- DL manuals
- Tabor Electronics
- Portable Generator
- 5251
- User Manual
Tabor Electronics 5251 User Manual
User Manual
Model 5251
250 MS/s PXIbus
Arbitrary Waveform Generator
Publication No. 100520
Tabor Electronics Ltd.
9 Hatasia Street, Nesher, Israel 20302
TEL: (972) 4 821 3393, FAX: (972) 4 821 3388
[www.taborelec.com]
PUBLICATION DATE: May 20, 2010
REVISION: 1.0
Copyright 2002 by Tabor Electronics. All rights reserved. This book or parts thereof may not be reproduced
in any form without written permission of the publisher.
Summary of 5251
Page 1
User manual model 5251 250 ms/s pxibus arbitrary waveform generator publication no. 100520 tabor electronics ltd. 9 hatasia street, nesher, israel 20302 tel: (972) 4 821 3393, fax: (972) 4 821 3388 [www.Taborelec.Com] publication date: may 20, 2010 revision: 1.0 copyright 2002 by tabor electronics. ...
Page 2
Warranty statement products sold by tabor electronics are warranted to be free from defects in workmanship or materials. Tabor electronics will, at its option, either repair or replace any hardware products, which prove to be defective during the warranty period. You are a valued customer. Our missi...
Page 3
Declaration of conformity we: tabor electronics ltd. 9 hatasia street, tel hanan israel 36888 declare, that the 250ms/s single channel arbitrary waveform generator model 5251 meet the intent of the requirements of the electro magnetic compatibility 89/336/eec as amended by 92/31/eec, 93/68/eec, 92/2...
Page 4: Table Of Contents
I table of contents chapter title page 1 getting started .................................................................................................................. 1-1 what’s in this chapter ........................................................................................................
Page 5
Te5251 user manual ii arbitrary (user) waveforms ........................................................................................ 1-12 sequenced waveforms .............................................................................................. 1-13 modulated waveforms ....................
Page 6
Contents (continued) iii 3 arbconnection© ............................................................................................................. 3-1 what’s in this chapter? ..................................................................................................... 3-3 introduction t...
Page 7
Te5251 user manual iv typing equations ........................................................................................................ 3-47 equation samples ....................................................................................................... 3-48 combining waveforms ........
Page 8
Contents (continued) v 3d modulation programming ......................................................................................... 4-61 psk modulation programming ...................................................................................... 4-63 run mode commands ......................
Page 9
Te5251 user manual vi delayed trigger characteristics ...................................................................................... 5-14 re-trigger characteristics ................................................................................................ 5-15 trigger slope ..............
Page 10
Contents (continued) vii reference oscillators adjustments ....................................................................................... 6-7 (setup 50mhz)................................................................................................................... 6-7 setup tcxo.........
Page 11
Te5251 user manual viii setup 34 ............................................................................................................................. 6-22 setup 35 ............................................................................................................................. 6...
Page 12: List Of Tables
Ix list of tables chapter title page 4 1, model 5251 scpi commands list summary ....................................................................... 4-8 4 2, instrument control commands summary ........................................................................... 4-14 4 3, instrument co...
Page 13
Te5251 user manual x 5-14, sinewave flatness test, dds output ............................................................................... 5-11 5-15, trigger, gate, and burst characteristics ............................................................................. 5-12 5-16, trigger delay ...
Page 14: List Of Figures
Xi list of figures chapter title page 1-1, the model 5251 ................................................................................................................ 1-4 1-2, arbconnection - control panels ....................................................................................... ...
Page 15
List of figures (continued) xii 3 6, the standard waveforms panel ........................................................................................ 3-11 3 7, the arbitrary & sequence panel ........................................................................................ 3-12 3 8, th...
Page 16
Te5251 user manual xiii 3 45, selecting pulse editor options ........................................................................................ 3-60 3 46, using the pulse editor .................................................................................................... 3-62 3 47, b...
Page 17
List of figures (continued) xiv.
Page 18: Chapter 1
Chapter 1 getting started title page what’s in this chapter ........................................................................................................ 1-3 conventions used in this manual ........................................................................................ 1-3 introd...
