Summary of Q150
Page 1
Www .Com ly ita k- o. User manual 150
Page 2: 1. Introduction
1. Introduction 2 1. Introduction ................................................................................................................... 3 1.1 h ow to use this manual .................................................................................................. 3 1.2p recautions ......
Page 3: 1. Introduction
1. Introduction 3 1. Introduction 1.1 how to use this manual this user manual is divided into four sections which cover introduction, overview, operation, and troubleshooting, respectively. Please read this manual carefully before install and operate this machine. Keep this manual handy and refer to...
Page 4: 1. Introduction
1. Introduction 4 gloves: when performing a certain maintenance work, machine may be hot and protective gloves are required to avoid being burnt. Safety glasses: wear safety glasses to avoid injury to the eyes. 1.2.2 protection q150 printer must not be exposed to water or rain, otherwise may cause d...
Page 5: 2. Overview
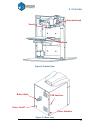
2. Overview 5 2. Overview q150 is designed with ultimate portability and simplicity in mind. The machine and software allow you to print great models with only a few keystrokes, even you are a first time user of q150 printer. Q150 uses a nozzle to deposit molten plastic, and the printed parts are st...
Page 6
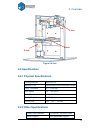
2. Overview 6 figure 2-2 inside view figure 2-3 back view platform extrusion head nozzle usb interface power interface roller shaft power on/off.
Page 7
2. Overview 7 ① usb cable ② power adapter (20 v) ③ filament tube ④ screws ⑤ cell board ⑥ extrusion head ⑦ abs spool figure 2-4 accessories ① pen knives ② tweezers ③ hex wrench ④ shovel ⑤ pliers ⑥ gloves ⑦ nozzle wrench figure 2-5 tool kit ⑤.
Page 8: 2.2 Specifications
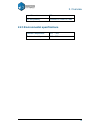
2. Overview 8 figure 2-6 axis 2.2 specifications 2.2.1 physical specifications printing material abs or pla material color white/black/red/yellow/blue/green layer thickness 0.2-0.35 mm print speed 10-100 cm 3 /h print size 120 120 120 mm printer weight 5 kg (11 lb) printer size 240 350 350 mm 2.2.2 ...
Page 9
2. Overview 9 input format stl os compatibility windows xp/vista/7/8; mac 2.2.3 environmental specifications ambient temperature 15°c ~30°c relative humidity 20%~50%.
Page 10: 3. Operation
3. Operation 10 3. Operation 3.1 preparation 3.1.1 installation figure 3-1 print head installation extrusion head the extrusion head of a q150 is fastened by three magnetic buckles. When assembling extrusion head, make sure the extrusion head is securely contacted with all the three buckles at right...
Page 11: 3. Operation
3. Operation 11 figure 3-2 print platform platform insert the cell board into the platform slot. Moderate force is recommended when inserting the cellboard. Figure 3-3 roller shaft roller shaft insert the roller shaft into the hole at the back of printer, and press it downward. The roller shaft shou...
Page 12: 3. Operation
3. Operation 12 material extrusion (top view) figure 3-4 material wiring (1) connect power adapter to power interface. (2) put a spool of material on the roller shaft, find the end of the material, insert it into filament tube, pass the material through the tube, and pass the tube through the top of...
Page 13: 3. Operation
3. Operation 13 and starts pulling it through the extrusion head. From the nozzle side, a string of melted filament will be extruded. (windows version) (mac version) figure 3-5 maintenance dialog 3.1.2 software installation the software is available for download on our site quant3d.Com . It is free ...
Page 14: 3. Operation
3. Operation 14 install the software, the printer drivers, and the sample files. Figure 3-6 software directory 3.1.3 driver installation connect the printer to a computer with a usb cable. The computer should pop up the “found new hardware wizard” window. Choose “no, not this time” option, and then ...
