scanning order so that transitions from large to small input ranges are infreq...
Page 36
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-9 ni 6232/6233 user manual avoid scanning faster than necessary designing your system to scan at slower speeds gives the pgia more time to settle to a more accurate level. Here are two examples to consider. Example 1 averaging many ai sampl...
Page 37
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-10 ni.Com each adc conversion. In ni-daqmx, software-timed acquisitions are referred to as having on-demand timing. Software-timed acquisitions are also referred to as immediate or static acquisitions and are typically used for reading a single sampl...
Page 38: Analog Input Triggering
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-11 ni 6232/6233 user manual be transferred to host memory. The device generates an error in this case. With continuous operations, if the user program does not read data out of the pc buffer fast enough to keep up with the data transfer, th...
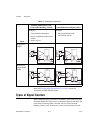
Page 39: Types of Signal Sources
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-12 ni.Com refer to the analog input ground-reference settings section for descriptions of diff and rse modes. Types of signal sources when configuring the input channels and making signal connections, first determine whether the signal sources are fl...
Page 40
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-13 ni 6232/6233 user manual two reference planes. Isolated front ends require a ground-reference point to the signal that is being measured. Floating signal sources a floating signal source is not connected to the building ground system (ea...
Page 41
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-14 ni.Com use diff input connections for any channel that meets any of the following conditions: • the input signal is low level (less than 1 v). • the leads connecting the signal to the device are greater than 3 m (10 ft). • the input signal require...
Page 42
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-15 ni 6232/6233 user manual with this type of connection, the pgia rejects both the common-mode noise in the signal and the ground potential difference between the signal source and the device ground, shown as v cm in the figure. Refer to t...
Page 43
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-16 ni.Com figure 4-5. Differential connections for floating signal sources this figure shows ai gnd connected to the ground reference point for the floating signal source. If you do not connect ai gnd, the source is not likely to remain within the co...
Page 44
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-17 ni 6232/6233 user manual signal connects to the positive input of the pgia, and the ground connects to the negative input of the pgia. You should only use single-ended input connections if the input signal meets the following conditions....
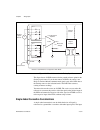
Page 45: Field Wiring Considerations
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-18 ni.Com figure 4-6. Single-ended connections for floating signal sources (rse configuration) refer to the ni 6232/6233 specifications for the usable range of v cm . Common-mode signal rejection considerations for signal sources that are already ref...
Page 46: Analog Input Timing Signals
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-19 ni 6232/6233 user manual • use individually shielded, twisted-pair wires to connect ai signals to the device. With this type of wire, the signals attached to the positive and negative input channels are twisted together and then covered ...
Page 47
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-20 ni.Com 1/sample period = sample rate figure 4-8. Interval sampling ai/convertclock controls the convert period, which is determined by the following equation: 1/convert period = convert rate by default, the ni-daqmx driver chooses the fastest chan...
Page 48
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-21 ni 6232/6233 user manual the pci-6220 m series device, a sampling rate of 40 khz for two channels would result in a convert clock rate of 80 khz. Maximum settling time for the amplifier is also very important. For example, to ensure accu...
Page 49
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-22 ni.Com figure 4-10. Pretriggered data acquisition example if an ai/referencetrigger pulse occurs before the specified number of pretrigger samples are acquired, the trigger pulse is ignored. Otherwise, when the ai/referencetrigger pulse occurs, th...
Page 50
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-23 ni 6232/6233 user manual using an internal source one of the following internal signals can drive ai/sampleclock. • counter n internal output • ai sample clock timebase (divided down) • a software pulse a programmable internal counter di...
Page 51
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-24 ni.Com a counter on your device internally generates ai/sampleclock unless you select some external source. Ai/starttrigger starts this counter and either software or hardware can stop it when a finite acquisition completes. When using an internal...
Page 52
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-25 ni 6232/6233 user manual sources for ai/sampleclock. You can configure the polarity selection for ai/sampleclocktimebase as either rising or falling edge. Ai convert clock signal use the ai convert clock (ai/convertclock) signal to initi...
Page 53
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-26 ni.Com using an external source use one of the following external signals as the source of ai/convertclock: • input pfi • rtsi • pxi_star routing ai convert clock signal to an output terminal you can route ai/convertclock (as an active low signal)...
Page 54
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-27 ni 6232/6233 user manual other timing requirements the sample and conversion level timing of m series devices work such that clock signals are gated off unless the proper timing requirements are met. For example, the device ignores both ...
Page 55
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-28 ni.Com ai/convertclocktimebase is not available as an output on the i/o connector. Ai hold complete event signal the ai hold complete event (ai/holdcompleteevent) signal generates a pulse after each a/d conversion begins. You can route ai/holdcomp...
