- DL manuals
- RKC INSTRUMENT
- Controller
- SRZ
- Instruction Manual
RKC INSTRUMENT SRZ Instruction Manual
Summary of SRZ
Page 1
Rkc instrument inc. Srz instruction manual module type controller ims01t04-e6.
Page 2
modbus is a registered trademark of schneider electric. company names and product names used in this manual are the trademarks or registered trademarks of the respective companies..
Page 3: Symbols
Ims01t04-e6 i-1 thank you for purchasing this rkc product. In order to achieve maximum performance and ensure proper operation of the instrument, carefully read all the instructions in this manual. Please place the manual in a convenient location for easy reference. Symbols : this mark indicates tha...
Page 4: Notice
Ims01t04-e6 i-2 this product is intended for use with industrial machines, test and measuring equipment. (it is not designed for use with medical equipment and nuclear energy plant.) this is a class a instrument. In a domestic environment, this instrument may cause radio interference, in which c...
Page 5: Contents
Ims01t04-e6 i-3 contents page 1. Outline ........................................................................... 1-1 1.1 features ...................................................................................................... 1-2 1.2 checking the product .....................................
Page 6
Ims01t04-e6 i-4 page 6. Rkc communication ................................................... 6-1 6.1 polling ........................................................................................................... 6-2 6.1.1 polling procedures ........................................................
Page 7
Ims01t04-e6 i-5 page 8. Communication data description ....................... 8-1 8.1 reference to communication data contents ............................................... 8-2 8.2 communication data of z-tio module ......................................................... 8-3 8.2.1 normal settin...
Page 8: Memo
I-6 ims01t04-e6 memo.
Page 9: Outline
Outline ims01t04-e6 1-1 1.1 features ........................................................................................... 1-2 1.2 checking the product ....................................................................... 1-3 1.2.1 z-tio module ..................................................
Page 10: 1.1 Features
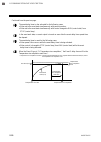
1. Outline 1-2 ims01t04-e6 1.1 features this chapter describes features, package contents and model code, etc. The module type controller has the following features: module type controller srz interfaces with the host computer via modbus or rkc communication protocols. The srz sets all of the data i...
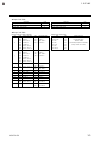
Page 11: 1.2 Checking The Product
1. Outline ims01t04-e6 1-3 1.2 checking the product before using this product, check each of the following: model code check that there are no scratches or breakage in external appearance (case, front panel, or terminal, etc.) check that all of the items delivered are complete. (refer to below...
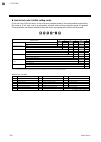
Page 12: 1.3 Model Code
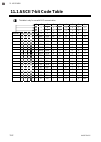
1. Outline 1-4 ims01t04-e6 1.3 model code check that the product received is correctly specified by referring to the following model code list: if the product is not identical to the specifications, please contact rkc sales office or the agent. 1.3.1 z-tio module suffix code z-tio-a □ □□□□ / □□ □□...
Page 13
1. Outline ims01t04-e6 1-5 output code table output type code output type code voltage output (0 to 1 v dc) 3 voltage output (1 to 5 v dc) 6 voltage output (0 to 5 v dc) 4 current output (0 to 20 ma dc) 7 voltage output (0 to 10 v dc) 5 current output (4 to 20 ma dc) 8 range code table [thermoco...
Page 14
1. Outline ims01t04-e6 1-6 quick start code 2 (initial setting code) quick start code 2 tells the factory to ship with each parameter preset to the values detailed as specified by the customer. Quick start code is not necessarily specified when ordering, unless the preset is requested. These param...
Page 15: 1.3.2 Z-Dio Module
1. Outline ims01t04-e6 1-7 1.3.2 z-dio module z-dio-a □-□□/□-□□□□□□□ (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) suffix code specifications hardware coding only quick start code1 (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) wiring type terminal type t connector type c digital input (di) none n 8 points a none n digital outp...
Page 16
1. Outline ims01t04-e6 1-8 continued from the previous page. do assignment code table [do1 to do4] code do1 do2 do3 do4 00 no assignment 01 do1 manual output do2 manual output do3 manual output do4 manual output 02 event 1 comprehensive output 1 event 2 comprehensive output 2 event 3 comprehensive...
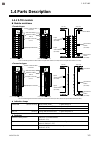
Page 17: 1.4 Parts Description
1. Outline ims01t04-e6 1-9 1.4 parts description 1.4.1 z-tio module module mainframe * the 2-channel type does not have neither an input select switch (for ch3) and nor an input select switch (for ch4). ** the 2-channel type does not have neither an input select switch (for ch3) and nor an input s...
Page 18
1. Outline ims01t04-e6 1-10 base mounting bracket used to fix the module on din rails and also to fix each module joined together. (base: rear) mounting holes (m3 screw) holes for screws to fix the base to a panel, etc. Customer must provide the m3 screws. Power supply terminals supply power to on...
Page 19: 1.4.2 Z-Dio Module
1. Outline ims01t04-e6 1-11 1.4.2 z-dio module module mainframe indication lamps fail/run [green or red] when normal (run): a green lamp is on self-diagnostic error (fail): a green lamp flashes instrument abnormality (fail): a red lamp is on rx/tx [green] during data send and receive: a green la...
Page 20: Memo
Ims01t04-e6 1-12 memo.
Page 21: Setting
Setting procedure to operation ims01t04-e6 2-1 1.1 ******** .............................................................................................. 1-2 1.2 ******* ................................................................................................ 1-3 1.3 ****** ....................
Page 22
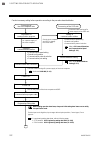
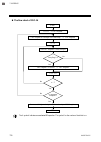
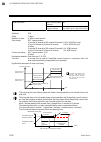
2. Setting procedure to operation 2-2 ims01t04-e6 conduct necessary setting before operation according to the procedure described below. Execute it after turning off a power supply of the srz unit. Processing of the host computer side preparation of communication program power-off turn on the power ...
Page 23
2. Setting procedure to operation ims01t04-e6 2-3 set the control run/stop transfer to the “run.” operation start setting of normal setting data set parameters in normal setting of data. Control run control action type? A position proportioning pid control adjustment of the valve position pid contro...
Page 24: Memo
2-4 ims01t04-e6 memo.
Page 25: Mounting
Mounting ims01t04-e6 3-1 3.1 mounting cautions ........................................................................... 3-2 3.2 dimensions ....................................................................................... 3-4 3.3 important points when joining modules ...........................
Page 26: 3.1 Mounting Cautions
3. Mounting 3-2 ims01t04-e6 3.1 mounting cautions this chapter describes installation environment, mounting cautions, dimensions and mounting procedures. (1) this instrument is intended to be used under the following environmental conditions. (iec 61010-1) [overvoltage category ii, pollution degree ...
Page 27
3. Mounting ims01t04-e6 3-3 depth for connector mount type module (connector type) space for connectors and cables must be considered when installing. 76.9 mm approx. 50 mm connector (plug) mounting the joint connector cover it is recommended to use a plastic cover on the connector on both sides...
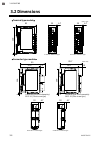
Page 28: 3.2 Dimensions
3. Mounting 3-4 ims01t04-e6 3.2 dimensions terminal type module connector type module connector type (sold separately): srzp-01 [front-screw type] 76.9 2.9 100 5 99 2.9 100 5 76.9 89.7 connector type (sold separately): srzp-02 [side-screw type] z-tio-at: 4-channel type 30 6.7 z-tio-bt: 2-channel...
Page 29
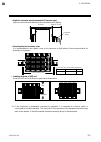
3. Mounting ims01t04-e6 3-5 3.3 important points when joining modules when joining the z-tio and z-dio modules, note the following: the maximum number of joined t-tio-a/b modules that can be connected to one host computer is 16. Srz unit example 1: when joining only z-tio-a modules (up to 16 modules...
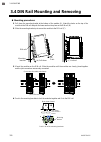
Page 30
3. Mounting 3-6 ims01t04-e6 3.4 din rail mounting and removing mounting procedures 1. Pull down the mounting bracket at the bottom of the module (a). Attach the hooks on the top of the module to the din rail and push the lower section into place on the din rail (b). 2. Slide the mounting bracket u...
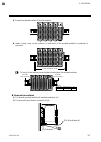
Page 31
3. Mounting ims01t04-e6 3-7 5. Connect the required number of function modules. 6. Install a plastic cover on the connector on both sides of the mounted modules for protection of connectors. Joint connector cover to firmly fix the modules, use end plates on both sides of the mounted modules. End pla...
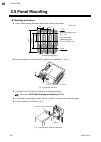
Page 32: 3.5 Panel Mounting
3. Mounting 3-8 ims01t04-e6 3.5 panel mounting mounting procedures 1. Refer to the mounting dimensions below when selecting the location. (unit: mm) (30) 30 0.2 38 70 0. 2 10 0 m3 recommended screw: m3 10 mounting dimensions base recommended tightening torque: 0.3 n・m (3 kgf・cm) 2. Remove the ...
Page 33: Wiring
Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-1 4.1 wiring cautions ................................................................................ 4-2 4.2 connecting precautions ................................................................... 4-4 4.3 terminal configuration .................................................
Page 34: 4.1 Wiring Cautions
4. Wiring 4-2 ims01t04-e6 4.1 wiring cautions this chapter describes wiring cautions, wiring layout and wiring of terminals. for thermocouple input, use the appropriate compensation wire. for rtd input, use low resistance lead wire with no difference in resistance between the three lead wires (3...
Page 35
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-3 when tightening a screw of the instrument, make sure to fit the screwdriver properly into the screw head mounted tilted or flat as shown in the right figure. Tightening the screw with excessive torque may damage the screw thread. for the connector type module, use the fol...
Page 36: 4.2 Connecting Precautions
4. Wiring 4-4 ims01t04-e6 4.2 connecting precautions connect connectors correctly in the right position. If it is forcibly pushed in with pins in the wrong positions, the pins may be bent resulting in instrument failure. when connecting or disconnecting the connectors, do not force it too far to...
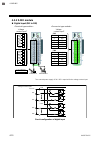
Page 37: 4.3 Terminal Configuration
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-5 4.3 terminal configuration 4.3.1 z-tio module input/output terminals z-tio-at 4-channel type thermocouple input tc rtd input rtd a b b voltage/current input in relay contact output no out3 triac output triac out3 voltage pulse/ current/voltage output out3 open collector o...
Page 38
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-6 thermocouple input tc 2 1 rtd input rtd a b b 3 2 1 voltage/current input in 2 1 relay contact output no out3 5 4 triac output triac out3 5 4 voltage pulse/ current/voltage output out3 5 4 open collector output out3 5 4 ch3 relay contact output no out4 5 4 triac output tria...
Page 39
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-7 input/output configurations by control specifications control type ch1 output terminal (out1) ch2 output terminal (out2) ch3 output terminal (out3) ch4 output terminal (out4) ch1 input terminal (input1) ch2 input terminal (input2) ch3 input terminal (input3) ch4 input termi...
