- DL manuals
- Radyne
- Modem
- DMD50
- Installation And Operation Manual
Radyne DMD50 Installation And Operation Manual
Part Number MN-DMD50
Revision 4
Comtech EF Data is an
AS9100 Rev B / ISO9001:2000 Registered Company
IMPORTANT NOTE: The information contained in this document supersedes all previously
published information regarding this product. This manual is subject to change without prior notice.
DMD50
Universal Satellite Modem
Installation and Operation Manual
Summary of DMD50
Page 1
Part number mn-dmd50 revision 4 comtech ef data is an as9100 rev b / iso9001:2000 registered company important note: the information contained in this document supersedes all previously published information regarding this product. This manual is subject to change without prior notice. Dmd50 univers...
Page 3: Errata A For Mn-Dmd50 Rev 4
Er-mndmd50-ea4 rev - plm c-0026227 errata a for mn-dmd50 rev 4 comtech ef data documentation update subject: chapter 7, technical specifications errata part number: er-mndmd50-ea4 (errata documents are not subject to revision.) plm co number: c-0026227 comments: see attached page(s). The new informa...
Page 4: Blank Page
Er-mndmd50-ea4 rev - plm c-0026227 blank page.
Page 5: Chapter 7. Technical
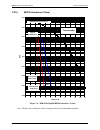
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–1 chapter 7. Technical specifications 7.1 data rates refer to section 7.21 7.2 modulator modulation bpsk, qpsk, oqpsk, 8psk, 8qam, 16qam if tuning range 50 to 90, 100 to 180 mhz in 1 hz steps l-band tuning range 950 to 2050 mhz in 1 hz steps impedance if, 75 ohm (50 ohm optiona...
Page 6
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–2 legacy turbo rates {0.495, 0.793} ldpc/tpc (optional) ldpc (bpsk) {1/2} ldpc (oqpsk/qpsk) {1/2, 2/3, 3/4} ldpc (8psk/8qam) {2/3, 3/4} ldpc (16qam) {3/4} turbo (bpsk) {21/44} turbo (qpsk/oqpsk) {1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 7/8} turbo...
Page 7
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–3 ldpc (oqpsk/qpsk) {1/2, 2/3, 3/4} ldpc (8psk/8qam) {2/3, 3/4} ldpc (16qam) {3/4} turbo (bpsk) {21/44} turbo (qpsk/oqpsk) {1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 7/8} turbo (8qam/8psk) {2/3, 3/4, 7/8} turbo (16qam) {3/4, 7/8} decoder options re...
Page 8
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–4 g.703 t2 (100) 6.312 mbps, 75 ohm unbalanced and 110 ohm balanced, b8zs and b6zs g.703 e2 8.448 mbps, 75 ohm bnc, unbalanced, hdb3 7.9 idr/esc t3/e3/sts1 interface (optional) g.703 t1 (dsx1) 1.544 mbps, 100-ohm balanced...
Page 9
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–5 7.16 hssi / g703 t2/e2 max hssi high-speed serial interface, 50-pin scsi-2 type connector (female) g.703 t1 (dsx1) 1.544 mbps, 100-ohm balanced, ami and b8zs g.703 e1 2.048 mbps, 75-ohm unbalanced and 120-ohm balanced, ...
Page 10
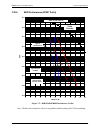
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–6 7.21 dmd50 data rate limits 7.21.1 non-dvb modulation code rate min data rate max data rate option card bpsk none 4800 10000000 bpsk vit 1/2 2400 10000000 bpsk vit 3/4 3600 10000000 bpsk vit 7/8 4200 10000000 bpsk seq 1...
Page 11
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–7 modulation code rate min data rate max data rate option card qpsk tpc 1/2 18000 9545400 ldpc/tpc card qpsk tpc 3/4 27000 15000000 ldpc/tpc card qpsk tpc 7/8 31500 17500000 ldpc/tpc card oqpsk none 9600 20000000 oqpsk vi...
Page 12
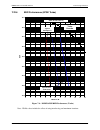
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–8 modulation code rate min data rate max data rate option card 8qam tpc 3/4 40500 20000000 ldpc/tpc card 8qam tpc 7/8 48000 20000000 ldpc/tpc card 8qam ldpc 2/3 36000 20000000 ldpc/tpc card 8qam ldpc 3/4 40500 20000000 ld...
Page 13
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–9 188 mode modulation code rate min data rate max data rate bpsk vit 1/2 2400 4607843 bpsk vit 2/3 2950 6143790 bpsk vit 3/4 3318 6911764 bpsk vit 5/6 3687 7679738 bpsk vit 7/8 3871 8063725 qpsk vit 1/2 4424 9215686 qpsk ...
Page 14
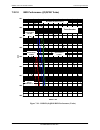
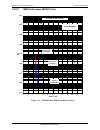
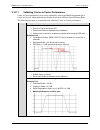
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–10 7.22 dmd50 ber specifications 7.22.1 ber performance (viterbi) figure 7-1 – dmd50 b/o/qpsk ber performance (viterbi) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding and v.35 descrambling. 1e-9 1e-8...
Page 15
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–11 7.22.2 ber performance (sequential) figure 7-2 – dmd50 b/o/qpsk ber performance (sequential) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding and v.35 descrambling. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-...
Page 16
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–12 7.22.3 ber performance (viterbi with reed-solomon) figure 7-3 – dmd50 b/o/qpsk ber performance (viterbi – w/rs) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1...
Page 17
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–13 7.22.4 ber performance (turbo) figure 7-4 – dmd50 b/o/qpsk ber performance (turbo) note: eb/no values include the effect of using interleaving and maximum iterations. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 ...
Page 18
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–14 7.22.5 ber performance (8psk trellis) figure 7-5 – dmd50 8psk ber performance (trellis) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding and v.35 descrambling. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-...
Page 19
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–15 7.22.6 ber performance (8psk turbo) figure 7-6 – dmd50 8psk ber performance (turbo) note: eb/no values include the effect of using interleaving and maximum iterations. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2...
Page 20
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–16 7.22.7 ber performance (16qam viterbi) figure 7-7 – dmd50 16qam ber performance (viterbi) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding and v.35 descrambling. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1...
Page 21
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–17 7.22.8 ber performance (16qam viterbi with reed-solomon) figure 7-8 – dmd50 16qam ber performance (viterbi w/rs) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 ...
Page 22
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–18 7.22.9 ber performance (16qam turbo) figure 7-9 – dmd50 16qam ber performance (turbo) note: eb/no values include the effect of using interleaving and maximum iterations. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1...
Page 23
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–19 7.22.10 ber performance ((o)qpsk turbo) figure 7-10 – dmd50 (o)qpsk ber performance (turbo) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 be r eb/no in db turbo decoder specification 1/2 rat...
Page 24
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–20 7.22.12 ber performance (bpsk turbo) figure 7-11 – dmd50 bpsk ber performance (turbo) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 be r eb/no in db turbo decoder specification 5/16 rate typ...
Page 25
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–21 7.22.13 ber performance (8psk turbo) figure 7-12 – dmd50 8psk ber performance (turbo) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 be r eb/no in db turbo decoder specification 3/4 rate typi...
Page 26
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–22 7.22.14 ber performance (16qam turbo) figure 7-13 – dmd50 16qam ber performance (turbo) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 be r eb/no in db turbo decoder specification 3/...
Page 27
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–23 7.22.15 b/o/qpsk ber performance (ldpc) figure 7-14 – dmd50 b/o/qpsk ber performance (ldpc) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 be r eb/no in db ldpc decoder typical performance b/...
Page 28
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–24 7.22.16 8psk/8qam ber performance (ldpc) figure 7-15 – dmd50 8psk/8qam ber performance (ldpc) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 be r eb/no in db ldpc decoder typical performance ...
Page 29
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–25 7.22.17 16qam ber performance (ldpc) figure 7-16 – dmd50 16qam ber performance (ldpc) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 be r eb/no in db ldpc decoder typical performance 16qam un...
Page 30
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–26 1/2 rate 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 1/2 rate 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 1e-3 4.2 db 5.3 db 6.2 db 3.9 db 4.9 db 5.8 db 1e-4 4.8 db 6.1 db 7.1 db 4.5 db 5.6 db 6.5 db 1e-5 5.5 db 6.8 db 7.9 db 5.1 db 6.3 db 7.2 db 1e-6 6.1 db 7.6 db 8.6 ...
