- DL manuals
- Panasonic
- Fax Machine
- KX-FP85
- Service Manual
Panasonic KX-FP85 Service Manual
Summary of KX-FP85
Page 1
© 2000 kyushu matsushita electric co., ltd. All rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and distribution is a violation of law. Kx-fp85 (for u.S.A.) compact plain paper fax order no. Kmf0004400c1 f7.
Page 2: Contents
1 introduction 3 1.1. Safety precautions 3 1.2. Insulation resistance test 3 1.3. For service technicians 3 1.4. Battery caution 3 1.5. Ac caution 4 1.6. Personal safety precautions 4 1.7. Service precautions 5 1.8. Features 6 1.9. Specifications 7 1.10. Optional accessories 7 1.11. Test chart 8 1.1...
Page 3: 1 Introduction
1 introduction 1.1. Safety precautions 1. Before servicing, unplug the ac power cord to prevent an electric shock. 2. When replacing parts, use only the manufacturer´s recommended components. 3. Check the condition of the power cord. Replace if wear or damage is evident. 4. After servicing, be sure ...
Page 4
1.5. Ac caution for safety, before closing the lower cabinet, please make sure of the following precautions. 1. The earth lead is fixed with the screw. 2. The ac connector is connected properly. 3. Wrap the earth lead around the core 3 times. 4. Wrap the ac lead around the core 2 times. 1.6. Persona...
Page 5
1.6.2. Live electrical sections all the electrical sections of the unit supplied with ac power by the ac power cord are live. Never disassemble the unit for service with the ac power supply plugged in. Caution: ac voltage is supplied to the primary side of the power supply unit. Therefore, always un...
Page 6
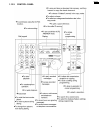
General · help function please refer to 2.1.3 when you don't know how to operate the unit, use the help function.(p.25) to print below features. Display: 1. Send guide 2. Quick set up 3. Feature list 4. Jog-dial 5. Tad operation 6. Fax snd/rcv 7. Copier 8. Q and a 9. Errors 10. Reports 11. Caller id...
Page 7
1.9. Specifications applicable lines: public switched telephone network document size: max. 216 mm (8 1/2") in width max. 600 mm (23 5/8") in length effective scanning width: 208 mm (8 3/16") recording paper size: letter: 216×279 mm (8 1/2"×11") legal: 216×356 mm (8 1/2"×14") effective printing widt...
Page 8
1.11. Test chart 1.11.1. Itu-t no.1 test chart 8 kx-fp85.
Page 9
1.11.2. Itu-t no.2 test chart 9 kx-fp85.
Page 10
1.12. Location of controls 1.12.1. Overview note: · the document will be ejected from the front of the unit. Install the unit on a desk or floor with a smooth surface and do not place anything in front of the unit. 10 kx-fp85.
Page 11
1.12.2. Control panel 11 kx-fp85.
Page 12
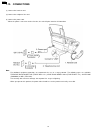
1.13. Connections (1) connect the handset cord. (2) connect the telephone line cord. (3) connect the power cord. · when the power is turned on for the first time, the unit will print some basic information. Note: · for additional equipment protection, we recommend the use of a surge protector. The f...
Page 13
1.14. Installation 1.14.1. Installation space the space required to install the unit is shown below. The dimensions given are necessary for the unit to operate efficiently. Note: · avoid excessive heat or humidity. · use the unit within the following ranges of temperature and humidity. · ambient tem...
Page 14
1.14.2. Installing the paper tray insert one tab on the paper tray into one slot on the back of the unit ( ) and then insert the other tab into the other slot ( ). Note: · do not place the unit in areas where the paper tray may be obstructed by a wall, etc. To use legal size paper please purchase a ...
Page 15
1.14.3. Installing the recording paper letter* or legal** size recording paper can be loaded. The unit can hold up to 50 sheets of 60 g/m 2 to 75 g/m 2 (16 lb. To 20lb.) paper or 30 sheets of 90 g/m 2 (24 lb.) paper. *letter=216 mm × 279 mm (8 1/2” × 11”) **legal=216 mm × 356 mm (8 1/2" × 14") if yo...
Page 16
1.14.4. Adding paper to the paper tray (1) pull the cassette open lever forward and remove all of the installed paper. (2) add paper to the removed paper and straighten. (3) fan the stack of paper. (4) pull the tension bar forward and hold open while inserting the paper. 1.14.5. Documents the unit c...
Page 17
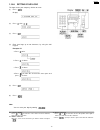
1.14.6. Setting your logo the logo can be your company, division or name. (1) press . Display: (2) press , then . (3) press . (4) enter your logo, up to 30 characters, by using the dial keypad. Example: bill a. Press twice. B. Press six times. C. Press six times. D. Press to move the cursor to the n...
Page 18
1.14.7. To select characters with the dial keypad 1.14.8. To select characters using the jog dial instead of pressing the dial keys, you can select characters using the jog dial. (1) rotate until the desired character is displayed. (2) press to move the cursor to the next space. · the character disp...
Page 19
1.14.9. Replacing the film cartridge when the unit runs out of ink film, the following message will be displayed. Display: install a new ink film. The following ink films are available for replacement. Each roll prints about 150 letter size pages. Refer to 1.10 optional accessories.(p.7) model no. K...
Page 20
(4) remove the stoppers and tags from the new ink film. Find the “t” shaped gear (blue). (5) insert the blue core of the front ink film roll into the right slot of the unit ( ). Insert the “t” shaped gear (blue) into the left slot of the unit ( ). Insert the back ink film roll ( ). (6) if the ink fi...
Page 21
1.15. Maintenance items and component locations 1.15.1. Outline maintenance and repairs are performed using the following steps. 1. Periodic maintenance inspect the equipment periodically and if necessary, clean any contaminated parts. 2. Check for breakdowns look for problems and consider how they ...
Page 22
1.15.2. Maintenance check items/component locations 22 kx-fp85.
Page 23
1.15.2.1. Maintenance list no. Operation check remarks 1 document path remove any foreign matter such as paper. — 2 rollers if the roller is dirty, clean it with a damp cloth then dry thoroughly. Refer to 1.15.3 maintenance(p.24). 3 platen roller if the platen is dirty, clean it with a damp cloth th...
