- DL manuals
- Suzuki
- Automobile
- Jimny
- Service Manual
Suzuki Jimny Service Manual
IMPORTANT
WARNING/CAUTION/NOTE
Please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully. To emphasize special information, the words
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE have special meanings. Pay special attention to the messages highlighted by
these signal words.
WARNING:
Indicates a potential hazard that could result in death or injury.
CAUTION:
Indicates a potential hazard that could result in vehicle damage.
NOTE:
Indicates special information to make maintenance easier or instructions clearer.
WARNING:
This service manual is intended for authorized Suzuki dealers and qualified service mechanics only.
Inexperienced mechanics or mechanics without the proper tools and equipment may not be able to
properly perform the services described in this manual.
Improper repair may result in injury to the mechanic and may render the vehicle unsafe for the driver
and passengers.
WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with a Supplemental Restraint or Air Bag System:
• Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
• If the air bag system and another vehicle system both need repair, Suzuki recommends that the air
bag system be repaired first, to help avoid unintended air bag system activation.
• Do not modify the steering wheel, instrument panel or any other air bag system component on or
around air bag system components or wiring. Modifications can adversely affect air bag system
performance and lead to injury.
• If the vehicle will be exposed to temperatures over 93°C (200°F), for example, during a paint baking
process, remove the air bag system components, that is air bag or inflator modules, SDM and/or
seat belt with pretensioner, beforehand to avoid component damage or unintended activation.
Summary of Jimny
Page 1
Important warning/caution/note please read this manual and follow its instructions carefully. To emphasize special information, the words warning, caution and note have special meanings. Pay special attention to the messages highlighted by these signal words. Warning: indicates a potential hazard th...
Page 2: Foreword
Foreword this manual contains procedures for diagnosis, maintenance, adjustments, minor service operations, replace- ment of components (service) and for disassembly and assembly of major components (unit repair-overhaul). Applicable model: jimny (sn413) of and after the vehicle identification numbe...
Page 4: Table of Contents
Table of contents general information general information 0a 0a maintenance and lubrication 0b 0b heating and air conditioning heater and ventilation 1a 1a air conditioning (optional) 1b 1b steering, suspension, wheels and tires steering, suspension, wheels and tires 3 3 front wheel alignment 3a 3a ...
Page 6: Section 0A
General information 0a-1 0a 6f2 6g 6h 6k 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 0a general information contents how to use this manual.................................0a-2 precautions......................................................0a-3 precaution for vehicles equipped with...
Page 7: How To Use This Manual
0a-2 general information how to use this manual 1) there is a “table of contents” on the third page of this manual, whereby you can easily find the section that offers the information you need. Also, there is a contents on the first page of each section, where the main items in that section are list...
Page 8: Precautions
General information 0a-3 precautions precaution for vehicles equipped with a sup- plemental restraint (air bag) system diagnosis • when troubleshooting air bag system, be sure to follow “air bag diagnostic system check” in section 10b. Bypassing these procedures may result in extended diagnostic tim...
Page 9
0a-4 general information servicing and handling warning: many of service procedures require disconnection of “air bag” fuse and all air bag (inflator) module(s) from initia- tor circuit to avoid an accidental deployment. Driver and passenger air bag (inflator) modules • for handling and storage of a...
Page 10
General information 0a-5 warning: sdm • during service procedures, be very careful when handling a sensing and diagnostic module (sdm). Never strike or jar the sdm. Never power up the air bag system when the sdm is not rigidly attached to the vehicle. All sdm and mounting bracket fasteners must be c...
Page 11
0a-6 general information caution: • even when the accident was light enough not to cause air bags to activate, be sure to inspect sys- tem parts and other related parts according to instructions under “repair and inspection required after an accident” in section 10b. • when servicing parts other tha...
Page 12
General information 0a-7 general precautions the warning and caution below describe some general precautions that you should observe when servic- ing a vehicle. These general precautions apply to many of the service procedures described in this manual, and they will not necessarily be repeated with ...
Page 13
0a-8 general information • when removing the battery, be sure to disconnect the negative cable first and then the positive cable. When reconnecting the battery, connect the positive cable first and then the negative cable, and replace the terminal cover. • when removing parts that are to be reused, ...
Page 14
General information 0a-9 • when disconnecting vacuum hoses, attach a tag describing the correct installation positions so that the hoses can be reinstalled correctly. • after servicing fuel, oil, coolant, vacuum, exhaust or brake systems, check all lines related to the system for leaks. • for vehicl...
Page 15
0a-10 general information precautions for catalytic converter for vehicles equipped with a catalytic converter, use only unleaded gasoline and be careful not to let a large amount of unburned gasoline enter the converter or it can be damaged. • conduct a spark jump test only when necessary, make it ...
Page 16
General information 0a-11 • when connecting connectors, also hold connectors and push them together until they lock securely (a click is heard). • when installing the wiring harness, fix it with clamps so that no slack is left. • when installing vehicle parts, be careful so that the wir- ing harness...
Page 17
0a-12 general information • never connect any tester (voltmeter, ohmmeter, or what- ever) to electronic control unit when its coupler is dis- connected. Attempt to do it may cause damage to it. • never connect an ohmmeter to electronic control unit with its coupler connected to it. Attempt to do it ...
Page 18
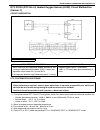
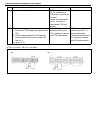
General information 0a-13 electrical circuit inspection procedure while there are various electrical circuit inspection methods, described here is a general method to check its open and short circuit by using an ohmmeter and a voltmeter. Open circuit check possible causes for the open circuit are as...
Page 19
0a-14 general information continuity check 1) measure resistance between connector terminals at both ends of the circuit being checked (between a-1 and c-1 in the figure). If no continuity is indicated (infinity or over limit), that means that the circuit is open between terminals a-1 and c-1. 2) di...
Page 20
General information 0a-15 short circuit check (wire harness to ground) 1) disconnect negative cable from battery. 2) disconnect connectors at both ends of the circuit to be checked. 3) measure resistance between terminal at one end of circuit (a-1 terminal in figure) and body ground. If continuity i...
Page 21
0a-16 general information • improperly formed or damaged terminals. Check each connector terminal in problem circuits carefully to ensure good contact tension by using the corresponding mating terminal. If contact tension is not enough, reform it to increase contact tension or replace. • poor termin...
Page 22: Identification Information
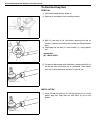
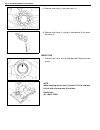
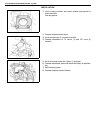
General information 0a-17 identification information body number the vehicle body number is punched on the chassis inside the tire housing on the right rear side. Engine identification number the number is punched on the cylinder block. Transmission identification number the automatic transmission i...
Page 23
0a-18 general information warning, caution and information labels the figure below shows main labels among others that are attached to vehicle component parts. When servicing and handling parts, refer to warning / caution instructions printed on labels. If any warning / caution label is found staine...
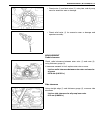
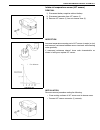
Page 24: Vehicle Lifting Points
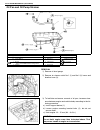
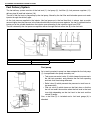
General information 0a-19 vehicle lifting points when using frame contact hoist warning: • before applying hoist to underbody, always take vehicle balance throughout service into consider- ation. Vehicle balance on hoist may change depending on what part to be removed. • before lifting up the vehicl...
Page 25
0a-20 general information when using floor jack in raising front or rear vehicle end off the floor by jacking, be sure to put the jack against the center portion of the front axle housing (1) or rear axle housing (2). To perform service with either front or rear vehicle end jacked up, be sure to pla...
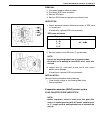
Page 26
General information 0a-21 abbreviations may be used in this manual abbreviations a abc atdc api atf alr ac a/t a/c abdc a/f a-elr anti-lock brake system after top dead center american petroleum institute automatic transmission fluid automatic locking retractor alternating current automatic transmiss...
Page 27
0a-22 general information l lh lspv left hand load sensing proportioning valve t tbi tcc tcm tp sensor tvv twc 2wd throttle body fuel injection (single-point fuel injection, spi) torque converter clutch transmission control module (a/t controller, a/t control mod- ule) throttle position sensor therm...
Page 28
General information 0a-23 symbols wire color symbols there are two kinds of colored wire used in this vehicle. One is single-colored wire and the other is dual-colored (striped) wire. The single-colored wire uses only one color symbol (i.E. “grn”). The dual-colored wire uses two color symbols (i.E. ...
Page 29: Fasteners Information
0a-24 general information fasteners information metric fasteners most of the fasteners used for this vehicle are metric fasteners. When replacing any fasteners, it is most impor- tant that replacement fasteners be the correct diameter, thread pitch and strength. Fastener strength identification most...
Page 30
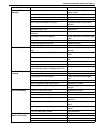
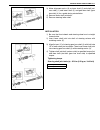
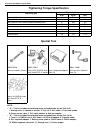
General information 0a-25 tightening torque chart thread diameter (nominal diameter) (mm) 4 5 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 strength an equivalent of 4t strength fastener n·m 1.5 3.0 5.5 13 29 45 65 105 160 kg-m 0.15 0.30 0.55 1.3 2.9 4.5 6.5 10.5 16 lb-ft 1.0 2.5 4.0 9.5 21.0 32.5 47.0 76.0 116.0 an equivalen...
Page 31
0a-26 general information.
Page 32: Section 0B
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-1 0a 6f1 0b 0b 6g 1a 6h 1b 6k 3 7a 3a 7a1 3b1 7b1 3c1 7c1 3d 7d 3e 7e 3f 7f 4a2 8a 4b 8b 8c 5 8d 5a 8e 5b 5c 9 5e 5e1 10 10a 6 10b 6-1 6a1 6a2 6a4 6b 6c 6e1 6e2 section 0b maintenance and lubrication contents maintenance schedule .................................. 0b-2...
Page 33: Maintenance Schedule
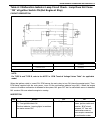
0b-2 maintenance and lubrication maintenance schedule maintenance schedule under normal driving conditions note: • this interval should be judged by odometer reading or months, whichever comes first. • this table includes service as scheduled up to 90,000 km (54,000 miles) mileage. Beyond 90,000 km ...
Page 34
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-3 interval km (x 1,000) 15 30 45 60 75 90 miles (x 1,000) 9 18 27 36 45 54 months 12 24 36 48 60 72 chassis and body clutch (pedal height and travel) – i – i – i brake discs and pads (thickness, wear, damage) i i i i i i brake drums and shoes (wear, damage) – i – i – i...
Page 35
0b-4 maintenance and lubrication maintenance recommended under severe driving conditions if the vehicle is usually used under the conditions corresponding to any severe condition code given below, it is recommended that applicable maintenance operation be performed at the particular interval as show...
Page 36: Maintenance Service
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-5 maintenance service engine drive belt water pump and generator drive belt inspec- tion 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) inspect belt for cracks, cuts, deformation, wear and cleanli- ness. If any defect exists, replace. Check belt for tension. Water pump an...
Page 37
0b-6 maintenance and lubrication 3) check belt for tension. Power steering pump and/or a/c compressor drive belt tension “a”: 6 – 9 mm (0.24 – 0.35 in.) deflection under 100 n (10 kg, 22 lb) pressure. 4) if belt tension is out of above specification, adjust it referring to “compressor drive belt” in...
Page 38
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-7 1) drain engine oil by removing drain plug. 2) after draining oil, wipe drain plug clean. Reinstall drain plug, and tighten it securely as specified below. Tightening torque (a) : 50 n·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft) 3) loosen oil filter by using oil filter wrench (special ...
Page 39
0b-8 maintenance and lubrication 6) replenish oil until oil level is brought to full level mark on dipstick. (oil pan and oil filter capacity). The filler inlet is at the top of the cylinder head cover. It is recommended to use engine oil of se, sf, sg, sh, sj or sl grade. Select the appropriate oil...
Page 40
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-9 when carrying out periodic maintenance, or the vehicle is raised for other service, check exhaust system as follows: • check rubber mountings for damage, deterioration, and out of position. • check exhaust system for leakage, loose connections, dents and damages. If ...
Page 41
0b-10 maintenance and lubrication replacement replace air cleaner filter with new one according to steps 1), 2) and 5), 6) of inspection procedure. Fuel lines and connections inspection 1) visually inspect fuel lines and connections for evidence of fuel leakage, hose cracking and damage. Make sure a...
Page 42
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-11 pcv (positive crankcase ventilation) valve inspection check crankcase ventilation hose and pcv hose for leaks, cracks or clog, and pcv valve for stick or clog. Refer to “pcv system” of section 6e for pcv valve checking procedure. Fuel evaporative emission control sy...
Page 43
0b-12 maintenance and lubrication brake drums and shoes inspection 1) remove wheel and brake drum. 2) check rear brake drums and brake linings for excessive wear and damage, while wheels and drums are removed. At the same time, check wheel cylinders for leaks. Replace these parts as necessary. For d...
Page 44
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-13 parking brake lever and cable inspection 1) inspect brake cable for damage and smooth movement. Replace cable if it is in deteriorated condition. 2) check tooth tip of each notch for damage or wear. If any damage or wear is found, replace parking lever. 3) check par...
Page 45
0b-14 maintenance and lubrication 3) rotate tires. For details, refer to “tire rotation” in section 3f. Wheel discs inspection inspect each wheel disc for dents, distortion and cracks. A disc in badly damaged condition must be replaced. Wheel bearing inspection 1) check front wheel bearing for wear,...
Page 46
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-15 rear 1) check shock absorber (1) for damage, deformation, oil leak- age and operation. 2) check bushings for wear and damage. 3) check coil spring (4), trailing arm (6) and lateral rod (5) for deformation and damage. 4) check trailing arm (6) and lateral rod bushing...
Page 47
0b-16 maintenance and lubrication manual transmission oil inspection 1) inspect transmission case for evidence of oil leakage. Repair leaky point if any. 2) make sure that vehicle is placed level for oil level check. 3) remove level plug (2) of transmission. 4) check oil level. Oil level can be chec...
Page 48
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-17 fluid cooler hose change replace inlet and outlet hoses of cooler hose and their clamps. For replacement procedure, refer to “oil cooler hoses” in section 7b. Transfer and differential oil inspection 1) check transfer case and differential for evidence of oil leak- ...
Page 49
0b-18 maintenance and lubrication steering system inspection 1) check steering wheel for play and rattle, holding vehicle in straight forward condition on the ground. Steering wheel play “a”: 0 – 30 mm (0 – 1.2 in.) 2) check universal joints of steering lower shaft (1) for rattle and damage. If ratt...
Page 50
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-19 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) inspection 1) visually check power steering system for fluid leakage and hose for damage and deterioration. Repair or replace defective parts, if any. 2) with engine stopped, check fluid level indicated on fluid tank or leve...
Page 51: Final Inspection
0b-20 maintenance and lubrication final inspection seats check that seat slides smoothly and locks securely at any position. Also check that reclining mechanism of front seat back allows it to be locked at any angle. Seat belt inspect belt system including webbing, buckles, latch plates, retractors ...
Page 52
Maintenance and lubrication 0b-21 gearshift or selector lever (transmission) check gear shift or selector lever for smooth shifting to all positions and for good performance of transmission in any position. With automatic transmission equipped vehicle, also check that shift indicator indicates prope...
Page 53
0b-22 maintenance and lubrication recommended fluids and lubricants engine oil se, sf, sg, sh, sj or sl (refer to “engine oil and oil filter” in this section for engine oil viscos- ity.) engine coolant (ethylene glycol base coolant) “antifreeze/anticorrosion coolant” brake fluid dot 3 manual transmi...
Page 54: Section 1A
Heater and ventilation 1a-1 6f1 6g 1a 6k 6k 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 1a heater and ventilation contents general description ....................................... 1a-2 diagnosis ........................................................ 1a-3 diagnosis table ...........
Page 55: General Description
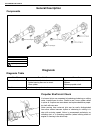
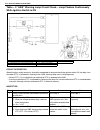
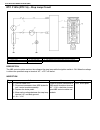
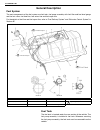
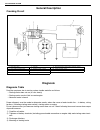
1a-2 heater and ventilation general description the heater, an in and out air selectable-type hot water heater, is so constructed that it is possible to assure an agreeable ventilation at all times by providing the ventilator air outlets at the center and both sides (right and left) of the instrumen...
Page 56: Diagnosis
Heater and ventilation 1a-3 diagnosis diagnosis table wiring circuit condition possible cause correction heater blower won’t work even when its switch is on. Blower fuse blown replace fuse to check for short. Blower resistor faulty check resistor. Blower fan switch faulty check blower fan switch. Bl...
Page 57: On Vehicle Service
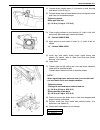
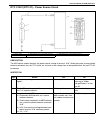
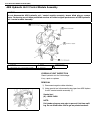
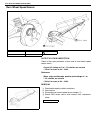
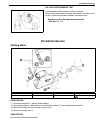
1a-4 heater and ventilation on vehicle service heater blower motor removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) disable air bag system, if equipped. Refer to “disabling air bag system” in section 10b. 3) remove column hole cover. 4) disconnect blower motor couplers. 5) remove blower motor...
Page 58
Heater and ventilation 1a-5 heater blower resistor removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) disable air bag system, if equipped. Refer to “disabling air bag system” in section 10b. 3) disconnect resistor coupler. 4) remove blower motor resistor (3) as shown figure. Inspection measure ...
Page 59
1a-6 heater and ventilation 4) disconnect blower fan switch coupler and a/c switch coupler (if equipped) 5) disconnect each heater control cables. 6) remove heater control lever assembly (1). 7) remove blower fan switch screw (3). 8) remove blower fan switch (2) as shown figure. Installation 1) inst...
Page 60
Heater and ventilation 1a-7 heater blower fan switch inspection check blower fan switch for each terminal-to-terminal continuity. For the detail refer to “wiring circuit” earlier in this section. Heater unit/boost ventilation removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) if equipped with a...
Page 61
1a-8 heater and ventilation caution: when the heater unit is disassembled and reassembled, locking force of the heater case lock may reduce. In such a case, tighten the heater case with a tapping screw of m4 ×l16 (1) as shown in the figure, or air may leak from its joint section..
Page 62: Section 1B
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-1 6f1 6f2 1b 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 1b air conditioning (optional) contents general description ....................................... 1b-3 major components and location ................. 1b-3 refrigerant circulation .................
Page 63
1b-2 air conditioning (optional) evacuating ................................................. 1b-23 evacuating procedure ............................ 1b-23 charging .................................................... 1b-25 charging procedure ............................... 1b-25 removing manifold g...
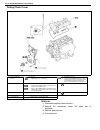
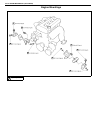
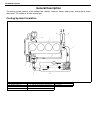
Page 64: General Description
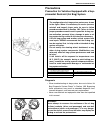
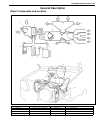
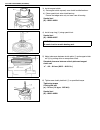
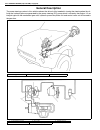
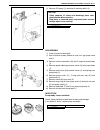
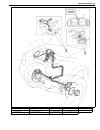
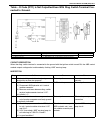
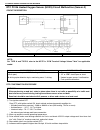
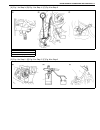
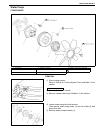
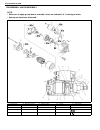
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-3 general description major components and location 1. Cooling unit 6. Suction hose 11. Foot air 16. Heater unit 2. Compressor 7. Receiver / dryer outlet pipe 12. Defroster air 17. A/c evaporator 3. Condenser assembly 8. Condenser outlet pipe 13. Demister air 18. Dual ...
Page 65
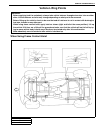
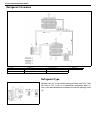
1b-4 air conditioning (optional) refrigerant circulation refrigerant type whether the a/c in the vehicle being serviced uses hfc-134a (r-134a) or cfc-12 (r-12) is indicated on compressor label (1). Also, it can be checked by the shape of the service (charge) valve (2). A: liquid 1. Compressor 4. Rec...
Page 66: Diagnosis
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-5 diagnosis general diagnosis table condition possible cause correction cool air won’t come out (a/c system won’t operative) no refrigerant perform recover, evacuation and charging. Fuse blown check fuses in main and circuit fuse boxes, and check short circuit to groun...
Page 67
1b-6 air conditioning (optional) cool air won’t come out or insufficient cooling (a/c system normal operative) insufficient or excessive charge of refrigerant check charge of refrigerant and system for leaks. Condenser clogged check condenser. A/c evaporator clogged or frosted check a/c evaporator a...
Page 68
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-7 abnormal noise diagnosis there are various types of noise, ranging from those produced in the engine compartment to those from the passenger compartment, also from rumbling noises to whistling noises. Abnormal noise from compressor abnormal noise from magnetic clutch...
Page 69
1b-8 air conditioning (optional) abnormal noise from crankshaft pulley abnormal noise from tension pulley abnormal noise from a/c evaporator abnormal noise from blower fan motor condition possible cause correction a large rattling noise is heard at idle or sud- den acceleration. Loosen crankshaft pu...
Page 70
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-9 quick checking of refrigerant charge the following procedure can be used for quickly checking whether the a/c system has a proper charge of refrigerant or not. Run engine at fast idle, and operate a/c at its maximum cooling capacity for a few minutes. Then, look at t...
Page 71
1b-10 air conditioning (optional) performance diagnosis 1) confirm that vehicle and environmental conditions are as fol- lows. • vehicle is not exposed to direct sun. • ambient temperature is within 15 – 35 °c (59 – 95 °f). 2) make sure that high pressure valve (1) and low pressure valve (2) of mani...
Page 72
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-11 8) check if each pressure on low side and on high side is within shaded range of the graph. If each gauge reading is out of specified pressure, correct defective part referring to “performance diagnosis table” in this section. Low side and high side pressure example...
Page 73
1b-12 air conditioning (optional) performance diagnosis table high pressure gauge low pressure gauge note: if ambient temperature is approximately 30 °c (86 °f), it is possible to diagnose a/c system in detail referring to “detail diagnosis table (ambient temperature at 30 °c (86 °f))” under “perfor...
Page 74
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-13 crossing point of center ventilation louver temperature and recirculation air inlet temperature detail diagnosis table (ambient temperature at 30°c (86°f)) condition possible cause correction crossing point is higher than accept- able range (“e” area) insufficient o...
Page 75
1b-14 air conditioning (optional) 0.05 – 0.15 (0.5 – 1.5) (4.2 – 21.3) 0.69 – 0.98 (7 – 10) (100 – 142) both low and high pres- sure sides indicate low readings. Continuous air bub- bles are visible through sight glass. Output air is slightly cold. Insufficient refrigerant in system. (refrigerant le...
Page 76
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-15 compressor drive belt inspection • check belt for wear and cracks, and replace as required. • check belt tension by measuring how much it deflects when pushed at intermediate point between compressor pulley (1) and crankshaft pulley (2) with about 100 n (10 kg, 22 l...
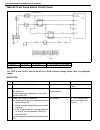
Page 77: Electronical Diagnosis
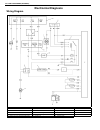
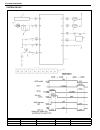
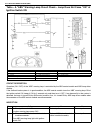
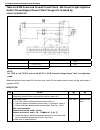
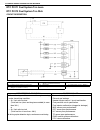
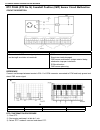
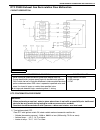
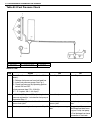
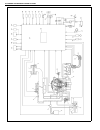
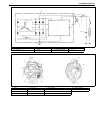
1b-16 air conditioning (optional) electronical diagnosis wiring diagram [a]: 4wd model 4. Dual pressure switch 9. Thermal switch 14. Circuit fuse box [b]: 2wd model 5. 4wd controller 10. Ignition switch 15. Main fuse box 1. Blower fan motor 6. Condenser cooling fan motor relay 11. A/c evaporator the...
