- DL manuals
- Samson
- Controller
- foundation 3787
- Mounting And Operating Instructions
Samson foundation 3787 Mounting And Operating Instructions - 4 Operation
4 Operation
Warning!
Before you take the control valve
into operation, carefully move the
control valve to its end position by
covering the hole (manual oper-
ation) on the cover plate (Fig. 11).
On doing so, check whether the
lever mechanism works properly.
If the maximum angle of rotation is
exceeded because the wrong lever
mechanism has been selected or in-
correctly sized, the positioner may
be ruined.
4.1 LEDs
There are two LEDs located inside the cover
used to monitor the positioner during start-
up, operation and to indicate possible faults.
General meaning of LEDs:
Red
Device start-up or error,
no control operation possible
Green
No error detected, control operation
or fail-safe position
(e.g. if not initialized)
Red and green
Error detected,
control operation possible
See table below for detailed description.
Description
LED
Device start-up:
Red on
No error detected:
Device connected to bus, cold start completed,
initialization required
Initialization or zero calibration running
Device is initialized, no valid set point
Device is initialized, valid set point, control operation
Green, generally
Green blinks slowly
Green blinks quickly
Green blinks 3x quickly + long interval
Green on
Error in the control loop:
Zero point error
Control loop fault
Red and green
Red and green blink slowly
Red and green blink quickly
Error leading to first initialization being cancelled
(Device does not go to standard operation)
Zero point error
Mechanics/pneumatics failure
Control loop fault
Red, generally
Red blinks slowly
Red on
Red blinks quickly
Device errors causing the control operation to be
left
Device has detected an internal fault
Red blinks 3x quickly + long interval
EB 8383-1 EN
29
Operation
Summary of foundation 3787
Page 1
Foundation tm fieldbus positioner type 3787 fig. 1 ⋅ type 3787 mounting and operating instructions eb 8383-1 en firmware r 1.42/k 1.40 edition november 2004.
Page 2
Contents page 1 design and principle of operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 1.1 optional limit switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 1.2 communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 2 attachment to the control valve . ...
Page 3
5 maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 6 servicing explosion-protected versions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 7 parameter description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36 7.1 general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 4
Safety instructions the device may only be assembled, started up, and operated by experienced personnel familiar with this product. In these mounting and operating instructions, the term "experienced person- nel" refers to individuals who are able to evaluate the responsibilities assigned to them as...
Page 5
Firmware modifications communication k1.00 k1.20 version compatible with user interface software version number: fisher-rosemount deltav in version 5.1 or higher national instruments fieldbus configurator in version 2.3 or higher. All host systems certified by the fieldbus foundation alteration to d...
Page 6
Technical data positioner travel direct attachment to type 3277 attachment acc. To iec 60534-6 adjustable 7.5 to 30 mm 7.5 to 120 mm or 30 to 120° for rotary actuators bus connection fieldbus interface as per en 61158-2, bus-powered physical layer class: 113 (not explosion-protected version) and 111...
Page 7
Versions accessories inductive limit switches two type sj 2 sn proximity switches for connection to a switching amplifier acc. To en 60947-5-6 communication data transmission in accordance with foundation tm fieldbus specification communication profile class: 31 ps, 32: interoperability test system ...
Page 8: 1.2 Communication
1 design and principle of operation the digital positioner compares the refer- ence variable, which is cyclically trans- mitted over the foundation tm fieldbus, with the travel or opening angle of the con- trol valve. It then delivers a corresponding signal pressure. It is suitable for attachment to...
Page 9
Configuration with ni-fbus tm configurator the positioner can also be configured using the ni-fbus tm configurator from national instruments. An interface card installed in a pc is re- quired to connect it to foundation tm fieldbus. The ni-fbus tm configurator can be used to configure the whole foun...
Page 10: 3277 Actuator
2 attachment to the control valve the positioner can be attached either di- rectly to a samson type 3277 actuator or to control valves with cast yokes or rod- type yokes according to iec 60534-6 (namur). In connection with an intermediate piece, the positioner can also be attached to rot- ary actuat...
Page 11
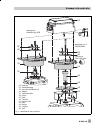
Actuator stem retracts side view of connection block with seal (new) with switch plate (old) fig. 3 ⋅ attachment and signal pressure connection for type 3277 actuators (top) and 3277-5 with 120 cm 2 (bottom) suppl y 18 17 19 1.2 d2 d1 17 16 15 1.2 16 17 15 actuator stem retracts internal signal pres...