Page 24
1.15.3. Maintenance 1.15.3.1. Cleaning the document feeder unit if misfeeding occurs frequently or if dirty patterns or bands appear on a transmitted document or on the original of a copied document, clean the document feeder. 1. Disconnect the power cord and the telephone line cord. 2. Open the fro...
Page 25: 2 Troubleshooting Guide
After confirming the problem by asking the user, troubleshoot according to the instructions and observe the following precautions. 2.1.2. Precautions 1. If there is a problem with the print quality or the paper feed, first check if the installation space and the print paper meets the specifications,...
Page 26
If the unit detects a problem, one or more of the following messages will appear on the display. 2.2. User recoverable errors note: the explanations given in the [ ] are for servicemen only. Cross reference: 1.8 features(p.6) 2.2.1 document jams(p.28) 3 adjustments(p.110) 26 kx-fp85.
Page 27
Cross reference:1 2.2.1 document jams(p.28) 2.2.2 recording paper jams(p.29) note: the explanations given in the [ ] are for servicemen only. 27 kx-fp85.
Page 28
2.2.1. Document jams if the unit does not release the document during feeding, remove the jammed document as follows. (1) open the front cover by pulling up the center part. (2) remove the jammed document carefully. (3) close the front cover securely. Note: · do not pull out the jammed paper forcibl...
Page 29
2.2.2. Recording paper jams if the unit does not eject any recording paper during reception or copying, the recording paper has jammed and the display will show the following massage. When paper has jammed under the film cartridge display: remove the jammed paper as follows. (1) open the front cover...
Page 30
(4) if the ink film is slack, tighten it by winding the gears. (5) close the back cover securely by pushing down on the dotted area at both ends ( ). Close the front cover securely ( ). 30 kx-fp85.
Page 31
2.3. Troubleshooting details 2.3.1. Outline troubleshooting is for recovering quality and reliability by determining the broken component and replacing, adjusting or cleaning it as required. First, determine the problem then decide the troubleshooting method. If you have difficulty finding the broke...
Page 32
2.3.3. Troubleshooting items table cross reference: 2.3.4 adf (auto document feed) section(p.34) 2.3.5 communication section(p.47) 2.3.7 analog board section(p.76) 2.3.10 operation panel section(p.84) 2.3.11 sensor section(p.85) 32 kx-fp85.
Page 33
2.3.3.1. Simple check list cross reference: 2.5 test functions(p.103) 33 kx-fp85.
Page 34
2.3.4. Adf (auto document feed) section 2.3.4.1. No document feed cross reference: 2.3.6 digital board section(p.66) 2.3.9 power supply board section(p.81) 2.3.11 sensor section(p.85) 2.5 test functions(p.103) 3 adjustments(p.110) 4 disassembly instructions(p.111) 6.4.5 stepping motor drive circuit(...
Page 35
2.3.4.2. Document jam cross reference: 2.3.11 sensor section(p.85) 4 disassembly instructions(p.111) 35 kx-fp85.
Page 36
2.3.4.3. Multiple feed · when using thick paper etc., sometimes the document will not be fed. Refer to 3.1 adjusting the feeder pressure(p.110). Fig. B cross reference: 1.15.3 maintenance(p.24) 3 adjustments(p.110) 4 disassembly instructions(p.111) note: when confirming if the characters are extende...
Page 37
2.3.4.4. Skew * we recommend making a copy of the fig. B document in 2.3.4.3 multiple feed (p.36) and using it. Cross reference: 1.15.2 maintenance check items/component locations(p.22) 2.3.4 adf (auto document feed) section(p.34) 2.3.4.3 multiple feed(p.36) 4 disassembly instructions(p.111) 37 kx-f...
Page 38
2.3.4.5. The recording paper does not feed * we recommend making a copy of the fig. B document in 2.3.4.3 multiple feed (p.36)and using it. Cross reference: 1.14.3 installing the recording paper(p.15) 2.3.6 digital board section(p.66) 2.3.9 power supply board section(p.81) 2.3.11 sensor section(p.85...
Page 39
2.3.4.6. Paper jam cross reference: 2.3.11 sensor section(p.85) 2.5 test functions(p.103) 4 disassembly instructions(p.111) 6.5 sensors and switches(p.155) 39 kx-fp85.
Page 40
2.3.4.7. Multiple feed and skew cross reference: 4 disassembly instructions(p.111) 9.1 operation panel section(p.180) 2.3.4.8. The sent fax data is skewed * we recommend making a copy of the fig. B document in 2.3.4.3 multiple feed(p.36) and using it. Cross reference: 2.3.4.4 skew(p.37) 2.3.4.9. The...
Page 41
2.3.4.10. Received or copied data is expanded * we recommend making a copy of the fig. B document in 2.3.4.3 multiple feed(p.36) and using it. Cross reference: 4 disassembly instructions(p.111) 41 kx-fp85.
Page 42
2.3.4.11. A blank page is copied * we recommend making a copy of the fig. B document in 2.3.4.3 multiple feed (p.36) and using it. Cross reference: 2.3.4.3 multiple feed(p.36) 2.3.4.12 a blank page is received(p.44) 2.5 test functions(p.103) 4 disassembly instructions(p.111) 6.4.3 thermal head(p.142...
Page 43
Fig. C 43 kx-fp85.
Page 44
2.3.4.12. A blank page is received cross reference: 2.3.4.11 a blank page is copied(p.42) 2.3.7 analog board section(p.76) 2.5 test functions(p.103) 2.3.4.13. Black or white vertical line * we recommend making a copy of the fig. B document in 2.3.4.3 multiple feed (p.36) and using it. Cross referenc...
Page 45
2.3.4.14. Black or white lateral line on print out * we recommend making a copy of the fig. B document in 2.3.4.3 multiple feed(p.36) and using it. Cross reference: 2.3.4.3 multiple feed(p.36) 2.3.4.11 a blank page is copied(p.42) 2.3.6 digital board section(p.66) 2.5 test functions(p.103) 4 disasse...
Page 46
2.3.4.15. An abnormal image is printed * we recommend making a copy of the fig. B document in 2.3.4.3 multiple feed (p.36) and using it. Cross reference: 2.3.4.3 multiple feed(p.36) 2.3.7 analog board section(p.76) 2.5 test functions(p.103) 4 disassembly instructions(p.111) 46 kx-fp85.
