- DL manuals
- NCR
- Printer
- 7158
- Owner's Manual
NCR 7158 Owner's Manual
Summary of 7158
Page 1
Ncr 7158 thermal receipt and impact printer release 1.0 owner's guide b005-0000-1112 issue d.
Page 2
The product described in this book is a licensed product of ncr corporation. Ncr is a registered trademark of ncr corporation. It is the policy of ncr corporation (ncr) to improve products as new technology, components, software, and firmware become available. Ncr, therefore, reserves the right to c...
Page 3: Preface
Owner's guide i preface important information to the user in order to ensure compliance with the product safety, fcc and ce marking requirements, you must use the power supply, power cord, and interface cable, which were shipped with this product or which meet the following parameters: power supply ...
Page 4: How to Use This Book
Ii owner's guide how to use this book use this book as a training guide for teaching users how to operate the printer or as a reference for programming the host computer to communicate with the printer. In addition, information is also provided about the character sets and graphics that are availabl...
Page 5: Table of Contents
Owner's guide iii table of contents chapter 1: about the printer introducing the 7158 printer................................................................1-1 standard features .................................................................................1-2 connectivity features .................
Page 6
Iv owner's guide chapter 3: using the printer printer controls.....................................................................................3-1 changing the receipt paper ................................................................3-3 replacing the ribbon cassette............................
Page 7
Owner's guide v check flip option ....................................................................3-28 basic troubleshooting ........................................................................3-29 printer beeps ...................................................................................
Page 8
Vi owner's guide standard receipt features.............................................................5-5 optional features ...........................................................................5-7 reliability .......................................................................................
Page 9
Owner's guide vii electrical interfaces ......................................................................5-26 switch settings..............................................................................5-27 character sets............................................................................
Page 10
Viii owner's guide chapter 7: programming guide command conventions .......................................................................7-1 list of commands and location.........................................................7-2 by command code ......................................................
Page 11
Owner's guide ix additional remote diagnostics .............................................7-19 comparison chart........................................................................7-20 command descriptions .....................................................................7-22 printer functio...
Page 12
X owner's guide print and eject slip...................................................................7-36 print and carriage return.......................................................7-37 feed n print lines.....................................................................7-37 feed n dot rows...
Page 13
Owner's guide xi select or cancel user-defined character set .......................7-58 define user-defined characters ............................................7-59 defining user-defined characters for the slip and receipt station ....................................................................
Page 14
Xii owner's guide transmit peripheral device status ........................................7-86 request alternate status (parallel only) ..............................7-87 transmit printer status ...........................................................7-88 transmit printer id.......................
Page 15
Owner's guide xiii set absolute vertical print position in page mode ...........7-127 set relative vertical print position in page mode.............7-128 macro commands ......................................................................7-129 start or end macro definition ............................
Page 16
Xiv owner's guide request printer id..................................................................7-152 return segment number status of flash memory ...........7-152 select flash memory sector to download..........................7-153 get firmware crc...............................................
Page 17: Revision Record
Owner's guide xv uninstalling the drivers ..............................................................8-17 troubleshooting ..................................................................................8-19 frequently asked questions.............................................................8...
Page 18
Xvi owner's guide radio frequency interference statements federal communications commission (fcc) information to user this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class a digital device, pursuant to part 15 of fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable pro...
Page 19: About The Printer
Chapter 1: about the printer introducing the 7158 printer the 7158 is an extremely fast, quiet, and reliable point-of-sale printer. It consists of two specialized printers in one compact package: a thermal printer on top that prints receipts, and an impact slip printer in front to print on forms and...
Page 20: Standard Features
1-2 chapter 1: about the printer standard features connectivity features industry standard rs-232c interface for communication with the host computer; other interfaces are available as options. • cash drawer kickout connector and software support for up to two cash drawers. Advanced interface design...
Page 21: Thermal Receipt Printer
Chapter 1: about the printer 1-3 thermal receipt printer • extremely fast and quiet thermal printhead. • no ribbon or ink cartridge to change. • drop-in paper loading. • double high, double wide, bold, inverse, underlined, superscript and subscrip, italics, scalable and rotated print modes. • reside...
Page 22: Impact Slip Printer
1-4 chapter 1: about the printer impact slip printer • bi-directional impact printhead designed for a very long life. • snap-on ribbon cassette. • prints on forms up to five plies. • horizontal flatbed slip table with an optional extension (which is standard with the micr check reader option). • for...
Page 23: Options
Chapter 1: about the printer 1-5 options connectivity options • rs-232c is supported on all printers. Usb is also supported on some later models. • communications cables are available for rs-232c and usb. • power supplies are available in 55 watt or 75 watt versions. • 3-pin to 6-pin power connectio...
Page 24: Model Identification Key
1-6 chapter 1: about the printer model identification key a758 model id key a 7 5 8 - x x x x 1 = no knife 5 = knife 0 = no micr 1 = micr 2 = micr and check flip 5 = check flip 0 = 512k flash memory (standard) 1 = 1mb flash memory 2 = 2mb flash memory 1 = standard color.
Page 25
Chapter 1: about the printer 1-7 the set of options installed on a particular printer can be determined by looking at the printer's model number. The printer's model number appears on a label on the right side of the printer. Four-digit model numbers are assigned to the various 7158 models based on ...
Page 26
1-8 chapter 1: about the printer.
Page 27: Setup Guide
Chapter 2: setup guide unpacking the printer save all packing materials in case you need to repack the printer. Check that the materials shipped with the printer match. • printer enclosed in a plastic bag and foam pack • thermal receipt paper roll (inside receipt bucket) • test printout protecting t...
Page 28: Choosing A Location
2-2 chapter 2: setup guide choosing a location 178 mm (7.0 in.) 280 mm (11.0 in.) 229 mm (9.0) 264 mm (10.4 in.) 347 mm (13.7 in.) extended slip table receipt cover the 7158 printer takes up relatively little counter space and may be set on or near the host computer. With the rs-232c interface, you ...
Page 29
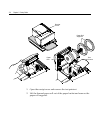
Chapter 2: setup guide 2-3 remove the packing restraints front cover cardboard support carriage foam restraint 1. Open the front cover, remove the foam restraint holding the carriage. 2. Remove the cardboard support from the slip path..
Page 30
2-4 chapter 2: setup guide receipt cover paper roll paper roll supports test printout 1. Open the receipt cover and remove the test printout. 2. Lift the thermal paper roll out of the paper bucket and remove the paper roll supports..
Page 31: Connecting The Cables
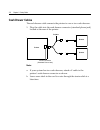
Chapter 2: setup guide 2-5 connecting the cables caution: connect the cables to the printer before plugging in the power supply. If power is received from the host computer, turn it off before connecting any cables. Back of printer strain relief dip switches communication connector (9-pin connector ...
Page 32: Cash Drawer Cables
2-6 chapter 2: setup guide cash drawer cables the cash drawer cable connects the printer to one or two cash drawers. 1. Plug the cable into the cash drawer connector (standard phone jack) located at the rear of the printer. Printer y-cable drawer drawer printer connector (standard phone jack) note: ...
Page 33: Power Supply Cable
Chapter 2: setup guide 2-7 power supply cable connect the power supply cable last. 1. Plug the power cord into the power supply. Communications cable to the communications connector strain relief cash drawer cable power supply or adapter cable cash drawer cable 2. Route the cash drawer and the power...
Page 34: Loading Receipt Paper
2-8 chapter 2: setup guide loading receipt paper 1. Tear off the end of the roll so that the edge is loose. 2. Place the roll into the paper bucket with the paper unrolling from the bottom of the roll, and with a few inches of paper extending over the cabinet front. Note: paper must unroll from the ...
Page 35
Chapter 2: setup guide 2-9 4. Remove the excess paper by tearing it against the tear-off blade. 5. Press the paper feed button to advance the paper..
Page 36
2-10 chapter 2: setup guide putting in the ribbon cassette note: you must use an approved ncr ribbon cassette with the check flip option to prevent jamming or other ribbon problems. 1. Unwrap and tighten the ribbon by turning the knob on the cassette in the direction of the arrow. Caution: do not re...
Page 37: Testing The Printer
Chapter 2: setup guide 2-11 testing the printer the configuration menu allows you to set general printer parameters. The test prints a list of various printer settings and partially cuts the paper if a knife is installed. The test printouts may vary depending on the printer model. To change the defa...
Page 38
2-12 chapter 2: setup guide configuration menu and print test samples (shown approximately 60% of size). Caution: be extremely careful changing any of the printer settings to avoid inadvertently changing other settings that might affect the performance of the printer. 3. Press the paper feed button ...
Page 39: Using The Printer
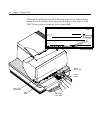
Chapter 3: using the printer printer controls front cover slip in led (green) slip or check extended slip table receipt receipt cover reset button on-line, paper status, error led (green) paper feed button the printer has the following controls: • the paper feed button advances the receipt paper. • ...
Page 40
3-2 chapter 3: using the printer the printer also indicates its status when it is first turned on, or after it has been reset, by beeping. A single beep indicates the printer has successfully completed its startup routine. But if the printer beeps in a single, double, or triple pattern at first powe...
Page 41: Changing The Receipt Paper
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-3 changing the receipt paper change the paper when either a colored stripe appears on the receipt paper or the printer’s on line, paper status, error led slowly flashes (indicating that 5 + 10 feet of paper remains on the roll). Change the paper as soon as possible to ...
Page 42
3-4 chapter 3: using the printer 1. Open the cover and remove the used roll. 2. Tear off the end of the new roll so that the edge is loose. 3. Place the roll into the paper bucket with the paper unrolling from the bottom of the roll, and with a few inches of paper extending over the cabinet front. P...
Page 43
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-5 replacing the ribbon cassette change the impact printer’s ribbon cassette if it is printing lightly. Note: you must use an approved ncr ribbon cassette with the check flip option to prevent jamming or other printing problems. Front cover ribbon cassette (shown in pos...
Page 44
3-6 chapter 3: using the printer 1. Open the printer’s front cover and pinch the tabs of the old ribbon cassette to remove it. Ribbon cassette knob mylar shield front cover ribbon cassette (shown in position) printhead 2. Unwrap and tighten the new ribbon by turning the knob on the cassette in the d...
Page 45: Printing On Forms Or Checks
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-7 printing on forms or checks there are several types of transactions that may require the insertion of a form or check into the printer: • credit card transaction • multiple-part forms such as credit transactions or merchandise returns • electronic funds transfers • c...