Page 31
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–27 2/3 rate 2/3 rate w/rs 2/3 rate 2/3 rate w/rs 1e-3 6.3 db 5.8 db 4.8 db 4.9 db 1e-4 7.3 db 6.1 db 5.6 db 5.1 db 1e-5 8.2 db 6.3 db 6.4 db 5.4 db 1e-6 9 db 6.5 db 7.2 db 5.6 db 1e-7 9.8 db 6.7 db 8.1 db 5.8 db 1e-8 10.4...
Page 32
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–28 turbo 0.495 turbo 0.793 turbo 0.495 turbo 0.793 1e-3 - - 5.6 db 7 db 1e-4 - - 6.1 db 7.4 db 1e-5 - - 6.6 db 7.8 db 1e-6 - - 7 db 8.2 db 1e-7 - - 7.5 db 8.6 db 1e-8 - - 8 db 9 db 1e-9 - - 8.5 db 9.4 db 1e-10 - - 9 db 9....
Page 33
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–29 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 1e-3 6.3 db 7.8 db 6 db 7.4 db 1e-4 6.7 db 7.9 db 6.4 db 7.5 db 1e-5 7 db 8 db 6.7 db 7.6 db 1e-6 7.4 db 8.1 db 7.1 db 7.7 db 1e-7 7.8 db 8.2 db 7.5 db 7.8 db 1e-8 8.2 db 8.3 db 7.9 ...
Page 34
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–30 7.22.18 acg output voltage the agc output voltage is a function of the input power level in dbm. The agc output voltage is found on the alarm connector pin 14 of j15. Figure 7-13. Agc voltage monitor er-mndmd50-ea4 rev...
Page 35: Errata B For Mn-Dmd50 Rev 4
Er-dmd50-eb4 rev - plm c-0028800 errata b for mn-dmd50 rev 4 comtech ef data documentation update subject: chapter 3, theory of operation errata part number: er-dmd50-eb4 (errata documents are not subject to revision.) plm co number: c-0028800 comments: the new information will be included in the ne...
Page 36: Blank Page
Er-dmd50-eb4 rev - plm c-0028800 blank page.
Page 37: Dmd50
Copyright © 2013 comtech ef data. All rights reserved. Printed in the usa. Comtech ef data, 2114 west 7th street, tempe, arizona 85281 usa, 480.333.2200, fax: 480.333.2161 dmd50 universal satellite modem installation and operation manual part number mn-dmd50 revision 4 comtech ef data is an as9100 r...
Page 38
Blank page.
Page 39: Table Of Contents
I table of contents chapter 1. Introduction ................................................................................................. 1–1 1.1 overview ................................................................................................................................................
Page 40
Table of contents revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 ii 3.7 clocking options ................................................................................................................................. 3–11 3.7.1 tx clock options ...................................................
Page 41
Table of contents revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 iii chapter 4. User interfaces ............................................................................................. 4–1 4.1 user interfaces ....................................................................................
Page 42
Table of contents revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 iv 5.4.8 143b async (j17) ...................................................................................................................................... 5–4 5.4.9 j18...........................................................
Page 43
Table of contents revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 v 6.2 troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................... 6–1 6.2.1 alarm faults .......................................................
Page 44
Table of contents revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 vi 7.22.3 ber performance (viterbi with reed-solomon) ............................................................................ 7–12 7.22.4 ber performance (turbo) ..................................................................
Page 45
Table of contents revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 vii c.1 states .................................................................................................................................................... C–1 c.2 carrier off .................................................
Page 46
Table of contents revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 viii appendix g. Aupc operation............................................................................................ G–1 g.1 automatic uplink power control (aupc operation) .....................................................
Page 47: Preface
Ix preface about this manual this manual describes the installation and operation of the dmd50 universal satellite modem. Conventions and references patents and trademarks see all of comtech ef data's patents and patents pending at http://patents.Comtechefdata.Com. Comtech ef data acknowledges that ...
Page 48
Preface revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 x electrical safety the dmd50 has been shown to comply with the en 60950-1 safety of information technology equipment (including electrical business machines) safety standard. The equipment is rated for a nominal operating range of 100 - 24...
Page 49
Preface revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 xi environmental the dmd50 must not be operated in an environment where the unit is exposed to precipitation; condensation; humid atmospheres above 95% rh; altitudes (unpressurized) greater than 2000 metres; excessive dust or vibration; fla...
Page 50
Preface revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 xii emc (electromagnetic compatibility) in accordance with european directive 2004/108/eec, the dmd50 has been shown, by independent testing, to comply with the following standards: emissions: en 55022 class b - limits and methods of measur...
Page 51
Preface revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 xiii warranty policy comtech ef data products are warranted against defects in material and workmanship for a period of two years from the date of shipment. During the warranty period, comtech ef data will, at its option, repair or replace ...
Page 52
Preface revision 4 dmd50 universal satellite modem mn-dmd50 xiv customer support support business hours - monday through friday - 8:00 a.M. To 5:00 p.M. (mst) comtech ef data & radyne • satellite modems • modem accessories • amplifiers • converters • transceivers • terminals tel: +1.480.333.4357 fax...
Page 53: Chapter 1. Introduction
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 1–1 chapter 1. Introduction this chapter provides an overview of the dmd50 universal satellite modem. When describing the equipment, it may be referred to as “the modem”, or “the unit”. 1.1 overview the dmd50 universal satellite modem (figure 1-1) offers the best features of a so...
Page 54
Dmd50 universal satellite modem introduction mn-dmd50 revision 4 1–2 1.2 configurations the unit can be configured in the following ways: features and options that are installed when the unit is ordered feature upgrades hardware options that are installed to a unit that is sent to a comtech facility...
Page 55: Chapter 2. Installation
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 2–1 chapter 2. Installation 2.1 unpacking and inspection inspect shipping containers for damage. If shipping containers are damaged, keep them until the contents of the shipment have been carefully inspected and checked for normal operation. The universal satellite modem and its ...
Page 56
Dmd50 universal satellite modem installation mn-dmd50 revision 4 2–2 2.2 installation requirements the modem is shipped fully assembled. It does not require removal of the covers for any purpose in installation. The power supply itself is designed for universal application using from 100 to 240 vac,...
Page 57
Dmd50 universal satellite modem installation mn-dmd50 revision 4 2–3 proper grounding protection required: the installation instructions require that the integrity of the protective earth must be ensured and that the equipment shall be connected to the protective earth connection at all times. There...
Page 58
Dmd50 universal satellite modem installation mn-dmd50 revision 4 2–4 2.5 modulator checkout the following descriptions assume that the unit is installed in a suitable location with prime ac power and supporting equipment available. 2.5.1 initial power-up before initial power up of the unit, it is a ...
Page 59: Chapter 3. Theory Of
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–1 chapter 3. Theory of operation 3.1 modem hardware the modem is based on a two printed circuit card (minimum configuration) design with additional optioned printed circuit cards available for additional features. The minimum configuration consists of an l-band/if assembly and ...
Page 60
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–2 in the modulator, analog in-phase (i) and quadrature (q) signals are generated on the digital baseband printed circuit card, routed to the l-band/if printed circuit card, and modulated at the desired frequency. The l-band or...
Page 61
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–3 the baseband printed circuit card also contains the monitor and control (m&c) circuitry responsible for: programmable part setup and initialization continuous control and adjustment of some functions calibration monitoring f...
Page 62
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–4 figure 3-3. Universal satellite modem functional block diagram 3.2.1 front panel the front panel includes a 2 x 16 backlit lcd display, indicator leds, and a numeric keypad (refer to chapter 4). 3.2.2 baseband processing the...
Page 63
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–5 3.2.3 tx baseband processing the tx data and clock enters the baseband processor, passes through a rate adapting fifo and enters the framer/drop processor. In idr, ibs, and d&i modes, the framer adds the appropriate framing ...
Page 64
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–6 3.3.1 terminal port this port supports an asynchronous control protocol as described in section 4. It is configured to support rs-232 signal levels. This port is intended for use in computer-based remote m&c. All functions o...
Page 65
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–7 3.3.4 modem monitor status the modems m&c system is connected to most of the circuitry on any board contained in the chassis. These connections provide status on the working condition of the circuitry as well as providing th...
Page 66
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–8 3.6 loopback features (terrestrial & if) the modem provides for a number of different loopbacks. The loopback supported are: if loopback – tx if port is looped back to the rx if port tx terrestrial loopback - tx data port is...
Page 67
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–9 figure 3-4. Loopback functional block diagram.
Page 68
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–10 figure 3-5. Loopback functional block diagram figure 3-6. Loopback functional block diagram.
