- DL manuals
- TA
- Controller
- UVR 64
- Operation And Installation Instructions Manual
TA UVR 64 Operation And Installation Instructions Manual
Summary of UVR 64
Page 1
Uvr 64 version p5.3 en manual version 2 four - circuit universal controller operation installation instructions en.
Page 3: Informations
Informations the hydraulic diagrams of this manual are only diagrams in principle. They do not describe or replace a professional system development. There is no guarantee for function if directly cop- ied. The settings of the menu functions ex works can be restored at any time using the yellow key ...
Page 4: Table of Contents
4 table of contents safety requirements ................................................................................................................. 5 maintenance ............................................................................................................................ 5 gener...
Page 5: Safety Requirements:
5 safety requirements: all installation and wiring work on the controller must only be carried out in a zero-volts state. The opening, connection and commissioning of the device may only be carried out by competent personnel. In so doing, all local security re- quirements must be adhered to. The dev...
Page 6: Generally Applicable Rules
6 generally applicable rules for the proper use of this unit: when used for floor and wall heaters: here, a safety thermostat must be used just as with conventional heater controllers. It has to switch off the heating loop pump if there is overheating regardless of the output from the controller to ...
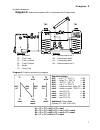
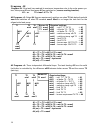
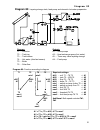
Page 7: Diagram 0
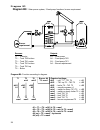
Diagram 0 7 hydraulic diagrams diagram 0: solar power system with 2 consumers and 2 feed pumps sensors outputs t1…. Collector a1…. Solar pump circuit 1 t2…. Tank 1 top a2…. Feed pump tank 2 t3…. Tank 1 bottom a3…. Feed pump tank 1 t4…. Tank 2 bottom a4…. Solar pump circuit 2 t5…. Boiler t6…. Tank 2 ...
Page 8: Diagram 0
Diagram 0 8 program 1: instead of the two solar pumps, one pump and a three-way valve are used (pump-valve system). The speed control (if activated) only operated when filling tank 1. Without a priority allocation, tank 2 is filled by priority. A1 ... Common pump a4 ... Valve (a4/s receives power wh...
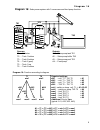
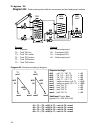
Page 9: Diagram 16
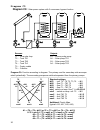
Diagram 16 9 diagram 16: solar power system with 3 consumers and feed pump function. Sensors outputs t1…. Collector a1…. Solar pump tank tk1 t2…. Tank 1 bottom a2…. Solar pump buffer tk2 t3…. Tank 2 bottom a3…. Solar pump pool tk3 t4…. Tank 3 (pool) a4…. Feed pump t5…. Tank 1 top t6…. Tank 2 bottom ...
Page 10: Diagram 16
Diagram 16 10 program 17: pump-valve system between tk1 und tk2 . Tk1 and tk2 are fed by a com- mon pump a1 and a three-way valve a2 . The speed control (if activated) only operated when filling tank 1. A1 ... Common pump a2 ... Valve (a2/s receives power when filling tank tk2 ) program 18: pump-val...
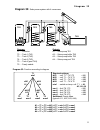
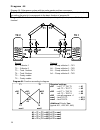
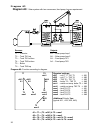
Page 11: Diagram 32
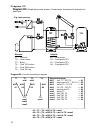
Diagram 32 11 diagram 32: solar power system with 4 consumers sensors outputs t1…. Collector a1…. Solar pump tk1 t2…. Tank 1 (tk1) a2…. Solar pump buffer tk2 t3…. Tank 2 (tk2) a3…. Solar pump buffer tk3 t4…. Tank 3 (tk3) a4…. Solar pump pool tk4 t5…. Tank 4 (pool tk4) t6…. Freely usable program 32: ...
Page 12: Diagram 32
Diagram 32 12 program 33: pump-valve system between tk1 und tk2 . Tk1 and tk2 are fed by a com- mon pump a1 and a three-way valve a2 . The speed control (if activated) only operated when filling tank 1. A1 ... Common pump a2 ... Valve (a2/s receives power when filling tank tk2 ) all programs +2: pum...
