- DL manuals
- SMC Networks
- Network Hardware
- 2888W-M
- Owner's Manual
SMC Networks 2888W-M Owner's Manual - System Configuration
Introduction
1-8
System Configuration
At each location where a unit is installed, it must be connected to
the local network using the power injector module. The following
figure illustrates the system component connections.
Indoor
Outdoor
LAN Switch
AC Power
Power
Injector
Wireless Bridge Unit
Ground Wire
Ethernet Cable
Ethernet Cable
External Antenna
RF Coaxial Cable
Summary of 2888W-M
Page 1
38 tesla irvine, ca 92618 phone: (949) 679-8000 eliteconnect™ universal 2.4ghz/5ghz wireless dual-band outdoor access point/bridge the easy way to make all your network connections may 2005 revision number: r01 f1.1.2.5.
Page 2
Copyright information furnished by smc networks, inc. (smc) is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by smc for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or ...
Page 3
I l imited w arranty limited warranty statement: smc networks, inc. (“smc”) warrants its products to be free from defects in workmanship and materials, under normal use and service, for the applicable warranty term. All smc products carry a standard 90-day limited warranty from the date of purchase ...
Page 4
L imited w arranty ii customers are responsible for all shipping charges from their facility to smc. Smc is responsible for return shipping charges from smc to customer. Warranties exclusive: if an smc product does not operate as warranted above, customer’s sole remedy shall be repair or replacement...
Page 5: Statement
Iii c ompliances federal communication commission interference statement this equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class b digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the fcc rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a...
Page 6: Ec Conformance Declaration
C ompliances iv wireless 5 ghz band statements: as the smc2888w access point/bridge can operate in the 5150-5250 mhz frequency band it is limited by the fcc, industry canada and some other countries to indoor use only so as to reduce the potential for harmful interference to co-channel mobile satell...
Page 7
C ompliances v • this device employs a radar detection feature required for european community operation in the 5 ghz band. This feature is automatically enabled when the country of operation is correctly configured for any european community country. The presence of nearby radar operation may resul...
Page 8
C ompliances vi operation using 5 ghz channels in the european community the user/installer must use the provided configuration utility to check the current channel of operation and make necessary configuration changes to ensure operation occurs in conformance with european national spectrum usage l...
Page 9
C ompliances vii declaration of conformity in languages of the european community english hereby, smc networks, declares that this radio lan device is in compliance with the essential requirements and other relevant provisions of directive 1999/5/ec. Finnish valmistajasmc networks vakuuttaa täten et...
Page 10: Safety Compliance
C ompliances viii safety compliance power cord safety please read the following safety information carefully before installing the wireless access point: warning: installation and removal of the unit must be carried out by qualified personnel only. • the unit must be connected to an earthed (grounde...
Page 11
C ompliances ix important! Before making connections, make sure you have the correct cord set. Check it (read the label on the cable) against the following: power cord set u.S.A. And canada the cord set must be ul-approved and csa certified. The minimum specifications for the flexible cord are: - no...
Page 12
C ompliances x veuillez lire à fond l'information de la sécurité suivante avant d'installer le wireless access point: avertissement: l’installation et la dépose de ce groupe doivent être confiés à un personnel qualifié. • ne branchez pas votre appareil sur une prise secteur (alimentation électrique)...
Page 13
C ompliances xi bitte unbedingt vor dem einbauen des access point die folgenden sicherheitsanweisungen durchlesen (germany) : warnung: die installation und der ausbau des geräts darf nur durch fachpersonal erfolgen. • das gerät sollte nicht an eine ungeerdete wechselstromsteckdose angeschlossen werd...
Page 14
C ompliances xii gegeben, wenn auch die an das gerät angeschlossenen geräte unter selv-bedingungen betrieben werden. • stromkabel. Dies muss von dem land, in dem es benutzt wird geprüft werden: u.S.A und kanada der cord muß das ul gepruft und war das csa beglaubigt. Das minimum spezifikation fur der...
Page 15
Xiii t able of c ontents 1 introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1 package checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2 hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4 integrated high-gain an...
Page 16
T able of c ontents xiv connect external antennas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-5 connect cables to the unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-7 connect the power injector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-7 align antennas . . . . . ...
Page 17
T able of c ontents xv entering commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3 keywords and arguments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3 minimum abbreviation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3 command completion . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 18
T able of c ontents xvi system clock commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-28 sntp-server ip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-29 sntp-server enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-30 sntp-server date-time . . ...
Page 19
T able of c ontents xvii wds commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-61 wds channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-62 wds mac-address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-62 wds enable . . . . . . . ...
Page 20
T able of c ontents xviii dns server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-92 ip address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-93 ip dhcp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-94 shutdown ....
Page 21: Glossary
T able of c ontents xix a troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1 b specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1 general specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1 antenna specifications . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 22
T able of c ontents xx.
Page 23
1-1 chapter 1 introduction the smc eliteconnect universal 2.4ghz/5ghz wireless dual-band outdoor access point/bridge system consists of two models that provide point-to-point or point-to-multipoint bridge links between remote ethernet lans, and wireless access point services for clients in the local...
Page 24: Package Checklist
Introduction 1-2 in addition, both wireless bridge models offer full network management capabilities through an easy-to-use web interface, a command-line interface, and support for simple network management protocol (snmp) tools. Radio characteristics – the ieee 802.11a and 802.11g standards use a r...
Page 25
Package checklist 1-3 • outdoor pole-mounting bracket kit • outdoor wall-mounting bracket kit • this user guide inform your dealer if there are any incorrect, missing or damaged parts. If possible, retain the carton, including the original packing materials. Use them again to repack the product in c...
Page 26: Hardware Description
Introduction 1-4 hardware description ethernet port rssi connector with protective cap grounding point screw integrated antenna bottom view top view (smc2888w-s) n-type external antenna connector (2.4 ghz) n-type external antenna connector (2.4 ghz) top view (smc2888w-m) n-type external antenna conn...
Page 27: Integrated High-Gain Antenna
Hardware description 1-5 integrated high-gain antenna the smc2888w-s wireless bridge includes an integrated high-gain (17 dbi) flat-panel antenna for 5 ghz operation. External antenna options the smc2888w-m master bridge unit does not include an integrated antenna, but provides various external ante...
Page 28: Power Injector Module
Introduction 1-6 power injector module the wireless bridge receives power through its network cable connection using power-over-ethernet technology. A power injector module is included in the wireless bridge package and provides two rj-45 ethernet ports, one for connecting to the wireless bridge (ou...
Page 29: Connector
Hardware description 1-7 the power injector module automatically adjusts to any ac voltage between 100-240 volts at 50 or 60 hz. No voltage range settings are required. Warning: the power injector module is designed for indoor use only. Never mount the power injector outside with the wireless bridge...
Page 30: System Configuration
Introduction 1-8 system configuration at each location where a unit is installed, it must be connected to the local network using the power injector module. The following figure illustrates the system component connections. Indoor outdoor lan switch ac power power injector wireless bridge unit groun...
Page 31: Features and Benefits
Features and benefits 1-9 features and benefits • smc2888w-s slave units support a 5 ghz high-gain 17 dbi antenna • smc2888w-m master units support 5 ghz point-to-multipoint links using various external antenna options • both smc2888w-s and smc2888w-m units also support access point services for the...
Page 32: System Defaults
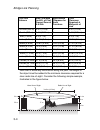
Introduction 1-10 system defaults the following table lists some of the wireless bridge’s basic system defaults. To reset the bridge defaults, use the cli command “reset configuration” from the exec level prompt. Feature parameter default identification system name dual band outdoor ap administratio...
Page 33
System defaults 1-11 snmp status enabled location null contact contact community (read only) public community (read/write) private traps enabled trap destination ip address null trap destination community name public system logging syslog disabled logging host disabled logging console disabled ip ad...
Page 34
Introduction 1-12 wireless interface 802.11a status enabled ssid smc turbo mode disabled radio channel default to first channel auto channel select enabled transmit power full maximum data rate 54 mbps beacon interval 100 tus data beacon rate (dtim interval) 2 beacons rts threshold 2347 bytes wirele...
Page 35
System defaults 1-13 wireless interface 802.11b/g status enabled ssid smc radio channel default to first channel auto channel select enabled transmit power full maximum data rate 54 mbps beacon interval 100 tus data beacon rate (dtim interval) 2 beacons rts threshold 2347 bytes wireless security 802...
Page 36
Introduction 1-14.
Page 37: Access Point Topologies
2-1 chapter 2 network configuration the dual-band outdoor access point / bridge system provides access point or bridging services through either the 5 ghz or 2.4 ghz radio interfaces. The wireless bridge units can be used just as normal 802.11a/b/g access points connected to a local wired lan, provi...
Page 38
Network configuration 2-2 the 802.11b and 802.11g frequency band, which operates at 2.4 ghz, can easily encounter interference from other 2.4 ghz devices, such as other 802.11b or g wireless devices, cordless phones and microwave ovens. If you experience poor wireless lan performance, try the follow...
Page 39
Access point topologies 2-3 infrastructure wireless lan the access point function of the wireless bridge provides access to a wired lan for 802.11a/b/g wireless workstations. An integrated wired/wireless lan is called an infrastructure configuration. A basic service set (bss) consists of a group of ...
Page 40
Network configuration 2-4 infrastructure wireless lan for roaming wireless pcs the basic service set (bss) defines the communications domain for each access point and its associated wireless clients. The bss id is a 48-bit binary number based on the access point’s wireless mac address, and is set au...