Page 46
3-8 chapter 3: using the printer although the illustration on the following page shows a check being inserted into the printer, these instructions apply to any type of form. The 7158 can print on forms up to five parts thick. Slip table extended slip table ¦ pay to the order of $ dollars 19 memo 200...
Page 47
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-9 to print on a form or check: 1. Insert the form or check (check shown in the illustration) from the front and place it on the slip table with the print side up. If the form is extra long, you may need to insert it from the side. A slight resistance may be felt when t...
Page 48
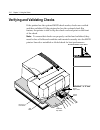
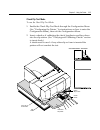
3-10 chapter 3: using the printer verifying and validating checks if the printer has the optional micr check reader, checks are verified and then validated. If the printer also has the optional check flip feature, the printer is able to flip the check over and print on the front of the check. Note: ...
Page 49
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-11 to verify and validate a check: 2. Place the check, face down on the slip table, with the bottom edge of the check to the right. Move the check to the right until it aligns against the check guide. 3. Slide the check straightforward into the printer until it stops. ...
Page 50
3-12 chapter 3: using the printer clearing check flip paper jams check check flip window door.
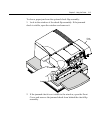
Page 51
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-13 to clear a paper jam from the optional check flip assembly: 1. Look in the window of the check flip assembly. If the jammed check is visible, open the window and remove it. Front cover 2. If the jammed check is not visible in the window, open the front cover and rem...
Page 52: Testing The Printer
3-14 chapter 3: using the printer testing the printer the configuration menu allows you to set general printer parameters. The test prints a list of various printer settings and partially cuts the paper if a knife is installed. The test printouts may vary depending on the printer model. The printout...
Page 53
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-15 configuration menu and print test samples (show approximately 60% of size)..
Page 54: Printer Configuration
3-16 chapter 3: using the printer printer configuration printers are generally shipped with all appropriate configuration settings pre-set at the factory. The only time the user should need to change the printer configuration is if a new option is installed or the firmware is changed. It is also pos...
Page 55: Configuring The Printer
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-17 • hardware options print density maximum power knife options paper low sensor printhead resistance micr option check flip option configuring the printer use the configuration menu to select functions or change various settings as indicated in the preceding sections....
Page 56
3-18 chapter 3: using the printer 1. Set dip switch 1 to on. Front of printer reset button front cover.
Page 57
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-19 2. Press the reset button while holding the paper feed button. The printer beeps, prints the current configuration, then prints the first selection. 3. Follow all the instructions on the scrolling menu..
Page 58: Communication Interface
3-20 chapter 3: using the printer 4. Press the paper feed button to make the selections. The instructions indicate whether to select something with a short click, a long click, or a series of short clicks. Indicate yes with a long click, no with a short click. Press and hold the paper feed button fo...
Page 59: Diagnostic Modes
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-21 diagnostic modes this function allows the user to put the printer into the following diagnostic modes: • normal mode: this is the normal operating mode of the printer. • datascope mode: the receipt printer prints incoming commands and data in hexadecimal format. • r...
Page 60
3-22 chapter 3: using the printer 3. Run a transaction from the host computer. All commands and data sent from the host computer will be printed as hexadecimal numbers as shown in the illustration. To exit the datascope mode: 1. 1. Enter the configuration menu again. 2. Disable the datascope mode. 3...
Page 61
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-23 7. Exit the configuration menu. The printer is in normal mode and can communicate with the host computer. Slip test mode to run the slip test mode: 1. Enable the slip test mode through the configuration menu, (see “configuring the printer,” for instructions on how t...
Page 62
3-24 chapter 3: using the printer 2. After enabling the micr test mode through the configuration menu, exit the configuration menu. 3. Insert a check into the slip station. (see “verifying and validating checks” section.) 4. The printer waits until a check is inserted and detected before the platen ...
Page 63
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-25 check flip test mode to run the check flip test mode: 1. Enable the check flip test mode through the configuration menu (see “configuring the printer,” for instructions on how to enter the configuration menu), then exit the configuration menu. 2. Insert a check as i...
Page 64: Emulation/software Options
3-26 chapter 3: using the printer 3. Push paper feed button. The check then goes through the flip routine only—no printing takes place. To exit the check flip test mode: 4. Enter the configuration menu again. 5. Disable the check flip test mode. 6. Exit the configuration menu. The printer is in norm...
Page 65: Hardware Options
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-27 default lines per inch this function allows the user to set the default lines per inch printed by the thermal receipt printer to 6, 7.52 or 8.13. (see “configuring the printer” for instructions on how to enter the configuration menu to change this setting.) carriage...
Page 66
3-28 chapter 3: using the printer knife option this function makes it possible to set the knife option if it is installed in the printer. This setting should only be changed if the option is added or removed. Paper low sensor paper low sensor setting makes it possible to enable or disable the paper ...
Page 67: Basic Troubleshooting
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-29 basic troubleshooting the 7158 printer is a simple, generally trouble-free printer, but from time to time minor problems may occur. For example, the power supply may be disconnected or the thermal printhead may overheat. The on line, paper status, error led on the o...
Page 68
3-30 chapter 3: using the printer if something is wrong with the printer, take the following general steps: • cycle the power of the printer and note its behavior. • check the on line, paper status, error led and compare its behavior to the table below. Status led behavior power off off firmware dow...
Page 69: Printer Beeps
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-31 printer beeps problem/symptom possible causes what to do printer beeps in a single, double, or triple pattern at first power on, the on line, paper status, error led blinks in the same pattern, and the printer won’t power up. The printer has a problem with its elect...
Page 70: Printer Will Not Print
3-32 chapter 3: using the printer printer will not print problem/symptom possible causes what to do the on line, paper status, error led is blinking and the printer won’t print. The receipt paper may be out, the cover open, the knife jammed, the supply voltage out of range, or the printhead temperat...
Page 71
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-33 on-line, paper status, error led flashes problem/symptom possible causes what to do on line, paper status, error led is blinking. Receipt paper is out. Change the paper now. Do not run a transaction without paper as the data may be lost. Change the paper immediately...
Page 72: Poor Forms Print Quality
3-34 chapter 3: using the printer poor forms print quality problem/symptom possible causes what to do printer starts to print, but stops while the form is being printed. Communication error or software error. Check the interface cable. Check that the software is working properly. Forms print is ligh...
Page 73
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-35 thermal printhead is dirty. Improper internal cable connections. Printhead is defective. Use recommended thermal receipt paper. Clean the thermal printhead with an alcohol pen. Do not spray the thermal printhead with household cleaner as this may damage it and the e...
Page 74
3-36 chapter 3: using the printer slip station, micr and flip problems problem/symptom possible causes what to do slip table led does not come on. Form or check not inserted properly. Line up the form or check against the check guide (wall) and slide it toward the back of the printer until it contac...
Page 75: Knife Does Not Operate
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-37 knife does not operate problem/symptom possible causes what to do receipt is not cut. Paper is jammed. The printer has a knife but the firmware is not configured for a knife. All other problems. Open the receipt cover, inspect the knife, and clear any jammed paper. ...
Page 76: Other Serious Problems
3-38 chapter 3: using the printer other serious problems the following problems all need to be corrected by a qualified service representative. See the next section, “contacting a service representative.” • micr check reader not operating properly • forms not feeding into the slip/forms area properl...
Page 77: Returning A Printer
Chapter 3: using the printer 3-39 returning a printer follow these instructions if you need to return a printer for servicing. 1. If you are sending the printer to ncr for repair, call ncr for a return material authorization number (rma#). Be prepared to answer questions concerning shipping and bill...
Page 78
3-40 chapter 3: using the printer a. Place receipt paper between the receipt cover and the printhead for protection. Front cover cardboard support carriage foam restraint b. Remove the ribbon cassette, move the carriage to the right, and place the foam restraint between the left side of the printer ...
Page 79: Printer & Media Supplies
Chapter 4: printer & media supplies ordering thermal paper thermal paper specifications the printer requires qualified thermal paper with the following dimensions: width diameter length 80 mm + .2 mm - .6 mm (3.15 + .008 in. - .024 in.) 90 mm max. (3.54 in.) 98 meters (322 ft.) 2.4 mil thick 73.5 me...
Page 80: Ordering Parts and Supplies
4-2 chapter 4: printer & media supplies ordering parts and supplies ordering cash drawers order cash drawers from the following suppliers: cash drawers number ncr 7052-k657 ordering power supply cord and adapters contact your sales representative to order the power supply and power cords listed in t...
Page 81: Forms Specifications
Chapter 4: printer & media supplies 4-3 ordering communication cables contact your sales representative to order the communication cables listed in the table. The numbers are for reference only. Suppliers may use other numbers. Communication cables length order number rs-232c 9-pin to 9 pin (0.7 met...
Page 82: Check Specifications
4-4 chapter 4: printer & media supplies check specifications check american standards ansi x9.13 and ansi x9.18, and international standard iso 1004 define specifications for paper. • minimum check size: 70 mm (2.75 in.) wide x 152 mm (6.00 in.) long • maximum check size: 95 mm (3.75 in.) wide x 222...
Page 83: Technical Specifications
Chapter 5: technical specifications functional description standard slip features print technology bidirectional, logic-seeking, nine wire impact printhead printhead features automatic homing and jam detection ink means 3 or 5 million character life carriage mounted ribbon cassette print resolution ...
Page 84
5-2 chapter 5: technical specifications forms capability * see notes on the following page. Maximum thickness .40 mm (.016 inch) max., 5 plies minimum .08 mm (.003 inch) minimum form reflectivity 60% minimum length: 68 mm (2.68 inches) w/o check flip option 70 mm (2.75 inches) with flip option minim...
Page 85
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-3 slip forms - recommendations the slip form should be flat and void of curls or wrinkles, especially at the top. Considerations for bound edges on slip paper (multi-page forms): • binding on the leading edge (top): best method, however paper feeding and inserti...
Page 86
5-4 chapter 5: technical specifications slip side guide paper holes and low reflection prohibited areas slip edge 19 mm (0.747 in.) 8 mm (0.315 in.) 6 mm (0.236 in.) slip/led sensor micr head slip sensor paper feed direction b a the slip/led sensors use a reflective photo sensor. • do not use paper ...
Page 87: Standard Receipt Features
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-5 micr reader – additional information • the check must be flat and void of curls, folds, or wrinkles (especially at the edges). Wrinkled checks may rub against the ribbon causing them to become ink-stained. • checks must be void of clips or staples. Paper jams,...
Page 88
5-6 chapter 5: technical specifications character sets pc code page 437 pc code page 850 pc code page 852 pc code page 858 pc code page 860 pc code page 863 pc code page 865 pc code page 866 resident additional flash memory for user-defined characters graphics 203 dpi x 203 dpi bit-mapped, input as ...
