- DL manuals
- Suzuki
- Engine
- F6A
- Service manual
Suzuki F6A Service manual
Summary of F6A
Page 1
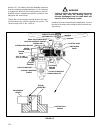
Haulster police vehicle service manual with 660 suzuki efi engine model 898487 part no. 2703285 for.
Page 2: Index
Index section 1 – fuel injection theory pages 1–26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Section 2 – periodic manintenance pages 27–32 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Section 3 – trouble shooting pages 33–42 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 3: Section 1
1 section 1 electronic fuel injection theory.
Page 4
2 electronic fuel injection theory management system description foreword this section provides information on the basic operation of the electronic fuel injection engine control system. The text covers what the electronic fuel injection engine control system does and how it works. Read this section...
Page 5
3 electronic fuel injection engine control technical instruction 1. Performance and configuration of engine control engine control system and micro computer this vehicle uses many different electronic control devices which make use of a microcomputer. Ones equipped in vehicles are: engine control sy...
Page 6
4 input circuit when a signal from each sensor enters ecm, it first passes through the input circuit, where any noise on each signal is removed and a sine wave signal such as a crank angle signal is converted to a pulse signal (rectanglar wave). Another function of the input circuit is to convert th...
Page 7
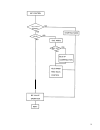
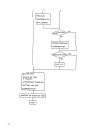
5 basic functions of engine control system basic functions of the engine control system include fuel injection control, idle speed control and ignition timing control that are synthetically controlled by ecm which has a built–in microcomputer. Outline of engine control functions electronic fuel inje...
Page 8
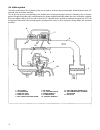
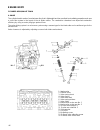
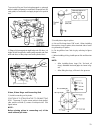
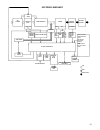
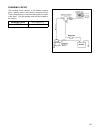
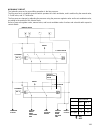
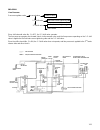
6 system configuration of each control function following block diagrams show configurations of sensors and actuators used for such control systems as fuel injection control, idle speed control, ignition control egr control and purging control. (1) fuel injection control pressure sensor key switch (...
Page 9
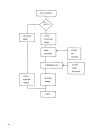
7 (3) ingition control sensor ignition coil 1 ignition coil 2 ignition coil 3 configuration of engine control system the engine control system consists of the following sub–systems. Intake air system this system supplies the air necessary for combustion. The air filtered by the air cleaner flows thr...
Page 10
8 air intake system the main components of the air intake system are air cleaner, air flow meter, air intake pipe, throttle body, air valve, isc solenoid valve and intake manifold. The air (by the amount corresponding to the throttle valve opening and engine speed) is filtered by the air cleaner, pa...
Page 11
9 description of intake system the air filtered by the air cleaner flows into the surge tank but only by such amount according to the opening of the throttle in the throttle body as well as the engine speed. The throttle valve in the throttle body regulates the air amount into the engine by its open...
Page 12
10 +f/b compensation +learning compensation +low speed compensation) x battery voltage compensation x water temperature compensation described below is how control is done at each time. (1) when the engine is at a stop the isc solenoid valve remains off or completely closed. Coolant temperature comp...
Page 13
11 key switch.
Page 14
12 fuel system fuel pump control the fuel pump of the electronic fuel injection system is controlled so that it operates only when the engine is running. This is a safety device to stop the fuel pump whenever the engine stops even if the ignition switch is on. (1) when the ignition switch is turned ...
Page 15
13 fuel pressure control system as the amount of injected fuel supply to the engine is controlled according to the injection signal (to determine how long the injector injects fuel) sent to the injector by the ecm, it is also necessary to control the fuel pressure. Otherwise, fuel injection increase...
Page 16
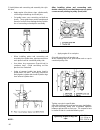
14 fuel injection control system injector a nozzle attached to the intake manifold is an injector. Equipped with an electromagnetic valve, it injects fuel according to the injection time calculated by the ecm. When electricity flows to the coil, it attracts the plunger and the needle valve, as it is...
Page 17
15 injectors 1 2 3 7 1 10 2 9 17.
Page 18
16 fuel injection control there are three types of fuel injection control for different injection methods: all cylinders synchronous injection, group injection and sequential injection as described below by using examples. Fuel injection control system synchronous injection at start when the engine ...
Page 19
17 k 1 is set to use as a remedy if the engine should have failed to start and an ignition plug converage have occurred. Also, when the cooling water temperature is low, the injection time at start is divided for effective spraying to ensure better start. (divided injection) criteria for execution o...
Page 20
18 warm–up increase compensation the fuel injection is increased according to the cooling water temperature and the engine speed to improve operation when the engine is cold. The lower the cooling water temperature, the larger the increase is. When this increase compensation is used, the air/fuel ra...
Page 21
19 • air/fuel ratio feedback compensation suzuki uses a rhodium catalytic converter to process c0, hc and nox contents in the exhaust gas. It oxidize co and hc and reduces nox simultaneously into non–toxic co2 h2o oz and n2 respectively; although only near the optimum air/fuel ratio range. In other ...
Page 22
20 • base air/fuel ratio compensation this base air/fuel ratio compensation is a long–term compensation. While the air fuel ratio feedback compensation is a short–term one. As the engine is subject to change, deviation (as shown by 1 and 2 below) occurs in the air/fuel ratio feedback compensation fa...
Page 23
21 (continued on next page).
Page 24
22.
Page 25
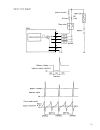
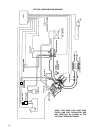
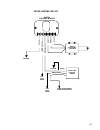
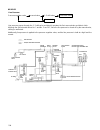
23 ignition system ignition signal system shown below is the basic ignition signal circuit. 1. Igniter (power unit) 2. Ignition coil 3. Distributor 4. Cas 5. Map (pressure sensor) 6. Tps 7. Wts 8. Vehicle speed sensor 9. Battery voltage 10. Test switch terminal the ecm calculates the energizing time...
Page 26
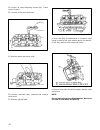
24 ignition control system the ignition control system controls the ignition to the optimum timing. There are two types: fixed ignition and soft igni- tion. Fixed ignition when the following conditions are met, the ignition timing is fixed to the initial set position of the crank angle signal. Condi...
Page 27
25 engine speed base ignition adv ance • when the idle switch is off the optimum basic advance is set according to the engine load (basic injection time) and the engine speed. Cooling water temperature compensation advance • warm–up compensation advance when the cooling water temperature is low, the...
Page 28
26 key switch.