Page 41: Bridge Link Topologies
Bridge link topologies 2-5 bridge link topologies the ieee 802.11 standard defines a wireless distribution system (wds) for bridge connections between bss areas (access points). The outdoor wireless bridge uses wds to forward traffic on links between units. Up to 16 wds links can be specified for a ...
Page 42: Point-to-Point Configuration
Network configuration 2-6 note: the external antennas offer longer range options using the 5 ghz radio, which makes this interface more suitable for bridge links. When using wds on a radio band, only wireless bridge units can associate to each other. Wireless clients can only associate with the wire...
Page 43
Bridge link topologies 2-7 master with omnidirectional antenna slave slave slave slave slave slave master with sector antenna slave slave slave.
Page 44
Network configuration 2-8.
Page 45: Radio Path Planning
3-1 chapter 3 bridge link planning the smc dual-band outdoor access point / bridge supports fixed point-to-point or point-to-multipoint wireless links. A single link between two points can be used to connect a remote site to larger core network. Multiple bridge links can provide a way to connect wid...
Page 46
Bridge link planning 3-2 this area is known as the first fresnel zone of the radio link. For a radio link not to be affected by obstacles along its path, no object, including the ground, must intrude within 60% of the first fresnel zone. The following figure illustrates the concept of a good radio l...
Page 47: Antenna Height
Radio path planning 3-3 • be sure there is enough clearance from buildings and that no building construction may eventually block the path. • check the topology of the land between the antennas using topographical maps, aerial photos, or even satellite image data (software packages are available tha...
Page 48
Bridge link planning 3-4 . Note that to avoid any obstruction along the path, the height of the object must be added to the minimum clearance required for a clear radio line-of-sight. Consider the following simple example, illustrated in the figure below. Total link distance max clearance for 60% of...
Page 49
Radio path planning 3-5 a wireless bridge link is deployed to connect building a to a building b, which is located three miles (4.8 km) away. Mid-way between the two buidings is a small tree-covered hill. From the above table it can be seen that for a three-mile link, the object clearance required a...
Page 50: Radio Interference
Bridge link planning 3-6 • the wireless bridge antennas at both ends of the link must be positioned with the same polarization direction, either horizontal or vertical antenna polarization — the wireless bridge’s integrated antenna sends a radio signal that is polarized in a particular direction. Th...
Page 51: Weather Conditions
Radio path planning 3-7 weather conditions when planning wireless bridge links, you must take into account any extreme weather conditions that are known to affect your location. Consider these factors: • temperature — the wireless bridge is tested for normal operation in temperatures from -33°c to 5...
Page 52: Ethernet Cabling
Bridge link planning 3-8 ethernet cabling when a suitable antenna location has been determined, you must plan a cable route form the wireless bridge outdoors to the power injector module indoors. Consider these points: • the ethernet cable length should never be longer than 100 m (328 ft) • determin...
Page 53
4-1 chapter 4 hardware installation before mounting antennas to set up your wireless bridge links, be sure you have selected appropriate locations for each antenna. Follow the guidance and information in chapter 2, “wireless link planning.” also, before mounting units in their intended locations, yo...
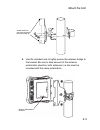
Page 54: Mount The Unit
Hardware installation 4-2 5. Align antennas at both ends of the link. Testing basic link operation set up the units over a very short range (15 to 25 feet), either outdoors or indoors. Connect the units as indicated in this chapter and be sure to perform all the basic configuration tasks outlined ab...
Page 55
Mount the unit 4-3 3. Use the included nuts to tightly secure the wireless bridge to the bracket. Be sure to take account of the antenna polarization direction; both antennas in a link must be mounted with the same polarization. Attach bracket to pole with mounting grooves facing up antenna polariza...
Page 56
Hardware installation 4-4 mounting on larger diameter poles in addition, there is a method for attaching the pole-mounting bracket to a pole that is 2 to 5 inches in diameter using an adjustable steel band clamp (not included in the kit). A steel band clamp up to 0.5 inch (1.27 cm) wide can be threa...
Page 57: Connect External Antennas
Connect external antennas 4-5 2. Position the bracket in the intended location and mark the position of the three mounting screw holes. 3. Drill three holes in the wall that match the screws and wall plugs included in the bracket kit, then secure the bracket to the wall. 4. Use the included nuts to ...
Page 58
Hardware installation 4-6 2. Connect the antenna to the bridge’s n-type connector. 3. Apply weatherproofing tape to the antenna connectors to help prevent water entering the connectors. Rf coaxial cable 2.4 ghz external omnidirectional antenna 2.4 ghz n-type connector 5 ghz n-type connector 5 ghz ex...
Page 59: Connect Cables To The Unit
Connect cables to the unit 4-7 connect cables to the unit 1. Attach the ethernet cable to the ethernet port on the wireless bridge. Note: the ethernet cable included with the package is 30 m (100 ft) long. To wire a longer cable (maximum 100 m, 325 ft), use the connector pinout information in append...
Page 60
Hardware installation 4-8 note: the wireless bridge’s ethernet port does not support power over ethernet (poe) based on the ieee 802.3af standard. Do not try to power the unit by connecting it directly to a network switch that provides ieee 802.3af poe. Always connect the unit to the included power ...
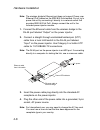
Page 61: Align Antennas
Align antennas 4-9 5. Check the led on top of the power injector to be sure that power is being supplied to the wireless bridge through the ethernet connection. Align antennas after wireless bridge units have been mounted, connected, and their radios are operating, the antennas must be accurately al...
Page 62
Hardware installation 4-10 strong central main lobe and smaller side lobes. The object of the alignment process is to set the antenna so that it is receiving the strongest signal from the central main lobe. To align the antennas in the link using the rssi output voltage, start with one antenna fixed...
Page 63
Align antennas 4-11 2. Pan the antenna horizontally back and forth while checking the rssi voltage. If using the pole-mounting bracket with the unit, you must rotate the mounting bracket around the pole. Other external antenna brackets may require a different horizontal adjustment. 3. Find the point...
Page 64
Hardware installation 4-12.
Page 65
5-1 chapter 5 initial configuration the wireless bridge offers a variety of management options, including a web-based interface, a command line interface (cli), or using snmp management software. Most initial configuration steps can be made through the web browser interface using the setup wizard (p...
Page 66: Initial Configuration Steps
Initial configuration 5-2 initial setup through the cli the wireless bridge provides access to the cli through a telnet connection. You can open a telnet session by performing these steps: 1. From the host computer, enter the telnet command and the ip address of the wireless bridge unit (default 192...
Page 67
Initial setup through the cli 5-3 at the exec prompt, type “country ?” to display the list of country codes. Check the code for your country, then enter the country command again followed by your country code (e.G., ie for ireland). Setting the ip address – by default, the wireless bridge is configu...
Page 68: Setup Wizard
Initial configuration 5-4 after configuring the wireless bridge’s ip parameters, you can access the management interface from anywhere within the attached network. The command line interface can also be accessed using telnet from any computer attached to the network. Using the web-based management s...
Page 69
Using the web-based management setup wizard 5-5 the home page displays the main menu. Launching the setup wizard – to perform initial configuration, click setup wizard on the home page, then click on the [next] button to start the process. 1. Service set id – enter the service set identifier in the ...
Page 70
Initial configuration 5-6 2. Radio channel – you must enable radio communications for the 802.11a and 802.11g radios and set the operating channel. • 802.11a.
Page 71
Using the web-based management setup wizard 5-7 turbo mode – if you select enable, the wireless bridge will operate in turbo mode with a data rate of up to 108 mbps. Normal mode supports 13 channels, turbo mode supports only 5 channels. (default: disable) 802.11a radio channel – set the operating ra...
Page 72
Initial configuration 5-8 note: available channel settings are limited by local regulations which determine which channels are available. 3. Ip configuration – either enable or disable (dynamic host configuration protocol (dhcp) for automatic ip configuration. If you disable dhcp, then manually ente...
Page 73
Using the web-based management setup wizard 5-9 4. Wds – to set up a wireless bridge link, you must configure the wds forwarding table by specifying the ethernet mac address of the bridge to which you want to forward traffic. For a slave bridge unit, you need to specify the mac address of the wirele...
Page 74
Initial configuration 5-10 5. Security (802.11g) – set the authentication type to “open system” to allow open access without authentication, or “shared key” to require authentication based on a shared key. Enable wired equivalent privacy (wep) to encrypt data transmissions. To configure other securi...
Page 75
Using the web-based management setup wizard 5-11 hexadecimal or ascii string of the appropriate length. The key can be entered as alphanumeric characters or hexadecimal (0~9, a~f, e.G., d7 0a 9c 7f e5). (default: 128 bit, hexadecimal key type) 64-bit manual entry: the key can contain 10 hexadecimal ...
Page 76
Initial configuration 5-12.
Page 77
6-1 chapter 6 system configuration before continuing with advanced configuration, first complete the initial configuration steps described in chapter 5 to set up an ip address for the wireless bridge. The wireless bridge can be managed by any computer using a web browser (internet explorer 5.0 or ab...
Page 78
System configuration 6-2 when the home page displays, click on advanced setup. The following page will display. The information in this chapter is organized to reflect the structure of the web screens for easy reference. However, it is recommended that you configure a user name and password as the f...
Page 79: Advanced Configuration
Advanced configuration 6-3 advanced configuration the advanced configuration pages include the following options. Menu description page system configures basic administrative and client access 6-4 identification specifies the system name, location and contact information 6-4 tcp / ip settings config...