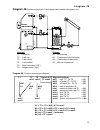
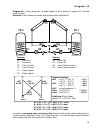
Page 13: Diagram 48
Diagram 48 13 diagram 48: burner requirement, 2 feed pumps and simple solar power unit sensors outputs t1…. Collector a1…. Solar pump t2…. Tank top a2…. Feed pump solid fuel boiler t3…. Tank center a3…. Feed pump oil/gas boiler t4…. Tank bottom a4…. Burner requirement t5…. Solid fuel boiler (“sfb”) ...
Page 14: Diagram 48
Diagram 48 14 program 49: if the tank has reached its maximum temperature due to the solar power sys- tem, solar pump a1 and feed pump a2 are switched on ( reverse cooling function ). A2 ... Or t4 > max1 & t5 all programs +2: output a4 (burner requirement) switches on when t2 falls below threshold m...
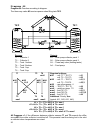
Page 15: Diagram 48
Diagram 48 15 all programs +8: this program enables controlling of two generators to each one consumer. Output a4 is switched with the difference diff4 between t2 and t3 instead of burner re- quirement. T2 is available for an additional forth generator. In this case threshold max4 oper- ates at t3 ....
Page 16: Diagram 48
Diagram 48 16 program 61: function similar to program 60, but output a3 does not only switch by the origin function, but additionally, if t5 is increasing min1 and is greater than t3 by diff3 a1 = t1 > (t4 + diff1) & t4 a2 = t5 > (t4 + diff2) & t5 > min1 & t4 a3 = t6 > (t3 + diff3) & t6 > min2 & t3 ...
Page 17: Diagram 48
Diagram 48 17 program 63: output a3 switches as described in program 61 and a4 as per program 62. A1 = t1 > (t4 + diff1) & t4 a2 = t5 > (t4 + diff2) & t5 > min1 & t4 a3 = t5 > (t3 + diff3) & t5 > min1 & t3 or t6 > (t3 + diff3) & t6 > min2 & t3 a4 = t5 > (t2 + diff4) & t5 > min1 & t2 or t6 > (t2 + di...
Page 18: Diagram 64
Diagram 64 18 t1 t2 sp 2 a4 a3 sp 1 a2 a1 t4 t3 diagram 64: solar power system with two solar panels and two consumers note: setting the time switch, the definition of the output corresponds to the actual output, but setting the priority it corresponds to the basic function of program 64. Program 64...
Page 19: Diagram 64
Diagram 64 19 t1 t2 sp 2 sp 1 t4 t3 a3 a4 a2 a1 program 66: 2 stop valves and 2 pumps instead of the 4 pumps in program 64. No feed pump function! Attention! If both valves are closed, both pumps will be switched off. Sensors outputs t1…. Collector 1 a1…. Pump tk1 t2…. Collector 2 a2…. Pump tk2 t3…....
Page 20: Diagram 64
Diagram 64 20 program 68: function according to diagram. The three-way valve a3 receives power when filling tank tk2 . Sensors outputs t1…. Collector 1 a1…. Solar pump collector panel 1 t2…. Collector 2 a2…. Solar pump collector panel 2 t3…. Tank 1 bottom a3…. Three-way valve (feeding tanks) t4…. Ta...
Page 21: Diagram 80
Diagram 80 21 diagram 80: layering storage tank, feed pump and domestic hot water preparation sensors outputs t1…. Collector a1…. Solar pumps t2…. Tank top a2…. Heat exchanger pump (hot water) t3…. Tank bottom a3…. Three-way valve layering storage t4…. Hot water (ultra-fast sensor) a4…. Feed pump t5...
Page 22: Diagram 80
Diagram 80 22 program 80: function according to diagram both solar pumps are switched on by the difference diff1 . The three-way valve a3 switches to the tank top, when t6 is increasing min2 or is greater than t2 by diff3 , but t2 has not ex- ceeded the threshold max3 . The speed controlled output a...
Page 23: Diagram 80
Diagram 80 23 program 88: a1 gets additionally the threshold min1 at t1 . The solid fuel boiler is not appli- cable. The domestic hot water preparation by a2 is also switching, if t4 is greater than t5 by diff2 . T5 could be a volume flow switch. A4 is used for burner requirement. A4 switches when t...
