- DL manuals
- Samsung
- Switch
- iES4028FP
- Management Manual
Samsung iES4028FP Management Manual
Summary of iES4028FP
Page 1
Ies4028f/4028fp/4024gp.
Page 2
Ies4028f ies4028fp ies4024gp e082008/st-r03 149100041800a 149100040200a 149100041700a 149100000020a.
Page 3: Copyright
Iii copyright this manual is proprietary to samsung electronics co., ltd. And is protected by copyright. No information contained herein may be copied, translated, transcribed or duplicated for any commercial purposes or disclosed to third parties in any form without the prior written consent of sam...
Page 4
Iv this page is intentionally left blank..
Page 5: About This Guide
V about this guide purpose this guide gives specific information on how to operate and use the management functions of the switch. Audience the guide is intended for use by network administrators who are responsible for operating and maintaining network equipment; consequently, it assumes a basic wo...
Page 6: July 2008 Revision
Vi • mac address aging attribute in “configuring the mac authentication reauthentication time” on page 3-103. • sym and fc attributes in “configuring interface connections” on page 3-130. • “setting multicast storm thresholds” on page 3-149. • “setting unknown unicast storm thresholds” on page 3-150...
Page 7
Vii • command usage and command attributes under “configuring the dhcp snooping information option” on page 3-118. • command usage under “configuring ports for dhcp snooping” on page 3-120. • command usage under “ip source guard” on page 3-123. • command usage under “configuring static binding for i...
Page 8
Viii • command usage and command attributes under “configuring mvr interface status” on page 3-270. • command usage under “switch clustering” on page 3-273. • introduction under “upnp” on page 3-277. • command usage under “jumbo frame” on page 4-33. • command usage under “copy” on page 4-35. • synta...
Page 9: April 2008 Revision
Ix • “spanning-tree port-bpdu-flooding” on page 4-240. • syntax and default setting under “spanning-tree mst cost” on page 4-244. • syntax for “switchport mode” on page 4-257. • removed note under “switchport ingress-filtering” on page 4-258. • removed note under “switchport allowed vlan” on page 4-...
Page 10
X this page is intentionally left blank..
Page 11: Contents
Xi contents chapter 1: introduction 1-1 key features 1-2 description of software features 1-3 system defaults 1-7 chapter 2: initial configuration 2-1 connecting to the switch 2-1 configuration options 2-1 required connections 2-2 remote connections 2-3 basic configuration 2-3 console connection 2-3...
Page 12
Contents xii managing firmware 3-21 downloading system software from a server 3-22 saving or restoring configuration settings 3-23 downloading configuration settings from a server 3-24 console port settings 3-25 telnet settings 3-27 configuring event logging 3-29 system log configuration 3-29 remote...
Page 13
Contents xiii configuring https 3-77 replacing the default secure-site certificate 3-78 configuring the secure shell 3-79 generating the host key pair 3-82 importing user public keys 3-84 configuring the ssh server 3-86 configuring 802.1x port authentication 3-88 displaying 802.1x global settings 3-...
Page 14
Contents xiv creating trunk groups 3-134 statically configuring a trunk 3-135 enabling lacp on selected ports 3-136 configuring parameters for lacp group members 3-138 configuring parameters for lacp groups 3-141 displaying lacp port counters 3-142 displaying lacp settings and status for the local s...
Page 15
Contents xv traffic segmentation 3-206 configuring global settings for traffic segmentation 3-207 configuring traffic segmentation sessions 3-207 private vlans 3-209 displaying current private vlans 3-209 configuring private vlans 3-210 associating vlans 3-211 displaying private vlan interface infor...
Page 16
Contents xvi displaying port members of multicast services 3-258 assigning ports to multicast services 3-259 igmp filtering and throttling 3-260 enabling igmp filtering 3-261 configuring igmp filter profiles 3-262 configuring igmp filtering and throttling for interfaces 3-263 multicast vlan registra...
Page 17
Contents xvii reload 4-13 show reload 4-14 prompt 4-14 end 4-15 exit 4-15 quit 4-16 system management commands 4-16 device designation commands 4-17 hostname 4-17 banner information commands 4-18 banner configure 4-18 banner configure company 4-19 banner configure dc-power-info 4-20 banner configure...
Page 18
Contents xviii databits 4-46 parity 4-46 speed 4-47 stopbits 4-47 disconnect 4-48 show line 4-48 event logging commands 4-49 logging on 4-49 logging history 4-50 logging host 4-51 logging facility 4-51 logging trap 4-52 clear log 4-53 show logging 4-53 show log 4-55 smtp alert commands 4-56 logging ...
Page 19
Contents xix rcommand 4-76 show cluster 4-76 show cluster members 4-77 show cluster candidates 4-77 upnp commands 4-77 upnp device 4-78 upnp device ttl 4-78 upnp device advertise duration 4-79 show upnp 4-79 debug commands 4-80 debug dot1x 4-80 debug radius 4-82 debug tacacs 4-84 snmp commands 4-86 ...
Page 20
Contents xx tacacs+ client 4-109 tacacs-server host 4-110 tacacs-server port 4-110 tacacs-server key 4-111 tacacs-server retransmit 4-111 tacacs-server timeout 4-112 show tacacs-server 4-113 aaa commands 4-114 aaa group server 4-114 server 4-115 aaa accounting dot1x 4-116 aaa accounting exec 4-117 a...
Page 21
Contents xxi dot1x re-authenticate 4-140 dot1x re-authentication 4-140 dot1x timeout quiet-period 4-141 dot1x timeout re-authperiod 4-141 dot1x timeout tx-period 4-142 dot1x intrusion-action 4-142 show dot1x 4-143 management ip filter commands 4-146 management 4-146 show management 4-147 general sec...
Page 22
Contents xxii show ip dhcp snooping 4-171 show ip dhcp snooping binding 4-171 ip source guard commands 4-172 ip source-guard 4-172 ip source-guard binding 4-174 show ip source-guard 4-175 show ip source-guard binding 4-175 access control list commands 4-176 ip acls 4-176 access-list ip 4-177 permit,...
Page 23
Contents xxiii lacp port-priority 4-208 lacp active/passive 4-209 show lacp 4-209 power over ethernet commands 4-213 power mainpower maximum allocation 4-214 power inline compatible 4-214 power inline 4-215 power inline maximum allocation 4-216 power inline priority 4-216 show power inline status 4-...
Page 24
Contents xxiv spanning-tree loopback-detection 4-242 spanning-tree loopback-detection release-mode 4-242 spanning-tree loopback-detection trap 4-243 spanning-tree mst cost 4-244 spanning-tree mst port-priority 4-245 spanning-tree protocol-migration 4-245 show spanning-tree 4-246 show spanning-tree m...
Page 25
Contents xxv switchport mode private-vlan 4-273 switchport private-vlan host-association 4-274 switchport private-vlan mapping 4-275 show vlan private-vlan 4-275 configuring protocol-based vlans 4-276 protocol-vlan protocol-group (configuring groups) 4-277 protocol-vlan protocol-group (configuring v...
Page 26
Contents xxvi lldp medtlv med-cap 4-302 lldp medtlv network-policy 4-302 show lldp config 4-303 show lldp info local-device 4-305 show lldp info remote-device 4-306 show lldp info statistics 4-307 class of service commands 4-308 priority commands (layer 2) 4-308 queue mode 4-308 switchport priority ...
Page 27
Contents xxvii static multicast routing commands 4-333 ip igmp snooping vlan mrouter 4-334 show ip igmp snooping mrouter 4-334 igmp filtering and throttling commands 4-335 ip igmp filter (global configuration) 4-336 ip igmp profile 4-336 permit, deny 4-337 range 4-337 ip igmp filter (interface confi...
Page 28
Contents xxviii this page is intentionally left blank..
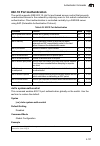
Page 29: Tables
Xxix tables table 1-1 differences in switch models 1-1 table 1-2 key features 1-2 table 1-3 system defaults 1-7 table 3-1 configuration options 3-3 table 3-2 main menu 3-4 table 3-3 logging levels 3-29 table 3-5 supported notification messages 3-52 table 3-6 https system support 3-77 table 3-7 802.1...
Page 30
Tables xxx table 4-21 switch cluster commands 4-73 table 4-22 debug commands 4-80 table 4-23 snmp commands 4-86 table 4-24 show snmp engine-id - display description 4-94 table 4-25 show snmp view - display description 4-95 table 4-26 show snmp group - display description 4-98 table 4-28 authenticati...
Page 31
Tables xxxi table 4-66 link type 4-237 table 4-66 ieee 802.1d-1998 4-237 table 4-66 ieee 802.1w-2001 4-237 table 4-67 default sta path costs 4-238 table 4-68 vlans 4-248 table 4-69 gvrp and bridge extension commands 4-249 table 4-70 editing vlan groups 4-254 table 4-71 configuring vlan interfaces 4-...
Page 32
Tables xxxii this page is intentionally left blank..
Page 33: Figures
Xxxiii figures figure 3-1 home page 3-2 figure 3-2 panel display 3-3 figure 3-3 system information 3-13 figure 3-4 switch information 3-14 figure 3-5 bridge extension configuration 3-16 figure 3-6 manual ip configuration 3-18 figure 3-7 dhcp ip configuration 3-19 figure 3-8 jumbo frames configuratio...
Page 34
Figures xxxiv figure 3-43 aaa authorization settings 3-74 figure 3-44 aaa authorization exec settings 3-75 figure 3-45 aaa authorization summary 3-76 figure 3-46 https settings 3-78 figure 3-47 https settings 3-79 figure 3-48 ssh host-key settings 3-83 figure 3-49 ssh user public-key settings 3-85 f...
Page 35
Figures xxxv figure 3-1 port multicast control 3-149 figure 3-2 port unknown unicast control 3-150 figure 3-88 mirror port configuration 3-151 figure 3-89 input rate limit port configuration 3-152 figure 3-90 port statistics 3-156 figure 3-91 displaying the global poe status 3-158 figure 3-92 settin...
Page 36
Figures xxxvi figure 3-131 port priority configuration 3-231 figure 3-132 traffic classes 3-233 figure 3-133 queue mode 3-234 figure 3-134 configuring queue scheduling 3-235 figure 3-135 ip dscp priority status 3-236 figure 3-136 mapping ip dscp priority values 3-237 figure 3-137 configuring class m...
Page 37: Chapter 1: Introduction
1-1 chapter 1: introduction this switch provides a broad range of features for layer 2 switching. It includes a management agent that allows you to configure the features listed in this manual. The default configuration can be used for most of the features provided by this switch. However, there are...
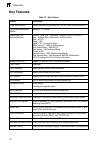
Page 38: Key Features
Introduction 1-2 1 key features table 1-2 key features feature description power over ethernet powers attached devices using ieee 802.3af power over ethernet (poe) configuration backup and restore backup to tftp server authentication and security measures console, telnet, web – user name / password,...
Page 39
Description of software features 1-3 1 description of software features this switch provides a wide range of advanced performance enhancing features. Flow control eliminates the loss of packets due to bottlenecks caused by port saturation. Broadcast storm suppression prevents broadcast traffic storm...
Page 40
Introduction 1-4 1 port configuration – you can manually configure the speed, duplex mode, and flow control used on specific ports, or use auto-negotiation to detect the connection settings used by the attached device. Use the full-duplex mode on ports whenever possible to double the throughput of s...
Page 41
Description of software features 1-5 1 spanning tree algorithm – this switch supports these spanning tree protocols: spanning tree protocol (stp, ieee 802.1d) – this protocol provides loop detection and recovery by allowing two or more redundant connections to be created between a pair of lan segmen...
Page 42
Introduction 1-6 1 this switch also supports several common methods of prioritizing layer 3/4 traffic to meet application requirements. Traffic can be prioritized based on the dscp field in the ip frame. When these services are enabled, the priorities are mapped to a class of service value by this s...
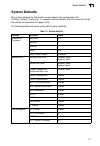
Page 43: System Defaults
System defaults 1-7 1 system defaults the system defaults for this switch are provided in the configuration file “factory_default_config.Cfg.” to reset the switch defaults, this file should be set as the startup configuration file (page 3-23). The following table lists some of the basic system defau...
Page 44
Introduction 1-8 1 snmp snmp agent enabled community strings “public” (read only) “private” (read/write) traps authentication traps: enabled link-up-down events: enabled snmp v3 view: defaultview group: public (read only); private (read/write) port configuration admin status enabled auto-negotiation...
Page 45
System defaults 1-9 1 ip settings ip address dhcp assigned subnet mask 255.255.255.0 default gateway 0.0.0.0 dhcp client: enabled bootp disabled multicast filtering igmp snooping snooping: enabled querier: disabled multicast vlan registration disabled system log status enabled messages logged levels...
Page 46
Introduction 1-10 1 this page is intentionally left blank..
Page 47: Connecting to The Switch
2-1 chapter 2: initial configuration connecting to the switch configuration options these switches include a built-in network management agent. The agent offers a variety of management options, including snmp, rmon (groups 1, 2, 3, 9) and a web-based interface. A pc may also be connected directly to...
Page 48: Required Connections
Initial configuration 2-2 2 • configure up to 8 static or lacp trunks • enable port mirroring • set broadcast storm control on any port • display system information and statistics required connections the switch provides an rs-232 serial port that enables a connection to a pc or terminal for monitor...
Page 49: Remote Connections
Basic configuration 2-3 2 remote connections prior to accessing the switch’s onboard agent via a network connection, you must first configure it with a valid ip address, subnet mask, and default gateway using a console connection, dhcp or bootp protocol. The ip address for this switch is obtained vi...
Page 50: Setting Passwords
Initial configuration 2-4 2 setting passwords note: if this is your first time to log into the cli program, you should define new passwords for both default user names using the “username” command, record them and put them in a safe place. Passwords can consist of up to 8 alphanumeric characters and...
Page 51
Basic configuration 2-5 2 manual configuration you can manually assign an ip address to the switch. You may also need to specify a default gateway that resides between this device and management stations that exist on another network segment. Valid ip addresses consist of four decimal numbers, 0 to ...
Page 52
Initial configuration 2-6 2 to automatically configure the switch by communicating with bootp or dhcp address allocation servers on the network, complete the following steps: 1. From the global configuration mode prompt, type “interface vlan 1” to access the interface-configuration mode. Press . 2. ...
Page 53
Basic configuration 2-7 2 community strings (for snmp version 1 and 2c clients) community strings are used to control management access to snmp version 1 and 2c stations, as well as to authorize snmp stations to receive trap messages from the switch. You therefore need to assign community strings to...
Page 54: Managing System Files
Initial configuration 2-8 2 see “snmp-server host” on page 4-90. The following example creates a trap host for each type of snmp client. Configuring access for snmp version 3 clients to configure management access for snmpv3 clients, you need to first create a view that defines the portions of mib t...
Page 55
Managing system files 2-9 2 • operation code — system software that is executed after boot-up, also known as run-time or firmware code. This code runs the switch operations and provides the cli and web management interfaces. See “managing firmware” on page 3-21 for more information. • diagnostic cod...
Page 56
Initial configuration 2-10 2 to save the current configuration settings, enter the following command: 1. From the privileged exec mode prompt, type “copy running-config startup-config” and press . 2. Enter the name of the start-up file. Press . Configuring power over ethernet the ubigate ies4028fp a...
Page 57: Using The Web Interface
3-1 chapter 3: configuring the switch using the web interface this switch provides an embedded http web agent. Using a web browser you can configure the switch and view statistics to monitor network activity. The web agent can be accessed by any computer on the network using a standard web browser (...
Page 58: Home Page
Configuring the switch 3-2 3 navigating the web browser interface to access the web-browser interface you must first enter a user name and password. The administrator has read/write access to all configuration parameters and statistics. The default user name and password for the administrator is “ad...
Page 59: Configuration Options
Panel display 3-3 3 configuration options configurable parameters have a dialog box or a drop-down list. Once a configuration change has been made on a page, be sure to click on the apply button to confirm the new setting. The following table summarizes the web page configuration buttons. Notes: 1. ...
Page 60: Main Menu
Configuring the switch 3-4 3 main menu using the onboard web agent, you can define system parameters, manage and control the switch, and all its ports, or monitor network conditions. The following table briefly describes the selections available from this program. Table 3-2 main menu menu descriptio...
Page 61
Main menu 3-5 3 snmpv3 3-46 engine id sets the snmp v3 engine id on this switch 3-46 remote engine id sets the snmp v3 engine id for a remote device 3-47 users configures snmp v3 users on this switch 3-48 remote users configures snmp v3 users from a remote device 3-50 groups configures snmp v3 group...
Page 62
Configuring the switch 3-6 3 port security configures per port security, including status, response for security breach, and maximum allowed mac addresses 3-97 802.1x 3-88 information displays global configuration settings for 802.1x port authentication 3-90 configuration configures the global confi...
Page 63
Main menu 3-7 3 port counters information displays statistics for lacp protocol messages 3-142 port internal information displays settings and operational state for the local side 3-143 port neighbors information displays settings and operational state for the remote side 3-145 port broadcast contro...
Page 64
Configuring the switch 3-8 3 trunk information displays individual trunk settings for sta 3-175 port configuration configures individual port settings for sta 3-178 trunk configuration configures individual trunk settings for sta 3-178 mstp 3-181 vlan configuration configures priority and vlans for ...
Page 65
Main menu 3-9 3 association each community vlan must be associated with a primary vlan 3-211 port information shows vlan port type, and associated primary or secondary vlans 3-212 port configuration sets the private vlan interface type, and associates the interfaces with a private vlan 3-213 trunk i...
Page 66
Configuring the switch 3-10 3 qos 3-238 diffserv 3-238 class map sets class maps 3-239 policy map sets policy maps 3-242 service policy defines service policy settings for ports 3-245 voip traffic setting 3-246 configuration voip traffic setting configuration 3-246 port configuration configures voip...
Page 67
Main menu 3-11 3 trunk configuration configures mvr interface type and immediate leave status 3-270 group member configuration statically assigns mvr multicast streams to an interface 3-271 dhcp snooping 3-116 configuration enables dhcp snooping and dhcp snooping mac-address verification 3-117 vlan ...
Page 68: Basic Configuration
Configuring the switch 3-12 3 basic configuration this section describes the basic functions required to set up management access to the switch, display or upgrade operating software, or reset the system. Displaying system information you can easily identify the system by displaying the device name,...
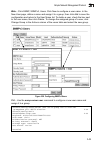
Page 69
Basic configuration 3-13 3 web – click system, system information. Specify the system name, location, and contact information for the system administrator, then click apply. (this page also includes a telnet button that allows access to the command line interface via telnet.) figure 3-3 system infor...
Page 70
Configuring the switch 3-14 3 displaying switch hardware/software versions use the switch information page to display hardware/firmware version numbers for the main board and management software, as well as the power status of the system. Field attributes main board • serial number – the serial numb...
Page 71
Basic configuration 3-15 3 cli – use the following command to display version information. Console#show version 4-32 unit 1 serial number: a622016032 hardware version: r01 epld version: 0.02 number of ports: 24 main power status: up redundant power status: not present agent (master) unit id: 1 loade...
Page 72
Configuring the switch 3-16 3 displaying bridge extension capabilities the bridge mib includes extensions for managed devices that support multicast filtering, traffic classes, and virtual lans. You can access these extensions to display default settings for the key variables. Field attributes • ext...
Page 73
Basic configuration 3-17 3 cli – enter the following command. Setting the switch’s ip address this section describes how to configure an ip interface for management access over the network. The ip address for the stack is obtained via dhcp by default. To manually configure an address, you need to ch...
Page 74
Configuring the switch 3-18 3 manual configuration web – click system, ip configuration. Select the vlan through which the management station is attached, set the ip address mode to “static,” enter the ip address, subnet mask and gateway, then click apply. Figure 3-6 manual ip configuration cli – sp...
Page 75
Basic configuration 3-19 3 using dhcp/bootp if your network provides dhcp/bootp services, you can configure the switch to be dynamically configured by these services. Web – click system, ip configuration. Specify the vlan to which the management station is attached, set the ip address mode to dhcp o...
Page 76: Enabling Jumbo Frames
Configuring the switch 3-20 3 web – if the address assigned by dhcp is no longer functioning, you will not be able to renew the ip settings via the web interface. You can only restart dhcp service via the web interface if the current address is still available. Cli – enter the following command to r...
Page 77: Managing Firmware
Basic configuration 3-21 3 managing firmware you can upload/download firmware to or from a tftp server. Just specify the method of file transfer, along with the file type and file names as required. By saving runtime code to a file on a tftp server, that file can later be downloaded to the switch to...
