Summary of Ray2
Page 1
User manual . Ray2 microwave link . Fw 1.3.X.X 2/18/2015 version 1.8.7 www.Racom.Eu racom s.R.O. • mirova 1283 • 592 31 nove mesto na morave • czech republic tel.: +420 565 659 511 • fax: +420 565 659 512 • e-mail: racom@racom.Eu.
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Table of contents important notice .................................................................................................................................. 7 quick start guide .....................................................................................................................
Page 4
7.3. Status ................................................................................................................................. 64 7.3.1. Status - general ...................................................................................................... 65 7.3.2. Status - radio ......
Page 5
10.5. Ray2-11 c,d parameters ............................................................................................... 184 10.6. Ray2-17 parameters ...................................................................................................... 185 10.6.1. Upper/lover limits ...............
Page 6
6.
Page 7: Important Notice
Important notice copyright © 2014 racom. All rights reserved. Products offered may contain software proprietary to racom s. R. O. (further referred to under the ab- breviated name racom). The offer of supply of these products and services does not include or infer any transfer of ownership. No part ...
Page 8: Quick Start Guide
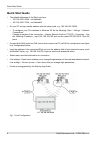
Quick start guide • the default addresses of the ray2 units are: ○ 192.168.169.169/24 - unit labeled l ○ 192.168.169.170/24 - unit labeled u • on your pc set up a similar address with the same mask, e.G. 192.168.169.180/24. ○ to configure your pc’s address in windows xp do the following: start – set...
Page 9: List Of Documentation
List of documentation user manuals ■ microwave link ray2 - this document user manual ray2-10, ray2-11, ray2-17, ray2-24 ■ microwave link ray11, 17, 24 1 user manual ray11, ray17, ray24 ■ microwave link ray10 2 user manual ray10 datasheets ■ ray2 - datasheet 3 ■ ray - datasheet 4 ■ ray - scada backbo...
Page 10
1. Ray2 – microwave link the microwave link ray2 is designed as a high-speed point-to-point wireless bridge for data transmission under the latest requirements of modern wireless transmission equipment. Ray2 works with an ethernet interface and can be used in backhaul networks as well as a last-mile...
Page 11
Standards etsi en 302 217-2-2 v2.1.1 radio parameters ray2-10 etsi en 300 440-2 v1.4.1 ray2-17 etsi en 300 440-2 v1.4.1 ray2-24 etsi en 301 489-1 v1.9.2, etsi en 301 489-17 v2.2.1 emc en 60950-2006/a1:2010 electrical safety note operation of the ray2-xx is described in this user manual. Operation of...
Page 12: 2. Implementation Notes
2. Implementation notes 2.1. Link calculation before a microwave link can be installed, an analysis and calculation of the microwave link must be made first. The analysis should take place before the site survey itself to get a clear idea about the di- mensions of the antennas. The analysis consists...
Page 13
P r received power level (dbm) p t transmitted power (dbm) g t transmitting antenna gain (dbi) g r receiving antenna gain (dbi) fsl free space loss (db) p r must be: p r > p s where: p s receiver sensitivity (dbm) the receiver’s sensitivity defines the minimum level of the received signal at which t...
Page 14
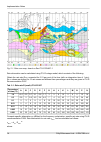
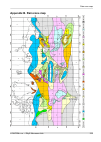
Fig. 2.1: rain zone map, based on rec.Itu-r pn.837-1 rain attenuation can be calculated using itu-r outage model, which consists of the following: obtain the rain rate r 0.01 exceeded for 0.01 per cent of the time (with an integration time of 1 min). R 0.01 values are defined for 15 rain zones and d...
Page 15
K h,v , α h,v constants for horizontal and vertical polarization. Constants are slightly different for each polarization, see next table according to itu-r p.838 tab. 2.2: constants k, α for horizontal and vertical polarization at 10, 11, 17 and 24 ghz α v k v α h k h 1.22 0.01 1.26 0.01 10 ghz 1.16...
Page 16
Is active we recommend using horizontal polarization in the direction with lower data traffic (typically up-link). 2.1.5. Multipath fading multipath fading is another dominant fading mechanism. A reflected wave causes a phenomenon known as multipath, meaning that the radio signal can travel multiple...
Page 17
2.1.6. Fresnel zones calculation the position of obstacles between points of the bridge can significantly influence the quality of the mi- crowave link. The radio signal doesn't only radiate along the line of sight, but also in the area around it, i.E. In the so-called 1st fresnel zone. Within this ...
Page 18
D total link distance (km) f frequency (ghz) tab. 2.3: 60 % of the 1st fresnel zone radius of zone r for frequency length of link d 24 ghz 17 ghz 11 ghz 0.75 m 0.89 m 1.10 m 0,5 km 1.06 m 1.25 m 1.56 m 1 km 1.50 m 1.77 m 2.21 m 2 km 2.12 m 2.50 m 3.13 m 4 km 2.60 m 3.07 m 3.84 m 6 km 3.00 m 3.54 m 4...
Page 19
30 cm ... 32.2 dbi 60 cm ... 37.8 dbi 99 cm ... 42 dbi step 2 - free space loss calculation fsl = 32.44 + 20log f + 20log d = 32.44 + 20log17.2·10 3 + 20log4 = 129.1 db step 3a - rain attenuation for 99.99% availability in rain zone b the rain rate is r 0.01 =32 (see fig. 2.1) for f=17 ghz k h =0.06...
Page 21: 3. Product
3. Product ray2 microwave links enable transmissions in both bands requiring license fees and those that are free. They work as a point-to-point link in a full duplex setting with transfer speeds of up to 360 mbps. Bandwidth can be configured from 1.75 up to 56 mhz. Modulation can be fixed or adapti...
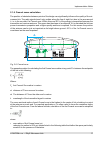
Page 22: 3.1. Mounting
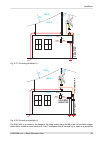
3.1. Mounting fig. 3.2: ray2 microwave link – antenna and fod unit the antenna is attached to the mast using a holder adjustable in two planes. The ray2 unit is then mounted on the antenna. There are two possible mounting positions – for horizontal and vertical polarization. Installation and adjustm...
Page 23: 3.3. Power Supply
The sfp status led function: the led status is controlled directly from the sfp module. Its function is specific for each sfp module. The typical behaviour is an indication of the received signal strength. Should the signal be in the proper power range (not too strong and not too weak), the led is s...
Page 24
The internal dc power source uses galvanic separation. If the galvanic separated power source is used and the dc power line needs to be grounded (either positive or negative wire), the middle pin of the 3-port dc connector can be used to make a connection between ground and the respective power wire...
Page 25: 3.4. Status Leds
3.4. Status leds fig. 3.8: status leds tab. 3.1: meaning of led status indicators function colour diode eth1 port flashing regularly: auto negotiation in progress flashing irregularly: link activity 10/100/1000 permanently lit: link 10/100/1000 green eth eth2 port flashing regularly: auto negotiatio...
Page 26: 3.6. Dimensions
3.6. Dimensions communication unit odu outer size 244 x 244 x 157 mm • weight ray2-10 — 2.8 kg • • ray2-11 — 2.8 kg • ray2-17 — 2.5 kg • ray2-24 — 2.5 kg diameters of supplied antennas ray2 units are ready for direct mounting to jirous 1 class 2 antennas. Individual datasheets are accessible here 2 ...
Page 27: 3.7. Ordering Codes
3.7. Ordering codes 3.7.1. Microwave units the proper pair (from the same sub-band) of lower and upper units should be selected when ordering the microwave link. This is not valid for ray2-17 and ray2-24 units. In such a case the same unit is used for both sides of the link. User manuals for ray10 3...
Page 28: 4. Accessories
4. Accessories 4.1. Overview short description racom-part-number antenna jirous antenna parabolic 0.38 m 10-11ghz with holder 28.0-29.0 dbi class 2 ant-jrma-380-10/11r antenna parabolic 0.65 m 10-11ghz with holder 34.1-35.5 dbi class 2 ant-jrma-650-10/11r antenna parabolic 0.9 m 10-11ghz with holder...
