- DL manuals
- Sailor
- Home Cinema speakers
- 250 FleetBroadband
- User Manual
Sailor 250 FleetBroadband User Manual
Summary of 250 FleetBroadband
Page 1
Sailor 500/250 fleetbroadband including 19” rack version user manual.
Page 3: Sailor
Sailor ® 500 fleetbroadband sailor ® 250 fleetbroadband including 19" rack version user manual document number: 98-125645-g release date: june 27, 2012.
Page 4: Disclaimer
Disclaimer any responsibility or liability for loss or damage in connection with the use of this product and the accompanying documentation is disclaimed by thrane & thrane. The information in this manual is provided for information purposes only, is subject to change without notice and may contain ...
Page 5: Safety Summary
Iii safety summary 1 the following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases of operation, service and repair of this equipment. Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific warnings elsewhere in this manual violates safety standards of design, manufacture and intend...
Page 6
Iv on the sailor 250 fleetbroadband, the minimum safety distance to the antenna panel on the focal line is 0.6 m, based on a radiation level of 10 w/m 2 . The radiation level is 100 w/m 2 at a distance of 0.2 m from the antenna panel. Refer to the drawing below. Pour une antenne sailor 250 fleetbroa...
Page 7
V service user access to the interior of the terminal is prohibited. Only a technician authorized by thrane & thrane may perform service - failure to comply with this rule will void the warranty. Access to the interior of the antenna is allowed, but only for replacement of certain modules - as descr...
Page 8
Vi maintenance personnel. Do not replace components with the power cable connected. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even with the power cable removed. To avoid injuries, always disconnect power and discharge circuits before touching them. Failure to comply with the rules above...
Page 9: About The Manual
Vii about the manual 2 intended readers this manual is a user manual for the sailor 500 fleetbroadband system and the sailor 250 fleetbroadband system. The readers of the manual include anyone who is using or intends to use one of these two systems. No specific skills are required to operate the sai...
Page 10: Related Documents
Viii • using the web interface explains how to use the built-in web interface of the terminal for configuration and daily use, and describes the available menus and settings, including advanced setup of interfaces. • troubleshooting contains a short troubleshooting guide and explains how to update s...
Page 11: Typography
Ix typography in this manual, typography is used as indicated below: bold is used for the following purposes: • to emphasize words. Example: “do not touch the antenna”. • to indicate what the user should select in the user interface. Example: “select settings > lan”. Italic is used to emphasize the ...
Page 12
X.
Page 13: Table Of Contents
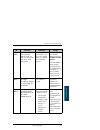
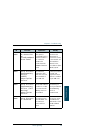
Xi table of contents safety summary ................................................................Iii chapter 1 introduction welcome ............................................................................ 1 features and interfaces ......................................................3 main u...
Page 14
Table of contents xii using the thrane ip handset ............................................77 chapter 4 using the web interface introduction .................................................................... 80 entering the sim pin in the web interface ....................... 85 using the dashb...
Page 15
Table of contents xiii reset button ................................................................... 243 list of reserved ip subnets .............................................. 245 supported at commands for pppoe ............................... 246 app. A conformity sailor 500 fleetbroadband ....
Page 16
Table of contents xiv.
Page 17: Introduction
1 chapter 1 1111 in tr oduc tion introduction 1 welcome congratulations on the purchase of your sailor fleetbroadband system! Sailor 500 fleetbroadband and sailor 250 fleetbroadband are maritime broadband systems, providing simultaneous high-speed data and voice communication via satellite through t...
Page 18
Chapter 1: introduction 2 welcome applications include: • internet browsing • e-mail • phone and fax services • large file transfers • video conferencing and streaming • vpn (virtual private network) access to corporate servers this chapter has the following sections: • features and interfaces • mai...
Page 19: Features And Interfaces
Chapter 1: introduction features and interfaces 3 1111 in tr oduc tion features and interfaces the sailor fleetbroadband system offers the following features and interfaces: simultaneous voice and data communication over bgan full duplex, single or multi-user, up to: sailor 500 fleetbroadband:492 kb...
Page 20: Main Units
Chapter 1: introduction 4 main units main units sailor 500/sailor 250 fleetbroadband the main difference between the sailor 500 fleetbroadband system and the sailor 250 fleetbroadband system lies in the antenna. • sailor 500 fleetbroadband uses the tt-3052a/b/c antenna, which is a maritime bgan clas...
Page 21
Chapter 1: introduction main units 5 1111 in tr oduc tion sailor ® fleetbroadband antennas sailor 500 fleetbroadband antenna the sailor 500 fleetbroadband system uses the tt-3052a/b/c antenna, which is a maritime 3-axis controlled bgan antenna. The antenna contains all functions for satellite tracki...
Page 22
Chapter 1: introduction 6 main units sailor 250 fleetbroadband antenna the sailor 250 fleetbroadband system uses the tt-3050a antenna, which is a medium size maritime 2-axis stabilized bgan antenna. For information on how to install the antenna, refer to the installation manual..
Page 23
Chapter 1: introduction main units 7 1111 in tr oduc tion sailor fleetbroadband terminal overview whether you have purchased a sailor 500 fleetbroadband system or a sailor 250 fleetbroadband system, the terminal is basically the same. For this reason this section covers both systems. The sailor flee...
Page 24
Chapter 1: introduction 8 main units the terminal is also available in a 19” rack version. The 19” rack terminal is the same as the basic version, except for the housing which fits in a 19” rack and has an additional power switch on the front panel. For information on how to install the terminal, re...
Page 25
Chapter 1: introduction main units 9 1111 in tr oduc tion thrane ip handset and cradle thrane ip handset the thrane ip handset communicates using internet protocols (ip). The handset is not strictly dedicated to the sailor fleetbroadband system, but can also be used in a public network as a standard...
Page 26: The Inmarsat Bgan System
Chapter 1: introduction 10 the inmarsat bgan system the inmarsat bgan system what is bgan? The broadband global area network (bgan) is a mobile satellite service that offers high-speed data up to 492 kbps and voice telephony. Bgan enables users to access e-mail, corporate networks and the internet, ...
Page 27
Chapter 1: introduction the inmarsat bgan system 11 1111 in tr oduc tion coverage the inmarsat ® bgan services are based on geostationary satellites situated above the equator. Each satellite covers a certain area (footprint). The coverage map below shows the footprints of the bgan system. For updat...
Page 28
Chapter 1: introduction 12 the inmarsat bgan system overview of the bgan fleetbroadband system a complete bgan fleetbroadband system includes the sailor fleetbroadband terminal with connected peripherals, a sailor 500 fleetbroadband antenna or a sailor 250 fleetbroadband antenna, the bgan satellite,...
Page 29
Chapter 1: introduction the inmarsat bgan system 13 1111 in tr oduc tion the bgan services supported by sailor fleetbroadband supported services the services currently supported by the sailor fleetbroadband comprise: • a packet-switched (ps) connection to the internet • a circuit-switched (cs) diale...
Page 30
Chapter 1: introduction 14 the inmarsat bgan system circuit-switched (dialed) service the following types of circuit-switched connection are available: • standard voice. A low-tariff connection for voice only. The voice signal is compressed to 4.0 kbps, which reduces the bandwidth use and consequent...
Page 31
Chapter 1: introduction the inmarsat bgan system 15 1111 in tr oduc tion terminal and assign a thrane ip handset in the web interface of the sailor fleetbroadband terminal. Supplementary services the bgan system also provides the following supplementary services: • call hold • call waiting • call fo...
Page 32
Chapter 1: introduction 16 the inmarsat bgan system service limitations sim lock the supplier may have locked the sim card to a specific provider. For further information, contact your supplier. Limitations in available services the services available depend on your airtime subscription. Your sim ca...
Page 33: Services And Interfaces
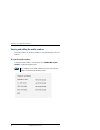
Chapter 1: introduction services and interfaces 17 1111 in tr oduc tion services and interfaces the following table shows which equipment and interfaces you can use to access the services listed in the left column. Service interface on the terminal phone/fax lan (poe) isdn 3.1 khz audio a analog tel...
Page 34
Chapter 1: introduction 18 services and interfaces.
Page 35: Getting Started
19 chapter 2 2222 gett ing s tar te d getting started 2 this chapter describes how to start up the system and make the first call or data session. It has the following sections: • before you start • starting up the terminal • connecting the thrane ip handset • connecting a computer • entering the si...