Page 12
With the actuator symbol "actuator stem extends" or "actuator stem retracts" to match the actuator version used. If not, remove the three fastening screws and the cover plate (18), turn the seal (17) by 180 ° and reinsert it. When the old connection block is used, turn the switch plate (19) to align...
Page 13
Table 1 required lever with associated clamp and distance plate actuator size cm 2 mounting kit order no. D1 (33 mm in length with clamp 17 mm in height) 120 (g 1/4) 120 (1/4 npt) 1400-6790 1400-6791 d1 (33 mm in length with clamp 17 mm in height) 240 and 350 1400-6370 d2 (44 mm in length with clamp...
Page 14: 2.2.1 Mounting Sequence
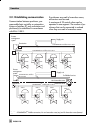
2.2 attachment acc. To iec 60534-6 the positioner is attached according to namur as shown in fig. 4 using an adapt- er housing. The valve travel is transmitted via the lever (18) and the shaft (25) to the bracket (28) in the adapter housing and then to the coupling pin (27) located on the lever of t...
Page 15
Fig. 4 ⋅ attachment according to iec 60534-6 (namur) 2 1,5 1 28 26 a b 24 25 22 32 31 20 19 19 21 20 23 18 27b 27a 29 30 attachment to namur rib mounting position attachment to rod 18 lever n1, n2 19 pin 20 plate 21 clamp 22 clamping plate 23 screw 24 pointer 25 shaft 26 lever of positioner 27a tran...
Page 16
For the assigned travel, see table 5. Intermediate values must be calculated. Move the clamp (21) beforehand to clasp the pin. 5. Measure the distance from the middle of the shaft (25) to the middle of the pin (19). This value must be entered later when the positioner is being con- figured. 2.2.2 pr...
Page 17
Insert nuts and secure the pin on the other side with a hex nut. Observe the mounting position a or b explained in table 5 and fig. 4. 4. Place the positioner onto the adapter housing, making sure the coupling pin (27) is positioned within the arms of the bracket (28). To do so, insert a 2.5 mm alle...
Page 18: Feeler Roll
For double-acting, springless rotary actua- tors, a reversing amplifier must be attached to the positioner housing on the side where it is connected to the actuator (see section 2.3.4). If the positioner is attached to a samson type 3278 rotary actuator, the air ex- hausted from the positioner is ad...
Page 19
Vent plug or filter check valve fig. 5 ⋅ attachment to rotary actuators 33 38 35 39 39 40 34 36 40 34 44 45 42 43 37 attachment to samson type 3278 attachment acc. To vdi/vde 3845 33 positioner 34 intermediate piece 35 lever with cam follower roll 36 adapter 37 transmission lever 38 screws 39 scale ...
Page 20: Cam Disk
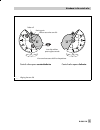
2.3.3 aligning and mounting the cam disk in rotary actuators with spring-return mech- anism, the actuator springs determine the fail-safe position and the direction of rota- tion of the control valve. With double-acting, springless rotary actua- tors, the direction of rotation depends on both the ac...
Page 21
Fig. 6 ⋅ aligning the cam disk control valve opens counterclockwise control valve opens clockwise feeler roll starting point holes to secure the cam disk view onto the actuator shaft from the positioner insert clip and then press tongues outwards eb 8383-1 en 21 attachment to the control valve.
Page 22: Double-Acting Actuators
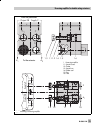
2.3.4 reversing amplifier for double-acting actuators for the use with double-acting actuators, the positioner must be fitted with a revers- ing amplifier. The reversing amplifier is listed as an acces- sory in the table 6 on page 17. The output signal pressure of the positioner is supplied at the o...
Page 23
Fig. 7 ⋅ mounting a reversing amplifier 1.3 1.2 1.1 1 output 38 supply 9 a 1 1.5 1.6 z a 2 1.4 a 1 a 2 output 38 supply 9 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.6 z a 1 from the positioner to the actuator 1 reversing amplifier 1.1 special screws 1.2 gasket 1.3 special nuts 1.4 rubber seal 1.5 plug 1.6 filter eb 8383-1 en 23...