Page 19
Te5251 user manual 1-2 fsk ............................................................................................................................1-15 psk ............................................................................................................................1-15 ask ..........
Page 20: What’S In This
1 getting started what’s in this chapter 1-3 what’s in this chapter this chapter contains general and functional description of the model 5251 arbitrary waveform generator. It also describes the front panel connectors and operational modes and provides description of all features available with the ...
Page 21: Te5251 Feature
Te5251 user manual 1-4 te5251 feature highlights • single slot pxi module • generates six types of waveforms: standard, arbitrary, sequenced, pulse, modulated and half-cycle waveforms • 250 ms/s sample clock frequency • 100 mhz sine and square waveforms • 14 digits frequency setting, limited by 1 μs...
Page 22: Arbconnection
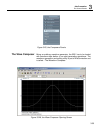
1 getting started arbconnection feature highlights 1-5 arbconnection feature highlights • three powerful tools in one software package: instrument control panel, waveform composer and fm signal composer • detailed virtual front panels control all 5251 functions and modes • wave, modulation and pulse...
Page 23
Te5251 user manual 1-6 figure 1-3, arbconnection - wave composer example figure 1-4, arbconnection – pulse composer example.
Page 24: Functional
1 getting started functional description 1-7 functional description detailed functional description is given following the general description of the features and functions available with the 5251. Output functions model 5251 is completely digital. There are no analog functions resident in its hardw...
Page 25: Supplied
Te5251 user manual 1-8 memory segmentation there is no need to use the entire memory every time an arbitrary waveform is generated. The waveform memory can be divided into smaller segments and different waveforms can be loaded into individual segment. The various segments may then be loaded into a s...
Page 26: Functional
1 getting started functional description 1-9 functional description a detailed functional description is given in the following paragraphs. The description is divided into logical groups: front panel connectors, operating modes, output type, output state and filters. Front panel connectors the 5251 ...
Page 27
Te5251 user manual 1-10 sclk in this smb connector accepts sample clock signals from an external source. Signal range is from dc to 250 mhz and amplitude level is pecl (positive ecl level). The purpose of this input is to replace the internal clock generator either for low noise applications or for ...
Page 28: Run Modes
1 getting started functional description 1-11 run modes the 5251 can be programmed to operate in one of four run modes: continuous, triggered, gated and (counted) burst. These modes are described below. Continuous mode in normal continuous mode, the selected waveform is generated continuously at the...
Page 29: Output Type
Te5251 user manual 1-12 output type the 5251 can output six types of waveforms: standard (fixed), arbitrary (user), sequenced, modulated, pulse and half-cycle waveforms. Description of the various waveform types that the instrument can generate is given below. Standard (fixed) waveforms the 5251 mus...
Page 30
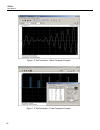
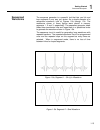
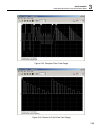
1 getting started functional description 1-13 sequenced waveforms the sequence generator is a powerful tool that lets you link and loop segments in any way you desire. As a simple example of a sequenced waveform, look at figures 1-5a through 1-5c. The waveforms shown in these figures were placed in ...
Page 31
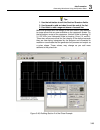
Te5251 user manual 1-14 figure 1-5c segment 3 – pulse waveform the following sequence was made of segment 2 repeated twice, segment 1 repeated four times, and segment 3 repeated two times. Figure 1- 5d. Sequenced waveforms modulated waveforms using the latest dds (direct digital synthesis) technolog...
Page 32
1 getting started functional description 1-15 fm the fm function modulates the 5251 carrier output in the frequency domain. You can modulate the output using the built-in waveforms standard waveforms, or download complex waveforms to the modulation memory. Fm can be used in continuous, triggered and...
Page 33
Te5251 user manual 1-16 ask ask (amplitude shift keying) function shifts the amplitude of the carrier frequency between two amplitude settings. The trigger input is used for programming the amplitude value. Trigger false state generates base amplitude and trigger true state generates shifted amplitu...
Page 34: Output State
1 getting started output state 1-17 output state the main outputs can be turned on or off. The internal circuit is disconnected from the output connector by a mechanical switch (relay). This feature is useful for connecting the main outputs to an analog bus. For safety reasons, when power is first a...
