- DL manuals
- SAF
- Receiver
- CFIP PhoeniX Series
- Configuration Manual
SAF CFIP PhoeniX Series Configuration Manual
Summary of CFIP PhoeniX Series
Page 1
Cfip phoenix series tdm/ip split mount system technical description & configuration guide product code: s0drfmd1 saf tehnika jsc 2015.
Page 2: Table Of Contents
Table of contents 1 overview .................................................................................................................................... 5 1.1 cfip phoenix tdm/ip split mount system ....................................................................................... 5 1.2...
Page 3
4.3.5 advanced protection configuration ........................................................................................................ 53 4.4 system configuration .................................................................................................................... 54 4.4.1 u...
Page 4
8 cfip discovery protocol ........................................................................................................... 110 8.1 cfip unit discovery procedure .................................................................................................... 110 8.2 discovery protocol ...
Page 5
Proprietary notice the information presented in this guide is the property of saf tehnika, jsc. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted without proper permission from saf tehnika, jsc. The specifications or information contained in this document are subject to change without notice...
Page 6
1.2 cfip phoenix feature summary 1.2.1 main features • split mount system solution • capacity: up to 363 mbps • channel bandwidth: 3.5 / 7 / 14 / 28 / 40 / 56 mhz • modulations: 4qam / 16qam / 32qam / 64qam / 128qam / 256qam • interfaces: 10 / 100 / 1000 eth + 20e1/t1 • traffic: ethernet only, eth+1...
Page 7
Figure 1.2 cfip phoenix odu 1.2.4 irfu mechanical features • indoor radio unit (idu+irfu) • 2u high • power consumption: 13-39w • dimensions 90x430x260 mm, weight 5.8 kg. Figure 1.3 cfip phoenix irfu 1.2.5 interfaces/management • cfip phoenix idu unit provides ethernet, e1, power, eow, alarm, serial...
Page 8
Figure 1.4 cfip phoenix idu connectors 1.3 cfip phoenix odu parameters • cfip phoenix is a good example of latest achievements in modem and transceiver development, providing both excellent radio parameters (system gain), due to use of qam modulations and efficient despite it consumes small amount o...
Page 9
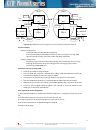
• the outgoing (tx) traffic at each site is passed to both odus, and both are always transmitting; • the incoming (rx) traffic is picked from one of the odus; • 1+1 configuration provides hardware redundancy and mitigates multipath fading; • both tx and rx switching is hitless. 1.4.3 cfip phoenix 1+...
Page 10
Figure 1.7 cfip phoenix 1+1 sd configuration 1.4.5 cfip phoenix ring topology • utilization of stp protocol allows cfip phoenix operation in ring topology (for ethernet traffic only) figure 1.8 cfip phoenix ring topology configuration cfip phoenix series tdm/ip split mount system technical descripti...
Page 11
1.5 technical specification cfip phoenix idu modem channel bandwidths 3.5, 7, 14, 28, 40, 56 mhz modulations 4qam, 16qam, 32qam, 64qam, 128qam, 256qam capacity 9 - 363 mbps supported odus cfip odu applications configuration 1+0, 1+1 (hsb, sd, fd), ring/mesh (with rstp), 2+0, 3+0, 4+0 (built-in ether...
Page 12
Ports cfip phoenix odu cfip phoenix irfu antenna n-type or flange a) n-type or flange b) tx and rx ports 1 if to idu n-type sma rssi bnc 2-port for multi-meter power --- (over if port) 2-pin power port (alternative to if port) mechanical & electrical operational use conforms to etsi en 300 019 class...
Page 13
Band frequency range duplex offset 10 ghz 10.15 – 10.68 ghz 65 mhz, 91 mhz, 300 mhz, 350 mhz 11 ghz 10.7 – 11.7 ghz 490 mhz, 500 mhz, 530 mhz 13 ghz 12.75 – 13.25 ghz 225 mhz, 266 mhz 15 ghz 14.4 – 15.35 ghz 315 mhz, 322 mhz, 420 mhz, 475 mhz, 490 mhz, 644 mhz, 728 mhz 18 ghz 17.7 – 19.7 ghz 1008 mh...