Page 78
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-17 a/c system inspection of ecm and its cir- cuits ecm and its circuits can be checked at ecm wiring couplers by measuring voltage. Voltage check 1) remove ecm from vehicle by referring to “engine control module” in section 6e. 2) connect ecm couplers (1) to ecm (2). 3...
Page 79
1b-18 air conditioning (optional) terminal arrangement of ecm coupler (viewed from harness side) 1. Blower fan motor 8. Compressor [a]: to “a/c” fuse (25a) in main fuse box 2. Dual pressure switch 9. Thermal switch [b]: to “heater” fuse (20a) in circuit fuse box 3. A/c switch 10. Main relay [c]: to ...
Page 80
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-19 ecm voltage values table for relation of a/c control terminal wire circuit measurement ground normal value condition e18-1 p compressor magnet clutch output ground to engine (fig b) 10 – 14 volt blower fan motor switch and a/c switch on with engine running 0 – 1 vol...
Page 81
1b-20 air conditioning (optional) e19-14 g/b ect sensor input ground to engine (fig b) 0.73 – 0.83 volts (315 – 355 Ω) engine coolant temperature at approximately 80 °c (176 °f) with engine running 0.35 – 0.45 volts (145 – 165 Ω) engine coolant temperature at approximately 110 °c (230 °f) with engin...
Page 82
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-21 refrigerant recovery, evacuating and charging operation procedure for refrigerant charging warning: • your eyes should not be exposed to refrigerant (liquid). Any liquid hfc-134a (r-134a) escaping by accident shows a temperature as low as approximately –6 °c (21 °f)...
Page 83
1b-22 air conditioning (optional) recovery refrigerant recovery when evacuating a/c system, always recover refrigerant by using equipment (1) for refrigerant recovery and recycling. Discharging refrigerant hfc-134a (r-134a) into atmosphere would cause adverse effect to environments. Replenishing com...
Page 84
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-23 when replacing compressor compressor oil is sealed in each new compressor by the amount required for a/c system. Therefore, when using a new compres- sor for replacement, drain oil from new compressor by the amount calculated as follows. “c” = “a” – “b” “c” : amount...
Page 85
1b-24 air conditioning (optional) 1) connect high charging hose (1) and low charging hose (2) of manifold gauge set (3) respectively as follows: high charging hose (1) → high pressure charging valve (4) on discharge hose low charging hose (2) → low pressure charging valve (5) on suction hose 2) atta...
Page 86
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-25 charging charging procedure the initial charging of the a/c system is performed from the high pressure side with the engine stopped. And next, this method must be followed by charging from the low pressure side with the engine running. 1) check to make sure that hos...
Page 87
1b-26 air conditioning (optional) 2) connect low charging hose (1) and high charging hose (2) of the manifold gauge set (3) in position. Thus open refriger- ant container valve (4) to purge the charging line. 3) open the high pressure side valve (5) and charge refrigerant to system. 4) after a while...
Page 88
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-27 8) after the system has been charged with specified amount (500 – 600 g) of refrigerant or when low pressure gauge (1) and high pressure gauge (2) have indicated the following specified amount, close low pressure side valve (3) on mani- fold gauge set (4). At this t...
Page 89
1b-28 air conditioning (optional) removing manifold gauge set when a/c system has been charged with a specified amount of refrigerant, remove manifold gauge set as follows: 1) close low pressure side valve of manifold gauge set. (the high pressure side valve is closed continuously during the process...
Page 90: On-Vehicle Service
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-29 on-vehicle service service precaution when servicing air conditioning system, note the following instructions. Refrigerant line • never use heat for bending pipes. When bending a pipe, try to make its bending radius as slight as possible. • keep internal parts of ai...
Page 91
1b-30 air conditioning (optional) handling refrigerant hfc-134a (r-134a) • always wear goggles to protect your eyes. • avoid you direct contact to liquid refrigerant. • do not heat refrigerant container higher than 40 °c (104 °f). • do not discharge refrigerant into atmosphere. • do not allow liquid...
Page 92
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-31 condenser assembly inspection check the following. • check clog of condenser fins. If, any clogs are found, condenser fins should be washed with water, and should be dried with compressed air. • check condenser fins for leakage and breakage. If any defects are found...
Page 93
1b-32 air conditioning (optional) receiver / dryer removal 1) recover refrigerant from a/c system by referring to “recov- ery” in this section. 2) remove front bumper referring to “front bumper” in section 8. 3) disconnect receiver / dryer outlet hose (1) and condenser outlet pipe (2) from receiver ...
Page 94
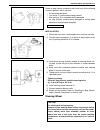
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-33 condenser cooling fan assembly assembly inspection 1) check continuity between each two terminals about the con- denser cooling fan motor (1). If check results are no continuity, replace condenser cooling fan motor. 2) connect battery to condenser cooling fan motor ...
Page 95
1b-34 air conditioning (optional) cooling unit (evaporator) removal 1) disconnect negative (–) cable at battery. 2) recover refrigerant from a/c system by referring to “recov- ery” in this section. Caution: be careful not to damage a/c evaporator fins. If a/c evaporator fin is bent, straighten a/c e...
Page 96
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-35 3) drain engine coolant and disconnect heater hoses (1) from heater unit. 4) disable air bag system referring to “disabling air bag sys- tem” in section 10b (if equipped). 5) remove attaching bolt (1). 6) disconnect suction hose (2) and receiver / dryer outlet pipe ...
Page 97
1b-36 air conditioning (optional) installation reverse removal procedure to install cooling unit, and then noting the following instructions. • if a/c evaporator thermistor removed, its should be rein- stalled in original position. • install uniformly the packing (1) to installation hole. • replenis...
Page 98
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-37 a/c evaporator thermistor (a/c evaporator temperature sensor) inspection check resistance between terminals for a/c evaporator ther- mistor (1). If check results are as not specified, replace thermistor. A/c evaporator temperature sensor resistance expansion valve i...
Page 99
1b-38 air conditioning (optional) installation reverse removal procedure for installation, and then note the fol- lowing instructions. • replenish specified amount of compressor oil to compressor suction side by referring to “replenishing compressor oil” in this section. • evacuate and charge refrig...
Page 100
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-39 a/c switch removal and installation refer to “heater control lever assembly” in section 1a. Inspection • press a/c switch button and check if there is continuity between terminals “a” and “b”. • with battery voltage (+) connected to terminal “c” and (–) to terminal ...
Page 101
1b-40 air conditioning (optional) 4) remove compressor drive belt (1) as follows. For vehicle with p/s loosen tension pulley bolts (2). For vehicle without p/s loosen tension pulley tightening nut (3) and adjusting bolt (4). 5) disconnect thermal switch connector. 6) disconnect suction and discharge...
Page 102
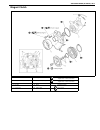
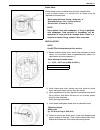
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-41 magnet clutch 1. Thermal switch 6. Magnet clutch coil a. Front head bolt : tighten bolt “a” first, and next “b”. 2. Compressor body assembly 7. Compressor pulley b. Front head bolt : tighten bolt “a” first, and next “b”. 3. O-ring 8. Circlip c. Clutch plate bolt 4. ...
Page 103
1b-42 air conditioning (optional) inspection • check clutch plate and clutch pulley for leaks of compressor oil. • check clutch bearing of compressor pulley for noise, wear and grease leakage. • measure resistance of magnet clutch coil (1) between mag- net clutch lead wire (2) and compressor body as...
Page 104
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-43 4) remove circlip (1) using special tool. Special tool (a) : 09900-06107 5) remove magnet clutch lead wire clamp screw, and discon- nect magnet clutch lead wire. 6) remove magnet clutch pulley (1) by using a puller (2). 7) remove snap ring (1) using special tool. Sp...
Page 105
1b-44 air conditioning (optional) 3) install magnet clutch. A) set magnet clutch squarely over clutch installation boss. B) place special tool onto clutch bearing. Ensure that edge rests only on inner race of bearing. Special tool (a) : 09991-06010 4) install snap ring (1) using special tool. Specia...
Page 106
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-45 lip type seal removal 1) remove magnet clutch referring to “magnet clutch” in this section. 2) remove front head mounting bolts (10 pcs). 3) remove front head (1) by pushing compressor shaft (2). 4) remove o-ring (5). 5) remove lip type seal from front head (1) usin...
Page 107
1b-46 air conditioning (optional) 2) coat special tool surface with compressor oil and place it on compressor shaft (1). Special tool (a) : 09991-06040 3) install o-ring (1) to compressor body assembly (2). 4) apply compressor oil to lip type seal and o-ring (1). 5) install front head (3) to compres...
Page 108: Required Service Materials
Air conditioning (optional) 1b-47 required service materials special tools material recommended suzuki product (part number) use compressor oil (refrigerant oil) compressor oil rs20 (150 cc) 99000-99088-00d0 • o-ring • each component 09900-06107 09991-06010 09991-06020 09991-06030 snap ring pliers (...
Page 109
1b-48 air conditioning (optional).
Page 110: Section 3
Steering, suspension, wheels and tires 3-1 6f1 6f2 6g 3 7b1 7c1 7b1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 3 steering, suspension, wheels and tires diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 111: General Diagnosis
3-2 steering, suspension, wheels and tires general diagnosis since the problems in steering, suspension, wheels and tires involve several systems, they must all be consid- ered when diagnosing a complaint. To avoid using the wrong symptom, always road test the vehicle first. Proceed with the followi...
Page 112
Steering, suspension, wheels and tires 3-3 shimmy, shake or vibration tire or wheel out of balance balance wheels or replace tire and/or wheel. Loose wheel bearings replace wheel bearing. Loose wheel hub nuts retighten. Worn tie rod ends replace tie rod end. Worn king pin bearings or king pins repla...
Page 113
3-4 steering, suspension, wheels and tires abnormal noise, front end worn, sticky or loose tie rod ends, drug rod ball joints, king pin bearings or axle shaft joints replace tie rod end, king pin bear- ing or axle shaft joint. Damaged shock absorbers or mountings replace or repair. Worn leading arm ...
Page 114: Tire Diagnosis
Steering, suspension, wheels and tires 3-5 tire diagnosis irregular and/or premature wear irregular and premature wear has many possible causes. Some of them are: incorrect inflation pressures lack of tire rotation, driv- ing habits, improper alignment. If the following conditions are noted rotation...
Page 115
3-6 steering, suspension, wheels and tires 1) ride vehicle to determine whether the front or rear waddles. 2) install tires and wheels that are known to be good (on similar vehicle) in place of those on wadding end of vehicle. If wadding end cannot be identified, substitute rear ones. 3) road test a...
Page 116: Vibration Diagnosis
Steering, suspension, wheels and tires 3-7 radial tire lead “lead” is the deviation of the vehicle from a straight path on a level rod even with no pressure on the steering wheel. Lead is usually caused by: 1) incorrect alignment. 2) uneven brake adjustment. 3) tire construction. The way in which a ...
Page 117
3-8 steering, suspension, wheels and tires.
Page 118: Section 3A
Front wheel alignment 3a-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 7a 3a 7b1 7c1 7d 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 3a front wheel alignment contents general description ........................................3a-2 toe setting ....................................................3a-2 camber .....................
Page 119: General Description
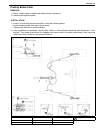
3a-2 front wheel alignment general description front alignment refers to the angular relationship between the front wheels, the front suspension attaching parts and the ground. Generally, the only adjustment required for front wheel alignment is toe setting. Camber and caster can’t be adjusted. Ther...
Page 120: Diagnosis
Front wheel alignment 3a-3 diagnosis diagnosis table for the details, refer to “diagnosis table” in section 3. Preliminary checks prior to adjusting front wheel alignment steering and vibration complaints are not always the result of improper alignment. An additional item to be checked is the possib...
Page 121
3a-4 front wheel alignment camber and caster check and adjustment should camber or caster be found out of specifications upon inspection, locate its cause first. If it is in damaged, loose, bent, dented or worn suspension parts and axle housing, they should be replaced. If it is in vehicle body, rep...
Page 122: Section 3B
Steering gear box (manual type) and linkage 3b-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 3b 7c1 7d 7e 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 3b steering gear box (manual type) and linkage contents general description ....................................... 3b-2 diagnosis ...................................................
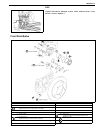
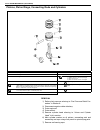
Page 123: General Description
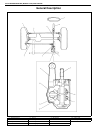
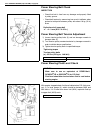
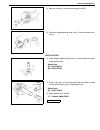
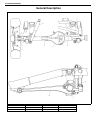
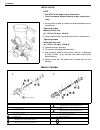
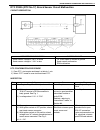
3b-2 steering gear box (manual type) and linkage general description 1. Steering gear box 5. Tie rod 9. Worm shaft 13. Sector shaft 2. Pitman arm 6. Steering lower shaft 10. Ball 14. Rack gear 3. Drag rod 7. Steering wheel 11. Ball nut 4. Knuckle arm 8. Steering upper shaft 12. Gear case.
Page 124: Diagnosis
Steering gear box (manual type) and linkage 3b-3 diagnosis diagnosis table refer to “diagnosis table” in section 3. Steering wheel play check check steering wheel for play and rattle, holding vehicle in straight forward condition on ground. Steering wheel play “a” : 10 – 30 mm (0.4 – 1.2 in.) if pla...
Page 125
3b-4 steering gear box (manual type) and linkage steering gear box oil level check oil surface should be up to the level as shown in figure. If not, add prescribed gear oil, sae 90. Steering gear box oil level “a” : 23 mm (0.91 in.) apply sealant to thread parts of breathing plug and tighten breath-...
Page 126
Steering gear box (manual type) and linkage 3b-5 3) measure worm shaft starting torque from its position in straight forward state as described in step 2). Starting torque for worm shaft (a) : 50 – 100 n·cm (5.0-10.0 kg-cm, 0.4-0.7 lb-ft) special tool (a) : 09944-18211 if measured torque is not with...
Page 127: On-Vehicle Service
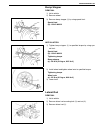
3b-6 steering gear box (manual type) and linkage on-vehicle service steering gear box removal 1) remove steering lower shaft joint bolt (2). 2) remove drag rod end nut from pitman arm (1). 3) disconnect drag rod end (2) from pitman arm (1), using spe- cial tool. Special tool (a) : 09913-65210 4) rem...
Page 128
Steering gear box (manual type) and linkage 3b-7 installation reverse removal procedure to install steering gear box. 1) install pitman arm (1) to sector shaft (2) of steering gear box with match marks (3) aligned as shown in figure and torque to specification. Tightening torque pitman arm mounting ...
Page 129
3b-8 steering gear box (manual type) and linkage tie rod and drag rod removal 1) hoist vehicle and remove wheel (s). 2) remove tie rod end nut from steering knuckle. 3) mark (3) one end of tie rod before removing the rod as shown in figure to distinguish the correct installing direction easy. 4) dis...
Page 130
Steering gear box (manual type) and linkage 3b-9 2) adjust tie rod (and/or drag rod) length to the measurement shown in figure; then tighten tie rod end lock nuts temporarily by finger. Tie rod and drag rod length tie rod length “a” : 1132 mm (44.6 in.) drag rod length “a” : 864.5 mm (34.0 in.) 3) a...
Page 131: Required Service Material
3b-10 steering gear box (manual type) and linkage tightening torque specifications required service material special tools fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft steering gear box oil plug 4 0.4 3.0 steering gear box adjusting bolt lock nut 30 3.0 22.0 pitman arm mounting nut 135 13.5 98.0 ...
Page 132: Section 3B1
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 6k 3b1 7d 7e 7f 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 3b1 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) contents general description ......................................3b1-2 diagnosis ......................................................
Page 133: General Description
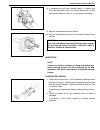
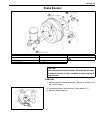
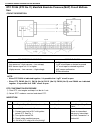
3b1-2 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) general description the power steering system in this vehicle reduces the driver’s effort needed in turning the steering wheel by uti- lizing the hydraulic pressure generated by the power steering (p/s) pump which is driven by the engine. It is an inte...
Page 134: Diagnosis
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-3 diagnosis diagnosis table condition possible cause correction steering wheel feels heavy (at low speed) fluid deteriorated, low viscosity, different type of fluid mixed change fluid. Pipes or hoses deformed, air entering through joint correct or replac...
Page 135
3b1-4 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) abnormal noise (see note “d”.) air drawn in due to insufficient fluid replenish fluid. Air drawn in through pipe or hose joints retighten or replace. Belt slipping (loose) adjust. Worn belt replace. Loose steering linkage retighten. Loose gear box fixi...
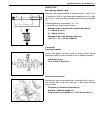
Page 136
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-5 steering wheel play check • with engine on, check steering wheel play as follows. Move steering wheel to the right and left from its straight position and measure along its circumference how much it must be turned before tires start to move. It should ...
Page 137
3b1-6 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) power steering belt check inspection • check that belt is free from any damage and properly fitted in pulley groove. • check belt tension by measuring how much it deflects when pushed at mid-point between pulley with about 10 kg (22 lb) force. Deflecti...
Page 138
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-7 idle-up system check 1) warm up engine to normal operating temperature. 2) turn a/c switch off, if equipped. 3) turn steering wheel fully and check idle speed. Engine idle speed drops a little momentarily when steering wheel is turned fully but returns...
Page 139
3b1-8 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) air bleeding procedure air bleeding from system 1) jack up the front end of vehicle and apply rigid rack. 2) fill p/s fluid reservoir with fluid up to specified level. 3) with engine running at idling speed, add fluid up to specified level. 4) when flu...
Page 140
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-9 3) after running engine at idling speed for 3 to 5 seconds, stop it and add fluid up to specified level. Repeat this step a few times. 4) set steering gear box (1) to state [a] as shown. 5) with engine running at idling speed, turn input shaft by using...
Page 141
3b1-10 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) hydraulic pressure in p/s circuit check 1) clean where pipe is connected thoroughly, then disconnect high pressure hose from high pressure pipe connector and connect oil pressure gauge (special tool) as shown. Special tool (a) : 09915-77410 (b) : 0991...
Page 142
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-11 5) relief pressure check a) increase engine speed to about 1,500 to 1,600 rpm. Close valve (6) gradually while watching pressure increase indicated on gauge (4) and take reading of relief pressure (maximum hydraulic pressure). If higher than 8,400 kpa...
Page 143: On-Vehicle Service
3b1-12 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) on-vehicle service power steering belt removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) loosen tension pulley bolts (2). 3) remove power steering belt (1). Inspection • check power steering belt for wear and cracks, and replace as required. Instlla...
Page 144
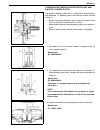
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-13 5) remove p/s pump (1) removing 3 mounting bolts (3). Disassembly 1) clean its exterior thoroughly. 2) with aluminum plates placed on vise first, grip pump case with it. 3) remove suction connector (10) and o-ring from pump body (1). 4) remove power s...
Page 145
3b1-14 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) cam ring and side plate check vane sliding surface of cam ring (2) for wear and damage. If any defect is found, replace pump assembly. Rotor and vane • check sliding surfaces of rotor and vane for wear and dam- age. • check clearance between rotor and...
Page 146
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-15 • check free length of relief valve spring (1). Replace pump assembly if any defective is found. Relief valve spring free length standard : 36.5 mm (1.44 in.) limit : 33.5 mm (1.32 in.) assembly reverse disassembly procedure for assembly, noting the f...
Page 147
3b1-16 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 7) apply power steering fluid to sliding surface of cam ring (1). 8) install cam ring (1) to pump body. The tapered end of cam ring (1) should face the side plate (2). 9) apply power steering fluid to each vane (2). 10) install vanes (10 pipes) (2) to...
Page 148
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-17 16) apply power steering fluid to relief valve (flow control valve) (1). 17) install relief valve (flow control valve) (1) to pump body. 18) apply power steering fluid to o-ring of plug (3). 19) install o-ring to plug (3). 20) tighten plug to specifie...
Page 149
3b1-18 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) installation install components in reverse order of removal procedure noting the following points. • tighten each bolt as specified below. Tightening torque oil pump mounting bolts (a) : 25 n·m (2.5 kg-m, 18.5 lb-ft) oil pump high pressure union bolt ...
Page 150
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-19 8) disconnect high pressure hose (2) and return hose (3) from gear box (1). 9) remove gear box assy from vehicle. Installation reverse removal procedure to install p/s gear box noting the fol- lowing points. • tightening torque specification. Tighteni...
Page 151
3b1-20 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) • install pitman arm (1) to sector shaft (2) of p/s gear box (3) with match marks “a” and “b” aligned as shown in figure and torque to specification. Tightening torque pitman arm mounting nut (a) : 135 n·m (13.5 kg-m, 98.0 lb-ft) • install lower shaft...
Page 152: Required Service Materials
Power steering (p/s) system (if equipped) 3b1-21 tightening torque specifications required service materials special tools fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft tension pulley bolt 25 2.5 18.0 oil pump mounting bolt 25 2.5 18.5 oil pump high pressure union bolt 60 6.0 43.5 oil pump cover b...
Page 153
3b1-22 power steering (p/s) system (if equipped).
Page 154: Section 3C
Steering wheel and column 3c-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 6k 7a 3c 7e 7f 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 3c steering wheel and column contents general description ....................................... 3c-2 diagnosis ........................................................ 3c-3 inspection and repair requ...
Page 155: General Description
3c-2 steering wheel and column general description this double tube type steering column has the following three important features in addition to the steering func- tion: • the column is energy absorbing, designed to compress in a front-end collision. • the ignition switch and lock are mounted conv...
Page 156: Diagnosis
Steering wheel and column 3c-3 diagnosis for maintenance service of the steering wheel and column, refer to “steering system inspection” in section 0b. For diagnosis of the steering wheel and column, refer to “diagnosis table” in section 3. For diagnosis of the air bag system, refer to “air bag diag...
Page 157
3c-4 steering wheel and column drive air bag (inflator) module (for vehicle with air bag system) removal 1) disconnect negative battery cable at battery terminal. 2) disable air bag system. Refer to “disabling air bag system” in section 10b. 3) remove steering wheel side cap (1) of left side. 4) loo...
Page 158
Steering wheel and column 3c-5 check air bag (inflator) module visually and if any of the following is found, replace it with a new one. • air bag being deployed • trim cover (1) (pad surface) being cracked • wire harness (3) or connector being damaged • air bag (inflator) module being damaged or ha...
Page 159
3c-6 steering wheel and column removal 1) disconnect negative battery cable at battery terminal. 2) remove steering wheel pad (for vehicle without air bag sys- tem) or driver air bag (inflator) module (for vehicle with air bag system) as follows. • vehicle without air bag system for type a a) remove...
Page 160
Steering wheel and column 3c-7 5) remove steering wheel (1) with special tool. Special tool (a) : 09944-36011 installation 1) check that vehicle’s front tires are at straight-ahead position. If equipped with air bag system, align contact coil to original position referring to “centering contact coil...
Page 161
3c-8 steering wheel and column 3) tighten steering shaft nut to specified torque. Tightening torque steering shaft nut (a) : 33 n·m (3.3 kg-m, 23.5 lb-ft) 4) install steering wheel pad (for vehicle without air bag system) or driver air bag (inflator) module (for vehicle with air bag system) as follo...
Page 162
Steering wheel and column 3c-9 4) from the position where contact coil became unable to turn any further (it stopped), turn it back clockwise about two and a half rotations and align center mark with alignment mark (1). Combination switch (for vehicle without air bag system)/contact coil and combina...
Page 163
3c-10 steering wheel and column 7) remove combination switch/contact coil and combination switch assembly (1) from steering column. Inspection • for vehicle with air bag system check contact coil and combination switch wire harness for any signs of scorching, melting or other damage. If it is dam- a...