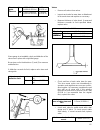
Page 29: Section 2
27 27 section 2 periodic maintenance.
Page 30
28 28 alternator belt inspection 1) disconnect negative battery lead at battery. 2) inspect belts for cracks, cuts, deformation, wear and cleanliness. Check belt for tension. The belt is in proper tension if it deflects 11 to 14mm (0.43–0.55in.) under thumb pressure (about 10 kg or 22 lbs.). Belt te...
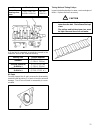
Page 31
29 29 3) refer to section 3 for valve lash inspection and adjustment procedures. 4) install engine valve cover and tighten bolts to specifications. Camshaft timing belt replacement refer to section 3 for camshaft timing belt removal and installation procedures. Engine oil filter change 1) loosen oil...
Page 32
30 30 another 3 minutes before checking the oil level. Add oil as necessary, to bring oil level to full level mark on dip stick. Note: steps 1–3 outlined above must be performed with engine not running. For step 4), be sure to have adequate ventilation while engine is running. It is recommended to u...
Page 33
31 31 reservoir tank 0.5 liters (1.1/0.9 us/imp pt.) total 4.7 liters (10.0/8.3 us/imp pt.) caution ! When changing engine coolant, use mixture of 50% water and 50% anti–freeze for regions where ambient temperatures fall lower than –16 degrees c (3 degrees f) in winter and mixture of 70% water and 3...
Page 34
32 32 spark plug tightening torque 25–30 n–m 2.5–3.0 kg–m 18.5–21.5 lb–ft air filter element cleaning and replacement air filter element 1) remove air cleaner cap. 2) take cleaner element out of the air cleaner case. 3) clean or replace with a new one. To clean element, blow off dust with compressed...
Page 35: Section 3
33 section 3 trouble shooting.
Page 36
34 condition possible cause correction poor starting (hard starting) starter will not run 1. Main fuse blown 2. Contact not closing in main switch, or this switch open–circuited 3. Run–down battery 4. Defective magnetic switch to starter 5. Loose battery terminal connection 6. Defective brushes in s...
Page 37
35 condition possible cause correction poor starting (hard starting) 6. Broken or slipped valve timing belt 7. Poor valve seating 8. Wrong kind of engine oil 9. Burnt valves 10. Sticky valve stem replace repair or replace replace replace correct or replace valve and guide not enough power inadequate...
Page 38
36 condition possible cause correction engine hesitates (momentary lack of response as the accelerator is depressed. Can occur at all vehicle speeds. Usually most severe when first trying to make the vehicle move, as from a stop sign.) abnormal condition in electrical system 1. Defective spark plug ...
Page 39
37 condition possible cause correction erratic idling (improper engine idling) abnormal condition in ignition system 1. Defective spark plug 2. Damaged or defective coils abnormal condition in fuel system 1. Incorrect idle adjustment 2. Clogged air cleaner elements others 1. Loose connection or disc...
Page 40
38 condition possible cause correction abnormal detonation abnormal condition in engine 1. Excessive carbon deposit on piston crowns or cylin- der head 2. Blown cylinder head gasket, resulting in low compres- sion pressure 3. Improper valve clearance 4. Valves tending to seize 5. Weakened valve spri...
Page 41
39 condition possible cause correction engine noise note: before check- ing the mechanical noise, make sure that: specified spark plug is used. Specified fuel is used. Crankshaft noise 1. Worn–down bearings, resulting in excessively large running clearances 2. Worn connecting–rod bearing 3. Distorte...
Page 42
40 condition possible cause correction high fuel consump- tion abnormal condition ignition system 1. Leak or loose connection of high tension cord 2. Defective spark plug (improper gap, heavy deposits, burned electrodes, etc...) abnormal condition in fuel system 1. Clogged air cleaner element abnorm...
Page 43
41 starting motor condition possible cause correction starter runs but pin- ion will not mesh into ring gear. 1. Worn pinion of starter clutch 2. Defective splines, resulting in sticky pinion plunging motion 3. Worn bushing 4. Worn teeth of ring gear replace repair or replace replace replace starter...
Page 44
42 charge light does not light with ignition on and engine off 1. Fuse blown 2. Light burned out 3. Loose wiring connection 4. Ic regulator check fuse replace light tighten loose connections replace alternator noise 1. Worn. Loose or otherwise defec- tive bearings replace.
Page 45: Section 4
43 section 4 engine mechanics.
Page 46
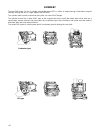
44 summary the type f6a engine (in–line 3–cylinder, total displacement 657 cc) offers an engine having a sleeveless compact structure through the use of a high–rigidity cast iron block. The cylinder head is made of aluminum alloy, with a 4–valve sohc design. The cylinder head of the 4–valve sohc typ...
Page 47
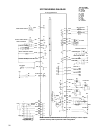
45 engine specifications model type carburetor efi no. And arrangement of cylinders in–line three–cylinder w traverse form of combustion chamber pentroof form valve mechanism sohc4 valve/drive total displacement (cc) 657 bore y stroke (mm) 65.0 × 66.0 compression ratio 10.5 maximum output (ps/rpm) 4...
Page 48
46 engine body cylinder head/valve train 4–valve the cylinder head is made of an aluminum alloy that is lightweight and has excellent heat radiating properties and uses a cross–flow system in the layout of the air intake valves. The combustion chambers have improved combustion efficiency by using a ...
Page 49
47 cylinder head gasket the head gasket uses carbon graphite as a parent material and the bore areas are made of stainless steel and given improved durability. Number of cylinders number of bearings copper a–a’ section b–b’ section material parent material bore sections oil holes carbon graphite sta...
Page 50
48 crankshaft the crankshaft is a 4–bearing type made of cast iron, and has reduced vibration and noise by providing balance or which offset the no. 1 ranking no. 3 crank. Thrust bearings oil hole upper journal bearing lower journal bearing specifications crankshaft journal diameter (mm) φ 44 ( φ 43...
Page 51
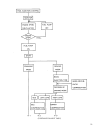
49 pistons/piston rings/piston pins pistons are made of aluminum alloy and have a slipper skirt, with a valve recess provided at the top of the piston. The first ring increases initial conformity having a barrel face form, and the second ring increases oil run–off properties with a tapered undercut ...
Page 52
50 timing belt/timing pulley/timing belt tensioner the timing drive system uses a quiet belt system. The rotation of the crankshaft is transmitted via the crankshaft timing pulley to the camshaft timing pulley by means of the timing belt. Since timing marks are engraved or cast in the timing pulley,...
