- DL manuals
- Proxim
- Adapter
- 7910
- User Manual
Proxim 7910 User Manual
Summary of 7910
Page 1
R ange lan2 serial adapter models 7910 and 7911 user’s guide 2.
Page 2
I copyright © 1999 proxim, inc., sunnyvale, ca. All rights reserved. This manual and the software described in it are copyrighted with all rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system or translated into any language in any for...
Page 3
Ii warranty return policy if you have a problem with your rangelan2 product, please call proxim technical support at (408) 731-2640. Proxim technical support will assist with resolving any technical difficulties you may have with your proxim product. If your product is found to be defective, you may...
Page 4: Contents
Iii contents 1. Introduction ................................................................. 1 the rangelan2 family ......................................................................... 2 system requirements .............................................................................. 3 the p...
Page 5
Iv 10. Advanced configuration menu .............................. 55 advanced parameters ............................................................................ 56 11. Display parameter values ...................................... 61 12. View statistics ...........................................
Page 6
V d. Parameters .............................................................. 107 radio parameters ................................................................................. 107 network parameters ............................................................................. 108 serial parame...
Page 7: 1. Introduction
1 1. Introduction congratulations on your purchase of the rangelan2 791x serial adapter, the radio module that replaces rs-232 serial cables with wireless rf (radio frequency) technology. By attaching a pair of rangelan2 serial adapters to the serial port of any two devices, you can transmit and rec...
Page 8: The Rangelan2 Family
2 the rangelan2 family rangelan2 791x serial adapter is part of a family of high- performance products that provides a complete wireless net- working solution. ❑ rangelan2 7100 is a wireless lan adapter that fits into a standard pc/at isa bus slot. ❑ rangelan2 7400 is a wireless lan adapter which fi...
Page 9: System Requirements
3 system requirements to begin using your rangelan2 791x serial adapter, you need the following minimum system requirements: ❑ at least one (1) device with a free rs-232 (serial) port (terminal, pc, etc.). ❑ at least one (1) other rangelan2 product. If the serial adapters are acting as a replacement...
Page 10: Figure 1
4 figure 1 rangelan2 791x serial adapter components.
Page 11: 2. Quick Installation
5 2. Quick installation you may follow the quick installation and configuration steps if all of the following conditions are true: ❑ you will use all of the software default values. ❑ you are using two (2) rangelan2 serial adapters as a replacement for an rs-232 cable. ❑ you are using no more than n...
Page 12: Figure 2
6 figure 2 attachment of the rangelan2 serial adapter antenna 2. Attach one end of an rs-232 cable to the rangelan2 serial adapter and the other end to a free serial port of a communication device, such as a terminal or a com- puter. Perform this step with both serial adapters. 3. Each rangelan2 791...
Page 13: Note:
7 4. Each rangelan2 791x serial adapter is preconfigured to use domain 0. If you have multiple pairs of serial adapters and each pair consists of one master and one station, set each pair to a unique domain number. Using the domain rotary switch on the underside of the rangelan2 serial adapter, set ...
Page 14
8.
Page 15: 3. Wireless Topologies
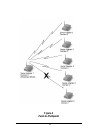
9 3. Wireless topologies the rangelan2 serial adapter supports numerous wireless topologies. The following sections describe four (4) basic wireless configurations supported by the rangelan2 serial adapter: point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, point-to-point using rangelan2 infrastructure, and point...
Page 16
10 in figure 3 above, serial adapters 1 and 2 can communicate with each other, as can serial adapters 3 and 4. Even though all four units may be in range of one another and may “hear” the others’ messages, each unit will filter out messages not intended for it. Since this topology establishes a one-...
Page 17: Point-to-Multipoint
11 point-to-multipoint the rangelan2 serial adapter may also operate in a point-to- multipoint topology. This configuration provides added flexibil- ity, allowing one centralized unit, operating in packetized mode, to communicate with multiple units placed in remote locations. When operating in pack...
Page 18: Figure 4
12 figure 4 point-to-multipoint.
Page 19
13 point-to-point using rangelan2 infrastructure you may also use your existing rangelan2 infrastructure and network to increase the range and flexibility of communications between serial adapters. A serial adapter configured as a station may synchronize to a rangelan2 access point which has the sam...
Page 20: Figure 5
14 figure 5 point-to-point using rangelan2 infrastructure.
