- DL manuals
- SafeNet
- Gateway
- 4000
- User Manual
SafeNet 4000 User Manual - Netman
Commands
Chapter 6. CLI Command Reference
78
netman
Parameters and
Attributes
none – specifies that the HA4000 gateways are
connected back-to-back, with no routers between
them. The HA4000 copies the MAC address from the
incoming packet.
arp – specifies that the destination is on the same
subnet as the HA4000 gateway’s local port (if the local
port is connected to a Layer 2 switch). The HA4000
uses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to derive the
MAC address of the destination device.
gateway – specifies that the HA4000 gateway’s local
port is connected to a router. The gateway IP address
identifies a device to send packets to for routing to
their destination.
ipAddress – specifies the IP address of the default
gateway.
Reboot Required
No.
Usage Guidelines
See “Layer 2 MAC Address Resolution” on page 27.
Syntax
netman {password <password> | login {enable |
disable <value>}}
Shortcut
None
User Type
Administrator
Hierarchy Level
Configuration
Description
Configures the Network Manager logon and password.
Parameters and
Attributes
password – assigns the network manager password.
password – specifies the network manager password.
A password is a character string with at least one
alphanumeric character. Passwords are case-sensitive;
they are suppressed from displaying when typed. A
password can include these special characters: ! @ # $
% ^ * ( ) _ + = - [ ] { } \ | ; : < >
Note: Although these characters are valid for use in
passwords, they may cause problems with third-party
scripting tools.
login – enables or disables the network manager
logon.
value – specifies the number, from 0 through 99, of
unsuccessful logon attempts allowed. A value of zero
allows unlimited unsuccessful logon attempts.
Reboot Required
No.
Usage Guidelines
See “Set Passwords” on page 35.
Summary of 4000
Page 1
Highassurance tm 4000 gateway t h e f o u n d a t i o n o f i n t e r n e t s e c u r i t y user's guide.
Page 2
© 2004 safenet, inc. All rights reserved. Safenet is a registered trademark and safeenterprise and highassurance are trademarks of safenet, inc. All other product and company names may be the property of their respective owners. Safenet, inc. (800) 533-3958 sales (800) 545-6608 customer support www....
Page 3: Contents
Contents iii contents chapter 1 product overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 product features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 led indicators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 4
Contents iv configure the ftp client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42 load software updates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 install certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 ...
Page 5: List of Figures
List of figures v list of figures figure 1-1 ha4000 gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 figure 3-1 management port and network management station on different subnets 19 figure 3-2 two remote ports on the same subnet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 6: List of Tables
List of tables vi list of tables table 1-1 front panel led indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 table 3-1 snmp trap types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33 table 3-2 ha4000 snmp agent parameters . . . . . ...
Page 7: Chapter 1
Chapter 1. Product overview 7 chapter 1 product overview the safenet highassurance™ 4000 (ha4000) gateway is a high-performance, integrated security appliance that offers ipsec encryption at multi-gigabyte rates. Supporting wire speed gigabit ethernet, the ha4000 enables secure remote data backup an...
Page 8: Product Features
Product features chapter 1. Product overview 8 product features z mounts in any standard 19-inch rack or on a tabletop z two gigabit ethernet data ports for encrypting and decrypting network traffic with single mode and multimode fiber gbic interfaces z fips 140-2 level 2 compliant, validated by the...
Page 9: Led Indicators
Sample deployments chapter 1. Product overview 9 led indicators table 1-1 shows how to interpret the leds on the ha4000 gateway’s front panel. Sample deployments the ha4000 device is deployed on either side of a wan-routed interface, between a switch and a router, securing the data transmitted acros...
Page 10: Tunnels
Management chapter 1. Product overview 10 in a branch-to-central office application, data is secured between each branch and the central office. Additionally, a secure tunnel is established between the two branch sites. This configuration can be used to transfer sensitive data between remote sites o...