Page 53
51 camshaft the camshaft is made of cast iron and is designed for high rigidity as a solid structure. The rear portion is formed as a single body by pressure–insertion of the signal rotor. 4–valve models ∅ 27.0 cam height (mm) in ex in ex 35.984 35.986 31.147 29.550 valves/valve springs valves are s...
Page 54
52 lubrication system the engine lubrication uses a wet sump system, which is full–flow filtration force–feed system that force–feeds the oil using a pump that is driven by the driveshaft. The oil is drawn up from the oil pump strainer, and passes through the oil filter before flowing into the main ...
Page 55
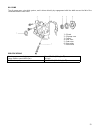
53 oil pump the oil pump uses a trochoid system, and is driven directly by engagement with the width across the flat of the crankshaft and the inner rotor. 1. Oil seal 2. Oil pump case 3. Gasket 4. Inner rotor 5. Outer rotor 6. Rotor plate 7. Relief valve specifications discharge pressure, discharge...
Page 56
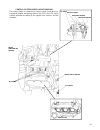
54 intake system air cleaner intake pipe air cleaner throttle body intake manifold engine exhaust system engine exhaust manifold exhaust pipe catalyst main muffler.
Page 57: Section 5
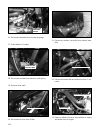
55 section 5 engine repair.
Page 58
56 general description engine 1. The engine is a water cooled, in–line, 3 cylinder, 4–stroke gasoline unit with its s.O.H.C. (single overhead camshaft) valve mechanism arranged for “v”–type configuration with12 valves (2 intake and 2 exhaust valves per cylinder). The single overhead camshaft is moun...
Page 59
57 engine lubrication the oil pump is of a trochoid type, and mounted on the crankshaft at crankshaft pulley side. Oil is drawn up through oil pump strainer and passed through pump to oil filter. The filtered oil flows into two paths in cylinder block. In one path, oil reaches crankshaft journal bea...
Page 60
58 note: throughout this manual, the three cylinders of the engine are identified by numbers: no. 1, no. 2 and no. 3 as counted from front end. Note: observe critically before starting to remove a component or part by loosening bolts, nuts and the like. What you may find before and during disassembl...
Page 61
59 4) remove timing belt outside cover. 5) remove timing belt tensioner after removing a part of the tensioner spring. 6) remove timing belt. Caution ! When timing belt has been removed, never turn crankshaft or camshaft. If camshaft must be turned, turn by crankshaft so that timing mark is deviated...
Page 62
60 19) loosen all valves adjusting screws fully. Leave screws in place. 20) remove rocker arm shaft caps. 21) remove intake rocker arm shaft. 22) remove camshaft caps, camshaft and exhaust rocker arms. 23) remove cylinder head. A) use valve lifter and attachment to compress valve spring in order to ...
Page 63
61 c) using special tool, drive valve guide out from combus- tion chamber side to valve spring side. Note: do not reuse valve guide once disassembled. Be sure to use new valve guide (oversize) when assem- bling. Note: place disassembled parts except valve stem oil seal and guide in order, so that th...
Page 64
62 caution ! Before pushing the piston out, scribe the cylinder number on its crown. Be sure to identify each piston, piston pin, connecting rod and bearing cap by using the cylinder number. A) from each piston, ease out piston pin circlips, as shown. B) force piston pin out. 33) remove oil pump cas...
Page 65
63 wash all disassembled parts clean, removing, grease, carbon and scales, before inspecting them to determine whether repair is necessary or not. Descale water jackets used compressed air to clear internal oil holes and passages. Do not disturb set combinations of valves, bear- ings, bearing caps, ...
Page 66
64 measuring surface of intake manifold seating face measuring surface of exhaust manifold seating face rocker–arm shaft and rocker arms shaft–to–arm clearance (in & ex): using a micrometer and a bore gauge, measure rocker shaft dia. And rocker arm i.D.. The difference between two readings is the ar...
Page 67
65 stem–to– guide l int 0.020–0.047 mm (0.0008–0.0018 in.) 0.07 mm (0.0035 in.) g clearance exh 0.035–0.062 mm (0.0014–0.0024 in.) 0.09 mm (0.0035 in.) if bore gauge is not available, check end deflection of the valve stem in place with a rigid dial gauge. Move stem end in the directions (1) and (2)...
Page 68
66 valve seats caution ! Valves to be checked and serviced for seating width and contact pattern must be those found satisfactory in regard to stem clearance in the guide and also requirements stated on preced- ing page under valves. Seating contact width: produce a contact pat- tern on each valve i...
Page 69
67 valve seat cutting valve seat angles for exhaust valve seat 2) intake valve seat: cutting sequence is the same as for exhaust valve seats but the second angle differs, as will be noted in below figure. Seat width (w) for intake valve seat 1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0434 – 0.0511 in.) valve seat angles for i...
Page 70
68 valve springs referring to the criterion–data given below, check to be sure that each spring is in sound condition, free of any evidence of breakage or weakening. Remember, weakened valve springs can be the cause of chatter, not to men- tion the possibility of reducing power output due to gas lea...
Page 71
69 journal wear: check camshaft journals and camshaft hous- ings for pitting, scratches, wear or damage. If any malcondition is found,replace camshaft or cylinder head with housing. Never replace cylin- der head without replacing housings. Check clearance by using gaging plastic. The procedure is as...
Page 72
70 cylinder bore dia. Limit 65.070 mm (2.5618 in.) taper and out–of–round limit 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.) piston and piston rings inspect the outer surface of each piston for evi- dence of burn and for scratch or groove marks. Minor flaws can be removed by sanding with fine grain sandpaper. De–carbon the...
Page 73
71 item standard limit ring clearance in top ring 0.03–0.07 mm (0.0012–0.0027 in.) 0.12 mm (0.0047 in.) clearance in the groove 2nd ring 0.02–0.06 mm (0.0008–0.0023 in.) 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.) piston ring end gap: to measure the end gap, insert the piston ring into the cylinder bore, locating it at th...
Page 74
72 connecting–rod big end bearings inspect bearings for signs of fusion, pitting, burn or flaking and observe the contact pattern. Bear- ings found in defective condition through this inspection must be replaced. Caution ! Bearings are not meant to be repaired by scrap- ing or sanding with sandpaper...
Page 75
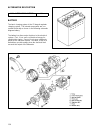
73 4) if the limit, indicated above, is exceeded, re–grind the crankpin to the undersize and use of the undersize bear- ing, both of which are stated below: bearing size crankpin diameter standard 35.982–36.000 mm (1.4167–1.4173 in.) 0.25 mm (0.0098 in.) undersize 35.732–35.750 mm (1.4068–1.4074 in....
