- DL manuals
- Racal Instruments
- Synthesizer
- 3152
- User Manual
Racal Instruments 3152 User Manual
Artisan Technology Group
is your source for quality
new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment
• FAST SHIPPING AND
DELIVERY
• TENS OF THOUSANDS OF
IN-STOCK ITEMS
• EQUIPMENT DEMOS
• HUNDREDS OF
MANUFACTURERS
SUPPORTED
• LEASING/MONTHLY
RENTALS
• ITAR CERTIFIED
SECURE ASSET SOLUTIONS
SERVICE CENTER REPAIRS
Experienced engineers and technicians on staff
at our full-service, in-house repair center
WE BUY USED EQUIPMENT
Sell your excess, underutilized, and idle used equipment
We also offer credit for buy-backs and trade-ins
www.artisantg.com/WeBuyEquipment
REMOTE INSPECTION
Remotely inspect equipment before purchasing with
our interactive website at
www.instraview.com
LOOKING FOR MORE INFORMATION?
Visit us on the web at
www.artisantg.com
for more
information on price quotations, drivers, technical
specifications, manuals, and documentation
Contact us:
(888) 88-SOURCE | sales@artisantg.com | www.artisantg.com
SM
View
Instra
Summary of 3152
Page 1
Artisan technology group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment • fast shipping and delivery • tens of thousands of in-stock items • equipment demos • hundreds of manufacturers supported • leasing/monthly rentals • itar certified secure asset solutions service center r...
Page 2: User Manual
User manual 3152 precision pll synthesizer publication no. 980793 racal instruments racal instruments, inc. 4 goodyear st., irvine, ca 92618-2002 tel: (800) racal-ate, (800) 722-2528, (949) 859-8999; fax: (949) 859-7139 racal instruments, ltd. 480 bath road, slough, berkshire, sl1 6be, united kingdo...
Page 3
Warranty statement all racal instruments, inc. Products are designed and manufactured to exacting standards and in full conformance to racal’s iso 9001 procedures. For the specific terms of your standard warranty, or optional extended warranty or service agreement, contact your racal customer servic...
Page 4: For Your Safety
For your safety before undertaking any troubleshooting, maintenance or exploratory procedure, read carefully the warnings and caution notices. This equipment contains voltage hazardous to human life and safety, and is capable of inflicting personal injury. If this instrument is to be powered from th...
Page 5
I table of contents model 3152 precision pll synthesizer getting started what’s in this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1 introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 6
Ii using the instrument overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1 output termination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1 input/output protection . . . . ...
Page 7
Iii scpi command reference what’s in this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1 introduction to scpi language . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1 command format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 8
Iv trig, gate and burst characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8 pll characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10 adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 9
V tables 3-1 default conditions after power on, reset or *rst . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2 3-2 amplitude and offset ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3 4-1 vxibus model 3152 scpi commands list summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6 5-1 cpu and vxi i...
Page 11: Getting Started
Getting started 1-1 1 getting started what’s in this chapter this chapter contains a general description of the vxibus model 3152 waveform synthesizer and an overall functional description of the instrument. It lists and describes various options available for this model. It also describes the model...
Page 12
Getting started 1-2 besides its normal continuous mode, the model 3152 offers a variety of interrupted modes. The output waveform may be gated, triggered, or may generate a counted burst of waveforms. A built-in trigger generator with a programmable period can replace an external trigger. The model ...
Page 13
Getting started 1-3 5. 407510-012 - model 3152 - 100ms/s waveform synthesizer, w/256k ram, 1ppm 6. 407510-002 - model 3152 - 100ms/s waveform synthesizer, w/512k ram, 1ppm 7. 407510-012 - model 3152 - 100ms/s waveform synthesizer, w/ 64k ram, 100ppm 8. 407510-022 - model 3152 - 100ms/s waveform synt...
Page 14
Getting started 1-4 supplied accessories the model 3152 is supplied with an instruction manual. The manual includes disks with vxiplug&play soft front panel and drivers along with wavecad for windows. A service manual is available upon request. Specifications instrument specifications are listed in ...
Page 15
Getting started 1-5 trigger input the trigger input accepts signals that stimulate the model 3152 to output waveforms. The trigger input is inactive when the instrument is in continuous operating mode. When placed in trigger, gated or burst mode, the trigger input is made active and waits for the ri...