Page 164
Steering wheel and column 3c-11 5) tighten steering column mounting nuts and bolts by hand and then tighten mounting nuts (1) first, and then tighten mounting bolts (2). Tightening torque steering column mounting bolts and nuts (a) : 14 n·m (1.4 kg-m, 10.5 lb-ft) 6) install steering column hole cove...
Page 165
3c-12 steering wheel and column removal 1) disconnect negative battery cable at battery terminal. 2) for vehicle equipped with air bag system, disable air bag system referring to “disabling air bag system” in section 10b. 3) if necessary, remove steering wheel and combination switch assembly referri...
Page 166
Steering wheel and column 3c-13 8) if equipped with shift (key) interlock cable (1), remove shift (key) interlock cable screw (2) and then disconnect its cable from ignition switch in order a) – c) as shown in the figure. 9) remove steering column from vehicle. 10) remove steering column seal (1) fr...
Page 167
3c-14 steering wheel and column 3) take measurement “a” as shown. If it is shorter than specified length, replace column assem- bly (1) with new one. Steering column assembly length “a” : 733.2 – 734.8 mm (28.87 – 28.93 in.) 4) check steering shaft joints and shaft for any damages such as crack, bre...
Page 168
Steering wheel and column 3c-15 4) insert steering lower shaft (1) to steering shaft. 5) put the steering column upper cover (3) on top of the steer- ing column (2), if necessary and then tighten steering col- umn mounting nuts (5) and bolts (4) by hand. 6) tighten mounting nuts (5) first and then m...
Page 169
3c-16 steering wheel and column 2) loosen and remove steering lock mounting bolts (2) using center punch (1) as shown. 3) turn ignition key to “acc” or “on” position and remove steering lock assembly from steering column. Installation 1) position oblong hole (1) of steering shaft in the center of ho...
Page 170
Steering wheel and column 3c-17 3) make alignment marks (3) on lower shaft (2) and shaft (col- umn side) (1) and lower shaft (2) and gear box shaft (gear box side) (4) for a guide during reinstallation. 4) remove lower shaft joint bolts. 5) remove steering lower shaft. Installation 1) be sure that f...
Page 171
3c-18 steering wheel and column checking steering column for accident damage checking procedure 1) check that two capsules (1) are attached to steering column bracket (2) securely. Check clearance between capsules (1) and steering column bracket (2). Clearance should be 0.0 mm (0.0 in.) on both side...
Page 172: Required Service Material
Steering wheel and column 3c-19 6) check steering shaft joints and shaft for any damages such as crack, breakage, malfunction or excessive play. If anything is found faulty, replace as lower joint assembly or column assembly. 7) check steering shaft for smooth rotation. If found defective, replace a...
Page 173
3c-20 steering wheel and column.
Page 174: Section 3D
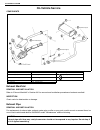
Front suspension 3d-1 6f1 6f2 6g 1a 6k 7a 7a1 3d 7f 8a 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 3d front suspension contents general description ....................................... 3d-2 4wd control system.................................... 3d-2 diagnosis ................................................
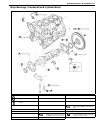
Page 175: General Description
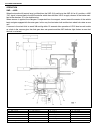
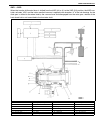
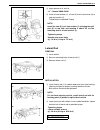
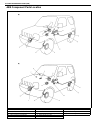
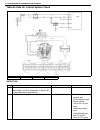
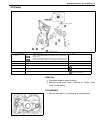
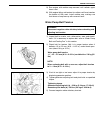
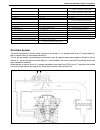
3d-2 front suspension general description 4wd control system the 4wd control system consists of a 4wd switch, a vacuum switch, a vacuum tank, two vacuum switching valves (vsv1 and vsv2) and air locking hub assemblies. The 4wd controller controls locking or unlocking of the air locking hub according ...
Page 176
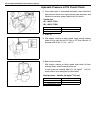
Front suspension 3d-3 1. Air locking hub assembly 4. Vsv2 7. 4wd controller 10. 4wd indicator light 13. Abs controller 2. Vsv1 5. Vacuum accumulation tank 8. Intake manifold 11. 4wd switch 14. Transfer 3. Check valve 6. Vacuum switch 9. Wheel spindle 12. Combination meter.
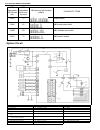
Page 177
3d-4 front suspension system circuit 1. 4wd controller 4. 4wd indicator lamp 7. Blower fan switch 10. Vacuum switch 13. Ig fuse 2. Vsv1 5. Ecm 8. A/c switch (if equipped) 11. Main fuse 14. A/c controller (if equipped) 3. Vsv2 6. Blower fan motor 9. 4wd switch 12. Ig switch 15. Coupler of 4wd control...
Page 178
Front suspension 3d-5 components and functions component function 4wd switch when the transfer shift lever is shifted to 4l or 4h position from 2h, this switch turns on and cause the 4wd control system to turn on. 4wd controller when the 4wd switch turns on, the 4wd controller activates vsv2 to lock...
Page 179
3d-6 front suspension operation 2wd → 4wd when the transfer shift control lever is shifted from the 2wd (2h) position to the 4wd (4h or 4l) position, a 4wd “on” signal is transmitted to the 4wd controller which then activates vsv2 to apply vacuum in the intake mani- fold to the chamber “b” in the hu...
Page 180
Front suspension 3d-7 4wd → 2wd when the transfer shift control lever is shifted from the 4wd (4h or 4l) to the 2wd (2h) position, the 4wd con- troller activates vsv1 and the intake manifold vacuum is applied to the chamber “a” in the hub housing. As the slide gear is shifted to the wheel side by th...
Page 181: Diagnosis
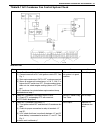
3d-8 front suspension diagnosis diagnosis table for description not found in the table below, refer to “diagnosis table” in section 3. 4wd control system 4wd control system diagnostic flow table before performing the trouble diagnosis, check that the air locking hub assemblies are in good condition ...
Page 182
Front suspension 3d-9 3 check 4wd switch circuit. 1) connect coupler to 4wd controller. 2) turn ignition switch on and check voltage between a7 terminal and ground. Transfer lever is in 2h : about 10 – 14 v transfer lever is in 4l or 4h : about 0 v is check result satisfactory? Go to step 4. Check 4...
Page 183
3d-10 front suspension 4wd controller and its circuit check voltage check check for input or output voltage of 4wd controller (1) (voltage between each circuit and body ground) with 4wd controller con- nector connected and ignition switch turned start (engine run). * : with engine running caution: •...
Page 184
Front suspension 3d-11 4wd control system check air locking hub 1) start engine and shift transfer shift control lever to 2h posi- tion. 2) connect vacuum pump gauge (special tool) to the spindle hose (2) which is disconnected from upper side pipe as shown. Apply vacuum and check operating sound fro...
Page 185
3d-12 front suspension 2) blow air from b and check that air comes out of c. If found faulty, replace. 3) connect 12 v-battery to vsv1 (vsv2) terminals and check continuity between a and b. Blow air from b and check that air comes out of a. If found faulty, replace. Vacuum switch 1) disconnect coupl...
Page 186
Front suspension 3d-13 check valve 1) remove check valve (1). 2) close b side of check valve with finger as shown and apply –50 cmhg vacuum by means of vacuum pump. Then check that vacuum is applied. Apply vacuum to another side of check valve and check that vacuum is not applied. Replace if defecti...
Page 187
3d-14 front suspension shock absorber and/or coil spring check 1) inspect shock absorber for oil leakage. If shock absorber is found faulty, replace it as an assembly unit, because it can not be disassembled. 2) shock absorber function check check and adjust tire pressures as specified. Bounce body ...
Page 188
Front suspension 3d-15 leading arm bushing / lateral rod bushing check inspect for damage, wear or deterioration. If defective, replace. Kingpin / kingpin bearing check 1) inspect for wear or deterioration. 2) inspect for crack, damage or deformation of kingpin. If defective, replace. Barfield joint...
Page 189
3d-16 front suspension wheel disc, nut and bearing check 1) inspect each wheel disc for dents, distortion and cracks. Disc in badly damaged condition must be replaced. 2) check wheel nuts for tightness and as necessary, retighten them to specification. Tightening torque wheel nuts (a) : 95 n·m (9.5 ...
Page 190: On-Vehicle Service
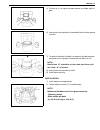
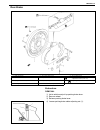
Front suspension 3d-17 on-vehicle service stabilizer bar / bushings removal 1) hoist vehicle. 2) remove front bumper. 3) disconnect stabilizer ball joints (right & left) (1) from front axle housing (2). 4) remove stabilizer bar mount bush bracket bolts (1). 5) remove stabilizer bar with its ball joi...
Page 191
3d-18 front suspension 2) when installing stabilizer, loosely assemble all components while insuring that stabilizer is centered, side-to-side. 3) tighten stabilizer bracket bolts (2) and stabilizer ball joint nuts to specified torque. Tightening torque stabilizer mount bracket bolts (a) : 20 n·m (2...
Page 192
Front suspension 3d-19 front shock absorber removal 1) hoist vehicle. 2) support front axle housing by using floor jack to prevent it from lowering, refer to “when using floor jack” under “vehi- cle lifting points” in section 0a. 3) remove shock absorber lower mounting bolt (6). 4) remove shock abso...
Page 193
3d-20 front suspension 4) support front axle housing by using floor jack. 5) remove shock absorber lower mounting bolt (1). 6) lower front axle housing (2) gradually as far down as where coil spring (1) can be removed. 7) remove coil spring (1). Installation install removed parts in reverse order of...
Page 194
Front suspension 3d-21 5) install wheel and tighten wheel nuts to specified torque. Tightening torque wheel nuts (a) : 95 n·m (9.5 kg-m, 69.0 lb-ft) 6) lower hoist. 7) confirm front end (wheel) alignment, referring to “prelimi- nary checks prior to adjusting front alignment” in section 3a. Bump stop...
Page 195
3d-22 front suspension 4) remove brake disc. 5) remove front wheel bearing lock nut as follows. For 2wd model : a) remove hub cap. B) remove front wheel bearing lock plate (1) by loosening 4 screws (2). For 4wd model : a) remove air locking hub assembly (1). B) remove front axle shaft circlip and wh...
Page 196
Front suspension 3d-23 6) remove front wheel bearing lock nut by using special tool. Special tool (a) : 09944-77020 (for 4wd) (a) : 09951-16050 (for 2wd) 7) remove front wheel bearing washer. 8) remove wheel hub complete (1) with bearings (2) and oil seal (4). Special tool (a) : 09943-35511 or 09943...
Page 197
3d-24 front suspension 11) using hydraulic press (1) and special tool remove wheel bearing (2). Special tool (a) : 09913-75520 12) remove hub bolts from hub. Installation 1) insert new stud in hub hole. Rotate stud slowly to assure ser- rations are aligned with those made by original bolt. 2) using ...
Page 198
Front suspension 3d-25 5) apply lithium grease to lip portion and hollow of oil seal (1). “a” : grease 99000-25010 6) install sensor rotor (3) as shown (if equipped with abs). 7) apply lithium grease inside wheel bearing thin. “a” : grease 99000-25010 8) install wheel hub complete with bearings and ...
Page 199
3d-26 front suspension for 2wd model: a) using lock plate (1), lock bearing lock nut. If lock screw hole is not aligned with screw hole in lock nut, turn lock nut in tightening direction till they align. Tightening torque wheel bearing lock washer screw (a) : 1.5 n·m (0.15 kg-m, 1.0 lb-ft) b) remove...
Page 200
Front suspension 3d-27 c) install front axle shaft circlip (1) and apply thin coat of grease to spline part of axle shaft. “a” : grease 99000-25010 d) clean mating surface of air locking hub and wheel hub. Install air locking hub assembly to wheel hub and tighten bolts to specified torque. Tightenin...
Page 201
3d-28 front suspension steering knuckle / wheel spindle removal 1) hoist vehicle and remove wheel. 2) remove wheel hub assembly, refer to “wheel hub / bearing / oil seal” in this section. 3) disconnect spindle vacuum hoses (1) from wheel spindle (for 4wd). 4) remove disc dust cover (1) and wheel spi...
Page 202
Front suspension 3d-29 7) remove lower and upper kingpins (1). 8) remove steering knuckle (1). 9) remove knuckle seal cover (1), knuckle seal (2) and knuckle seal retainer (3) from front axle housing (4). 10) remove spindle oil seal by using special tool. Special tool (a) : 09913-50121 11) remove sp...
Page 203
3d-30 front suspension installation 1) set knuckle seal cover (2), knuckle seal (4) and knuckle seal retainer (5) on front axle housing (6). 2) apply grease within the knuckle (1). Amount of grease to be applied within the knuckle (1) is approximately 100 g (for 4wd). “a” : grease 99000-25030 3) app...
Page 204
Front suspension 3d-31 8) press-fit spindle bushing (2) to wheel spindle (1) by using special tool. Set cut part (4) of spindle bushing (2) as shown in figure (opposite side of the groove (3) of wheel spindle). Special tool (a) : 09922-55131 9) press-fit spindle oil seal (1) until it becomes flush w...
Page 205
3d-32 front suspension 14) blow air into pipes at the top and the front of wheel spindle and check that it comes out of the hole as shown in figure (for 4wd). 15) connect spindle vacuum hoses to wheel spindle (for 4wd). 16) connect tie rod and drag rod to steering knuckle, refer to “tie rod and drag...
Page 206
Front suspension 3d-33 5) remove oil seal (1) from axle housing (for 4wd). 6) drain out kingpin bearing outer race (1) from front axle hous- ing (2). Installation 1) install kingpin bearing outer race (1) to front axle housing by using special tools. Special tool (a) : 09944-68510 (b) : 09924-74510 ...
Page 207
3d-34 front suspension 4) install axle shaft (2) to front axle housing (1) (for 4wd). 5) install knuckle to front axle housing. For details, refer to “steering knuckle / wheel spindle” in this section. 6) refill front axle (differential) housing with new specified gear oil (for 4wd). Refer to “maint...
Page 208
Front suspension 3d-35 2) apply grease to oil seal lip. “a” : grease 99000-25010 3) install oil seal retainer (1), oil seal (2) and oil seal cover (3) to steering knuckle (4). Tighten bolts to specified torque tightening torque knuckle seal cover bolts (a) : 10 n·m (1.0 kg-m, 7.5 lb-ft) lateral rod ...
Page 209
3d-36 front suspension leading arm / bushing removal 1) hoist vehicle. 2) remove air locking hub vacuum pipe clamp bolts (2) (for 4wd). 3) support front axle housing by using floor jack. 4) remove shock absorber lower mounting bolt, refer to “front shock absorber” in this section. 5) remove mounting...
Page 210
Front suspension 3d-37 installation 1) install bushings (1) by using hydraulic press and special tools, noting the following point. • install bushings (1) so that either face of bushing are aligned with housing edge of leading arm (2), also the length between the aligned side end of bushing and lead...
Page 211
3d-38 front suspension front axle housing removal 1) hoist vehicle. 2) remove front wheels. 3) drain front differential gear oil (for 4wd). 4) remove caliper carrier bolts (r&l) and suspend caliper. 5) remove right and left brake disc. 6) remove wheel speed sensor (if equipped with abs). 7) disconne...
Page 212
Front suspension 3d-39 9) remove knuckle seal cover bolts, take off knuckle seal cover (1), knuckle seal and knuckle seal retainer. 10) remove upper and lower kingpins (2) from steering knuckle. 11) remove knuckle with hub assembly from axle housing (for 2wd model) or draw out right and left axle sh...
Page 213
3d-40 front suspension 19) lower floor jack until tension of suspension coil spring becomes a little loose and remove right and left sides lower mounting bolt of shock absorber (1). 20) remove front mounting bolts of leading arm. 21) lower front axle housing gradually. 22) remove axle housing. Insta...
Page 214
Front suspension 3d-41 3) install air locking hub vacuum pipe and tighten clamp bolts to specified torque (for 4wd). Tightening torque vacuum pipe clamp bolts (a) : 5.5 n·m (0.55 kg-m, 4.0 lb-ft) 4) install stabilizer bar, refer to “stabilizer bar / bushings” in this section. 5) install lateral rod ...
Page 215
3d-42 front suspension 9) install right and left axle shafts to axle housing (for 4wd). Install knuckle to axle housing (for 2wd). 10) install kingpins (2) and knuckle seal cover (1) to steering knuckle (r&l), refer to “steering knuckle / wheel spindle” in this section. 11) install right and left br...
Page 216
Front suspension 3d-43 17) tighten lateral rod (1) mounting bolt and nut to specified torque. Tightening torque lateral rod bolt and nut (a) : 90 n·m (9.0 kg-m, 65.0 lb-ft) 18) tighten right and left shock absorber lower mounting nuts and leading arm mounting nuts to specified torque. Tightening tor...
Page 217: Required Service Material
3d-44 front suspension tightening torque specifications required service material fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft stabilizer mount bracket bolt 20 2.0 14.5 stabilizer ball joint nut 50 5.0 36.5 shock absorber lock nut 29 2.9 21.0 shock absorber lower nut 90 9.0 65.0 brake caliper car...
Page 218: Special Tool
Front suspension 3d-45 special tool 09917-47910 09913-50121 09913-65210 09913-75520 vacuum pump gauge oil seal remover tie rod end remover bearing installer 09951-76010 09924-74510 09942-15510 09943-35511 or 09943- 35512 bearing installer bearing installer handle sliding hammer brake drum remover 09...
Page 219
3d-46 front suspension 09944-66020 09913-85210 09951-16030 09951-26010 bearing installer oil seal installer bush remover bush remover plate.
Page 220: Section 3E
Rear suspension 3e-1 6f1 6f2 6g 1a 6k 7a 7a1 7b1 3e 8a 8b 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 3e rear suspension contents general description ....................................... 3e-2 diagnosis ........................................................ 3e-3 diagnosis table ............................
Page 221: General Description
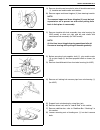
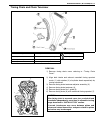
3e-2 rear suspension general description 1. Rear axle housing 4. Bearing oil seal 7. Brake drum 10. Bump stopper 2. Rear wheel bearing 5. Oil seal protector 8. Rear axle shaft 11. Coil spring 3. Bearing retainer ring 6. Lateral rod 9. Shock absorber 12. Trailing arm.
Page 222: Diagnosis
Rear suspension 3e-3 diagnosis diagnosis table refer to “diagnosis table” in section 3. Rear shock absorber check • inspect for deformation or damage. • inspect bushings for wear or damage. • inspect for evidence of oil leakage. Replace any defective part. Trailing arm, lateral rod, axle housing and...
Page 223
3e-4 rear suspension rear suspension fasteners check each bolt and nut fastening suspension parts for tightness. Tighten loose one, if any, to specified torque, referring to “tighten- ing torque specifications” of this section. Bearing retainer and axle shaft oil seal check • when brake drum has bee...
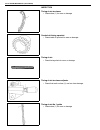
Page 224: On-Vehicle Service
Rear suspension 3e-5 • check wheel bearings for wear. When measuring thrust play, apply a dial gauge to axle shaft center after removing wheel center cap from wheel disc. When measurement exceeds limit, replace bearing. Rear wheel bearing thrust play limit : 0.8 mm (0.03 in.) • by rotating wheel act...
Page 225
3e-6 rear suspension 3) remove upper mounting bolt (2). 4) remove lower mounting bolt (3). 5) remove shock absorber (1). Installation 1) install shock absorber (1), refer to figure for proper installing direction of bush and washer (2). Tighten bolts (3) temporarily by hand. 2) remove floor jack. 3)...
Page 226
Rear suspension 3e-7 4) remove shock absorber lower mounting bolt (2). 5) lower rear axle housing (2) gradually as far down as where coil spring (1) can be removed. 6) remove coil spring (1). 7) remove spring rubber seat (1). 1. Shock absorber.
Page 227
3e-8 rear suspension installation 1) install spring rubber seat (1). 2) install coil spring (2) on spring seat (1) of axle housing and then raise axle housing. 3) install shock absorber lower mounting bolt. Tighten bolt temporarily by hand. 4) install brake flexible hose e-ring. 5) install wheel and...
Page 228
Rear suspension 3e-9 bump stopper removal 1) hoist vehicle. 2) remove wheel. 3) remove bump stopper (1) by using special tool. Special tool (a) : 09941-66010 installation 1) tighten bump stopper (1) to specified torque by using spe- cial tool. Special tool (a) : 09941-66010 tightening torque bump st...
Page 229
3e-10 rear suspension installation 1) install lateral rod to vehicle body and rear axle housing. Tighten bolt and nut temporarily by hand. 2) lower hoist and with vehicle in non-loaded condition, tighten lateral rod bolt and nut to specified torque. Tightening torque lateral rod bolt and nut (a) : 9...
Page 230
Rear suspension 3e-11 7) remove bushings (1) by using hydraulic press and special tools. Special tool (a) : 09924-74510 (b) : 09951-16030 (c) : 09951-26010 installation 1) install bushings (1) by using hydraulic press and special tools, noting the following points. Special tool (a) : 09913-85210 (b)...
Page 231
3e-12 rear suspension • install bushings so that either face of bushing are aligned with housing edge of leading arm, also the length between the aligned side end of bushing and trailing arm (1) are within specification below. Specification for trailing arm bushing protrusion “a” : 8.5 – 10.5 mm (0....
Page 232
Rear suspension 3e-13 4) remove wheel speed sensor (4) from rear axle housing (if equipped with abs). 5) disconnect brake pipe(s) (2) from wheel cylinder and put wheel cylinder bleeder plug cap (1) onto pipe to prevent fluid from spilling. 6) remove brake back plate nuts (3) from axle housing. 7) us...
Page 233
3e-14 rear suspension 10) in order to remove the retainer ring (1) from the shaft (3), grind with a grinder (2) two parts of the bearing retainer ring (1) as illustrated till it becomes thin. 11) break with a chisel the thin ground retainer ring, and it can be removed. 12) using special tools, remov...
Page 234
Rear suspension 3e-15 installation install removed parts in reverse order of removal procedure, not- ing the following. 1) aligning serrations between new stud bolt(s) (1) and flange, install new stud bolt(s) (1) by tightening nut (2) as shown. 2) press-fit wheel bearing (1) and retainer ring (2) as...
Page 235
3e-16 rear suspension 7) install rear axle shaft to rear axle housing (2) and tighten brake back plate nuts (4) to specified torque. Tightening torque brake back plate nuts (a) : 23 n·m (2.3 kg-m, 17.0 lb-ft) 8) connect brake pipe (3) to wheel cylinder and tighten brake pipe flare nut to specified t...
Page 236
Rear suspension 3e-17 16) upon completion of all jobs, depress brake pedal with about 30 kg (66 lbs) load over ten times so as to obtain proper drum-to shoe clearance. Adjust parking brake cable. (for adjustment, refer to “parking brake check and adjustment” in section 5.) 17) tighten parking brake ...
Page 237
3e-18 rear suspension rear axle housing removal 1) hoist vehicle and remove wheels. 2) remove rear axle shaft, refer to “rear axle shaft and wheel bearing” in this section. 3) disconnect brake pipe (3) from flexible hose (1) and remove e-ring (2). 4) remove brake pipe clamps and pipes from axle hous...
Page 238
Rear suspension 3e-19 10) loosen rear mounting nuts of trailing arm (2) but don’t remove bolt. 11) remove shock absorber (1) lower mounting bolt. 12) lower floor jack until tension of suspension coil spring becomes a little loose and remove rear mount bolts of trailing arm. 13) lower rear axle housi...
Page 239
3e-20 rear suspension 3) install lower part of shock absorber (1) to right and left sides of axle housing and tighten bolts (2) temporarily by hand. 4) install lateral rod (1) and install bolts in proper direction as shown. At this time, mount bolt and nut but don’t tighten them. 5) clean mating sur...
Page 240
Rear suspension 3e-21 11) connect brake flexible hose (2) to bracket on axle housing and secure it with e-ring (1). 12) connect brake pipe to brake flexible hose and tighten brake pipe flare nut to specified torque. Tightening torque brake pipe flare nut (a) : 16 n·m (1.6 kg-m, 11.5 lb-ft) 13) clean...
