- DL manuals
- Suzuki
- Motorcycle
- 2006 GSR600
- Service Manual
Suzuki 2006 GSR600 Service Manual
Summary of 2006 GSR600
Page 1
Gsr600 9 9 5 0 0 - 3 6 1 6 0 - 0 1 e.
Page 2: Group Index
Group index general information 1 periodic maintenance 2 engine 3 fi system diagnosis 4 fuel system and throttle body 5 exhaust system 6 cooling and lubrication system 7 chassis 8 electrical system 9 servicing information 10 emission control information 11 wiring diagram 12 foreword this manual cont...
Page 3: How To Use This Manual
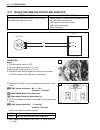
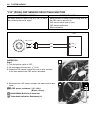
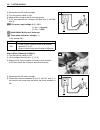
How to use this manual to locate what you are looking for: 1. The text of this manual is divided into sections. 2. The section titles are listed in the group index. 3. Holding the manual as shown at the right will allow you to find the first page of the section easily. 4. The contents are listed on ...
Page 4
Symbol listed in the table below are the symbols indicating instructions and other information necessary for servic- ing. The meaning of each symbol is also included in the table. Symbol definition symbol definition torque control required. Data beside it indicates specified torque. Apply thread loc...
Page 5: Manual
Abbreviations used in this manual a abdc : after bottom dead center ac : alternating current acl : air cleaner, air cleaner box api : american petroleum institute atdc : after top dead center atm pressure : atmospheric pressure : atmospheric pressure sensor (aps, ap sensor) a/f : air fuel mixture b ...
Page 6
M mal-code : malfunction code (diagnostic code) max : maximum mil : malfunction indicator lamp (led) min : minimum n nox : nitrogen oxides o ohc : over head camshaft ops : oil pressure switch p pcv : positive crankcase ventilation (crankcase breather) r rh : right hand rom : read only memory s sae :...
Page 7
Wire color b : black g : green p : pink bl : blue gr : gray r : red br : brown lbl : light blue w : white dg : dark green lg : light green y : yellow dgr : dark gray o : orange b/bl : black with blue tracer b/br : black with brown tracer b/g : black with green tracer b/lg : black with light green tr...
Page 8: General Information
1 general information 1-1 general information contents country and area codes the following codes stand for the applicable country(-ies) and area(-s). Model code country or area efective frame no. Gsr600 e-02 e-19 e-24 u.K. Eu australia js1b9111100 100001 – js1b9111100 100001 – js1b9111300 100001 – ...
Page 9: Warning/caution/note
1-2 general information warning/caution/note please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully. To emphasize special information, the symbol and the words warning, caution and note have special meanings. Pay special attention to the mes- sages highlighted by these signal words. Indicates...
Page 10
General information 1-3 * if parts replacement is necessary, replace the parts with suzuki genuine parts or their equiva- lent. * when removing parts that are to be reused, keep them arranged in an orderly manner so that they may be reinstalled in the proper order and orientation. * be sure to use s...
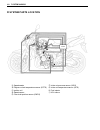
Page 11: Serial Number Location
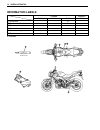
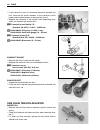
1-4 general information suzuki gsr600k6 (’06-model) • difference between illustration and actual motorcycle may exist depending on the markets. Serial number location the frame serial number or v.I.N. (vehicle identification number) 1 is stamped on the right side of the steering head pipe. The engin...
Page 12
General information 1-5 fuel, oil and engine coolant recommendation fuel gasoline used should be graded 91 octane (research method) or higher. Unleaded gasoline is recom- mended. Engine oil oil quality is a major contributor to your engine’s performance and life. Always select good quality engine oi...
Page 13
1-6 general information engine coolant use an anti-freeze/engine coolant compatible with an aluminum radiator, mixed with distilled water only. Water for mixing use distilled water only. Water other than distilled water can corrode and clog the aluminum radiator. Anti-freeze/engine coolant the engin...
Page 14: Break-In Procedures
General information 1-7 break-in procedures during manufacture only the best possible materials are used and all machined parts are finished to a very high standard but it is still necessary to allow the moving parts to “break-in” before subjecting the engine to maximum stresses. The future performa...
Page 15: Information Labels
1-8 general information information labels a: attached gsr600 gsr600u e-02 e-19 e-24 e-19 1 noise label a 2 fuel caution label a a 3 tire information label a a a a 4 general information label a a 5 general warning label a a 6 id plate a a a a chain cover.
Page 16: Specifications
General information 1-9 specifications dimensions and dry mass overall length .......................................................................... 2 090 mm overall width ........................................................................... 795 mm overall height .............................
Page 17
1-10 general information chassis front suspension .................................................................... Telescopic, coil spring, oil damped rear suspension ..................................................................... Link type, coil spring, oil damped front fork stroke..........
Page 18: Periodic Maintenance
Periodic maintenance 2-1 2 periodic maintenance contents periodic maintenance schedule .................................................... 2- 2 periodic maintenance chart..................................................... 2- 2 lubrication points ......................................................
Page 19
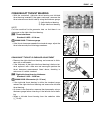
2-2 periodic maintenance periodic maintenance schedule the chart below lists the recommended intervals for all the required periodic service work necessary to keep the motorcycle operating at peak performance and economy. Mileages are expressed in terms of kilome- ters, miles and time for your conve...
Page 20
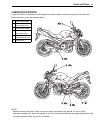
Periodic maintenance 2-3 lubrication points proper lubrication is important for smooth operation and long life of each working part of the motorcycle. Major lubrication points are indicated below. Note: * before lubricating each part, clean off any rusty spots and wipe off any grease, oil, dirt or g...
Page 21: Maintenance And Tune-Up
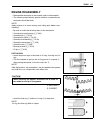
2-4 periodic maintenance maintenance and tune-up procedures this section describes the servicing procedures for each item of the periodic maintenance requirements. Air cleaner • lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) • remove the air cleaner box cover 1 by removing the screws and iap sensor. • remo...
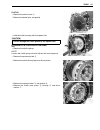
Page 22
Periodic maintenance 2-5 spark plug spark plug and ignition coil/plug cap removal • lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) • remove the air cleaner box. ( 5-13) • disconnect all lead wire couplers 1 from ignition coil/plug caps. • remove the ignition coil/plug caps. • remove the spark plugs. 099...
Page 23
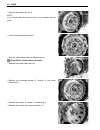
2-6 periodic maintenance spark plug gap • measure the spark plug gap with a thickness gauge. • adjust the spark plug gap if necessary. spark plug gap: standard: 0.7 – 0.8 mm 09900-20803: thickness gauge electrode’s condition • check the condition of the electrode. • if it is extremely worn or bu...
Page 24
Periodic maintenance 2-7 valve clearance • lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) • remove the air cleaner box. ( 5-13) • disconnect the cmp sensor coupler 1. • remove the pair control solenoid valve 2. • remove the spark plugs. ( 2-5) • loosen the throttle body clamp screws at the intake pipe si...
Page 25
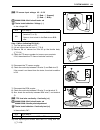
2-8 periodic maintenance • remove the valve timing inspection plug 1. • turn the crankshaft to bring the “top” line on the starter clutch to the index mark and also to bring the notches a on the left ends of both camshafts (ex. And in.) to the positions as shown. • in this condition, read the valve ...
Page 26: 170
Periodic maintenance 2-9 • turn the crankshaft 360 degrees (one rotation) to bring the “top” line on the starter clutch to the index mark of valve tim- ing inspection hole and also to bring the notches a to the position as shown. • read the clearance at the rest of the valves c and adjust the cleara...
Page 27
2-10 periodic maintenance note: * be sure to apply engine oil to tappet shim top and bottom faces. * when seating the tappet shim, be sure the figure printed sur- face faces the tappet. Note: reinstall the camshafts in the specified manner. ( 3-97) • after replacing the tappet shim and camshafts, r...
Page 28
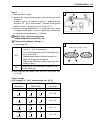
Periodic maintenance 2-11 (intake side) measured v a lve clearance (mm) suffix no . 120 125 130 135 140 145 150 155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200 205 210 215 220 present shim size (mm) 1.20 1.25 1.30 1.35 1.40 1.45 1.50 1.55 1.60 1.65 1.70 1.75 1.80 1.85 1.90 1.95 2.00 2.05 2.10 2.15 2.20 0.00...