Page 11
Fips 140-2 level 2 operation chapter 1. Product overview 11 z hmac-sha1-06 authentication z manual keys or ike key management caution md5 is not a fips-approved authentication algorithm. Therefore, using md5 authentication in a security policy removes the ha4000 from fips-compliant note: operation..
Page 12: Chapter 2
Chapter 2. Installation 12 chapter 2 installation perform the tasks in this chapter in the sequence they are presented. Unpack the shipping carton remove all product components from the shipping carton and compare the contents to the packing list. Keep all packaging in case it is necessary to return...
Page 13: Required Hardware
Required hardware chapter 2. Installation 13 z air flow make sure that there is sufficient flow of air around the ha4000 so that safe operation is not compromised. Maintain a clearance of at least three inches (7.62 cm) on each side of the ha4000 gateway to ensure adequate air intake and exhaust. If...
Page 14: Connect The Cables
Mount the ha4000 in a rack chapter 2. Installation 14 connect the cables before beginning, make sure that the necessary cables are available. For more information on cabling requirements and specifications, see appendix c, "cable specifications." 1. Connect the ha4000 rs-232 craft port directly to a...
Page 15
Mount the ha4000 in a rack chapter 2. Installation 15 notes: z if you experience a problem during system initialization, go to chapter 5, "troubleshooting." z until you configure your security policies, the ha4000 gateway’s default mode of operation passes all packets in the clear..
Page 16: Chapter 3
Chapter 3. Configuration 16 chapter 3 configuration ha4000 management is performed out of band. Use the management interface to configure the device remotely through the command line interface (cli) and monitor snmp-based performance. This chapter describes the tasks required to configure the ha4000...
Page 17: Command Shortcuts
Configure the management port chapter 3. Configuration 17 command shortcuts some cli commands have specific shortcuts. For a list, go to table 6-1 on page 65. Shortcuts are also included in the detailed information available on each cli command in chapter 6, "cli command reference." for other comman...
Page 18: Assign Ip Addresses
Configure the management port chapter 3. Configuration 18 note: usernames and passwords are case-sensitive. 6. At the password prompt, enter the default password, safenet. The password you type does not display. Note: change the default password when you configure the ha4000 gateway. 7. When you are...
Page 19
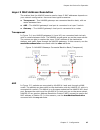
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 19 figure 3-1 management port and network management station on different subnets example this example configures the default gateway for router #1 in figure 3-1. The example enters configuration mode for the management interface, assigns a d...
Page 20: Control
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 20 assign the remote port ip address the remote port ip address identifies the ha4000 to the untrusted network, typically a wan, campus lan, or man. Changing the remote port ip address directly affects the ha4000 gateway’s ipsec policies, inc...
Page 21: Assign Ike Default Gateway
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 21 these are some possible configurations and the associated command: examples z enable auto-negotiation and flow control on the remote port: config-ifremote> auto enable z disable auto-negotiation and flow control on the remote port, exit co...
Page 22
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 22 figure 3-2 two remote ports on the same subnet routed network in a routed network, a router is placed between the initiating ha4000 #1 and the wan. Use the ikedefaultgateway command on ha4000 #1 (see figure 3-3) to specify router r2’s loca...
Page 24
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 24 example this example enters remote interface configuration mode on the ha4000, disables ike id validation, exits configuration mode, and saves the configuration. Admin> config t config> interface remote config-ifremote> ikeidvalidation dis...
Page 25
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 25 example this example enters remote interface configuration mode on the ha4000, sets the ike id type to subject distinguished name, exits configuration mode, and saves the configuration. Admin> config t config> interface remote config-ifrem...
Page 26
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 26 local port auto-negotiation and flow control auto-negotiation and flow control is configured on a per port basis. If the device that the ha4000 is connected to on the local network side does not support auto-negotiation or flow control, di...