Page 29
Surge protection 1gb eth cat.6 lpz2-lpz3 ip20 -40/+85°c oth-dl-cat.6-60v cat5e cable double shell outdoor ftp cat5e cable teldor cab-cat5e-ftp-tld cat6 connector connector tc-con, stp rj45, cat6, 8p8c, wire, pleated, awg24, ubnt con-rj45-ubnt-cat6 connector rj45, cat6, awg 24-22, harting con-rj45-hr...
Page 30: 4.2. Details
4.2. Details antenna the overview of different jirous antenna types is listed in section 3.6, “dimensions”. The antenna choice determines radio link properties. The radio link calculation should be performed to determine proper antenna size. Rough calculation can be done using a simple on-line calcu...
Page 31
• set-ray2-ext35 • cable bushing lengthening, pg21, 35 mm power supply dc • pws-ac/dc-ad-55b • orig. Part no: ad-55b • fod unit power supply 50 w, 24 v, ups function, meanwell • datasheet 3 power supply poe • pwr-poe36u-1at • orig. Part no: poe36u-1at • fod unit power supplies – 30 w poe adapters, 1...
Page 32
• hol-poe-phi-4a • 4x eth poe power supply, 19" rack mountable surge protection • oth-dl-1grj45 • orig. Part no: dl-1grj45 • protection from the voltage spikes • datasheet 7 • oth-dl-cat.6-60v • orig. Part no: dl-cat. 6-60 v • datasheet 8 cat5e cable • cab-cat5e-ftp-tld • orig. Part no: plu030078 • ...
Page 33
• set-ray2-tlg-ext35 • orig. Part no: telegärtner mfp8 cat.6a awg 22-27 + racom set-ray2-ext35 connector rj45, cat6a, awg 24-22, telegärtner • set rj45 connector (telegärtner) and cable bushing lengthening (35mm) • datasheet 11 sfp module rj45 • sfp-rj45-avago • orig. Part no: abcu-5730arz sfp modul...
Page 34
• cab-fib-2f-dlc/x-ofa-5m • orig. Part no: dlc0rac2fyyy pigtail, 2-fibres, single mode, lc-connector — loose end, yyy meters, ofa • cab-fib-ofa-1f-lc/x-ofa-5m • orig. Part no: lc0rac1fyyy pigtail, 1-fibre, single mode, lc-connector — loose end, yyy meters, ofa • datasheet 15 dc cable • cab-dc-2x1.5 ...
Page 35
Raytool • set-ray tool • set of tools for installation of the bracket and mounting of con- nectors. These are branded tools which allow complete installa- tion of the microwave bridge. Extended descriptions see www.Racom.Eu, microwave link, accessories 19 e-shop accessories easiest to order here: e-...
Page 36: 5. Step-By-Step Guide
5. Step-by-step guide the following chapters will guide you step by step through preparation, installation and activation of the ray2 link: • pre-installation check out • installation • advanced configuration • troubleshooting pre-installation checklist familiarise yourself with the controls and pre...
Page 37: 5.1. Service Access
Warning during operation, never bring the waveguides of the stations close to each other. There is a risk of damaging sensitive input circuits. 5.1. Service access the ray2 link is supplied with a default configuration of access parameters: unit l has the service ip address 192.168.169.169 and mask ...
Page 38
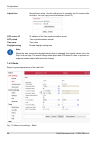
5.1.1. Menu link settings - general • station name – station can be assigned with a name, e.G. The place of installation. • station location – for easier inclusion the network hierarchy, it is possible to enter the station’s loc- ation fig. 5.2: configuration menu link settings - general ray2 microw...
Page 39
5.1.2. Menu link - service access - services • ipv4 address – enter a valid ip address to access the drive. The default ip address has to be replaced with a valid address. Keeping the default address will probably lead to future problems in the network. • netmask – enter the network mask. • gateway ...
Page 40: 5.3. Link Test
5.1.3. Menu link - service access - users • edit - enter the menu. • new password – choose a password and enter it. • confirm password – enter the password again to confirm. Fig. 5.4: configuration menu link settings – service access – services 5.1.4. Menu maintenance - feature keys the firmware of ...
Page 41
• status bar displays link: ok. If the alarm message appears at local or peer, this doesn’t necessarily mean there is a problem. The message indicates that the limit at any of the monitored parameters has been exceeded. Es- sential is the link: ok message on the status bar. • the status screen conta...
Page 42: 6. Installation
6. Installation 6.1. Line of sight test before you install the device to a mast tube, verify visually that the view in the direction of the remote unit is unobstructed. Line of sight considerations: • free fresnel zones. Signal needs space wider than the diameter of the antenna. • trees at the lower...
Page 43
Fig. 6.3: left-side mounting – horizontal rx polarization fig. 6.4: right-side mounting – vertical rx polarization fig. 6.5: right-side mounting – horizontal rx polarization 43 © racom s.R.O. – ray2 microwave link installation.
Page 44
Changing the mounting method an antenna bracket is supplied as standard partly assembled, and ready for right-side mounting. On changing the jirous antenna bracket for left-side mounting the adjustment bolt (part no. 11) and swivel bolt (part no. 6) need to be unscrewed, then shift the bracket body ...
Page 45
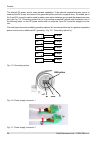
6.2.2. Mounting the fod unit on the antenna ray2 microwave bridge equipment is generally supplied as several component parts packaged separ- ately in a box. • two parabolic antennas with assembled mounting plates. There are also 4 screws in a small plastic bag in the box. • two brackets for mounting...
Page 46
B. Slide the antenna bracket onto the mast tube and clamp to the mast by tightening the nuts. Recommendation: keep the gap between the two saddle plates (part no. 3) as wide as possible, so the horizontal angle adjustement screw can fit in this gap. The range of horizontal adjustement is consequentl...
Page 47
D. Tighten both bolts to the plate before continuing with installation to prevent any unnecessary movements of the equipment. Before precisely adjusting the vertical direction of the antenna upon completing installation it will be necessary to unscrew them again as the lower bolt (part no. 8) passes...
Page 48
F. The precise horizontal direction the antenna is pointing in can be adjusted using the bolt with two nuts (part no. 10 and 12). Once the direction has been set the antenna is fixed in place by tightening the nuts against the bracket to prevent further movement of the antenna. The vertical directio...
Page 49
6.2.3. Lubrication and preservation of the antenna pivot before fitting the fod unit bush onto the antenna pivot ensure that the "o" ring (part no. 1) is in the correct position. It is also essential to prevent moisture getting in between these two parts. This moisture could cause oxidation which wo...
Page 50: 6.3. Connectors Assembly
6.3. Connectors assembly the fod communication unit can be connected to the user network by metallic or fibre ethernet cable. The unit is equipped with those connectors: ■ e1+poe – gigabit metallic ethernet port. This port is can power the unit with any power over eth- ernet power source working acc...
Page 51
Assembly procedure: fig. 6.25: bushing and connector assembly fig. 6.26: bushing incl. Lengthening and connector assembly • put on the cable: the nut no.1, rubber sealing no.2, bushing no.3 and o-ring no.4. • attach the appropriate connector no.5 to the cable. • plug the connector no.5 into the ray2...
Page 52: 6.4. Grounding
All necessary parts are delivered as an accessory set-ray2-con-b. If the lengthening is needed use the extension set-ray2-ext35 containing the parts no.6 and no.7. The rubber sealing is delivered with three different internal diameters to fit different cable diameters. The rubber is diagonally cut t...
Page 53
R eth eth 230 v~ poe lpz 0 a lpz 0 b lpz 1 lightning arrester fig. 6.27: grounding installation 1 eth eth 230 v~ poe r lpz 0 a lpz 0 b lpz 1 grounding kit lightning arrester bonding bar fig. 6.28: grounding installation 2 the ray2 unit is grounded to the flange at the fixing screws using an m8 screw...
Page 54
Conductor. The conductor should have a green/yellow plastic cover along its whole length. For grounding a ray grounding kit can be ordered as an accessory (see chapter 4, accessories) containing a grounding terminal zsa16, 40 cm grounding strip 15 mm wide, and 100 cm of cable with grounding lugs. Fo...