Page 80: System Identification
System configuration 6-4 system identification the system information parameters for the wireless bridge can be left at their default settings. However, modifying these parameters can help you to more easily distinguish different devices in your network. The wireless bridge allows the selection of t...
Page 81
Advanced configuration 6-5 system name – an alias for the wireless bridge, enabling the device to be uniquely identified on the network. (default: dual band outdoor ap; range: 1-22 characters) outdoor bridge band – selects the radio band used for bridge links. • a – bridging is supported on the 802....
Page 82
System configuration 6-6 cli commands for system identification – enter the global configuration mode and use the system name command to specify a new system name. Use the snmp-server location and snmp-server contact commands to indicate the physical location of the wireless bridge and define a syst...
Page 83: Tcp / Ip Settings
Advanced configuration 6-7 tcp / ip settings configuring the wireless bridge with an ip address expands your ability to manage the wireless bridge. A number of wireless bridge features depend on ip addressing to operate. Note: you can use the web browser interface to access ip addressing only if the...
Page 84
System configuration 6-8 dhcp client (enable) – select this option to obtain the ip settings for the wireless bridge from a dhcp (dynamic host configuration protocol) server. The ip address, subnet mask, default gateway, and domain name server (dns) address are dynamically assigned to the wireless b...
Page 85
Advanced configuration 6-9 • default gateway: the default gateway is the ip address of the router for the wireless bridge, which is used if the requested destination address is not on the local subnet. • if you have management stations, dns, or other network servers located on another subnet, type t...
Page 86: Radius
System configuration 6-10 radius remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) is an authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to radius-aware devices on the network. An authentication server contains a database of user credentials for each user t...
Page 87
Advanced configuration 6-11 primary radius server setup – configure the following settings to use radius authentication on the access point. • ip address: specifies the ip address or host name of the radius server. • port: the udp port number used by the radius server for authentication messages. (r...
Page 88
System configuration 6-12 • key: a shared text string used to encrypt messages between the access point and the radius server. Be sure that the same text string is specified on the radius server. Do not use blank spaces in the string. (maximum length: 255 characters) • timeout: number of seconds the...
Page 89: Pppoe Settings
Advanced configuration 6-13 to display the current settings for the primary and secondary radius servers. Pppoe settings the wireless bridge uses a point-to-point protocol over ethernet (pppoe) connection, or tunnel, only for management traffic between the wireless bridge and a remote pppoe server (...
Page 90
System configuration 6-14 ppp over ethernet – enable pppoe on the rj-45 ethernet interface to pass management traffic between the unit and a remote pppoe server. (default: disable) pppoe username – the user name assigned for the pppoe tunnel. (range: 1-63 alphanumeric characters) pppoe password – th...
Page 91
Advanced configuration 6-15 ip allocation mode – this field specifies how ip adresses for the pppoe tunnel are configured on the rj-45 interface. The allocation mode depends on the type of service provided by the pppoe server. If automatic mode is selected, dhcp is used to allocate the ip addresses ...
Page 92: Authentication
System configuration 6-16 authentication wireless clients can be authenticated for network access by checking their mac address against the local database configured on the access point, or by using a database configured on a central radius server. Alternatively, authentication can be implemented us...
Page 93
Advanced configuration 6-17 ethernet supplicant setup – allows the access point to act as an 802.1x supplicant so it can be authenticated through its ethernet port with a radius server on the local network. When enabled, a unique md5 user name and password needs to be configured. (default: disabled)...
Page 94
System configuration 6-18 mac authentication – you can configure a list of the mac addresses for wireless clients that are authorized to access the network. This provides a basic level of authentication for wireless clients attempting to gain access to the network. A database of authorized mac addre...
Page 95
Advanced configuration 6-19 note: client station mac authentication occurs prior to the ieee 802.1x authentication procedure configured for the access point. However, a client’s mac address provides relatively weak user authentication, since mac addresses can be easily captured and used by another s...
Page 96
System configuration 6-20 • supported: the access point supports 802.1x authentication only for clients initiating the 802.1x authentication process (i.E., the access point does not initiate 802.1x authentication). For clients initiating 802.1x, only those successfully authenticated are allowed to a...
Page 97
Advanced configuration 6-21 local mac authentication – configures the local mac authentication database. The mac database provides a mechanism to take certain actions based on a wireless client’s mac address. The mac list can be configured to allow or deny network access to specific clients. • syste...
Page 98
System configuration 6-22 • permission: select allow to permit access or deny to block access. If delete is selected, the specified mac address entry is removed from the database. • update: enters the specified mac address and permission setting into the local database. • mac authentication table: d...
Page 99
Advanced configuration 6-23 command. To display the current settings, use the show authentication command from the exec mode. Ap(config)#mac-authentication server local 7-59 ap(config)#address filter default denied 7-56 ap(config)#address filter entry 00-70-50-cc-99-1a denied 7-57 ap(config)#address...
Page 100
System configuration 6-24 cli commands for radius mac authentication – use the mac-authentication server command from the global configuration mode to enable remote mac authentication. Set the timeout value for re-authentication using the mac-authentication session-timeout command. Be sure to also c...
Page 101
Advanced configuration 6-25 cli commands for 802.1x authentication – use the 802.1x supported command from the global configuration mode to enable 802.1x authentication. Set the session and broadcast key refresh rate, and the re-authentication timeout. To display the current settings, use the show a...
Page 102: Filter Control
System configuration 6-26 filter control the wireless bridge can employ vlan tagging support and network traffic frame filtering to control access to network resources and increase security. Native vlan id – the vlan id assigned to wireless clients that are not assigned to a specific vlan by radius ...
Page 103
Advanced configuration 6-27 traffic that has an unknown vlan id or no vlan tag is dropped. When vlan support is disabled, the wireless bridge does not tag traffic passing to the wired network and ignores the vlan tags on any received frames. Note: before enabling vlans on the wireless bridge , you m...
Page 104
System configuration 6-28 note: the specific configuration of radius server software is beyond the scope of this guide. Refer to the documentation provided with the radius server software. When vlan filtering is enabled, the access point must also have 802.1x authentication enabled and a radius serv...
Page 105
Advanced configuration 6-29 • enable: wireless bridge filters ethernet protocol types based on the configuration of protocol types in the filter table. If a protocol has its status set to “on,” the protocol is filtered from the wireless bridge. Cli commands for vlan support– from the global configur...
Page 106: Snmp
System configuration 6-30 you want to filter. To display the current settings, use the show filters command from the exec mode. Snmp you can use a network management application to manage the wireless bridge via the simple network management protocol (snmp) from a management station. To implement sn...
Page 107
Advanced configuration 6-31 snmp – enables or disables snmp management access and also enables the wireless bridge to send snmp traps (notifications). Snmp management is disabled by default. Community name (read only) – defines the snmp community access string that has read-only access. Authorized m...
Page 108
System configuration 6-32 trap destination community name – the community string sent with the notification operation. (maximum length: 23 characters; default: public) cli commands for snmp – use the snmp-server enable server command from the global configuration mode to enable snmp. To set read/wri...
Page 109: Administration
Advanced configuration 6-33 administration changing the password management access to the web and cli interface on the wireless bridge is controlled through a single user name and password. You can also gain additional access security by using control filters (see “filter control” on page 6-26). To ...
Page 110
System configuration 6-34 cli commands for the user name and password – use the username and password commands from the cli configuration mode. Upgrading firmware you can upgrade new wireless bridge software from a local file on the management workstation, or from an ftp or tftp server. After upgrad...
Page 111
Advanced configuration 6-35 before upgrading new software, verify that the wireless bridge is connected to the network and has been configured with a compatible ip address and subnet mask. If you need to download from an ftp or tftp server, take the following additional steps: • obtain the ip addres...
Page 112
System configuration 6-36 firmware upgrade local – downloads an operation code image file from the web management station to the wireless bridge using http. Use the browse button to locate the image file locally on the management station and click start upgrade to proceed. • new firmware file: speci...
Page 113
Advanced configuration 6-37 note: if you have upgraded system software, then you must reboot the wireless bridge to implement the new operation code. Cli commands for downloading software from a tftp server – use the copy tftp file command from the exec mode and then specify the file type, name, and...
Page 114: System Log
System configuration 6-38 system log the wireless bridge can be configured to send event and error messages to a system log server. The system clock can also be synchronized with a time server, so that all the messages sent to the syslog server are stamped with the correct time and date. Enabling sy...
Page 115
Advanced configuration 6-39 logging console – enables the logging of error messages to the console. Logging level – sets the minimum severity level for event logging. The system allows you to limit the messages that are logged by specifying a minimum severity level. The following table lists the err...
Page 116
System configuration 6-40 cli commands for system logging– to enable logging on the wireless bridge, use the logging on command from the global configuration mode. The logging level command sets the minimum level of message to log. Use the logging console command to enable logging to the console. Us...
Page 117
Advanced configuration 6-41 the wireless bridge acts as an sntp client, periodically sending time synchronization requests to specific time servers. You can configure up to two time server ip addresses. The wireless bridge will attempt to poll each server in the configured sequence. Sntp server – co...
Page 118
System configuration 6-42 cli commands for sntp– to enable sntp support on the wireless bridge, from the global configuration mode specify sntp server ip addresses using the sntp-server ip command, then use the sntp-server enable command to enable the service. Use the sntp-server timezone command to...