Page 36: Before You Start
Chapter 2: getting started 20 before you start before you start operation at high temperatures if the terminal is installed in a location where the ambient temperature may exceed 45 c, we recommend placing the terminal where unintentional contact is avoided. Note that the maximum allowed ambient te...
Page 37
Chapter 2: getting started before you start 21 2222 gett ing s tar te d connector panel the drawings below show the connector panel of each terminal version. The only difference is the terminal block on the 19” rack terminal. Connector panel on sailor fleetbroadband terminal: connector panel on sail...
Page 38: Starting Up The Terminal
Chapter 2: getting started 22 starting up the terminal starting up the terminal sim card note that the sailor fleetbroadband terminal requires a sim card dedicated to fleetbroadband. The terminal can only access the bgan network when the right type of sim card is installed. For information on how to...
Page 39
Chapter 2: getting started starting up the terminal 23 2222 gett ing s tar te d 19” rack terminal: using the front power switch if you have the 19” rack variant of the sailor fleetbroadband terminal, flip the switch in the front panel to “1” to switch on the terminal. Note to be able to use the powe...
Page 40
Chapter 2: getting started 24 starting up the terminal using the ignition system normally the ignition function is not used in maritime installations. Instead you may want to use the remote on/off function described in the next section. If you have connected the ignition system of your vessel to the...
Page 41
Chapter 2: getting started starting up the terminal 25 2222 gett ing s tar te d power up completed when the terminal is switched on, the power indicator in the led panel of the terminal lights green. You can now access the terminal settings, but the terminal is not ready for making calls or running ...
Page 42
Chapter 2: getting started 26 connecting the thrane ip handset connecting the thrane ip handset power supply (poe) the thrane ip handset is powered from the lan interface, using power over ethernet. The total output power from all 4 interfaces is • 64 w at 24 v dc power supply • 32 w at 12 v dc powe...
Page 43: Connecting A Computer
Chapter 2: getting started connecting a computer 27 2222 gett ing s tar te d if the handset is not ready for making calls, it may be because the bgan terminal is waiting for a sim pin. To check this, enter the handset menu system and select bgan > status > pin status. You can enter the sim pin using...
Page 44
Chapter 2: getting started 28 entering the sim pin for the terminal 3. When the computer and the terminal are ready, check the connection e.G. By accessing the built-in web interface of the terminal with your browser. For further information, see accessing the web interface on page 82. You may have ...
Page 45
Chapter 2: getting started entering the sim pin for the terminal 29 2222 gett ing s tar te d entering the sim pin using a phone or thrane ip handset to enter the sim pin if you have a phone connected to the terminal, you can use it to enter the sim pin for the terminal at start up. Do as follows: • ...
Page 46
Chapter 2: getting started 30 entering the sim pin for the terminal if you enter 10 wrong puks, the sim card will no longer be functional. Contact your airtime provider for a new sim card. Thrane ip handset: after having entered the user name and password for the terminal you have 3 attempts to ente...
Page 47
Chapter 2: getting started entering the sim pin for the terminal 31 2222 gett ing s tar te d if your sim card uses a pin and the pin has not yet been entered, the web interface will open on the pin page. 2. Type in the pin and click ok. When the pin is accepted, the web interface opens the dashboard...
Page 48
Chapter 2: getting started 32 registering with the bgan network registering with the bgan network registration procedure when the sim pin is accepted by the terminal, the sailor fleetbroadband system automatically starts the registration procedure on the bgan network. You can monitor the registratio...
Page 49
Chapter 2: getting started registering with the bgan network 33 2222 gett ing s tar te d led indications during the registration procedure this table shows how the startup procedure is signalled with the light indicators. If an error occurs, the indicators will light yellow or red, depending on the ...
Page 50
Chapter 2: getting started 34 registering with the bgan network indications in the web interface the dashboard in the web interface also shows the status during and after registration. When the system is ready, the antenna status field shows tracking and the status field shows ready (unless a call o...
Page 51: Making The First Call
Chapter 2: getting started making the first call 35 2222 gett ing s tar te d making the first call when the antenna and terminal indicators in the led panel on the terminal both light steady green, you are ready to make or receive the first call. The following sections provide a short guide to makin...
Page 52
Chapter 2: getting started 36 making the first call • mobile number: the mobile number of the terminal/handset you are calling. The first part of the number is always 870, which is the “country code” for the bgan system. Example: if you are calling from denmark and the mobile number for standard voi...
Page 53
Chapter 2: getting started standard connection to the internet (default) 37 2222 gett ing s tar te d standard connection to the internet (default) by default, the terminal does not automatically connect to the internet when you connect your computer or other equipment to the lan interface. You must ...
Page 54
Chapter 2: getting started 38 standard connection to the internet (default) activating the connection using the thrane ip handset (only handset number 0501) to activate the connection using the thrane ip handset, do as follows: 1. Connect the thrane ip handset to one of the lan ports (preferably por...
Page 55: Operating The System
39 chapter 3 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em operating the system 3 this chapter describes how to use the sailor fleetbroadband systems. It has the following sections: • general • using a phone or fax machine • multi-voice (optional) • voice distress (optional) • using a computer • using the thra...
Page 56: The Thrane Ip Handset
Chapter 3: operating the system 40 general the thrane ip handset when you connect the thrane ip handset to one of the lan (poe) connectors on the terminal you can use the handset display and keypad to enter the pin or to view the status of the terminal. The menu system in the thrane ip handset inclu...
Page 57
Chapter 3: operating the system general 41 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em the web interface of the terminal the web interface is a built-in web server for setting up and controlling the terminal, using a connected computer with a browser. With the web interface you can: • enter the sim pin for t...
Page 58
Chapter 3: operating the system 42 general • change the sim pin for the terminal • set up user rights (requires administrator password) • set up remote management and activation • set up restricted dialling • set up multi-voice • set up voice distress for information on how to use the web interface,...
Page 59: Services And Interfaces
Chapter 3: operating the system general 43 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em services and interfaces the following table shows which equipment and interfaces you can use to access the services listed in the left column. Service interface on the terminal phone/fax lan (poe) isdn 3.1 khz audio a anal...
Page 60: Using A Phone Or Fax Machine
Chapter 3: operating the system 44 using a phone or fax machine using a phone or fax machine available interfaces three types of voice equipment connect to the terminal: standard analogue phone or g3 fax machine: the terminal has two phone connectors for connecting standard analogue phones or fax ma...
Page 61: Selecting The Call Type
Chapter 3: operating the system using a phone or fax machine 45 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em selecting the call type definition the phone connection can use one of the following call types: • standard voice, which is a low-tariff voice connection compressed to 4.0 kbps • 3.1 khz audio, which i...
Page 62
Chapter 3: operating the system 46 using a phone or fax machine • phone/fax. Select the call type for each port in the web interface under settings > phone/fax. For further information, see configuring the phone/fax interface on page 114. • ip handset. Select the call type for each handset in the we...
Page 63
Chapter 3: operating the system using a phone or fax machine 47 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em phone numbers for incoming calls the mobile numbers for your system are listed in your airtime subscription. For example, you may have • 1 number for standard voice • 1 number for 3.1 khz audio • 1 num...
Page 64: Making A Call
Chapter 3: operating the system 48 using a phone or fax machine • ip handset. Select the call type for each handset in the web interface under settings > ip handset > call settings. For further information, see setting the call types for ip handsets on page 132. Making or receiving a phone call maki...
Page 65: Receiving A Call
Chapter 3: operating the system using a phone or fax machine 49 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em if there was an error establishing the connection, refer to the troubleshooting guide on page 209. If you are using the thrane ip handset, the handset may show an error message. Depending on the type o...
Page 66
Chapter 3: operating the system 50 using a phone or fax machine making a call to the terminal to make a call to a phone connected to the terminal, dial + • + is the international call prefix 1 used in front of the country code for international calls. • mobile number. The first part of the mobile nu...
Page 67: Using The Local Exchange
Chapter 3: operating the system using a phone or fax machine 51 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em using the local exchange before you can use the local exchange, you must enable it in the web interface of the terminal. For information on how to set up the local exchange function, see setting up the...
Page 68: Making Local Phone Calls
Chapter 3: operating the system 52 using a phone or fax machine making local phone calls you can make local calls between various phones connected to the terminal. Local phone numbers always start with 0. For an overview of the numbers assigned to each type of interface, see local numbers and specia...