Page 56
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-29 ni 6232/6233 user manual you also can specify whether the measurement acquisition begins on the rising edge or falling edge of ai/starttrigger. Routing ai start trigger to an output terminal you can route ai/starttrigger out to any outpu...
Page 57
Chapter 4 analog input ni 6232/6233 user manual 4-30 ni.Com figure 4-14. Reference trigger final buffer using a digital source to use ai/referencetrigger with a digital source, specify a source and an edge. The source can be any of the following signals: • input pfi • rtsi • pxi_star the source also...
Page 58
Chapter 4 analog input © national instruments corporation 4-31 ni 6232/6233 user manual using a digital source to use ai/sampleclock, specify a source and a polarity. The source can be any of the following signals: • input pfi • rtsi • pxi_star the source also can be one of several other internal si...
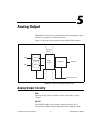
Page 59: Analog Output
© national instruments corporation 5-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 5 analog output ni 6232/6233 devices have two ao channels that are controlled by a single clock and are capable of waveform generation. Figure 5-1 shows the analog output circuitry of ni 6232/6233 devices. Figure 5-1. Ni 6232/6233 analo...
Page 60
Chapter 5 analog output ni 6232/6233 user manual 5-2 ni.Com dacs. It allows you to download the points of a waveform to your m series device without host computer interaction. Ao sample clock the ao sample clock signal reads a sample from the dac fifo and generates the ao voltage. Isolation barrier ...
Page 61
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual hardware-timed generations with a hardware-timed generation, a digital hardware signal controls the rate of the generation. This signal can be generated internally on your device or provided externally. Hardware-...
Page 62: Analog Output Triggering
Chapter 5 analog output ni 6232/6233 user manual 5-4 ni.Com regeneration is the repetition of the data that is already in the buffer. Standard regeneration is when data from the pc buffer is continually downloaded to the fifo to be written out. New data can be written to the pc buffer at any time wi...
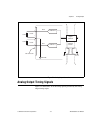
Page 63: Analog Output Timing Signals
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-5 ni 6232/6233 user manual figure 5-2. Analog output connections analog output timing signals figure 5-3 summarizes all of the timing options provided by the analog output timing engine. Load load v out v out + – + – ao 1 ao 0 channel 1 ch...
Page 64
Chapter 5 analog output ni 6232/6233 user manual 5-6 ni.Com figure 5-3. Analog output timing options ni 6232/6233 devices feature the following ao (waveform generation) timing signals. • ao start trigger signal • ao pause trigger signal • ao sample clock signal • ao sample clock timebase signal ao s...
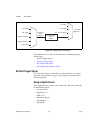
Page 65
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-7 ni 6232/6233 user manual the source also can be one of several internal signals on your daq device. Refer to device routing in max in the ni-daqmx help or the labview 8.X help for more information. You also can specify whether the wavefo...
Page 66
Chapter 5 analog output ni 6232/6233 user manual 5-8 ni.Com deasserted and another edge of the sample clock is received, as shown in figure 5-5. Figure 5-5. Ao/pausetrigger with other signal source using a digital source to use ao/pausetrigger, specify a source and a polarity. The source can be one ...
Page 67
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-9 ni 6232/6233 user manual using an internal source one of the following internal signals can drive ao/sampleclock. • ao sample clock timebase (divided down) • counter n internal output a programmable internal counter divides down the ao s...
Page 68
Chapter 5 analog output ni 6232/6233 user manual 5-10 ni.Com figure 5-6. Ao/sampleclock and ao/starttrigger ao sample clock timebase signal the ao sample clock timebase (ao/sampleclocktimebase) signal is divided down to provide a source for ao/sampleclock. You can route any of the following signals ...
Page 69
Chapter 5 analog output © national instruments corporation 5-11 ni 6232/6233 user manual • finite generation • continuous generation • waveform generation you can perform these generations through programmed i/o, interrupt, or dma data transfer mechanisms. Some of the applications also use start tri...
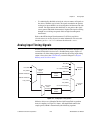
Page 70: Digital Input and Output
© national instruments corporation 6-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 6 digital input and output ni 6232/6233 devices have six static digital input lines, p0.. These lines also can be used as pfi inputs. The voltage input and output levels and the current drive level of the di and do lines are listed in t...
Page 71
Chapter 6 digital input and output ni 6232/6233 user manual 6-2 ni.Com connecting digital i/o signals the di signals p0. Are referenced to p0.Gnd and do signals p1. Are referenced to p1.Gnd. Figures 6-1 and 6-2 show p0. And p1. On the ni 6232 and the ni 6233 device, respectively. Digital input and o...
Page 72: Logic Conventions
Chapter 6 digital input and output © national instruments corporation 6-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual figure 6-2. Ni 6233 digital i/o connections (do sink) caution exceeding the maximum input voltage or maximum working voltage ratings, which are listed in the ni 6232/6233 specifications , can damage th...