Page 14
Cfip phoenix odu cfip odu rsl at 10 -6 (dbm) and total payload capacity (mbps) bw**, mhz modulation fec *** 6 ghz 7 ghz 8 ghz 10 ghz 11 ghz 13 ghz 15 ghz 18 ghz 23 ghz 26 ghz 38 ghz bit rate, mbps 3.5 4qam strong -97 -95 -95 -97 -96 -95 -93,5 -95 -97 -96,5 -93,5 3 16qam strong -90,5 -88 -88 -90 -89 ...
Page 15
Cfip odu rsl at 10 -6 (dbm) and total payload capacity (mbps) bw**, mhz modulation fec*** 6 ghz 7 ghz 8 ghz 10 ghz 11 ghz 13 ghz 15 ghz 18 ghz 23 ghz 26 ghz 38 ghz bit rate, mbps 40 4qam strong -89 -87.5 -88 -87.5 -88 -88 -88 -88 -87.5 -89.5 -83.5 49 16qam strong -82.5 -81.5 -81.5 -81 -82 -82 -81.5 ...
Page 16
1.6 cable requirements idu-odu cable idu–odu cable is a 50 Ω coaxial cable intended to interconnect the indoor unit with the outdoor unit. Any type of 50 Ω cable of good quality can be used; the cable should be equipped with n–type male connectors on each end. There are two n–type male connectors in...
Page 17
Figure 1.10 cable for connecting the voltmeter to the cfip phoenix odu rssi port 1.7 labelling the label can be found on the front side of the unit. The label contains the following information (see samples in the picture below): - model name. The model name example is: cfip-idu-phoenix for cfip pho...
Page 18
Figure 1.13 label of the cfip phoenix irfu low band side, operating in 6 ghz band p/n translation for cfip phoenix odu: - “s” designates cfip split mount series product; - “18” designates frequency range (18 ghz) of the unit; - “rf” designates standard power radio; - “u” designates unified band odu ...
Page 19
2 configuration and management 2.1 connecting cfip phoenix idu to power source in case ac/dc power supply, 48vdc, 80w (eu - p/n i0ab4810, us – p/n i0ab4811, aus - i0ab4818) provided by saf tehnika jsc is used to power up cfip phoenix idu, interconnect idu and power source through appropriate connect...
Page 20
Figure 2.1 cfip phoenix idu dc power cable connector of type 2esdv-02 after successful powering of phoenix idu there are four ways to adjust and read settings and operation parameters of the cfip phoenix equipment: 1. Using web terminal connected to the 10/100/1000base-t port, 2. Using telnet termin...
Page 21
Prompt command “system reset” resetting with command prompt command “system reset cold” restarts modem and cpu of the management controller. Resets all management counters. 2.3 web interface this section describes operation of web interface. 2.3.1 10/100/1000base-t ports 10/100/1000base-t port is us...
Page 22
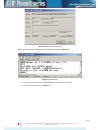
• ie v. 6.0 • mozilla firefox v. 2.0.0.11 • google chrome figure 2.4 supported browsers: “internet explorer”, “mozilla firefox” and “google chrome” after web browsers selection, open it and enter address of the cfip phoenix idu (figure 2.5). (!) the ip address of cfip phoenix idu is 192.168.205.10 f...
Page 23
Figure 2.6 web interface - main window 2.3.4 interface description web interface consists of four parts, they are: 1. Top panel, that allows to log out and gives information about device type, software version, device name, ip, serial number and uptime; 2. Menu panel that is used to open links to ot...
Page 24
Figure 2.7 web interface - main window with section numbering 2.3.5 command execution there is “ip configuration” page shown in figure 2.8. The entire page is divided into smaller fragments: 1. The header of page; 2. Sub-header of single type configuration parameters; 3. Execution controls related t...
Page 25
“execute for both” is available in “main configuration” section during configuration of modem or atpc parameters for local and remote radio sides simultaneously. Connection between both management cpus must be established in order to complete successfully configuration execution for both sides. “rol...
Page 26
Figure 2.9 starting configuration wizard initially, you can specify preferable system name, location name, passwords for guest and admin accounts. The next time you will try to access the web gui management, you will be asked to enter the user name (guest or admin) and user password. By default, sys...
Page 27
Figure 2.11 step 2. Defining ip address, mask, default gateway and remote ip address the third screen of the wizard is devoted to the modem and radio configuration and requires specifying utilized bandwidth (from 3.5 to 56 mhz), modulation type (4qam, 16qam, 32qam, 64qam, 128qam or 256qam), e1 chann...