Page 47
2.3.5. Communication section find the problem in the table shown below, and refer to the corresponding troubleshooting procedure in 2.3.5.1 defective facsimile section p.48. No. Symptom content possible cause 1 the paper is not fed properly when faxing. (nor in the copy mode.) troubleshooting proble...
Page 48
2.3.5.1. Defective facsimile section 2.3.5.1.1. Transmit problem cross reference: 1.15.3 maintenance(p.24) 2.3.4 adf (auto document feed) section(p.34) 2.3.10 operation panel section(p.84) 48 kx-fp85.
Page 49
2.3.5.1.2. Sometime there is a transmit problem note: "596: transmit level set" represents a service code. (refer to 2.4.4 service function table(p.91).) 49 kx-fp85.
Page 50
2.3.5.1.3. Receive problem first confirm whether the recording paper is installed properly or not before starting troubleshooting. (refer to "remarks".) note: "596: transmit level set" represents a service code. (refer to 2.4.4 service function table(p.91).) remarks: regarding the reception problem,...
Page 51
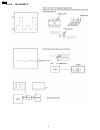
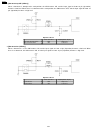
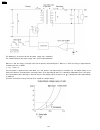
2.3.5.1.4. The unit can copy, but cannot transmit/receive cross reference: 2.3.7 analog board section(p.76) 2.5 test functions(p.103) 2.3.5.1.5. The unit can copy, but cannot either transmit/receive long distance or internationl communications the following two causes can be considered for this symp...
Page 52
(cause and countermeasure) as shown in the chart above, the total handshaking time must be reduced, but because of the long distance connection and linking of several stations, the line connection time cannot be reduced. Accordingly, the following countermeasures should be tried. (a)... As the 35 se...
Page 53
(cause c) this model is fax1 and the other party is fax2. For transmission from this model to fax2, fax2 executes automatic reception and transmits a ced signal (2100 hz) followed by a dis signal. As the echo cancelers stops as described in cause b, the echo of the dis signal returns to fax2. On the...
Page 54
2.3.5.1.7. How to output the journal report 1. Press the menu button two times. 2. Rotate jog dial until the “ journal report ” is displayed. 3. Press the set button. 4. The report prints out. Cross reference: 1.8 features(p.6) error code table: (1) code (2) result (3) mode symptom counter- measure*...
Page 55
55 kx-fp85.
Page 56
Cross reference: 2.5 test functions(p.103) 56 kx-fp85.
Page 57
Cross reference: 2.5 test functions(p.103) 57 kx-fp85.
Page 58
Cross reference: 2.5 test functions(p.103) 58 kx-fp85.
Page 59
Cross reference: 2.5 test functions(p.103) 59 kx-fp85.
Page 60
60 kx-fp85.
Page 61
61 kx-fp85.
Page 62
Cross reference: 2.5 test functions(p.103) 62 kx-fp85.
Page 63
2.3.5.2. Remote programming if, after the call is connected, the customer describes the situation and it is determined that the problem can be corrected by making parameter changes, this function makes it possible to change parameters such as the user code and service code from another fax (using dt...
Page 64
2.3.5.2.2. Program mode table code function set value default remote setting 001 set date and time mm/dd/yy hh:mm jan/01/00 ng 002 your logo --------- none ng 003 your telephone number --------- none ng 004 transmission report mode 1:error / 2:on/3:off error ok 006 fax ring count 1~4 2 ok tad/fax ri...
Page 65
Code function set value default remote setting 591 fax auto redial line disconnection time set 001~999sec 045 ok 592 cng transmit select 1:off / 2:all / 3:auto all ok 593 time between ced and 300 bps 1:75ms / 2:500ms / 3:1sec 75ms ok 594 overseas dis detection 1:1st / 2:2nd 1st ok 595 receive error ...
Page 66
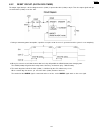
2.3.6. Digital board section when the unit fails to boot up the system, take the troubleshooting procedures very carefully. It may have a serious problem. The symptom: no response when the power is turned on. (no lcd display, and keys are not accepted.) the first step is to check the power source. I...
Page 67
2.3.6.1. Digital block diagram you also need to check the signal lines listed here [list 1] when the unit fails to boot up the system. Those signal lines should remain normal. Other signal lines are not directly related to that failure even if they have faults or troubles. As long as these signals r...
Page 68
Ng wave pattern (refer to ng example) 68 kx-fp85.
Page 69
Normal wave patterns remarks: when you use an oscilloscope to judge whether a signal to be tested is normal or ng, perform the signal check in exactly the same order as in [list 1]. (if the asic fails to access the rom, the asic cannot access sram or dram normally.) the digital circuit actually oper...
Page 70
I/o and pin no. Diagram 70 kx-fp85.
Page 71
After the power is turned on, the asic initializes and checks each ic. The rom, sram, and modem are checked. If initialization fails for the ics , the system will not boot up. In this case, please find the cause as follows. Cross reference: 2.3.6.3 ng example(p.74) 2.3.6.4 check the status of the di...
Page 72
Cross reference: 2.3.6.4 check the status of the digital board(p.75) other ng example while the power is on and the lcd displays the following. 72 kx-fp85.
Page 73
2.3.6.2. Flash memory (ic501) if the unit is working correctly but the voice guidance (voice prompt) is not audible, you should check the flash memory. A voice message is pre-recorded in the flash memory (ic512). So, when you find an ic512 malfunction and replace it with a new one. You have to pre-r...
Page 74
2.3.6.3. Ng example 74 kx-fp85.
Page 75
2.3.6.4. Check the status of the digital board 75 kx-fp85.
Page 76
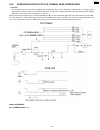
2.3.7. Analog board section this chapter provides the testing procedures required for the analog parts. A signal route to be tested is determined depending upon purposes. For example, the handset tx route begins at the handset microphone and the signal is output to the telephone line. The signal mai...
Page 77
2.3.7.2. Defective its (integrated telephone system) section 1. No handset and speakerphone transmission / reception perform a signal test in the its or the ncu section and locate a defective point (where the signal disappears) on each route between the handset microphone and telephone line (sending...
Page 78
4. No tone dialing cross reference: 2.3.7.1 check sheet(p.76) 78 kx-fp85.
Page 79
2.3.8. Digital speakerphone the digital speakerphone has different features from the analog speakerphone. The analog speakerphone switches between tx or rx. Either tx or rx is able to pass through a telephone line or speaker, depending on the tx and rx signal (voice) level. The higher-level signal (...