Page 69: Dialling Functions
Chapter 3: operating the system using a phone or fax machine 53 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em dialling functions local numbers and special-purpose numbers there are a number of dialling functions available in the terminal. The following list shows the allocated special-purpose numbers for the t...
Page 70: Dialling Prefixes
Chapter 3: operating the system 54 using a phone or fax machine dialling prefixes apart from the numbers above, the terminal uses the following dialling prefixes: • 1* before the phone number will force the connection to use standard voice. • 2* before the phone number will force the connection to u...
Page 71: Handling Waiting Calls
Chapter 3: operating the system using a phone or fax machine 55 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em handling waiting calls during a call, if a second party tries to call you, you may hear a call waiting indication. The call waiting indication is two beeps and a pause of 3 seconds, then two beeps agai...
Page 72: Holding A Call
Chapter 3: operating the system 56 using a phone or fax machine holding a call during a call, you may place the initial call on hold while another call is made. Thrane ip handset: select options > hold in the thrane ip handset. For further details, refer to the section “handling calls” in the user m...
Page 73: Transferring A Call
Chapter 3: operating the system using a phone or fax machine 57 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em transferring a call when you receive a call, you can transfer this call to another phone connected to the terminal. Thrane ip handset: select options > transfer in the thrane ip handset. For further de...
Page 74: Handling Delays
Chapter 3: operating the system 58 using a phone or fax machine sending or receiving a fax message handling delays when sending or receiving fax messages over satellite, both fax units must be capable of handling longer delays without timing out. Some fax machines have an overseas mode, which enable...
Page 75: Receiving A Fax Message
Chapter 3: operating the system using a phone or fax machine 59 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em • mobile number. The first part of the mobile number is always 870, which is the “country code” for the bgan system. Use the 3.1 khz mobile number if you are calling a g3 fax and the udi number if you ...
Page 76: Multi-Voice (Optional)
Chapter 3: operating the system 60 multi-voice (optional) multi-voice (optional) you can add multi-voice to your airtime subscription, enabling you to have up to 9 simultaneous calls. You can subscribe to multi-voice with or without additional numbers. For details on how to set up multi-voice using ...
Page 77: Handset Contexts
Chapter 3: operating the system multi-voice (optional) 61 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em handset contexts calls to the terminal are treated differently depending on the handset context. There are 3 possible handset contexts, which are explained in this section: • call type groups • directly assi...
Page 78: Directly Assigned Handsets
Chapter 3: operating the system 62 multi-voice (optional) directly assigned handsets the mobile numbers are assigned to individual handsets. Only the assigned handset will ring when the belonging number is called. For information on how to assign a number to a handset, see • setting the call types f...
Page 79: Unassigned Handsets
Chapter 3: operating the system multi-voice (optional) 63 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em unassigned handsets these are ip handsets that are not assigned a number, and that do not belong to a call type group. Use this handset context if you want to create a group of ip handsets that can be called...
Page 80
Chapter 3: operating the system 64 multi-voice (optional) additional numbers for multi-voice in addition to the phone numbers for incoming standard voice, 3.1 khz audio and udi/rdi, your subscription may include extra phone numbers that can be assigned to specific handsets. If you want to use the ad...
Page 81: Voice Distress (Optional)
Chapter 3: operating the system voice distress (optional) 65 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em voice distress (optional) with the voice distress feature you can make distress and urgency calls using the fleetbroadband service. The voice distress system includes a fleetbroadband system, a sailor 377...
Page 82: Using A Computer
Chapter 3: operating the system 66 using a computer using a computer interfaces the terminal has four lan connectors for connecting computers or other lan equipment. For information on how to connect to the interfaces, see the installation manual for the sailor fleetbroadband systems. Router functio...
Page 83
Chapter 3: operating the system using a computer 67 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em • using a standard ip connection, several users can share the data connection simultaneously. This type of connection is ideal for tcp/ip traffic such as e-mail, file transfer, and internet and intranet access. Th...
Page 84: Connecting To The Internet
Chapter 3: operating the system 68 using a computer connecting to the internet default setup by default, any ip device that is connected to the terminal belongs to the default network user group. It uses a standard shared ip connection, which you must manually activate from the web interface. For fu...
Page 85
Chapter 3: operating the system using a computer 69 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em start/stop standard ip on the lan interface by default, standard ip is not automatically activated on the terminal. If you want standard ip to be automatically activated at start-up, the administrator can enable a...
Page 86
Chapter 3: operating the system 70 using a computer start/stop streaming ip on the lan interface to start or stop a streaming session, click the link with the name of your streaming profile under streaming profiles on lan at the bottom of the dashboard. For information on setup of the network user g...
Page 87
Chapter 3: operating the system using a computer 71 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em accessing the terminal from a remote location preparing the terminal for remote management there are three steps you must go through before you can access the terminal from a remote location: 1. Set up the termina...
Page 88
Chapter 3: operating the system 72 using a computer activating a data connection with an sms to be able to activate a data connection on the terminal from a remote location, the terminal must be set up as described in remote activation on page 191. Send an sms to the mobile number of the terminal. T...
Page 89
Chapter 3: operating the system using a computer 73 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em • is the address from step 3 above. • is the port you defined in remote management on page 189. Example: if the ip address of the terminal is 161.30.180.12 and the incoming port number defined in the remote manage...
Page 90: Overview
Chapter 3: operating the system 74 using a computer using pppoe (point-to-point protocol over ethernet) overview you can establish a pppoe connection to the bgan network using the sailor fleetbroadband system. Use pppoe if you want to control your connection independently of the web interface and th...
Page 91
Chapter 3: operating the system using a computer 75 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em configuring the connected equipment for pppoe to use pppoe with your sailor system, first enable pppoe in your terminal. Refer to enabling pppoe (point-to-point protocol over ethernet) on page 111. After enabling ...
Page 92
Chapter 3: operating the system 76 using a computer if you need a certain service, for example a streaming class, you must type in a specified text string when asked for a service name. The following table shows the service names supported by the terminal. For a list of supported at commands and the...
Page 93: Tracking The Terminal
Chapter 3: operating the system using the thrane ip handset 77 3333 o p er ati n g t h e sy st em tracking the terminal the sailor fleetbroadband system can be used for tracking purposes. You can set up the terminal to report its position to a server at certain time intervals or after moving a speci...
Page 94
Chapter 3: operating the system 78 using the thrane ip handset.
Page 95: Using The Web Interface
79 chapter 4 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e using the web interface 4 this chapter describes how to use the web interface to operate, set up and configure your sailor fleetbroadband system. It has the following sections: • introduction • entering the sim pin in the web interface • using the dashb...
Page 96: Introduction
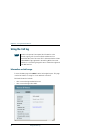
Chapter 4: using the web interface 80 introduction introduction the web interface what is the web interface? The web interface is built into the terminal and is used for operating, setting up and configuring the system. You can access the web interface from a computer with a standard internet browse...
Page 97
Chapter 4: using the web interface introduction 81 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e proxy settings when accessing the web interface if you are connecting your computer using a lan or wlan interface, the proxy server settings in your browser must be disabled before accessing the web interface. Most ...
Page 98
Chapter 4: using the web interface 82 introduction accessing and navigating the web interface accessing the web interface to access the web interface, do as follows: 1. Connect your computer to the terminal. 2. Start up the terminal. For details, see getting started on page 19. 3. Open your browser ...
Page 99
Chapter 4: using the web interface introduction 83 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e overview of the web interface when the web interface opens, the title bar shows the name of the product. The web interface consists of the following sections. • the navigation pane holds the main menu. Clicking an i...
Page 100
Chapter 4: using the web interface 84 introduction icons in the icon bar the following icons may appear in the icon bar in the web interface: navigating the web interface • to expand a menu, click the menu in the navigation pane. • to access status and settings, click the relevant subject in the nav...
Page 101
Chapter 4: using the web interface entering the sim pin in the web interface 85 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e entering the sim pin in the web interface do you need a sim pin? If a computer is connected when you start up the terminal, you can access the web interface and enter the sim pin here. T...
Page 102: Using The Dashboard
Chapter 4: using the web interface 86 using the dashboard using the dashboard overview the dashboard is used for control and inspection of ongoing communication and for viewing properties and status of the terminal and antenna. For information on how to start or stop your data sessions from the dash...
