- DL manuals
- RKS
- Power Supply
- H-PCP-J
- Instruction Manual
RKS H-PCP-J Instruction Manual - Contents
IMS01J02-E4
i-3
CONTENTS
Page
1. OUTLINE ............................................................................... 1
1.1 Features .......................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Handling Procedures ....................................................................................... 2
1.3 Checking the Product ...................................................................................... 3
1.4 Confirmation of the Model Code ...................................................................... 4
1.5 System Configuration ...................................................................................... 6
1.6 Parts Description ........................................................................................... 12
2. SPECIFICATIONS .............................................................. 14
3. MOUNTING ......................................................................... 20
3.1 Mounting Cautions ......................................................................................... 20
3.2 Dimensions .................................................................................................... 21
3.3 Mounting the Mother Block ............................................................................ 22
3.4 Mounting the Module Mainframe ................................................................... 24
3.5 Removing the Module Mainframe .................................................................. 24
4. WIRING .............................................................................. 25
4.1 Wiring ............................................................................................................ 25
4.2 Connections ................................................................................................... 27
4.2.1 DO connector connection ................................................................................... 28
4.2.2 Connection to the host computer ....................................................................... 30
4.2.3 Connection to the operation panel ..................................................................... 37
4.2.4 Connection to the touch panel ........................................................................... 38
4.2.5 Multiple control unit connections ........................................................................ 41
5. SETTINGS BEFORE OPERATION .................................... 43
5.1 Protocol Selection and Host Communication Setting .................................... 43
5.2 Unit Address Setting ...................................................................................... 48
5.3 Start-up Procedures ...................................................................................... 49
5.4 Communication Requirements ...................................................................... 50
Summary of H-PCP-J
Page 1
Sr mini hg system ims01j02-e4 h-pcp-j instruction manual rkc instrument inc. ® power supply/cpu module.
Page 2
All rights reserved, copyright 2004, rkc instrument inc. modbus is a registered trademark of schneider electric. the name of each programmable controller (plc) means the products of each manufacturer. company names and product names used in this manual are the trademarks or registered tradem...
Page 3: Symbols
Ims01j02-e4 i-1 thank you for purchasing this rkc product. In order to achieve maximum performance and ensure proper operation of your new instrument, carefully read all the instructions in this manual. Please place the manual in a convenient location for easy reference. Symbols : this mark indicate...
Page 4: Notice
Ims01j02-e4 i-2 this product is intended for use with industrial machines, test and measuring equipment. (it is not designed for use with medical equipment and nuclear energy.) this is a class a instrument. In a domestic environment, this instrument may cause radio interference, in which case th...
Page 5: Contents
Ims01j02-e4 i-3 contents page 1. Outline ............................................................................... 1 1.1 features .......................................................................................................... 1 1.2 handling procedures ..................................
Page 6
Ims01j02-e4 i-4 page 6. Rkc communication .................................................... 52 6.1 protocol ......................................................................................................... 52 6.1.1 polling .....................................................................
Page 7
Ims01j02-e4 i-5 page 8.2.6 scale correction ............................................................................................... 175 8.2.7 output change rate limiter ................................................................................ 177 8.2.8 alarm hold function ...............
Page 8: Memo
I-6 ims01j02-e4 memo.
Page 9: 1. Outline
Ims01j02-e4 1 1. Outline this manual describes the specifications, mounting, wiring and communication of the h-pcp-j module. This manual should be used in conjunction with hardware quick manual (ims01v01-e). 1.1 features h-pcp-j module (power supply/cpu module) is made up of the cpu section and the...
Page 10: 1.2 Handling Procedures
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 2 1.2 handling procedures conduct handling according to the procedure described below. Checking the product see 1.3 checking the product (p. 3) see 1.4 confirmation of the model code (p. 4) mounting see 3. Mounting (p. 20) settings prior to operation power supply/ground wiring...
Page 11: 1.3 Checking The Product
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 3 1.3 checking the product when unpacking your new instrument, please confirm that the following products are included. If any of the products are missing, damaged, or if your manual is incomplete, please contact rkc sales office or agent for replacement. power supply/cpu mo...
Page 12: H-Pcp- J -
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 4 1.4 confirmation of the model code the model code for the instrument you received is listed below. Please confirm that you have received the correct instrument by checking the model code label, located on the left side of the module, with this list. If the product you receiv...
Page 13
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 5 initial code (1) ti alarm 1 function n: no alarm function : see ti/ai alarm code table (p. 5) (2) ti alarm 2 function n: no alarm function : see ti/ai alarm code table (p. 5) alarm code table ti/ai alarm code table the selected alarm function will be common for all the mod...
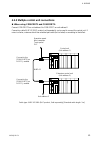
Page 14: 1.5 System Configuration
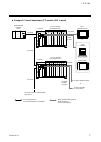
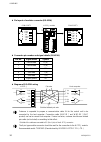
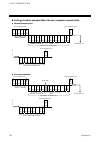
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 6 1.5 system configuration the system configuration example that used operation panel, host computer, touch panel and programmable controller (hereafter called plc) is shown. example 1: plc is used rs-422a sr mini hg system control unit function module (10 modules max.) h-pc...
Page 15
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 7 example 2: current transformer (ct) monitor (plc is used) rs-422a sr mini hg system control unit h-ct-a module (10 modules max.) h-pcp-j programmable controller (plc) up to 16 units per communication port of plc rkc operation panel rs-422a rs-485 rs-232c host computer touc...
Page 16
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 8 example 3: rkc operation panel is used sr mini hg system control unit function module (10 modules max.) h-pcp-j when the rkc operation panel is connected: up to 8 units rs-422a sr mini hg system control unit function module (10 modules max.) h-pcp-j rs-422a rs-485 rs-232c ...
Page 17
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 9 example 4: host computer or touch panel is used rs-422a rs-485 sr mini hg system control unit function module (10 modules max.) h-pcp-j when the host computer is connected: up to 16 units when the is touch panel connected: up to 16 units sr mini hg system control unit func...
Page 18
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 10 usable modules the following function modules can be used in combination with the h-pcp-j module. However, usable module is different by protocol. rkc communication protocol/modbus protocol function module type temperature control module h-tio-a h-tio-b h-tio-c h-tio-d ...
Page 19
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 11 precautions for plc communication system configuration when a system is configured by connecting a plc, the protocol dedicated to the plc (for temperature control) cannot be used together with the current transformer (ct) monitor. mitsubishi melsec series h-pcp-j module...
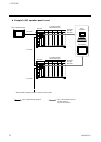
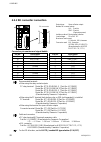
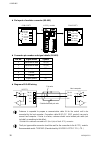
Page 20: 1.6 Parts Description
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 12 1.6 parts description h-pcp-j module (1) (3) (4) (7) (6) (5) (2) front side (10) (11) (8) (9) no. Name description (1) unit address setting switch set unit address number of control unit setting range: 0 to 15 (0 to f, hexadecimal) (2) status indication lamps rx1 (data re...