Page 55
Fig. 6.31: protective conductor at the fod unit fig. 6.32: grounding the fod unit fig. 6.33: protective conductor at the mast on a zsa16 terminal fig. 6.34: ray grounding kit 55 © racom s.R.O. – ray2 microwave link installation.
Page 56
Fig. 6.35: separated lightning conductor note - it is always better not to install the microwave unit directly under the lightning conductor holders. There is lower probability of unit being polluted by birds. It is necessary to install the ethernet lead so that there is no excessive mechanical stre...
Page 57: 6.5. Start Up
6.5. Start up connect a power supply to the installed fod unit and connect the configuration pc. Use an internet browser (such as mozilla firefox) to enter the configuration menu. 6.5.1. Noise on the site this is particularly true for installation of links working in free bands, where the user has n...
Page 58
Main and side lobes 5 4 -40° 0 10 20 -10 g[dbi] -20° 20° 40° 0° 6 -40° 0 10 20 -10 g[dbi] -20° 20° 40° 0° -40° 0 10 20 -10 g[dbi] -20° 20° 40° 0° 2 1 3 a – a b – b c – c cross-sec tion a – a c r o ss-sec t io n c – c -40° 0 10 20 g[dbi] -20° 20° 0° main beam side lobe a a b b c c 40° 2 1 3 6 4 5 fig...
Page 59
Fig. 6.40: radiation diagram – incorrect adjustment the resulting rss helps distinguish between the states a-a and c-c which appear similar. It also helps in situations where simple search for a maximum doesn’t work as shown in the illustration “incorrect adjustment”. Real radiation diagrams are mor...
Page 60
6.5.3. Link test basic parameters of the link are shown in the menu status – brief, its quality is characterized by rss and snr. Values on status screens can be refreshed manually by pressing the refresh button or in real time with a period of several seconds after activating the start button. Press...
Page 61: 7. Configuration
7. Configuration 7.1. Introduction controls the following configuration buttons are used for configuration: apply and save parameters. Apply set parameters are overwritten with original values. Cancel reload the current values of the unit / both units. Refresh show values of individual parameters as...
Page 62: 7.2. Status Bar
Fig. 7.2: login rollback function if you interrupt the connection on an operating link by entering inappropriate radio link parameters, the original parameters will be restored after 1 minute. The connection is automatically restored. 7.2. Status bar fig. 7.3: status bar 1 the status bar is located ...
Page 63
All states except for the state of ok are highlighted with a triangle.: fig. 7.4: status bar 2 example of a complete page - status bar, menu and control buttons: fig. 7.5: page example 63 © racom s.R.O. – ray2 microwave link configuration.
Page 64: 7.3. Status
7.3. Status fig. 7.6: menu status ray2 microwave link – © racom s.R.O. 64 configuration.
Page 65
The status menu provides basic information about local and remote station. Information is valid the moment the page is open, or the refresh button is hit. The status – brief tab shows only the most important values whereas the status – detailed tab provides further details. Below is a list of all va...
Page 66
Received signal strength. If atpc is enabled, the atpc letters are dis- played as well as information about threshold value for activation of power control loop: “current rss atpc / threshold rss” rss [dbm] signal to noise ratio. If atpc is enabled, the atpc letters are displayed as well as informat...
Page 67: 7.4. Link Settings
7.4. Link settings 7.4.1. General setup of general parameters of the link. Fig. 7.7: menu link settings – general unit type indicator. Unit code unit serial number. Serial no. Ip address in the standard dotted decimal notation, including the bit width of netmask after the forward slash. Ipv4 address...
Page 68
Manual time setup. Use the dialog box to manually set the current date and time. You can copy time from browser (local pc). Adjust time ip address of the time synchronization server. Ntp source ip time synchronization interval. Ntp period time zone time zone enable daylight saving time daylight savi...
Page 69
Radio unit type: l(ower) or u(pper) part of the frequency band. Radio type horizontal or vertical polarization based on the physical installation. Indic- ates the polarization of received signal. Local and peer are indicated sep- arately. The proper position of the cable is sideways down. Notice for...
Page 70
7.4.3. Service access services access routes for link configuration. Fig. 7.9: menu link settings – service access – services there are two modes of accessing the internal management system of the microwave link: standard and direct service channel standard: both units are configured with the separa...
Page 71
To the same sub-net. There is no need for internal vlan to handle the internal service traffic between both units of the microwave link. No additional internal service ad- dresses exist. Note: it is strongly recommended to use management vlan to encapsulate and prioritize the management traffic when...
Page 72
Enables access via ssh protocol. Provides secure access to cli. If preventing unau- thorized access to the unit is the number one priority, leave only this server on. Cli (ssh) enabling snmp server. Off by default. Snmp snmp community string. Can contain both lower and uppercase letters, numbers, fo...
Page 73
Users list and setup of users. There can be different users on either side of the link. Fig. 7.10: menu link settings – service access – users service access has three levels of permissions: • guest – read only access (up to 10 users) • admin – read/write access for configuration settings - most com...
Page 74
The group has all the rights of group cli_guest plus: right to configure the link. Has the right to view and modify all settings. A group can contain a maximum of 10 users. Cli_admin same rights as cli_admin plus: right to configure user accounts including ssh keys. This group contains the user supe...
Page 75
Edit user clicking edit next to a username opens a screen with configuration of the given account. User name username the group to which the user belongs. Group password can be set or deleted. Delete – user will not have a password. The user will only be able to log in with an ssh key. In order to d...
Page 76
For the super user, the add user button is active. You can use it to create a new user from groups cli_quest or cli_admin. Name of new user. Username the group to which this user will belong. Group password for this user. New password repeat password. Confirm password if you want the user to have ac...
Page 77
7.4.4. Alarm limits alarms status fig. 7.11: menu link settings – alarms status overview of alarms all system alarms are listed on this screen. Inactive alarms are colored white with an "ok" text label. Active alarms are colored according to the severity of the alarm (see below) with a text message ...
Page 78
The system warning is generated when the current transfer capa- city of radio channel is lower than the threshold set in this paramet- er. 0 net bitrate [mbps] interruption of radio link. Ticked air link down corresponding user eth link (eth1/eth2) on station interrupted. Note: the ethx link system ...
Page 79: 7.5. Switch Settings
7.5. Switch settings 7.5.1. Status port status the unit internal ethernet switch port status fig. 7.14: menu switch settings - port status port name identification of the internal switch port. The switch ports are connected to an external port or to an internal device (radio modem, management cpu). ...
Page 80
Dual mode with lc connector fibre single mode with lc connector fibre with rj45 connector copper there can be one of the following scenarios: message scenario the sfp vendor string read out of sfp module. The vendor, model, connector (rj45/lc) and wavelength values are shown. Separate sfp ok window ...
Page 81
Rmon counters the unit internal ethernet switch rmon counters fig. 7.15: menu switch settings - rmon counters the remote network monitoring (rmon) mib was developed by the ietf to support monitoring and protocol analysis of lans. Port name identification of the internal switch port. The switch ports...
Page 82
The external port (with rj45 interface) labeled "e1+poe". The external port (with sfp interface) labeled "e2". The internal port to radio modem, i.E. Link to the peer unit. The internal port to management cpu. Eth1 eth2 air cpu the internal switch port rmon counters these counters provide a set of e...
Page 83
Added to a modified frame. If the original fcs is invalid, the new fcs is made invalid too and this counter is incremented. The number of frames sent that have a unicast destination mac address. Out unicasts the number of good frames sent that have a multicast destination mac address. Note: this doe...
Page 84
Histogram counters mode frame size histogram counters can count received and/or transmitted octets. The mode of histogram counters is indicated here. Measure time this is the time interval, the diff column is valid for. The diff column shows the difference of the actual value of the counters at the ...
Page 85
Register dump fig. 7.17: menu switch settings - register dump the exact contents of the internal switch configuration and diagnostic registers can be listed for dia- gnostic purposes. All registers are separated into several groups. Groups global switch parameters. Globals global port related parame...
