Summary of Q200
Page 1
Www.Quant3d.Com user manual 200
Page 2: 1. Introduction
1. Introduction 2 1. Introduction .................................................................................................................. 3 1.1 h ow to use this manual ................................................................................................. 3 1.2 p recautions .......
Page 3: 1. Introduction
1. Introduction 3 1. Introduction 1.1 how to use this manual this user manual is divided into four sections which cover the introduction, overview, operation, and troubleshooting. Please study this manual carefully before installation, and use the printer according to these instructions. Keep this m...
Page 4: 1. Introduction
1. Introduction 4 warning: indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in serious injury. Gloves: when performing certain maintenance procedures, the machine may be hot and gloves are required to avoid burns. Safety glasses: wear safety glasses to avoid injury to yo...
Page 5: 2. Overview
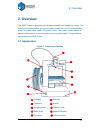
2. Overview 5 2. Overview the q200 printer is designed with ultimate portability and simplicity in mind. The system and software allow you to print great models with only a few keystrokes, even if you have never used a 3d printer before. The system uses a nozzle to deposit molten plastic, so printed...
Page 6
2. Overview 6 figure 2. Accessories ① usb cable ② power adapter (20 v) ③ filament tube ④ screws ⑤ cellboard figure 3. Tool kit ① pen knives ② tweezers ③ hex wrench ④ shovel ⑤ pliers ⑥ gloves ⑦ nozzle wrench ⑧ clip.
Page 7
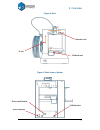
2. Overview 7 figure 4. Axis figure 5. Back view of printer extruder axis z axis platform axis power on/off button power interface usb interface.
Page 8: 2.2 Specifications
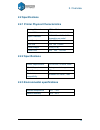
2. Overview 8 2.2 specifications 2.2.1 printer physical characteristics printing material abs or pla material color white layer thickness 0.20–0.40 or 0.25-0.35mm, depending on model print speed 10-100 cm 3 /h print size 140 140 135mm printer weight 5 kg (11 lb) printer size 245 260 350 mm 2.2.2 spe...
Page 9: 3. Operation
3. Operation 9 3. Operation 3.1 preparation 3.1.1 installation the printer assemble the four parts first following the diagram above. Extrude head (1) remove extruder guard from extruder head (2) unscrew the scew (d) and fix the extruder head onto the holder (3) make sure the extruder is parallel wi...
Page 10: 3. Operation
3. Operation 10 platform: raise the platform axis to a height at which you can reach under it to insert the screws. Line up the screw holes (e, f) on the platform with the screw holes on the heater base and insert the screws in from the bottom and tighten them. Perfboard: fix the perfboard on the pl...
Page 11: 3. Operation
3. Operation 11 the filament into the hole at the top of the extruder head and hold it there with some gentle pressure until the extruder motor grabs it and starts pulling it through the extrusion head. The extruder will then automatically extrude a thin filament of material. (windows version) (mac ...
Page 12: 3. Operation
3. Operation 12 3.1.2 installing the software start the upx.Xx setup.Exe file and install it to the specified directory (default is program files/up). Note: this installs the up software, the up drivers, and the up sample files into your program files/up folder. 3.1.3 installing drivers connect the ...
Page 13: 3. Operation
3. Operation 13 click ―browse‖, and choose c: \program files\up\driver, then ―next‖. The following dialogue box pops up. Choose ―continue anyway‖, and the drivers will install automatically. If you have any problems installing the drivers, or get a "winusb.Dll not found" error, please refer to the d...
Page 14: 3. Operation
3. Operation 14 3.2 using the basic functions 3.2.1 start the program click on the icon on the desktop. The program should open as follows: 3.2.2 loading a 3d model click ―file / open‖ or on the toolbar and select the model you want to open. Up only supports stl files (which is the standard input fo...
Page 15: 3. Operation
3. Operation 15 (mac version) tip: you can open several models and print them all at the same time. Just repeat the open model procedure for each model you want to add. See the ―placing models on the build platform‖ section for more information. Unloading the model: click the left mouse button on th...
Page 16: 3. Operation
3. Operation 16 fixing stl files: the up software has an option that attempts to fix models with bad surfaces. Under the ―edit‖ menu you will see a ―fix‖ option. Select the model with inverted surfaces, and click the ―fix‖ option to try and fix it. Merging models: several separate models can be merg...
Page 17: 3. Operation
3. Operation 17 3.2.3 view options to observe the target model in different ways, use the mouse to control the view. Rotate: press the middle mouse button and move the mouse: the view can be rotated and observed from different angles. Pan: press ctrl and the middle mouse button at the same time and ...
Page 18: 3. Operation
3. Operation 18 3.2.4 model transformations model transformation can be achieved through the edit menu or the toolbar: (windows version) moving the model: click the ―move‖ button and choose, or input, the distance you want to move in the text box. Then choose the axis (direction) in which you want t...