Page 76
74 out of round and taper (uneven wear): an unevenly worn crankshaft journal or crankpin shows up as difference in diameter at a cross section or along its length (or both). This differ- ence, if any, is to be determined from micrometer readings taken as shown in figure below. If any of the journals...
Page 77
75 item standard limit journal–to– bearing clear- ance 0.020–0.040 mm (0.0008–0.0016 in.) 0.065 mm (0.0026 in.) 4) if the limit is exceeded, re–grind the journals to the undersize and use the undersize bearing. Bearing size journal diameter standard 43.982–44.00 mm (1.7316–1.7322 in.) 0.25 mm unders...
Page 78
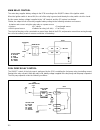
76 oil pump 1) inspect oil seal lip for fault or other damage. Replace as necessary. 2) inspect outer and inner gears, gear plate, and oil pump case for excessive wear or damage. Radial clearance: check radial clearance between outer rotor and case, using thickness gauge. If clearance exceeds its li...
Page 79
77 engine reassembly note: all parts to be used in reassembly must be perfectly clean. Oil sliding and rubbing surfaces of engine parts with engine oil just before using them in reassembly. Have liquid packing ready for use. Bond no.1215 is specified for it. Use it wherever its use is specified in o...
Page 80
78 tightening torque for bearing cap bolts 55–60 n–m 5.5–6.0 kg–m 40.0–43.0 lb–ft gradual and uniform tightening is important for bearing cap bolts. Make sure that the four caps become tight equally and uniformly to the specified torque. Note: after tightening cap bolts, check to be sure that cranks...
Page 81
79 to prevent oil lip seal from being damaged or upturned when installing oil pump to crankshaft, fit special tool (oil seal guide) to crankshaft, and apply engine oil to special tool. 3) edge of oil pump gasket might bulge out: if it does, cut bulge off with sharp knife, making edge smooth and flus...
Page 82
80 3) install piston and connecting rod assembly into cylin- der bore. Apply engine oil to pistons, rings, cylinder walls, connecting rod bearings and crank pins. Put guide hoses over connecting rod bolts as shown. These guide hoses protect crankpin and thread of rod bolt from damage during installa...
Page 83
81 oil pump strainer install oil pump strainer to oil pump. Bearing in mind that “o” ring is often forgotten and left out in reassembly. Absence of this ring defeats the purpose served by the strainer. Oil pan 1) clean mating surfaces of oil pan and cylinder block. Remove oil, old sealant, and dusts...
Page 84
82 2) install valve spring seat to cylinder head. 3) install new valve stem seal to valve guide. After apply- ing engine oil to seal and the install seal to valve guide. After installation, check to be sure that seal is properly fixed to valve guide. Do not reuse oil seal from disassembly. Be sure t...
Page 85
83 crankshaft camshaft & rocker–arm shaft 1) apply engine oil to exhaust rocker arm at its cam–rid- ing face and install it to valve stem end face and rocker– arm adjust screw. 2) place camshaft on camshaft journal of cylinder head at such angle that no. 1 piston is at top dead center of exhaust str...
Page 86
84 note: valve clearance is adjusted after all parts are assembled. So it is not adjusted at this point. Leave rocker arm adjusting screw as loose as possible. Intake manifold and carburetor 1) install intake manifold gasket to cylinder head. Use new gasket. Note: clean cylinder head mating surface ...
Page 87
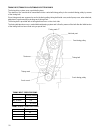
85 3) install key and camshaft timing belt pulley. When installing pulley, direct its timing marked side to timing belt outside cover side. Tighten pulley bolt to specified torque with special tool applied as shown in figure below. Tightening torque for pulley bolt 50–60 n–m 5.0–6.0 kg–m 36.5–43.0 l...
Page 88
86 note: when installing timing belt, match arrow mark on timing belt with rotating direction of crankshaft. In this state, no. 1 piston is at top dead cen- ter of compression stroke. Belt tensioner timing belt 9) after putting on belt, adjust belt tensioner as shown in figure above. The belt tensio...
Page 89
87 11) install crankshaft pulley and water pump pulley. Oil filter install oil filter. Caution ! For oil filter installation refer to section 1 of this manual. Exhaust manifold and cover 1) install exhaust manifold gasket to cylinder head. Use new gasket. Note: clean cylinder head mating surface wit...
Page 90
88 warm engine in 0.12 mm (0.0047 in.) warm engine ex 0.12 mm (0.0047 in.) caution ! When using specification for warm engine, warm up engine until engine cooling fan starts run- ning and take measurement or make adjustment within 20 to 30 minutes after engine is stopped. Checking and adjusting proc...
Page 91
89 6) upon completion of check and adjustment, install cyl- inder valve cover and torque bolts to specification. Tightening torque for cylinder head cover bolts 9–12 n–m 0.9–1.2 kg–m 7.0–8.5 lb–ft engine oil refer to section 1 of this manual. Engine oil filter for removal and installation of filter,...
Page 92
90 note: prior to checking oil pressure, check the following. Oil level in oil pan. If level is low, add oil to full level line on oil dip stick. Oil quality. If oil is discolored, or deteriorated, change oil. For particular oil to be used , refer to table in section 1. Oil leak. If oil leak is foun...
Page 93
91 note: should indicating hand of the vacuum gauge oscil- late violently, turn adjusting nut (a) to steady it. Standard vacuum (sea level) 40–48 cmhg (15.8–18.8 in.Hg) at specified idling speed. 4) after checking, remove vacuum gauge. 5) before reinstalling vacuum checking switch, be sure to wrap i...
Page 94
92 recommended torque specifications.
Page 95: Section 6
93 section 6 engine control system.
Page 96
94 summary mpi (multi–point injection) type efi (electronic fuel injection) is used in engine control, achieving optimal air–fuel ratio control. Additionally, by combining (integrating) the at controller with the ecm (engine control module), space saving is achieved and maintenance qualities are imp...
Page 97
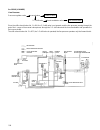
95 isc valve throttle body pressure sensor throttle sensor water temperature sensor injectors crank angle sensor o 2 sensor ignition coil control system parts layout diagram the control system is composed of sensors, which send data con- cerning the engine and driving status to the ecm, the ecm, whi...
Page 98
96 system configuration drawing pcv v a l v e isc v a l v e w a ter tempera ture sensor throttle sensor o2 sensor ca t a l ytic converter air cleaner crank angle sensor inject or ecm canister fuel pump pressure ignition coil pressure sensor fuel fil ter regula t o r note: fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel ...