Page 78
Configuring the switch 3-22 3 downloading system software from a server when downloading runtime code, the new operation code file will overwrite the existing file. Versions of the code prior to 1.1.0.10 require the operation code file being transferred to have the same destination file name as the ...
Page 79
Basic configuration 3-23 3 cli – to download new firmware from a tftp server, enter the ip address of the tftp server, select “opcode” as the file type, then enter the source and destination file names. When the file has finished downloading, and then restart the switch for the new code to take effe...
Page 80
Configuring the switch 3-24 3 downloading configuration settings from a server you can download the configuration file under a new file name and then set it as the startup file, or you can specify the current startup configuration file as the destination file to directly replace it. Note that the fi...
Page 81: Console Port Settings
Basic configuration 3-25 3 cli – enter the ip address of the tftp server, specify the source file on the server, set the startup file name on the switch, and then restart the switch. To select another configuration file as the start-up configuration, use the boot system command and then restart the ...
Page 82
Configuring the switch 3-26 3 • speed – sets the terminal line’s baud rate for transmit (to terminal) and receive (from terminal). Set the speed to match the baud rate of the device connected to the serial port. (range: 9600, 19200, or 38400 baud; default: 9600 baud) • stop bits – sets the number of...
Page 83: Telnet Settings
Basic configuration 3-27 3 cli – enter line configuration mode for the console, then specify the connection parameters as required. To display the current console port settings, use the show line command from the normal exec level. Telnet settings you can access the onboard configuration program ove...
Page 84
Configuring the switch 3-28 3 • password 2 – specifies a password for the line connection. When a connection is started on a line with password protection, the system prompts for the password. If you enter the correct password, the system shows a prompt. (default: no password) • login 2 – enables pa...
Page 85: Configuring Event Logging
Basic configuration 3-29 3 configuring event logging the switch allows you to control the logging of error messages, including the type of events that are recorded in switch memory, logging to a remote system log (syslog) server, and displays a list of recent event messages. System log configuration...
Page 86
Configuring the switch 3-30 3 web – click system, log, system logs. Specify system log status, set the level of event messages to be logged to ram and flash memory, then click apply. Figure 3-15 system logs cli – enable system logging and then specify the level of messages to be logged to ram and fl...
Page 87
Basic configuration 3-31 3 web – click system, log, remote logs. To add an ip address to the host ip list, type the new ip address in the host ip address box, and then click add. To delete an ip address, click the entry in the host ip list, and then click remove. Figure 3-16 remote logs cli – enter ...
Page 88
Configuring the switch 3-32 3 displaying log messages the logs page allows you to scroll through the logged system and event messages. The switch can store up to 2048 log entries in temporary random access memory (ram; i.E., memory flushed on power reset) and up to 4096 entries in permanent flash me...
Page 89
Basic configuration 3-33 3 configured email recipients. For example, using level 7 will report all events from level 7 to level 0. (default: level 7) • smtp server list – specifies a list of up to three recipient smtp servers. The switch attempts to connect to the other listed servers if the first f...
Page 90: Resetting The System
Configuring the switch 3-34 3 cli – enter the host ip address, followed by the mail severity level, source and destination email addresses and enter the sendmail command to complete the action. Use the show logging command to display smtp information. Resetting the system this feature restarts the s...
Page 91: Setting The System Clock
Basic configuration 3-35 3 web – click system, reset. Enter the amount of time the switch should wait before rebooting. Click the reset button to reboot the switch or click the cancel button to cancel a configured reset. If prompted, confirm that you want reset the switch or cancel a configured rese...
Page 92
Configuring the switch 3-36 3 setting the time manually you can set the system time on the switch manually without using sntp. Cli – this example sets the system clock time and then displays the current time and date . Configuring sntp you can configure the switch to send time synchronization reques...
Page 93
Basic configuration 3-37 3 cli – this example configures the switch to operate as an sntp unicast client and then displays the current time and settings. Configuring ntp the ntp client allows you to configure up to 50 ntp servers to poll for time updates. You can also enable authentication to ensure...
Page 94
Configuring the switch 3-38 3 web – select sntp, configuration. Modify any of the required ntp parameters, and click apply. Figure 3-21 ntp client configuration cli – this example configures the switch to operate as an ntp client and then displays the current settings. Console(config)#ntp authentica...
Page 95
Basic configuration 3-39 3 setting the time zone sntp uses coordinated universal time (or utc, formerly greenwich mean time, or gmt) based on the time at the earth’s prime meridian, zero degrees longitude, which passes through greenwich, england. To display a time corresponding to your local time, y...
Page 96
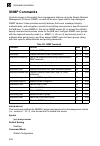
Configuring the switch 3-40 3 simple network management protocol snmp is a communication protocol designed specifically for managing devices on a network. Equipment commonly managed with snmp includes switches, routers and host computers. Snmp is typically used to configure these devices for proper ...
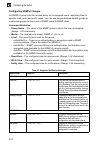
Page 97: Enabling Snmp Agent Status
Simple network management protocol 3-41 3 note: the predefined default groups and view can be deleted from the system. You can then define customized groups and views for the snmp clients that require access. Enabling snmp agent status enables snmpv3 service for all management clients (i.E., version...
Page 98
Configuring the switch 3-42 3 setting community access strings you may configure up to five community strings authorized for management access by clients using snmp v1 and v2c. All community strings used for ip trap managers should be listed in this table. For security reasons, you should consider r...
Page 99
Simple network management protocol 3-43 3 specifying trap managers and trap types traps indicating status changes are issued by the switch to specified trap managers. You must specify trap managers so that key events are reported by this switch to your management station (using network management pl...
Page 100
Configuring the switch 3-44 3 top of the snmp configuration page (for version 1 or 2c clients), or define a corresponding “user name” in the snmpv3 users page (for version 3 clients). (range: 1-32 characters, case sensitive) • trap udp port – specifies the udp port number used by the trap manager. (...
Page 101
Simple network management protocol 3-45 3 web – click snmp, configuration. Enter the ip address and community string for each management station that will receive trap messages, specify the udp port, trap version, trap security level (for v3 clients), trap inform settings (for v2c/v3 clients), and t...
Page 102
Configuring the switch 3-46 3 configuring snmpv3 management access to configure snmpv3 management access to the switch, follow these steps: 1. If you want to change the default engine id, it must be changed first before configuring other parameters. 2. Specify read and write access views for the swi...
Page 103
Simple network management protocol 3-47 3 specifying a remote engine id to send inform messages to an snmpv3 user on a remote device, you must first specify the engine identifier for the snmp agent on the remote device where the user resides. The remote engine id is used to compute the security dige...
Page 104
Configuring the switch 3-48 3 configuring snmpv3 users each snmpv3 user is defined by a unique name. Users must be configured with a specific security level and assigned to a group. The snmpv3 group restricts users to a specific read, write, and notify view. Command attributes • user name – the name...
Page 105
Simple network management protocol 3-49 3 web – click snmp, snmpv3, users. Click new to configure a user name. In the new user page, define a name and assign it to a group, then click add to save the configuration and return to the user name list. To delete a user, check the box next to the user nam...
Page 106
Configuring the switch 3-50 3 configuring remote snmpv3 users each snmpv3 user is defined by a unique name. Users must be configured with a specific security level and assigned to a group. The snmpv3 group restricts users to a specific read, write, and notify view. To send inform messages to an snmp...
Page 107
Simple network management protocol 3-51 3 web – click snmp, snmpv3, remote users. Click new to configure a user name. In the new user page, define a name and assign it to a group, then click add to save the configuration and return to the user name list. To delete a user, check the box next to the u...
Page 108
Configuring the switch 3-52 3 configuring snmpv3 groups an snmpv3 group sets the access policy for its assigned users, restricting them to specific read, write, and notify views. You can use the pre-defined default groups or create new groups to map a set of snmp users to snmp views. Command attribu...
Page 109
Simple network management protocol 3-53 3 linkdown * 1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.3 a linkdown trap signifies that the snmp entity, acting in an agent role, has detected that the ifoperstatus object for one of its communication links is about to enter the down state from some other state (but not from the notp...
Page 110
Configuring the switch 3-54 3 web – click snmp, snmpv3, groups. Click new to configure a new group. In the new group page, define a name, assign a security model and level, and then select read and write views. Click add to save the new group and return to the groups list. To delete a group, check t...
Page 111
Simple network management protocol 3-55 3 cli – use the snmp-server group command to configure a new group, specifying the security model and level, and restricting mib access to defined read and write views. Setting snmpv3 views snmpv3 views are used to restrict user access to specified portions of...
Page 112
Configuring the switch 3-56 3 web – click snmp, snmpv3, views. Click new to configure a new view. In the new view page, define a name and specify oid subtrees in the switch mib to be included or excluded in the view. Click back to save the new view and return to the snmpv3 views list. For a specific...
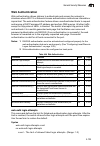
Page 113: User Authentication
User authentication 3-57 3 cli – use the snmp-server view command to configure a new view. This example view includes the mib-2 interfaces table, and the wildcard mask selects all index entries. User authentication you can configure this switch to authenticate users logging into the system for manag...
Page 114: Configuring User Accounts
Configuring the switch 3-58 3 configuring user accounts the guest only has read access for most configuration parameters. However, the administrator has write access for all parameters governing the onboard agent. You should therefore assign a new administrator password as soon as possible, and stor...
Page 115
User authentication 3-59 3 web – click security, user accounts. To configure a new user account, specify a user name, select the user’s access level, then enter a password and confirm it. Click add to save the new user account and add it to the account list. To change the password for a specific use...
Page 116
Configuring the switch 3-60 3 multiple user name/password pairs with associated privilege levels for each user that requires management access to the switch. Radius uses udp while tacacs+ uses tcp. Udp only offers best effort delivery, while tcp offers a connection-oriented transport. Also, note tha...
Page 117
User authentication 3-61 3 - accounting port number – udp port on authentication server used for accounting messages. (range: 1-65535; default: 1813) - number of server transmits – number of times the switch tries to authenticate logon access via the authentication server. (range: 1-30; default: 2) ...
Page 118
Configuring the switch 3-62 3 web – click security, authentication settings. To configure local or remote authentication preferences, specify the authentication sequence (i.E., one to three methods), fill in the parameters for radius or tacacs+ authentication if selected, and click apply. Figure 3-3...
Page 119
User authentication 3-63 3 cli – specify all the required parameters to enable logon authentication. Console(config)#authentication login radius 4-103 console(config)#radius-server auth-port 181 4-106 console(config)#radius-server acct-port 183 4-106 console(config)#radius-server retransmit 5 4-108 ...
Page 120: Configuring Encryption Keys
Configuring the switch 3-64 3 configuring encryption keys the encryption key feature provides a central location for the management of all radius and tacacs+ server encryption keys. Command attributes • radius settings - global – provides globally applicable radius encryption key settings. - server ...
Page 121
User authentication 3-65 3 - confirm secret text string – re-type the string entered in the previous field to ensure no errors were made. The switch will not change the encryption key if these two fields do not match. - change – clicking this button adds or modifies the selected encryption key. Web ...
Page 122
Configuring the switch 3-66 3 • accounting for users that access management interfaces on the switch through the console and telnet. • accounting for commands that users enter at specific cli privilege levels. • authorization of users that access management interfaces on the switch through the conso...
Page 123
User authentication 3-67 3 cli – specify the group name for a list of radius servers, and then specify the index number of a radius server to add it to the group. Configuring aaa tacacs+ group settings the aaa tacacs+ group settings screen defines the configured tacacs+ servers to use for accounting...
Page 124
Configuring the switch 3-68 3 the method name is only used to describe the accounting method(s) configured on the specified accounting servers, and do not actually send any information to the servers about the methods to use. • service request – specifies the service as either 802.1x (user accountin...
Page 125
User authentication 3-69 3 cli – specify the accounting method required, followed by the chosen parameters. Aaa accounting update this feature sets the interval at which accounting updates are sent to accounting servers. Command attributes periodic update - specifies the interval at which the local ...
Page 126
Configuring the switch 3-70 3 aaa accounting 802.1x port settings this feature applies the specified accounting method to an interface. Command attributes • port/trunk - specifies a port or trunk number. • method name - specifies a user defined method name to apply to the interface. This method must...
Page 127
User authentication 3-71 3 aaa accounting exec command privileges this feature specifies a method name to apply to commands entered at specific cli privilege levels. Command attributes • commands privilege level - the cli privilege levels (0-15). • console/telnet - specifies a user-defined method na...
Page 128
Configuring the switch 3-72 3 aaa accounting exec settings this feature specifies a method name to apply to console and telnet connections. Command attributes method name - specifies a user defined method name to apply to console and telnet connections. Web – click security, aaa, accounting, exec se...
Page 129
User authentication 3-73 3 web – click security, aaa, summary. Figure 3-42 aaa accounting summary cli – use the following command to display the currently applied accounting methods, and registered users. Console#show accounting 4-122 accounting type : dot1x method list : default group list : radius...
Page 130
Configuring the switch 3-74 3 authorization settings aaa authorization is a feature that verifies a user has access to specific services. Command attributes • method name – specifies an authorization method for service requests. The “default” method is used for a requested service if no other method...
Page 131
User authentication 3-75 3 authorization exec settings this feature specifies an authorization method name to apply to console and telnet connections. Command attributes method name - specifies a user-defined method name to apply to console and telnet connections. Web – click security, aaa, authoriz...
Page 132
Configuring the switch 3-76 3 authorization summary the authorization summary displays the configured authorization methods and the interfaces to which they are applied. Command attributes • accounting type - displays the accounting service. • method list - displays the user-defined or default autho...
Page 133: Configuring Https
User authentication 3-77 3 configuring https you can configure the switch to enable the secure hypertext transfer protocol (https) over the secure socket layer (ssl), providing secure access (i.E., an encrypted connection) to the switch’s web interface. Command usage • both the http and https servic...
Page 134
Configuring the switch 3-78 3 web – click security, https settings. Enable https and specify the port number, then click apply. Figure 3-46 https settings cli – this example enables the http secure server and modifies the port number. Replacing the default secure-site certificate when you log onto t...
Page 135
User authentication 3-79 3 • private password – password stored in the private key file. This password is used to verify authorization for certificate use, and is verified when downloading the certificate to the switch. Web – click security, https settings. Fill in the tftp server, certificate and p...
Page 136
Configuring the switch 3-80 3 notes: 1. You need to install an ssh client on the management station to access the switch for management via the ssh protocol. 2. The switch supports both ssh version 1.5 and 2.0 clients. Command usage the ssh server on this switch supports both password and public key...
Page 137
User authentication 3-81 3 6. Authentication – one of the following authentication methods is employed: password authentication (for ssh v1.5 or v2 clients) a. The client sends its password to the server. B. The switch compares the client's password to those stored in memory. C. If a match is found,...
Page 138
Configuring the switch 3-82 3 generating the host key pair a host public/private key pair is used to provide secure communications between an ssh client and the switch. After generating this key pair, you must provide the host public key to ssh clients and import the client’s public key to the switc...
Page 139
User authentication 3-83 3 web – click security, ssh, host-key settings. Select the host-key type from the drop-down box, select the option to save the host key from memory to flash (if required) prior to generating the key, and then click generate. Figure 3-48 ssh host-key settings cli – this examp...
Page 140
Configuring the switch 3-84 3 importing user public keys a user’s public key must be uploaded to the switch in order for the user to be able to log in using the public key authentication mechanism. If the user’s public key does not exist on the switch, ssh will revert to the interactive password aut...
Page 141
User authentication 3-85 3 web – click security, ssh, ssh user public-key settings. Select the user name and the public-key type from the respective drop-down boxes, input the tftp server ip address and the public key source file name, and then click copy public key. Figure 3-49 ssh user public-key ...
Page 142
Configuring the switch 3-86 3 cli – this example imports an sshv2 dsa public key for the user admin and then displays admin’s imported public keys. Note that public key authentication through ssh is only supported for users configured locally on the switch. Configuring the ssh server the ssh server ...
Page 143
User authentication 3-87 3 • ssh authentication retries – specifies the number of authentication attempts that a client is allowed before authentication fails and the client has to restart the authentication process. (range: 1-5 times; default: 3) • ssh server-key size – specifies the ssh server key...
Page 144
Configuring the switch 3-88 3 configuring 802.1x port authentication network switches can provide open and easy access to network resources by simply attaching a client pc. Although this automatic configuration and access is a desirable feature, it also allows unauthorized personnel to easily intrud...
Page 145
User authentication 3-89 3 • each switch port that will be used must be set to dot1x “auto” mode. • each client that needs to be authenticated must have dot1x client software installed and properly configured. • the radius server and 802.1x client support eap. (the switch only supports eapol in orde...
Page 146
Configuring the switch 3-90 3 configuring 802.1x global settings the 802.1x protocol provides port-based client authentication. The 802.1x protocol must be enabled globally for the switch system before port settings are active. Command attributes 802.1x system authentication control – sets the globa...
Page 147
User authentication 3-91 3 • re-authentication – sets the client to be re-authenticated after the interval specified by the re-authentication period. Re-authentication can be used to detect if a new device is plugged into a switch port. (default: disabled) • max-request – sets the maximum number of ...
Page 148
Configuring the switch 3-92 3 cli – this example sets the 802.1x parameters on port 2. For a description of the additional fields displayed in this example, see “show dot1x” on page 4-143. Console(config)#interface ethernet 1/2 4-188 console(config-if)#dot1x port-control auto 4-138 console(config-if...
Page 149
User authentication 3-93 3 displaying 802.1x statistics this switch can display statistics for dot1x protocol exchanges for any port. Table 3-7 802.1x statistics parameter description rx eapol start the number of eapol start frames that have been received by this authenticator. Rx eapol logoff the n...
Page 150
Configuring the switch 3-94 3 web – select security, 802.1x, statistics. Select the required port and then click query. Click refresh to update the statistics. Figure 3-54 displaying 802.1x port statistics cli – this example displays the 802.1x statistics for port 4. Filtering ip addresses for manag...
Page 151
User authentication 3-95 3 • ip address can be configured for snmp, web and telnet access respectively. Each of these groups can include up to five different sets of addresses, either individual addresses or address ranges. • when entering addresses for the same group (i.E., snmp, web or telnet), th...
Page 152: General Security Measures
Configuring the switch 3-96 3 cli – this example allows snmp access for a specific client. General security measures this switch supports many methods of segregating traffic for clients attached to each of the data ports, and for ensuring that only authorized clients gain access to the network. Priv...
Page 153: Configuring Port Security
General security measures 3-97 3 • ip source guard – filters untrusted dhcp messages on unsecure ports by building and maintaining a dhcp snooping binding table. (see “ip source guard” on page 3-123.) note: the priority of execution for the filtering commands is port security, port authentication, n...
Page 154: Web Authentication
Configuring the switch 3-98 3 • security status – enables or disables port security on the port. (default: disabled) • max mac count – the maximum number of mac addresses that can be learned on a port. (range: 0 - 1024, where 0 means disabled) • trunk – trunk number if port is a member (page 3-135 a...
Page 155
General security measures 3-99 3 configuring web authentication web authentication is configured on a per-port basis, however there are four configurable parameters that apply globally to all ports on the switch. Command attributes • system authentication control – enables web authentication for the...
Page 156
Configuring the switch 3-100 3 configuring web authentication for ports web authentication is configured on a per-port basis. The following parameters are associated with each port. Command attributes • port – indicates the port being configured • status – configures the web authentication status fo...
Page 157
General security measures 3-101 3 displaying web authentication port information this switch can display web authentication information for all ports and connected hosts. Command attributes • interface – indicates the ethernet port to query. • ip address – indicates the ip address of each connected ...
Page 158: Network Access
Configuring the switch 3-102 3 web – click security, web authentication, re-authentication. Figure 3-60 web authentication port re-authentication cli – this example forces the re-authentication of all hosts connected to port 1/5. Network access ( mac address authentication) some devices connected to...
Page 159
General security measures 3-103 3 • configured static mac addresses are added to the secure address table when seen on a switch port. Static addresses are treated as authenticated without sending a request to a radius server. • when port status changes to down, all mac addresses are cleared from the...
Page 160
Configuring the switch 3-104 3 cli – this example sets and displays the reauthentication time. Configuring mac authentication for ports configures mac authentication on switch ports, including setting the maximum mac count, applying a mac address filter, and enabling dynamic vlan assignment. Command...
Page 161
General security measures 3-105 3 note: mac authentication cannot be configured on trunk ports. Ports configured as trunk members are indicated on the network access port configuration page in the “trunk” column. Web – click security, network access, port configuration. Figure 3-62 network access po...