Page 103
Chapter 4: using the web interface using the dashboard 87 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e properties the properties section of the dashboard shows the following information: • airtime provider. The name of your airtime provider. • gps position. The gps position of your sailor fleetbroadband system...
Page 104
Chapter 4: using the web interface 88 using the dashboard • satellite selection. The satellite selected for logon. For further information, see selecting the preferred bgan satellite on page 165. • current satellite. The satellite to which the system is currently logged on. • unit serial number. The...
Page 105
Chapter 4: using the web interface using the dashboard 89 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e viewing information on calls and data sessions the following sections in the dashboard show information on calls and data sessions. • ongoing calls is a list of calls that are currently active. The list shows...
Page 106: Using The Phone Book
Chapter 4: using the web interface 90 using the phone book using the phone book general usage overview in the phone book you can: • look up phone numbers. • look up short-dial numbers for easy dialling from a handset. • modify or delete existing names and phone numbers, or add new names and phone nu...
Page 107
Chapter 4: using the web interface using the phone book 91 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e accessing the phone book to access the phone book, select phone book from the left navigation pane. The phone book shows all entries with entry number, name and phone number. Empty place holders are also inc...
Page 108
Chapter 4: using the web interface 92 using the phone book short dial the entry number in the phone book is the short dial number. When making a call from the terminal you can use this number instead of dialling the entire phone number. Simply dial 00 followed by # or off-hook key. Example: to call ...
Page 109
Chapter 4: using the web interface using the phone book 93 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e editing phone book entries adding a new entry to add a new entry, do as follows: 1. In the phone book, locate the empty entry number where you want to add the new phone number and click new. 2. Type in the n...
Page 110
Chapter 4: using the web interface 94 using the phone book viewing and editing the mobile numbers the mobile numbers are the phone numbers to use when making a call to the terminal. To view the mobile numbers to view the mobile numbers of the terminal, select phone book > mobile numbers from the lef...
Page 111
Chapter 4: using the web interface using the phone book 95 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e additional numbers: if you have additional numbers in your subscription, you can enter them as well. Below is an example of a mobile numbers list with additional numbers. To enter or edit the mobile numbers ...
Page 112: Using The Call Log
Chapter 4: using the web interface 96 using the call log using the call log information on total usage to enter the calls page select calls from the left navigation pane. This page contains information on usage for circuit-switched connections. The listed information includes: • time connected using...
Page 113
Chapter 4: using the web interface using the call log 97 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e exporting the call log you can export the call log file and save it on your computer for archiving, surveillance or other tracking purposes. The call log holds information on all calls and data sessions since ...
Page 114
Chapter 4: using the web interface 98 using the call log for information on the available types of service, see the bgan services supported by sailor fleetbroadband on page 13. You can sort each of the lists by clicking the title of the column you wish to sort by. If a list covers more than one page...
Page 115: Handling Sms Messages
Chapter 4: using the web interface handling sms messages 99 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e handling sms messages sending an sms message to send an sms message from the terminal, do as follows: 1. Click messages from the left navigation pane. This page contains new incoming messages. 2. In the lef...
Page 116
Chapter 4: using the web interface 100 handling sms messages if the message text is too long for one sms, the message is sent as two or more sms messages. The field below the message field shows the number of sms messages used to send the message. 4. Type in the phone number in the recipient field. ...
Page 117
Chapter 4: using the web interface handling sms messages 101 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e options for messages in the sent folder the sent folder contains sms messages that have been sent. To access the sent folder, select messages > sent from the navigation pane. The status column shows the st...
Page 118
Chapter 4: using the web interface 102 handling sms messages select phone book > mobile numbers. If the mobile numbers are not listed in the web interface, refer to the documents provided with your airtime subscription. Receiving a message if a message has arrived, the icon bar at the top of the web...
Page 119
Chapter 4: using the web interface handling sms messages 103 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e options for new sms messages to see new messages, click messages from the left navigation pane. Besides viewing the new messages, you have a number of options for what to do with each message: • click arch...
Page 120
Chapter 4: using the web interface 104 handling sms messages configuring message settings setting up the default message options you can set up general options for your outgoing messages. These settings apply by default to all your outgoing messages. Note, however, that you can change the delivery n...
Page 121
Chapter 4: using the web interface handling sms messages 105 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e viewing or changing sms service centre number the sms service centre number identifies the sms service centre used when sending and receiving sms messages. The sms service centre number is stored on the si...
Page 122: Setting Up The Interfaces
Chapter 4: using the web interface 106 setting up the interfaces setting up the interfaces the settings page (antenna properties) the settings page shows properties of the connected antenna and contains a field for enabling or disabling the l-band interface on the terminal. To access the settings pa...
Page 123
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 107 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e enabling or disabling the l-band interface the l-band interface is used for connecting a broadband receiver for reception of position data. To enable or disable the l-band interface, do as follows: 1. ...
Page 124
Chapter 4: using the web interface 108 setting up the interfaces you can also set up the local ip address used by the connected devices to access the terminal. The drawing below shows the default setup. To change the local ip addresses, do as follows: 1. From the left navigation pane, select setting...
Page 125
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 109 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e • if you select enabled, the terminal assigns dynamic ip addresses to devices connected to the terminal. • if you select disabled, you need to set up a static ip address in the connected device. 3. If ...
Page 126
Chapter 4: using the web interface 110 setting up the interfaces the mail server in this example has the ip address 192.168.0.100. 1. Select lan > port forwarding in the left navigation pane. 2. Select enabled to generally enable port forwarding. 3. Type in the incoming port range. 4. Type in the de...
Page 127
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 111 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e if you do not know the ip address, you can look it up in the dashboard of the web interface under ongoing data sessions. Enabling pppoe (point-to-point protocol over ethernet) what is pppoe by using pp...
Page 128
Chapter 4: using the web interface 112 setting up the interfaces enabling pppoe in the sailor fleetbroadband terminal to enable pppoe in the terminal do as follows: 1. Select settings > lan > pppoe. 2. Select enabled. 3. Click apply. 4. Restart the terminal for the setting to take effect. For inform...
Page 129
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 113 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e setting up static routing when you have an external gateway connected to your terminal, the terminal is not automatically able to “see” the network on the other side of the gateway. However, you can se...
Page 130
Chapter 4: using the web interface 114 setting up the interfaces the values for the new entry are now in the list. This means that the terminal can communicate with the destination ip address on the other side of the gateway. Configuring the phone/fax interface to configure the phone/fax interface d...
Page 131
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 115 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 2. If you have additional numbers from your airtime provider and you want to assign them to the phone/fax ports, use the assigned number drop down list to select the number you want to use for each por...
Page 132
Chapter 4: using the web interface 116 setting up the interfaces configuring the isdn interface to configure the isdn interface, do as follows: 1. Select settings > isdn. 2. If you have additional numbers from your airtime provider and you want to assign them to the isdn ports, use the assigned numb...
Page 133
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 117 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 3. Set the call type(s) for incoming calls. You can select standard, 3.1 khz audio, udi and/or rdi. Note that sailor 250 fleetbroadband only supports standard or 3.1 khz audio. 4. Set the msn (multiple...
Page 134
Chapter 4: using the web interface 118 setting up the interfaces the call. If you make a local call to one of the local numbers 0401 or 0402, only the called device will accept the call. 5. Set the call type for outgoing calls. • if you select automatic, the call type will be determined by the calli...
Page 135
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 119 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e setting the common interface settings overview the settings under common are common for all interfaces. Definition of access point name (apn) the apn is used by the network user to establish a connecti...
Page 136
Chapter 4: using the web interface 120 setting up the interfaces to set up the common interface settings to set up the common interface settings, do as follows: 1. Select settings > common. 2. Select the apn. You have the following options: • sim default. The apn is taken from the sim card. This is ...
Page 137
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 121 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e • if you select disabled, your streaming connection will not be buffered. This means the data is delivered immediately, but may vary slightly in transmission speed. 4. Click apply. Setting up call serv...
Page 138
Chapter 4: using the web interface 122 setting up the interfaces do as follows: 1. Select settings > common > call forward from the left navigation pane. 2. Click ok next to read current settings to display the phone numbers for call forwarding for the subscription. These numbers are operator contro...
Page 139
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 123 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e call barring do as follows to bar incoming and/or outgoing calls to and from the terminal: 1. Select settings > common > call barring from the left navigation pane. 2. Click ok next to read current set...
