- DL manuals
- National Instruments
- Network Hardware
- NI 653x
- User Manual
National Instruments NI 653x User Manual
Summary of NI 653x
Page 1
Daq 653 x user manual high-speed digital i/o devices for pci, pxi , compactpci, at, eisa, and pcmcia bus systems 653 x user manual ™ january 2001 edition part number 321464c-01.
Page 2
Support worldwide technical support and product information ni.Com national instruments corporate headquarters 11500 north mopac expressway austin, texas 78759-3504 usa tel: 512 794 0100 worldwide offices australia 03 9879 5166, austria 0662 45 79 90 0, belgium 02 757 00 20, brazil 011 284 5011, can...
Page 3: Important Information
Important information warranty the at-dio-32hs, daqcard-6533 for pcmcia, pci-6534, pci-dio-32hs, pxi-6533, and pxi-6534 devices are warranted against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one year from the date of shipment, as evidenced by receipts or other documentation. National ins...
Page 4: Compliance
Compliance fcc/canada radio frequency interference compliance* determining fcc class the federal communications commission (fcc) has rules to protect wireless communications from interference. The fcc places digital electronics into two classes. These classes are known as class a (for use in industr...
Page 5
• connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected. • consult the dealer or an experienced radio/tv technician for help. Canadian department of communications this class b digital apparatus meets all requirements of the canadian interference-ca...
Page 6: Conventions
Conventions the following conventions appear in this manual: angle brackets that contain numbers separated by an ellipsis represent a range of values associated with a bit or signal name—for example, dbio. » the » symbol leads you through nested menu items and dialog box options to a final action. T...
Page 7: Contents
© national instruments corporation vii 653x user manual contents chapter 1 getting started with your 653 x 653 x device overview ..................................................................................................1-1 control lines ..........................................................
Page 8
Contents 653x user manual viii ni.Com choosing whether or not to use a programmable delay .............................. 2-8 choosing continuous or finite data transfer ................................................ 2-9 finite transfers.................................................................
Page 9
Contents © national instruments corporation ix 653x user manual external req signal source ...........................................................................3-2 handshaking i/o timing diagrams...............................................................................3-4 comparing the di...
Page 10: 653
© national instruments corporation 1-1 653x user manual 1 getting started with your 653 x the 653x user manual describes installing, configuring, setting up, and programming applications for your at-dio-32hs, daqcard-6533 for pcmcia, pci-6534, pci-dio-32hs, pxi-6533, pxi-6534, or pci/pxi-7030/6533 d...
Page 11: What You Need to Get Started
Chapter 1 getting started with your 653x 653x user manual 1-2 ni.Com use group 1 and 2 to: • generate or receive digital patterns and waveforms timed by a ttl clock • transfer data between two devices using one of six configurable handshaking protocols • acquire a digital pattern every time the stat...
Page 12
Chapter 1 getting started with your 653x © national instruments corporation 1-3 653x user manual choosing your programming software when programming your national instruments measurement hardware, you can use either national instruments application software or another application development environ...
Page 13
Chapter 1 getting started with your 653x 653x user manual 1-4 ni.Com using labview, measurement studio, or virtualbench software greatly reduces the development time for your data acquisition and control application. Ni-daq driver software the ni-daq driver software shipped with your 653 x device ha...
Page 14: Installing Your Software
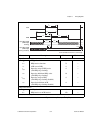
Chapter 1 getting started with your 653x © national instruments corporation 1-5 653x user manual to download a free copy of the most recent version of ni-daq, click download software at ni.Com . Find ni-daq compatibility for your device using the following table: installing your software install app...
Page 15: Installing Your 653
Chapter 1 getting started with your 653x 653x user manual 1-6 ni.Com remove the device from the package and inspect the device for loose components or any sign of damage. Notify national instruments if the device appears damaged in any way. Do not install a damaged device into your computer. Store y...
Page 16
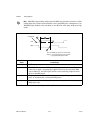
Chapter 1 getting started with your 653x © national instruments corporation 1-7 653x user manual installing the pxi-6533, pxi-6534, or pxi-7030/6533 you can install a pxi-653 x or pxi-7030/6533 device any available 5 v peripheral slot in your pxi or compactpci chassis. Note your pxi device has conne...
Page 17: Configuring The 653
Chapter 1 getting started with your 653x 653x user manual 1-8 ni.Com 5. Insert the at-dio-32hs into an at (16-bit isa) or eisa slot. It can be a tight fit, but do not force the device into place. 6. Screw the mounting bracket of the at-dio-32hs to the back panel rail of the computer. 7. Visually ver...
Page 18
Chapter 1 getting started with your 653x © national instruments corporation 1-9 653x user manual to create a virtual channel, or to learn about other capabilities of max, read the max online help by selecting help»help topics and select ni-daq from the menu. In mac os to view and test current resour...
