- DL manuals
- Rabbit
- Microcontrollers
- 2000
- Reference Manual
Rabbit 2000 Reference Manual - Table Of Contents
Instruction Reference Manual
iii
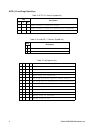
Table of Contents
1. Alphabetical Listing of Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2. Instructions Listed by Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
3. Document Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4. Processor Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5. OpCode Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6. Quick Reference Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Summary of 2000
Page 1
Rabbit 2000 /3000 microprocessor instruction reference manual 019–0098 c • 020416 this manual (or an even more up-to-date revision) is available for free download at the rabbit website: www.Rabbitsemiconductor.Com.
Page 2
Ii rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor.
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Instruction reference manual iii table of contents 1. Alphabetical listing of instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2. Instructions listed by group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 3. Docume...
Page 4
Iv rabbit 2000 microprocessor.
Page 5
Instruction reference manual 1 1. Alphabetical listing of instructions a adc a,n ..............................14 adc a,r ..............................14 adc a,(hl) .........................13 adc a,(ix+d) ......................13 adc a,(iy+d) ......................13 adc hl,ss .......................
Page 6
2 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor ld (mn),hl ..........................47 ld (mn),ix ...........................47 ld (mn),iy ...........................47 ld (mn),ss ...........................47 ld (sp+n),hl .......................48 ld (sp+n),ix ........................48 ld (sp+n),iy ..............
Page 7
Instruction reference manual 3 2. Instructions listed by group a. Load immediate data ld dd,mn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52 ld ix,mn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56 ld iy,mn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 8
4 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor exx . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33 h. Stack manipulation pop ip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73 pop ix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73 pop iy . ...
Page 9
Instruction reference manual 5 res b,r . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78 set b,(hl) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96 set b,(ix+d) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96 set b,(iy+d) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 10
6 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor altd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 and hl,de . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 and ix,de . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 and iy,de . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
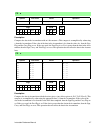
Page 11: 3. Document Conventions
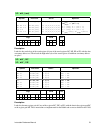
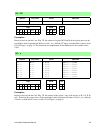
Instruction reference manual 7 3. Document conventions instruction table key • opcode : a hexidecimal representation of the value that the mnemonic instruction represents. • instruction : the mnemonic syntax of the instruction. • clocks : the number of clock cycles it takes to complete this instruct...
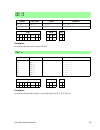
Page 12
8 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor altd, i/o and flags table keys table 2: altd (“a” column) symbol key table 3: ioi and ioe (“i” column) symbol key table 4: flag register key flag description f r sp • altd selects alternate flags • altd selects alternate destination register • altd operation is a sp...
Page 13
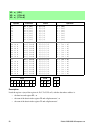
Instruction reference manual 9 document symbols key table 5: symbols rabbit z180 meaning b b bit select (000 = bit 0, 001 = bit 1, 010 = bit 2, 011 = bit 3, 100 = bit 4, 101 = bit 5, 110 = bit 6, 111 = bit 7) cc cc condition code select (00 = nz, 01 = z, 10 = nc, 11 = c) d d 7-bit (signed) displacem...
Page 14
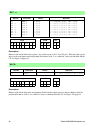
10 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor condition codes table 6: condition code description condition flag=value description nz z=0 not zer0 z z=1 zero nc c=0 no carry (c=0) c c=1 carry (c=1) p s=0 minus m s=1 positive lz l/v=0 for logic operations, logic zero (all of the four most significant bits of th...
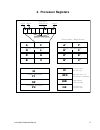
Page 15: 4. Processor Registers
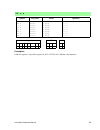
Instruction reference manual 11 4. Processor registers s z lv c sign zero logical/ overflow carry ix iy sp pc index register index register stack pointer program counter general purpose external interrupt internal interrupt interrupt priority extension of program counter eir iir ip xpc accumulator f...
Page 16
12 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor.