Page 21
1. Outline ims01j02-e4 13 continued from the previous page. No. Name description (3) modular connector (com.Port3) connector for connection with the host computer, touch panel or operation panel (conforming to rs-232c/rs-422a/rs-485) (4) do connector connector for digital output (5) power terminals ...
Page 22: 2. Specifications
14 ims01j02-e4 2. Specifications basic functions data supervision: operating and system data control unit diagnosis: function modules configuration check self-diagnostic: check item: rom/ram check watchdog timer power supply monitoring if error occurs in self-diagnosis, the hardware will automatic...
Page 23
2. Specifications ims01j02-e4 15 digital output number of outputs: 8 points output type: open collector output number of common points: vcc: 2 points, gnd: 2 points (8 points/common) isolation method: photocoupler isolation load voltage: 12 to 24 v dc maximum load current: 0.1 a/point, 0.8 a/commo...
Page 24
2. Specifications ims01j02-e4 16 communication functions com.Port1/com.Port2 interface: based on rs-422a, eia standard based on rs-485, eia standard specify when ordering connection method: rs-422a: 4-wire system, half-duplex multi-drop connection rs-485: 2-wire system, half-duplex multi-drop co...
Page 25
2. Specifications ims01j02-e4 17 synchronous method: start/stop synchronous type communication speed: 9600 bps, 19200 bps, 38400 bps communication speed can be selected with switch data bit configuration: start bit: 1 data bit: 7 or 8 parity bit: without, odd or even without for 8 data bits stop bit...
Page 26
2. Specifications ims01j02-e4 18 com.Port3 interface: based on rs-232c, eia standard based on rs-422a, eia standard based on rs-485, eia standard specify when ordering connection method: rs-232c: point-to-point connection rs-422a: 4-wire system, half-duplex multi-drop connection rs-485: 2-wire sys...
Page 27
2. Specifications ims01j02-e4 19 signal logic: rs-232c signal voltage logic 3 v or more 0 (space) 3 v or less 1 (mark) rs-422a/rs-485 signal voltage logic v (a) v (b) 2 v 0 (space) v (a) v (b) 2 v 1 (mark) voltage between v (a) and v (b) is the voltage of (a) terminal for the (b) terminal....
Page 28: 3. Mounting
20 ims01j02-e4 3. Mounting this chapter describes the mounting procedures for the h-pcp-j modules. For details of the mounting procedures for other modules and the mounting position of the control unit, see the hardware quick manual (ims01v01-e). 3.1 mounting cautions (1) this instrument is intende...
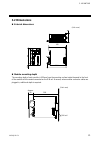
Page 29: 3.2 Dimensions
3. Mounting ims01j02-e4 21 3.2 dimensions external dimensions 4 48 (unit: mm) 96 3. 5 100 110 module mounting depth the mounting depth of each module is 108 mm from the mounting surface inside the panel to the front of the module with the module mounted on the din rail. However, when modular con...
Page 30
3. Mounting ims01j02-e4 22 3.3 mounting the mother block the mother block can be mounted to a panel or din rail. Mount the h-pcp-j module on the left side of the control unit. panel mounting directions 1. Refer to both the panel mounting dimensions below and the external dimensions in previous sec...
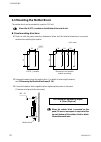
Page 31
3. Mounting ims01j02-e4 23 din rail mounting directions 1. Remove the module mainframe from the mother block. For details of removing the module mainframe, see 3.5 removing the module mainframe (p. 24). 2. Pull down both locking devices at the bottom of the mother block. (figure 1) 3. Attach the t...
Page 32
3. Mounting ims01j02-e4 24 3.4 mounting the module mainframe it engages the module with the mother block that is mounted on din rail or a panel. 1. Place the module mainframe opening on top of the mother block tab. (figure 1) 2. Snap the lower part of module mainframe on to the mother block. (figure...
Page 33: 4. Wiring
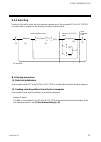
Ims01j02-e4 25 4. Wiring 4.1 wiring power supply wiring: use power supply as specified in power supply rated voltage range. power supply wiring must be twisted and have a low voltage drop. provide separate power supply for this instrument independent of other input/output circuits, motors, equ...
Page 34
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 26 terminal configuration 200-240 v ac l n 13 12 24 v dc power terminals 13 12 100-120 v ac l n 13 12 ground terminal 12 13 14 14 power supply use power supply as specified in power supply rated voltage range. 90 to 132 v ac [including power supply voltage variations] (50/6...
Page 35: 4.2 Connections
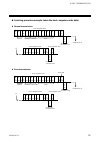
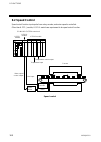
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 27 4.2 connections connect connectors correctly in the right position. If it is forcibly pushed in with pins in the wrong positions, the pins may be bent resulting in instrument failure. when connecting or disconnecting the connectors, do not force it too far to right and l...
Page 36
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 28 4.2.1 do connector connection do connector 10 1 20 11 connector pin number and signal details pin no. Description pin no. Description 20 vcc (com) 10 vcc (com) 19 gnd (com) 9 gnd (com) 18 unused 8 do8 17 unused 7 do7 16 unused 6 do6 15 unused 5 do5 14 unused 4 do4 13 unu...
Page 37
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 29 open collector output wiring example 12 to 24 v dc load load 10 1 9 8 com ( ) com ( ) do1 do8 20 19 pc relay terminal connecting example pc relay terminal rt1s-od08-24v-s (manufactured by panasonic corporation) h-pcp-j module expansion cable ay1584 (manufactured by panason...
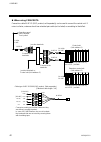
Page 38
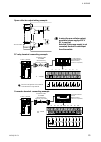
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 30 4.2.2 connection to the host computer connection block diagram the communication interface for control unit are rs-232c *, rs-422a and rs-485. When using the rs-422a or rs-485, a maximum of 16 control units can be connected. However, when connecting to the computer which o...
Page 39
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 31 rs-232c * use d-sub 25-pin modular conversion connector (recommended type: tm12rv-64-h manufactured by hirose electric co., ltd.) when connector of host computer is d-sub 25-pin. Control unit connect to the [com.Port3] on h-pcp-j module cable type: w-bf-28-3000 (rkc produc...
Page 40
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 32 diagram of rs-232c wiring host computer h-pcp-j shielded wire *short rs and cs within connector sd (txd) rd (rxd) sg sg sd (txd) rd (rxd) sg rs (rts) cs (cts) 2 4 3 6 * customer is requested to prepare a communication cable fit for the control unit to be connected by the h...