Page 29
2-12 periodic maintenance (exhaust side) ho w t o use this char t : i. Measure v alv e clear ance . “engine is cold” ii. Measure present shim siz e . Iii. Match clear ance in v e rtical column with present shim siz e in hor iz ontal column. Example v alv e clear ance is 0.33 mm present shim siz e 1....
Page 30
Periodic maintenance 2-13 engine oil and oil filter engine oil replacement • keep the motorcycle upright. • place an oil pan below the engine, and drain oil by removing the oil drain plug 1 and filler cap 2. • tighten the drain plug 1 to the specified torque, and pour fresh oil through the oil fille...
Page 31
2-14 periodic maintenance oil filter replacement • drain the engine oil as described in the engine oil replace- ment procedure. • remove the oil filter 1 with the special tool. 09915-40610: oil filter wrench • apply engine oil lightly to the gasket of the new oil filter before installation. • inst...
Page 32
Periodic maintenance 2-15 engine idle speed note: warm up the engine before adjusting the engine idle speed. • start the engine, turn the throttle stop screw 1 and set the engine idle speed as follows. engine idle speed: 1 300 ± 100 r/min throttle valve synchronization inspect the throttle valve s...
Page 33
2-16 periodic maintenance clutch • loosen the lock-nut 1 and turn in the adjuster 2 all the way into the clutch lever assembly. • from that position, turn out the adjuster screw 3 rotations. • lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) • loosen the lock-nut 3 and fully turn in the clutch cable adjuster...
Page 34
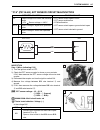
Periodic maintenance 2-17 cooling system engine coolant level check • keep the motorcycle upright. • check the engine coolant level by observing the engine cool- ant reservoir. A full line b lower line • if the level is below the lower line, lift and support the fuel tank ( 5-3) and add engine cool...
Page 35
2-18 periodic maintenance air bleeding the cooling circuit • add engine coolant up to the radiator inlet. • support the motorcycle upright. • slowly swing the motorcycle, right and left, to bleed the air trapped in the cooling circuit. • add engine coolant up to the radiator inlet. • start up the en...
Page 36
Periodic maintenance 2-19 drive chain visually check the drive chain for the possible defects listed below. (support the motorcycle by a jack and a wooden block, turn the rear wheel slowly by hand with the transmission shifted to neutral.) * loose pins * excessive wear * damaged rollers * improper c...
Page 37
2-20 periodic maintenance • count out 21 pins (20 pitches) on the chain and measure the distance between the two points. If the distance exceeds the service limit, the chain must be replaced. drive chain 20-pitch length: service limit: 336.5 mm adjusting • loosen or tighten both chain adjuster bol...
Page 38
Periodic maintenance 2-21 cleaning and lubricating • clean the drive chain with kerosine. If the drive chain tends to rust quickly, the intervals must be shortened. • after washing and drying the chain, oil it with a heavyweight motor oil. Do not use trichloroethylene, gasoline or any similar solven...
Page 39
2-22 periodic maintenance brake brake fluid level check • keep the motorcycle upright and place the handlebars straight. • remove the right frame cover. ( 8-4) • check the brake fluid level relative to the lower limit lines on the front and rear brake fluid reservoirs. • when the level is below the...
Page 40
Periodic maintenance 2-23 brake pads front brake the extent of brake pad wear can be checked by observing the grooved limit line a on the pad. When the wear exceeds the grooved limit line, replace the pads with new ones. ( 8-54) rear brake the extent of brake pad wear can be checked by observing th...
Page 41
2-24 periodic maintenance brake light switch • adjust the rear brake light switch so that the brake light will come on just before pressure is felt when the brake pedal is depressed. Air bleeding from brake fluid circuit air trapped in the brake fluid circuit acts like a cushion to absorb a large pr...
Page 42
Periodic maintenance 2-25 front brake • fill the reservoir with brake fluid to the top of the inspection window. Place the reservoir cap to prevent dirt from entering. • attach a hose to the air bleeder valve and insert the free end of the hose into a receptacle. • squeeze and release the brake leve...
Page 43
2-26 periodic maintenance tires tire tread condition operating the motorcycle with excessively worn tires will decrease riding stability and consequently invite a dangerous situation. It is highly recommended to replace a tire when the remaining depth of tire tread reaches the following specificatio...
Page 44
Periodic maintenance 2-27 front fork inspect the front forks for oil leakage, scoring or scratches on the outer surface of the inner tubes. Replace any defective parts, if necessary. ( 8-14) rear suspension inspect the rear shock absorbers for oil leakage and check that there is no play in the swin...
Page 45
2-28 periodic maintenance exhaust pipe bolt and nut • tighten the exhaust pipe bolts, muffler mounting bolts and muffler connecting bolts to the specified torque. Tighten initially at 1 000 km (2 months) and every 12 000 km (24 months) thereafter. Set chamfer side to muffler side. Set chamfer side t...
Page 46
Periodic maintenance 2-29 chassis bolts and nuts check that all chassis bolts and nuts are tightened to their specified torque. (refer to page 2-30 for the loca- tions of the following nuts and bolts on the motorcycle.) tighten initially at 1 000 km (2 months) and every 6 000 km (12 months) thereaft...
Page 47
2-30 periodic maintenance.
Page 48: Compression Pressure Check
Periodic maintenance 2-31 compression pressure check the compression pressure reading of a cylinder is a good indicator of its internal condition. The decision to overhaul the cylinder is often based on the results of a compression test. Periodic mainte- nance records kept at your dealership should ...
Page 49: Oil Pressure Check
2-32 periodic maintenance oil pressure check check the engine oil pressure periodically. This will give a good indication of the condition of the moving parts. Oil pressure specification if the oil pressure is lower or higher than the specification, the following causes may be considered. Low oil pr...
Page 50: Sds Check
Periodic maintenance 2-33 sds check using sds, take the sample of data from the new motorcycle and at the time of periodic maintenance at your dealership. Save the data in the computer or by printing and filing the hard copies. The saved or filed data are useful for troubleshooting as they can be co...
Page 51
2-34 periodic maintenance data at 3 000 r/min under no load data at the time of racing 3 000 r/min check the manifold absolute pressure. Xxx mmhg throttle: quick wide open throttle: slowly open secondary throttle valve opens closes in according with the engine r/min..
Page 52
Periodic maintenance 2-35 data of intake negative pressure during idling (100 °c) data of secondary throttle valve operation at the time of starting check the manifold absolute pressure. Approx. Xxx mmhg closes fully in approx. Xx sec..
Page 53: Engine
Engine 3-1 engine contents 3 engine components removable with engine in place ............3- 2 engine removal and installation...................................................3- 3 engine removal ................................................................................3- 3 engine installatio...
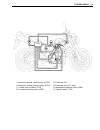
Page 54
3-2 engine engine components removable with engine in place the parts listed below can be removed and reinstalled without removing the engine from the frame. Refer to page listed in each section for removal and reinstallation instructions. Engine center engine right side engine left side item remova...
Page 55
Engine 3-3 engine removal and installation engine removal before taking the engine out of the frame, wash the engine using a steam cleaner. Engine removal is sequentially explained in the following steps. Reinstall the engine by reversing the removal procedure. • remove the under covers. ( 8-5) • l...
Page 56
3-4 engine radiator • disconnect the radiator inlet hoses 1 and 2. • disconnect the oil cooler water hose 3. • open the hose clamp 4. • remove the radiator mounting bolts. • move the radiator forward. • disconnect the radiator hose 5. • disconnect the cooling fan coupler 6. • disconnect the horn cou...
Page 57
Engine 3-5 • remove the front engine cover 8. Exhaust pipe and muffler joint • remove the exhaust pipe and muffler joint. ( 6-3) • remove the o2 sensor. ( 6-3) • remove the radiator mounting bracket 1. Electric parts and pair hose • remove the regulator/rectifier 1. • disconnect the oil pressure s...
Page 58
3-6 engine • disconnect the starter motor lead wire 3. • disconnect the engine ground lead wire 4. • disconnect the respective lead wire couplers. Ckp sensor 5 generator 6 side-stand 7 gp switch 8 ect sensor 9 • disconnect the ignition coil/plug cap lead wire couplers 0 and cmp sensor lead wire coup...