Page 19: Using Your 653
© national instruments corporation 2-1 653x user manual 2 using your 653 x to begin using your 653 x device, navigate this chapter in the following order: 1. Choose the correct mode of operation to perform using the table below. 2. Follow the instructions for the application you want to perform. 3. ...
Page 20: Lines—Unstrobed I/o
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-2 ni.Com controlling and monitoring static digital lines—unstrobed i/o this section explains how to control and monitor static digital lines through software-timed reads and writes to and from the digital lines of your 653 x device. Configuring digital li...
Page 21
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-3 653x user manual advantages of using the wired-or driver include: • the ability to connect two or more wired-or outputs together without damaging the drivers. • the ability to connect wired-or outputs to open-collector drivers, to gnd ...
Page 22
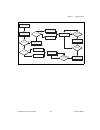
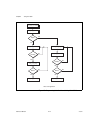
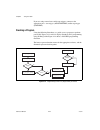
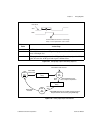
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-4 ni.Com connecting signals connect digital input signals to the i/o connector using the pinout diagrams, figures c-1, 653x i/o connector 68-pin assignments , and c-2, 68-to-50-pin adapter pin assignments . Creating a program using the following flowchart...
Page 23
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-5 653x user manual figure 2-1. Programming unstrobed i/o in ni-daq s figure 2-2. Programming unstrobed i/o in labview/labview rt programming the control/timing lines as extra unstrobed data lines if you want to use the control/timing lin...
Page 24: Devices—Handshaking I/o
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-6 ni.Com • labview—use one of the top-level vis: the read from digital line vi to read from a digital port, and the write to digital line vi to write to a digital port. The digital channel number is 4 and the port width is 4. If one of the control/timing ...
Page 25
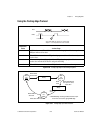
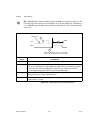
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-7 653x user manual deciding which handshaking protocol to use the 653 x device supports several different handshaking protocols to communicate with your peripheral device. The protocol you select will determine the timing of the ack and ...
Page 26
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-8 ni.Com to set the direction of the pclk signal: • ni-daq c interface—set the nd_clock_reverse_mode to nd_on in set_daq_device_info. • labview—set the clock reverse mode attribute to on in the dio parameter vi. Note for more information on labview vis an...
Page 27
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-9 653x user manual the state machine diagrams in chapter 3, timing diagrams , show more precisely where this delay occurs in the handshaking sequence. Choosing continuous or finite data transfer you can transfer data indefinitely to/from...
Page 28
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-10 ni.Com you have the option to allow it to regenerate data that has already been outputted. As in continuous input, you specify the device to allow regeneration though the olddatastop parameter in the dig_db_config function and the data overwrite/regene...
Page 29
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-11 653x user manual figure 2-3. Connecting signals if you are using the burst protocol, make the connection to the appropriate pclk pin on the 653 x device. Choosing the startup sequence to avoid invalid or missing data when the ack and ...
Page 30
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-12 ni.Com controlling the startup sequence does not apply to buffered (block) operations. In a buffered operation, the ni-daq c interface configures and enables the 653 x device at the same time, when you start the actual data transfer. For buffered opera...
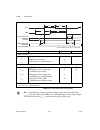
Page 31
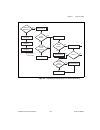
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-13 653x user manual figure 2-4. Programming buffered handshaking i/o in ni-daq read? Dig_grp_mode dig_grp_config read? Continuous? No dig_db_config yes dig_block_in dig_block_out dig_block_in dig_block_out yes no yes no yes dig_db_halfre...
Page 32
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-14 ni.Com figure 2-5. Programming unbuffered handshaking i/o in ni-daq dig_grp_config input? Dig_grp_mode dig_grp_status ready? Dig_in_grp dio_grp_config done? Dig_out_grp dig_grp_status ready? Done? Dig_in_grp dio_grp_config* no yes no yes no yes yes no ...
Page 33
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-15 653x user manual figure 2-6. Programming handshaking input in labview/labview rt dio start vi dio parameter vi dio clear vi buffered operation? Dio config vi yes burst mode? No no no reverse pclk direction? Yes yes finite buffer? Dio ...
Page 34
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-16 ni.Com figure 2-7. Programming handshaking output in labview/labview rt by default, for output buffered transfers the 6534 device will preload the on board memory with data before starting the output operation. This is done to eliminate or reduce the i...
Page 35: Waveforms—Pattern I/o
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-17 653x user manual the preloading process will cause a small delay between the start command in software and the actual start of data transfer. If this is a concern, you may disable the preloading by calling the following function/vi be...
Page 36
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-18 ni.Com deciding transfer direction you can choose to send data from your 653 x device to the peripheral device (output), or from the peripheral device to your 653 x device (input). Choosing an internal or external req source in pattern i/o, the 653 x d...
Page 37
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-19 653x user manual for example, if you specify a timebase of 100 khz and a timebase divisor of 25, the resulting acquisition/generation rate would be 4 khz. 100 khz/25 = 4 khz. Note if you are using a version of ni-daq prior to version ...
