- DL manuals
- Qsan Technology
- Storage
- P300H61
- User Manual
Qsan Technology P300H61 User Manual - 4.6
83
This is much better than hard drive crash when it is writing data or rebuilding a failed hard
drive.
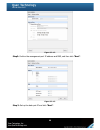
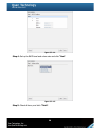
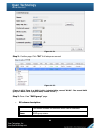
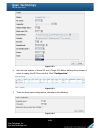
“S.M.A.R.T.” can display S.M.A.R.T. information of hard drives. The number is the
current value; the number in parenthesis is the threshold value. The threshold values from
different hard drive vendors are different; please refer to hard drive vendors’ specification
for details.
S.M.A.R.T. only supports SATA drives. SAS drives do not have this function now. It will
show N/A in the web page for SAS drives.
Figure 4.5.4.1 (SAS drives)
Figure 4.5.4.2 (SATA drives)
4.6
System maintenance
Summary of P300H61
Page 1
1 qsan iscsi subsystem p300h61 / p300h71 gbe iscsi to sata ii / sas raid subsystem user manual version 7.79 (mar, 2011) qsan technology, inc. Http://www.Qsantechnology.Com user manual# qum201106-p300h61_p300h71.
Page 2: Preface
2 preface copyright copyright@2011, qsan technology, inc. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted without written permission from qsan technology, inc. Trademarks all products and trade names used in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their re...
Page 3: Table Of Contents
3 table of contents chapter 1 overview ................................................................. 6 1.1 features .......................................................................................6 1.1.1 highlights .............................................................................
Page 4: Chapter 5
4 4.4 volume configuration ..................................................................56 4.4.1 physical disk ............................................................................................................. 57 4.4.2 raid group .........................................................
Page 5: Appendix
5 6.2 event notifications ....................................................................135 6.3 how to get support ...................................................................142 appendix ................................................................................ 146 a. Compatibili...
Page 6: Chapter 1
6 chapter 1 overview 1.1 features qsan subsystem can provide non-stop service with a high degree of fault tolerance by using qsan raid technology and advanced array management features. P300h61 / p300h71 subsystem connects to the host system by iscsi interface. It can be configured to numerous raid ...
Page 7
7 snapshot-on-the-box (qsnap) is a fully usable copy of a defined collection of data that contains an image of the data as it appeared at the point in time, which means a point-in-time data replication. It provides consistent and instant copies of data volumes without any system downtime. Snapshot-o...
Page 8: 1.2
8 data protection qsnap writeable snapshot connection availability load balancing and failover support on the 8 iscsi gbe ports dimension (w x d x h) 447 x 490 x 130 (mm) (p300h61) 447 x 490 x 171 (mm) (p300h71) power supply 2 x 500w psu (p300h61) 3 x 500w psu (p300h71) cache protection hot pluggabl...
Page 9
9 vd virtual disk. Each rd could be divided into several vds. The vds from one rg have the same raid level, but may have different volume capacity. Lun logical unit number. A logical unit number (lun) is a unique identifier which enables it to differentiate among separate devices (each one is a logi...
Page 10
10 s.M.A.R.T. Self-monitoring analysis and reporting technology. Wwn world wide name. Hba host bus adapter. Ses scsi enclosure services. Nic network interface card. Bbm battery backup module • part 2: iscsi iscsi internet small computer systems interface. Lacp link aggregation control protocol. Mpio...
Page 11
11 1.2.2 raid levels there are different raid levels with different degree of data protection, data availability, and performance to host environment. The description of raid levels are on the following: raid 0 disk striping. Raid 0 needs at least one hard drive. Raid 1 disk mirroring over two disks...
Page 12: 1.3
12 the below graphic is the volume structure which qsan has designed. It describes the relationship of raid components. One rg (raid group) consists of a set of vds (virtual disk) and owns one raid level attribute. Each rg can be divided into several vds. The vds in one rg share the same raid level,...
Page 13
13 the target is the storage device itself or an appliance which controls and serves volumes or virtual volumes. The target is the device which performs scsi command or bridge to an attached storage device. Figure 1.3.1 the host side needs an iscsi initiator. The initiator is a driver which handles ...
Page 14: 1.4
14 google groups: http://groups.Google.Com/group/open-iscsi/threads?Gvc=2 http://groups.Google.Com/group/open-iscsi/topics open-iscsi wiki: http://www.Open-iscsi.Org/cgi-bin/wiki.Pl 3. Atto iscsi initiator is available for mac. Website: http://www.Attotech.Com/xtend.Html 4. Solaris iscsi initiator v...
Page 15
15 7. Front-end: 4 x gbe iscsi ports per controller 8. Lcm for quick management 9. Hot pluggable bbm support (optional) 10. Sas jbod expansion port for expansion 11. Qsata board support for sata drives (optional) 12. Two power supplies (p300h61) three power supplies (p300h71) 13. Redundant fans • ra...
Page 16
16 1. Management ui via lcm serial console ssh telnet http web ui secured web (https) 2. Notification via email snmp trap browser pop-up windows syslog windows messenger 3. Isns support 4. Dhcp support • iscsi features 1. Iscsi jumbo frame support 2. Header/data digest support 3. Chap authentication...
Page 17
17 • power and environment ac input: 100-240v ~ 7a-4a 500w with pfc (auto switching) dc output: 3.3v-21a; 5v-39a; 12v-30a operating temperature: 0 to 40 ℃ relative humidity: 5% to 95% non-condensing • dimensions 3u16 19 inch rackmount chassis (p300h61) 4u24 19 inch rackmount chassis (p300h71) 447mm ...