Page 162
Configuring the switch 3-106 3 displaying secure mac address information authenticated mac addresses are stored in the secure mac address table. Information on the secure mac entries can be displayed and selected entries removed from the table. Command attributes • network access mac address count –...
Page 163: Mac Authentication
General security measures 3-107 3 cli – this example displays all entries currently in the secure mac address table. Mac authentication each port’s mac authentication settings are configured independently. Configuring mac authentication parameters for ports use the mac authentication port configurat...
Page 164: Access Control Lists
Configuring the switch 3-108 3 web – click security, mac authentication. Modify the maximum mac count and intrusion action. Click apply. Figure 3-64 mac authentication port configuration cli – this example configures the maximum mac count to 32 and sets the intrusion action to block all traffic for ...
Page 165
General security measures 3-109 3 the order in which active acls are checked is as follows: 1. User-defined rules in the ingress mac acl for ingress ports. 2. User-defined rules in the ingress ip acl for ingress ports. 3. Explicit default rule (permit any any) in the ingress mac acl for ingress port...
Page 166
Configuring the switch 3-110 3 configuring a standard ip acl command attributes • action – an acl can contain any combination of permit or deny rules. • address type – specifies the source ip address. Use “any” to include all possible addresses, “host” to specify a specific host address in the addre...
Page 167
General security measures 3-111 3 configuring an extended ip acl command attributes • action – an acl can contain any combination of permit or deny rules. • source/destination address type – specifies the source or destination ip address. Use “any” to include all possible addresses, “host” to specif...
Page 168
Configuring the switch 3-112 3 web – specify the action (i.E., permit or deny). Specify the source and/or destination addresses. Select the address type (any, host, or ip). If you select “host,” enter a specific address. If you select “ip,” enter a subnet address and the mask for an address range. S...
Page 169
General security measures 3-113 3 configuring a mac acl command attributes • action – an acl can contain any combination of permit or deny rules. • source/destination address type – use “any” to include all possible addresses, “host” to indicate a specific mac address, or “mac” to specify an address...
Page 170
Configuring the switch 3-114 3 web – specify the action (i.E., permit or deny). Specify the source and/or destination addresses. Select the address type (any, host, or mac). If you select “host,” enter a specific address (e.G., 11-22-33-44-55-66). If you select “mac,” enter a base address and a hexa...
Page 171
General security measures 3-115 3 binding a port to an access control list after configuring the access control lists (acl), you can bind the ports that need to filter traffic to the appropriate acls. You can assign one ip access list to any port. Command usage • each acl can have up to 32 rules. • ...
Page 172: Dhcp Snooping
Configuring the switch 3-116 3 dhcp snooping the addresses assigned to dhcp clients on unsecure ports can be carefully controlled using the dynamic bindings registered with dhcp snooping (or using the static bindings configured with ip source guard). Dhcp snooping allows a switch to protect a networ...
Page 173
General security measures 3-117 3 - if a dhcp packet from a client passes the filtering criteria above, it will only be forwarded to trusted ports in the same vlan. - if a dhcp packet is from server is received on a trusted port, it will be forwarded to both trusted and untrusted ports in the same v...
Page 174
Configuring the switch 3-118 3 configuring vlans for dhcp snooping use the dhcp snooping vlan configuration page to enable or disable dhcp snooping on specific vlans. Command usage • when dhcp snooping is enabled globally on the switch, and enabled on the specified vlan, dhcp packet filtering will b...
Page 175
General security measures 3-119 3 command usage • dhcp snooping (see page 3-117) must be enabled for option 82 information to be inserted into request packets. • when option 82 is enabled, the requesting client (or an intermediate relay agent that has used the information fields to describe itself) ...
Page 176
Configuring the switch 3-120 3 cli – this example enables dhcp snooping information option, and sets the policy as replace . Configuring ports for dhcp snooping use the dhcp snooping port configuration page to configure switch ports as trusted or untrusted. Command usage • a trusted interface is an ...
Page 177
General security measures 3-121 3 command attributes • trust status – enables or disables port as trusted. Web – click dhcp snooping, information option configuration. Figure 3-73 dhcp snooping port configuration cli – this example shows how to enable the dhcp snooping trust status for ports . Conso...
Page 178
Configuring the switch 3-122 3 displaying dhcp snooping binding information binding table entries can be displayed on the binding information page. Command attributes • store dhcp snooping binding entries to flash. – writes all dynamically learned snooping entries to flash memory. This function can ...
Page 179: Ip Source Guard
General security measures 3-123 3 ip source guard ip source guard is a security feature that filters ip traffic on network interfaces based on manually configured entries in the ip source guard table, or dynamic entries in the dhcp snooping table when enabled (see “dhcp snooping” on page 3-116). Ip ...
Page 180
Configuring the switch 3-124 3 command attributes • filter type – configures the switch to filter inbound traffic based source ip address, or source ip address and corresponding mac address. (default: none) • none – disables ip source guard filtering on the port. • sip – enables traffic filtering ba...
Page 181
General security measures 3-125 3 configuring static binding for ip source guard use the ip source guard static configuration page to bind a static address to a port. Table entries include a mac address, ip address, lease time, entry type (static, dynamic), vlan identifier, and port identifier. All ...
Page 182
Configuring the switch 3-126 3 web – click ip source guard, static configuration. Select the vlan and port to which the entry will be bound, enter the mac address and associated ip address, then click add. Figure 3-76 static ip source guard binding configuration cli – this example configures a stati...
Page 183
General security measures 3-127 3 web – click ip source guard, dynamic information. Figure 3-77 dynamic ip source guard binding information cli – this example shows how to configure a static source-guard binding on port 5 . Console#show ip source-guard binding 4-175 macaddress ipaddress lease(sec) t...
Page 184: Port Configuration
Configuring the switch 3-128 3 port configuration displaying connection status you can use the port information or trunk information pages to display the current connection status, including link state, speed/duplex mode, flow control, and auto-negotiation. Field attributes (web) • name – interface ...
Page 185
Port configuration 3-129 3 field attributes (cli) basic information: • port type – indicates the port type. (100base-tx, 1000base-t, or sfp) • mac address – the physical layer address for this port. (to access this item on the web, see “setting the switch’s ip address” on page 3-17.) configuration: ...
Page 186
Configuring the switch 3-130 3 current status: • link status – indicates if the link is up or down. • port operation status – provides detailed information on port state. (displayed only when the link is up.) • operation speed-duplex – shows the current speed and duplex mode. • flow control type – i...
Page 187
Port configuration 3-131 3 trunk. If not used, the success of the link process cannot be guaranteed when connecting to other types of switches. However, this switch does provide a means of safely forcing a link to operate at 1000 mbps, full-duplex using the giga phy mode attribute described below. C...
Page 188
Configuring the switch 3-132 3 back pressure is used for half-duplex operation and ieee 802.3-2005 (formally ieee 802.3x) for full-duplex operation. Avoid using flow control on a port connected to a hub unless it is actually required to solve a problem. Otherwise back pressure jamming signals may de...
Page 189
Port configuration 3-133 3 cli – select the interface, and then enter the required settings. Console(config)#interface ethernet 1/13 4-188 console(config-if)#description rd sw#13 4-189 console(config-if)#shutdown 4-195 . Console(config-if)#no shutdown console(config-if)#no negotiation 4-190 console(...
Page 190: Creating Trunk Groups
Configuring the switch 3-134 3 creating trunk groups you can create multiple links between devices that work as one virtual, aggregate link. A port trunk offers a dramatic increase in bandwidth for network segments where bottlenecks exist, as well as providing a fault-tolerant link between two devic...
Page 191
Port configuration 3-135 3 statically configuring a trunk command usage • when configuring static trunks, you may not be able to link switches of different types, depending on the manufacturer’s implementation. However, note that the static trunks on this switch are cisco etherchannel compatible. • ...
Page 192
Configuring the switch 3-136 3 cli – this example creates trunk 2 with ports 1 and 2. Just connect these ports to two static trunk ports on another switch to form a trunk. Enabling lacp on selected ports command usage • to avoid creating a loop in the network, be sure you enable lacp before connecti...
Page 193
Port configuration 3-137 3 command attributes • member list (current) – shows configured trunks (port). • new – includes entry fields for creating new trunks. - port – port identifier. (range: 1-28 on ies4028f/ies4028fp, 1-24 on ies4024gp) web – click port, lacp, configuration. Select any of the swi...
Page 194
Configuring the switch 3-138 3 cli – the following example enables lacp for ports 1 to 6. Just connect these ports to lacp-enabled trunk ports on another switch to form a trunk. Configuring parameters for lacp group members dynamically creating a port channel – ports assigned to a common port channe...
Page 195
Port configuration 3-139 3 command attributes set port actor – this menu sets the local side of an aggregate link; i.E., the ports on this switch. • port – port number. (range: 1-28 on ies4028f/ies4028fp, 1-24 on ies4024gp) • system priority – lacp system priority is used to determine link aggregati...
Page 196
Configuring the switch 3-140 3 web – click port, lacp, aggregation port. Set the system priority, admin key, and port priority for the port actor. You can optionally configure these settings for the port partner. (be aware that these settings only affect the administrative state of the partner, and ...
Page 197
Port configuration 3-141 3 cli – the following example configures lacp parameters for ports 1-4. Ports 1-4 are used as active members of the lag. Configuring parameters for lacp groups use the aggregator page to configure system parameters which apply to specific lacp groups. Command attributes • ad...
Page 198
Configuring the switch 3-142 3 web – click port, lacp, aggregator. Set the admin key for the required lacp group, and click apply. Figure 3-83 lacp aggregation group configuration cli – the following example sets the lacp admin key for port channel 1. Displaying lacp port counters you can display st...
Page 199
Port configuration 3-143 3 web – click port, lacp, port counters information. Select a member port to display the corresponding information. Figure 3-84 lacp - port counters information cli – the following example displays lacp counters. Displaying lacp settings and status for the local side you can...
Page 200
Configuring the switch 3-144 3 web – click port, lacp, port internal information. Select a port channel to display the corresponding information. Figure 3-85 lacp - port internal information admin state, oper state administrative or operational values of the actor’s state parameters: • expired – the...
Page 201
Port configuration 3-145 3 cli – the following example displays the lacp configuration settings and operational state for the local side of port channel 1. Displaying lacp settings and status for the remote side you can display configuration settings and the operational state for the remote side of ...
Page 202
Configuring the switch 3-146 3 web – click port, lacp, port neighbors information. Select a port channel to display the corresponding information. Figure 3-86 lacp - port neighbors information cli – the following example displays the lacp configuration settings and operational state for the remote s...
Page 203
Port configuration 3-147 3 setting broadcast storm thresholds broadcast storms may occur when a device on your network is malfunctioning, or if application programs are not well designed or properly configured. If there is too much broadcast traffic on your network, performance can be severely degra...
Page 204
Configuring the switch 3-148 3 web – click port, port/trunk broadcast control. Set the threshold and mark the enabled field for the required interface, then click apply. Figure 3-87 port broadcast control cli – specify any interface, and then enter the threshold. The following disables broadcast sto...
Page 205
Port configuration 3-149 3 setting multicast storm thresholds you can protect your network from excess multicast traffic by setting thresholds for each port. Any multicast packets exceeding the specified threshold will then be dropped. Command attributes • port - port number. (range: 1-28 on ies4028...
Page 206
Configuring the switch 3-150 3 setting unknown unicast storm thresholds you can protect your network from excess unknown unicast traffic by setting thresholds for each port. Any multicast packets exceeding the specified threshold will then be dropped. Command attributes • port - port number. (range:...
Page 207: Configuring Port Mirroring
Port configuration 3-151 3 configuring port mirroring you can mirror traffic from any source port to a target port for real-time analysis. You can then attach a logic analyzer or rmon probe to the target port and study the traffic crossing the source port in a completely unobtrusive manner. Command ...
Page 208: Configuring Rate Limits
Configuring the switch 3-152 3 configuring rate limits this function allows the network manager to control the maximum rate for traffic received on a port or transmitted from a port. Rate limiting is configured on ports at the edge of a network to limit traffic into or out of the switch. Packets tha...
Page 209: Showing Port Statistics
Port configuration 3-153 3 showing port statistics you can display standard statistics on network traffic from the interfaces group and ethernet-like mibs, as well as a detailed breakdown of traffic based on the rmon mib. Interfaces and ethernet-like statistics display errors on the traffic passing ...
Page 210
Configuring the switch 3-154 3 transmit discarded packets the number of outbound packets which were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space. Transmit errors th...
Page 211
Port configuration 3-155 3 received frames the total number of frames (bad, broadcast and multicast) received. Broadcast frames the total number of good frames received that were directed to the broadcast address. Note that this does not include multicast packets. Multicast frames the total number o...
Page 212
Configuring the switch 3-156 3 web – click port, port statistics. Select the required interface, and click query. You can also use the refresh button at the bottom of the page to update the screen. Figure 3-90 port statistics.
Page 213
Power over ethernet settings 3-157 3 cli – this example shows statistics for port 13. Power over ethernet settings the ies4028fp and ies4024gp switches can provide dc power to a wide range of connected devices, eliminating the need for an additional power source and cutting down on the amount of cab...
Page 214: Switch Power Status
Configuring the switch 3-158 3 switch power status use the main power status page to display the power over ethernet settings for the switch. Command attributes • maximum available power – the configured power budget for the switch. • system operation status – the poe power service provided to the s...
Page 215
Power over ethernet settings 3-159 3 setting a switch power budget a maximum poe power budget for the switch (power available to all switch ports) can be defined so that power can be centrally managed, preventing overload conditions at the power source. If the power demand from devices connected to ...
Page 216: Configuring Port Poe Power
Configuring the switch 3-160 3 web – click poe, power port status. Figure 3-93 displaying port poe status cli – this example displays the poe status and priority of port 1. Configuring port poe power if a device is connected to a switch port and the switch detects that it requires more than the powe...
Page 217
Power over ethernet settings 3-161 3 command attributes • port – the port number on the switch. (range: 1-24) • admin status – enables poe power on the port. Power is automatically supplied when a device is detected on the port, providing that the power demanded does not exceed the switch or port po...
Page 218: Address Table Settings
Configuring the switch 3-162 3 address table settings switches store the addresses for all known devices. This information is used to pass traffic directly between the inbound and outbound ports. All the addresses learned by monitoring traffic are stored in the dynamic address table. You can also ma...
Page 219
Address table settings 3-163 3 cli – this example adds an address to the static address table, but sets it to be deleted when the switch is reset. Displaying the address table the dynamic address table contains the mac addresses learned by monitoring the source address for traffic entering the switc...
Page 220: Changing The Aging Time
Configuring the switch 3-164 3 cli – this example also displays the address table entries for port 1. Changing the aging time you can set the aging time for entries in the dynamic address table. Command attributes • aging status – enables/disables the function. (default: enabled) • aging time – the ...
Page 221
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-165 3 spanning tree algorithm configuration the spanning tree algorithm (sta) can be used to detect and disable network loops, and to provide backup links between switches, bridges or routers. This allows the switch to interact with other bridging devices (tha...
Page 222
Configuring the switch 3-166 3 mstp – when using stp or rstp, it may be difficult to maintain a stable path between all vlan members. Frequent changes in the tree structure can easily isolate some of the group members. Mstp (which is based on rstp for fast convergence) is designed to support indepen...
Page 223
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-167 3 configuring port and trunk loopback detection when port loopback detection is enabled and a port receives it’s own bpdu, the detection agent drops the loopback bpdu, sends an snmp trap, and places the port in discarding mode. This loopback state can be r...
Page 224: Displaying Global Settings
Configuring the switch 3-168 3 cli – this command enables loopback detection for port 1/5, configures automatic release-mode, and enables snmp trap notification for detected loopback bpdu’s. Displaying global settings you can display a summary of the current bridge sta information that applies to th...
Page 225
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-169 3 these additional parameters are only displayed for the cli: • spanning tree mode – specifies the type of spanning tree used on this switch: - stp: spanning tree protocol (ieee 802.1d) - rstp: rapid spanning tree (ieee 802.1w) - mstp: multiple spanning tr...
Page 226
Configuring the switch 3-170 3 web – click spanning tree, sta, information. Figure 3-99 displaying spanning tree information cli – this command displays global sta settings, followed by settings for each port. Note: the current root port and current root cost display as zero when this device is not ...
Page 227: Configuring Global Settings
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-171 3 configuring global settings global settings apply to the entire switch. Command usage • spanning tree protocol 12 uses rstp for the internal state machine, but sends only 802.1d bpdus. This creates one spanning tree instance for the entire network. If mu...
Page 228
Configuring the switch 3-172 3 • priority – bridge priority is used in selecting the root device, root port, and designated port. The device with the highest priority becomes the sta root device. However, if all devices have the same priority, the device with the lowest mac address will then become ...
Page 229
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-173 3 configuration settings for rstp the following attributes apply to both rstp and mstp: • path cost method – the path cost is used to determine the best path between devices. The path cost method is used to determine the range of values that can be assigne...
Page 230
Configuring the switch 3-174 3 web – click spanning tree, sta, configuration. Modify the required attributes, and click apply. Figure 3-100 configuring spanning tree.
Page 231
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-175 3 cli – this example enables spanning tree protocol, sets the mode to mst, and then configures the sta and mstp parameters. Displaying interface settings the sta port information and sta trunk information pages display the current status of ports and trunk...
Page 232
Configuring the switch 3-176 3 • designated port – the port priority and number of the port on the designated bridging device through which this switch must communicate with the root of the spanning tree. • oper link type – the operational point-to-point status of the lan segment attached to this in...
Page 233
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-177 3 should be assigned to ports attached to faster media, and higher values assigned to ports with slower media. (path cost takes precedence over port priority.) • internal admin path cost – the path cost for the mst. See the preceding item. • priority – def...
Page 234
Configuring the switch 3-178 3 cli – this example shows the sta attributes for port 5. Configuring interface settings you can configure rstp attributes for specific interfaces, including port priority, path cost, link type, and edge port. You may use a different priority or path cost for ports of th...
Page 235
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-179 3 the following interface attributes can be configured: • spanning tree – enables/disables sta on this interface. (default: enabled). • bpdu flooding - enables/disables the flooding of bpdus to other ports when global spanning tree is disabled (page 3-171)...
Page 236
Configuring the switch 3-180 3 • admin link type – the link type attached to this interface. - point-to-point – a connection to exactly one other bridge. - shared – a connection to two or more bridges. - auto – the switch automatically determines if the interface is attached to a point-to-point link...
Page 237
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-181 3 web – click spanning tree, sta, port configuration or trunk configuration. Modify the required attributes, then click apply. Figure 3-102 configuring spanning tree per port cli – this example sets sta attributes for port 7. Configuring multiple spanning ...
Page 238
Configuring the switch 3-182 3 note: all vlans are automatically added to the ist (instance 0). To ensure that the msti maintains connectivity across the network, you must configure a related set of bridges with the same msti settings. Command attributes • mst instance – instance identifier of this ...
Page 239
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-183 3 cli – this example sets the priority for msti 1, and adds vlan 1 to this msti. It then displays the sta settings for instance 1, followed by settings for each port. Console(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration 4-233 console(config-mst)#mst 1 priority ...
Page 240
Configuring the switch 3-184 3 displaying interface settings for mstp the mstp port information and mstp trunk information pages display the current status of ports and trunks in the selected mst instance. Command attributes • mst instance id – instance identifier to configure. (default: 0) note: th...
Page 241
Spanning tree algorithm configuration 3-185 3 cli – this displays sta settings for instance 0, followed by settings for each port. The settings for instance 0 are global settings that apply to the ist, the settings for other instances only apply to the local spanning tree. Console#show spanning-tree...
Page 242
Configuring the switch 3-186 3 configuring interface settings for mstp you can configure the sta interface settings for an mst instance using the mstp port configuration and mstp trunk configuration pages. Field attributes the following attributes are read-only and cannot be changed: • sta state – d...
Page 243: Vlan Configuration
Vlan configuration 3-187 3 web – click spanning tree, mstp, port configuration or trunk configuration. Enter the priority and path cost for an interface, and click apply. Figure 3-105 displaying mstp interface settings cli – this example sets the mstp attributes for port 4. Vlan configuration ieee 8...
Page 244
Configuring the switch 3-188 3 this switch supports the following vlan features: • up to 255 vlans based on the ieee 802.1q standard • distributed vlan learning across multiple switches using explicit or implicit tagging and gvrp protocol • port overlapping, allowing a port to participate in multipl...
Page 245
Vlan configuration 3-189 3 untagged vlans – untagged (or static) vlans are typically used to reduce broadcast traffic and to increase security. A group of network users assigned to a vlan form a broadcast domain that is separate from other vlans configured on the switch. Packets are forwarded only b...