Page 86
7.5.2. Interface port port settings fig. 7.18: menu switch settings - port phyter is responsible for ethernet signal conversion between wire (e.G. Cat7 cable) and internal switch bus. Port name identification of the internal switch port. The switch ports are connected to an ex- ternal port or to an ...
Page 87
With rj45 connector copper there can be one of the following scenarios: message scenario the sfp vendor string read out of sfp module. The vendor, model, connector (rj45/lc) and wavelength values are shown. Sfp ok separate window with more detailed information can be opened by clicking the more... L...
Page 88
Detect function, it is then required to establish the link at half-duplex mode only. Refer to ieee 802.3 clauses 28 and 40 for a full description of auto-negotiation. 1000base-x auto-negotiation is defined in clause 37 of the ieee 802.3 specific- ation. It is used to auto-negotiate duplex and flow c...
Page 89
Own by detecting activity on the ethernet cable. The energy detect modes only apply to the copper media. In the first sense mode, if the phy detects energy on the line, it starts to auto-ne- gotiate sending flps (fast link pulse) for 5 seconds. If at the end of 5 seconds the auto-negotiation is not ...
Page 90
The switch port is disabled and it will not receive or transmit any frames. Disabled the switch examines all frames, learning source addresses (sa) from all good frames (except those from mgmt frames) and re- ceives and transmits all frames as a normal switch. Forwarding only mgmt frames are allowed...
Page 91
To be received from a given input port but may or may not be allowed to be trans- mitted out of a port or ports. The possible values are 1522, 2048 and 10240 bytes. Note: the definition of frame size is counting the frame bytes from mac_da through layer2 crc of the frame. Pause limit in [frame] limi...
Page 92
Pirl port based ingress rate limiting, see also the functional diagram fig. 7.20: menu switch settings - pirl the device supports per port tcp/ip ingress rate limiting along with independent storm prevention. Port based ingress rate limiting accommodates information rates from 64 kbps to 1 mbps in i...
Page 93
Possible actions: - discard the frame - pass the frame and send flow control frame back to the source - pass the traffic ebs: excess burst size cbs: committed burst size cir: committed information rate all bucket calculations done in units of tokens passed frame size based token update ebs limit cbs...
Page 94
Pirl - resource configuration fig. 7.22: menu switch settings - pirl resource each port can be assigned up to five different ingress rate resources. Ray2 microwave link – © racom s.R.O. 94 configuration.
Page 95
Each resource defines a rule (filter) for the incoming frame. If the rule is met, the frame is affected (as set by the ebs limit action parameter). If the incoming frame doesn't meet any rule, it is not affected by pirl. The frame is accepted and forwarded further to the switch engine. Port name ide...
Page 96
Bucket rate factor this is a factor which determines the amount of tokens that need to be decremented for each rate resource decrement (which is done periodically based on the com- mitted information rate). Bucket increment bucket increment (bi) indicates the amount of tokens that need to be added f...
Page 97
Flow control gets de-asserted when the ingress rate resource has enough room to accept at least one frame of size specified by the cbs limit. For example, if the cbs limit is programmed to be 2k bytes, then the flow control will get de-asserted if there is at least 2k bytes worth of tokens available...
Page 98
Egress queue control see also output queue diagram. Fig. 7.23: menu switch settings - egress queue port name identification of the internal switch port. The switch ports are connected to an ex- ternal port or to an internal device (radio modem, management cpu). The external port (with rj45 interface...
Page 99
Use strict for priority 3 and use weighted round robin for prior- ities 2,1 and 0 strict pri 3 use strict for priorities 3 and 2 and use weighted round robin for priorities 1 and 0 strict pri 3, 2 use a strict priority scheme for all priorities strict speed guard the speed guard controls automatical...
Page 100
Weight table the weighted round robin alternate weighting can be defined here. The sequence of the output queue numbers (0,1, 2 or 3) defines the sequence of the output queue frame egressing. This sequence can be up to 128 items long. Ray2 microwave link – © racom s.R.O. 100 configuration.
Page 101
7.5.3. Qos the qos classification is handled in the switch ingress block. The ingress block does not perform the qos switching policy, which is the task of the queue controller. See the functional diagram. 802.1p fig. 7.24: menu switch settings - 802.1p this qos technique also known as class of serv...
Page 102
The external port (with rj45 interface) labeled "e1+poe". The external port (with sfp interface) labeled "e2". The internal port to radio modem, i.E. Link to the peer unit. The internal port to management cpu. Eth1 eth2 air cpu enabled the qos classification according to ieee 802.1p priority bits is...
Page 103
Dscp fig. 7.25: menu switch settings - dscp the dscp stands for differentiated services code point which is a 6-bit value stored within the ip header. The qos techniques using those bits are called diffserv or differentiated services. Port name identification of the internal switch port. The switch ...
Page 104
7.5.4. Advanced trunk fig. 7.26: menu switch settings - advanced - trunk port trunking is supported by the device using any combinations of ports. The ports that are to be as- sociated with the trunk need to have all the port member's defined with the same id (trunkid) and the enabled parameter has ...
Page 105
The hash computed for address table lookups is used for the trunkmask selection. Use this parameter to reach better load balancing between the ports in the trunk. Hash port name identification of the internal switch port. The switch ports are connected to an external port or to an internal device (r...
Page 106
Monitoring, policy fig. 7.27: menu switch settings - advanced - monitoring, policy setup of monitoring and policy functions. Ingress monitor destination frames that are targeted toward an ingress monitor destination leave via the port selected by this parameter. This includes frames received on a po...
Page 107
Ingress monitor source when this parameter is enabled, any frame that ingresses this port is also sent to the ingress monitor destination port. The frame is sent to this port even if it is discarded due to switching policy but the frame will not be forwarded if it contains an error (such as crc, etc...
Page 108
Atu settings fig. 7.28: menu switch settings - advanced - atu settings setup of atu (address translation unit) table related parameters. Aging timeout [s] atu age time. This value determines the time that each atu entry remains valid in the database, since its last access as a source address, before...
Page 109
Reserv. Multicast da this parameter enables individual multicast da addresses to be affected by re- served multicast to cpu parameter. Port name identification of the internal switch port. The switch ports are connected to an external port or to an internal device (radio modem, management cpu). The ...
Page 110
Do not egress any frame with an unknown da (unicast or multic- ast) unknown do not egress any frame with an unknown multicast da unknown multicast do not egress any frame with an unknown unicast da unknown unicast egress all frames with an unknown da (unicast and multicast) none sa filtering source ...
Page 111
Flush all non-static adresses in the atu. Define the desired limit for the ports. Re-enable the ports. Sa priority override when any other than "none" mode is selected, sa atu priority overrides can occur on this port. An sa atu priority override occurs when the source address of a frame results in ...
Page 112
Atu fig. 7.29: menu switch settings - advanced - atu the address translation unit (atu) in the device supports user commands to access the contents of the mac address database. There is one static record which can't be deleted. This is the management cpu record. The unicast frames directed to manage...
Page 113
The switch, the vid assigned to the frame is used to access the vtu. The vtu returns the fid associated with that vid for mac address lookups in to the atu. Mac mac address associated with this atu entry in the database number defined by the fid. Entry state the entry state parameter is used to dete...
Page 114
Fig. 7.30: menu switch settings - advanced - atu - edit ray2 microwave link – © racom s.R.O. 114 configuration.
Page 115
Vlan fig. 7.31: menu switch settings - advanced - vlan setup of vlan related and global parameters. Link authorization guard user data flow to the remote unit can be established dependent on remote station authorization. The authorization is secured by using ssh keys. See user manual section 8.3.3, ...
Page 116
User data flow through the air channel is enabled even if the remote unit is not authorized. Disabled user data flow through the air channel is enabled only if the re- mote unit is authorized. The link authorization guard parameter value of the remote unit is ignored. Enabled remove one provider tag...
Page 117
Vlan violation is detected. Vlan barriers (both port based and 802.1q based) can be bypassed by vlan tunnel. Use port based vlans only. The vid assigned to the frame is the port's default vid which is used as the vid in the provider tag if the frame egresses a provider port. Disabled enable 802.1q f...