Page 18
18 c. Mechanical loading - mounting of the equipment in the rack should be such that a hazardous condition is not achieved due to uneven mechanical loading. D. Circuit overloading - consideration should be given to the connection of the equipment to the supply circuit and the effect that overloading...
Page 19: Chapter 2
19 chapter 2 installation 2.1 package contents the package contains the following items: 1. P300h61 / p300h71 subsystem (x1) 2. Hdd trays (x16) (p300h61) hdd trays (x24) (p300h71) 3. Power cords (x2) (p300h61) power cords (x3) (p300h71) 4. Rs-232 cables (x2), one is for console (black color, phone j...
Page 20
20 drive slot numbering (p300h61) slot 1 slot 5 slot 9 slot 13 slot 2 slot 6 slot 10 slot 14 slot 3 slot 7 slot 11 slot 15 slot 4 slot 8 slot 12 slot 16 drive slot numbering (p300h71) slot 1 slot 7 slot 13 slot 19 slot 2 slot 8 slot 14 slot 20 slot 3 slot 9 slot 15 slot 21 slot 4 slot 10 slot 16 slo...
Page 21
21 lcd display. Power led: blue power on. Off power off. Access led: orange host is accessing. Off host is no access. Status led: red system is failure. Off system is good. Mute button. Up button. Down button. Enter button. Esc button. 2.3.3 install drives remove a drive tray. Then install a hdd. To...
Page 22
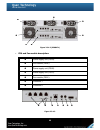
22 figure 2.2.3.3 • hdd tray description: hdd fault led: red hdd is failure. Off hdd is good. Hdd activity led: blue hdd is active. Violet blinking hdd is accessing. Off no hdd. Latch for tray kit removal. Hdd tray handhold. 2.3.4 rear view figure 2.3.4.1 (p300h61).
Page 23
23 figure 2.3.4.2 (p300h71) • psu and fan module description: power supply unit (psu3). Fan module (fan2). Power supply unit (psu2). Power supply unit (psu1). Fan module (fan1). Controller 1. Controller 2. Figure 2.3.4.3.
Page 24
24 • connector, led and button description: gigabit ports (x4). Led (from left to right) controller health led: green controller status normal or in the booting. Red other than above status. Master slave led: green master controller. Off slave controller. Dirty cache led: orange data on the cache wa...
Page 25: Deployment
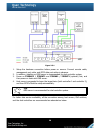
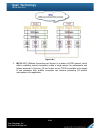
25 figure 2.4.1 1. Bbm (battery backup module) supports hot pluggable. Regardless of the subsystem is turned on or off. 2. Remove the cover of bbm. 3. Insert the bbm. 4. Tighten the bbm and use screws to lock the both sides. 5. Done. 2.5 deployment please refer to the following topology and have all...
Page 26
26 figure 2.5.1 1. Setup the hardware connection before power on servers. Connect console cable, management port cable, and iscsi data port cables in advance. 2. In addition, installing an isns server is recommended for dual controller system. 3. Power on p300h61 / p300h71 and j300h61 / j300h71 (opt...
Page 27
27 figure 2.5.2 the following topology is the connections for console and ups (optional). Figure 2.5.3.
Page 28
28 1. Using rs-232 cable for console (back color, phone jack to db9 female) to connect from controller to management pc directly. 2. Using rs-232 cable for ups (gray color, phone jack to db9 male) to connect from controller to apc smart ups serial cable (db9 female side), and then connect the serial...
Page 29: Chapter 3
29 chapter 3 quick setup 3.1 management interfaces there are three management methods to manage qsan subsystem, describe in the following: 3.1.1 serial console use console cable (null modem cable) to connect from console port of qsan subsystem to rs 232 port of management pc. Please refer to figure ...
Page 30
30 figure 3.1.3.1 figure 3.1.3.2 press “enter” button, the lcm functions “system info.”, “alarm mute”, “reset/shutdown”, “quick install”, “volume wizard”, “view ip setting”, “change ip config” and “reset to default” will rotate by pressing (up) and (down). When there is warning event or error event ...
Page 31
31 default gateway: 192.168.10.254 • lcm menu hierarchy: [firmware version x.X.X] [system info.] [ram size xxx mb] [alarm mute] [yes no] [reset] [yes no] [reset/shutdown] [shutdown] [yes no] [quick install] raid 0 raid 1 raid 3 raid 5 raid 6 raid 0+1 xxx gb [apply the config] [yes no] [local] raid 0...
Page 32
32 caution before power off, it is better to execute “shutdown” to flush the data from cache to physical disks. 3.1.4 web ui qsan subsystem supports graphic user interface (gui) to operate. Be sure to connect the lan cable. The default ip setting is dhcp; open the browser and enter: http://192.168.1...
Page 33
33 figure 3.1.4.2 there are seven indicators and three icons at the top-right corner. Figure 3.1.4.3 • indicator description: raid light: green raid works well. Red raid fails. Temperature light: green temperature is normal. Red temperature is abnormal. Voltage light: green voltage is normal. Red vo...
Page 34: 3.2
34 controller alive and well. Return to home page. Logout the management web ui. Mute alarm beeper. Tips if the status indicators in internet explorer (ie) are displayed in gray, but not in blinking red, please enable “internet options” “advanced” “play animations in webpages” options in ie. The def...
