- DL manuals
- NC
- Utility Vehicle
- SW6
- Maintenance Instructions Manual
NC SW6 Maintenance Instructions Manual
Summary of SW6
Page 1
Sw6 site dumper maintenance instruction manual nc engineering (hamiltonsbawn) ltd 2 killyrudden road, hamiltonsbawn, co armagh, bt61 9sf tel: 028 38871970 fax: 028 38870362 email: sales@nc-engineering.Com www.Nc-engineering.Com revision-e orginalinstructions.
Page 2
2 dear customer even if you have operated this type of equipment before, it is very important that your new equipment operations and instructions are explained to you by a dealer representative following delivery of your equipment. This will explain the operating controls and enable you to gain maxi...
Page 3: Foreword
3 foreword this manual has been produced to provide information on the correct operating and maintenance procedures for the nc dumper the procedures in this publication relate specifically to the nc dumper all information, specifications and illustrations used in this manual are correct at the time ...
Page 4: Contents
4 contents page no. Declaration of conformity 5 noise level declaration 6 vibration declaration 7 technical information 8 maintenance decals descriptions 15 safety decals and descriptions 17 6t pst maintenance manual 19 service record 20 service schedules 21 torque settings 24 fluids and lubricants ...
Page 5
5 engineering (hamiltonsbawn)ltd. Manufacturers of agricultural and industrial equ i pment 2 killyrudden road, hamiltonsbawn, tel: 028 38871970 richhill, co. Armagh. Fax: 028 3887 0362 northern ireland. E.Mail: info@nc engineering.Com 8t619sf www.Nc-engineering.Com ec – declaration of conformity mac...
Page 6: Noise Level Declaration
6 noise level declaration the noise levels are measured according to iso6395:1998 the noise level of this machine is l wa 103db ( a ) l pa 85db ( a ) l wa :- a - weighted sound power level. L pa :- a - weighted sound pressure level..
Page 7: Vibration Declaration.
7 vibration declaration. The absence of a harmonised test code together with variable conditions under which this equipment may be used allows only representative figures to be quotes. Whole body vibration level : a w (m/s²) = 0.25 hand / arm : a ha ( m/s² ) ≤ 2.4 the above figures are for reference...
Page 8: Technical Specifications
8 technical specifications capacity: max. Safe load: 6000 kg heaped: 3150l struck: 2215l water: 1645l engine: jcb444t 4 cylinder turbo displacement: 4.4 l max. Power: 74.5kw/100bhp @ 2200 rpm max. Torque: 425nm @ 1300 rpm emissions: euro 2 compliant transmission: torque converter c/w 4 speed forward...
Page 9: Technical Specifications
9 technical specifications basic engine data emission compliance tier 2 / stage 2 rated speed 2200rpm number of cylinders 4 nominal bore size 103mm ( 4.055 in ) stroke 132mm ( 5.16 in ) cylinder arrangement in line combustion cycle 4-stroke firing order (1 at front {crankshaft pulley} end) 1-3-4-2 d...
Page 10: Technical Specifications
10 technical specifications torque + angle explanation insufficient preload of a bolted joint can cause major problems, such as cylinder head warp, leaking gasket joints etc. There are several methods of achieving an accurate preload of a bolted joint, the two main methods used on the jcb 444 engine...
Page 11: Technical Specifications
11 technical specifications engine torque figures item torque setting angle nm lbf ft fan belt tensioner retaining bolts 22-26 16-19 - item torque setting angle nm lbf ft oil sump retaining bolts a 22-26 16-19 - oil sump plug b 40-60 30-44 - item torque setting angle nm lbf ft rocker cover retaining...
Page 12: Technical Specifications
12 technical specifications engine torque figures item torque setting angle nm lbf ft water inlet connector retaining 22-26 16-19 - bolts item torque setting angle nm lbf ft water temperature sender / switch 22-26 16-19 - item torque setting angle nm lbf ft cold start advance switch 22-24 16-19 - it...