Page 140
Chapter 4: using the web interface 124 setting up the interfaces call waiting you can set up whether or not you want to receive notification of waiting calls while you are making a call or transmitting data. Do as follows: 1. Select settings > common > call waiting from the left navigation pane. 2. ...
Page 141
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 125 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e line identification you can set up the terminal to show your number when you are making a call or transmitting data. Do as follows: 1. Select settings > common > line identification from the left navig...
Page 142
Chapter 4: using the web interface 126 setting up the interfaces closed user group your subscription may include one or more closed user groups. A closed user group is a group of users permitted to make calls to each other but not to users outside the group. To define the settings for these user gro...
Page 143
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 127 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 4. To allow outgoing access for the activated user group(s), select outgoing access under settings for active closed user group. Note that if you selected subscribed above, this setting will not be use...
Page 144
Chapter 4: using the web interface 128 setting up the interfaces setting up the local exchange function if the local exchange is not used, the default behaviour is such that incoming calls will cause all connected phones to ring. If you want to be able to call a specific phone connected to the termi...
Page 145
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 129 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e • the caller dials nothing after the recorded message. 3. Select the call types you want to direct to the local exchange. For example, if you use 3.1 khz audio for a fax machine only, you do not want t...
Page 146
Chapter 4: using the web interface 130 setting up the interfaces connecting and configuring ip handsets if you want to view or change the settings for the new ip handset, do as follows: 1. Connect the ip handset to one of the lan ports of the terminal. If it is a thrane ip handset, the handset start...
Page 147
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 131 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 5. In the ip handset, enter the local number and the password you just entered in the web interface. For the thrane ip handset. Do as follows: 1. In the thrane ip handset, enter the menu system (select...
Page 148
Chapter 4: using the web interface 132 setting up the interfaces setting the call types for ip handsets in the call settings page you can set the call types for each local number and see whether restricted dialling is enabled for that number. For further information on restricted dialling, see restr...
Page 149
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 133 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 3. For each handset, select the call types you want to enable for incoming and outgoing calls. The call types are described in more detail in selecting the call type on page 45. • for incoming calls, y...
Page 150
Chapter 4: using the web interface 134 setting up the interfaces setting up the thrane ip handset compatibility if you are connecting your thrane ip handset(s) to the terminal through a separate router with nat, you must use thrane ip handsets with software version 1.8 or newer and set up the handse...
Page 151
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 135 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e configuring the discrete i/o interface i/o pins and their functions the i/o interface on the terminal has 5 configurable i/o pins. You can set up the function of each pin in the web interface. The defa...
Page 152
Chapter 4: using the web interface 136 setting up the interfaces • normally open: the internal switch at pin 2 is normally open (no connection to ground). When an alarm occurs, the switch is closed (connected to ground). The switch is opened again when all warnings/errors are cleared. Pin 3: mute ou...
Page 153
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 137 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e • active high (default): connect pin 5 permanently to ground. Connect pin 8 to positive dc voltage (10.5-32 v dc) when the ignition is on. To switch off, disconnect pin 8 from the positive dc voltage. ...
Page 154
Chapter 4: using the web interface 138 setting up the interfaces configuring the i/o interface to configure the i/o pins, do as follows: 1. Select settings > discrete i/o. 2. For each pin you want to use, select enabled. 3. For each pin, select the function of the pin. Refer to the previous section,...
Page 155
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 139 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 6. If you are using a mute output, select the call types (both incoming and outgoing) that should activate the mute function under mute output. 7. Click apply. Setting up tracking the sailor fleetbroad...
Page 156
Chapter 4: using the web interface 140 setting up the interfaces to set up tracking, do as follows: 1. Select settings > tracking..
Page 157
Chapter 4: using the web interface setting up the interfaces 141 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 2. Type in the server ip address, server port, client port and encryption key for your server connection. • ip address. The ip address of the server that the sailor fleetbroadband terminal will report ...
Page 158
Chapter 4: using the web interface 142 setting up the interfaces 7. Under distance report, select enabled or disabled and type in the following: • when moved. Enter the distance the vessel should be moved before sending a report. • max one report per. Enter the minimum time that should pass between ...
Page 159: Managing Lan Network Users
Chapter 4: using the web interface managing lan network users 143 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e managing lan network users introduction the network management system with the built-in router functionality the system offers a flexible use of the data channel of the bgan service. You can configure...
Page 160
Chapter 4: using the web interface 144 managing lan network users how the users connect to the inmarsat bgan network. The network user groups can allow or restrict certain services for different users. For example, you may want to define: • one network user group allowing both standard and streaming...
Page 161
Chapter 4: using the web interface managing lan network users 145 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e access to the network management settings access to the network management settings requires an administrator password. The default user name is admin and the default password is 1234. The administrat...
Page 162
Chapter 4: using the web interface 146 managing lan network users editing a network user group for further explanation of the terms used below, see definitions for network terms on page 157. To edit a network user group, do as follows: 1. Select settings > lan > network user groups. When you are pro...
Page 163
Chapter 4: using the web interface managing lan network users 147 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 2. Click edit next to the network user group you want to set up..
Page 164
Chapter 4: using the web interface 148 managing lan network users 3. Type in a name for the group. 4. Select enabled or disabled. 5. Select the type of internet connection. • router mode means the connection will be shared with other users, and the nat module of the terminal will make the necessary ...
Page 165
Chapter 4: using the web interface managing lan network users 149 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e there are four options for setting the apn. Unless you have special requirements, it is recommended to use the sim default, or to set the common apn to sim default, and then select common here. You ha...
Page 166
Chapter 4: using the web interface 150 managing lan network users select a profile from the primary scroll list. This profile is used by this network user group as a first choice, when possible. There are several predefined profiles: standard, streaming 8 kbps, streaming 16 kbps, streaming 32 kbps, ...
Page 167
Chapter 4: using the web interface managing lan network users 151 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e managing network devices overview a network device, in this context, is an ethernet hardware device, identified by its unique mac address. When a network device with dynamic ip address is connected to...
Page 168
Chapter 4: using the web interface 152 managing lan network users locking an ip address to a mac address when the device is locked to an ip address, the terminal will always assign this ip address to the mac address of this device (if dhcp is enabled and the internet connection is not a bridge mode ...
Page 169
Chapter 4: using the web interface managing lan network users 153 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e using the network classification table overview the network classification table is used to define which network devices, ip addresses and/or lan ports are associated with which network user groups. E...
Page 170
Chapter 4: using the web interface 154 managing lan network users adding or editing an entry in the network classification table to add a new entry to the table or to edit an existing entry, do as follows: 1. Select settings > lan > network classification table. If you are prompted, enter the admini...
Page 171
Chapter 4: using the web interface managing lan network users 155 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 2. Click edit next to the entry you want to edit, or click add at the bottom of the list. 3. Click add next to a network device you want to use, or type in the mac address manually at the top of the p...
Page 172
Chapter 4: using the web interface 156 managing lan network users removing an entry in the network classification table in the network classification table, click delete next to the entry you want to delete. Changing the priority in the network classification table to change the priority of an entry...
Page 173
Chapter 4: using the web interface managing lan network users 157 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e definitions for network terms apn (access point name) apns are provided from the airtime provider. They may also be defined on the sim card the apn is used by the network user to establish a connectio...
Page 174
Chapter 4: using the web interface 158 managing lan network users profiles a profile is a collection of quality of service (qos) settings and other settings defining the mode in which data is transmitted on an interface. For example, a profile is used to define whether a connection should be a stand...
Page 175
Chapter 4: using the web interface managing lan network users 159 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e starting/stopping data sessions the administrator can start and stop data sessions for all network user groups connected to the terminal. To start or stop a data session, do as follows: 1. Select conn...
Page 176: Uploading Software
Chapter 4: using the web interface 160 uploading software uploading software introduction the next pages describe how to upload software from your computer to the terminal and how to download the latest software version from the internet to your computer. You can upload software from your computer t...
Page 177
Chapter 4: using the web interface uploading software 161 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e uploading software from your computer to upload software from your computer to the terminal, do as follows: 1. Download the new software as described in the next section, or acquire the software from thrane &...
Page 178
Chapter 4: using the web interface 162 uploading software 3. In the field upload software to terminal, click browse... 4. Browse to the new software version and accept it. 5. Click the upload button. Note that the upload procedure takes a couple of minutes. Note when upload is done, your terminal au...