Page 69
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–11 3.7 clocking options the modem supports a number of different clocking options that can be recovered from the satellite or the terrestrial links. The various clocking options allow users to determine which clock will best f...
Page 70
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–12 3.7.1.1 scte: serial clock transmit external the scte clock is the transmit terrestrial clock associated with the data interface. Scte is an external clock received from the terrestrial equipment and the modem utilizes the ...
Page 71
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–13 clock source priority rx sat 1 of 5 scte 2 of 5 sct 3 of 5 exc bnc 4 of 5 ext idi 5 of 5 refer to front panel setup menus or web browser manual mn-dmdremoteop 3.7.2.1 rx sat clock the rx sat clock is recovered from the sate...
Page 72
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–14 3.7.3 ext ref: external reference, top bnc port, j10 this is not actually a clock, but does have some clocking implications. When the external reference is used, the master oscillator within the modem is locked to the exter...
Page 73
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–15 3.9 reed-solomon codec refer to figure 3-8, figure 3-9, and table 3-1. Utilizing a reed-solomon (r-s) outer codec concatenated with a convolutional inner codec is an effective way to produce very low error rates even for po...
Page 74
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–16 figure 3-8. Reed-solomon encoder functional block diagram figure 3-9. Reed-solomon decoder functional block diagram table 3-1. Reed-solomon codes type of service data rate (kbps) r-s code (n, k, t) 1 bandwidth expansion [ (...
Page 75
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–17 3.10 asynchronous overhead operation (framing/multiplexer capability) the asynchronous framing/multiplexer is capable of multiplexing a relatively low-speed overhead channel onto the terrestrial data stream resulting in a s...
Page 76
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–18 kbps baud rate example for standard ibs kbps baud rate example for enhanced mode 1344 19200 1408 19200 1472 19200 1536 19200 1600 19200 1664 19200 1728 19200 1792 19200 1856 19200 1920 19200 1984 19200 2048 19200 3.11 stand...
Page 77
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–19 in this mode, the overhead signaling bytes 16 and 48 can be used to implement a significantly higher speed es to es data channel under software control. When implemented, this rate is 16 times that of the normal ibs standar...
Page 78
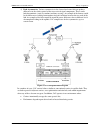
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–20 3.14 doubletalk carrier-in-carrier option space segment costs are typically the most significant operating expense for any satellite-based service, having a direct impact on the viability and profitability of the service. F...
Page 79
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–21 3.14.2 application requirements the following conditions are necessary in order to operate doubletalk carrier-in-carrier: • link must be full duplex. • a radyne dmd50 must be used at the end of the link where the cancellati...
Page 80
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–22 4) link asymmetries: various asymmetries in the forward and return link can produce differences in the relative power of the two received signal components. These can be both deterministic (static) or random (and time varyi...
Page 81
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–23 3.14.3 operational recommendations the rules for cnc operation are summarized below: • both earth stations share the same footprint so each sees both carriers; • cnc carriers are operated in pairs; • one outbound with multi...
Page 82
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–24 3.14.4 system functionality and operational considerations figure 3-2 illustrates a conventional, full duplex satellite link where two carriers are placed in non-overlapping channels. Figure 3-11. Conventional fdma link fig...
Page 83
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–25 figure 3-12. Same link using radyne dmd50 and doubletalk carrier-in-carrier traditional full duplex link duplex link with doubletalk carrier-in-carrier figure 3-13. Duplex link optimization because acquiring the delay and f...
Page 84
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–26 table 3-4. Spectral efficiency using doubletalk carrier-in-carrier modulation and code rate spectral efficiency (bps/hz) traditional scpc carrier-in-carrier bpsk 1/2 0.50 1.00 qpsk 1/2 1.00 2.00 qpsk 2/3 1.33 2.67 qpsk 3/4 ...
Page 85
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–27 figure 3-14. Doubletalk carrier-in-carrier signals referring to figure 3-5: modem 1 and modem 2 transmit signals s1 and s2 respectively. The satellite receives, translates, and retransmits the composite signal. The downlink...
Page 86
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–28 3.14.6 margin requirements typical interfering signal cancellation is 28 to 35 db (depending on the product). The residual interfering signal appears as noise causing a slight degradation of the eb/no. To compensate for the...
Page 87
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–29 3.14.9.1 symmetric data rate link consider the following example: satellite & transponder galaxy 18 @ 123º w, 13k/13k earth station 1 phoenix, az – 4.6 m earth station 2 phoenix, az – 2.4 m data rate 512 kbps / 512 kbps the...
Page 88
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–30 link parameters and lst summary for qpsk, ldpc 2/3 with carrier-in-carrier is as follows:.
Page 89
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–31 the link budget summary for the different modcod combinations is as follows: s. No. Modulation & fec allocated bw (mhz) peb (mhz) leased bw (mhz) savings compared to original psd ratio (db) 1 8-qam, ldpc 2/3 0.3584 1.1468 1...
Page 90
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–32 3.14.9.2 asymmetric data rate link as occupied (or allocated) bandwidth of a carrier-in-carrier circuit is dictated by the larger of the two carriers, it is strongly recommended that the smaller carrier be spread as much as...
Page 91
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–33 3.14.9.3 power limited links carrier-in-carrier can provide substantial savings even when the original link is power limited. Spreading the carrier by using a lower modulation and/or fec along with latest fec such as versaf...
Page 92
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–34 3.14.10 carrier-in-carrier commissioning and deployment prior to commissioning a carrier-in-carrier link, it is critical that the link is fully tested in non carrier-in-carrier mode and all system issues including external ...
Page 93
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–35 3.14.11 validating carrier-in-carrier performance carrier-in-carrier performance can be easily validated by verifying that eb/no degradation due to carrier-in-carrier is within published specification for the observed power...
Page 94
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–36 3.14.12 operational references 3.14.13 carrier-in-carrier link budget calculation the following steps are required for calculating the link budget for a carrier-in-carrier link: 1. Calculate the link budget for both carrier...
Page 95
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–37 3.14.14 estimating psd ratio psd can be estimated from a link budget using downlink eirp and symbol rate: psd = downlink eirp – 10 * log (symbol rate) psd ratio example: carrier downlink eirp symbol rate power spectral dens...
Page 96
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–38 3.14.14.2 estimating psd ratio from satmaster 3.14.14.3 estimating psd ratio using spectrum analyzer psd ratio or cnc ratio can also be estimated using a spectrum analyzer capable of integrating the signal power in a given ...
Page 97
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–39 3.14.15 doubletalk carrier-in-carrier specifications operating mode requires the two links to share a common carrier frequency (outbound and inbound symbol rates do not have to be equal) power spectral density ratio and cnc...
Page 98
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–40 3.14.17 glossary allocated bandwidth bandwidth or allocated bandwidth or occupied bandwidth is the frequency space required by a carrier on a transponder. For example, a duplex e1 (2.048 mbps) circuit with 8-psk modulation,...
Page 99
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–41 c/n carrier power (c) to noise (n) ratio: unit is db c/no carrier power (c) to noise density (n o ) ratio: unit is dbhz co+no/no carrier density (c o ) + noise (n o ) to noise density (n o ) ratio: unit is db c/n = c/n o – ...
Page 100
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–42 3.15 satellite control channel (scc) the scc format uses a variable overhead rate to transmit an asynchronous data channel in addition to the normal data channel. The scc asynchronous mode implemented on the dmd50 is "passt...
Page 101
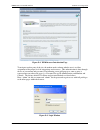
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–43 3.15.2 aggregate data rate the aggregate data rate equals the following: user data rate + in-band rate + synchronizing overhead rate because scc must adjust the overhead so that there are an equal number of user data bits i...
Page 102
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–44 user data rate in-band rate control ratio aggregate data rate overhead ratio 6,312,000 19,200 1/3 6,337,606 1.004 6,312,000 19,200 1/1 6,350,418 1.006 3.15.4 actual overhead rate calculation the following is the actual calc...
Page 103
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–45 3.15.5 scc overhead channel setup 1. Set the framing mode (located under mod and demod data menus) to scc. After doing this, two new menus will appear to the right of the framing menu, for both the mod and demod. The new me...
Page 104
Dmd50 universal satellite modem theory of operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 3–46 3.16 edmac satellite framing/deframing mode the modem supports edmac satellite framing. Edmac can be enables for both modulator and demodulator satellite framing when modem is configured in closed net applications. Edmac sa...
Page 105: Chapter 4. User Interfaces
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–1 chapter 4. User interfaces 4.1 user interfaces this section contains information pertaining to the user interfaces for the modem. There are four user intefaces available for the modem. These are: • front panel interface – refer to section 4.2. • terminal interface - :refer to...