Page 73
Chapter 6 digital input and output ni 6232/6233 user manual 6-4 ni.Com getting started with dio applications in software you can use ni 6232/6233 devices in the following digital i/o applications: • static digital input • static digital output note for more information about programming digital i/o ...
Page 74: Counters
© national instruments corporation 7-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 7 counters ni 6232/6233 devices have two general-purpose 32-bit counter/timers and one frequency generator, as shown in figure 7-1. The general-purpose counter/timers can be used for many measurement and pulse generation applications. C...
Page 75
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-2 ni.Com figure 7-1. M series counters the counters have seven input signals, although in most applications only a few inputs are used. For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the default counter terminals section. Counter 0 counter 0 sou...
Page 76: Counter Input Applications
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual counter input applications counting edges in edge counting applications, the counter counts edges on its source after the counter is armed. You can configure the counter to count rising or falling edges on its source ...
Page 77
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-4 ni.Com figure 7-3. Single point (on-demand) edge counting with pause trigger buffered (sample clock) edge counting with buffered edge counting (edge counting using a sample clock), the counter counts the number of edges on the source input after the co...
Page 78
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-5 ni 6232/6233 user manual non-cumulative buffered edge counting non-cumulative edge counting is similar to buffered (sample clock) edge counting. However, the counter resets after each active edge of the sample clock. You can route the sample ...
Page 79
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-6 ni.Com pulse-width measurement in pulse-width measurements, the counter measures the width of a pulse on its gate input signal. You can configure the counter to measure the width of high pulses or low pulses on the gate signal. You can route an interna...
Page 80
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-7 ni 6232/6233 user manual buffered pulse-width measurement buffered pulse-width measurement is similar to single pulse-width measurement, but buffered pulse-width measurement takes measurements over multiple pulses. The counter counts the numb...
Page 81
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-8 ni.Com of rising (or falling) edges occurring on the source input between the two active edges of the gate signal. You can calculate the period of the gate input by multiplying the period of the source signal by the number of edges returned by the coun...
Page 82
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-9 ni 6232/6233 user manual figure 7-9. Buffered period measurement note that if you are using an external signal as the source, at least one source pulse should occur between each active edge of the gate signal. This condition ensures that corr...
Page 83
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-10 ni.Com buffered semi-period measurement in buffered semi-period measurement, on each edge of the gate signal, the counter stores the count in a hardware save register. A dma controller transfers the stored values to host memory. The counter begins cou...
Page 84
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-11 ni 6232/6233 user manual you can route the signal to measure (f1) to the gate of a counter. You can route a known timebase (ft) to the source of the counter. The known timebase can be 80mhztimebase. For signals that might be slower than 0.02...
Page 85
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-12 ni.Com figure 7-12. Method 1b method 2—measure high frequency with two counters in this method, you measure one pulse of a known width using your signal and derive the frequency of your signal from the result. This method is good for high frequency si...
Page 86
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-13 ni 6232/6233 user manual figure 7-13. Method 2 method 3—measure large range of frequencies using two counters by using two counters, you can accurately measure a signal that might be high or low frequency. This technique is called reciprocal...
Page 87
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-14 ni.Com figure 7-14. Method 3 then route the counter 0 internal output signal to the gate input of counter 1. You can route a signal of known frequency (f2) to the counter 1 source input. F2 can be 80mhztimebase. For signals that might be slower than 0...
Page 88
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-15 ni 6232/6233 user manual consider a frequency measurement on a 50 khz signal using an 80 mhz timebase. This frequency corresponds to 1600 cycles of the 80 mhz timebase. Your measurement may return 1600 ±1 cycles depending on the phase of the...
Page 89
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-16 ni.Com for information on connecting counter signals, refer to the default counter terminals section. Position measurement you can use the counters to perform position measurements with quadrature encoders or two-pulse encoders. You can measure angula...
Page 90
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-17 ni 6232/6233 user manual figure 7-15. X1 encoding x2 encoding the same behavior holds for x2 encoding except the counter increments or decrements on each edge of channel a, depending on which channel leads the other. Each cycle results in tw...
Page 91
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-18 ni.Com channel z behavior—when it goes high and how long it stays high—differs with quadrature encoder designs. You must refer to the documentation for your quadrature encoder to obtain timing of channel z with respect to channels a and b. You must th...
Page 92
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-19 ni 6232/6233 user manual for information on connecting counter signals, refer to the default counter terminals section. Two-signal edge-separation measurement two-signal edge-separation measurement is similar to pulse-width measurement, exce...
Page 93
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-20 ni.Com figure 7-20. Single two-signal edge-separation measurement buffered two-signal edge-separation measurement buffered and single two-signal edge-separation measurements are similar, but buffered measurement measures multiple intervals. The counte...