Page 246
Configuring the switch 3-190 3 forwarding tagged/untagged frames if you want to create a small port-based vlan for devices attached directly to a single switch, you can assign ports to the same untagged vlan. However, to participate in a vlan group that crosses several switches, you should create a ...
Page 247
Vlan configuration 3-191 3 displaying basic vlan information the vlan basic information page displays basic information on the vlan type supported by the switch. Field attributes • vlan version number 16 – the vlan version used by this switch as specified in the ieee 802.1q standard. • maximum vlan ...
Page 248
Configuring the switch 3-192 3 displaying current vlans the vlan current table shows the current port members of each vlan and whether or not the port supports vlan tagging. Ports assigned to a large vlan group that crosses several switches should use vlan tagging. However, if you just want to creat...
Page 249
Vlan configuration 3-193 3 • name – name of the vlan (1 to 32 characters). • status – shows if this vlan is enabled or disabled. - active: vlan is operational. - suspend: vlan is suspended; i.E., does not pass packets. • ports / channel groups – shows the vlan interface members. Cli – current vlan i...
Page 250
Configuring the switch 3-194 3 web – click vlan, 802.1q vlan, static list. To create a new vlan, enter the vlan id and vlan name, mark the enable checkbox to activate the vlan, and then click add. Figure 3-109 configuring a vlan static list cli – this example creates a new vlan. Console(config)#vlan...
Page 251
Vlan configuration 3-195 3 adding static members to vlans (vlan index) use the vlan static table to configure port members for the selected vlan index. Assign ports as tagged if they are connected to 802.1q vlan compliant devices, or untagged they are not connected to any vlan-aware devices. Or conf...
Page 252
Configuring the switch 3-196 3 web – click vlan, 802.1q vlan, static table. Select a vlan id from the scroll-down list. Modify the vlan name and status if required. Select the membership type by marking the appropriate radio button in the list of ports or trunks. Click apply. Figure 3-110 configurin...
Page 253
Vlan configuration 3-197 3 adding static members to vlans (port index) use the vlan static membership by port menu to assign vlan groups to the selected interface as a tagged member. Command attributes • interface – port or trunk identifier. • member – vlans for which the selected interface is a tag...
Page 254
Configuring the switch 3-198 3 configuring vlan behavior for interfaces you can configure vlan behavior for specific interfaces, including the default vlan identifier (pvid), accepted frame types, ingress filtering, gvrp status, and garp timers. Command usage • gvrp – garp vlan registration protocol...
Page 255
Vlan configuration 3-199 3 • garp leave timer 17 – the interval a port waits before leaving a vlan group. This time should be set to more than twice the join time. This ensures that after a leave or leaveall message has been issued, the applicants can rejoin before the port actually leaves the group...
Page 256
Configuring the switch 3-200 3 web – click vlan, 802.1q vlan, port configuration or trunk configuration. Fill in the required settings for each interface, click apply. Figure 3-112 configuring vlans per port cli – this example sets port 3 to accept only tagged frames, assigns pvid 3 as the native vl...
Page 257
Vlan configuration 3-201 3 qinq tunneling uses a single service provider vlan (spvlan) for customers who have multiple vlans. Customer vlan ids are preserved and traffic from different customers is segregated within the service provider’s network even when they use the same customer-specific vlan id...
Page 258
Configuring the switch 3-202 3 process transmits the packet. Packets entering a qinq tunnel port are processed in the following manner: 1. New spvlan tags are added to all incoming packets, no matter how many tags they already have. The ingress process constructs and inserts the outer tag (spvlan) i...
Page 259
Vlan configuration 3-203 3 4. After successful source and destination lookups, the packet is double tagged. The switch uses the tpid of 0x8100 to indicate that an incoming packet is double-tagged. If the outer tag of an incoming double-tagged packet is equal to the port tpid and the inner tag is 0x8...
Page 260
Configuring the switch 3-204 3 5. Configure the qinq tunnel access port to join the spvlan as an untagged member (see “adding static members to vlans (vlan index)” on page 3-195). 6. Configure the spvlan id as the native vid on the qinq tunnel access port (see “configuring vlan behavior for interfac...
Page 261
Vlan configuration 3-205 3 cli – this example sets the switch to operate in qinq mode. Adding an interface to a qinq tunnel follow the guidelines in the preceding section to set up a qinq tunnel on the switch. Use the vlan port configuration or vlan trunk configuration screen to set the access port ...
Page 262: Traffic Segmentation
Configuring the switch 3-206 3 web – click vlan, 802.1q vlan, 802.1q tunnel configuration or tunnel trunk configuration. Set the mode for a tunnel access port to 802.1q tunnel and a tunnel uplink port to 802.1q tunnel uplink. Click apply. Figure 3-114 tunnel port configuration cli – this example set...
Page 263
Vlan configuration 3-207 3 configuring global settings for traffic segmentation use the traffic segmentation status page to enable traffic segmentation, and to block or forward traffic between uplink ports assigned to different client sessions. Command attributes • traffic segmentation status – enab...
Page 264
Configuring the switch 3-208 3 web – click vlan, traffic segmentation, session configuration. Set the session number, specify whether an uplink or downlink is to be used, select the interface, and click apply. Figure 3-116 traffic segmentation session configuration cli – this example enables traffic...
Page 265: Private Vlans
Vlan configuration 3-209 3 private vlans private vlans provide port-based security and isolation between ports within the assigned vlan. This switch supports private vlans with primary/secondary associated groups. A primary vlan contains promiscuous ports that can communicate with all other ports in...
Page 266
Configuring the switch 3-210 3 web – click vlan, private vlan, information. Select the desired port from the vlan id drop-down menu. Figure 3-117 private vlan information cli – this example shows the switch configured with primary vlan 5 and secondary vlan 6. Port 3 has been configured as a promiscu...
Page 267
Vlan configuration 3-211 3 web – click vlan, private vlan, configuration. Enter the vlan id number, select primary or community type, then click add. To remove a private vlan from the switch, highlight an entry in the current list box and then click remove. Note that all member ports must be removed...
Page 268
Configuring the switch 3-212 3 cli – this example associates community vlans 6 and 7 with primary vlan 5. Displaying private vlan interface information use the private vlan port information and private vlan trunk information menus to display the interfaces associated with private vlans. Command attr...
Page 269
Vlan configuration 3-213 3 cli – this example shows the switch configured with primary vlan 5 and community vlan 6. Port 3 has been configured as a promiscuous port and mapped to vlan 5, while ports 4 and 5 have been configured as host ports and associated with vlan 6. This means that traffic for po...
Page 270: Protocol Vlans
Configuring the switch 3-214 3 web – click vlan, private vlan, port configuration or trunk configuration. Set the pvlan port type for each port that will join a private vlan. Assign promiscuous ports to a primary vlan. Assign host ports to a community vlan. After all the ports have been configured, ...
Page 271
Vlan configuration 3-215 3 command usage to configure protocol-based vlans, follow these steps: 1. First configure vlan groups for the protocols you want to use (page 3-193). Although not mandatory, we suggest configuring a separate vlan for each major protocol running on your network. Do not add po...
Page 272
Configuring the switch 3-216 3 cli – this example shows the switch configured with protocol group 2 which matches rfc 1042 ip traffic. Configuring the protocol vlan system use the protocol vlan system configuration menu to map a protocol vlan group to a vlan. Command usage when a frame enters a port...
Page 273
Link layer discovery protocol 3-217 3 link layer discovery protocol link layer discovery protocol (lldp) is used to discover basic information about neighboring devices on the local broadcast domain. Lldp is a layer 2 protocol that uses periodic broadcasts to advertise information about the sending ...
Page 274
Configuring the switch 3-218 3 this attribute must comply with the rule: (4 * delay interval) ≤ transmission interval • reinitialization delay – configures the delay before attempting to re-initialize after lldp ports are disabled or the link goes down. (range: 1-10 seconds; default: 2 seconds) when...
Page 275
Link layer discovery protocol 3-219 3 cli – this example sets several attributes which control basic lldp message timing. Configuring lldp interface attributes use the lldp port/trunk configuration to specify the message attributes for individual interfaces, including whether messages are transmitte...
Page 276
Configuring the switch 3-220 3 • tlv type – configures the information included in the tlv field of advertised messages. - port description – the port description is taken from the ifdescr object in rfc 2863, which includes information about the manufacturer, the product name, and the version of the...
Page 277
Link layer discovery protocol 3-221 3 power (the endpoint device could use this information to decide to enter power conservation mode). Note that this device does not support poe capabilities. - inventory – this option advertises device details useful for inventory management, such as manufacturer,...
Page 278
Configuring the switch 3-222 3 cli – this example sets the interface to both transmit and receive lldp messages, enables snmp trap messages, enables med notification, and specifies the tlv, med-tlv, dot1-tlv and dot3-tlv parameters to advertise. Displaying lldp local device information use the lldp ...
Page 279
Link layer discovery protocol 3-223 3 • chassis id – an octet string indicating the specific identifier for the particular chassis in this system. • system name – an string that indicates the system’s administratively assigned name (see “displaying system information” on page 3-12). • system descrip...
Page 280
Configuring the switch 3-224 3 web – click lldp, local information. Figure 3-126 lldp local device information cli – this example displays lldp information for the local switch. Console#show lldp info local-device 4-305 lldp local system information chassis type : mac address chassis id : 00-01-02-0...
Page 281
Link layer discovery protocol 3-225 3 this example displays detailed information for a specific port on the local switch. Displaying lldp remote port information use the lldp remote port/trunk information screen to display information about devices connected directly to the switch’s ports which are ...
Page 282
Configuring the switch 3-226 3 displaying lldp remote information details use the lldp remote information details screen to display detailed information about an lldp-enabled device connected to a specific port on the local switch. Field attributes • local port – the local port to which a remote lld...
Page 283
Link layer discovery protocol 3-227 3 web – click lldp, remote information details. Select an interface from the drop down lists, and click query. Figure 3-128 lldp remote information details cli – this example displays lldp information for an lldp-enabled remote device attached to a specific port o...
Page 284
Configuring the switch 3-228 3 displaying device statistics use the lldp device statistics screen to general statistics for lldp-capable devices attached to the switch, and for lldp protocol messages transmitted or received on all local interfaces. Field attributes general statistics on remote devic...
Page 285
Link layer discovery protocol 3-229 3 cli – this example displays lldp statistics received from all lldp-enabled remote devices connected directly to this switch. Displaying detailed device statistics use the lldp device statistics details screen to display detailed statistics for lldp-capable devic...
Page 286
Configuring the switch 3-230 3 web – click lldp, device statistics details. Figure 3-130 lldp device statistics details cli – this example displays detailed lldp statistics for an lldp-enabled remote device attached to a specific port on this switch. Class of service configuration class of service (...
Page 287: Layer 2 Queue Settings
Class of service configuration 3-231 3 layer 2 queue settings setting the default priority for interfaces you can specify the default port priority for each interface on the switch. All untagged packets entering the switch are tagged with the specified default port priority, and then sorted into the...
Page 288
Configuring the switch 3-232 3 cli – this example assigns a default priority of 5 to port 3. Mapping cos values to egress queues this switch processes class of service (cos) priority tagged traffic by using four egress queues for each port, with service schedules based on strict or weighted round ro...
Page 289
Class of service configuration 3-233 3 command attributes • priority – cos value. (range: 0-7, where 7 is the highest priority) • traffic class 19 – output queue buffer. (range: 0-3, where 3 is the highest cos priority queue) web – click priority, traffic classes. The current mapping of cos values t...
Page 290
Configuring the switch 3-234 3 selecting the queue mode you can set the switch to service the queues based on a strict rule that requires all traffic in a higher priority queue to be processed before lower priority queues are serviced, or use weighted round-robin (wrr) queuing that specifies a relat...
Page 291: Layer 3/4 Priority Settings
Class of service configuration 3-235 3 note: this switch does not allow the queue service weights to be set. The weights are fixed as 1, 2, 4, 8, for queues 0 through 3 respectively. Command attributes • wrr setting table 20 –displays a list of weights for each traffic class (i.E., queue). • weight ...
Page 292
Configuring the switch 3-236 3 enabling ip dscp priority the switch allows you to enable or disable the ip dscp priority. Command attributes • ip dscp priority status – the following options are: - disabled – disables the priority service. (default setting: disabled) - ip dscp – maps layer 3/4 prior...
Page 293
Class of service configuration 3-237 3 mapping dscp priority the dscp is six bits wide, allowing coding for up to 64 different forwarding behaviors. The dscp retains backward compatibility with the three precedence bits so that non-dscp compliant devices will not conflict with the dscp mapping. Base...
Page 294: Quality Of Service
Configuring the switch 3-238 3 cli – the following example globally enables dscp priority service on the switch, maps dscp value 0 to cos value 1 (on port 1), and then displays the dscp priority settings. * mapping specific values for ip dscp is implemented as an interface configuration command, but...
Page 295
Quality of service 3-239 3 2. You should create a class map before creating a policy map. Otherwise, you will not be able to select a class map from the policy rule settings screen (see page 3-244). Configuring quality of service parameters to create a service policy for a specific category or ingre...
Page 296
Configuring the switch 3-240 3 • add class – opens the “class configuration” page. Enter a class name and description on this page, and click add to open the “match class settings” page. Enter the criteria used to classify ingress traffic on this page. • remove class – removes the selected class. Cl...
Page 297
Quality of service 3-241 3 web – click qos, diffserv, then click add class to create a new class, or edit rules to change the rules of an existing class. Figure 3-137 configuring class maps cli - this example creates a class map call “rd_class,” and sets it to match packets marked for dscp service v...
Page 298
Configuring the switch 3-242 3 creating qos policies this function creates a policy map that can be attached to multiple interfaces. Command usage • to configure a policy map, follow these steps: - create a class map as described on page 3-239. - open the policy map page, and click add policy. - whe...
Page 299
Quality of service 3-243 3 policy rule settings - class settings - • class name – name of class map. • action – shows the service provided to ingress traffic by setting a cos, dscp, or ip precedence value in a matching packet (as specified in match class settings on page 3-239). • meter – the maximu...
Page 300
Configuring the switch 3-244 3 web – click qos, diffserv, policy map to display the list of existing policy maps. To add a new policy map click add policy. To configure the policy rule settings click edit classes. Figure 3-138 configuring policy maps.
Page 301
Quality of service 3-245 3 cli – this example creates a policy map called “rd-policy,” sets the average bandwidth the 1 mbps, the burst rate to 1522 bps, and the response to reduce the dscp value for violating packets to 0. Attaching a policy map to ingress queues this function binds a policy map to...
Page 302: Voip Traffic Configuration
Configuring the switch 3-246 3 voip traffic configuration when ip telephony is deployed in an enterprise network, it is recommended to isolate the voice over ip (voip) network traffic from other data traffic. Traffic isolation can provide higher voice quality by preventing excessive packet delays, p...
Page 303
Quality of service 3-247 3 web – click qos, voip traffic setting, configuration. Enable auto detection, specify the voice vlan id, the set the voice vlan aging time. Click apply. Figure 3-140 configuring voip traffic cli – this example enables voip traffic detection and specifies the voice vlan id a...
Page 304
Configuring the switch 3-248 3 address oui numbers must be configured in the telephony oui list so that the switch recognizes the traffic as being from a voip device. • 802.1ab – uses lldp to discover voip devices attached to the port. Lldp checks that the “telephone bit” in the system capability tl...
Page 305
Quality of service 3-249 3 cli – this example configures voip traffic settings for port 2 and displays the current voice vlan status. Configuring telephony oui voip devices attached to the switch can be identified by the manufacturer’s organizational unique identifier (oui) in the source mac address...
Page 306
Configuring the switch 3-250 3 web – click qos, voip traffic setting, oui configuration. Enter a mac address that specifies the oui for voip devices in the network. Select a mask from the pull-down list to define a mac address range. Enter a description for the devices, then click add. Figure 3-142 ...
Page 307: Multicast Filtering
Multicast filtering 3-251 3 multicast filtering multicasting is used to support real-time applications such as videoconferencing or streaming audio. A multicast server does not have to establish a separate connection with each client. It merely broadcasts its service to the network, and any hosts th...
Page 308
Configuring the switch 3-252 3 layer 2 igmp (snooping and query) igmp snooping and query – if multicast routing is not supported on other switches in your network, you can use igmp snooping and query (page 3-253) to monitor igmp service requests passing between multicast clients and servers, and dyn...
Page 309
Multicast filtering 3-253 3 static igmp host interface – for multicast applications that you need to control more carefully, you can manually assign a multicast service to specific interfaces on the switch (page 3-259). Configuring igmp snooping and query parameters you can configure the switch to f...
Page 310
Configuring the switch 3-254 3 • igmp report delay — sets the time between receiving an igmp report for an ip multicast address on a port before the switch sends an igmp query out of that port and removes the entry from its list. (range: 5-25 seconds; default: 10) • igmp query timeout — the time the...
Page 311
Multicast filtering 3-255 3 cli – this example modifies the settings for multicast filtering, and then displays the current status. Enabling igmp immediate leave the switch can be configured to immediately delete a member port of a multicast service if a leave packet is received at that port and the...
Page 312
Configuring the switch 3-256 3 command attributes • vlan id – vlan identifier. (range: 1-4094). • immediate leave – sets the status for immediate leave on the specified vlan. (default: disabled) web – click igmp snooping, igmp immediate leave. Select the vlan interface to configure, set the status f...
Page 313
Multicast filtering 3-257 3 web – click igmp snooping, multicast router port information. Select the required vlan id from the scroll-down list to display the associated multicast routers. Figure 3-145 displaying multicast router port information cli – this example shows that port 11 has been static...
Page 314
Configuring the switch 3-258 3 web – click igmp snooping, static multicast router port configuration. Specify the interfaces attached to a multicast router, indicate the vlan which will forward all the corresponding multicast traffic, and then click add. After you have finished adding interfaces to ...
Page 315
Multicast filtering 3-259 3 web – click igmp snooping, ip multicast registration table. Select a vlan id and the ip address for a multicast service from the scroll-down lists. The switch will display all the interfaces that are propagating this multicast service. Figure 3-147 ip multicast registrati...
Page 316
Configuring the switch 3-260 3 • multicast ip – the ip address for a specific multicast service • port or trunk – specifies the interface attached to a multicast router/switch. Web – click igmp snooping, igmp member port table. Specify the interface attached to a multicast service (via an igmp-enabl...
Page 317
Multicast filtering 3-261 3 igmp throttling sets a maximum number of multicast groups that a port can join at the same time. When the maximum number of groups is reached on a port, the switch can take one of two actions; either “deny” or “replace”. If the action is set to deny, any new igmp join rep...
Page 318
Configuring the switch 3-262 3 configuring igmp filter profiles when you have created an igmp profile number, you can then configure the multicast groups to filter and set the access mode. Command usage • each profile has only one access mode; either permit or deny. • when the access mode is set to ...
Page 319
Multicast filtering 3-263 3 cli – this example configures profile number 19 by setting the access mode to “permit” and then specifying a range of multicast groups that a user can join. The current profile configuration is then displayed. Configuring igmp filtering and throttling for interfaces once ...
Page 320
Configuring the switch 3-264 3 web – click igmp snooping, igmp filter/throttling port configuration or igmp filter/throttling trunk configuration. Select a profile to assign to an interface, then set the throttling number and action. Click apply. Figure 3-151 igmp filter and throttling port configur...
Page 321: Multicast Vlan Registration
Multicast vlan registration 3-265 3 multicast vlan registration multicast vlan registration (mvr) is a protocol that controls access to a single network-wide vlan most commonly used for transmitting multicast traffic (such as television channels or video-on-demand) across a service provider’s networ...
Page 322
Configuring the switch 3-266 3 configuring global mvr settings the global settings for multicast vlan registration (mvr) include enabling or disabling mvr for the switch, selecting the vlan that will serve as the sole channel for common multicast streams supported by the service provider, and assign...
Page 323
Multicast vlan registration 3-267 3 web – click mvr, configuration. Enable mvr globally on the switch, select the mvr vlan, add the multicast groups that will stream traffic to attached hosts, and then click apply. Figure 3-152 mvr global configuration cli – this example first enables igmp snooping,...
Page 324
Configuring the switch 3-268 3 web – click mvr, port or trunk information. Figure 3-153 mvr port information cli – this example shows information about interfaces attached to the mvr vlan. Displaying port members of multicast groups you can display the multicast groups assigned to the mvr vlan eithe...
Page 325
Multicast vlan registration 3-269 3 web – click mvr, group ip information. Figure 3-154 mvr group ip information cli – this example following shows information about the interfaces associated with multicast groups assigned to the mvr vlan. Console#show mvr interface 4-344 mvr group ip status members...