Page 89: Optional Features
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-7 optional features paper cutter rotary partial cut knife leaves 5.0 mm (0.2 inch) uncut on left edge. Slip table kits extends slip table 38 mm (1.5 in.) or 76 mm (3.0 in.) in front. The 76 mm slip table comes standard with the micr and flip options. Micr reader...
Page 90: Reliability
5-8 chapter 5: technical specifications reliability the numbers in the table refer to the mean cycles between failure (mcbf) for the items indicated. Thermal receipt printer 45 million lines impact slip printer 15 million lines impact printhead 200 million characters knife 1.5 million cuts micr chec...
Page 91: Certifications
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-9 certifications emi: • fcc, class a • industry canada, class a • vcci, class a • ce mark, class b • austel, class b safety: • ul 1950 • csa 22.2 no. 950 • ce mark (en60950).
Page 92: Temperature and Humidity
5-10 chapter 5: technical specifications physical and operating environment temperature and humidity temperature in degrees %humidity operating: w/ knife 5c to 28c ( 41f to 82f) 10 to 90 28c to 45c ( 82f to 113f) 10 to 35 operating: w/o knife 5c to 35c ( 41f to 95f) 5 to 90 35c to 50c ( 95f to 122f)...
Page 93: Receipt Media
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-11 minimum form length (feed direction) for forms inserted from the front up to the slip stop is 68 mm (2.68 inches) w/o check flip option and 70 mm (2.75 inches) w/flip option. Minimum form width (print direction) is 51 mm (2.00 inches). These minimums ensure t...
Page 94: Migration
5-12 chapter 5: technical specifications migration the 7158’s standard command set allows it to work with software written for ncr or other esc/pos™ compliant printers. The 7158 supports two modes of operation: “a756 emulation” and “a758 native” modes. When the 7158 is configured for a756 emulation ...
Page 95
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-13 slip format maximum print line width: 120.7 mm (4.752 inches) starting 3.20 mm ± 1.5 mm (.125 inch ± .060 inch) from the right edge of the form. Standard font compressed font character cell 10 half dots x 7 dots 10 half dots x 7 dots character size 7 x 7 7 x ...
Page 96
5-14 chapter 5: technical specifications slip throughput bi-directional line speed is based on a printhead speed of 260 cps. Throughput (±5%) at the standard line spacing (7.2 lpi) depends on line length expressed in characters: line length character density lines per minute 40 chars. 13.9 cpi (stan...
Page 97: Character Format
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-15 character format the 7158 can place 66 standard characters, or 80 compressed characters, or 33 rotated characters, or 330 adjacent bits of graphics (660 addressable positions) in the 121 mm (4.752 inch) wide print zone. Minimum line height is 7 dots (.097 inc...
Page 98
5-16 chapter 5: technical specifications dimension standard compressed rotated mm inch mm inch mm inch a .36 .0144 .30 .0117 .36 .0144 b .35 .0139 .35 .0139 .35 .0139 c 1.46 .0576 1.19 .0468 2.56 .1008 d 2.47 .0973 2.47 .0973 1.76 . 0695 e 1.83 .0720 1.48 .0585 3.66 .1440 f n/a n/a n/a n/a 2.11 .083...
Page 99: Receipt Printing
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-17 receipt printing receipt format, 80mm paper width print line width: 576 dots @ 8 dots/mm centered on 80 mm. Standard font compressed font character cell 13 x 24 dots 10 x 24 dots character per line 44 @ 15.6 cpi 56 @ 20.3 cpi nominal margins 4.25 mm (.167 inc...
Page 100
5-18 chapter 5: technical specifications print zone cut edge 44 standard columns = 71.5 mm (2.815 in.) 56 compressed columns = 70 mm (2.756 in.) cut edge paper width = 80 mm (3.15 in.) top margin, 17.8 mm (.70 in.) minimum printable zone, 576 dots = 72 mm (2.835 in.) nominal margins, 4 mm (0.157 in....
Page 101
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-19 when printing graphics or logos, converted from 6 dot/mm to 8 dot/mm (i.E. Designed for 7156), the printable zone is expanded to 598 dots. Character pattern for standard 15.6 cpi pitch.
Page 102
5-20 chapter 5: technical specifications character character cell 11 dots 1.368 mm 0.054 in. 13 dots 1.625 mm 0.064 in. 24 dots 3.00 mm 0.118 in. 19 dots 2.388 mm 0.094 in. B - upper case m - lower case g - with descender Ö - with ascender $ - both ascender and decsender # - graphic symbol character...
Page 103
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-21 receipt throughput: maximum throughput is achieved at any dot coverage up to 25%, which includes any amount of text. But above that, throughput is dependent on the dot coverage and available electrical power. 25% dot coverage (max speed) 50% dot coverage and ...
Page 104
5-22 chapter 5: technical specifications allowable duty cycle (measured over one minute of continuous printing) amount of dot coverage ambient temperature 25 °c 35°c 50°c 20% 100% 50% 20% 40% 50% 25% 10% 100% 20% 10% 4% partial cut knife the "partial cut" produces a partial cut that leaves 5.0 ± 1.5...
Page 105: Interface Description
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-23 interface description human interfaces • receipt paper-loading door, on top of the cabinet. The receipt station will not print when this door is open. See “loading receipt paper”. • ribbon cassette-loading door, in front of the cabinet. The slip station will ...
Page 106
5-24 chapter 5: technical specifications front cover slip in led (green) slip or check extended slip table receipt receipt cover front of printer reset button front cover on-line, paper status, error led (green) paper feed button.
Page 107: Power Requirements
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-25 dip switch back of printer off switch 1 is shown in the on position on dip switch 4 3 2 1 location of human and electrical interfaces power requirements the 7158 draws 24vdc ±10% power from its standard 55w, or optional 75w, remote supply. The 7158 printer ca...
Page 108: Electrical Interfaces
5-26 chapter 5: technical specifications electrical interfaces the 7158 rs-232c is equipped with a 9 pin male d-shell connector, which will accept an rs-232 cable with a mating female d-shell. The 7158 is equipped with a 3 pin female, which mates with the integral shielded cable on the power supply....
Page 109: Switch Settings
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-27 switch settings these are out-of-service tests or printer settings invoked via the 4 position dip switch in the back of the printer. Level 1 diagnostics is entered (or exited) by turning switch 1 on (or off) and resetting or power cycling the printer. Switch ...
Page 110
5-28 chapter 5: technical specifications code page 437.
Page 111
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-29 code page 850
Page 112
5-30 chapter 5: technical specifications code page 852.
Page 113
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-31 code page 858.
Page 114
5-32 chapter 5: technical specifications code page 860
Page 115
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-33 code page 863.
Page 116
5-34 chapter 5: technical specifications code page 865.
Page 117
Chapter 5: technical specifications 5-35 code page 866.
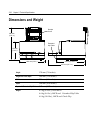
Page 118: Dimensions and Weight
5-36 chapter 5: technical specifications dimensions and weight 178 mm (7.0 in.) 280 mm (11.0 in.) 229 mm (9.0 in.) 264 mm (10.4 in.) 347 mm (13.7 in.) extended slip table receipt cover height 178 mm (7.0 inches) height with cover open 280 mm (11.0 inches) width 229 mm (9.0 inches) depth 264 mm (10.4...
Page 119: Communication Interface
Chapter 6: communication interface communication overview in order for the printer to communicate with the host, a communication link must be set up. The 7158 printer supports either the rs-232c or usb interfaces. The rs-232c interface has a protocol associated with it that the host must understand ...
Page 120: Using Basic to Send Commands
6-2 chapter 6: communication interface using basic to send commands in basic, printer commands are sent as a string of characters preceded by the lprint command. For example: lprint chr$(&h0a) sends the hexadecimal number 0a to the printer, which causes the printer to print the contents of its print...
Page 121: Rs-232C Interface
Chapter 6: communication interface 6-3 rs-232c interface the rs-232c interface uses either the xon/xoff (software) or dtr/dsr (hardware) protocol to control the flow of information between the computer and the printer. For xon/xoff, a particular character is sent back and forth between the host and ...
Page 122
6-4 chapter 6: communication interface if the application sends data at 9600 baud and pauses between lines for as short a time as 50 milliseconds, the printer will never be able to print at full speed. However, if the application sends data at 19.2 k baud and does not pause between lines, the printe...
Page 123: Rs-232C Communications
Chapter 6: communication interface 6-5 no delay after each line characters/line lines/receipt transmit time (19.2 k baud) process time* 20 20 0.2 seconds 0.5 seconds 20 40 0.4 seconds 1.0 seconds 44 20 0.44 seconds 0.5 seconds 44 40 0.88 seconds 1.0 seconds rs-232c communications the 7158 offers an ...
Page 124: Xon/xoff Protocol
6-6 chapter 6: communication interface [dtr space] - when ready to accept data. - remaining space in the 4k buffer rises above 512 bytes. ** [xon sent] - when ready to accept data after power on. - remaining space in the 4k buffer rises above 512 bytes. ** [xoff sent] - in an error state. - remainin...
Page 125: Dtr/dsr Protocol
Chapter 6: communication interface 6-7 xon character = hexadecimal 11. Xoff character = hexadecimal 13. Dtr/dsr protocol the dtr signal is used to control data transmission to and from the printer. It is driven low when the printer is ready to receive data and driven high when it cannot accept any m...
Page 126: Connector Pin-Outs
6-8 chapter 6: communication interface connector pin-outs this section describes the pin settings for the connectors on the back of the printer. Communication connectors the following illustrations show the rs-232c communication connectors and pin assignments. The connectors are located at the rear ...
Page 127
Chapter 6: communication interface 6-9 cash drawer connector a 6-contact modular jack (rj11) is available to drive a cash drawer with dedicated feedback, or up to two cash drawers without feedback. The following illustration shows the pinouts for the cash drawer connector. Pin 1 pin 6 the following ...
Page 128
6-10 chapter 6: communication interface.
Page 129: Chapter 7:
Chapter 7: programming guide command conventions the following information describes how each command is organized: name: name of command. Ascii: the ascii control code. Hexadecimal: the hexadecimal control code. Decimal: the decimal control code. Value: a description of the command operands. Range:...
Page 130: By Command Code
7-2 chapter 7: programming guide list of commands and location commands control all operations and functions of the printer. This includes selecting the size and placement of characters and graphics on the receipt or the slip and feeding and cutting the paper. Any of the commands may be used in any ...