Page 179
Chapter 4: using the web interface uploading software 163 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e downloading software from the internet to download the latest software from the internet to the terminal, do as follows: 1. Make sure you have a connection to the internet from your terminal. 2. Open the web ...
Page 180
Chapter 4: using the web interface 164 uploading software the terminal will now connect to the internet through the bgan network, using your airtime subscription. It may take a minute or two to obtain the new software version. When the new software version is found, the web interface shows the new s...
Page 181
Chapter 4: using the web interface selecting the preferred bgan satellite 165 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e selecting the preferred bgan satellite overview by default the terminal is set up to automatically find the most appropriate satellite to connect to (“auto” mode). However, if you are loca...
Page 182
Chapter 4: using the web interface 166 selecting the preferred bgan satellite the sailor fleetbroadband terminates all ongoing connections and deregisters from the current satellite before registering on the new satellite. Note if you have selected a satellite, your sailor fleetbroadband system will...
Page 183: Selecting The Language
Chapter 4: using the web interface selecting the language 167 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e selecting the language the default language of the web interface is english. You can change the language to french, german, russian, spanish, mandarin (chinese) or japanese. To change the language, do as ...
Page 184: Administration
Chapter 4: using the web interface 168 administration administration accessing the administration settings logging on the administration settings require an administration user name and password. To log on as administrator, do as follows: 1. Select administration from the left navigation pane. 2. En...
Page 185
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 169 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 3. Click logon. The administration page is now updated to let you change the user name and password, save/load a configuration or log off administration. Resetting the administrator password if you have forgotten...
Page 186
Chapter 4: using the web interface 170 administration changing the administrator password to change the administrator password, do as follows: 1. After entering the administrator user name and password in the administration page, locate the section change administrator logon. 2. Type in the existing...
Page 187
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 171 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e saving a configuration to a file if you need to reuse a configuration in another terminal of the same type and software version, you can save your current configuration to a file, which can then be loaded into th...
Page 188
Chapter 4: using the web interface 172 administration call charges if you know the tariff for your subscribed services, you can enter these tariffs in the web interface and automatically calculate the charges for your calls and data sessions. To enter the call tariffs, do as follows: 1. From the lef...
Page 189
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 173 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 3. Enter the tariff for each of the services. 4. Click apply. The entered tariffs are used for estimating the charges for calls and data sessions. The estimated charge is listed for each call or data session in t...
Page 190
Chapter 4: using the web interface 174 administration for the standard data connection, and/or a time interval from start to end for a streaming connection. If you have entered the call charges in the menu call charges, the system automatically calculates and displays the maximum charges for your da...
Page 191
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 175 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 6. Click apply to save the settings. Using profiles what is a profile? A profile is a collection of quality of service (qos) settings and other settings defining the mode in which data is transmitted. For example...
Page 192
Chapter 4: using the web interface 176 administration selecting the profiles for a network user group when you set up a network user group, you select the profiles to use for that network user group. You select a primary profile and optionally one or more secondary profiles. For further information ...
Page 193
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 177 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e defining new profiles when you define your profiles you can select subscribed for many of the settings. If you select subscribed, the value given in your airtime subscription is automatically used. To define a ne...
Page 194
Chapter 4: using the web interface 178 administration 2. Click edit next to one of the user defined profiles. 3. Fill in the name you want for your profile..
Page 195
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 179 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e 4. Select the traffic class from the drop-down list. You may select subscribed or one of the following: • conversational is real-time two-way conversation. It is primarily used for voice over ip and video confere...
Page 196
Chapter 4: using the web interface 180 administration 6. In the delivery order field, select from the scroll list whether or not data should be delivered in the same order it was sent. Yes means the data packets are delivered in the same order they were sent. 7. In the maximum sdu size (byte) field,...
Page 197
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 181 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e using traffic flow filters purpose of the traffic flow filters the purpose of the traffic flow filters is to assign different priorities to different types of traffic in order to optimize performance. Example: wh...
Page 198
Chapter 4: using the web interface 182 administration defining traffic flow filters to define the traffic flow filters, do as follows: 1. From the left navigation pane, select administration > traffic flow filters. 2. Click the link new entry. 3. Select a number in the eval.Prec. Index drop-down lis...
Page 199
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 183 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e the evaluation precedence index defines the order in which the traffic flow filters are applied to packets. 0 is first, then 1, 2 etc. 4. Select the profile from the drop-down list. The available profiles are the...
Page 200
Chapter 4: using the web interface 184 administration example of a list of traffic flow filters below is an example of a list of traffic flow filters. In this example, data packets are filtered in the following order: 1. The filter with evaluation precedence index 0 checks for udp packets (protocol ...
Page 201
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 185 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e setting up the use of sim pin in the terminal enabling or disabling the use of a sim pin to enable or disable the use of a pin to access the terminal, do as follows: 1. Select administration > sim pin. 2. Under r...
Page 202
Chapter 4: using the web interface 186 administration changing the sim pin to change the pin used to access the terminal, do as follows: 1. Select administration > sim pin. 2. Under change pin type in the old pin. 3. Type in the new pin and retype it on the next line. 4. Click apply. The new pin set...
Page 203
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 187 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e setting up user permissions you can allow or deny users who are not administrators access to certain functions and make these pages read-only. This is useful if you want to protect the system against unintended c...
Page 204
Chapter 4: using the web interface 188 administration 2. For each item under allow users to:, select • yes to allow access or • no to block access to the settings. Change general settings means change the settings on the settings main page, that is enabling/disabling the l-band interface. Control co...
Page 205
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 189 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e remote management you can set up the terminal so that it can be controlled from a remote location, either using the web interface or at commands. To set up the terminal for remote management, do as follows: 1. Fr...
Page 206
Chapter 4: using the web interface 190 administration 2. Select whether remote access should be enabled or disabled for the web server and/or for at commands. 3. Type in the incoming port numbers to use for the web server and for at commands. 4. Under trusted ip addresses, type in the ip addresses o...
Page 207
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 191 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e remote activation if you want to remotely control the terminal, it must have activated a connection. You can do this by sending an sms to the terminal. The terminal must be powered up and logged on to the satelli...
Page 208
Chapter 4: using the web interface 192 administration 3. Select whether confirmation by sms should be enabled or disabled. 4. Enter the password. It can be up to 32 characters long. The characters 0-9, a-z and a-z are allowed. The password is mandatory and must match the password in the activation s...
Page 209
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 193 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e link monitoring you can monitor the external ip connection of the sailor 500 fleetbroadband system using the link monitoring feature. With this feature activated, the terminal will send out ping commands (icmp ec...
Page 210
Chapter 4: using the web interface 194 administration 6. Click apply. When a data session is started with the default network user group, the terminal will start sending ping commands to the primary ip address the number of times specified at retries. If no response is received, it will send the sam...
Page 211
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 195 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e to setup the terminal for restricted dialing, do as follows: 1. From the left navigation pane, select administration > restricted dialing. 2. Select whether restricted dialing should be enabled or disabled. 3. Ty...
Page 212
Chapter 4: using the web interface 196 administration multi-voice if you wish to have more simultaneous voice calls, you can add multi-voice to your airtime subscription. When multi-voice is enabled in your terminal, you can have up to 9 simultaneous calls using ip handsets (max 6 for sailor 250 fle...
Page 213
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 197 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e terminal. Refer to the manufacturer documentation for your multi-voice pbx. 3. If you want to assign additional numbers, select use additional numbers. 4. Type in the voip apn used for multi-voice. You find the m...
Page 214
Chapter 4: using the web interface 198 administration voice distress to set up the terminal for voice distress, do as follows: 1. Connect your voice distress system as described in the manual for the voice distress system. 2. From the left navigation pane, select administration > voice distress sett...
Page 215
Chapter 4: using the web interface administration 199 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e • the distress ip handset display should show (designated for distress), and • the alarm panel should show fb (connected to fleetbroadband terminal)..
Page 216
Chapter 4: using the web interface 200 help desk and diagnostic report help desk and diagnostic report accessing the help desk if you need help with airtime-related issues you may call the help desk. By default, the help desk is the phone number for your airtime provider, if it is available on the s...
Page 217
Chapter 4: using the web interface help desk and diagnostic report 201 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e generating a diagnostic report the diagnostic report contains relevant information for troubleshooting. When contacting your distributor for support, please enclose this file. To generate a diagn...
Page 218: Event Logging and Self Test
Chapter 4: using the web interface 202 event logging and self test event logging and self test viewing the event list or the event log overview when an event is registered, the web interface shows an event icon in the icon bar as long as the event is active. The event list only shows events that are...