Page 28
Figure 2.13 step 4 checking settings and executing configuration to verify the settings, we can go to ‘status’ or the main screen, which is the first option in the navigation panel. If there are no ‘red fields’, everything is set correctly and the link is up. 2.4 command prompt interface cfip equipm...
Page 29
2.4.1 rs-232 serial management port rs-232 serial management port provides terminal management via a connected pc or another terminal device or modem. The terminal connected to serial management port provides the same management functionality as telnet interfaces (refer to chapter 2.3.2). In order t...
Page 30
Figure 2.15 putty configuration - 1 2) go to “keyboard” category and change “the backspace key” to “control-h”: figure 2.16 putty configuration - 2 3) press “open” and after pressing “enter” key following prompt should appear: cfip phoenix series tdm/ip split mount system technical description and c...
Page 31
Figure 2.17 putty serial prompt password is disabled by default. See chapters 3...7 for available commands. 2.4.2 telnet connection the telnet connection to the cfip phoenix is carried out using the ethernet management connection. Please refer to chapter 2.3.2 for ethernet management port connection...
Page 32
Figure 2.19 putty telnet prompt see chapters 3...7 for available commands. 2.4.3 initial configuration with command prompt configuration steps using command prompt are as follows: 1. Check the system settings with command ‘status’ 2. Configuration required parameters: – tx power with the command ‘ra...
Page 33
Led name description odu green – ok yellow blinks – odu tx mute. Yellow – rx level alarm; odu temperature failure; idu psu to odu state alarm. Red – tx pll error alarm; rx pll error alarm; odu rx los; odu tx los; odu rx failure; odu tx failure; odu frequency failure. Red blinks – no data from odu. I...
Page 34
3 status window the main window in the web gui is status window that shows all main system parameters, and, in case of failure or any other problems, it tints a specific parameter in red. To have a better understanding on status window, we will go through every field. Figure 3.1 “main status” page 1...
Page 35
• rx level (or rsl) at both ends must not differ significantly from the previously calculated value. • modulation indicates which modulation mode is used. For better operation the same modulation must be set at both ends. • radial mse is explained below in the chapter 3.1.1. • ldpc is explained belo...
Page 36
30. Idu temperature – shows the idu internal temperature in degrees by celsius and fahrenheit (command line - diagnostics or status); 31. Odu temperature – shows the odu internal temperature in degrees by celsius and fahrenheit (command line - odu status); 32. Modem temperature – shows the temperatu...
Page 37
Figure 3.2 ldpc decoder structure ldpc stress value thresholds @ ber 1.0⋅10 -6 : - for strong fec mode ~ 4.0⋅10 -2 ; - for weak fec mode ~ 1.0⋅10 -2 as long as ldpc stress value is under the specified thresholds, the amount of errors (and ber itself) on the output of ldpc remains at zero level. 3.2 ...
Page 38
Figure 3.4 ethernet aggregation/protection status 1. Clear max n/d time – clear maximum no data time; 2. State – displays current device state status – active or standby; 3. Previous state – displays previous device state status; 4. Max n/d time: - displays maximum disconnection time between devices...
Page 39
Figure 3.5 diagnostics data 1. Inventory information - displays the cfip phoenix idu and odu product code, serial number and additional hardware information; 2. Download system information - allows saving system information (output from “full system information page”) in separate txt file on your ha...
Page 40
4 detailed configuration in web graphic user interface configuration section in web interface allows customizing your system to suit your specific needs. 4.1 odu configuration the odu configuration window provides the configuration of cfip phoenix radio part parameters. Below is a short explanation ...
Page 41
4.1.2 atpc configuration to configure atpc, it is necessary to set rx (remote) “min” and “max” values and enable the atpc feature. Atpc update period and atpc delta are recommended to be left unchanged. It is also possible to change the limit of tx power correction. Figure 4.2 atpc configuration 1. ...
Page 42
Atpc algorithm acm can be implemented together with automatic transmit power control (atpc), complimentary features that enhance overall system performance. Atpc reduces the average transmitted power as well as cci and adjacent-channel interference (aci), which is caused by extraneous power from a s...
Page 43
4.2 idu configuration 4.2.1 modem configuration figure 4.4 modem configuration 1. Modem data status – shows if management cpu was able to read data from modem; 2. Modem standard – allows switching between etsi and ansi (fcc) standards, changing available bandwidths to 3.5/7/14/28/40/56 mhz and 5/10/...