Page 94: Counter Output Applications
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-21 ni 6232/6233 user manual counter output applications simple pulse generation single pulse generation the counter can output a single pulse. The pulse appears on the counter n internal output signal of the counter. You can specify a delay fro...
Page 95
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-22 ni.Com figure 7-23. Single pulse generation with start trigger retriggerable single pulse generation the counter can output a single pulse in response to each pulse on a hardware start trigger signal. The pulses appear on the counter n internal output...
Page 96
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-23 ni 6232/6233 user manual pulse train generation continuous pulse train generation this function generates a train of pulses with programmable frequency and duty cycle. The pulses appear on the counter n internal output signal of the counter....
Page 97
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-24 ni.Com frequency generation you can generate a frequency by using a counter in pulse train generation mode or by using the frequency generator circuit. Using the frequency generator the frequency generator can output a square wave at many different fr...
Page 98
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-25 ni 6232/6233 user manual frequency output can be routed out to any output pfi or rtsi terminal. All pfi terminals are set to high-impedance at startup. In software, program the frequency generator as you would program one of the counters for...
Page 99: Counter Timing Signals
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-26 ni.Com nyquist frequency of the system. Figure 7-28 shows an example of pulse generation for ets; the delay from the trigger to the pulse increases after each subsequent gate active edge. Figure 7-28. Pulse generation for ets for information on connec...
Page 100
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-27 ni 6232/6233 user manual counter n source signal the selected edge of the counter n source signal increments and decrements the counter value depending on the application the counter is performing. Table 7-3 lists how this terminal is used i...
Page 101
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-28 ni.Com routing counter n source to an output terminal you can route counter n source out to any output pfi or rtsi terminal. All pfis are set to high-impedance at startup. Counter n gate signal the counter n gate signal can perform many different oper...
Page 102
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-29 ni 6232/6233 user manual routing a signal to counter n aux each counter has independent input selectors for the counter n aux signal. Any of the following signals can be routed to the counter n aux input. • rtsi • input pfi • ai/referencetri...
Page 103
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-30 ni.Com counter n hw arm signal the counter n hw arm signal enables a counter to begin an input or output function. To begin any counter input or output function, you must first enable, or arm, the counter. In some applications, such as buffered semi-p...
Page 104: Default Counter Terminals
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-31 ni 6232/6233 user manual routing counter n internal output to an output terminal you can route counter n internal output to any output pfi or rtsi terminal. All output pfis are set to high-impedance at startup. Frequency output signal the fr...
Page 105: Counter Triggering
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-32 ni.Com you can use these defaults or select other sources and destinations for the counter/timer signals in ni-daqmx. Refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview 8.X help for more information on how to connect your signals ...
Page 106: Other Counter Features
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-33 ni 6232/6233 user manual pause trigger you can use pause triggers in edge counting and continuous pulse generation applications. For edge counting acquisitions, the counter stops counting edges while the external trigger signal is low and re...
Page 107
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-34 ni.Com the filter setting for each input can be configured independently. On power up, the filters are disabled. Figure 7-29 shows an example of a low-to-high transition on an input that has its filter set to 125 ns (n = 5). Figure 7-29. Filter exampl...
Page 108
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-35 ni 6232/6233 user manual prescaling on each counter (prescaling can be disabled). Each prescaler consists of a small, simple counter that counts to eight (or two) and rolls over. This counter can run faster than the larger counters, which si...
Page 109
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-36 ni.Com figure 7-31. Duplicate count prevention example on the first rising edge of the gate, the current count of 7 is stored. On the next rising edge of the gate, the counter stores a 2 since two source pulses occurred after the previous rising edge ...
Page 110
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-37 ni 6232/6233 user manual figure 7-32. Duplicate count example example application that prevents duplicate count with duplicate count prevention enabled, the counter synchronizes both the source and gate signals to the 80 mhz timebase. By syn...
Page 111
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-38 ni.Com normally, the counter value and counter n internal output signals change synchronously to the source signal. With duplicate count prevention, the counter value and counter n internal output signals change synchronously to the 80 mhz timebase. N...
Page 112
Chapter 7 counters © national instruments corporation 7-39 ni 6232/6233 user manual in daqmx, the device uses 80 mhz source mode if the user performs the following: • performs a position measurement • selects duplicate count prevention otherwise, the mode depends on the signal that drives counter n ...
Page 113
Chapter 7 counters ni 6232/6233 user manual 7-40 ni.Com other internal source mode in other internal source mode, the device synchronizes signals on the falling edge of the source, and counts on the following rising edge of the source, as shown in figure 7-35. Figure 7-35. Other internal source mode...