Page 35
35 figure 3.2.1.2 step2: confirm the management port ip address and dns, and then click “next”. Figure 3.2.1.3 step 3: set up the data port ip and click “next”..
Page 36
36 figure 3.2.1.4 step 4: set up the raid level and volume size and click “next”. Figure 3.2.1.5 step 5: check all items, and click “finish”..
Page 37
37 figure 3.2.1.6 step 6: done. 3.2.2 volume creation wizard “volume create wizard” has a smarter policy. When the system is inserted with some hdds. “volume create wizard” lists all possibilities and sizes in different raid levels, it will use all available hdds for raid level depends on which user...
Page 38
38 figure 3.2.2.1 step 2: please select the combination of the rg capacity, or “use default algorithm” for maximum rg capacity. After rg size is chosen, click “next”. Figure 3.2.2.2.
Page 39
39 step 3: decide vd size. User can enter a number less or equal to the default number. Then click “next”. Figure 3.2.2.3 step 4: confirmation page. Click “finish” if all setups are correct. Then a vd will be created. Step 5: done. The system is available now. Figure 3.2.2.4 (figure 3.2.2.4: a virtu...
Page 40: Chapter 4
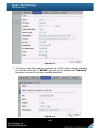
40 chapter 4 configuration 4.1 web ui management interface hierarchy the below table is the hierarchy of web gui. System configuration system setting system name / date and time / system indication network setting mac address / address / dns / port login setting login configuration / admin password ...
Page 41: 4.2
41 system information system information event log download / mute / clear upgrade browse the firmware to upgrade firmware synchronization synchronize the slave controller’s firmware version with the master’s reset to factory default sure to reset to factory default? Import and export import/export ...
Page 42
42 figure 4.2.1.1 check “change date and time” to set up the current date, time, and time zone before using or synchronize time from ntp (network time protocol) server. Click “confirm” in system indication to turn on the system indication led. Click again to turn off. 4.2.2 network setting “network ...
Page 43
43 figure 4.2.2.1 4.2.3 login setting “login setting” can set single admin, auto logout time and admin / user password. The single admin is to prevent multiple users access the same system in the same time. 1. Auto logout: the options are (1) disabled; (2) 5 minutes; (3) 30 minutes; (4) 1 hour. The ...
Page 44
44 figure 4.2.3.1 check “change admin password” or “change user password” to change admin or user password. The maximum length of password is 12 characters. 4.2.4 mail setting “mail setting” can enter 3 mail addresses for receiving the event notification. Some mail servers would check “mail-from add...
Page 45
45 figure 4.2.4.1 4.2.5 notification setting “notification setting” can set up snmp trap for alerting via snmp, pop-up message via windows messenger (not msn), alert via syslog protocol, and event log filter for web ui and lcm notifications..
Page 46
46 figure 4.2.5.1 “snmp” allows up to 3 snmp trap addresses. Default community setting is “public”. User can choose the event log levels and default setting enables error and warning event log in snmp. There are many snmp tools. The following web sites are for your reference: snmpc: http://www.Snmpc...
Page 47: 4.3
47 be received. It allows up to 3 messenger addresses. User can choose the event log levels and default setting enables the warning and error event logs. Using “system log server”, user can choose the facility and the event log level. The default port of syslog is 514. The default setting enables ev...
Page 48
48 (figure 4.3.1.1: there are 4 iscsi data ports on each controller. 4 data ports are set with static ip.) • ip settings: user can change ip address by checking the gray button of lan port, click “ip settings for iscsi ports”. There are 2 selections, dhcp (get ip address from dhcp server) or static ...
Page 49
49 the following is the description of multi-homed / trunking / lacp functions. 1. Multi-homed: default mode. Each of iscsi data port is connected by itself and is not link aggregation and trunking. This function is also for multipath functions. Select this mode can also remove the setting of trunki...
Page 50
50 for example, lan1 and lan2 are set as trunking mode. Lan3 and lan4 are set as lacp mode. To remove trunking / lacp setting, check the gray button of lan port, click “delete link aggregation”. Then it will pop up a message to confirm. • ping host: user can ping the corresponding host data port fro...
Page 51
51 figure 4.3.2.1 4.3.3 node “node” can view the target name for iscsi initiator. P300h61 / p300h71 supports up to 32 multi-nodes. There are 32 default nodes created for each controller. Figure 4.3.3.1 • chap: chap is the abbreviation of challenge handshake authentication protocol. Chap is a strong ...
Page 52
52 to use chap authentication, please follow the procedures. 1. Select one of 32 default nodes from one controller. 2. Check the gray button of “op.” column, click “authenticate”. 3. Select “chap”. Figure 4.3.3.2 4. Click “ok”. Figure 4.3.3.3 5. Go to “/ iscsi configuration / chap account” page to c...
Page 53
53 figure 4.3.3.4 8. Click “ok”. 9. In “authenticate” of “op” page, select “none” to disable chap. • change portal: users can change the portals belonging to the device node of each controller. 1. Check the gray button of “op.” column next to one device node. 2. Select “change portal”. 3. Choose the...
Page 54
54 1. Check the gray button of “op.” column next to one device node. 2. Select “rename alias”. 3. Create an alias for that device node. 4. Click “ok” to confirm. 5. An alias appears at the end of that device node. Figure 4.3.3.6 figure 4.3.3.7 tips after setting chap, the initiator in host should be...