Page 38
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-20 ni.Com data is in the buffer, transfer stops. If the stop trigger arrives before all the pretrigger data is acquired, ni-daq returns an error. Figure 2-9. Stopping data transfer using a trigger start and stop trigger when using a start and stop trigger...
Page 39
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-21 653x user manual • the polarity (whether to trigger on data that matches or mismatches the specified pattern) for example, if you want to start acquisition when the two least significant bits of your data are 1 and 0, you would specif...
Page 40
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-22 ni.Com the data overwrite/regenerate parameter in the digital buffer control vi, called by the dio start vi. Continuous output similarly, with continuous output, the 653 x device continuously reads data from computer memory. As the device retrieves dat...
Page 41
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-23 653x user manual monitoring data transfer to monitor your data transfer once data transfer starts: • ni-daq c interface—call dig_block_check to monitor finite data transfer. For continuous transfers, use get_daq_device_info to obtain ...
Page 42
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-24 ni.Com if you are using external start and/or stop triggers, connect to the appropriate pins—start trigger (ack/starttrig) and/or stop trigger (stoptrig). Creating a program using the following flowcharts as a guide, create a program to perform pattern...
Page 43
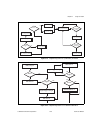
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-25 653x user manual figure 2-13. Programming pattern i/o (continuous) in ni-daq figure 2-14. Programming pattern i/o in labview/labview rt dig_db_halfready is the next half buffer ready? Dig_db_transfer dig_block_clear acquisition comple...
Page 44
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-26 ni.Com note if you are performing a finite pattern output operation, you can call the dio wait vi instead of the dio write vi after the dio start vi. For more information about these vis, see the labview help . By default, for output buffered transfers...
Page 45
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-27 653x user manual deciding which lines you want to monitor you need to specify which of the lines in your acquisition you want to monitor for changes. Specify which bits are significant to you by using a software line mask in the dig_t...
Page 46
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-28 ni.Com the three types of trigger signals available are the start trigger, the stop trigger, or the start and stop trigger. Start trigger a start trigger is a trigger that initiates a pattern i/o upon receipt of a hardware trigger on the ack (starttrig...
Page 47
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-29 653x user manual figure 2-18. Using a start and stop trigger pattern-matching trigger instead of using an external signal on the start/stop trigger pins on the i/o connector, you may start or stop (not both) an operation once a user-s...
Page 48
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-30 ni.Com figure 2-19. Pattern-detection trigger example tip to prevent a transient data value during line switching from falsely causing a match, set a valid pattern for at least 60 ns to guarantee detection. In addition, keep glitches to less than 20 ns...
Page 49
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-31 653x user manual choosing dma or interrupt transfers when using dma (by default), the 6534 device transfers data in 32-byte blocks and the 6533 device transfers data in 4 byte blocks. Therefore, at any time during a continuous operati...
Page 50
Chapter 2 using your 653x 653x user manual 2-32 ni.Com figure 2-20. Programming change detection (continuous) in ni-daq figure 2-21. Programming change detection (single buffer) in ni-daq dig_db_halfready is the next half buffer ready? Dig_db_transfer dig_block_clear acquisition complete? Yes yes no...
Page 51
Chapter 2 using your 653x © national instruments corporation 2-33 653x user manual figure 2-22. Programming change detection for labview/labview rt dio config vi trigger config vi dio read vi done? Dio clear vi yes no dio start vi specify data mask here.
Page 52: Timing Diagrams
© national instruments corporation 3-1 653x user manual 3 timing diagrams this chapter contains timing diagrams for the handshaking and pattern i/o modes. You can use these diagrams to get a detailed understanding about what happens in hardware when using these modes. Note all timing diagrams are in...
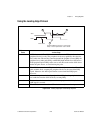
Page 53
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-2 ni.Com figure 3-1. Internal request timing diagram external req signal source use an external request when you want to time data transfers using an external signal on the req pin of the i/o connector. You can select the polarity of the req signal. If ac...
Page 54
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-3 653x user manual during, or after the req edge. If startrig is asserted too close to the req edge, it may not be recognized until the next req edge. To avoid this uncertainty, you can observe an optional setup time of 15 ns, in other w...
Page 55
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-4 ni.Com handshaking i/o timing diagrams this section compares of the handshaking i/o protocols and includes timing diagrams for each: • handshaking sequence for input operation • state machine for input operation • timing specification for input operatio...
Page 56
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-5 653x user manual in order for the 653 x device to communicate with peripheral devices in handshaking mode, it is important to verify that: • you are using complementary protocols. For example, use 8255-emulation protocol with long-puls...
Page 57
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-6 ni.Com figure 3-3. Burst transfer example (input) figure 3-4. Burst transfer example (output) note since data is transferred only when both the 653 x device and the peripheral device are ready (and thus ack and req are asserted), it is not reasonable to...