Page 44
Availability based on the priority. As a result, high-priority services such as voice enjoy 99.995% availability, while low-priority services like video streaming are allocated lower priorities. Use of qos prioritizing defines which services should be transmitted under any link condition and which s...
Page 45
The following real-world example illustrates the benefits of acm. Consider a cfip link operating at 23 ghz with 56 mhz channel spacing and 45.9 dbi (120 cm) antenna gain. The link is operating in a moderate rain region similar to central europe with a distance of 15 kilometers. The system operation ...
Page 46
• e1 and e1 far loopback modes loop signal back to local end and to remote end respectively in bounds of e1 interface. E1 loopback mode must be set on the particular channel you need to test. If no e1 channels are selected, e1 loopback mode is not available. E1 loopbacks are named “interface” and “i...
Page 47
4.3 protection configuration this section describes 1+1 protection implementation for phoenix idu. The possible 1+1 configuration modes are frequency diversity (fd), hot standby (hsb) and space diversity (sd). Figure 4.9 1+1 interconnection of twocfip phoenix idus (with power protection ports – p/n ...
Page 48
Ethernet switch modem idu4 192.168.205.13 odu3 odu4 odu1 odu2 idu1 192.168.205.10 ethernet switch modem modem idu3 192.168.205.12 idu2 192.168.205.11 ethernet switch modem protection mode: working protection mode: protection protection mode: working protection mode: protection p1 p4 p3 p2 protection...
Page 49
Figure 4.11 cfip phoenix configuration for 1+1 fd mode please refer to chapter 4.3.5 for details of 1+1 configuration parameters and configuration possibilities via cli. After successful 1+1 fd configuration, the screen of ‘protection configuration’ in web gui should look as follows: figure 4.12 pro...
Page 50
Ethernet switch modem idu4 192.168.205.13 odu3 odu4 odu1 odu2 idu1 192.168.205.10 ethernet switch modem modem idu3 192.168.205.12 idu2 192.168.205.11 ethernet switch modem protection mode: working protection mode: protection protection mode: working protection mode: protection p1 p2 protection cable...
Page 51
Example of configuration for hsb mode: figure 4.14 cfip phoenix configuration for 1+1 hsb mode after successful 1+1 hsb configuration, the screen of ‘protection configuration’ in web gui should look as follows: figure 4.15 protection configuration window after successful hsb configuration configurat...
Page 52
• it is recommended that ‘standby’ and ‘activetry’ times remain default. Idu will remain in appropriate state during forcing it to another state for this specified time. Example of configuration for sd mode: figure 4.16 cfip phoenix configuration for 1+1 sd mode the same commands can be executed usi...
Page 53
1. Value – denotes the names of cfip phoenix units in 1+1 configuration. ‘local’ and ‘local alternate’ designates both units (working and protection) at the local side and ‘remote’ and ‘remote alternate’ designates both units of remote side. 2. Protection status – denotes that cfip phoenix 1+1 prote...
Page 55
4.4.1 user configuration figure 4.22 user configuration 1. Guest – enter new password (length: 4..30 characters) – allows entering preferable ‘guest’ account password and enabling the account. By default guest account is disabled. Maximal length of the password cannot exceed 30 symbols. Guest accoun...
Page 56
4.4.2 name configuration figure 4.24 name configuration 1. System name (max length: 16 characters) – allows entering preferable system name. Maximum length of the system name cannot exceed 16 symbols. Default name is ‘saf’ (command line – system name ); 2. Location name (max length: 16 characters) –...
Page 58
2. Open advanced ethernet information page / download ethernet statistics – allows to open/save advanced ethernet statistics. Link on the top of the page allow you to save advanced ethernet statistics page in separate txt file on your hard disk drive; 3. System returned - in case of error or incorre...
Page 59
4.5.1 ethernet management port ip configuration figure 4.29 ethernet management port ip configuration 1. Ip address – allows specifying ip address of cfip phoenix you are currently logged in. Default ip address is 192.168.205.10. (command line – net ip addr ); 2. Ip mask – allows specifying ip mask ...
Page 60
Figure 4.31 static route configuration 1. Static routes – shows the list of existing static routes, as well as allows you to choose specific route you are willing to change or delete. By default there is one route which depends on earlier entered ip settings (command line – net route); 2. Network ad...