Page 59
Engine 3-7 engine sprocket and gear shift lever • disengage the gearshift lever 1. • remove the engine sprocket cover 2. • remove the clamp 3. • remove the clutch push rod 4. • remove the speed sensor rotor 5. • remove the engine sprocket nut 6 and its washer. Note: when loosening the engine sprocke...
Page 60
3-8 engine • remove the engine sprocket 9. Engine mounting • support the engine using an engine jack. • remove the engine mounting bolts 1. • remove the engine mounting bolt 2. • remove the engine mounting bolt/nut 3..
Page 61
Engine 3-9 • remove the engine mounting nut 4. • loosen the engine mounting thrust adjuster lock-nut 5 with the special tool. • loosen the engine mounting thrust adjuster 6. 09940-14980: engine mounting thrust adjuster socket wrench note: do not remove the engine mounting bolt 7 at this stage. • r...
Page 62
3-10 engine • tighten the engine mounting thrust adjuster 2 to the speci- fied torque. engine mounting thrust adjuster: 23 n·m (2.3 kgf-m) • tighten the engine mounting thrust adjuster lock-nut 3 to the specified torque with the special tool. engine mounting thrust adjuster lock-nut: 45 n·m (4.5...
Page 63
Engine 3-11 • tighten all engine mounting bolts and nuts to the specified torque. Note: the engine mounting nuts are self-locking. Once the nuts have been removed, they are no longer of any use. A left b right length item n·m kgf-m item mm abc 55 5.5 bolt ac 55 12 75 7.5 b 40 3 45 4.5 d 305 4 23 2.3...
Page 64
3-12 engine • install the engine sprocket and its washer. • apply a small quantity of thread lock to the driveshaft thread portion. 99000-32050: thread lock “1342” • tighten the engine sprocket nut 1 to the specified torque. engine sprocket nut: 115 n·m (11.5 kgf-m) • install the speed sensor ro...
Page 65
Engine 3-13 • replace the exhaust pipe gaskets and muffler connectors with new ones. Note: be sure to face the tabs a on the exhaust pipe gaskets 1 to the engine side when installing them. • tighten the exhaust pipe bolts, muffler mounting bolts and muffler connecting bolts to the specified torque. ...
Page 66: Engine Disassembly
3-14 engine engine disassembly • remove the spark plugs. ( 2-5) starter motor • remove the starter motor 1. Cylinder head cover and pair reed valve • remove the cylinder head cover 1 and its gaskets. • remove the pair reed valves 2 and their gaskets. Identify the position of each removed part. Orga...
Page 67
Engine 3-15 camshafts • remove the valve timing inspection cap 1. • turn the crankshaft to bring the line a on the starter clutch to the index mark b of the valve timing inspection hole and also to bring the cams to the position as shown. • remove the cam chain tension adjuster cap bolt 2. • remove ...
Page 68
3-16 engine • remove the intake camshaft 6. • remove the exhaust camshaft 7. • remove the dowel pins. Cylinder head • remove the water hose 1. • remove the thermostat cover 2 and thermostat. Thermostat inspection ( 7-9) • remove the ect sensor 3. Ect sensor inspection ( 7-7) • remove the cylinder ...
Page 69
Engine 3-17 clutch • remove the clutch cover 1. • remove the dowel pins and gasket. • hold the clutch housing with the special tool. 09920-53740: clutch sleeve hub holder • remove the clutch springs. Note: loosen the clutch spring set bolts little by little and diagonally. • remove the pressure pl...
Page 70
3-18 engine • remove the clutch push rod 8. Note: if it is difficult to pull out the push rod 8, use a magnetic hand or a wire. • unlock the clutch sleeve hub nut. • hold the clutch sleeve hub with the special tool. 09920-53740: clutch sleeve hub holder • remove the clutch sleeve hub nut. • remove...
Page 71
Engine 3-19 • remove the thrust washer f. • remove the oil pump drive gear g from the primary driven gear assembly h. Oil pump • remove the snap ring 1. • remove the oil pump driven gear 2. Note: do not drop the snap ring 1 into the crankcase. 09900-06107: snap ring priers • remove the pin 3 and w...
Page 72
3-20 engine • remove the gearshift shaft assembly 3 and washer 4. Note: do not drop the washer 4 into the crankcase. • remove the gearshift cam plate bolt 5 and gearshift cam plate 6. • remove the gearshift cam stopper 7. Starter idle gear • remove the starter idle gear cover 1. • remove the dowel p...
Page 73
Engine 3-21 • remove the starter clutch cover 8. • remove the dowel pins and gasket. • remove the concaved washer 9, starter idle gear no.2 0 and shaft a. Starter clutch • hold the starter clutch with the special tool. 09920-34830: starter clutch holder • remove the starter clutch bolt and washer....
Page 74
3-22 engine generator cover • remove the generator cover 1. • remove the dowel pins and gasket. Generator rotor • hold the generator rotor with the special tool. 09930-44520: rotor holder • remove the generator rotor bolt. • install a bolt a of suitable size to the left end of crankshaft. Suitable...
Page 75
Engine 3-23 gear position switch • remove the gear position switch 1. Crankcase breather (pcv) cover • remove the crankcase breather cover 1. Oil filter • remove the oil filter with the special tool. 09915-40610: oil filter wrench oil cooler • remove the oil cooler 1. Oil pan • remove the oil pan ...
Page 76
3-24 engine oil pressure regulator • remove the oil pressure regulator case 1. • remove the oil pressure regulator 2. Oil pressure switch • remove the oil pressure switch 1. • remove the oil pipe 2. Oil strainer • remove the oil strainer 3 and its o-ring. Lower crank case • remove the lower crankcas...
Page 77
Engine 3-25 middle crankcase • remove the crankcase bolts (m6). • remove the crankcase bolts (m6), clamp 1 and regula- tor/rectifier backet 2. • remove the crankshaft journal bolts (m9). Note: loosen the crankcase bolts diagonally with the smaller sizes first. Crankshaft • loosen the bearing cap bol...
Page 78
3-26 engine • remove the piston pin circlip 1. • separate the piston and conrod by driving out the piston pin. Note: scribe the cylinder number on the piston head..
Page 79: And Service
Engine 3-27 engine components inspection and service cylinder head cover • clean and check the gasket groove a and pair reed valve gasket mating surfaces b of cylinder head cover. • if it is damaged, replace the cylinder head cover with a new one. Cmp sensor removal • remove the cmp sensor 1 from th...
Page 80
3-28 engine inspection • inspect the reed valve for the carbon deposit. • if the carbon deposit is found in the reed valve, replace the pair reed valve with a new one. Installation • set new gasket to the pair reed valve as shown. Pcv hose • remove the pcv hose from the crankcase breather cover. • i...
Page 81
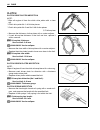
Engine 3-29 camshaft journal wear • determine whether or not each journal is worn down to the limit by measuring the oil clearance with the camshaft installed in place. • use the plastigauge 1 to read the clearance at the widest portion, which is specified as follows: camshaft journal oil clearanc...
Page 82
3-30 engine • if the camshaft journal oil clearance measured exceeds the limit, measure the inside diameter of the camshaft journal holder and outside diameter of the camshaft journal. • replace the camshaft or the cylinder head depending upon which one exceeds the specification. camshaft journal ...
Page 83
Engine 3-31 cam chain tensioner inspection • check the contacting surface of the cam chain tensioner. • if it is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Cam chain guide inspection • check the contacting surfaces of the cam chain guides. • if they are worn or damaged, replace them with the new on...
Page 84
3-32 engine • install the special tool 3 between the valve spring and cylin- der head. • using the special tools, compress the valve spring and remove the two cotter halves from the valve stem. 09916-14510: valve lifter 09916-14530: valve lifter attachment 09916-84511: tweezers 09919-28610: sleeve...
Page 85
Engine 3-33 valve stem runout • support the valve using v-blocks and check its runout using the dial gauge as shown. • if the runout exceeds the service limit, replace the valve. valve stem runout: service limit: 0.05 mm 09900-20607: dial gauge (1/100 mm) 09900-20701: magnetic stand 09900-21304:...
Page 86
3-34 engine valve stem deflection • lift the valve about 10 mm from the valve seat. • measure the valve stem deflection in two directions, perpen- dicular to each other, by positioning the dial gauge as shown. • if the deflection measured exceeds the limit, then determine whether the valve or the gu...