Page 118
The vid priority value assigned to the frame's vid (in the vlan database) is used to overwrite the frame's previously determined queue qpri (queue priority). The qpri is used internally to map the frame to one of the egress queues inside the switch. Qpri override will not affect the contents of the ...
Page 119
Entering this port with a da that is currently 'static' in the atu. This applies to unicast as well as multicast frames. While enabled, the unicast frames with the management cpu da can go from the eth1 and eth2 ports in to the cpu port. The static record with the cpu da in the atu table has to be c...
Page 120
Stu fig. 7.32: menu switch settings - advanced - stu the per vlan spanning tree unit (stu) in the device supports user commands to access and modify the contents of the port state database. Primary key the icon indicates which parameter field is taken as the unique identifier in the database. This f...
Page 121
Fig. 7.33: menu switch settings - advanced - stu - edit 121 © racom s.R.O. – ray2 microwave link configuration.
Page 122
Vtu fig. 7.34: menu switch settings - advanced - vtu the vtu (vlan table unit) records form the vlan table. Primary key the icon indicates which parameter field is taken as the unique identifier in the database. This field entry ensures each record is unique and must not be duplicated. Vid vlan id. ...
Page 123
Vid policy this parameter is used to indicate that frames assigned with this vid can have layer 2 policy actions applied to it if the port's policy vtu (menu advanced/mon- itoring, policy/policy) is enabled to do so. Member tag this parameters is used to indicate which ports are members of the vlan ...
Page 124: 7.6. Tools
7.6. Tools 7.6.1. Maintenance restart fig. 7.36: menu tools - restart target restart of selected unit, local or peer. Restart mode reboot management system. Warm restart the whole station as if power was removed. Cold system restart performs the selected restart. Ray2 microwave link – © racom s.R.O....
Page 125
Backup fig. 7.37: menu tools - backup saving and restoring unit configuration. User accounts are not affected by those functions. Settings (local & peer) configuration is saved to backup file which is downloaded to management pc. The backup file name contains the date, time and ray2 serial number as...
Page 126
It is possible to make a temporary backup of the unit configuration. The backup is stored directly in the unit flash memory. Settings - internal backup (local) note: the internal backup is deleted if factory settings or firmware upgrade are performed. L p o l o s u make a temporary backup of the uni...
Page 127
Button is located next to the dc connector within the port marked "p". Disconnect the power supply from the unit. Keep the hw button depressed while reconnecting the power. The led marked sys starts to flash red after a few seconds. Keep the hw button pressed another 5 seconds until the red status l...
Page 128
Feature keys fig. 7.38: menu tools - feature keys the sub-set of ray2 parameters is affected by use of feature keys. The feature keys limiting data transfer speed [mbps] are now available. Speed of the transferred data is determined by a combination of the radio channel bandwidth (parameter bandwidt...
Page 129
Firmware fig. 7.39: menu tools - firmware if a new firmware version is released for the given microwave link type, you can upload it to your ray2 units. Info firmware version information about the current firmware package version on local and peer unit. Radio firmware version iinformation about the ...
Page 130
File name name of the uploaded firmware file. File size [b] size of the uploaded firmware file. Version in buffer information about firmware version prepared in the buffer for installation into the unit (local, peer). This firmware must first be prepared in the firmware upload section (see above). C...
Page 131
Radio adaptation fig. 7.40: menu tools - radio adaptation radio type important: applies only to links equipped with ray2-17 and ray2-24 units. Hardware of these links is universal for the entire frequency band. To facilitate the configuration of radio parameters, units are coded for l (lower) and u ...
Page 132
7.6.2. Live data bar indicators fig. 7.41: menu tools - bar indicators graphical indication of ber, snr and rss. Refresh one-time update of displayed values. Start, stop use the start button to start automatic update of displayed values with a period of 1 second. Use the stop button to stop it. Ray2...
Page 133
Rx constellation diagram fig. 7.42: menu tools - rx constellation constellation diagram shows the quality of received signal. Rx modulation modulation level of rx channel. Buffer number of plotted points. Refresh one-time update of diagram. 133 © racom s.R.O. – ray2 microwave link configuration.
Page 134
Frequency spectrum analyzer fig. 7.43: menu tools - frequency analyzer a very useful tool for identifying in-band interference and locating a free channel. It is not a full-blown spectrum analyzer as it scans the spectrum with 7mhz channel resolution. The accuracy of measured results is given by the...
Page 135
7.6.3. History the unit continuously stores information about the values of important variables. Stored values can be viewed using three methods - thumbnails, viewer and data thumbnails preview all values for the last 24 hours. Click on a thumbnail to open the viewer with a chart. Fig. 7.44: menu to...
Page 136
Instantaneous value of unit supply voltage. Voltage received signal strength. Rss signal-to-noise ratio of the received signal. Snr instantaneous bit error rate on link. Ber instantaneous transmission capacity. Net bitrate instantaneous speed (20s average) of incoming user data on the user eth- erne...
Page 137
The values are saved in the following resolutions and history lengths: resolution 1 minute, length of history 7 days resolution 15 minutes, length of history 30 days resolution 1 day, length of history about 180 days interval selecting width of interval to be displayed. Based on the interval width, ...
Page 138
Data numerical view of all values fig. 7.46: menu tools - history - data quantities detailed graphical view of values for selected interval. Plotted - shows only the values that are selected for the graph. Local, peer, all - shows all logged values. Filtering of values from local, remote or both. Ra...
Page 139
7.6.4. Logs shows internal unit logs. Individual tabs allow total or filtered view. Fig. 7.47: menu tools - logs when you first open the screen, it is necessary to start browsing logs by pressing the refresh button. Maximum length of displayed logs is 250 entries. If you need to display longer histo...
Page 140
7.6.5. Ping the ping tool allows sending icmp pings to a selected address fig. 7.48: menu tools - ping start the test by clicking on send. The result is displayed in the text window. Destination destination address in dotted decimal notation. The default address 127.0.0.1 is the localhost address - ...
Page 141: 7.7. Help
7.7. Help help from help menu the help screen displays contents of the embedded help. The help text is displayed in the whole con- figuration window. The text structure corresponds to individual configuration screens. Fig. 7.49: help menu every item of this help opens the specific help menu. 141 © r...
Page 142
Help from configuration menu clicking the name of the specific parameter in the configuration menu brings up the help belonging to this parameter. The help text is displayed in the pop up window: fig. 7.50: parameter help there is a go to help link within the help text. It displays the whole configu...
Page 143
Clicking the question mark icon in the upper right corner of the configuration screen brings a summary help for the configuration screen in the pop up window: fig. 7.52: summary help the help window can be moved by dragging the hints bar. Resize it by dragging the bottom corner. 143 © racom s.R.O. –...
Page 144: 8. Command Line Interface
8. Command line interface the command line interface (cli) provides an alternative to https access. Cli allows you to work in a text regime interface using an ssh (putty) or telnet client. 8.1. Connection via cli 8.1.1. Telnet use the telnet client to connect to the unit with service ip address 192....
Page 145: 8.2. Working With Cli
8.2. Working with cli • overview of cli options cli_help fig. 8.1: cli menu • parameters of cli commands are listed in the help. For example: help listing -h target unit -t local, default option -t l both, both units, command item for remote unit has peer_ prefix -t b peer, opposite unit, when readi...
Page 146
• entering more parameters in both units cli_cnf_set -t b radio_tx_chan=17128000 peer_radio_rx_chan=17128000 • put parameters containing spaces in quotation marks: cli_time_set -t b -t '2012-11-27 10:55:00' set time in both units 8.2.1. Ssh keys • generation using ssh-keygen [user@laptop ~]$ ssh-key...
Page 147
8.3. Configuration with cli 8.3.1. Configuration file • configuration backup cli_cnf_backup_get saves the configuration of both units to file cnf_backup.Tgz into the working directory. • configuration restore cli_cnf_set -t b -b cnf_backup.Tgz restores configuration of both units from file cnf_backu...