Page 131
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-3 code (hexadecimal) command page 16 n add n extra dot rows 39 17 print 40 18 open form 23 18 cancel print data in page mode 121 19 perform full knife cut 24 1a perform partial knife cut 24 1b followed by the bmp file data characters download bmp logo 74 1b 07 generate...
Page 132
7-4 chapter 7: programming guide code (hexadecimal) command page 1b 34 m a0 a1 a2 read from user data storage 147 1b 3a 30 30 30 copy character set from rom to ram 62 1b 3c return home 25 1b 3d n select peripheral device (for multi- drop) 25 1b 3f n cancel user-defined characters 63 1b 40 initialize...
Page 133
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-5 code (hexadecimal) command page for micr read 1b 63 31 n select receipt or slip for setting line spacing 28 1b 63 33 n select paper sensors to output paper end signals (parallel only) 29 1b 63 34 n select sensors to stop printing 30 1b 63 35 n enable or disable panel...
Page 134
7-6 chapter 7: programming guide code (hexadecimal) command page 1d 00 request printer id 152 1d 01 return segment number status of flash memory 152 1d 02 n select flash memory sector to download 153 1d 03 n real time request to printer (dle sequence) 107 1d 04 n real time status transmission (gs se...
Page 135
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-7 code (hexadecimal) command page 1d 48 n select printing position for hri characters 114 1d 49 n transmit printer id 89 1d 49 40 n transmit printer id, remote diagnostics extension 91 1d 4c nl nh set left margin 51 1d 50 x y set horizontal and vertical minimum motion ...
Page 136: By Function
7-8 chapter 7: programming guide by function all items in bold are new or have additional functionality when compared to the 7156. Printer function commands code (hexadecimal command page 10 clear printer 22 11 close form 23 18 open form 23 19 perform full knife cut 24 1a perform partial knife cut 2...
Page 137
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-9 1b 7a n select or cancel parallel printing mode on r&j 32 1c select slip station 33 1d 56 m select cut mode and cut paper 34 1d 56 m n select cut mode and cut paper 34 1e select receipt station 35 1f 74 print test form 35 vertical positioning and print commands code ...
Page 138
7-10 chapter 7: programming guide horizontal positioning commands code (hexadecimal command page 09 horizontal tab 45 1b 14 n set column 45 1b 24 n1 n2 set absolute starting position 46 1b 44 [n] k 00 set horizontal tabs 47 1b 5c n1 n2 set relative print position 48 1b 61 n select justification 50 1...
Page 139
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-11 print characteristic commands code (hexadecimal command page 12 select double-wide characters 53 13 select single-wide characters 53 1b 12 select 90 degree counter-clockwise rotated print 54 1b 16 n select pitch (column width) 55 1b 20 n set character right-side spa...
Page 140
7-12 chapter 7: programming guide graphics commands code (hexadecimal command page 1b followed by the bmp file data characters download bmp logo 74 1b 2a m n1 n2 d1…dn select bit image mode 75 1b 4c n1 n2 d1…dn select double-density graphics (in a756 emulation mode) 78 1b 59 n1 n2 d1…dn select doubl...
Page 141
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-13 real time code (hexadecimal command page 10 04 n real time status transmission (dle sequence) 103 10 05 n real time request to printer (gs sequence) 107 1d 03 n real time request to printer (dle sequence) 107 1d 04 n real time status transmission (gs sequence) 103 1...
Page 142
7-14 chapter 7: programming guide page mode commands code (hexadecimal command page 0c print and return to standard mode/print and eject slip 120 18 cancel print data in page mode 121 1b 0c print data in page mode 121 1b 4c select page mode 122 1b 53 select standard mode 123 1b 54 n select print dir...
Page 143
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-15 micr parsing code (hexadecimal command page 1b 77 50 define parsing format, save in nvram 132 1b 77 70 define parsing format, do not save permanently 132 check flip commands code (hexadecimal command page 1b 77 46 check flip command 146 user data storage commands co...
Page 144
7-16 chapter 7: programming guide flash download commands code (hexadecimal command page 1b 5b 7d switch flash download mode 151 1d 00 request printer id 152 1d 01 return segment number status of flash memory 152 1d 02 n select flash memory sector to download 153 1d 06 get firmware 153 1d 07 return ...
Page 145: Comparison to 7156
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-17 comparison to 7156 new features there are a number of new firmware features in the a758 native mode. These include: 1. Page mode on the receipt 2. Additional code pages 3. Additional character attributes 4. Flip 5. More flexible handling of user-defined characters a...
Page 146
7-18 chapter 7: programming guide additional character attributes the 7158 includes support for additional character attributes including bold, italics, underline, black/white reverse print, superscript, subscript, and scaling. Flip the 7158 can flip a check on command. Additional flexibility when u...
Page 147
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-19 macro capability the 7158 supports the ability to record and execute a series of commands called a macro. Additional remote diagnostics the 7158 supports 5 additional remote diagnostics. • number of flash cycles • number of knife jams • numbers of cover openings • m...
Page 148: Comparison Chart
7-20 chapter 7: programming guide comparison chart the following table details the list of commands whose behavior differs from the 7156 because of the physical differences of a 6 dots/mm head ( 7156 ) versus an 8 dots/mm head ( 7158 ). Command description difference between 7156 and 7158 configured...
Page 149
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-21 command description difference between 7156 and 7158 configured ina 756 emulation mode. Graphics scales the graphics to provide the best match. 1b 5c n1 n2 set relative print position the parameter to this command is in units of dots. However, the command moves and ...
Page 150: Command Descriptions
7-22 chapter 7: programming guide command descriptions printer function commands the printer function commands control the following basic printer functions and are described in order of their hexadecimal codes: 1. Station select 2. Platen control 3. Resetting the printer 4. Cutting the paper 5. Ope...
Page 151
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-23 exceptions: in printers with the parallel interface, this command also returns paper exhaust to the paper status line if an alternate status has been requested. A dle command followed by an 04 or 05 is interpreted as a “real time command”. (see real time commands) c...
Page 152
7-24 chapter 7: programming guide perform full knife cut ascii: em or esc i hexadecimal: 19 or 1b 69 decimal: 25 or 27 105 cuts the receipt, leaving .20 inch (5 mm) of paper. This command is implemented the same as partial knife cut (1a, 1b 6d). There are two codes for this command. Both codes perfo...
Page 153
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-25 return home ascii: esc hexadecimal: 1b 3c decimal: 27 60 moves the impact printhead (unless already there) to the home position. Related information: the printer is able to detect carriage motor jams, eliminating the need to home the printhead after each slip transa...
Page 154
7-26 chapter 7: programming guide initialize printer ascii: esc @ hexadecimal: 1b 40 decimal: 27 64 default: receipt slip character pitch 15.6 cpi 13.9 cpi column width 44 characters 66 characters extra dot rows 2 3 character set code page 437 code page 437 printing position column one column one cl...
Page 155
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-27 select receipt or slip for printing; slip for micr read ascii: esc c 0 n hexadecimal: 1b 63 30 n decimal: 27 99 48 n value of n : 1, 2, 3 receipt selected 4 slip selected default of n : 1 selects the station for printing. When slip is selected, the printer waits (ba...
Page 156
7-28 chapter 7: programming guide select receipt or slip for setting line spacing ascii: esc c 1 n hexadecimal: 1b 63 31 n decimal: 27 99 49 n value of n: 1, 2, 3 select receipt 4 select slip default of n : 1 selects which station receives the effects of the following commands: 1. Select default lin...
Page 157
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-29 select paper sensors to output paper end signals (parallel only) ascii: esc c 3 n hexadecimal: 1b 63 33 n decimal: 27 99 51 n value of n : if either bit 0 or bit 1 is on, the paper roll near-end sensor is selected as the paper sensor outputting paper-end signals. If...
Page 158
7-30 chapter 7: programming guide select sensors to stop printing ascii: esc c 4 n hexadecimal: 1b 63 34 n decimal: 27 99 52 n value of n : bit of n bit function bit 0, 1 stop receipt on receipt low bit 4 stop slip if trailing edge uncovered bit 5 stop slip if leading edge uncovered default: 0 deter...
Page 159
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-31 enable or disable online switch ascii: esc c 6 n hexadecimal: 1b 63 36 n decimal: 27 99 54 n value of n : 0, 1 since the 7158 does not have an online switch, this command is ignored. Set slip paper waiting time ascii: esc f m n hexadecimal: 1b 66 m n decimal: 27 102...
Page 160
7-32 chapter 7: programming guide generate pulse to open cash drawer ascii: esc p n p1 p2 hexadecimal: 1b 70 n p1 p2 decimal: 27 112 n p1 p2 value of n : 0, 48 = drawer 1 1, 49 = drawer 2 value of p1 : 0 - 255 value of p2 : 0 - 255 sends a pulse to open the cash drawer. Formulas: the value for eithe...
Page 161
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-33 select slip station ascii: fs hexadecimal: 1c decimal: 28 selects the slip station for all functions. The receipt station is the default setting after the printer is initialized or the clear printer (0x10) command is received..
Page 162
7-34 chapter 7: programming guide select cut mode and cut paper ascii: gs v m gs v m n hexadecimal: 1d 56 m 1d 56 m n decimal: 29 86 m 29 86 m n value of m : selects the mode as shown in the table value of n : determines cutting position only if m is 65 or 66. M feed and cut mode 0, 48 full cut (no ...
Page 163
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-35 select receipt station ascii: rs hexadecimal: 1e decimal: 31 selects the receipt station for all functions. The receipt station is the default setting after the printer is initialized or the clear printer (0x10) command is received. Print test form ascii: ax t hexad...
Page 164
7-36 chapter 7: programming guide vertical positioning and print commands the vertical positioning and print commands control the vertical print positions of characters on the receipt and slip. Print and feed paper one line ascii: lf hexadecimal: 0a decimal: 10 prints one line from the buffer and fe...
Page 165
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-37 print and carriage return ascii: cr hexadecimal: 0d decimal: 13 prints one line from the buffer and feeds paper one line. The printer can be set through the configuration menu to ignore or use this command. Some applications expect the command to be ignored while ot...
Page 166
7-38 chapter 7: programming guide feed n dot rows ascii: nak n hexadecimal: 15 n decimal: 21 n value of n: receipt slip n/203 inch n/72 inch range of n : 0 – 127 a756 emulation mode 0 – 255 a758 native mode feeds paper n dot rows without printing. Receipt moves n rows if the print buffer is empty..
Page 167
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-39 add n extra dot rows ascii: syn n hexadecimal: 16 n decimal: 22 n value of n: receipt slip n/203 inch n/72 inch range of n : 0 - 12 default: receipt slip 3 3 adds n extra dot rows to the character height to increase space between print lines or decrease number of li...