Page 35
Te5251 user manual 1-18 this page was intentionally left blank.
Page 36: Chapter 2
Chapter 2 configuring the instrument title page installation overview .......................................................................................................... 2-3 unpacking and initial inspection ..................................................................................... ...
Page 37
Te5251 user manual 2-2.
Page 38: Installation
2 e r r o r ! B o o k m a r k n o configuring the instrument installation overview 2-3 installation overview this chapter contains information and instructions necessary to prepare the model 5251 for operation. Details are provided for initial inspection, grounding requirements, repackaging instruct...
Page 39: Operating
Te5251 user manual 2-4 operating environment the 5251 is intended for operation within a pxi chassis chassis as a plug-in module. Ensure the pxi chassis being used to host the 5251 fully conforms to the latest pxi specifications, including 3.3v supply rail. The 5251 is intended for indoor use and sh...
Page 40: Calibration
2 e r r o r ! B o o k m a r k n o configuring the instrument calibration 2-5 caution the outer shells of the front panel terminals (output, sync out, trig in, sclk in, 10m ref in) are connected to the instrument’s chassis and therefore to the safety ground. Caution do not attempt to float the output...
Page 41: Preparation For
Te5251 user manual 2-6 note if the instrument is to be shipped to tabor electronics for calibration or repair, attach a tag to the instrument identifying the owner. Note the problem, symptoms, and service or repair desired. Record the model and serial number of the instrument. Show the returned auth...
Page 42: Installing
2 e r r o r ! B o o k m a r k n o configuring the instrument installing instrument drivers 2-7 installing instrument drivers the 5251 is a plug & play instrument, meaning that after you install it in your pxi chassis, windows will automatically detect its presence and will ask you to supply the appr...
Page 43
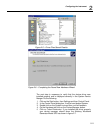
Te5251 user manual 2-8 2. Insert the 5251 board into a free pxi slot. 3. Power on your pxi chassis 4. Power on the computer. Windows should first detect the new hardware device with a “found new hardware wizard” message box. 5. Windows then displays the “found new hardware wizard” as shown in figure...
Page 44
2 e r r o r ! B o o k m a r k n o configuring the instrument 2-9 figure 2-2 – install hardware device drivers press next and you’ll now be prompted to select the location of your driver files on your computer as shown in figure 2-3. Check the “specify a location” option only. Figure 2-3 – locate d...
Page 45
Te5251 user manual 2-10 the 5251 is supplied with an installation at this time, cd. Insert this cd into your cd-rom drive. If you already have the instrument drivers installed somewhere on your computer, you can specify your custom location. Either type in the complete path or click on the browse bu...
Page 46
2 e r r o r ! B o o k m a r k n o configuring the instrument 2-11 figure 2-5 – driver files search results figure 2-6 – completing the found new hardware wizard the next step is necessary to verify that the device driver was installed properly and is displayed correctly in the system device manger...
Page 47: Installing Software
Te5251 user manual 2-12 figure 2-7 – device manager click on “x” to remove the system properties dialog box from the screen. Installing software utilities the 5251 is supplied with a cd that contains the following programs: ivi driver, arbconnection, device driver and some other utilities to aid yo...
Page 48: Installing Ivi
2 e r r o r ! B o o k m a r k n o configuring the instrument installing ivi drivers and arbconnection 2-13 before you write your own code. Arbconnection has a command editor feature that allows direct low-level programming of the 5251 using scpi commands, just as you will be using them in your progr...
Page 49
Te5251 user manual 2-14 figure 2-8 – install preparation after finishing the “preparing to install” phase, the install wizard shown in figure 2-9 will take you to the first installation step assuming that no problems were detected. Figure 2-9 – first installation step.
Page 50
2 e r r o r ! B o o k m a r k n o configuring the instrument 2-15 press next and type the customer details at the “customer i nformation” window, as shown in figure 2-10. Figure 2-10 – customer information step after typing the customer details press next and select the setup type. You can select f...