Page 19: 3. Operation
3. Operation 19 rotating the model: click the ―rotate‖ button on the toolbar, choose or input how many degrees you want to rotate in the text box, then choose the axis to rotate around. For example: rotate the model around y axis by 30 o . Procedure: 1. Click ―rotate‖; 2. Input 30 in the text box;3....
Page 20: 3. Operation
3. Operation 20 unit conversion: this option is provided as a convenient way to convert metric models to imperial, and vice versa. To convert an imperial model to metric, select the 25.4 option from the scale menu and click ―scale‖ again . To convert from metric to imperial, select the 0.03937 optio...
Page 21: 3. Operation
3. Operation 21 3.3 getting ready to print 3.3.1 initializing the printer before anything can be printed, the printer must be initialized. Click the ―initialize‖ option under the ―3d print‖ m enu. The printer will beep and the initialization procedure will begin. The printer will then return the pla...
Page 22: 3. Operation
3. Operation 22 3.3.2 calibrating the nozzle height this section is probably the most important of the entire manual. Please read it carefully to ensure that you understand the nozzle height setup procedure, as it is vital to successful 3d printing. To print successfully, the platform should be set ...
Page 23: 3. Operation
3. Operation 23 in the above example, this tells the printer that, after being initialized, and when a print job begins, the platform is 135.9mm away from the nozzle. To figure out the correct nozzle distance, please follow these steps: 1 - open the ―maintain‖ dialogue box from the ―3d print‖ menu. ...
Page 24: 3. Operation
3. Operation 24 only increased the number by 3mm instead of 4mm. The reason for this is that we do not want to crash the platform into the nozzle, so we want to increase the height in smaller and smaller increments as we get closer to the nozzle. 4 - once you are about 1mm away from the nozzle, star...
Page 25: 3. Operation
3. Operation 25 the path in the above picture is thick, seems just stick on the surface of the perfboard, and it can be easily pulled by nails. So click ―no‖, the height will increase 0.1mm and test again. The last path in the above picture is quite wide and thin, and its surface is not flat. Viewed...
Page 26: 3. Operation
3. Operation 26 3.3.3 leveling the print platform after you have correctly calibrated your nozzle height, check that the nozzle is at the same distance at all four corners of the print platform. If it is not, you may need to adjust the platform until it is level with the nozzle at all 4 corners. The...
Page 27: 3. Operation
3. Operation 27 3.3.4 other maintenance options click ―maintain‖ on the ―3d print‖ menu, and the following dialog box pops up: (windows version) (mac version) extrude: squeezes material out of the nozzle. Click on this button, and the nozzle is heated. When the temperature is high enough (260°c), th...
Page 28: 3. Operation
3. Operation 28 new spool: this is used so the printer can keep track of how much material has been used, and warn you if you don‘t have enough material left to print your model. Click this button and enter the value of how many grams of material you have on the current spool. If it is a new spool, ...
Page 29: 3. Operation
3. Operation 29 the ―bottom‖ button returns the platform to the lowest position. Set nozzle height: takes whatever value you have in the ―to‖ box and transfers it to the nozzle box of the setup screen. 3.3.5 preparing the platform before printing, the platform must be prepared so that the model adhe...
Page 30: 3. Operation
3. Operation 30 3.3.6 print setup options click menu ―3d print->setup‖. The following dialog box pops up: print options z resolution: sets the print resolution (layer thickness) of the printer. This can be between 0.2mm per layer to 0.4mm per layer (depending on the printer model). Optimize: disable...
Page 31: 3. Operation
3. Operation 31 the default value for this parameter is set to 2mm. Nozzle: represents the distance between nozzle and the print platform when it is at the bottom position. It is essential that this value be correctly set for good printing. See section 3.3.2. For instructions on calibrating your pri...
Page 32: 3. Operation
3. Operation 32 the part has an outer wall thickness of solid plastic (about 1.5mm), but its interior is filled with a reasonably small scaffold structure. On previous software version this was referred to as ―loose‖ the part has an outer wall thickness of solid plastic (about 1.5mm), but its interi...
Page 33: 3. Operation
3. Operation 33 angle: angle at which support material gets used. For example if 10° is used, support material only gets used if angle of surface is greater than 10° from horizontal (so support material is almost not used unless there is a direct overhang), if set to 50° than support material is use...
Page 34: 3. Operation
3. Operation 34 area: the surface area above which support material gets used. When you choose 5mm 2 , for example, there will be no support if the overhanging area is less than 5mm 2 . Benefit? A little material is saved and a slightly faster print speed is achieved. Other options stable support: s...
Page 35: 3. Operation
3. Operation 35 4. Printing tip: one of the keys to successful printing on the up is platform preparation and preheating. Particularly with large parts, there is a tendency for the edges of the part to lift from the platform (which is a little colder than the center) and cause the parts to warp. The...