Page 21: Point-to-Multipoint Using A
15 point-to-multipoint using a rangelan2 access point as a base unit a serial adapter may communicate directly with a workstation that has either a rangelan2 isa card, a rangelan2 pc card, or is on the same ethernet segment as a rangelan2 access point. One configuration that utilizes this feature is...
Page 22: Note:
16 figure 6 above shows a simple configuration of this topology. Desktop 1 is on the same network as a rangelan2 access point. Serial adapters 1 and 2 are configured as stations and are synchronized to the access point, which is configured as a master. Desktop 1 is running a custom-made application ...
Page 23: Note:
17 4. Pass-through and packetized modes the serial adapter’s serial interface can be set for two kinds of operating modes: pass-through mode and packetized mode. The format of the information presented to the unit’s serial port is dramatically different depending on which of these modes is selected....
Page 24
18.
Page 25: Rotary Switches
19 5. Understanding the hardware rotary switches the rangelan2 serial adapter is designed for easy config- uration by setting two rotary switches located on the bottom of the unit. The rotary switches are shown in figure 7 below. Use the switch setting tool, enclosed in the product package, to chang...
Page 26: Figure 7
20 figure 7 rotary switches the pairing domain there is an additional feature associated with domain 8 on the domain switch called the pairing domain. When the pairing domain is not used, two serial adapters will each send out a series of handshaking messages and exchange ip addresses to enable comm...
Page 27: Note:
21 when the unit is reset. This allows the user to permanently configure a pair of serial adapters to communicate exclusively with one another. Follow these steps to permanently bind a pair of serial adapters: 1. Ensure that both units are turned off. 2. Using the switch setting tool, turn the domai...
Page 28: Led Indicators
22 to reset the unit back to the default setting, manually set the destination address to 0.0.0.0 or reset the unit to factory de- faults from within the software configuration menu. When using this feature, have only two serial adapters config- ured to domain 8 on the rotary switch at any point in ...
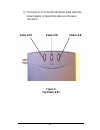
Page 29: Figure 8
23 ❑ the serial led on the left side blinks green when the serial adapter is transmitting data over the serial connection. Figure 8 top panel leds status led radio led serial led.
Page 30
24 there are also four leds on the back panel of the rangelan2 791x serial adapter: ❑ the green master led, located between the dc power jack and the serial interface, is on steady when the unit is set as a master. ❑ the yellow sync led, located between the dc power jack and the serial interface, is...
Page 31: Figure 9
25 figure 9 back panel leds override led master led sync led.
Page 32: Serial Port Specification
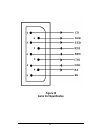
26 serial port specification figure 10 and the table below provide the specification of the 9- pin serial port located on the rangelan2 serial adapter. The serial adapter is wired as a dce (data communication equip- ment), like a modem. The unit is designed to connect directly to a dte (data termina...
Page 33: Figure 10
27 figure 10 serial port specification.
Page 34: Antenna Options
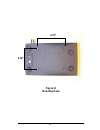
28 antenna options the serial adapter is shipped with a standard directly-connected antenna. To install the antenna, screw it clockwise onto the antenna connector. Proxim sells several antenna alternatives, including higher gain omnidirectional and directional antennas. Each of these antennas ship w...
Page 35: Figure 11
29 figure 11 mounting holes 2.10” 2.75”.
Page 36
30
Page 37: 6. Configuration
31 6. Configuration you need to configure the rangelan2 serial adapter using the software menus if any of the following conditions apply: ❑ you plan to operate a serial adapter in broadcast mode. ❑ you want to set security ids on your serial adapters. ❑ you want to operate in packetized mode. ❑ you ...
Page 38
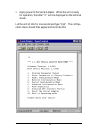
32 3. Apply power to the serial adapter. When the unit is ready for operation, the letter “u” will be displayed on the terminal screen. Let the unit sit idle for one second and type “$$$”. The configu- ration menu should then appear and look like this:.
Page 39
33 type the number of the menu option and to view the sub-menus. Hit at any time to back up one menu. To simplify the menu options, all of the configuration menus will appear in a tree diagram format within this manual. The tree diagram for the main menu, shown in the screen shot above, looks like t...
Page 40
34.
Page 41: 7. Radio Configuration Menu
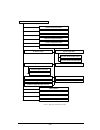
35 7. Radio configuration menu this section discusses the radio configuration values that can be manually configured by the user. The software tree below shows the options available in the radio configuration menu: d o tted l in e - v is ib le w h e n c o n fig u re d a s a m as ter d a s h ed l in ...