Page 27
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 27 layer 2 mac address resolution the method that the ha4000 uses to resolve layer 2 mac addresses depends on your network configuration. Here are three typical scenarios: z transparent – two ha4000 gateways are connected back-to-back, with n...
Page 28
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 28 figure 3-5 arp used to resolve layer 2 mac addresses gateway in figure 3-6, the ha4000 #2’s local port is connected to router r4. The destination station s2 is on a different subnet than ha4000 #2’s local port. To send packets to station s...
Page 30: Configure Df Bit Handling
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 30 when the ha4000 detects an ip payload that exceeds 1460 bytes, the ha4000 notifies the local device of the required mtu size. Note that the pmtu is a layer 3-based number, and, therefore, does not include layer 2 ethernet header overhead. ...
Page 32: Set Session Timer
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 32 set session timer a timer can be set to end a session after a specified interval of user inactivity with the session timer command. At the config> prompt, enter this command: session timer cli number> where number is the number of minutes ...
Page 34: Name The Ha4000
Prepare the device for operation chapter 3. Configuration 34 display trap status to display the status of the traps, use the trap list command. It displays all traps and lists their status as enabled or disabled. At the config> prompt, enter this command: snmp-server trap list example config> snmp-s...
Page 35: Administrative Tasks
Administrative tasks chapter 3. Configuration 35 example this example uses the snmp-server command to provide identifying information about the ha4000. Note the quotation mark usage. Config> snmp-server contact "jane doe" config> snmp-server location "building c, san jose" config> snmp-server name "...
Page 36
Administrative tasks chapter 3. Configuration 36 set the administrator password 1. Log in as administrator (username super). 2. Go into configuration mode; enter this command: configure terminal 3. At the config> prompt, enter this command: password 4. Enter the current password. 5. Enter the new pa...
Page 38: Reboot The Ha4000
Administrative tasks chapter 3. Configuration 38 reboot the ha4000 the reboot command stops all operations on the ha4000 and begins the boot process, the same process initiated when the power is cycled on the device. Caution save any configuration changes prior to rebooting the unit; unsaved changes...
Page 39: View Configurations
Administrative tasks chapter 3. Configuration 39 example this example saves the running configuration and reboots the ha4000: admin> copy system:running nvram:config admin> reboot view configurations the show command displays information about saved and running configurations, ip addresses, and vers...
Page 40
Administrative tasks chapter 3. Configuration 40 example in this example, the show nvram:config command displays the configuration saved in the ha4000 file system. Admin> show nvram:config interface management ip address 192.168.10.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.10.1 ipsec disabled ipsec phase1 3des sha1 ...
Page 41: Chapter 4
Chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 41 chapter 4 maintenance tasks perform these maintenance tasks on a regular or as-needed basis: z create a backup copy of the file system. Z configure the ftp client for file downloads. Z download software updates. Z install a certificate on the ha4000. Z physically insp...
Page 42: Restore The Backup
Install software updates chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 42 restore the backup if the ha4000’s file system is damaged or corrupted, you can restore it from the backup. 1. Log on as network manager. 2. At the admin> prompt, enter this command: copy nvram:fs-backup nvram:fs 3. Reboot the device, enter th...
Page 43: Load Software Updates
Install certificates chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 43 load software updates when a new software image is downloaded, the ha4000 data is not affected. Saved security policies and configurations are preserved. The ha4000 remains operational during software downloads. Note: before downloading any softwa...
Page 44: Install A New Certificate
Install certificates chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 44 when replacing the certificate, make sure to set the ha4000 gateway’s internal clock, as described in “configure df bit handling” on page 30. The date and time settings are required to track certificate expiration dates. Caution installing a new c...
Page 45: Physical Inspection
Physical inspection chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 45 physical inspection the ha4000 is housed in a tamper-evident chassis. Periodically check the chassis for evidence of tampering. Items to look for include stripped screws and damaged seals. Figure 4-1 shows the seal location. Figure 4-1 tamper evide...