Page 55
55 figure 4.3.4.1 (figure 4.3.4.1: iscsi session.) check the gray button of session number, click “list connection”. It can list all connection(s) of the session. Figure 4.3.4.2 (figure 4.3.4.2: iscsi connection.) 4.3.5 chap account “chap account” can manage a chap account for authentication. P300h6...
Page 56: 4.4
56 figure 4.3.5.1 3. Click “ok”. Figure 4.3.5.2 4. Click “delete” to delete chap account. 4.4 volume configuration “volume configuration” is designed for setting up the volume configuration which includes “physical disk”, “raid group”, “virtual disk”, “snapshot”, “logical unit”, and “qreplica” (opti...
Page 57
57 figure 4.4.1 4.4.1 physical disk “physical disk” can view the status of hard drives in the system. The followings are operational steps: 1. Check the gray button next to the number of slot, it will show the functions which can be executed. 2. Active function can be selected, and inactive function...
Page 58
58 figure 4.4.1.3 (figure 4.4.1.3: physical disks in slot 1,2,3 are created for a rg named “rg-r5”. Slot 4 is set as dedicated spare disk of the rg named “rg-r5”. The others are free disks.) step 4: the unit of size can be changed from (gb) to (mb). It will display the capacity of hard drive in mb. ...
Page 59
59 status the status of hard drive: “online” the hard drive is online. “rebuilding” the hard drive is being rebuilt. “transition” the hard drive is being migrated or is replaced by another disk when rebuilding occurs. “scrubbing” the hard drive is being scrubbed. Health the health of hard drive: “go...
Page 60
60 command queuing newer sata and most scsi disks can queue multiple commands and handle one by one. Default is “enabled”. • pd operation description: set free disk make the selected hard drive be free for use. Set global spare set the selected hard drive to global spare of all rgs. Set dedicated sp...
Page 61
61 figure 4.4.2.1 step 2: confirm page. Click “ok” if all setups are correct. Figure 4.4.2.2 (figure 4.4.2.2: there is a raid 0 with 4 physical disks, named “rg-r0”. The second raid group is a raid 5 with 3 physical disks, named “rg-r5”.) step 3: done. View “raid group” page. • rg column description...
Page 62
62 total (gb) (mb) total capacity of this raid group. The unit can be displayed in gb or mb. Free (gb) (mb) free capacity of this raid group. The unit can be displayed in gb or mb. #pd the number of physical disks in a raid group. #vd the number of virtual disks in a raid group. Status the status of...
Page 63
63 activate activate the raid group after disk roaming; it can be executed when rg status is offline. This is for online disk roaming purpose. Deactivate deactivate the raid group before disk roaming; it can be executed when rg status is online. This is for online disk roaming purpose. Parity check ...
Page 64
64 step 1: click “create”, enter “name”, select raid group from “rg name”, enter required “capacity (gb)/(mb)”, change “stripe height (kb)”, change “block size (b)”, change “read/write” mode, set virtual disk “priority”, select “bg rate” (background task priority), andchange “readahead” option if ne...
Page 65
65 figure 4.4.3.2 (figure 4.4.3.2: create a vd named “vd-01”, from “rg-r0”. The second vd is named “vd-02”, it’s initializing.) step 3: done. View “virtual disk” page. • vd column description: the button includes the functions which can be executed. Name virtual disk name. Size (gb) (mb) total capac...
Page 66
66 “online” the virtual disk is online. “offline” the virtual disk is offline. “initiating” the virtual disk is being initialized. “rebuild” the virtual disk is being rebuilt. “migrate” the virtual disk is being migrated. “rollback” the virtual disk is being rolled back. “parity checking” the virtua...
Page 67
67 rg name the rg name of the virtual disk • vd operation description: create create a virtual disk. Extend extend the virtual disk capacity. Parity check execute parity check for the virtual disk. It supports raid 3 / 5 / 6 / 30 / 50 / 60. Regenerate parity: “yes” regenerate raid parity and write. ...
Page 68
68 “disabled” disable av-media mode. (default) type: “raid” the virtual disk is normal. (default) “backup” the virtual disk is for clone usage. Attach lun attach to a lun. Detach lun detach to a lun. List lun list attached lun(s). Set clone set the target virtual disk for clone. Clear clone clear cl...
Page 69
69 step 1: create snapshot space. In “/ volume configuration / virtual disk”, check to the gray button next to the vd number; click “set snapshot space”. Step 2: set snapshot space. Then click “ok”. The snapshot space is created. Figure 4.4.4.1 figure 4.4.4.2 (figure 4.4.4.2: “vd-01” snapshot space ...
Page 70
70 figure 4.4.4.4 figure 4.4.4.5 (figure 4.4.4.5: this is the snapshot list of “vd-01”. There are two snapshots. Snapshot vd “snapvd-01” is exposed as read-only, “snapvd-02” is exposed as read-write.) step 5: attach a lun to a snapshot vd. Please refer to the next section for attaching a lun. Step 6...
Page 71
71 health the health of snapshot: “good” the snapshot is good. “failed” the snapshot fails. Exposure snapshot vd is exposed or not. Right the right of snapshot: “read-write” the snapshot vd can be read / write. “read-only” the snapshot vd is read only. #lun number of lun(s) that snapshot vd is attac...
Page 72
72 figure 4.4.5.1 figure 4.4.5.2 (figure 4.4.5.2: vd-01 is attached to lun 0 and every host can access. Vd-02 is attached to lun 1 and only the initiator node which is named “iqn.1991-05.Com.Microsoft:qsan” can access.) • lun operation description: attach attach a logical unit number to a virtual di...