Page 61
For the purpose of illustration, we use b class ip network address 10.0.10.11 for the remote side cfip and 10.0.10.10 for the local side cfip, while the ip address of our management pc lan adapter will is 10.0.0.1. The steps of the configuration procedure are as follows: 1) enter the remote side (fa...
Page 62
Figure 4.34 internet protocol (tcp/ip) properties 4) go to the remote side web gui, choose “tools configuration file” and press “cfg write”. 5) repeat step 4) for the local side web gui. 4.6 ethernet configuration the ethernet configuration window provides the speed settings for all four lan ports...
Page 63
3. Link – shows whether link with appropriate port is established. If link is off, according field will be shown in red; 4. Duplex (actual) – shows if port is currently operating in full or half duplex mode; 5. Rx flow – shows if ‘flow control’ is enabled or disabled for ingress traffic; 6. Tx flow ...
Page 64
4.6.2 protocol transparency figure 4.37 protocol transparency 1. Represents four lan (local area network) ports of the cfip phoenix switch, as well as wan (wide area port) connected to modem ethernet interface; 2. Stp – allows enabling/disabling spanning tree protocol (stp) transparency by passing t...
Page 65
4.7 aggregation configuration link aggregation in n+0 mode allows utilizing up to 1000 mbps ethernet layer 2 throughput by using independent frequency pair for each link. Traffic is being balanced (n+0) by internal switches of master link. In case of link aggregation n+0 traffic distribution between...
Page 66
Figure 4.40 ethernet aggregation configuration for master 1. Role – choose “master”; 2. Mode – choose “aggregation” for link aggregation 2+0; 3. Revertive mode – in case of “enabled” setting link will automatically reconfigure back to 2+0 operation when unit/cable/link failure is resolved. In case o...
Page 67
Figure 4.41 ethernet aggregation configuration for slave 1. Role – choose “slave”; 2. Mode – choose “aggregation” for link aggregation 2+0 or “protection” for link protection 1+1; 3. Revertive mode – in case of “enabled” setting link will automatically reconfigure back to 2+0 operation when unit/cab...
Page 70
When vlans are not used (figure 4.44), user data and management data are not separated either logically, or physically. When using vlans (figure 4.45), it is necessary to use external switches (switch 3 and switch 4). These switches add/remove vlan tags per port basis. Thus, management data and user...
Page 71
Ext. Switch 1 int. Switch 1 cpu 1 int. Switch 2 cpu 2 cfip1 cfip2 user dat a mm dat a port 1 port 2 port 3 mng wan wan mng ext. Switch 2 user dat a mm dat a port 1 port 2 port 3 vlan b vlan a&b vlan b vlan b vlan b vlan a vlan a vlan a&b vlan a user data user data vlan a lan1 lan1 lan2 lan2 figure 4...
Page 72
Figure 4.48 vlan configuration of cfip phoenix link 4.9 qos 4.9.1 general configuration qos status provides control over main qos parameters, accordingly allowing enabling or disabling qos 802.1p, diffserv or port based priorities and change priority queuing mode. Figure 4.49 qos general configurati...
Page 74
If any queues are empty, the highest non-empty queue gets one more weighting. For example, if q2 is empty, q3:q2:q1:q0 becomes (8+1):0:2:1. In case of fixed queuing mode, highest priority buffer (q3) will pass packets as long as its buffer is full. By default weighted priority queuing mode is enable...
Page 75
Figure 4.53 dscp mapping 1. Dscp mapping – allows assigning queues for different dscp classes. You may have up to 64 different traffic dscp classes; 2. By pressing „execute configuration” changes made to the corresponding section apply only for the local side cfip phoenix. If „rollback on” is select...
Page 76
4.10 spanning tree configuration 4.10.1 spanning tree configuration figure 4.54 spanning tree protocol – bridge configuration bridge configuration - values 2-4 take effect only if a given bridge is root: 1. Bridge id – value from (0..61440); this parameter and mac address determine whether a given b...
Page 77
14. Bridge id – displays the bridge id of current root bridge; 15. Root port – currently elected root port is being shown; 16. Root path cost – displays the path cost from current bridge to root bridge; 17. Port 1 lan – stp parameters of lan port; 18. Port 2 wan – stp parameters of wan port: - prior...