Page 99
97 system flowchart air cleaner isc valve throttle body tps ps intake manifold engine exhaust manifold wts cas o 2 sensor ternary catalyst injector throttle opening amount intake air pressure cool- ant temp engine rpm cyl- inder differ- enti- ation exhaust gas oxy- gen con- centra- tion fuel pump fu...
Page 100
98 system wiring diagram efi (& at) controller 5v cas 16 +b br/r crank angle sensor +b 216 w/r vehicle speed sensor 5v spd throttle sensor ltg/r ltg – light green w – white br – brown y – yellow gy – gray b – black g – green bl – blue r – red pk – pink p – purple or – orange 26 vcc 5v pressure senso...
Page 101
99 fuel system the fuel system comprises of the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel pressure regulator, delivery pipe, injectors and fuel feed line. The fuel in the fuel tank is drawn up by the fuel pump, filtered by the fuel filter, transported to the delivery pipe, and injected by the injector...
Page 102
100 1 4 2 3 ecm 1. Filter 2. Solenoid coil 3. Ball valve 4. Injector terminal +12v (via relay) injector #1 br/b br br/w 1 1# 10 2# 2 3# b/bl b color code b – black br – brown w – white bl – blue injectors the injector is a device which injects fuel in the delivery pipe into the intake manifold under...
Page 103
101 air intake system air that has been filtered by the air cleaner passes through the throttle body and is distributed to the intake manifold of each cylinder. The intake air amount is indirectly measured by measuring the intake air pressure using the pressure sensor. When the throttle valve is ful...
Page 104
102 6 7 ics valve 3 5 4 2 1 1. Valve pintle 2. Screw shaft 3. Magnet (rotor) 4. Coil 5. Bearing 6. Throttle valve 7. Bimetal type limiter valve +12v (via relay) b/r isc valve 11 sma 12 smb 13 smc 14 smd 9 e01 e1 17 ecm r/b r r/y r/bl b/bl b color code b – black r – red y – yellow bl – blue n s s n 8...
Page 105
103 input–output system throttle sensor vcc vta e2 ecm 5v 26 33 34 vcc vta e2 ltg/r gy/y bl/y v t a output terminal votage(v) fully closed throttle lever turn angle fully open color code ltg – light green gy – gray r – red bl – blue y – yellow thw water temperature gauge e2 water temperature sensor ...
Page 106
104 pressure sensor ltg/r ltg/y bl/y vcc e2 pm 26 25 34 vcc pm e2 ecm 5v 5v 2 1 1. Zirconia element 2. Housing o 2 sensor s–r bl/y 24 34 ox e2 ecm color code r – red bl – blue y – yellow pressure sensor (pm) the pressure sensor is a sensor that is installed on the throttle body, detects changes in t...
Page 107
105 1 2 1. Crank angle sensor 2. Element +b cas gnd crank angle sensor br/r +b 16 cas 5v ecm color code br – brown r – red signal rotor vehicle speed sensor controller period between pulses crank angle sensor (cas) the crank angle sensor is installed on the sensor case and houses an element which co...
Page 108
106 emission system the emission system is composed of a fuel vapor gas emission prevention device, blow–by gas recovery device, and ternary catalyst device. Information label 1 7 3 2 4 5 6 1. Throttle body 2. Evapo–canister 3. Air 4. Evaporation gas 5. Fuel tank 6. Intake manifold 7. Cylinder infor...
Page 109
107 5 1 2 3 4 (when engine load is low) (when engine load is high) 1 2 3 4 1. Breather hose 2. Pcv valve 3. Intake manifold 4. Exhaust manifold 5. Throttle valve blow–by gas recovery device the blow–by gas recovery device is provided in order to return unconsumed gas (consisting mainly of hc) that h...
Page 110
108 control system the ecm (engine control module) is incorporated into the efi(&at) controller housed behind the engine compartment under the center panel of the storage compartment. The ecm performs optimal actuator control during driving by processing data input from the sensors. The following ar...
Page 111
109 fuel injection control a speed density method is used whereby ecm calculates the air intake amount according to the engine rpm (crank angle sensor) and intake manifold pressure (pressure sensor), and determines the basic injection time. The fuel injection method (timing) and fuel injection amoun...
Page 112
110 feedback mode: during normal driving, sequential control, which performs injection in the order 1–3–2 for each cylinder, is used. Injection is performed in the exhaust sequence of each cylinder. The fuel injection amount is calculated by adding following correction to the basic fuel injection ti...
Page 113
111 isc stepper motor control the isc stepper motor is controlled in the following modes according to various conditions. Operation shutdown: when the battery voltage is less than 9.0 v, operation of the isc is halted. Initialization: when the ignition key is switched from on to off, initializing is...
Page 114
112 main relay control the main relay supplies battery voltage to the ecm according to the on/off status of the ignition switch. When the ignition switch is turned on, the coil of the relay is ground, and thereby the relay switch circuit is closed. By this means, battery voltage is applied to the ”+...
Page 115
113 diagnosis (self–diagnosis) function the ecm is provided with a self–diagnosis function, whereby it illuminates the check engine lamp in the combination meter when there is an abnormality in an input signal, providing notification of the occurrence of an abnormal condition. Further, when control ...
Page 116
114 code retrieval procedure note: • when there are multiple failure locations, all of the codes are displayed 3 times each in order of priority of code. • see section 2b for at system diagnosis codes. Note: the jumper will perform diagnostic checks on various electrical components. 3. Place the gea...
Page 117
115 16 vehicle speed sensor – no signal for a length of time at pin 16 (orange wire) of the 26 pin ecu connector. 19 water temperature sensor – voltage at pin 32 (green/white wire) of the 34 pin ecu connector is either higher than 4.85v or lower than 0.15v. Failsafe mode: control system sot that coo...
Page 118
116.
Page 119: Section 7
117 section 7 engine removal.
Page 120
118 engine removal this section covers the removal of the suzuki 660 engine from the model 898487 on–road cushman police vehicle. The engine and transmission are to be removed from the vehicle as an assembly. Procedure 1. Disconnect negative (–) and positive cables from battery terminals. Ecm 2. Rem...
Page 121
119 8. Disconnect lead wires from water temperature sender. 9. Remove air cleaner hose. 10. Remove fuel tank cap to release fuel vapor pressure in fuel tank and then reinstall it. Fuel line vacuum line 11. Disconnect vacuum and fuel lines. 12. Disconnect lead wires from alternator terminals. Acceler...
Page 122
120 lead to oil pressure gauge 16. Disconnect lead wire from oil pressure gauge. 17. Drain radiator of coolant. Transmission cooler lines 18. Disconnect and drain transmission cooling lines. 19. Remove drive shaft. Oil hose disconnects 20. Disconnect oil hose from oil filter. 21. Disconnect catalyti...