Page 73
73 4.4.6 example the following is an example to create volumes. This example is to create two vds and set a global spare disk. • example this example is to create two vds in one rg, each vd shares the cache volume. The cache volume is created after system boots up automatically. Then set a global sp...
Page 74
74 figure 4.4.6.2 (figure 4.4.6.2: creating a raid 5 with 3 physical disks, named “rg-r5”.) step 2: create vd (virtual disk). To create a data user volume, please follow the procedures. Figure 4.4.6.3 1. Select “/ volume configuration / virtual disk”. 2. Click “create”. 3. Input a vd name, choose a ...
Page 75
75 figure 4.4.6.4 (figure 4.4.6.4: creating vds named “vd-r5-1” and “vd-r5-2” from raid group “rg-r5”, the size of “vd-r5-1” is 50gb, and the size of “vd-r5-2” is 64gb. There is no lun attached.) step 3: attach a lun to a vd. There are 2 methods to attach a lun to a vd. 1. In “/ volume configuration...
Page 76
76 tips the matching rules of access control are from the luns’ created time, the earlier created lun is prior to the matching rules. Step 4: set a global spare disk. To set a global spare disk, please follow the procedures. 1. Select “/ volume configuration / physical disk”. 2. Check the gray butto...
Page 77: 4.5
77 to delete the virtual disk, please follow the procedures: 1. Select “/ volume configuration / virtual disk”. 2. Check the gray button next to the vd number; click “delete”. There will pop up a confirmation page, click “ok”. 3. Done. Then, the vd is deleted. Tips when deleting vd directly, the att...
Page 78
78 1. Temperature sensors: 1 minute. 2. Voltage sensors: 1 minute. 3. Hard disk sensors: 10 minutes. 4. Fan sensors: 10 seconds . When there are 3 errors consecutively, system sends error event log. 5. Power sensors: 10 seconds, when there are 3 errors consecutively, system sends error event log. 6....
Page 79
79.
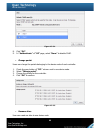
Page 80
80 figure 4.5.1.1 if “auto shutdown” is checked, the system will shutdown automatically when voltage or temperature is out of the normal range. For better data protection, please check “auto shutdown”. For better protection and avoiding single short period of high temperature triggering auto shutdow...
Page 81
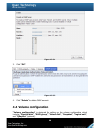
81 first, connect the cable(s) between the system and apc smart-ups via rs-232. Then set up the following values for what the system will do the actions when power fails. Figure 4.5.2.2 (figure 4.5.2.2: with smart-ups.) • ups column description: ups type select ups type. Choose smart-ups for apc, no...
Page 82
82 “communication lost” “ups reboot in progress” “ups shutdown in progress” “batteries failed. Please change them now!” battery level (%) current power percentage of battery level. The system will shutdown either “shutdown battery level (%)” or “shutdown delay (s) ” reaches the condition. User shoul...
Page 83: 4.6
83 this is much better than hard drive crash when it is writing data or rebuilding a failed hard drive. “s.M.A.R.T.” can display s.M.A.R.T. Information of hard drives. The number is the current value; the number in parenthesis is the threshold value. The threshold values from different hard drive ve...
Page 84
84 “maintenance” allows the operations of system functions which include “system information” to show the system version and details, “event log” to view system event logs to record critical events, “upgrade” to the latest firmware, “firmware synchronization” to synchronized firmware versions on bot...
Page 85
85 “event log” can view the event messages. Check the checkbox of info, warning, and error to choose the level of event log display. Click “download” button to save the whole event log as a text file with file name “log-modelname-serialnumber-date-time.Txt”. Click “clear” button to clear all event l...
Page 86
86 tips please plug-in any of the first four hard drives, then event logs can be saved and displayed in next system boot up. Otherwise, the event logs cannot be saved and would be disappeared. 4.6.3 upgrade “upgrade” can upgrade controller firmware, jbod firmware, change operation mode, and activate...
Page 87
87 please prepare new controller firmware file named “xxxx.Bin” in local hard drive, then click “browse” to select the file. Click “confirm”, it will pop up a warning message, click “ok” to start to upgrade firmware. Figure 4.6.3.2 when upgrading, there is a progress bar running. After finished upgr...
Page 88
88 “reset to factory default” allows user to reset subsystem to factory default setting. Figure 4.6.5.1 reset to default value, the password is: 1234, and ip address to default dhcp. Default ip address: 192.168.10.50 (dhcp) default subnet mask: 255.255.255.0 default gateway: 192.168.10.254 4.6.6 imp...
Page 89: 4.7
89 “reboot and shutdown” can “reboot” and “shutdown” the system. Before power off, it’s better to execute “shutdown” to flush the data from cache to physical disks. The step is necessary for data protection. Figure 4.6.7.1 4.7 home/logout/mute in the right-upper corner of web ui, there are 3 individ...
Page 90: Chapter 5
90 chapter 5 advanced operations 5.1 volume rebuild if one physical disk of the rg which is set as protected raid level (e.G.: raid 3, raid 5, or raid 6) is failed or has been unplugged / removed, then the status of rg is changed to degraded mode, the system will search/detect spare disk to rebuildt...
Page 91
91 sometimes, rebuild is called recover; they are the same meaning. The following table is the relationship between raid levels and rebuild. • rebuild operation description: raid 0 disk striping. No protection for data. Rg fails if any hard drive fails or unplugs. Raid 1 disk mirroring over 2 disks....