Page 119
Advanced configuration 6-43 wireless distribution system (wds) the ieee 802.11 standard defines a wireless distribution system (wds) for connections between wireless bridges. The access point uses wds to forward traffic on bridge links between units. When using wds, only wireless bridge units can as...
Page 120
System configuration 6-44 mode – the wireless bridge is set to operate as a slave or master unit: • master mode: in a point-to-multipoint network configuration, only one wireless bridge unit must be a master unit (all others must be slave units). A master wireless bridge provides support for up to 1...
Page 121: Bridge
Advanced configuration 6-45 mac address – the physical layer address of the wireless bridge unit at the other end of the wireless link. (12 hexadecimal digits in the form “xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx”) port status – enables or disables the wireless bridge link. Note: the ethernet mac address for each bridge u...
Page 122
System configuration 6-46 bridge aging time – changes the aging time for entries in the dynamic address table: • ethernet: the time after which a learned ethernet port entry is discarded. (range: 60-1800 seconds; default: 100 seconds) • wireless 802.11a (g): the time after which a learned wireless e...
Page 123: Spanning Tree Protocol (Stp)
Advanced configuration 6-47 cli commands for bridging– the following example shows how to set the mac address aging time for the wireless bridge. Spanning tree protocol (stp) the spanning tree protocol (stp) can be used to detect and disable network loops, and to provide backup links between switche...
Page 124
System configuration 6-48 device (except for the root device) which incurs the lowest path cost when forwarding a packet from that device to the root device. Then it selects a designated bridging device from each lan which incurs the lowest path cost when forwarding a packet from that lan to the roo...
Page 125
Advanced configuration 6-49 enable – enables/disables stp on the wireless bridge. (default: enabled) forward delay – the maximum time (in seconds) this device waits before changing states (i.E., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is required because every device must receive informati...
Page 126
System configuration 6-50 hello time – interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a configuration message. (range: 1-10 seconds) • default: 2 • minimum: 1 • maximum: the lower of 10 or [(max. Message age / 2) -1] maximum age – the maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without rec...
Page 127
Advanced configuration 6-51 assigned to ports with slower media. (path cost takes precedence over port priority.) • range: 1-65535 • default: ethernet interface: 19; wireless interface: 40 priority – defines the priority used for this port in the spanning tree protocol. If the path cost for all port...
Page 128
System configuration 6-52 port fast (fast forwarding) – you can enable this option if an interface is attached to a lan segment that is at the end of a bridged lan or to an end node. Since end nodes cannot cause forwarding loops, they can pass directly through to the spanning tree forwarding state. ...
Page 129
Advanced configuration 6-53 cli commands for stp– the following example configures spanning tree paramters for the bridge and wireless port 5. Ap(config)#bridge stp-bridge priority 40000 7-70 ap(config)#bridge stp-bridge hello-time 5 7-68 ap(config)#bridge stp-bridge max-age 38 7-69 ap(config)#bridg...
Page 130: Rssi
System configuration 6-54 rssi the rssi value displayed on the rssi page represents a signal to noise ratio. A value of 30 would indicate that the power of the received signal is 30 dbm above the signal noise threshold. This value can be used to align antennas (see page 4-9) and monitor the quality ...
Page 131
Advanced configuration 6-55 rssi – the rssi value for a selected port can be displayed and a representative voltage output can be enabled. • output activate: enables or disables the rssi voltage output on the external rssi connector. (default: enabled) • port number:selects a specific wds port for w...
Page 132: Radio Interface
System configuration 6-56 radio interface the ieee 802.11a and 802.11g interfaces include configuration options for radio signal characteristics and wireless security features. The configuration options are nearly identical, but depend on which interface is operating as the bridge band. Both interfa...
Page 133: Radio Settings A (802.11A)
Radio interface 6-57 radio settings a (802.11a) the ieee 802.11a interface operates within the 5 ghz band, at up to 54 mbps in normal mode or up to 108 mbps in turbo mode. Enable – enables radio communications on the wireless interface. (default: enabled) description – adds a comment or description ...
Page 134
System configuration 6-58 mode. Ssid broadcast – when enabled, the access point radio does not include its ssid in beacon messages. Nor does it respond to probe requests from clients that do not include a fixed ssid. (default: disable) turbo mode – the normal 802.11a wireless operation mode provides...
Page 135
Radio interface 6-59 auto channel select – enables the wireless bridge to automatically select an unoccupied radio channel. (default: enabled) transmit power – adjusts the power of the radio signals transmitted from the wireless bridge. The higher the transmission power, the farther the transmission...
Page 136
System configuration 6-60 using higher dtim values reduces the power used by stations in power save mode, but delays the transmission of broadcast/ multicast frames. (range: 1-255 beacons; default: 2 beacons) fragment length – configures the minimum packet size that can be fragmented when passing th...
Page 137
Radio interface 6-61 maximum associations – (access point mode only) sets the maximum number of clients that can be associated with the access point radio at the same time. (range: 1-64 per radio: default: 64) cli commands for the 802.11a wireless interface – from the global configuration mode, ente...
Page 138
System configuration 6-62 ap(config)#interface wireless a 7-99 enter wireless configuration commands, one per line. Ap(if-wireless a)#description rd-ap#3 7-99 ap(if-wireless a)#ssid r&d 7-100 ap(if-wireless a)#no turbo 7-103 ap(if-wireless a)#channel 44 7-102 ap(if-wireless a)#closed-system 7-101 ap...
Page 139: Radio Settings G (802.11G)
Radio interface 6-63 radio settings g (802.11g) the ieee 802.11g standard operates within the 2.4 ghz band at up to 54 mbps. Also note that because the ieee 802.11g standard is an extension of the ieee 802.11b standard, it allows clients with 802.11b wireless network cards to associate to an 802.11g...
Page 140
System configuration 6-64 with each other. For example, in the united states you can deploy up to three access points in the same area (e.G., channels 1, 6, 11). Also note that the channel for wireless clients is automatically set to the same as that used by the access point to which it is linked. (...
Page 141
Radio interface 6-65 stop sending the ssid in beacon messages. Select a radio channel or set selection to auto using the channel command. Set any other parameters as required. To view the current 802.11g radio settings, use the show interface wireless g command. Ap(config)#interface wireless g 7-99 ...
Page 142: Security (Bridge Mode)
System configuration 6-66 security (bridge mode) wired equivalent privacy (wep) and advanced encryption standard (aes) are implemented for security in bridge mode to prevent unauthorized access to network data. To secure bridge link data transmissions, enable wep or aes encryption for the bridge rad...
Page 143
Radio interface 6-67 setting up ieee 802.11 wired equivalent privacy (wep) shared keys prevents unauthorized access to the wireless bridge network. Be sure to define at least one static wep key for data encryption. Also, be sure that the wep keys are the same for all bridge units in the wireless net...
Page 144
System configuration 6-68 advanced encryption standard (aes) aes has been designated by the national institute of standards and technology as the successor to the data encryption standard (des) encryption algorithm, and will be used by the u.S. Government for encrypting all sensitive, nonclassified ...
Page 145
Radio interface 6-69 configuring aes encryption keys on the wireless bridge provides far more robust security than using wep. Also, a unique aes key can be used for each bridge link in the wireless network, instead of all bridges sharing the same wep keys. Data encryption setup – enable or disable t...
Page 146
System configuration 6-70 command. To view the current security settings, use the show interface wireless a command. Note: the index and length values used in the key command must be the same values used in the encryption and transmit-key commands. Ap(config)#interface wireless a 7-99 enter wireless...
Page 147
Radio interface 6-71 cli commands for aes security – from the 802.11a interface configuration mode, use the encryption command to enable aes encryption. To enter aes keys, use the key command. To view the current security settings, use the show interface wireless a command. Note: the key type value ...
Page 148
System configuration 6-72 security (access point mode) a radio band set to access point mode is configured by default as an “open system,” which broadcasts a beacon signal including the configured ssid. Wireless clients can read the ssid from the beacon, and automatically reset their ssid to allow i...
Page 149
Radio interface 6-73 wireless clients. A summary of wireless security considerations is listed in the following table. Security mechanism client support implementation considerations wep built-in support on all 802.11a and 802.11g devices • provides only weak security • requires manual key managemen...
Page 150
System configuration 6-74 note: although a wep static key is not needed for wep over 802.1x, wpa over 802.1x, and wpa psk modes, you must enable wep encryption through the web or cli in order to enable all types of encryption in the access point. Wired equivalent privacy (wep) wep provides a basic l...
Page 151
Radio interface 6-75 authentication and data encryption. Also, be sure that the wep shared keys are the same for each client in the wireless network. Authentication type setup – sets the access point to communicate as an open system that accepts network access attempts from any client, or with clien...
Page 152
System configuration 6-76 shared key setup – select 64 bit, 128 bit, or 152 bit key length. Note that the same size of encryption key must be supported on all wireless clients. 152 bit key length is only supported on 802.11a radio. (default: 128 bit) key type – select the preferred method of enterin...
Page 153
Radio interface 6-77 four settings without having to update the client keys. Note: key index and type must match that configured on the clients. The configuration settings for wep are summarized below: cli commands for static wep shared key security – from the 802.11a or 802.11g interface configurat...
Page 154
System configuration 6-78 show interface wireless a or show interface wireless g command. Note: the index and length values used in the key command must be the same values used in the encryption and transmit-key commands. Ap(config)#interface wireless g 7-99 enter wireless configuration commands, on...
Page 155
Radio interface 6-79 cli commands for wep over 802.1x security – from the 802.11a or 802.11g interface configuration mode, use the authentication command to select open system authentication. Use the multicast-cipher command to select wep cipher type. Then set 802.1x to required with 802.1x command,...