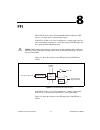
Page 114: Pfi
© national instruments corporation 8-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 8 pfi ni 6232/6233 devices have 10 programmable function interface (pfi) signals—six input signals and four output signals. Each pfi /p0. Can be configured as a timing input signal for ai or counter/timer functions or a static digital i...
Page 115
Chapter 8 pfi ni 6232/6233 user manual 8-2 ni.Com figure 8-2. Ni 6232/6233 pfi output circuitry when a terminal is used as a timing input or output signal, it is called pfi x (where x is an integer from 0 to 9). When a terminal is used as a static digital input or output, it is called p0. X or p1. X...
Page 116: Connecting Pfi Input Signals
Chapter 8 pfi © national instruments corporation 8-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual exporting timing output signals using pfi terminals you can route any of the following timing signals to any pfi terminal. • ai hold complete event • counter n source • counter n gate • counter n internal output • frequenc...
Page 117: Pfi Filters
Chapter 8 pfi ni 6232/6233 user manual 8-4 ni.Com figure 8-3. Pfi input signals connections pfi filters you can enable a programmable debouncing filter on each pfi, rtsi, or pxi_star signal. When the filters are enabled, your device samples the input on each rising edge of a filter clock. M series d...
Page 118: I/o Protection
Chapter 8 pfi © national instruments corporation 8-5 ni 6232/6233 user manual the filter setting for each input can be configured independently. On power up, the filters are disabled. Figure 8-4 shows an example of a low-to-high transition on an input that has its filter set to 125 ns (n = 5). Figur...
Page 119: Programmable Power-Up States
Chapter 8 pfi ni 6232/6233 user manual 8-6 ni.Com consult the device specifications for details. However, you should avoid these fault conditions by following these guidelines. • do not connect any digital output line to any external signal source, ground signal, or power supply. • understand the cu...
Page 120
Chapter 8 pfi © national instruments corporation 8-7 ni 6232/6233 user manual figure 8-5. Ni 6232 digital i/o connections (do source) p1. P1.Vcc p1.0 p1.1 p1.Gnd p0.0 p0.Gnd p1.Gnd p0.Gnd digital isolators.
Page 121
Chapter 8 pfi ni 6232/6233 user manual 8-8 ni.Com figure 8-6. Ni 6233 digital i/o connections (do sink) caution exceeding the maximum input voltage or maximum working voltage ratings, which are listed in the ni 6232/6233 specifications , can damage the daq device and the computer. Ni is not liable f...
Page 122
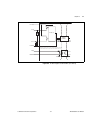
© national instruments corporation 9-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 9 isolation and digital isolators ni 6232/6233 devices are isolated data acquisition devices. As shown in figure 9-1, the analog input, analog output, counters, and pfi/static dio circuitry are referenced to an isolated ground . The bus...
Page 123: Digital Isolation
Chapter 9 isolation and digital isolators ni 6232/6233 user manual 9-2 ni.Com the non-isolated ground is connected to the chassis ground of the pc or chassis where the device is installed. The isolated ground is not connected to the chassis ground of the pc or chassis. The isolated ground can be at ...
Page 124: Digital Routing and Clock
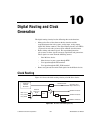
© national instruments corporation 10-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 10 digital routing and clock generation the digital routing circuitry has the following three main functions. • manages the flow of data between the bus interface and the acquisition/generation sub-systems (analog input, analog output,...
Page 125
Chapter 10 digital routing and clock generation ni 6232/6233 user manual 10-2 ni.Com 80 mhz timebase the 80 mhz timebase can be used as the source input to the 32-bit general-purpose counter/timers. The 80 mhz timebase can be generated from either of the following. • onboard oscillator • external si...
Page 126
Chapter 10 digital routing and clock generation © national instruments corporation 10-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual 10 mhz reference clock the 10 mhz reference clock can be used to synchronize other devices to your m series device. The 10 mhz reference clock can be routed to the rtsi terminals. Other d...
Page 127
Chapter 10 digital routing and clock generation ni 6232/6233 user manual 10-4 ni.Com • share trigger signals between devices many national instruments daq, motion, vision, and can devices support rtsi. In a pci system, the rtsi bus consists of the rtsi bus interface and a ribbon cable. The bus can r...
Page 128
Chapter 10 digital routing and clock generation © national instruments corporation 10-5 ni 6232/6233 user manual using rtsi as outputs rtsi are bidirectional terminals. As an output, you can drive any of the following signals to any rtsi terminal. • ai/starttrigger • ai/referencetrigger • ai/convert...
Page 129
Chapter 10 digital routing and clock generation ni 6232/6233 user manual 10-6 ni.Com using rtsi terminals as timing input signals you can use rtsi terminals to route external timing signals to many different m series functions. Each rtsi terminal can be routed to any of the following signals. • ai c...