Page 92: 5.2
92 5.2 rg migration and moving to do migration, the total size of rg must be larger or equal to the original rg. It does not allow expanding the same raid level with the same hard disks of original rg. There is a similar function “move” which will move the member disks of rg to totally different phy...
Page 93
93 tips “migrate” function will migrate the member disks of rg to the same physical disks but it should increase the number of disks or it should be different raid level. “move” function will move the member disks of rg to totally different physical disks. To migrate the raid level, please follow be...
Page 94: 5.3
94 figure 5.2.4 5.3 vd extension to extend vd size, please follow the procedures. 1. Select “/ volume configuration / virtual disk”. 2. Check the gray button next to the vd number; click “extend”. 3. Change the size. The size must be larger than the original, and then click “ok” to start extension. ...
Page 95: 5.4
95 5.4 qsnap snapshot-on-the-box (qsnap) captures the instant state of data in the target volume in a logical sense. The underlying logic is copy-on-write -- moving out the data which would be written to certain location where a write action occurs since the time of data capture. The certain locatio...
Page 96
96 4. There are two methods to take snapshot. In “/ volume configuration / virtual disk”, check the gray button next to the vd number; click “take snapshot”. Or in “/ volume configuration / snapshot”, click “take snapshot”. 5. Enter a snapshot name, and then click “ok”. A snapshot vd is created. 6. ...
Page 97
97 1. There are two methods to set auto snapshot. In “/ volume configuration / virtual disk”, check the gray button next to the vd number; click “auto snapshot”. Or in “/ volume configuration / snapshot”, click “auto snapshot”. 2. The auto snapshot can be set monthly, weekly, daily, or hourly. 3. Do...
Page 98
98 the data in snapshot vd can rollback to original vd. Please follow the procedures. 1. Select “/ volume configuration / snapshot”. 2. Check the gray button next to the snap vd number which user wants to rollback the data; click “rollback”. 3. Done, the data in snapshot vd is rollback to original v...
Page 99
99 figure 5.4.4.1 on linux and unix platform, a command named sync can be used to make the operating system flush data from write caching into disk. For windows platform, microsoft also provides a tool – sync, which can do exactly the same thing as the sync command in linux/unix. It will tell the os...
Page 100: 5.5
100 1. If there are two or more snapshots existed, the system will try to remove the oldest snapshots (to release more space for the latest snapshot) until enough space is released. 2. If there is only one snapshot existed, the snapshot will fail. Because the snapshot space is run out. For example, ...
Page 101: 5.6
101 1. Check the firmware version of two systems first. It is better that either systems have the same firmware version or system-2 firmware version is newer. 2. All physical disks of the rg should be moved from system-1 to system-2 together. The configuration of both rg and vd will be kept but lun ...
Page 102
102 figure 5.6.2 3. Here are the objects, a source vd and a target vd. Before starting clone process, it needs to deploy the vd clone rule first. Click “configuration”. Figure 5.6.3 4. There are three clone configurations, describe on the following. Figure 5.6.4.
Page 103
103 snapshot space: figure 5.6.5 this setting is the ratio of source vd and snapshot space. The default ratio is 2 to 1. It means when the clone process is starting, the system will automatically use the free rg space to create a snapshot space which capacity is double the source vd. Threshold: (the...
Page 104
104 figure 5.6.7 when running out of snapshot space, the vd clone process will be stopped because there is no more available snapshot space. If this option has been checked, system will clear the snapshots of clone in order to release snapshot space automatically, and the vd clone will restart the t...
Page 105
105 figure 5.6.9 7. Now, the clone target “targetvd_r6” has been set. Figure 5.6.10 8. Click “start clone”, the clone process will start. Figure 5.6.11 9. The default setting will create a snapshot space automatically which the capacity is double size of the vd space. Before starting clone, system w...
Page 106
106 figure 5.6.12 10. After initiating the snapshot space, it will start cloning. Figure 5.6.13 11. Click “schedule clone” to set up the clone by schedule. Figure 5.6.14 12. There are “set clone schedule” and “clear clone schedule” in this page. Please remember that “threshold” and “restart the task...
Page 107
107 figure 5.6.15 • run out of snapshot space while vd clone while the clone is processing, the increment data of this vd is over the snapshot space. The clone will complete, but the clone snapshot will fail. Next time, when trying to start clone, it will get a warning message “this is not enough of...
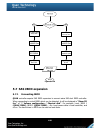
Page 108: 5.7
108 figure 5.6.16 5.7 sas jbod expansion 5.7.1 connecting jbod qsan controller suports sas jbod expansion to connect extra sas dual jbod controller. When connecting to a dual jbod which can be detected, it will be displayed in “show pd for:” of “/ volume configuration / physical disk”. For example, ...
Page 109
109 figure 5.7.1.1 (figure 5.7.1.1: display all pds in jbod 1.) “/ enclosure management / hardware monitor” can display the hardware status of sas jbods..
Page 110
110 figure 5.7.1.2.
Page 111
111 figure 5.7.1.3 “/ enclosure management / s.M.A.R.T.” can display s.M.A.R.T. Information of all pds, including local and all sas jbods..
Page 112
112 figure 5.7.1.4 (figure 5.7.1.4: disk s.M.A.R.T. Information of jbod 1, although s.M.A.R.T. Supports sata disk only.) sas jbod expansion has some constraints as described in the followings: 1 user could create raid group among multiple chassis, max number of disks in a single raid group is 32. 2 ...