Page 80
Cross reference: 2.3.7 analog board section (p.76). 80 kx-fp85.
Page 81
2.3.9. Power supply board section 2.3.9.1. Key components for troubleshooting check the following parts first: f101, d101-d104, c106, q101, pc101 and ic101. This comes from our experience with experimental tests. For example: power supply and lightning surge voltage test, withstanding voltage test, ...
Page 82
2.3.9.2. Toroubleshooting flow chart 82 kx-fp85.
Page 83
2.3.9.3. Broken parts repair details (d101, d102, d103, d104) check for a short-circuit in terminal 4. If d101, d102, d103 and d104 are short-circuits, f101 will melt (open). In this case, replace all of the parts (d101, d102, d103, d104, f101). (q101) the worst case of q101 is a short-circuit betwe...
Page 84
2.3.10. Operation panel section 2.3.10.1. No key operation cross reference: 2.5 test functions(p.103) 2.3.10.2. No lcd indication cross reference: 2.5 test functions(p.103) 84 kx-fp85.
Page 85
2.3.11. Sensor section refer to 6.5 sensors and switches(p.155) for the circuit descriptions. The test function makes the sensor circuit check easier. (refer to 2.5 test functions(p.103).) for example, as for "cover open sensor", "co" is turned on/off on the display when you open or close the front ...
Page 86
2.3.11.5. Check the paper top senser (ps501)........................"paper jammed" 2.3.12. Cis (contact image sensor) section refer to 6.4.4 scanning block(p.144). Cross reference: 2.5 test functions(p.103) 86 kx-fp85.
Page 87
87 kx-fp85.
Page 88
2.3.13. Thermal head section refer to 6.4.3 thermal head(p.142). 88 kx-fp85.
Page 89
The programming functions are used to program the various features and functions of the machine, and to test the machine. There are 2 basic categories of programming functions, the user mode and the service mode. The service mode is further broken down into the normal and special programs. The norma...
Page 90
2.4.3. User mode (the list below is an example of the system setup list the unit prints out.) note: the above values are the default values. 90 kx-fp85.
Page 91
2.4.4. Service function table code function set value effective range default remarks 501 pause time set x 100 msec 001~600 50 ---------- 502 flash time x 10 ms 01~99 70 ---------- 503 dial speed select 1:10 pps 2:20 pps 1, 2 1 ---------- 510 vox time 1:6 sec 2:4sec 1, 2 1 ---------- 511 vox sense 1...
Page 92
Code function set value effective range default remarks 593 time between ced and 300bps 1:75 msec 2:500 msec 3:1 sec 1~3 1 see symptom/countermeasure table for long distance and international calls in 2.3.5.1.5 the unit can copy, but cannot either transmit/receive long distance or internationl commu...
Page 93
Note: the above values are the default values. Code function set value effective range default remarks 880 history list see 2.4.6 history(p.94). 881 journal 2 list see 2.4.7.3 printout example(p.101). 882 journal 3 list see 2.4.7.3 printout example(p.101). 890 tel/fax 1st ring back tone 1:on 2:off 1...
Page 94
2.4.6. History note: see the following descriptions of this report. Item no. (1) ~ (47) are corresponding to the listed items in 2.4.6.1 descriptions of the history report(p.95). 94 kx-fp85.
Page 95
2.4.6.1. Descriptions of the history report (1) rom version eprom version (2) sum eprom internal data calculation. (3) your logo the user logo recorded in the unit. If it is not recorded, none will be displayed. (4) your telephone number the user telephone number recorded in the unit. If it is not r...
Page 96
(25) num(ber of recording message the number of messages recorded in tam. (26) number of pc scan the number of times multifunction was used for the scanner. (the number of pages scanned. If the unit does not have a pc interface, none will be printed.) (27) number of pc-print the number of times mult...
Page 97
(47) number of iq-fax pages transmitted 97 kx-fp85.
Page 98
Journal 2 and journal 3 shown below, which are special journals giving the additional detailed information about the latest 35 communications, can be printed by service code 881 or 882. Remote printing function for the journal reports (journal, journal 2 and journal 3) is also available for how to r...
Page 99
2.4.7.1. Journal 2 refer to journal 2 in 2.4.7.3 printout example(p.101). Journal 2 displays the additional detailed information about the last 35 communications. Descriptions: (1) rcv. Mode indicates which receive mode the unit was in when the unit received a fax message. This information is also d...
Page 100
2.4.7.2. Journal 3 refer to journal 3 in 2.4.7.3 printout example(p.101). Descriptions: (6) encode compression code: mh/mr (7) mslt mslt means minimum scan line time. Used only at the factory. (8) eqm eqm means eye quality monitor. Used only at the factory. (9) error line(rx) when an error occurs wh...
Page 101
2.4.7.3. Printout example 101 kx-fp85.
Page 102
102 kx-fp85.
Page 103
2.5. Test functions the codes listed below can be used to perform simple checks of some of the unit’s functions. When complaints are received from customers, they provide an effective tool for identifying the locations and causes of malfunctions. Cross reference: 2.5.1 dtmf single tone transmit sele...
Page 104
Note: the numbers in the boxes (xxx) indicate the keys to be input for the various test modes. Cross reference: 2.3.8 digital speakerphone(p.79) 6.5 sensors and switches(p.155) 2.5.1. Dtmf single tone transmit selection note: after performing this check, do not forget to turn the setting off. Otherw...
Page 105
2.5.2. Button code table note: these codes (00, 01) are only for the data in the history report. 105 kx-fp85.
Page 106
2.5.3. Print test pattern 1. Platen roller (reference pattern) 106 kx-fp85.
Page 107
2. Left margin/top margin (reference pattern) 107 kx-fp85.
Page 108
3. Thermal head 1 dot (reference pattern) 108 kx-fp85.
Page 109
4. Use this test pattern to confirm the torque limiter for ink film and platen roller timing. (reference pattern) 109 kx-fp85.
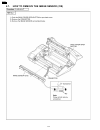
Page 110: 3 Adjustments
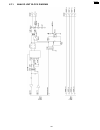
3 adjustments 3.1. Adjusting the feeder pressure if misfeeding of a document such as multiple feeding or no feeding occurs frequently, try to adjust the feeder pressure by following the steps below. 1. Open the front cover by pulling up the center part. 2. Shift the position of the green lever by us...