Page 130
Chapter 10 digital routing and clock generation © national instruments corporation 10-7 ni 6232/6233 user manual the filter setting for each input can be configured independently. On power up, the filters are disabled. Figure 10-3 shows an example of a low-to-high transition on an input that has its...
Page 131
Chapter 10 digital routing and clock generation ni 6232/6233 user manual 10-8 ni.Com pxi clock and trigger signals note pxi clock and trigger signals are only available on pxi devices. Other devices use rtsi. Pxi_clk10 pxi_clk10 is a common low-skew 10 mhz clock reference clock for synchronization o...
Page 132
Chapter 10 digital routing and clock generation © national instruments corporation 10-9 ni 6232/6233 user manual an m series device is not a star trigger controller. An m series device may be used in the first peripheral slot of a pxi system, but the system will not be able to use the star trigger f...
Page 133
Chapter 10 digital routing and clock generation ni 6232/6233 user manual 10-10 ni.Com figure 10-4. Filter example enabling filters introduces jitter on the input signal. For the 125 ns and 6.425 µs filter settings, the jitter is up to 25 ns. On the 2.55 ms setting, the jitter is up to 10.025 µs. Whe...
Page 134: Bus Interface
© national instruments corporation 11-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 11 bus interface the bus interface circuitry of ni 6232/6233 devices efficiently moves data between host memory and the measurement and acquisition circuits. Ni 6232/6233 devices are available for the following platforms. • pci • pxi n...
Page 135: Pxi Considerations
Chapter 11 bus interface ni 6232/6233 user manual 11-2 ni.Com each dma controller supports packing and unpacking of data through the fifos to connect different size devices and optimize pci bus utilization and automatically handles unaligned memory buffers. Pxi considerations note pxi clock and trig...
Page 136: Data Transfer Methods
Chapter 11 bus interface © national instruments corporation 11-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual using pxi with compactpci using pxi-compatible products with standard compactpci products is an important feature provided by pxi hardware specification revision 2.1 . If you use a pxi-compatible plug-in module...
Page 137
Chapter 11 bus interface ni 6232/6233 user manual 11-4 ni.Com interrupt request (irq) irq transfers rely on the cpu to service data transfer requests. The device notifies the cpu when it is ready to transfer data. The data transfer speed is tightly coupled to the rate at which the cpu can service th...
Page 138: Triggering
© national instruments corporation 12-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual 12 triggering a trigger is a signal that causes an action, such as starting or stopping the acquisition of data. When you configure a trigger, you must decide how you want to produce the trigger and the action you want the trigger to c...
Page 139
Chapter 12 triggering ni 6232/6233 user manual 12-2 ni.Com • analog output generation • counter behavior.
Page 140: Device-Specific Information
© national instruments corporation a-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual a device-specific information this appendix contains device pinouts, specifications, cable and accessory choices, and other information for the ni 6232 and ni 6233 m series isolated devices. To obtain documentation for devices not liste...
Page 141
Appendix a device-specific information ni 6232/6233 user manual a-2 ni.Com figure a-1. Ni 6232 pinout table a-1. Ni 6232 device default ni-daqmx counter/timer pins counter/timer signal default pin number (name) port ctr 0 src 13 (pfi 0) p0.0 ctr 0 gate 32 (pfi 1) p0.1 ctr 0 aux 33 (pfi 2) p0.2 ctr 0...
Page 142
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview 8.X help . Ni 6232 specifications refer to the ni 6232/6233 ...
Page 143: Ni 6233
Appendix a device-specific information ni 6232/6233 user manual a-4 ni.Com vision, and motion devices. Since pxi devices use pxi backplane signals for timing and synchronization, no cables are required. Cables in most applications, you can use the following cables: • sh37f-37m- x —37-pin female-to-m...
Page 144
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-5 ni 6232/6233 user manual figure a-2. Ni 6233 pinout table a-2. Ni 6233 device default ni-daqmx counter/timer pins counter/timer signal default pin number (name) port ctr 0 src 13 (pfi 0) p0.0 ctr 0 gate 32 (pfi 1) p0.1 ctr...
Page 145
Appendix a device-specific information ni 6232/6233 user manual a-6 ni.Com note for more information about default ni-daqmx counter inputs, refer to connecting counter signals in the ni-daqmx help or the labview 8.X help . Ni 6233 specifications refer to the ni 6233 specifications , available on the...
Page 146
Appendix a device-specific information © national instruments corporation a-7 ni 6232/6233 user manual vision, and motion devices. Since pxi devices use pxi backplane signals for timing and synchronization, no cables are required. Cables in most applications, you can use the following cables: • sh37...
Page 147: Troubleshooting
© national instruments corporation b-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual b troubleshooting this section contains some common questions about m series devices. If your questions are not answered here, refer to the national instruments knowledgebase at ni.Com/kb . It contains thousands of documents that answer...