Page 78
4. By pressing „execute configuration” changes made to the corresponding section apply only for the local side; 5. Vlan (1 – 4094) – map vlan id or vlan ids range for each instance. Up to seven instances; 6. Write to config file - saves to configuration file all the changes made on the whole page (c...
Page 79
4.11 snmp v1/v2 configuration the snmp v1/v2 configuration pages provide configuration of snmp communities, host and trap addresses. Saf nms system will work only when snmp is properly configured. Explanation of customization fields: 4.11.1 snmp community configuration figure 4.57 snmp community con...
Page 80
Figure 4.58 snmp allowed hosts configuration 1. Snmp host list – shows the list of available v1/v2 snmp hosts; adds or deletes the host ip address to the cfip snmp v1/v2 host table. If the snmp host connected to the cfip is not added to the cfip snmp v1/v2 host table, the cfip will not respond to th...
Page 81
5 performance and alarm management 5.1 alarm management 5.1.1 alarms and events structure all alarms and events are placed in indexed table. Low level raw alarms and events are placed in the first table. Raw alarms and events are merged in groups, which are placed in the second indexed group table. ...
Page 82
12 12 idu temperature fault temperature is out of defined range 13 13 no data from main psu idu adc no data from idu adc connected via i2c interface 14 14 main supply 48v failure main supply voltage is out of defined range 15 15 idu psu state one of the possible psu state "off","idle","ok","overload...
Page 83
44 35 no data from modem no data from modem connected via uart interface 45 36 acquire status alarm modem acquire failure status 46 37 last acquire error status modem last acquire failure status 47 38 radial mse radial mse is out of defined range 48 39 ldpc decoder stress ldpc decoder stress is out ...
Page 84
Grouped. Complete list of alarm individual ids and group ids can be seen in the table above or using the command ‘alarm list’ in the command prompt. To configure representation of alarms, refer to chapter 5.2.5. Figure 5.2 alarm status window 5.1.4 alarm log to view alarms history, go to ‘performanc...
Page 85
Figure 5.4 alarm configuration window alarm threshold configuration screen allows you to define specific threshold levels to bound alarms to desirable values, so that you are able to adapt alarm system to your individual needs. Alarms in bold font represent group alarms and alarms in normal font – i...
Page 86
Figure 5.5 alarm threshold configuration window 5.1.6 alarm management commands to manage alarms in command prompt, the commands are as follows: alarm management commands command description log show [] the management controller maintains event log, - events include configuration changes, management...
Page 87
5.2 performance management the main aim of the performance management is to register mostly critical device performance event values in predefined time intervals. 5.2.1 performance management data collection the performance parameters are collected within time intervals of 1 min., 15 min. And 1 hour...
Page 88
Figure 5.6 functional architecture for data collection, history and thresholding treatment 5.2.2 performance values threshold seconds (ts) the ts is defined as one second period during which the detected value is outside of predefined thresholds. The current value of the counter associated with ts s...
Page 89
Figure 5.7 selecting performance log parameters figure 5.8 performance log window time interval can be chosen between 1 min, 15 min or 1 hr. You can also define the start time and the start date. When start values are defined, it is also possible to define the end time and the end date. Ts (threshol...
Page 90
Figure 5.9 performance log configuration window the main advantage in terms of demonstration means is obtained from ‘performance graphs’, which are found in ‘performance performance graph’ section. You are able to choose between 9 parameters – rx level; tx level; radial mse; ldpc stress; modem tem...
Page 91
1. Time scale selector. User can select the scale and accuracy (1 / 15 / 60 minutes). The lower accuracy, the longer the period available for data (mechanism of the performance management system) 2. Updates the performance graph; the latest data is shown 3. Shows / hides period settings (point 5) 4....
Page 92
Figure 5.12 equalizer graph – normal operation during normal operation frequency response curve is smooth and the only equalizer tap towers are in the centre of equalizer taps graph, otherwise frequency response curve will appear jagged and many equalizer taps will become visible. The latter case mo...
Page 93
5.3 ethernet modem statistics ethernet modem statistics window shows the full ethernet and framing statistics of cfip modem since unit start or statistics reset. All statistics are also accessible using command prompt command ethernet statistics all. Explanation of fields: figure 5.14 ethernet modem...
Page 94
2. Modem state – shows if the modem is operating correctly; 3. Clear statistics – resets all statistics counters (not available for “guest” account); 4. Truncated frames – number of truncated received frames; 5. Long events – frames having byte count greater than maximum frame size parameter (1518, ...