Page 241: Required Service Materials
3e-22 rear suspension tightening torque specifications required service materials fastening portion tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft shock absorber upper and lower bolt 85 8.5 61.5 bump stopper 50 5.0 36.5 lateral rod bolt and nut 90 9.0 65.0 trailing arm nut (front and rear) brake back plate nut 23...
Page 242: Special Tools
Rear suspension 3e-23 special tools 09913-75520 09913-85210 09924-74510 1) 09927-18411 universal puller bearing installer oil seal installer bearing installer handle 2) 09921-57810 bearing remover 09941-66010 09942-15510 09943-35511 or 09943-35512 09944-96010 bearing outer race remover bump stopper ...
Page 243
3e-24 rear suspension.
Page 244: Section 3F
Wheels and tires 3f-1 6f1 6f2 6g 3f 8a 8b 8c 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 3f wheels and tires contents general description ........................................ 3f-2 tires .............................................................. 3f-2 wheels .................................................
Page 245: General Description
3f-2 wheels and tires general description tires this vehicle is equipped with following tire. Tire size : 205/70 r15 or 175/80 r15 the tires are of tubeless type. The tires are designed to operate satisfactorily with loads up to the full rated load capacity when inflated to the recommended inflation...
Page 246
Wheels and tires 3f-3 replacement wheels wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have excessive lateral or radial runout, leak air through welds, have elongated bolt holes, if lug nuts won’t stay tight, or if they are heavily rusted. Wheels with greater runout than shown in “how to measure...
Page 247: Diagnosis
3f-4 wheels and tires diagnosis diagnosis table refer to “diagnosis table” in section 3. Balancing wheels there are two types of wheel and tire balance: static and dynamic. Static balance, as shown in figure, is equal distribution of weight around wheel. Wheels that are statically unbalanced cause b...
Page 248
Wheels and tires 3f-5 warning: wheel spin should be limited to 35 mph (55 km/h) as indicated on speedometer. This limit is necessary because speedometer only indicates one-half of actual wheel speed when one drive wheel is spinning and the other drive wheel is stopped. Unless care is taken in limiti...
Page 249
3f-6 wheels and tires maintenance and minor adjustments wheel and tire wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peening are not approved. All damaged wheels should be replaced. Studs if a broken stud is found, see section 3e (rear) or section 3d (front) for note and replacement procedure. Matched...
Page 250
Wheels and tires 3f-7 lower than recommended pressure can cause: 1) tire squeal on turns 2) hard steering 3) rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread 4) tire rim bruises and rupture 5) tire cord breakage 6) high tire temperatures 7) reduced handling 8) high fuel consumption tire placard the t...
Page 251: On-Vehicle Service
3f-8 wheels and tires on-vehicle service wheel removal 1) loosen wheel nuts by approximately 180° (half a rotation). 2) hoist vehicle. 3) remove wheel. Installation wheel nuts must be tightened in sequence and to proper torque to avoid bending wheel or brake drum or disc as shown. Tightening order :...
Page 252
Wheels and tires 3f-9 tire mounting and demounting use tire changing machine to mount or demount tires. Follow equipment manufacturer’s instructions. Do not use hand tools or tire irons alone to change tires as they may damage tire beads or wheel rim. Rim bead seats should be cleaned with wire brush...
Page 253
3f-10 wheels and tires.
Page 254: Section 4B
Propeller shafts 4b-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 6k 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 4b 8d 8e 9 8e 9 10 10a 10b section 4b propeller shafts contents general description ....................................... 4b-2 components ................................................. 4b-2 diagnosis .........................................
Page 255: General Description
4b-2 propeller shafts general description components diagnosis diagnosis table propeller shaft joint check if universal joints are suspected of producing chattering or rattling noise, inspect them for wear. Check to see if cross spider rattles in yokes or if splines are worn down and replace defecti...
Page 256: On-Vehicle Service
Propeller shafts 4b-3 on-vehicle service propeller shafts removal 1) hoist vehicle. 2) drain transmission oil only when servicing propeller shaft no. 1. 3) before removing propeller shaft (2), give match marks (1) on each joint flange (3) and propeller shaft (2) as shown. 4) remove propeller shaft(s...
Page 257
4b-4 propeller shafts installation install propeller shaft(s) reversing removal procedure noting fol- lowing points : • when installing propeller shaft, align the match marks. Otherwise, vibration may occur during driving. • use following specification to torque universal joint flange. Tightening to...
Page 258
Propeller shafts 4b-5 universal joint disassembly 1) using special tool, remove 4 circlips (1). Special tool (a) : 09900-06108 2) apply penetrate lubricant between bearing race outer diame- ter and shaft yoke bore. 3) using a set of special tool, push spider bearing race (1) out 3 – 4 mm (0.12 – 0.1...
Page 259
4b-6 propeller shafts 6) push out bearing race (2) on flange yoke (1) in the same way as step 2). 7) holding bearing race (2) by a vise (3), tap flange yoke (1) and take out race. 8) take out bearing race (2) on the opposite side of flange yoke (1) in the same way as step 5) to step 6). Reassembly 1...
Page 260: Required Service Material
Propeller shafts 4b-7 3) insert bearing race into opposite side of shaft yoke until it is flush with side face of shaft yoke, tapping it by a copper hammer. 4) in the same way as step 2) to step 3), insert bearing races into flange yoke. 5) using round bar of 22 – 24 mm (0.87 in. – 0.94 in.) in diam...
Page 261: Special Tool
4b-8 propeller shafts special tool 09900-06108 09926-48010 snap ring pliers (closing type) universal joint disassem- bling tool set.
Page 262: Section 5
Brakes 5-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 6k 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 5 9 10 10a 10b 9 10 10a 10b section 5 brakes contents general description ......................................... 5-3 diagnosis .......................................................... 5-4 road testing brakes...................................... ...
Page 263
5-2 brakes master cylinder............................................ 5-38 fill reservoir ................................................ 5-40 lspv (load sensing proportioning valve) assembly (if equipped) ................................. 5-42 lspv assembly ..........................................
Page 264: General Description
Brakes 5-3 general description when the foot brake pedal is depressed, hydraulic pressure is developed in the master cylinder to actuate pis- tons (two in front and four in rear). The master cylinder is a tandem master cylinder. Three (or two) brake pipes are connected to the master cylin- der and t...
Page 265: Diagnosis
5-4 brakes diagnosis road testing brakes brakes should be tested on dry, clean, smooth and reasonably level roadway which is not crowned. Road test brakes by making brake applications with both light and heavy pedal forces at various speeds to determine if the vehicle stops evenly and effectively. A...
Page 266
Brakes 5-5 diagnosis table condition possible cause correction not enough braking force brake oil leakage from brake lines locate leaking point and repair. Brake disc or pads stained with oil clean or replace. Overheated brakes determine cause and repair. Poor contact of shoes on brake drum repair f...
Page 267
5-6 brakes excessive pedal travel (pedal stroke too large) partial brake system failure check brake systems and repair as necessary. Insufficient fluid in master cylinder reservoirs fill reservoirs with approved brake fluid. Check for leaks and air in brake systems. Check warning light. Bleed system...
Page 268
Brakes 5-7 brake warning light turns on when brake is applied brake fluid leaking from brake line investigate leaky point, correct it and add brake fluid. Insufficient amount of brake fluid add brake fluid. Faulty p & differential valve (differential switch) replace. Brake warning light fails to tur...
Page 269
5-8 brakes brake pedal free height adjustment 1) check brake pedal free height. If it is not within specification, check and adjust following item 2) and 3). Brake pedal free height “a” from wall lh steering vehicle : 221 – 227 mm (8.70 – 8.94 in.) rh steering vehicle : 217 – 223 mm (8.54 – 8.78 in....
Page 270
Brakes 5-9 excessive pedal travel check 1) start engine. 2) depress brake pedal a few times. 3) with brake pedal depressed with approximately 30 kg (66 ibs) load, measure brake pedal to wall clearance “d” or “e”. Clearance “d” or “e” between brake pedal and wall lh steering vehicle clearance “d” : o...
Page 271
5-10 brakes rear brake shoe check inspection should be carried out on following points after brake pedal travel (pedal to wall clearance) check, even when pedal travel is normal. Amount of brake shoe wear can be checked as follows. 1) hoist vehicle. 2) remove rubber plug (1) from brake back plate. 3...
Page 272
Brakes 5-11 rear drum brake shoe adjustment rear brake has self-adjusting mechanism but it does require adjustment for proper drum to shoe clearance when brake shoe has been replaced or brake drum has been removed for some other service. Adjustment is automatically accomplished by depressing brake p...
Page 273
5-12 brakes if number of notches is out of specification, adjust cable by refer- ring to adjustment procedure described on the following so as to obtain specified parking brake stroke. Adjustment after confirming that above 5 conditions are all satisfied, adjust parking brake lever stroke by looseni...
Page 274
Brakes 5-13 check air tightness 1) start engine. 2) stop engine after running for 1 to 2 minutes. 3) depress brake pedal several times with the same load as in ordinary braking and observe pedal travel. If pedal goes down deep the first time but its travel decreases as it is depressed the second and...
Page 275
5-14 brakes check air tightness under load 1) with engine running, depress brake pedal. Then stop engine while holding brake pedal depressed. 2) hold brake pedal depressed for 30 seconds. If pedal height does not change, condition is good. But it isn’t if pedal rises. H : hold h : hold t : 30 second...
Page 276
Brakes 5-15 fluid pressure test (if equipped with lspv) test procedure for lspv assembly is as follows. Before testing, confirm the following. • fuel tank is filled with fuel fully. • vehicle is equipped with spare tire, tools, jack and jack han- dle. 1) stop vehicle on level floor and place approxi...
Page 277
5-16 brakes 4) if rear brake pressure is not within specification, adjust it by changing stay position as follows. • if rear brake pressure is higher than specification, move stay “a” to direction “l” and if it is lower, to direction “r”. • repeat steps 3) and 4) until rear brake pressure is within ...
Page 278: On-Vehicle Service
Brakes 5-17 on-vehicle service air bleeding of brake system bleeding operation is necessary to remove air whenever it entered hydraulic brake system. Hydraulic lines of brake system consists of two separate lines, one for front wheel brakes and the other for rear wheel brakes. Air bleeding is necess...
Page 279
5-18 brakes 4) when fluid pressure in the cylinder is almost depleted, retighten bleeder plug. 5) repeat this operation until there are no more air bubbles in hydraulic line. 6) when bubbles stop, depress and hold brake pedal and tighten bleeder plug. Tightening torque front caliper bleeder plug (b)...
Page 280
Brakes 5-19 pipe inspect the tube for damage, cracks, dents and corrosion. If any defect is found, replace it. Front disc brake 1. Caliper pin bolt 10. Carrier bolt 2. Boot 11. Brake caliper carrier 3. Cylinder slide bush : apply rubber grease to mating surface of caliper 12. Pad clip 4. Bleeder plu...
Page 281
5-20 brakes brake pad removal 1) hoist vehicle and remove wheel. 2) remove caliper pin bolts (2). 3) remove caliper (1) from caliper carrier. 4) remove pads (3). Inspection check pad lining for wear. When wear exceeds limit, replace with new one. Brake pad thickness (lining + pad rim) standard : 15 ...
Page 282
Brakes 5-21 installation 1) install pad shim (1) (to outside pad) and pads (2) to caliper carrier (3). 2) install caliper and torque caliper pin bolts (1) to specification. Tightening torque brake caliper pin bolts (a) : 22 n·m (2.2 kg-m, 16.0 ib-ft) 3) install wheel and torque front wheel nuts to s...
Page 283
5-22 brakes caliper assembly removal 1) hoist vehicle and remove wheel. 2) remove brake flexible hose mounting bolt from caliper. As this will allow fluid to flow out of hose, have a container ready beforehand. 3) remove caliper pin bolts. 4) remove caliper from carrier. Disassembly 1) before disass...
Page 284
Brakes 5-23 inspection cylinder slide bush check slide bush for smooth movement as shown. If it is found faulty, correct or replace. Apply rubber grease to bush outer surface. Rubber grease should be the one whose viscosity is less affected by such low temperature as – 40 °c (– 40 °f). Bush dust boo...
Page 285
5-24 brakes assembly 1) check that slide bushes and boots for wear, corrosion, dam- age, movement or deterioration. If it is found faulty, correct or replace. Apply rubber grease to bush outer surface. And then make sure that each bush slides easily through each caliper bolt hole. 2) tighten bleeder...
Page 286
Brakes 5-25 5) fit boot as it is in figure into boot groove in cylinder with fin- gers. 6) insert piston into cylinder by hand and fit boot in boot groove in piston. 7) to confirm that boot is fitted in its groove in cylinder properly, pull piston out of cylinder a little but do not take it all out....
Page 287
5-26 brakes 3) install brake flexible hose (4) as shown and torque hose mounting bolt (3) to specification. Tightening torque front brake flexible hose bolt (a) : 23 n·m (2.3 kg-m, 17.0 lb-ft) 4) install wheel and torque wheel nuts to specification. 5) after completing installation, fill reservoir w...
Page 288
Brakes 5-27 inspection check disc surface for scratches in wearing parts. Scratches on disc surface noticed at the time of specified inspection or replace- ment are normal and disc is not defective unless they are serious. But when there are deep scratches or scratches all over disc sur- face, repla...
Page 289
5-28 brakes check for front brake after installation mount tires and make certain that they rotate smoothly, with a force of less than 3.0 kg (6.6 ib). If tire rotation is heavy, check the following: • piston, piston seal and cylinder slide bush of caliper for installation. • wheel bearings for brea...
Page 290
Brakes 5-29 rear brake brake drum removal 1) hoist vehicle and pull up parking brake lever. 2) remove wheel. 3) release parking brake lever. 4) loosen parking brake cable adjusting nut (1). 1. Brake back plate 5. Shoe return spring lower 9. Shoe hold down pin 2. Brake shoe 6. Adjuster lever 10. Whee...
Page 291
5-30 brakes 5) to increase clearance between brake shoe and brake drum, remove rubber plug from brake back plate and turn adjuster downward with flat-head screw driver. 6) remove brake drum (1) off by using 8 mm bolts (2). Inspection brake drum inspect drum for cleanliness. Check wear of its braking...
Page 292
Brakes 5-31 brake shoe where lining is worn out beyond service limit, replace shoe. If one of brake linings is to service limit, all linings must be replaced at the same time. Brake shoe thickness (lining + shoe rim) “a” standard (lining + rim) : 6.5 mm (0.26 in.) service limit : 3.0 mm (0.12 in.) i...
Page 293
5-32 brakes brake shoe removal 1) remove brake drum referring to “brake drum” in this sec- tion. 2) remove shoe return spring lower (3), spring and rod assem- bly (4) and shoe hold down springs (2) by turning shoe hold down pins (1). 3) remove parking brake shoe lever (5) from brake back plate. Insp...
Page 294
Brakes 5-33 2) install shoe hold down springs (2) by pushing them down in place and turning hold down pins (1). 3) install shoe return spring and parking brake shoe lever spring. 4) for procedure hereafter, refer to “brake drum” in this sec- tion. Wheel cylinder removal 1) remove brake drum referrin...
Page 295
5-34 brakes installation 1) apply sealant to wheel cylinder. Then take off bleeder plug cap from brake pipe and connect pipe (for pipes) (3) to wheel cylinder just enough to prevent fluid from leaking. “a” : sealant 99000-31090 2) tighten wheel cylinder to brake back plate (1) to specified torque. 3...
Page 296
Brakes 5-35 7) using special tools, draw out rear axle shaft with brake back plate. Special tool (a) : 09943-35511 (b) : 09942-15510 8) remove wheel bearing retainer and wheel sensor ring (if equipped with abs), refer to “rear axle shaft and wheel bearing” in section 3e. 9) remove brake back plate f...
Page 297: Master Cylinder
5-36 brakes master cylinder master cylinder reservoir removal 1) disconnect reservoir lead wire at coupler. 2) clean outside of reservoir (1). 3) take out fluid with syringe or such. 4) remove reservoir connector pin (2) by using special tool. Special tool (a) : 09922-85811 remove reservoir (1). Cau...
Page 298
Brakes 5-37 installation 1) when using new grommets, lubricate them with the same fluid as the one to fill reservoir with. Then press-fit grommets to master cylinder. Grommets must be seated in place. 2) install reservoir (1) and drive in reservoir pin (2). 3) connect reservoir lead wire. 4) fill re...
Page 299
5-38 brakes installation 1) install master cylinder as shown and torque attaching nuts to specification. Tightening torque master cylinder nuts (a) : 13 n·m (1.3 kg-m, 9.5 ib-ft) 2) attach hydraulic lines and torque flare nuts to specification. Tightening torque brake pipe flare nuts (b) : 16 n·m (1...
Page 300
Brakes 5-39 disassembly 1) remove circlip (1). 2) remove primary piston. 3) [for vehicle with abs] pull out primary piston assembly straight so as not to cause any damage to inside o cylinder wall. Pull out secondary piston assembly straight so as not to cause any damage to inside of cylinder wall a...
Page 301
5-40 brakes • rinse cylinder in clean brake fluid. Shake excess rinsing fluid from cylinder. Do not use a cloth to dry cylinder, as lint from cloth cannot be kept from cylinder bore surfaces. Assembly 1) install secondary piston assembly into cylinder. 2) install primary piston in cylinder. 3) depre...
Page 302
Brakes 5-41 fluid to fill reservoir with is indicated on reservoir cap of that vehi- cle with embossed letters or in owner’s manual supplied with it. Add fluid up to max line..
Page 303
5-42 brakes lspv (load sensing proportioning valve) assembly (if equipped) removal 1) clean around reservoir cap and take out fluid with syringe or such. 2) hoist vehicle. 3) disconnect brake pipes from lspv. 4) remove lspv assembly from vehicle. 5) remove spring and stay from lspv. Installation ins...
Page 304
Brakes 5-43 lspv assembly inspection and adjustment 1) confirm the following before inspection and adjustment. • fuel tank is filled with fuel fully. • vehicle is equipped with spare tire, tools, jack and jack han- dle. • vehicle is free from any other load. • place it on level floor. 2) push up lsp...
Page 305: P (Proportioning) Valve
5-44 brakes p (proportioning) valve removal 1) clean around reservoir cap and take out fluid with syringe or such. 2) disconnect brake pipes from p valve. 3) remove p valve. Installation 1) install p valve (2). Tightening torque p valve bolts (a) : 25 n·m (2.5 kg-m, 18.0 lb-ft) 2) tighten flare nuts...
Page 306: Brake Booster
Brakes 5-45 brake booster removal 1) remove master cylinder assembly, referring to “maser cylin- der” in the section. 2) disconnect brake vacuum hose (2) from booster (1). 3) remove brake pipes (3). 1. Brake master cylinder assembly 5. Nut 9. Brake vacuum hose 2. Brake booster assembly 6. Clevis pin...
Page 307
5-46 brakes 4) disconnect push rod clevis pin (4) from brake pedal arm (3). 5) remove attaching nuts (6) and then booster as shown. Installation 1) install booster to dash panel as shown, then connect booster push rod clevis (2) to pedal arm (3) with clevis pin (4) and clip (5). 2) tighter booster a...
Page 308
Brakes 5-47 clearance between booster piston rod and master cylinder piston the length of booster piston rod (1) is adjusted to provide speci- fied clearance “a” between piston rod end and master cylinder piston (2). • before measuring clearance, push piston rod several times so as to make sure reac...
Page 309
5-48 brakes brake hose/pipe front brake hose/pipe for left-hand steering vehicle [a] : for vehicle without abs x : view x 5. Brake caliper 12. To front left brake caliper [b] : for vehicle with abs y : view y 6. 4 way joint 13. To rear brake f : front side z : view z 7. 5 way joint a-d: clamp r : ri...
Page 310
Brakes 5-49 for right-hand steering vehicle [a] : for vehicle without abs x : view x 5. Brake caliper 12. To front left brake caliper [b] : for vehicle with abs y : view y 6. 4 way joint 13. To rear brake f : front side z : view z 7. 5 way joint 14. Front brake master cylinder r : right side 1. E-ri...
Page 311
5-50 brakes removal 1) raise, suitably support vehicle. Remove wheel if necessary. 2) clean dirt and foreign material from both hose end or pipe end fittings. Remove brake hose and pipe. Installation 1) install brake hose and pipe by reversing removal procedure, noting the following points. For inst...
Page 312
Brakes 5-51 rear brake hose/pipe removal 1) raise, suitably support vehicle. Remove wheel if necessary. 2) clean dirt and foreign material from both hose end or pipe end fittings. Remove brake hose and pipe. Installation 1) install brake hose and pipe by reversing removal procedure, noting the follo...
Page 313
5-52 brakes parking brake lever/cable parking brake lever removal 1) hoist vehicle and release parking brake lever. 2) disconnect negative cable at battery. 3) remove parking brake lever cover. 4) disconnect lead wire of parking brake switch at coupler. 5) remove adjusting nut. 6) loosen bracket nut...
Page 314
Brakes 5-53 parking brake cable removal 1) raise, suitably support vehicle and remove wheel if necessary. 2) remove parking brake cable. Installation 1) install it by reversing removal procedure, noting the following points. • install clamps properly referring to figure below. • tighten bolts and nu...
Page 315: Required Service Material
5-54 brakes tightening torque specifications required service material fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft brake caliper carrier bolt 85 8.5 61.5 brake caliper pin bolt 22 2.2 16.0 front brake flexible hose bolt 23 2.3 17.0 rear brake back plate nut 23 2.3 17.0 master cylinder nut 13 1.3...
Page 316: Special Tool
Brakes 5-55 special tool 09900-20205 09900-20602 09900-20701 09956-02210 micrometer (0 – 25 mm) dial gauge (1/1000 mm) magnetic stand brake circuit plug 09922-85811 09942-15510 09943-35511 09950-78220 connector pin remover sliding hammer brake drum remover (front wheel hub remover) flare nut wrench ...
Page 317
5-56 brakes.
Page 318: Section 5E
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 6k 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8e 5e 9 10 10a 10b 10 10a 10b section 5e antilock brake system (abs) contents general description ....................................... 5e-2 system schematic ....................................... 5e-3 abs component parts l...
Page 319: General Description
5e-2 antilock brake system (abs) general description the abs (antilock brake system) is a system to prevent each wheel to lock during hard braking or braking on a slippery road by controlling the fluid pressure from master cylinder to each brake (either brake caliper or wheel cylinder). The abs of t...
Page 320
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-3 system schematic 1. Wheel speed sensor (right front) 7. Wheel speed sensor (left rear) 13. Abs hydraulic unit 2. Stop lamp switch 8. “abs” warning lamp 14. G sensor 3. Abs control module 9. Abs pump motor transistor 15. Data link connector 4. Wheel speed sensor (righ...
Page 321
5e-4 antilock brake system (abs) abs component parts location 1. Wheel speed sensor (right front) 6. Abs hydraulic unit / control module assembly 11. Proportioning valve 2. Stop lamp switch 7. Monitor connector [a] : for lh steering vehicle 3. “abs” warning lamp 8. Wheel speed sensor (left front) [b...
Page 322
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-5 abs control module self-diagnosis function abs control module diagnoses conditions of the system compo- nent parts (whether or not there is any abnormality) all the time and indicates the results (warning of abnormality occurrence and dtc) through the “abs” warning l...
Page 323: Diagnosis
5e-6 antilock brake system (abs) diagnosis to ensure that the trouble diagnosis is done accurately and smoothly, observe “precautions in diagnosing trou- bles” and follow “abs diagnostic flow table”. Precaution in diagnosing troubles • if the vehicles was operated in any of the following ways, “abs”...
Page 324
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-7 1) malfunction analysis a) customer complaint analysis record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this purpose, use of such a questionnaire form as shown below will facilitate collecting information to the...