Page 87
Engine 3-35 • cool down the new valve guides in a freezer for about one hour and heat the cylinder head to 100 °c – 150 °c with a hot plate. • apply engine oil to the valve guide hole. • drive the valve guide into the hole using the valve guide installer 1 and attachment 2. 09916-53310: valve guid...
Page 88
3-36 engine • if the seat width w measured exceeds the standard value or seat width is not uniform, reface the seat using the seat cutter. valve seat width w: standard: 0.9 – 1.1 mm if the valve seat is out of specification, re-cut the seat. Valve seat servicing • the valve seats 1 for both the in...
Page 89
Engine 3-37 • clean and assemble the head and valve components. Fill the intake and exhaust ports with gasoline to check for leaks. • if any leaks occur, inspect the valve seat and face for burrs or other things that could prevent the valve from sealing. Valve spring the force of the coil spring kee...
Page 90
3-38 engine • install the valve spring with the small-pitch portion a facing cylinder head. B large-pitch portion c upward d paint • put on the valve spring retainer 2, and using the special tool 3, press down the spring, fit the cotter halves 4 to the stem end, and release the lifter to allow the c...
Page 91
Engine 3-39 intake pipe • remove the intake pipes 1. • apply suzuki super grease to the o-rings. • install the intake pipes. Water bypass union • remove the water bypass union 1. • apply suzuki bond to the thread part of water bypass union and tighten it to the specified torque. 99000-31140: suzuk...
Page 92
3-40 engine clutch clutch drive plates inspection note: * wipe off engine oil from the clutch drive plates with a clean rag. * clutch drive plate no.1: 40 friction pieces * clutch drive plate no.2 and no.3: 48 friction pieces a friction piece • measure the thickness of drive plates with a vernier ca...
Page 93
Engine 3-41 clutch bearing inspection • inspect the clutch release bearing for any abnormality, partic- ularly cracks, to decide whether it can be reused or should be replaced. • smooth engagement and disengagement of the clutch depends on the condition of this bearing. Clutch sleeve hub/primary dri...
Page 94
3-42 engine • if a large resistance is felt for rotation, inspect the starter clutch bearing or the starter clutch contacting surface on the starter driven gear for wear and damage. • if they are found to be damaged, replace them with the new ones. Generator inspection ( 9-10) reassembly • when ins...
Page 95
Engine 3-43 water pump disassembly/inspection ( 7-12) gearshift system gearshift shaft/gearshift arm disassembly • remove the following parts from the gearshift shaft/gearshift arm. 1 washer 4 gearshift cam drive plate 2 snap ring 5 plate return spring 3 gearshift shaft return spring gearshift shaf...
Page 96
3-44 engine oil pressure regulator • inspect the operation of the oil pressure regulator by pushing on the piston with a proper bar. • if the piston does not operate, replace the oil pressure regula- tor with a new one. Oil strainer • inspect the oil strainer body for damage. • clean the oil straine...
Page 97
Engine 3-45 transmission disassembly disassemble the countershaft and driveshaft. Pay attention to the following points: • remove the 6th drive gear snap ring 1 from its groove and slide it towards the 3rd/4th drive gears 2. • slide the 6th 3 and 2nd 4 drive gears toward the 3rd/4th drive gears 2, t...
Page 98
3-46 engine reassembly assemble the countershaft and driveshaft in the reverse order of disassembly. Pay attention to the following points: note: * rotate the bearings by hand to inspect for smooth rotation. Replace the bearings if there is anything unusual. * before installing the gears, apply engi...
Page 99
Engine 3-47 transmission parts location 1 countershaft 2 driveshaft.
Page 100
3-48 engine cylinder crankcase servicing ( 3-51) cylinder distortion • check the gasketed surface of the cylinder for distortion with a straightedge and thickness gauge, taking a clearance read- ing at several places as indicated. • if the largest reading at any position of the straightedge exceeds...
Page 101
Engine 3-49 piston and piston ring piston diameter • using a micrometer, measure the piston outside diameter at 15 mm a from the piston skirt end. • if the measurement is less than the limit, replace the piston. piston diameter: service limit: 66.845 mm at 15 mm from the skirt end 09900-20203: m...
Page 102
3-50 engine piston ring-to-groove clearance • measure the side clearances of the 1st and 2nd piston rings using the thickness gauge. • if any of the clearances exceed the limit, replace both the pis- ton and piston rings. 09900-20803: thickness gauge 09900-20205: micrometer (0 – 25 mm) piston ri...
Page 103
Engine 3-51 crankcase gearshift fork and gearshift cam removal • remove the gearshift cam bearing retainer screws 1 and gearshift fork shaft retainer 2 from the lower crankcase. • remove the gearshift fork shafts 3 and gearshift 4 forks from the lower crankcase. • remove the gearshift cam 5 and its ...
Page 104
3-52 engine gearshift fork thickness • measure the gearshift fork thickness using the vernier cali- pers. shift fork thickness: standard: 4.8 – 4.9 mm 09900-20102: vernier calipers gearshift cam bearing and gearshift shaft bearing inspection • inspect the gearshift cam bearing for abnormal noise...
Page 105
Engine 3-53 • remove the oil seal 1. • remove the gearshift shaft bearing with the special tool. 09921-20240: bearing remover set (15 mm) installation • install the bearings with the special tool. 09913-70210: bearing installer set (1, 222) (3 32) note: the stamped mark side of the gearshift s...
Page 106
3-54 engine • install the gearshift forks and their shafts as shown. 6 for 3rd/4th drive gears (17e-3w) 7 for 6th driven gear (17e-1e) 8 for 5th driven gear (17e-1f) • apply a small quantity of thread lock to the bearing retainer screws 9. • tighten the bearing retainer screws 9 and gearshift fork s...
Page 107
Engine 3-55 oil jet removal • remove the piston cooling oil jets 1 from the upper crank- case. • remove the oil jet 2 (for transmission) from the lower crank- case. • remove the oil jet 3 (for cam chain tension adjuster) from the cylinder head. Inspection and cleaning • check the oil jets for cloggi...
Page 108
3-56 engine installation • fit new o-ring 1 to each piston cooling oil jet as shown and apply engine oil to them. • install each piston cooling oil jet with the bolt. Note: apply a small quantity of thread lock to the bolts and tighten them to the specified torque. 99000-32050: thread lock “1342” ...
Page 109
Engine 3-57 • remove the water jacket plugs 3. • remove the oil gallery plugs 4 (for lower crankcase side). Installation • apply engine coolant to the o-rings of the water jacket plugs 1. 99000-99032-11x: suzuki coolant • apply thread lock to the oil gallery plug 2. 99000-32050: thread lock “134...
Page 110
3-58 engine crankshaft and conrod crankshaft runout • support the crankshaft with “v” blocks as shown, with the two end journals resting on the blocks. • set up the dial gauge, as shown. • rotate the crankshaft slowly to read the runout. • replace the crankshaft if the runout is greater than the lim...
Page 111
Engine 3-59 conrod big end side clearance • inspect the conrod side clearance by using a thickness gauge. • if the clearance exceeds the limit, remove the conrod and inspect the conrod big end width and the crank pin width. • if the width exceed the limit, replace conrod or crankshaft. conrod big ...
Page 112
3-60 engine • remove the bearing caps and measure the width of the com- pressed plastigauge using the envelope scale. This measure- ment should be taken at the widest part of the compressed plastigauge. conrod big end oil clearance: standard: 0.032 – 0.056 mm service limit: 0.080 mm • if the oil c...
Page 113
Engine 3-61 crank pin o.D. 09900-20202: micrometer (25 – 50 mm) bearing thickness code o.D. Specification 1 30.992 – 31.000 mm 2 30.984 – 30.992 mm 3 30.976 – 30.984 mm color c (part no.) thickness yellow (12164-29g00-0d0) 1.492 – 1.496 mm brown (12164-29g00-0c0) 1.488 – 1.492 mm black (12164-...
Page 114
3-62 engine crankshaft journal bearing inspection • inspect each bearing of upper and middle crankcases for any damage. Selection • place the plastigauge axially along the crankshaft journal, avoiding the oil hole, as shown. 09900-22301: plastigauge • mate the middle crankcase with the upper crank...
Page 115
Engine 3-63 • check the corresponding crankcase journal i.D. Code number a, “a” or “b” which is stamped on the rear of upper crank- case. • check the corresponding crankshaft journal o.D. Code num- ber b, “a”, “b” or “c” which is stamped on the crankshaft. bearing selection table crankcase i.D. ...