Page 24: 3 Connections
3 connections 3.1 pneumatic connections the air connections are either 1/4 npt or g 1/4 tapped holes. Customary fittings for metal and copper pipes or plastic tubes can be used. Note! The supply air must be dry and free from oil and dust. Observe the maintenance instruc- tions for upstream pressure ...
Page 25: 3.1.2 Supply Air Pressure
3.1.2 supply air pressure the required supply air pressure depends on the bench range and the operating direc- tion (fail-safe position) of the actuator. The bench range is mentioned on the name- plate as spring range or signal pressure range. Actuator stem extends: required supply air pressure = up...
Page 26
Caution! The terminal assignment specifiedin the certificate must be adhered to. Reversing the assignment of the elec- trical terminals may cause the explo- sion protection to become ineffective! Do not tamper with enameled screws inside or on the housing. Note on the selection of cables and wires: ...
Page 27
Limit switches for operation of the limit switches, switch- ing amplifiers have to be connected in the output circuit. Their function is to control the limit values of the control circuit according to namur, thus ensuring operational relia- bility of the positioner. If the positioner is installed in...
Page 28
3.2.1 establishing communication communication between positioner, pro- grammable logic controller or automation system or between pc and workstation and positioner(s) is established in accordance with en 61158-2. If positioners are used in hazardous areas, ex-barriers must be used. A maximum of 32 ...
Page 29: 4 Operation
4 operation warning! Before you take the control valve into operation, carefully move the control valve to its end position by covering the hole (manual oper- ation) on the cover plate (fig. 11). On doing so, check whether the lever mechanism works properly. If the maximum angle of rotation is excee...
Page 30: Tion Switches
4.2 write protection and simula- tion switches there are two microswitches inside the hinged cover to activate the write protection and enable simulation. When the write protection switch is on, the configuration data of the positioner are write-protected and cannot be overwritten. The switch must b...
Page 31: 4.4.2 Initialization
4.4.2 initialization after connecting the supply air and electri- cal connections to the bus cable, initializa- tion must be started. During initialization, the positioner adapts itself optimally to the friction conditions and signal pressure re- quirements of the control valve. Caution! Initializat...
Page 32
Final position at a reference variable larger than 125 % (function deactivated). Fail-safe position "actuator stem re- tracts": direction of action: increasing/decreas- ing (), the globe valve closes with in- creasing reference variable final position at a reference variable less than − 2.5% (functi...
Page 33: 4.5.1 Initialization
4.5 operation via trovis-view in addition to using the fieldbus configura- tion or operating system via fieldbus com- munication, the positioner can also be oper- ated with samson’s trovis-view user in- terface via the serial port integrated in the device. You can configure all the parameters using ...
Page 34: Ches
Max_hub maximum travel/angle of rotation in per- cent of the rated travel/nominal angle. The integrated leds and the parameters self_calib_status self_calib_warnung indicate if the initialization has been suc- cessfully completed or whether errors have occurred. 4.5.2 testing the control valve upon ...
Page 35: 5 Maintenance
Adjusting the switching point: the limit switches are marked gw1 and gw2 on the inside of the case cover. Yel- low tags and the associated adjustment screws (fig. 11) are located below these markings. Each switching position can optionally be indi- cated when the tag has entered the field, or when i...
Page 36: 7 Parameter Description
7 parameter description 7.1 general the section is based on: fieldbus foundation specification "function block application process part 1 to 3" revision 1.4. Fieldbus foundation specification "transducer block application process part 1 to 2" revision ps 3.0. 7.2 device description (dd) the followin...
Page 37
7.3.1 legends assigned to the parameters r = read w = write index = relative index of the parameter in each block o/s = out of service man = manual auto = automatic cas = cascade rcas = remote cascade rout = remote output s = static parameter n = non-volatile parameter d = dynamic parameter 7.3.2 no...
Page 38: 7.4 Block Structure
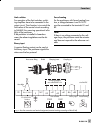
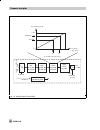
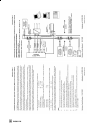
7.4 block structure foundation fieldbus assigns all functions and data of a device to three different block types. Each block type has a different area of application. A foundation fieldbus device has the following block types: one resource block the resource block contains all the hardware specific...