Page 123
121 5550 24. Place transmission or floor jack under “engine with transmission”. Place wood blocks between trans- mission and jack so that engine with transmission is held horizontally even when motor mount bolts are removed. 5559 25. Place engine hoist lift arm through right hand door, and attach wi...
Page 124
122 5554 28. Carefully remove engine with transmission..
Page 125: Section 8
123 section 8 ignition system.
Page 126
124 general description ignition system this vehicle uses a full–transistor type, direct–ignition system, comprising of (3) ignition coils, (3) spark plugs and the engine control module or ecm. The ecm also has the function of controlling the automatic transmis- sion shift points, if vehicle is so e...
Page 127
125 ignition coil ignition coil test ignition coil resistance primary 1.08–1.32 Ω resistance (cold) secondary 22.1–29.2 k/ Ω measure primary and secondary coil resistances ( at 20 ° c or 68 ° f). If the resistance is out of range in either the primary or secondary circuit, replace the ignition coil ...
Page 128
126 condition possible cause correction engine cranks, but will not start or hard to start no spark blown fuse for ignition coil loose connection or disconnection of lead wires faulty spark plug(s) replace connect securely adjust, clean or replace poor fuel economy or engine performance faulty spark...
Page 129
127 ignition timing control low rpm (starting) mode: when the engine speed is 600 rpm or lower, ignition is adjusted to btdc5 ° . Connection occurs in the interval from 75 ° btdc to 5 ° btdc. Ignition timing adjustment mode: when diagnositc jumper (p.N. 2700920) in place, the ignition timing is fixe...
Page 130
128.
Page 131: Section 9
129 section 9 fuel system.
Page 132
130 air cleaner general description in the air cleaner case, a dry–type air cleaner element is provided for filtering out dirt and dust from air being drawn into the engine for combustion. A damaged element must be replaced with a new one, since it allows dust particles to enter the engine if used a...
Page 133
131 maintenance services air cleaner element air cleaner element should be cleaned or replaced peri- odically according to following method. Cleaning 1) remove engine access cover. 2) remove air cleaner case cap. 3) take out air cleaner element from air cleaner case and blow off dust with compressed...
Page 134
132 fuel filter fuel filter is mounted on the chassis above the differen- tial. Fuel enters the filter through its inlet hole and after pass- ing through the filtering element, comes out of its outlet hole connected to the fuel pump. This filter is not meant to be disassembled. It is of a cartridge ...
Page 135
133 fuel pump removal 1) disconnect negative battery cable. 2) remove fuel filler can to release fuel vapor pres- sure in the fuel tank. After releasing, reinstall the cap. 3) disconnect fuel pump lead wires at the fuel pump. Note: there is a positive (+) and negative (–) wire, and a (+) positive in...
Page 136
134 installation 1) install filter and clamp, and connect inlet and outlet hoses to fuel filter. 2 1 3 4 5 1. Fuel filter 2. Fuel line 3. Fuel pump 4. Carbon canister 5. Regulator 2) connect negative cable to battery. 3) after installation, start engine and check system for leaks. Fuel tank removal ...
Page 137: Section 10
135 section 10 cooling system.
Page 138
136 engine cooling system radiator cap a pressure–vent cap is used on the radiator. The cap contains a pressure valve and vacuum valve. The pres- sure valve is held against its seat by a spring of pre–de- termined strength which protects the cooling system by relieving the pressure if the pressure i...
Page 139
137 water reservoir tank a “see through” plastic reservoir tank is connected to the radiator by a hose. As the vehicle is driven, the coolant is heated and expands. The portion of the coolant dis- placed by this expansion flows from the radiator into the reservoir tank. When the vehicle is stopped a...
Page 140
138 coolant draining 1) remove radiator cap. 2)loosen drain plug (1) on radiator to drain coolant. Removal of radiator hoses 1) drain cooling system 2) to remove the hoses, loosen the screw on each hose clamp and pull hose end off. Alternator belt 1) loosen alternator drive belt tension 2) remove al...
Page 141
139 6) remove tensioner and timing belt. 7) remove water pump..
Page 142
140 inspection of components thermostat 1) make sure that the air bleed valve of thermostat is clear. Should this valve be clogged, engine would tend to overheat. 2) check valve seat for some foreign objects being stuck which might prevent valve from seating tight. Note: check interference between w...
Page 143
141 note: special care must be used when installing belt tensioner and timing belt. Be sure to refer to section 3 of this manual. Torque each bolt and nut to specification. 5) install crankshaft pulley and pump drive belt. 6)adjust intake and exhaust valve lashes. (for adjust- ment and related data,...
Page 144
142 3) tighten alternator adjusting bolt and pivot bolts. 4) if it is necessary to replace belt, refer to section 10 for procedure. Warning ! All adjustments described above are to be per- formed with engine not running. Coolant the coolant recovery system is standard. The coolant in the radiator ex...
Page 145
143 note: if proper quality antifreeze is used, there is no need to add extra inhibitors or additives that claim to improve system. They may be harmful to proper operation of system, and are unnecessary expense. Cooling system service cooling system should be serviced as follows: 1) check cooling sy...
Page 146
144 caution ! Be sure to replace old gasket used for bolt “a” with new one. Tightening torque for bolt “a” 2–4 n–m 0.2–0.4 kg–m 1.5–2.5 lb–ft. 10) run engine, with radiator cap removed, until radiator upper hose is hot. 11) with engine idling, add coolant to radiator until level reaches the bottom o...
Page 147: Section 11
145 section 11 cranking system.
Page 148
146 cranking system the cranking system is mainly composed of the battery, starting motor, ignition switch, and inhibitor switch (at models). Starting motor the starting motor uses a solenoid shift type. Magnetic switch assembly brush, assmebly permanent magnets armature drive lever 60a st main fuse...
Page 149
147 cranking circuit the cranking circuit consists of the battery, starting motor, ignition switch, and related, electrical wiring. These components are connected electrically as shown in the figure. Only the starting motor will be covered in this section. Manufacturer nippondenso output 0.6 kw.
Page 150
148 starting motor the starting motor consists of parts shown below and has permanent magnets mounted in the starter motor yoke (hous- ing). The magnetic switch assembly and parts in the starting motor are enclosed in the housing so that they will be protected against possible dirt and water exposur...
Page 151
149 possible symptoms do to starting system trouble would be as follows: starting motor does not run (or runs slowly) starting motor runs but fails to crank engine abnormal noise is heard proper diagnosis must be made to determine exactly where the cause of each trouble lies, in battery, wiring harn...