Page 40
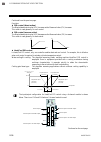
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-8 power supply terminals, communication terminals (common to both terminal and connector type module) connecting to the base terminals as an example, the method of connecting to the power terminals (terminal numbers 1 and 2) is shown below. 1. Remove the module mainframe ...
Page 41
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-9 ct input connector (optional) 1 2 3 4 4 3 2 1 pin no. Description 1 2 ct4 (ch4) 3 4 ct3 (ch3) pin no. Description 1 2 ct2 (ch2) 3 4 ct1 (ch1) for the ct input, use the following our ct cable (with socket) and current transformer (ct). [sold separately] cable type: w-bw-03...
Page 42: 4.3.2 Z-Dio Module
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-10 4.3.2 z-dio module digital input (di1 to di8) * an external power supply of 24 v dc is required for the voltage contact input. Voltage contact input di1 com com 24 v dc di4 di5 di8 circuit configuration of digital input cn3 pin no. Description 1 di4 2 di3 3 di2 4 di1 5 c...
Page 43
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-11 digital output (do1 to do8) * an external power supply of 12 to 24 v dc is required for the open collector output. Relay contact output do1 do4 load com load do5 do8 load load com open collector output com do1 12 to 24 v dc do4 load com load do5 do8 load load circuit con...
Page 44: Warning
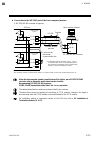
4. Wiring 4-12 ims01t04-e6 4.4 connection to host computer configurations that can be connected to a host computer examples of configurations of srz units that can be connected to a host computer are shown below. “srz unit” refers to a unit consisting of only z-tio modules, or a unit in which z-ti...
Page 45
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-13 when two or more srz units are connected (distributed arrangement) regardless of the number of units, a maximum of 16 srz z-tio modules and a maximum of 16 srz z-dio modules can be connected respectively. However, the maximum number of srz modules that can be connected o...
Page 46
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-14 terminal number and signal details terminal no. Signal name symbol 3 send data/receive data t/r (a) 4 send data/receive data t/r (b) 5 signal ground sg wiring figure connection to the rs-485 port of the host computer (master) host computer (master) rs-485 pair wire s...
Page 47
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-15 connection to the rs-232c port of the host computer (master) a rs-232c/rs-485 converter is required. Host computer (master) rs-485 pair wire r sg t/r (b) t/r (a) sg 5 r t/r (a) 3 4 t/r (b) rs-232c sg 5 t/r (a) 3 4 t/r (b) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) z-tio module (slave) z-tio mo...
Page 48
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-16 connection to the usb of the host computer (master) when the host computer (os: windows 98se or higher) is corresponding to the usb connector, our communication converter com-k (sold separately) can be used. Rs-485 sg 5 t/r (a) 3 4 t/r (b) 5 1 sg 3 t/r(b) 2 t/r (a) 4 unu...
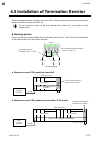
Page 49
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-17 4.5 installation of termination resistor when connecting termination resistors to each end of the rs-485 communication line, follow the procedure below to connect the resistor to the srz end. For the termination resistor on the host computer side, connect it so as to satis...
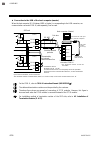
Page 50
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-18 when two or more srz units are connected (distributed arrangement) rs-485 rs-485 termination resistor host computer (master) srz unit (slave) z-tio module z-dio module srz unit (slave) z-tio module z-dio module rs-485 z-tio module srz unit (slave) internal communication ...
Page 51
4. Wiring ims01t04-e6 4-19 4.6 connections for loader communication each function module (z-tio, z-dio) is equipped standard with a loader communication connector. The module loader communication connector, our com-k usb communication converter (sold separately) 1 , and a personal computer can be co...
Page 52: Memo
4-20 ims01t04-e6 memo.
Page 53: Settings
Settings before operation ims01t04-e6 5-1 5.1 module address setting ................................................................... 5-2 5.2 protocol selections and communication speed setting ................... 5-3 5.3 operating precautions ........................................................
Page 54: 5.1 Module Address Setting
5. Settings before operation 5-2 ims01t04-e6 5.1 module address setting set communication setting before mounting and wiring of the z-tio module. Do not separate the module mainframe from the base with the power turned on. If so, instrument failure may result. address setting switches set an addre...
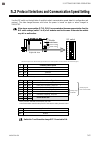
Page 55
5. Settings before operation ims01t04-e6 5-3 5.2 protocol selections and communication speed setting use the dip switch on the right side of module to select communication speed, data bit, configuration and protocol. The data changes become valid when the power is turned on again or when changed to ...
Page 56: 5.3 Operating Precautions
5. Settings before operation 5-4 ims01t04-e6 5.3 operating precautions check the following items before starting operation, then turn on the power. power on when first powered on, the unit starts with the operation mode set to “control” and the run/stop switch set to stop (control is stopped) (fai...
Page 57
5. Settings before operation ims01t04-e6 5-5 5.4 communication requirements processing times during data send/receive when the host computer is using either the polling or selecting procedure for communication, the following processing times are required for controller to send data: - response wai...
Page 58
5. Settings before operation ims01t04-e6 5-6 rs-485 (2-wire system) send/receive timing rs-485 communication is conducted through two wires, therefore the transmission and reception of data requires precise timing. polling procedure a: response send time after the controller receives [enq] + int...
Page 59: Rkc
Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-1 6.1 polling .............................................................................................. 6-2 6.1.1 polling procedures .................................................................................... 6-2 6.1.2 polling procedures example ...........
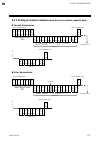
Page 60: 6.1 Polling
6. Rkc communication 6-2 ims01t04-e6 6.1 polling rkc communication uses the polling/selecting method to establish a data link. The basic procedure is followed ansi x3.28-1976 subcategories 2.5 and b1 basic mode data transmission control procedure (fast selecting is the selecting method used in srz)....
Page 61
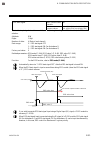
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-3 (1) data link initialization host computer sends eot to the controllers to initiate data link before polling sequence. (2) data sent from host computer - polling sequence the host computer sends the polling sequence in the following two types of formats: format...
Page 62
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-4 3. Identifier (2 digits) the identifier specifies the type of data that is requested from the srz. Always attach the enq code to the end of the identifier. Refer to 6.4 communication data list (p. 6-13). 4. Enq the enq is the transmission control character that i...
Page 63
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-5 memory area soak time monitor and area soak time become the following data: when data range is 0 hour 00 minute to 99 hours 59 minutes: data range is 0:00 to 99:59, punctuation of time unit is expressed in colon “: (3ah).” when data range is 0 minute 00 secon...
Page 64
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-6 (6) ack (acknowledgment) an acknowledgment ack is sent by the host computer when data received is correct. When the srz receives ack from the host computer, the srz will send any remaining data of the next identifier without additional action from the host comput...
Page 65
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-7 6.1.2 polling procedure example (when the host computer requests data) normal transmission e o t 0 1 k 1 s 1 e n q a c k 04h 30h 31h 4bh 31h 53h 31h 05h 06h s t x s 1 0 1 4 0 0 . 0 e t x b c c 02h 53h 31h 30h 31h 20h 20h 20h 34h 30h 30h 2eh 30h 03h e o t 04h s ...
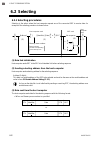
Page 66: 6.2 Selecting
6. Rkc communication 6-8 ims01t04-e6 6.2 selecting 6.2.1 selecting procedures selecting is the action where the host computer requests one of the connected srz to receive data. An example of the selecting procedure is shown below: host computer send [ ] srz send host computer send [data] [bcc] (1) (...
Page 67
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-9 when the memory area number is specified for the stx, memory area number, identifier, data, etb, etx and bcc, refer to 6.1 polling (p. 6-2). If the length of send data (from stx to bcc) exceeds 136 bytes, it is divided into blocks by etb. In this case, the succ...
Page 68
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-10 the data that receipt of letter is impossible the srz sends nak when received a following data. Plus sign and the data that gained plus sing only minus sign (there is no figure) . Only minus sign and decimal point (period) (4) ack (acknowledgment) an acknowledg...
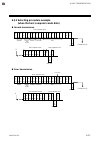
Page 69
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-11 6.2.2 selecting procedure example (when the host computer sends data) normal transmission e o t 0 1 s t x k 1 s 1 0 1 4 0 0 . 0 e t x b c c 04h 30h 31h 02h 4bh 31h 53h 31h 30h 31h 20h 20h 20h 34h 30h 30h 2eh 30h 03h a c k 06h s t x p 1 0 1 e t x b c c e o t 02...
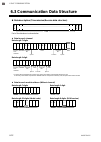
Page 70
6. Rkc communication 6-12 ims01t04-e6 6.3 communication data structure data description (transmission/receive data structure) s t x e t x b c c part of the data above is shown below. data for each channel data length 7 digits 0 1 1 0 0 . 0 , 0 2 ... Data length 1 digit 0 1 , 0 2 * to select data...
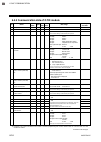
Page 71
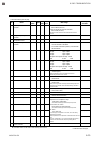
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-13 6.4 communication data list 6.4.1 reference to communication data list no. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 1 model code id 32 ro m model code (character) 2 rom version vr 8 ro m rom version 3 measured value (pv) m1 7...
Page 72
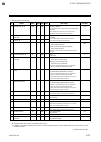
6. Rkc communication 6-14 ims01t04-e6 6.4.2 communication data of z-tio module no. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 1 model code id 32 ro m model code (character) 2 rom version vr 8 ro m rom version 3 measured value (pv) m1 7 ro c input scale low to input...
Page 73
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-15 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 19 memory area soak time monitor tr 7 ro c 0 minutes 00 seconds to 199 minutes 59 seconds: 0:00 to 199:59 (min:sec) 0 hours 00 minutes to 99 hours...
Page 74
6. Rkc communication 6-16 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 36 lba deadband ★ n1 7 r/w c 0 to input span varies with the setting of the decimal point position. 0 (0.0) 37 set value (sv) ★ s1 7 r/w c setting...
Page 75
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-17 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 46 manual reset ★ mr 7 r/w c 100.0 to +100.0 % if the integral function is valid, set to ro (only reading data is possible). When integral acti...
Page 76
6. Rkc communication 6-18 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 62 output distribution bias dw 7 r/w c 100.0 to 100.0 % 0.0 63 output distribution ratio dq 7 r/w c 9.999 to 9.999 1.000 64 proportional cycle...
Page 77
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-19 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 80 eds value learning times nt 7 r/w c 0 to 10 times (0: no learning mode) 1 81 eds start signal nu 1 r/w c 0: eds start signal off 1: eds start s...
Page 78
6. Rkc communication 6-20 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 87 display unit pu 7 r/w c 0: c 1: f use to select the temperature unit for thermocouple (tc) and rtd inputs. Based on model code when not speci...
Page 79
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-21 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 97 event 1 type xa 7 r/w c 0: none 1: deviation high (using sv monitor value) 1 2: deviation low (using sv monitor value) 1 3: deviation high/low ...