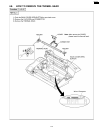
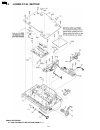
Page 111: 4 Disassembly Instructions
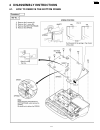
4 disassembly instructions 4.1. How to remove the bottom frame 111 kx-fp85.
Page 112
4.2. How to remove the operation panel block 112 kx-fp85.
Page 113
4.3. How to remove the operation board and lcd 113 kx-fp85.
Page 114
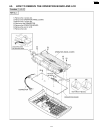
4.4. How to remove the analog, digital and power boards and ac inlet 114 kx-fp85.
Page 115
4.5. How to remove the motor block 115 kx-fp85.
Page 116
116 kx-fp85.
Page 117
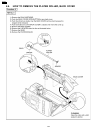
4.6. How to remove the separation roller 117 kx-fp85.
Page 118
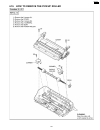
4.7. How to remove the image sensor (cis) 118 kx-fp85.
Page 119
4.8. How to remove the termal head 119 kx-fp85.
Page 120
4.9. How to remove the platen roller, back cover 120 kx-fp85.
Page 121
4.10. How to remove the pickup roller 121 kx-fp85.
Page 122
4.11. How to remove the cassette plate 122 kx-fp85.
Page 123
4.12. How to remove the document tray 123 kx-fp85.
Page 124
4.13. Installation position of the lead wires 124 kx-fp85.
Page 125
5 how to replace the flat package ic even if you do not have the special tools (for example, a spot heater) to remove the flat ic, with some solder (large amount), a soldering iron and a cutter knife, you can easily remove the ics that have more than 100 pins. 5.1. Preparation · solder sparkle solde...
Page 126
5.3. Flat package ic installation procedure 1. Temporarily fix the flat package ic, soldering the two marked pins. *check the accuracy of the ic setting with the corresponding soldering foil. 2. Apply flux to all pins of the flat package ic. 3. Solder the pins, sliding the soldering iron in the dire...
Page 127: 6 Circuit Operations
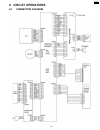
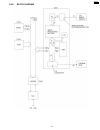
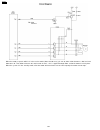
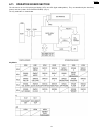
6 circuit operations 6.1. Connection diagram 127 kx-fp85.
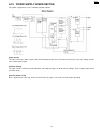
Page 128
6.2. General block diagram the following is an outline of each device ic on the digital board. (refer to 6.2.1 general block diagram(p.129).). 1. Asic (ic501) composed mainly of an address decoder and a modem control. Controls the general fax operations. Controls the operation panel i/f. Controls th...
Page 129
6.2.1. General block diagram cross reference: 6.7.1 analog unit block diagram(p.167) 129 kx-fp85.
Page 130
6.3. Control section 6.3.1. Block diagram 130 kx-fp85.
Page 131
6.3.2. Memory map 131 kx-fp85.
Page 132
This custom ic is used for the general fax operations. 1. Cpu: this model uses a z80 equivalent to the cpu operating at 8 mhz. Most of the peripheral functions are performed by custom-designed lsis. Therefore, the cpu only works for processing the results. 2. Rtc: real time clock 3. Decoder: decodes...
Page 133
6.3.4. Rom (ic502) this 512kb rom (eprom or maskrom) carries a common area of 32kb and bank areas which each have 8kb (bk4~bk63). The addresses from 0000h to 7fffh are for the common area and from 8000h to 9fffh are for the bank areas. 6.3.5. Static ram (ic504) this 32kb ram carries a common area of...
Page 134
Descriptions of pin distribution (ic501) no. Signal i/o power supplied voltage description 1 ain1 a 3.3v ccd image signal input 2 ain2 a 3.3v thermistor temperature watch input 3 ain3 a 3.3v ----------- 4 amon a 3.3v analog signal monitor terminal 5 vssb gnd power source (analog gnd) 6 vddb 3.3v pow...
Page 135
No. Signal i/o power supplied voltage description 66 xout o 3.3v system clock (24mhz) 67 xin i 3.3v system clock (24mhz) 68 vss gnd power source (gnd) 69 vdd (5v) 5v power source (+5v) 70 xtest o 5v 24mhz clock 71 cpuclk o 5v not used 72 test1 i 5v high fixed 73 test2 i 5v high fixed 74 test3 i 5v h...
Page 136
No. Signal i/o power supplied voltage description 133 xoreset o 5v reset output 134 vdd (5v) 5v power source (+5v) 135 vss gnd power source (gnd) 136 xreseti i 5v reset input 137 wderr o 5v watched error output signal 138 xrstswi i 5v input port (mpos) 139 xrstswo o 5v output port (volin sel2) 140 x...
Page 137
6.3.7. Reset circuit (watch dog timer) the output signal from pin 1 of the voltage detect ic (ic507) is input to the asic (ic501) 136 pin. Then the output signal from pin 133 of the asic (ic501) resets the asic. 1. During a momentary power interruption, a positive reset pulse of 46~51 msec is genera...
Page 138
6.3.8. Sram and rtc backup circuit 1. Function this unit has a lithium battery (bat501) which works for the sram (ic504) and real time clock ic (rtc: inside ic501). The user parameters for autodial numbers, the system setup data and others are stored in the sram (ic504). The rtc continues to work, b...
Page 139
6.3.9. Supervision circuit for the thermal head temperature 1. Function the thermistor changes the resistor according to the temperature and uses the thermistor´s characteristics. The output of pin 169 of ic501 becomes a low level. Then when it becomes a high level, it triggers point a. In point c, ...
Page 140
6.4. Facsimile section 6.4.1. Image data flow during facsimile operation copy (fine, super-fine, half tone) 1. Line information is read by cis (to be used as the reference white level) via route 1, and is input to ic501. Refer to 6.4.2. Block diagram. 2. In ic501, the data is adjusted to a suitable ...
Page 141
6.4.2. Block diagram 141 kx-fp85.
Page 142
6.4.3. Thermal head 1. Function this unit utilizes the state of the art thermal printer technology. The ink film is chemically processed. The ink film is comprised of two parts: an ink layer and a base film. When the thermalhead contacts this ink film, it emits heat momentarily, and the ink layer is...