Page 13: Technical Specifications
13 technical specifications engine torque figures item torque setting angle nm lbf ft inlet manifold retaining bolts 22-26 16-19 - item torque setting angle nm lbf ft high pressure fuel pipes 25-29 19-22 - item torque setting angle nm lbf ft power take off (pto) pump bolts - sae ‘a’ - m10 bolts 43-5...
Page 14: Technical Specifications
14 technical specifications engine torque figures item torque setting angle nm lbf ft starter motor retaining bolts 43-51 32-38 - item torque setting angle nm lbf ft alternator retaining bolts 47 34.7 item torque setting angle nm lbf ft oil cooler drain plug 20-25 15-18 item torque setting angle nm ...
Page 15
15 maintenance decal descriptions the machine is fitted with a maintenance decal. It is important that before using the ma- chine the decal is understood and all the checks have been carried out. The decal must be clean and readable at all times. If the decal needs to be replaced it can be obtained ...
Page 16
16 maintenance decal descriptions ref no. Symbols description. 15 grease point - steering ram. 16 grease point - drive shafts. 17 transfer box oil level. 18 transmission oil filter. 19 oil pressure filter. 20 axle oil. 21 engine oil filter. 22 fuel filter. 23 check drive shaft bolts. 24 air filter e...
Page 17: Safety Decals
17 safety decals and descriptions safety decals the machine is fitted with a number of safety decals placed in areas to draw the attention of the users. It is important that before using the machine theses decals are read and un- derstood. The decals must be clean and readable at all times, if they ...
Page 18
18 safety decals and descriptions part no. Symbol. Descriptions. Dec~1920-011 gear locations. Dec~1920-012 seat belt must be worn. Dec~1920-013 don’t operate controls until operators manual has been read. Dec~1920-014 recommended brake fluid. Dec~1920-015 recommended brake fluid ( circular ) dec~192...
Page 19: 6T Pst Maintenance Manual
19 6t pst maintenance manual the following maintenance sections are provided to ensure safe working practices. The procedures in this booklet should be followed. No attempt should be made to shortcut any of the steps. You or others could be killed or seriously injured if the machine is not correctly...
Page 20: Service Record Sheet
20 service record sheet first 50 hr. Date……………………. Hour reading………….. First 100 hr. Date……………………. Hour reading………….. First 500 hr. Date……………………. Hour reading………….. First 1000 hr. Date……………………. Hour reading………….. First 1500 hr. Date……………………. Hour reading………….. First 2000 hr. Date……………………. Hour readin...
Page 21: Service Schedules
21 service schedules calendar equilivants 50 hours = weekly 100 hours = fortnightly 500 hours = six months 1000 hours = yearly 2000 hours = 2 years service checks should be carried out at which ever interval occurs first. Do not use a machine which is due for a service. Make sure any defects found d...
Page 22: Axle
22 axle service points & fluid levels operation 10 hr 50 hr 100 hr 1000 hr 2000 hr hubs check for leaks ● ● ● ● axle oil level (incl. Hubs when applicable) check ● ● ● ● axle oil change ● ● ● tightness of mounting bolts (torque to 970nm / 715lbf ft) ● ● ● ● ● tightness of wheel rim nuts (torque to 6...
Page 23: Service Schedules
23 service schedules dumper chassis grease points operation 10 hr 50 hr 100 hr 500 hr 1000 hr skip pivot pins (2 no pins) ● slew ring (4 no points) ● ● tipping ram pins (2 no pins) ● slew rams (2 no points) ● drive shafts (3 no points) ● ● skip stopper flap (1 no point) ● centre point articulation (...
Page 24: Torque Settings
24 torque settings use these torque settings only where no torque setting has been specified in the text. Values are for dry threads and may be within 3% of the figures stated. For lubricated threads the values should be reduced by one third. Unf grade “s” bolts bolt size hexagon (a/f) torque settin...