Page 46: Audit Log Resources
Audit logs chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 46 audit log resources the audit log is a fixed-length list of entries. When a log file is full, another log file is started. This continues until the specified maximum number of log files is reached. At that point, the information in the first log file is ove...
Page 47
Audit logs chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 47 z where to send the data when an event is enabled, the output can be sent to the terminal, recorded in the log file, or both. To change the display settings, set the terminal and logfile attributes. For example, to turn off the terminal display but continue...
Page 48
Audit logs chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 48 for parameter and attribute descriptions, go to “log” on page 76. Attributes are case-sensitive. To specify multiple attributes on a single command, insert them in a quoted string (enclosed in quotation marks), as the first example below shows. Logging chan...
Page 49
Audit logs chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 49 view log file status the show logging command displays a summary of the active log file, including the events being logged, log file name, and file size. 1. Log on as network manager. 2. At the admin> prompt, enter this command: show logging example admin> ...
Page 51
Restore factory settings chapter 4. Maintenance tasks 51 when clearing configurations or policies, the factory settings become effective when the device is rebooted. When clearing all settings, the ha4000 automatically reboots. Example this example clears the ha4000’s saved configuration, replaces i...
Page 52: Chapter 5
Chapter 5. Troubleshooting 52 chapter 5 troubleshooting possible problems and solutions table 5-1 ha4000 troubleshooting category symptom explanation and possible solutions leds power led is off. • make sure the power cable is attached and plugged in to both the device and the power outlet. Failure ...
Page 53
Possible problems and solutions chapter 5. Troubleshooting 53 browser can’t make a connection to the ha4000 gateway’s management port. • verify that the correct management port ip address is being entered for the connection. • verify that http is configured correctly for your access method (unsecure...
Page 54
Possible problems and solutions chapter 5. Troubleshooting 54 configuration continued the device on the wan side (remote port connection) of the ha4000 is dropping packets. • set the pmtu size to a number that doesn’t exceed the mtu of the device with the smallest mtu in the path. To get this number...
Page 55
Possible problems and solutions chapter 5. Troubleshooting 55 ipsec policies traffic is not processing as expected. • verify the policy priorities. The policy with the highest priority number is processed first. • verify the filter information: local and remote ip addresses and subnets, protocol, an...
Page 56: Diagnostic Commands
Diagnostic commands chapter 5. Troubleshooting 56 diagnostic commands a set of commands is available to assist with diagnosing and troubleshooting unexpected behavior of your ha4000 and security policies. Some of these commands are self-explanatory; enter the others only upon request by safenet cust...
Page 57
Diagnostic commands chapter 5. Troubleshooting 57 example ops> show ipsec aessupport ops> aes is not supported view discarded packets the show ipsec discards command displays a summary of the number of discarded and aborted packets. To obtain the reason for the discards, use the all attribute. For e...
Page 58
Diagnostic commands chapter 5. Troubleshooting 58 view sas the show ipsec sa command displays the active sas on the ha4000 gateway. In addition to verifying that a specific sa is active on the ha4000, this command also displays its spi and lifetime. Syntax show ipsec sa response table 5-4 describes ...
Page 59
Diagnostic commands chapter 5. Troubleshooting 59 response the command response displays precisely what the ha4000 is enforcing and in what order (see table 5-5). Given a packet with specific selectors, you can determine how the packet will be handled by checking it against the spd in descending ord...
Page 60
Diagnostic commands chapter 5. Troubleshooting 60 example admin> show ipsec spd ----------------------------------------------------------- security policy database enforcement order -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
Page 61
Diagnostic commands chapter 5. Troubleshooting 61 example admin> show ipsec statistics transmit localif remoteif total bytes (including crc) in good pkts :0 0 total bytes (including crc) in good+bad pkts :0 0 unicast pkts w/o error :0 0 multicast pkts w/o error :0 0 broadcast pkts w/o error :0 0 flo...