Page 16
Getting started 1-6 gated mode in gated mode, the model 3152 circuits are armed to generate output waveforms as long as a gating signal is true. Unlike the triggered mode, the gated mode is level sensitive. When the gating signal goes false, the waveform at the output connector is first completed an...
Page 18
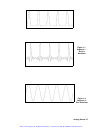
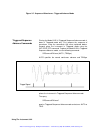
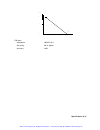
Getting started 1-8 figure 1-3 segment 3 - pulse waveform the following sequence was made of segment 2 repeated twice, segment 1 repeated four times and segment 3 repeated twice. Figure 1-4 sequenced waveforms output state the main output can be turned on or off. The internal circuit is disconnected...
Page 19
Getting started 1-9 backplane synchronization multiple model 3152s may be synchronized and operated together inside one vxibus chassis. With one instrument configured as master and the rest of the instruments configured as slaves, the instruments are phase-locked to the start phase on the master mod...
Page 20
Getting started 1-10 the fail led may be illuminated during normal operation if the model 3152 stops communication. The access led (amber) illuminates each time a command has been received by the model 3152. This light remains on during shared memory data transfer. The pll on led is off during norma...
Page 21: Configuring The Instrument
Configuring the instrument 2-1 2 configuring the instrument installation overview this chapter contains information and instructions necessary to prepare the model 3152 for operation. Details are provided for initial inspection, grounding safety requirements, repacking instructions for storage or sh...
Page 22
Configuring the instrument 2-2 when using test fixtures, keep the lid closed while power is applied to the device under test. Safe operation requires that the computer lid be closed at all times during operation. Carefully read the “safety precautions” instructions that are supplied with your comput...
Page 23
Configuring the instrument 2-3 note if the instrument is to be shipped to racal instruments for calibration or repair, attach a tag to the instrument identifying the owner. Note the problem, symptoms, and service or repair desired. Record the model and serial number of the instrument. Show the work ...
Page 25
Configuring the instrument 2-5 installation the instrument can be installed in any slot except slot 0 in a vxibus mainframe. When inserting the instrument into the mainframe, it should be gently rocked back and forth to seat the connectors into the backplane receptacle. The ejectors will be at right...
Page 27: Using The Instrument
Using the instrument 3-1 3 using the instrument overview this chapter contains information about how to operate the model 3152. Unlike bench-type instruments, the model 3152 must be programmed to turn on functions, change parameters and configure various operating modes. The instrument can be progra...
Page 28
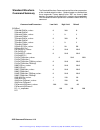
Using the instrument 3-2 table 3-1 default conditions after power on, reset or *rst output state: off operating mode: continuous filter state: off filter type: 20 mhz ecltrg0-1: off ttltrg0-7: off output trigger source: bit sync state: off std. Wave frequency: 1 mhz arb. Wave sample clock: 1 mhz amp...
Page 29
Using the instrument 3-3 table 3-2 amplitude and offset ranges amplitude window maximum offset $1.6 v ±8 v 0 to ±7.19 v $160 mv ±800 mv 0 to 719 mv $10 mv ±80 mv 0 to 75 mv to calculate the maximum offset available for a particular amplitude setting, use the following inequality: v amplitude + * v o...
Page 30
Using the instrument 3-4 alternatively, if just the first parameters need to be changed, omit the commas. The other parameters will be set to the power-up default values: appl:squ 4e6,2 queries can also be made on all parameters associated with a standard function using the appl: ? Query. For exampl...
Page 31
Using the instrument 3-5 the command: apply:ramp {,,, , ,} programs the synthesizer to output a ramp waveform with frequency, amplitude, offset, delay, rise time, and fall time parameters. The default settings for these functions are: 1 mhz, 5 vp-p, 0 v, 0%, 10% and 10%. The command: apply:sinc {,,,...
Page 32
Using the instrument 3-6 the query: apply:? Queries parameters associated with the specified function shape. Returns a string of values depending on the parameters that are available for the selected function shape. The query: apply? Queries parameters associated with the currently selected function...
Page 35
Using the instrument 3-9 the command: voltage:offset sets the offset for the currently active function. The default offset is 0 v. The query: voltage:offset? Queries the output offset for the currently selected function and returns a value in volts. Selecting the filter type before selecting the fil...