Page 80
6. Rkc communication 6-22 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 104 event 2 type xb 7 r/w c 0: none 1: deviation high (using sv monitor value) 1 2: deviation low (using sv monitor value) 1 3: deviation high/low...
Page 81
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-23 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 111 event 3 type xc 7 r/w c 0: none 1: deviation high (using sv monitor value) 1 2: deviation low (using sv monitor value) 1 3: deviation high/low...
Page 82
6. Rkc communication 6-24 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 118 event 4 type xd 7 r/w c 0: none 1: deviation high (using sv monitor value) 1 2: deviation low (using sv monitor value) 1 3: deviation high/low...
Page 83
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-25 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 125 ct ratio xs 7 r/w c 0 to 9999 ctl-6-p-n: 800 ctl-12-s56-10l -n: 1000 126 ct assignment zf 1 r/w c 0: none 3: out3 1: out1 4: out4 2: out2 ch1:...
Page 84
6. Rkc communication 6-26 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 140 action (high) at input error wh 1 r/w c 0: normal control 1: manipulated output value at input error 0 141 action (low) at input error wl 1 r/...
Page 85
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-27 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 157 at differential gap time gh 7 r/w c 0.0 to 50.0 seconds 10.0 158 proportional band adjusting factor [heat-side] kc 7 r/w c 0.01 to 10.00 tim...
Page 86
6. Rkc communication 6-28 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 177 action at feedback resistance (fbr) input error sy 1 r/w c 0: action depending on the valve action at stop 1: control action continued 0 178 f...
Page 87
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-29 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 196 pv transfer function ts 1 r/w c 0: unused 1: used 0 197 operation mode assignment 1 (logic output selection function) logic output 1 to 4 ea 7...
Page 88
6. Rkc communication 6-30 ims01t04-e6 6.4.3 communication data of z-dio module no. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 1 model code id 32 ro m model code (character) 2 rom version vr 8 ro m rom version 3 digital input (di) state 1 l1 7 ro m least significant...
Page 89
6. Rkc communication ims01t04-e6 6-31 continued from the previous page. No. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value 15 do output distribution ratio o9 7 r/w c 9.999 to 9.999 1.000 16 do proportional cycle time v0 7 r/w c 0.1 to 100.0 seconds relay contact outp...
Page 90: Memo
6-32 ims01t04-e6 memo.
Page 91: Modbus
Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-1 7.1 communication protocol .................................................................. 7-2 7.1.1 message format ........................................................................................ 7-2 7.1.2 function code ................................................
Page 92: 7.1 Communication Protocol
7. Modbus 7-2 ims01t04-e6 7.1 communication protocol the master controls communication between master and slave. A typical message consists of a request (query message) sent from the master followed by an answer (response message) from the slave (srz). When master begins data transmission, a set of ...
Page 93: 7.1.2 Function Code
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-3 7.1.2 function code function code contents function code (hexadecimal) function contents 03h read holding registers measured value, control output value, current transformer input measured value, event status, etc. 06h preset single register set value, pid constants, even...
Page 94: 7.1.4 Slave Responses
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-4 7.1.4 slave responses (1) normal response in the response message of the read holding registers, the slave returns the read out data and the number of data items with the same slave address and function code as the query message. in the response message of the preset si...
Page 95: 7.1.5 Calculating Crc-16
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-5 7.1.5 calculating crc-16 the cyclic redundancy check (crc) is a 2 byte (16-bit) error check code. After constructing the data message, not including start, stop, or parity bit, the master calculates a crc code and appends this to the end of the message. The slave will calcu...
Page 96
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-6 the flow chart of crc-16 start ffffh crc register 0 n shift crc register 1 bit to the right carry flag is 1 no yes crc register a001h crc register n + 1 n no yes n 7 no yes is message complete ? End crc register next byte of the message crc register revers...
Page 97
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-7 example of a crc calculation in the ‘c’ language this routine assumes that the data types ‘uint16’ and ‘uint8’ exists. Theses are unsigned 16-bit integer (usually an ‘unsigned short int’ for most compiler types) and unsigned 8-bit integer (unsigned char). ‘z_p’ is a point...
Page 98
7. Modbus 7-8 ims01t04-e6 7.2 register read and write 7.2.1 read holding registers [03h] the query message specifies the starting register address and quantity of registers to be read. The contents of the holding registers are entered in the response message as data, divided into two parts: the high...
Page 99
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-9 7.2.2 preset single register [06h] the query message specifies data to be written into the designated holding register. The write data is arranged in the query message with high-order 8-bit first and low-order 8-bit next. Only r/w holding registers can be specified. Example...
Page 100
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-10 7.2.3 diagnostics (loopback test) [08h] the master’s query message will be returned as the response message from the slave. This function checks the communication system between the master and slave. Example: loopback test for slave address 1 query message slave address 01...
Page 101
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-11 7.2.4 preset multiple registers [10h] the query message specifies the starting register address and quantity of registers to be written. The write data is arranged in the query message with high-order 8-bit first and low-order 8-bit next. Only r/w holding registers can be ...
Page 102
7. Modbus 7-12 ims01t04-e6 7.3 data processing precautions the numeric range of data used in modbus protocol is 0000h to ffffh. Only the set value within the setting range is effective. Ffffh represents 1. the modbus protocol does not recognize data with decimal points during communication. Exa...
Page 103
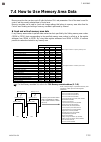
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-13 7.4 how to use memory area data memory area function can store up to 8 individual sets of svs and parameters. One of the areas is used for control, and the currently selected area is control area. Memory area data can be used to check and change settings that belong to mem...
Page 104
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-14 [example 1] when data on the event 1 set value in memory area 2 of ch1 is read 1. The memory area number, “2” is written to the ch1 setting memory area number (0500h). Data in memory area 2 is called up to the ch1 register addresses. Ch1 register addresses setting memory a...
Page 105
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-15 control area transfer any memory area used for control is specified by the memory area transfer (006eh to 0071h). The area (0076h to 00c5h) now used for control is called control area. The memory area number (control area) can be changed at either run or stop. Register a...
Page 106
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-16 [example] when performing control by calling up data in memory area 3 of ch1 1. The memory area number, “3” is written to the memory area transfer (006eh). Data in memory area 3 is called up to the ch1 register addresses. Ch1 register addresses memory area transfer 006eh 3...
Page 107
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-17 7.5 how to use data mapping when this communication method is used, 16 types of data (mapping data) can be specified as desired for the z-tio and z-dio modules, and read/write can be performed continuously. Z-tio module z-dio module register address to specify mapping data...
Page 108
7. Modbus 7-18 ims01t04-e6 7.6 communication data list 7.6.1 reference to communication data list no. Name chan- nel resister address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 1 measured value (pv) ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 0000 0001 0002 0003 0 1 2 3 ro c input scale low to input scale hig...
Page 109
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-19 7.6.2 communication data of z-tio module no. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 1 measured value (pv) ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 0000 0001 0002 0003 0 1 2 3 ro c input scale low to input scale high varies with the setting of t...
Page 110
7. Modbus 7-20 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 10 burnout state monitor ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 0021 0022 0023 0024 33 34 35 36 ro c 0: off 1: on 11 event 1 state monitor ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 0025 0026 ...
Page 111
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-21 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 22 unused 0045 ・ ・ ・ 0060 69 ・ ・ ・ 96 23 pid/at transfer ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 0061 0062 0063 0064 97 98 99 100 r/w c 0: pid control 1: autotuning (...
Page 112
7. Modbus 7-22 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 36 proportional band [heat-side] ★ ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 0092 0093 0094 0095 146 147 148 149 r/w c tc/rtd inputs: 0 to input span (unit: c [f]) va...
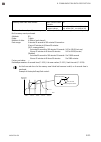
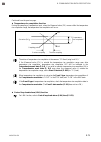
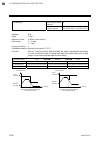
Page 113
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-23 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 44 manual reset ★ ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 00b2 00b3 00b4 00b5 178 179 180 181 r/w c 100.0 to +100.0 % if the integral function is valid, set to ro (o...
Page 114
7. Modbus 7-24 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 56 rs bias * ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 00e2 00e3 00e4 00e5 226 227 228 229 r/w c input span to +input span varies with the setting of the decimal point...
Page 115
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-25 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 66 eds mode (for disturbance 1) ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 010a 010b 010c 010d 266 267 268 269 r/w c 0: no function 1: eds function mode 2: learning mode...
Page 116
7. Modbus 7-26 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 81 startup tuning (st) ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 0146 0147 0148 0149 326 327 328 329 r/w c 0: st unused 1: execute once * 2: execute always * when the s...
Page 117
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-27 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 87 decimal point position ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 017e 017f 0180 0181 382 383 384 385 r/w c 0: no decimal place 1: one decimal place 2: two decimal pl...
Page 118
7. Modbus 7-28 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 96 event 1 type ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 01a2 01a3 01a4 01a5 418 419 420 421 r/w c 0: none 1: deviation high (using sv monitor value) 1 2: deviation lo...
Page 119
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-29 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 103 event 2 type ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 01be 01bf 01c0 01c1 446 447 448 449 r/w c 0: none 1: deviation high (using sv monitor value) 1 2: deviation l...
Page 120
7. Modbus 7-30 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 110 event 3 type ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 01da 01db 01dc 01dd 474 475 476 477 r/w c 0: none 1: deviation high (using sv monitor value) 1 2: deviation l...
Page 121
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-31 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 117 event 4 type ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 01f6 01f7 01f8 01f9 502 503 504 505 r/w c 0: none 1: deviation high (using sv monitor value) 1 2: deviation l...
Page 122
7. Modbus 7-32 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 124 ct ratio ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 0212 0213 0214 0215 530 531 532 533 r/w c 0 to 9999 ctl-6-p-n: 800 ctl-12-s56- 10l-n: 1000 125 ct assignment ch1 ...
Page 123
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-33 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 135 undershoot suppression factor ch1 unused ch3 unused 023e unused 0240 unused 574 unused 576 unused r/w c 0.000 to 1.000 water cooling: 0.10...
Page 124
7. Modbus 7-34 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 149 output change rate limiter (down) [cool-side] ch1 unused ch3 unused 0276 unused 0278 unused 630 unused 632 unused r/w c 0.0 to 100.0 % of ...
Page 125
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-35 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 163 proportional band limiter (high) [heat-side] ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 02ae 02af 02b0 02b1 686 687 688 689 r/w c tc/rtd inputs: 0 to input span (uni...
Page 126
7. Modbus 7-36 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 178 control motor time ch1 unused ch3 unused 02ea unused 02ec unused 746 unused 748 unused r/w c 5 to 1000 seconds 10 179 integrated output ...
Page 127
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-37 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 191 setting change rate limiter unit time ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 031e 031f 0320 0321 798 799 800 801 r/w c 1 to 3600 seconds 60 192 soak time unit ch...