Page 58
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-7 653x user manual the 653 x device can either drive an output clock signal onto the pclk line or receive an input clock signal from the pclk line. By default, the pclk line is set for input during output transfers, and set for output du...
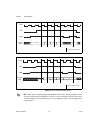
Page 59
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-8 ni.Com figure 3-5. Burst input timing diagram (default) parameter description minimum maximum input parameters t rs setup time from req valid to pclk 12 — t rh hold time from pclk to req invalid 0 — t dis setup time from input data valid to pclk 4 — t d...
Page 60
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-9 653x user manual figure 3-6. Burst output timing diagram (default) parameter description minimum maximum input parameters t pc pclk cycle time 50 — t pw pclk high pulse duration 20 — t pl pclk low pulse duration 20 — t rs setup time fr...
Page 61
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-10 ni.Com figure 3-7. Burst input timing diagram (pclk reversed) parameter description minimum maximum input parameters t pc pclk cycle time 50 — t pw pclk high pulse duration 20 — t pl pclk low pulse duration 20 — t rs setup time from req valid to pclk f...
Page 62
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-11 653x user manual figure 3-8. Burst output timing diagram (pclk reversed) parameter description minimum maximum input parameters t rs setup time from req valid to pclk 12 — t rh hold time from pclk to req invalid 0 — output parameters ...
Page 63
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-12 ni.Com using asynchronous protocols all handshaking protocols except burst are asychronous. The asynchronous protocols include 8255 emulation, level ack, leading edge, trailing edge, and long pulse. When using these protocols, you have the following op...
Page 64
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-13 653x user manual 653 x device terminology differs from 8255 terminology. • input—the req line carries the 8255 stb (strobe) input signal, and the 653 x device ack line carries the 8255 ibf (input buffer full) output signal. • output—t...
Page 65
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-14 ni.Com figure 3-10. 8255 emulation input state machine wait for space wait for req programmable delay wait for req when req unasserted, latch input data when 6533 device has space for data, input data. Clear ack when req asserted initial state: ack set...
Page 66
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-15 653x user manual figure 3-11. 8255 emulation output handshaking sequence reference point action steps 1 when the 653 x device has data to output, it asserts the ack signal, then waits for the peripheral device to assert req to indicat...
Page 67
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-16 ni.Com figure 3-12. 8255 emulation output state machine wait for data wait for req programmable delay wait for req when req unasserted when 6533 device has data to output, output data. When req asserted initial state: ack cleared output data, then send...
Page 68
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-17 653x user manual figure 3-13. 8255 emulation output timing diagram parameter description minimum maximum input parameters t r*r req low duration 75 — t rr* req high duration 75 — t a*r ack falling edge to req rising edge 0 — t dir inp...
Page 69
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-18 ni.Com using the level-ack protocol in level-ack protocol, the 653 x device asserts the ack signal when ready for a transfer and holds the ack signal level until an active-going edge occurs on the req line. After the req edge occurs, the 653 x device d...
Page 70
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-19 653x user manual figure 3-15. Level ack input state machine wait for space wait for req programmable delay programmable delay wait for req when req asserted clear ack when 6533 device has space for data, input data.* when req unassert...
Page 71
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-20 ni.Com figure 3-16. Level ack input timing diagram parameter description minimum maximum input parameters t rr* req pulse width 75 — t r*r req inactive duration 75 — t ar ack to next req 0 — t dir(1) input data setup to req active (with req-edge latchi...
Page 72
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-21 653x user manual note with req edge latching enabled (default), the req edge determines when data will be latched. Input data valid has to be held before the active going req edge a minimum of t rdi ns. With req edge disabled, input d...
Page 73
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-22 ni.Com figure 3-18. Level ack output state machine wait for data wait for req programmable delay programmable delay wait for req when req asserted clear ack when 6533 device has data to output, output data.* when req unasserted initial state: ack clear...
Page 74
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-23 653x user manual figure 3-19. Level ack output timing diagram note with req edge latching disabled (default), output data valid will hold t rdo ns after the req edge is asserted. With req edge latching enabled, that data will be held ...
Page 75
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-24 ni.Com using protocols based on signal edges the 653 x device can communicate via pulses on the ack and req lines. The three edge protocols are: • trailing-edge protocol—the trailing edge of the ack or req pulse indicates that the 653 x device or perip...
Page 76
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-25 653x user manual using the trailing-edge protocol figure 3-20. Trailing edge input handshaking sequence figure 3-21. Trailing edge input state machine reference point action steps initial state ack is deasserted. The 653 x device wait...
Page 77
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-26 ni.Com figure 3-22. Trailing edge input timing diagram note when req-edge latching is enabled (default), the req edge determines when data will be latched. Input data valid needs to be held t r*di after the trailing edge of req occurs. When req-edge la...
Page 78
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-27 653x user manual figure 3-23. Trailing edge output handshaking sequence figure 3-24. Trailing edge output state machine reference point action steps initial state ack is deasserted. 1 the 653 x device sends an ack pulse of programmabl...