Page 39
The samson type 3787 foundation fieldbus positioner contains the following blocks: one resource block. One standard advanced positioner valve transducer block. Two function blocks: one analog output function block, one pid function block. Fig. 12 ⋅ block structure rcas_in cas_in out mode_blk (manual...
Page 40: 7.4.1 Resource Block
7.4.1 resource block the resource block contains all the data that clearly identifies the device. It is, so to speak, the electronic nameplate of the device. The resource block’s parameters include, for example, device type, device name, manufac- turer id, serial number as well as parameters which a...
Page 41
Clr_fstate d index: 30 access: r, w writing a clear to this parameter will clear the fault state of the analog output function block. Confirm_time s index: 33 access: r, w default: default of confirmation time for event report. If the device does not receive any confirmation within this time, the ev...
Page 42
Device_ ser_num n index: 44 access: r serial number of the device, allows together with manufac_id and dev_type the clear identification of the field device. Fault_state n index: 28 access:r shows current status of the fault state of the analog output function block. Features s index: 17 access: r s...
Page 43
Manufac_id s index: 10 access:r display: shows the manufacturer identification number. 0 x 00e099 = samson ag max_notify s index: 31 access: r display shows the maximum number of unacknowledged event reports possible. 8 memory_size s index: 22 access:r shows available configuration memory in kilobyt...
Page 44
Rs_state d index: 7 access: r display: shows the actual operating state of the resource block. Online standard operation, the block is in the operating mode auto. Standby the resource block is in the operating mode o/s. Online linking the configured links among the function blocks are still not set ...
Page 45
Text_input_3 n index: 52 access:r,w freely available space for entering text. Update_evt d index: 35 access:r this alert is generated by any change to the static data, including date and time. Write_alm d index: 40 access:r, w shows status of the write protection alarm. Note: this alert is generated...
Page 46: 7.4.2 Transducer Block
7.4.2 transducer block the transducer block enables the input and output variables of a function block to be in- fluenced. In this way, measured and control data can be calibrated, characteristics can be linearized or physical variables can be converted with the aid of process data. Parameters of th...
Page 47
Note: when initialization based on maximum range (default) is selected, the positioner can be started up directly after being attached to the control valve via the self_calib_cmd par- ameter. The results of the initialization are saved in self_calib_status. When this type of initializa- tion is used...
Page 48
Alert_key s index: 4 access:r, w input: default: the identification number of the plant unit. This information can be used by the fieldbus host system to sort the alarms and events. 1...255 0 note: the value 0 (default) is not a tolerated value and is therefore rejected with an error message when wr...
Page 49
Charact s index: 42 access:r, w input: default: selection of characteristics to assign the correction value to the travel range/angle of rotation. Linear equal percentage equal percentage reverse samson butterfly linear samson butterfly equal percentage vetec rotary linear vetec rotary equal percent...
Page 50
Final_value_cutoff_lo s index: 16 access:r, w range: default: final position if the set point falls below the entered value, the valve is moved towards the final position that corresponds to 0 % of the manipulated variable. This is done by completely venting or filling the actuator (depending on the...
Page 51
Max_hub n index: 58 access:r maximum possible travel /angle of rotation maximum travel/angle of rotation detected during initialization stated in percent of the rated travel/nominal angle. Mode_blk n index: 5 access:r, w option: shows/used to select the actual operating mode of the resource block, p...
Page 52
Self_calib_status d index: 56 access:r display: status of sequence started with self_calib_cmd. Undetermined running aborted range error defective mechanics / pneumatics timeout proportional range restricted rated travel or transmission error mechanical error pneumatical error initialization status:...
Page 53
Strategy s index: 3 access:r, w default: the strategy field can be used to identify grouping of blocks to allow a faster analysis of the blocks. Enter the same number in the strategy parameter of each block to group blocks. 0 note: this data is not checked or processed by the transducer block. St_re...
Page 54
Transducer_state d index: 32 access:r display: state of transducer block. See actual mode of transducer block forced venting active lower travel limit active upper travel limit active end position active at end position active at > transducer_type s index: 10 access:r type of transducer, here "stand...
Page 55
Valve_model_num s index: 26 access:r, w type/version of the valve associated with the positioner. Valve_sn s index: 27 access:r, w serial number of the valve associated with the positioner. Valve_type s index: 28 access: r, w input: default: valve type uninitialized undefined linear (control valve w...