Page 41
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 33 rs-422a rs-422a connect to the [com.Port1] connect to the [com.Port2] w-bf-02 rs-232c connect to the [com.Port1] or [com.Port3] on h-pcp-j module cable type: w-bf-02-3000 (rkc product, sold separately) [standard cable length: 3 m] w-bf-28-3000 (rkc product, sold separately...
Page 42
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 34 pin layout of modular connector (rs-422a) h-pcp-j module com.Port1 sg 6 t (a) 5 t (b) 4 sg 3 r (b) 2 r (a) 1 com.Port3 1 r (a) 2 r (b) 3 sg 4 t (b) 5 t (a) 6 sg connector pin number and signal details (rs-422a) pin no. Signal name symbol 1 receive data r (a) 2 receive da...
Page 43
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 35 rs-485 rs-485 rs-232c connect to the communication connector connect to the [com.Port1] or [com.Port3] on h-pcp-j module cable type: w-bf-01-3000 (rkc product, sold separately) [standard cable length: 3 m] rs-232c/rs-485 converter host computer control unit t/r(b) t/r(a) s...
Page 44
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 36 pin layout of modular connector (rs-485) h-pcp-j module com.Port1 sg 6 unused 5 unused 4 sg 3 t/r (b) 2 t/r (a) 1 com.Port3 1 t/r (a) 2 t/r (b) 3 sg 4 unused 5 unused 6 sg connector pin number and signal details (rs-485) pin no. Signal name symbol 1 send/receive data t/r...
Page 45
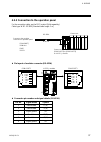
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 37 4.2.3 connection to the operation panel for the connection cable, use the rkc product (sold separately). Cable type: w-bf-02-3000 [standard cable length: 3 m] control unit connect to the modular connector on operation panel [com.Port] opm-hl4 [cn3] opc-h connect to the [com....
Page 46
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 38 4.2.4 connection to the touch panel rs-232c pin layout of modular connector (rs-232c) h-pcp-j module com.Port3 sg 6 unused 5 rd 4 sg 3 sd 2 unused 1 connector pin number and signal details (rs-232c) pin no. Signal name symbol 1 unused - 2 send data sd (txd) 3 signal gr...
Page 47
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 39 rs-422a pin layout of modular connector (rs-422a) h-pcp-j module com.Port1 sg 6 t (a) 5 t (b) 4 sg 3 r (b) 2 r (a) 1 com.Port3 1 r (a) 2 r (b) 3 sg 4 t (b) 5 t (a) 6 sg connector pin number and signal details (rs-422a) pin no. Signal name symbol 1 receive data r (a) 2 ...
Page 48
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 40 rs-485 pin layout of modular connector (rs-485) h-pcp-j module com.Port1 sg 6 unused 5 unused 4 sg 3 t/r (b) 2 t/r (a) 1 com.Port3 1 t/r (a) 2 t/r (b) 3 sg 4 unused 5 unused 6 sg connector pin number and signal details (rs-485) pin no. Signal name symbol 1 send/receive...
Page 49
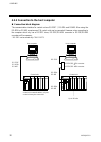
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 41 4.2.5 multiple control unit connections when using com.Port1 and com.Port2: connect com.Port2 on unit address 1 to com.Port1 on unit address 2. Connection cable w-bf-02 (rkc product, sold separately) can be used to connect the control unit. If noise is a factor, customer s...
Page 50
4. Wiring ims01j02-e4 42 when using com.Port3: connection cable w-bf-01 (rkc product, sold separately) can be used to connect the control unit. If noise is a factor, customer should use a twisted pair cable (not included) or something to that effect. Junction terminals control unit (unit address 1...
Page 51: Warning
Ims01j02-e4 43 5. Settings before operation 5.1 protocol selection and host communication setting protocol, data bit configuration, communication speed and initialize method can be set with the dip switches located in the h-pcp-j module. Com.Port1/com.Port2 setting switch (sw2) com.Port3 setting swi...
Page 52
5. Settings before operation ims01j02-e4 44 com.Port1/com.Port2 setting switch (sw2) sw2 data bit configuration 1 2 off off data 8-bit, without parity, stop 1-bit on off data 7-bit, odd parity, stop 1-bit off on data 7-bit, even parity, stop 1-bit on on data 7-bit, even parity, stop 2-bit factory ...
Page 53
5. Settings before operation ims01j02-e4 45 com.Port1/com.Port2 setting switch (sw2) sw2 protocol 5 6 7 8 off off off off rkc communication protocol (based on ansi x3.28-1976 subcategory 2.5 b1) see 6. Rkc communication (p. 52). On off off off modbus protocol see 7. Modbus (p. 105). Off on off off m...
Page 54
5. Settings before operation ims01j02-e4 46 com.Port3 setting switch (sw3) sw3 data bit configuration 1 2 off off data 8-bit, without parity, stop 1-bit on off data 7-bit, odd parity, stop 1-bit off on data 7-bit, even parity, stop 1-bit on on data 7-bit, even parity, stop 2-bit factory set value:...
Page 55
5. Settings before operation ims01j02-e4 47 com.Port3 setting switch (sw3) sw3 modbus mode selection 7 off modbus mode 1 (data time interval judges time-out with 24-bit time or more.) this mode is based on modbus rtu standard. On modbus mode 2 (data time interval judges time-out with 24-bit time 2...
Page 56: 5.2 Unit Address Setting
5. Settings before operation ims01j02-e4 48 5.2 unit address setting when each control unit is multi-drop connected to host computer, set the unit address of each control unit using the unit address setting switch at the front of the h-pcp-j module. For this setting, use a small blade screwdriver. 8...
Page 57: 5.3 Start-Up Procedures
5. Settings before operation ims01j02-e4 49 5.3 start-up procedures check prior to power on check the following items before turning on the power to the control unit. operation environments conform to 3.1 mounting cautions (p. 20). wiring and connections conform to 4. Wiring (p. 25). power s...
Page 58
5. Settings before operation ims01j02-e4 50 5.4 communication requirements processing times during data send/receive the sr mini hg system requires the following processing times during data send/receive. Whether the host computer is using either the polling or selecting procedure for communicatio...
Page 59
5. Settings before operation ims01j02-e4 51 rs-485 (2-wire system) send/receive timing the sending and receiving of rs-485 communication is conducted through two wires; consequently, the transmission and reception of data requires precise timing. Typical polling and selecting procedures between th...
Page 60: 6. Rkc Communication
52 ims01j02-e4 6. Rkc communication 6.1 protocol rkc communication uses the polling/selecting method to establish a data link. The basic procedure is followed ansi x3.28-1976 subcategories 2.5 and b1 basic mode data transmission control procedure (fast selecting is the selecting method used in sr mi...
Page 61
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 53 polling procedures (1) data link initialization host computer sends eot to the controllers to initiate data link before polling sequence. (2) data sent from host computer - polling sequence host computer sends polling sequence with the format shown below: 1. Add...