Page 79
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-28 ni.Com figure 3-25. Trailing edge output timing diagram note when req-edge latching is disabled (default), output data valid will be held t r*do(1) ns after the trailing edge of req occurs. With req-edge latching enabled, output data will be held at mo...
Page 80
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-29 653x user manual using the leading-edge protocol figure 3-26. Leading edge input handshaking sequence reference point action steps initial state ack is deasserted. The 653 x device waits for an active req to indicate that the peripher...
Page 81
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-30 ni.Com figure 3-27. Leading edge input state machine wait for space wait for req programmable delay programmable delay wait for req when req asserted when 6533 device has space for data, input data.* clear ack pulse when req unasserted initial state: a...
Page 82
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-31 653x user manual figure 3-28. Leading edge input timing diagram parameter description minimum maximum input parameters t rr* req pulse width 75 — t r*r req inactive duration 75 — t ar ack to next req 0 — t dir(1) input data setup to r...
Page 83
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-32 ni.Com note with req edge latching enabled (default), the req edge determines when data will be latched. Input data valid has to be held before an active going req edge a minimum of t rdi ns. With req edge disabled, it has to be held t adi after the ne...
Page 84
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-33 653x user manual figure 3-30. Leading edge output state machine wait for data wait for req programmable delay programmable delay wait for req when req asserted clear ack pulse when req unasserted initial state: ack cleared when 653 x ...
Page 85
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-34 ni.Com figure 3-31. Leading edge output timing diagram note with req edge latching disabled (default), output data valid will hold t rdo ns after the req edge occurs. With req edge latching enabled, that data will be held for at most t rdo ns after the...
Page 86
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-35 653x user manual using the long-pulse protocol figure 3-32. Long pulse input handshaking sequence reference point action steps initial state ack is deasserted. The 653 x device waits for an active req to indicate that the peripheral d...
Page 87
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-36 ni.Com figure 3-33. Long pulse input state machine wait for space wait for req programmable delay programmable delay wait for req when req asserted when 6533 device has space for data, input data.* clear ack pulse when req unasserted initial state: ack...
Page 88
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-37 653x user manual figure 3-34. Long pulse input timing diagram parameter description minimum maximum input parameters t rr* req pulse width 75 — t r*r req inactive duration 75 — t ar ack to next req 0 — t dir(1) input data setup to req...
Page 89
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-38 ni.Com note with req edge latching enabled (default) req edge determines when data will be latched. Input data valid has to be held before active going req edge a minimum of t rdi ns. With req edge disabled, it has to be held t adi after the next activ...
Page 90
Chapter 3 timing diagrams © national instruments corporation 3-39 653x user manual figure 3-36. Long pulse output state machine wait for data wait for req programmable delay programmable delay wait for req when req asserted when 6533 device has data to output, output data.* clear ack pulse when req ...
Page 91
Chapter 3 timing diagrams 653x user manual 3-40 ni.Com figure 3-37. Long pulse output timing diagram note with req edge latching disabled (default), output data valid will hold t rdo ns after the req edge with req edge latching enabled, that data will be held for at most t rdo ns after the req edge ...
Page 92: Specifications
© national instruments corporation a-1 653x user manual a specifications this appendix lists features and specifications for your 653 x devices and the pci/pxi-7030/6533 device. Specifications are typical at 25 ° c unless otherwise noted. Digital i/o number of channels .................................
Page 93
Appendix a specifications 653x user manual a-2 ni.Com absolute max input voltage range ..........–0.3 to 5 v power-on state for outputs ......................High-impedance, pulled up or down (selectable) data transfers (all devices except daqcard)................Interrupt, dma memory at-dio-32hs .....
Page 94
Appendix a specifications © national instruments corporation a-3 653x user manual pattern i/o direction................................................. Input or output maximum sample rate (internally timed, for small transfers 1 )..................... 20 mhz minimum sample rate (internal clock rate...
Page 95
Appendix a specifications 653x user manual a-4 ni.Com power requirement +5 vdc (±5%) (with light output load) ...........................500 ma power available at i/o connector pci-dio-32hs, pxi-6533, at-dio-32hs, pci-6534, and pxi-6534 ........................+4.65 to +5.25 vdc at 1 a daqcard-6533 ...
Page 96
Appendix a specifications © national instruments corporation a-5 653x user manual nonoperational random vibration (pxi only) .............................................. 5 to 500 hz, 2.5 g rms , 3 axes note random vibration profiles were developed in accordance with mil-t-28800e and mil-std-810e m...
Page 97: Using Pxi With Compactpci
© national instruments corporation b-1 653x user manual b using pxi with compactpci you can use your pxi-653 x device as a plug-in device in a standard compactpci chassis, but you will not be able to access pxi-specific functions, such as rtsi bus features detailed in the pxi specification , rev. 1....
Page 98: Connecting Signals With
© national instruments corporation c-1 653x user manual c connecting signals with accessories this appendix describes how to connect signals to your 653 x device. Use the first part of the appendix to acquaint yourself with the device control signals. Then go to appropriate pinout diagrams (68 or 50...