Page 168
7-40 chapter 7: programming guide print ascii: etb hexadecimal: 17 decimal: 23 prints one line from the buffer and feeds paper one line. Executes lf on receipt. Executes lf on slip if previous character was not a cr. Set line spacing to 1/6 inch ascii: esc 2 hexadecimal: 1b 32 decimal: 27 50 default...
Page 169
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-41 set line spacing ascii: esc 3 n hexadecimal: 1b 33 n decimal: 27 51 n value of n: n/406 inches on receipt n/144 inches in slip range of n: 0 – 255 default: receipt .13 inch (3.37 mm or 7.52 lines per inch, 3 extra dot rows.) slip .14 inch (7.2 lines per inch, 3 extr...
Page 170
7-42 chapter 7: programming guide print and feed paper ascii: esc j n hexadecimal: 1b 4a n decimal: 27 74 n value of n: n/203 inches receipt n/144 inches slip range of n: 0 - 255 prints one line from the buffer and feeds the paper. On the receipt station, the line height equals the character height ...
Page 171
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-43 print and feed n lines ascii: esc d n hexadecimal: 1b 64 n decimal: 27 100 n value of n: number of lines to be printed and fed. Range of n: 1 – 255 (0 is interpreted as 1 on the receipt station) prints one line from the buffer and feeds paper n lines at the current ...
Page 172
7-44 chapter 7: programming guide reverse feed n dots ascii: gs nak n hexadecimal: 1d 15 n decimal: 29 21 n value of n: n dots at 1/72 inch range of n : 0 – 127 a756 emulation mode 0 – 255 a758 native mode reverses the paper feed in the slip station by n dots at 1/72 inch (ncr 7150™ command). This c...
Page 173
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-45 horizontal positioning commands the horizontal positioning commands control the horizontal print positions of characters on the receipt and slip. Horizontal tab ascii: ht hexadecimal: 09 decimal: 9 moves the print position to the next tab position set by the set hor...
Page 174
7-46 chapter 7: programming guide set absolute starting position ascii: esc $ n1 n2 hexadecimal: 1b 24 n1 n2 decimal: 27 36 n1 n2 value of n: number of dots to be moved from the beginning of the line. Value of n1 :remainder after dividing n by 256. Value of n2 :integer after dividing n by 256. The v...
Page 175
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-47 set horizontal tabs ascii: esc d [n] k nul hexadecimal: 1b 44 [n] k 00 decimal: 27 68 [n] k 0 value of n: column for tab minus one. N is always less than or equal to the current selected column width. Value of k: 0 - 32 default: every 8 characters from column. 1 (9,...
Page 176
7-48 chapter 7: programming guide set relative print position ascii: esc \ n1 n2 hexadecimal: 1b 5c n1 n2 decimal: 27 92 n1 n2 value of n: to move the relative starting position right of the current position by n dots: n1 = remainder after dividing n by 256. N2 = integer after dividing n by 256. The...
Page 177
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-49 65,516/256 = 255, remainder of 236 n1 = 236 n2 = 255 to move to the right: determine the value of n by multiplying the number of columns to move right of the current position by 10 (slip or receipt standard pitch) or 8 (receipt compressed pitch). The example shows h...
Page 178
7-50 chapter 7: programming guide select justification ascii: esc a n hexadecimal: 1b 61 n decimal: 27 97 n value of n: 0, 48 = left aligned 1, 49 = center aligned 2, 50 = right aligned range of n: 0 – 2, 48-50 default: 0 (left aligned) specifies the alignment of the characters, graphics, logos, and...
Page 179
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-51 set left margin ascii: gs l nl nh hexadecimal: 1d 4c nl nh decimal: 29 76 nl nh range of nl: 0 - 255 range of nh: 0 - 255 default : 576 dots (the maximum printable area) sets the left margin of the printing area. The left margin is set to (((nh x 256) + nl) times ho...
Page 180
7-52 chapter 7: programming guide set printing area width ascii: gs w nl nh hexadecimal: 1d 57 nl nh decimal: 29 87 nl nh range of nl: 0 – 255 range of nh: 0 - 255 default: 576 dots (the maximum printable area) sets the width of the printing area. If the setting exceeds the printable area, the maxim...
Page 181
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-53 print characteristic commands these commands control what the printed information looks like: selection of character sets, definition of custom-defined characters, and setting of margins. The commands are described in order of their hexadecimal codes select double-w...
Page 182
7-54 chapter 7: programming guide select 90 degree counter-clockwise rotated print ascii: esc dc2 hexadecimal: 1b 12 decimal: 27 18 rotates characters 90 degrees counter-clockwise. The command remains in effect until the printer is reset or until a clear printer (0x10), select or cancel upside-down ...
Page 183
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-55 select pitch (column width) ascii: esc syn n hexadecimal: 1b 16 n decimal: 27 22 n value of n: 0 = standard pitch 1 = compressed pitch default: 0 (standard pitch) selects the character pitch for a print line. Formulas: the following table provides the print characte...
Page 184
7-56 chapter 7: programming guide set character right-side spacing ascii: esc sp n hexadecimal: 1b 20 n decimal: 27 32 n range of n: 0 - 32 default : 0 sets the right side character spacing to [n x horizontal or vertical motion units]. Values for this command are set independently in standard and pa...
Page 185
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-57 select print modes ascii: esc ! N hexadecimal: 1b 21 n decimal: 27 33 n value of n: pitch selection (standard, compressed, double high, or double wide.) value of n bit function 0 1 bit 0 pitch standard pitch 1 44 col/line, 15.6 cpi (rec) 66 col/line, 13.9 cpi (slip)...
Page 186
7-58 chapter 7: programming guide related information: the bits in this command perform the same function as the standalone functions: 1b 16 n select pitch 1b 45 n emphasized 12 double-wide 13 single-wide 1b 2d n underline select or cancel user-defined character set ascii: esc % n hexadecimal: 1b 25...
Page 187
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-59 define user-defined characters receipt slip ascii: esc & 3 c1 c2 n1 d1 ... Nn dn esc & 0 c1 c2 d1 ... Dn hexadecimal: 1b 26 3 c1 c2 n1 d1 ... Nn dn 1b 26 0 c1 c2 d1 ... Dn decimal: 27 38 3 c1 c2 n1 d1 ... Nn dn 27 38 0 c1 c2 d1 ... Dn defines and enters downloaded c...
Page 188
7-60 chapter 7: programming guide defining user-defined characters for the slip and receipt station defines and enters downloaded characters into ram. (define user-defined characters—continued on the next page) top of character top of character receipt characters (1b 26 3) slip characters (1b 26 0) ...
Page 189
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-61 n = 1-10 (standard pitch), 12 and less accepted but ignored n = 1-8 (compressed pitch), 12 and less accepted but ignored d = the column data for the nth character as specified by d1 ... Dn the number of bytes for a particular character cell is 3 x n1. The bytes are ...
Page 190
7-62 chapter 7: programming guide select or cancel underline mode ascii: esc - n hexadecimal: 1b 2d n decimal: 27 45 n value of n: 0, 48 = cancel underline mode 1, 49 = select underline mode default of n: 0 (cancels underline mode) turns underline mode on or off. Underlines cannot be printed for spa...
Page 191
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-63 cancel user-defined characters ascii: esc ? N hexadecimal: 1b 3f n decimal: 27 63 n value of n: specified character code range of n: 32 - 255 cancels the pattern defined for the character code specified by n. After the user-defined character is canceled, the corresp...
Page 192
7-64 chapter 7: programming guide select double strike a756 emulation a758 native ascii: esc g esc g n hexadecimal: 1b 47 1b 47 n decimal: 27 71 27 71 n value of n: 0 = off 1 = on turns double strike mode on for the slip station. Overprints a second pass of the print line on the slip station to impr...
Page 193
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-65 select or cancel italic print ascii: esc i n hexadecimal: 1b 49 n decimal: 27 73 n value of n: 0 = off 1 = on (when 0 and 1 are the least significant bit, lsb) default: 0 (off) turns italic print mode on or off. This command is only available in a758 native mode. It...
Page 194
7-66 chapter 7: programming guide select international character set ascii: esc r n or esc t n hexadecimal: 1b 52 n or 1b 74 n decimal: 27 82 n or 27 116 n a758 native mode a756 emulation value of n: 0 = code page 437 0 = code page 437 1 = code page 850 1 = code page 850 2 = code page 852 3 = code p...
Page 195
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-67 select or cancel unidirectional printing mode ascii: esc u n hexadecimal: 1b 55 n decimal: 27 85 n value of n: 0 = select bi-directional 1 = select unidirectional default: 0 toggles between unidirectional and bi-directional printing on the slip station. Unidirection...
Page 196
7-68 chapter 7: programming guide select or cancel upside down printing mode ascii: esc { n hexadecimal: 1b 7b n decimal: 27 123 n value of n: 0 = cancel 1 = set default: 0 (cancel) prints upside-down characters. The character order is inverted in the buffer so text is readable. The command remains ...
Page 197
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-69 select character size ascii: gs ! N hexadecimal: 1d 21 n decimal: 29 33 n value of n: 1 - 8 = vertical number of times normal font 1 – 8 = horizontal number of times normal font range of n: 00 – 07, 10 – 17, … 70 – 77 default of n: 0 selects the character height usi...
Page 198
7-70 chapter 7: programming guide this command is effective for all characters (except for hri characters). In standard mode, the vertical direction is the paper feed direction, and the horizontal direction is perpendicular to the paper feed direction. However, when character orientation changes in ...
Page 199
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-71 select or cancel white/black reverse print mode ascii: gs b n hexadecimal: 1d 42 n decimal: 29 66 n value of n: 0 = off 1 = on (only the lowest bit is used.) range of n: 0 – 255 default of n: 0 (off) turns on white/black reverse printing mode. This command is only a...
Page 200
7-72 chapter 7: programming guide select superscript or subscript modes ascii: ax enq n hexadecimal: 1f 05 n decimal: 31 05 n value of n: 0 = normal character size 1 = select subscript size 2 = select superscript size default: 0 (normal size) turns superscript or subscript modes on or off. This attr...
Page 201
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-73 summary of rotated printing the table shows the combinations of set/cancel upside-down print, set/cancel rotated print (clockwise), and rotated print (counterclockwise). Rotated ccw is mutually exclusive with the other two commands. Unintended consequences may resul...