Page 143
143 kx-fp85.
Page 144
6.4.4. Scanning block the scanning block of this device consists of a control circuit and a contact image sensor made up of a celfoc lens array, an led array, and photoelectric conversion elements. When an original document is inserted and the start button pressed, pin 20 of ic501 goes to a high lev...
Page 145
6.4.5. Stepping motor drive circuit 1. Function the stepping motor works for both transmission and reception. 2. Motor during motor driving, pin 163 of asic ic501 becomes a high level, and q503, q501 turns on. As a result, +24v is supplied to the motor coil. Stepping pulses are output from gate arra...
Page 146
When the motor suspends while it is in the receive mode (about 70~80 msec), pin 163 of asic ic501 becomes a low level and q503 turns off. Then q501 also turns off, and instead of +24 v, +5 v is supplied through d501 so that the motor is held in place. When the system is in the stand-by mode, all of ...
Page 147
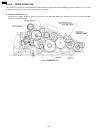
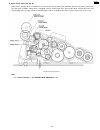
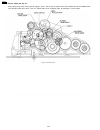
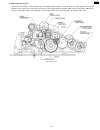
6.4.6. Gear section this model provides a motor-driven gear mechanism for transmitting/copying documents and printing fax data. In this chapter, you will see how the gears work to select and operate a mode and how the gear section, sensors and rollers mechanically work during the main operations (fa...
Page 148
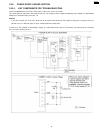
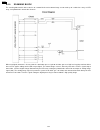
6.4.6.2. Mode operation once a mode is selected, the drive motor gear rotates clockwise (cw) and then the controlling positions of swing gears a, b and c determine which gears convey their drive power in each mode. A. Transmit mode (see fig. A.) : swing gear a engages gear e and conveys its power to...
Page 149
B. Paper-pickup mode (see fig. B) : swing gear c engages gear h and provides its power to the pick up roller gear and platen idler gear and pick up idler gear. The gear drive as follows: swing arm c → engaging → gear h → platen idler gear → pick up idler gear → pickup roller gear. The pickup roller ...
Page 150
C. Receive mode (see fig. C.) : after paper pick up mode, swing gear b engages gear c and conveys its power to the platen roller gear and ink ribbon drive gear through platen drive gear. Then, the platen roller feeds recording paper for printing the received data. Fig. C: receive mode 150 kx-fp85.
Page 151
D. Copy mode (see fig. D.) : documents pre-feeding → transmit mode go → recording paper feeding → pick up mode go. Next swing gear a and b engages gear e and gear c respectively and conveys these power to the separation roller gear and the platen roller gear. Then the separation roller feeds documen...
Page 152
6.4.6.3. Mechanical movements in the main operations (transmitting documents, receiving faxes and copying) 6.4.6.3.1. Idle status note: see “sensor locations” in 6.5 sensors and switches(p.155). 152 kx-fp85.
Page 153
6.4.6.3.2. Transmitting documents cross reference: 2.3.11 sensor section(p.85). 6.4.6.3.3. Receiving fax note: see “sensor locations” in 6.5 sensors and switches(p.155). 153 kx-fp85.
Page 154
6.4.6.3.4. Copying note: see “sensor locations” in 6.5 sensors and switches(p.155). Cross reference: 2.3.11 sensor section(p.85) 154 kx-fp85.
Page 155
6.5. Sensors and switches all of the sensor and switches are shown below. Sensor circuit location sensor sensor or switch name message error operation panel sw352 document set sw [check document] sw353 document top sw [remove document] digital pcb sw501 film end/cover open [check cover] or [check fi...
Page 156
1. [document top sw (sw353)] when a document is brought to the read position, the sw becomes on, and the input signal of ic301-16 pin (operation) becomes a low level. When there is no document at the read position, the sw becomes off, and the input signal of ic301-16 pin (operation) becomes a high l...
Page 157
3. [cover open/film end sw (sw501)] when the operation panel cover is closed and a film is set, the sw becomes on, and the input signal of ic501-130 pin (digital) becomes a low level. When the cover is opened, the sw becomes off, and the input signal of ic501-130 pin (digital) becomes a high level. ...
Page 158
5. [paper top sensor (ps501)] when the recording paper is loaded on the print head, the shelter plate shuts the sensor light, and the photo transistor becomes off. The input signal of ic501-131 pin becomes a high level. Usually, the shelter plate is lifted, the photo transistor becomes on, and the i...
Page 159
6.6. Modem section 6.6.1. Function the unit uses a 1 chip modem (ic505) that serves as an interface between the control section for fax transmission and reception and the telephone line. During a transmitting operation, the digital image signals are modulated and sent to the telephone line. During a...
Page 160
3. Facsimile call time series as shown in the following diagram, the facsimile call time series is divided into five phases. Phase a : call setting call setting can be manual/automatic. Phase b : pre-message procedure phase b is a pre-processing procedure and sequence for confirming the status of th...
Page 161
6. Explanation of communication and compression technology a. G3 communication signals (t. 30 binary process) for g3 facsimile communication, this is the procedure for exchanging control signals between the sending and receiving machines both before and after transmission of image signals. Control s...
Page 162
Bit no. Dis/dtc dcs 9 transmitter --- t.4 operation 10 receiver --- t.4 operation receiver --- t.4 operation 11, 12, 13, 14 0, 0, 0, 0 0, 1, 0, 0 1, 0, 0, 0 1, 1, 0, 0 0, 0, 1, 0 0, 1, 1, 0 1, 0, 1, 0 1, 1, 1, 0 0, 0, 0, 1 0, 1, 0, 1 1, 0, 0, 1 1, 1, 0, 1 0, 0, 1, 1 0, 1, 1, 1 1, 0, 1, 1 1, 1, 1, 1 ...
Page 163
Bit no. Dis/dtc dcs 43 r16×15.4 lines/mm and/or 400×400 pels/25.4 mm r16×15.4 lines/mm and/or 400×400 pels/25.4 mm 44 inch based resolution preferred resolution type selection "0" : neuritic based resolution "1" : inch based resolution 45 metric based resolution preferred don’t care 46 minimum scan ...