Page 106
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–2 4.2.1 lcd front panel display the front panel display is a 2 line by 16-character lcd display. The display is lighted and the brightness can be set to increase when the front panel is currently in use. The lcd display automatica...
Page 107
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–3 normal operation, yellow means that there is a condition not proper for normal operation, and red indicates a fault condition that will result in lost communications. Table 4-3. Led color reference led color function modem led i...
Page 108
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–4 4.3 parameter setup the four cursor control arrow keys are used to navigate the menu tree and select the parameter to be set. After arriving at a parameter that needs to be modified, depress . The first space of the modifiable p...
Page 109
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–5 idr: (iess-308) for data rates 1.544, 2.048, 6.312, 8.448 mbps framing type: 96 kbps (idr) scrambler type: v.35 spectrum mask: intelsat for data rates framing type: 1/15 (ibs) scrambler type: iess-309 spectrum mask: intelsat ibs...
Page 110
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–6 dvb: per en301-421 & en301-210 data rates: all rates framing type: dvb scrambler type: dvb spectrum mask: dvb 0.25, 0.35 closed net: all possible combinations allowed, however, dvb settings requires the dvb network spec. Activat...
Page 111
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–7 allows you to offset output power by up to 1 dbm. This is intended as a correction for user cabinet connectors. Data (menu) data rate (bps) {refer to technical specs for data rates} allows the user to set the data rate in bps st...
Page 112
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–8 in-band rate {150, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200} allows the user to select the rate of in-band data for the es to es, async overhead channel. Only displayed when effiecient d&i with enhanced async are selected. Scc ct...
Page 113
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–9 nearside: enables nearside local aupc function. In the event the local demodulator losses lock due to signal loss, the output power level will adjust itself to the nominal level. This nominal power should be set to a level high ...
Page 114
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–10 ef aupc: when configured for ef aupc, this setting is compared against the local received e b /n o and commands to the remote modem to increase or decrease transmit power. Nearside: when configured for nearside aupc, this setti...
Page 115
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–11 rx 2047 ber: reports the ber measurement of the receiver 2047 pattern test mode of the remote modem. Ber is reported from the 1x10 -5 to 1x10 -7 in tenth decade steps. If the pattern does not synchronize or is out of range, ‘no...
Page 116
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–12 ibs: (iess-309) for data rates framing type: 1/15 (ibs) descrambler type: iess-309 spectrum mask: intelsat drop & insert: data rates: n x 64, n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 16, 20, 24, 30 framing type: 1/15 (ibs) descramb...
Page 117
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–13 modulation {qpsk, bpsk, oqpsk, 8psk, 16qam} allows the user to select the demodulation type. Spectral mask {intelsat 0.35, dvb 0.35, dvb 0.25, dvb 0.20} allows the user to set the spectral shape of tx data filter. Sweep range (...
Page 118
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–14 sequential {1/2, 3/4, 7/8} trellis {8psk} turbo ≤ 20mbps {.793, .495, 3/4, 7/8} turbo >20mbps {.750, .875} csc {3/4} dvb vit {2/3, 5/6} dvb trellis {3/4, 5/6, 7/8, 8/9} ldpc (b/o/qpsk) {1/2, 2/3, 3/4} ldpc (8psk) {2/3, 3/4} ldp...
Page 119
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–15 allows the user to simulate the framing used by the satellite control channel option (pass thru mode only). The scc ctl ratio is the ratio of overhead in-band data to synchronizing words. Only displayed when scc framing is sele...
Page 120
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–16 4.4.4 interface menu options and parameters tx setup (menu) circuit id allows the user entry of a tx circuit identifier. Circuits can be given up to an 11 character alphanumeric identity such as link1. Terr interface standard i...
Page 121
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–17 automatically corrects. If g.703 interface is selected, this selection cannot be changed. Sct clk src {sct, scr} allows the user to select sct source.Sct is the internally generated sct clock. Scr is the rx satellite clock. Scr...
Page 122
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–18 terr interface standard interface {rs422 serial,rs232 serial, v.35} optional hardware interfaces: {m2p parallel, dvb parallel, asi} {hssi} {ethernet 10/100 base-t} {g.703: t1 ami, t1 b8zs, , e1 bal, e1 unbal, t2 bal, t2 unbal, ...
Page 123
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–19 allows the user to edit the tx edit map and specify the terrestrial slots that will be dropped into the assigned satellite channels. The satellite channels are fixed and the number of channels are determined by the data rate. T...
Page 124
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–20 tx async mode (menu) tx async mode {es-es, esc enhanced} es-es is the normal ibs async channel. Esc enhanced can be selected in closed net and uses the overhead signaling bytes in the ibs overhead to pass asynchronous data. Es ...
Page 125
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–21 raw ber displays the estimated channel error rate (before decoding) measured by the modem. Corrected ber the cber display shows an estimated corrected bit error rate of the modem. Depending on the symbol rate the modem is runni...
Page 126
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–22 js4 status {see the note above} displays the current status of the lan port. Wan status {see the note above} displays the current status of the wan port. Voltages (menu) +1.5v rx supply displays the measured voltage of the 1.5 ...
Page 127
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–23 current alarms (menu) tx major (menu)status edit table fpga cfg {pass/fail, unmasked/masked} indicates a transmit fpga configuration failure. Dsp cfg {pass/fail, unmasked/masked} indicates a transmit dsp configuration failure. ...
Page 128
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–24 indicates the framing unit is unable to find the expected terrestrial framing pattern. Dni m-frame lock {pass/fail, unmasked/masked} indicates the framing unit is unable to find the expected inter- frame pattern. Tx dvb frm loc...
Page 129
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–25 rx minor (menu) buff underflow {pass/fail, unmasked/masked} indicates that a doppler buffer underflow has occurred. Buff near empty {pass/fail, unmasked/masked} indicates that the doppler buffer is about to underflow. Buff near...
Page 130
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–26 indicates that there are more than one in 1000 bits in error in ibs mode. Rx dvb frm lock {pass/fail, unmasked/masked} indicates that the rx satellite data stream framing is not dvb. Common (menu) terr fpga cfg {pass/fail, unma...
Page 131
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–27 ext clock act {pass/fail, unmasked/masked} indicates the external clock activity. Ext ref act {pass/fail, unmasked/masked} indicates the external reference activity. Ext ref lock {pass/fail, unmasked/masked} indicates the exter...
Page 132
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–28 signal lock frame lock multiframe lock lb synth pll if synth pll ethernet wan rx minor (menu) buff underflow buff near empty buff near full buff overflow rx data activity sat ais dni frame lock dni m-frame lock insert crc t1/e1...
Page 133
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–29 common (menu) terr fpga cfg codec fpga cfg codec dev cfg voltage (menu) +1.5v rx supply +1.5v tx supply +3.3v supply +5v supply +12v supply -12v supply +20v supply ext clock act ext ref act ext ref lock clear latched ((enter)) ...
Page 134
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–30 t1e1 satterr alm {pass, fail} map summary {none, bk 1; bk 2; bk 1, 2; bk 3; bk 1, 3; bk 2, 3; bk 1, 2, 3; bk 4; bk 1,4; bk 2,4; bk 1, 2,4; bk 3,4; bk 1, 3,4; bk 2, 3,4; bk 1, 2, 3,4} summary alarm is given when criteria meets t...
Page 135
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–31 bklt timeout {00 - 99} allows the user to enter the length of time (in minutes ) of keyboard inactivity before the backlight shuts off. 00 = no timeout. Key click {on, off} allows the user to enable or disable the audible beep ...
Page 136
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–32 tcp/ip (menu) boot mode {default, non-vol, bootp, ip test} default: during initialization (boot up), the modem will restore the web setting to the standard ip mask and addresses supplied by the modem. The modem will be taken of...
Page 137
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–33 server ip addr {xxx.Xxx.Xxx.Xxx} hexidecimal address {ddd.Ddd.Ddd.Ddd} decimal address the ip address of the boot server and the address of the snmp trap server when snmp is active. If a server is used and there is no local rou...
Page 138
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–34 the mib2 context allows a user with appropriate authentication to access the mib2 oids and the snmp oids. These are of interest primarily to network operators not controlling the satellite link. The dev context allows a user wi...
Page 139
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–35 guest: users are able to navigate most of the site, and view modem parameter settings. Oper: users can monitor and and control parameter settings, and change their own authentication passwords. Admin: at this highest access rig...
Page 140
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–36 user 3 access group {no group, guest, oper, admin} access rights represent the following: no group: denies access guest: users are able to navigate most of the site, and view modem parameter settings. Oper: users can monitor an...