Page 25: Fluids & Lubricants
25 fluids & lubricants engine lubricating oil new engines do not require a running-in period. The dumper should be used in a normal work cycle immediately. Glazing of the piston cylinder bores, resulting in excessive oil consumption, could occur if the engine is gently run in. Under no circumstance ...
Page 26: Fluids & Lubricants
26 fluids & lubricants fuel specification the quality and grade of fuel can seriously affect the lubrication and overall service life of the fuel injection pump. It is vitally important that the correct grade of fuel is used. Pre- filters and water separators must be checked daily and cleaned if nec...
Page 27: Fluids & Lubrication
27 fluids & lubrication gearbox oil nc recommend fuchs titan t04hd10 (up to 30°c ambient) alternative suppliers 1 : shell spirax cx10, mobil trans hd10, bp autran 4 10 nc recommend t04hd30 (for temperatures above 30°c ambient) alternative suppliers 1 : shell spirax cx30, mobil trans hd30, bp autran ...
Page 28: Fluids & Lubrication
28 fluids & lubrication non-geared slew ring nc recommend fuchs renolit ep2 grease alternative suppliers 1 : general grease points multi purpose grease 1 do not mix different type of oils / grease as they may react with each other. If topping up use the same type of oil or fully drain oil before usi...
Page 29: For Your Safety
29 for your safety if the dumper develops a fault • park the machine in a safe area if possible. If this is not possible take measures to warn others of the machine position. • remove the start switch key. • contact a qualified person to rectify the fault. • do not place any part of the body in any ...
Page 30: Maintenance
30 maintenance before you start • clean the machine before starting any maintenance. • allow the machine to cool. • ensure strict cleanliness is observed at all times. • do not smoke near any fluids. • beware of scalding from hot oils, check oil temperature before draining. • when checking fluid lev...
Page 31: Battery Location
31 battery location the battery is located in the left-hand footstep assembly. It is accessed by turning the key lock (a) on the side and then pulling the step (b) upwards and towards the step. Battery • always wear safety glasses when working on the battery. • always disconnect the negative (-) bat...
Page 32: Maintenance
32 maintenance air cleaner servicing the air cleaner needs serviced when the red line on the visual indicator line (a) reads 75 kpa, the box on the indicator labelled service when red (b) will also be filled. This should be one of the daily machine checks. Maximum protection for the engine against d...
Page 33: Maintenance
33 maintenance checking coolant level always check the coolant level when engine is cold this is a pressurised cooling system to prevent scalding never remove the filler cap when the coolant is hot hot coolant will burn you. Always check the engine is cool before checking the coolant level or draini...
Page 34: Maintenance
34 maintenance checking engine oil level • clean away all dirt from around the dipstick and tube. • ensure the engine oil is warm (not hot) and dumper is positioned on firm, level ground. • pull the dipstick (a) from the engine, wipe the oil off the dipstick using clean paper roll. • put the dipstic...
Page 35: Maintenance
35 maintenance draining engine oil it is illegal to pollute, drains, sewers or the ground. Clean up all spilt fluids and or lubricants. Used fluids and or lubricants, filters and contaminated materials must be disposed of in accordance with local regulations. Use authorised waste disposal sites. • e...
Page 36: Maintenance
36 maintenance gearbox lubrication to ensure proper lubrication and operating temperatures it is important that the appropriate lubricants are used and the correct oil level maintained. This level should be checked daily. Nc recommend fuchs titan t04 hd10. Gearbox oil level checking ensure the engin...
Page 37: Maintenance
37 maintenance changing gearbox oil • when changing the oil it is essential to renew the oil filter and clean out the suction strainer. • ensure the transmission oil is cool but warm to allow it to flow easily. • drain the oil by removing the strainer (b). • oil will gush out, keep clear of hot oil ...
Page 38: Maintenance
38 maintenance towing procedure reconnecting drive shafts the propshafts must have both ends on exactly the same plane as shown in x. The yokes must not be at right angles as in y or at an intermediate angle as shown in z. When reconnecting always apply loctite 242 to the threads of all flange bolts...