Page 62: Show All Commands
Diagnostic commands chapter 5. Troubleshooting 62 show all commands the show all command displays a concatenation of the information displayed by these show commands: z date z ipsec discards all z ipsec sa z ipsec spd all z ipsec statistics z logging z nvram:config z system:running z version the sho...
Page 63: Chapter 6
Chapter 6. Cli command reference 63 chapter 6 cli command reference cli overview this chapter explains cli command syntax conventions and usage, and provides detailed information on each command. Commands are listed in alphabetical order. Command hierarchy the cli has three command hierarchy levels:...
Page 65: User Types
Cli overview chapter 6. Cli command reference 65 user types the ha4000 has two levels of logon privileges, identified by user type: z the network manager configures the ha4000. The network manager’s username is admin. Z the administrator sets passwords and logon restrictions. The administrator’s use...
Page 67: Configure
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 67 configure copy ftp:fs copy ftp:policy syntax configure terminal shortcut con t user type network manager and administrator hierarchy level command description enters configuration mode. Reboot required no. Usage guidelines use this command to enter differ...
Page 68: Copy Nvram:fs
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 68 copy nvram:fs copy nvram:fs-backup copy nvram:logs syntax copy nvram:fs nvram:fs-backup shortcut none user type network manager hierarchy level command description creates a backup copy of the ha4000 file system. Reboot required no. Usage guidelines see “...
Page 69: Copy Nvram:policy
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 69 copy nvram:policy copy system:running date syntax copy nvram:policy {ftp:policy [filename>]} shortcut none user type network manager hierarchy level command description copies the policy file from the ha4000 gateway’s file system to an ftp host. Parameter...
Page 70: Dfbit-Handling
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 70 dfbit-handling exit parameters year – 2003 through 2100 month – 01 through 12 day – 01 through 31 hour – 00 through 23 minutes – 00 through 59 seconds – 00 through 59 reboot required no. Usage guidelines see “set date and time” on page 31. Syntax dfbit-ha...
Page 71: Ftp-Client
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 71 ftp-client help syntax ftp-client ftp_ipaddress> ftp_userid> ftp_password> [ftp_directory>] shortcut none user type network manager hierarchy level configuration description configures ftp client access to an ftp server for file transfers. Parameters ftp_...
Page 75: Ipsec
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 75 ipsec reboot required local and remote port ip addresses require a reboot or policy reload to take effect. Management port ip addresses take effect immediately. Usage guidelines see “assign ip addresses” on page 18 and “configure the local interface” on p...
Page 77: Log-File
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 77 log-file macaddrresolutionmechanism usage guidelines see “configure log file events” on page 46. Syntax log-file number> [size_in_kbytes>] shortcut none user type network manager hierarchy level configuration description configures log file resources. Par...
Page 78: Netman
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 78 netman parameters and attributes none – specifies that the ha4000 gateways are connected back-to-back, with no routers between them. The ha4000 copies the mac address from the incoming packet. Arp – specifies that the destination is on the same subnet as ...
Page 79: Password
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 79 password syntax password password> shortcut none user type administrator hierarchy level configuration description sets the administrator password. Parameters password – character string with at least one alphanumeric character. Passwords are case-sensiti...
Page 80: Pmtu
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 80 pmtu reboot reload policies syntax pmtu number> shortcut none user type network manager hierarchy level configuration description specifies the maximum transmission unit of the path (end-to-end mtu). Parameters and attributes number – specifies the pmtu s...
Page 81: Session
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 81 session show reboot required no. Usage guidelines none. Syntax session timer cli number> shortcut none user type network manager hierarchy level configuration description specifies the interval of inactivity before a user is logged out. Parameters and att...
Page 82: Snmp-Server
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 82 snmp-server attributes all – displays a concatenation of the information provided by the show attributes listed below (date through version). For technical support use only. Date – displays the internal clock’s date and time settings. Http – displays the ...