Page 156
System configuration 6-80 wi-fi protected access (wpa) wpa employs a combination of several technologies to provide an enhanced security solution for 802.11 wireless networks. The access point supports the following wpa components and features: ieee 802.1x and the extensible authentication protocol ...
Page 157
Radio interface 6-81 when a radius server has authenticated a user’s credentials will encryption keys be sent to the access point and client. Note: to implement wpa on wireless clients requires a wpa-enabled network card driver and 802.1x client software that supports the eap authentication type tha...
Page 158
System configuration 6-82 uses tkip unicast data encryption keys for wpa clients and wep unicast keys for wep clients. The global encryption key for multicast and broadcast traffic must be the same for all clients, therefore it restricts encryption to a wep key. When access is opened to both wpa and...
Page 159
Radio interface 6-83 the wpa configuration parameters are described below: authentication type setup – when using wpa, set the access point to communicate as an open system to disable wep keys. Note: although wep keys are not needed for wpa, you must enable wep encryption through the web or cli in o...
Page 160
System configuration 6-84 • tkip: tkip provides data encryption enhancements including per-packet key hashing (that is, changing the encryption key on each packet), a message integrity check, an extended initialization vector with sequencing rules, and a re-keying mechanism. • aes: aes has been desi...
Page 161
Radio interface 6-85 the configuration settings for wpa are summarized below: cli commands for wpa pre-shared key security – from the 802.11a or 802.11g interface configuration mode, use the authentication command to set the access point to “open system.” use the wep encryption command to enable all...
Page 162
System configuration 6-86 authentication. To view the current 802.11g security settings, use the show interface wireless a or show interface wireless g command (not shown in example). Cli commands for wpa over 802.1x security – from the 802.11a or 802.11g interface configuration mode, use the authen...
Page 163: Status Information
Status information 6-87 status information the status page includes information on the following items: ap status the ap status window displays basic system configuration settings, as well as the settings for the wireless interfaces. Ap system configuration – the ap system configuration table displa...
Page 164
System configuration 6-88 • system up time: length of time the management agent has been up. • mac address: the physical layer address for this device. • system name: name assigned to this system. • system contact: administrator responsible for the system. • ip address: ip address of the management ...
Page 165
Status information 6-89 • radio authentication type: shows the bridge is set as an open system. • 802.1x: shows if ieee 802.1x access control for wireless clients is enabled. Cli commands for displaying system settings – to view the current wireless bridge system settings, use the show system comman...
Page 166: Station Status
System configuration 6-90 station status the station status window shows wireless clients currently associated with the access point. The station status page displays basic connection information for all associated stations. Note that this page is automatically refreshed every five seconds. • statio...
Page 167
Status information 6-91 • associated: shows if the station has been successfully associated with the access point. • forwarding allowed: shows if the station has passed authentication and is now allowed to forward traffic. • key type: displays one of the following: • disabled: the client is not usin...
Page 168: Event Logs
System configuration 6-92 event logs the event logs window shows the log messages generated by the wireless bridge and stored in memory. The event logs table displays the following information: • log time: the time the log message was generated. • event level: the logging level associated with this ...
Page 169
Status information 6-93.
Page 170
System configuration 6-94.
Page 171: Accessing The Cli
7- 1 chapter 7 command line interface using the command line interface accessing the cli when accessing the management interface for the wireless bridge via a telnet connection, the wireless bridge can be managed by entering command keywords and parameters at the prompt. Using the wireless bridge’s ...
Page 172
Command line interface 7-2 gateway if you are managing the wireless bridge from a different ip subnet. For example: after you configure the wireless bridge with an ip address, you can open a telnet session by performing these steps. 1. From the remote host, enter the telnet command and the ip addres...
Page 173: Entering Commands
Entering commands 7-3 entering commands this section describes how to enter cli commands. Keywords and arguments a cli command is a series of keywords and arguments. Keywords identify a command, and arguments specify configuration parameters. For example, in the command “show interface ethernet,” sh...
Page 174: Getting Help On Commands
Command line interface 7-4 getting help on commands you can display a brief description of the help system by entering the help command. You can also display command syntax by following a command with the “?” character to list keywords or parameters. Showing commands if you enter a “?” at the comman...
Page 175: Partial Keyword Lookup
Entering commands 7-5 the command “show interface ?” will display the following information: partial keyword lookup if you terminate a partial keyword with a question mark, alternatives that match the initial letters are provided. (remember not to leave a space between the command and question mark....
Page 176: Understanding Command Modes
Command line interface 7-6 understanding command modes the command set is divided into exec and configuration classes. Exec commands generally display information on system status or clear statistical counters. Configuration commands, on the other hand, modify interface parameters or enable certain ...
Page 177: Configuration Commands
Entering commands 7-7 configuration commands configuration commands are used to modify wireless bridge settings. These commands modify the running configuration and are saved in memory. The configuration commands are organized into three different modes: • global configuration - these commands modif...
Page 178: Command Line Processing
Command line interface 7-8 command line processing commands are not case sensitive. You can abbreviate commands and parameters as long as they contain enough letters to differentiate them from any other currently available commands or parameters. You can use the tab key to complete partial commands,...
Page 179: Command Groups
Command groups 7-9 command groups the system commands can be broken down into the functional groups shown below. Command group description page general basic commands for entering configuration mode, restarting the system, or quitting the cli 7-10 system management controls user name, password, brow...
Page 180: General Commands
Command line interface 7-10 the access mode shown in the following tables is indicated by these abbreviations: gc (global configuration), ic-e (ethernet interface configuration), and ic-w (wireless interface configuration). General commands configure this command activates global configuration mode....
Page 181: End
General commands 7-11 command mode exec example related commands end (page 7-11) end this command returns to the previous configuration mode. Default setting none command mode global configuration, interface configuration example this example shows how to return to the configuration mode from the in...
Page 184: Show History
Command line interface 7-14 show history this command shows the contents of the command history buffer. Default setting none command mode exec command usage • the history buffer size is fixed at 10 commands. • use the up or down arrow keys to scroll through the commands in the history buffer. Exampl...
Page 185: System Management Commands
System management commands 7-15 example the console port settings are fixed at the values shown below. System management commands these commands are used to configure the user name, password, browser management options, and a variety of other system information. Ap#show line console line information...
Page 186: Country
Command line interface 7-16 country this command configures the wireless bridge’s country code, which identifies the country of operation and sets the authorized radio channels. Syntax country country_code> country_code - a two character code that identifies the country of operation. See the followi...
Page 187
System management commands 7-17 default setting us - for units sold in the united states 99 (no country set) - for units sold in other countries command mode exec command usage • if you purchased an wireless bridge outside of the united states, the country code must be set before radio functions are...
Page 188: Prompt
Command line interface 7-18 example prompt this command customizes the cli prompt. Use the no form to restore the default prompt. Syntax prompt string no prompt string - any alphanumeric string to use for the cli prompt. (maximum length: 255 characters) default setting dual outdoor command mode glob...
Page 189: System Name
System management commands 7-19 system name this command specifies or modifies the system name for this device. Use the no form to restore the default system name. Syntax system name name no system name name - the name of this host. (maximum length: 32 characters) default setting outdoor bridge comm...
Page 190: Password
Command line interface 7-20 example password after initially logging onto the system, you should set the password. Remember to record it in a safe place. Use the no form to reset the default password. Syntax password password no password password - password for management access. (length: 3-16 chara...
Page 191: Ip Http Server
System management commands 7-21 default setting 80 command mode global configuration example related commands ip http server (page 7-21) ip http server this command allows this device to be monitored or configured from a browser. Use the no form to disable this function. Syntax ip http server no ip ...
Page 192: Show System
Command line interface 7-22 show system this command displays basic system configuration settings. Default setting none command mode exec example ap#show system system information ========================================================= serial number : 0000000000 system up time : 0 days, 0 hours, 1...
Page 193: Show Version
System logging commands 7-23 show version this command displays the software version for the system. Default setting none command mode exec example system logging commands these commands are used to configure system logging on the wireless bridge. Ap#show version version v1.1.2.1b05 ap# command func...
Page 194: Logging On
Command line interface 7-24 logging on this command controls logging of error messages; i.E., sending debug or error messages to memory. The no form disables the logging process. Syntax logging on no logging on default setting none command mode global configuration command usage the logging process ...
Page 195: Logging Console
System logging commands 7-25 default setting none command mode global configuration example logging console this command initiates logging of error messages to the console. Use the no form to disable logging to the console. Syntax logging console no logging console default setting disabled command m...
Page 196: Logging Facility-Type
Command line interface 7-26 default setting error command mode global configuration command usage messages sent include the selected level down to the emergency level. Example logging facility-type this command sets the facility type for remote logging of syslog messages. Syntax logging facility-typ...
Page 197: Show Logging
System logging commands 7-27 default setting 16 command mode global configuration command usage the command specifies the facility type tag sent in syslog messages. (see rfc 3164.) this type has no effect on the kind of messages reported by the wireless bridge. However, it may be used by the syslog ...
Page 198: System Clock Commands
Command line interface 7-28 example system clock commands these commands are used to configure sntp and system clock settings on the wireless bridge. Ap#show logging logging information ============================================ syslog state : disabled logging host state : enabled logging console ...
Page 200: Sntp-Server Enable
Command line interface 7-30 sntp-server enable this command enables sntp client requests for time synchronization with ntp or sntp time servers specified by the sntp-server ip command. Use the no form to disable sntp client requests. Syntax sntp-server enable no sntp-server enable default setting di...