Page 37
Using the instrument 3-11 assigning the validating source for ttltrg the ttltrg signals, when enabled and placed on the backplane, can be asserted with signals coming from a number of sources. Use the following command to assign the signal source for the active ttltrg line: output:trigger:source {bi...
Page 39
Using the instrument 3-13 hclock generates a trigger signal at intervals equal to half of the period of the sample clock. This option is useful for synchronizing two-point waveforms on an oscilloscope (sine and square waveforms above 10 mhz). The query: output:sync:source? Queries the validating sig...
Page 40
Using the instrument 3-14 f(m) ' & a 2 % a 2 [e m 7.7t &1] f(m) ' ae &m 2 /t 2 & a 2 f(m) ' ae &m 2 /t 2 & a 2 f(m) ' sine(2. B. M r ).A 2. B. M r for triangle and sinc: freq # 200khz points = 500 freq > 200khz points = 100mhz freq the equations used for generating exponential, gausian and sinc func...
Page 41
Using the instrument 3-15 the command: pulse:delay sets the pulse delay in percent of the pulse period. For example, if the pulse period is 100 ms, 10% will delay the first transition of the pulse by 10 ms. Delay is measured from trigger to the first turning point. The query: pulse:delay? Queries th...
Page 42
Using the instrument 3-16 the query: pulse:transition:trailing? Queries the pulse fall time setting and returns a value in percent. Selecting an operating mode the model 3152 offers four operating modes: continuous, triggered, gated and burst. The selected waveform is repeated continuously when the ...
Page 43
Using the instrument 3-17 gated mode operates on standard waveforms, arbitrary waveforms, and on sequences of waveforms. Observe the limitations of the gating signal as listed in the specification section of this manual. To place the model 3152 in gated mode, use the following commands: init:cont of...
Page 44
Using the instrument 3-18 the query: trigger:count? Queries the burst count and returns an integer. Selecting the trigger source when an external source is not available, the operator has the option to use either the built-in trigger generator or a ttltrg signal to stimulate its output. Use the foll...
Page 45
Using the instrument 3-19 selecting the trigger slope the trigger slope command selects the sensitive edge of the trigger signal that is applied to the trig in connector. The model 3152 can be made sensitive to either positive or negative transitions. Use the following command to select the edge sen...
Page 46
Using the instrument 3-20 using the soft trigger there are a number of commands that are available to trigger the model 3152. The soft trigger command is one of them. To use the soft trigger command, place the instrument in the trig:sour ext mode. Soft trigger is ignored in the internal or ttltrg mo...
Page 47
Using the instrument 3-21 memory management commands arbitrary memory can be divided into smaller segments; up to 4096 different arbitrary waveforms can be generated with the model 3152. The length of each segment is left totally to the user’s discretion. To partition the arbitrary waveform memory, ...
Page 48
Using the instrument 3-22 first, define the work area. Define the segment number and its associated length. Segment length must be an even number. For example, to use segment number 8 and give it a length of 1000 points, use this command: trace:define 8,1000 next, make segment 8 the active segment. ...
Page 49
Using the instrument 3-23 “#” non-zero ascii digit high byte (binary) low byte (binary) ascii digit start of data block number of digits to follow byte count: 2x number of points 2 bytes per data point figure 3-1 definite length arbitrary block data format 6-bits of data are sent to the model 3152 a...
Page 50
Using the instrument 3-24 note t h e m o d e l 3 1 5 2 o p e r a t e s i n i n t e r l a c e d mode where two memory cells generate one byte of data. Segment size can be programmed in even-numbers only and the generator can accept binary blocks of data that are multiples of 4 only. For example, 2000...
Page 52
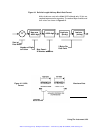
Using the instrument 3-26 generating sequenced waveforms what are sequenced waveforms? Sequenced waveforms are made of a number of arbitrary waveforms which can be linked and repeated in various manners. Sequenced waveforms are generated from waveforms stored in a library of memory segments. Before ...
Page 54
Using the instrument 3-28 figure 3-6 shows a sequence of waveforms that were stored in three different memory segments. Note that segment number 2 is generated first and repeated twice, segment 3 follows once and then segment 1 is repeated four times. Sequence commands the following is an overview o...