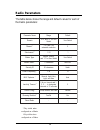
Page 42: Radio Parameters
36 radio parameters the table below shows the range and default values for each of the radio parameters: e m a n r et e m a r a p e g n a r tl u af e d ni a m o d e s u r of " u " d n a , 5 1 - 0 h ct i w s h ct i w s e s u * l e n n a h c r of 0 d n a , 5 1 - 1 n oi t c el e s ci t a m ot u a 0 * l...
Page 43
37 note that changes to these parameters will not take effect until either the radio or the serial adapter is reset. A rangelan2 serial adapter may be set as either a masterora station using the station type parameter within the configura- tion menu. You may also choose “u” for use switch to use the...
Page 44: Note:
38 in order to establish communications, all stations and the master must be configured with the same domain number. Radios on different domains cannot communicate with each other. The domain is a software filter which does not affect the actual radio frequency or the frequency hopping sequence. You...
Page 45
39 each master can select one of 15 channels to establish commu- nication with its stations. Each channel number sets a unique frequency hopping sequence allowing for multiple subnetworks with higher data rate transmission capability in the same air space. You may think of the channel as a pipe. In ...
Page 46: Note:
40 for example, you can use channel 1, subchannel 1 for adapter pair a and channel 1, subchannel 2 for adapter pair b. The two pairs will not communicate with one another. However, they are still sharing the 1.6 mbps pipe since they are both using channel 1. The subchannels are designated 1 through ...
Page 47
41 the repeating enabled parameter gives the ability to enable or disable the rangelan2 repeating feature. When enabled, a serial adapter, acting as a master, may repeat signals coming from one station and destined for another station. These two stations must be out of range of one another, but both...
Page 48: Note:
42 there is no inactivity timeout set by default, but you may change this to any interval of 10 seconds. This parameter is visible only when the serial adapter is set as a station. A master unit does not have a sleep mode. Note: configuring a serial adapter with an inactivity timeout may cause data ...
Page 49: Note:
43 you may choose to disable a serial adapter’s ability to roam with the roaming enabled parameter. This feature is enabled by default; however, if you want a rangelan2 serial adapter to communicate with one and only one other rangelan2 product, you may disable this feature. This parameter is visibl...
Page 50
44.
Page 51
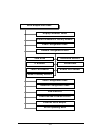
45 8. Network configuration menu this section describes the network configuration parameters for the rangelan2 serial adapter. The software tree below shows the options available: d isp lay p aram eter v alu es r eset p aram eters to f acto ry d efau lts r ad io c o n fig u ratio n m en u s en d m o...
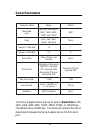
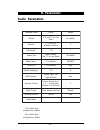
Page 52: Network Parameters
46 network parameters e m a n r et e m a r a p e g n a r tl u af e d e d o m d n e s ,) t ni o p ot t ni o p ( p c t ,) t ni o p ot t ni o p ( p d u t s a c d a o r b d n a )t ni o p ot t ni o p ( p c t s s e r d d a n oi t a ni t s e d - - s s e r d d a p i - s s e r d d a tl u af e d k s a m t e n...
Page 53
47 broadcast message. Broadcast mode uses the udp transport layer protocol to send data. As stated above, udp is faster than tcp but does not ensure reliable message delivery. However, if your application ensures the reliability of data transmission, there should be no negative side effects to using...
Page 54: Note:
48 cate with the wired infrastructure, it will be necessary to change the default address to one which is on the same subnet as the wired stations so that ip packets are routed correctly. You can override the default address using the ip address option in the configuration menu. This parameter will ...
Page 55
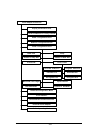
49 9. Serial configuration menu this section describes the serial configuration parameters for the rangelan2 serial adapter. The software tree below shows the options available: d isp la y p a ra m e te r v a lu e s r e se t pa ra m e te rs to f a c to ry d e fa u lts r a d io c o n fig u ra tio n m...
Page 56: Serial Parameters
50 serial parameters e m a n r et e m a r a p e g n a r tl u af e d et a r d u a b ) s p b ( , 0 0 8 4 , 0 0 4 2 , 0 0 2 1 , 0 0 3 , 0 0 4 8 3 , 0 0 2 9 1 , 0 0 6 9 0 0 2 5 1 1 d n a , 0 0 6 7 5 0 0 6 9 yt ir a p , k r a m , d d o , n e v e e n o n d n a , e c a p s e n o n st i b p ot s f o r e b m...