Page 62
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 54 1. Stx stx is the transmission control character which indicates the start of the text transmission (identifier and data). 2. Identifier (2 digits) the identifier indicates the type of data (measured value, status and set value) sent to the host computer. See 6.2 ...
Page 63
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 55 (4) eot send (ending data transmission from the sr mini hg system) in the following cases, the sr mini hg system sends eot to terminate the data link: when the specified identifier is invalid when there is an error in the data format when all the data has be...
Page 64
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 56 polling procedure example (when the host computer requests data) normal transmission e o t 0 1 s 1 e n q a c k 04h 30h 31h 53h 31h 05h 06h s t x s 1 0 1 4 0 0 . 0 e t x b c c 02h 53h 31h 30h 31h 20h 20h 34h 30h 30h 2eh 30h 03h 67h e o t 04h s t x p 1 0 1 e t x b...
Page 65: 6.1.2 Selecting
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 57 6.1.2 selecting selecting is the action where the host computer requests one of the connected sr mini hg system to receive data. An example of the selecting procedure is shown below: selecting procedures (1) data link initialization host computer sends eot to th...
Page 66
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 58 (3) data sent from the host computer the host computer sends data for the selecting sequence with the following format: if the length of send data (from stx to bcc) exceeds 128 bytes, it is divided into blocks by etb. In this case, the succeeding divided data is s...
Page 67
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 59 selecting procedure example (when the host computer sends data) normal transmission e o t 0 1 s t x s 1 0 1 4 0 0 . 0 e t x b c c 04h 30h 31h 02h 53h 31h 30h 31h 20h 20h 34h 30h 30h 2eh 30h 03h 57h a c k 06h s t x p 1 0 1 e t x b c c e o t 02h 50h 31h 30h 31h ...
Page 68
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 60 6.1.3 communication data structure data description (transmission/receive data structure) s t x e t x b c c part of the data above is shown below. data for each channel data length 6 digits 0 1 1 0 0 . 0 , 0 2 ... ... 2 0 ... Data length 1 digit 0 1 , 0 2 ... ...
Page 69
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 61 6.2 communication identifier list if you add or delete a function module, or change the arrangement of the modules, or replace a module with a different model, be sure to perform “module initialization (identifier: cl)” (p. 84) before setting the data. “module ini...
Page 70
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 62 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value alarm 1 status [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] aa 1 ro c 0: off 1: on alarm 2 status [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] ab 1 ro c 0: off 1: on burnout status [h-ti...
Page 71
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 63 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value pid/at transfer * [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] g1 1 r/w c 0: pid control operation 1: at (autotuning) operation 0 * autotuning (at) is the function which...
Page 72
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 64 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value temperature set value (sv) [h-tio-, h-cio-a] s1 6 r/w c tc/rtd input: within input range (within setting limiter) voltage/current input: within display...
Page 73
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 65 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value alarm 1 set value [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] a1 6 r/w c tc/rtd input: within input range or span range voltage/current input, h-sio-a: within display s...
Page 74
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 66 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value operation mode transfer [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] ei 1 r/w c 0: unused if set to “unused,” no control, monitor or alarm monitor is performed. 1: monit...
Page 75
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 67 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value initial setting mode [h-pcp-j] in 1 r/w u 0: normal communication normal communication is possible. 1: extended communication (initialize setting mode) ...
Page 76
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 68 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value temperature rise completion trigger 1 [h-tio-, h-cio-a] hs 1 r/w c 0: unused 1: used do not set “1: used” in h-tio-h/j module and h-sio-a module, becau...
Page 77
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 69 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value control loop break alarm (lba) status [h-tio-, h-cio-a] ap 1 ro c 0: off 1: on lba use selection [h-tio-, h-cio-a] hp 1 r/w c 0: unused 1: used 0 lba ...
Page 78
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 70 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ao corresponding channel setting [h-ao-a/b] oy 6 r/w c 1 to 20 (tio channel) 1 to 40 (ai and ti channel) setting will be valid in recorder output mode. ...
Page 79
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 71 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value event do status [h-do-c] q3 6 ro m 0 to 255 a contact output status is expressed as a bit image in decimal number. Event do manual output value [h-do-c]...
Page 80
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 72 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ti measured value [h-ti-a/b/c] m7 6 ro c within input range ti alarm 1 status [h-ti-a/b/c] af 1 ro c 0: off 1: on ti alarm 2 status [h-ti-a/b/c] ag 1 ro...
Page 81
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 73 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value event di contact input monitor [h-di-b] l4 6 ro m 0 to 255 a contact input status is expressed as a bit image in decimal number. Event di logic input mo...
Page 82
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 74 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value h-ct-a module heater break alarm status [h-ct-a] ah 1 ro c 0: normal 1: break 2: welding comprehensive alarm status [h-pcp-j] aj 6 ro u 0 to 2047 * alar...
Page 83
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 75 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value h-do-g manipulated output value [h-do-g] d0 6 ro c 5.0 to 105.0 % h-do-g do output status [h-do-g] d2 6 ro c 0 to 65535 * output status is expressed a...
Page 84
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 76 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value plc scanning time setting * [h-pcp-j] st 6 r/w u 0 to 3000 ms 10 integral time limiter at at end [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] gy 6 r/w u 1 to 3600 second...
Page 85: Warning
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 77 6.3 initial setting (extended communication) this section describes the initialize setting changing procedure when this system is changed to extended communication (initialize setting mode). Change the setting correctly in accordance with precautions in each item....
Page 86
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 78 data of identifier h3 with h-tio-/h-cio-a module is different from h-sio-a module. Data is discriminated by channel number (module number). Identifier h3: for h-cio-a module ....... Cascade di function selection for h-sio-a module ..... Di process selection for ...
Page 87
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 79 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value input error determination point (low) [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] aw 6 r/w c tc/rtd input: within input range input range (low) voltage/current input, h...
Page 88
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 80 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value on/off control differential gap (upper) [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] iv 6 r/w c 0.00 to 10.00 of span 0.02 on/off control differential gap (lower) [h-...
Page 89
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 81 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value hot/cold start selection [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] xn 1 r/w c 0: hot start at restarting operation mode → same as mode before the power failure output...
Page 90
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 82 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value control run/stop holding * [h-pcp-j] x1 1 r/w u 0: not hold start-up from control stop status 1: hold start-up from before the stop status 2: start-up ...
Page 91
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 83 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value alarm 1 differential gap [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] ha 6 r/w u 0.00 to 10.00 of span 0.10 alarm 2 differential gap [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] hb 6 r...
Page 92
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 84 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value alarm 1 action at input error [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] oa 1 r/w u 0: normal alarm action 1: forced alarm on when temperature measured value exceeds ...