Page 141
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–37 hw/fw config (menu) firmware rev displays the installed firmware revision. M&c rev displays the installed monitor and control revision. Main board (menu) only the appropriate of the vco adjustment screens listed below will be d...
Page 142
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–38 front panel board indicates the radyne assembly number for the front panel board. Features (menu) 5012.2840.2417 {____.____.____} allows the user to install purchased feature upgrades (see appendix a). Contact the ustomer servi...
Page 143
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–39 4.4.8 test menu options and parameters tx test pattern {none, 2047, 2^15-1, 2^23-1} allows the user to enable the tests listed above. Rx test pattern {none, 2047, 2^15-1, 2^23-1} allows the user to enable the tests listed above...
Page 144
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–40 baseband tx:sends tx data to the receive input to the bb card. Carrier type {normal, cw, dual, offset, pos fir, neg fir} allows the user to set the type of carrier. Normal: causes the modulator to output normal modulation. Cw: ...
Page 145
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–41 the terminal mode uses eight “screens,” each of which have the basic contents of the three modem monitor and control areas as set in the front panel matrix columns. This screen is used for setting the parameters of the modulato...
Page 146
Dmd50 universal satellite modem user interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 4–42 4.8 terminal screens for terminal screens, refer to the remote protocol manual. 4.9 rs485 remote port interface (rllp protocol) the remote port allows for complete control and monitoring of all parameters and functions via an r...
Page 147: Chapter 5. Rear Panel
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–1 chapter 5. Rear panel interfaces this section discusses the electrical interfaces available from the rear panel. All locations are as viewed from the rear of the unit unless otherwise specified. 5.1 connections all connections are made to labeled connectors located on the rea...
Page 148
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–2 figure 5-1. Universal satellite modem rear panel configurations 5.2 compact flash the compact flash slot is located on the right side as viewed from the rear of the unit. A 128 mbit flash memory card stores all the modem m...
Page 149
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–3 5.3.2 dc power input/switch the optional dc power input and switch (figure 5-1) is available for all dmd50 products. The unit may be powered from a 48v ± 5vdc vdc source with a maximum unit power consumption of 3 a. Refer ...
Page 150
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–4 table 5-2. Alarm port 15-pin female “d” connector (j15) pin no. Signal name signal direction 1 mod fault - c mf-c no direction 2 mod fault – nc mf-nc no direction 3 mod fault – no mf-no no direction 4 demod fault - c df-c ...
Page 151
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–5 pin no. Signal name signal direction 7 no connection --- --- 8 no connection --- --- 9 no connection --- --- 5.4.9 j18 factory use only. 5.4.10 eia-530 (j19) the eia-530 port is an rs-422/v.35/rs-232 connection. It is a 25...
Page 152
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–6 pin no. Signal name signal direction 22 data mode b (+) dm-b output 23 data terminal ready b (+) tr-b input 24 terminal timing a (-) tt-a input 25 no connection --- --- 5.4.11 remote (j20) the remote port is a rs-485 or rs...
Page 153
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–7 5.6 esc alarm (j1) the esc (engineering service circuits) alarms port is a 25-pin female “d” connector. Refer to table 5-6 for pinouts. Table 5-6. Esc alarm port 25-pin female “d” connector (j1) pin no. Signal name signal ...
Page 154
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–8 5.7 64k audio (j2) the 64k audio port allows for communications between earth stations. It is a 9-pin female “d” connector that complies with iess 308. Refer to table 5-7 for pinouts in audio mode and table 5-8 for pinouts...
Page 155
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–9 5.8 k data (j3) the 8k data port allows for communications between earth stations. It is a 15-pin female “d” connector that complies with iess 308. Refer to table 5-9 for pinouts. Table 5-9. 8k data port 15-pin female “d” ...
Page 156
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–10 5.9.1 switch interface (j5) the switch interface port is a 68-pin high-density female connector. Refer to table 5-11 for pinouts. Table 5-11. Switch interface port 68-pin high-density female connector (j5) pin no. Signal ...
Page 157
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–11 pin no. Signal name signal direction 52 idr esc audio output channel - 2b escaudrx 2b output 53 idr esc backward alarm input - 4 escbwi 4 input 54 ibs es transmit data – b idr esc backward alarminput - 2 tx-b bwi 2 input ...
Page 158
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–12 5.10 ethernet data interface (optional) the optional dmd50 ethernet data interface provides four rj-45, auto-crossover and auto- sensing, 10/100 ethernet data ports. Js1 through js4 may be referred to port 1 through port ...
Page 159
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–13 5.13 asi/dvb/m2p interface (optional) 5.13.1 asi in (j1) the asi in port (j1) is supported on the bnc connector. The interface complies with dvb asi electrical specifications. 5.13.2 asi out (j2) the asi out port (j2) is ...
Page 160
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–14 5.13.4 dvb/m2p out (j4) the dvb or m2p out port (j4) is also supported on the db-25 female connector. It complies with rs-422 electrical specifications. Refer to table 5-15 for dvb and table 5-16 for m2p pinouts for this ...
Page 161
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–15 5.14 ethernet data interface (optional) the optional dmd50 ethernet data interface provides four rj-45, auto-crossover, auto- sensing, 10/100 ethernet data ports where: js1 is port 1 js2 is port 2 js3 is port 3 js4 is por...
Page 162
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–16 5.15.1 64k audio (j2) the 64k audio port allows for communications between earth stations. It is a 9-pin female “d” connector that complies to iess 308. Refer to table 5-18 for pinouts in audio mode and table 5-19 for pin...
Page 163
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–17 5.15.2 8k data (j3) the 8k data port allows for communications between earth stations. It is a 15-pin female “d” connector that complies with iess 308. Refer to table 5-20 for pinouts. Table 5-20. 8k data port 15-pin fema...
Page 164
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–18 5.15.4 esc alarm (j5) the esc (engineering service circuits) alarms port is a 25-pin female “d” connector. Refer to table 5-22 for pinouts. Table 5-22. Esc alarm port 25-pin female “d” connector (j1) pin no. Signal name s...
Page 165
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–19 5.16 hssi / ethernet (j1) the hssi (high-speed serial interface) (j1) complies with the hssi functional and electrical specifications. The physical interface is a 50-pin scsi-2 type connector. Electrical levels are ecl. G...
Page 166
Dmd50 universal satellite modem rear panel interfaces mn-dmd50 revision 4 5–20 5.18 gige interface the optional ethernet data interface provides a three port rj45 10/100/1000 base-t interface. The ethernet interface supports auto-crossover and auto-sensing. The ethernet port are referred to as js1 t...
Page 167: Troubleshooting
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 6–1 chapter 6. Maintenance and troubleshooting this section discusses unit maintenance and troubleshooting for the universal satellite modem. The unit contains a lithium battery. Danger of explosion exists if the battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or equi...
Page 168
Dmd50 universal satellite modem maintenance and troubleshooting mn-dmd50 revision 4 6–2 6.2.1 alarm faults 6.2.1.1 major tx alarms alarm possible cause fpga cfg indicates a transmit fpga hardware failure. Dsp cfg indicates a transmit fpga failure. Sct clock pll indicates that the tx sct clock pll is...
Page 169
Dmd50 universal satellite modem maintenance and troubleshooting mn-dmd50 revision 4 6–3 6.2.1.4 minor rx alarms alarm possible cause buff underflow indicates that a doppler buffer underflow has occurred. Buff near empty indicates that the doppler buffer is about to underflow. Buff near full indicate...
Page 170
Dmd50 universal satellite modem maintenance and troubleshooting mn-dmd50 revision 4 6–4 6.2.2 alarm masks the modem performs a high degree of self-monitoring and fault isolation. The alarms for these faults are separated into the following three categories: active alarms common equipment alarms back...
Page 171
Dmd50 universal satellite modem maintenance and troubleshooting mn-dmd50 revision 4 6–5 6.3 ibs fault conditions and actions figure 6-1 and table 6-1 illustrate the ibs fault conditions and actions to be taken at the earth station, at the terrestrial data stream, and the satellite. These faults incl...
Page 172
Dmd50 universal satellite modem maintenance and troubleshooting mn-dmd50 revision 4 6–6 table 6-1. Ibs fault conditions and actions (includes drop and insert) fault detected on terrestrial link (across interface a) action in earth station action to terrestrial (across interface h) action to satellit...