Page 24: Diagram 96
Diagram 96 24 diagram 96: solar power system with two consumers and two feed pump functions sensors outputs t1…. Collector a1…. Solar pump loop 1 t2…. Tank tk1 top a2…. Feed pump tk2 t3…. Tank tk1 center a3…. Feed pump tk3 t4…. Tank tk1 bottom a4…. Solar pump loop 2 t5…. Tank tk2 bottom t6…. Tank tk...
Page 25: Diagram 96
Diagram 96 25 program 97: instead of the two solar pumps , one pump and a three-way valve are used (pump-valve system). The speed control (if activated) only operated when filling loop 1 ( t3 ). A1 ... Common pump a4 ... Valve (a4/s receives power when filling tank tk1 bottom) all programs +2: inste...
Page 26: Diagram A0
Diagram a0 26 diagram a0: solar system with two consumers, feed pump, burner requirement sensors outputs t1…. Collector a1…. Solar pump loop 1 t2…. Tank tk1 top a2…. Solar pump loop 2 t3…. Tank tk1 bottom a3…. Feed pump tk1 t4…. Tank tk2 bottom a4…. Feed pump tk2 t5…. Boiler t6…. Tank tk2 top progra...
Page 27: Diagram A0
Diagram a0 27 all programs +1 : instead of the two solar pumps, one pump and a three-way valve are used (pump-valve system). The speed control (if activated) only operated when filling tk 1 ( t3 ). A1 ... Common pump a2 ... Valve (a2/s receives power when filling tank tk2 ) all programs +2: output a...
Page 28: Diagram B0
Diagram b0 28 diagram b0: solar power system, 2 feed pump functions, burner requirement sensors outputs t1…. Collector a1…. Solar pump t2…. Tank tk2 bottom a2…. Feed pump tk2 t3…. Tank tk1 center a3…. Feed pump tk1 t4…. Tank tk1 bottom a4…. Burner requirement t5…. Tank tk1 top t6…. Boiler program b0...
Page 29: Diagram B0
Diagram b0 29 all programs +1: the feeding of the hot water tank is normally done by the difference buffer t5 – hot water tank t2 . This program considers also the boiler temperature t6 . A1 = t1 > (t4 + diff1) & t4 a2 = t5 > (t2 + diff2) & t2 min1 or t6 > (t2 + diff4) & t2 min2 a3 = t6 > (t3 + diff...
Page 30: Diagram C0
Diagram c0 30 diagram c0: solar power system with 3 consumers, bypass function sensors outputs t1…. Flow solar loop a1…. Primary solar pump t2…. Tank tk1 a2…. Solar pump tk1 t3…. Tank tk2 a3…. Solar pump tk2 t4…. Tank tk3 a4…. Solar pump tk3 t5…. Freely usable t6…. Collector program c0: function acc...
Page 31: Diagram C0
Diagram c0 31 all programs +1: instead of both pumps a2 and a3 one pump a2 and a three-way valve a3 are deployed. (pump-valve system between tk1 and tk2). A2 ... Common pump or bypass valve a3 ... Valve (a3/s receives power when filling tank tk2 ( t3 )) all programs +2: instead of both pumps a2 and ...
Page 32: Diagram D0
Diagram d0 32 t1 t2 t3 t6 min1 min2 diff1 diff2 diff3 diff4 a1 a2 a3 a4 t4 t5 max1 max4 max2 max3 required settings: diff1 …coll. T1 – sp1 t4 a1 diff2 …heat source t2 – tk1 t4 a2 diff3 …boiler t3 – tk1 t4 a3 diff4 …tk1 t6 – tk2 t5 a4 min1 …heat source t2 a2 min2 …boiler t3 a3 max1 …limit tk1 t4 a1 m...
Page 33: Diagram D0
Diagram d0 33 program d1: threshold min2 is active at sensor t6 and switches output a4 . Program d2: instead of the independent temperature difference between t6 and t5 the dif- ference between t6 and t4 applies. Hence it is possible to heat one consumer from four generators. A4 = t6 > (t4 + diff4) ...
Page 34: Diagram D0
Diagram d0 34 program d5: instead of the independent temperature difference t6 – t5 the controller com- pares the sensors t6 and t3 . A1 = t1 > (t4 + diff1) & t4 a2 = t2 > (t4 + diff2) & t2 > min1 & t4 a3 = t3 > (t4 + diff3) & t4 a4 = t6 > (t3 + diff4) & t6 > min2 & t3 program d6: output a4 switches...