Page 116
3-64 engine crankshaft journal o.D. Specification 09900-20202: micrometer (25 – 50 mm) bearing thickness specification note: upper and middle crankshaft journal bearings are the same. Installation • when fitting the crankshaft journal bearings to the upper and middle crankcases, be sure to fix...
Page 117
Engine 3-65 crankshaft thrust bearing • with the crankshaft, right-side thrust bearing and left-side thrust bearing inserted in the upper crankcase, measure the thrust clearance on the left side by using the thickness gauge. L: left-side thrust bearing r: right-side thrust bearing note: pull the cra...
Page 118
3-66 engine thrust bearing selection table • after selecting a left-side thrust bearing, insert it and again perform the thrust clearance measurement to make sure it falls within the standard range. A color code note: right-side thrust bearing has the same specification as the green (12228-17e00-0...
Page 119: Engine Reassembly
Engine 3-67 engine reassembly • reassemble the engine in the reverse order of disassembly. • the following steps require special attention or precautionary measures should be taken. Note: apply engine oil to each running and sliding part before reas- sembling. • be sure to install the following item...
Page 120
3-68 engine • 1st ring 5 and 2nd ring 6 have letters “it” and “t” marked on the side. Be sure to bring the marked side to the top when fit- ting them to the piston. • position the gaps of the three ring as shown. Before inserting each piston into the cylinder, check that the gaps are so located. C 2...
Page 121
Engine 3-69 • install the pistons and conrods into the cylinders from upside. Note: when installing the pistons, the indent c of each piston head must be brought to the exhaust side. • check that id code d on each conrod faces intake side. • apply molybdenum oil solution to the crank pin bear- ings ...
Page 122
3-70 engine • set the crankshaft to the conrods and upper crankcase. • apply molybdenum oil solution to the crank pin and bearing surface. molybdenum oil solution • when fitting the conrod cap, make sure that i.D. Code a on each conrod faces intake side. • apply engine oil to the bearing cap bolts...
Page 123
Engine 3-71 • insert the right and left thrust bearings with oil groove b fac- ing the crank web. Note: right thrust bearing has green painting. Crankcase • clean the mating surfaces of the crankcases. • install the dowel pins 1 and o-ring 2 to the upper crank- case..
Page 124
3-72 engine • apply suzuki bond to the mating surface of the middle crankcase. 99000-31140: suzuki bond “1207b” note: use of suzuki bond is as follows: * make surfaces free from moisture, oil, dust and other foreign materials. * spread on surfaces thinly to form an even layer, and assemble the cra...
Page 125
Engine 3-73 • install the regulator/rectifier bracket 3 and tighten the other crankcase bolts a little at a time to equalize the pressure. crankcase bolt: (m6) initial: 6 n·m (0.6 kgf-m) final : 11 n·m (1.1 kgf-m) note: fit the clamp to the crankcase bolt a. Note: fit a new gasket to the crankcase...
Page 126
3-74 engine transmission • install the bearing pins 1 and the c-rings 2 on the middle crankcase. • install the countershaft assembly on the middle crankcase. Note: align the c-ring with the groove of bearing and the bearing pin with the indent on the bearing. • install the driveshaft assembly on the...
Page 127
Engine 3-75 • apply suzuki bond to the mating surface. 99000-31140: suzuki bond “1207b” note: use of suzuki bond is as follows: * make surfaces free from moisture, oil, dust and other foreign materials. * spread on surfaces thinly to form an even layer, and assemble the crankcases within few minut...
Page 128
3-76 engine • tighten the crankcase bolts a little at a time to equalize the pressure. crankcase bolt: (m6) initial: 6 n·m (0.6 kgf-m) final : 11 n·m (1.1 kgf-m) (m8) initial : 15 n·m (1.5 kgf-m) final : 26 n·m (2.6 kgf-m) note: * fit new copper washer to the crankcase bolts a. * fit new gasket wa...
Page 129
Engine 3-77 oil strainer • install the o-ring. • apply suzuki super grease “a” to the o-ring. 99000-25010: suzuki super grease “a” (or equivalent grease) • install the oil strainer 1 as shown and tighten the oil strainer bolts to the specified torque. oil strainer bolt: 10 n·m (1.0 kgf-m) oil pr...
Page 130
3-78 engine oil pan • apply suzuki bond to the mating surface. ( 3-75) 99000-31140: suzuki bond “1207b” • install the oil pan. Note: fit the gasket washer to the oil pan bolt a. • tighten the oil pan bolts diagonally to the specified torque. oil pan bolt: 10 n·m (1.0 kgf-m) oil cooler • apply s...
Page 131
Engine 3-79 crankcase breather cover • apply suzuki bond to the mating surface. 99000-31140: suzuki bond “1207b” • install the crankcase breather cover 1. crankcase breather cover bolt: 10 n·m (1.0 kgf-m) • apply suzuki super grease “a” to the o-ring. 99000-25010: suzuki super grease “a” (or e...
Page 132
3-80 engine • tighten the water pump mounting bolts to the specified torque. water pump mounting bolt: 10 n·m (1.0 kgf-m) note: pass the gear position switch lead wire 1 under the water pump lib. • apply engine coolant to the o-ring. • install the water inlet cover 2. water inlet cover bolt: 10 ...
Page 133
Engine 3-81 • apply suzuki bond to the mating surfaces. 99000-31140: suzuki bond “1207b” note: use of suzuki bond is as follows: * make surfaces free from moisture, oil, dust and other foreign materials. * spread on surfaces thinly to form an even layer, and assemble the covers within few minutes....
Page 134
3-82 engine generator cover • apply suzuki bond lightly to the mating surfaces at the parting line between the upper and middle crankcases as shown. 99000-31140: suzuki bond “1207b” • install the dowel pins 1 and new gasket 2. • install the generator cover and tighten the generator cover bolts to ...
Page 135
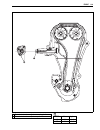
Engine 3-83 cam chain drive sprocket • install the cam chain drive sprocket onto the crankshaft. Note: when installing the cam chain drive sprocket, align the wide spline teeth a and b. Cam chain tensioner and cam chain guide • install the cam chain. • apply a small quantity of thread lock to the ca...
Page 136
3-84 engine starter clutch • install the washer 1. • install the starter clutch assembly onto the crankshaft. Note: when installing the starter clutch assembly, align the wide spline teeth a and b. • install the starter clutch bolt with the washer. • hold the starter clutch with the special tool and...
Page 137
Engine 3-85 • install the starter clutch cover and tighten its bolt as shown. Note: fit a new gasket washer to the starter clutch cover bolt c as shown. starter clutch cover bolt: 10 n·m (1.0 kgf-m) • install the starter idle gear no.1 shaft 6, thrust washer 7, bearing 8, starter idle gear no.1 9,...
Page 138
3-86 engine note: hook the return spring end a to the stopper 5. • check the gearshift cam stopper moves smoothly. • locate the gearshift cam in the neutral position. • install the gearshift cam stopper plate 6. Note: align the gearshift cam pin b with the gearshift cam stopper plate hole c. • apply...
Page 139
Engine 3-87 oil pump • install the o-ring to the oil pump and apply suzuki super grease “a” to it. Note: set the oil pump shaft end a to the water pump shaft. 99000-25010: suzuki super grease “a” (or equivalent grease) • install the oil pump with the oil pump mounting bolts and then tighten them t...
Page 140
3-88 engine • install the oil pump drive gear 1 to the primary driven gear assembly. • install the primary driven gear assembly. Note: be sure to engage the oil pump driven gear with drive gear and primary driven gear with drive gear. • install the bearing 3 and spacer 4 and apply engine oil to them...
Page 141
Engine 3-89 • lock the clutch sleeve hub nut with a center punch. • install the spring washer seat 9 and spring washer 0 onto the clutch sleeve hub correctly. • install the clutch push rod a into the countershaft. • install the clutch push piece b, bearing c and thrust washer d to the countershaft. ...
Page 142
3-90 engine • insert the clutch drive plates and driven plates one by one into the clutch sleeve hub in the prescribed order. Note: insert the outermost drive plate claws b to the other slits c of clutch housing as shown. *1: direction of outside drive plate: a no.2 drive plate...1 pc [48 friction p...