Page 36: 3. Operation
3. Operation 36 (windows version) (mac version) print options: speed: fine, normal or fast. This simply determines the speed at which the printer moves. As a general rule, the slower you print, the better the quality of the parts. For tall parts, running at fast speed can be problematic as the print...
Page 37: 3. Operation
3. Operation 37 tip: once the print has started, you can unplug the pc from the printer. The print job is stored in the printer‘s internal memory, so the pc is no longer required. Calculating model costs the main factor that will affect model cost is the part interior fill structure, and support mat...
Page 38: 3. Operation
3. Operation 38 3. Gently slide the spatula under the model and slowly wiggle it back and forth to pry loose the model. Remember to use gloves as the platform and model may still be hot. Caution: it is strongly recommended that you ware the gloves to remove the model from the perfboard. Removing sup...
Page 39: 3. Operation
3. Operation 39 the support material gets removed using a combination of tools. Some material can easily be cracked off by hand. Support material close to the model is easier to remove using tools such as wood carving chisels, long nose pliers, or wire cutters. It takes some practice to get comforta...
Page 40: 3. Operation
3. Operation 40 6. Maintenance changing the material first withdraw the leftover material from the printer. Initialize the printer and choose ― 3d print->maintain‖. Click ―withdraw‖ and the system automatically begins to heat the nozzle. When the nozzle reaches the correct temperature, the printer w...
Page 41: 3. Operation
3. Operation 41 after the calibration model is printed, measure the x1 and x2 length, as shown in the pictures below. Open the ―calibrate‖ box form the ―3d print‖ menu and enter the me asured x1 and x2 values into the appropriate boxes..
Page 42: 3. Operation
3. Operation 42 important note: before you enter any new calibration values, always click the ―reset‖ button, otherwise the new values get added to the old ones. Before you enter any new values, the bar at the very top of the screen should read: xy: 0.00 deg / xz: 0.00 deg. Next, take down the front...
Page 43: 3. Operation
3. Operation 43 tip: many users also soak their nozzle in acetone to clean them, or even use an ultrasonic cleaning bath to help clean their nozzles removing / changing the nozzle should the nozzle become blocked, you may need to remove it in order to unblock, or change it. To remove the nozzle, use...
Page 44: 3. Operation
3. Operation 44 cleaning the platform if you are using the special green paint on your platform, the platform requires cleaning after a few prints to get it back to a smooth surface. Simply remove the platform from the machine and soak it in water for a few hours and the paint will peel of easily. O...
Page 45: 3. Operation
3. Operation 45 7.0. Tips & tricks large parts can sometimes have their corners lift from the platform, which causes the part to distort. This is caused by uneven heat across the surface of the platform. Preheating the platform before beginning large parts is essential to minimize this lifting. Also...
Page 46: 3. Operation
3. Operation 46 regularly check your nozzle height! It can change for a number of reasons, some of which you may not even be aware of. To check your nozzle height, refer to section 3.3.2 to get the best results out of your up printer, the print platform must be perfectly lined up with the nozzle. Th...
Page 47: 4. Troubleshooting
4. Troubleshooting 47 8. Troubleshooting problem or error message solution no power verify power cord is securely plugged in. Extruder or platform fails to reach operating temperature 1. 1. Verify printer has initialized. If not, initialize the printer 2. 2. Heater is damaged, replace the heater mat...
Page 48: 4. Troubleshooting
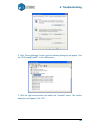
4. Troubleshooting 48 2. Click ―device manager‖ button, and the following dialog box will popup. Find the ―3dprinter@freemc‖ in the usb section. 3. Click the right mouse button and select the ―uninstall‖ option. The confirm dialog box will appear. Click ―ok‖..
Page 49: 4. Troubleshooting
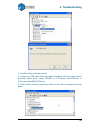
4. Troubleshooting 49 4. Install the latest software version. 5. Unplug the usb cable, then plug again. Windows will find a new device. Manually select driver folder (default is c:\program files\up\driver or c:\program files(x86)\up\driver); 6. There should now be a new driver section in the device ...
Page 50: 4. Troubleshooting
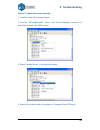
4. Troubleshooting 50 option 2: update the driver manually. 1. Install the latest up software version. 2. Find the ―3dprint@freemc‖ driver in the ―device manager‖ dialog box (it should be located in the usb section). 3. Select ―update driver.‖ in the right click menu. 4. Select the up driver folder ...
Page 51: 4. Troubleshooting
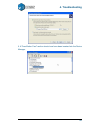
4. Troubleshooting 51 5. A ―free motion card‖ section should now have been inserted into the device manager..
Page 52
Www.Quant3d.Com ve rs io n q 20 0 1.