Page 95
35. Excessive defers – packets deferred in excess of 6,071 nibble times in 100 mbps mode, or 24,287 bit-times in 10 mbps mode; 36. Non-exc. Defers – packets deferred for at least one attempt, but less than an excessive defer; 37. Broadcasts – packets, which destination address contained broadcast ad...
Page 96
Figure 5.15 ethernet switch statistics 1. Shows the time during which statistics have been gathered; 2. Clear statistics – resets all statistics counters (not available for “guest” account); 3. Txoctets - the total number of good bytes of data transmitted by a port (excluding preamble but including ...
Page 97
8. Txunicastpkts - the number of good packets transmitted by a port that are addressed to a unicast address; 9. Txcollisions - the number of collisions experienced by a port during packet transmissions; 10. Txsinglecollision - the number of packets successfully transmitted by a port that have experi...
Page 98
32. Rxfcserrors – the number of packets received by a port that have a length (excluding framing bits, but including fcs) between 64 and 1522 bytes inclusive, and have a bad fcs with an integral number of bytes; 33. Rxgoodoctets – the total number of bytes in all good packets received by a port (exc...
Page 99
6 miscellaneous controls in web graphic user interface these controls are located in the navigation panel under the “tools” item. 6.1 ethernet/configuration files this section allows working with cfip configuration script. The management module has ram and eeprom chips on-board. When cfip is booted ...
Page 100
Figure 6.1 configuration (cfg & ethernet) files cfip phoenix series tdm/ip split mount system technical description and configuration guide • rev. 1.13 • © saf tehnika jsc 2015 100
Page 101
1. Download cfg file – allows downloading system configuration file and saving it on your hard drive. 2. Upload configuration file - allows uploading system configuration file to cfip phoenix flash memory. In order to load configuration file from system memory, cfg restore should be used (refer to n...
Page 102
15. Saved configuration file - shows contents of system configuration file saved in eeprom memory. Commands contained in this configuration file are executed at every system start-up; 16. Running configuration file - shows currently running system configuration file (command line – eth config). In o...
Page 103
Figure 6.2 license management 1. Show active license – if non-active license is selected, pressing this button will switch selection back to currently active license (command line – license status); 2. License status – shows if management cpu was able to read license data (command line – license sta...
Page 104
13. 28000 khz – shows the maximum modulation that can be used together with 28 mhz channel bandwidth (command line – license status); 14. 30000 khz – shows the maximum modulation that can be used together with 30 mhz channel bandwidth (command line – license status); 15. 40000 khz – shows the maximu...
Page 105
The following files are required for the cfip to start: – ‘boot.Ini’ file, - device boot configuration file. This file is a text file and contains the name of the firmware file which must be executed on start-up. The file name can be freely changed, but its default name is ‘boot.Ini’; hereinafter, i...
Page 106
Tfs edit edits the specified file. This command is applied for editing configuration backup files and boot configuration file (boot.Ini). For example, edit boot.Ini,be – file ‘boot.Ini’ will be opened for editing. ‘be’ specifies that this file will be saved with attributes ‘b’ and ‘e’. If boot.Ini f...
Page 107
7 software update to simplify the firmware update process, saf tehnika jsc provides special update package, as a new version is available. This update pack is available as archive (e.G. Zip), which includes firmware file (with *.Elf.Ezip,ec extension), upgrade instructions, release notes and mib fil...
Page 108
Use command “ls” to list files on cfip flash disk. Use command “delete ” to delete the file from the cfip flash disk. 6. Proceed with steps 5. And 6. In chapter 7.1. You can also use any preferable ftp client if you wish. 7.2 uploading file via serial port (xmodem) file upload via serial port takes ...
Page 109
Figure 7.3 xmodem file send for cfip when upload is complete, the following information will be displayed (figure 7.4): figure 7.4 hyperterminal 5. Enter ‘reset’ command to exit from micromonitor mode and restart the cfip. 6. Proceed with steps 5. And 6. In chapter 7.1. Cfip phoenix series tdm/ip sp...
Page 110
8 cfip discovery protocol discovery protocol is layer 3 network protocol. This feature allows gathering information from connected cfip devices. The protocol discovers the ip address and software version of connected cfip unit. Discovery protocol uses udp packets sent on port 78. Discovery protocol ...