Page 201: Sntp-Server Date-Time
System clock commands 7-31 sntp-server date-time this command sets the system clock. Default setting 00:14:00, january 1, 1970 command mode global configuration example this example sets the system clock to 17:37 june 19, 2003. Related commands sntp-server enable (page 7-30) sntp-server daylight-sav...
Page 202: Sntp-Server Timezone
Command line interface 7-32 command usage the command sets the system clock back one hour during the specified period. Example this sets daylight savings time to be used from july 1st to september 1st. Sntp-server timezone this command sets the time zone for the wireless bridge’s internal clock. Syn...
Page 203: Show Sntp
System clock commands 7-33 degrees longitude. To display a time corresponding to your local time, you must indicate the number of hours and minutes your time zone is east (before) or west (after) of utc. Example show sntp this command displays the current time and configuration settings for the sntp...
Page 204: Snmp Commands
Command line interface 7-34 snmp commands controls access to this wireless bridge from management stations using the simple network management protocol (snmp), as well as the hosts that will receive trap messages. Snmp-server community this command defines the community access string for the simple ...
Page 205: Snmp-Server Contact
Snmp commands 7-35 default setting • public - read-only access. Authorized management stations are only able to retrieve mib objects. • private - read/write access. Authorized management stations are able to both retrieve and modify mib objects. Command mode global configuration command usage if you...
Page 206: Snmp-Server Enable Server
Command line interface 7-36 example related commands snmp-server location (page 7-38) snmp-server enable server this command enables snmp management access and also enables this device to send snmp traps (i.E., notifications). Use the no form to disable snmp service and trap messages. Syntax snmp-se...
Page 208: Snmp-Server Location
Command line interface 7-38 example related commands snmp-server enable server (page 7-36) snmp-server location this command sets the system location string. Use the no form to remove the location string. Syntax snmp-server location text no snmp-server location text - string that describes the syste...
Page 209: Show Snmp
Flash/file commands 7-39 show snmp this command displays the snmp configuration settings. Command mode exec example flash/file commands these commands are used to manage the system code or configuration files. Ap#show snmp snmp information ============================================ service state :...
Page 210: Bootfile
Command line interface 7-40 bootfile this command specifies the image used to start up the system. Syntax bootfile filename> filename - name of the image file. Default setting none command mode exec command usage • the file name should not contain slashes (\ or /), the leading letter of the file nam...
Page 211: Copy
Flash/file commands 7-41 copy this command copies a boot file, code image, or configuration file between the wireless bridge’s flash memory and a ftp/tftp server. When you save the configuration settings to a file on a ftp/tftp server, that file can later be downloaded to the wireless bridge to rest...
Page 212: Delete
Command line interface 7-42 • the destination file name should not contain slashes (\ or /), the leading letter of the file name should not be a period (.), and the maximum length for file names on the ftp/tftp server is 255 characters or 32 characters for files on the wireless bridge. (valid charac...
Page 213: Dir
Flash/file commands 7-43 default setting none command mode exec caution: beware of deleting application images from flash memory. At least one application image is required in order to boot the wireless bridge. If there are multiple image files in flash memory, and the one used to boot the wireless ...
Page 214
Command line interface 7-44 command usage file information is shown below: example the following example shows how to display all file information: column heading description file name the name of the file. Type (2) operation code and (5) configuration file file size the length of the file in bytes....
Page 215: Radius Client
Radius client 7-45 radius client remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) is a logon authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access for radius-aware devices to the network. An authentication server contains a database of credentials, such as users...
Page 216: Radius-Server Port
Command line interface 7-46 command mode global configuration example radius-server port this command sets the radius server network port. Syntax radius-server [secondary] port port_number> • secondary - secondary server. • port_number - radius server udp port used for authentication messages. (rang...
Page 217: Radius-Server Key
Radius client 7-47 radius-server key this command sets the radius encryption key. Syntax radius-server [secondary] key key_string> • secondary - secondary server. • key_string - encryption key used to authenticate logon access for client. Do not use blank spaces in the string. (maximum length: 20 ch...
Page 218: Radius-Server Timeout
Command line interface 7-48 example radius-server timeout this command sets the interval between transmitting authentication requests to the radius server. Syntax radius-server [secondary] timeout number_of_seconds • secondary - secondary server. • number_of_seconds - number of seconds the access po...
Page 219: Authentication
Authentication 7-49 example authentication the access point supports ieee 802.1x access control for wireless clients. This control feature prevents unauthorized access to the network by requiring a 802.1x client application to submit user credentials for authentication. Client authentication is then...
Page 220
Command line interface 7-50 client mac addresses can also be used for authentication on the access point. For local mac authentication, first define the default filtering policy using the address filter default command. Then enter the mac addresses to be filtered, indicating if they are allowed or d...
Page 222
Command line interface 7-52 • when 802.1x is supported, the access point supports 802.1x authentication only for clients initiating the 802.1x authentication process (i.E., the access point does not initiate 802.1x authentication). For stations initiating 802.1x, only those stations successfully aut...
Page 223
Authentication 7-53 command usage • the access point uses eapol (extensible authentication protocol over lans) packets to pass dynamic unicast session and broadcast keys to wireless clients. The 802.1x broadcast-key-refresh-rate command specifies the interval after which the broadcast keys are chang...
Page 224: 802.1X Session-Timeout
Command line interface 7-54 example 802.1x session-timeout this command sets the time period after which a connected client must be re-authenticated. Use the no form to disable 802.1x re-authentication. Syntax 802.1x session-timeout seconds> no 802.1x session-timeout seconds - the number of seconds....
Page 225: 802.1X Supplicant
Authentication 7-55 802.1x supplicant this command sets the user name and password used for authentication of the access point when operating as a 802.1x supplicant and enables supplicant authentication. Use the no form to disable the feature. Syntax 802.1x supplicant eth_password password> 802.1x s...
Page 226: Address Filter Default
Command line interface 7-56 command mode global configuration command usage • ethernet and wds user names and passwords must be set before enabling the 802.1x supplicant feature for the specified port. • the access point currently only supports eap-md5 chap for 802.1x supplicant authentication. Exam...
Page 228: Address Filter Delete
Command line interface 7-58 example related commands address filter default (page 7-56) show authentication (page 7-60) address filter delete this command deletes a mac address from the filter table. Syntax address filter delete mac-address> mac-address - physical address of client. (enter six pairs...
Page 230: Show Authentication
Command line interface 7-60 mac-authentication session-timeout this command sets the interval at which associated clients will be re-authenticated with the radius server authentication database. Use the no form to disable reauthentication. Syntax mac-authentication session-timeout seconds> seconds -...
Page 231: Wds Commands
Wds commands 7-61 example wds commands the commands described in this section are used to configure the wireless distribution system (wds) forwarding table. Ap#show authentication authentication information ========================================================= mac authentication server : remote ...
Page 233: Wds Enable
Wds commands 7-63 command mode global configuration command usage • you can only configure one mac address per wireless port id. • the ethernet mac address for each bridge unit is printed on the label on the back of the unit. • when trying to connect to other bridges, please input the ethernet mac a...
Page 235: Bridge Commands
Bridge commands 7-65 bridge commands the commands described in this section are used to set the mac address table aging time and spanning tree parameters for both the ethernet and wireless interfaces. Command function mode page bridge timeout sets the aging time for the address table gc 7-66 bridge ...
Page 236: Bridge Timeout
Command line interface 7-66 bridge timeout this command sets the aging time for both the ethernet port and the wireless interface. Syntax bridge timeout interface-id> seconds> • interface-id - an identifier that specifies the interface. (0 for ethernet, 2 for 802.11a wireless) • seconds - the time t...
Page 237
Bridge commands 7-67 default setting spanning tree is enabled. Command mode global configuration command usage the spanning tree protocol (stp) can be used to detect and disable network loops, and to provide backup links between switches, bridges or routers. This allows the wireless bridge to intera...
Page 238
Command line interface 7-68 default setting 15 seconds command mode global configuration command usage this command sets the maximum time (in seconds) the root device will wait before changing states (i.E., discarding to learning to forwarding). This delay is required because every device must recei...
Page 239: Bridge Stp-Bridge Max-Age
Bridge commands 7-69 command mode global configuration command usage this command sets the time interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a configuration message. Example bridge stp-bridge max-age use this command to configure the spanning tree bridge maximum age globally for the wire...
Page 240: Bridge Stp-Bridge Priority
Command line interface 7-70 command usage this command sets the maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without receiving a configuration message before attempting to reconfigure. All device ports (except for designated ports) should receive configuration messages at regular intervals. Any port ...
Page 241: Bridge Stp-Port Path-Cost
Bridge commands 7-71 command usage bridge priority is used in selecting the root device, root port, and designated port. The device with the highest priority becomes the stp root device. However, if all devices have the same priority, the device with the lowest mac address will then become the root ...
Page 242: Bridge Stp-Port Priority
Command line interface 7-72 command usage • this command is used by the spanning tree protocol to determine the best path between devices. Therefore, lower values should be assigned to ports attached to faster media, and higher values assigned to ports with slower media. • path cost takes precedence...
Page 243: Bridge Stp-Port Portfast
Bridge commands 7-73 • where more than one port is assigned the highest priority, the port with lowest numeric identifier will be enabled. Example related commands bridge stp-port path-cost (page 7-71) bridge stp-port portfast use this command to set an interface to fast forwarding. Use the no form ...