Page 93
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 85 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value this identifier is unused with this module (h-pcp-j). (h-pcp-a/b module do type selection) vp 6 r/w u 0000 to 9999 do not set this module (h-pcp-j). Set...
Page 94
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 86 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value di function selection [h-di-a] xk 6 r/w m 0: unused 1: function mode 1 memory area transfer (enable terminal is used) after area selection setting, t...
Page 95
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 87 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ai input range number [h-ai-a/b] vk 6 r/w c 0: 0 to 10 mv dc 1: 10 to 10 mv dc 2: 0 to 100 mv dc 3: 100 to 100 mv dc 4: 0 to 1 v dc 5: 1 to 1 v dc...
Page 96
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 88 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ai alarm 1 type selection [h-ai-a/b] xc 1 r/w u 0: process high alarm 1: process low alarm 2 to 6: no alarm function the factory set value varies depen...
Page 97
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 89 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value display scale high [h-tio-h/j, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] xv 6 r/w c span 10000 or less 1 (within 9999 to 10000) h-tio-h/j, h-cio-a: 100.0 h-sio-a: 300 display...
Page 98
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 90 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value event do function selection [h-do-c] xf 6 r/w c 0 to 30 * 0 event do corresponding channel setting [h-do-c] xg 6 r/w c 1 to 40 * 1 event do mode select...
Page 99
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 91 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value cascade di function selection [h-cio-a] h3 1 r/w m 0: unused 1: cascade control on/off only 2: auto/manual transfer only 3: di1 valid (cascade control o...
Page 100
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 92 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ti input range number [h-ti-a/b/c] xj 6 r/w c 0 to 120 if the input range number is changed, all of the settings corresponding to the channels in the r...
Page 101
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 93 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value event di type selection 1 [h-di-b] r1 6 r/w l 0 to 30 * (17 to 30: not settable) 0 event di type selection 2 [h-di-b] r2 6 r/w l 0 to 30 * (17 to 30: no...
Page 102
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 94 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value number of hba trigger points [h-ct-a] dh 6 r/w u 0 to 255 times 5 positioning adjustment counter [h-tio-k] fv 6 r/w c 0 to 100 a 0 h-pcp-j module do de...
Page 103
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 95 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value h-sio-a input frequency at full scale [h-sio-a] jf 6 r/w c 10 to 50000 hz 130 h-sio-a control range [h-sio-a] sc 6 r/w c 0.00 to 50.00 % 10.00 h-sio-a o...
Page 104
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 96 continued from the previous page. Name iden- tifier digits attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value pv bias unit selection [h-tio-h/j, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] jw 1 r/w u 0: % (of span) 1: unit of input range 0 * h-pcp-j module do type selection [h-pcp-j] vu...
Page 105
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 97 event output function the event output function enables up to 8 points to be output per module of unique alarms different from ordinary temperature and ai alarms (extension alarm output function), control unit operations (status output function) and comparison r...
Page 106
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 98 continued from the previous page. status output function this function is used to output the control unit action status other than the extension alarm output in addition to the ordinary alarm output status (alarm 1 status, etc.). Event do function selection (id...
Page 107
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 99 continued from the previous page. data comparison output function this function is used to output the result of comparison between the measured value and measured value (or set value and set value) within the same group. Event do function selection (identifier: ...
Page 108
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 100 continued from the previous page. [relationship between output and comparison] computing equation: the output turns on at (data 2) (data 1) 0 this means: the output turns on if (data 2) is smaller than or equal to (data 1). {data 2 data 1} the output turns...
Page 109
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 101 continued from the previous page. Event di type selection (identifier: r1 to r4) event di corresponding channel selection (identifier: e1 to e4) note setting data description 0 input always off always on at “reversal” selection 1 event di input 1 to 80 0: off 1: ...
Page 110
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-ee4 102 positioning adjustment counter item setting data (setting counter value) description status 0 normal status opening adjustment 1 opening adjustment star, open-side output start (motor time: 110 %) automatic 2 capture the open-side opening value after 3 seconds...
Page 111
6. Rkc communication ims01j02-e4 103 input range table thermocouple input (h-tio-a/b/c/d/e/g/k/p/r, h-ti-b/c, h-cio-a) input type range no. 0 to 400 c 0 0 to 800 c 1 0 to 1300 c 2 0.0 to 400.0 c 46 0.0 to 800.0 c 47 k 0.0 to 1300.0 c 1 80 0 to 800 f 3 0.0 to 800.0 f 48 0 to 2400 f 4 0.0 t...
Page 112
6. Rkc communication 104 ims01j02-e4 rtd input (h-tio-a/b/c/d/e/f/g/k/p/r, h-ti-a/b, h-cio-a) input type range no. 0.0 to 400.0 c 59 0 to 400 c 38 200 to 200 c 39 200.0 to 200.0 c 58 jpt100 50.00 to 150.00 c 1 106 300 to 900 f 41 0 to 800 f 40 0.0 to 800.0 f 60 300.0 to 900.0 f 2 ...
Page 113: 7. Modbus
Ims01j02-e4 105 7. Modbus 7.1 protocol the master controls communication between master and slave. A typical message consists of a request (query message) sent from the master followed by an answer (response message) from the slave. When master begins data transmission, a set of data is sent to the ...
Page 114: 7.1.2 Function Code
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 106 7.1.2 function code function code contents function code (hexadecimal) function contents 03h read holding registers measured value (pv), control output value, current transformer input measured value, alarm status, etc. 06h preset single register set value (sv), pv bias, ...
Page 115: 7.1.4 Slave Responses
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 107 7.1.4 slave responses (1) normal response in the response message of the read holding registers, the slave returns the read out data and the number of data items with the same slave address and function code as the query message. in the response message of the preset si...
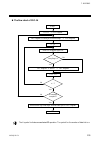
Page 116: 7.1.5 Calculating Crc-16
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 108 7.1.5 calculating crc-16 the cyclic redundancy check (crc) is a 2 byte (16-bit) error check code. After constructing the data message, not including start, stop, or parity bit, the master calculates a crc code and appends this to the end of the message. The slave will calcu...
Page 117
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 109 the flow chart of crc-16 start ffffh crc register 0 n shift crc register right 1 bit carry flag is 1 no yes crc register a001h crc register n + 1 n no yes n 7 no yes is message complete ? Crc register next byte of the message crc register end reverse with ...
Page 118
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 110 example of a crc calculation in the ‘c’ language this routine assumes that the data types ‘uint16’ and ‘uint8’ exists. Theses are unsigned 16-bit integer (usually an ‘unsigned short int’ for most compiler types) and unsigned 8-bit integer (unsigned char). ‘z_p’ is a point...
Page 119: 7.2 Message Format
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 111 7.2 message format 7.2.1 read holding registers [03h] the query message specifies the starting register address and quantity of registers to be read. The contents of the holding registers are entered in the response message as data, divided into two parts: the high-order 8-...