Page 57: Local Serial Adapter
51 you may also change the default settings for parity, number of stop bits, and number of data bits to match the settings of your rs-232 application. The serial adapter will support any combination of 7 or 8 data bits, 1 or 2 stop bits, and one of the following parity settings: even, odd, mark, spa...
Page 58
52 cts pin, notifying the remote rs-232 host that data may be sent over the connection. This function regulates the data exchange between two rs-232 hosts. In addition to this basic function, the serial adapter’s flow control options regulate the data exchange between the serial adapter and its atta...
Page 59
53 the maximum line length refers to the maximum number of characters the serial adapter must receive before transmitting the message. The maximum value for this parameter is 1456, which corresponds to the maximum size of an ethernet packet minus the space required for the transport layer and other ...
Page 60
54.
Page 61
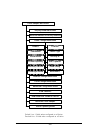
55 10. Advanced configuration menu * f o r u s e w h ile in p a c k e tiz e d m o d e o n ly d ispla y p a ra m e te r v a lu e s r e se t pa ra m e te rs to fa c to ry d e fa u lts r a dio c o n fig ura tio n m e n u n e tw ork c on fig ura tio n m e n u s e ria l c o n fig ura tio n m e n u ip ad ...
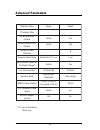
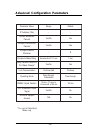
Page 62: Advanced Parameters
56 advanced parameters e m a n r et e m a r a p e g n a r tl u af e d r et li f s s e r d d a p i - - t s a c d a o r b t p e c c a st e k c a p o n / s e y s e y t ni o p - ot -t ni o p t p e c c a st e k c a p o n / s e y s e y u n e m - ot - e p a c s e r et c a r a h c - $ y al e d u n e m - ot ...
Page 63
57 the ip address filter parameter allows you filter out packets received by the serial adapter from any ip address other than one specified ip address. You may specify only one ip ad- dress from which to accept messages. The default for this parameter is to receive packets from any ip address. The ...
Page 64
58 and loses communication with its destination unit. You may set the unit to either reestablish the connection and continue trans- missions or to halt communications to provide an alert that the connection has been lost. If the serial adapter loses communication while set to continue, the unit will...
Page 65
59 if you have written, or plan to write, a custom application to allow communication between the rangelan2 serial adapter and an ethernet device, set the tcp close connection signal parameter to “yes.” when this parameter is enabled, the serial adapter will close an existing tcp connection upon rec...
Page 66
60
Page 67
61 11. Display parameter values the serial adapter displays all of the relevant parameters in one centralized location. By choosing “display parameter values,” you can view the current and configured values for the radio, network, serial, and advanced parameters. Current values are already in use by...
Page 68
62 r adio param eters n etw ork p aram eters baud r ate (current) baud r ate (configured) p arity (current) p arity (configured) # s top bits (current) # s top bits (configured) # data bits (current) # data bits (configured) e cho mode max. Line length input t im eout (m s) line delim iters generate...
Page 69: 12. View Statistics
63 12. View statistics you can view statistics about the rangelan2 serial adapter from the view statistics menu. The following diagram illustrates the software tree: d isp lay param eter v alu e s r es et p ara m eters to f ac to ry d e fa u lts r ad io c o n fig u ratio n m en u n etw o rk c o n fi...
Page 70: Serial Errors Statistics
64 serial errors statistics this category displays the number of errors occurring in the serial interface of the serial adapter during operation. The serial adapter will record the number of framing errors that occur when a character is received over the serial line without a valid stop bit. A parit...
Page 71: 13. Performance Hints
65 13. Performance hints this section provides the user with ideas for how to increase performance with proxim wireless products. Microwave ovens microwave ovens operate in the same frequency band as rangelan2 products. Therefore, if you use a microwave within range of rangelan2 equipment, you may n...
Page 72
66 proper antenna placement can help improve range. Here are some guidelines: ❑ the antenna should be placed in a vertical position. ❑ do not place a sheet of metal (like a filing cabinet) between two antennas. ❑ two antennas that are communicating should be in the same plane. For example, do not li...