Page 244
Command line interface 7-74 • since end-nodes cannot cause forwarding loops, they can be passed through the spanning tree state changes more quickly than allowed by standard convergence time. Fast forwarding can achieve quicker convergence for end-node devices, and also overcome other stp related ti...
Page 246: Filtering Commands
Command line interface 7-76 filtering commands the commands described in this section are used to control access to the management interface from the wireless interface and filter traffic using specific ethernet protocol types. Filter local-bridge this command disables communication between wireless...
Page 247: Filter Ap-Manage
Filtering commands 7-77 command usage this command can disable wireless-to-wireless communications between clients via the access point. However, it does not affect communications between wireless clients and the wired network. Example related commands filter ethernet-type enable (page 7-78) filter ...
Page 248: Filter Ethernet-Type Enable
Command line interface 7-78 filter ethernet-type enable this command checks the ethernet type on all incoming and outgoing ethernet packets against the protocol filtering table. Use the no form to disable this feature. Syntax filter ethernet-type enable no filter ethernet-type enable default disable...
Page 249
Filtering commands 7-79 filter ethernet-type protocol this command sets a filter for a specific ethernet type. Use the no form to disable filtering for a specific ethernet type. Syntax filter ethernet-type protocol protocol> no filter ethernet-type protocol protocol> protocol - an ethernet protocol ...
Page 250: Show Filters
Command line interface 7-80 show filters this command shows the filter options and protocol entries in the filter table. Command mode exec example pppoe commands the commands described in this section configure pppoe management tunnel connection parameters for the ethernet port. Ap#show filters prot...
Page 251: Ip Pppoe
Pppoe commands 7-81 ip pppoe this command enables point-to-point protocol over ethernet (pppoe) on the ethernet interface. Use the no form to disable pppoe on the ethernet interface. Syntax ip pppoe no ip pppoe default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (ethernet) pppoe lcp echo-f...
Page 252: Pppoe Ip Allocation Mode
Command line interface 7-82 command usage the access point uses a pppoe connection, or tunnel, only for management traffic between the access point and a remote pppoe server (typically at an isp). Examples of management traffic that may initiated by the access point and carried over a pppoe tunnel a...
Page 253: Pppoe Ipcp Dns
Pppoe commands 7-83 example related commands pppoe local ip (page 7-86) pppoe remote ip (page 7-86) pppoe ipcp dns this command requests allocation of ip addresses for dynamic naming system (dns) servers from the device at the remote end of the pppoe tunnel. Syntax pppoe ipcp dns no pppoe ipcp dns d...
Page 254: Pppoe Lcp Echo-Interval
Command line interface 7-84 pppoe lcp echo-interval this command sets the link control protocol (lcp) echo interval for the pppoe tunnel. Syntax pppoe lcp echo-interval interval> interval - the interval between sending echo requests. (range: 1-60 seconds) default setting 10 command mode interface co...
Page 255: Pppoe Lcp Echo-Failure
Pppoe commands 7-85 pppoe lcp echo-failure this command sets the link control protocol (lcp) echo timeout for the pppoe tunnel. Syntax pppoe lcp echo-failure timeout> timeout - the number of timeouts allowed. (range: 1-10) default setting 3 command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usa...
Page 256: Pppoe Local Ip
Command line interface 7-86 pppoe local ip this command sets the local ip address for the pppoe tunnel. Syntax pppoe local ip ip-address> ip-address - ip address of the local end of the pppoe tunnel. Default setting none command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage if the pppoe ip a...
Page 257: Pppoe Username
Pppoe commands 7-87 default setting none command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage if the pppoe ip allocation mode is set to static, the remote ip address must be entered with this command, and the local ip address must be entered with the pppoe local ip command. Example related ...
Page 258: Pppoe Password
Command line interface 7-88 command usage you must enter a user name with this command, and a password with the pppoe password command. Example related commands pppoe password (page 7-88) pppoe password this command sets the password for the pppoe tunnel. Syntax pppoe password string> string - passw...
Page 259: Pppoe Service-Name
Pppoe commands 7-89 pppoe service-name this command sets the service name for the pppoe tunnel. Syntax pppoe service-name string> string - service name assigned by the service provider. (range: 1-63 alphanumeric characters) default setting none command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command...
Page 260: Show Pppoe
Command line interface 7-90 example show pppoe this command shows information about the pppoe configuration. Command mode privileged exec example ap#(if-ethernet)#pppoe restart ap# ap#show pppoe pppoe information ====================================================== state : link up username : mike ...
Page 261: Ethernet Interface Commands
Ethernet interface commands 7-91 ethernet interface commands the commands described in this section configure connection parameters for the ethernet interface. Interface ethernet this command enters ethernet interface configuration mode. Syntax interface ethernet default setting none command mode gl...
Page 262: Dns Server
Command line interface 7-92 example to specify the 10/100base-tx network interface, enter the following command: dns server this command specifies the address for the primary or secondary domain name server to be used for name-to-address resolution. Syntax dns primary-server server-address> dns seco...
Page 263: Ip Address
Ethernet interface commands 7-93 related commands show interface ethernet (page 7-96) ip address this command sets the ip address for the (10/100base-tx) ethernet interface. Use the no form to restore the default ip address. Syntax ip address ip-address> netmask> gateway> no ip address • ip-address ...
Page 264: Ip Dhcp
Command line interface 7-94 • you must assign an ip address to this device to gain management access over the network or to connect the wireless bridge to existing ip subnets. You can manually configure a specific ip address using this command, or direct the device to obtain an address from a dhcp s...
Page 265: Shutdown
Ethernet interface commands 7-95 command usage • you must assign an ip address to this device to gain management access over the network or to connect the wireless bridge to existing ip subnets. You can manually configure a specific ip address using the ip address command, or direct the device to ob...
Page 266: Show Interface Ethernet
Command line interface 7-96 command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage this command allows you to disable the ethernet port due to abnormal behavior (e.G., excessive collisions), and reenable it after the problem has been resolved. You may also want to disable the ethernet port fo...
Page 267: Wireless Interface Commands
Wireless interface commands 7-97 example wireless interface commands the commands described in this section configure connection parameters for the wireless interface. Ap#show interface ethernet ethernet interface information ======================================== ip address : 192.168.2.2 subnet m...
Page 268
Command line interface 7-98 dtim-period configures the rate at which stations in sleep mode must wake up to receive broadcast/multicast transmissions ic-w 7-104 fragmentation- length configures the minimum packet size that can be fragmented ic-w 7-105 rts-threshold sets the packet size threshold at ...
Page 269: Interface Wireless
Wireless interface commands 7-99 interface wireless this command enters wireless interface configuration mode. Syntax interface wireless a • a - 802.11a radio interface. • g - 802.11g radio interface default setting none command mode global configuration example to specify the wireless interface, en...
Page 270: Ssid
Command line interface 7-100 default setting none command mode interface configuration (wireless) example ssid this command configures the service set identifier (ssid). Syntax ssid string> string - the name of a basic service set supported by the access point. (range: 1 - 32 characters) default set...
Page 271: Closed-System
Wireless interface commands 7-101 closed-system this command closes access to clients without a pre-configured ssid. Use the no form to disable this feature. Syntax closed-system no closed-system default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage when ssid broadca...
Page 272: Channel
Command line interface 7-102 command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage the maximum transmission distance is affected by the data rate. The lower the data rate, the longer the transmission distance. Example channel this command configures the radio channel through which the local ...
Page 273: Turbo
Wireless interface commands 7-103 example turbo this command sets the wireless bridge to an enhanced mode (not regulated in ieee 802.11a) that provides a higher data rate of up to 108 mbps. Default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (wireless - 802.11a) command usage • the normal ...
Page 274: Beacon-Interval
Command line interface 7-104 beacon-interval this command configures the rate at which beacon signals are transmitted from the wireless bridge. Syntax beacon-interval interval> interval - the rate for transmitting beacon signals. (range: 20-1000 milliseconds) default setting 100 command mode interfa...
Page 275: Fragmentation-Length
Wireless interface commands 7-105 default setting 2 command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage • the delivery traffic indication map (dtim) packet interval value indicates how often the mac layer forwards broadcast/multicast traffic. This parameter is necessary to wake up remote b...
Page 276: Rts-Threshold
Command line interface 7-106 default setting 2346 command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage • if the packet size is smaller than the preset fragment size, the packet will not be segmented. • fragmentation of the pdus (package data unit) can increase the reliability of transmissio...
Page 277: Transmit-Power
Wireless interface commands 7-107 default setting 2347 command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage • if the threshold is set to 0, the wireless bridge always sends rts signals. If set to 2347, the wireless bridge never sends rts signals. If set to any other value, and the packet si...
Page 278: Max-Association
Command line interface 7-108 default setting full command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage • the “min” keyword indicates minimum power. • the longer the transmission distance, the higher the transmission power required. Power selection is not just a trade off between coverage ar...
Page 281
Wireless interface commands 7-111 • aes has been designated by the national institute of standards and technology as the successor to the data encryption standard (des) encryption algorithm, and will be used by the u.S. Government for encrypting all sensitive, nonclassified information. Because of i...
Page 283: Transmit-Key
Wireless interface commands 7-113 • to enable aes encryption, use the encryption command to specify the key type, and use the key command to configure a key for each wireless port. • if wep is enabled, all units in the wireless bridge network must be configured with the same keys. • the wep key leng...
Page 284: Multicast-Cipher
Command line interface 7-114 command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage • if you use wep key encryption, the wireless bridge uses the transmit key to encrypt multicast and broadcast data signals that it sends to other nodes. Other keys can be used for decryption of data from other...