Page 55
Using the instrument 3-29 use this command up to 4095 times, each time for a different step and for a different segment number and repeat combination. Note that the same segment number can be used for different sequence steps. The seq:def command does not change the func:mode setting. Unless the fun...
Page 56
Using the instrument 3-30 trigger signal figure 3-7 sequenced waveforms - triggered advance mode triggered sequence advance commands placing the model 3152 in triggered sequence advance mode is done in triggered mode only. First, prepare the sequence of waveforms using the commands that were explain...
Page 57
Using the instrument 3-31 backplane inter- module synchronization although multiple model 3152s within one chassis run off a common clock (clk10), their outputs are not synchronized to each other. If the same waveform length and clock rates for two modules are selected and both are displayed on an o...
Page 58
Using the instrument 3-32 the sample clock rate has no effect on phase offset accuracy. However, when trying to synchronize modules that are programmed to output waveforms with few memory points, a ±1 count error between modules may be seen. To remove this error, use the following command: phase[1]:...
Page 59
Using the instrument 3-33 phase offset resolution depends on the number of waveform samples. For instance, if you have 1000 waveform samples, there is no problem with adjusting the phase offset in 1 ee increments (360 ee / 1000 only 10 waveform samples, the best phase offset increments are only 36 e...
Page 60
Using the instrument 3-34 phase2:lock? Queries the pll’s state. It returns a “0” (off) or “1” (on). Phase2:adjust? Queries the pll offset. It returns a value in degrees. Phase2:fine? Queries the pll’s fine offset. It returns a value in degrees. Using the frequency counter in pll mode, the model 3152...
Page 61
Using the instrument 3-35 the pm in is sensitive to voltage levels. Applying 1 v to this input generates a phase offset of 20 e. Likewise, applying -1 v to this input generates a phase offset of -20 e. You may apply 20 v to this input and generate a phase offset of 400 e. The applied frequency range...
Page 62
Using the instrument 3-36 system-related commands system-related commands are used to place the instrument in a known state, clear the instrument to its defaults, or to query the generator for its errors or identity. The following is an overview of the system-related commands. The query: system:erro...
Page 65: Scpi Command Reference
Scpi command reference 4-1 4 scpi command reference what’s in this chapter this chapter contains reference information for programming the model 3152. Standard commands for programmable instruments (scpi) convention rules and syntax are explained in detail. Table 4-1 lists all scpi commands used for...
Page 67
Scpi command reference 4-3 a semicolon ( ; ) is used to separate commands within the same subsystem, and can also minimize typing. For example, sending the following command string: trig:sour:adv int;burs on;int:rate 5e-3 is the same as sending the following three commands: trig:sour:adv int trig:bu...
Page 68
Scpi command reference 4-4 ieee-std-488.2 common commands the ieee-std-488.2 standard defines a set of common commands that perform functions like reset, trigger and status operations. Common commands begin with an asterisk ( * ), are four to five characters in length, and may include one or more pa...
Page 69
Scpi command reference 4-5 arbitrary block parameters arbitrary block parameters are used for loading waveforms into the synthesizer's memory. Depending on which option is installed, the model 3152 can accept binary blocks up to 1046576 bytes. The following command uses an arbitrary block parameter ...
Page 71
Scpi command reference 4-7 keyword parameter form (default in bold) scpi 1993.0 notes :ramp not confirmed :delay (10;0;99.9) not confirmed :transition not confirmed [:leading] (10;0;99.9) not confirmed :trailing (10;0;99.9) not confirmed :sinc not confirmed :ncycle (10;4;100) not confirmed :gaussian...
Page 74
Scpi command reference 4-10 standard waveform command summary the standard waveform commands control the various parameters of the standard output functions. Optional modes are omitted from these commands. Factory defaults after *rst are shown in bold typeface. Parameter low and high limits are give...
Page 75
Scpi command reference 4-11 arbitrary waveform, sequence, and shared memory command summary arbitrary waveform commands allow the definition of segments and their corresponding lengths, addition and deletion of segments, and the loading waveform data. Sequence commands control which segments are lin...
Page 76
Scpi command reference 4-12 trigger command summary the trigger commands control the trigger modes of the model 3152. The model 3152 can be placed in triggered, gated or burst mode. Trigger source is selectable from an external source, internal trigger generator, backplane ttltrg 0-7, and software t...