Page 56
Xd_error_ext d index: 33 access:r display: extended error messages of the transducer block. None (0) failure mechanics failure in measurement not initialized selfcalibration failed zero point error internal control loop disturbed (reset over self_calib_cmd -> reset ‘control loop fault‘). Travel time...
Page 57: 7.4.3 Function Blocks
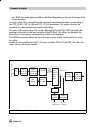
7.4.3 function blocks the function blocks contain the fundamental automation functions of the fieldbus device. There are various types of function blocks such as analog input function block , analog out- put function block and pid block. Each of these function blocks is used to process various appli...
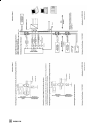
Page 58
Fig. 14 ⋅ analog output function block rcas_in cas_in readback pv out 100 % 0 % 0 ˚c pv_scale sp_lo_lim sp pv sp readback out xd_scale mode_blk out mode_blk (manual) sp (e.G. In °c) (e.G. In %) set point ramps sp_rate_dn sp_rate_up pv, xd scaling xd_scale pv_scale xd, pv scaling xd_scale, pv_scale s...
Page 59
Parameters of the analog output function block alert_key s index: 4 access: r, w input: default: the identification number of the plant unit. This information may be used in the fieldbus host system for sorting alarms and events. 1...255 0 note: the value 0 (default) is not a tolerated value and is ...
Page 60
Fstate_val s index: 24 access:r, w input: default: determines set point for the ao function block to be used when the fault state is activated. Value and range of pv_scale ± 10 % 0 note: this value is used when the option "fault state to value" is selected in io_opts. Grant_deny d index: 13 access:r...
Page 61
Mode_blk n index: 5 access:r, w display: shows the actual mode of the ao block, the target modes, permitted modes supported by the ao block and normal mode. Rcas cas auto man o/s the ao block supports the following modes: o/s (out of service) the ao algorithm of the block is not executed. The last v...
Page 62
Rcas_out d index: 28 access:r shows the analog reference variable (value and status) after ramping. This value is made available to the fieldbus host system to perform back calculations when the operating mode changes or with limited signals. Note: this parameter is only active in rcas mode. Readbac...
Page 63
Simulate d index: 10 access:r, w using the simulation the value and status of the process variable pv of the block can be simulated. Note: during simulation, the value of out is not passed onto the transducer block. The transducer block keeps the last valid value stored before the simulation was act...
Page 64
Status_opts s index: 15 access:r, w in o/s option: default: used to select available status options to determine the treatment and processing of the status: uninitialized propagate fault backward status of the transducer is passed on to the upstream connected block using the status of bkcal_out. Uni...
Page 65
7.4.3.2 pid function block (pid controller) a pid function block includes the input channel processing, the pid control and the analog output channel processing. The configuration of the pid block (pid controller) is dependent on each automation task. Simple control loops, feedforward controls, casc...
Page 66
Nent rate, the manipulated variable is calculated depending on the rate of change of the system deviation. An output value out is formed from the calculated manipulated variable corresponding to the out_scale, out_hi_lim and out_lo_lim parameters. This output value can be passed on to a downstream c...
Page 67
Parameters of the pid function block ack_option s index: 46 access:r, w option: default: this parameter allows you to choose whether an alarm should be automatically acknowledged in the device, i.E. Without any influence from the fieldbus host system. Undefined no option hi_hi_alm high high alarm hi...
Page 68
Alert_key s index: 4 access:r, w input: default: the identification number of the plant unit. This information may be used in the fieldbus host system for sorting alarms and events. 1...255 0 note: the value 0 (default) is not a tolerated value and is therefore rejected with an error message when wr...
Page 69
Bypass s index: 17 access:r, w in man, o/s option: default: this parameter allows the calculation of the manipulated variable by means of the pid control algorithm to be switched on or off. Unintialized same as on off bypass switched off: the manipulated variable determined by the pid control algori...
Page 70
Default: 2 reserved for block alarms. 3...7 the violation of the limit for the high deviation is issued with the corresponding priority (3= low priority, 7= high priority) to notify the user. 8...15 the violation of the limit for the high deviation is issued with the corresponding priority (8= low p...
Page 71
Ff_val n index: 40 access:r, w input: used to input and displays the feedforward value and status. Range and unit of the ff_scale note: the feedforward input is multiplied by the gain (ff_gain) before it is added to the calculated output value out. Gain s index: 23 access:r, w default: used to input...