Page 325
5e-8 antilock brake system (abs) 2) driving test test drive the vehicle at 40 km/h for more than a minute and check if any trouble symptom (such as abnor- mal lighting of “abs” warning lamp) exists. If the malfunction dtc is confirmed again at ignition switch on, driving test as described in above i...
Page 326
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-9 “abs” warning lamp check turn ignition switch on and check that “abs” warning lamp comes on for about 2 seconds and then goes off. If any faulty condition is found, advance to diagnostic flow table-a, b or c. Diagnostic trouble code (dtc) check 1) test drive vehicle ...
Page 327
5e-10 antilock brake system (abs) dtc check (using suzuki scan tool) 1) connect suzuki scan tool to data link connector after set- ting cartridge for abs to it. Special tool (a) : suzuki scan tool 2) turn ignition switch on. 3) read dtc according to instructions displayed on suzuki scan tool and pri...
Page 328
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-11 diagnostic trouble code (dtc) table dtc (displayed on suzuki scan tool) dtc (indicated by abs warn- ing lamp) abs warning light flashing pattern diagnostic items – 12 normal c1015 15 g sensor circuit (for 4wd model only) c1016 16 stop lamp switch circuit c1021 21 rf...
Page 329
5e-12 antilock brake system (abs) system circuit c1057 57 power source c1061 61 abs pump motor circuit c1063 63 abs solenoid valve circuit c1071 71 abs control module 1. Battery 5-5. Solenoid valves 14. Stop lamp switch 2. Main fuses 6. Combination meter 15. Ecm 3. Ignition switch 7. Right rear whee...
Page 330
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-13 terminal circuit a1 idle up signal a2 stop lamp switch a3 right front wheel speed sensor (+) a4 right front wheel speed sensor (–) a5 – a6 right rear wheel speed sensor (–) a7 right rear wheel speed sensor (+) a8 – a9 – a10 – a11 g sensor signal a12 diagnosis switch...
Page 331
5e-14 antilock brake system (abs) table – a “abs” warning lamp circuit check – lamp does not come “on” at ignition switch on circuit description operation (on / off) of the “abs” warning lamp is controlled by the abs control module and abs lamp driver module. If the antilock brake system is in good ...
Page 332
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-15 table – b “abs” warning lamp circuit check – lamp comes “on” steady refer to table – a for system circuit diagram and circuit description. Inspection 3 1) remove combination meter. Is bulb of abs warning lamp in good condition? “r/bl” circuit shorted to ground. If o...
Page 333
5e-16 antilock brake system (abs) table – c “abs” warning lamp circuit check – lamp flashes continuously while ignition switch is on circuit description when the diag. Switch terminal is shorted or connected to the ground with the ignition switch on, the diag. Trou- ble code (dtc) is indicated by fl...
Page 334
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-17 table – d code (dtc) is not outputted even with diag. Switch terminal con- nected to ground. Circuit description when the diag. Switch terminal is connected to the ground with the ignition switch turned on, the abs control module outputs a diagnostic trouble code by...
Page 335
5e-18 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1015 (dtc 15) – g sensor circuit description while a vehicle is at stop or running, if the potential difference between the sensor signal terminal “a11” and the sensor ground terminal “a13” is not within the specified voltage value, or if the signal voltage whi...
Page 336
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-19 inspection step action yes no 1 is g sensor installed floor securely? Go to step 2. Tighten sensor or bracket screw securely. If not, use new screw. 2 1) ignition switch off. 2) remove g sensor with bracket. 3) check for proper connection to g sensor. 4) if ok, then...
Page 337
5e-20 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1016 (dtc 16) – stop lamp circuit description the abs control module monitors the voltage at the stop lamp while the ignition switch is on. When the voltage is without the specified range at terminal “a2”, a dtc will be set. Inspection 1. Main fuse 4. Ig fuse 7...
Page 338
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-21 dtc c1021 (dtc 21), dtc c1022 (dtc 22) – right front wheel speed sensor circuit dtc c1025 (dtc 25), dtc c1026 (dtc 26) – left front wheel speed sensor circuit dtc c1031 (dtc 31), dtc c1032 (dtc 32) – right rear wheel speed sensor circuit dtc c1035 (dtc 35), dtc c103...
Page 339
5e-22 antilock brake system (abs) inspection step action yes no 1 1) disconnect the applicable sensor connector with ignition switch off. 2) measure resistance between sensor terminals. Resistance of wheel speed sensor: 1.4 – 1.8 k Ω (at 20°c, 68°f) 3) measure resistance between each terminal and bo...
Page 340
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-23 1. Abs hydraulic unit / control module connector 2. Lock position 3. Unlock position.
Page 341
5e-24 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1041 (dtc 41), dtc c1042 (dtc 42) – right front solenoid circuit dtc c1045 (dtc 45), dtc c1046 (dtc 46) – left front solenoid circuit dtc c1055 (dtc 55), dtc c1056 (dtc 56) – rear solenoid circuit description the abs control module monitors the voltage of the t...
Page 342
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-25 dtc c1057 (dtc 57) – power source circuit description the abs control module monitors the power source voltage at terminal “a18”. When the power source voltage becomes extremely low, this dtc will be set. As soon as the voltage rises to the specified level, the set ...
Page 343
5e-26 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1061 (dtc 61) – abs pump motor circuit description the abs control module monitors the voltage at the terminal “a23” of the pump motor circuit constantly with the ignition switch turned on. It sets this dtc when the voltage at the terminal “a23” does not become...
Page 344
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-27 dtc c1063 (dtc 63) – abs fail safe circuit description the abs control module monitors the voltage at the terminal of the solenoid circuit constantly with the ignition switch turned on. Also, immediately after the ignition switch is turned “on”, perform an initial c...
Page 345
5e-28 antilock brake system (abs) dtc c1071 (dtc 71) – abs control module description this dtc will be set when an internal fault is detected in the abs control module. Inspection step action yes no 1 1) ignition switch off. 2) disconnect connectors from abs control module. 3) check for proper conne...
Page 346: On-Vehicle Service
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-29 on-vehicle service precaution when connectors are connected to abs hydraulic unit / control module assembly, do not disconnect connectors of sensors, fuse etc. And turn ignition switch on. Then dtc will be set in abs con- trol module. Abs hydraulic unit operation ch...
Page 347
5e-30 antilock brake system (abs) abs hydraulic unit / control module assembly hydraulic unit inspection check hydraulic unit for fluid leakage. If any, repair or replace. Removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) using special tool, disconnect brake pipes from abs hydrau- lic unit / contr...
Page 348
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-31 3) disconnect abs hydraulic unit / control module assembly connector (1) by pulling up lock. 4) remove abs hydraulic unit / control module assembly with its bracket. 5) remove three bolts (3) and take out abs hydraulic unit / control module assembly (1) from bracket...
Page 349
5e-32 antilock brake system (abs) front wheel speed sensor output voltage inspection 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) hoist vehicle a little. 3) disconnect connector of wheel speed sensor. 4) connect voltmeter between connector terminals. 5) while turning wheel at a speed of approximately 1 full rota...
Page 350
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-33 reference when using oscilloscope for this check, check if peak-to-peak voltage (1) meets specification and waveform is complete. Peak-to-peak voltage at 1 to 1 1/3 rotation per second : 340 mv or more at 42 – 54 hz removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2...
Page 351
5e-34 antilock brake system (abs) sensor ring inspection • check ring teeth for being missing, damaged or deformed. • turn drive shaft and check if ring rotation is free from eccen- tricity and looseness. • check that no foreign material is attached. If any faulty is found, repair or replace. Instal...
Page 352
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-35 front wheel sensor ring removal 1) remove wheel hub with sensor ring. Refer to “wheel hub / bearing / oil seal” in section 3d. 2) remove sensor ring (1) from wheel hub (2) as shown. Inspection • check ring teeth for being missing, damaged or deformed. • check sensor...
Page 353
5e-36 antilock brake system (abs) rear wheel speed sensor output voltage inspection check in the same procedure as that used of front wheel speed sensor check. Output ac voltage at 1 to 1 1/3 rotation per second : 100 mv or more at 38 – 49 hz reference when using oscilloscope, peak-to-peak voltage a...
Page 354
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-37 5) remove rear wheel speed sensor (1) from rear axle housing. Sensor inspection • check sensor for damage. • check sensor for resistance. Resistance between terminals of sensor : 1.4 – 1.8 k Ω at 20 °c (68 °f) resistance between sensor terminal and sensor body : 1 m...
Page 355
5e-38 antilock brake system (abs) rear wheel sensor ring removal 1) remove rear axle shaft. Refer to “rear axle shaft and wheel bearing” in section 3e. 2) in order to remove sensor ring (3) from retainer ring (2), grind with a grinder one part of the sensor ring (3) as illus- trated till it becomes ...
Page 356
Antilock brake system (abs) 5e-39 g sensor removal 1) turn ignition switch “off” and disconnect battery negative cable. 2) remove rear center console box. 3) disconnect connector from g sensor (2). 4) remove g sensor (2) from floor. Inspection connect positive cable of 12 volt battery to “a” termina...
Page 357: Special Tool
5e-40 antilock brake system (abs) tightening torque specification special tool fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft brake pipe flare nuts 16 1.6 11.6 abs hydraulic unit / control module assembly bracket bolts 11 1.1 8.0 abs hydraulic unit / control module assembly bolts 9 0.9 6.5 front wh...
Page 358: Section 6
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-1 6f2 6g 6h 6k 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8b 6 8d 8e 8b 9 10a 10b section 6 engine general information and diagnosis general information and engine diagnosis .............................................................................. 6-1 engine mechanical ....
Page 359
6-2 engine general information and diagnosis diagnostic trouble code (dtc) table ......... 6-16 fail-safe table............................................ 6-19 visual inspection ....................................... 6-20 engine basic inspection ............................ 6-21 engine diagnosis t...
Page 360: General Information
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-3 general information statement on cleanliness and care an automobile engine is a combination of many machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with tolerances that are measured in the thousands of an millimeter (ten thousands of an inch). Accordingly, ...
Page 361
6-4 engine general information and diagnosis precaution on fuel system service • work must be done with no smoking, in a well-ventilated area and away from any open flames. • as fuel feed line (between fuel pump and fuel delivery pipe) is still under high fuel pressure even after engine was stopped,...
Page 362
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-5 fuel pressure relief procedure after making sure that engine is cold, release fuel pressure as fol- lows. 1) place transmission gear shift lever in “neutral” (shift selector lever to “p” range for a/t model), set parking brake, and block drive wheels. 2) ...
Page 363: Engine Diagnosis
6-6 engine general information and diagnosis engine diagnosis general description this vehicle is equipped with an engine and emission control system which are under control of ecm. The engine and emission control system in this vehicle are controlled by ecm. Ecm has an on-board diagnos- tic system ...
Page 364
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-7 driving cycle a “driving cycle” consists of engine startup and engine shutoff. 2 driving cycles detection logic the malfunction detected in the first driving cycle is stored in ecm memory (in the form of pending dtc and freeze frame data) but the malfunct...
Page 365
6-8 engine general information and diagnosis in the 2nd through the 4th frames, the freeze frame data of each malfunction is stored in the order as the malfunction is detected. These data are not updated. Shown in the table below are examples of how freeze frame data are stored when two or more malf...
Page 366
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-9 on-board diagnostic system (vehicle without immobilizer indicator lamp) ecm diagnosis troubles which may occur in the area including the following parts when the ignition switch is on and the engine is running, and indicates the result by turning on or fl...
Page 367
6-10 engine general information and diagnosis precaution in diagnosing trouble • don’t disconnect couplers from ecm, battery cable at battery, ecm ground wire harness from engine or main fuse before confirming diagnostic information (dtc, freeze frame data, etc.) stored in ecm memory. Such disconnec...
Page 368
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-11 engine diagnostic flow table refer to the following pages for the details of each step. Step action yes no 1 customer complaint analysis 1) perform customer complaint analysis referring to the followings. Was customer complaint analysis performed? Go to ...
Page 369
6-12 engine general information and diagnosis 1. Customer complaint analysis record details of the problem (failure, complaint) and how it occurred as described by the customer. For this purpose, use of such an inspection form will facilitate collecting information to the point required for proper a...
Page 370
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-13 customer problem inspection form (example) note: the above form is a standard sample. It should be modified according to conditions characteristic of each market..
Page 371
6-14 engine general information and diagnosis malfunction indicator lamp (mil) check 1) turn on ignition switch (but the engine at stop) and check that mil lights. If mil does not light up (or mil dims), go to “diagnostic flow table a-1” for troubleshooting. If mil flushes, go to “diagnostic flow ta...
Page 372
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-15 4) after completing the check, turn the ignition switch off posi- tion and disconnect service wire from monitor coupler. Diagnostic trouble code (dtc) clearance [using suzuki scan tool] 1) connect suzuki scan tool to data link connector in the same manne...
Page 373
6-16 engine general information and diagnosis diagnostic trouble code (dtc) table dtc no. Detecting item detecting condition (dtc will set when detecting :) mil (vehicle with immo- bilizer indi- cator lamp) mil (vehicle without immobi- lizer indica- tor lamp) p0105 (no.11) manifold absolute pressure...
Page 374
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-17 p0335 (no.23) crankshaft position sensor circuit malfunction no signal for 2 sec. During engine crank- ing 1 driving cycle 1 driving cycle p0340 (no.15) camshaft position sensor circuit malfunction no signal during engine running 1 driving cycle 1 drivin...
Page 375
6-18 engine general information and diagnosis dtc no. Detecting item detecting condition (dtc will set when detecting :) mil p0702 transmission control system electrical refer to section 7b. These dtcs can not be read on vehicle without immobilizer indicator lamp (by ecm application of suzuki scan t...
Page 376
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-19 fail-safe table when any of the following dtcs is detected, ecm enters fail-safe mode as long as malfunction continues to exist but that mode is canceled when ecm detects normal condition after that. Dtc no. Detected item fail-safe operation (symptom) p0...
Page 377
6-20 engine general information and diagnosis visual inspection visually check following parts and systems. Inspection item referring section • engine oil – level, leakage section 0b • engine coolant – level, leakage section 0b • fuel – level, leakage section 0b • a/t fluid – level, leakage section ...
Page 378
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-21 engine basic inspection this check is very important for troubleshooting when ecm has detected no dtc and no abnormality has been found in visual inspection. Follow the flow table carefully. Step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? G...
Page 379
6-22 engine general information and diagnosis [a] fig. 1 for step 5 / [b] fig. 2 for step 7 / [c] fig. 3 for step 8 10 check fuel supply as follows : 1) check to make sure that enough fuel is filled in fuel tank. 2) turn on ignition switch for 2 seconds and then off. See fig. 5. Is fuel return press...
Page 380
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-23 [d] fig. 4 for step 7 or 8 / [e] fig. 5 for step 10 / [f] fig. 6 for step 13 engine diagnosis table perform troubleshooting referring to following table when ecm has no dtc and no abnormality found in visual inspection and engine basic inspection previou...
Page 381
6-24 engine general information and diagnosis engine has no power engine overheating refer to “overheating” of this table. • faulty ignition coil ignition coil assembly in section 6f. • faulty knock sensor knock sensor malfunction in this sec- tion. • fuel pressure out of specification diagnostic fl...
Page 382
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-25 excessive detonation (the engine makes sharp metallic knocks that change with throt- tle opening. Sounds like pop corn popping.) engine overheating refer to “overheating” of this table. • faulty spark plug spark plugs in section 6f. • clogged fuel filter...
Page 383
6-26 engine general information and diagnosis excessive engine oil consumption • sticky piston ring pistons, piston rings, connecting rods and cylinders in section 6a1. • worn piston and cylinder pistons, piston rings, connecting rods and cylinders in section 6a1. • worn piston ring groove and ring ...
Page 384
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-27 condition possible cause reference item excessive hydrocar- bon (hc) emission or excessive carbon mon- oxide (co) emission • faulty ignition coil ignition coil assembly in section 6f. • fuel pressure out of specification diagnostic flow table b-3 • lead ...
Page 385
6-28 engine general information and diagnosis scan tool data as the data values given below are standard values estimated on the basis of values obtained from the normally operating vehicles by using a scan tool, use them as reference values. Even when the vehicle is in good condi- tion, there may b...
Page 386
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-29 ∆ ✱ ✱ ✱ ✱ o2s b1 s2 (heated oxy- gen sensor-2) when engine is running at 2000 r/min. For 3 min or longer after warming up. 0.01 – 0.95 v ∆ ✱ ✱ ✱ ✱ psp sw no load to power steering. Off desired idle (desired idle speed) at idling with no load after warmin...
Page 387
6-30 engine general information and diagnosis scan tool data definitions fuel system (fuel system status) air / fuel ratio feedback loop status displayed as either open or closed loop. Open indicates that ecm ignores feedback from the exhaust oxygen sensor. Closed indicates final injection duration ...
Page 388
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-31 throttle pos (absolute throttle position, %) when throttle position sensor is fully closed position, throttle opening is indicated as 0% and 100% full open position. Oxygen sensor b1 s1 (heated oxygen sensor-1, v) it indicates output voltage of ho2s-1 in...
Page 389
6-32 engine general information and diagnosis fuel tank level (%) this parameter indicates approximate fuel level in the fuel tank. As the detectable range of the fuel level sensor is set as 0 to 100%, however, with some models whose fuel tank capacity is smaller, the indicated fuel level may be onl...
Page 390
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-33 inspection of ecm and its circuits ecm and its circuits can be checked at ecm wiring connectors by measuring voltage and resistance. Voltage check 1) remove ecm from body referring to section 6e. 2) check voltage at each terminal of connectors connected....
Page 391
6-34 engine general information and diagnosis ecm terminal voltage values table for type a (see note) note: • type a is other than follows. • type b is left hand steering vehicle equipped with fasten seat belt light and egr valve or right hand steering vehicle equipped with fasten seat belt light an...
Page 392
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-35 for type b (see note) e19 26 manifold absolute pressure sensor 3.3 – 4.0 v ignition switch on barometric pressure : 100 kpa (760 mmhg) 27 a/c evaporator temp. Sensor 2.0 – 2.3 v ignition switch on a/c evaporation temp. Sensor at 25 °c (77 °f) 28 egr valv...
Page 393
6-36 engine general information and diagnosis for type a (see note) e19 18 egr valve (stepper motor coil 1, if equipped) 10 – 14 v ignition switch on position leaving engine off 19 ignition coil #2 – – 20 ignition coil #1 – – 21 fuel injector no.2 10 – 14 v ignition switch on 22 power source for sen...
Page 394
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-37 for type b (see note) e18 14 diag. Switch terminal (without immobilizer indicator lamp) 4 – 5 v ignition switch on 15 test switch terminal (without immo- bilizer indicator lamp) 4 – 5 v ignition switch on 16 a/c (input) signal 10 – 14 v ignition switch o...
Page 395
6-38 engine general information and diagnosis for type a (see note) e18 9 ignition switch 10 – 14 v ignition switch on 10 main relay 10 – 14 v ignition switch off 0.4 – 1.5 v ignition switch on 11 ignition switch 10 – 14 v ignition switch on 12 rear defogger switch (if equipped) 10 – 14 v ignition s...
Page 396
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-39 for type b (see note) e17 4 blank – – 5 overdrive cut signal (a/t) 0 – 1.0 v ignition switch on and ect less than 60 °c 10 – 14 v ignition switch on and ect more than 60 °c 6 d-range idle up signal (a/t) 10 – 14 v ignition switch on and shift select swit...
Page 397
6-40 engine general information and diagnosis e17 5 overdrive cut signal (a/t) 0 – 1.0 v ignition switch on and ect less than 60° c 10 – 14 v ignition switch on and ect more than 60 °c 6 d-range idle up signal (a/t) 10 – 14 v ignition switch on and shift select switch in other than p and n range 0 –...
Page 398
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-41 resistance check 1) disconnect ecm couplers (1) from ecm with ignition switch off. 2) check resistance between each terminal of couplers discon- nected. Caution: never touch terminals of ecm itself or connect voltmeter or ohmmeter (2). Caution: • be sure...
Page 399
6-42 engine general information and diagnosis component location note: the figure shows left-hand steering vehicle. For right-hand steering vehicle, parts with (*) are installed at the other side. 1. Iat sensor a : immobilizer indicator lamp (if equipped) a : ecm 2. Tp sensor b : a/c condenser fan m...
Page 400
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-43 table a-1 malfunction indicator lamp circuit check - lamp does not come “on” at ignition switch on (but engine at stop) circuit description when the ignition switch is turned on, ecm causes the main relay to turn on (close the contact point). Then, ecm b...
Page 401
6-44 engine general information and diagnosis table a-2 malfunction indicator lamp circuit check - lamp remains “on” after engine starts wiring diagram / circuit description refer to table a-1. Inspection 2 ecm power and ground circuit check does engine start? Go to step 3. Go to “table a-5 ecm powe...
Page 402
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-45 table a-3 malfunction indicator lamp circuit check - mil flashes at ignition switch on wiring diagram / circuit description refer to table a-1. Inspection table a-4 malfunction indicator lamp circuit check - mil does not flash, just remains on or just re...
Page 403
6-46 engine general information and diagnosis table a-5 ecm power and ground circuit check - mil doesn’t light at ignition switch on and engine doesn’t start though it is cranked up circuit description when the ignition switch tuned on, the main relay turns on (the contact point closes) and the main...
Page 404
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-47 [a] fig. 1 for step 2 and 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 2 / [c] fig. 3 for step 2 3 fuse check is main “fi” fuse in good condition? See fig. 1. Go to step 4. Check for short in cir- cuits con- nected to this fuse. 4 ecm power circuit check 1) turn off ignition...
Page 405
6-48 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0105 (dtc no.11) manifold absolute pressure (map) circuit malfunc- tion circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) clear dtc, start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min. 2) select “dtc” mode on scan tool and check dtc. Inspection dtc detectin...
Page 406
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-49 [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 3 check wire harness. 1) disconnect map sensor connector with ignition switch off. 2) check for proper connection of map sensor at “g” and “b/bl” wire terminals. 3) if ok, then with ignition switch on, check ...
Page 407
6-50 engine general information and diagnosis map sensor individual check 1) disconnect connector from map sensor (1). 2) remove map sensor (1). 3) arrange 3 new 1.5 v batteries (2) in series (check that total voltage is 4.5 – 5.0 v) and connect its positive terminal to “vin” terminal of sensor and ...
Page 408
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-51 dtc p0110 (dtc no.18) intake air temp. (iat) circuit malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) clear dtc, start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min. 2) select “dtc” mode no scan tool and check dtc. Inspection dtc detecting condition ...
Page 409
6-52 engine general information and diagnosis [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 / [c] fig. 3 for step 6 3 check wire harness. 1) disconnect iat sensor connector with igni- tion switch off. 2) check for proper connection to iat sensor at “lg/b” and “b/bl” wire terminals. See fig. 2. 3) if...
Page 410
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-53 dtc p0115 (dtc no.19) engine coolant temperature (ect) circuit malfunc- tion circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) clear dtc, start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min. 2) select “dtc” mode on scan tool and check dtc. Dtc detecting condition...
Page 411
6-54 engine general information and diagnosis inspection [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 5 / [c] fig. 3 for step 6 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 check ect sensor and its circuit. 1) connect scan tool with ig...
Page 412
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-55 dtc p0120 (dtc no.13) throttle position circuit malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) clear dtc, start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min. 2) select “dtc” mode on scan tool and check dtc. Dtc detecting condition possible cause •...
Page 413
6-56 engine general information and diagnosis inspection [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 / [c] fig. 3 for step 4 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 check tp sensor and its circuit. 1) connect scan tool to dlc w...
Page 414
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-57 dtc p0121 throttle position circuit range / performance problem wiring diagram refer to dtc p0120 section. Circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. Clear dtc with ignition switch on, check vehicle and environmental cond...
Page 415
6-58 engine general information and diagnosis [a] fig. 1 for step 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 4 / [c] fig. 3 for step 3 and 4 fig. 4 for step 5 4 check tp sensor and its circuit. 1) turn ignition switch on. 2) check voltage at terminal e19-16 of ecm connector connected, when throttle valve is at idle po...