Page 128
7. Modbus 7-38 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 203 address of interacting modules ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 034e 034f 0350 0351 846 847 848 849 r/w c 1 (interact with its own module address) 0 to 99...
Page 129
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-39 7.6.3 communication data of z-dio module no. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 1 digital input (di) state 0000 0 ro m bit data bit 0: di1 bit 1: di2 bit 2: di3 bit 3: di4 bit 4: di5 bit 5: di6 bit 6: di7 bit 7: d...
Page 130
7. Modbus 7-40 ims01t04-e6 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 9 do output distribution selection ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 ch5 ch6 ch7 ch8 0048 0049 004a 004b 004c 004d 004e 004f 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 r/w c 0: do...
Page 131
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-41 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 19 do output assignment 1 [do1 to do4] 00a8 168 r/w m 0 to 13 (refer to page 8-158) based on model code when not specifying: 0 20 do output ...
Page 132
7. Modbus 7-42 ims01t04-e6 7.6.4 memory area data address (z-tio) the register addresses, 0500h to 0553h are used for checking and changing each set value belonging to the memory area. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 1 setting memory a...
Page 133
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-43 continued from the previous page. No. Name chan- nel register address attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hex dec 13 proportional band [cool-side] ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 0530 0531 0532 0533 1328 1329 1330 1331 r/w c tc/rtd inputs: 1 (0.1) to input span (unit: c ...
Page 134
7. Modbus 7-44 ims01t04-e6 7.6.5 data mapping address (z-tio, z-dio) register address for data mapping no. Name register address number of data items attri- bute data range factory set value hex dec 1 register address setting 1 read/write address : 1500h 1000 4096 1 r/w decimal: 1 to 4095 (1: no...
Page 135
7. Modbus ims01t04-e6 7-45 register address for data read/writes no. Name register address number of data items attri- bute data range factory set value hex dec 1 data specified by register address setting 1 (1000h) 1500 5376 1 differs depending on data specified. 2 data specified by register addr...
Page 136: Memo
7-46 ims01t04-e6 memo.
Page 137: Communication
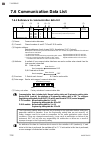
Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-1 8.1 reference to communication data contents ................................... 8-2 8.2 communication data of z-tio module ............................................. 8-3 8.2.1 normal setting data items ..................................................
Page 138: 8.1
8. Communication data description 8-2 ims01t04-e6 8.1 reference to communication data contents (1) name: communication data name (2) rkc communication identifier: communication identifier of rkc communication (3) modbus register address: modbus communication data register addresses of each channel t...
Page 139
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-3 8.2 communication data of z-tio module 8.2.1 normal setting data items model code rkc communication identifier id modbus register address this value is the type identifier code of the z-tio module. Attribute: ro digits: 32 digits number of data: 1 (d...
Page 140
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-4 comprehensive event state rkc communication identifier aj modbus register address ch1: 0004h (4) ch3: 0006h (6) ch2: 0005h (5) ch4: 0007h (7) each event state such as event 1 to event 4, heater break alarm, temperature rise completion or burnout is e...
Page 141
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-5 operation mode state monitor rkc communication identifier l0 modbus register address ch1: 0008h (8) ch3: 000ah (10) ch2: 0009h (9) ch4: 000bh (11) each operation mode state of the z-tio module is expressed in bit data items. Attribute: ro digits: 7 d...
Page 142
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-6 error code rkc communication identifier er modbus register address 000ch (12) each error state of the z-tio module is expressed in bit data items. Attribute: ro digits: 7 digits number of data: 1 (data of each module) data range: 0 to 63 (bit data) t...
Page 143
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-7 manipulated output value (mv) monitor [cool-side] rkc communication identifier o2 modbus register address ch1: 0011h (17) ch3: 0013h (19) ch2: unused ch4: unused cool-side output value of heat/cool pid control. Attribute: ro digits: 7 digits number o...
Page 144
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-8 remote setting (rs) input value monitor rkc communication identifier s2 modbus register address ch1: 001dh (29) ch3: 001fh (31) ch2: 001eh (30) ch4: 0020h (32) input value used in remote mode. Monitors the sv selected by the remote sv selection funct...
Page 145
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-9 event 1 state monitor rkc communication identifier aa modbus register address ch1: 0025h (37) ch3: 0027h (39) ch2: 0026h (38) ch4: 0028h (40) event 2 state monitor rkc communication identifier ab modbus register address ch1: 0029h (41) ch3: 002bh (43...
Page 146
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-10 output state monitor rkc communication identifier q1 modbus register address 0039h (57) on/off state of output (out1 to out4) is expressed as a bit image in decimal number. Attribute: ro digits: 7 digits number of data: 1 (data of each module) data ...
Page 147
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-11 memory area soak time monitor rkc communication identifier tr modbus register address ch1: 003ah (58) ch3: 003ch (60) ch2: 003bh (59) ch4: 003dh (61) monitors the time elapsed for memory area operation (soak time) when ramp/soak control by using mul...
Page 148
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-12 integrated operating time monitor rkc communication identifier ut modbus register address 003eh (62) this value is an integrated operating time of the z-tio module. Attribute: ro digits: 7 digits number of data: 1 (data of each module) data range: 0...
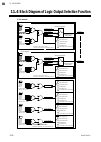
Page 149
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-13 logic output monitor 1 rkc communication identifier ed logic output monitor 2 rkc communication identifier ee logic output monitor modbus register address 0044h (68) each logic output state of the z-tio module is expressed in bit data items. Attribu...
Page 150
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-14 pid/at transfer rkc communication identifier g1 modbus register address ch1: 0061h (97) ch3: 0063h (99) ch2: 0062h (98) ch4: 0064h (100) activation or deactivation of the autotuning (at) function is selected. Attribute: r/w digits: 1 digit number of...
Page 151
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-15 continued from the previous page. requirements for autotuning (at) cancellation if the autotuning (at) is canceled according to any of the following conditions, the controller immediately changes to pid control. The pid values will be the same as ...
Page 152
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-16 auto/manual transfer rkc communication identifier j1 modbus register address ch1: 0065h (101) ch3: 0067h (103) ch2: 0066h (102) ch4: 0068h (104) use to transfer the auto mode or manual mode. Auto mode: automatic control is performed. Manual mode: th...
Page 153
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-17 remote/local transfer rkc communication identifier c1 modbus register address ch1: 0069h (105) ch3: 006bh (107) ch2: 006ah (106) ch4: 006ch (108) use to transfer the remote mode or local mode. Local mode: control is performed at the local set value ...
Page 154
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-18 memory area transfer rkc communication identifier za modbus register address ch1: 006eh (110) ch3: 0070h (112) ch2: 006fh (111) ch4: 0071h (113) this item selects the memory area (control area) to use for control. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits num...
Page 155
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-19 interlock release rkc communication identifier ar modbus register address ch1: 0072h (114) ch3: 0074h (116) ch2: 0073h (115) ch4: 0075h (117) the event state is turned off when the event on state is continued by the event interlock function. Attribu...
Page 156
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-20 event 1 set value (ev1) rkc communication identifier a1 modbus register address ch1: 0076h (118) ch3: 0078h (120) ch2: 0077h (119) ch4: 0079h (121) event 2 set value (ev2) rkc communication identifier a2 modbus register address ch1: 007ah (122) ch3:...
Page 157
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-21 control loop break alarm (lba) time rkc communication identifier a5 modbus register address ch1: 0086h (134) ch3: 0088h (136) ch2: 0087h (135) ch4: 0089h (137) the lba time sets the time required for the lba function to determine there is a loop fai...
Page 158
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-22 lba deadband rkc communication identifier n1 modbus register address ch1: 008ah (138) ch3: 008ch (140) ch2: 008bh (139) ch4: 008dh (141) control loop break alarm (lba) deadband gives a neutral zone to prevent the control loop break alarm (lba) from ...
Page 159
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-23 set value (sv) [local set value (sv)] rkc communication identifier s1 modbus register address ch1: 008eh (142) ch3: 0090h (144) ch2: 008fh (143) ch4: 0091h (145) set value (sv) is desired value of the control. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits number ...
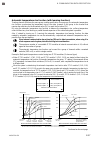
Page 160
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-24 continued from the previous page. Function: in heat/cool pid control, only one module enables heat and cool control. For example, this is effective when cool control is required in extruder cylinder temperature control. Manipulated output (mv) 100 %...
Page 161
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-25 derivative time [heat-side] rkc communication identifier d1 modbus register address ch1: 009ah (154) ch3: 009ch (156) ch2: 009bh (155) ch4: 009dh (157) derivative time [cool-side] rkc communication identifier d2 modbus register address ch1: 00aah (1...
Page 162
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-26 control response parameter rkc communication identifier ca modbus register address ch1: 009eh (158) ch3: 00a0h (160) ch2: 009fh (159) ch4: 00a1h (161) the control response for the set value (sv) change can be selected among slow, medium, and fast. A...
Page 163
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-27 overlap/deadband rkc communication identifier v1 modbus register address ch1: 00aeh (174) ch3: 00b0h (176) ch2: 00afh (175) ch4: 00b1h (177) this is the overlapped range of proportional bands (on the heat and cool sides) or the deadband range when h...
Page 164
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-28 manual reset rkc communication identifier mr modbus register address ch1: 00b2h (178) ch3: 00b4h (180) ch2: 00b3h (179) ch4: 00b5h (181) in order to eliminate the offset occurring in proportional (p) control, the manipulated output value is manually...
Page 165
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-29 setting change rate limiter (up) rkc communication identifier hh modbus register address ch1: 00b6h (182) ch3: 00b8h (184) ch2: 00b7h (183) ch4: 00b9h (185) setting change rate limiter (down) rkc communication identifier hl modbus register address c...
Page 166
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-30 area soak time rkc communication identifier tm modbus register address ch1: 00beh (190) ch3: 00c0h (192) ch2: 00bfh (191) ch4: 00c1h (193) this is the time required until transferred to the link area number when performing ramp/soak control. Attribu...
Page 167
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-31 link area number rkc communication identifie lp modbus register address ch1: 00c2h (194) ch3: 00c4h (196) ch2: 00c3h (195) ch4: 00c5h (197) memory area numbers for linking the corresponding memory areas are set when ramp/soak control is performed. A...
Page 168
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-32 heater break alarm (hba) set value rkc communication identifier a7 modbus register address ch1: 00c6h (198) ch3: 00c8h (200) ch2: 00c7h (199) ch4: 00c9h (201) hba is to set the set values for the heater break alarm (hba) function. The hba function d...
Page 169
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-33 continued from the previous page. Heater break alarm (hba) type b can be used with continuous control output (voltage/current continuous output). The hba function assumes that the heater current value is proportional* to the control output value of ...
Page 170
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-34 heater break determination point rkc communication identifier ne modbus register address ch1: 00cah (202) ch3: 00cch (204) ch2: 00cbh (203) ch4: 00cdh (205) set the heater break determination point for the heater break alarm (hba) type b. Attribute:...