Page 35: Installing Instructions
Installing instructions 35 installing instructions installing the sensor(s): the sensors must be arranged and installed properly for the system to function correctly. To this end, make sure that they are completely inserted in the immersion sleeves. The threaded cable connections provided can be use...
Page 36: Installing Instructions
Installing instructions 36 hot water sensor: when the control system is used in hot water systems with an ex- ternal heat exchanger and variable-speed pump, changes in the amount of tempera- ture have to be reacted to quickly . Hence, the hot water sensor has to be put directly on the heat exchanger...
Page 37: Installing Instructions
Installing instructions 37 installing the unit caution! Always pull the mains plug before opening the case! Unscrew the 4 screws at the edges of the case. The controlling electronic is situated in the cover plate and is connected by a ribbon cable to the mains module, which is set in the basin of th...
Page 38: Installing Instructions
Installing instructions 38 w..... Root c s...... Make contact no Ö...... Break contact nc note: the system has to be grounded properly to protect it from damage due to lightening. Sensor failures due to storms and static electricity are usually the result of improper ground- ing. Data line (dl) the ...
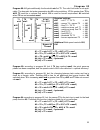
Page 39: Selector Switch
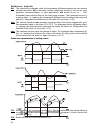
Selector switch 39 selector switch the selector switch has 16 different positions. Each position has two functions (e.G. Switch position diff2 / t2 ). The value, which is nearer to the selector switch, will be displayed without pressing of the yellow key “ eingabe ” (e.G. T2 ). By pressing the yello...
Page 40: Selector Switch
Selector switch 40 diff: the output will be released, when the temperature difference between two set sensors exceeds this value. Diff is the basic function (differential control) of this unit for most programs. Recommendation: in solar applications, diff should be set to 7 - 10k. Somewhat lower val...
Page 41: Selector Switch
Selector switch 41 uhr: setting of the actual time, important for correct function of time windows. The controller has a power reserve of approx. 24 hours, i.E. When blackout longer than 24 hours oc- curs, time must be set again. F>a: menu for assignment of each time window to one of the 4 outputs. ...
Page 42: Selector Switch
Selector switch 42 program selection (progr.), assignment of priority (vorr.) position of selector switch: prog. / vorr. Pressing the yellow „ eingabe “ key for 2 seconds causes entry or exit to/from the sub menu normal (short) pressing switches from one position to the next the value can be changed...
Page 43: Additional Functions
Additional functions 43 additional functions programming procedure („menü“) position of selector switch: vers. / menü pressing the yellow „ eingabe “ key for 2 seconds causes entry or exit to/from the sub menu normal (short) pressing switches from one position to the next the value can be changed wi...
Page 44: Additional Functions
Additional functions 44 entry to sub menu „ after-running time “ hst – hystereses : setting of the hystereses for exact balancing of the system ew = all hystereses at 3k per 64°c entry to sub menu „ hystereses “ pd1 – pump speed control for output a1 : sub menu for the speed processor for activation...
Page 45: Additional Functions
Additional functions 45 sensor type solar collectors reach standstill temperatures of 200 to 300°c. No value above 200°c is expected due to the sensor installation point and physical properties (dry steam does not conduct heat well, for instance). The standard pt1000 series sensors can be permanentl...
Page 46: Additional Functions
Additional functions 46 function control function control allows detection of sensor interruption or short circuit (error code ff1 – ff6 ), missing circulation caused by too high temperatures (>40k) between solar panel and consumer after 10 minutes pump-run (error code ff7 ) and circulation error (e...
Page 47: Additional Functions
Additional functions 47 collector excess temperature limit steam builds up when the system is not circulating. When it automatically switches on again, the pump does not have the pressure to lift the fluid level above the highest point in the system (collector feed line). If there is no circulation,...
Page 48: Additional Functions
Additional functions 48 start function (ideal for tube collectors) in the morning, solar power systems sometimes do not “start” quickly enough because the warm heat transfer medium does not reach the collector sensor. Flat collector panels and forced-circulation vacuum tubes generally lack sufficien...
Page 49: Additional Functions
Additional functions 49 priority menu when the consumers with lower priority are being filled, the unit monitors the irradiation at the radiation sensor or the collector temperature. If a radiation threshold c is reached or the collector temperature is exceeded by a value calculated from the thresho...