Page 152
150 condition possible cause correction starter motor running too slow (low torque) if battery and wiring are satisfactory, inspect starter motor 1. Insufficient contact of magnetic switch main contacts 2. Layer short–circuit of armature 3. Disconnected, burnt or worn commutator 4. Poor grounding of...
Page 153
151 starter motor inspection inspect armature inspect commutator for dirt or burn. Correct with emery cloth or lathe, if necessary. Check commutator for uneven wear. If deflection of dial gauge pointer exceeds limit, repair or replace. Note: below specification presupposes that armature is free from...
Page 154
152 ground test check commutator and armature core. If there is conti- nuity, armature is grounded and must be replaced. Open circuit test check for continuity between segments, if there is no continuity at any test point, there is an open circuit and armature must be replaced. Inspect brushes check...
Page 155
153 performance test caution ! These tests must be performed within 3–5 seconds to avoid burning out coil. Pull–in test connect battery to magnetic switch as shown. Check that plunger moves outward. If plunger does not move, replace the starter solenoid. Hold–in test while connected as above with pl...
Page 156
154.
Page 157: Section 12
155 section 12 charging system.
Page 158
156 alternator description max. Alternator output 45a battery the basic charging system is the ic integral regulator charging system. The internal components are con- nected electrically as shown in the following schematic diagram battery. The battery has three major functions in the electrical syst...
Page 159
157 carrier and holddown the battery carrier and hold–down clamp should be clean and free from corrosion before installing the bat- tery. The carrier should be in good condition so it will support the battery securely and keep it level. Make certain there are no parts in carrier before installing th...
Page 160
158 warning ! Departure from these conditions or pro- cedures described below could result in: 1) serious personal injury (particularly to eyes) or property damage from such causes as battery explosion, battery acid or electrical burns. 2) damage to electronic components of either vehicle. Never exp...
Page 161
159 belt tension spec- ification 11–14 mm (0.43–0.55 in.) as deflection note: when replacing belt with new one, adjust belt ten- sion to 10–12 mm (0.40–0.47 in.) 3) if the belt is too tight or too loose, adjust it to specifi- cation by adjusting alternator position. 4) tighten alternator adjusting b...
Page 162
160 undercharged battery this conditions, as evidenced by slow cranking or indi- cator clear with red dot can be caused by one or more of the following conditions even though indicator light may be operating normally. Following procedure also applies to vehicle with voltmeter and ammeter. 1) connect...
Page 163: Section 13
161 section 13 speed limiter.
Page 164
162 system operation trombetta’s p613–k1 throttle control solenoid kit con- sists of a “three wire,” dual coil solenoid, electromechani- cal control module and stainless steel sheathed pull cable. The sheathed pull cable allows the solenoid to be mounted away from hostile environments, such as engin...
Page 165
163 speed limiting circuit 845219 control module ground black green/yellow white/black red white black ground black orange/green white/green +12v fuse panel speed limit module 2700918 845218 speed limit solenoid +12v fuse panel vehicle speed input from speed sensor.
Page 166
164.
Page 167: Section 14
165 section 14 chassis.
Page 168
166 storage before storing the vehicle or battery for an extended period, the battey should be thoroughly cleaned, fully charged and the electrolyte brought up to the proper level. During storage, batteries should be periodically recharged. Charging interval depends on the average temperature at whi...
Page 169
167 see your authorized cushman dealer for nec- essary maintenance and service. • when replacement parts are required, use genu- ine cushman parts or parts with equivalent characteristics including type, strength and material. Failure to do so may result in product malfunction and possible injury to...
Page 170
168 the wheel cylinder. Fluid present in the boot area indicates a leaking wheel cylinder. Refer to figure 7. 3. Clean the brake backing plate. Reassembly 4. Apply a thin layer of high temperature lubricant to the brake backing plate where the brake shoes make contact (6 places) and brake adjuster. ...
Page 171
169 shoes until a slight drag is felt while turning front wheel assembly. 4. Reinstall the adjusting hole cover. Rear brake adjustment notice • this brake is self adjusting and needs adjustment only on initial installation. 1. Raise the vehicle off the ground. Warning ! • support the vehicle on appr...
Page 172
170 speedometer gear brake drum hub speedometer gear brake adjuster dust shield wheel cylinder adjustment hole cover brake shoes wheel mounting screw shoe retainer brake lever figure 11 (typical) rear brake assembly master cylinder master cylinder failures may usually be recognized by repeated loss ...
Page 173
171 1 2 3 4401 figure 12 1. Brake rod 2. Locknut 3. Push rod rebuild procedure for master cylinder if cylinder is to be rebuilt, remove from vehicle and pro- ceed as follows: 1. Remove filler cup and gasket and pour fluid from res- ervoir. (do not reuse fluid). 2. Remove boot from cylinder. 3. Remov...
Page 174
172 rust or score and hone if necessary. Dip cups and pistons in brake fluid and reassemble parts into the cylinder. Install the wheel cylinder on the vehicle and connect the brake line. Bleed the entire brake system. Check for leaks prior to returning vehicle to service. Notice • severe pitting, sc...
Page 175
173 steering gear driven steering gear inside surface machined to provide clearance for nut idler bolt without lubrication fitting key upper housing lower housing figure 15 pinion gear shaft washer cluster gear nut washer retaining ring ball bearing bolt retaining ring disassembly with the horn wire...
Page 176
174 direction 15 ° . It is better to have the allowable roughness than the maximum permitted backlash. If it is necessary to readjust the idler bolt, the locating washers (part no. 816449) must be rotated to prevent the serrations from falling into the same marks. Tighten the nut securing the steeri...
Page 177
175 front fork disassembly 1. Raise vehicle high enough to provide room for the fork to be removed from from bottom of vehicle. Warning ! • when it is necessary to raise the vehicle for any repair or service, use jackstands to provide ade- quate support. Do not rely on hydraulic or mechanical jacks ...
Page 178
176 warning ! • when it is necessary to raise the vehicle for any repair or service, use jackstands to provide ade- quate support. Do not rely on hydraulic or mechanical jacks. Notice • the complete steering gear must be removed to adjust fork pivot bearings. Refer to the steering gear overhaul sect...
Page 179
177 figure 22 1. Axle nut 2. Axle lock 3. Jam nut 4. Lubrication seals 5. Bearing cone 6. Hub 7. Lockwasher 8. Special washer 9. Bearing adjusting nut 10. Oil slinger 11. Bearing cup 12. Bearing backing ring 1 7 2 8 3 9 4 10 5 11 12 6 12 11 5 10 4 3. Remove special washer, jam nut and bearing adjust...