Page 111
Figure 8.1 cidr notation (routing prefix) is related to network mask that is also necessary in order to manage cfip unit. The ip address of your pc ethernet adapter and cfip unit should be from the same subnet in order to manage the cfip unit. In the table below some examples are given for cidr nota...
Page 112
Figure 8.2 8.2.3 discovery of ip address and firmware version of remote cfip unit connected to router in case one ip address of remote units is known for this purpose the command “dp remote ” should be executed in ‘cmd’. Instead of place the ip address of your pc ethernet adapter that is connected t...
Page 113
9 rssi port rssi (received signal strength indicator) port is used to adjust the alignment of antenna for best performance (for both rough and fine adjustment); this can be done using digital multimeter which is connected to the rssi port. The output of the rssi port is dc voltage and varies dependi...
Page 114
10 pinouts 10.1 ethernet rj-45 port the pinouts of rj45 socket are as follows: figure 10.1 ethernet rj-45 port pinouts 10.2 e1 port rj-45 pinouts the pinouts of cfip phoenix idu rj-45 sockets for e1 channels are shown in figure 10.2. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 in (rx) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 gnd gnd not used out (tx) ...
Page 115
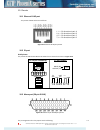
Pin type pin number pin type pin number alarm input 1 1 ground 12 alarm input 2 2 ground 13 alarm input 3 3 alarm output 4 nc 15 alarm input 4 4 alarm output 3 nc 16 alarm output 4 no 6 alarm output 2 nc 17 alarm output 3 no 7 alarm output 1 nc 18 alarm output 2 no 8 alarm output 4 com 23 alarm outp...
Page 116
Figure 10.5 1+1 protection port pinouts 10.6 1+1 protection cable connector 1 pin wire connector 2 pin 1 pair 1a 4 2 pair 1b 5 3 pair 2a 7 4 pair 3a 1 5 pair 3b 2 6 pair 2b 8 7 pair 4a 3 8 pair 4b 6 figure 10.6 1+1 protection cable pinouts pins direction description 1 in rin- 2 in rin+ 3 out prot_cl...
Page 117
10.7 power protection port figure 10.7 power protection port and cable (p/n s0acpr11) pinouts cfip phoenix series tdm/ip split mount system technical description and configuration guide • rev. 1.13 • © saf tehnika jsc 2015 117.
Page 118
11 available accessories surge protection p/n: clala001 surge protection with gas tube p/n: clala003 ac/dc power supply, 48vdc, 80w eu - p/n i0ab4810, us - p/n i0ab4811, aus - p/n i0ab4818 flexible waveguide ubr-pbr (see the list of available test equipment below) cfip phoenix 1+1 protection bus cab...
Page 119
Coaxial attenuator 40 db p/n cla40a01 saf adapted omt for arkivator antenna for dual-polarization (see the list of available test equipment below) rssi cable for odu align 1m bnc − 2 plug-in p/n clgcrs01 cfip odu mounting bracket (for 1xodu p/n: clgrfb05; for 2xodu p/n: clgrfb06) test equipment (see...
Page 120
C08tst02 test equipment 7/8 ghz 7/8ghz test suite, contains two waveguide-to-coaxial adapters, two attenuators, 40 db, coaxial cable, 40 cm long c11tst02 test equipment 10/11 ghz test equipment 10/11 ghz c15tst02 test equipment 13/15 ghz 13/15ghz test suite, contains two waveguide-to-coaxial adapter...
Page 121
12 list of abbreviations 3g – third generation ac – alternating current aci – adjacent-channel interference acm – adaptive coding and modulation agc – automatic gain control ascii - american standard code for information interchange atpc – automatic transmit power control ber – bit-error ratio bnc c...
Page 122
Ram – random access memory rsl – received signal level rssi – received signal strength indicator rx – receive snmp - simple network management protocol snr – signal-to-noise ratio stm-1 – synchronous transport module - 1 tcp/ip – internet protocol suite (transmission control protocol / internet prot...
Page 123
13 saf tehnika jsc contacts saf tehnika a/s technical support can be reached by: - email: techsupport@saftehnika.Com - telephone: +371 67046840 - fax: +371 67046809 cfip phoenix series tdm/ip split mount system technical description and configuration guide • rev. 1.13 • © saf tehnika jsc 2015 123.