Page 148
Activated refuse to make a connection with any other communication unit. The units are locked using the unique authorization keys. The keys are exchanged between the units concerned. The authorization keys can be backed up to an external medium to be able to make a service unit exchange, if necessar...
Page 149: 9. Troubleshooting
9. Troubleshooting • polarization incorrect install the unit with the correct horizontal or vertical polarization: the arrow mark (placed just next to the status led) indicates the unit rx polarization. When the arrow is perpendicular to the earth, the unit receives a signal in vertical polarization...
Page 150
Limited. Though, in most situations the rss reading accuracy is better than ± 2db, the absolute rss value should not be used for accurate comparisons e.G. Between two links. • problem with https certificate see the appendix g, https certificate • overexcited receiver a natural property of each radio...
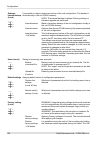
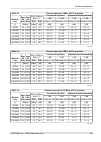
Page 151: 10. Technical Parameters
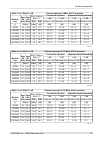
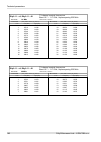
10. Technical parameters 10.1. General parameters 10.1.1. Technical parameters overview ray2-24 ray2-17 ray2-11 ray2-10 type 24.0 – 24.25 17.1 – 17.3 a, b: a: band [ghz], sub-bands a,b.. 10.695 – 11.695 10.30 – 10.59 b: 10.125 – 10.675 one universal unit unit l and u odu inits optional min 60 option...
Page 152
Fixed qpsk, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 qam or acm modulation ldpc fec 1 gb eth. (10/100/1000) (ieee 802.3ac 1000base-t) , mtu 10240 b, recommended cable s/ftp cat7 user interface rj45 1000base‐sx / 1000base‐lx, mtu 10240 b, user exchangable sfp user interface sfp usb-a service poe, 40 - 60 vdc , ieee 802....
Page 153
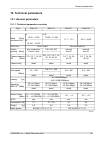
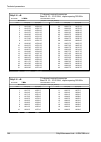
10.1.2. Link speed nominal link speed user data rate [mbps] ray2 - xx 56 mhz to 56 mhz 40 mhz 28 / 30 mhz 14 mhz 7 mhz 3.5 mhz 1.75 mhz modulation / cs accp accp accp acap accp accp accp accp accp 85.8 72.9 50.1 38.3 36.8 19.9 8.5 4.9 2.5 qpsk 169.9 160.2 110.0 84.1 80.9 38.8 17.2 9.6 4.9 16-qam 206...
Page 154
Acm switching according to snr state snr degrade / improve [db] ray2 - xx 56 mhz to 56 mhz 40 mhz 28 mhz 20 mhz 14 mhz 7 mhz 3.5 mhz 1.75 mhz modulation / cs accp accp accp accp accp accp accp accp accp - 19.0 - 19.0 - 19.0 - 19.0 - 19.0 - 19.0 - 19.0 - 19.0 - 19.0 qpsk 17.0 23.0 17.0 23.0 17.0 23.0...
Page 155
10.1.3. Frequency overview 10 ghz and 11 ghz, for cs 28 mhz 10 g hz a nd 1 1 g hz b an ds o ve rv ie w r ay 10 .32 2 10 .35 0 10 .37 8 10 .40 6 10 .49 0 10 .51 8 10 .54 6 10 .57 4 28 m h z c s c en tr al f re qu en ci es 1 0 10 .3 08 ch 1 2 3 4 7 8 9 10 10 .5 88 a r ay 10 .16 8 10 .19 6 10 .22 4 10 ...
Page 156
10.2. Nominal frequency tables description 1) tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, 3) duplex frequency 490 mhz 4) 2) cept 12-06 annex c 5) 6) (freq.Table: rcinfo11_a_490, rcinfo11_a_490_n) 7) (freq.Table: rcinfo11_b_490, rcinfo11_b_490_n) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [...
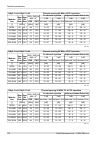
Page 157: 10.3. Ray2-10 Parameters
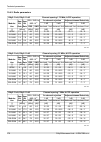
10.3. Ray2-10 parameters 10.3.1. Upper/lover limits tx power ray2-10-xa, ray2-10-xb max min modulation [dbm] [dbm] 13 -10 qpsk 11 -10 16-qam 11 -10 32-qam 10 -10 64-qam 9 -10 128-qam 8 -10 256-qam ver. 1.2 duplex spacing ray2-10-xa, ray2-10-xb [mhz] sub-band all combinations of channels a all combin...
Page 158
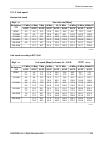
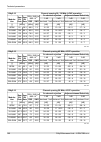
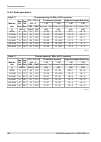
10.3.2. Radio parameters channel spacing 1.75 mhz; accp operation ray2-10 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [...
Page 159
Channel spacing 14 mhz; accp operation ray2-10 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [db] [db] [dbm] [mbps] [-] -...
Page 160
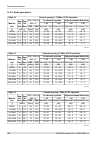
Channel spacing 28 / 30 mhz; acap operation ray2-10 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [db] [db] [dbm] [mbps] ...
Page 161
Channel spacing 56 mhz to; accp operation ray2-10 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [db] [db] [dbm] [mbps] [-...
Page 162
10.3.3. Nominal frequencies, band 10.30 – 10.59 ghz tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.30 – 10.59 ghz default duplex 168 mhz bandwidth: 1.75 mhz channel arrangements based on 7 mhz channelsduplex range 57.75 – 285.25 mhz ( freq.Table: rcinfo10_a_default:6 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. ...
Page 163
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.30 – 10.59 ghz default duplex 168 mhz bandwidth: 3.5 mhz channel arrangements based on 7 mhz channelsduplex range 59.5 – 283.5 mhz ( freq.Table: rcinfo10_a_default:6 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 1 10302.75 2 10306.25 3 10309.7...
Page 164
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.30 – 10.59 ghz default duplex 168 mhz bandwidth: 14 mhz vo-r/14/12.2012-17 duplex range 70 – 273 mhz ( freq.Table: rcinfo10_a_default:6 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 1 10308 2 10315 10483 6 10371 10539 3 10329 10497 7 10385 105...
Page 165
10.3.4. Nominal frequencies, band 10.15 – 10.65 ghz tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.15 – 10.65 ghz, duplex spacing 350 mhz bandwidth: 1.75 mhz based on 3.5 mhz channels ( freq.Table: rcinfo10_b_default:5 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 1 10151.375 10501.375 43 ...
Page 166
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.15 – 10.65 ghz, duplex spacing 350 mhz bandwidth: 3.5 mhz cept/erc/rec 12-05 e ( freq.Table: rcinfo10_b_default:5 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 1 10152.25 10502.25 22 10225.75 10575.75 2 10155.75 10505.75 23 10229.25 10579.25 3...
Page 167
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.15 – 10.65 ghz, duplex spacing 350 mhz bandwidth: 14 mhz cept/erc/rec 12-05 e + 7 mhz based channels ( freq.Table: rcinfo10_b_default:5 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 1 10161 10511 6 10231 10581 1c 10168 10518 6c 10238 10588 2 1...
Page 168
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.15 – 10.65 ghz, duplex spacing 350 mhz bandwidth: 56 mhz cept/erc/rec 12-05 e ( freq.Table: rcinfo10_b_default:5 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 1 10182 10532 3 10238 10588 2 10210 10560 4 10266 10616 3 10238 10588 4 10266 10616 ...
Page 169
10.4. Ray2-11 a,b parameters 10.4.1. Upper/lover limits tx power ray2-11-xa, ray2-11-xb max min modulation [dbm] [dbm] 24 -15 qpsk 22 -15 16-qam 22 -15 32-qam 21 -15 64-qam 20 -15 128-qam 19 -15 256-qam ver. 2.2 duplex spacing ray2-11-xa, ray2-11-xb [mhz] sub-band 490, 530 a 490, 530 b ver. 2.5 sub-...