Page 120
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 112 7.2.2 preset single register [06h] the query message specifies data to be written into the designated holding register. The write data is arranged in the query message with high-order 8-bit first and low-order 8-bit next. Only r/w holding registers can be specified. Example...
Page 121
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 113 7.2.3 diagnostics (loopback test) [08h] the master’s query message will be returned as the response message from the slave. This function checks the communication system between the master and slave (sr mini hg system control unit). Example: loopback test for slave address ...
Page 122
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 114 7.2.4 preset multiple registers [10h] the query message specifies the starting register address and quantity of registers to be written. The write data is arranged in the query message with high-order 8-bit first and low-order 8-bit next. Only r/w holding registers can be s...
Page 123: 7.3 Communication Data
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 115 7.3 communication data 7.3.1 data configuration the numeric range of data used in modbus protocol is 0000h to ffffh. Only the set value within the setting range is effective. Ffffh represents 1. Data processing with decimal points data with decimal points the modbus prot...
Page 124
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 116 data with 3 digits below decimal point h-do-g output ratio set value cascade gain example: when heater break alarm set value 1 is 20.0 a, 20.0 is processed as 200, 200 = c8h heater break alarm high 00h set value 1 low c8h data without decimal points status error code ov...
Page 125
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 117 continued from the previous page. Di process selection positioning adjustment counter heater break alarm status (h-ct-a) h-di-a module input status h-do-g output cycle time h-do-g master channel setting h-do-g auto/manual transfer ai status ai zero point correction ai full ...
Page 126
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 118 data whose decimal point’s presence and/or position depends on input range the position of the decimal point changes depending on the input range type because the modbus protocol does not recognize data with decimal points during communication. The following data can have...
Page 127
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 119 7.3.2 data processing precautions with modbus protocol, the maximum number of channels per slave address is 20. the accessible data (holding register) address range is from 0000h to 1fffh. If data exceeding the 1fffh is accessed, an error response message is returned. ...
Page 128
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 120 7.3.3 communication data list if you add or delete a function module, or change the arrangement of the modules, or replace a module with a different model, be sure to perform “module initialization (register addresses: 02bfh)” (p. 127, 153) before setting the data. “module ...
Page 129
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 121 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value status [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] ro c the respective channel status is assigned to each bit in the holding register. Bit 0: alarm 1 status bit 1: alarm 2 status bit 2: burnout stat...
Page 130
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 122 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value comprehensive alarm status [h-pcp-j] ro u the respective channel status is assigned to each bit in the holding register. Bit 0: logical or of alarm 1 status in all channels bit 1: lo...
Page 131
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 123 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value pid/at transfer * [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w c 0: pid control operation 1: at (autotuning) operation 0 * autotuning (at) is the function which automatically measures, calculates...
Page 132
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 124 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value heat-side proportional band [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w c 0.1 to 1000.0 % of span h-tio-, h-cio-a: 3.0 h-sio-a: 300.0 cool-side proportional band [h-tio-, h-cio-a] r/w c 0.1 to...
Page 133
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 125 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value alarm 1 set value [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w c tc/rtd input: within input range or span range voltage/current input, h-sio-a: within display scale range or span range see factor...
Page 134
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 126 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value heat-side proportioning cycle time [h-tio-, h-cio-a] r/w c 1 to 100 seconds setting will be invalid in voltage/current output. 20 a cool-side proportioning cycle time [h-tio-, h-ci...
Page 135
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 127 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value temperature rise completion trigger [h-tio-, h-cio-a] r/w c 0: unused 1: used 1 do not set “1: used” in h-tio-h/j module and h-sio-a module, because temperature rise completion is n...
Page 136
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 128 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value alarm interlock release [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-ti-, h-ai-] wo u 1: release (1 only) cascade on/off [h-cio-a] r/w c 0: off 1: on setting will be valid in master channel. 0 cascade gai...
Page 137
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 129 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value output limiter low [for heat/cool control: cool-side output limiter (high)] [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w c [heat control, position proportioning control and speed control] 5.0 % ...
Page 138
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 130 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value h-sio-a control range [h-sio-a] r/w c 0.00 to 50.00 % 10.00 h-sio-a input frequency at full scale [h-sio-a] r/w c 10 to 50000 hz 130 h-sio-a output scale high [h-sio-a] r/w c h-sio-a...
Page 139
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 131 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value decimal point position [h-tio-h/j, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w c 0: no decimal place 1: one decimal place 2: two decimal places 3: three decimal places h-tio-h/j, h-cio-a: 1 h-sio-a: 0 inp...
Page 140
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 132 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value at bias [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w c within input span range 0 * on/off control differential gap (upper) [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w c 0.00 to 10.00 of span 0.02 on/off ...
Page 141
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 133 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value start determination point 1 [h-tio-, h-cio-a] r/w c 0.0 to 100.0 of span (deviation setting from the temperature set value) setting will be invalid in h-sio-a module. 3.0 control ...
Page 142
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 134 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value temperature rise completion hold function [h-pcp-j] r/w u 0: not hold 1: hold 1 interval time setting com.Port1/ com.Port2 [h-pcp-j] r/w u 0 to 100 ms 1 interval time setting com.Por...
Page 143
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 135 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value pv bias unit selection [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w u 0: % (of span) 1: unit of input range 0 * integral time limiter at at end [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w u 1 to 3600 seconds...
Page 144
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 136 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value number of alarm delay times [h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a] r/w u 0 to 255 times 0 do function selection [h-do-a/b/d] r/w m 00 to 88 * the factory set value varies depending on the speci...
Page 145
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 137 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value di using selection [h-di-a] r/w m 0 to 255 * 255 h-pcp-j module do type selection [h-pcp-j] r/w c 0: no alarm function 1: alarm 1/ti alarm 1 2: alarm 2/ti alarm 2 3: burnout 4: heate...
Page 146
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 138 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value cascade tracking [h-cio-a] r/w m 0: not provided cascade monitored value becomes zero. 1: provided cascade monitored value just before is hold. 0 cascade data selection [h-cio-a] r/w...
Page 147
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 139 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value positioning adjustment counter [h-tio-k] r/w c 0 to 100 * 0 h-ct-a module heater break alarm status [h-ct-a] ro c 0: normal 1: break 2: welding h-di-a module input status [h-di-a] ro...
Page 148
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 140 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value h-do-g manipulated output value [h-do-g] ro c 5.0 to 105.0 % h-do-g output limiter high [h-do-g] r/w c output limiter low to 105.0 % 100.0 h-do-g output limiter low [h-do-g] r/w c ...
Page 149
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 141 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ai measured value [h-ai-a/b] ro c within display scale range * ai status [h-ai-a/b] ro c the respective channel status is assigned to each bit in the holding register. Bit 0: ai alar...