Page 113: 5.8
113 5.7.2 upgrade firmware of jbod before upgrade, it’s better to use “export” function to backup all configurations to a file. To upgrade the firmware of jbod, please follow the procedures. 1. Please login subsystem as username admin first, and then go “/ system maintenance / upgrade”. Figure 5.7.2...
Page 114
114 figure 5.8.1 2. Mc/s: mc/s (multiple connections per session) is a feature of iscsi protocol, which allows combining several connections inside a single session for performance and failover purposes. In this way, i/o can be sent on any tcp/ip connection to the target. If one connection fails, an...
Page 115: 5.9
115 figure 5.8.2 difference: mc/s is implemented on iscsi level, while mpio is implemented on the higher level. Hence, all mpio infrastructures are shared among all scsi transports, including fiber channel, sas, etc. Mpio is the most common usage across all os vendors. The primary difference between...
Page 116
116 link aggregation is the technique of taking several distinct ethernet links to let them appear as a single link. It has a larger bandwidth and provides the fault tolerance ability. Beside the advantage of wide bandwidth, the i/o traffic remains operating until all physical links fail. If any lin...
Page 117: 5.10
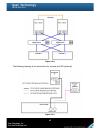
117 figure 5.9.2 caution before using trunking or lacp, he gigabit switch must support trunking or lacp and enabled. Otherwise, host can not connect the link with storage device. 5.10 dual controllers 5.10.1 perform i/o please refer to the following topology and have all the connections ready. To pe...
Page 118
118 figure 5.10.1.1 5.10.2 ownership when creating rg, it will be assigned with a prefered owner, the default owner is controller 1. To change the rg ownership, please follow the procedures. 1 select “/ volume configuration / raid group”. 2 check the gray button next to the rg name; click “set prefe...
Page 119
119 figure 5.10.2.2 (figure 5.10.2.2: the rg ownership is changed to the other controller.) 5.10.3 controller status there are four statuses described on the following. It can be found in “/ system maintenance / system information”. 1. Normal: dual controller mode. Both of controllers are functional...
Page 120: 5.11
120 tips isns server is recommended for dual controller system. 5.11 qreplica qreplica function will help users to replicate data easily through lan or wan from one subsystem to another. The procedures of qreplica are on the following: 1. Copy all data from source vd to target vd at the beginning (f...
Page 121
121 figure 5.11.1 2. The setting can be reverted by select “disable qreplica” in the operation menu. Figure 5.11.2 • create backup virtual disk on the target subsystem 1. Before creating the replication job on the source subsystem, user has to create a virtual disk on the target subsystem and set th...
Page 122
122 figure 5.11.3 2. The backup virtual disk needs to be attached to a lun id before creating replication job. And the virtual disk of “backup” type can only be attached with “read-only” permission to prevent it from being modified incautiously. Figure 5.11.4.
Page 123
123 • create replication job on the source subsystem 1. If the license key is activated on the subsystem correctly, a new qreplica tab will be added on the web ui. Click “create” to create a new replication job. Figure 5.11.5 2. Select the source virtual disk which will be replicated to the target s...
Page 124
124 figure 5.11.7 4. The qreplica uses standard iscsi protocol for data replication. User has to log on the iscsi node to create the iscsi connection for the data transmission. Enter the chap information if necessary and select the target node to log no. Click “next” to continue. Figure 5.11.8 5. Ch...
Page 125
125 figure 5.11.9 6. A new replication job is created and listed on the qreplica page. Figure 5.11.10 • run the replication job 1. Click the “op.” button on the replication job to open operation menu. Click “start” to run the replication job. Figure 5.11.11 2. Click “start” again to confirm the exec...
Page 126
126 figure 5.11.12 3. User can monitor the replication job from the “status” information and the progress is expressed by percentage. Figure 5.11.13 • create multi-path on the replication job 1. Click the “create multi-path” in the operation menu of the replication job. Figure 5.11.14 2. Enter the i...
Page 127
127 figure 5.11.15 3. Select the iscsi node to log on and click “next”. Figure 5.11.16 4. Choose the same target virtual disk and click “next”..
Page 128
128 figure 5.11.17 5. A new target will be added in this replication job as a redundancy path. Figure 5.11.18 • configure the replication job to run by schedule 1. Click “schedule” in the operation menu of the replication job..
Page 129
129 figure 5.11.19 2. The replication job can be scheduled to run by hour, by day, by week or by month. The execution time can be configurable per user’s need. If the scheduled time of execution is arrived but the pervious replication job is stilling going, the scheduled execution will be ignored on...
Page 130
130 the qreplica uses qsnap, the snapshot technique of qsan, to help user to replicate the data without stop accessing to the source virtual disk. If the snapshot space is not configured on the source virtual disk in advance, the subsystem will allocate snapshot space for the source virtual disk aut...
Page 131
131 the source virtual disk to the target virtual disk. Next time, when the rest snapshot space has been used over 50%, in other words, the total snapshot space has been used over 75%, the subsystem will start the replication job again. “restart the task an hour later if failed” setting is used when...
Page 132
132 figure 5.11.23 here are more details about these two methods for setup the replication job at the first time. Method 1: skip full copy of replication job for a new, clean virtual disk. For a new created virtual disk which has not been accessed, the subsystem will recognized it and skip full copy...