Page 17: 5. Opcode Descriptions
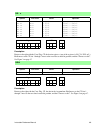
Instruction reference manual 13 5. Opcode descriptions description the data in the accumulator is summed with the carry flag and with the data in memory whose location is: • held in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement value d, or • the sum of the data i...
Page 18
14 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description the 8-bit constant n is summed with the carry flag and with the data in the accumulator. The sum is then stored in the accumulator. Description the data in the accumulator is summed with the carry flag, cf, and with the data in register r (any of the re...
Page 19
Instruction reference manual 15 description the data in the register pair hl is summed with the carry flag and with the data in word register ss (any of the word registers bc, de, hl, or sp). The result is stored in hl. Description the data in the accumulator is summed with the data in the memory lo...
Page 20
16 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description the data in the accumulator is summed with the 8-bit constant n. The result is stored in the accumulator. Description the data in the accumulator is summed with the data in register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). The result is stored i...
Page 21
Instruction reference manual 17 description the data in the word register hl is summed with the data in the word register ss (any of the word registers bc, de, hl, or sp). The result is stored in hl. Add hl,ss opcode instruction clocks operation —— 09 19 29 39 add hl,ss add hl,bc add hl,de add hl,hl...
Page 22
18 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description the data in index register ix is summed with the word register xx (any of the word registers bc, de, ix, or sp) and the result is stored in ix. The data in index register iy is summed with the word register yy (any of the word registers bc, de, iy, or s...
Page 23
Instruction reference manual 19 description this is an instruction prefix. Causes the instruction immediately following to affect the alternate flags, or use the alternate registers for the destination of the data, or both. For some instructions altd causes special alternate register uses, unique to...
Page 24
20 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description performs a logical and operation between the byte in the accumulator and the byte whose address is: • in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement value d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a disp...
Page 25
Instruction reference manual 21 description performs a logical and operation between the word in word register hl and the word in word register de. The relative bits of each byte are compared (i.E., the bit 1 of both bytes are compared, the bit 2 of both bytes are compared, etc.) and the associated ...
Page 26
22 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description performs a logical and operation between the byte in the accumulator and the 8-bit constant n. The relative bits of each byte are compared (i.E., the bit 1 of both bytes are compared, the bit 2 of both bytes are compared, etc.) and the associated bit in...
Page 27
Instruction reference manual 23 description tests the bit b (any of the bits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7) of the byte whose address is: • contained in the register pair hl, or • the sum of data in index register ix plus a displacement value d, or • the data in index register iy plus a displacement val...
Page 28
24 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description tests the bit b (any of the bits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7) of the byte in the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). The zero flag, z, is set if the tested bit is 0, reset if the bit is 1. Description if the data in word register hl ...
Page 29
Instruction reference manual 25 description if the data in index register ix or iy does not equal zero, then that register is set to 1. These instructions are implemented for the rabbit and are not available for the z180. Description this instruction is used to call a subroutine. First the data in t...
Page 30
26 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description the carry flag is inverted: if it is set, it becomes cleared. If it is not set, it becomes set. Description compares the data in the accumulator with the data whose address is (a) contained in word register hl, (b) the sum of the data in index register ...
Page 31
Instruction reference manual 27 description compares the data in the accumulator with an 8-bit constant n. This compare is accomplished by subtracting n from the accumulator. If the value of the data in the accumulator is less than the value of n, then the sign flag and the carry flag are set. If th...
Page 32
28 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description the data in the accumulator is inverted (one’s complement). Example if the data in the accumulator is 1100 0101, after the instruction cpl the accumulator will contain 0011 1010. Description decrements the byte whose address is: • in word register hl, o...
Page 33
Instruction reference manual 29 description decrements the data in index register ix or iy. Description decrements the data in the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). Dec ix dec iy opcode instruction clocks operation dd 2b dec ix 4 (2,2) ix = ix - 1 fd 2b dec iy 4(2,2) iy = iy ...