Page 39: Maintenance
39 maintenance brake system the brake system is filled with high grade hydraulic oil. Do not use conventional brake fluid. This will cause serious damage to the dumper and degrades the brake performance to dangerous levels. Nc recommend fuchs renoil hvz15 the brake system is filled via a fluid reser...
Page 40: Maintenance
40 maintenance transmission parking brake the parking brake is mounted on the transmission gearbox and can be accessed from the underside of the dumper. Wear can occur either by stretching of the handbrake cable, or wear on the disc pads themselves, causing a reduction in efficiency. Brake pads gene...
Page 41: Maintenance
41 maintenance adjusting the parking brake (continued) on this machine the parking brake when fully engaged disconnects the transmission drive. The machine is prevented from driving with the park brake engaged. To complete the test move the park brake lever fractionally forward until the warning lig...
Page 42: Maintenance
42 maintenance axles the axles have totally enclosed & sealed multi-plate brakes and compensate automatically for brake wear. As the brakes wear ensure the fluid reservoir is kept topped up to the max level. Over a period of time wear may necessitate replacement of the friction discs and / or the sl...
Page 43: Maintenance
43 maintenance hydraulic system the hydraulic system provides power to the steering, skip swivel and skip tip functions. The hydraulics consists of an engine driven pump drawing oil from a tank. In the tank there is a suction strainer, filter and breather cap fitted, the tank is made from a transpar...
Page 44: Maintenance
44 maintenance hydraulics during any hydraulic maintenance extreme care should be taken to ensure cleanliness of the hydraulic circuit. By observing strict hydraulic cleanliness the machine will benefit from fewer hydraulic failures through contamination. Always • thoroughly clean the machine before...
Page 45: Maintenance
45 maintenance draining hydraulic oil before draining the hydraulic tank ensure the hydraulic oil is warm not hot and the skip is fully lowered. • place a suitable container under the tank and remove the drain plug (a) allowing the oil to fully drain. • remove the blanking plate (b) and ensure insid...
Page 46: Maintenance
46 maintenance storage if the dumper is to be stored for a long period of time the following procedures should be applied. • thoroughly wash down the exterior of the machine and remove any build-up of material. • grease all greasing points. • start the engine to warm it up. Drain the engine oil and ...
Page 47: Maintenance
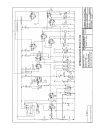
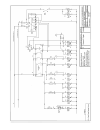
47 maintenance electrics relay & fuse box layout description specification battery 663 type: 800cca, 115ampere-hour capacity alternator 95a belt driven the alternator is very sensitive to temperature. High temperatures will affect the performance of the alternator and may eventually cause damage to ...
Page 48
48.
Page 49
49.
Page 50: Fault Finding
50 fault finding introduction the dumper must be correctly parked and prepared. Maintenance personnel must be suitably qualified and trained. Failure to observe these this notice could result in serious injury of yourself or others the fault finding procedures are given in the form of flow charts ea...
Page 51: Fault Finding
51 fault finding chart a1—dumper will not start or difficult to start (no exhaust smoke) cause remedy no fuel in tank. Check the level in the fuel tank and replenish as required. Display gauge not powering up. • check battery. • check main line fuses 30a & 100a. • check fuses in fuse box behind the ...
Page 52: Fault Finding
52 fault finding chart a2—dumper will not start or difficult to start (exhaust smoke) cause remedy cold starting aid not working (if fitted). Check for the correct operation of the cold start advance. Intake air insufficient. Visually check the air intake and exhaust intake for blockage or obstructi...
Page 53: Fault Finding
53 fault finding chart a3—engine will not crank or cranks slowly cause remedy starting electrical connections loose or corroded. Clean and tighten connections. Battery charge low. Check battery voltage, charge the battery or replace as required. Make sure that the alternator is functioning correctly...