Page 15: 3. Operation
3. Operation 15 click “browse”, and choose c: \program files\up\driver, then “next”. Figure 3-8 snap shots of software installation the following dialogue box pops up. Choose “continue anyway” , and the drivers will install automatically. Figure 3-9 snap shots of software installation if you have an...
Page 16: 3. Operation
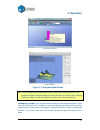
3. Operation 16 3.2 using the basic functions 3.2.1 start the program click on the icon in a computer desktop. The program should open up as the following: figure 3-10 program startup screen 3.2.2 loading a 3d model click “file / open” or on the toolbar and select the model you want to load. Up! Sof...
Page 17: 3. Operation
3. Operation 17 (windows version) (mac version) figure 3-11 program model screen tip: you can open several models and print them all at the same time. Just repeat the open model procedure for each model you want to add. See the “placing models on the build platform” section for more information. Unl...
Page 18: 3. Operation
3. Operation 18 figure 3-12 manu option of unloading models saving a model: choose the model you want to save, then click “save”. The file is saved in up3 format and its size is 12%~18% of the original stl file. This is a convenient format for users to archive or transfer models. Note on stl files: ...
Page 19: 3. Operation
3. Operation 19 figure 3-14 fixing stl problems merging models: separate models can be merged into one model by using “merge” option from the “edit” menu. Simply open all the models that you want to merge and arrange them the way you want on the platform and click on the “merge” option. When you the...
Page 20: 3. Operation
3. Operation 20 figure 3-15 preset view options 3.2.4 model transformations model transformation can be achieved through edit menu or push buttons on the toolbar: (windows version) figure 3-16 model transformation options moving a model: click the “move” button and, in the text box, choose, or input...
Page 21: 3. Operation
3. Operation 21 procedure: 1. Click on “move” ; 2. Input “-5” in the text box; 3. Click the “z axis”. Figure 3-17 move a model tip: if you hold down the ‘ctrl’ key, you can simply drag the model to whatever position you want. Rotating a model: click the “rotate” button on the toolbar, in the text bo...
Page 22: 3. Operation
3. Operation 22 scaling a model: click “scale”, choose or input a scaling ratio in the text box, then either scale the model uniformly along all three axes by clicking the scale button again, or choose the axis along which you want to scale the model, if you only want to scale along one axis. Exampl...
Page 23: 3. Operation
3. Operation 23 auto place: clicking the “auto place” button on the far right of the toolbar, can automatically place all the loaded models on the platform in an optimized position. When there is more than one model on the platform, using “auto place” is always recommended. Manually place models: pr...
Page 24: 3. Operation
3. Operation 24 (windows version) (mac version) figure 3-19 initializing a printer tip: under the condition that your printer is not responding properly, the first thing to try is to re-initialize the printer by clicking the ‘initialize’ option in the ‘3d print’ menu. 3.3.2 preparing platform before...
Page 25: 3. Operation
3. Operation 25 mechanical bond with the bottom surface, which prevents the model from lifting. When inserting or extracting a cell board into the platform slot, moderate strength should be well-distributed, without using strong force, and hold the metal guides on both sides to prevent the print pla...
Page 26: 3. Operation
3. Operation 26 figure 3-20 "print" dialog the snapshot of "print" dialog in figure 3-20 shows that the distance of the from platform to nozzle is 135.9mm, after the printer is initialized, and before the printing starts. To figure out the correct nozzle height, please follow the following steps: 1 ...
Page 27: 3. Operation
3. Operation 27 (mac version) figure 3-21 "maintain" dialog 2 - in the text box, type in the height to which you want the platform to move, and click the “to” button. In the above example, the platform move s to 122mm above the platform’s original position figure 3-22 gap between platform and nozzle...
Page 28: 3. Operation
3. Operation 28 4 - once the platform is about 1mm away from the nozzle, start increasing the number in the text box by 0.1mm increment and click the “to” button. Repeat this step, until the platform is within 0.2mm away from the nozzle. 5 - click the “set nozzle height” in the maintenance dialogue ...