Page 77
Scpi command reference 4-13 the commands are presented exactly as they should be typed in your program. Optional nodes were omitted from these commands. Factory defaults after *rst or front panel reset are shown in bold typeface. Parameter low and high limits are given where applicable. Command and ...
Page 78
Scpi command reference 4-14 the following is a complete listing of all common commands and queries which are used in the model 3152. *cls - clear the status byte summary register and all event registers. *ese - enable bits in the standard event enable register. The selected bits are then reported to...
Page 79
Scpi command reference 4-15 *sre? - query the status byte enable register. The synthesizer returns a decimal value in the range of 0 to 63 or 128 to 191 since bit 6 (rsq) cannot be set. The binary-weighted sum of the number represents the value of the bits of the service request enable register. *st...
Page 80
Scpi command reference 4-16 an event register defines which bits in the corresponding event register are logically ored together to form a single summary bit. The user can read from and write to an enable register. Querying an enable register will not clear it. The *cls command does not clear enable...
Page 82
Scpi command reference 4-18 the status byte register (stb) the status byte summary register contains conditions from the other registers. Query data waiting in the synthesizer's output buffer is immediately reported through the message available bit (bit 4). Bits in the summary register are not latc...
Page 83
Scpi command reference 4-19 service request enable register (sre) the service request enable register is an 8-bit register that enables corresponding summary messages in the status byte register. Thus, the application programmer can select reasons for the synthesizer to issue a service request by al...
Page 84
Scpi command reference 4-20 bit 3 - device dependent error. This bit is set when an error in a device function occurs. For example, the following command will cause a dde error: voltage 7.25;:voltage:offset 4.1 both of the above parameters are legal and within the specified limits, however, the synt...
Page 85
Scpi command reference 4-21 error messages in general, whenever the model 3152 receives an invalid scpi command, it automatically generates an error. Errors are stored in a special error queue and may be retrieved from this buffer one at a time. Errors are retrieved in first-in-first-out (fifo) orde...
Page 86
Scpi command reference 4-22 -148,"character data not allowed". A character data element was encountered where prohibited by the instrument. -200,"execution error". This is the generic syntax error for the instrument when it cannot detect more specific errors. Execution error as defined in ieee-488.2...
Page 87
Maintenance and performance checks 5-1 5 maintenance and performance checks what’s in this chapter this chapter provides maintenance, service information, performance tests, and the information necessary to adjust and troubleshoot the model 3152 waveform synthesizer. Warning the procedures described...
Page 88
Maintenance and performance checks 5-2 special handling of static sensitive devices mos devices are designed to operate at very high impedance levels for low power consumption. As a result, any normal static charge that builds up on your person or clothing may be sufficient to destroy these devices ...
Page 89
Maintenance and performance checks 5-3 2. Keep the soldering iron in contact with the pc board for a minimum time to avoid damage to the components or printed conductors. 3. To desolder components, use a commercial "solder sucker" or a solder-removing solder - wick, size 3. 4. Always replace a compo...
Page 90
Maintenance and performance checks 5-4 recommended test equipment recommended test equipment for troubleshooting, calibration and performance checking is listed below. Test instruments other than those listed may be used only if their specifications equal or exceed the required characteristics. Test...
Page 91
Maintenance and performance checks 5-5 3. Connect the model 3152 output to the counter’s input. Change the frequency setting as required for the test and verify the reading on the counter display as follows: 3152 setting counter reading 10.00000 hz 9.999000 hz - 10.00100 hz 100.0000 hz 99.99000 hz -...
Page 92
Maintenance and performance checks 5-6 equipment: dmm, 50s feedthrough termination 1. Configure the model 3152 as follows: function: sine frequency: 1.000 mhz amplitude: 1.61 v remote commands: :res :outp on :func sin :freq 1e6 :volt 1.61 :volt:offs 5 2. Set the dmm to dcv measurements 3. Connect th...
Page 93
Maintenance and performance checks 5-7 2. Connect the model 3152 output to the oscilloscope input. Use the 20 db attenuator and set the oscilloscope input impedance to 50s. 3. Set the oscilloscope and verify that the rise and fall times are less than 6 ns. Verify that overshoot and ringing are less ...