Page 416
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-59 dtc p0130 (dtc no.14) heated oxygen sensor (ho2s) circuit malfunction (sensor-1) circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. Clear dtc with ignition switch on, check vehicle and environmental condition for : – altitude (ba...
Page 417
6-60 engine general information and diagnosis inspection [a] fig. 1 for step 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 is there dtc(s) other than ho2s-1 (dtc p0130)? Go to applicable dtc diag. Flow table. ...
Page 418
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-61 dtc p0133 heated oxygen sensor (ho2s) circuit slow response (sensor-1) wiring diagram refer to dtc p0130 section. Circuit description fig. 1 dtc confirmation procedure refer to dtc p0130 section. Inspection dtc detecting condition possible cause • when r...
Page 419
6-62 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0135 (dtc no.14) heated oxygen sensor (ho2s) heater circuit mal- function (sensor-1) circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) clear dtc with ignition switch on, start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min. 3) sta...
Page 420
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-63 inspection [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 check heater for operation. 1) check voltage at terminal e19-7. See fig. 1. 2) warm up...
Page 421
6-64 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0136 heated oxygen sensor (ho2s) circuit malfunction (sensor-2) circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. Clear dtc with ignition switch on, check vehicle and environmental condition for : – altitude (barometric pre...
Page 422
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-65 6) repeat above steps 5) 4 times. 7) increase vehicle speed to about 50 mph (80 km/h) in 3rd gear or 2 range. 8) release accelerator pedal and with engine brake applied, keep vehicle coasting (fuel cut condition) for 10sec. Or more. 9) stop vehicle (don’...
Page 423
6-66 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0141 heated oxygen sensor (ho2s) heater circuit malfunction (sen- sor-2) circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off once and then on. 2) clear dtc, start engine and warm up engine to normal operating temperature. 3) k...
Page 424
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-67 inspection fig. 1 for step 2 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 check ho2s-2 heater and its circuit. 1) warm up engine to normal operating tem- perature. 2) stop engine. 3) turn ...
Page 425
6-68 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0171 fuel system too lean dtc p0172 fuel system too rich circuit description [a] : signal to decrease amount of fuel injection [d] : a/f mixture becomes richer (oxygen concentration decreases) 1. Injector [b] : signal to increase amount of fuel inje...
Page 426
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-69 dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) clear dtc with ignition switch on. 3) check vehicle and environmental condition for : – altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmhg, 75 kpa or more) – ambient temp. : –10 °...
Page 427
6-70 engine general information and diagnosis 5 check fuel injectors and circuit. 1) using sound scope (4) or such, check operating sound of each injector (5) when engine is run- ning. Cycle of operating sound should vary according to engine speed. See fig. 3. If no sound or an unusual sound is hear...
Page 428
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-71 [a] fig. 1 for step 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 4 / [c] fig. 3 for step 5 [d] fig. 4 for step 5 / [e] fig. 5 for step 5 / [f] fig. 6 for step 6 1. Fuel delivery pipe 2. Fuel feed hose 3. Fuel pressure gauge & 3 way joint.
Page 429
6-72 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0300 random misfire detected (misfire detected at 2 or more cylinders) dtc p0301 cylinder 1 misfire detected dtc p0302 cylinder 2 misfire detected dtc p0303 cylinder 3 misfire detected dtc p0304 cylinder 4 misfire detected circuit description ecm mo...
Page 430
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-73 dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) clear dtc with ignition switch on. 3) check vehicle and environmental condition for : – altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmhg, 75 kpa or more) – ambient temp. : –10 °...
Page 431
6-74 engine general information and diagnosis 3 check ignition system. 1) remove spark plugs and check them for; • air gap : 1.0 – 1.1 mm (0.040 – 0.043 in.) see fig. 1. • carbon deposits / insulator damage / plug type if abnormality is found, adjust, clean or replace by referring to section 6f. (se...
Page 432
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-75 [a] fig. 1 for step 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 / [c] fig. 3 for step 4 / [d] fig. 4 for step 5 / [e] fig. 5 for step 4 7 check evap canister purge valve for closing. 1) disconnect purge hose (1) from evap canister. 2) place finger against the end of disco...
Page 433
6-76 engine general information and diagnosis [f] fig. 6 for step 5 / [g] fig. 7 for step 7.
Page 434
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-77 dtc p0325 (dtc no.17) knock sensor circuit malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) clear dtc, start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min. 2) select “dtc” mode on scan tool and check dtc. Inspection dtc detecting condition possible c...
Page 435
6-78 engine general information and diagnosis [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3.
Page 436
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-79 dtc p0335 (dtc no.23) crankshaft position (ckp) sensor circuit malfunction circuit description reference connect oscilloscope between terminals e19-23 of ecm connector connected to ecm and body ground and check ckp sensor signal. Dtc confirmation procedu...
Page 437
6-80 engine general information and diagnosis inspection step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 check ckp sensor and connector for proper installation. Is ckp sensor installed properly and connector connected securely? Go to ste...
Page 438
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-81 [a] fig. 1 for step 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 6 / [c] fig. 3 for step 6 fig. 4 for step 7.
Page 439
6-82 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0340 (dtc no.15) camshaft position (cmp) sensor circuit malfunction circuit description reference connect oscilloscope between terminals e19-11 of ecm connector connected to ecm and body ground and check cmp sensor signal. Dtc confirmation procedure...
Page 440
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-83 inspection step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 check cmp sensor and connector for proper installa- tion. Is cmp sensor installed properly and connector con- nected securely? Go to...
Page 441
6-84 engine general information and diagnosis [a] fig. 1 for step 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 6 / [c] fig. 3 for step 6 fig. 4 for step 7.
Page 442
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-85 dtc p0400 exhaust gas recirculation flow malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. Clear dtc with ignition switch on, check vehicle and environmental condition for : – altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m,...
Page 443
6-86 engine general information and diagnosis 2) start engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature (70 – 110 °c, 158 – 230 °f) and run it at idle for 5 min. 3) increase vehicle speed to 50 – 55 mph, 80 – 88 km/h in 5th gear or in “d” range. 4) hold throttle valve at that opening position f...
Page 444
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-87 [a] fig. 1 for step 7 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 and 4 4 with ignition switch at on, check voltage between e19-28, 17, 29, 18 terminals of ecm and body ground. See fig. 2. Is voltage within 10 – 14 v? Go to step 5. Go to step 8. 5 do you have suzuki scan to...
Page 445
6-88 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0420 catalyst system efficiency below threshold circuit description ecm monitors oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas which has passed the three way catalytic converter by ho2s-2. When the catalyst is functioning properly, the variation cycle of ...
Page 446
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-89 dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. Clear dtc with ignition switch on, check vehicle and environmental condition for : – altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmhg, 75 kpa or more) – ambient temp. : –10 °c, 14 ...
Page 447
6-90 engine general information and diagnosis test result confirmation flow table inspection step action yes no 1 check dtc in “dtc” mode and pending dtc in “on board test” or “pending dtc” mode. Is dtc or pending dtc displayed? Proceed to applicable dtc diag. Flow table. Go to step 2. 2 set scan to...
Page 448
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-91 dtc p0443 purge control valve circuit malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) clear dtc with ignition switch on. 2) select “dtc” mode on scan tool and check dtc. Inspection fig. 1 for step 2 1. Evap canister purge vale dtc detecting...
Page 449
6-92 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0481 a/c condenser fan control circuit malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) clear dtc with ignition switch on. 3) start engine and then turn both a/c switch and heater blower switch on for 2 sec ...
Page 450
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-93 inspection [a] fig. 1 for step 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 check a/c condenser fan control relay and its circuit. 1) turn ignition switch on. 2) ...
Page 451
6-94 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0500 (dtc no.16) vehicle speed sensor (vss) malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) clear dtc and warm up engine to normal operating temperature. 2) increase vehicle speed to 50 mph, 80 km/h in 3rd gear or “2” range while obser...
Page 452
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-95 inspection [a] fig. 1 for step 5 / [b] fig. 2 for step 4 and step 6 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 does speedometer indicate vehicle speed? Go to step 3. Go to step 5. 3 chec...
Page 453
6-96 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0505 idle control system malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) clear dtc with ignition switch on. 3) start engine and run it at idle for 1 min. 4) check dtc and pending dtc. Inspection 1. Iac valv...
Page 454
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-97 [a] fig. 1 for step 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 4 3 check idle air control system. 1) connect suzuki scan tool to dlc with igni- tion switch off, set parking brake and block drive wheels. See fig. 1. 2) warm up engine to normal operating tem- perature. 3) cl...
Page 455
6-98 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p0601 internal control module memory check sum error (dtc no.71) dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) clear dtc with ignition switch on and then turn ignition switch off. 3) start engine and run it at idle if possible. 4) check ...
Page 456
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-99 dtc p1450 barometric pressure sensor low / high input dtc p1451 barometric pressure sensor performance problem wiring diagram / circuit description barometric pressure sensor is installed in ecm. Dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. 2)...
Page 457
6-100 engine general information and diagnosis [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 table 1 3 check map sensor 1) remove map sensor from intake manifold and connect vacuum pump gauge to map sensor. See fig. 2. 2) connect scan tool to dlc and turn ignition switch on. 3) check intake manifold...
Page 458
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-101 dtc p1500 engine starter signal circuit malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) clear dtc with ignition switch on, crank engine and run it at idle for 3 min. 3) check pending dtc in “on board test” or “...
Page 459
6-102 engine general information and diagnosis inspection step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 check for voltage at terminal e17-13 (case of type a) (see note) or e18-20 (case of type b) (see note) of ecm connector connected, ...
Page 460
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-103 dtc p1510 ecm back-up power supply malfunction circuit description battery voltage is supplied so that diagnostic trouble code memory, values for engine control learned by ecm, etc. Are kept in ecm even when the ignition switch is turned off. Dtc confir...
Page 461
6-104 engine general information and diagnosis dtc p1570 (dtc no.21) abs signal circuit malfunction circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) clear dtc, start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min. 2) select “dtc” mode on scan tool and check dtc. Inspection dtc detecting condition possible ca...
Page 462
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-105 dtc p1600 serial communication problem between ecm and tcm circuit description the serial data line is pulled up to about 12 v by ecm and tcm transmits information to ecm through it by con- trolling its grounding. Tcm constantly sends information while ...
Page 463
6-106 engine general information and diagnosis [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 4 3 is it about 12 v at step 2? “b/r” wire open, poor e21-11 connection or tcm power or ground cir- cuit open. If wires and connections are ok, substitute a known-good tcm and recheck. Go to step 4. 4 check si...
Page 464
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-107 dtc p1717 a/t drive range (park / neutral position) signal circuit malfunc- tion circuit description dtc confirmation procedure 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) clear dtc with ignition switch on. 3) start engine and shift selector lever to “d” range. 4) ...
Page 465
6-108 engine general information and diagnosis inspection [a] fig. 1 for step 3 / [b] fig. 2 for step 4 / [c] fig. 3 for step 6 step action yes no 1 was “engine diag. Flow table” performed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table”. 2 is suzuki scan tool available? Go to step 3. Go to step 4. 3 ...
Page 466
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-109 [d] table 1 for step 3 and 4 table b-1 fuel injector circuit check inspection scan tool voltmeter suzuki scan tool display voltage at e17-6 selector lever position “p” and “n” range p/n range 10 – 14v “r”, “d”, “2” and “l” range d range 0 – 1v step acti...
Page 467
6-110 engine general information and diagnosis table b-2 fuel pump and its circuit check inspection 1. Ignition switch 3. Main relay 5. Fuel pump relay [a] : case of type a is shown (see note) 2. Main relay 4. Main fuse 6. Fuel pump [b] : case of type b is shown (see note) note: for type a and type ...
Page 468
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-111 [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 / [c] fig. 3 for step 4 4 check fuel pump relay for operation. 1) check resistance between each two termi- nals of fuel pump relay. See fig.3. Fuel pump relay resistance between terminals “a” and “b” : infin...
Page 469
6-112 engine general information and diagnosis table b-3 fuel pressure check inspection 1. Injector 3. Fuel pump (b) : hose 2. Delivery pipe (a) : fuel pressure gauge (c) : attachment step action yes no 1 check fuel pressure (refer to section 6e for details). 1) release fuel pressure from fuel feed ...
Page 470
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-113 fig. 1 for step 1 special tool (a) : 09912-58441 (b) : 09912-58431 (c) : 09912-58490
Page 471
6-114 engine general information and diagnosis table b-4 idle air control system check inspection 1. Main fuse 2. Fuse box 3. Main relay 4. Iac valve step action yes no 1 check engine idle speed and iac duty referring to “idle speed / iac duty inspection” in section 6e. Is idle speed within specific...
Page 472
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-115 3 is engine idle speed kept specified speed even with headlight on? System is in good condi- tion. Check iac system for operation referring to step 3 or step 4 of dtc p0505 diag. Flow table. 4 was idle speed higher than specification in step 1? Go to st...
Page 473
6-116 engine general information and diagnosis fig. 1 for step 10 table 1 for step 9 and 10 scan tool or voltmeter suzuki scan tool display voltage at e17-6 selector lever position “p” and “n” range p/n range 10 – 14v “r”, “d”, “2” and “l” range d range 0 – 1v.
Page 474
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-117 table b-5 a/c signal circuits check (vehicle with a/c) 1. A/c compressor magnet clutch 4. A/c condenser fan 7. Evaporator temp. Sensor 2. A/c switch 5. Refrigerant pressure switch [a] : case of type a is shown (see note) 3. Blower fan 6. Ect sensor [b] ...
Page 475
6-118 engine general information and diagnosis inspection fig. 1 for step 1 step action yes no 1 check evaporator temp. Sensor. 1) disconnect ecm connectors with ignition switch at off position. 2) check resistance between e19-14 terminal and e19-10 terminal. Reference value (refer to characteristic...
Page 476
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-119 table b-6 electric load signal circuit check inspection 1. Rear defogger switch 3. Blower fan switch [b] : case of type b is shown (see note) 2. Light switch [a] : case of type a is shown (see note) note: for type a and type b, refer to the note in “ecm...
Page 477
6-120 engine general information and diagnosis [a] fig. 1 for step 2 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 table 1 for step 2 and 3 scan tool or voltmeter suzuki scan tool voltage at e18-17, e17-16 or e18-12 voltage at e18-24 or e17-13 ignition switch on, small light, heater blower fan and rear defogger all turne...
Page 478
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-121 table b-7 a/c condenser fan control system check inspection step action yes no 1 check fan control system. 1) connect scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. See fig. 1. 2) start engine and select “data list” mode on scan tool. 3) warm up engine unti...
Page 479
6-122 engine general information and diagnosis [a] fig. 1 for step 1 / [b] fig. 2 for step 3 fig. 3 for step 4 4 check a/c condenser fan (1). 1) turn ignition switch off. 2) disconnect fan motor connector (2). 3) check for proper connection to motor at “r/bl” and “b” terminals. 4) if ok, connect bat...
Page 480: Special Tool
Engine general information and diagnosis 6-123 special tool 09912-58441 09912-58431 09912-58490 09912-58421 pressure gauge pressure hose 3-way joint & hose checking tool set (see note “a”.) 09912-57610 09917-47010 09930-88530 09931-76011 checking tool plate vacuum pump gauge injector test lead suzuk...
Page 481
6-124 engine general information and diagnosis.
Page 482: Section 6A1
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-1 6f1 6g 6h 6k 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8c 6a1 8e 9 9 10b section 6a1 engine mechanical (m13 engine) contents general description ......................................6a1-2 engine .........................................................6a1-2 engine lubrication ...
Page 483: General Description
6a1-2 engine mechanical (m13 engine) general description engine the engine is water-cooled, in line 4 cylinders, 4 stroke cycle gasoline unit with its dohc (double overhead camshaft) valve mechanism arranged for “v” type valve configuration and 16 valves (4 valves / one cylinder). The double overhea...
Page 484
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-3 engine lubrication the oil pump is of a trochoid type, and mounted under the crankshaft. Oil is drawn up through the oil pump strainer and passed through the pump to the oil filter. The filtered oil flows into 2 paths in cylinder block. In one path, oil reaches t...
Page 485: Diagnosis
6a1-4 engine mechanical (m13 engine) diagnosis diagnosis table refer to “engine diagnosis table” in section 6. Compression check check compression pressure on all 4 cylinders as follows: 1) warm up engine. 2) stop engine after warming up. 3) disconnect accelerator cable (1) from clamp (2) (for left ...
Page 486
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-5 10) disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on engine) for m/t vehicle, and depress accelerator pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open. 11) crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the highest pressure on compression gauge. Compression ...
Page 487
6a1-6 engine mechanical (m13 engine) engine vacuum check the engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a good indi- cator of the condition of the engine. The vacuum checking proce- dure is as follows: 1) warm up engine to normal operating temperature. 2) stop engine and turn off the all elec...
Page 488
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-7 oil pressure check • oil level in oil pan. If oil level is low, add oil up to full level mark (hole) (1) on oil level gauge. • oil quality. If oil is discolored, or deteriorated, change it. For particular oil to be used, refer to the table in section 0b. • oil le...
Page 489
6a1-8 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6) before reinstalling oil pressure switch (2), be sure to wrap its screw threads with sealing tape (1) and tighten switch to specified torque. Tightening torque oil pressure switch (a) : 14 n.M (1.4 kg-m, 10.5 lb-ft) 7) start engine and check oil pressure switch...
Page 490
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-9 valve lash (clearance) 1) remove negative cable at battery. 2) remove cylinder head cover referring to “cylinder head cover” in this section. 3) using 17 mm wrench, turn crankshaft pulley (1) clockwise until cam lobes (2) become perpendicular to shim faces (3) at...
Page 491
6a1-10 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 2) lift valve by turning crankshaft and then remove camshaft housing bolts (1) where the shim to be replaced. 3) install special tool with camshaft housing bolts as shown in figure. Special tool (a) : 09916-67020 tightening torque camshaft housing bolts (for tig...
Page 492
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-11 5) using a micrometer (2), measure the thickness of the removed shim (1), and determine replacement shim by cal- culating the thickness of new shim with the following formula and table. Intake side a = b + c – 0.20 mm (0.008 in.) exhaust side a = b + c – 0.30 mm...
Page 493
6a1-12 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 8) lift valve by turning crankshaft counterclockwise (in opposite direction against above step 4) and remove special tool. Special tool (a) : 09916-67020 9) install camshaft housing (1) and tighten them to specified torque. Tightening torque camshaft housing bol...
Page 494: On-Vehicle Service
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-13 on-vehicle service air cleaner element removal 1) open air cleaner case by unhooking its clamps. 2) remove air cleaner element from case. Inspection check air cleaner element for dirt. Replace excessively dirty ele- ment. Cleaning blow off dust by compressed air...
Page 495
6a1-14 engine mechanical (m13 engine) air cleaner assembly removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) disconnect iat sensor coupler (1). 3) disconnect breather hose from air cleaner outlet no.2 hose (2). 4) remove air cleaner outlet no.2 hose fastening bolt (3). 5) loosen air cleaner outlet...
Page 496
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-15 cylinder head cover removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) disconnect accelerator cable (1) from clamp (2) (for left hand steering vehicle only). 3) remove cylinder head upper cover (3). 4) disconnect ignition coil couplers (1). 5) remove ignition c...
Page 497
6a1-16 engine mechanical (m13 engine) installation 1) install new spark plug hole gaskets (1) and new cylinder head cover gasket (2) to cylinder head cover (3) as shown in figure. 2) remove oil, old sealant, and dust from sealing surface on cylinder head and cover. After cleaning, apply sealant “a” ...
Page 498
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-17 3) install cylinder head cover to cylinder head. 4) tighten bolts in such order as indicated in figure a little at a time till they are tightened to specified torque. Tightening torque cylinder head cover bolts (a) : 8 n·m (0.8 kg-m, 6.0 lb-ft) 5) connect breath...
Page 499
6a1-18 engine mechanical (m13 engine) throttle body and intake manifold removal 1) relieve fuel pressure referring to “fuel pressure relief pro- cedure” in section 6. 2) disconnect negative cable at battery. 3) drain coolant by loosening drain plug (1). 1. Intake manifold 7. Evap canister purge valv...
Page 500
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-19 4) remove air cleaner outlet no.1 (1) and no.2 (2) hoses and breather hose (3). 5) remove intake manifold bracket (1) with main harness from intake manifold. 6) disconnect the following electric lead wires: • iac valve (2) • tp sensor (3) • evap canister purge v...
Page 501
6a1-20 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 13) remove intake manifold (1) with throttle body (2) and egr pipe (3) from cylinder head (4), and then its gasket. Installation reverse removal procedure for installation noting the followings. • use new intake manifold gasket and egr pipe gasket. • tighten lon...
Page 502
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-21 exhaust manifold removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) disconnect heated oxygen sensor coupler (1) (if equipped) and detach it from its stay. 3) remove exhaust manifold cover (2). 4) remove exhaust manifold stiffener (1). 1. Exhaust manifold 4. Exh...
Page 503
6a1-22 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 5) disconnect exhaust pipe (1) from exhaust manifold. 6) remove exhaust manifold (1) and its gasket from cylinder head. Installation 1) install new gasket to cylinder head. Then install exhaust manifold. Tighten manifold nuts to specified torque. Tightening torq...
Page 504
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-23 3) install exhaust manifold stiffener (1). Tighten exhaust manifold stiffener bolts to specified torque. Tightening torque exhaust manifold stiffener bolts (a) : 50 n·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft) 4) install exhaust manifold cover (1). 5) connect heated oxygen sensor...
Page 505
6a1-24 engine mechanical (m13 engine) oil pan and oil pump strainer removal 1) remove oil level gauge. 2) remove air cleaner outlet no.1 (1) and no.2 (2) hoses and breather hose (3). 3) to facilitate and ensure removal of oil pan, increase clear- ance between engine and vehicle body according to the...
Page 506
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-25 4) drain engine oil by removing drain plug. 5) remove clutch housing (torque converter housing for a/t vehicle) lower plate (1). 6) remove oil pan and then oil pump strainer (1) from cylinder block. Clean • inside of oil pan and oil pump strainer screen. • clean...
Page 507
6a1-26 engine mechanical (m13 engine) installation 1) apply sealant continuously to oil pan mating surface as shown in figure. “a” sealant : 99000-31150 sealant amount for oil pan width “a” : 3 mm, 0.12 in. Height “b” : 2 mm, 0.08 in. 2) install new o-rings (1) in the position as shown in figure and...
Page 508
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-27 6) lower engine and tighten engine mounting bracket bolts to specified torque. Tightening torque engine mounting bracket bolts (a) : 50 n·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft) 7) install oil level gauge. 8) refill engine with engine oil referring to “engine oil and filter ch...
Page 509
6a1-28 engine mechanical (m13 engine) timing chain cover removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) remove a/c compressor and/or p/s pump belt (if equipped). 3) remove generator belt. 4) drain engine oil. [a] : sealant application amount 3. Oil seal : apply engine oil to oil seal lip. 8. Cy...
Page 510
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-29 5) drain coolant. 6) disconnect radiator inlet and outlet hoses from each pipe. 7) disconnect a/t fluid hoses (1) (vehicle with a/t) and release its clamps. Place some container under radiator to receive a/t fluid which will flow out when hose is disconnected. 8...
Page 511
6a1-30 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 12) remove crankshaft pulley bolt. To lock crankshaft pulley (1), use special tool with it as shown in figure. Special tool (a) : 09917-68221 13) remove crankshaft pulley (1). If it is hard to remove, use special tools as shown in figure. If bolts of special too...
Page 512
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-31 inspection • check oil seal (1) lip for fault or other damage. Replace as necessary. Special tool (a) : 09913-75520 installation reverse removal procedure to install timing chain cover, noting the following points. 1) apply sealant “a” to mating surface of cylin...
Page 513
6a1-32 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 3) install crankshaft pulley (1). Tighten bolt (2) to specified torque. To lock crankshaft pulley, use special tool with it as shown in figure. Special tool (a) : 09917-68221 tightening torque crankshaft pulley bolt (a) : 150 n·m (15.0 kg-m, 108.5 lb-ft) 4) inst...