Page 72
Hi_pri s index: 50 access:r, w input: default: determines the action to be taken when the high alarm limit (hi_lim) is exceeded. 0 the violation of the high alarm limit is not evaluated. 1 no message issued when a violation of the high alarm occurs. 2 reserved for block alarms. 3...7 the violation o...
Page 73
Lo_lim s index: 53 access:r, w input: default: input of the alarm limit for the low alarm (lo_alm). If the pv value exceeds this limit, the lo_alm alarm status parameter is issued. Range and limit of the pv_scale -3402823466 x 10 38 lo_pri s index: 52 access:r, w input: default: determines the actio...
Page 74
Out n index: 9 access:r, w in man, o/s shows the manipulated variable, value, limit and status of the pid function block. Note: if the man mode in mode_blk is selected, the output value out can be entered manually here. The unit used is taken on by the out_scale parameter group. The input range corr...
Page 75
Reset s index: 24 access:r, w default: used to input the time constant for the integral function. 3402823466 x 10 38 (maximum possible value) note: the integral function is cleared by setting to 0 seconds. Rout_in n index: 33 access:r, w used to input and display the manipulated variable (value and ...
Page 76
Default: uninitialized note: this parameter is only active in the pid block in the rcas and rout modes. If it is set to "uninitialized", the pid block cannot be placed into rcas or rout modes. Sp n index: 8 access:r, w in auto, man, o/s input: used to input the set point (reference variable) in auto...
Page 77
Status_opts index: 14 access:r, w in o/s option: default: used to select available status options to determine the treatment and processing of the status: uninitialized ifs if bad in fault state of the downstream connected ao function block initiated, if the controlled variable (in) changes the stat...
Page 78: 7.5 Other Parameters
7.5 other parameters 7.5.1 stale counter the stale counter is used to assess the "quality" of a process variable received via a cyclically configured link (publisher subscriber link). The process variables that are "connected" among various function blocks are transferred using these links. For this...
Page 79: 8. Diagnostic Messages
8. Diagnostic messages 8.1 messages of the xd_error_ext parameter (transducer block) failure mechanics this message is issued when the entered rated travel is not reached on initialization. - check mechanics and pneumatics in the valve - compare the specifications in the transducer block, which desc...
Page 80
Forced venting active forced venting is activated, i.E. The signal at terminals +81 and -82 is smaller than 3v. The control valve moves to the fail-safe position irrespective of the control loop. It is auto- matically reset as soon as there is a 6v to 24 v dc signal at terminals +81 and -82. Device ...
Page 81
- check mechanics and pneumatics in the valve - compare the specifications in the transducer block, which describe the valve as well as the actuator and the mechanical structure, with the actual valve. Reinitialize. Data integrity error checksum error algorithm error set point value - actual value e...
Page 82
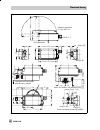
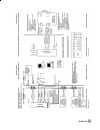
Dimensional drawing 39 35 14 198 78.5 40 86 30.5 164 150 27 14 28 56 58 n1=113 n2=200 39 50 78.5 45 50 82 150 164 27 75 56 50 86 46 28.5 28.5 output 1 (a1) output 2 (a2) supply (z) output (38) supply (9) m20 x1.5 direct attachment pneumatic connections g 1/4 or npt 1/4 attachment with intermediate p...
Page 83
Eb 8383-1 en 83.
Page 84
84 eb 8383-1 en.
Page 85
Eb 8383-1 en 85.
Page 86
86 eb 8383-1 en.
Page 87
Eb 8383-1 en 87.
Page 88
88 eb 8383-1 en.
Page 89
Eb 8383-1 en 89.
Page 90
90 eb 8383-1 en.
Page 91
Eb 8383-1 en 91.
Page 92
92 eb 8383-1 en.
Page 93
Eb 8383-1 en 93.
Page 94
94 eb 8383-1 en.
Page 95
Eb 8383-1 en 95.
Page 96
Samson ag ⋅ mess- und regeltechnik weismüllerstraße 3 ⋅ 60314 frankfurt ⋅ germany phone: +49 69 4009-0 ⋅ fax: +49 69 4009-1507 internet: http://www.Samson.De s/z 2004- 11 eb 8383-1 en.