Page 171
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-35 pv bias rkc communication identifier pb modbus register address ch1: 00d2h (210) ch3: 00d4h (212) ch2: 00d3h (211) ch4: 00d5h (213) pv bias adds bias to the measured value (pv). The pv bias is used to compensate the individual variations of the sens...
Page 172
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-36 pv low input cut-off rkc communication identifier dp modbus register address ch1: 00deh (222) ch3: 00e0h (224) ch2: 00dfh (223) ch4: 00e1h (225) pv low input cut-off is used with square root extraction function. The measured value less than the pv l...
Page 173
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-37 rs digital filter rkc communication identifier f2 modbus register address ch1: 00e6h (230) ch3: 00e8h (232) ch2: 00e7h (231) ch4: 00e9h (233) this item is the time of the first-order lag filter to eliminate noise against the remote setting input. At...
Page 174
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-38 output distribution selection rkc communication identifier dv modbus register address ch1: 00eeh (238) ch3: 00f0h (240) ch2: 00efh (239) ch4: 00f1h (241) select whether or not the manipulated output value of the specified master channel is output fr...
Page 175
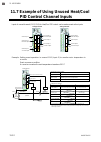
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-39 continued from the previous page. operation flow example: using two z-tio modules (4ch type) master/slave: master/slave module address ch input output master channel (heater 2) module address 0 ch1 sensor input control output slave channel (heater...
Page 176
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-40 output distribution bias rkc communication identifier dw modbus register address ch1: 00f2h (242) ch3: 00f4h (244) ch2: 00f3h (243) ch4: 00f5h (245) the bias which is added to the manipulated output value of the master channel that is distributed to...
Page 177
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-41 minimum on/off time of proportioning cycle rkc communication identifier vi modbus register address ch1: 00feh (254) ch3: 0100h (256) ch2: 00ffh (255) ch4: 0101h (257) this is the minimum on/off time of the time proportioning cycle. Attribute: r/w di...
Page 178
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-42 manual manipulated output value rkc communication identifier on modbus register address ch1: 0102h (258) ch3: 0104h (260) ch2: 0103h (259) ch4: 0105h (261) use to set the output value in the manual control. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits number of ...
Page 179
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-43 area soak time stop function rkc communication identifier rv modbus register address ch1: 0106h (262) ch3: 0108h (264) ch2: 0107h (263) ch4: 0109h (265) select the event for which the area soak time is to be stopped when an event state occurs. Attri...
Page 180
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-44 eds mode (for disturbance 1) rkc communication identifier ng modbus register address ch1: 010ah (266) ch3: 010ch (268) ch2: 010bh (267) ch4: 010dh (269) eds mode (for disturbance 2) rkc communication identifier nx modbus register address ch1: 010eh ...
Page 181
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-45 continued from the previous page. For the eds action time, set the approximate time for a single disturbance response to converge. This time will be automatically computed when tuning is performed, and will be the action time of the eds control. In ...
Page 182
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-46 continued from the previous page. requirements for normal end and suspending [normal end] when the eds action time elapses after eds control starts following eds start signal input. when a new eds start signal is input (in this case, eds contr...
Page 183
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-47 continued from the previous page. Example: eds action selection when the number of learning times is set at 3 (when there is one disturbance pattern) if it is impossible to satisfy a control response to the last learning result, the learning can be ...
Page 184
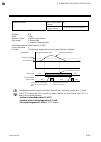
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-48 eds value 1 (for disturbance 1) rkc communication identifier ni modbus register address ch1: 0112h (274) ch3: 0114h (276) ch2: 0113h (275) ch4: 0115h (277) eds value 1 (for disturbance 2) rkc communication identifier nj modbus register address ch1: ...
Page 185
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-49 eds transfer time (for disturbance 1) rkc communication identifier nn modbus register address ch1: 0122h (290) ch3: 0124h (292) ch2: 0123h (291) ch4: 0125h (293) eds transfer time (for disturbance 2) rkc communication identifier no modbus register a...
Page 186
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-50 eds action wait time (for disturbance 1) rkc communication identifier nr modbus register address ch1: 0132h (306) ch3: 0134h (308) ch2: 0133h (307) ch4: 0135h (309) eds action wait time (for disturbance 2) rkc communication identifier ny modbus regi...
Page 187
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-51 eds start signal rkc communication identifier nu modbus register address ch1: 013eh (318) ch3: 0140h (320) ch2: 013fh (319) ch4: 0141h (321) this is the input signal to start or end the mode (tuning, learning, and eds function) of eds mode selection...
Page 188
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-52 operation mode rkc communication identifier ei modbus register address ch1: 0142h (322) ch3: 0144h (324) ch2: 0143h (323) ch4: 0145h (325) this mode is used to select “unused,” “monitor,” “monitor event function,” or “control” for each channel. At...
Page 189
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-53 startup tuning (st) rkc communication identifier st modbus register address ch1: 0146h (326) ch3: 0148h (328) ch2: 0147h (327) ch4: 0149h (329) use to set the number of execution times of startup tuning (st). Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits number o...
Page 190
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-54 continued from the previous page. caution for using the startup tuning (st) for startup tuning (st) at power on or transfer from stop to run, always set the heater power to on simultaneously with the start of tuning or before the start of tuning...
Page 191
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-55 continued from the previous page. procedure for using the startup tuning (st) the setting procedure when executing startup tuning (st) only one time at power on is shown below as a setting example. When startup tuning (st) is executed with power o...
Page 192
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-56 automatic temperature rise learning rkc communication identifier y8 modbus register address ch1: 014ah (330) ch3: 014ch (332) ch2: 014bh (331) ch4: 014dh (333) use to select use/unuse of the automatic temperature rise learning function. Attribute: r...
Page 193
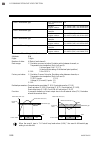
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-57 automatic temperature rise function (with learning function): treating channels that have the same group number specification as one group, the automatic temperature rise function synchronizes the temperature rise of the other channels in the group ...
Page 194
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-58 continued from the previous page. requirements for automatic temperature rise start when all the channels in a group satisfy the following conditions, automatic temperature rise is executed. Operation state run/stop transfer run 1 pid/at transfer ...
Page 195
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-59 continued from the previous page. procedure for using the automatic temperature rise function 1. Set the automatic temperature rise group 2. Automatic temperature rise learning on 3. Control stop for each z-tio module channel, set an automatic tem...
Page 196
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-60 communication switch for logic rkc communication identifier ef modbus register address 014eh (334) on/off signal that applies the signal of event information occurring in the higher system as input to a logic computation result (logic output). Attri...
Page 197: Warning
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-61 8.2.2 engineering setting data items setting procedure of engineering setting data items when run/stop switching (rkc communication identifier: rs, modbus register address: 006dh) is set to “0: stop (control stop),” engineering setting data can be...
Page 198
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-62 continued from the previous page. Data type items default value engineering burnout direction 0: upscale setting data event 1 channel setting 1 (channel 1) event 2 channel setting event 3 channel setting event 4 channel setting event 1 hold action 0...
Page 199
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-63 continued from the previous page. Data type items default value engineering setting data integral time limiter (low) [cool-side] 1 second setting (no decimal place): 0 seconds 0.1 seconds setting (one decimal place): 0.0 seconds derivative time limi...
Page 200
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-64 when an event type parameter is changed when an event type setting is changed, the corresponding event settings will be initialized. Reset these settings to the values that you wish to use. Event 1 type (rkc communication identifier: xa, modbus ad...
Page 201
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-65 when the control action parameter is changed when the control action setting (rkc communication identifier: xe, modbus address: 0232h to 0235h) is changed, the settings in the following table will be changed. Reset the settings to the values that ...
Page 202
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-66 when the decimal point position parameter is changed when the input decimal point position is changed (rkc communication identifier: xu, modbus address: 017eh to 0181h), the decimal point positions of the settings in the following table are automa...
Page 203
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-67 continued from the previous page. Items processed by limiter processing: data type items engineering event 1 differential gap 1 at bias setting data event 2 differential gap 1 proportional band limiter (high) [heat-side] 2 event 3 differential gap 1...
Page 204
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-68 when the eds transfer time decimal point position parameter is changed when the eds transfer time decimal point position is changed (rkc communication identifier: ns, modbus address: 0312h to 0315h), the decimal point positions of the settings in ...
Page 205
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-69 data explanation input type rkc communication identifier xi modbus register address ch1: 0176h (374) ch3: 0178h (376) ch2: 0177h (375) ch4: 0179h (377) input type number is a number to indicate an input type. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits number...
Page 206
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-70 continued from the previous page. hardware selection the voltage (low) or (high) input group is selected by the input select switch at the side of the module. Turn the measured value input switch by a small screwdriver. Input select switch (for ch...
Page 207
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-71 decimal point position rkc communication identifier xu modbus register address ch1: 017eh (382) ch3: 0180h (384) ch2: 017fh (383) ch4: 0181h (385) use to select the decimal point position of the input range. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits number of...
Page 208
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-72 continued from the previous page. Function: the input range can be changed for temperature input. For voltage (v)/current (i) input, display scaling can be made in the range of 19999 to 19999. Example [temperature input]: when the range of 200.0 ...
Page 209
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-73 input error determination point (high) rkc communication identifier av modbus register address ch1: 018ah (394) ch3: 018ch (396) ch2: 018bh (395) ch4: 018dh (397) input error determination point (low) rkc communication identifier aw modbus register ...
Page 210
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-74 burnout direction rkc communication identifier bs modbus register address ch1: 0192h (402) ch3: 0194h (404) ch2: 0193h (403) ch4: 0195h (405) use to select burnout direction in input break. When input break is detected by the module, the measured va...
Page 211
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-75 output assignment (logic output selection function) rkc communication identifier e0 modbus register address ch1: 019ah (410) ch3: 019ch (412) ch2: 019bh (411) ch4: 019dh (413) this is used to assign the output function (control output, logic output ...
Page 212
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-76 energized/de-energized (logic output selection function) rkc communication identifier na modbus register address ch1: 019eh (414) ch3: 01a0h (416) ch2: 019fh (415) ch4: 01a1h (417) energized/de-energized can be selected for any of outputs 1 (out1) t...
Page 213
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-77 event 1 type rkc communication identifier xa modbus register address ch1: 01a2h (418) ch3: 01a4h (420) ch2: 01a3h (419) ch4: 01a5h (421) event 2 type rkc communication identifier xb modbus register address ch1: 01beh (446) ch3: 01c0h (448) ch2: 01bf...
Page 214
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-78 continued from the previous page. Related parameters: comprehensive event state (p. 8-4), event state monitor (p. 8-9), event set value (p. 8-20), output assignment (p. 8-75), event interlock (p. 8-83), event differential gap (p. 8-84), event delay ...
Page 215
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-79 continued from the previous page. temperature rise completion function during the sampling of temperature input, when the measured value (pv) comes within the temperature rise completion range, the temperature rise completion will occur. Pv1 pv2 s...
Page 216
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-80 event 1 channel setting rkc communication identifier fa modbus register address ch1: 01a6h (422) ch3: 01a8h (424) ch2: 01a7h (423) ch4: 01a9h (425) event 2 channel setting rkc communication identifier fb modbus register address ch1: 01c2h (450) ch3:...