Page 173: Chapter 7. Technical
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–1 chapter 7. Technical specifications 7.1 data rates refer to section 7.21 7.2 modulator modulation bpsk, qpsk, oqpsk, 8psk, 8qam, 16qam if tuning range 50 to 90, 100 to 180 mhz in 1 hz steps l-band tuning range 950 to 2050 mhz in 1 hz steps impedance if, 75 ohm (50 ohm optiona...
Page 174
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–2 legacy turbo rates {0.495, 0.793} ldpc/tpc (optional) ldpc (bpsk) {1/2} ldpc (oqpsk/qpsk) {1/2, 2/3, 3/4} ldpc (8psk/8qam) {2/3, 3/4} ldpc (16qam) {3/4} turbo (bpsk) {21/44} turbo (qpsk/oqpsk) {1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 7/8} turbo...
Page 175
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–3 ldpc (oqpsk/qpsk) {1/2, 2/3, 3/4} ldpc (8psk/8qam) {2/3, 3/4} ldpc (16qam) {3/4} turbo (bpsk) {21/44} turbo (qpsk/oqpsk) {1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 7/8} turbo (8qam/8psk) {2/3, 3/4, 7/8} turbo (16qam) {3/4, 7/8} decoder options re...
Page 176
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–4 g.703 t2 (100) 6.312 mbps, 75 ohm unbalanced and 110 ohm balanced, b8zs and b6zs g.703 e2 8.448 mbps, 75 ohm bnc, unbalanced, hdb3 7.9 idr/esc t3/e3/sts1 interface (optional) g.703 t1 (dsx1) 1.544 mbps, 100-ohm balanced...
Page 177
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–5 7.16 hssi / g703 t2/e2 max hssi high-speed serial interface, 50-pin scsi-2 type connector (female) g.703 t1 (dsx1) 1.544 mbps, 100-ohm balanced, ami and b8zs g.703 e1 2.048 mbps, 75-ohm unbalanced and 120-ohm balanced, ...
Page 178
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–6 7.21 dmd50 data rate limits 7.21.1 non-dvb modulation code rate min data rate max data rate option card bpsk none 4800 10000000 bpsk vit 1/2 2400 10000000 bpsk vit 3/4 3600 10000000 bpsk vit 7/8 4200 10000000 bpsk seq 1...
Page 179
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–7 modulation code rate min data rate max data rate option card qpsk tpc 1/2 18000 9545400 ldpc/tpc card qpsk tpc 3/4 27000 15000000 ldpc/tpc card qpsk tpc 7/8 31500 17500000 ldpc/tpc card oqpsk none 9600 20000000 oqpsk vi...
Page 180
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–8 modulation code rate min data rate max data rate option card 8qam tpc 3/4 40500 20000000 ldpc/tpc card 8qam tpc 7/8 48000 20000000 ldpc/tpc card 8qam ldpc 2/3 36000 20000000 ldpc/tpc card 8qam ldpc 3/4 40500 20000000 ld...
Page 181
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–9 188 mode modulation code rate min data rate max data rate bpsk vit 1/2 2400 4607843 bpsk vit 2/3 2950 6143790 bpsk vit 3/4 3318 6911764 bpsk vit 5/6 3687 7679738 bpsk vit 7/8 3871 8063725 qpsk vit 1/2 4424 9215686 qpsk ...
Page 182
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–10 7.22 dmd50 ber specifications 7.22.1 ber performance (viterbi) figure 7-1 – dmd50 b/o/qpsk ber performance (viterbi) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding and v.35 descrambling. 1e-9 1e-8...
Page 183
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–11 7.22.2 ber performance (sequential) figure 7-2 – dmd50 b/o/qpsk ber performance (sequential) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding and v.35 descrambling. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-...
Page 184
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–12 7.22.3 ber performance (viterbi with reed-solomon) figure 7-3 – dmd50 b/o/qpsk ber performance (viterbi – w/rs) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1...
Page 185
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–13 7.22.4 ber performance (turbo) figure 7-4 – dmd50 b/o/qpsk ber performance (turbo) note: eb/no values include the effect of using interleaving and maximum iterations. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 ...
Page 186
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–14 7.22.5 ber performance (8psk trellis) figure 7-5 – dmd50 8psk ber performance (trellis) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding and v.35 descrambling. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-...
Page 187
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–15 7.22.6 ber performance (8psk turbo) figure 7-6 – dmd50 8psk ber performance (turbo) note: eb/no values include the effect of using interleaving and maximum iterations. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2...
Page 188
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–16 7.22.7 ber performance (16qam viterbi) figure 7-7 – dmd50 16qam ber performance (viterbi) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding and v.35 descrambling. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1...
Page 189
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–17 7.22.8 ber performance (16qam viterbi with reed-solomon) figure 7-8 – dmd50 16qam ber performance (viterbi w/rs) note: eb/no values include the effect of using differential decoding. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 ...
Page 190
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–18 7.22.9 ber performance (16qam turbo) figure 7-9 – dmd50 16qam ber performance (turbo) note: eb/no values include the effect of using interleaving and maximum iterations. 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1...
Page 191
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–19 7.22.10 ber performance ((o)qpsk turbo) figure 7-10 – dmd50 (o)qpsk ber performance (turbo) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 eb/no in db be r turbo decoder specification 1/2 rat...
Page 192
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–20 7.22.11 ber performance (8psk turbo) figure 7-11 – dmd50 8psk ber performance (turbo) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 eb/no in db be r turbo decoder specification 3/4 rate typi...
Page 193
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–21 7.22.12 ber performance (16qam turbo) figure 7-12 – dmd50 16qam ber performance (turbo) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 eb/no in db be r turbo decoder specification 3/...
Page 194
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–22 7.22.13 1/2 rate b/o/qpsk ber performance (ldpc) figure 7-13 – dmd50 rate 1/2 b/o/qpsk ber performance (ldpc) 1e-9 1e-8 1e-7 1e-6 1e-5 1e-4 1e-3 1e-2 1e-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 eb/no in db be r 1/2 rate ldpc dec...
Page 195
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–23 7.22.14 2/3 rate q/8psk/8qam ber performance (ldpc) figure 7-14 – dmd50 rate 2/3 q/8psk/8qam ber performance (ldpc) 1e-09 1e-08 1e-07 1e-06 1e-05 1e-04 1e-03 1e-02 1e-01 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 eb/no in db be r 2/...
Page 196
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–24 7.22.15 3/4 rate q/8psk, 8/16qam ber performance (ldpc) figure 7-15 – dmd50 rate 2/3 q/8psk/8qam ber performance (ldpc) 1e-09 1e-08 1e-07 1e-06 1e-05 1e-04 1e-03 1e-02 1e-01 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 eb/no in db be ...
Page 197
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–25 1/2 rate 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 1/2 rate 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 1e-3 4.8 db 5.2 db 6 db 4.3 db 4.7 db 5.5 db 1e-4 5.2 db 5.7 db 6.4 db 4.7 db 5.2 db 5.9 db 1e-5 5.6 db 6.1 db 6.9 db 5.1 db 5.6 db 6.4 db 1e-6 5.9 db 6.5 db 7.4 db...
Page 198
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–26 turbo 0.495 turbo 0.793 turbo 0.495 turbo 0.793 1e-3 2.5 db 3.3 db 2.2 db 3 db 1e-4 2.7 db 3.7 db 2.3 db 3.2 db 1e-5 3 db 4.1 db 2.5 db 3.4 db 1e-6 3.2 db 4.4 db 2.6 db 3.6 db 1e-7 3.5 db 4.8 db 2.7 db 3.8 db 1e-8 3.7 ...
Page 199
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–27 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 1e-3 8.9 db 10.3 db 8.1 db 9.5 db 1e-4 9.8 db 11.1 db 9 db 10.3 db 1e-5 10.7 db 11.9 db 9.9 db 11.1 db 1e-6 11.5 db 12.7 db 10.7 db 11.9 db 1e-7 12.4 db 13.5 db 11.6 db 12.7 db 1e-8 ...
Page 200
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–28 table 7-13a – bpsk ber performance (ldpc) ber specification typical 1/2 rate 1/2 rate 1e-5 2 db 1.7 db 1e-9 2.3 db 2 db 1/2 rate 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 1/2 rate 3/4 rate 7/8 rate 1e-3 - 3.2 db 4 db - 2.8 db 3.7 db 1e-4 - 3....
Page 201
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–29 table 7-16. Open network performance ber specification typical ibs idr ibs idr 1/2 rate 3/4 rate 3/4 rate 3/4 rate 1e-3 4.1 db 5.2 db 4.2 db 4.35 db 1e-4 4.6 db 6.0 db 4.9 db 5.25 db 1e-5 5.3 db 6.7 db 5.6 db 5.9 db 1e...