Page 202: Graphics Commands
7-74 chapter 7: programming guide graphics commands these commands are used to enter and print graphics data and are described in order of their hexadecimal codes. Download bmp logo ascii: esc followed by the bmp file data characters hexadecimal: 1b followed by the bmp file data characters decimal: ...
Page 203
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-75 select bit image mode ascii: esc * m n1 n2 d1 ... Dn hexadecimal: 1b 2a m n1 n2 d1 ... Dn decimal: 27 42 m n1 n2 d1 ... Dn sets the print resolution and enters one line of graphics data into the print buffer. Excess data is accepted but ignored. Any print command is...
Page 204
7-76 chapter 7: programming guide in single density, one byte (7 dots) is printed in each full dot column; in double density, one byte is printed in each half/full dot column. *adjacent horizontal dots (overlapping dots) are not printed on the slip. **in a758 native mode. There are 8 vertical dots. ...
Page 205
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-77 top of bit image 24-dot single-density mode—receipt only dn msb lsb d1 d2 d3 d4 d7 d5 d6 dn.
Page 206
7-78 chapter 7: programming guide select double-density graphics ascii: esc y n1 n2 d1 … dn or esc l n1 n2 d1 ... Dn hexadecimal: 1b 59 n1 n2 d1 ... Dn or 1b 4c n1 n2 d1 … dn decimal: 27 89 n1 n2 d1 ... Dn or 27 76 n1 n2 d1 ... Dn value of n: value of n (8-dot single density mode) value of n (24-dot...
Page 207
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-79 select the current logo (downloaded bit image) ascii: gs # n hexadecimal: 1d 23 n decimal: 29 35 n range of n: 0 – 255 selects a logo to be defined or printed. The active logo n remains in use until this command is sent again with a different logo n. When this comma...
Page 208
7-80 chapter 7: programming guide exceptions: this command is only valid for the receipt station. However, it will be processed correctly regardless of whether the receipt station is currently selected..
Page 209
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-81 define downloaded bit image ascii: gs * n1 n2 d1 ... Dn] hexadecimal: 1d 2a n1 n2 d1 ... Dn] decimal: 29 42 n1 n2 d1 ... Dn value of n1: see the following table. Value of n2: see the following table. Value of d: see the following table. Value of n1 value of n2 value...
Page 210
7-82 chapter 7: programming guide d1 d2 dn d top of g raphic dn m sb lsb c olum n colum n o ne 72 x 8 m ax. Row o ne row 64 m ax. 64 65 d exceptions: see the illustration for the print downloaded bit image command (1d 2f) for a representation of the bit image. Related information: see 1d 22 n (selec...
Page 211
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-83 print downloaded bit image ascii: gs / m hexadecimal: 1d 2f m decimal: 29 47 m value and range of m: value of m print mode vertical dpi 1 horizontal dpi* 0 1 2 3 normal double wide double high quadruple 203 203 101 101 203 101 203 101 1 dot density measured in dots ...
Page 212
7-84 chapter 7: programming guide convert 6 dots/mm bitmap to 8 dots/mm bitmap ascii: ax eot n hexadecimal: 1f 04 n decimal: 31 04 n value: 0 = off 1 = on default: 0 (off) selects or cancels 6 dot/mm in a756 emulation mode. When the 6 dot/mm emulation is selected, logos and graphics are expanded hor...
Page 213: Status Commands
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-85 status commands status command introduction the 7158 has three methods of providing status to the application. These methods are through batch status commands, real time status commands, and auto status back. An application may use one or more of these methods to un...
Page 214
7-86 chapter 7: programming guide batch mode for rs-232c printers, these commands enable the printer to communicate with the host computer following the selected handshaking protocol, either dtr/dsr or xon/xoff. They are stored in the printer's data buffer as they are received, and are handled by th...
Page 215
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-87 request alternate status (parallel only) ascii: esc u n hexadecimal: 1b 75 n decimal: 27 117 n value and range of n: value of n function description 00 drawer 1 high = open low = closed or not present 01 drawer 2 high = open low = closed or not present 02 paper low ...
Page 216
7-88 chapter 7: programming guide transmit printer status ascii: esc v hexadecimal: 1b 76 decimal: 27 118 sends status data to the host computer. The printer sends one byte to the host computer when it is not busy or in a fault condition. In dtr/dsr protocol, the printer waits for dsr = space. Statu...
Page 217
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-89 transmit printer id ascii gs i n hexadecimal 1d 49 n decimal 29 73 n value of n 1, 49 = printer model id 2, 50 = type id 3, 51 = rom version id transmits the printer id specified by n as follows: n printer id specification id (hexadecimal) 1, 49 printer model id ncr...
Page 218
7-90 chapter 7: programming guide type id (n=4) bit off/on hex decimal function 0 off 00 0 no logo definition loaded by application. On 01 1 logo loaded by application. 1 - - - undefined 2 - - - undefined 3 - - - undefined 4 off 00 0 not used. Fixed to off. 5 - - - undefined 6 - - - undefined 7 off ...
Page 219
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-91 transmit printer id, remote diagnostics extension ascii: gs i @ n hexadecimal: 1d 49 40 n decimal: 29 73 64 n values of n: refer to table range of n: 32 – 255 (not all defined but reserved) performs the remote diagnostic function specified by n. Eighteen remote diag...
Page 220
7-92 chapter 7: programming guide value of n remote diagnostic item function asc hex dec “ 22 34 serial # not available, cannot clear serial # item # 23 35 serial # return serial #, preceded by n to identify printer returns 12 bytes in above example: #1234567890 $ 24 36 class/model #, 15 digit ascii...
Page 221
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-93 value of n remote diagnostic item function asc hex dec â 83 131 receipt lines tally return receipt lines tally, preceded by n to identify printer returns 10 bytes in above example: â00010000 ä 84 132 knife cut tally, 8 digit ascii numeric, max 99,999,999 write to nv...
Page 222
7-94 chapter 7: programming guide value of n remote diagnostic item function asc hex dec É 90 144 hours on tally, 8 digit ascii numeric, max 99,999,999 write to nvram æ 91 145 hours on tally write to nvram, and print on receipt to verify Æ 92 146 hours on tally clear hours on tally to 0 ô 93 147 hou...
Page 223
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-95 value of n remote diagnostic item function asc hex dec ¡ ad 173 cover openings tally write to nvram, and print on receipt to verify « ae 174 cover openings tally clear cover openings tally to 0 » af 175 cover openings tally return cover openings tally, returns 10 by...
Page 224
7-96 chapter 7: programming guide transmit status ascii: gs r n hexadecimal: 1d 72 n decimal: 29 114 n value of n: 1, 49 = printer status 2, 50 = cash drawer status 3, 51 = slip paper status 4, 52 = flash memory status transmits the status specified by n. This is a batch mode command which transmits...
Page 225
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-97 printer status (n = 1 or n = 49) bit off/on hex decimal status for transmit status 0 off on 00 01 0 1 receipt paper adequate. Receipt paper low. 1 off on 00 02 0 2 receipt paper adequate. Receipt paper low. 2 off on 00 04 0 4 receipt paper present. Receipt paper exh...
Page 226
7-98 chapter 7: programming guide slip paper status (n = 3 or n = 51) value of byte returned slip status 0 there is no more printing space on the current slip, or the slip paper is not selected. 1 to 8 remaining print area on the current slip, in number of lines, at the currently set line spacing, w...
Page 227
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-99 recognizing data from the printer an application sending various real time and non-real time commands to which the printer responds can determine which command a response belongs to by the table below. Responses to transmit peripheral device status (1b 75) and trans...
Page 228
7-100 chapter 7: programming guide real time commands these commands provide an application interface to the printer even when the printer is not handling other commands (rs-232c communication interface only): 1. Real time status transmission (gs sequence and dle sequence) 2. Real time request to pr...
Page 229
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-101 alternate implementation the alternate implementation uses the dle (0x10) sequences as implemented on other printers. An application using these dle (0x10) sequences and the original 7156 clear printer command (0x10) must distinguish for the printer between the new...
Page 230
7-102 chapter 7: programming guide moving data through the buffer another consideration is that an application should take care not to let the buffer fill up with real time commands when the printer is busy at the rs-232c interface. A busy condition at the rs-232c interface can be determined by bit ...
Page 231
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-103 real time status transmission gs sequence dle sequence ascii: gs eot n dle eot n hexadecimal: 1d 04 n 10 04 n decimal: 29 4 n 16 4 n value of n: gs/dle sequence 1 = transmit printer status 2 = transmit rs-232c busy status 3 = transmit error status 4 = transmit rece...
Page 232
7-104 chapter 7: programming guide related information: 1 = transmit printer status bit status hex decimal function 0 off 00 0 fixed to off 1 on 02 2 fixed to on 2 off on 00 04 0 4 one or both cash drawers open both cash drawers closed 3 off on 00 08 0 8 not busy at the rs-232c interface printer is ...
Page 233
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-105 3 = transmit error status bit status hex decimal function 0 off 00 0 fixed to off 1 on 02 2 fixed to on 2 off on 00 04 0 4 no slip motor or flip jam slip motor or flip jam occurred 3 off on 00 08 0 8 no knife error knife error occurred 4 on 10 16 fixed to on 5 off ...
Page 234
7-106 chapter 7: programming guide 5 = transmit slip paper status bit status hex decimal function 0 off 00 0 fixed to off 1 on 02 2 fixed to on 2 off on 00 04 0 4 slip paper selected receipt paper selected 3 off on 00 08 0 8 not waiting for slip waiting for slip 4 on 10 16 fixed to on 5 off on 00 20...
Page 235
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-107 real time request to printer gs sequence dle sequence ascii: gs etx n or dle enq n hexadecimal: 1d 03 n or 10 05 n decimal: 29 3 n or 16 5 n value of n: 1 = recover and restart 2 = recover and clear buffers 3 = cancel slip waiting the printer responds to a request ...
Page 236
7-108 chapter 7: programming guide recovers from an error after clearing the receive and print buffers. Print settings that are normally preserved from line to line, such as character height and width, are still preserved with this command. This sequence is ignored except when the printer is busy du...
Page 237
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-109 real time printer status transmission ascii: gs enq hexadecimal: 1d 05 decimal: 29 5 transmits one byte status of the printer in real time. Value of byte: bit status hex decimal function 0 off on 00 01 0 1 receipt paper adequate receipt paper low 1 off on 00 02 0 2...
Page 238
7-110 chapter 7: programming guide auto status back select or cancel automatic status back ascii: gs a n hexadecimal: 1d 61 n decimal: 29 97 n value of n: status of asb enables or disables automatic status back (asb) and specifies the status items. This command is a batch mode command; that is, it i...