Page 326
Configuring the switch 3-270 3 configuring mvr interface status each interface that participates in the mvr vlan must be configured as an mvr source port or receiver port. If only one subscriber attached to an interface is receiving multicast services, you can enable the immediate leave function. Co...
Page 327
Multicast vlan registration 3-271 3 - non-mvr – an interface that does not participate in the mvr vlan. (this is the default type.) • immediate leave – configures the switch to immediately remove an interface from a multicast stream as soon as it receives a leave message for that group. (this option...
Page 328
Configuring the switch 3-272 3 • the ip address range from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 is used for multicast streams. Mvr group addresses cannot fall within the reserved ip multicast address range of 224.0.0.X. Command attributes • interface – indicates a port or trunk. • member – shows the ip addr...
Page 329: Switch Clustering
Switch clustering 3-273 3 switch clustering switch clustering is a method of grouping switches together to enable centralized management through a single unit. Switches that support clustering can be grouped together regardless of physical location or switch type, as long as they are connected to th...
Page 330: Configuring Cluster Members
Configuring the switch 3-274 3 • cluster ip pool – an “internal” ip address pool that is used to assign ip addresses to member switches in the cluster. Internal cluster ip addresses are in the form 10.X.X.Member-id. Only the base ip address of the pool needs to be set since member ids can only be be...
Page 331
Switch clustering 3-275 3 web – click cluster, member configuration. Figure 3-159 cluster member configuration cli – this example creates a new cluster member by specifying the candidate switch mac address and setting a member id. Displaying information on cluster members use the cluster member info...
Page 332
Configuring the switch 3-276 3 web – click cluster, member information. Figure 3-160 cluster member information cli – this example shows information about cluster member switches. Displaying information on cluster candidates use the cluster candidate information page to display information about dis...
Page 333: Upnp
Upnp 3-277 3 cli – this example shows information about cluster candidate switches. Upnp universal plug and play (upnp) is a set of protocols that allows devices to connect seamlessly and simplifies the deployment of home and office networks. Upnp achieves this by issuing upnp device control protoco...
Page 334: Upnp Configuration
Configuring the switch 3-278 3 using upnp under windows vista – to access or manage the switch with the aid of upnp under windows vista, open the network and sharing center, and enable network discovery. Then click on the node representing your local network under the network sharing center. An entr...
Page 335
Upnp 3-279 3 cli – this example enables upnp, sets the device advertise duration to 200 seconds, the device ttl to 6, and displays information about basic upnp configuration. Console(config)#upnp device 4-78 console(config)#upnp device advertise duration 200 4-79 console(config)#upnp device ttl 6 4-...
Page 336
Configuring the switch 3-280 3 this page is intentionally left blank..
Page 337: Accessing The Cli
4-1 chapter 4: command line interface this chapter describes how to use the command line interface (cli). Using the command line interface accessing the cli when accessing the management interface for the switch over a direct connection to the server’s console port, or via a telnet connection, the s...
Page 338: Telnet Connection
Command line interface 4-2 4 telnet connection telnet operates over the ip transport protocol. In this environment, your management station and any network device you want to manage over the network must have a valid ip address. Valid ip addresses consist of four numbers, 0 to 255, separated by peri...
Page 339: Entering Commands
Entering commands 4-3 4 entering commands this section describes how to enter cli commands. Keywords and arguments a cli command is a series of keywords and arguments. Keywords identify a command, and arguments specify configuration parameters. For example, in the command “show interfaces status eth...
Page 340: Showing Commands
Command line interface 4-4 4 showing commands if you enter a “?” at the command prompt, the system will display the first level of keywords for the current command class (normal exec or privileged exec) or configuration class (global, acl, interface, line or vlan database). You can also display a li...
Page 341: Partial Keyword Lookup
Entering commands 4-5 4 the command “show interfaces ?” will display the following information: partial keyword lookup if you terminate a partial keyword with a question mark, alternatives that match the initial letters are provided. (remember not to leave a space between the command and question ma...
Page 342: Exec Commands
Command line interface 4-6 4 current mode. The command classes and associated modes are displayed in the following table: exec commands when you open a new console session on the switch with the user name and password “guest,” the system enters the normal exec command mode (or guest mode), displayin...
Page 343: Configuration Commands
Entering commands 4-7 4 configuration commands configuration commands are privileged level commands used to modify switch settings. These commands modify the running configuration only and are not saved when the switch is rebooted. To store the running configuration in non-volatile storage, use the ...
Page 344: Command Line Processing
Command line interface 4-8 4 for example, you can use the following commands to enter interface configuration mode, and then return to privileged exec mode command line processing commands are not case sensitive. You can abbreviate commands and parameters as long as they contain enough letters to di...
Page 345: Command Groups
Command groups 4-9 4 command groups the system commands can be broken down into the functional groups shown below . Table 4-4 command groups command group description page general basic commands for entering privileged access mode, restarting the system, or quitting the cli 4-10 system management di...
Page 346: General Commands
Command line interface 4-10 4 the access mode shown in the following tables is indicated by these abbreviations: acl (access control list configuration) mst (multiple spanning tree) cm (class map configuration) ne (normal exec) gc (global configuration) pe (privileged exec) ic (interface configurati...
Page 347
General commands 4-11 4 enable this command activates privileged exec mode. In privileged mode, additional commands are available, and certain commands display additional information. See “understanding command modes” on page 4-5. Syntax enable [level] level - privilege level to log into the device....
Page 348
Command line interface 4-12 4 example related commands enable (4-11) configure this command activates global configuration mode. You must enter this mode to modify any settings on the switch. You must also enter global configuration mode prior to enabling some of the other configuration modes, inclu...
Page 349
General commands 4-13 4 example in this example, the show history command lists the contents of the command history buffer: the ! Command repeats commands from the execution command history buffer when you are in normal exec or privileged exec mode, and commands from the configuration command histor...
Page 350
Command line interface 4-14 4 command usage this command resets the entire system. The switch will wait the designated amount of time before resetting. If a delayed reset has already been scheduled, then the newly configured reset will overwrite the original delay configuration. The configured delay...
Page 351
General commands 4-15 4 command mode global configuration example end this command returns to privileged exec mode. Default setting none command mode global configuration, interface configuration, line configuration, vlan database configuration, and multiple spanning tree configuration. Example this...
Page 352: System Management Commands
Command line interface 4-16 4 quit this command exits the configuration program. Default setting none command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage the quit and exit commands can both exit the configuration program. Example this example shows how to quit a cli session: system management co...
Page 353: Device Designation Commands
System management commands 4-17 4 device designation commands hostname this command specifies or modifies the host name for this device. Use the no form to restore the default host name. Syntax hostname name no hostname name - the name of this host. (maximum length: 255 characters) default setting n...
Page 354: Banner Information Commands
Command line interface 4-18 4 banner information commands these commands are used to configure and manage administrative information about the switch, its exact data center location, details of the electrical and network circuits that supply the switch, as well as contact information for the network...
Page 355
System management commands 4-19 4 command usage the administrator can batch-input all details for the switch with one command. When the administrator finishes typing the company name and presses the enter key, the script prompts for the next piece of information, and so on, until all information has...
Page 356
Command line interface 4-20 4 default setting none command mode global configuration command usage input strings cannot contain spaces. The banner configure company command interprets spaces as data input boundaries. The use of underscores ( _ ) or other unobtrusive non-letter characters is suggeste...
Page 357
System management commands 4-21 4 banner configure department this command is used to configure the department information displayed in the banner. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax banner configure department dept-name no banner configure company dept-name - the name of the dep...
Page 358
Command line interface 4-22 4 command mode global configuration command usage input strings cannot contain spaces. The banner configure equipment-info command interprets spaces as data input boundaries. The use of underscores ( _ ) or other unobtrusive non-letter characters is suggested for situatio...
Page 359
System management commands 4-23 4 banner configure ip-lan this command is used to configure the device ip address and subnet mask information displayed in the banner. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax banner configure ip-lan ip-mask no banner configure ip-lan ip-mask - the ip ad...
Page 360
Command line interface 4-24 4 example banner configure manager-info this command is used to configure the manager contact information displayed in the banner. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax banner configure manager-info name mgr1-name phone-number mgr1-number [name2 mgr2-name...
Page 361
System management commands 4-25 4 banner configure mux this command is used to configure the mux information displayed in the banner. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax banner configure mux muxinfo no banner configure mux muxinfo - the circuit and pvc to which the switch is conne...
Page 362
Command line interface 4-26 4 command usage input strings cannot contain spaces. The banner configure note command interprets spaces as data input boundaries. The use of underscores ( _ ) or other unobtrusive non-letter characters is suggested for situations where white space is necessary for clarit...
Page 363: System Status Commands
System management commands 4-27 4 system status commands this section describes commands used to display system information. Show startup-config this command displays the configuration file stored in non-volatile memory that is used to start up the system. Default setting none command mode privilege...
Page 364
Command line interface 4-28 4 - spanning tree settings - interface settings - any configured settings for the console port and telnet example related commands show running-config (4-29) console#show startup-config building startup-config, please wait... !00 !01_00-16-b6-f0-6f-fd_00 ! Phymap 00-16-b6...
Page 365
System management commands 4-29 4 show running-config this command displays the configuration information currently in use. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • use this command in conjunction with the show startup-config command to compare the information in running mem...
Page 366
Command line interface 4-30 4 example related commands show startup-config (4-27) console#show startup-config building startup-config, please wait... !00 !01_00-16-b6-f0-6f-fd_00 ! Phymap 00-16-b6-f0-6f-fd ! Sntp server 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 ! Ntp poll 16 ! No dot1q-tunnel system-tunnel-control ! ...
Page 367
System management commands 4-31 4 show system this command displays system information. Command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage • for a description of the items shown by this command, refer to “displaying system information” on page 3-12. • the post results should all display “pass.”...
Page 368
Command line interface 4-32 4 example show version this command displays hardware and software version information for the system. Command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage see “displaying switch hardware/software versions” on page 3-14 for detailed information on the items displayed b...
Page 369: Frame Size Commands
System management commands 4-33 4 show memory this command shows the location and size of free system memory. Command mode privileged exec example frame size commands this section describes commands used to configure the ethernet frame size on the switch. Jumbo frame this command enables support for...
Page 370: File Management Commands
Command line interface 4-34 4 connections, all devices in the collision domain would need to support jumbo frames. • the current setting for jumbo frames can be displayed with the show system command (page 4-31). Example file management commands managing firmware firmware can be uploaded and downloa...
Page 371
System management commands 4-35 4 copy this command moves (upload/download) a code image or configuration file between the switch’s flash memory and a tftp server. When you save the system code or configuration settings to a file on a tftp server, that file can later be downloaded to the switch to r...
Page 372
Command line interface 4-36 4 • the boot rom and loader cannot be uploaded or downloaded from the tftp server. You must follow the instructions in the release notes for new firmware, or contact your distributor for help. • for information on specifying an https-certificate, see “replacing the defaul...
Page 373
System management commands 4-37 4 the following example shows how to download a configuration file: this example shows how to copy a secure-site certificate from an tftp server. It then reboots the switch to activate the certificate: this example shows how to copy a public-key used by ssh from a tft...
Page 374
Command line interface 4-38 4 command usage • if the file type is used for system startup, then this file cannot be deleted. • “factory_default_config.Cfg” cannot be deleted. Example this example shows how to delete the test2.Cfg configuration file from flash memory. Related commands dir (4-38) dele...
Page 375
System management commands 4-39 4 example the following example shows how to display all file information: whichboot this command displays which files were booted when the system powered up. Command mode privileged exec example this example shows the information displayed by the whichboot command. S...
Page 376: Line Commands
Command line interface 4-40 4 command mode global configuration command usage • a colon (:) is required after the specified unit number and file type. • if the file contains an error, it cannot be set as the default file. Example related commands dir (4-38) whichboot (4-39) line commands you can acc...
Page 378
Command line interface 4-42 4 command usage • there are three authentication modes provided by the switch itself at login: - login selects authentication by a single global password as specified by the password line configuration command. When using this method, the management interface starts in no...
Page 379
System management commands 4-43 4 number of times a user can enter an incorrect password before the system terminates the line connection and returns the terminal to the idle state. • the encrypted password is required for compatibility with legacy password settings (i.E., plain text or encrypted) w...
Page 380
Command line interface 4-44 4 related commands silent-time (4-45) exec-timeout (4-14) exec-timeout this command sets the interval that the system waits until user input is detected. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax exec-timeout [seconds] no exec-timeout seconds - integer that specifies...
Page 381
System management commands 4-45 4 default setting the default value is three attempts. Command mode line configuration command usage • when the logon attempt threshold is reached, the system interface becomes silent for a specified amount of time before allowing the next logon attempt. (use the sile...
Page 383
System management commands 4-47 4 command usage communication protocols provided by devices such as terminals and modems often require a specific parity bit setting. Example to specify no parity, enter this command: speed this command sets the terminal line’s baud rate. This command sets both the tr...
Page 384
Command line interface 4-48 4 default setting 1 stop bit command mode line configuration example to specify 2 stop bits, enter this command: disconnect this command terminates an ssh, telnet, or console connection. Syntax disconnect session-id session-id – the session identifier for an ssh, telnet o...
Page 385: Event Logging Commands
System management commands 4-49 4 command mode normal exec, privileged exec example to show all lines, enter this command: event logging commands this section describes commands used to configure event logging on the switch. Logging on this command controls logging of error messages, sending debug o...
Page 386
Command line interface 4-50 4 command mode global configuration command usage the logging process controls error messages saved to switch memory or sent to remote syslog servers. You can use the logging history command to control the type of error messages that are stored in memory. You can use the ...
Page 387
System management commands 4-51 4 default setting flash: errors (level 3 - 0) ram: warnings (level 7 - 0) command mode global configuration command usage the message level specified for flash memory must be a higher priority (i.E., numerically lower) than that specified for ram. Example logging host...
Page 388
Command line interface 4-52 4 default setting 23 command mode global configuration command usage the command specifies the facility type tag sent in syslog messages. (see rfc 3164.) this type has no effect on the kind of messages reported by the switch. However, it may be used by the syslog server t...
Page 390
Command line interface 4-54 4 example the following example shows that system logging is enabled, the message level for flash memory is “errors” (i.E., default level 3 - 0), the message level for ram is “informational” (i.E., default level 7 - 0). The following example displays settings for the trap...
Page 392: Smtp Alert Commands
Command line interface 4-56 4 smtp alert commands these commands configure smtp event handling, and forwarding of alert messages to the specified smtp servers and email recipients. Logging sendmail host this command specifies smtp servers that will be sent alert messages. Use the no form to remove a...
Page 393
System management commands 4-57 4 logging sendmail level this command sets the severity threshold used to trigger alert messages. Syntax logging sendmail level level level - one of the system message levels (page 4-50). Messages sent include the selected level down to level 0. (range: 0-7; default: ...
Page 394
Command line interface 4-58 4 logging sendmail destination-email this command specifies the email recipients of alert messages. Use the no form to remove a recipient. Syntax [no] logging sendmail destination-email email-address email-address - the source email address used in alert messages. (range:...
Page 395: Time Commands
System management commands 4-59 4 example time commands the system clock can be dynamically set by polling a set of specified time servers (ntp or sntp). Maintaining an accurate time on the switch enables the system log to record meaningful dates and times for event entries. If the clock is not set,...
Page 396
Command line interface 4-60 4 sntp client this command enables sntp client requests for time synchronization from ntp or sntp time servers specified with the sntp servers command. Use the no form to disable sntp client requests. Syntax [no] sntp client default setting disabled command mode global co...
Page 397
System management commands 4-61 4 sntp server this command sets the ip address of the servers to which sntp time requests are issued. Use the this command with no arguments to clear all time servers from the current list. Syntax sntp server [ip1 [ip2 [ip3]]] ip - ip address of a time server (ntp or ...
Page 398
Command line interface 4-62 4 example related commands sntp client (4-60) show sntp this command displays the current time and configuration settings for the sntp client, and indicates whether or not the local time has been properly updated. Command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage th...
Page 399
System management commands 4-63 4 • this command enables client time requests to time servers specified via the ntp servers command. It issues time synchronization requests based on the interval set via the ntp poll command. • sntp and ntp clients cannot both be enabled at the same time. Example rel...
Page 400
Command line interface 4-64 4 example related commands ntp client (4-62) ntp poll (4-64) show ntp (4-66) ntp poll this command sets the interval between sending time requests when the switch is set to ntp client mode. Use the no form to restore to the default. Syntax ntp poll seconds no ntp poll sec...
Page 401
System management commands 4-65 4 command usage you can enable ntp authentication to ensure that reliable updates are received from only authorized ntp servers. The authentication keys and their associated key number must be centrally managed and manually distributed to ntp servers and clients. The ...
Page 402
Command line interface 4-66 4 example related commands ntp authenticate (4-64) show ntp this command displays the current time and configuration settings for the ntp client, and indicates whether or not the local time has been properly updated. Command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage...
Page 403
System management commands 4-67 4 clock timezone-predefined this command uses predefined time zone configurations to set the time zone for the switch’s internal clock. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax clock timezone-predefined offset-city no clock timezone-predefined • offset - select ...
Page 404
Command line interface 4-68 4 default setting none command mode global configuration command usage this command sets the local time zone relative to the coordinated universal time (utc, formerly greenwich mean time or gmt), based on the earth’s prime meridian, zero degrees longitude. To display a ti...
Page 405
System management commands 4-69 4 • e-minute - the minute summer-time will end. (range: 0-59 minutes) • offset - summer-time offset from the regular time zone, in minutes. (range: 0-99 minutes) default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • in some countries or regions, c...
Page 406
Command line interface 4-70 4 command usage • in some countries or regions, clocks are adjusted through the summer months so that afternoons have more daylight and mornings have less. This is known as summer time, or daylight savings time (dst). Typically, clocks are adjusted forward one hour at the...
Page 407
System management commands 4-71 4 • b-hour - the hour when summer-time will begin. (range: 0-23 hours) • b-minute - the minute when summer-time will begin. (range: 0-59 minutes) • e-week - the week of the month when summer-time will end. (range: 1-5) • e-day - the day of the week summer-time will en...
Page 409: Switch Cluster Commands
System management commands 4-73 4 switch cluster commands switch clustering is a method of grouping switches together to enable centralized management through a single unit. Switches that support clustering can be grouped together regardless of physical location or switch type, as long as they are c...
Page 410
Command line interface 4-74 4 command usage • to create a switch cluster, first be sure that clustering is enabled on the switch (the default is enabled), then set the switch as a cluster commander. Set a cluster ip pool that does not conflict with any other ip subnets in the network. Cluster ip add...
Page 411
System management commands 4-75 4 cluster ip-pool this command sets the cluster ip address pool. Use the no form to reset to the default address. Syntax cluster ip-pool ip-address no cluster ip-pool ip-address - the base ip address for ip addresses assigned to cluster members. The ip address must st...
Page 412
Command line interface 4-76 4 command usage • the maximum number of cluster members is 36. • the maximum number of switch candidates is 100 . Example rcommand this command provides access to a cluster member cli for configuration. Syntax rcommand id member-id member-id - the id number of the member ...
Page 413: Upnp Commands
System management commands 4-77 4 show cluster members this command shows the current switch cluster members. Command mode privileged exec example show cluster candidates this command shows the discovered candidate switches in the network. Command mode privileged exec example upnp commands universal...
Page 414
Command line interface 4-78 4 upnp device this command enables upnp on the device. Use the no form to disable upnp. Syntax [no] upnp device default setting enabled command mode global configuration command usage you must enable upnp before you can configure time out settings for sending of upnp mess...
Page 415
System management commands 4-79 4 example in the following example, the ttl is set to 6. Upnp device advertise duration this command sets the duration for which a device will advertise its presence on the local network. Syntax upnp device advertise duration value value - a time out value expressed i...
Page 417
System management commands 4-81 4 an 802.1x system event occurs. When debugging is enabled for the packet classification, debug messages will be shown when the switch sends or receives an eapol packet. • use the debug dot1x show state-machine command to show debug messages for all state-machine rela...
Page 418
Command line interface 4-82 4 when the debug state-machine option is selected, messages similar to those shown below are displayed when a change occurs in the state-machine. Debug radius this command configures debug settings for radius processes. Use the no form to disable debug mode for radius. Sy...
Page 419
System management commands 4-83 4 command mode privileged exec command usage • use the debug radius command without any classification or feature to enable debugging for all radius processes. • use the debug radius all command to enable debugging for all of the classification options (i.E., config, ...