Page 143
Engine 3-91 • install the pressure plate e. • install the clutch springs. • hold the clutch housing with the special tool. 09920-53740: clutch sleeve hub holder • tighten the clutch spring set bolts to the specified torque. clutch spring set bolt: 10 n·m (1.0 kgf-m) note: tighten the clutch spri...
Page 144
3-92 engine cylinder head • fit the dowel pins 1 and new cylinder head gasket 2 to the cylinder. • place the cylinder head on the cylinder. Note: when installing the cylinder head, keep the cam chain taut. • tighten the cylinder head bolts (m10) in the following four-step. Step 1: • tighten the cyli...
Page 145
Engine 3-93 • apply suzuki super grease “a” to the o-rings and install them into the cylinder head. 99000-25010: suzuki super grease “a” (or equivalent grease) • fit the gasket 2 and tighten the ect sensor. ect sensor: 18 n·m (1.8 kgf-m) • install the thermostat 3. Note: the jiggle valve a of th...
Page 146
3-94 engine • the camshafts are identified by the embossed letters. • before replacing the camshafts on cylinder head, apply molybdenum oil solution to their journals and cam faces. • apply molybdenum oil solution to the camshaft jour- nal holders. molybdenum oil solution note: before installing t...
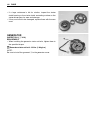
Page 147
Engine 3-95 • pull the cam chain lightly. • the exhaust camshaft sprocket has an arrow marked “1” c. Turn the exhaust camshaft so that the arrow is aligned with the gasket surface of the cylinder head. • engage the cam chain with the exhaust camshaft sprocket. • bind the cam chain and sprocket with ...
Page 148
3-96 engine • install the dowel pins 3. • install the o-rings 4 to the camshaft journal holders. • install the camshaft journal holders. Note: * each camshaft journal holder is identified with an embossed letter. “a”: no.1 and no.2 cylinders “b”: no.3 and no.4 cylinders * check that embossed letter ...
Page 149
Engine 3-97 • tighten the camshaft journal holder bolts in the ascending order of numbers to the specified torque. camshaft journal holder bolt: 10 n·m (1.0 kgf-m) cam chain tension adjuster • retract the push rod by pushing the stopper 1. • install new gasket. • install the cam chain tension adju...
Page 150
3-98 engine • install the gasket 4 and cam chain tension adjuster cap bolt 5. Note: click sound is heard when the cam chain tension adjuster cap bolt is installed. • tighten the cam chain tension adjuster cap bolt to the speci- fied torque. cam chain tension adjuster cap bolt: 23 n·m (2.3 kgf-m) •...
Page 151
Engine 3-99 a cam chain tension adjuster mounting bolt b cam chain tension adjuster cap bolt item n·m kgf-m a 10 1.0 b 23 2.3.
Page 152
3-100 engine • tighten the valve timing inspection plug 7 to the specified torque. valve timing inspection plug: 11 n·m (1.1 kgf-m) cylinder head cover and pair reed valve • pour engine oil in each oil pocket in the cylinder head. Note: be sure to check the valve clearance. ( 2-7) • install the p...
Page 153
Engine 3-101 • tighten the head cover bolts to the specified torque. head cover bolt: initial: 10 n·m (1.0 kgf-m) final : 14 n·m (1.4 kgf-m) starter motor • install the new o-ring 1 to the starter motor. • apply suzuki super grease “a” to the o-ring. 99000-25010: suzuki super grease “a” (or equi...
Page 154: Fi System Diagnosis
Fi system diagnosis 4-1 4 contents fi system diagnosis precautions in servicing .................................................................. 4- 3 electrical parts ........................................................................... 4- 3 fuse.................................................
Page 155: Fi System Diagnosis
4-2 fi system diagnosis contents fi system diagnosis “c31” (p0705) gp switch circuit malfunction ....................... 4-72 “c32” (p0201), “c33” (p0202), “c34” (p0203) or “c35” (p0204) fuel injector circuit malfunction....................................... 4-74 “c41” (p0230-h/l) fp relay circuit ...
Page 156: Precautions In Servicing
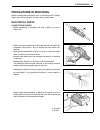
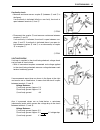
Fi system diagnosis 4-3 precautions in servicing when handling the component parts or servicing the fi system, observe the following points for the safety of the system. Electrical parts connector/coupler • when connecting a connector, be sure to push it in until a click is felt. • with a lock type ...
Page 157
4-4 fi system diagnosis • when connecting meter probe from the terminal side of the coupler (where connection from harness side not being possi- ble), use extra care not to force and cause the male terminal to bend or the female terminal to open. Connect the probe as shown to avoid opening of female...
Page 158
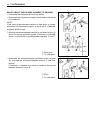
Fi system diagnosis 4-5 • when disconnecting and connecting the ecm, make sure to turn off the ignition switch 1, or electronic parts may get damaged. • battery connection in reverse polarity is strictly prohibited. Such a wrong connection will damage the components of the fi system instantly when r...
Page 159
4-6 fi system diagnosis electrical circuit inspection procedure while there are various methods for electrical circuit inspection, described here is a general method to check for open and short circuit using an ohmmeter and a voltmeter. Open circuit check possible causes for the open circuits are as...
Page 160
Fi system diagnosis 4-7 continuity check • measure resistance across coupler b (between a and c in the figure). If no continuity is indicated (infinity or over limit), the circuit is open between terminals a and c. 1 ecm • disconnect the coupler b and measure resistance between couplers a and b. If ...
Page 161
4-8 fi system diagnosis short circuit check (wire harness to ground) • disconnect the negative cable from the battery. • disconnect the connectors/couplers at both ends of the circuit to be checked. Note: if the circuit to be checked branches to other parts as shown, disconnect all connectors/couple...
Page 162
Fi system diagnosis 4-9 using the multi-circuit tester • use the suzuki multi-circuit tester set (09900-25008). • use well-charged batteries in the tester. • be sure to set the tester to the correct testing range. Using the tester • incorrectly connecting the + and - probes may cause the inside of t...
Page 163
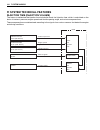
4-10 fi system diagnosis fi system technical features injection time (injection volume) the factors to determine the injection time include the basic fuel injection time, which is calculated on the basis of intake air pressure, engine speed and throttle opening angle, and various compensations. Thes...
Page 164
Fi system diagnosis 4-11 compensation of injection time (volume) the following different signals are output from the respective sensors for compensation of the fuel injection time (volume). Injection stop control signal description atmospheric pressure sensor signal when atmospheric pressure is low,...
Page 165
4-12 fi system diagnosis fi system parts location a speedometer f intake air pressure sensor (iaps) b engine coolant temperature sensor (ects) g intake air temperature sensor (iats) c ignition coil h fuel injector d speed sensor i ho2 sensor e cam shaft position sensor (cmps) ecm.
Page 166
Fi system diagnosis 4-13 j secondary throttle valve actuator (stva) n fuel pump (fp) k secondary throttle position sensor (stps) o fuel pump relay (fp relay) l throttle position sensor (tps) p atmospheric pressure sensor (aps) m crankshaft position sensor (ckp) q tip-over sensor (tos) ecm.
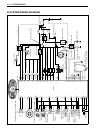
Page 167
4-14 fi system diagnosis fi system wiring diagram ho2 sensor 10 a 15 a 15 a 30 a 10 a speedometer b/y g/r r/bl gr/w gr/b gr/y gr/r y/r y/b o/g w/bl # 1 # 2 # 3 # 4 # 1 # 2 # 3 # 4 y g w/g p y/g b/y b/w b/w b/w b/w w/b g p/w b/lg b g/w g/bl p/b y/w g/b g/b b g/y b/bl b/br r br camshaft position senso...
Page 168: Ecm Terminal
Fi system diagnosis 4-15 ecm terminal terminal no. Circuit terminal no. Circuit 1 stva signal (stva. 2a) u ckp sensor signal (ckp–) 2 stva signal (stva. 1a) v serial data for self-diagnosis 3 immobilizer indicator light w power source for fuel injector (vm) 4 immobilizer communication x ecm ground (...
Page 169: Self-Diagnosis Function
4-16 fi system diagnosis self-diagnosis function the self-diagnosis function is incorporated in the ecm. The function has two modes, “user mode” and “dealer mode”. The user can only be notified by the lcd (display) panel and led (fi light). To check the function of the individual fi system devices, ...