Page 217
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-81 event 1 hold action rkc communication identifier wa modbus register address ch1: 01aah (426) ch3: 01ach (428) ch2: 01abh (427) ch4: 01adh (429) event 2 hold action rkc communication identifier wb modbus register address ch1: 01c6h (454) ch3: 01c8h (...
Page 218
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-82 function: hold action when hold action is on, the event action is suppressed at start-up or stop to run until the measured value (pv) has entered the non-event range. [ with hold action ] [ without hold action ] on on event status time deviation h...
Page 219
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-83 event 1 interlock rkc communication identifier lf modbus register address ch1: 01aeh (430) ch3: 01b0h (432) ch2: 01afh (431) ch4: 01b1h (433) event 2 interlock rkc communication identifier lg modbus register address ch1: 01cah (458) ch3: 01cch (460)...
Page 220
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-84 event 1 differential gap rkc communication identifier ha modbus register address ch1: 01b2h (434) ch3: 01b4h (436) ch2: 01b3h (435) ch4: 01b5h (437) event 2 differential gap rkc communication identifier hb modbus register address ch1: 01ceh (462) ch...
Page 221
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-85 event 1 delay timer rkc communication identifier td modbus register address ch1: 01b6h (438) ch3: 01b8h (440) ch2: 01b7h (439) ch4: 01b9h (441) event 2 delay timer rkc communication identifier tg modbus register address ch1: 01d2h (466) ch3: 01d4h (...
Page 222
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-86 continued from the previous page. The event delay timer is also activated for the following cases. when set to the event state simultaneously with power turned on. when set to the event state simultaneously with control changed to run (control s...
Page 223
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-87 force on of event 1 action rkc communication identifier oa modbus register address ch1: 01bah (442) ch3: 01bch (444) ch2: 01bbh (443) ch4: 01bdh (445) force on of event 2 action rkc communication identifier ob modbus register address ch1: 01d6h (470...
Page 224
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-88 continued from the previous page. Example: when “0: event output turned on at input error occurrence” is selected input range: 0 to 400 c input error determination point (high): 300 c input error determination point (low): 50 c action area at inp...
Page 225
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-89 ct ratio rkc communication identifier xs modbus register address ch1: 0212h (530) ch3: 0214h (532) ch2: 0213h (531) ch4: 0215h (533) use to set the number of turns (ratio) of the current transformer that is used with the heater break alarm (hba). At...
Page 226
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-90 heater break alarm (hba) type rkc communication identifier nd modbus register address ch1: 021ah (538) ch3: 021ch (540) ch2: 021bh (539) ch4: 021dh (541) use to select the heater break alarm (hba) type. Attribute: r/w digits: 1 digit number of data:...
Page 227
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-91 number of heater break alarm (hba) delay times rkc communication identifier dh modbus register address ch1: 021eh (542) ch3: 0220h (544) ch2: 021fh (543) ch4: 0221h (545) to prevent producing a false alarm, the alarm function waits to produce an ala...
Page 228
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-92 hot/cold start rkc communication identifier xn modbus register address ch1: 0222h (546) ch3: 0224h (548) ch2: 0223h (547) ch4: 0225h (549) use to select the start mode at power recovery. Attribute: r/w digits: 1 digit number of data: 4 (data of each...
Page 229
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-93 start determination point rkc communication identifier sx modbus register address ch1: 0226h (550) ch3: 0228h (552) ch2: 0227h (551) ch4: 0229h (553) determination point always set to hot start 1 when recovered from power failure. The start determin...
Page 230
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-94 sv tracking rkc communication identifier xl modbus register address ch1: 022ah (554) ch3: 022ch (556) ch2: 022bh (555) ch4: 022dh (557) to select use/unuse of sv tracking. Attribute: r/w digits: 1 digit number of data: 4 (data of each channel) data ...
Page 231
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-95 mv transfer function [action taken when changed to manual mode from auto mode] rkc communication identifier ot modbus register address ch1: 022eh (558) ch3: 0230h (560) ch2: 022fh (559) ch4: 0231h (561) the manipulated output value used for manual c...
Page 232
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-96 continued from the previous page. Function: pid control (direct action) the manipulated output value (mv) increases as the measured value (pv) increases. This action is used generally for cool control. pid control (reverse action) the manipulate...
Page 233
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-97 continued from the previous page. position proportioning pid control position proportioning pid control converts the control output value of the controller into the corresponding signal to control a motor driven valve (control motor) and then perf...
Page 234
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-98 continued from the previous page. The settings vary as shown below depending on whether or not there is feedback resistance (fbr) input. Configure settings for position proportional pid control in the order of the arrows (→). (×: valid, : invalid) ...
Page 235
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-99 continued from the previous page. brilliant ii pid control pid control is a control method of achieving stabilized control result by setting p (proportional band), i (integral time) and d (derivative time) constants, and is widely used. However ev...
Page 236
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-100 integral/derivative time decimal point position rkc communication identifier pk modbus register address ch1: 0236h (566) ch3: 0238h (568) ch2: 0237h (567) ch4: 0239h (569) use to select a decimal point position of integral time and derivative time....
Page 237
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-101 undershoot suppression factor rkc communication identifier kb modbus register address ch1: 023eh (574) ch3: 0240h (576) ch2: unused ch4: unused this is a factor to restrict undershooting on the cool side. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits number of d...
Page 238
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-102 on/off action differential gap (upper) rkc communication identifier iv modbus register address ch1: 0246h (582) ch3: 0248h (584) ch2: 0247h (583) ch4: 0249h (585) on/off action differential gap (lower) rkc communication identifier iw modbus registe...
Page 239
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-103 action (high) at input error rkc communication identifier wh modbus register address ch1: 024eh (590) ch3: 0250h (592) ch2: 024fh (591) ch4: 0251h (593) action (low) at input error rkc communication identifier wl modbus register address ch1: 0252h ...
Page 240
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-104 manipulated output value at input error rkc communication identifier oe modbus register address ch1: 0256h (598) ch3: 0258h (600) ch2: 0257h (599) ch4: 0259h (601) when the measured value reaches input error determination point and action at input ...
Page 241
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-105 output change rate limiter (up) [heat-side] rkc communication identifier ph modbus register address ch1: 0262h (610) ch3: 0264h (612) ch2: 0263h (611) ch4: 0265h (613) output change rate limiter (down) [heat-side] rkc communication identifier pl mo...
Page 242
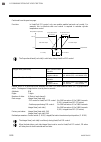
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-106 continued from the previous page. If the output change rate is set smaller, it will cause slow control response and affect derivative action. When the output change rate limiter is used, you may not be able to obtain appropriate pid constants by au...
Page 243
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-107 output limiter high [heat-side] rkc communication identifier oh modbus register address ch1: 026ah (618) ch3: 026ch (620) ch2: 026bh (619) ch4: 026dh (621) output limiter low [heat-side] rkc communication identifier ol modbus register address ch1: ...
Page 244
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-108 at bias rkc communication identifier gb modbus register address ch1: 0282h (642) ch3: 0284h (644) ch2: 0283h (643) ch4: 0285h (645) use to set a bias to move the set value only when autotuning is activated. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits number of...
Page 245
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-109 at cycles rkc communication identifier g3 modbus register address ch1: 0286h (646) ch3: 0288h (648) ch2: 0287h (647) ch4: 0289h (649) the number of on/off cycles is selected when the autotuning (at) function is executed. Attribute: r/w digits: 1 di...
Page 246
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-110 output value with at turned on rkc communication identifier op modbus register address ch1: 028ah (650) ch3: 028ch (652) ch2: 028bh (651) ch4: 028dh (653) output value with at turned off rkc communication identifier oq modbus register address ch1: ...
Page 247
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-111 at differential gap time rkc communication identifier gh modbus register address ch1: 0292h (658) ch3: 0294h (660) ch2: 0293h (659) ch4: 0295h (661) use to set an on/off action differential gap time for autotuning. This function prevents the at fun...
Page 248
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-112 proportional band adjusting factor [heat-side] rkc communication identifier kc modbus register address ch1: 0296h (662) ch3: 0298h (664) ch2: 0297h (663) ch4: 0299h (665) proportional band adjusting factor [cool-side] rkc communication identifier k...
Page 249
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-113 derivative time adjusting factor [heat-side] rkc communication identifier ke modbus register address ch1: 029eh (670) ch3: 02a0h (672) ch2: 029fh (671) ch4: 02a1h (673) derivative time adjusting factor [cool-side] rkc communication identifier kh mo...
Page 250
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-114 integral time limiter (high) [heat-side] rkc communication identifier i6 modbus register address ch1: 02b6h (694) ch3: 02b8h (696) ch2: 02b7h (695) ch4: 02b9h (697) integral time limiter (low) [heat-side] rkc communication identifier i7 modbus regi...
Page 251
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-115 derivative time limiter (high) [heat-side] rkc communication identifier d6 modbus register address ch1: 02beh (702) ch3: 02c0h (704) ch2: 02bfh (703) ch4: 02c1h (705) derivative time limiter (low) [heat-side] rkc communication identifier d7 modbus ...
Page 252
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-116 integral time limiter (high) [cool-side] rkc communication identifier i8 modbus register address ch1: 02ceh (718) ch3: 02d0h (720) ch2: unused ch4: unused integral time limiter (low) [cool-side] rkc communication identifier i9 modbus register addre...
Page 253
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-117 open/close output neutral zone rkc communication identifier v2 modbus register address ch1: 02deh (734) ch3: 02e0h (736) ch2: unused ch4: unused use to set open/close output neutral zone. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits number of data: 4 (data of e...
Page 254
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-118 feedback adjustment rkc communication identifier fv modbus register address ch1: 02e6h (742) ch3: 02e8h (744) ch2: unused ch4: unused feedback adjustment function is to adjust controller's output value to match the feedback resistance (fbr) of the ...
Page 255
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-119 integrated output limiter rkc communication identifier oi modbus register address ch1: 02eeh (750) ch3: 02f0h (752) ch2: unused ch4: unused this is a restricted value when the output on the open or closed side is integrated. Attribute: r/w digits: ...
Page 256
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-120 st proportional band adjusting factor rkc communication identifier ki modbus register address ch1: 02f6h (758) ch3: 02f8h (760) ch2: 02f7h (759) ch4: 02f9h (761) st integral time adjusting factor rkc communication identifier kj modbus register addr...
Page 257
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-121 automatic temperature rise group rkc communication identifier y7 modbus register address ch1: 0306h (774) ch3: 0308h (776) ch2: 0307h (775) ch4: 0309h (777) group number when conducting an automatic temperature rise. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits...
Page 258
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-122 automatic temperature rise gradient data rkc communication identifier r2 modbus register address ch1: 030eh (782) ch3: 0310h (784) ch2: 030fh (783) ch4: 0311h (785) this parameter is used to set the temperature change per one minute when the automa...