Page 34
30 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description decrements the data in word register ss (any of the word registers bc, de, hl, or sp). Description this instruction’s mnemonic stands for decrement and jump if not zero. It decrements the data in register b then, if the data in b does not equal 0, it ad...
Page 35
Instruction reference manual 31 description exchanges the byte in the register h with the data whose address is the data in the stack pointer register plus 1; and exchanges the byte in the register l with the data whose address is the data in the stack pointer . This instruction has been modified fr...
Page 36
32 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description exchanges the data in word register af with the data in the alternate word register af'. Description • ex de,hl exchanges the data in word register de with the data in word register hl. If the altd instruction is present then the data in de is exchanged...
Page 37
Instruction reference manual 33 description exchanges the data in word registers bc, de, and hl, with the data in their respective alternate word regis- ters bc', de', and hl'. Description increments the byte whose address is: • held in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix...
Page 38
34 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description • inc ix increments the data in index register ix. • inc iy increments the data in index register iy. Description increments the data in the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). Inc ix inc iy opcode instruction clocks operation dd 2...
Page 39
Instruction reference manual 35 description increments the data in word register ss (any of the word registers bc, de, hl, or sp). Inc ss opcode instruction clocks operation —— 03 13 23 33 inc ss inc bc inc de inc hl inc sp 2 2 2 2 2 ss = ss + 1 bc = bc + 1 de = de + 1 hl = hl + 1 sp = sp + 1 flags ...
Page 40
36 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description these instructions are implemented for the rabbit and are not available for the z180. • ioi: the ioi prefix allows the use of existing memory access instructions as internal i/o instructions. When prefixed, a 16-bit memory instruction accesses the i/o s...
Page 41
Instruction reference manual 37 description the interrupt priority register, ip is an 8-bit register that forms a stack of the current priority and the other previous 3 priorities. Ipset 0 forms the lowest priority; ipset 3 forms the highest priority. These instruc- tions are privileged. They are im...
Page 42
38 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description the ipres instruction rotates the contents of the interrupt priority register 2-bits to the right, replacing the current priority with the previous priority. It is impossible to interrupt during the execution of this instruction. This instruction is pri...
Page 43
Instruction reference manual 39 description • jp (hl): the data in hl is loaded into the program counter. Thus the address of the next instruction fetched is the data in hl. • jp (ix): the data in index register ix is loaded into the program counter. Thus the address of the next instruction fetched ...
Page 44
40 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description if the condition f is true then the 16-bit data mn is loaded into the program counter, pc. If the condition is false then the program counter increments normally. The condition f is one of the following: nz, zero flag not set; z, zero flag set; nc, carr...
Page 45
Instruction reference manual 41 description if condition cc is true then the 8-bit signed displacement value e is added to the program counter, pc. Since the instruction takes two increments of the pc to complete, two is subtracted from the displacement value so that the displacement take place from...
Page 46
42 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description this instruction is similar to the call routine in that it transfers program execution to the subroutine address specified by the 16-bit operand mn. The lcall instruction is special in that it allows calls to be made to a computed address in xmem. Note ...
Page 47
Instruction reference manual 43 description • ld (bc),a: loads the memory location whose address is the data in word register bc with the data in the accumulator. • ld (de),a: loads the memory location whose address is the data in word register de with the data in the accumulator. • ld (hl),n: loads...
Page 48
44 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description loads the data in register l into the memory location whose address is the sum of the data in word register hl and a displacement value d. Then, loads the data in register h into the memory location whose address is the sum of the data in word register ...
Page 49
Instruction reference manual 45 description • ld (ix+d),hl: loads the data in register l into the memory location whose address is the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement value d. Then, loads the data in register h into the memory location whose address is the sum of the data in ...
Page 50
46 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description • ld (iy+d),hl: loads the data in register l into the memory location whose address is the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement value d. Then, loads the data in register h into the memory location whose address is the sum of the data ...