Page 150
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 142 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ai input range number [h-ai-a/b] r/w c 0: 0 to 10 mv dc 1: 10 to 10 mv dc 2: 0 to 100 mv dc 3: 100 to 100 mv dc 4: 0 to 1 v dc 5: 1 to 1 v dc 6: 0 to 5 v dc 7: 1 to 5 v dc 8: ...
Page 151
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 143 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ai alarm 1 type selection [h-ai-a/b] r/w u 0: process high alarm 1: process low alarm 2 to 6: no alarm function the factory set value varies depending on the specifications when orde...
Page 152
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 144 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ti measured value [h-ti-a/b/c] ro c within input range ti status [h-ti-a/b/c] ro c the respective channel status is assigned to each bit in the holding register. Bit 0: ti alarm 1 st...
Page 153
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 145 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ti alarm 1 differential gap [h-ti-a/b/c] r/w u 0.00 to 10.00 % of span 0.10 ti alarm 2 differential gap [h-ti-a/b/c] r/w u ti alarm 1 type selection [h-ti-a/b/c] r/w u 0: process hig...
Page 154
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 146 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value ao output value monitor [h-ao-a/b] ro c display scale range * data will be valid in manual mode. Ao output set value [h-ao-a/b] r/w c display scale range * setting will be valid in m...
Page 155
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 147 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value event di contact input monitor [h-di-b] ro m the respective channel status is assigned to each bit in the holding register. Bit 0: ch1 (di1) bit 1: ch2 (di2) bit 2: ch3 (di3) bit 3: ...
Page 156
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 148 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value event di type selection 1 [h-di-b] r/w l 0 to 30 * (17 to 30: not settable) 0 event di type selection 2 [h-di-b] r/w l 0 to 30 * (17 to 30: not settable) 0 event di type selection 3 ...
Page 157
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 149 continued from the previous page. Name attri- bute struc- ture data range factory set value event do status [h-do-c] ro m the respective channel status is assigned to each bit in the holding register. Bit 0: ch1 (do 1) bit 1: ch2 (do 2) bit 2: ch3 (do 3) bit 3: ch4 (do 4) b...
Page 158: 7.4 Data Map
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 150 7.4 data map if you add or delete a function module, or change the arrangement of the modules, or replace a module with a different model, be sure to perform “module initialization (register addresses: 02bfh)” (p. 127, 153) before setting the data. “module initialization” s...
Page 159: 7.4.2 Data Map List
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 151 continued from the previous page. (4) correspondence module: the function module name that data becomes valid is written. Data of following address with h-tio-/h-cio-a module is different from h-sio-a module. Data is discriminated by channel number (module number). Address...
Page 160
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 152 (2) read/write data address ch name address ch name 00c8h ( 200) ch1 temperature set value (sv) 01cch ( 460) ch1 heat-side proportioning h-tio-, h-cio-a cycle time motor speed set value h-tio-, h-cio-a 00dbh ( 219) ch20 h-sio-a 01dfh ( 479) ch20 00dch ( 220) ch1 pid/a...
Page 161
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 153 continued from the previous page. Address ch name address ch name memory area number 0384h ( 900) ch21 heater break alarm set 02bdh ( 701) (for each control unit) value 2 h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a 03abh ( 939) ch60 h-ct-a temperature rise 03ach ( 940) do not use this ...
Page 162
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 154 (3) read/write data (initial data) when setting initial setting data items, stop control by normal setting data control start/stop selection.” address ch name address ch name 03e8h (1000) ch1 setting change rate limiter 04d8h (1240) ch1 h-sio-a correction trigger h-tio-, h...
Page 163
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 155 continued from the previous page. Address ch name address ch name 05b4h (1460) ch1 setting limiter low temperature rise h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a 06a5h (1701) completion hold function 05c7h (1479) ch20 (for each control unit) 05c8h (1480) ch1 input error determination h-p...
Page 164
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 156 continued from the previous page. Address ch name address ch name alarm 2 differential gap 06eah (1770) do not use this address 06b9h (1721) (for each control unit) range h-tio-, h-cio-a, h-sio-a 06f3h (1779) alarm 1 type selection 06f4h (1780) di using selection 06bah...
Page 165
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 157 (4) read only data address ch name 085ch (2140) ch1 h-ct-a module heater break alarm status h-ct-a 0897h (2199) ch60 0898h (2200) h-di-a module input status (for each module) 08a1h (2209) h-di-a 08a2h (2210) do not use this address range 08abh (2219) 08ach (2220) ch1 ca...
Page 166
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 158 (5) h-do-g module data address ch name 0bb8h (3000) ch1 h-do-g manipulated output value h-do-g 0c57h (3159) ch160 0c58h (3160) ch1 h-do-g output limiter high h-do-g 0cf7h (3319) ch160 0cf8h (3320) ch1 h-do-g output limiter low h-do-g 0d97h (3479) ch160 0d98h (3480) ch1 h-do...
Page 167
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 159 (6) h-ai-a/b module data address ch name address ch name 1194h (4500) ch1 ai measured value ai alarm 1 differential gap h-ai-a/b 139ch (5020) (for each control unit) 11bbh (4539) ch40 h-ai-a/b 11bch (4540) ch1 ai status ai alarm 2 differential gap h-ai-a/b 139dh (5021) ...
Page 168
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 160 (7) h-ti-a/b/c module data address ch name address ch name 13ech (5100) ch1 ti measured value ti alarm 2 hold action h-ti-a/b/c 1531h (5425) (for each control unit) 1413h (5139) ch40 h-ti-a/b/c 1414h (5140) ch1 ti status ti alarm 1 interlock h-ti-a/b/c 1532h (5426) (for...
Page 169
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 161 (8) h-ao-a/b module data address ch name 157ch (5500) ch1 ao output value monitor h-ao-a/b 15a3h (5539) ch160 15a4h (5540) ch1 ao output set value h-ao-a/b 15cbh (5579) ch160 15cch (5580) ch1 ao function selection h-ao-a/b 15f3h (5619) ch160 15f4h (5620) ch1 ao correspondin...
Page 170
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 162 (9) h-di-b module data (event di data) address ch name address ch name 1770h (6000) event di contact input 1a18h (6680) event di corresponding monitor (for each module) channel selection 4 (for h-di-b each event input logic 1779h (6009) 1a67h (6759) circuit) h-di-b 177a...
Page 171
7. Modbus ims01j02-e4 163 (10) h-do-c module data (event do data) address ch name 1c84h (7300) event do status (for each module) 1c8dh (7309) h-do-c 1c8eh (7310) do not use this address range 1c97h (7319) 1c98h (7320) event do manual output value (for each module) 1ca1h (7329) h-do-c 1ca2h (7330) do...