Page 219
Chapter 4: using the web interface event logging and self test 203 4444 usin g the web in te rf ac e to view the event log, select helpdesk > event log from the left navigation pane. Self test the self test performs system test on the sailor fleetbroadband system, similar to the tests that are perfo...
Page 220: Site Map
Chapter 4: using the web interface 204 site map • the status of the connection to the air interface (iai-2). This field should normally show “registered”, unless the system is still in the startup process. • ongoing data sessions (ip address) and connection status, e.G. Active or suspended. • ongoin...
Page 221: Troubleshooting
205 chapter 5 555 tr ouble sho ot ing troubleshooting 5 this chapter gives guidelines for troubleshooting and provides an overview of the different means of status signalling. It has the following sections: • getting support • uploading software • part numbers • troubleshooting guide • status signal...
Page 222
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 206 getting support system support if you need assistance with problems caused by the terminal or antenna, please call a distributor in your area. A list of certified partners and distributors is available on thrane & thrane’s web site: thrane.Com . Select maritime and sel...
Page 223: Uploading Software
Chapter 5: troubleshooting uploading software 207 555 tr ouble sho ot ing uploading software viewing software version status to view the version of the embedded software in the terminal, do as follows: 1. Connect a computer. 2. Enter the web interface and see the software version field in the dashbo...
Page 224: Part Numbers
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 208 part numbers part numbers system units tt-3740a sailor 500 fleetbroadband system tt-3742a sailor 250 fleetbroadband system tt-3670a thrane ip handset & cradle, wired item part number sailor 500 fleetbroadband antenna 403052a/b/c sailor fleetbroadband terminal or sailor...
Page 225: Troubleshooting Guide
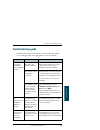
Chapter 5: troubleshooting troubleshooting guide 209 555 tr ouble sho ot ing troubleshooting guide the below table provides information on some of the problems that might occur, including possible causes and remedies to solve the problems. Problem possible cause remedy no signal or weak signal from ...
Page 226
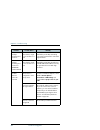
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 210 troubleshooting guide 256 kbps streaming does not work the elevation angle to the satellite is too low. Availability of 256 kbps streaming can only be guaranteed in areas with high elevation. 128 kbps streaming does not work on sailor 250 fleetbroadband the elevation a...
Page 227
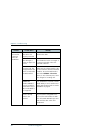
Chapter 5: troubleshooting troubleshooting guide 211 555 tr ouble sho ot ing multi-voice: voice call is not put through the mobile number is not correctly typed into the web interface. Check that all mobile numbers from your airtime subscription are correctly typed into the web interface. See viewin...
Page 228
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 212 troubleshooting guide a phone/fax connection cannot be established. The cable is not properly connected connect the cable. The cable type or connector type is not correct. For information on the correct type of connector and cable, refer to the installation manual. Inc...
Page 229
Chapter 5: troubleshooting troubleshooting guide 213 555 tr ouble sho ot ing an isdn connection cannot be established the cable is not properly connected. Connect the cable. You have connected to the lan interface. Connect the cable to the interface marked isdn. The cable type or connector type is n...
Page 230
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 214 troubleshooting guide no phones are ringing on incoming calls the mute function is activated from an external device connected to the i/o interface of the terminal. If the mute function should not be activated, deactivate it from the external device. The call types for...
Page 231
Chapter 5: troubleshooting troubleshooting guide 215 555 tr ouble sho ot ing a lan connection cannot be established. The cable is not properly connected. Connect the cable. The cable type or connector type is not correct. For information on the correct type of connector and cable, refer to the insta...
Page 232
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 216 troubleshooting guide an ip handset connection cannot be established. The cable is not properly connected. Connect the cable. You have connected to the isdn interface. Remove the cable and connect to one of the lan connectors instead. There is no power (poe) in the lan...
Page 233
Chapter 5: troubleshooting troubleshooting guide 217 555 tr ouble sho ot ing the administrator password does not work. Someone has changed the administrator password. If the correct password is not found, you have to reset the password. Contact your supplier for a reset code. You must provide the se...
Page 234: Status Signalling
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 218 status signalling status signalling overview there are many ways of troubleshooting if an error occurs. The terminal has different means of status signalling, to help you find the cause of a problem: • indicators. • event messages. • event log. Indicators, event messag...
Page 235
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 219 555 tr ouble sho ot ing light indicators overview the terminal has a number of leds, placed in the panel at the top of the terminal: • a green power indicator, • a green/red/orange terminal indicator, • a green/red/orange antenna indicator, • a green ...
Page 236
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 220 status signalling power indicator terminal indicator antenna indicator behaviour meaning green power ok. Flashing green the terminal is powering up. Flashing orange the terminal is closing down. Off no power. Behaviour meaning steady green ready. Bgan registration comp...
Page 237
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 221 555 tr ouble sho ot ing message indicator lan indicator functions flashing green please wait - process in progress. Slow flashing: the antenna is starting up rapid flashing: sky scan orange warning - temporary malfunction. User action is required. Red...
Page 238
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 222 status signalling activity indicator link/speed indicator poe indicator event messages display of event messages the terminal can detect events during post (power on self test) or cm (continuous monitoring). When the terminal detects an event that requires your action,...
Page 239
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 223 555 tr ouble sho ot ing when your terminal issues an event message, the terminal indicator or the antenna indicator in the led panel on top of the terminal signals the event, according to the tables terminal indicator and antenna indicator in the prev...
Page 240
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 224 status signalling list of events the following list explains most of the events that may show in the web interface of the terminal. Note that the list is not complete. Note events with “info” level are not included in this list. Only events that can appear in the alarm...
Page 241
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 225 555 tr ouble sho ot ing 00300 to 00309 gps module error the gps module is out of function. The terminal cannot obtain a valid gps position. Contact your distributor. 00330 to 00339 isdn failure the isdn interface on the terminal cannot be used. Contac...
Page 242
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 226 status signalling 01020 to 01029 too low temperature warning low ambient temperature is causing the performance of the terminal to be degraded or halted. The terminal will assume radio silence if the problem is in the acm module of the antenna. Move the terminal to a w...
Page 243
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 227 555 tr ouble sho ot ing 01120 to 01129 too high temperature warning high ambient temperature is causing the performance of the system to be degraded or halted. If the problem is in the terminal: all poe ports are shut down, except port 1 and the bit r...
Page 244
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 228 status signalling 01500 to 01509 sim card missing no sim card is detected in the sim slot. Insert sim card. If the sim card is already inserted, try removing and reinserting it. 01600 to 01609 sos calls only the sim card is not accepted by the network. Only emergency c...
Page 245
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 229 555 tr ouble sho ot ing 02000 to 02009 satellite signal weak the signal from the satellite is weak. Check the line of sight to the satellite. Check in the web interface under settings > satellite selection that you have selected auto, or a satellite c...
Page 246
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 230 status signalling 03500 to 03509 2-wire calibration failure 2-wire calibration failed on the phone/fax interface, because of: 1. Common mode balance error. 2. The phone is off hook. 3. Wires are shorted to each other or shorted to ground. 1. Check the wires to your pho...
Page 247
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 231 555 tr ouble sho ot ing 08002 one or more ports has poe disabled due to power limitations the power supply to the terminal has dropped critically. Poe is disabled to ensure enough power to the antenna. Ensure a stable power supply to the terminal. 080...
Page 248
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 232 status signalling 0800b poe overvoltage protection is activated overvoltage is detected in the terminal. The terminal will be shut down in 10 minutes. Do not use the terminal. Contact your distributor. 0800d antenna overvoltage protection is activated overvoltage is de...
Page 249
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 233 555 tr ouble sho ot ing 0802c firmware update still fails after several retries the terminal was unable to upload new firmware to the antenna. Contact your distributor. 0802d firmware update failed the terminal was unable to upload new firmware to the...
Page 250
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 234 status signalling 08031 failed to enter normal operation antenna failed to start up normally. Reboot the terminal. Contact your distributor if the problem persists. 08032 firmware image version lower than active antenna version the firmware in the antenna is newer than...
Page 251
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 235 555 tr ouble sho ot ing 08036 radio silence is activated the radio silence function is activated. No transmission is allowed. If the radio silence function should not be active, enter the web interface and select settings > discrete i/o. Then uncheck ...