Page 239
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-111 the bits of n are defined in the table. Bit off/on hex decimal status for asb 0 off on 00 01 0 1 cash drawer status disabled. Cash drawer status enabled. 1 off on 00 02 0 2 rs-232c busy status disabled. Rs-232c busy status enabled. 2 off on 00 04 0 4 error status d...
Page 240
7-112 chapter 7: programming guide first byte (printer information) bit off/on hex decimal status for asb 0 off 00 0 not used. Fixed to off. 1 off 00 0 not used. Fixed to off. 2 off on 00 04 0 4 one or both cash drawers open. Both cash drawers closed. 3 off on 00 08 0 8 not busy at the rs232c interf...
Page 241
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-113 third byte (paper sensor information) bit off/on hex decimal status for asb 0 off on 00 01 0 1 receipt paper adequate receipt paper low 1 off on 00 02 0 2 receipt paper adequate receipt paper low 2 off on 00 04 0 4 receipt paper present. Receipt paper exhausted. 3 ...
Page 242: Bar Code Commands
7-114 chapter 7: programming guide bar code commands these commands format and print bar codes and are described in order of their hexadecimal codes. Note: 7156 firmware can be set for module widths in bar codes ranging from 2 dots to 4 dots per module (dpm) for the narrow modules. The default is 3 ...
Page 243
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-115 select pitch for hri characters ascii: gs f n hexadecimal: 1d 66 n decimal: 29 102 n value of n: pitch 0 = standard pitch at 15.2 cpi on receipt 1 = compressed pitch at 19 cpi on receipt default: 0 (standard pitch at 15.2 cpi) selects standard or compressed font fo...
Page 244
7-116 chapter 7: programming guide values: first variation: string terminated with nul character m = 0 – 6, 10 d = 32 - 126 (see the table) n = 1 - 255 (see the table) selects the bar code type and prints a bar code for the ascii characters entered. If the width of the bar code exceeds one line, the...
Page 245
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-117 the check digit is calculated for upc and jan (ean) codes if it is not sent from the host computer. Six-character zero-suppressed upc-e tags are generated from full 11 or 12 characters sent from the host computer according to standard upc-e rules. Start/stop charac...
Page 246
7-118 chapter 7: programming guide m bar code d n, length 65 upc-a 48- 57 (ascii numerals) fixed length: 11, 12 66 upc-e 48- 57 fixed length: 11, 12 67 jan13 (ean) 48- 57 fixed length: 12, 13 68 jan8 (ean) 48- 57 fixed length: 7, 8 69 code 39 48- 57, 65- 90 (ascii alphabet), 32, 36, 37, 43, 45, 46, ...
Page 247
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-119 exceptions: illegal data cancels this command. The command is valid only at the beginning of a line. Pdf 417 format cannot be printed on the slip. Barcodes on the slip are always right justified. Pdf417 and code 93 are only available in a758 native mode. Select bar...
Page 248: Page Mode Commands
7-120 chapter 7: programming guide page mode commands page mode is one of two modes, which the 7158 printer uses to operate. Standard mode is typical of how most printers operate by printing data as it is received and feeding paper as the various paper feed commands are received. Page mode is differ...
Page 249
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-121 cancel print data in page mode ascii: can hexadecimal: 18 decimal: 24 deletes all the data to be printed in the “page” area. Any data from the previously selected “page” area that is also part of the current data to be printed is deleted. This command has the same ...
Page 250
7-122 chapter 7: programming guide select page mode ascii: esc l hexadecimal: 1b 4c decimal: 27 76 switches from standard mode to page mode. After printing has been completed either by the print and return to standard mode (ff) command or select standard mode (1b 53) the printer returns to standard ...
Page 251
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-123 select standard mode ascii: esc s hexadecimal: 1b 53 decimal: 27 83 switches from page mode to standard mode. In switching from page mode to standard mode, data buffered in page mode are cleared, the printing area set by set print area in page mode (1b 57) is initi...
Page 252
7-124 chapter 7: programming guide select print direction in page mode ascii: esc t n hexadecimal: 1b 54 n decimal: 27 84 n value of n: start position selects the printing direction and start position in page mode. See the illustration. 0 = upper left corner proceeding across page to the right (a) 1...
Page 253
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-125 set printing area in page mode ascii: esc w n1, n2 ...N8.] hexadecimal: 1b 57 n1, n2 ...N8] decimal: 27 87 n1,n2 ...N8] range: 0 - 255 default: n1-4 = 0 n5 = 64 n6 = 2 n7 = 64 n8 = 2 sets the position and size of the printing area in page mode. The command can be s...
Page 254
7-126 chapter 7: programming guide 4. Dy = [(n7 + n8 x 256) x (vertical direction of the fundamental calculation pitch)] keep the following notes in mind for this command. 5. The fundamental calculation pitch depends on the vertical or horizontal direction. 6. The maximum printable area in the x dir...
Page 255
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-127 set absolute vertical print position in page mode ascii: gs $ nl nh hexadecimal: 1d 24 nl nh decimal: 29 36 nl nh formulas: [(nl + nh x 256) x (vertical or horizontal motion unit)] inches. Sets the absolute vertical print starting position for buffer character data...
Page 256
7-128 chapter 7: programming guide set relative vertical print position in page mode ascii: gs \ nl nh hexadecimal: 1d 5c nl nh decimal: 29 92 nl nh sets the relative vertical print starting position from the current position. This command can also change the horizontal and vertical motion unit. The...
Page 257: Macro Commands
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-129 macro commands these commands are used to select and perform a user-defined sequence of printer operations. Start or end macro definition ascii: gs : hexadecimal: 1d 3a decimal: 29 58 starts or ends macro definition. Macro definition begins when this command is rec...
Page 258
7-130 chapter 7: programming guide execute macro ascii: gs ^ r t m hexadecimal: 1d 5e r t m decimal: 29 94 r t m value of r: the number of times to execute the macro. Value of t: the waiting time for executing the macro. Executes a macro. After waiting for a specified period the led indicators blink...
Page 259: Micr Commands
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-131 micr commands micr reading these commands control the magnetic ink character recognition (micr) check reader, including how it parses the character strings on checks. The section, micr parsing, describes how to create a parsing format and how to create and maintain...
Page 260
7-132 chapter 7: programming guide micr parsing this section describes micr parsing in detail and includes several examples of useful parsing variations. It also describes how to create a parsing format and how to create and maintain an exception table. Define parsing format, save in nvram ascii: es...
Page 261
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-133 parsing parameter string options variable length fields variable length field name selector comments transit number t full 9 digit routing/transit number bank number b digits 4-8 of transit number check digit d digit 9 of transit number account number a check seria...
Page 262
7-134 chapter 7: programming guide other parameters error number e one digit returned 0 1 read ok read error: bad character, empty field invalid length, check digit invalid status s two digits returned 01 09 08 05 07 04 10 11 00 no micr data mexican check canadian check error in transit number error...
Page 263
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-135 ten parameters are more than enough to specify all variable length fields with a field separator each and other status information that may be helpful to an application. More than 10 parameters are not recommended because they use up space in non-volatile memory (n...
Page 264
7-136 chapter 7: programming guide sample parsing formats the following strings show various sample formats that you can use assuming they meet your parsing format needs. Included with the sample format is a description of the data that is returned to the application. Esc w p 18 a • maximum 18 chara...
Page 265
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-137 esc w p 018 x a • always 18 characters in the account number with spaces and dashes replaced with 0 • final carriage return esc w p t 18 x a 04c • all characters in the transit number • all characters in the account number (up to 18) with spaces and dashes removed ...
Page 266
7-138 chapter 7: programming guide esc w p t '/ a '/ c '/ s • all characters in the transit number • field separator: / • all characters in the account number • field separator: / • all characters in the check number • field separator: / • two-digit status • final carriage return.
Page 267
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-139 notes all parameters are ascii characters, i.E. Greater than or equal to 0x20, with the exception of a non-ascii character enclosed in single quotes as a field separator. This applies both to parameter specifications sent from application to printer, and to micr da...
Page 268
7-140 chapter 7: programming guide once a parsing format is specified, the following values are returned: micr characters ascii hexadecimal numerics space dash field separator* country code* 0...9 - 0x30...0x39 0x20 0x2d *as specified in the parsing parameter string.
Page 269
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-141 check serial number parsing the check serial number most banks print the check serial number in three easily recognizable spots. The printer firmware will look for the number in these spots, using the following ordered algorithm. The examples use letters to represe...
Page 270
7-142 chapter 7: programming guide if all of these searches fail to produce the distinct check serial number, and the check serial number field has been specified in the parsing parameter string options, no check serial number will be returned. If it is imbedded within the account number field, it w...
Page 271
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-143 loading the exception table the exception table begins at word 20 in nvram. Each entry takes five words. There is room for eight exceptions with a sumcheck written in the last word. An application can load local exceptions into the printer using the write nvram com...
Page 272
7-144 chapter 7: programming guide exception table entry format each exception table entry consists of five words. The first two words contain the first eight characters of the transit number by packing the low order nibble of the numeric transit number characters. For canadian checks, eliminate the...
Page 273
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-145 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 (check #, four characters) and 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 (account #, 10 characters) then stored in the other three words of the table entry using: 0x1b 0x73 0x24 0x4a 27 0x1b 0x73 0x00 0x00 28 0x1b 0x73 0x00 0x00 29 example 2 t22137-632t001 6042202o927540 275...
Page 274: Check Flip Command
7-146 chapter 7: programming guide which reads and returns word k in nvram. When the exception table is full, a new entry can replace an older, less frequently used entry, by merely rewriting the words for that table entry. Check flip command check flip command ascii: esc w f hexadecimal: 1b 77 46 d...
Page 275
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-147 read from user data storage ascii: esc 4 m a0 a1 a2 hexadecimal: 1b 34 m a0 a1 a2 decimal: 27 52 m a0 a1 a2 value of m: 0 – 255 reads m bytes of data from the user data storage flash page at the address specified. Read from non-volatile memory ascii: esc j k hexade...
Page 276
7-148 chapter 7: programming guide select memory type (sram/flash) where to save logos or user-defined fonts ascii: gs " n hexadecimal: 1d 22 n decimal: 29 34 n value of n: 48 - 51 specifies whether to load the logos or user-defined characters to flash memory or to ram (volatile memory). The selecti...
Page 277
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-149 flash allocation ascii: gs " u n1 n hexadecimal: 1d 22 55 n1 n2 decimal: 29 34 85 n1 n2 default value of n1: 1 (see below) default value of n2: 1 (see below) n1 is the number of 64k sectors used for logos and user-defined characters. N2 is the number of 64k sectors...