Page 202
Dmd50 universal satellite modem technical specifications mn-dmd50 revision 4 7–30 7.22.16 acg output voltage the agc output voltage is a function of the input power level in dbm. The agc output voltage is found on the alarm connector pin 14 of j15. Figure 7-13. Agc voltage monitor.
Page 203
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 a–1 appendix a. Product options a.1 hardware options the following enhanced interface cards are available. A.2 g.703/idr esc interface the modem can be equipped with either a g.703 t1/e1/t2/e2 /idr esc interface or g.703 t1/e1/t2/e2/t3/e3/sts1idr esc. A.3 internal high stability ...
Page 204
Dmd50 universal satellite modem product options mn-dmd50 revision 4 a–2 a.9 hssi / g.703 high-speed serial interface 50-pin scsi-2 type connector. Complies with cisco systems in hssi design specification, revision 3.0. The g.703 interface supports t1, e1, t2, e2 rates balanced or unbalanced. It does...
Page 205: Appendix B. Front Panel
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 b–1 appendix b. Front panel upgrade procedure b.1 introduction the universal satellite modem offers the ability to perform field upgrades of the modem’s feature set quickly and easily from the front panel. Purchased upgrades will become part of the modems permanent configuration....
Page 206
Dmd50 universal satellite modem front panel upgrade procedure mn-dmd50 revision 4 b–2 2. Contact radyne with the unit id and desired upgrades. The modem’s unit id can be found on the front panel as follows: a. From the modem’s main menu, scroll right to the system menu. B. Scroll down. C. Scroll rig...
Page 207
Dmd50 universal satellite modem front panel upgrade procedure mn-dmd50 revision 4 b–3 b.4 demonstration procedure the procedure for enabling a 30-day demo of the options is similar to the procedure used for permanently updating the modems feature set. The one big difference being that at the end of ...
Page 208
Dmd50 universal satellite modem front panel upgrade procedure mn-dmd50 revision 4 b–4 your radyne sales representative will ask you for this number along with the features you wish to demo. 3. Once your order has been processed, you will be issued a 12-digit demonstration code. This code can only be...
Page 209
Dmd50 universal satellite modem front panel upgrade procedure mn-dmd50 revision 4 b–5 b.4.1 running in demonstration mode because of the possible interruption in traffic when the demonstration mode expires, several indicators are used to inform an operator that the modem is indeed, operating in demo...
Page 210
Dmd50 universal satellite modem front panel upgrade procedure mn-dmd50 revision 4 b–6 b.4.2 canceling demonstration mode at any time, a demonstration may be canceled and have the modem return to its normal operation. Once the demonstration has been canceled, it cannot be restarted using the old demo...
Page 211
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 c–1 appendix c. Carrier control c.1 states the dmd2050 transmitter will turn off the carrier output automatically when the modem determines there is a major alarm. This is done to prevent the carrier from outputting an unknown spectrum and possibly disturbing adjacent carriers. T...
Page 212
Dmd50 universal satellite modem carrier control mn-dmd50 revision 4 c–2 c.5 carrier vsat modulator output is turned off before reprogramming modulator functions that may alter the output spectrum through the front panel, and the user is required to enter “yes” to re-enable output after the change. W...
Page 213: Appendix D. Web Browser
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 d–1 appendix d. Web browser setup guide d.1 introduction the dmd20/50/2050 web browser allows for connection to radyne products through the ethernet port. The web interface allows for complete control and monitoring of all equipment parameters and functions via a 10base-t etherne...
Page 214
Dmd50 universal satellite modem web browser setup guide mn-dmd50 revision 4 d–2 • guest: users are able to navigate most of the site, and view modem parameter settings. • oper: users can monitor and control modem parameter settings, and change their own authentication passwords. • admin: at this hig...
Page 215
Dmd50 universal satellite modem web browser setup guide mn-dmd50 revision 4 d–3 d.3 change web user name any of the three available user names can be modified. 1. Go to submenu, press then move the cursor to any position and press along with the ‘right arrow’ key to clear all text to the right of th...
Page 216
Dmd50 universal satellite modem web browser setup guide mn-dmd50 revision 4 d–4 figure d-1. Web browser introduction page to navigate to other parts of the site, the modem needs to know who the user is to allow assignment of the proper level of transactions and resources. This authentication is done...
Page 217
Dmd50 universal satellite modem web browser setup guide mn-dmd50 revision 4 d–5 upon completion of a successful login, the user will be able to access the other screens within the web browser. D.7 web page appearance this page displays the monitor and control section of the modem web interface. With...
Page 218
Dmd50 universal satellite modem web browser setup guide mn-dmd50 revision 4 d–6 blank page.
Page 219: Appendix E. Strap Codes
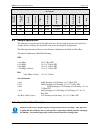
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–1 appendix e. Strap codes e.1 strap codes the strap code is a quick set key that sets many of the modem parameters. For quick setup of the modem, strap codes are very helpful. When a strap code is entered, the modem is automatically configured for the code’s corresponding data ...
Page 220
Dmd50 universal satellite modem strap codes mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–2 strap codes dis = disable s tr ap c o d e (d eci m al ) d at a r at e (k bps ) o ver h ea d c ode r a te t yp e fr a m ing ty pe s c ra m b le r ty pe d ro p an d i n ser t r eed -s ol om on m odul a tio n m ode 128 8448 96k 3/4 vit...
Page 221
Dmd50 universal satellite modem strap codes mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–3 strap codes dis = disable s tr ap c o d e (d eci m al ) d at a r at e (k bps ) o ver h ea d c ode r a te t yp e fr a m ing ty pe s c ra m b le r ty pe d ro p an d i n ser t r eed -s ol om on m odul a tio n m ode 52 1920 16/15 3/4 vi...
Page 222
Dmd50 universal satellite modem strap codes mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–4 strap codes dis = disable s tr ap c o d e (d eci m al ) d at a r at e (k bps ) o ver h ea d c ode r a te t yp e fr a m ing ty pe s c ra m b le r ty pe d ro p an d i n ser t r eed -s ol om on m odul a tio n m ode 23 1024 16/15 1/2 vi...
Page 223
Dmd50 universal satellite modem strap codes mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–5 strap codes dis = disable s tr ap c o d e (d eci m al ) d at a r at e (k bps ) o ver h ea d c ode r a te t yp e fr a m ing ty pe s c ra m b le r ty pe d ro p an d i n ser t r eed -s ol om on m odul a tio n m ode 176 4000 1 1/2 vit n...
Page 224
Dmd50 universal satellite modem strap codes mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–6 e.3.1 case 1: idr 8.448 mbps, 3/4 rate viterbi starting with the data rate = 512 kbps modulator: method 1 - under interface menu: set interface type set tx clock selection set mode to idr under mod data menu: set code rate to 3/4 vi...
Page 225
Dmd50 universal satellite modem strap codes mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–7 e.3.2 case 2: ibs 1.544 mbps, 3/4 rate viterbi starting with the data rate – 512 kbps modulator: method 1 - under interface menu: set interface type set tx clock selection set framing to 1/15 set mode to ibs under mod data menu: set...
Page 226
Dmd50 universal satellite modem strap codes mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–8 e.3.3 case 3: closed network, 3/4 rate viterbi, ibs overhead starting with the data rate = 512 kbps modulator: method 1 - under interface menu: set interface type set tx clock selection set mode to idr: under mod data menu: set code...
Page 227
Dmd50 universal satellite modem strap codes mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–9 e.3.4 case 4: loop timing example method 1 - under interface menu: under tx setup menu: set intf to rs-422 set sct source to scr set tx clock to scte set mode to ibs method 2 - under interface menu: under tx setup menu: set intf to ...
Page 228
Dmd50 universal satellite modem strap codes mn-dmd50 revision 4 e–10 blank page.
Page 229: Setup
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 f–1 appendix f. Tcp/ip ethernet setup f.1 introduction the modem supports snmp, ftp protocols and the web browser. Utilization of the protocols is dependent upon proper set up of the tcp-ip menus. This document is to be used only as a guideline for setting up the tcp-ip menus. Co...
Page 230
Dmd50 universal satellite modem tcp/ip ethernet setup mn-dmd50 revision 4 f–2 c. Non-vol: this will allow for setting up all required ip addresses and will store the information to the non-volatile memory. Upon power cycle, the modem will restore the saved settings into the correct fields. D. Ip tes...
Page 231
Dmd50 universal satellite modem tcp/ip ethernet setup mn-dmd50 revision 4 f–3 f.3 network configuration summary if the above steps were followed and the information was entered, then the following would be the tcp / ip configuration summary for a ‘no router specified’ setup: 1. Boot mode = non-vol 2...