Page 170
Fi system diagnosis 4-17 dealer mode the defective function is memorized in the computer. Use the special tool’s coupler to connect to the dealer mode coupler. The memorized malfunction code is displayed on lcd (display) panel. Malfunction means that the ecm does not receive signal from the devices....
Page 171
4-18 fi system diagnosis in the lcd (display) panel, the malfunction code is indicated from small code to large code. *1 to get the proper signal from the throttle position sensor, the sensor basic position is indicated in the lcd (display) panel. The malfunction code is indicated in three digits. I...
Page 172
Fi system diagnosis 4-19 tps adjustment 1. Adjust the engine rpm to 1 300 r/min. ( 2-15) 2. Connect the special tool (mode select switch) to the dealer mode coupler at the wiring harness. 3. If the throttle position sensor adjustment is necessary, remove the air cleaner box ( 5-13) and follow the ...
Page 173: Fail-Safe Function
4-20 fi system diagnosis fail-safe function fi system is provided with fail-safe function to allow the engine to start and the motorcycle to run in a mini- mum performance necessary even under malfunction condition. Item fail-safe mode starting ability running ability cmp sensor when camshaft positi...
Page 174
Fi system diagnosis 4-21 the engine can start and can run even if the above signal is not received from each sensor. But, the engine running condition is not complete, providing only emergency help (by fail-safe circuit). In this case, it is nec- essary to bring the motorcycle to the workshop for co...
Page 175: Fi System Troubleshooting
4-22 fi system diagnosis fi system troubleshooting customer complaint analysis record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this purpose, use of such an inspection form such as below will facilitate collecting information required for prope...
Page 176
Fi system diagnosis 4-23 note: the above form is a standard sample. The form should be modified according to conditions and characteris- tics of each market. Visual inspection • prior to diagnosis using the mode select switch or sds, perform the following visual inspections. The rea- son for visual ...
Page 177
4-24 fi system diagnosis self-diagnostic procedures note: * do not disconnect couplers from the ecm, the battery cable from the battery, ecm ground wire harness from the engine or main fuse before confirming the malfunction code (self-diag- nostic trouble code) stored in memory. Such disconnection w...
Page 178
Fi system diagnosis 4-25 use of sds diagnostic procedures * do not disconnect couplers from ecm, the battery cable from the battery, ecm ground wire harness from the engine or main fuse before confirming the malfunction code (self-diagnostic trouble code) stored in memory. Such disconnection will er...
Page 179
4-26 fi system diagnosis use of sds diagnosis reset procedure • after repairing the trouble, turn off the ignition switch and turn on again. • click the dtc inspection button 1. • check the dtc. • the previous malfunction history code (past dtc) still remains stored in the ecm. Therefore, erase the ...
Page 180
Fi system diagnosis 4-27 show data when trouble (displaing data at the time of dtc) ecm stores the engine and driving conditions (in the form of data as shown in the figure) at the moment of the detection of a malfunction in its memory. This data is called “show data when trouble”. Therefore, it is ...
Page 181
4-28 fi system diagnosis malfunction code and defective condition dtc no. Detected item detected failure condition check for c00 no fault ––––––––––– ––––––––––– c11 cmp sensor the signal does not reach ecm for 3 sec. Or more, after receiving the starter signal. Cmp sensor wiring and mechan- ical pa...
Page 182
Fi system diagnosis 4-29 dtc no. Detected item detected failure condition check for c21 iat sensor the sensor voltage should be the fol- lowing. 0.15 v sensor voltage in other than the above range, c21 (p0110) is indicated. Iat sensor, lead wire/coupler connection p0110 h sensor voltage is higher th...
Page 183
4-30 fi system diagnosis dtc no. Detected item detected failure condition check for c29 stp sensor the sensor should produce following voltage. 0.15 v sensor voltage in other than the above range, c29 (p1654) is indicated. Stp sensor, lead wire/coupler connection p1654 h sensor voltage is higher tha...
Page 184
Fi system diagnosis 4-31 dtc no. Detected item detected failure condition check for c44 ho2 sensor ho2 sensor output voltage is not input to ecm during engine operation and running condition. (sensor voltage 0.1 v) in other than the above value, c44 (p0130) is indicated. Ho2 sensor circuit open or s...
Page 185
4-32 fi system diagnosis “c11” (p0340) cmp sensor circuit malfunction inspection step 1 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) remove the air cleaner box. ( 5-13) 4) check the cmp sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the cmp senso...
Page 186
Fi system diagnosis 4-33 step 2 1) crank the engine a few seconds with the starter motor, and measure the cmp sensor peak voltage at the coupler. 2) repeat the above test procedure a few times and measure the highest peak voltage. cmp sensor peak voltage: 0.7 v and more (+ b/y – - b/br) 1 peak vol...
Page 187
4-34 fi system diagnosis “c12” (p0335) ckp sensor circuit malfunction inspection step 1 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) check the ckp sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the ckp sensor resistance. 4) disconnect the ckp sens...
Page 188
Fi system diagnosis 4-35 5) if ok, then check the continuity between each terminal and ground. ckp sensor continuity: ∞Ω (infinity) (black – ground) (green – ground) are the resistance and continuity ok? 6) after repairing the trouble, clear the dtc using sds tool. ( 4-26) step 2 1) crank the eng...
Page 189
4-36 fi system diagnosis “c13” (p0105-h/l) iap sensor circuit malfunction inspection step 1 (when indicating c13:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) check the iap sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the iap sensor input volta...
Page 190
Fi system diagnosis 4-37 4) disconnect the iap sensor coupler. 5) turn the ignition switch to on. 6) insert the needle pointed probes to the lead wire coupler. 7) measure the voltage at the red wire and ground. 8) if ok, then measure the voltage at the red wire and b/br wire. iap sensor input volt...
Page 191
4-38 fi system diagnosis 6) disconnect the ecm coupler. 7) check the continuity between g/b wire b and terminal 9. 8) if ok, then check the continuity between b/br wire c and ter- minal s. iaps lead wire continuity: continuity () 09900-25008: multi-circuit tester set 09900-25009: needle pointed...
Page 192
Fi system diagnosis 4-39 7) disconnect the ecm coupler. 8) check the continuity between red wire a and terminal a. 9) also, check the continuity between g/b wire b and terminal 9. iaps lead wire continuity: continuity () 09900-25008: multi-circuit tester set 09900-25009: needle pointed probe se...
Page 193
4-40 fi system diagnosis step 3 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) remove the iap sensor. 3) connect the vacuum pump gauge to the vacuum port of the iap sensor. Arrange 3 new 1.5 v batteries in series 1 (check that total - voltage is 4.5 – 5.0 v) and connect - terminal to the ground - terminal 2...
Page 194
Fi system diagnosis 4-41 output voltage (vcc voltage 4.5 – 5.0 v, ambient temp. 20 – 30 °c) altitude (reference) atmospheric pressure output voltage (m) (mmhg) kpa (v) 0 610 760 708 100 95 3.1 – 3.6 611 1 524 707 635 94 86 2.8 – 3.4 1 525 2 438 634 568 85 77 2.6 – 3.1 2 439 3 048 567 526 76 70 2.4 –...
Page 195
4-42 fi system diagnosis “c14” (p0120-h/l) tp sensor circuit malfunction inspection step 1 (when indicating c14:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) remove the air cleaner box and lift up the throttle body. ( 5-13) 4) check the tp sensor coupler for lo...
Page 196
Fi system diagnosis 4-43 tp sensor input voltage: 4.5 – 5.5 v (+ red – - ground) (+ red – - b/br) 09900-25008: multi-circuit tester set tester knob indication: voltage () is the voltage ok? Step 1 (when indicating p0120-h:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank...
Page 197
4-44 fi system diagnosis step 1 (when indicating p0120-l:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) remove the air cleaner box and lift up the throttle body. ( 5-13) 4) check the tp sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then check the tp sensor l...
Page 198
Fi system diagnosis 4-45 step 2 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) disconnect the tp sensor coupler. 3) install the test harness to the tp sensor. 4) check the continuity between terminal a and ground. tp sensor continuity: ∞Ω (infinity) (terminal a – ground) 09900-25008: multi-circuit teste...
Page 199
4-46 fi system diagnosis are the continuity and resistance ok? 8) after repairing the trouble, clear the dtc using sds tool. ( 4-26) step 3 1) connect the tp sensor coupler 1 to the test harness. 2) turn the ignition switch to on. 3) measure the tp sensor output voltage at the coupler (between + p/...