Page 420
Command line interface 4-84 4 when the debug packet option is selected, messages similar to those shown below are displayed when a radius reply packet is received. Debug tacacs this command configures debug settings for tacacs processes. Use the no form to disable debug mode for tacacs. Syntax [no] ...
Page 421
System management commands 4-85 4 tacacs configuration commands are entered. When debugging is enabled for the database classification, debug messages will be shown when a memory operation is applied to the tacacs database. When debugging is enabled for the event classification, debug messages will ...
Page 422: Snmp Commands
Command line interface 4-86 4 snmp commands controls access to this switch from management stations using the simple network management protocol (snmp), as well as the error types sent to trap managers. Snmp version 3 also provides security features that cover message integrity, authentication, and ...
Page 423
Snmp commands 4-87 4 example show snmp this command can be used to check the status of snmp communications. Default setting none command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage this command provides information on the community access strings, counter information for snmp input and output pr...
Page 425
Snmp commands 4-89 4 related commands snmp-server location (4-89) snmp-server location this command sets the system location string. Use the no form to remove the location string. Syntax snmp-server location text no snmp-server location text - string that describes the system location. (maximum leng...
Page 427
Snmp commands 4-91 4 command to enable the sending of traps or informs and to specify which snmp notifications are sent globally. For a host to receive notifications, at least one snmp-server enable traps command and the snmp-server host command for that host must be enabled. • some notification typ...
Page 428
Command line interface 4-92 4 related commands snmp-server enable traps (4-92) snmp-server enable traps this command enables this device to send simple network management protocol traps or informs (i.E., snmp notifications). Use the no form to disable snmp notifications. Syntax [no] snmp-server enab...
Page 430
Command line interface 4-94 4 related commands snmp-server host (4-90) show snmp engine-id this command shows the snmp engine id. Command mode privileged exec example this example shows the default engine id. Snmp-server view this command adds an snmp view which controls user access to the mib. Use ...
Page 431
Snmp commands 4-95 4 command usage • views are used in the snmp-server group command to restrict user access to specified portions of the mib tree. • the predefined view “defaultview” includes access to the entire mib tree. Examples this view includes mib-2. This view includes the mib-2 interfaces t...
Page 433
Snmp commands 4-97 4 show snmp group four default groups are provided – snmpv1 read-only access and read/write access, and snmpv2c read-only access and read/write access. Command mode privileged exec example console#show snmp group group name: r&d security model: v3 read view: defaultview write view...
Page 435
Snmp commands 4-99 4 command usage • the snmp engine id is used to compute the authentication/privacy digests from the password. You should therefore configure the engine id with the snmp-server engine-id command before using this configuration command. • before you configure a remote user, use the ...
Page 436: Authentication Commands
Command line interface 4-100 4 authentication commands you can configure this switch to authenticate users logging into the system for management access using local or radius authentication methods. You can also enable port-based authentication for network client access using ieee 802.1x. User accou...
Page 437
Authentication commands 4-101 4 username this command adds named users, requires authentication at login, specifies or changes a user's password (or specify that no password is required), or specifies or changes a user's access level. Use the no form to remove a user name. Syntax username name {acce...
Page 438
Command line interface 4-102 4 example this example shows how to set the access level and password for a user. Enable password after initially logging onto the system, you should set the privileged exec password. Remember to record it in a safe place. This command controls access to the privileged e...
Page 439: Authentication Sequence
Authentication commands 4-103 4 authentication sequence three authentication methods can be specified to authenticate users logging into the system for management access. The commands in this section can be used to define the authentication method and sequence. Authentication login this command defi...
Page 440
Command line interface 4-104 4 related commands username - for setting the local user names and passwords (4-101) authentication enable this command defines the authentication method and precedence to use when changing from exec command mode to privileged exec command mode with the enable command (s...
Page 441: Radius Client
Authentication commands 4-105 4 radius client remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) is a logon authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to radius-aware devices on the network. An authentication server contains a database of multiple user ...
Page 442
Command line interface 4-106 4 command mode global configuration example radius-server auth-port this command sets the radius server network port for authentication messages. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax radius-server auth-port port_number no radius-server auth-port port_number - r...
Page 443
Authentication commands 4-107 4 radius-server attribute 4 this command sets the ip address of the network access server (nas) to use in the attribute 4 address field in packets sent to the radius server. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax radius-server attribute 4 nas_ip_address ...
Page 444
Command line interface 4-108 4 command mode global configuration example radius-server retransmit this command sets the number of retries. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax radius-server retransmit number_of_retries no radius-server retransmit number_of_retries - number of times the swi...
Page 445: Tacacs+ Client
Authentication commands 4-109 4 show radius-server this command displays the current settings for the radius server. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example tacacs+ client terminal access controller access control system (tacacs+) is a logon authentication protocol that uses softwa...
Page 446
Command line interface 4-110 4 tacacs-server host this command specifies a tacacs+ server. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax [no] tacacs-server index host {host_ip_address} [port port_number] [timeout timeout] [retransmit retransmit] [key key] • index - specifies the index number of the...
Page 447
Authentication commands 4-111 4 example tacacs-server key this command sets the tacacs+ encryption key. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax tacacs-server key key_string no tacacs-server key key_string - encryption key used to authenticate logon access for the client. Do not use blank spac...
Page 448
Command line interface 4-112 4 tacacs-server timeout this command sets the interval between transmitting authentication requests to the tacacs+ server. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax tacacs-server timeout number_of_seconds no tacacs-server timeout number_of_seconds - number of second...
Page 449
Authentication commands 4-113 4 show tacacs-server this command displays the current settings for the tacacs+ server. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example console#show tacacs-server remote tacacs+ server configuration: global settings: communication key with tacacs+ server: serv...
Page 450: Aaa Commands
Command line interface 4-114 4 aaa commands the authentication, authorization, and accounting (aaa) feature provides the main framework for configuring access control on the switch. The aaa functions require the use of configured radius or tacacs+ servers in the network. Aaa group server use this co...
Page 455
Authentication commands 4-119 4 aaa accounting update this command enables the sending of periodic updates to the accounting server. Use the no form to disable accounting updates. Syntax aaa accounting update [periodic interval] no aaa accounting update interval - sends an interim accounting record ...
Page 459: Web Server Commands
Authentication commands 4-123 4 default setting none command mode privileged exec example web server commands this section describes commands used to configure web browser management access to the switch. Ip http port this command specifies the tcp port number used by the web browser interface. Use ...
Page 460
Command line interface 4-124 4 command mode global configuration example related commands ip http server (4-124) ip http server this command allows this device to be monitored or configured from a browser. Use the no form to disable this function. Syntax [no] ip http server default setting enabled c...
Page 461
Authentication commands 4-125 4 command usage • both http and https service can be enabled independently on the switch. However, you cannot configure the http and https servers to use the same udp port. • if you enable https, you must indicate this in the url that you specify in your browser: https:...
Page 462: Telnet Server Commands
Command line interface 4-126 4 default setting 443 command mode global configuration command usage • you cannot configure the http and https servers to use the same port. • if you change the https port number, clients attempting to connect to the https server must specify the port number in the url,...
Page 463: Secure Shell Commands
Authentication commands 4-127 4 example secure shell commands this section describes the commands used to configure the ssh server. However, note that you also need to install a ssh client on the management station when using this protocol to configure the switch. Note: the switch supports both ssh ...
Page 464
Command line interface 4-128 4 to use the ssh server, complete these steps: 1. Generate a host key pair – use the ip ssh crypto host-key generate command to create a host public/private key pair. 2. Provide host public key to clients – many ssh client programs automatically import the host public ke...
Page 465
Authentication commands 4-129 4 public key authentication – when an ssh client attempts to contact the switch, the ssh server uses the host key pair to negotiate a session key and encryption method. Only clients that have a private key corresponding to the public keys stored on the switch can access...
Page 466
Command line interface 4-130 4 • the ssh server uses dsa or rsa for key exchange when the client first establishes a connection with the switch, and then negotiates with the client to select either des (56-bit) or 3des (168-bit) for data encryption. • you must generate the host key before enabling t...
Page 467
Authentication commands 4-131 4 ip ssh authentication-retries this command configures the number of times the ssh server attempts to reauthenticate a user. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax ip ssh authentication-retries count no ip ssh authentication-retries count – the number o...
Page 470
Command line interface 4-134 4 example related commands ip ssh crypto host-key generate (4-132) show ip ssh this command displays the connection settings used when authenticating client access to the ssh server. Command mode privileged exec example show ssh this command displays the current ssh serv...
Page 472
Command line interface 4-136 4 example console#show public-key host host: rsa: 1024 35 1568499540186766925933394677505461732531367489083654725415020245593199868 5443583616519999233297817660658309586108259132128902337654680172627257141 34287629413011961955667825956641048695742788814620651941746772984...
Page 473: 802.1X Port Authentication
Authentication commands 4-137 4 802.1x port authentication the switch supports ieee 802.1x (dot1x) port-based access control that prevents unauthorized access to the network by requiring users to first submit credentials for authentication. Client authentication is controlled centrally by a radius s...
Page 474
Command line interface 4-138 4 dot1x default this command sets all configurable dot1x global and port settings to their default values. Command mode global configuration example dot1x max-req this command sets the maximum number of times the switch port will retransmit an eap request/identity packet...
Page 475
Authentication commands 4-139 4 default force-authorized command mode interface configuration example dot1x operation-mode this command allows single or multiple hosts (clients) to connect to an 802.1x-authorized port. Use the no form with no keywords to restore the default to single host. Use the n...
Page 476
Command line interface 4-140 4 dot1x re-authenticate this command forces re-authentication on all ports or a specific interface. Syntax dot1x re-authenticate [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - stack unit. (range: 1) - port - port number. (range: 1-28 on ies4028f/ies4028fp, 1-24 on i...
Page 477
Authentication commands 4-141 4 example related commands dot1x timeout re-authperiod (4-141) dot1x timeout quiet-period this command sets the time that a switch port waits after the max request count has been exceeded before attempting to acquire a new client. Use the no form to reset the default. S...
Page 478
Command line interface 4-142 4 example dot1x timeout tx-period this command sets the time that an interface on the switch waits during an authentication session before re-transmitting an eap packet. Use the no form to reset to the default value. Syntax dot1x timeout tx-period seconds no dot1x timeou...
Page 479
Authentication commands 4-143 4 example show dot1x this command shows general port authentication related settings on the switch or a specific interface. Syntax show dot1x [statistics] [interface interface] • statistics - displays dot1x status for each port. • interface • ethernet unit/port - unit -...
Page 480
Command line interface 4-144 4 - max-req – maximum number of times a port will retransmit an eap request/identity packet to the client before it times out the authentication session (page 4-138). - status – authorization status (authorized or not). - operation mode – shows if single or multiple host...
Page 481
Authentication commands 4-145 4 example console#show dot1x global 802.1x parameters system-auth-control: enable 802.1x port summary port name status operation mode mode authorized 1/1 disabled single-host forceauthorized n/a 1/2 enabled single-host auto yes . . . 1/24 disabled single-host forceautho...
Page 482
Command line interface 4-146 4 management ip filter commands this section describes commands used to configure ip management access to the switch. Management this command specifies the client ip addresses that are allowed management access to the switch through various protocols. Use the no form to ...
Page 484: General Security Measures
Command line interface 4-148 4 general security measures this switch supports many methods of segregating traffic for clients attached to each of the data ports, and for ensuring that only authorized clients gain access to the network. Private vlans and port-based authentication using ieee 802.1x ar...
Page 485: Port Security Commands
General security measures 4-149 4 port security commands these commands can be used to enable port security on a port. When using port security, the switch stops learning new mac addresses on the specified port when it has reached a configured maximum number. Only incoming traffic with source addres...
Page 486: Network Access
Command line interface 4-150 4 command usage • if you enable port security, the switch stops learning new mac addresses on the specified port when it has reached a configured maximum number. Only incoming traffic with source addresses already stored in the dynamic or static address table will be acc...
Page 487
General security measures 4-151 4 network-access aging use this command to enable aging for authenticated mac addresses stored in the secure mac address table. Use the no form of this command to disable address aging. Syntax [no] network-access aging default setting disabled command mode global conf...
Page 488
Command line interface 4-152 4 network-access mode use this command to enable network access authentication on a port. Use the no form of this command to disable network access authentication. Syntax [no] network-access mode mac-authentication default setting disabled command mode interface configur...
Page 489
General security measures 4-153 4 network-access max-mac-count use this command to set the maximum number of mac addresses that can be authenticated on a port interface via all forms of authentication. Use the no form of this command to restore the default. Syntax network-access max-mac-count count ...
Page 490
Command line interface 4-154 4 have same vlan configuration, or they are treated as an authentication failure. • if dynamic vlan assignment is enabled on a port and the radius server returns no vlan configuration, the authentication is still treated as a success, and the host assigned to the default...
Page 491
General security measures 4-155 4 mac-authentication reauth-time use this command to set the time period after which a connected mac address must be re-authenticated. Use the no form of this command to restore the default value. Syntax mac-authentication reauth-time seconds no mac-authentication rea...
Page 492
Command line interface 4-156 4 mac-authentication max-mac-count use this command to set the maximum number of mac addresses that can be authenticated on a port via 802.1x authentication or mac authentication. Use the no form of this command to restore the default. Syntax mac-authentication max-mac-c...
Page 493
General security measures 4-157 4 show network-access use this command to display the mac authentication settings for port interfaces. Syntax show network-access [interface interface] • interface - specifies a port interface. • ethernet unit/port - unit - this is unit 1. - port - port number. (range...
Page 495: Web Authentication
General security measures 4-159 4 web authentication web authentication allows stations to authenticate and access the network in situations where 802.1x or network access authentication methods are infeasible or impractical. The web authentication feature allows unauthenticated hosts to request and...
Page 496
Command line interface 4-160 4 default setting 3 login attempts command mode global configuration example web-auth quiet-period this command defines the amount of time a host must wait after exceeding the limit for failed login attempts, before it may attempt web authentication again. Use the no for...
Page 497
General security measures 4-161 4 command mode global configuration example web-auth system-auth-control this command globally enables web authentication for the switch. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax [no] web-auth system-auth-control default setting disabled command mode global conf...
Page 498
Command line interface 4-162 4 web-auth re-authenticate (port) this command ends all web authentication sessions connected to the port and forces the users to re-authenticate. Syntax web-auth re-authenticate interface interface • interface - specifies a port interface. • ethernet unit/port - unit - ...
Page 499
General security measures 4-163 4 show web-auth this command displays global web authentication parameters. Syntax show web-auth default setting none command mode privileged exec example show web-auth interface this command displays interface-specific web authentication parameters and statistics. Sy...
Page 500: Dhcp Snooping Commands
Command line interface 4-164 4 example show web-auth summary this command displays a summary of web authentication port parameters and statistics. Command mode privileged exec example dhcp snooping commands dhcp snooping allows a switch to protect a network from rogue dhcp servers or other devices w...
Page 501
General security measures 4-165 4 ip dhcp snooping this command enables dhcp snooping globally. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax [no] ip dhcp snooping default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • network traffic may be disrupted when malicious dhcp...
Page 502
Command line interface 4-166 4 port. If the received packet is a dhcp ack message, a dynamic dhcp snooping entry is also added to the binding table. - if dhcp snooping is enabled globally, and also enabled on the vlan where the dhcp packet is received, but the port is not trusted, it is processed as...
Page 503
General security measures 4-167 4 ip dhcp snooping vlan this command enables dhcp snooping on the specified vlan. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax [no] ip dhcp snooping vlan vlan-id vlan-id - id of a configured vlan (range: 1-4094) default setting disabled command mode global c...
Page 504
Command line interface 4-168 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • a trusted interface is an interface that is configured to receive only messages from within the network. An untrusted interface is an interface that is configured to receive messages from out...
Page 505
General security measures 4-169 4 command usage if mac address verification is enabled, and the source mac address in the ethernet header of the packet is not same as the client’s hardware address in the dhcp packet, the packet is dropped. Example this example enables mac address verification. Relat...
Page 506
Command line interface 4-170 4 example this example enables the dhcp snooping information option. Ip dhcp snooping information policy this command sets the dhcp snooping information option policy for dhcp client packets that include option 82 information. Syntax ip dhcp snooping information policy {...
Page 507
General security measures 4-171 4 example clear ip dhcp snooping database flash this command removes all dynamically learned snooping entries from flash memory. Command mode privileged exec example show ip dhcp snooping this command shows the dhcp snooping configuration settings. Command mode privil...
Page 508: Ip Source Guard Commands
Command line interface 4-172 4 ip source guard commands ip source guard is a security feature that filters ip traffic on network interfaces based on manually configured entries in the ip source guard table, or static and dynamic entries in the dhcp snooping table when enabled (see “dhcp snooping com...
Page 509
General security measures 4-173 4 • when enabled, traffic is filtered based upon dynamic entries learned via dhcp snooping, or static addresses configured in the source guard binding table. • table entries include a mac address, ip address, lease time, entry type (static-ip-sg-binding, dynamic-dhcp-...
Page 510
Command line interface 4-174 4 ip source-guard binding this command adds a static address to the source-guard binding table. Use the no form to remove a static entry. Syntax ip source-guard binding mac-address vlan vlan-id ip-address interface ethernet unit/port no ip source-guard binding mac-addres...
Page 511
General security measures 4-175 4 related commands ip source-guard (4-172) ip dhcp snooping (4-165) ip dhcp snooping vlan (4-167) show ip source-guard this command shows whether source guard is enabled or disabled on each interface. Command mode privileged exec example show ip source-guard binding t...
Page 512: Ip Acls
Command line interface 4-176 4 access control list commands access control lists (acl) provide packet filtering for ip frames (based on address, protocol, or layer 4 protocol port number or tcp control code) or any frames (based on mac address or ethernet type). To filter packets, first create an ac...
Page 515
Access control list commands 4-179 4 permit, deny (extended acl) this command adds a rule to an extended ip acl. The rule sets a filter condition for packets with specific source or destination ip addresses, protocol types, source or destination protocol ports, or tcp control codes. Use the no form ...
Page 516
Command line interface 4-180 4 “match” and 0 bits to indicate “ignore.” the bitmask is bitwise anded with the specified source ip address, and then compared with the address for each ip packet entering the port(s) to which this acl has been assigned. • the control-code bitmask is a decimal number (r...
Page 518: Mac Acls
Command line interface 4-182 4 example related commands show ip access-list (4-181) show ip access-group this command shows the ports assigned to ip acls. Command mode privileged exec example related commands ip access-group (4-181) mac acls the commands in this section configure acls based on hardw...
Page 519
Access control list commands 4-183 4 access-list mac this command adds a mac access list and enters mac acl configuration mode. Use the no form to remove the specified acl. Syntax [no] access-list mac acl_name acl_name – name of the acl. (maximum length: 16 characters) default setting none command m...
Page 521
Access control list commands 4-185 4 • protocol – a specific ethernet protocol number. (range: 600-fff hex.) • protocol-bitmask – protocol bitmask. (range: 600-fff hex.) default setting none command mode mac acl command usage • new rules are added to the end of the list. • the ethertype option can o...
Page 522
Command line interface 4-186 4 mac access-group this command binds a port to a mac acl. Use the no form to remove the port. Syntax mac access-group acl_name in • acl_name – name of the acl. (maximum length: 16 characters) • in – indicates that this list applies to ingress packets. Default setting no...
Page 523: Acl Information
Access control list commands 4-187 4 acl information show access-list this command shows all acls and associated rules, as well as all the user-defined masks. Command mode privileged exec example show access-group this command shows the port assignments of acls. Command mode privileged executive exa...
Page 524: Interface Commands
Command line interface 4-188 4 interface commands these commands are used to display or set communication parameters for an ethernet port, aggregated link, or vlan. Interface this command configures an interface type and enters interface configuration mode. Use the no form to remove a trunk. Syntax ...
Page 525
Interface commands 4-189 4 default setting none command mode global configuration example to specify port 24, enter the following command: description this command adds a description to an interface. Use the no form to remove the description. Syntax description string no description string - comment...
Page 526
Command line interface 4-190 4 default setting • auto-negotiation is enabled by default. • when auto-negotiation is disabled, the default speed-duplex setting for both 100base-tx and gigabit ethernet ports is 100full. Command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • the ...
Page 527
Interface commands 4-191 4 command usage • when auto-negotiation is enabled the switch will negotiate the best settings for a link based on the capabilities command. When auto-negotiation is disabled, you must manually specify the link attributes with the speed-duplex and flowcontrol commands. • if ...
Page 528
Command line interface 4-192 4 command usage when auto-negotiation is enabled with the negotiation command, the switch will negotiate the best settings for a link based on the capabilites command. When auto-negotiation is disabled, you must manually specify the link attributes with the speed-duplex ...