Page 514
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-33 oil pump removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) remove timing chain cover, referring to “timing chain cover” in this section. Disassembly 1) remove rotor plate (1) by removing its mounting bolts. [a] : sealant application amount 4. Timing chain cove...
Page 515
6a1-34 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 2) remove outer rotor (1) and inner rotor (2). 3) remove relief valve (1), spring (2) and retainer (3) by remov- ing circlip (4). Inspection • check oil seal lip for fault or other damage. Replace as nec- essary. Special tool (a) : 09913-75520 note: when install...
Page 516
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-35 • check outer (1) and inner rotors (2), rotor plate, and oil pump case for excessive wear or damage. • check relief valve (1) for excessive wear or damage and operates smoothly. Measurement radial clearance check radial clearance between outer rotor (1) and case...
Page 517
6a1-36 engine mechanical (m13 engine) assembly 1) wash, clean and then dry all disassembled parts. 2) apply thin coat of engine oil to inner and outer rotors, oil seal lip portion, and inside surfaces of oil pump case and plate. 3) install outer (1) and inner rotors (2) to oil pump case. 4) install ...
Page 518
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-37 timing chain and chain tensioner removal 1) remove timing chain cover referring to “timing chain cover”. 2) align both intake and exhaust camshaft timing sprocket marks (1) with notches (2) of cylinder head respectively by turning crankshaft. 3) remove timing ch...
Page 519
6a1-38 engine mechanical (m13 engine) inspection timing chain tensioner • check shoe (1) for wear or damage. Crankshaft timing sprocket • check teeth of sprocket for wear or damage. Timing chain • check timing chain for wear or damage. Timing chain tensioner adjuster • check that tooth surface (1) a...
Page 520
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-39 installation 1) check that match marks (1) on intake and exhaust camshaft timing sprockets are in match with notches (2) on cylinder head as shown in figure. 2) set key (3) and turn crankshaft to position key on upside of crankshaft. 3) install timing chain by a...
Page 521
6a1-40 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6) apply engine oil to sliding surface of chain tensioner (1) and install chain tensioner and spacer. Tighten tensioner bolt to specified torque tightening torque timing chain tensioner bolt (a) : 22 n·m (2.2 kg-m, 16.0 lb-ft) 7) check that match marks (1) on in...
Page 522
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-41 10) apply engine oil to timing chain and then turn crankshaft clockwise by 2 revolutions and check that match marks (1) on intake and exhaust camshaft timing sprockets are in match with notches (2) on cylinder head and key (3) is on upside of crankshaft as shown...
Page 523
6a1-42 engine mechanical (m13 engine) camshaft, tappet and shim removal 1) remove cylinder head cover and oil pan referring to “cylin- der head cover” and “oil pan and oil pump strainer” in this section. 2) remove timing chain cover referring to “timing chain cover” in this section. 3) remove timing...
Page 524
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-43 7) remove tappets (1) with shims (2). Inspection cam wear using a micrometer, measure cam height “a”. If measured height is below its limit, replace camshaft. Cam height “a” of camshaft camshaft runout set camshaft between two “v” blocks, and measure its runout ...
Page 525
6a1-44 engine mechanical (m13 engine) check clearance by using gauging plastic. Checking procedure is as follows. 1) clean housings and camshaft journals. 2) remove all tappets with shims. 3) install camshafts to cylinder head. 4) place a piece of gauging plastic to full width of journal of camshaft...
Page 526
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-45 wear of tappet and shim check tappet and shim for pitting, scratches or damage. If any malcondition is found, replace. Measure cylinder head bore and tappet outside diameter to deter- mine cylinder head-to-tappet clearance. If clearance exceeds limit, replace ta...
Page 527
6a1-46 engine mechanical (m13 engine) installation 1) install tappets and shims to cylinder head. Apply engine oil around tappet and then install it to cylinder head. 2) install camshafts (1). Apply engine oil to sliding surface of each camshaft and camshaft journal then install them as shown in fig...
Page 528
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-47 5) after applying engine oil to housing bolts, tighten them tem- porarily first. Then tighten them by the following numerical order in figure. Tighten a little at a time and evenly among bolts and repeat tightening sequence two or three times before they are tig...
Page 529
6a1-48 engine mechanical (m13 engine) valves and cylinder head 1. Valve cotters 6. Intake valve 11. Cylinder head gasket : “top” mark provided on gasket comes to crankshaft pulley side, facing up. 2. Valve spring retainer 7. Exhaust valve 12. Knock pin 3. Valve spring 8. Valve guide tightening torqu...
Page 530
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-49 removal 1) relieve fuel pressure referring to “fuel pressure relief pro- cedure” in section 6. 2) disconnect negative cable at battery. 3) drain engine oil. 4) drain coolant by loosening drain plug (1). 5) remove air cleaner outlet no.1 and no.2 hoses and breath...
Page 531
6a1-50 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 9) disconnect accelerator cable (1) from throttle body. 10) disconnect the following hoses: • brake booster hose (2) from intake manifold • canister purge hose (3) from evap canister purge valve • fuel feed and return hoses (4) from each pipe • water hose from t...
Page 532
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-51 19) remove exhaust manifold stiffener (1). 20) loosen cylinder head bolts in such order as indicated in fig- ure by using a 12 corner socket wrenches and remove them. 21) check all around cylinder head for any other parts required to be removed or disconnected a...
Page 533
6a1-52 engine mechanical (m13 engine) disassembly 1) for ease in servicing cylinder head, remove intake manifold, injectors and exhaust manifold from cylinder head. 2) using special tools (valve lifter), compress valve spring and then remove valve cotters (1) by using special tool (for- ceps). Speci...
Page 534
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-53 inspection valve guides using a micrometer and bore gauge, take diameter readings on valve stems and guides to check stem-to-guide clearance. Be sure to take reading at more than one place along the length of each stem and guide. If clearance exceeds limit, repl...
Page 535
6a1-54 engine mechanical (m13 engine) valves • remove all carbon from valves. • inspect each valve for wear, burn or distortion at its face and stem end, as necessary, replace it. • measure thickness “a” of valve head. If measured thickness exceeds limit, replace valve. Valve head thickness “a” (in ...
Page 536
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-55 • valve seat repair: a valve seat not producing a uniform contact with its valve or showing width of seating contact that is out of specified range must be repaired by regrinding or by cutting and regrinding and finished by lapping. 1) exhaust valve seat: use va...
Page 537
6a1-56 engine mechanical (m13 engine) • check cylinder head for cracks on intake and exhaust ports, combustion chambers, and head surface. Using a straightedge and thickness gauge, check flatness of gasketed surface at a total of 2 locations. If distortion limit, given below, is exceeded, correct ga...
Page 538
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-57 valve springs • referring to data given below, check to be sure that each spring is in sound condition, free of any evidence of break- age or weakening. Remember, weakened valve springs can cause chatter, not to mention possibility of reducing power output due t...
Page 539
6a1-58 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 2) install valve guide to cylinder head. Heat cylinder head uniformly to a temperature of 80 to 100 °c (176 to 212 °f) so that head will not be distorted, and drive new valve guide into hole with special tools. Drive in new valve guide until special tool (valve ...
Page 540
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-59 6) install valve to valve guide before installing valve to valve guide, apply engine oil to stem seal, valve guide bore and valve stem. 7) install valve spring and spring retainer. Each valve spring has top end (large-pitch end (1)) and bot- tom end (small-pitch...
Page 541
6a1-60 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 4) make sure that oil jet (venturi plug) (1) is installed and if it is, that it is not clogged. When installing it, be sure to tighten to specified torque. Tightening torque venturi plug (a) : 5 n·m (0.5 kg-m, 3.5 lb-ft) 5) install cylinder head to cylinder bloc...
Page 542
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-61 6) install exhaust manifold stiffener and exhaust pipe referring to “exhaust manifold” in this section. 7) install camshafts, timing chain and chain cover referring to “camshaft, tappet and shim”, “timing chain and chain tensioner” and “timing chain cover” in th...
Page 543
6a1-62 engine mechanical (m13 engine) pistons, piston rings, connecting rods and cylinders removal 1) relieve fuel pressure referring to “fuel pressure relief pro- cedure” in section 6. 2) disconnect negative cable at battery. 3) drain engine oil. 4) drain coolant. 5) remove cylinder head referring ...
Page 544
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-63 8) install guide hose (1) over threads of rod bolts. This prevents damage to bearing journal and rod bolt threads when removing connecting rod. 9) decarbon top of cylinder bore before removing piston from cylinder. 10) push piston and connecting rod assembly out...
Page 545
6a1-64 engine mechanical (m13 engine) • using a cylinder gauge (1), measure cylinder bore in thrust and axial directions at two positions (“a” and “b”) as shown in figure. If any of the following conditions is noted, rebore cylinder. 1) cylinder bore dia. Exceeds limit. 2) difference of measurements...
Page 546
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-65 • piston clearance: measure cylinder bore diameter and piston diameter to find their difference which is piston clearance. Piston clearance should be within specification as given below. If it is out of specification, rebore cylinder and use oversize piston. Pis...
Page 547
6a1-66 engine mechanical (m13 engine) • piston pin clearance: check piston pin clearance in small end and piston. Replace connecting rod and/or piston if its small end is badly worn or damaged or if measured clearance exceeds limit. Piston pin clearance in connecting rod small end 0.003 – 0.014 mm (...
Page 548
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-67 • connecting rod alignment: mount connecting rod on aligner to check it for bow and twist. If limit is exceeded, replace it. Connecting rod alignment limit on bow : 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.) limit on twist : 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.) • connecting rod bolt diameter (plasti...
Page 549
6a1-68 engine mechanical (m13 engine) • rod bearing : inspect bearing shells for signs of fusion, pitting, burn or flak- ing and observe contact pattern. Bearing shells found in defective condition must be replaced. Two kinds of rod bearing are available; standard size bear- ing and 0.25 mm (0.0098 ...
Page 550
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-69 6) if clearance can not be brought to within its limit even by using a new standard size bearing, regrind crankpin to undersize and use 0.25 mm undersize bearing. Assembly 1) install piston pin to piston (1) and connecting rod (2): a) after applying engine oil t...
Page 551
6a1-70 engine mechanical (m13 engine) installation 1) apply engine oil to pistons, rings, cylinder walls, connecting rod bearings and crankpins. 2) install guide hoses (1) over connecting rod bolts. These guide hoses protect crank pin and threads of rod bolt from damage during installation of connec...
Page 552
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-71 5) install bearing cap (1): point arrow mark (2) on cap to crankshaft pulley side. After applying oil to rod bolts and tighten cap nuts (3) gradu- ally as follows. A) tighten all cap nuts to 15 n·m (1.5 kg-m, 11.0 lb-ft). B) retighten them to 45°. C) repeat step...
Page 553
6a1-72 engine mechanical (m13 engine) engine mountings tightening torque.
Page 554: Unit Repair Overhaul
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-73 unit repair overhaul engine assembly removal 1) relieve fuel pressure referring to “fuel pressure relief pro- cedure” in section 6. 2) disconnect negative cable at battery. 3) remove engine hood after disconnecting windshield washer hose. 4) remove a/c compresso...
Page 555
6a1-74 engine mechanical (m13 engine) a) for right hand steering vehicle: with hose connected, detach a/c compressor from its bracket. B) for left hand steering vehicle: i) recover refrigerant from refrigeration system using recov- ery and recycling equipment. Ii) disconnect magnet clutch lead wire....
Page 556
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-75 18) remove heated oxygen sensor bracket from cylinder head and detach no.1 heated oxygen sensor coupler from its bracket. 19) release accelerator cable (1) from clamp (2) (for left hand steering vehicle only) and disconnect accelerator cable from throttle body. ...
Page 557
6a1-76 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 26) remove bolts and nuts fastening cylinder block and trans- mission. 27) install board (1) or the like on a/c condenser. This prevents damage to condenser fins when lifting and lowering engine assembly. 28) install lifting device. 29) remove right and left eng...
Page 558
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-77 installation 1) lower engine assembly into engine compartment. Connect engine to transmission. Hard-tighten bolts and nuts fastening cylinder block and transmission. 2) tighten right and left engine mounting bracket bolts to speci- fied torque. Tightening torque...
Page 559
6a1-78 engine mechanical (m13 engine) • install seal ring and exhaust pipe to exhaust manifold. Tighten pipe fasteners to specified torque. Tightening torque exhaust pipe bolts (a) : 50 n·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.5 lb-ft) 6) reverse disconnected hoses, cables and electric wires for connection. 7) install air...
Page 560
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-79 main bearings, crankshaft and cylinder block tightening torque 4. Venturi plug 12. Input shaft bearing do not reuse. 5. Main bearing 13. Flywheel apply engine oil to inside / sliding surface. 6. Sensor plate 14. Main bearing cap “a” : 3 mm (0.12 in.) 7. Cranksha...
Page 561
6a1-80 engine mechanical (m13 engine) removal 1) remove engine assembly from vehicle as previously out- lined. 2) remove clutch cover, clutch disc and flywheel (drive plate for a/t) by using special tool. Special tool (a) : 09924-17810 3) remove the following parts from engine as previously out- lin...
Page 562
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-81 inspection main bearing cap no.1 bolt measure each thread diameter of bearing cap no.1 bolts (1) at “a” on 60 mm (2.36 in.) from seat side of flange bolt and “b” on 90 mm (3.54 in.) from seat side of flange bolt by using a micrometer (2). Calculate difference in...
Page 563
6a1-82 engine mechanical (m13 engine) tighten bearing cap no.1 bolts (1) – (10) and no.2 bolts (11) – (20) gradually as follows. 1) tighten bolts (1) – (10) to 30 n·m (3.0 kg-m, 22.0 lb-ft) according to numerical order in figure. 2) in the same manner as in step 1), tighten them to 50 n·m (5.0 kg-m,...
Page 564
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-83 • upper half of bearing (1) has an oil groove (2) as shown in figure. Install this half with oil groove to cylinder block. • lower half of bearing does not have an oil groove. Visual inspection check bearings for pitting, scratches, wear or damage. If any malcon...
Page 565
6a1-84 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 5) remove bearing caps and using scale (1) on gauging plastic (2) envelop, measure gauging plastic width at its widest point. If clearance exceeds its limit, replace bearing. Always replace both upper and lower inserts as a unit. A new standard bearing may produ...
Page 566
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-85 2) next, check bearing cap bore diameter without bearing. On mating surface of cylinder block, five alphabets are stamped as shown in figure. Three kinds of alphabets (“a”, “b” and “c”) represent the fol- lowing cap bore diameters. Stamped alphabets on cylinder ...
Page 567
6a1-86 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 4) from number stamped on crank web no.2 and alphabets stamped on cylinder block, determine new standard bearing to be installed to journal, by referring to table shown below. For example, if number stamped on crank web no.2 is “1” and alphabet stamped on cylind...
Page 568
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-87 • if necessary, regrind crankshaft journal and select undersize bearing to use with it as follows. A) regrind journal to the following finished diameter. Finished diameter 44.732 – 44.750 mm (1.7611 – 1.7618 in.) 1) using micrometer, measure reground journal dia...
Page 569
6a1-88 engine mechanical (m13 engine) flywheel • if ring gear is damaged, cracked or worn, replace flywheel. • if the surface contacting clutch disc is damaged, or exces- sively worn, replace flywheel. • check flywheel for face runout with a dial gauge. If runout exceeds its limit, replace flywheel....
Page 570
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-89 3) using micrometer, measure piston diameter. Measurement position for piston diameter “a” : 19.5 mm (0.77 in.) 4) calculate cylinder bore diameter to be rebored as follows. D = a + b – c d : cylinder bore diameter to be rebored. A : piston diameter as measured....
Page 571
6a1-90 engine mechanical (m13 engine) installation 1) install sensor plate (1) to crankshaft (2) and tighten bolts to specified torque. Tightening torque sensor plate bolts (a) : 11 n·m (1.1 kg-m, 8.0 lb-ft) 2) install main bearings to cylinder block. Upper half of bearing (1) has an oil groove (2)....
Page 572
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-91 5) install crankshaft to cylinder block. 6) install bearing cap to cylinder block, making sure to point arrow mark (on each cap) to crankshaft pulley side. Fit them sequentially in ascending order, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5, starting from pulley side. After applying engi...
Page 573
6a1-92 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 8) install rear oil seal housing (1) and tighten bolts to specified torque by using special tool. Special tool (a) : 09911-97720 tightening torque rear oil seal housing bolts : 11 n·m (1.1 kg-m, 8.0 lb-ft) 9) install flywheel (drive plate for a/t). Using special...
Page 574: Required Service Material
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-93 required service material tightening torque specification material recommended suzuki product (part number) use sealant suzuki bond no. 1207c (99000-31150) • to apply to mating surface of cylinder block and oil pan. • to apply to mating surface of cylinder block...
Page 575: Special Tool
6a1-94 engine mechanical (m13 engine) special tool crankshaft bearing cap no.1 bolts (for inspection of crankshaft thrust play) 50.0 5.0 36.5 crankshaft bearing cap no.2 bolts 22.0 2.2 16.0 sensor plate bolts 11.0 1.1 8.0 crankshaft bearing cap no.1 bolts a) tighten 50 n·m b) turn 60° a) tighten 5.0...
Page 576
Engine mechanical (m13 engine) 6a1-95 09915-67310 09915-77310 09915-78211 09916-14510 vacuum gauge oil pressure gauge oil pressure gauge attachment valve lifter 09916-14521 09916-34542 09916-34550 09916-37320 valve lifter attachment reamer handle reamer (5.5 mm) reamer (10.5 mm) 09916-44910 09916-56...
Page 577
6a1-96 engine mechanical (m13 engine) 09924-17810 09926-58010 09944-36011 flywheel holder bearing puller attachment steering wheel remover.
Page 578: Section 6B
Engine cooling 6b-1 6b section 6b engine cooling contents general description ........................................6b-2 cooling system circulation ...........................6b-2 radiator cap .................................................6b-3 coolant reservoir ....................................
Page 579: General Description
6b-2 engine cooling general description the cooling system consists of the radiator cap, radiator, reservoir, hoses, water pump, cooling fan & clutch, thermostat. The radiator is of tube-and-fin type. Cooling system circulation 1. Radiator inlet hose 5. Water pump 9. Heater outlet hose 2. Radiator o...
Page 580
Engine cooling 6b-3 radiator cap a pressure-vent cap is used on the radiator. The cap contains a pressure valve (1) and ventilation valve (2). The cap has its face marked 1.1, which means that its pressure valve opens at 1.1 kg/cm 2 (15.6 psi, 110 kpa). Coolant reservoir a “see-through” plastic rese...
Page 581
6b-4 engine cooling water pump the centrifugal type water pump is used in the cooling system. The pump impeller is supported by a totally sealed bearing. The water pump can not be disassembled. Thermostat a wax pellet type thermostat is used in the cooling system. The temperature at which the valve ...
Page 582: Diagnosis
Engine cooling 6b-5 diagnosis condition possible cause correction engine overheats • loose or broken water pump belt • not enough coolant • faulty thermostat • faulty water pump • dirty or bent radiator fins • coolant leakage on cooling system • defective cooling fan clutch • plugged radiator • faul...
Page 583: Maintenance
6b-6 engine cooling maintenance coolant the coolant recovery system is standard. The coolant in the radiator expands with heat, and the overflow is col- lected in the reservoir. When the system cools down, the coolant is drawn back into the radiator. The cooling system has been filled at the factory...
Page 584
Engine cooling 6b-7 coolant level to check level, look at “see-through” reservoir. It is not necessary to remove radiator cap to check coolant level. When engine is cool, check coolant level in reservoir (1). A normal coolant level should be between “full” (2) and “low” (3) marks on reservoir (1). I...
Page 585
6b-8 engine cooling 5) tighten hose clamps and inspect all hoses. Replace hoses whenever cracked, swollen or otherwise deteriorated. 6) clean frontal area of radiator core. Cooling system flush and refill 1) remove radiator cap when engine is cool: turn cap slowly to the left until it reaches a “sto...
Page 586
Engine cooling 6b-9 9) run engine, with radiator cap removed, until radiator upper hose is hot. 10) with engine idling, add coolant to radiator until level reaches the bottom of filler neck. Install radiator cap, making sure that the ear of cap lines up with reservoir hose. Water pump belt tension 1...
Page 587: On-Vehicle Service
6b-10 engine cooling on-vehicle service cooling system component caution: • check to make sure that engine coolant temperature is cold before removing any part of cooling system. • disconnect negative cable at battery before removing any part. 1. Radiator 6. Thermostat 11. Water outlet cap 2. Reserv...
Page 588
Engine cooling 6b-11 coolant draining 1) remove radiator cap (1). 2) loosen drain plug on radiator to drain coolant. 3) after draining coolant, be sure to tighten drain plug securely. 4) fill cooling system. Refer to “coolant” in this section. Cooling water pipes or hoses removal 1) drain cooling sy...
Page 589
6b-12 engine cooling inspection 1) make sure that air bleed valve (1) of thermostat is clear. Should this valve be clogged, engine would tend to overheat. 2) check valve seat for some foreign matters being stuck which prevent valve from seating tight. 3) check thermostatic movement of wax pellet as ...
Page 590
Engine cooling 6b-13 water pump belt and cooling fan removal 1) remove radiator shroud securing bolts (1). 2) remove radiator by referring to “radiator” in this section. 3) loosen water pump drive belt tension. 4) remove cooling fan by removing securing nuts. Remove power steering and/or compressor ...
Page 591
6b-14 engine cooling radiator removal 1) drain cooling system. 2) remove radiator shroud. 3) disconnect water hoses from radiator. 4) with automatic transmission (a/t) vehicle, disconnect addi- tional two fluid hoses from radiator. Place some container under radiator to receive a/t fluid which will ...
Page 592
Engine cooling 6b-15 water pump components removal 1) drain cooling system. Refer to step 6) of “cooling system flush and refill” in this section. 2) remove the radiator shroud. 3) remove radiator referring to “radiator” in this section. 4) loosen water pump drive belt tension. Then remove water pum...
Page 593
6b-16 engine cooling inspection • rotate water pump by hand to check for smooth operation. If pump does not rotate smoothly or makes an abnormal noise, replace it. Installation 1) apply sealant to water pump (1). “a” : sealant 99000-31150 sealant quantity for mating surface of water pump width “a” :...
Page 594: Required Service Material
Engine cooling 6b-17 required service material tightening torque specification material recommended suzuki product (part number) use ethylene glycol base coolant (anti-freeze / anti-corrosion coolant) – additive to engine cooling system for improving cooling efficiency and for protection against rus...
Page 595
6b-18 engine cooling.
Page 596: Section 6C
Engine fuel 6c-1 6f1 7a 7a1 7a 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 6g 6c 6k 9 10 10a 10b section 6c engine fuel contents general description ....................................... 6c-2 fuel system ................................................. 6c-2 fuel tank ...........................................
Page 597: General Description
6c-2 engine fuel general description fuel system the main components of the fuel system are fuel tank, fuel pump assembly with fuel filter and fuel level gauge and fuel cut valve, fuel feed line, fuel return line and fuel vapor line. For the details of fuel flow and fuel vapor flow, refer to “fuel d...
Page 598
Engine fuel 6c-3 fuel pump assembly the fuel pump assembly (1) consists of fuel pump (6), fuel filter (2), fuel level gauge (5) and fuel cut valve (4). Fuel pump for structure and operation of the fuel pump, refer to “fuel deliv- ery system” in section 6e. Fuel cut valve the fuel cut valve consists ...
Page 599: On-Vehicle Service
6c-4 engine fuel on-vehicle service before work, refer to “precaution on fuel system service” in sec- tion 6. Fuel lines due to the fact that fuel feed line is under high pressure, use spe- cial care when servicing it. Inspection visually inspect fuel lines for evidence of fuel leakage, hose crack a...