Page 73: 14. Troubleshooting
67 14. Troubleshooting the rangelan2 791x serial adapter is designed to be very easy to install and operate. If you do experience difficulties, however, use the information in this chapter to help diagnose and solve the problem. If you cannot resolve the problem, contact proxim, as described in appe...
Page 74: 3 Blinks: Software Error
68 3 blinks: software error 4 blinks: failed to initialize the radio 5 blinks: memory full 6 blinks: miscellaneous error 7 blinks: failed to initialize the tcp/ip stack commonly asked technical support questions n oi t s e u q m ot p m y s / m el b o r p r e w s n a / n oi t ul o s el bi s s o p s' ...
Page 75
69 n oi t s e u q m ot p m y s / m el b o r p r e w s n a / n oi t ul o s el bi s s o p s' r e s u ni r et p a h c e di u g e ht p u g ni r b t' n a c i . U n e m n oi t a r u gi f n o c s g ni tt e s la ni m r et r u o y t a ht yf ir e v . 1 la ir e s e ht n o t e s e s o ht h ct a m .R et p a d a ...
Page 76: Overview
70 a. Packetized mode specification overview the purpose of the serial adapter is to accept information from a serial line and transmit it reliably via radio to another rangelan2 station, or to a wired station through a rangelan2 access point. Serial adapters receiving information transfer it to an ...
Page 77
71 tions where developing special software to interact with the serial adapter is undesirable. For some applications, the pass-through mode of operation is not ideal. For example, because the pass-through serial adapter takes all information arriving at its serial line as data to be sent out over th...
Page 78
72 the modem command protocol (mcp) is an application layer protocol by which an external computer may exchange com- mands, status information, and data with the serial adapter over the serial adapter’s rs-232 serial line. Since the protocol is an application layer protocol, it contains no provision...
Page 79: Ppx-1 Protocol
73 ppx-1 protocol the following is the format of the ppx-1 packet: byte soh ;start of header for synchronization (ascii 01h) byte len h ;high byte of length byte len l ;low byte of length byte header ;= not(len l) + check ;not(len h), this is an ; arithmetic sum bytes data ;this is where the mcp com...
Page 80: Modem Command Protocol (McP)
74 modem command protocol (mcp) this section describes the modem command protocol. All of the commands which the serial adapter will accept are listed below. Each command begins with a command byte which tells the serial adapter which command the message contains. Some commands cause the serial adap...
Page 81: Transmit Data Packet
75 the external computer creates a command packet, it should place a unique number (from 0 to 127) into the seqno field of the packet. When the serial adapter later generates a response to that packet, it will place this same value in the seqno field of the response. In this way, the external comput...
Page 82
76 the four byte address field is the ip address of the destination node. Broadcast addresses (for example, x.Y.Z.255) can also be used. Request radio signal strengths purpose: to request the serial adapter to measure the strength of rf energy on its current radio channel and report the signal stren...
Page 83: Go to Standby
77 go to standby purpose: the purpose of this command is to place the serial adapter in standby mode in order to conserve current. For this command to work properly, the rts line at the serial adapters serial connector must be inactive. The serial adapter can be removed from standby mode by assertin...
Page 84: Set Network Subchannel
78 message format: byte command (ascii ‘c’, 43h) byte seqno byte radio channel (1 to 15) set network subchannel purpose: to set the subchannel of the serial adapter’s network protocol. Response expected from serial adapter: “subchannel confirma- tion” message format: byte command (ascii ‘s’, 53h) by...
Page 85: Station Search
79 the meaning of the baud rate argument is as follows: value of baudrate field baud rate 2 300 3 1200 4 2400 5 4800 6 9600 7 19200 8 38400 9 57600 a 115200 station search purpose: to send a broadcast message asking any station receiv- ing the message to reply with its ip address. Response expected ...
Page 86: Call Up Configuration Menu
80 call up configuration menu purpose: to invoke the serial adapter configuration menu from packetized mode. Response expected from serial adapter: none byte command (ascii ‘m’, 4dh) override rangelan2 parameters purpose: to allow a serial adapter application to set the domain, security id, and mast...
Page 87: Data Packet Received
81 mcp responses from serial adapter this section describes the format of mcp response messages passed from the serial adapter to an external computer. Data packet received purpose: this is the message used by the serial adapter to deliver packets to the external computer which have been received by...
Page 88: Signal Strength Report
82 the statusind field does not show whether the destination node has received the message. Message format: byte response (ascii ‘t’, 74h) byte seqno (from original command) byte len h (from original command) byte len l (from original command) byte destaddr h (from original command) byte destaddr 3 ...