Page 170
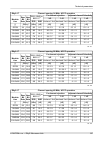
10.4.2. Radio parameters channel spacing 1.75 mhz; accp operation ray2-11-xa, ray2-11-xb adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [...
Page 171
Channel spacing 14 mhz; accp operation ray2-11-xa, ray2-11-xb adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [db] [db] [db...
Page 172
Channel spacing 40 mhz; accp operation ray2-11-xa, ray2-11-xb adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [db] [db] [db...
Page 173
10.4.3. Nominal frequencies, duplex 490 mhz ray2-11 - xa, ray2-11 - xb tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 490 mhz bandwidth: 1.75 mhz channel arrangements based on 28 mhz channels ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_490_default:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_490_default:13 ) c...
Page 174
Ray2-11 - xa, ray2-11 - xb tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 490 mhz bandwidth: 3.5 mhz channel arrangements based on 28 mhz channels ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_490_default:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_490_default:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [m...
Page 175
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 490 mhz bandwidth: 7 mhz channel arrangements based on 28 mhz channels ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_490_default:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_490_default:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 33 1 10713 11...
Page 176
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 490 mhz bandwidth: 14 mhz channel arrangements based on 28 mhz channels ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_490_default:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_490_default:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 17 1 10716 1...
Page 177
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 490 mhz bandwidth: 30 mhz ic ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_490_default:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_490_default:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 8 1 10725 11215 9 10965 11455 2 10755 11245 10 10995 11...
Page 178
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 490 mhz bandwidth: 56 mhz cept 12-06, annex c ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_490_default:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_490_default:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 9 1 10737 11227 10 10989 11479 2 10765...
Page 179
10.4.4. Nominal frequencies, duplex 530 mhz tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 530 mhz bandwidth: 1.75 mhz channel arrangements based on 28 mhz channels ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_530:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_530:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower ...
Page 180
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 530 mhz bandwidth: 3.5 mhz channel arrangements based on 28 mhz channels ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_530:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_530:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [m...
Page 181
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 530 mhz bandwidth: 7 mhz itu-r f.387 , annex 5 ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_530:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_530:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 33 1 10712.5 11242.5 34 10943.5 11473.5 2 10719.5 112...
Page 182
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 530 mhz bandwidth: 14 mhz itu-r f.387 , annex 5 ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_530:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_530:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 17 1 10716 11246 18 10954 11484 2 10730 11260 19 109...
Page 183
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 530 mhz bandwidth: 40 mhz (itu) itu-r f.387 rec.1.1, ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_530:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_530:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 6 1 10715 11245 7 10955 11485 2 10755 11285 8 1...
Page 184
Tx channel nominal frequencies band 10.7 – 11.7 ghz, duplex spacing 530 mhz bandwidth: 56 (cs 80) mhz cept 12-06, annex c ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_a_530:13 ) ( freq. Table: rcinfo11_b_530:13 ) ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] upper [mhz] 6 1 10755 11285 7 10995 11525 2 10795 11325 8 ...
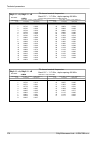
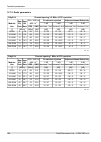
Page 185: 10.6. Ray2-17 Parameters
10.6. Ray2-17 parameters 10.6.1. Upper/lover limits tx power ray2-17 max min modulation [dbm] [dbm] 5 -25 qpsk 5 -25 16-qam 5 -25 32-qam 5 -25 64-qam 5 -25 128-qam 5 -25 256-qam ver. 2.0 optional duplex spacing ray2-17 default min channel width [mhz] [mhz] [mhz] 73.5 60 3.5 73.5 60 7 87.5 65 14 84 7...
Page 186
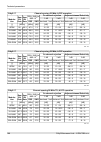
10.6.2. Radio parameters channel spacing 3.5 mhz; accp operation ray2-17 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [d...
Page 187
Channel spacing 14 mhz; accp operation ray2-17 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [db] [db] [dbm] [mbps] [-] -...
Page 188
Channel spacing 50 mhz; accp operation ray2-17 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [db] [db] [dbm] [mbps] [-] -...
Page 189
10.6.3. Nominal frequencies ray2-17 tx channel nominal frequencies duplex spacing range 63 – 189 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo17_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ### u19 17168.0 ### no more channels u2...
Page 190
Ray2-17 tx channel nominal frequencies duplex spacing range 63 – 189 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo17_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] u19 17168.0 u20 17171.5 u21 17175.0 l1 17105.0 u22 17178.5 l2 17108...
Page 191
Ray2-17 tx channel nominal frequencies duplex spacing range 66.5 – 182 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo17_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ### ### ### ### u21 17175.0 ### u22 17178.5 ### ### ### u23 17182...
Page 192
Ray2-17 tx channel nominal frequencies duplex spacing range 70 – 168 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo17_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] u24 17185.5 u25 17189.0 u26 17192.5 u27 17196.0 l4 17115.5 u28 1719...
Page 193
Ray2-17 tx channel nominal frequencies duplex spacing range 70 – 154 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo17_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] l6 17122.5 u26 17192.5 l7 17126.0 u27 17196.0 l8 17129.5 u28 17199....
Page 194
Ray2-17 tx channel nominal frequencies duplex spacing range 84 – 140 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo17_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ### ### l8 17129.5 u32 17213.5 l9 17133.0 u33 17217.0 l10 17136.5 u...
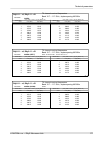
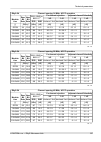
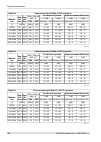
Page 195: 10.7. Ray2-24 Parameters
10.7. Ray2-24 parameters 10.7.1. Upper/lover limits tx power ray2-24 max min modulation [dbm] [dbm] 10 -30 qpsk 10 -30 16-qam 10 -30 32-qam 10 -30 64-qam 10 -30 128-qam 10 -30 256-qam ver. 1.0 optional duplex spacing ray2-24 default min channel width [mhz] [mhz] [mhz] 73.5 60 3.5 73.5 60 7 87.5 65 1...
Page 196
10.7.2. Radio parameters channel spacing 3.5 mhz; accp operation ray2-24 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [d...
Page 197
Channel spacing 14 mhz; accp operation ray2-24 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [db] [db] [dbm] [mbps] [-] -...
Page 198
Channel spacing 50 mhz; accp operation ray2-24 adjacent channel selectivity co-channel rejection rss / snr for ber 10 -6 user bit rate raw bit rate modula- tion 3 db 1 db 3 db 1 db declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit declared / limit snr rss [db] [db] [db] [db] [db] [dbm] [mbps] [-] -...
Page 199
10.7.3. Nominal frequencies 24.00-24.25 ghz ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.00 – 24.25 ghz, duplex spacing 73.5 mhz bandwidth: 3.5 mhz duplex spacing range 63 – 238 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism250_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No....
Page 200
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.00 – 24.25 ghz, duplex spacing 73.5 mhz bandwidth: 7 mhz duplex spacing range 63 – 238 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism250_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [...
Page 201
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.00 – 24.25 ghz, duplex spacing 87.5 mhz bandwidth: 14 mhz duplex spacing range 66.5 – 231 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism250_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Uppe...
Page 202
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.00 – 24.25 ghz, duplex spacing 84 mhz bandwidth: 28 mhz duplex spacing range 70 – 217 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism250_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [m...
Page 203
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.00 – 24.25 ghz, duplex spacing 70 mhz bandwidth: 40 mhz duplex spacing range 70 – 203 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism250_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [m...
Page 204
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.00 – 24.25 ghz, duplex spacing 84 mhz bandwidth: 56 mhz duplex spacing range 84 – 189 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism250_default:14) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [m...
Page 205
10.7.4. Nominal frequencies 24.05-24.25 ghz ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.05 – 24.25 ghz, default duplex sp. 73.5 mhz bandwidth: 3.5 mhz duplex spacing range 63 – 189 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism200:13) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upp...
Page 206
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.05 – 24.25 ghz, default duplex sp. 73.5 mhz bandwidth: 7 mhz duplex spacing range 63 – 189 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism200:13) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz]...