Page 99
Appendix c connecting signals with accessories 653x user manual c-2 ni.Com making 68-pin signal connections caution do not make connections that exceed any of the maximum input or output ratings on the 653 x , listed in appendix a, specifications . This includes connecting any power signals to groun...
Page 100: Signal Descriptions
Appendix c connecting signals with accessories © national instruments corporation c-3 653x user manual note in figure c-1, the * indicates that you can reverse the pin assignments of the ack1 (starttig1) and req1 pins, or the ack2 (starttig2) and req2 pins. To do this, set the ack-req exchange attri...
Page 101
Appendix c connecting signals with accessories 653x user manual c-4 ni.Com table c-3. Signal descriptions pins signal name signal type signal description based on mode used 2, 9 req control group 1 and group 2 request lines handshaking i/o —request. A control line that indicates whether the peripher...
Page 102
Appendix c connecting signals with accessories © national instruments corporation c-5 653x user manual 23, 57–58, 25–26, 60–61, 28 dioc data port c bidirectional data lines port c is referred to as port number 2 in software. Dioc7 is the msb; dioc0 is the lsb. 29, 31–32, 34, 63–64, 66–67 diod data p...
Page 103
Appendix c connecting signals with accessories 653x user manual c-6 ni.Com making 50-pin signal connections figure c-2. 68-to-50-pin adapter pin assignments use table c-4 to find the accessories designed to connect to your 653 x device. Diob4 diob0 diob7 diob5 dioa7 dioa1 dioa0 dioa4 req1 pclk1 (out...
Page 104
Appendix c connecting signals with accessories © national instruments corporation c-7 653x user manual to use your 653 x device with cables, signal conditioning modules, and other accessories that require an at-dio-32f pinout, use the r6850-d1, an optional 68-to-50-pin device adapter. Using a pshr68...
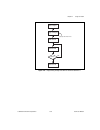
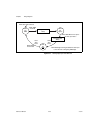
Page 105: Hardware Considerations
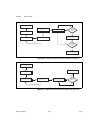
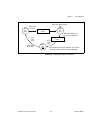
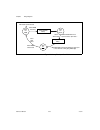
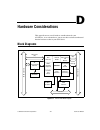
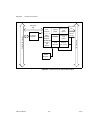
© national instruments corporation d-1 653x user manual d hardware considerations this appendix covers several hardware considerations for your 653 x device. As an advanced user, you can use these sections to understand how the hardware works in your 653 x device. Block diagrams figure d-1. At-dio-3...
Page 106
Appendix d hardware considerations 653x user manual d-2 ni.Com figure d-2. Daqcard-6533 for pcmcia block diagram daq-dio counters and timers dma/ interrupt requests handshaking and control data latches and drivers data lines data lines (32) (16) pcmcia interface pcmcia i/o channel control lines (8) ...
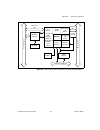
Page 107
Appendix d hardware considerations © national instruments corporation d-3 653x user manual figure d-3. Pci-dio-32hs, pci/pxi-7030/6533, and pxi-6533 block diagram daq-dio counters and timers dma/ interrupt requests handshaking and control data latches and drivers data lines data lines (32) (32) mite...
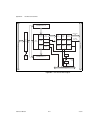
Page 108
Appendix d hardware considerations 653x user manual d-4 ni.Com figure d-4. Pci/pxi-6534 block diagram handshaking and control request processing data latches and drives internal fifos bus interface dma/irq counter and timers clock selection daq-dio bus interface scarab interface scarab interface fpg...
Page 109: Power-On State
Appendix d hardware considerations © national instruments corporation d-5 653x user manual power-on state when the computer is first turned on, all lines are configured for input and in the high-impedance state. By default, the data and control lines in the 653 x device are pulled down, even if the ...
Page 110
Appendix d hardware considerations 653x user manual d-6 ni.Com you can connect the +5 v pin to the cpull and dpull pins to control the bias of the 653 x device control and data lines, as described in the power-on state section earlier in this chapter. Caution do not connect the +5 v power pin direct...
Page 111
Appendix d hardware considerations © national instruments corporation d-7 653x user manual using the schottky-diode termination scheme you can terminate a cable that acts as a uniform transmission line in several ways. If your 653 x device is driving a cable, use the following termination scheme: co...
Page 112
Appendix d hardware considerations 653x user manual d-8 ni.Com figure d-5. Transmission line terminations note run the signal lines through special metal conduits to protect them from magnetic fields caused by electric motors, welding equipment, breakers, or transformers. If you are using the schott...
Page 113
Appendix d hardware considerations © national instruments corporation d-9 653x user manual there is no specific cutoff frequency at which termination becomes necessary. Note a purely resistive termination scheme is not recommended because of the current drawn by the termination resistors. For exampl...