Page 180
178 3584 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 front wheel (brake side) figure 24 1. Front fork side arm 2. Brake anchor link 3. Brake arm 4. Cotter pin 5. Castle nut 6. Washer 7. Axle nut & lockwasher 8. Axle lock 9. Brake hose and protector brake link bushings (not shown, refer to safety warning regarding brake link ...
Page 181: Section 15
179 section 15 transmission automatic.
Page 182
180 summary the three–speed automatic transmission uses an a–type manufactured by aishin. The at controller is integrated with the epi controller. 2 5 4 6 8 7 9 10 11 14 13 12 3 1 1. Input shaft 2. Torque converter 3. Oil pump 4. Second brake 5. Direct clutch 6. Forward clutch 7. One–way clutch 8. F...
Page 183
181 model a172 specifications items specifications engine f6a con- verter torque type 3–element 1–stage 2–phase stall torque ratio 2.07 pump oil type trochoid oil pump drive method engine drive type forward 3–stage, reverse 1 stage planetary gear train shift position p range: change gear neutral, ou...
Page 184
182 power transmission mechanism planetary gear unit this unit is used for shifting during driving, and switching between forward, reverse, and neutral. Unit is composed of a sun gear, planetary gear, and internal gear. This unit is provided on the front rear and by combination of connections is abl...
Page 185
183 one–way clutch this clutch connects the input shaft and front internal gear. In the driving range excluding reverse, direct line pressure is applied from the manual valve, and gear is always connected. Direct clutch this clutch connects the input shaft and sun gear. Operates in 3rd gear and reve...
Page 186
184 power transmission path 1 st gear (l range) operating clutch forward clutch: connects input shaft and front internal gear first reverse brake: fixes rear gear input/output input front internal gear output: rear internal gear rotating status of each gear front rear input rpm n i rpm internal gear...
Page 187
185 2 nd gear since n i > n i , the output rpm is slowed in relation to the input rpm. Since the rotation of the sun gear was reverse in 1st gear, the front carrier was slowed to that extent, but in 2nd gear the sun gear is fixed, so the slowing of the front gear is less than that in 1st gear. Accor...
Page 188
186 reverse the rear carrier is fixed, and the sun gear rotates turns in a forward direciton, so the rear internal gear turns in a reverse direction. Thus the output shaft rotation is reversed, and the vehicle moves backward. Operating brake, clutch direct clutch: connects input shaft and sun gear 1...
Page 189
187 hydraulic mechanism valve body the valve body distributes the hydraulic pressure generated by the oil pump to the clutch and brake. Internally, is comprised of a manifold valve, which distributes the basic hydraulic pressure, shift valves, which switch hydraulic pressure to the clutch and brake,...
Page 190
188 1–2 shift valve manual valve [d], [2] range pressure regulator valve 1–2 shift valve shift solenoid no. 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 forward clutch drain direct clutch second brake tightening side first reverse brake manual valve [d], [2] range manual valve [d], [2] range locost module valve shift solenoid n...
Page 191
189 hydraulic circuit the hydraulic pressure for gear shifting operation is the line pressure. The line pressure is a hydraulic pressure which operates the clutch and brake, and is switched by the manual valve, 1–2 shift valve, and 2–3 shift valve. The line pressure changes by adjusting the pressure...
Page 192
190 1 st gear (l range) line pressure pressure regulator valve manual valve forward clutch 2–3 shift valve locost modulator valve first reverse brake since the shift solenoid valve no. 1 is on, the 2–3 shift valve is not operate, and the line pressure passing through the port of the l range of the m...
Page 193
191 1st gear (d, 2 range) line pressure pressure regulator valve manual valve forward clutch since solenoid valve no. 1 is on, the 2–3 shift valve is not operated, the line pressure is halted at the 2–3 shift valve. Shift solenoid valve no. 2 is off, the 1–2 shift valve is operated, and the line pre...
Page 194
192 2nd gear 2nd brake servo tightening side line pressure pressure regulator valve manual valve forward clutch 1–2 shift valve since shift solenoid valve no. 1 is on, the pilot pressure is drained, and the 2–3 shift valve does not operate. Since shift solenoid valve no. 2 is on, the line pressure i...
Page 195
193 3rd gear 2nd brake servo tightening side line pressure pressure regulator valve manual valve forward clutch 1–2 shift valve 2nd brake servo tightening side 2–3 shift valve direct clutch since shift solenoid valve no. 1 is off, the 2–3 shift valve operates. The line pressure operates the forward ...
Page 196
194 reverse line pressure pressure regulator valve manual valve 1–2 shift valve 1st reverse brake direct clutch line pressure passes through the 1–2 shift valve and directly operates the first reverse brake and direct clutch. Although the shift solenoid valves no. 1 and no. 2 are off, since the line...
Page 197
195 control mechanism gearshift control shifting in the epi models is performed using shift solenoid valves no. 1 and no. 2, which are controlled by the at controller that is integrated with the epi controller, and in manual valve that is controlled by the selector lever. When the selector lever is ...
Page 198
196 at controller the controller is installed behind the engine compartment under the storage compart- ment center section, and is integrated with the epi controller. The output signals of the shift solenoids no. 1, no. 2, and no. 3 are transmitted according to the input signals from each sensor and...
Page 199
197 thermistor (between thw and e2 terminals) resistance k Ω (5.74) 2.28 ∼ 2.61 (1.15) (0.584) 0.303~0.326 0 20 40 60 80 ( ° c) temperature each shift solenoid terminal pressure hi (battery voltage) lo (about 0v) solenoid off solenoid on vcc vta e2 throttle sensor ecm 5v ltg/r gy/y bl/y 26 vcc vta 3...
Page 200
198 diagnosis (with failsafe function) the controller is provided with a diagnosis function, which detects and displays abnormalities in the input/output signals and controller main unit. However, abnormalities in mechanical parts such as the power transmission system and hydraulic system cannot be ...
Page 201
199 diagnostic code table error code diagnosis item diagnosis content failsafe control 12 normal 41 shift solenoid no. 1 (direct clutch solenoid) open circuit performs normal control shifts between 2 nd and 3 rd gear, does not enter 1 st gear short solenoid off 42 shift solenoid no. 2 (2nd brake sol...
Page 202
200 other mechanisms oil pump a trochoid type oil pump is installed on the at case input shaft side. It is driven by means of a torque converter shell case. Thus, when the engine stops, lubrication is not performed in the at. 1 2 fwd 1. Oil cooler 2. Water pipe oil cooler a pipe type oil cooler is i...