Page 89: Standby Confirmation
83 serial adapter version report purpose: this packet is generated by the serial adapter in re- sponse to a request serial adapter version command. The packet contains the 4-byte ip address of the serial adapter, along with the version string and a code indicating the radio type. Message format: byt...
Page 90: Radio Channel Confirmation
84 message format: byte response (ascii ‘i’, 69h) byte seqno (from original command) byte ipaddr h (serial adapter’s ip address) byte ipaddr 3 byte ipaddr 2 byte ipaddr l 7 bytes string (7 byte rom version number string) byte radio type: 03= rangelan2 ex- tended range, 04= rangelan2 ex- tended range...
Page 91: Baud Rate Confirmation
85 message format: byte response (ascii ‘s’, 73h) byte seqno (from original command) byte subchannel (1 to 15, from original com mand) baud rate confirmation purpose: this message is sent after a set baud rate command is received by the serial adapter. Note that this message is sent at the old baud ...
Page 92: Rs-232 Pin Status Reply
86 rs-232 pin status reply byte response (ascii ‘p’, 70h) byte seqno byte status 0= success 1= error 4 bytes ip address of remote node byte pin status the pin status byte b will consist of the following fields: b0: 1 if dtr is asserted b1: 1 if dsr is asserted b2: 1 if rts is asserted b3: 1 if cts i...
Page 93
87 b. Serial adapter tcp/ip specification the fundamental obstacle to allowing a serial adapter to commu- nicate with a wired workstation is that the two units communicate in different ways. To address this discrepancy, the user must have a custom application programmed by someone familiar with tcp/...
Page 94
88 that windows sockets programs require a compiler, such as visual c++, in order to be executed. On unix machines, berkeley sockets is available on most of the common platforms. 5. The data sent to the serial adapter must be formatted appro- priately. A four-byte header precedes the user data that ...
Page 95
89 bit 4 is set if cd is asserted on the sending side. Bit 5 is set if the sending host has sent a break; this bit should be set to 0. Bit 6: reserved and always set to 0. Bit 7: reserved and always set to 0. Messages received from the serial adapter will contain the four- byte header before the act...
Page 96
90 7. The default gateway address and subnet mask parameters on the serial adapter must be set to the appropriate values for your network. See your network administrator for details. 8. It is also possible to do a station search from a wired worksta- tion to determine the ip address of any serial ad...
Page 97: Note:
91 sample tcp/ip communication programs on the following pages are four pieces of sample code written in berkeley sockets as an example of the type of custom code which must be written so that the serial adapter can communicate with nodes on an ethernet network. Note: if your custom program makes us...
Page 98
92 23 24 25 /* open the log file */ 26 logfile= fopen(“proxlink.Log”, “wb”); 27 if (!Logfile) { 28 printf(“error: couldn’t open log file”); 29 exit(1); 30 } 31 32 /* create socket */ 33 sock= socket(af_inet, sock_stream, 0); 34 if (sock 35 perror(“opening stream socket”); 36 exit(2); 37 } 38 39 /*...
Page 99
93 65 /* establish the tcp connection. Accept() returns a new 66 socket number for the connection, allowing listen() to 67 (if desired) continue to listen on the old socket. 68 69 parameters to accept() are: the socket that the 70 previous listen() call was using, a sockaddr structure, 71 and the le...
Page 100: Sample Tcp Send Program
94 sample tcp send program 1 /******************************************************* 2 * tcpsend.C 3 * sends a message to a serial adapter using tcp 4 * 5 *******************************************************/ 6 7 #include 8 #include 9 #include 10 #include 11 #include 12 13 #define data “half a l...
Page 101
95 40 hp= gethostbyname(argv[1]); 41 if (hp==0) { 42 fprintf(stderr, “%s: unknown host”, argv[1]); 43 exit(2); 44 } 45 memcpy( (char *)&server.Sin_addr, (char *)hp->h_addr, hp-h_length); 46 server.Sin_port= htons(atoi(argv[2])); 47 48 /* use the connect() socket call to initiate a tcp connection w...
Page 102: Sample Udp Receive Program
96 sample udp receive program 1 /******************************************************** 2 * udprecv.C 3 * receives a series of messages from a serial adapter using udp. 4 * 5 *******************************************************/ 6 7 #include 8 #include 9 #include 10 #include 11 12 main() 13 { 1...