Page 114
Appendix d hardware considerations 653x user manual d-10 ni.Com rtsi and pxi trigger bus interfaces you can use the seven bidirectional rtsi lines on the rtsi bus to share signals between devices. Use the rtsi bus interface to synchronize multiple cards or change control signals with multiple device...
Page 115
Appendix d hardware considerations © national instruments corporation d-11 653x user manual rtsi and pxi bus triggers the seven rtsi lines on the rtsi bus provide a very flexible interconnection scheme for any device sharing the rtsi or pxi-trigger bus. Any control signal on the device can connect t...
Page 116
© national instruments corporation e-1 653x user manual e optimizing your transfer rates use this appendix to determine the maximum transfer rate for your device, optimize transfer rates, and to see example benchmark results. Determining the maximum transfer rates the maximum sustainable transfer ra...
Page 117
Appendix e optimizing your transfer rates 653x user manual e-2 ni.Com obtaining the fastest transfer rates to achieve the highest transfer rates possible, consider the following: • burst mode is the fastest handshaking protocol. You can further increase speed by using short cables. • minimize the nu...
Page 118
Appendix e optimizing your transfer rates © national instruments corporation e-3 653x user manual interpreting benchmark results use benchmark results to get a general idea of what transfer rates to expect for an application. Since these results are system dependent, they are not to be used as speci...
Page 119
Appendix e optimizing your transfer rates 653x user manual e-4 ni.Com at-dio-32hs the following benchmarks are results using a dell dimension xps, 600 mhz, piii, and windows 98 se. Pci-dio-32hs the following benchmarks are results using a gateway 550 mhz piii, 128 mb ram, and windows 98 se. Table e-...
Page 120
Appendix e optimizing your transfer rates © national instruments corporation e-5 653x user manual pxi-6533 the following benchmarks are results using a pxi-8170, 450 mhz piii, and windows 98. Pattern i/o– continuous retransmit output 4 1.81 1.81 burst protocol– continuous input 19.93 19.6 19.05 burs...
Page 121
Appendix e optimizing your transfer rates 653x user manual e-6 ni.Com daqcard-6533 for pcmcia the following benchmarks are results using a pxi-8170, 450 mhz piii, and windows 98. Pci-6534 the following benchmarks are results using a dell dimension xps t600r, 600 mhz piii, 128 mb ram, and windows 98 ...
Page 122
Appendix e optimizing your transfer rates © national instruments corporation e-7 653x user manual pxi-6534 the following benchmarks are results using a pxi-8170, 450 mhz piii, and windows 98. Burst protocol– single shot* input 20 20 20 output 20 20 20 burst protocol– continuous retransmit** output 2...
Page 123
Appendix e optimizing your transfer rates 653x user manual e-8 ni.Com pci-7030/6533 with labview rt the following benchmarks are results using a 133 mhz amd 486dx5 class processor, and the real-time operating system running on labview rt. Pxi-6533 with labview rt the following benchmarks are results...
Page 124
Appendix e optimizing your transfer rates © national instruments corporation e-9 653x user manual pattern i/o– continuous retransmit output 2.50 1.25 1.25 burst protocol– continuous input 19.98 19.97 19.97 output 19.97 17.72 8.60 table e-10. Pci-7030/6533 benchmark results (continued) mode benchmark...
Page 125: Technical Support Resources
© national instruments corporation f-1 653x user manual f technical support resources web support national instruments web support is your first stop for help in solving installation, configuration, and application problems and questions. Online problem-solving and diagnostic resources include frequ...
Page 126: Worldwide Support
Appendix f technical support resources 653x user manual f-2 ni.Com worldwide support national instruments has offices located around the world to help address your support needs. You can access our branch office web sites from the worldwide offices section of ni.Com . Branch office web sites provide...
Page 127: Glossary
© national instruments corporation g-1 653x user manual glossary prefix meaning value k- kilo- 10 3 µ- micro- 10 – 6 m- milli- 10 –3 m- mega- 10 6 n- nano- 10 –9 numbers/symbols ° degrees – negative of, or minus less than > greater than ≤ less than or equal to ≥ greater than or equal to Ω ohms / per...
Page 128
Glossary 653x user manual g-2 ni.Com a a amps ack acknowledge—handshaking signal driven by the 653 x device, indicating that it is ready to transfer data ade application development environment api application programming interface—a standardized set of subroutines or functions along with the parame...
Page 129
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-3 653x user manual channel pin or wire lead to which you apply or from which you read the analog or digital signal. For digital signals, you group channels to form ports. Ports usually consist of either four or eight digital channels. Compactpci core spe...
Page 130
Glossary 653x user manual g-4 ni.Com default setting a default parameter value recorded in the driver. In many cases, the default input of a control is a certain value (often 0) that means use the current default setting . Device a plug-in data acquisition board, card, or pad that can contain multip...
Page 131
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-5 653x user manual g group a collection of one, two, or four ports and an associated timing controller. All buffered operations must be performed on groups. H handshaking i/o data-transfer mode in which the 653 x device engages in a two-way communication...