Page 83
Commands chapter 6. Cli command reference 83 user type network manager hierarchy level configuration description defines snmp parameters. Parameters and attributes no – negates a previously entered snmp command with the same parameters. Community – specifies the snmp community string to validate snm...
Page 85: Appendix A
Appendix a. Mib support 85 appendix a mib support the ha4000 gateway supports snmp v2-c. Supported mibs include these: z mib ii (www.Ietf.Org/rfc/rfc 1213.Txt, limited to these groups): system group interfaces group the ha4000 also uses these proprietary mibs, which are included on the ha4000 gatewa...
Page 86: Appendix B
Appendix b. Product specifications 86 appendix b product specifications table b-1 system specifications interfaces • two gigabit fiber ports • 10/100 mbps auto-sensing lan port • rs-232c port electrical/mechanical dimensions • 19-inch rack mount design • 4” h x 17” w x 15” d (10.16 cm h x 43.18 cm w...
Page 87: Appendix C
Appendix c. Cable specifications 87 appendix c cable specifications db-9 null modem cable figure c-1 db-9 null model cable specifications table c-1 null model pin connections pin pin 2 rd (receive data) 3 td 3 td (transmit data) 2 rd 5 sg (signal ground) 5 sg.
Page 88
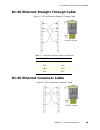
Rj-45 ethernet straight through cable appendix c. Cable specifications 88 rj-45 ethernet straight through cable figure c-2 rf-45 ethernet straight-through cable rj-45 ethernet crossover cable figure c-3 rj-45 ethernet crossover cable table c-2 straight-through cable connections rj-45 pin rj-45 pin 1...
Page 89
Rj-45 ethernet crossover cable appendix c. Cable specifications 89 table c-3 crossover cable connections rj-45 pin rj-45 pin 1 rx+ 3 tx+ 2 rc- 6 tx- 3 tx+ 1 rc+ 6 tx- 2 rc-.
Page 90: Appendix D
Appendix d. Electrostatic discharge 90 appendix d electrostatic discharge electrostatic discharge (esd) can damage electronic components and equipment. Esd occurs when electronic components are improperly handled and can result in complete or intermittent failures. Always follow esd-prevention proce...
Page 91: Appendix E
Appendix e. Regulatory information 91 appendix e regulatory information safety/emissions/immunity specifications fcc information (usa) this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class b digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to p...
Page 92: European Notice
European notice appendix e. Regulatory information 92 european notice products with the ce marking comply with both the emc directive (89/336/eec) and the low voltage directive (73/23/eec) issued by the commission of the european community..
Page 93: Glossary
Glossary 93 glossary a action component of an ipsec rule. Packets that match a specified filter have an action applied to them. The set of possible actions are: bypass the packet (send it in the clear), discard the packet, reject the packet, or apply ipsec processing to it. Advanced encryption stand...
Page 94
Glossary 94 confidentiality ensures that the content of the message (user data) has not been revealed. Condition filtering component of an ipsec rule. The condition identifies the packets a specified action will be applied to. Crl see certificate revocation list. D des see data encryption standard. ...
Page 95
Glossary 95 two parties. If the hmac is correct, it proves that it must have been added by the source. Hmac see hash message authentication code. I ike see internet key exchange. Internet key exchange (ike) protocol that ipsec uses to dynamically authenticate ipsec peers, negotiate security services...
Page 96
Glossary 96 pki see public key infrastructure. Plaintext original, unencrypted message that anyone can read. Policy set of rules that define levels of security for various types of traffic. The policy identifies classes of traffic and applies different services to them. Policy group collection of ip...
Page 97
Glossary 97 security association (sa) processing performed on a specific packet. It associates security services and a key with the traffic to be protected and the remote peer with whom ipsec traffic is being exchanged. An sa is created when hosts communicate for the first time, and remains active u...