Page 103: Sample Udp Send Program
97 41 if (bind(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&name, sizeof(name)) 42 perror(“binding datagram socket”); 43 exit(1); 44 } 45 46 /* find assigned port value and print it out. Getsockname() gets 47 the local ip address and port number associated with a socket. */ 48 length= sizeof(name); 49 if (getsockname(...
Page 104
98 13 #define data1 0 14 15 main(argc, argv) 16 int argc; 17 char *argv[]; 18 { 19 int i, sock; 20 short datalength; 21 short networkdatalength; 22 long npackets= 0; 23 char buf[1024]; 24 struct sockaddr_in name; 25 struct hostent *hp, *gethostbyname(); 26 27 if (argc 28 printf(“usage: udpsend hostn...
Page 105
99 55 name.Sin_family= af_inet; 56 /* htons() converts a 16-bit integer from host to network byte order */ 57 name.Sin_port= htons(atoi(argv[2])); 58 59 /* construct message, including serial adapter header. */ 60 buf[0]= data1; 61 buf[3]= 0x1b; 62 datalength= strlen(data); 63 networkdatalength= hto...
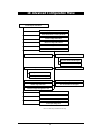
Page 106: C. Menu Structure
100 c. Menu structure d otted line - v isible w hen configured as a m aster d ashed line - v isible w hen configured as a s tation d o m ain c han nel s ub chan nel m aste r/s tatio n m a ster n am e r epe ating e nab le d m ac op tim ize in activity t im e out (sec .) r o am ing c onfig. R oam ing ...
Page 107
101 radio param eters netw ork parameters baud rate (current) baud rate (configured) p arity (current) p arity (configured) # stop bits (current) # stop bits (configured) # data b its (current) # data bits (configured) e cho mode max. Line length input t imeout (m s) line delim iters generate x on/x...
Page 108
102 d otted l in e - v is ib le w h en c on fig u red as a m as ter d as h ed l in e - v is ib le wh en c on fig u red as a s tation d isp la y pa ra m e te r v a lu e s r e se t pa ra m e te rs to f a c to ry d e fa u lts d o m a in c h a n n e l s u b c h a n n e l s ta tio n t y p e m a ste r n a...
Page 109
103 d isp lay param eter values r eset param eters to facto ry d efau lts r ad io c on fig u ratio n m en u send m o d e d estin atio n ad d ress ip ad d ress su b n et m ask l ocal po rt n u m b er r em o te po rt n u m b er d efau lt g atew ay add ress n etw o rk c o n fig u ratio n m en u serial ...
Page 110
104 d ispla y pa ra m e te r v a lu e s r e se t pa ra m e te rs to fa c to ry d e fa u lts r a d io c onfigu ra tion m e n u n e tw ork c o nfigu ra tion m e n u ba u d r a te pa rity n u m be r o f s top bits n um b e r of d a ta bits e c h o m od e g e ne ra te x on /x o ff r e c og nize x o n /x...
Page 111
105 * f or u s e w h ile in p ac k e tiz e d m od e o n ly d ispla y pa ra m e te r v a lue s r e se t p a ra m e te rs to f a c tory d e fa ults r a dio c o nfigu ra tion m e nu n e tw ork c o nfigura tion m e nu s e ria l c o nfigu ra tion m e nu ip ad dre ss filte r r e c e ive bro a dc a st m e ...
Page 112
106 d isp la y param eter v alu es r e set p ara m eters to f acto ry d efau lts r a d io c o n fig u ratio n m en u n e tw o rk c o n fig u ratio n m en u s erial c o n fig u ratio n m en u a d va n ced c o n fig u ratio n m en u f ram in g parity o ve rru n se ria l e rro rs pa ckets a c cep ted p...
Page 113: D. Parameters
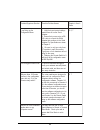
107 d. Parameters radio parameters e m a n r et e m a r a p e g n a r tl u af e d ni a m o d e s u r of " u " d n a , 5 1 - 0 h ct i w s h ct i w s e s u * l e n n a h c r of 0 d n a , 5 1 - 1 n oi t c el e s ci t a m ot u a 0 * l e n n a h c b u s 5 1 - 1 1 e p y t n oi t at s , n oi t at s ,r et s...