Page 132
Glossary 653x user manual g-6 ni.Com m m mega—the standard metric prefix for 1 million or 10 6 , when used with units of measure such as volts and hertz measurement & automation explorer (max) a controlled centralized configuration environment that allows you to configure all of your national instru...
Page 133
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-7 653x user manual pretrigger acquiring data that occurs before a trigger propagation delay the amount of time required for a signal to pass through a circuit protocol the exact sequence of bits, characters and control codes used to transfer data between...
Page 134
Glossary 653x user manual g-8 ni.Com sample rate the number of samples a system takes over a given time period, usually expressed in samples per second software trigger a programmed event that triggers an event such as data acquisition stoptrig see control signals strobed i/o any operation where eve...
Page 135
Glossary © national instruments corporation g-9 653x user manual w wired-or output driver that drives its output pin to 0 v for logic low, but tri-states the pin (puts the pin in the high-impedance state) for logic high.
Page 136: Index
© national instruments corporation i-1 653x user manual index numbers +5 v signal, description (table), c-5 653 x devices. See also hardware; specific device name. Configuring, 1-8 to 1-9 installing, 1-6 to 1-8 overview, 1-1 to 1-2 requirements for getting started, 1-2 software programming choices, ...
Page 137
Index 653x user manual i-2 ni.Com long-pulse protocol input handshaking sequence (figure), 3-35 input state machine (figure), 3-36 input timing diagram (figure), 3-37 output handshaking sequence (figure), 3-38 output state machine (figure), 3-39 output timing diagram (figure), 3-40 polarity for hand...
Page 138
Index © national instruments corporation i-3 653x user manual dma or interrupt transfers, 2-31 finite, 2-30 overview, 2-26 port and timing controller combinations (table), 2-26 to 2-27 programming, 2-31 to 2-33 continuous change detection in ni-daq (figure), 2-32 labview/labview rt (figure), 2-33 si...
Page 139
Index 653x user manual i-4 ni.Com rate of data transfer, 2-18 to 2-19 triggering data transfer, 2-19 to 2-21 width of data to transfer, 2-17 delay, programmable, handshaking protocol, 2-8 to 2-9 digital i/o specifications, a-1 to a-2 digital lines. See static digital lines. Digital patterns and wave...
Page 140
Index © national instruments corporation i-5 653x user manual output handshaking sequence (figure), 3-15 output state machine (figure), 3-16 output timing diagram (figure), 3-17 asynchronous protocol, 3-12 burst protocol input timing diagram, 3-5 to 3-11 default timing diagram (figure), 3-8 pclk rev...
Page 141
Index 653x user manual i-6 ni.Com board, rtsi, and pxi bus clocks, d-10 rtsi and pxi bus triggers, d-11 sink and source current, d-9 i initialization order, handshaking i/o, 2-11 to 2-12 installation at-dio-32hs, 1-7 to 1-8 daqcard-6533 for pcmcia, 1-8 pci-dio-32hs, pci-6534, or pci-7030/6533 device...
Page 142
Index © national instruments corporation i-7 653x user manual o optimizing transfer rates, e-1 to e-9 benchmark results, e-3 to e-9 at-dio-32hs (table), e-4 daqcard-6533 for pcmcia (table), e-6 pci-6534, e-6 to e-7 pci-7030/6533 with labview rt (table), e-8 pci-dio-32hs (table), e-4 to e-5 pxi-6533 ...
Page 143
Index 653x user manual i-8 ni.Com transfer example (figure), 3-6 description (table), c-4 frequency selection for programmable delay, 2-8 to 2-9 handshaking i/o and pattern i/o (table), c-1 signal direction for burst protocol, 2-7 to 2-8 physical specifications, a-4 pin assignments 50-pin signal con...
Page 144
Index © national instruments corporation i-9 653x user manual output timing diagram (figure), 3-17 overview, 3-12 to 3-13 burst input timing diagrams default input timing diagram (figure), 3-8 pclk reversed (figure), 3-10 transfer example (figure), 3-6 burst output timing diagrams output timing diag...
Page 145
Index 653x user manual i-10 ni.Com pin assignments (figure), c-6 68-pin signal connections, c-2 to c-3 accessories (table), c-3 pin assignments (figure), c-2 change detection, 2-31 control signals (table), c-1 handshaking i/o, 2-10 to 2-11 optional equipment, c-7 pattern i/o, 2-23 to 2-24 signal des...
Page 146
Index © national instruments corporation i-11 653x user manual stop trigger change detection, 2-28 pattern i/o, 2-19 to 2-20 system integration, by national instruments, f-1 t technical support resources, f-1 to f-2 terminating cables. See cable selection and termination. Timing diagrams, 3-1 to 3-4...
Page 147
Index 653x user manual i-12 ni.Com w waveforms. See pattern i/o. Web support from national instruments, f-1 wired-or output, unstrobed i/o, 2-2 to 2-3 worldwide technical support, f-2.