Page 259
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-123 output average processing time for eds rkc communication identifier nv modbus register address ch1: 0316h (790) ch3: 0318h (792) ch2: 0317h (791) ch4: 0319h (793) processing time for obtaining the output value average, which is used internally. Att...
Page 260
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-124 setting change rate limiter unit time rkc communication identifier hu modbus register address ch1: 031eh (798) ch3: 0320h (800) ch2: 031fh (799) ch4: 0321h (801) set the time unit for setting change rate limiter (up/down). Attribute: r/w digits: 7 ...
Page 261
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-125 setting limiter high rkc communication identifier sh modbus register address ch1: 0326h (806) ch3: 0328h (808) ch2: 0327h (807) ch4: 0329h (809) setting limiter low rkc communication identifier sl modbus register address ch1: 032ah (810) ch3: 032ch...
Page 262
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-126 operation mode assignment 1 (logic output selection function) logic output 1 to 4 rkc communication identifier ea modbus register address ch1: 0332h (818) ch3: 0334h (820) ch2: 0333h (819) ch4: 0335h (821) operation mode assignment 2 (logic output ...
Page 263
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-127 sv select function rkc communication identifier km modbus register address ch1: 033ah (826) ch3: 033ch (828) ch2: 033bh (827) ch4: 033dh (829) select the slave action in response to the set input from the master when operation is switched from loca...
Page 264
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-128 cascade control function/cascade control 2 function cascade control monitors the controlled object temperature in the master unit and then corrects the set value in the slave unit depending on the deviation between the target value (set value) an...
Page 265
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-129 ratio setting function ratio setting exercises control with the product of the set value (sv) from the master multiplied by a fixed ratio as the slave set value (sv). Example: ratio setting control using ch1 to ch3 of the z-tio module specify ch1...
Page 266
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-130 operation flow (common procedure for sv select function operation) 1. Set sv select function operation 2. Set the master channel module address 3. Select the master channel set the function that you wish to have operate in the slave channel of th...
Page 267
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-131 adjustment after control starting examples of using the ratio and bias for each function are given below. Example 1: remote sv function when the master and slave setting limiter range is 0 to 400 c rs ratio of slave: 0.500, rs bias of slave: 2...
Page 268
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-132 continued from the previous page. Example 3: ratio setting function when the master and slave setting limiter range is 0 to 400 c rs ratio of slave: 0.500, rs bias of slave: 20 c master set value (sv): 200 c slave set value (sv): 120 c rs...
Page 269
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-133 remote sv function master channel module address rkc communication identifier mc modbus register address ch1: 033eh (830) ch3: 0340h (832) ch2: 033fh (831) ch4: 0341h (833) in the slave channel, set the module address number of the module that incl...
Page 270
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-134 remote sv function master channel selection rkc communication identifier mn modbus register address ch1: 0342h (834) ch3: 0344h (836) ch2: 0343h (835) ch4: 0345h (837) in the slave channel, select the channel number that will be the master in the m...
Page 271
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-135 output distribution master channel module address rkc communication identifier dy modbus register address ch1: 0346h (838) ch3: 0348h (840) ch2: 0347h (839) ch4: 0349h (841) to output the manipulated output value computed in the master channel from...
Page 272
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-136 output distribution master channel selection rkc communication identifier dz modbus register address ch1: 034ah (842) ch3: 034ch (844) ch2: 034bh (843) ch4: 034dh (845) in the slave channel, select the channel number that will be the master in the ...
Page 273
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-137 address of interacting modules rkc communication identifier rl modbus register address ch1: 034eh (846) ch3: 0350h (848) ch2: 034fh (847) ch4: 0351h (849) in the z-tio module, set the module address number of the module with the channel that you wi...
Page 274
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-138 channel selection of interacting modules rkc communication identifier rm modbus register address ch1: 0352h (850) ch3: 0354h (852) ch2: 0353h (851) ch4: 0355h (853) in the z-tio module, select the interacting channel number of the module to be link...
Page 275
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-139 continued from the previous page. Example 1: switching the memory areas of all channels of two z-tio modules base interacting module: ch1 of modules address 0 module to be linked: ch2 to ch4 of module address 0 ch1 to ch4 of module address 1 z-tio ...
Page 276
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-140 continued from the previous page. Example 2: switching the memory areas of all channels of two z-tio modules using one z-dio module base interacting module: z-dio module (module address 16) module to be linked: ch1 to ch4 of module address 0 ch1 to...
Page 277
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-141 control run/stop holding setting rkc communication identifier x1 modbus register address 035ah (858) it is set whether or not the operation mode before the power supply is turned off is held when the power supply is turned on or power failure recov...
Page 278: Memo
Ims01t04-e6 8-142 memo.
Page 279
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-143 8.3 communication data of z-dio module 8.3.1 normal setting data items model code rkc communication identifier id modbus register address this value is the type identifier code of the z-dio module. Attribute: ro digits: 32 digits number of data: 1 ...
Page 280
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-144 digital input (di) state 1 rkc communication identifier l1 digital input (di) state 2 rkc communication identifier l6 digital input (di) state modbus register address 0000h (0) each digital input (di) state of the z-dio module is expressed in bit d...
Page 281
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-145 digital output (do) state 1 rkc communication identifier q2 digital output (do) state 2 rkc communication identifier q3 digital output (do) state modbus register address 0001h (1) each digital output (do) state of the z-dio module is expressed in b...
Page 282
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-146 error code rkc communication identifier er modbus register address 0002h (2) each error state of the z-dio module is expressed in bit data items. Attribute: ro digits: 7 digits number of data: 1 (data of each module) data range: 0 to 2 (digits) the...
Page 283
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-147 run/stop transfer rkc communication identifier sr modbus register address 0046h (70) use to transfer the run (control run) or stop (control stop). Attribute: r/w digits: 1 digit number of data: 1 (data of each channel) data range: 0: stop (control ...
Page 284
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-148 continued from the previous page. Modbus: 0 to 255 (bit data) the do manual output is assigned as a bit image in binary numbers. Bit image: 0000000000000000 bit 15 ····················· bit 0 bit data: 0: off 1: on factory set value: 0 related para...
Page 285
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-149 do output distribution selection rkc communication identifier do modbus register address ch1: 0048h (72) ch5: 004ch (76) ch2: 0049h (73) ch6: 004dh (77) ch3: 004ah (74) ch7: 004eh (78) ch4: 004bh (75) ch8: 004fh (79) select whether or not the manip...
Page 286
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-150 continued from the previous page. operation flow example: when using one z-tio module (4ch type) and one z-dio module master/slave: master/slave module address ch/do input ourpur master channel (heater 2) module address 0 ch1 sensor input control...
Page 287
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-151 do output distribution bias rkc communication identifier o8 modbus register address ch1: 0050h (80) ch5: 0054h (84) ch2: 0051h (81) ch6: 0055h (85) ch3: 0052h (82) ch7: 0056h (86) ch4: 0053h (83) ch8: 0057h (87) the bias which is added to the manip...
Page 288
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-152 do proportional cycle time rkc communication identifier v0 modbus register address ch1: 0060h (96) ch5: 0064h (100) ch2: 0061h (97) ch6: 0065h (101) ch3: 0062h (98) ch7: 0066h (102) ch4: 0063h (99) ch8: 0067h (103) use to set do proportional cycle ...
Page 289
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-153 continued from the previous page. Function: the do minimum on/off time of the proportioning cycle is used to prevent output on or off when the output is greater than 0 % or less than 100 %. This is useful when you wish to establish a minimum on/off...
Page 290: Warning
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-154 8.3.2 engineering setting data items setting procedure of engineering setting data items when run/stop switching (rkc communication identifier: rs, modbus register address: 0046h) is set to “0: stop (control stop),” engineering setting data can b...
Page 291
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-155 continued from the previous page. di assignment table set value di1 di2 di3 di4 di5 di6 di7 di8 0 no assignment 1 memory area transfer (1 to 8) 1 auto/man 4 2 rem/loc 4 3 interlock release eds start signal 1 4 soak stop 5 run/stop 4 6 rem/loc 4 7...
Page 292
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-156 memory area setting signal rkc communication identifier e1 modbus register address 00a5h (165) use to select the memory area setting signal for memory area transfer. Attribute: r/w digits: 1 digit number of data: 1 (data of each module) data range:...
Page 293
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-157 do signal assignment module address 1 [do1 to do4] rkc communication identifier lq modbus register address 00a6h (166) do signal assignment module address 2 [do5 to do8] rkc communication identifier lr modbus register address 00a7h (167) specify th...
Page 294
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-158 do output assignment 1 [do1 to do4] rkc communication identifier lt modbus register address 00a8h (168) do output assignment 2 [do5 to do8] rkc communication identifier lx modbus register address 00a9h (169) assignments to digital outputs (do1 to d...
Page 295
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-159 continued from the previous page. 1 logical or of event 1 (ch1 to ch4) 2 logical or of event 2 (ch1 to ch4) 3 logical or of event 3 (ch1 to ch4) 4 logical or of event 4 (ch1 to ch4) 5 temperature rise completion status (on when temperature rise com...
Page 296
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-160 do output distribution master channel module address rkc communication identifier dd modbus register address ch1: 00b2h (178) ch5: 00b6h (182) ch2: 00b3h (179) ch6: 00b7h (183) ch3: 00b4h (180) ch7: 00b8h (184) ch4: 00b5h (181) ch8: 00b9h (185) to ...
Page 297
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-161 do output distribution master channel selection rkc communication identifier dj modbus register address ch1: 00bah (186) ch5: 00beh (190) ch2: 00bbh (187) ch6: 00bfh (191) ch3: 00bch (188) ch7: 00c0h (192) ch4: 00bdh (189) ch8: 00c1h (193) select t...
Page 298
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-162 do manipulated output value (mv) at stop mode rkc communication identifier oj modbus register address ch1: 00c2h (194) ch5: 00c6h (198) ch2: 00c3h (195) ch6: 00c7h (199) ch3: 00c4h (196) ch7: 00c8h (200) ch4: 00c5h (197) ch8: 00c9h (201) manipulate...
Page 299
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-163 continued from the previous page. Related parameters: digital output (do) state (p. 8-145), run/stop transfer (p. 8-147), do output distribution selection (p. 8-149), do output distribution bias (p. 8-151), do output distribution ratio (p. 8-151), ...
Page 300
8. Communication data description ims01t04-e6 8-164 interval time rkc communication identifier zx modbus register address 00dbh (219) rs-485 sets the transmission transfer time to accurately assure the sending/receiving selection timing. Attribute: r/w digits: 7 digits number of data: 1 (data of eac...
Page 301: Trouble
Trouble shooting ims01t04-e6 9-1 10.1 solutions for problems .................................................................... 9-2.
Page 302: Solutions For Problems
9. Troubleshooting 9-2 ims01t04-e6 solutions for problems this section explains possible causes and treatment procedures if any abnormality occurs in the instrument. For any inquiries, please contact rkc sales office or the agent, to confirm the specifications of the product. If it is necessary to r...