Page 207
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.05 – 24.25 ghz, default duplex sp. 87.5 mhz bandwidth: 14 mhz duplex spacing range 66.5 – 182 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism200:13) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [m...
Page 208
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.05 – 24.25 ghz, default duplex sp. 84 mhz bandwidth: 28 mhz duplex spacing range 70 – 168 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism200:13) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ...
Page 209
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.05 – 24.25 ghz, default duplex sp. 70 mhz bandwidth: 40 mhz duplex spacing range 70 – 154 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism200:13) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ...
Page 210
Ray2-24 tx channel nominal frequencies band 24.05 – 24.25 ghz, default duplex sp. 84 mhz bandwidth: 56 mhz duplex spacing range 84 – 140 mhz (freq.Table: rcinfo24_ism200:13) basic channels (default duplex) optional channels ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ch.No. Lower [mhz] ch.No. Upper [mhz] ...
Page 211: 11.1. Frequency
11. Safety, environment, licensing 11.1. Frequency ray2 microwave links designed for operation in licensed bands must be used in accordance with license issued by the telecommunications authority for the area the device is operating in. Ray2 microwave links must comply with the maximum permitted rad...
Page 212
Equipment is transported, stored, operated and controlled in the proper manner. The same applies to equipment maintenance. • in order to prevent damage to the radio modem and other terminal equipment the supply must always be disconnected upon connecting or disconnecting the cable to the radio modem...
Page 213: 11.5. Warranty
11.5. Warranty racom supplied parts or equipment ("equipment") are covered under warranty for inherently faulty parts and workmanship for a warranty period as stated in the delivery documentation from the date of dispatch to the customer. The warranty does not cover custom modifications to software....
Page 214
11.6. Declaration of conformity www.Racom.Eu racom s.R.O. • mirova 1283 • 592 31 nove mesto na morave • czech republic tel.: +420 565 659 511 • fax: +420 565 659 512 • e-mail: racom@racom.Eu we, the manufacturer of the above mentioned product, hereby declare that: 1999/5/ec the declaration of confor...
Page 215
Www.Racom.Eu racom s.R.O. • mirova 1283 • 592 31 nove mesto na morave • czech republic tel.: +420 565 659 511 • fax: +420 565 659 512 • e-mail: racom@racom.Eu we, the manufacturer of the above mentioned product, hereby declare that: 1999/5/ec the declaration of conformity is based on the following d...
Page 216
Www.Racom.Eu racom s.R.O. • mirova 1283 • 592 31 nove mesto na morave • czech republic tel.: +420 565 659 511 • fax: +420 565 659 512 • e-mail: racom@racom.Eu we, the manufacturer of the above mentioned product, hereby declare that: 1999/5/ec the declaration of conformity is based on the following d...
Page 217
11.7. Country of origin declaration country of origin declaration producer: racom s.R.O. Address: mirova 1283, 592 31 nove mesto na morave, czech republic vat no: cz46343423 we, the manufacturer, hereby declare that country of origin of the ray microwave links and its accessories is the czech republ...
Page 218
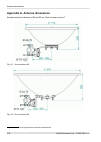
Appendix a. Antenna dimensions example antenna's diameter of 68 and 90 cm. More on www.Racom.Eu 1 . Fig. A.1: jirous antenna 68 fig. A.2: jirous antenna 90 1 http://www.Racom.Eu/eng/products/microwave-link.Html#download ray2 microwave link – © racom s.R.O. 218 antenna dimensions.
Page 219
Appendix b. Rain zone map 219 © racom s.R.O. – ray2 microwave link rain zone map.
Page 220
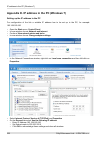
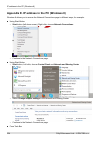
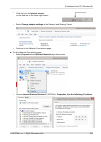
Appendix c. Ip address in the pc (windows xp) setting up the ip address in the pc for configuration of the link a suitable ip address has to be set up in the pc, for example 192.168.169.160 • open the start menu, settings, network connections, local area connection • in the window local area connect...
Page 221
Checking the ip address in the pc in windows xp proceed in the following manner: • interconnect the configured unit and pc with an ethernet cable • open the start menu and click run... • enter command cmd • enter command ipconfig and read the pc ip address and mask: checking the pc - unit connection...
Page 222
Appendix d. Ip address in the pc (windows 7) setting up the ip address in the pc for configuration of the link a suitable ip address has to be set up in the pc, for example 192.168.169.160 • open the start menu, control panel • in new window choose network and internet • continue view network status...
Page 223
Checking the ip address in the pc in windows 7 proceed in the following manner: • interconnect the configured unit and pc with an ethernet cable • under the start menu, type the command cmd in the search programs and files box and press enter. • inside the cmd.Exe window that opens, enter the comman...
Page 224
Appendix e. Ip address in the pc (windows 8) windows 8 allows you to access the network connections page in different ways, for example: ■ using start button ○ start button (left down corner), right click, choose network connections ○ continue to the network connections page. ■ using start button ○ ...
Page 225
○ click the icon for internet access on the task bar in the lower right corner ○ select change adapter settings in the network and sharing center ○ continue to the network connections page. ■ on the network connections page: ○ select properties from ethernet network drop down menu ○ choose internet ...
Page 226
■ enter ip address 192.168.169.160 ■ set subnet mask to 255.255.255.0 ■ click ok to acknowledge these settings and close all windows checking the ip address in the pc in windows 8 proceed in the following manner: • interconnect the configured unit and pc with an ethernet cable • right click on the s...
Page 227
Appendix f. Ssh key generation linux use “ssh-keygen” command. Windows use "puttygen.Exe" software, which is typically located in the c:\program files\putty\ directory and apply the "generate" button. To use cli (command line interface) access the unit with a putty client. Access is protected by a k...
Page 228
Putty access with key in putty menu fill in the address, e.G. Root@192.168.169.169 and the name of the link, e.G. Ray 17 racom. Go to connection / ssh / auth in the left column and locate the key c:\downloads\ray.Ppk go back to session and save the configuration. To connect select the name of the co...
Page 229
Appendix g. Https certificate when switching from older versions of the firmware the access certificate for https is changed. New web browser configuration must take place in order to remove the link between the microwave link management ip address and the previous https certificate. Mozilla firefox...
Page 230
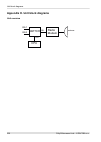
Appendix h. Unit block diagrams unit overview cpu eth1 eth2 air antenna switch radio modem cpu ray2 microwave link – © racom s.R.O. 230 unit block diagrams.
Page 231
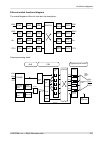
Ethernet switch functional diagram the overall diagram of the unit, see also the description: cpu qos egress queue pirl eth1 eth2 air qos qos qos pirl pirl egress queue egress queue egress queue eth1 eth2 air switch phy phy radio modem radio modem phy phy pirl cpu cpu cpu frame processing detail: ip...
Page 232: Index
Index a accessories, 28 acm, 68 address default, 8 ip, 70 ip in ray, 39 mac, 66 address ip pc windows 7, 222 pc windows 8, 224 pc windows xp, 220 alarms, 77 antenna dimensions, 26, 218 assembly, 42 lubrication, 45, 49 atpc, 68 authorization, 147 b backup, 125 bandwidth, 68 box contens, 9 c calculati...
Page 233
Link configuration, 40 length, 18 microwave, 10 lldp protocol, 70 logs, 139 m mapping 802.1p, 101 dscp, 103 microwave link, 10 n name plate, 26 o ordering codes, 27 p parameters basic, 10 setup, 60 table, 151 ping, 140 pirl, 92 polarization cross, 44 indication, 65 mounting, 42 port parameters, 86 p...
Page 234
234.
Page 235
Appendix i. Revision history 2014-05-28 revision 1.0 first issue 2014-06-04 revision 1.1 name plate changes 2014-07-15 revision 1.2 ray2-11 c,d user speed and cs correction 2014-07-25 revision 1.3 accessory supplemented 2014-08-12 revision 1.4 ray2-11 a,b frequency range corrected 2014-09-01 revisio...