Page 29: 3. Operation
3. Operation 29 tip: if you happen to crash the platform into the nozzle while making height adjustment, it is good practice to re-initialize the printer before undertaking any other operations. 3.3.4 other maintenance options click “maintain” on the “3d print” menu, and the following dialog box pop...
Page 30: 3. Operation
3. Operation 30 molten filament for a while, and machine beeps again when it finishes extruding. This function is frequently used when changing new material (see section 6), and it can be also used to test whether the nozzle is working properly withdraw: withdraws the material from the extrusion hea...
Page 31: 3. Operation
3. Operation 31 pause print: this button allows you to pause an ongoing print job, and you can resume the print job from where it was stopped. This function is very useful if you, for example, want to change different material color during a printing process. Another popular use for pausing a print ...
Page 32: 3. Operation
3. Operation 32 3.3.6 print setup options click menu “3d print->setup”. The following dialog box pops up: figure 3-26 setup dialog print options z resolution: set the print resolution (layer thickness) of the printer. This can be a choice between 0.2mm to 0.35mm per layer. Base height: this is the v...
Page 33: 3. Operation
3. Operation 33 part options surface: this parameter determines how many layers are needed to form the bottom of a part. For example, if value is set to 3, the machine will print 3 complete layers before going into non-solid mode. This does not, however, affect the side wall thickness on non-solid p...
Page 34: 3. Operation
3. Operation 34 the part has an outer wall thickness of solid plastic (about 1.5mm), but its interior is filled with a largely spaced support structure. In previous version, this was referred as “big hole” figure 3-27 support structure generated by different infill options shell mode: this mode prin...
Page 35: 3. Operation
3. Operation 35 please check the following pictures for the differences of the two printing modes. Figure 3-28 shell mode and surface mode.
Page 36: 3. Operation
3. Operation 36 support options dense: for a model printed by q150 3d printer, the inside of the model is either hollow or use infill structure to support the contour of the model. Up! Software is smart enough to figure out which the portion of a model can be hollow, and how the model is generated w...
Page 37: 3. Operation
3. Operation 37 for 3d printing, a lot of discussions are related to support structure, which can affect print quality, time to print, material consumption, easiness of support removal, and etc.. The basic idea is that the less support structure generated, the better, because the material consumed w...
Page 38: 3. Operation
3. Operation 38 figure 3-31 infill gap area: the surface area above which support structure gets generated. If the value is set to 5 mm 2 , for instance, there will be no support structure generated for all the overhanging surface with area less than 5 mm 2 . Benefit? Material is saved and faster pr...
Page 39: 4. Printing
4. Printing 39 4. Printing tip: one of the keys to successful printing on up! Mini is platform preparation and preheating, particularly with large parts. Generally, platform is heated, but not evenly. The edges are always a little colder than the center of the platform, which is the primary reason t...
Page 40: 4. Printing
4. Printing 40 when the "door" is opened, the heat generated from extrusion head is blown away fast by the wind from the fan, and models can be solidified in very short time so that the surfaces in these models can have better quality. Regular models, if printed with "door" open, could have warping ...
Page 41: 4. Printing
4. Printing 41 print options: speed: fine, normal or fast. This option determines the speed up! Printer prints. As a general rule, the slower you print, the better the print quality. For tall parts, printing at fast speed could be problematic, because printer could vibrate to a certain extent to whi...
Page 42: 4. Printing
4. Printing 42 model info: 30 30 30 mm layer thickness: 0.2 mm figure 4-3 different parts with different settings the prices shown in figure 4-3 are based on the abs material sold on quant3d.Com the easiest way to calculate how much material one print is about to consume is to use the “print preview...
Page 43: 5. Model Removal
5. Model removal 43 5. Model removal 1. After a print job finishes, printer gives off beeps, and nozzle and platform are not long heated. 2. Remove the cell board from the print platform with the printed part 3. Gently slide the shovel, an accessory that comes with the machine, under the printed mod...
Page 44: 5. Model Removal
5. Model removal 44 figure 5-1 removing model after print 4. Removing support material figure 5-2 support structure 3d printed models are composed of two parts. One part is the model itself, and the other one is the support structure used to support any overhanging portion of the model. The support ...