Page 94
Maintenance and performance checks 5-8 4. Tune the spectrum analyzer to the carrier frequency and adjust the gain so the fundamental corresponds to 0 db. 5. Connect the model 3152 output to spectrum analyzer input through a 20db feedthrough attenuator. 6. Set the model 3152 freq setting and verify t...
Page 95
Maintenance and performance checks 5-9 gated - external signal at the trig in connector enables the model 3152 output. The last cycle of the output waveform is always completed. Burst - each transition at the front panel trig in connector stimulates the model 3152 to generate a burst of pre-selected...
Page 96
Maintenance and performance checks 5-10 burst 1. Configure the model 3152 as follows: function: sine wave frequency: 1.000 khz operating mode: burst remote commands: :res :outp on :freq 10e3 :init:cont off :burst:stat on :trig:coun 10 2. Set the oscilloscope and verify that the model 3152 outputs a ...
Page 97
Maintenance and performance checks 5-11 4. Set pulse/function generator to output 2 vp-p square waveforms. Change 3152 and pulse/function generator frequency and verify counter phase readings as shown below. 3152 freq. Pulse generator setting freq. Setting counter reading 10.00 mhz 10.00 mhz 0 e ±77...
Page 98
Maintenance and performance checks 5-12 8. Change the model 3152 phas2:adj setting to 0 e and phas2:fine setting to 36 e. Verify counter phase readings as shown below. Note the exact phase reading. 3152 freq. Pulse generator setting freq. Setting counter reading 10.00 khz 10.00 khz recorded result f...
Page 99
Maintenance and performance checks 5-13 note if not otherwise specified, configure the instrument to factory defaults before each adjustment by sending the *rst command. Always connect the output bnc connector through a 50s s feedthrough termination. Pulse response adjustment equipment: oscilloscope...
Page 100
Maintenance and performance checks 5-14 amplitude adjustment equipment: dmm, 50s feedthrough termination 1. Configure the model 3152 as follows: function: sine frequency: 1 khz amplitude: 16 v remote commands: :res :outp on :freq 1e3 :volt 16 2. Connect the model 3152 output to the dmm input through...
Page 101
Maintenance and performance checks 5-15 vco adjustment equipment: dmm 1. Configure the model 3152 as follows: function: sinewave output: on remote commands: :res 2. Connect the dmm “v” input to u515 pin 1 and the dmm “common” input to case ground. Set the dmm to dcv measurements. 3. Adjust r536 unti...
Page 102
Maintenance and performance checks 5-16 2. Make the following connections: a. Connect function generator output to the input of the 50s “t”connector. B. Connect one end of the 50s “t” connector to the 3152 trig in and the other end to the counter channel a input. C. Connect the 3152 out to the count...
Page 103
Maintenance and performance checks 5-17 the troubleshooting procedure should also be initiated whenever the synthesizer fails to perform either completely or partially. It is also required to troubleshoot the model 3152 whenever the instrument fails to fully comply with its published specifications....
Page 104
Maintenance and performance checks 5-18 problems in the cpu and the digital circuit may cause a complete malfunction of the entire instrument. The cpu would not start generating control signals. This makes it impossible to troubleshoot the remaining circuits. Check the various components associated ...
Page 106
Maintenance and performance checks 5-20 clock synthesizer checkout problems with the clock synthesizer circuits can be detected if the model 3152 accepts word serial commands and responds correctly to word serial queries, but fails to output the correct waveform frequency. If there is a problem with...
Page 107
Maintenance and performance checks 5-21 sequence generator checkout problems with the sequence generator circuits can be detected if the model 3152 accepts word serial commands and responds correctly to word serial queries, but fails to output sequences or bursts. If there is a problem with the sequ...
Page 108
Maintenance and performance checks 5-22 the next checkout is done on the model 3152 configured to operate in burst mode with 5 bursts. Use the following command to configure the model 3152: remote commands: :func:mode user :trac:sel 1 :init:cont off :trig:burs: on :trig:coun 5 :outp on connect an ex...
Page 109
Maintenance and performance checks 5-23 engine board circuit checkout as described in the paragraph main board circuit checkout, the model 3152 is made of two boards. If the engine board is removed from the main board, reinstall it before continuing with the following checks. The following circuit c...