Page 51
Te5251 user manual 2-16 figure 2-11 – selecting setup type if you select the custom option, proceed to change your destination folder, as shown in figure 2-12, by pressing the browse button, select the appropriate path, press ok and then press next. Figure 2-12 – selecting destination.
Page 52
2 e r r o r ! B o o k m a r k n o configuring the instrument 2-17 the final step to complete the installation process, you’ll be prompted to restart your computer. You can select to either restart your computer immediately or do it later, but remember that the software will not function properly if ...
Page 53: Chapter 3
3-1 chapter 3 arbconnection title page what’s in this chapter? ....................................................................................................... 3-3 introduction to arbconnection ............................................................................................. 3-3 i...
Page 54
Te5251 user manual 3-2 the composers panels ............................................................................................... 3-34 the wave composer ............................................................................................... 3-35 the toolbar ...........................
Page 55: What’S In This
3 arbconnection what’s in this chapter? 3-3 what’s in this chapter? This chapter contains information how to install, invoke and use arbconnection. Introduction to arbconnection and examples how to program instrument controls and parameters and how to generate waveforms and download them to the 5251...
Page 56: Quitting
Te5251 user manual 3-4 quitting arbconnection before you start roaming through menus and editing commands, we strongly recommend that you make yourself familiar with arbconnection basics and concept. For now quit the program and spend some more time with this section of the manual. Point the mouse c...
Page 57: The Opening
3 arbconnection the opening screen 3-5 the opening screen invoke arbconnection by double clicking on the icon. If you cannot find the icon on your desktop, click on start, programs and arbconnection. The opening screen will show. If you installed the program correctly, your screen should look as sho...
Page 58: Arbconnection
Te5251 user manual 3-6 the standard windows menu bar is the top bar. It provides access to main system controls like saving files, and viewing or removal of screen images. The second bar is called link bar. It provides direct access to different instruments that are active on the active interface bu...
Page 59: The Control
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-7 the control panels the control panels look and feel just as if you would operate an instrument from its front panel. They even look like instrument front panels, so operating function and changing parameters is easy and intuitive. Let’s look at the first panel ...
Page 60: The Operation
Te5251 user manual 3-8 note after you change the displayed readout, the 5251 will be updated with the new parameter only after you press the execute button. Digital display – the display is used for displaying and reading various 5251 parameters, just as you would use it on your instrument. Note nor...
Page 61
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-9 figure 3-4, the operations panels main the main panel, as shown in figure 3-5, is the first panel you see after invoking arbconnection. Notice how buttons and led’s are grouped; this is done specifically so that common parameters are placed in functional groups...
Page 62
Te5251 user manual 3-10 if you are connected properly to a pc and arbconnection has detected your instrument, then every time you press a button, you are getting an immediate action on the 5251. It is different if you are changing parameters on the display; doing this, you’ll have to press the execu...
Page 63
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-11 standard the standard panel, as shown in figure 3-6, is accessible after you click on the standard button in the panels bar. The standard waveform panel groups allow (from left to right) adjustment of waveforms and their associated parameters. The functional g...
Page 64
Te5251 user manual 3-12 the frequency control lets you program the output frequency of the selected waveform shape. The frequency parameter may be modified when the led illuminates. You can use the dial, keyboard, or the [ ↑] [↓} keys to adjust the readout to the required setting. After you modify t...
Page 65
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-13 sclk the sclk (sample clock) group is comprised of parameters that control the sample clock frequency. The sample clock setting affects the 5251 in arbitrary mode only. The sample clock rate is programmed in units of s/s (samples per second) and will affect th...
Page 66
Te5251 user manual 3-14 using the memory partition table if you want to learn more about waveform memory and segment control, you should refer to section 2 of this manual. In general, the 5251 can generate arbitrary waveforms but, before it can generate waveforms, they must be downloaded to the inst...
Page 67
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-15 the clear all key will remove all segments from the table and will let you start designing your segment table from fresh. Click on the close to discard of the contents of the dialog box without saving your last actions and to remove the segment table from the ...
Page 68
Te5251 user manual 3-16 the state field shows the current status of the memory segment. It can be free, if no file has yet been assigned to this segment number, or mapped, if file name has been assigned to the segment but the download button has not been used yet to move the file to the 5251 memory,...