Page 50: Additional Functions
Additional functions 50 after-running time during the start phase, the pumps may repeatedly switch on and off for a long time, espe- cially with solar and heating systems with long hydraulic system lines. This response can be reduced by using a speed control or increasing the pump after-run time. Af...
Page 51: Additional Functions
Additional functions 51 pump speed control the pump speed control can be used to change the delivered quantity - i.E. The volume flow - of usual commercial circulating pumps in 30 steps. This provides constant levels of (differen- tial) temperatures in the system. Setting of optional sensors and tem...
Page 52: Additional Functions
Additional functions 52 differential control f = keeps the temperature constant between two sensors. Keeping the temperature difference constant between t1 and t2 , for instance, allows for “shifting” operation of the collector. If t1 drops due to lower irradiation, the difference be- tween t1 and t...
Page 53: Additional Functions
Additional functions 53 pump standstill the wave packet method (standard) allows for variations in the volume flow by a factor of 10 in 30 increments. If the flow rate is too low, flap valves may cause a system standstill. In addition, low power stages at low speeds may cause the rotors to stop. Suc...
Page 54: Additional Functions
Additional functions 54 pump speed processor a 2 – absolute value control : sensor t2 being kept constant by pump speed. The speed increases as temperature t2 does. A-2 means that speed increases as temperature t2 drops (= inverse mode) ew = a 0 (switched off) c60 – desired value for absolute value ...
Page 55: Additional Functions
Additional functions 55 di0 = no differential part, ew = 5 u6 – lower speed limit: limiting the speed for avoiding a rotor stand- still. The controller varies the speed between step 30 and down to “ u ” (e.G. 6) ew = 1 n18 – actual speed stage: if speed control is activated, „ n 2 “ shows the actual...
Page 56: Additional Functions
Additional functions 56 auxiliary output a5 the auxiliary output can be linked via “ and ” ( ) (german: und) resp. “ or ” ( ) conditions with the outputs 1 to 4 or/and the time windows 1 to 3. Inverse mode is possible ( , ): auxiliary output is linked with the switched off output resp. The not fulfi...
Page 57: Additional Functions
Additional functions 57 example: (using all linking symbols): aut – automatic mode. Three possibilities: aut – aux. Output is switched according to the links. Aus (off) – aux. Output is switched off perma- nently. Ein (on) – aux. Output is switched on permanently. Ew = aus a1o – aux. Output is linke...
Page 58
58 instructions for troubleshooting: in general, all of the settings in the menus and the terminals should be checked if there is an error. Malfunction, but “realistic” temperatures: check the program number. Check the thresholds for on/off (min/max) and the set differential temperatures (diff). Hav...
Page 59: Table of Settings:
59 table of settings: if the control system fails unexpectedly, all of the settings should be reset for initial configura- tion. In this case, problems are inevitable if all of the setting values are entered in the follow- ing table. If there are questions, this table has to be provided. Only then i...
Page 60
60 ew cs ew cs function control fco sensor t1 f1n difference temperature fdn sensor t2 f2n circulation error fc0 sensor t3 f3n value l l70 °c sensor t4 f4n sensor t5 f5n sensor t6 f6n collector excess temperature utb start function stf switch-off temperature 140°c °c start function active a 0 switch...
Page 61: Technical Data
61 technical data power supply: 230v +-10%, 50- 60hz, power input: max. 3 va fuse: 3.15 a fast acting (device & output) supply cable: 3x 1mm² h05vv-f conforming to en 60730-1 protection class: ip40 allowed ambient temperature: 0 to 45°c sensors: pt1000, accuracy between 0 and 1000°c: +-0.35k tank se...
Page 62: Eu Declaration of Conformity
Eu declaration of conformity document- nr. / date: ta17010 / 02/02/2017 company / manufacturer: technische alternative rt gmbh address: a- 3872 amaliendorf, langestraße 124 this declaration of conformity is issued under the sole responsibility of the manufacturer. Product name: uvr64 product brand: ...
Page 64: Guarantee Conditions
Guarantee conditions note: the following guarantee conditions do not in any way limit the legal right to a guaran- tee, rather expand your rights as a consumer. 1. The company technische alternative rt gmbh provides a two-year guarantee from the date of purchase by the end consumer for all the devic...