Page 285
Wireless interface commands 7-115 command usage • wpa enables the access point to support different unicast encryption keys for each client. However, the global encryption key for multicast and broadcast traffic must be the same for all clients. This command sets the encryption type that is supporte...
Page 288: Wpa-Preshared-Key
Command line interface 7-118 example related commands wpa-clients (page 7-116) wpa-preshared-key (page 7-118) wpa-preshared-key this command defines a wi-fi protected access (wpa) preshared-key. Syntax wpa-preshared-key type> value> • type - input format. (options: ascii, hex) • value - the key stri...
Page 289: Wpa-Psk-Type
Wireless interface commands 7-119 example related commands wpa-clients (page 7-116) wpa-mode (page 7-117) wpa-psk-type this command defines the wi-fi protected access (wpa) preshared-key type. Syntax wpa-psk-type type> type - input format. (options: alphanumeric, hex) default setting hex command mod...
Page 290: Shutdown
Command line interface 7-120 shutdown this command disables the wireless interface. Use the no form to restart the interface. Syntax shutdown no shutdown default setting interface enabled command mode interface configuration (wireless) example show interface wireless this command displays the status...
Page 291: Show Station
Wireless interface commands 7-121 example show station this command shows the wireless clients associated with the access point. Command mode exec ap#show interface wireless a wireless interface information ========================================================= ----------------identification-----...
Page 292: Iapp Commands
Command line interface 7-122 example iapp commands the command described in this section enables the protocol signaling required to ensure the successful handover of wireless clients roaming between different 802.11f-compliant access points. In other words, the 802.11f protocol can ensure successful...
Page 293: Vlan Commands
Vlan commands 7-123 default enabled command mode global configuration command usage the current 802.11 standard does not specify the signaling required between access points in order to support clients roaming from one access point to another. In particular, this can create a problem for clients roa...
Page 294: Vlan
Command line interface 7-124 note: before enabling vlans on the wireless bridge , you must configure the connected lan switch port to accept tagged vlan packets with the wireless bridge ’s native vlan id. Otherwise, connectivity to the wireless bridge will be lost when you enable the vlan feature. T...
Page 295: Native-Vlanid
Vlan commands 7-125 example related commands native-vlanid (page 7-125) native-vlanid this command configures the native vlan id for the wireless bridge. Syntax native-vlanid vlan-id> vlan-id - native vlan id. (range: 1-64) default setting 1 command mode global configuration command usage when vlans...
Page 296
Command line interface 7-126.
Page 297
A-1 appendix a troubleshooting check the following items before you contact local technical support. 1. If wireless bridge units do not associate with each other, check the following: • check the power injector led for each bridge unit to be sure that power is being supplied • be sure that antennas ...
Page 298
Troubleshooting a-2 3. If the wireless bridge cannot be configured using telnet, a web browser, or snmp software: • be sure to have configured the wireless bridge with a valid ip address, subnet mask and default gateway. • check that you have a valid network connection to the wireless bridge and tha...
Page 299: General Specifications
B-1 appendix b specifications general specifications maximum channels (outdoor) 802.11a: us & canada: 9 (normal mode), 3 (turbo mode) japan: 4 (normal mode), 1 (turbo mode) etsi: 11 channels (normal mode), 4 (turbo mode) taiwan: 4 (normal mode), 1 (turbo mode) 802.11g: fcc/ic: 1-11 etsi: 1-13 france...
Page 300
Specifications b-2 modulation types 802.11a: bpsk, qpsk, 16-qam, 64-qam 802.11g: cck, bpsk, qpsk, ofdm 802.11b: cck, bpsk, qpsk network configuration bridge mode: point-to-point and point-to-multipoint access point mode: infrastructure operating frequency 802.11a: 5.15 ~ 5.25 ghz (lower band) us/can...
Page 301
General specifications b-3 network management web-browser, telnet, snmp temperature operating: -33 to 55 °c (-27.4 to 131 °f) storage: -40 to 80 °c (-40 to 176 °f) humidity 5% to 95% (non-condensing) emc compliance (class b) fcc class b (us) rtted 1999/5/ec dgt (taiwan) radio signal certification fc...
Page 302: Antenna Specifications
Specifications b-4 antenna specifications 17 dbi integrated panel frequency range 5.150 - 5.850 ghz gain 17 dbi vswr 1.8 : 1 max polarization linear, vertical/horizontal hpbw horizontal: 20° vertical: 22° front-to-back ratio >25 db power handling 10 w (cw) impedance 50 ohms connector sma female.
Page 303
Antenna specifications b-5 17 dbi integrated panel antenna link budget (5.825 ghz, cable loss 1 db, fade margin 5 db) modulation/rates transmit power (dbm) receive sensitivity (dbm) maximum range (km) with 17 dbi panel* normal mode bpsk (6 mbps) 20 -88 15.4 bpsk (9 mbps) 20 -87 14.7 qpsk (12 mbps) 2...
Page 304
Specifications b-6.
Page 305
C-1 appendix c cables and pinouts twisted-pair cable assignments for 10/100base-tx connections, a twisted-pair cable must have two pairs of wires. Each wire pair is identified by two different colors. For example, one wire might be green and the other, green with white stripes. Also, an rj-45 connec...
Page 306
Cables and pinouts c-2 10/100base-tx pin assignments use unshielded twisted-pair (utp) or shielded twisted-pair (stp) cable for rj-45 connections: 100-ohm category 3 or better cable for 10 mbps connections, or 100-ohm category 5 or better cable for 100 mbps connections. Also be sure that the length ...
Page 307: Straight-Through Wiring
Twisted-pair cable assignments c-3 straight-through wiring because the 10/100 mbps input port on the power injector uses an mdi pin configuration, you must use “straight-through” cable for network connections to hubs or switches that only have mdi-x ports. However, if the device to which you are con...
Page 308: 8-Pin Din Connector Pinout
Cables and pinouts c-4 8-pin din connector pinout the ethernet cable from the power injector connects to an 8-pin din connector on the wireless bridge. This connector is described in the following figure and table. 8-pin din ethernet port pinout pin signal name 1 transmit data plus (td+) 2 transmit ...
Page 309
8-pin din connector pinout c-5 8-pin din to rj-45 cable wiring to construct an extended ethernet cable to connect from the power injector’s rj-45 output port to the wireless bridge’s 8-pin din connector, follow the wiring diagram below. Use category 5 or better utp or stp cable, maximum length 100 m...
Page 310
Cables and pinouts c-6.
Page 311
Glossary-1 glossary 10base-t ieee 802.3 specification for 10 mbps ethernet over two pairs of category 3 or better utp cable. 100base-tx ieee 802.3u specification for 100 mbps fast ethernet over two pairs of category 5 or better utp cable. Access point an internetworking device that seamlessly connec...
Page 312
Glossary glossary-2 basic service set (bss) a set of 802.11-compliant stations and an access point that operate as a fully-connected wireless network. Beacon a signal periodically transmitted from the access point that is used to identify the service set, and to maintain contact with wireless client...
Page 313
Glossary glossary-3 file transfer protocol (ftp) a tcp/ip protocol used for file transfer. Hypertext transfer protocol (http) http is a standard used to transmit and receive all data over the world wide web. Internet control message protocol (icmp) a network layer protocol that reports errors in pro...
Page 314
Glossary glossary-4 open system a security option which broadcasts a beacon signal including the access point’s configured ssid. Wireless clients can read the ssid from the beacon, and automatically reset their ssid to allow immediate connection to the nearest access point. Orthogonal frequency divi...
Page 315
Glossary glossary-5 simple network time protocol (sntp) sntp allows a device to set its internal clock based on periodic updates from a network time protocol (ntp) server. Updates can be requested from a specific ntp server, or can be received via broadcasts sent by ntp servers. Trivial file transfe...
Page 316
Glossary glossary-6.
Page 317
Index-1 a advanced encryption standard see aes aes 6-82 configuring 6-68 aes, configuring 6-66, 7-110 authentication 6-16, 7-109 configuring 6-16, 7-109 mac address 6-18, 7-56, 7-57 type 5-10, 6-72, 7-101 b basic service set see bss beacon interval 6-59, 7-104 rate 6-59, 7-104 bootp 7-93, 7-94 bpdu ...
Page 318
Index index-2 filter 6-26, 7-56 address 6-16, 7-56 between wireless clients 6-28, 7-76 local bridge 6-28, 7-76 local or remote 6-16, 7-59 management access 6-28, 7-77 protocol types 6-28, 7-78 vlans 6-26, 7-123 firmware displaying version 6-35, 7-23 upgrading 6-34, 6-36, 7-41 fragmentation 7-105 g g...
Page 319
Index index-3 password configuring 6-33, 7-20 management 6-33, 7-20 poe 4-8 specifications b-2 port priority sta 7-72 power over ethernet see poe power supply, specifications b-2 psk 6-81, 7-117 r radio channel 802.11a interface 6-58, 7-102 802.11g interface 6-63, 7-102 configuring 5-6 radius 6-10, ...
Page 320
Index index-4 temporal key integrity protocol see tkip time zone 6-41, 7-32 tkip 6-81, 7-114 transmit power, configuring 6-59, 7-107 trap destination 6-31, 7-37 trap manager 6-31, 7-37 troubleshooting a-1 u upgrading software 6-34, 7-41 user name, manager 6-33, 7-19 user password 6-33, 7-19, 7-20 v ...
Page 322
Smc2888w-s smc2888w-m.