Page 252
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 236 status signalling 08046 timeout of startup sequence - no antenna or antenna temperature too low the start-up sequence of the terminal has timed out because: • the antenna is not properly connected, or • the antenna temperature is too low to start up. Check that the ant...
Page 253
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 237 555 tr ouble sho ot ing 0804c the chosen satellite is not visible at current gps position the terminal is set up to use a satellite that is not visible at the current gps position. Enter the web interface and select settings > satellite selection. The...
Page 254
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 238 status signalling 08056 usim rejected the type of usim card inserted in the terminal is not correct for your terminal. Make sure you have the correct type of usim card. For example, an usim card for a land- mobile system will not work for a maritime system and vice ver...
Page 255
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 239 555 tr ouble sho ot ing 08064 no connection to fleetbroadband alarm panel the system is configured for voice distress but there is no connection between the terminal and the sailor 3771 alarm panel check that the alarm panel is connected correctly to ...
Page 256
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 240 status signalling 08079 multi-voice control connection error not possible to establish connection to multi- voice server check that multi- voice is included in your subscription. Check that the multi-voice apn entered in the web interface under administration > multi-v...
Page 257
Chapter 5: troubleshooting status signalling 241 555 tr ouble sho ot ing 0900c antenna - temperature too low the temperature is too low for the antenna to work properly. Leave the antenna on and wait for it to warm up. 0900d antenna - temperature too high the temperature is too high for the antenna ...
Page 258: Logging Of Events
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 242 logging of events logging of events diagnostic report when contacting your distributor for support, please include a diagnostic report. The diagnostic report contains information relevant for the service personnel during troubleshooting. To generate the diagnostic repo...
Page 259: Reset Button
Chapter 5: troubleshooting reset button 243 555 tr ouble sho ot ing reset button how to access the reset button the terminal has a reset button placed next to the sim slot behind the sim cover. The functions of this button is described in the next section. To press the reset button, use a pointed de...
Page 260
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 244 reset button function of the reset button the reset button on the terminal has the following functions: action function with the terminal running, press the reset button normally. The terminal ip address and ip netmask are temporarily set to the default value (default ...
Page 261
Chapter 5: troubleshooting list of reserved ip subnets 245 555 tr ouble sho ot ing list of reserved ip subnets some ip subnets are reserved for internal use in the terminal. If any of these addresses are assigned to external equipment connected to the terminal, the terminal and connected equipment w...
Page 262
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 246 supported at commands for pppoe supported at commands for pppoe overview of supported at commands you can use pppoe to issue at commands to the terminal, for example specifying quality of service parameters or which apn to use. The following at commands are supported: ...
Page 263
Chapter 5: troubleshooting supported at commands for pppoe 247 555 tr ouble sho ot ing at+cgeqreq usage: at+cgeqreq is the requested quality of service (qos). This is used to specify the qos for the connection. With this command you can start a streaming context. Syntax: at+cgeqreq=,,,, , • is the c...
Page 264
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 248 supported at commands for pppoe • is the guaranteed bit rate up link (8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256) • is the guaranteed bit rate down link (8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256) example: at+cgeqmin=1,1,64,64,64,64 at+cgtft usage: at+cgtft is the traffic flow template (tft). This command...
Page 265
Chapter 5: troubleshooting supported at commands for pppoe 249 555 tr ouble sho ot ing at+cgdscont usage: at+cgdscont is used to specify the secondary contexts relation to a primary context. The secondary context’s cid must be different from the primary context’s cid. The secondary context’s qos mus...
Page 266
Chapter 5: troubleshooting 250 supported at commands for pppoe if you have any technical questions about the pppoe feature please refer to your local distributor, who can assist you with the configuration..
Page 267: Conformity
251 appendix a aaaa co n fo rm it y conformity a sailor 500 fleetbroadband ce (r&tte) the sailor 500 fleetbroadband is ce certified (r&tte directive) as stated in the “declaration of conformity with r&tte directive”, enclosed in copy on the next page..
Page 269
Appendix a: conformity sailor 500 fleetbroadband 19" rack 253 aaaa co n fo rm it y sailor 500 fleetbroadband 19" rack ce (r&tte) the sailor 500 fleetbroadband 19" rack is ce certified (r&tte directive) as stated in the “declaration of conformity with r&tte directive”, enclosed in copy on the next pa...
Page 271: Sailor 250 Fleetbroadband
Appendix a: conformity sailor 250 fleetbroadband 255 aaaa co n fo rm it y sailor 250 fleetbroadband ce (r&tte) the sailor 250 fleetbroadband is ce certified (r&tte directive) as stated in “declaration of conformity with r&tte directive”, enclosed in copy on the next page..
Page 273
Appendix a: conformity sailor 250 fleetbroadband 19" rack 257 aaaa co n fo rm it y sailor 250 fleetbroadband 19" rack ce (r&tte) the sailor 250 fleetbroadband 19" rack is ce certified (r&tte directive) as stated in “declaration of conformity with r&tte directive”, enclosed in copy on the next page..
Page 275: Glossary
259 glossary bbbb glos sar y glossary b a apn access point name. The access point name is used by the terminal operator to establish the connection to the required destination network. B bgan broadband global area network. A satellite network based on geostationary satellites, delivering data rates ...
Page 276
Glossary 260 e ecef the earth-centred earth-fixed or conventional terrestrial coordinate system rotates with the earth and has its origin at the centre of the earth. The x axis passes through the equator at the prime meridian. The z axis passes through the north pole but it does not exactly coincide...
Page 277
Glossary 261 bbbb glos sar y isdn integrated services digital network. A circuit-switched telephone network system, designed to allow digital transmission of voice and data over ordinary telephone copper wires, resulting in higher quality and speed than are available with analogue. K kbps kilobits p...
Page 278
Glossary 262 p pdp packet data protocol. A network protocol used by external packet data networks that communicate with a gprs network. Pin personal identification number. A code number used to provide access to a system that has restricted access. Poe power over ethernet post power on self test. A ...
Page 279
Chapter glossary: 263 bbbb glos sar y rf radio frequency. Electromagnetic wave frequencies between about 3 kilohertz and about 300 gigahertz including the frequencies used for communications signals (radio, television, cell-phone and satellite transmissions) or radar signals. S sas satellite access ...
Page 280
Chapter glossary: 264 u udi unrestricted digital information utc coordinated universal time. The international atomic time (tai) with leap seconds added at irregular intervals to compensate for the earth’s slowing rotation. Leap seconds are used to allow utc to closely track ut1, which is mean solar...
Page 281: Index
265 index cccc inde x index c numerics 2-wire interface local numbers, 53 setting call type, 115 a activation remote, 191 additional numbers ip handsets, 132 isdn interface, 116 phone interface, 115 additional numbers description, 64 enable, 196 administration settings, 168 administration, remote, 1...
Page 282
Index 266 ce compliance, 251 clearing logs, 173, 174 clearing usage counter, 173, 174 closed user group, 126 common network settings, 119 compression, header, 157 computer, connecting to lan, 27 configuration exporting to file, 171 importing from file, 171 isdn, 116 lan, 107 conformity, 251 connecti...
Page 283
Index 267 cccc inde x i ignition function, 24 imei number, 87 importing configuration, 171 inbox for sms messages replying, forwarding or deleting, 103 indicator functions, 219 installation manual document number, viii interfaces and services combinations, 17 internal calls, 52 internet connection, ...
Page 284
Index 268 messages configuring outgoing, 104 forwarding, 103 opening in web interface, 103 receiving in web interface, 102 replying, 103 sending, 101 microwave radiation, iii mobile numbers viewing and editing, 94 monitoring the external ip connection, 193 multi-voice additional numbers, 64 descript...
Page 285
Index 269 cccc inde x q quality of voice, 45 quick dial, 48 r radiation, iii redial, 53 registering on the bgan network, 32 remote activation by sms, 192 trusted mobile number, 192 remote control, 191 remote management, 189 remote on/off, 24 restricted dialling, 194 router function, 66 router mode, ...
Page 286
Index 270 subnet ip, reserved, 245 supplementary services setting up, 116 supported, 15 using, 55 support contact information, 205 t telephone interface local numbers, 53 setting call type, 115 tools for setting up the terminal, 39 total usage viewing, 89, 96 tracking, 139 traffic flow filters, 181 ...
Page 288
98-125645-g info@thrane.Com • thrane.Com.