Page 51
Instruction reference manual 47 description • ld (mn),a: loads the memory location whose address is mn with the data in the accumula- tor. • ld (mn),hl: loads the memory location whose address is mn with the data in register l, then loads the memory location whose address is 1 plus mn with the data ...
Page 52
48 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description these instructions are implemented for the rabbit and are not available for the z180. • ld (sp+n),hl: loads the data in the register l into the memory location whose address is the sum of the data in the stack pointer, sp, and the displacement n. Then l...
Page 53
Instruction reference manual 49 description loads the accumulator with the data whose address in memory is: • the data in word register bc, or • the data in word register de, or • the 16-bit constant mn. Ld a,(bc) ld a,(de) ld a,(mn) opcode instruction clocks operation 0a ld a,(bc) 6 (2,2,2) a = (bc...
Page 54
50 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description • ld a,eir: loads the accumulator with the data in the external interrupt register, eir. The eir is used to specify the most significant byte (msb) of the external interrupt address. The value loaded in the eir is concatenated with the appropriate exter...
Page 55
Instruction reference manual 51 description loads the low-order byte of the word register dd (any of the word registers bc, de, hl or sp) with the data at memory address mn. Then loads the high-order byte of the word register dd with data at memory address mn plus 1. Description loads the alternate ...
Page 56
52 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description loads the register pair dd (any of the register pairs bc, de, hl, or sp) with the 16-bit value mn. Description • ld eir,a: loads the external interrupt register, eir, with the data in the accumulator. The eir is used to specify the most significant byte...
Page 57
Instruction reference manual 53 description • ld hl,(mn): loads the register l with the data whose address is mn and loads the register h with the data whose address is mn plus 1. • ld hl,(hl+d): loads the register l with the data whose address is the data in word register hl plus a displacement d. ...
Page 58
54 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description loads the register l with the data whose address is the data in index register sp plus a displacement d. Then loads the register h with the data whose address is the data in index register sp plus a displacement d plus 1. This instruction is implemented...
Page 59
Instruction reference manual 55 description loads the low order byte of index register ix with the data whose address is mn. Then loads the high order byte of ix with the data whose address is mn plus 1. Description loads the low order byte of index register ix with the data whose address is the dat...
Page 60
56 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description • ld ix,hl: loads the index register ix with the data in word register hl. This instruction is implemented for the rabbit and is not available for the z180 • ld ix,mn: loads the index register ix with the 16-bit constant mn. • ld iy,hl: loads the index ...
Page 61
Instruction reference manual 57 description loads the low order byte of index register iy with the data whose address is the data in the stack pointer reg- ister sp plus a displacement n. Then loads the high order byte of iy with the data whose address is the data in the stack pointer register plus ...
Page 62
58 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description loads the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l) with the data whose address is: • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a di...
Page 63
Instruction reference manual 59 description loads the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l) with the 8-bit constant n. Ld r,n opcode instruction clocks operation —— 3e n 06 n 0e n 16 n 1e n 26 n 2e n ld r,n ld a,n ld b,n ld c,n ld d,n ld e,n ld h,n ld l,n 4 (2,2) 4 (2,2) 4 (2,2) 4...
Page 64
60 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description loads the one-byte register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l) with the data in another one-byte register g (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). Ld r,g opcode instruction clocks operation r,g a b c d e h l ld r,g 2 r = g a 7f 78 7...
Page 65
Instruction reference manual 61 description loads the stack pointer register, sp, with the data in (a) the word register hl, (b) the data in index register ix, or (c) the data in index register iy. These are privileged instructions. Description loads the extension of the program counter, xpc, with t...
Page 66
62 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description • ldd: loads the memory location whose address is in word register de with the data at the address in word register hl. Then it decrements the data in word registers bc, de, and hl. • lddr: while the data in the register pair bc does not equal 0 then th...
Page 67
Instruction reference manual 63 description these instructions are used to access 20-bit addresses. In all cases, the four most significant bits of the 20-bit address (bits 19 through 16) are defined as the four least significant bits of the accumulator (bits 3 though 0). The ldp instructions bypass...