Page 200
Fi system diagnosis 4-47 “c15” (p0115-h/l) ect sensor circuit malfunction inspection step 1 (when indicating c15:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) check the ect sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the ect sensor voltage at the wire side coupler. 3) disconnect the co...
Page 201
4-48 fi system diagnosis step 1 (when indicating p0115-h:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) check the ect sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then check the ect sensor lead wire continuity. 3) disconnect the ect sensor coupler and ecm coupler. 4) check the continuity between b/bl...
Page 202
Fi system diagnosis 4-49 step 1 (when indicating p0115-l:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) check the ect sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the output voltage. 3) disconnect the ect sensor coupler. 4) check the continuity between b/bl wire a and ground. If the soun...
Page 203
4-50 fi system diagnosis step 2 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) disconnect the ect sensor coupler. 3) measure the ect sensor resistance. ect sensor resistance: approx. 2.3 – 2.6 k Ω at 20 °c (terminal – terminal) 09900-25008: multi-circuit tester set tester knob indication: resistance (...
Page 204
Fi system diagnosis 4-51 “c21” (p0110-h/l) iat sensor circuit malfunction inspection step 1 (when indicating c21:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) check the iat sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the iat sensor voltage at ...
Page 205
4-52 fi system diagnosis step 1 (when indicating p0110-h:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) check the iat sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then check the iat sensor lead wire continuity. 4) disconnect the iat sensor coupler and ecm co...
Page 206
Fi system diagnosis 4-53 step 1 (when indicating p0110-l:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) check the iat sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then check the iat sensor lead wire continuity. 4) disconnect the iat sensor coupler. 5) check ...
Page 207
4-54 fi system diagnosis step 2 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) measure the iat sensor resistance. iat sensor resistance: approx. 2.45 kΩ at 20 °c (terminal – terminal) 09900-25008: multi-circuit tester set tester knob indication: resistance (Ω) is the resistance ok? iat sensor specif...
Page 208
Fi system diagnosis 4-55 “c22” (p1450-h/l) ap sensor circuit malfunction inspection step 1 (when indicating c22:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) check the ap sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the ap sensor input voltage....
Page 209
4-56 fi system diagnosis 4) disconnect the ap sensor coupler. 5) turn the ignition switch to on. 6) measure the voltage at the r wire and ground. 7) if ok, then measure the voltage at the red wire a and b/br wire b. ap sensor input voltage: 4.5 – 5.5 v (+ r – - ground) (+ r – - b/br) 09900-25008...
Page 210
Fi system diagnosis 4-57 6) disconnect the ecm coupler. 7) check the continuity between g/y wire c and terminal p. 8) if ok, then check the continuity between b/br wire b and ter- minal s. aps lead wire continuity: continuity () 09900-25008: multi-circuit tester set 09900-25009: needle pointed ...
Page 211
4-58 fi system diagnosis 7) disconnect the ecm coupler. 8) check the continuity between r wire a and terminal a. 9) if ok, then check the continuity between g/y wire c and ter- minal p. aps lead wire continuity: continuity () 09900-25008: multi-circuit tester set 09900-25009: needle pointed pro...
Page 212
Fi system diagnosis 4-59 step 3 1) remove the ap sensor. 2) connect the vacuum pump gauge to the vacuum port of the ap sensor. Arrange 3 new 1.5 v batteries in series 1 (check that total voltage is 4.5 – 5.0 v) and connect - terminal to the ground terminal 2 and + terminal to the vcc terminal 3. 3) ...
Page 213
4-60 fi system diagnosis “c23” (p1651-h/l) to sensor circuit malfunction inspection step 1 (when indicating c23:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) check the to sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the to sensor resistance. 4)...
Page 214
Fi system diagnosis 4-61 step 1 (when indicating p1651-h:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) check the to sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then check the to sensor lead wire continuity. 4) disconnect the to sensor coupler. 5) check the...
Page 215
4-62 fi system diagnosis step 1 (when indicating p1651-l:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) check the to sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then check the to sensor lead wire continuity. 4) disconnect the to sensor coupler. 5) check the...
Page 216
Fi system diagnosis 4-63 step 2 1) connect the to sensor coupler and ecm coupler. 2) insert the needle pointed probes to the lead wire coupler. 3) turn the ignition switch to on. 4) measure the voltage at the wire side coupler between b and b/br wires. to sensor voltage (normal): 0.4 – 1.4 v (+ b ...
Page 217
4-64 fi system diagnosis “c28” (p1655) stv actuator circuit malfunction inspection step 1 1) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 2) remove the air cleaner box. ( 5-13) 3) check the stva lead wire coupler for loose or poor contacts. 4) turn the ignition switch to on to check the stv operation. (...
Page 218
Fi system diagnosis 4-65 step 2 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) disconnect the stva lead wire coupler. 3) check the continuity between each terminal and ground. stva continuity: ∞Ω (infinity) (terminal – ground) 4) if ok, then measure the stva resistance (between terminal a and terminal b) ...
Page 219
4-66 fi system diagnosis active control inspection 1) set up the sds tool. (refer to the sds operation manual for further details.) 2) turn the ignition switch to on. 3) click “secondary throttle operating control” 1. 4) click each button 2. At this time, if an operation sound is heard from the stva...
Page 220
Fi system diagnosis 4-67 “c29” (p1654-h/l) stp sensor circuit malfunction inspection step 1 (when indicating c29:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) remove the air cleaner box and lift up the throttle body. ( 5-13) 4) check the stp sensor coupler for ...
Page 221
4-68 fi system diagnosis stp sensor input voltage: 4.5 – 5.5 v (+ r – - ground) (+ r – - b/br) 09900-25008: multi-circuit tester set tester knob indication: voltage () is the voltage ok? Step 1 (when indicating p1654-h:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. (...
Page 222
Fi system diagnosis 4-69 step 1 (when indicating p1654-l:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank. ( 5-3) 3) remove the air cleaner box and lift up the throttle body. ( 5-13) 4) check the stp sensor coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then check the stp sensor...
Page 223
4-70 fi system diagnosis step 2 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) remove the air cleaner box and lift up the throttle body. ( 5-13) 3) disconnect the stp sensor coupler. 4) install the test harness to the stp sensor. 5) check the continuity between each terminal and ground. stp sensor contin...
Page 224
Fi system diagnosis 4-71 8) if ok, then measure the stp sensor resistance at the wire terminals (between terminal a and terminal c). stp sensor resistance: approx. 4.69 kΩ 09900-25008: multi-circuit tester set 09900-28630: tps test wire harness tester knob indication: resistance (Ω) are the co...
Page 225
4-72 fi system diagnosis “c31” (p0705) gp switch circuit malfunction inspection step 1 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) check the gp switch coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the gp switch voltage. 3) support the motorcycle with a jack. 4) fold the side-stand to up positio...
Page 226
Fi system diagnosis 4-73 is the voltage ok? 9) after repairing the trouble, clear the dtc using sds tool. ( 4-26) yes • p wire open or shorted to ground • if wire and connection are ok, intermittent trou- ble or faulty ecm. • recheck each terminal and wire harness for open circuit and poor connecti...
Page 227
4-74 fi system diagnosis “c32” (p0201), “c33” (p0202), “c34” (p0203) or “c35” (p0204) fuel injector circuit malfunction inspection step 1 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) lift and support the fuel tank ( 5-3) 3) check the injector coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then measure the in...
Page 228
Fi system diagnosis 4-75 5) if ok, then check the continuity between each terminal and ground. injector resistance: ∞Ω (infinity) are the resistance and continuity ok? 6) after repairing the trouble, clear the dtc using sds tool. ( 4-26) step 2 1) turn the ignition switch to on. 2) measure the in...
Page 229
4-76 fi system diagnosis “c41” (p0230-h/l) fp relay circuit malfunction inspection step 1 (when indicating c41:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) remove the seat tail cover. ( 8-4) 3) check the fp relay coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then check the fp relay. ( 5-6) is the fp rela...
Page 230
Fi system diagnosis 4-77 step 1 (when indicating p0230-h:) 1) turn the ignition switch to off. 2) remove the seat tail cover. ( 8-4) 3) check the fp relay coupler for loose or poor contacts. If ok, then check the fp relay. ( 5-6) is the fp relay ok? 4) after repairing the trouble, clear the dtc us...