Page 303
9. Troubleshooting ims01t04-e6 9-3 z-tio/z-dio module problem possible cause solution fail/run lamp does not light up power not being supplied check external breaker etc. Appropriate power supply voltage not being supplied check the power supply power supply terminal contact defect retighten the t...
Page 304
9. Troubleshooting ims01t04-e6 9-4 rkc communication problem possible cause solution no response wrong connection, no connection or disconnection of the communication cable confirm the connection method or condition and connect correctly breakage, wrong wiring, or imperfect contact of the communic...
Page 305
9. Troubleshooting ims01t04-e6 9-5 modbus problem possible cause solution no response wrong connection, no connection or disconnection of the communication cable confirm the connection method or condition and connect correctly breakage, wrong wiring, or imperfect contact of the communication cable...
Page 306: Memo
9-6 ims01t04-e6 memo.
Page 307: Specifications
Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-1 10.1 z-tio module ................................................................................ 10-2 10.2 z-dio module ............................................................................. 10-16.
Page 308: 10.1 Z-Tio Module
10. Specifications 10-2 ims01t04-e6 10.1 z-tio module measured input number of inputs: 4 point or 2 point (isolated between each input) input type: temperature, current, voltage (low) and feedback resistance input group * thermocouple (tc) k, j, t, s, r, e, b, n (jis-c1602-1995) pl ii (nbs), w5r...
Page 309
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-3 sampling cycle: 250 ms influence of external resistance: approx. 0.125 v/ (converted depending on tc types) influence of input lead: approx. 0.02 / of pv (rtd input) 10 or less per wire input impedance: tc input: 1 m or more voltage (low) input: 1 m or m...
Page 310
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-4 output (out1 to out4) number of outputs: 4 points or 2 points output contents: used for control output or logic output output type: relay contact output contact type: 1a contact contact rating (resistive load): 250 v ac 3 a, 30 v dc 1 a electrical life: 300,00...
Page 311
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-5 performance (at the ambient temperature 23 ±2 c, mounting angle 3) input accuracy: measured input: input type input range accuracy k, j, t, plii, e less than −100 c 2.0 c 100 c or more, less than 500 c 1.0 c 500 °c or more (0.2 of reading +1 digit...
Page 312
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-6 control control method: a) brilliant ii pid control (direct action/reverse action is selectable) b) brilliant ii heat/cool pid control (water cooling) c) brilliant ii heat/cool pid control (air cooling) d) brilliant ii heat/cool pid control (cooling gain linear)...
Page 313
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-7 brilliant ii heat/cool pid control ( only ch1 and ch3 can be set ) setting range: a) proportional band (p) * temperature input: 0 to input span (unit: c [f]) (varies with the setting of the decimal point position) voltage/current input: 0.0 to 1000.0 of ...
Page 314
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-8 brilliant ii position proportioning pid control without fbr ( only ch1 and ch3 can be set ) setting range: a) proportional band (p) * temperature input: 0 to input span (unit: c [f]) (varies with the setting of the decimal point position) voltage/current i...
Page 315
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-9 event function number of events: 4 points/channel event action: deviation high, deviation low, deviation high/low, band, process high, process low, sv high, sv low, mv high [heat-side] *, mv low [heat-side] *, mv high [cool-side], mv low [cool-side] deviation hi...
Page 316
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-10 heater break alarm (hba) [time-proportional control output (optional)] number of hba: 4 points or 2 points setting range: 0.0 to 100.0 a (0.0: hba function off) [hba function off: the current value monitoring is available] ct assignment: 0 (hba function off) 1 ...
Page 317
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-11 communication interface: based on rs-485 eia standard connection method: 2-wire system, half-duplex multi-drop connection synchronous method: start/stop synchronous type communication speed: 4800 bps, 9600 bps, 19200 bps, 38400 bps data bit configuration: start...
Page 318
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-12 logic output function number of logic output points: 8 points input: event output 1 (ch1 to ch4), event output 2 (ch1 to ch4), event output 3 (ch1 to ch4), event output 4 (ch1 to ch4), heater break alarm1 to 4, communication switch for logic 1 to 4, fail signal...
Page 319
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-13 output distribution function setting range: output distribution master channel module address: 1, 0 to 99 master channel selection: 1 to 99 output distribution bias: 100.0 to 100.0 % output distribution ratio: 9.999 to 9.999 output distribution selection: ...
Page 320
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-14 master-slave mode setting range: address of interacting modules: 1, 0 to 99 channel selection of interacting modules: 1 to 99 selection switch of interacting modules: 0 (no interaction) 1 (interact with other channels) bit 0: memory area number bit 1: operatio...
Page 321
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-15 general specifications insulation resistance: between measuring terminal and grounding: 20 m or more at 500 v dc between power supply terminal and grounding: 20 m or more at 500 v dc between power supply and measuring terminals: 20 m or more at 500 v dc w...
Page 322: 10.2 Z-Dio Module
10. Specifications 10-16 ims01t04-e6 10.2 z-dio module digital input (di) number of inputs: none or 8 points (di1 to di8) isolated input (each common block) number of commons: 2 points (di 4 points/common) input method: voltage contact input (sink type) open state: 5 v or less close state: 17.5 v ...
Page 323
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-17 digital input (di) function the following z-tio functions can be assigned as digital input: setting range: di function assignment: 0 to 29 (refer to p. 1-6) signal details: memory area transfer, area set *, operation mode, interlock release, auto/manual transfe...
Page 324
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-18 communication interface: based on rs-485 eia standard connection method: 2-wire system, half-duplex multi-drop connection synchronous method: start/stop synchronous type communication speed: 4800 bps, 9600 bps, 19200 bps, 38400 bps data bit configuration: start...
Page 325
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-19 self-diagnostic function function stop: date back-up error (error code 2) action stop (error number is not displayed [operation: impossible]): power supply voltage monitoring watchdog timer instrument status: when a self-diagnostic error occurs: all output off ...
Page 326
10. Specifications ims01t04-e6 10-20 allowable ambient temperature: 10 to 50 c allowable ambient humidity: 5 to 95 rh (absolute humidity: max.W.C 29.3 g/m 3 dry air at 101.3 kpa) installation environment conditions: indoor use altitude up to 2000 m transportation and storage environment conditio...
Page 327: Appendix
Appendix ims01t04-e6 11-1 11.1 ascii 7-bit code table ................................................................. 11-2 11.2 current transformer (ct) dimensions ......................................... 11-3 11.3 cover ...............................................................................
Page 328: 11.1 Ascii 7-Bit Code Table
11. Appendix 11-2 ims01t04-e6 11.1 ascii 7-bit code table this table is only for use with rkc communication. B7 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 b6 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 b5 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 b5 to b7 b4 b3 b2 b1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 0 0 0 0 nul dle sp 0 @ p ‘ p 0 0 0 1 1 soh dc1 ! 1 a q a q 0 0 1 0 2 stx dc2 ” 2 b r b r 0 0 1 ...
Page 329
11. Appendix ims01t04-e6 11-3 11.2 current transformer (ct) dimensions ctl-6-p-n (for 0 to 30 a) (unit: mm) 130 25 14.5 21 5.8 15 10 ctl-12-s56-10l-n (for 0 to 100 a) (unit: mm) 100 40 15 30 40 30 12 7. 5.
Page 330: 11.3 Cover
11. Appendix 11-4 ims01t04-e6 11.3 cover when mounting and removing the terminal cover, apply pressure very carefully for avoid damage to the terminal cover. power terminal cover (standard equipment) power terminal cover parts code ksrz-518a(1) ordering code 00514689 joint connector cover (stand...
Page 331
11. Appendix ims01t04-e6 11-5 terminal cover (optional) terminal cover parts code ksrz-510a(1) ordering code 00501925 this section can be removed by bending it. Remove and then use it depending on the wiring condition..
Page 332: 11.4
11. Appendix 11-6 ims01t04-e6 11.4 block diagram of logic output selection function z-tio module output 1 ch1 (output assignment) ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ output 4 0: 2: 4: 1: 3: 5: no assignment operation mode 2 remote/local operation mode 1 auto/manual unused [d o not set this one] (operation mode assignment) (o...
Page 333
11. Appendix ims01t04-e6 11-7 11.5 peak current suppression function when the output type is time proportional output, the peak current suppression function changes the start timing of the proportional cycle so that the outputs of the channels do not turn on simultaneously. The peak current suppress...
Page 334
11. Appendix ims01t04-e1 11-8 the use of peak current suppression function in the load used in the three phase power supply system may not suppress the peak current. This is because the peak current suppression function works on condition that the target (object) channels are time-proportionally con...
Page 335: 11.6 Example of Using Di/do
11. Appendix ims01t04-e6 11-9 11.6 example of using di/do example of using di using one z-dio module to configure memory area settings and perform auto/man switching in two z-tio modules set value setting items (engineering setting data).
Page 336
11. Appendix ims01t04-e6 11-10 example of using do when outputting events (used as an alarm) and temperature rise completion of two z-tio modules from one z-dio module.
Page 337
11. Appendix ims01t04-e6 11-11 example of output distribution from z-dio module when outputting distribution of control output of ch1 and ch2 of z-tio module from z-dio module.
Page 338: Pid Control Channel Inputs
11. Appendix 11-12 ims01t04-e6 11.7 example of using unused heat/cool pid control channel inputs inputs of unused channels (ch2, ch4) for heat/cool pid control can be used as event action inputs. Sensor input 2 ou tp ut 1 out put 2 ou tp ut 3 out put 4 in p u t 1 input 2 in put 3 inpu t 4 ch1 ch2 ch...
Page 339: Alphabetical Order
Index ims01t04-e6 a-1 alphabetical order a action (high) at input error ······················ 6-26, 7-33, 8-103 action (low) at input error ······················· 6-26, 7-33, 8-103 action at feedback resistance (fbr) input error ························································ 6-28, 7-35, ...
Page 340
Index a-2 ims01t04-e6 do signal assignment module address 1 [do1 to do4] ························································ 6-31, 7-40, 8-157 do signal assignment module address 2 [do5 to do8] ························································ 6-31, 7-40, 8-157 e eds action time (for dis...
Page 341
Index ims01t04-e6 a-3 input select switch ················································· 8-70 input type ············································· 6-19, 7-26, 8-69 integral time [cool-side] ··························· 6-16, 7-22, 8-24 integral time [heat-side] ··························· 6-16...
Page 342
Index a-4 ims01t04-e6 p pid/at transfer ······································ 6-15, 7-21, 8-14 proportional band [cool-side] ···················· 6-16, 7-22, 8-23 proportional band [heat-side] ···················· 6-16, 7-22, 8-23 proportional band adjusting factor [cool-side] ·····················...
Page 343
The first edition: may 2006 [imq00] the sixth edition: jan. 2018 [imq00].
Page 344: Ims01T04-E6
Ims01t04-e6 jan. 2018 rkc instrument inc. Headquarters: 16-6, kugahara 5-chome, ohta-ku tokyo 146-8515 japan phone: 03-3751-9799 (+81 3 3751 9799) e-mail: info@rkcinst.Co.Jp website: http://www.Rkcinst.Com/ r.