Page 68
64 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description these instructions are used to access 20-bit addresses. In all cases, the four most significant bits of the 20-bit address (bits 19 through 16) are defined as the four least significant bits of the accumulator (bits 3 though 0). The ldp instructions byp...
Page 69
Instruction reference manual 65 description these instructions are used to access 20-bit addresses. In all cases, the four most significant bits of the 20-bit address (bits 19 through 16) are defined as the four least significant bits of the accumulator (bits 3 though 0). The ldp instructions bypass...
Page 70
66 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description these instructions are used to access 20-bit addresses. In all cases, the four most significant bits of the 20-bit address (bits 19 through 16) are defined as the four least significant bits of the accumulator (bits 3 though 0). The ldp instructions byp...
Page 71
Instruction reference manual 67 description this instruction is similar to the jp mn instruction in that it transfers program execution to the memory loca- tion specified by the 16-bit address, mn. Ljp is special in that it allows a jump to be made to a computed address in xmem. Note that the value ...
Page 72
68 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description a multiplication operation is performed on the contents of the 16-bit binary integers contained in the bc and de registers. The signed 32-bit result is placed in the hl (bits 31 through 16) and bc (bits 15 through 0) reg- isters. If the multiplier is ne...
Page 73
Instruction reference manual 69 description subtracts the value of the data in the accumulator from zero and stores the result in the accumulator. Description no operation is performed during this cycle. Neg opcode instruction clocks operation ed 44 neg 4 (2,2) a = 0 - a flags altd i/o s z l/v c f r...
Page 74
70 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description performs a logical or operation between the byte in the accumulator and the byte whose address is (a) in the word register hl, (b) the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or (c) the sum of the data in index register iy and a displ...
Page 75
Instruction reference manual 71 description performs a logical or between the data in word register hl and the data in word register de. The relative bits of each byte are compared (i.E., the bit 1 of both bytes are compared, the bit 2 of both bytes are compared, etc.) and the associated bit in the ...
Page 76
72 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description • or n: performs a logical or operation between the byte in the accumulator and the 8-bit con- stant n. • or r: performs a logical or operation between the byte in the accumulator an the byte in register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). ...
Page 77
Instruction reference manual 73 description • pop ip: loads the interrupt priority register, ip, with the data at the memory location in the stack pointer, sp, and then increments the data in sp. This privileged instruction was imple- mented for the rabbit and is not available for the z180. • pop ix...
Page 78
74 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description loads the low order byte of the word register zz (any of the word registers af, bc, de, or hl) with the data at the memory address in the stack pointer, sp, then loads the high order byte of zz with the data at the mem- ory address immediately following...
Page 79
Instruction reference manual 75 description • push ip: loads the location in memory whose address is 1 less that the data held in the stack pointer, sp, with the data in the interrupt priority register ip. Then decrements sp. This instruc- tion was implemented for the rabbit and is not available for...
Page 80
76 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description loads the memory location with the address 1 less than the data in the stack pointer, sp, with the high order byte of the data in word register zz (any of the word register af, bc, de, or hl), and loads the memory loca- tion with the address two less th...
Page 81
Instruction reference manual 77 description resets bit b (any of the bits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7) of the data whose address is: • held in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d. The b...
Page 82
78 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description resets bit b (any of the bits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7) of the data whose address is held in the register r (any of the register a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). The bit is reset by performing a logical and between the selected bit and its complement. Res b,r ...
Page 83
Instruction reference manual 79 description ret transfers execution from a subroutine to the program that called it. First it loads the low order byte of the program counter, pc, with the data at the memory address in the stack pointer, sp, then loads the high order byte of pc with the data at the m...
Page 84
80 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description if the condition f is false, then the instruction is ignored. If the condition f is true, then the instruction loads the low order byte of the program counter, pc, with the data at the memory address in the stack pointer, sp, then loads the high order b...