Page 529
Interface commands 4-193 4 • avoid using flow control on a port connected to a hub unless it is actually required to solve a problem. Otherwise back pressure jamming signals may degrade overall performance for the segment attached to the hub. Example the following example enables flow control on por...
Page 530
Command line interface 4-194 4 giga-phy-mode this command forces two connected ports in to a master/slave configuration to enable 1000base-t full duplex. Use the no form to restore the default mode. Syntax giga-phy-mode mode no giga-phy-mode mode • master - sets the selected port as master. • slave ...
Page 531
Interface commands 4-195 4 shutdown this command disables an interface. To restart a disabled interface, use the no form. Syntax [no] shutdown default setting all interfaces are enabled. Command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage this command allows you to disable a ...
Page 532
Command line interface 4-196 4 command usage • when traffic exceeds the threshold specified for broadcast and multicast or unknown unicast traffic, packets exceeding the threshold are dropped until the rate falls back down beneath the threshold. • due to an asic chip limitation in the ies4028fp and ...
Page 533
Interface commands 4-197 4 command usage statistics are only initialized for a power reset. This command sets the base value for displayed statistics to zero for the current management session. However, if you log out and back into the management interface, the statistics displayed will show the abs...
Page 534
Command line interface 4-198 4 example show interfaces counters this command displays interface statistics. Syntax show interfaces counters [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - stack unit. (range: 1) - port - port number. (range: 1-28 on ies4028f/ies4028fp, 1-24 on ies4024gp) • port-c...
Page 535
Interface commands 4-199 4 command usage if no interface is specified, information on all interfaces is displayed. For a description of the items displayed by this command, see “showing port statistics” on page 3-153. Example show interfaces switchport this command displays the administrative and op...
Page 536
Command line interface 4-200 4 command mode normal exec, privileged exec command usage if no interface is specified, information on all interfaces is displayed . Example this example shows the configuration setting for port 24. Console#show interfaces switchport ethernet 1/24 broadcast threshold: en...
Page 537
Interface commands 4-201 4 priority for untagged traffic indicates the default priority for untagged frames (page 4-286). Gvrp status shows if garp vlan registration protocol is enabled or disabled (page 4-250). Allowed vlan shows the vlans this interface has joined, where “(u)” indicates untagged a...
Page 538: Link Aggregation Commands
Command line interface 4-202 4 link aggregation commands ports can be statically grouped into an aggregate link (i.E., trunk) to increase the bandwidth of a network connection or to ensure fault recovery. Or you can use the link aggregation control protocol (lacp) to automatically negotiate a trunk ...
Page 539
Link aggregation commands 4-203 4 • stp, vlan, and igmp settings can only be made for the entire trunk via the specified port-channel. Dynamically creating a port channel – ports assigned to a common port channel must meet the following criteria: • ports must have the same lacp system priority. • po...
Page 540
Command line interface 4-204 4 lacp this command enables 802.3ad link aggregation control protocol (lacp) for the current interface. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [no] lacp default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage • the ports on both ends of an l...
Page 541
Link aggregation commands 4-205 4 example the following shows lacp enabled on ports 11-13. Because lacp has also been enabled on the ports at the other end of the links, the show interfaces status port-channel 1 command shows that trunk 1 has been established. Lacp system-priority this command confi...
Page 542
Command line interface 4-206 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage • port must be configured with the same system priority to join the same lag. • system priority is combined with the switch’s mac address to form the lag identifier. This identifier is used to indicate a spe...
Page 543
Link aggregation commands 4-207 4 • once the remote side of a link has been established, lacp operational settings are already in use on that side. Configuring lacp settings for the partner only applies to its administrative state, not its operational state, and will only take effect the next time a...
Page 546
Command line interface 4-210 4 command mode privileged exec example console#show lacp 1 counters port channel : 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- eth 1/11 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- lacpdus sent : 21 lacpdus rec...
Page 547
Link aggregation commands 4-211 4 console#show lacp 1 internal port channel : 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- oper key : 4 admin key : 0 eth 1/1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- lacpdus internal: 30 sec lacp system ...
Page 548
Command line interface 4-212 4 console#show lacp 1 neighbors port channel 1 neighbors ------------------------------------------------------------------------- eth 1/11 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- partner admin system id: 32768, 00-00-00-00-00-00 partner...
Page 549
Power over ethernet commands 4-213 4 power over ethernet commands the commands in this group control the power that can be delivered to attached poe devices through switch ports on the ies4028fp and ies4024gp. The switch’s power management enables total switch power and individual port power to be c...
Page 550
Command line interface 4-214 4 power mainpower maximum allocation this command defines a power budget for the switch (i.E., the power available to all switch ports). Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax power mainpower maximum allocation watts watts - the power budget for the switc...
Page 551
Power over ethernet commands 4-215 4 this switch can detect 802.3af compliant devices and the more recent 802.3af non-compliant devices that also reflect the test voltages back to the switch. It cannot detect other legacy devices that do not reflect back the test voltages. • for legacy devices to be...
Page 552
Command line interface 4-216 4 power inline maximum allocation this command limits the power allocated to specific ports. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax power inline maximum allocation milliwatts no power inline maximum allocation milliwatts - the maximum power budget for the...
Page 553
Power over ethernet commands 4-217 4 - if a device is connected to a critical or high-priority port and causes the switch to exceed its budget, port power is still be turned on if the switch can drop power to one or more lower-priority ports and keep within its budget. Power will be dropped from low...
Page 554
Command line interface 4-218 4 show power mainpower use this command to display the current power status for the switch. Command mode privileged exec example table 4-59 show power inline status parameters parameter description admin the power mode set on the port (see power inline on page -215) oper...
Page 556
Command line interface 4-220 4 example the following example configures the switch to mirror received packets from port 6 to 11: show port monitor this command displays mirror information. Syntax show port monitor [interface] interface - ethernet unit/port (source port) • unit - stack unit. (range: ...
Page 557: Rate Limit Commands
Rate limit commands 4-221 4 rate limit commands this function allows the network manager to control the maximum rate for traffic received on an interface. Rate limiting is configured on interfaces at the edge of a network to limit traffic into the network. Packets that exceed the acceptable amount o...
Page 558: Address Table Commands
Command line interface 4-222 4 address table commands these commands are used to configure the address table for filtering specified addresses, displaying current entries, clearing the table, or setting the aging time. Mac-address-table static this command maps a static address to a destination port...
Page 559
Address table commands 4-223 4 command usage the static address for a host device can be assigned to a specific port within a specific vlan. Use this command to add static addresses to the mac address table. Static addresses have the following characteristics: • static addresses will not be removed ...
Page 561
Address table commands 4-225 4 mac-address-table aging-time this command sets the aging time for entries in the address table. Use the no form to restore the default aging time. Syntax mac-address-table aging-time seconds no mac-address-table aging-time seconds - aging time. (range: 10-30000 seconds...
Page 562: Spanning Tree Commands
Command line interface 4-226 4 spanning tree commands this section includes commands that configure the spanning tree algorithm (sta) globally for the switch, and commands that configure sta for the selected interface. Table 4-64 spanning tree commands command function mode page spanning-tree enable...
Page 563
Spanning tree commands 4-227 4 spanning-tree this command enables the spanning tree algorithm globally for the switch. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [no] spanning-tree default setting spanning tree is enabled. Command mode global configuration command usage the spanning tree algorithm (sta) ...
Page 565
Spanning tree commands 4-229 4 example the following example configures the switch to use rapid spanning tree: spanning-tree forward-time this command configures the spanning tree bridge forward time globally for this switch. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax spanning-tree forward-time ...
Page 566
Command line interface 4-230 4 command mode global configuration command usage this command sets the time interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a configuration message. Example related commands spanning-tree forward-time (4-229) spanning-tree max-age (4-230) spanning-tree max-age ...
Page 567
Spanning tree commands 4-231 4 related commands spanning-tree forward-time (4-229) spanning-tree hello-time (4-229) spanning-tree priority this command configures the spanning tree priority globally for this switch. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax spanning-tree priority priority no sp...
Page 568
Command line interface 4-232 4 command mode global configuration command usage the spanning-tree system-bpdu-flooding command has no effect if bpdu flooding is disabled on a port (see the spanning-tree port-bpdu-flooding command, page 4-240). Example spanning-tree pathcost method this command config...
Page 569
Spanning tree commands 4-233 4 default setting 3 command mode global configuration command usage this command limits the maximum transmission rate for bpdus. Example spanning-tree mst configuration this command changes to multiple spanning tree (mst) configuration mode. Default setting • no vlans ar...
Page 570
Command line interface 4-234 4 command mode mst configuration command usage • use this command to group vlans into spanning tree instances. Mstp generates a unique spanning tree for each instance. This provides multiple pathways across the network, thereby balancing the traffic load, preventing wide...
Page 571
Spanning tree commands 4-235 4 • you can set this switch to act as the msti root device by specifying a priority of 0, or as the msti alternate device by specifying a priority of 16384. Example name this command configures the name for the multiple spanning tree region in which this switch is locate...
Page 572
Command line interface 4-236 4 command usage the mst region name (page 4-235) and revision number are used to designate a unique mst region. A bridge (i.E., spanning-tree compliant device such as this switch) can only belong to one mst region. And all bridges in the same region must be configured wi...
Page 573
Spanning tree commands 4-237 4 default setting enabled command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) example this example disables the spanning tree algorithm for port 5. Spanning-tree cost this command configures the spanning tree path cost for the specified interface. Use the no fo...
Page 574
Command line interface 4-238 4 default setting by default, the system automatically detects the speed and duplex mode used on each port, and configures the path cost according to the values shown below. Path cost “0” is used to indicate auto-configuration mode. When the short path cost method is sel...
Page 575
Spanning tree commands 4-239 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • this command defines the priority for the use of a port in the spanning tree algorithm. If the path cost for all ports on a switch are the same, the port with the highest priority (that is, l...
Page 576
Command line interface 4-240 4 related commands spanning-tree portfast (4-240) spanning-tree portfast this command sets an interface to fast forwarding. Use the no form to disable fast forwarding. Syntax [no] spanning-tree portfast default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (ether...
Page 577
Spanning tree commands 4-241 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • when enabled, bpdus are flooded to all other ports on the switch or to all other ports within the receiving port’s native vlan as specified by the spanning-tree system-bpdu-flooding command (...
Page 578
Command line interface 4-242 4 spanning-tree loopback-detection this command enables the detection and response to spanning tree loopback bpdu packets on the port. Use the no form to disable this feature. Syntax spanning-tree loopback-detection no spanning-tree loopback-detection default setting ena...
Page 579
Spanning tree commands 4-243 4 command usage • if the port is configured for automatic loopback release, then the port will only be returned to the forwarding state if one of the following conditions is satisfied: - the port receives any other bpdu except for it’s own, or; - the port’s link status c...
Page 580
Command line interface 4-244 4 spanning-tree mst cost this command configures the path cost on a spanning instance in the multiple spanning tree. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax spanning-tree mst instance_id cost cost no spanning-tree mst instance_id cost • instance_id - instance iden...
Page 581
Spanning tree commands 4-245 4 spanning-tree mst port-priority this command configures the interface priority on a spanning instance in the multiple spanning tree. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax spanning-tree mst instance_id port-priority priority no spanning-tree mst instance_id por...
Page 582
Command line interface 4-246 4 command mode privileged exec command usage if at any time the switch detects stp bpdus, including configuration or topology change notification bpdus, it will automatically set the selected interface to forced stp-compatible mode. However, you can also use the spanning...
Page 583
Spanning tree commands 4-247 4 items displayed for specific interfaces, see “displaying interface settings” on page 3-175. Example console#show spanning-tree spanning-tree information --------------------------------------------------------------- spanning tree mode: mstp spanning tree enable/disabl...
Page 584: Vlan Commands
Command line interface 4-248 4 show spanning-tree mst configuration this command shows the configuration of the multiple spanning tree. Command mode privileged exec example vlan commands a vlan is a group of ports that can be located anywhere in the network, but communicate as though they belong to ...
Page 585
Vlan commands 4-249 4 gvrp and bridge extension commands garp vlan registration protocol defines a way for switches to exchange vlan information in order to automatically register vlan members on interfaces across the network. This section describes how to enable gvrp for individual interfaces and g...
Page 586
Command line interface 4-250 4 show bridge-ext this command shows the configuration for bridge extension commands. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage see “displaying basic vlan information” on page 3-191 and “displaying bridge extension capabilities” on page 3-16 for a d...
Page 587
Vlan commands 4-251 4 show gvrp configuration this command shows if gvrp is enabled. Syntax show gvrp configuration [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - stack unit. (range: 1) - port - port number. (range: 1-28 on ies4028f/ies4028fp, 1-24 on ies4024gp) • port-channel channel-id (range...
Page 588
Command line interface 4-252 4 will consider whether or not other participants are also declaring this attribute. “in” permutations indicate that the sender does not look for other participants declaring this attribute, and simply assumes that there are such participants. Example clear gvrp statisti...
Page 590: Editing Vlan Groups
Command line interface 4-254 4 show garp timer this command shows the garp timers for the selected interface. Syntax show garp timer [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - stack unit. (range: 1) - port - port number. (range: 1-28 on ies4028f/ies4028fp, 1-24 on ies4024gp) • port-channel ...
Page 591
Vlan commands 4-255 4 command mode global configuration command usage • use the vlan database command mode to add, change, and delete vlans. After finishing configuration changes, you can display the vlan settings by entering the show vlan command. • use the interface vlan command mode to define the...
Page 592: Configuring Vlan Interfaces
Command line interface 4-256 4 • you can configure up to 255 vlans on the switch. Note: the switch allows 255 user-manageable vlans. One extra, unmanageable vlan (vlan id 4093) is maintained for switch clustering. Example the following example adds a vlan, using vlan id 105 and name rd5. The vlan is...
Page 593
Vlan commands 4-257 4 example the following example shows how to set the interface configuration mode to vlan 1, and then assign an ip address to the vlan: related commands shutdown (4-195) switchport mode this command configures the vlan membership mode for a port. Use the no form to restore the de...
Page 595
Vlan commands 4-259 4 • with ingress filtering enabled, a port will discard received frames tagged for vlans for it which it is not a member. • ingress filtering does not affect vlan independent bpdu frames, such as gvrp or sta. However, they do affect vlan dependent bpdu frames, such as gmrp. Examp...
Page 599
Vlan commands 4-263 4 configuring ieee 802.1q tunneling ieee 802.1q tunneling (qinq tunneling) uses a single service provider vlan (spvlan) for customers who have multiple vlans. Customer vlan ids are preserved and traffic from different customers is segregated within the service provider’s network ...
Page 600
Command line interface 4-264 4 reconfigured to overcome a break in the tree. It is therefore advisable to disable spanning tree on these ports. Dot1q-tunnel system-tunnel-control this command sets the switch to operate in qinq mode. Use the no form to disable qinq operating mode. Syntax [no] dot1q-t...
Page 601
Vlan commands 4-265 4 • when a tunnel uplink port receives a packet from a customer, the customer tag (regardless of whether there are one or more tag layers) is retained in the inner tag, and the service provider’s tag added to the outer tag. • when a tunnel uplink port receives a packet from the s...
Page 602
Command line interface 4-266 4 example related commands show interfaces switchport (4-199) show dot1q-tunnel this command displays information about qinq tunnel ports. Command mode privileged exec example related commands switchport dot1q-tunnel mode (4-264) console(config)#interface ethernet 1/1 co...
Page 603
Vlan commands 4-267 4 configuring port-based traffic segmentation if tighter security is required for passing traffic from different clients through downlink ports on the local network and over uplink ports to the service provider, port-based traffic segmentation can be used to isolate traffic for i...
Page 604
Command line interface 4-268 4 command usage • when traffic segmentation is enabled, the forwarding state for the uplink and downlink ports assigned to different client sessions is shown below. • when traffic segmentation is disabled, all ports operate in normal forwarding mode based on the settings...
Page 605
Vlan commands 4-269 4 command mode global configuration command usage • a port cannot be configured in both an uplink and downlink list. • a port can only be assigned to one traffic-segmentation session. • a downlink port can only communicate with an uplink port in the same session. Therefore, if an...
Page 607: Configuring Private Vlans
Vlan commands 4-271 4 configuring private vlans private vlans provide port-based security and isolation between ports within the assigned vlan. This switch supports two types of private vlans: primary/ secondary associated groups, and stand-alone isolated vlans. A primary vlan contains promiscuous p...
Page 608
Command line interface 4-272 4 4. Use the switchport private-vlan host-association command to assign a port to a secondary vlan. 5. Use the switchport private-vlan mapping command to assign a port to a primary vlan. 6. Use the show vlan private-vlan command to verify your configuration settings. Pri...
Page 610
Command line interface 4-274 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • to assign a promiscuous port to a primary vlan, use the switchport private-vlan mapping command. To assign a host port to a community vlan, use the private-vlan host association command. • to...
Page 611
Vlan commands 4-275 4 switchport private-vlan mapping use this command to map an interface to a primary vlan. Use the no form to remove this mapping. Syntax switchport private-vlan mapping primary-vlan-id no switchport private-vlan mapping primary-vlan-id – id of primary vlan. (range: 1-4094, no lea...
Page 612
Command line interface 4-276 4 example configuring protocol-based vlans the network devices required to support multiple protocols cannot be easily grouped into a common vlan. This may require non-standard devices to pass traffic between different vlans in order to encompass all the devices particip...
Page 613
Vlan commands 4-277 4 protocol-vlan protocol-group (configuring groups) this command creates a protocol group, or adds specific protocols to a group. Only one frame type and protocol type can be added to a protocol group. Use the no form to remove a protocol group. Syntax protocol-vlan protocol-grou...
Page 614
Command line interface 4-278 4 command usage • when creating a protocol-based vlan, do not assign interfaces to the protocol vlan via any of the standard vlan commands. If you assign interfaces using any of the other vlan commands (such as vlan on page 4-255), the switch will admit traffic of any pr...
Page 615: Configuring Voice Vlans
Vlan commands 4-279 4 show protocol-vlan protocol-group-vid this command shows the mapping from protocol groups to vlans. Syntax show protocol-vlan protocol-group-vid default setting the mapping for all protocol groups is displayed. Command mode privileged exec example this shows that traffic matchi...
Page 616
Command line interface 4-280 4 voice vlan this command enables voip traffic detection and defines the voice vlan id. Use the no form to disable the voice vlan. Syntax voice vlan voice-vlan-id no voice vlan voice-vlan-id - specifies the voice vlan id. (range: 1-4094) default setting disabled command ...
Page 617
Vlan commands 4-281 4 default setting 1440 minutes command mode global configuration command usage the voice vlan aging time is the time after which a port is removed from the voice vlan when voip traffic is no longer received on the port. Example the following example configures the voice vlan agin...
Page 618
Command line interface 4-282 4 • selecting a mask of ff-ff-ff-00-00-00 identifies all devices with the same oui (the first three octets). Other masks restrict the mac address range. Selecting ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff specifies a single mac address. Example the following example adds a mac oui to the oui te...
Page 620
Command line interface 4-284 4 command usage • security filtering discards any non-voip packets received on the port that are tagged with the voice vlan id. Voip traffic is identified by source mac addresses configured in the telephony oui list, or through lldp that discovers voip devices attached t...
Page 622: Lldp Commands
Command line interface 4-286 4 lldp commands link layer discovery protocol (lldp) is used to discover basic information about neighboring devices on the local broadcast domain. Lldp is a layer 2 protocol that uses periodic broadcasts to advertise information about the sending device. Advertised info...
Page 623
Lldp commands 4-287 4 * vendor-specific options may or may not be advertised by neighboring devices. Lldp basic-tlv system-name configures an lldp-enabled port to advertise its system name ic 4-296 lldp dot1-tlv proto-ident* configures an lldp-enabled port to advertise the supported protocols ic 4-2...
Page 624
Command line interface 4-288 4 lldp this command enables lldp globally on the switch. Use the no form to disable lldp. Syntax [no] lldp default setting enabled command mode global configuration example lldp holdtime-multiplier this command configures the time-to-live (ttl) value sent in lldp adverti...
Page 625
Lldp commands 4-289 4 lldp medfaststartcount this command specifies the amount of med fast start lldpdus to transmit during the activation process of the lldp-med fast start mechanism. Syntax lldp medfaststartcount packets seconds - amount of packets. (range: 1-10 packets; default: 4 packets) defaul...
Page 626
Command line interface 4-290 4 notification are included in the transmission. An snmp agent should therefore periodically check the value of lldpstatsremtablelastchangetime to detect any lldpremtableschange notification-events missed due to throttling or transmission loss. Example lldp refresh-inter...