Page 45: 5. Model Removal
5. Model removal 45 figure 5-3 support structure removal it takes some practice to get comfortable with removing support structure, but it can become quite satisfying as you discover the shapes of your new creation. Caution: always wear safety glasses when removing support structure, especially when...
Page 46: 5. Model Removal
5. Model removal 46.
Page 47: 6. Maintenance
6. Maintenance 47 6. Maintenance 6.1 changing the material withdraw the leftover material from printer. Initialize printer and choose “3d print->maintain”. Click “withdraw” . Printer automatically begins heating up nozzle. When temperature of nozzle reaches about 260°c , printer gives off beep, and ...
Page 48: 6. Maintenance
6. Maintenance 48 6.2 vertical calibration the vertical calibration procedure is to ensure that the print platform of up! Printer is level and that printer prints consistently in the x, y and z axes. First, the software provides a calibration model located in the directory "example". Print the calib...
Page 49: 6. Maintenance
6. Maintenance 49 figure 6-3 snapshot of calibration dialog important note: before you enter any new calibration values, always click the “reset” button, otherwise the new values get added to the old ones. Before you enter any new values, the bar at the very top of the screen should read: xy: 0.00 d...
Page 50: 6. Maintenance
6. Maintenance 50 6.3 cleaning print nozzle nozzle may be covered with some oxidized abs after a lot of prints. These oxidized abs could be melt during a print job, and create burnt marks on the model being printed. To avoid this problem, nozzle needs to be cleaned regularly. Firstly, in order to me...
Page 51: 6. Maintenance
6. Maintenance 51 6.4 removing / changing nozzle if your nozzle gets clogged, you need to remove it from print head, and clean it or change a new one. To remove nozzle, use the nozzle wrench provided in the toolkit that comes with your q150 printer. Generally, it is much easier to remove the nozzle ...
Page 52: 7. Tips & Tricks
7. Tips & tricks 52 7. Tips & tricks how to print a large part? Large parts can sometimes have their corners warping from the print platform, which can cause the part to distort. This is caused by uneven temperature across the surface of the platform. Preheating the platform before printing large pa...
Page 53: 8. Troubleshooting
8. Troubleshooting 53 8. Troubleshooting problem or error message solution no power verify power cord is securely plugged in. Extrusion head or platform fails to reach operating temperature 1. Verify printer is initialized. If not, initialize the printer 2. Heating block is damaged, replace it extru...
Page 54: 8. Troubleshooting
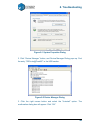
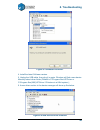
8. Troubleshooting 54 figure 8-1 system properties dialog 2. Click “device manager” button, and device manager dialog pops up. Find the entry “3dprinter@freemc” in the usb section. Figure 8-2 device manager dialog 3. Click the right mouse button and select the “uninstall” option. The confirmation di...
Page 55: 8. Troubleshooting
8. Troubleshooting 55 figure 8-3 uninstall old driver 4. Install the latest software version. 5. Unplug the usb cable, then plug it in again. Windows will find a new device. Manually select driver folder (default is c:\program files\up\driver or c:\program files(x86)\up\driver if windows is a 64bit ...
Page 56: 8. Troubleshooting
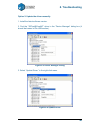
8. Troubleshooting 56 option 2: update the driver manually. 1. Install the latest software version. 2. Find the “3dprint@freemc” driver in the “device manager” dialog box (it should be located in the usb section). Figure 8-5 device manager dialog 3. Select “update driver.” in the right click menu. F...
Page 57: 8. Troubleshooting
8. Troubleshooting 57 4. Select the up! Driver folder (the default is c:\program files\up\driver). Figure 8-7 select driver directory 5. A “free motion card” section should now have been created in device manager. Figure 8-8 "free motion card" entry created.
Page 58
Www ly ita k- .O .Com ve rs io n q 15 0 1.