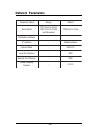
Page 114: Network Parameters
108 network parameters e m a n r et e m a r a p e g n a r tl u af e d e d o m d n e s ,) t ni o p ot t ni o p ( p c t ,) t ni o p ot t ni o p ( p d u t s a c d a o r b d n a )t ni o p ot t ni o p ( p c t s s e r d d a n oi t a ni t s e d - - s s e r d d a p i - s s e r d d a tl u af e d k s a m t e ...
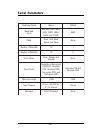
Page 115: Serial Parameters
109 serial parameters e m a n r et e m a r a p e g n a r tl u af e d et a r d u a b ) s p b ( , 0 0 8 4 , 0 0 4 2 , 0 0 2 1 , 0 0 3 , 0 0 4 8 3 , 0 0 2 9 1 , 0 0 6 9 0 0 2 5 1 1 d n a , 0 0 6 7 5 0 0 6 9 yt ir a p , k r a m , d d o , n e v e e n o n d n a , e c a p s e n o n st i b p ot s f o r e b ...
Page 116
110 advanced configuration parameters e m a n r et e m a r a p e g n a r tl u af e d r et li f s s e r d d a p i - - t s a c d a o r b t p e c c a st e k c a p o n / s e y s e y t ni o p - ot -t ni o p t p e c c a st e k c a p o n / s e y s e y u n e m - ot - e p a c s e r et c a r a h c - $ y al e ...
Page 117
111 e. Procedure for downloading new software at some point in the future, you may need to upgrade the rangelan2 serial adapter software. To do this, choose the download new software version option from the main menu. You need to use the xmodem protocol to complete the download. Commonly used serial...
Page 118: Note:
112 note: do not choose the “download new software version” menu item unless you are prepared to perform a soft- ware download to the device. Once you proceed past the warning messages, there is no way to exit the download process. The unit will not become operational again until after a download of...
Page 119: F. Glossary
113 f. Glossary access point — an internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks together. Assert — to set a flow control pin to the “on” position. Bandwidth — the size (in hertz) of the frequency range that a signal transmission occupies. Typical narrow band signals oc-...
Page 120
114 inhibit — to set a flow control pin to the “off” position. Interference — a situation that occurs when an unwanted rf signal occupies the same frequency band as a desired signal. Ip address (internet protocol address) — a 32-bit address assigned to tcp/ip hosts. Mac address (media access control...
Page 121
115 g. How to reach technical support if you’re having a problem using rangelan2 791x serial adapter and can’t resolve it with the information in chapter 14, gather the following information and contact proxim technical support: ❑ what are the configuration settings? ❑ what were you doing when the e...
Page 122: H. U.S. Specifications
116 h. U.S. Specifications the following technical specification is for reference purposes only. Actual product’s performance and compliance with local telecommunica- tions regulations may vary from country to country. Proxim, inc. Will only ship products that are type approved in the destination co...
Page 123: Index
117 index a access point. See rangelan2: access point advanced configuration menu 55. See also configuration menu antenna 3, 5, 28, 65, 116 placement 66 b baud rate 50 break signal duration 58 broadcast mode 47, 57. See also point-to-multipoint c channel 39, 113, 116 configuration menu 31–34 advance...
Page 124
118 e echo mode 51, 69 eeprom 1 escape parameters 57 escape-to-menu character 57 escape-to-menu delay 57 extension point. See rangelan2: extension point f fcc ii, 116 flow control 51 generate dsr 52 recognize dtr 52 recognize rts 52 recognize xon/xoff 52 use dtr remotely 52 use rts remotely 53 frami...
Page 125
119 microwave ovens 65 mounting 28–31 n network configuration menu 45–48. See also configuration menu notify remote nodes of pin status change 57 null modem cable 26 number of data bits 51 number of stop bits 51 o operating mode 58. See also packetized mode; pass-through mode output power 116 overri...
Page 126
120 repeating 41 rma i roam config 42 roaming enabled 43 rotary switch 1, 19–22, 24 domain 3, 7, 19, 20–22, 31, 38 station type 3, 6, 19, 37 router 16, 48 rs-232 cable 3, 17, 26, 31. See also serial port s security id 13, 31, 40, 46 send mode 46. See also broadcast mode; point-to-point serial config...
Page 127
121 u u.S. Specifications 116–117 udp 46, 64, 114 v view statistics 63 w windows sockets. See sockets x xmodem 111 xon/off. See flow control.