Page 600
Engine fuel 6c-5 4) insert hose of a hand operated pump into fuel filler hose (1) and drain fuel in space “a” in the figure (drain fuel through it till fuel stops). 5) hoist vehicle. 6) remove exhaust center pipe referring to “components” in section 6k and rear propeller shaft referring to “propelle...
Page 601
6c-6 engine fuel 12) remove fuel tank (1) from vehicle. Remove fuel tank protec- tor (3) and inlet valve (2) as necessary. Fuel tank purging procedure the following procedure is used for purging the fuel tank. 1) after removing fuel tank, remove all hoses and fuel pump assembly from fuel tank. 2) dr...
Page 602
Engine fuel 6c-7 installation 1) install fuel pump (1) assembly to fuel tank. Refer to “fuel pump assembly” in this section. Install protector to fuel tank. 2) install inlet valve to fuel tank. If deformed or damaged in any other way, replace with a new one. 3) connect fuel filler and breather hoses...
Page 603
6c-8 engine fuel inspection check fuel pump assembly for damage. Check fuel suction filter (1) for evidence of dirt and contamination. If present, replace or clean and check for presence of dirt in fuel tank. For inspection of fuel pump itself, refer to “table b – 3 fuel pres- sure check” in section...
Page 604
Engine fuel 6c-9 installation 1) clean mating surfaces of fuel pump assembly and fuel tank. 2) install new gasket (2) and plate (3) to fuel pump assembly (1) then install fuel pump assembly to fuel tank. Tightening torque fuel pump assembly bolts (a) : 10 n·m (1.0 kg-m, 7.5 lb-ft) 3) connect wire ha...
Page 605: Special Tool
6c-10 engine fuel tightening torque specification special tool fastening part tightening torque n•m kg-m lb-ft fuel pump assembly bolt 10 1.0 7.5 09919-47020 quick joint remover.
Page 606: Section 6E
Engine and emission control system 6e-1 6f1 6f2 6g 7c1 7d 7e 7a 7a1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 6h 6e 10 10a 10b section 6e engine and emission control system contents general description ....................................... 6e-3 air intake system ......................................... 6e-5 f...
Page 607
6e-2 engine and emission control system egr system (if equipped)...................... 6e-38 evaporative emission (evap) control system.................................................... 6e-39 pcv system ........................................... 6e-41 special tools ..................................
Page 608: General Description
Engine and emission control system 6e-3 general description the engine and emission control system is divided into 4 major sub-systems: air intake system, fuel delivery system, electronic control system and emission control system. Air intake system includes air cleaner, throttle body, iac valve and...
Page 609
6e-4 engine and emission control system.
Page 610
Engine and emission control system 6e-5 air intake system the main components of the air intake system are air cleaner (1), air cleaner outlet hose (2), throttle body (3), idle air control valve (4) and intake manifold (5). The air (by the amount corresponding to the throttle valve (6) opening and e...
Page 611
6e-6 engine and emission control system fuel delivery system the fuel delivery system consists of the fuel tank (1), fuel pump (2), fuel filter (3), fuel pressure regulator (11), delivery pipe (9) and fuel injectors (10). The fuel in the fuel tank is pumped up by the fuel pump, filtered by the fuel ...
Page 612
Engine and emission control system 6e-7 electronic control system the electronic control system consists of 1) various sensors which detect the state of engine and driving condi- tions, 2) ecm which controls various devices according to the signals from the sensors and 3) various controlled devices....
Page 613
6e-8 engine and emission control system engine & emission control input / output table input output electric control device diagnosis switch terminal (vehicle without immobilizer indicator lamp) barometric pressure sensor (vehicle with immobilizer indicator lamp) stop lamp switch starter switch igni...
Page 614
Engine and emission control system 6e-9 ecm input / output circuit diagram for type a (see note) note: type a is other than follows. Type b is left hand steering vehicle equipped with fasten seat belt light and egr valve or right hand steering vehicle equipped with fasten seat belt light and immobil...
Page 615
6e-10 engine and emission control system 1. Ckp sensor 20. Power steering pressure switch (if equipped) 39. Ignition coil assembly (for no.1 and no.4 spark plugs) 2. Cmp sensor 21. A/c switch 40. Ignition coil assembly (for no.2 and no.3 spark plugs) 3. Vss 22. A/c refrigerant pressure switch (if eq...
Page 616
Engine and emission control system 6e-11 for type b (see note) note: see note in “ecm input / output circuit diagram” for applicable model..
Page 617
6e-12 engine and emission control system 1. Ckp sensor 20. Power steering pressure switch (if equipped) 39. Ignition coil assembly (for no.1 and no.4 spark plugs) 2. Cmp sensor 21. A/c switch 40. Ignition coil assembly (for no.2 and no.3 spark plugs) 3. Vss 22. A/c refrigerant pressure switch (if eq...
Page 618
Engine and emission control system 6e-13 ecm terminal arrangement table for type a (see note) connec- tor terminal wire color circuit connec- tor terminal wire color circuit e19 1 b ground for ecm e18 7 w backup power source 2 b/r ground for drive circuit 8 r/g immobilizer indicator lamp (if equippe...
Page 619
6e-14 engine and emission control system for type b (see note) connec- tor terminal wire color circuit connec- tor terminal wire color circuit e19 1 b ground for ecm e18 7 w backup power source 2 b/r ground for drive circuit 8 r/g immobilizer indicator lamp (if equipped) 3 b/r ground for drive circu...
Page 620: On-Vehicle Service
Engine and emission control system 6e-15 on-vehicle service accelerator cable adjustment 1) with throttle valve closed, check accelerator pedal play which should be within following specification. If measured value is out of specification, adjust it to specifi- cation with cable adjusting nut (1). A...
Page 621
6e-16 engine and emission control system 1) connect suzuki scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off, if it is available. 2) warm up engine to normal operating temperature. 3) check engine idle speed and “iac duty” as follows: a) when using suzuki scan tool: i) select “data list” mode on scan tool t...
Page 622
Engine and emission control system 6e-17 idle mixture inspection / adjustment (vehicle without heated oxygen sensor) all vehicles not equipped with heated oxygen sensor are shipped with their co % factory adjusted as follows. Engine idle mixture (co %) 0.5 – 1.5 % at specified idle speed idle mixtur...
Page 623
6e-18 engine and emission control system air intake system throttle body on-vehicle inspection • check that throttle valve lever (1) moves smoothly. Removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) drain cooling system. 3) disconnect accelerator cable (1) from throttle valve lever. 1. Throttle bo...
Page 624
Engine and emission control system 6e-19 4) disconnect air cleaner outlet no.2 hose (1) from throttle body. 5) disconnect electric connector from tp sensor (1) and iac valve (2). 6) remove throttle body from intake manifold. 7) disconnect engine coolant hoses from throttle body. Disassembly 1) remov...
Page 625
6e-20 engine and emission control system installation 1) clean mating surfaces and install throttle body gasket to intake manifold. Use new gasket. 2) connect engine coolant hoses. 3) install throttle body (1) to intake manifold. 4) connect connectors to tp sensor (2) and iac valve (3) securely. 5) ...
Page 626
Engine and emission control system 6e-21 idle air control valve (iac valve) removal 1) remove throttle body from intake manifold referring to “throttle body” in this section for removal. 2) remove iac valve from throttle body. Inspection 1) connect each connector to iac valve (1), tp sensor and iat ...
Page 627
6e-22 engine and emission control system fuel delivery system fuel pressure inspection 1) relieve fuel pressure in fuel feed line referring to “fuel pres- sure relief procedure” in section 6. 2) disconnect fuel feed hose from fuel delivery pipe. 3) connect special tools and hose between fuel deliver...
Page 628
Engine and emission control system 6e-23 6) start engine and warm it up to normal operating tempera- ture. 7) measure fuel pressure at idling. If measured pressure doesn’t satisfy specification, refer to “diagnostic flow table b-3” in section 6 and check each possibly defective part. Replace if foun...
Page 629
6e-24 engine and emission control system 3) fuel pressure should be felt at fuel feed hose (1) for 2 sec- onds after ignition switch on. If fuel pressure is not felt, advance to “diagnostic flow table b-3” in section 6. Removal remove fuel tank from body according to procedure described in “fuel tan...
Page 630
Engine and emission control system 6e-25 installation for installation, reverse removal procedure and note following precautions. • use new o-ring (1). • apply thin coat of gasoline to o-ring to facilitate installation. • tighten fuel pressure regulator bolts to specified torque. Tightening torque f...
Page 631
6e-26 engine and emission control system removal 1) relieve fuel pressure according to procedure described in “fuel pressure relief procedure” in section 6. 2) disconnect battery negative cable at battery. 3) disconnect fuel injector couplers and release wire harness from clamps. 4) remove clamp bol...
Page 632
Engine and emission control system 6e-27 5) put graduated cylinder under injector as shown. 6) operate fuel pump and apply fuel pressure to injector as fol- lows: a) when using suzuki scan tool : i) connect suzuki scan tool to dlc with ignition switch off. Ii) turn ignition switch on, clear dtc and ...
Page 633
6e-28 engine and emission control system installation for installation, reverse removal procedure and note following precautions. • replace injector o-ring (1) with new one using care not to damage it. • check if cushion (2) is scored or damaged. If it is, replace with new one. • apply thin coat of ...
Page 634
Engine and emission control system 6e-29 electronic control system engine control module (ecm) removal 1) disconnect battery negative cable at battery. 2) disable air bag system, refer to “disabling air bag system” in section 10b if equipped. 3) remove glove box. 4) disconnect ecm (1) and tcm (3) (i...
Page 635
6e-30 engine and emission control system throttle position sensor (tp sensor) inspection 1) disconnect negative cable at battery and connector from tp sensor. 2) using ohmmeter, check resistance between terminals under each condition given in table below. If check result is not satisfactory, replace...
Page 636
Engine and emission control system 6e-31 intake air temperature sensor (iat sensor) removal 1) disconnect battery negative cable at battery. 2) disconnect connector from iat sensor (1). 3) remove iat sensor (1) from air cleaner case (2). Inspection immerse temperature sensing part of iat sensor in w...
Page 637
6e-32 engine and emission control system engine coolant temperature sensor (ect sensor) removal 1) disconnect battery negative cable at battery. 2) drain coolant referring to step 6) of “cooling system flush and refill” in section 6b. 3) disconnect connector from ect sensor. 4) remove ect sensor (1)...
Page 638
Engine and emission control system 6e-33 • tighten ect sensor (1) to specified torque. Tightening torque ect sensor (a) : 15 n·m (1.5 kg-m, 11.5 lb-ft) • connect connector to ect sensor (1) securely. • refill coolant referring to “cooling system flush and refill” in section 6b. Heated oxygen sensor ...
Page 639
6e-34 engine and emission control system 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) for sensor-1, remove exhaust manifold cover (1) and dis- connect connector of heated oxygen sensor and release its wire harness from clamps. 3) for sensor-2, disconnect connector of heated oxygen sensor and release ...
Page 640
Engine and emission control system 6e-35 crankshaft position sensor inspection check crankshaft position sensor referring to step 2 and 6 of “dtc p0335 (no.23) flow table” in section 6. If malfunction is found, replace. Removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) remove generator drive belt,...
Page 641
6e-36 engine and emission control system vehicle speed sensor (vss) inspection check vehicle speed sensor referring to step 7 of “dtc p0500 (no.16) flow table” in section 6. If malfunction is found, replace. Fuel level sensor (gauge) inspection refer to “fuel meter / fuel gauge unit” in section 8. R...
Page 642
Engine and emission control system 6e-37 fuel cut operation inspection 1) warm up engine to normal operating temperature. 2) while listening to sound of injector (1) by using sound scope (2) or such, increase engine speed to higher than 3,000 r/ min. 3) check to make sure that sound to indicate oper...
Page 643
6e-38 engine and emission control system 2) connect battery (3) to a/c condenser fan motor coupler (2) as shown in figure, then check that the a/c condenser fan motor (1) operates smoothly. If a/c condenser fan motor does not operate smoothly, replace motor. Reference current data of a/c condenser f...
Page 644
Engine and emission control system 6e-39 removal 1) disconnect negative cable at battery. 2) disconnect egr valve connector. 3) remove egr pipe. 4) remove egr valve and gasket from cylinder head. Inspection 1) check resistance between following terminals of egr valve (1) in each pair. If found fault...
Page 645
6e-40 engine and emission control system 1) disconnect purge hose (1) from evap canister. 2) place finger against the end of disconnected hose and check that vacuum is not felt there when engine is cool and running at idle speed. 3) connect purge hose to evap canister and warm up engine to normal op...
Page 646
Engine and emission control system 6e-41 evap canister inspection 1) check outside of evap canister visually. 2) disconnect vacuum hoses from evap canister. 3) check that there should be no restriction of flow through purge pipe (1) and air pipe (2) when air is blown (4) into tank pipe (3). If any f...
Page 647: Special Tools
6e-42 engine and emission control system 4) after checking vacuum, stop engine and remove pcv valve (1). Shake valve and listen for the rattle of check needle inside the valve. If valve does not the rattle, replace valve. 5) after checking, remove plug and install pcv valve (1). Special tools 09912-...
Page 648
Engine and emission control system 6e-43 tightening torque specifications 09931-76030 16/14 pin dlc cable tech 2 kit (suzuki scan tool) (see note “c”.) note: • “a”: this kit includes the following items. 1. Tool body & washer, 2. Body plug, 3. Body attachment-1, 4. Holder, 5. Return hose & clamp, 6....
Page 649
6e-44 engine and emission control system.
Page 650: Section 6F
Ignition system (electronic ignition system) 6f-1 6g 6f2 6g 6h 7d 7e 7f 7a1 7a1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 6k 6f 7a 10 10a 10b section 6f ignition system (electronic ignition system) contents general description ........................................ 6f-2 diagnosis ......................................
Page 651: General Description
6f-2 ignition system (electronic ignition system) general description the ignition system is an electronic (distributorless) ignition system. It consists of the parts as described below and has an electronic ignition control system. • ecm it detects the engine and vehicle conditions through the sign...
Page 652: Diagnosis
Ignition system (electronic ignition system 6f-3 system wiring diagram diagnosis 1. Ignition switch 7. No.1 spark plug 2. Main relay 8. No.2 spark plug 3. Ignition coil assembly for no.1 and no.4 spark plugs 9. No.3 spark plug 4. Ignition coil assembly for no.2 and no.3 spark plugs 10. No.4 spark pl...
Page 653
6f-4 ignition system (electronic ignition system) ignition system diagnostic flow table step action yes no 1 was “engine diagnostic flow table” in section 6 per- formed? Go to step 2. Go to “engine diag. Flow table” in section 6. 2 ignition spark test 1) check all spark plugs for condition and type ...
Page 654: On-Vehicle Service
Ignition system (electronic ignition system 6f-5 on-vehicle service ignition spark test 1) disconnect all injector connectors (1) from injectors. 2) remove cylinder head upper cover. 3) remove spark plug and check it for condition and type refer- ring to “spark plugs” in this section. 4) if ok, conn...
Page 655
6f-6 ignition system (electronic ignition system) 5) install high-tension cords (2) to spark plugs and ignition coil assemblies (1) while gripping each cap. Spark plugs 1) pull out high-tension cords by gripping their caps and then remove ignition coil assemblies referring to “ignition coil assembly...
Page 656
Ignition system (electronic ignition system 6f-7 4) if any abnormality is found, adjust air gap, clean with spark plug cleaner or replace them with specified new plugs. For iridium/platinum spark plugs, replace them with new plugs. Spark plug air gap “a” 1.0 – 1.1 mm (0.040 – 0.043 in.) spark plug t...
Page 657
6f-8 ignition system (electronic ignition system) 6) measure resistance between terminals as follows by using analog type ohmmeter. If check result is not satisfactory, replace ignition coil assem- bly. Secondary coil resistance “a” – “b” : 7.5 – 14 k Ω (at 20°c, 68°f) 7) install ignition coil assem...
Page 658
Ignition system (electronic ignition system 6f-9 5) fix ignition timing to initial one as follows. A) when using suzuki scan tool: select “misc” mode on suzuki scan tool and fix ignition timing to initial one. B) without using suzuki scan tool: (vehicle without immobi- lizer indicator lamp) disconne...
Page 659: Special Tools
6f-10 ignition system (electronic ignition system) special tools tightening torque specification 09931-76011 09931-76030 tech 1a kit (suzuki scan tool) (see note “a”.) mass storage cartridge for tech 1a 16/14 pin dlc adapter for tech 1a tech 2 kit (suzuki scan tool) (see note “b”. ) note: • “a” : th...
Page 660: Section 6G
Cranking system 6g-1 6f1 6f2 6h 7c1 7d 7e 7c1 7b1 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 6g 7a1 10a 10b section 6g cranking system contents general description ....................................... 6g-2 cranking circuit............................................ 6g-2 diagnosis .................................
Page 661: General Description
6g-2 cranking system general description cranking circuit diagnosis diagnosis table possible symptoms due to starting system trouble would be as follows: • starting motor does not run (or runs slowly) • starting motor runs but fails to crank engine • abnormal noise is heard proper diagnosis must be ...
Page 662
Cranking system 6g-3 condition possible cause correction motor not running (no operating sound of magnetic switch) shift lever switch is not in p or n, or not adjusted (a/t) shift in p or n, or adjust switch. Battery run down recharge battery. Battery voltage too low due to battery deteriora- tion r...
Page 663
6g-4 cranking system performance test pull-in test connect battery to magnetic switch as shown. Check that plunger and pinion move outward. If plunger and pinion don’t move, replace magnetic switch. Hold-in test while connected as above with plunger out, disconnect negative lead from terminal “m”. C...
Page 664: On-Vehicle Service
Cranking system 6g-5 no-load performance test connect battery and ammeter to starter as shown. Check that starter rotates smoothly and steadily with pinion mov- ing out. Check that ammeter indicates specified current. Specified current (no-load performance test) : 90 a max. At 11 v on-vehicle servic...
Page 665
6g-6 cranking system disassembly and reassembly note: • make sure to apply grease before assembly, where are indicated “a” in the figure below. • spare parts have been lubricated. 1. Front housing 6. Over-running clutch 11. Magnetic switch 16. Packing 21. Rear bracket 2. Bush 7. Lever 12. Ball 17. Y...
Page 666: Specifications
Cranking system 6g-7 specifications voltage 12 volts output 0.9 kw 1.2 kw rating 30 seconds direction of rotation clockwise as viewed from pinion side brush length 12.3 mm (0.48 in.) 12.3 mm (0.48 in.) number of pinion teeth 8 performance condition guarantee around at 20° c (68 °f) no load character...
Page 667
6g-8 cranking system.
Page 668: Section 6H
Charging system 6h-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6k 7d 7e 7f 7c1 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 7a 6h 7b1 10b section 6h charging system contents general description ....................................... 6h-2 battery .......................................................... 6h-2 generator ................................
Page 669: General Description
6h-2 charging system general description battery the battery has three major functions in the electrical system. • it is a source of electrical energy for cranking the engine. • it acts as a voltage stabilizer for the electrical system. • it can, for a limited time, provide energy when the electrica...
Page 670
Charging system 6h-3 built-in indicator (if equipped) the battery has a built-in temperature compensated indicator in the top of the battery. This indicator is to be used with the follow- ing diagnostic procedure. When checking the indicator, make sure that the battery has a clean top. A light may b...
Page 671
6h-4 charging system when keeping battery on vehicle over a long period of time, follow instructions given below. • weekly, start the engine and run it until it reaches normal operating temperature with engine speed of 2,000 to 3,000 rpm. Make sure all electric switches are off before storing the ve...
Page 672
Charging system 6h-5 1. Generator with regulator assembly 3. Stator coil 5. Field coil (rotor coil) 7. Main switch 2. I.C. Regulator 4. Diode 6. Charge indicator light 8. Battery 1. Pulley 5. Stator core 9. Front housing ig: ignition terminal 2. Pulley nut 6. Field coil 10. Rear housing l: lamp term...
Page 673: Diagnosis
6h-6 charging system diagnosis battery common causes of failure a battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however, with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If the battery performs satisfactorily during test but fails to operate properly for no appar- ent reason, the followings ...
Page 674
Charging system 6h-7 how to use the temperature-corrected state-of-charge graph suppose your s.G. Reading is 1.28 and the battery temperature is –5 °c (23 °f). Locate the intersection of the –5 °c line and the 1.28 s.G. Line. The intersection is within the “a” zone (shaded area in the graph) and tha...
Page 675
6h-8 charging system undercharged battery this condition, as evidenced by slow cranking or indicator clear with red dot can be caused by one or more of the following condi- tions even though indicator lamp may be operating normal. Following procedure also applies to cars with voltmeter and ammeter. ...
Page 676: On-Vehicle Service
Charging system 6h-9 2) ground f terminal and start engine, then measure voltage at b terminal as shown in left figure. • voltage is higher than standard value it is considered that generator itself is good but ic regulator has been damaged, replace ic regulator. • voltage is lower than standard val...
Page 677
6h-10 charging system 1) set parking brake and place automatic transmission in park (neutral on manual transmission). Turn off ignition, turn off lights and all other electrical loads. 2) check electrolyte level. If it is below low level line, add dis- tilled water. 3) attach end of one jumper cable...
Page 678
Charging system 6h-11 dismounting 1) disconnect negative cable (3). 2) disconnect positive cable (2). 3) remove retainer (5). 4) remove battery (1). Handling when handling battery, following safety precautions should be followed: • hydrogen gas is produced by battery. A flame or spark near battery m...
Page 679: Unit Repair Overhaul
6h-12 charging system unit repair overhaul generator dismounting 1) disconnect negative (–) cable (2) at battery (1). 2) remove bolts (2) and then canister (1) together with its bracket. 3) disconnect “b” terminal wire (3) and coupler (2) from gener- ator (1). 4) remove generator belt. Refer to “wat...
Page 680
Charging system 6h-13 remounting 1) mount generator on the generator bracket. 2) tighten generator bolts. Tightening torque generator pivot bolt (a) : 23 n·m (2.3 kg-m, 16.5 lb-ft) (b) : 50 n·m (5.0 kg-m, 36.0 lb-ft) 3) install generator (cooling fan) belt. Refer to “water pump belt and cooling fan”...
Page 681
6h-14 charging system inspection rotor 1) using ohmmeter, check for continuity between slip rings of rotor (1). If there is no continuity, replace rotor. Standard resistance between slip rings of rotor 1.8 – 2.1 Ω Ω Ω Ω 2) using ohmmeter, check that there is no continuity between slip ring and rotor...
Page 682
Charging system 6h-15 2) using ohmmeter, check that there is no continuity between coil leads (2) and stator core. If there is continuity, replace stator (1). Brush and brush holder check each brush for wear by measuring its length. If brush is found worn down to service limit, replace brush. Brush ...
Page 683
6h-16 charging system drive end bearing check that the bearing is not rough or worn. End housing bearing check that the bearing is not rough or worn. When removal is necessary, use bearing puller to remove end housing bearing (1). Replace brush 1) unsolder and remove the brush and spring. 2) run the...
Page 684: Specifications
Charging system 6h-17 specifications battery 55b24r type 38b20r type generator tightening torque specification rated capacity 36 ah/5hr, 12 volts electrolyte 3.1 l (6.55/5.46 us/lmp pt) electrolyte s.G. 1.28 when fully charged at 20 °c (68 °f) rated capacity 28 ah/5hr, 12 volts electrolyte 2.1 l (4....
Page 685
6h-18 charging system.
Page 686: Section 6K
Exhaust system 6k-1 6f1 6f2 6g 6h 7d 7e 7f 7d 7e 7f 8a 8b 8c 8d 8e 9 7a1 6k 7c1 section 6k exhaust system contents general description ........................................6k-1 maintenance ....................................................6k-1 on-vehicle service ...................................
Page 687: On-Vehicle Service
6k-2 exhaust system on-vehicle service components exhaust manifold removal and installation refer to “exhaust manifold” in section 6a1 for removal and installation procedures of exhaust manifold. Inspection check seals for deterioration or damage. Exhaust pipe removal and installation for replacemen...