Page 110
Maintenance and performance checks 5-24 change the model 3152 setting to triggered. Use an external pulse generator to apply a ttl level, 200 khz signal to the trig in connector. Proceed with the checks given in table 5-7b. Table 5-7b engine board checkout procedure - #2 step test point expected res...
Page 111: Specifications
Specifications a-1 a specifications vxibus general information module form single slot vxibus c-size module connectors p1, p2 protocol a16/a24/d16 slave, message-based vxibus revision 1.4 scpi revision 1993.0 logical address settings 1 - 255, configured via dip switches interrupt level settings 1 - ...
Page 112
Specifications a-2 triggering characteristics trigger input impedance 1 k 6 , ±5% level ±10 v resolution 10 mv sensitivity 100 mv rms accuracy ±(5% of level + 150 mv) maximum input voltage 30 v rms minimum pulse width 20 ns slope positive or negative going edges, programmable modes normal continuous...
Page 113
Specifications a-3 internal internal programmable rate generator system delay from external trigger input to waveform output standard waveforms 120ns + 2 sample clock periods ± 1 sample clock period arbitrary waveforms 150ns + 2 sample clock periods ± 1 sample clock period external input from: 1) fr...
Page 114
Specifications a-4 output on green - output on/off front panel input/output connectors main output signal output (bnc) marker/sync output marker/sync output (bnc) trigger input external trigger source input (bnc) sample frequency input sample frequency input (bnc) pm input phase control input (bnc) ...
Page 115
Specifications a-5 pressure (for 10 c rise) 0.5 mm h 0 o 2 environmental operating temperature 0 c - 55 c o o storage temperature -40 c - +70 c o o humidity (non-condensing) 11 c - 30 c 95% +5% o o 31 c - 40 c 75% +5% o o 41 c - 50 c 45% +5% o o altitude operating 10000 ft storage 15000ft vibration ...
Page 116
Specifications a-6 range 0 to ±7.190 v within ±8 v window 0 to ±719.0 mv within ±800 mv window 0 to ±71.90 mv within ±80 mv window resolution 4 digits accuracy ±(1% +1% of amplitude +20 mv) ±8 v window ±(1% +1% of amplitude +2 mv) ±800 mv window ±(1% +1% of amplitude +200 µv) ±80mv window filters 50...
Page 117
Specifications a-7 triangle frequency range 100 µhz to 1 mhz, usable to 10 mhz adjustable parameters start phase 0 to 360° power 1 to 9 square frequency range 100 µhz to 50 mhz adjustable parameters duty cycle 1% to 50% pulse/ramp frequency range 100 µhz to 1 mhz adjustable parameters delay 0% to 99...
Page 118
Specifications a-8 range 1% to 100% of amplitude arbitrary waveforms waveform memory 64k (256k or 512k) optional) points memory segmentation number of segments 1 to 4096 min segment size 10 point vertical resolution 12 bits (4096 points) sampling clock source internal synthesizer, external clock, ec...
Page 119
Std. Waveform frequency ext. Lock frequency 10mhz 200khz 500hz 200khz 10mhz specifications a-9 accuracy same as frequency standard stability same as frequency standard pll characteristics operation automatically locks to external signal pll input characteristics same as trig in external lock frequen...
Page 120
Waveform samples max. Lock frequency 200,000 10 500hz 10mhz specifications a-10 coarse phase offset control range ±180 % resolution std. Waveforms 0.72 % , frequency setting from 500 hz to 200 khz; 360 % x frequency (in mhz) / 100, frequency setting from 200 khz to 10 mhz arbitrary waveforms 360 % /...
Page 123
Racal instruments repair and calibration request form to allow us to better understand your repair requests, we suggest you use the following outline when calling and include a copy with your instrument to be sent to the racal repair facility. Model serial no. Date company name purchase order # bill...
Page 124: Support Offices
Support offices racal instruments, inc. 4 goodyear street irvine, ca 92718-2002 phone: 1-714-859-8999 1-800-racal-ate 1-800-722-2528 fax: 1-714-849-2505 racal instruments ltd 480 bath road slough, berkshire sl1 6be, england phone: +44 (0) 1628 604455 fax: +44 (0) 1628 662017 racal systems electroniq...
Page 125
Artisan technology group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment • fast shipping and delivery • tens of thousands of in-stock items • equipment demos • hundreds of manufacturers supported • leasing/monthly rentals • itar certified secure asset solutions service center r...