Page 164
B. Redundancy compression process coding mode this unit uses one-dimensional mh format. 164 kx-fp85.
Page 165
6.6.2. Modem circuit operation the modem (ic505) has all the hardware satisfying the ccitt standards mentioned previously. When the asic ic501 (77) is brought to a low level, the modem (ic505) is chip-selected and the resistors inside ic are selected by the select signals from asic (ic501) adr0-adr4...
Page 166
6.7. Description of block diagram in analog section 1. Function the analog section works as an interface between the telephone line. The analog gate array (ic551) on the digital board exchanges fax tx and rx signals between the modem (ic505) and the analog section. The control signals transmitted to...
Page 167
6.7.1. Analog unit block diagram 167 kx-fp85.
Page 168
6.8. Ncu section 6.8.1. General ncu is the interface with the telephone line. It is composed of renmote fax activation circuit, bell detection circuit, pulse dial circuit, cpc detection circuit, line amplifier and sidetone circuits and multiplexer. The following is a brief explanation of each circui...
Page 169
6.8.5. Line amplifier and side tone circuits 1. Circuit operation the reception signal output from the line transformer t101 is input to pin (3) of ic101 via c129 and r115, and then the signal is amplified at pin (1) of ic101 and sent to the reception system at 10db. The transmission signal goes thr...
Page 170
6.8.8. Calling line identification circuit 1. Function this unit is compatible with the caller id service offered by your local telephone company. To use this feature, you must subscribe to a caller id service. The data for the caller id from the telephone exchange is sent during the interval betwee...
Page 171
171 kx-fp85.
Page 172
6.9. Its (integrated telephone system) and monitor section 6.9.1. General the general its operation is performed by the special ic505 which has a handset circuit. The alarm tone, the key tone, and the beep are output from the asic ic501 (digital board). During the pulse dial operation, the monitor t...
Page 173
6.11. Operation board section the unit consists of a lcd (liquid crystal display), keys and leds (light-emitting diodes). They are controlled by the gate array (ic301) and asic (ic501: on the digital board). (fig.-a) the key matrix table is shown below. Key matrix 173 kx-fp85.
Page 174
6.12. Lcd section the gate array (ic301) works only for writing the ascii code from the data bus (d4~d7). V0 is supplied for the crystal drive. R303(r377) and r305(r379) are density control resistors. Consequently, in this unit, the timing (positive clock) is generated by the lcd interface circuitry...
Page 175
6.13. Power supply board section this power supply board uses the switching regulator method. [input circuit] the input current goes into the input rectifier circuit through the filter circuit. The filter circuit decreases the noise voltage and the noise electric field strength. [rectifier circuit] ...
Page 176
The following is an overview of how the power supply unit is controlled. The control method of this power supply unit is pulse width modulation. When q 1 is on, the energy is charged in the transfer primary coil according to e 1 . When q 1 is off, the energy is output from the secondary transfer as ...
Page 177
[surge absorber circuit] this circuit is for absorbing surge voltage generated by the transformer. [control circuit and detecting circuit] the control circuit amplifies the output with increased voltage detected in the error detecting circuit. Then it drives the main transistor. In this power supply...
Page 178: Diodes
7 terminal guide of the ic´s transistors and diodes 178 kx-fp85.
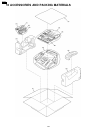
Page 179: 8 Fixtures And Tools
8 fixtures and tools 179 kx-fp85.
Page 180: Location
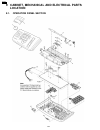
9 cabinet, mechanical and electrical parts location 9.1. Operation panel section 180 kx-fp85.
Page 181
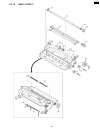
9.2. Upper cabinet section 181 kx-fp85.
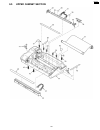
Page 182
9.2.1. Back cover section 9.2.1.1. Back cover 1 182 kx-fp85.
Page 183
9.2.1.2. Back cover 2 183 kx-fp85.
Page 184
9.3. Lower/p.C.B. Section cross reference: 4.1 how to remove the bottom frame(p.111) 184 kx-fp85.
Page 185
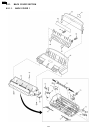
9.4. Motor section 9.5. Actual size of screws and washer 185 kx-fp85.
Page 186
10 accessories and packing materials 186 kx-fp85.
Page 187: 11 Replacement Parts List
This replacement parts list is for kx-fp85 only. Refer to the simplified manual (cover) for other areas. Notes: 1. The marking (rtl) indicates that the retention time is limited for this item. After the discontinuation of this assembly in production, the item will continue to be available for a spec...
Page 188
Ref. No. Part no. Part name & description remarks 80 pfdg1165y gear, platen 81 pfde1130y1 lever, lock 82 pfus1258z spring, lock lever 83 pfhs1029z cover, back tension sheet 84 pfdg1160z gear, back tension 85 pfus1232z spring, back tension 86 pfdg1164z gear, pickup idler 87 pfdg1166z gear, platen idl...
Page 189
Ref. No. Part no. Part name & description remarks (battery) bat501 pfsu1004z battery (coils) l513 pqlqr1et coil l514 pqlqr2ka20t coil l516 pqlqr2ka113t coil l517 pqlqr1et coil l518 pqlqr2ka20t coil l519 pqlqr2ka20t coil l520 pqlqr2ka113t coil l522 pqlqr2ka20t coil l523 pqlqr2ka20t coil l525 pqlqr2ka...
Page 190
Ref. No. Part no. Part name & description remarks r577 erj3geyj183 18k r578 erj3geyj183 18k r579 erj3geyj154 150k r580 erj3geyj184 180k r581 erj3geyj103 10k r582 erj3geyj4r7 4.7 r584 erj3geyj103 10k r587 erj3geyj103 10k r591 erj3geyj222 2.2k r592 erj3geyj102 1k r593 erj3gey0r00 0 r594 erj3geyj103 10...
Page 191
Ref. No. Part no. Part name & description remarks c607 ecuv1h104zfv 0.1 s c608 ecuv1h104zfv 0.1 s c609 ecea1cks100 10 c610 ecuv1h104zfv 0.1 s c611 ecuv1c104kbv 0.1 c612 ecuv1h102kbv 0.001 c613 ecuv1h101jcv 100p c614 ecuv1h104zfv 0.1 s c615 ecuv1c393kbv 0.039 c616 ecuv1c104kbv 0.1 c617 ecuv1h102kbv 0...