Page 133
133 2. It is better that there is no host connected to the source virtual disk. Then run “vd clone” to synchronize the data between source and target virtual disks. 3. After the data is synchronized, change the cloning job to a qreplica job by selecting “change to qreplica” at the drop down menu of ...
Page 134
134 figure 5.11.26 7. Select the replication job to rebuild. Figure 5.11.27 8. Follow the steps as creating a new replication job. 9. If a wrong target virtual disk is selected when rebuilding the replication job, an error message of “the rebuilding source and target vds are mismatched” will be pop-...
Page 135: Chapter 6
135 chapter 6 troubleshooting 6.1 system buzzer the system buzzer features are listed below: 1. The system buzzer alarms 1 second when system boots up successfully. 2. The system buzzer alarms continuously when there is error occurred. The alarm will be stopped after error resolved or be muted. 3. T...
Page 136
136 error sata prd mem fail failed to init sata prd memory manager error sata revision id fail failed to get sata revision id error sata set reg fail failed to set sata register error sata init fail core failed to initialize the sata adapter error sata diag fail sata adapter diagnostics failed error...
Page 137
137 • rms events level type description info console login login from via console ui info console logout logout from via console ui info web login login from via web ui info web logout logout from via web ui info log clear all event logs are cleared warning send mail fail failed to send event to . •...
Page 138
138 error vd move failed failed to complete move of vd . Info rg activated rg has been manually activated. Info rg deactivated rg has been manually deactivated. Info vd rewrite started rewrite at lba info vd rewrite finished rewrite at lba warning vd rewrite failed rewrite at lba warning rg degraded...
Page 139
139 info vd erase started vd starts erasing process. • snapshot events level type description warning snap mem failed to allocate snapshot memory for vd . Warning snap space overflow failed to allocate snapshot space for vd . Warning snap threshold the snapshot space threshold of vd has been reached...
Page 140
140 info pd upgrade started jbod pd [] starts upgrading firmware process. Info pd upgrade finished jbod pd [] finished upgrading firmware process. Warning pd upgrade failed jbod pd [] upgrade firmware failed. Info pd freed jbod pd has been freed from rg . Info pd inserted jbod disk is inserted into ...
Page 141
141 • system maintenance events level type description info system shutdown system shutdown. Info system reboot system reboot. Info system console shutdown system shutdown from via console ui info system web shutdown system shutdown from via web ui info system button shutdown system shutdown via pow...
Page 142: 6.3
142 • clone events level type description info vd clone started vd starts cloning process. Info vd clone finished vd finished cloning process. Warning vd clone failed the cloning in vd failed. Info vd clone aborted the cloning in vd was aborted. Info vd clone set the clone of vd has been designated....
Page 143
143 qsan support form version: 1.1 customer information customer name contact email target information model name (*) hardware version mb (main board): db (daughter board): serial number (1) firmware version (*)(2) backplane / chassis model backplane version target configuration (*) raid configurati...
Page 144
144 connect diagram attached file name: problem description (*) reproduce step (*) screenshot attached file name: qsan description fields marked as (*) are must. At least, these informations are must to have. Fields marked as (1)(2)(3)(4), you can get them on the following descriptions. (1) in / mai...
Page 145
145 this form can be got from qsan ftp. Ftp://ftp.Qsan.Com.Tw/qsan_support_form.Doc.
Page 146: Appendix
146 appendix a. Compatibility list • gbe iscsi hba card vendor model bus type i/o port bios fw comment hp nc380t pci-e gigabit 2 1.9.6 n/a iscsi offload hp nc7170 pci-x gigabit 2 hp nc360t pci-e gigabit 2 ibm netxtreme 1000 t pci-x gigabit 2 intel pwla8492mt pci-x gigabiti 2 qlogic qla4052 pci-x gig...
Page 147: Microsoft Iscsi Initiator
147 a7k2000 3.5 hitachi deskstar 7k2000 hds722020ala330 2tb 7200 3gb/s 32 jkaoa3ma 3.5 hitachi deskstar 7k1000.C hds721010cla332 1tb 7200 3gb/s 32 jp4oa3ma 3.5 seagate constellation es st32000644ns 2tb 7200 3gb/s 64 sn11 3.5 seagate constellation es st31000524ns 1tb 7200 3gb/s 32 sn11 3.5 western di...
Page 148
148 figure b.1 3. Click “done”. Figure b.2 figure b.3.
Page 149
149 4. It can connect to an iscsi disk now. • mpio 5. If running mpio, please continue. 6. Click “discovery” tab to connect the second path. 7. Click “discover portal”. Input ip address or dns name of the target. Figure b.4 figure b.5 8. Click “ok”..
Page 150
150 figure b.6 figure b.7 9. Click “targets” tab, select the second path, and then click “connect”. 10. Enable “enable multi-path” checkbox. Then click “ok”. 11. Done, it can connect to an iscsi disk with mpio. • mc/s 12. If running mc/s, please continue. 13. Select one target name, click “propertie...
Page 151
151 figure b.8 figure b.9 15. Click “add…”. 16. Click “advanced…”..
Page 152
152 figure b.10 figure b.11 17. Select initiator ip and target portal ip, and then click “ok”. 18. Click “connect”. 19. Click “ok”. Figure b.12 figure b.13 20. Done. • disconnect 21. Select the target name, click “disconnect”, and then click “yes”..
Page 153
153 figure b.14 22. Done, the iscsi device disconnect successfully..
Page 154: System Information
154 system information p300h61 / p300h71 sw version 2.0.1.