Page 172: 8. Functions
164 ims01j02-e4 8. Functions 8.1 output ratio output ratio function multiplies value (gradient) set with output ratio in manipulated output value of master channel (temperature control module h-tio-), and it is function to output the consequence as manipulated output value from slave channel (digit...
Page 173
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 165 output ratio action manipulated output value of master channel and slave channel are output within the output limiter range. Master channel (h-tio module) output limiter high manipulated output value of master channel 0 % 100 % pid computation result output limiter low...
Page 174
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 166 assignment of the master channels it is possible to assign the master channel corresponding to the slave channel if in the same unit. The master channel is assigned by “h-do-g master channel setting.” h-do-g master channel setting setting range: 0 to the number of h-ti...
Page 175
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 167 h-do-g master channel setting example slave channel no. (h-do-g module) h-do-g master channel setting slave channel no. (h-do-g module) h-do-g master channel setting 1 1 17 5 2 1 18 5 3 2 19 5 4 2 20 6 5 2 21 6 6 2 22 6 7 2 23 7 8 3 24 7 9 3 25 7 10 3 26 8 11 3 27 8 12 3...
Page 176: 8.2 Speed Control
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 168 8.2 speed control speed control function inputs pulse from rotary encoder, and motor speed is controlled. Other than h-pcp-j module, h-sio-a module are requirement to do speed control function. Sr mini hg system control unit h-tio-b module h-pcp-j module h-sio-a module m...
Page 177: 8.2.1 Display Scale
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 169 8.2.1 display scale this function scales the display range of the input value between 9999 to 10000. However, the maximum span is 10000. H-sio-a input frequency at full scale: sets the frequency of encoder when display scale high value (full scale) is displayed. Settin...
Page 178: 8.2.2 Measuring Method
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 170 8.2.2 measuring method can be selected periodic computation method or pulse count method. periodic computation method frequency is obtained by measuring the time required for certain pulse intervals. The number of measured pulses can be set in the pulse range of 1 to 1...
Page 179: 8.2.3 Output Scale
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 171 8.2.3 output scale this function scales the output range between 9999 to 10000. H-sio-a output scale high: sets the value equivalent to display scale of control output high limit. Setting rage: h-sio-a output scale low to 10000 h-sio-a output scale low: sets the value ...
Page 180: 8.2.5 Controls
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 172 8.2.5 controls this instrument controls with open loop control or pid control (closed loop control). (1) open loop control in a deviation between the motor speed measured value and set value is larger than the h-sio-a control range set value, or the h-sio-a open/closed l...
Page 181
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 173 (2) pid control (closed loop control) if a deviation between the motor speed measured value and set value is within the control range set value, and the h-sio-a open/closed loop control transfer is “0: closed loop control,” the instrument performs pid control. Pi control...
Page 182
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 174 control response parameters this is the function of enabling the setting of response to set value change in select any one of 3 steps (slow, medium, fast) in pid control. In order to achieve faster controlled object response to set value change, select fast. However, s...
Page 183: 8.2.6 Scale Correction
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 175 8.2.6 scale correction this is the function of correcting the motor speed measured value and control output when the motor speed measured value differs from the actually measured value or motor speed set value differs from the actually measured value. H-sio-a correction ...
Page 184
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 176 example: correction in the following value. Control output: voltage output 0 to 10 v dc motor speed set value: 250 mm/min display scale high: 300 mm/min motor speed measured value: 245 mm/min display scale low: 0 mm/min actual measured value: 240 mm/min output scale high...
Page 185
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 177 8.2.7 output change rate limiter the output change rate limiter limits the variation of manipulated output (mv) for a time unit. You can set an output variation, and control the output, when your object requires to avoid sudden variation. The output variation limiter is ...
Page 186: 8.2.8 Alarm Hold Function
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 178 8.2.8 alarm hold function in the alarm hold function, the alarm function is kept invalid even if the motor speed measured value is in the alarm range when the power is on or the operation mode is switched to run from stop. The alarm function is held until it passes with ...
Page 187: 8.2.9 Assignment of Channels
8. Functions ims01j02-e4 179 8.2.9 assignment of channels channel number of h-sio-a modules uses the same kind of channel number as h-tio- modules and h-cio-a modules. If the h-sio-a modules are mounted together with h-tio- modules and h-cio-a modules, the channel numbers are continued. Channel nu...
Page 188: 9. Troubleshooting
180 ims01j02-e4 9. Troubleshooting this section lists some basic causes and solutions to be taken when any problem would arise in this instrument. If you cannot solve a problem, please contact rkc sales office or the agent, on confirming the type name and specifications of the product. If the instru...
Page 189
9. Troubleshooting ims01j02-e4 181 h-pcp-j module problem probable cause solution run lamp does not light up power not being supplied check external breaker etc. Appropriate power supply voltage not being supplied check the power supply power supply terminal contact defect retighten the terminals ...
Page 190
9. Troubleshooting ims01j02-e4 182 rkc communication problem probable cause solution no response wrong connection, no connection or disconnection of the communication cable confirm the connection method or condition and connect correctly breakage, wrong wiring, or imperfect contact of the communic...
Page 191
9. Troubleshooting ims01j02-e4 183 modbus problem probable cause solution no response wrong connection, no connection or disconnection of the communication cable confirm the connection method or condition and connect correctly breakage, wrong wiring, or imperfect contact of the communication cable...
Page 192
9. Troubleshooting ims01j02-e4 184 plc communication problem probable cause solution tx1 (data transmission) lamp does not flash rx1 (data reception) lamp does not flash wrong connection, no connection or disconnection of the communication cable confirm the connection method or condition and conne...
Page 193
9. Troubleshooting ims01j02-e4 185 continued from the previous page. Problem probable cause solution tx1 (data transmission) lamp and rx1 (data reception) lamp are flashed alternately setting of plc becomes write inhibit setting of plc is turned into write enable (write enable in run, shift to monit...
Page 194: 10. Ascii 7-Bit Code Table
186 ims01j02-e4 10. Ascii 7-bit code table this table is only for use with rkc communication. B7 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 b6 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 b5 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 b5 to b7 b4 b3 b2 b1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 0 0 0 0 nul dle sp 0 @ p ‘ p 0 0 0 1 1 soh dc1 ! 1 a q a q 0 0 1 0 2 stx dc2 ” 2 b r b r 0 0 1 1 3 etx dc3 # 3...
Page 195
The first edition: sep. 2004 [imq00] the fourth edition: feb. 2013 [imq00].
Page 196: Ims01J02-E4
Ims01j02-e4 feb. 2013 rkc instrument inc. Headquarters: 16-6, kugahara 5-chome, ohta-ku tokyo 146-8515 japan phone: 03-3751-9799 (+81 3 3751 9799) fax: 03-3751-8585 (+81 3 3751 8585) e-mail: info@rkcinst.Co.Jp website: http://www.Rkcinst.Com/ r.