Page 278
7-150 chapter 7: programming guide erase user flash sector ascii: gs @ n hexadecimal: 1d 40 n decimal: 29 64 n value of n: 49 - 50 erases a page of flash memory and sends a carriage return when the operation is complete. N = 49 (ascii n = 1) this command erases all sectors available for user-defined...
Page 279: Flash Download Commands
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-151 flash download commands these commands are used to load firmware into the printer. The commands are listed in numerical order according to their hexadecimal codes. Each command is described and the hexadecimal, decimal, and ascii codes are listed. There are three w...
Page 280
7-152 chapter 7: programming guide request printer id ascii: gs nul hexadecimal: 1d 00 decimal: 29 0 returns ack (06 hex) + 12 bytes ascii string describing the flash memory boot sector firmware part number. Ex : 189-1234567a return segment number status of flash memory ascii: gs soh hexadecimal: 1d...
Page 281
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-153 select flash memory sector to download ascii: gs stx n hexadecimal: 1d 02 n decimal: 29 2 n value of n: the flash sector to which the next download operation applies range of n: 0 – 7 (512k) 0 – 15 (1 mb) 0 – 31 (2 mb) selects the flash sector (nn) for which the ne...
Page 282
7-154 chapter 7: programming guide return microprocessor crc ascii: gs bel hexadecimal: 1d 07 decimal: 29 7 returns the crc calculated over the boot sector code space. Formulas: ack erase the flash memory ascii: gs so hexadecimal: 1d 0e decimal: 29 14 causes the entire flash memory (except the boot)...
Page 283
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-155 erase selected flash sector ascii: gs dle n hexadecimal: 1d 10 n decimal: 29 16 n value and range of n: 0 – 7 = 512k bytes flash 0 – 15 = 1m bytes flash 0 – 31 = 2m bytes flash erases the previously selected sector. The printer transmits ack when the sector has bee...
Page 284
7-156 chapter 7: programming guide download to active flash sector ascii: gs dc1 al ah cl ch d1…dn hexadecimal: 1d 11 al ah cl ch d1…dn decimal: 29 17 al ah cl ch d1…dn value of al = low byte of the address value of ah = high byte of the address value of cl = low byte of the count value of ch = high...
Page 285
Chapter 7: programming guide 7-157 reboot the printer ascii: gs (space) hexadecimal: 1d ff decimal: 29 255 ends the load process and reboots the printer. Before executing this command, the printer should have firmware loaded and external switches set to the runtime settings. Application software for...
Page 286
7-158 chapter 7: programming guide.
Page 287: Universal Serial Bus
Chapter 8: universal serial bus about the universal serial bus the universal serial bus (usb) is a peripheral bus for personal computers that was first released in january 1996. Since that time, virtually all intel architecture personal computers have the hardware to support usb, and a large number ...
Page 288
8-2 chapter 8: universal serial bus additional pos devices. Some pos systems are required to host more peripherals than can be supported by two rs-232 ports typical in a platform. With the addition of one (or two) usb connectors, the platform can now support the additional devices that had previousl...
Page 289: Host Configuration
Chapter 8: universal serial bus 8-3 checking for usb support on the host computer to make usb work, the pos must be factory equipped with a usb port. With the required hardware in place, windows 98 and 95 (os r2.1) natively support plug-and-play usb with a built-in driver; windows nt does not, and t...
Page 290
8-4 chapter 8: universal serial bus note: even though the host may have a usb port, windows nt does not natively support plug-and-play usb because it does not have a built-in driver. You will need to load the ncr windows nt usb driver (see “installing the usb printer drivers”)..
Page 291
Chapter 8: universal serial bus 8-5 configuring ncr pos printers for usb installing the ncr 7158 usb upgrade kit if you’re upgrading the printer, you may need to upgrade the firmware and must install a usb board. If your printer is factory configured for usb, proceed to “configuring the printer.” to...
Page 292
8-6 chapter 8: universal serial bus 7. Return dip switch no.1 to the original off (down) position. 8. When you’re finished, plug the printer in again. The led remains on without blinking. The printer is now operational. You can print out a diagnostics form to verify that the boot and flash versions ...
Page 293
Chapter 8: universal serial bus 8-7 4. Remove the options board by gripping it at the connector end and lifting up. You may need to wiggle it slightly back and forth as you pull. 5. Firmly seat the usb board onto the controller board (where you just removed the options board) by carefully aligning t...
Page 294: Configuring The Printer
8-8 chapter 8: universal serial bus configuring the printer usb is a plug-and-play environment. As such, neither the printer nor the host requires user configuration to work. However, since the ncr solution simulates a serial communication interface, you must configure “handshaking” on the printer f...
Page 295
Chapter 8: universal serial bus 8-9 dip switch back of printer off switch 1 is shown in the on position on dip switch 4 3 2 1 3. Open the front cover of the printer and press the reset button, while pressing the paper feed button. The printer beeps, prints the current configuration, then waits for y...
Page 296
8-10 chapter 8: universal serial bus follow the instructions on the scrolling menu, pressing the paper feed button to make selections. Indicate yes with a long click, and no with a short click. • press and hold the paper feed button for at least one second for a long click. • press the paper feed bu...
Page 297
Chapter 8: universal serial bus 8-11 8. Follow the instructions to select either xon/off or dtr/dsr, then skip the remaining communications parameters. 9. When you have finished, set dip switch 1 to off (down). 10. Press the reset button. The printer resets with the new selection. You can verify the...
Page 298: Installing The Drivers
8-12 chapter 8: universal serial bus installing the usb printer drivers you must have lpin d370-1111-0100 to install the required drivers to support the usb printers note: nt users should exit out of all windows programs before starting installation. Load from ncr lpin d370-1111-0100 1. Insert disk ...
Page 299
Chapter 8: universal serial bus 8-13 2. To start the installation program, plug one end of the usb cable into the usb connector port on the printer. Route the cable from the printer, as shown, to provide strain relief and plug the other end into the host computer. Make sure the usb symbol on the con...
Page 300: Checking The Installation
8-14 chapter 8: universal serial bus checking the installation you’ll need to verify that the device drivers were installed correctly: windows 95 and 98: 1. Open the device manager window, as you did in “checking for usb support.” 2. Scroll down to “universal serial bus controllers.” the following d...
Page 301
Chapter 8: universal serial bus 8-15 3. Scroll back up to “ports.” you should see a com number and port description for the ncr printer. If the devices are missing or are not listed correctly, the installation wasn’t successful. You will need to reinstall the drivers. Windows nt: go the windows star...
Page 302: Running The Edgeport Utility
8-16 chapter 8: universal serial bus configuring serial port number assignments this section described how the ncr usb solution assigns serial port numbers (e.G., comx) to the printer. The information that determines the assigned port number is stored in the host computer and not in the printer. Thi...
Page 303: Uninstalling The Drivers
Chapter 8: universal serial bus 8-17 serial port configuration methods automatic (default). When the printer is plugged into the usb port of the host and the drivers are loaded, the printer will default to the next available serial port number. In many cases this is exactly what is desired. You can ...
Page 304
8-18 chapter 8: universal serial bus windows nt: windows nt users will need to run the edgeport configuration utility to uninstall the drivers. 1. Press windows start menu button. 2. Choose programs, then inside out networks utilities. 3. Choose edgeport configuration utility. 4. Click the advanced ...
Page 305: Troubleshooting
Chapter 8: universal serial bus 8-19 troubleshooting problem solution device not working. Check for conflicting usb devices. Check comport assignment in application. Reconnect usb connector to pc..
Page 306: Frequently Asked Questions
8-20 chapter 8: universal serial bus frequently asked questions usb printer performance under windows 95 normally sending output to a usb printer results in a print speed slightly faster than that obtained using the highest baud rate of 115200 under rs-232. Our performance testing typically yields b...
Page 307: Index
Index —a— a758 printer advanced interface design, 1-2 configuration, 3-16 connectivity features, 1-2 description, 5-1 dimensions, 5-36 documentation, 4-4 electronics and software, 1-2 introducing, 1-1 migration, 5-12 optional features, 5-7 ordering supplies, 4-1 receipt features, 5-5 reliability, 5-...
Page 308
Index-2 code page 850, 5-29 code page 852, 5-30 code page 858, 5-31 code page 860, 5-32 code page 863, 5-33 code page 865, 5-34 code page 866, 5-35 character sets, 5-27 check flip clearing jams, 3-12 commands, 7-146 check flip commands, 7-146 check flip test, 3-25 checks printing, 3-7 validating, 3-...
Page 309: —D—
Index-3 connecting cables cash drawer, 2-6 power supply, 2-7 connector cash drawer, 6-9 rs-232c communication, 6-8 consumables. See paper contacting a service representative, 3-38 —d— data moving through buffer, 7-102 datascope mode, 3-21 default lines per inch, 3-27 description interface, 5-23, 5-3...
Page 310: —I—
Index-4 humidity, 5-10 —i— impact slip printer, 1-4 options, 1-5 interface description, 5-23, 5-36 electrical, 5-26 human, 5-23 timing, 6-5 —j— jams check flip, 3-12 checks, 3-12 —k— knife not cutting, 3-37 partial cut, 5-22 —l— lines per inch default, 3-27 loading paper receipt, 2-8 locating the pr...
Page 311: —P—
Index-5 ordering adapters, 4-2 cash drawers, 4-2 communication cable, 4-3 documentation, 4-4 paper, 4-1 power supply, 4-2 power supply cord, 4-2 ribbon cassettes, 4-4 slip table, 4-4 supplies, 4-1 overview communication, 6-1 —p— packing material repacking printer, 3-39 packing restraints, 2-3 removi...
Page 312: —R—
Index-6 checks, 3-7 forms, 3-7 receipt, 5-17 slip, 5-12 printing problems receipt, 3-34 problems contacting a service representative, 3-38 flashing led, 3-33 knife, 3-37 other, 3-38 paper out, 3-33 poor forms print quality, 3-34 poor receipt print quality, 3-34 printer beeps, 3-31 printer not printi...
Page 313: —S—
Index-7 —s— sample printout configuration menu, 2-12, 3-19 print test, 2-12 sending commands basic, 6-2 dos, 6-1 service representative contacting, 3-38 settings communication, 3-20 rs-232c serial interface, 3-20 switch, 5-27 slip duty cycle, 5-16 format, 5-13 media, 5-10 positioning, 5-12 printing,...
Page 314: —W—
Index-8 —w— weight, of printer, 5-36 —x— xon/xoff protocol, 6-6.