Page 627
Lldp commands 4-291 4 command mode global configuration command usage when lldp is re-initialized on a port, all information in the remote systems lldp mib associated with this port is deleted. Example lldp tx-delay this command configures a delay between the successive transmission of advertisement...
Page 629
Lldp commands 4-293 4 therefore periodically check the value of lldpstatsremtablelastchangetime to detect any lldpremtableschange notification-events missed due to throttling or transmission loss. Example lldp mednotification this command enables the transmission of snmp trap notifications about lld...
Page 630
Command line interface 4-294 4 lldp basic-tlv management-ip-address this command configures an lldp-enabled port to advertise the management address for this device. Use the no form to disable this feature. Syntax [no] lldp basic-tlv management-ip-address default setting enabled command mode interfa...
Page 631
Lldp commands 4-295 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage the port description is taken from the ifdescr object in rfc 2863, which includes information about the manufacturer, the product name, and the version of the interface hardware/software. Example lldp b...
Page 632
Command line interface 4-296 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage the system description is taken from the sysdescr object in rfc 3418, which includes the full name and version identification of the system's hardware type, software operating system, and netwo...
Page 633
Lldp commands 4-297 4 command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage this option advertises the protocols that are accessible through this interface. Example lldp dot1-tlv proto-vid this command configures an lldp-enabled port to advertise port related vlan information. ...
Page 634
Command line interface 4-298 4 command usage the port’s default vlan identifier (pvid) indicates the vlan with which untagged or priority-tagged frames are associated (see “switchport native vlan” on page 4-259). Example lldp dot1-tlv vlan-name this command configures an lldp-enabled port to adverti...
Page 635
Lldp commands 4-299 4 command usage this option advertises link aggregation capabilities, aggregation status of the link, and the 802.3 aggregated port identifier if this interface is currently a link aggregation member. Example lldp dot3-tlv mac-phy this command configures an lldp-enabled port to a...
Page 636
Command line interface 4-300 4 command usage refer to “frame size commands” on page 4-33 for information on configuring the maximum frame size for this switch. Example lldp dot3-tlv poe this command configures an lldp-enabled port to advertise its power-over-ethernet (poe) capabilities. Use the no f...
Page 637
Lldp commands 4-301 4 command usage this option advertises extended power-over-ethernet capability details, such as power availability from the switch, and power state of the switch, including whether the switch is operating from primary or backup power (the endpoint device could use this informatio...
Page 638
Command line interface 4-302 4 command usage this option advertises location identification details. Example lldp medtlv med-cap this command configures an lldp-med-enabled port to advertise its media endpoint device capabilities. Use the no form to disable this feature. Syntax [no] lldp medtlv med-...
Page 639
Lldp commands 4-303 4 command usage this option advertises network policy configuration information, aiding in the discovery and diagnosis of vlan configuration mismatches on a port. Improper network policy configurations frequently result in voice quality degradation or complete service disruption....
Page 640
Command line interface 4-304 4 example console#show lldp config lldp global configuation lldp enable : yes lldp transmit interval : 30 lldp hold time multiplier : 4 lldp delay interval : 2 lldp reinit delay : 2 lldp notification interval : 5 lldp med fast start counts : 4 lldp port configuration int...
Page 641
Lldp commands 4-305 4 show lldp info local-device this command shows lldp global and interface-specific configuration settings for this device. Syntax show lldp info local-device [detail interface] • detail - shows detailed information. • interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - stack unit. (range: 1...
Page 642
Command line interface 4-306 4 show lldp info remote-device this command shows lldp global and interface-specific configuration settings for remote devices attached to an lldp-enabled port. Syntax show lldp info remote-device [detail interface] • detail - shows detailed information. • interface • et...
Page 643
Lldp commands 4-307 4 show lldp info statistics this command shows statistics based on traffic received through all attached lldp-enabled interfaces. Syntax show lldp info statistics [detail interface] • detail - shows detailed information. • interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - stack unit. (rang...
Page 644: Class Of Service Commands
Command line interface 4-308 4 class of service commands the commands described in this section allow you to specify which data packets have greater precedence when traffic is buffered in the switch due to congestion. This switch supports cos with four priority queues for each port. Data packets in ...
Page 645
Class of service commands 4-309 4 command mode global configuration command usage • strict priority requires all traffic in a higher priority queue to be processed before lower priority queues are serviced. • wrr uses a relative weight for each queue which determines the number of packets the switch...
Page 646
Command line interface 4-310 4 • this switch provides eight priority queues for each port. It is configured to use weighted round robin, which can be viewed with the show queue bandwidth command. Inbound frames that do not have vlan tags are tagged with the input port’s default ingress user priority...
Page 647
Class of service commands 4-311 4 command usage • cos values assigned at the ingress port are also used at the egress port. • this command sets the cos priority for all interfaces. Example the following example shows how to change the cos assignments: related commands show queue cos-map (4-312) show...
Page 648
Command line interface 4-312 4 example show queue cos-map this command shows the class of service priority map. Syntax show queue cos-map [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - stack unit. (range: 1) - port - port number. (range: 1-28 on ies4028f/ies4028fp, 1-24 on ies4024gp) • port-cha...
Page 649
Class of service commands 4-313 4 priority commands (layer 3 and 4) this section describes commands used to configure layer 3 and layer 4 traffic priority on the switch. Map ip dscp (global configuration) this command enables ip dscp mapping (i.E., differentiated services code point mapping). Use th...
Page 650
Command line interface 4-314 4 default setting the dscp default values are defined in the following table. Note that all the dscp values that are not specified are mapped to cos value 0. Command mode interface configuration (ethernet, port channel) command usage • the precedence for priority mapping...
Page 651
Class of service commands 4-315 4 show map ip dscp this command shows the ip dscp priority map. Syntax show map ip dscp [interface] interface • ethernet unit/port - unit - stack unit. (range: 1) - port - port number. (range: 1-28 on ies4028f/ies4028fp, 1-24 on ies4024gp) • port-channel channel-id (r...
Page 652: Quality Of Service Commands
Command line interface 4-316 4 quality of service commands the commands described in this section are used to configure differentiated services (diffserv) classification criteria and service policies. You can classify traffic based on access lists, ip precedence or dscp values, or vlans. Using acces...
Page 653
Quality of service commands 4-317 4 notes: 1. You can configure up to 16 rules per class map. You can also include multiple classes in a policy map. 2. You should create a class map (page 4-317) before creating a policy map (page 4-319). Otherwise, you will not be able to specify a class map with th...
Page 655
Quality of service commands 4-319 4 policy-map this command creates a policy map that can be attached to multiple interfaces, and enters policy map configuration mode. Use the no form to delete a policy map and return to global configuration mode. Syntax [no] policy-map policy-map-name policy-map-na...
Page 656
Command line interface 4-320 4 command mode policy map configuration command usage • use the policy-map command to specify a policy map and enter policy map configuration mode. Then use the class command to enter policy map class configuration mode. And finally, use the set and police commands to sp...
Page 657
Quality of service commands 4-321 4 average bandwidth to 100,000 kbps, the burst rate to 1522 bytes, and configure the response to drop any violating packets. Police this command defines an policer for classified traffic. Use the no form to remove a policer. Syntax [no] police rate-kbps burst-byte [...
Page 658
Command line interface 4-322 4 service-policy this command applies a policy map defined by the policy-map command to the ingress queue of a particular interface. Use the no form to remove the policy map from this interface. Syntax [no] service-policy input policy-map-name • input - apply to the inpu...
Page 659
Quality of service commands 4-323 4 example show policy-map this command displays the qos policy maps which define classification criteria for incoming traffic, and may include policers for bandwidth limitations. Syntax show policy-map [policy-map-name [class class-map-name]] • policy-map-name - nam...
Page 660: Multicast Filtering Commands
Command line interface 4-324 4 command mode privileged exec example multicast filtering commands this switch uses igmp (internet group management protocol) to query for any attached hosts that want to receive a specific multicast service. It identifies the ports containing hosts requesting a service...
Page 661
Multicast filtering commands 4-325 4 ip igmp snooping this command enables igmp snooping on this switch. Use the no form to disable it. Syntax [no] ip igmp snooping default setting enabled command mode global configuration example the following example enables igmp snooping. Ip igmp snooping vlan st...
Page 663
Multicast filtering commands 4-327 4 command usage • the igmp snooping leave-proxy feature suppresses all unnecessary igmp leave messages so that the non-querier switch forwards an igmp leave packet only when the last dynamic member port leaves a multicast group. • the leave-proxy feature does not f...
Page 664
Command line interface 4-328 4 show ip igmp snooping this command shows the igmp snooping configuration. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage see “configuring igmp snooping and query parameters” on page 3-253 for a description of the displayed items. Example the following ...
Page 665
Multicast filtering commands 4-329 4 example the following shows the multicast entries learned through igmp snooping for vlan 1: igmp query commands (layer 2) this section describes commands used to configure layer 2 igmp query on the switch. Ip igmp snooping querier this command enables the switch ...
Page 666
Command line interface 4-330 4 example ip igmp snooping query-count this command configures the query count. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax ip igmp snooping query-count count no ip igmp snooping query-count count - the maximum number of queries issued for which there has been no resp...
Page 667
Multicast filtering commands 4-331 4 default setting 125 seconds command mode global configuration example the following shows how to configure the query interval to 100 seconds: ip igmp snooping query-max-response-time this command configures the query report delay. Use the no form to restore the d...
Page 668
Command line interface 4-332 4 ip igmp snooping router-port-expire-time this command configures the query timeout. Use the no form to restore the default. Syntax ip igmp snooping router-port-expire-time seconds no ip igmp snooping router-port-expire-time seconds - the time the switch waits after the...
Page 669
Multicast filtering commands 4-333 4 ip igmp snooping vlan mrouter this command statically configures a multicast router port. Use the no form to remove the configuration. Syntax [no] ip igmp snooping vlan vlan-id mrouter interface • vlan-id - vlan id (range: 1-4094) • interface • ethernet unit/port...
Page 670
Command line interface 4-334 4 command mode privileged exec command usage multicast router port types displayed include static. Example the following shows that port 11 in vlan 1 is attached to a multicast router: igmp filtering and throttling commands in certain switch applications, the administrat...
Page 671
Multicast filtering commands 4-335 4 ip igmp filter (global configuration) this command globally enables igmp filtering and throttling on the switch. Use the no form to disable the feature. Syntax [no] ip igmp filter default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • igmp fil...
Page 672
Command line interface 4-336 4 command usage a profile defines the multicast groups that a subscriber is permitted or denied to join. The same profile can be applied to many interfaces, but only one profile can be assigned to one interface. Each profile has only one access mode; either permit or den...
Page 673
Multicast filtering commands 4-337 4 command mode igmp profile configuration command usage enter this command multiple times to specify more than one multicast address or address range for a profile. Example ip igmp filter (interface configuration) this command assigns an igmp filtering profile to a...
Page 674
Command line interface 4-338 4 ip igmp max-groups this command sets the igmp throttling number for an interface on the switch. Use the no form to restore the default setting. Syntax ip igmp max-groups number no ip igmp max-groups number - the maximum number of multicast groups an interface can join ...
Page 675
Multicast filtering commands 4-339 4 command usage when the maximum number of groups is reached on a port, the switch can take one of two actions; either “deny” or “replace.” if the action is set to deny, any new igmp join reports will be dropped. If the action is set to replace, the switch randomly...
Page 676
Command line interface 4-340 4 show ip igmp profile this command displays igmp filtering profiles created on the switch. Syntax show ip igmp profile [profile-number] profile-number - an existing igmp filter profile number. (range: 1-4294967295) default setting none command mode privileged exec examp...
Page 677
Multicast filtering commands 4-341 4 example multicast vlan registration commands this section describes commands used to configure multicast vlan registration (mvr). A single network-wide vlan can be used to transmit multicast traffic (such as television channels) across a service provider’s networ...
Page 678
Command line interface 4-342 4 default setting • mvr is disabled. • no mvr group address is defined. • the default number of contiguous addresses is 0. • mvr vlan id is 1. Command mode global configuration command usage • use the mvr group command to statically configure all multicast group addresse...
Page 679
Multicast filtering commands 4-343 4 mvr (interface configuration) this command configures an interface as an mvr receiver or source port using the type keyword, enables immediate leave capability using the immediate keyword, or configures an interface as a static member of the mvr vlan using the gr...
Page 680
Command line interface 4-344 4 • immediate leave applies only to receiver ports. When enabled, the receiver port is immediately removed from the multicast group identified in the leave message. When immediate leave is disabled, the switch follows the standard rules by sending a group-specific query ...
Page 681
Multicast filtering commands 4-345 4 default setting displays global configuration settings for mvr when no keywords are used. Command mode privileged exec command usage enter this command without any keywords to display the global settings for mvr. Use the interface keyword to display information a...
Page 682
Command line interface 4-346 4 the following shows information about the interfaces associated with multicast groups assigned to the mvr vlan: status shows the mvr status and interface status. Mvr status for source ports is “active” if mvr is globally enabled on the switch. Mvr status for receiver p...
Page 683: Ip Interface Commands
Ip interface commands 4-347 4 ip interface commands an ip addresses may be used for management access to the switch over your network. The ip address for this switch is obtained via dhcp by default. You can manually configure a specific ip address, or direct the device to obtain an address from a bo...
Page 684
Command line interface 4-348 4 • if you select the bootp or dhcp option, ip is enabled but will not function until a bootp or dhcp reply has been received. Requests will be broadcast periodically by this device in an effort to learn its ip address. (bootp and dhcp values can include the ip address, ...
Page 685
Ip interface commands 4-349 4 related commands show ip redirects (4-350) ip dhcp restart this command submits a bootp or dhcp client request. Default setting none command mode privileged exec command usage • this command issues a bootp or dhcp client request for any ip interface that has been set to...
Page 686
Command line interface 4-350 4 related commands show ip redirects (4-350) show ip redirects this command shows the default gateway configured for this device. Default setting none command mode privileged exec example related commands ip default-gateway (4-348) ping this command sends icmp echo reque...
Page 687
Ip interface commands 4-351 4 - network or host unreachable - the gateway found no corresponding entry in the route table. • press to stop pinging. Example related commands interface (4-188) console#ping 10.1.0.9 type esc to abort. Ping to 10.1.0.9, by 5 32-byte payload icmp packets, timeout is 5 se...
Page 688
Command line interface 4-352 4 this page is intentionally left blank..
Page 689: Software Features
A-1 appendix a: software specifications software features management authentication local, radius, tacacs, port authentication (802.1x), mac authentication, web authentication, https, ssh general security measures access control lists (ip, mac - 100 rules), port authentication (802.1x), port securit...
Page 690: Management Features
Software specifications a-2 a multicast filtering igmp snooping (layer 2) multicast vlan registration quality of service diffserv supports class maps, policy maps, and service policies additional features bootp client link layer discovery protocol sntp (simple network time protocol) snmp (simple net...
Page 691
Management information bases a-3 a ieee 802.3ac vlan tagging ieee 802.3af-2003 power over ethernet (poe) dhcp client (rfc 2131) dhcp options (rfc 2132) https igmpv1 (rfc 1112) igmpv2 (rfc 2236) igmpv3 (rfc 3376) - partial support radius+ (rfc 2618) rmon (rfc 1757 groups 1,2,3,9) snmp (rfc 1157) snmp...
Page 692
Software specifications a-4 a snmp target mib, snmp notification mib (rfc 3413) snmp user-based sm mib (rfc 3414) snmp view based acm mib (rfc 3415) tacacs+ authentication client mib tcp mib (rfc 2012) trap (rfc 1215) udp mib (rfc 2013).
Page 693: Appendix B: Troubleshooting
B-1 appendix b: troubleshooting problems accessing the management interface table b-1 troubleshooting chart symptom action cannot connect using telnet, web browser, or snmp software • be sure the switch is powered up. • check network cabling between the management station and the switch. • check tha...
Page 694: Using System Logs
Troubleshooting b-2 b using system logs if a fault does occur, refer to the installation guide to ensure that the problem you encountered is actually caused by the switch. If the problem appears to be caused by the switch, follow these steps: 1. Enable logging. 2. Set the error messages reported to ...
Page 695: Glossary
Glossary-1 glossary access control list (acl) acls can limit network traffic and restrict access to certain users or devices by checking each packet for certain ip or mac (i.E., layer 2) information. Boot protocol (bootp) bootp is used to provide bootup information for network devices, including ip ...
Page 696
Glossary glossary-2 packets sent back from the dhcp server. This information can be used by dhcp servers to assign fixed ip addresses, or set other services or policies for clients. Extensible authentication protocol over lan (eapol) eapol is a client authentication protocol used by this switch to v...
Page 697
Glossary-3 glossary ieee 802.1s an ieee standard for the multiple spanning tree protocol (mstp) which provides independent spanning trees for vlan groups. Ieee 802.1x port authentication controls access to the switch ports by requiring users to first enter a user id and password for authentication. ...
Page 698
Glossary glossary-4 layer 2 data link layer in the iso 7-layer data communications protocol. This is related directly to the hardware interface for network devices and passes on traffic based on mac addresses. Link aggregation see port trunk. Link aggregation control protocol (lacp) allows ports to ...
Page 699
Glossary-5 glossary the size of each region, and prevents vlan members from being segmented from the rest of the group. Network time protocol (ntp) ntp provides the mechanisms to synchronize time across the network. The time servers operate in a hierarchical-master-slave configuration in order to sy...
Page 700
Glossary glossary-6 traffic shaping. These features effectively provide preferential treatment to specific flows either by raising the priority of one flow or limiting the priority of another flow. Remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) radius is a logon authentication protocol that use...
Page 701
Glossary-7 glossary terminal access controller access control system plus (tacacs+) tacacs+ is a logon authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to tacacs-compliant devices on the network. Transmission control protocol/internet protocol (tcp/ip) protoco...
Page 702
Glossary glossary-8 this page is intentionally left blank..
Page 703: Index
Index-1 numerics 802.1q tunnel 3-200, 4-263 configuration, guidelines 3-203, 4-263 configuration, limitations 3-203 description 3-200 ethernet type 3-204, 4-265 interface configuration 3-204, 3-205, 4-264–4-265 mode selection 3-205, 4-264 status, configuring 3-204, 4-264 tpid 3-204, 4-265 uplink 3-2...
Page 704
Index-2 index cos configuring 3-230, 4-308 dscp 3-237, 4-313 layer 3/4 priorities 3-235, 4-313 queue mapping 3-232, 4-310 queue mode 3-234, 4-308 traffic class weights 3-234 d debug commands 4-80 default gateway, configuration 3-17, 4-349 default priority, ingress port 3-231, 4-309 default settings,...
Page 705
Index-3 index igmp filter profiles, configuration 3-262, 4-336 filtering, enabling 3-261 filtering/throttling 3-260, 4-335 filtering/throttling, configuring profile 4-337 filtering/throttling, creating profile 4-336 filtering/throttling, enabling 3-260, 4-336 filtering/throttling, interface settings...
Page 706
Index-4 index tlv, port description 3-220, 4-294 tlv, system capabilities 3-220, 4-295 tlv, system description 3-220, 4-295 tlv, system name 3-220, 4-296 lldp-med 3-217 notification, status 3-221, 4-293 tlv 3-220 tlv, inventory 3-221, 4-301 tlv, location 3-220, 4-301 tlv, network policy 3-220, 4-302...
Page 707
Index-5 index p packet filtering 3-108, 4-176 password, changing privilege mode 4-102 password, line 4-42 passwords 2-4, 3-58 administrator setting 3-58, 4-101 path cost 3-168, 3-176 method 3-173, 4-232 sta 3-168, 3-176, 4-232 port authentication 3-88, 4-137 port power displaying status 3-159, 4-217...
Page 708
Index-6 index global settings, displaying 3-168, 4-246 interface settings, configuring 3-178, 4-236–4-243 interface settings, displaying 3-175, 4-246 s secure shell 3-79, 4-127 configuration 3-79, 4-127 security, general measures 3-96, 4-148 serial port, configuring 3-25, 4-40 simple network managem...
Page 709
Index-7 index trap manager 2-7, 3-43, 4-90 troubleshooting b-1 trunk configuration 3-134, 4-202 lacp 3-136, 4-204 static 3-135, 4-203 type length value see also lldp-med tlv type length value see lldp tlv u unknown unicast storm, threshold 3-150, 4-195 upgrading software 3-22, 4-35 upnp 3-277, 4-78 ...
Page 710
Index-8 index this page is intentionally left blank..
Page 711
This page is intentionally left blank..
Page 712
Ies4028f/4028fp/4024gp.