Page 148
Appendix b troubleshooting ni 6232/6233 user manual b-2 ni.Com reference the signal to the same ground level as the device reference. There are various methods of achieving this reference while maintaining a high common-mode rejection ratio (cmrr). These methods are outlined in the connecting analog...
Page 149: Analog Output
Appendix b troubleshooting © national instruments corporation b-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual analog output i am seeing glitches on the output signal. How can i minimize it? When you use a dac to generate a waveform, you may observe glitches on the output signal. These glitches are normal; when a dac s...
Page 150: Technical Support and
© national instruments corporation c-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual c technical support and professional services visit the following sections of the national instruments web site at ni.Com for technical support and professional services: • support —online technical support resources at ni.Com/support i...
Page 151
Appendix c technical support and professional services ni 6232/6233 user manual c-2 ni.Com • calibration certificate —if your product supports calibration, you can obtain the calibration certificate for your product at ni.Com/calibration . If you searched ni.Com and could not find the answers you ne...
Page 152: Glossary
© national instruments corporation g-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual glossary numbers/symbols % percent. + positive of, or plus. – negative of, or minus. ± plus or minus. Less than. > greater than. Less than or equal to. Greater than or equal to. / per. º degree. Ω ohm. A a amperes—the unit of electric c...
Page 153
Glossary ni 6232/6233 user manual g-2 ni.Com ai 1. Analog input. 2. Analog input channel signal. Ai gnd analog input ground signal. Ai sense analog input sense signal. Analog a signal whose amplitude can have a continuous range of values. Analog input signal an input signal that varies smoothly over...
Page 154
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual asic application-specific integrated circuit—a proprietary semiconductor component designed and manufactured to perform a set of specific functions for a specific customer. Asynchronous 1. Hardware—a property of an event that o...
Page 155
Glossary ni 6232/6233 user manual g-4 ni.Com cascading process of extending the counting range of a counter chip by connecting to the next higher counter. Ce european emissions control standard. Channel pin or wire lead to which you apply or from which you read the analog or digital signal. Analog s...
Page 156
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-5 ni 6232/6233 user manual counter/timer a circuit that counts external pulses or clock pulses (timing). D d gnd digital ground signal. D-sub connector a serial connector. Dac digital-to-analog converter—an electronic device, often an integrated circuit,...
Page 157
Glossary ni 6232/6233 user manual g-6 ni.Com data transfer a technique for moving digital data from one system to another. Options for data transfer are dma, interrupt, and programmed i/o. For programmed i/o transfers, the cpu in the pc reads data from the daq device whenever the cpu receives a soft...
Page 158
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-7 ni 6232/6233 user manual digital signal a representation of information by a set of discrete values according to a prescribed law. These values are represented by numbers. Digital trigger a ttl level signal having two discrete levels—a high and a low l...
Page 159
Glossary ni 6232/6233 user manual g-8 ni.Com f fifo first-in-first-out memory buffer—a data buffering technique that functions like a shift register where the oldest values (first in) come out first. Many daq products and instruments use fifos to buffer digital data from an a/d converter, or to buff...
Page 160
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-9 ni 6232/6233 user manual function 1. A built-in execution element, comparable to an operator, function, or statement in a conventional language. 2. A set of software instructions executed by a single line of code that may have input and/or output param...
Page 161
Glossary ni 6232/6233 user manual g-10 ni.Com in. Inch or inches. Instrument driver a set of high-level software functions that controls a specific gpib, vxi, or rs232 programmable instrument or a specific plug-in daq device. Instrument drivers are available in several forms, ranging from a function...
Page 162
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-11 ni 6232/6233 user manual k khz kilohertz—a unit of frequency; 1 khz = 10 3 = 1,000 hz. Ks 1,000 samples. L labview a graphical programming language. Led light-emitting diode—a semiconductor light source. Lowpass filter a filter that passes signals bel...
Page 163
Glossary ni 6232/6233 user manual g-12 ni.Com mite mxi interface to everything—a custom asic designed by national instruments that implements the pci bus interface. The mite supports bus mastering for high-speed data transfers over the pci bus. Module a board assembly and its associated mechanical p...
Page 164
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-13 ni 6232/6233 user manual ni-pgia see instrumentation amplifier . Non-referenced signal sources signal sources with voltage signals that are not connected to an absolute reference or system ground. Also called floating signal sources. Some common examp...
Page 165
Glossary ni 6232/6233 user manual g-14 ni.Com power source an instrument that provides one or more sources of ac or dc power. Also known as power supply. Ppm parts per million. Pretriggering the technique used on a daq device to keep a continuous buffer filled with data, so that when the trigger con...