Page 85
Instruction reference manual 81 description loads the interrupt priority register, ip, with the data whose address is in the stack pointer, sp. Then loads the low order byte of the program counter, pc, with the data whose address is 1 higher than the data in sp and loads the high order byte of the p...
Page 86
82 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description rotates to the left with the carry flag, cf, the data whose address is: • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d. Bits 0 throug...
Page 87
Instruction reference manual 83 description rotates to the left with the carry flag, cf, the contents of register de. Each bit in the register moves to the next highest-order bit position (bit 0 moves to bit 1, etc.) while the cf moves to bit 0 and bit 15 moves to the cf. See figure 1 on page 82. Th...
Page 88
84 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description rotates to the left with the carry flag, cf, the contents of the accumulator. Each bit in the register moves to the next highest-order bit position (bit 0 moves to bit 1, etc.) while the cf moves to bit 0 and bit 7 moves to the cf. See figure 1 on page ...
Page 89
Instruction reference manual 85 description rotates to the left the data whose address is: • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d. Each bit in the register moves to the nex...
Page 90
86 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description rotates to the left the data in the register r (any of the register a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). Each bit in the register moves to the next highest-order bit position (bit 0 moves to bit 1, etc.) while bit 7 moves to both bit 0 and the cf. See figure 2 on p...
Page 91
Instruction reference manual 87 description rotates to the right with the carry flag, cf, the data whose address is: • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d. Bit 0 moves to ...
Page 92
88 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description rotates to the right with the carry flag, cf, the data in word register de or hl. Bit 0 moves to the cf, bits 1 through 15 move to the next lowest-order bit position, and the cf moves to bit 15. See figure 3 on page 87. These instructions were implement...
Page 93
Instruction reference manual 89 description rotates to the right with the carry flag, cf, the data in register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). Bit 0 moves to the cf, bits 1 through 7 move to the next lowest-order bit position, and the cf moves to bit 7. See figure 3 on page 87. Desc...
Page 94
90 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description rotates to the right the data whose address is: • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d. Each bit in the register moves to the...
Page 95
Instruction reference manual 91 description rotates to the right the data in the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). Each bit in the regis- ter moves to the next lowest-order bit position (bit 7 moves to bit 6, etc.) while bit 0 moves to both bit 7 and the cf. See figure 4 on p...
Page 96
92 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description pushes the current program counter, pc, onto the stack and then resets the pc to the interrupt vector address represented by iir:v , where iir is the address of the interrupt table and v is the offset into the table. The address of the vector table can ...
Page 97
Instruction reference manual 93 description subtracts the carry flag, cf, and the data whose address is: • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d from the data in the accumul...
Page 98
94 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description • sbc a,n: subtracts the carry flag, cf, and the 8-bit constant n from the data in the accumu- lator. • sbc a,r: subtracts the carry flag, cf, and the data in the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l) from the data in the accumulator....
Page 99
Instruction reference manual 95 description subtracts the carry flag, cf, and the data in word register ss (any of the word registers bc, de, hl, or sp) from the data in word register hl. The difference is stored in hl. These operations output an inverted carry: • the carry flag is set if the accumu...
Page 100
96 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description sets bit b (any of the bits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7) of the byte whose address is • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d. S...
Page 102
98 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description arithmetically shifts to the left the bits of the data whose address is • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d. Bits 0 throug...
Page 103
Instruction reference manual 99 description arithmetically shifts to the left the bits of the data in register r (any of a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). Bits 0 through 6 are each shifted to the next highest-order bit position (bit 0 moves to bit 1, etc.). Bit 7 is shifted to the carry flag, cf. Bit 0 is re...
Page 104
100 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description arithmetically shifts to the right the bits in the data whose address is • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d. Bits 7 thro...
Page 105
Instruction reference manual 101 description arithmetically shifts to the right the bits in the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). Bits 7 through 1 are shifted to the next lowest-order bit position (bit 7 is shifted to bit 6, etc.). Bit 7 is also copied to itself. Bit 0 is shi...
Page 106
102 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description logically shifts to the right the bits of the data whose address is • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d. Each bit is shif...