Page 54: Fault Finding
54 fault finding chart a4—engine starts then stops cause remedy no fuel supply in tank. Check the level in the fuel tank and replenish as required. Engine starting under load. Check for added loading form malfunctioning accessories or driven units, brakes dragging and other changes in the vehicle lo...
Page 55: Fault Finding
55 fault finding chart a5—engine poor running cause remedy condition occurs only at idle. Refer to chart a6 for possible poor running at idle faults. Engine is cold. Cold starting aid is not working. Check for the correct operation of the cold start advance. If the engine will not reach operating te...
Page 56: Fault Finding
56 fault finding chart a6—engine poor running at idle cause remedy engine is cold. Cold starting aid is not working. Check for the correct operation of the cold start advance. If the engine will not reach operating temperature, refer to chart d3. Idle speed too low for accessories. Adjust the idle s...
Page 57: Fault Finding
57 fault finding chart a7—engine excessive noise cause remedy drive belt squeal, insufficient tension or abnormally high loading. Check the tensioner and inspect the drive belt for deterioration. Make sure the water pump, tensioner pulley, fan and alternator turn freely. Check for paint/oil or other...
Page 58: Fault Finding
58 fault finding chart a8—engine compression knocks cause remedy fuel is aerated. Check the fuel system for loose connections and possible air ingress points. Rectify and bleed the fuel system. Fuel is contaminated or incorrect grade of diesel used. Refer to fluids & lubricants section for recommend...
Page 59: Fault Finding
59 fault finding chart a9—engine reduced power output cause remedy no fuel supply in the tank. Check the level in the fuel tank and replenish as required. Oil level incorrect. Check oil level. Engine overloaded. Check for added loading from malfunctioning accessories or driven units, brakes dragging...
Page 60: Fault Finding
60 fault finding chart a9—engine reduced power output (continued) cause remedy exhaust leak at the manifold or turbocharger. Check/correct leaks in the manifold or turbocharger gaskets. Look for a cracked manifold. Extra injector sealing washer installed under injector. Remove extra injector sealing...
Page 61: Fault Finding
61 fault finding chart a10—engine will not reach maximum rpm cause remedy tachometer faulty (if fitted). Verify the engine speed with a hand held tachometer. Measure on the fan drive pulley and this will be the engine rpm. Engine overloaded. Verify high idle speed without load. Investigate operation...
Page 62: Fault Finding
62 fault finding chart a11—engine rpm surges cause remedy fuel level low. Check/fill fuel tank. If the condition occurs at idle, the idle speed is set too low for the accessories. Check the engine idle rpm setting. Throttle adjustment incorrectly set or binding. Check the engine maximum rpm is as sp...
Page 63: Fault Finding
63 fault finding chart a12—engine excessive vibration cause remedy engine not running smoothly/missing. Refer to chart a5. Oil level over full. Check oil level. If the condition occurs at idle, the idle speed is set too low for the accessories. Check the engine idle rpm setting. Fan damaged or acces...
Page 64: Fault Finding
64 fault finding chart a13—engine exhaust smoke excessive (black smoke) cause remedy engine being lugged down. Use appropriate gear for the task. Air intake or exhaust system is blocked. Visually check the air intake and exhaust intake for blockage or obstruction-remove as required. Check the air fi...
Page 65: Fault Finding
65 fault finding chart a14—engine exhaust smoke excessive (white/blue smoke) cause remedy fuel is contaminated or incorrect grade of diesel used. Refer to fluids & lubricants section for recommended diesel fuels. If the fuel is suspect, verify by operating the engine with clean fuel from a temporary...
Page 66: Fault Finding
66 fault finding chart a15—engine will not shut off cause remedy electrical fuel shut-off solenoid (esos) valve not functioning properly. Check for correct operation of the esos. Worn or malfunction fuel injection pump (fip). Injection pump not delivering fuel. Check for operation of the fip. The fi...