Page 166
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-15 ni 6232/6233 user manual r range the maximum and minimum parameters between which a sensor, instrument, or device operates with a specified set of characteristics. This may be a voltage range or a frequency range. Real time 1. Displays as it comes in;...
Page 167
Glossary ni 6232/6233 user manual g-16 ni.Com scan rate reciprocal of the scan interval. Scc signal conditioning carriers—a compact, modular form factor for signal conditioning modules. Scxi signal conditioning extensions for instrumentation—the national instruments product line for conditioning low...
Page 168
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-17 ni 6232/6233 user manual software applications the programs that run on your computer and perform a specific user- oriented function, such as accounting, program development, measurement, or data acquisition. In contrast, operating system functions ba...
Page 169
Glossary ni 6232/6233 user manual g-18 ni.Com t out output delay time. Transducer a device that responds to a physical stimulus (heat, light, sound, pressure, motion, flow, and so on), and produces a corresponding electrical signal. See also sensor . Trigger 1. Any event that causes or starts some f...
Page 170
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-19 ni 6232/6233 user manual v m measured voltage. V oh volts, output high. V ol volts, output low. V out volts out. V s signal source voltage. Virtual channel see channel . W waveform 1. The plot of the instantaneous amplitude of a signal as a function o...
Page 171: Index
© national instruments corporation i-1 ni 6232/6233 user manual index symbols .Net languages documentation, xviii numerics 10 mhz reference clock, 10-3 100 khz timebase, 10-2 20 mhz timebase, 10-2 80 mhz source mode, 7-39 80 mhz timebase, 10-2 a a/d converter, 4-2 accessories, 2-4, a-3, a-6 choosing...
Page 172
Index ni 6232/6233 user manual i-2 ni.Com getting started with applications in software, 5-10 glitches on the output signal, 5-2 signals, 5-5 timing signals, 5-5 trigger signals, 5-4 triggering, 5-4 troubleshooting, b-3 ansi c documentation, xviii ao fifo, 5-1 ao pause trigger signal, 5-7 ao sample ...
Page 173
Index © national instruments corporation i-3 ni 6232/6233 user manual for ground-referenced signal sources, 4-14 for non-referenced signal sources, 4-15 single-ended considerations, 4-16 single-ended for floating signal sources, 4-17 single-ended for grounded signal sources, 4-17 single-ended, nrse ...
Page 174
Index ni 6232/6233 user manual i-4 ni.Com data transfer methods, 11-3 changing, 11-4 dma, 11-3 irq, 11-4 programmed i/o, 11-4 declaration of conformity (ni resources), c-1 default counter terminals, 7-31 device cabling, 2-4 information, a-1 multiple synchronization, 10-3 specifications, 1-2 diagnost...
Page 175
Index © national instruments corporation i-5 ni 6232/6233 user manual f features, counter, 7-33 field wiring considerations, 4-18 filters counter, 7-33 pfi, 8-4 pxi_star, 10-9 rtsi, 10-6 floating signal sources, 4-13 freq out signal, 7-31 frequency division, 7-25 generation, 7-24 generator, 7-24 mea...
Page 176
Index ni 6232/6233 user manual i-6 ni.Com isolation barrier, 4-2, 5-2 isolators, 9-1 k knowledgebase, c-1 l labview documentation, xvii labwindows/cvi documentation, xviii low impedance sources, 4-6 m m series information, a-1 specifications, xix measurement studio documentation, xviii measurements ...
Page 177
Index © national instruments corporation i-7 ni 6232/6233 user manual non-buffered hardware-timed acquisitions, 4-11 generations, 5-3 non-cumulative buffered edge counting, 7-5 non-referenced signal sources, differential connections, 4-15 nrse configuration, 4-16 o order of channels for scanning, 4-...
Page 178
Index ni 6232/6233 user manual i-8 ni.Com retriggerable single pulse generation, 7-22 routing clock, 10-1 digital, 10-1 rse configuration, 4-16 rtsi, 10-3 connector pinout, 3-3, 10-4 filters, 10-6 using as outputs, 10-5 using terminals as timing input signals, 10-6 s sample clock edge counting, 7-4 ...
Page 179
Index © national instruments corporation i-9 ni 6232/6233 user manual connections, nrse configuration, 4-16 connections, rse configuration, 4-16 software configuring ai ground-reference settings, 4-5 ni resources, c-1 programming devices, 2-5 timed acquisitions, 4-9 software-timed acquisitions, 4-9 ...
Page 180
Index ni 6232/6233 user manual i-10 ni.Com v voltage connecting analog input signals, 4-11 connecting analog voltage, 5-4 w waveform generation signals, 5-5 web resources, c-1 wiring, field, 4-18 x x1 encoding, 7-16 x2 encoding, 7-17 x4 encoding, 7-17.