Page 107
Instruction reference manual 103 description logically shifts to the right the bits in the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). Each bit is shifted to the next lowest-order bit position (bit 7 shifts to bit 6, etc.) bit 0 shift to the carry flag, cf. Bit 7 is reset. See figure 7...
Page 108
104 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description subtracts from the data in the accumulator the data whose address is • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and a displacement d. The result is s...
Page 109
Instruction reference manual 105 description subtracts from the data in the accumulator the data in the register r (any of the registers a, b, c, d, e, h, or l). The result is stored in the accumulator. Sub r opcode instruction clocks operation —— 97 90 91 92 93 94 95 sub r sub a sub b sub c sub d s...
Page 110
106 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor description performs an exclusive or operation between the data in the accumulator and the data whose address is: • the data in word register hl, or • the sum of the data in index register ix and a displacement d, or • the sum of the data in index register iy and ...
Page 111
Instruction reference manual 107 description performs an exclusive or operation between the byte in the accumulator and the 8-bit constant n. The corre- sponding bits of each byte are compared (i.E., the bit 1 of both bytes are compared, the bit 2 of both bytes are compared, etc.) and the associated...
Page 112
108 rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor.
Page 113: 6. Quick Reference Table
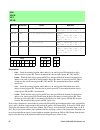
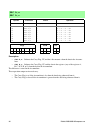
Instruction reference manual 111 6. Quick reference table key • instruction : the mnemonic syntax of the instruction. • opcode : the binary bytes that represent the instruction. • clock cycles : the number of clock cycles that the instruction takes to complete. The numbers in parenthesis are a break...
Page 114
112 rabbit 2000 microprocessor and ix,de 11011101 11011100 4 (2,2) f * * l 0 ix = ix & de n and iy,de 11111101 11011100 4 (2,2) f * * l 0 iy = iy & de n and n 11100110 ----n--- 4 (2,2) fr * * l 0 a = a & n and r 10100-r- 2 fr * * l 0 a = a & r bit b,(hl) 11001011 01-b-110 7 (2,2,1,2) f s - * - - (hl...
Page 115
Instruction reference manual 113 ipset 3 11101101 01011110 4 (2,2) - - - - ip = {ip[5:0], 11} np ipres 11101101 01011101 4 (2,2) - - - - ip = {ip[1:0], ip[7:2]} np jp (hl) 11101001 4 (2,2) - - - - pc = hl jp (ix) 11011101 11101001 6 (2,2,2) - - - - pc = ix jp (iy) 11111101 11101001 6 (2,2,2) - - - -...
Page 116
114 rabbit 2000 microprocessor ld hl,ix 11011101 01111100 4 (2,2) r - - - - hl = ix n ld hl,iy 11111101 01111100 4 (2,2) r - - - - hl = iy n ld ix,(mn) 11011101 00101010 ----n--- ----m--- 13 (2,2,2,2,1,2,2) s - - - - ixl = (mn); ixh = (mn+1) ld ix,(sp+n) 11011101 11000100 ----n--- 11 (2,2,2,1,2,2) -...
Page 118
116 rabbit 2000 microprocessor rrc (hl) 11001011 00001110 10 (2,2,1,2,3) f b * * l * (hl) = {(hl)[0],(hl)[7,1]}; cy = (hl)[0] rrc (ix+d) 11011101 11001011 ----d--- 00001110 13 (2,2,2,2,2,3) f b * * l * (ix+d) = {(ix+d)[0],(ix+d)[7,1]}; cy = (ix+d)[0] rrc (iy+d) 11111101 11001011 ----d--- 00001110 13...
Page 119
Rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor instruction reference manual part number 019–0098 c • 020416 • printed in u.S.A. ©2001 rabbit semiconductor • all rights reserved. Rabbit semiconductor reserves the right to make changes and improvements to its products without providing notice. Dynamic c is a registe...
Page 120
Ii rabbit 2000/3000 microprocessor.