Page 67: Fault Finding
67 fault finding chart b1—fuel consumption excessive cause remedy additional load on engine. Check/repair accessories and vehicle components. Operator technique. Review operation for correct gear shifts, deceleration and idling. Fuel leaks. Check for external leaks and engine lubricating oil dilutio...
Page 68: Fault Finding
68 fault finding chart b2—fuel/oil leaking from exhaust manifold cause remedy operating for extended periods under light or no load. Review operation for correct gear shifts, deceleration and idling. Intake air or exhaust leaks. Refer to charts a13 & a14. Turbocharger lubricating oil drain line obst...
Page 69: Fault Finding
69 fault finding chart c1—lubricating oil consumption excessive cause remedy oil leaks. Inspect the engine for visible signs of leaks. Pay particular attention to the seals, gaskets, oil cooler and external connections. Oil level over full. Check oil level. Incorrect lubricating oil. (specification ...
Page 70: Fault Finding
70 fault finding chart c2—lubricating oil contaminated cause remedy coolant in the lubricating oil, internal engine component leaks. Refer to chart d1. Lubricating oil sludge excessive. Change oil & filter. Review/reduce the lubricating oil change intervals. If operating in arduous conditions change...
Page 71: Fault Finding
71 fault finding chart c3—lubricating oil pressure low cause remedy incorrect lubricating oil. (specification of viscosity). Make sure the correct lubricating oil is being used, refer to fluids & lubricants section. Look for reduced viscosity from dilution with fuel. Fuel dilution in lubricating oil...
Page 72: Fault Finding
72 fault finding chart c4—lubricating oil pressure high cause remedy incorrect lubricating oil. (specification of viscosity). Make sure the correct lubricating oil is being used, refer to fluids & lubricants section. Look for reduced viscosity from dilution with fuel. Fuel dilution in lubricating oi...
Page 73: Fault Finding
73 fault finding chart d1—coolant loss cause remedy incorrect coolant level. Check the level. Coolant leaking from engine radiator. Visually inspect the radiator hoses and connections to locate the leak. If oil is present in the coolant, check for an engine oil cooler leak. External engine coolant l...
Page 74: Fault Finding
74 fault finding chart d2—coolant over temperature cause remedy incorrect coolant level. Check the level. Ensure low level is not a result of a coolant leak. Refer to chart d1. Radiator matrix blocked with dirt or chaff. Clean radiator matrix. Air flow to the radiator restricted clean the mesh grill...
Page 75: Fault Finding
75 fault finding chart d3—coolant under temperature chart d4—coolant contaminated cause remedy air flow across radiator excessive. Check/repair the mesh grill on the bonnet. Check/repair the fan shroud, anti recirculation sealing. Check fan blades replace if necessary. Temperature gauge sensor fault...
Page 76: Fault Finding
76 fault finding chart e1—dumper gearbox a if the transmission is noisy start at check 1 b if the transmission is overheating start at check 4 c if the transmission will not pull start at check 12 d if there is no drive in one or both directions start at check 17 e if the transmission is jumping out...
Page 77: Fault Finding
77 fault finding chart e1—dumper gearbox (continued) check action 9 does the noise continue when the direction selector is in forward or reverse? Yes: check 10 no: check 11 10 is the transmission misaligned? Yes: renew mountings and check position. No: check “converter out” pressure and flow. 11 are...
Page 78: Fault Finding
78 fault finding chart e1—dumper gearbox (continued) check action 24 is the counter shaft or it bearings worn or damaged? Yes: renew damaged parts. No: check 25 25 is there excessive backlash in the gears? Yes: adjust by checking shaft end float. No: check 26 26 is the main shaft pilot bearing worn?...
Page 79: Fault Finding
79 fault finding chart e1—dumper gearbox (continued) check action 40 are chips wedged between splines of shaft or gear? Yes: remove chips no: ensure that clutch is disengaged when dump pedal is pressed. 41 are steel chips embedded in the bronze? Yes: continue using, chips will either embed blow bron...