Page 232
Dmd50 universal satellite modem tcp/ip ethernet setup mn-dmd50 revision 4 f–4 the computer tcp/ip must be properly configured in order to obtain connectivity. The following set-up procedure can be used as a guide to aide in this setup. The following instructions apply only to windows 2000 or xp clas...
Page 233
Dmd50 universal satellite modem tcp/ip ethernet setup mn-dmd50 revision 4 f–5 figure f-3. Local area connection properties box 4. Select “use the following ip address”. Enter in the ip address that is offset by 5 or so numbers from the equipment address (the computer and the equipment that it is con...
Page 234
Dmd50 universal satellite modem tcp/ip ethernet setup mn-dmd50 revision 4 f–6 f.5 testing the ethernet connection using the ping program (optional) make sure that connectivity and settings are correct. The ping command will report if the host (equipment) is responding correctly. Open the msdos comma...
Page 235
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 g–1 appendix g. Aupc operation g.1 automatic uplink power control (aupc operation) the modem has an optional built-in provision for automatic uplink power control, aupc. Aupc is useful when operating power levels are affected by environmental changes in the atmosphere. Aupc attem...
Page 236
Dmd50 universal satellite modem aupc operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 g–2 when the rain diminishes, local modem will see the remote e b /n o begin to increase. Local modem will lower its power level. The operation is therefore a feedback control loop with the added complication of a significant time de...
Page 237
Dmd50 universal satellite modem aupc operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 g–3 ef aupc, also provides some control over the rate of power change; while the radyne and near side aupc use a optimized rate for rain fade compensation. The aupc menu functions and their descriptions are shown on tables g-1 and g-...
Page 238
Dmd50 universal satellite modem aupc operation mn-dmd50 revision 4 g–4 blank page.
Page 239: (D&i)
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–1 appendix h. Drop and insert (d&i) h.1 drop and insert (d&i) the drop and insert (d&i) function provides an interface between a full t1 or e1 trunk whose framing is specified in ccitt g.704 and a fractional nx64 kbps satellite channel. The drop and insert functionality conform...
Page 240
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–2 figure h-1. Looped modems figure h-2. Looped modems with separate d&i trunks.
Page 241
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–3 h.1.1 drop only when drop is enabled and insert is disabled, the unit performs a drop-only function. Framed e1 or t1 data is input via the send data in port, the selected timeslots are dropped into the ibs frame structure,...
Page 242
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–4 figure h-5. Insert only with internal frame source h.1.3 mode selection d&i can be easily configured to support several commonly used terrestrial data formats. For e1 data, the user can choose between pcm-30, pcm-30c, pcm-...
Page 243
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–5 h.1.3.3 pcm-31 the pcm-31 mode of operation supports an e1 interface with no multiframe alignment (mfas) or channel associated signaling (cas). The user may independently program n timeslots to drop and n timeslots to inse...
Page 244
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–6 figure h-6. Multidestinational communications example : for a modem w/ drop & insert enabled at a data rate of 256 (with timeslots assigned 1 - 1, 2 - 2, etc.). At a data rate of 256, the modem will allow 4 channels to ass...
Page 245
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–7 for the receive side: 1. With rx side channels configured as follows: ch1 to ts1, ch2 to ts2, ch3 to ts3, and ch4 to ts4. 2. After the timeslots are assigned properly, scroll to the mapping menu and use the above procedure...
Page 246
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–8 • it contributes to the terrestrial framing mode selection process. Trying to select a t1-type drop mode such as t1-esf with the mod data rate set to 1920000 bps (a valid e1 d&i rate but not a valid t1 rate) will result in...
Page 247
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–9 1920000 bps will result in an error message. In turn, the selection of the terrestrial framing formats influences the satellite channel to terrestrial timeslot mappings in the following manner: the selection of t1-d4, t1-e...
Page 248
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–10 h.2.4 d&i sample configurations and d&i clock setup options the following are several examples of how to configure the modem for d&i. Also, refer to figures 3-14 through 3-17 for the d&i clocking setup options available. ...
Page 249
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–11 under demodulator: under demod if: set frequency to desired value under demodulator: set network spec. = drop & insert example 2: multidestinational remote site programming drop 512 kbps from a t1 trunk, 3/4 rate viterbi....
Page 250
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–12 figure h-7. Transmit trunk and receive trunk figure h-8. Single trunk figure h-9. Rx only with trunk.
Page 251
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–13 figure h-10. Rx only no trunk h.3 d&i maps and map editing the drop and insert multiplexer is programmed by loading it with a transmit and receive map. Maps always contain 30 entries, although, only the first “n” entries ...
Page 252
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–14 the modem is equipped with eight permanently stored default maps, which are designated rom 1 through rom 8. The user may also define, modify, and save an additional eight maps which are designated user 1 through user 8. R...
Page 253
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–15 the mapping of channels to time slots is arbitrary; it is not necessary to map ch1 to ts1, ch2 to ts2, etc. The channel to the time slot mapping may be in any order within the constraints of the number of available channe...
Page 254
Dmd50 universal satellite modem drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 h–16 rom map 7 could also be used as the template for an active transmit (drop) and/or active receive (insert) map with a modulator and/or demodulator configured for 1024 kbps operation. This would be used with t1 or e1 frames...
Page 255: Insert (D&i)
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 i–1 appendix i. Efficient drop and insert (d&i) i.1 introduction the following paragraphs describe the menu structure and procedure for configuring a modem for efficient drop & insert mode. I.2 prerequisite in order for a modem to be configured for efficient drop & insert, the mo...
Page 256
Dmd50 universal satellite modem efficient drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 i–2 aupc installed optional, required if desired i.3 efficient drop & insert mode with efficient drop & insert, the terrestrial interface selections, terrestrial framing modes, terrestrial to satellite mapping, es to...
Page 257
Dmd50 universal satellite modem efficient drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 i–3 i.3.1 calculating the required satellite bandwidth in order to calculate the satellite bandwidth (i.E. The symbol rate), we must first calculate the efficient d&i rate (i.E. The data rate plus the overhead requir...
Page 258
Dmd50 universal satellite modem efficient drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 i–4 summary and examples: the following examples further illustrate how to calculate the efficient d&i rate which can be summarized for n timeslots as: efficient d&i rate = data rate + (n * 250 bps) with e1 signaling...
Page 259
Dmd50 universal satellite modem efficient drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 i–5 example 2b: change to e1-pcm30 framing (e1 signaling), standard es to es overhead add 10 * 2000 bps to our previous calculation gives 662500 bps still saving over 20,000 bps compared to the drop & insert open net...
Page 260
Dmd50 universal satellite modem efficient drop and insert (d&i) mn-dmd50 revision 4 i–6 blank page.
Page 261: Appendix J. Ethernet Data
Mn-dmd50 revision 4 j–1 appendix j. Ethernet data interface setup j.1 configuring the modem to use the ethernet data interface (optional) when the optional ethernet data interface card is installed, all of the ethernet related menus become available and can be used to control the interface as follow...
Page 262
Dmd50 universal satellite modem ethernet data interface setup mn-dmd50 revision 4 j–2 when available buffer space is almost gone, the modem will force a collision on the input port when it senses an incoming packet. This collision will cause the transmitting station to back off and retry the transmi...
Page 263
Dmd50 universal satellite modem ethernet data interface setup mn-dmd50 revision 4 j–3 j.1.5 setting up the dmd20/dmd20 lbst ethernet bridge to operate like a fifo in certain circumstances, it may be desirable to have the ethernet interface operate in a fifo like manner with no reordering of packets....
Page 264
Dmd50 universal satellite modem ethernet data interface setup mn-dmd50 revision 4 j–4 j.1.6 packet statistics the following statistics are available under the monitor menu when the ethernet data interface is selected. Total packets: this counter displays the total number of ethernet packets received...
Page 265
Metric conversions units of length unit millimeter centimeter inch foot yard meter kilometer mile 1 millimeter 1 0.1 0.0394 0.0033 0.0011 0.001 1 x 10 -6 6.214 x 10 -7 1 centimeter 10 1 0.3937 0.0328 0.0109 0.01 1 x 10 -5 6.214 x 10 -6 1 inch 25.4 2.54 1 0.0833 0.0278 0.0254 2.54 x 10 -5 1.578 x 10 ...
Page 266
2114 west 7 th street tempe arizona 85281 usa 480 • 333 • 2200 phone 480 • 333 • 2161 fax.