Page 192
Ref. No. Part no. Part name & description remarks r135 erj3geyj472 4.7k r136 erj3gey0r00 0 r137 erj3gey0r00 0 r138 erj3geyj102 1k r141 erj3geyj101 100 r142 erj3geyj472 4.7k r143 erj3geyj103 10k r144 erj3geyj103 10k r151 erj3geyj222 2.2k r153 erj3geyj562 5.6k r156 erj3geyj153 15k r158 erds2tj331 330 ...
Page 193
Ref. No. Part no. Part name & description remarks r353 erj3geyj123 12k r354 erj3geyj682 6.8k r355 erj3geyj223 22k r356 erj3geyj334 330k r357 erj3geyj222 2.2k r385 erj3gey0r00 0 (capacitors) c302 ecuv1c104kbv 0.1 s c303 ecea0jks101 100 c304 ecuv1c104kbv 0.1 s c305 ecuv1h101jcv 100p c308 ecuv1h331jcv ...
Page 194
Ref. No. Part no. Part name & description remarks znr101 erzv10dk471u varistor (resistors) r101 erds2tj105 1m r102 erds2tj334 330k r103 erds2tj334 330k r104 erg1sj104 100k r105 erx2sjr22 0.22 r106 erg2sj470 47 r108 erds2fj150 15 r109 erds2tj220 22 r121 pq4r10xj103 10k s r122 erj6geyj621 620 r124 pq4...
Page 195
12 for the schematic diagrams note: 1. Dc voltage measurements are taken with an oscilloscope or a tester with a ground. 2. The schematic diagrams and circuit board may be modified at any time with the development of new technology. 3. 195 kx-fp85.
Page 196
12.1. Memo 196 kx-fp85.
Page 197
13 printed circuit board 13.1. Digital board: bottom view r557 r599 r602 sw501 ic504 c583 c612 28 15 11 4 c539 l521 c604 c608 l524 c614 c613 c628 r612 c594 l519 l520 r561 c563 c556 c567 c575 l516 r558 c558 c559 c561 c578 c621 c636 c508 q505 r519 r524 r525 q506 c638 r507 r508 c501 r509 c510 r510 r511...
Page 198
13.2. Digital board: component view (component view) d502 f502 q501 q504 ref-ch auto-ch pcb-ch +12v -12v 1.25a c514 r502 r501 l506 l505 bat501 cn509 cn503 c626 c629 x501 video ftg pfup1190z dg l503 l504 11 11 1 1 32 17 15 14 1 16 1 22 23 1 1 5 1 1 11 4 8 5 2 1 1 10 1 3 c506 c505 c516 cn508 c529 1 c5...
Page 199
13.3. Analog board: bottom view ic107 c176 r187 ic108 r225 r224 r227 r228 c216 r186 q121 r226 r193 c183 c217 c181 r194 1 12 53 4 8 5 r195 c147 dg +5vd +5va +24v ag c149 r144 r143 q124 c155 j153 r230 q108 q123 r168 r166 r151 r170 c162 q107 r162 c215 r167 c204 c201 c203 c211 l103 l104 c186 d118 q114 c...
Page 200
13.4. Analog board: component view pc102 r202 cn102 c173 r190 znr101 cn104 cn103 sw102 sw101 c212 q116 e d112 c172 q105 r146 c170 r155 pc103 c153 c223 c152 c150 c136 c182 c145 c218 c219 c221 d103 d102 cn105 2 1 d104 cn106 q125 c139 11 17 10 r163 q112 r178 e e e c166 pcb-ch pfup1191z r158 d110 r200 l...
Page 201
13.5. Operation board sw318 12 3 45 6 78 0 redial/p a use flash monit or/sp-phone 9 sw317 sw320 sw316 sw313 sw312 sw315 sw326 sw319 sw333 sw322 sw307 mute iq-f ax sw310 sw305 a u to answer help menu pcb-ch colla te q uick scan resolution st op copy/ st ar t/ set v ol+ v ol- sw303 sw304 sw308 sw323 c...
Page 202
13.6. Power supply board for continued c101 f101 d104 d103 d102 d101 r102 c102 c106 r103 r105 j1 c105 c103 j2 j3 d107 q101 s g d r108 c202 c205 d201 1 1 ic202 c203 r203 r202 cn301 1 c201 mitsumi elec. Co., ltd. R106 t101 l103 c119 r109 d106 c108 r104 d105 r205 j4 znr101 l101 ic101 c109 d108 ic201 kr...
Page 203
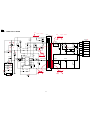
14 schematic diagram 14.1. Digital board si clk .... .... Krxd/ktxd ksclk klatch kstart .... .... .... Stb1 stb2 thdat thclk thlat .... .... Tx0 tx1 tx2 tx3 txe fax tx signal fax rx signal q511 r595 330 r594 10k +5vd r531 0 c534 j15p x501 32.768khz c531 j15p r554 47 c554 j10p l513 c552 j10p r555 1m ...
Page 204
14.2. Analog board fax tx signal fax rx signal 12v handset sp-phone fax tx 2.0v handset sp-phone fax rx +5vd r174 47k 47k(1/2w) r215 r184 10k +24va d118 2 1 4 3 ( ) d103 250v 0.33u c198 10k r143 ( ) c121 sa101 300v r115 56k 2 1 5 3 +5vd +24va -1 ic110 1 2 3 4 8 q115 +5vd +12va 270k r122 pc104 1 2 3 ...
Page 205
14.3. Operation board +5v1 +5v2 c310 z0.1u c311 z0.1u r303 27k r305 680 ( ) r304 +5v2 r301 470 r302 470 +5v1 sw302 help sw303 vol+ sw304 vol- sw306 menu sw307 mute sw308 collate sw309 quick scan sw311 9 sw312 5 sw313 2 sw314 copy/start/set sw316 * sw317 4 sw318 1 sw319 redial/pause sw321 record sw32...
Page 206
14.4. Power supply board d102 d101 c106 180/200 c203 470/16 c119 r106 220p 47/2 r137 47k r136 47k r102 330k r103 330k r121 10k c108 1000p1k c201 470/35 r202 1.5k/2 r225 vr201 r224 27k 5k 3.3k r222 r221 2.2k 2.2k pc101 d105 l103 r109 22 c105 2200pf r126 5.6k c122 0.22/16 c123 560pf c109 47/35 d103 c1...
Page 207
207 kx-fp85 y(q) kxfp85 printed in japan.