Page 69
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-17 description of the various buttons in the segment table is given below. Append – adds segment number at the end of the table insert – adds a segment above a highlighted segment line delete – removes a highlighted segment save – saves current table settings (do...
Page 70
Te5251 user manual 3-18 figure 3-10, the sequence table the sequence table is demonstrated in figure 3-10. To access the sequence table, click anywhere on the sequence table area. If it was not yet, it will turn white as opposed to the segment table area that turns gray. There are four major element...
Page 71
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-19 adv – this parameter flags the advance mode for the specific segment. This flag is active when the advance mode is stepped. When set to 0, the sequence will advance through the list automatically until a segment that is flagged 1 is encountered. When 1 is enco...
Page 72
Te5251 user manual 3-20 and its delay parameter, to the re-trigger state and its parameter and to the burst counter. To change trigger parameters, point and click on one of these led’s. The value that is associated with the lit led is displayed on the digital display. You can use the dial, keyboard,...
Page 73: The Modulation
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-21 the modulation panels the modulation functions were designed over five separate panels, as shown in figures 3-13 through 3-17. The panels are invoked by pressing the modulation header and then one of the modulation panels that appear below it (figure 3-12). Th...
Page 74
Te5251 user manual 3-22 other hand, you can select the arbitrary modulating wave option where you can use any shape however, you must load the modulating waveform from an external application, such as the fm composer in arbconnection. Click on the button next to the required modulating waveform shap...
Page 75
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-23 depth the depth parameter programs the modulation depth, or index in percent of the un-modulated cw amplitude. The depth is symmetrical about the center of the cw amplitude. Figure 3-14, the am panel sweep the sweep group contains parameters for controlling sw...
Page 76
Te5251 user manual 3-24 figure 3-15, the sweep modulation panel ask/fsk/psk the ask/fsk/psk panel contains parameters for controlling the ask, fsk and the psk functions. To select the required function, click on the appropriate button and adjust the parameters in the associated group. The various co...
Page 77
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-25 figure 3-16, the ask/fsk/psk modulation panel fsk control data the control data button in the fsk group provides access to the data string that controls the sequence of base frequency and shifted frequency. It contains a list of “0” and “1” and the output will...
Page 78
Te5251 user manual 3-26 “0/1” phase in psk, the carrier waveform (cw) has two phase settings: an initial phase which is set by the “0” phase parameter and shifted phase which is set by the “1” phase. The control data table has a list of “0” and “1” values that flag when the phase shifts from base to...
Page 79
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-27 figure 3-17, the frequency hop panel variable hold the hold parameter determines how long will certain step of frequency dwells on this specific setting before it will step to the next frequency setting. By selecting the variable hold, the hold time changes au...
Page 80: The Auxiliary
Te5251 user manual 3-28 the auxiliary panels the auxiliary tab provides access to a group of panels that control some auxiliary and utility functions. There are six panels in this group: counter/timer, which provides access to the auxiliary counter/timer function; pulse generator, which provides acc...
Page 81
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-29 figure 3-19, the counter/timer panel display the display group has controls to select the display mode and to select if the display shows measurement or gate time readings. In normal mode, the counter is armed to receive signal at the trigger input. When signa...
Page 82
Te5251 user manual 3-30 pulse generator the pulse generator panel contains controls that select the pulse function and adjusts the pulse parameters. The pulses are generated digitally suing the arbitrary waveform memory and digital computation and therefore, there are some limitations to the minimum...
Page 83
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-31 half cycle the half cycle panel contains controls that select the half cycle functions and adjust the half cycle parameters. The half cycle functions are generated with variable and controllable delay between the halves. If triggered mode, one half at a time i...
Page 84: The System Panels
Te5251 user manual 3-32 the system panels the system tab provides access to a group of panels that control some general system parameters and provides access to the calibration. There are two panels in this group: general/system, which provides access to some system commands, utilities and filters; ...
Page 85
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-33 figure 3-23, the general/filters panel clear queue – clears the error queue. The error queue can buffer up to 35 errors and then generates an error queue overflow message while ignoring new errors. This command clears the error queue and allows fresh errors to...
Page 86: The Composers
Te5251 user manual 3-34 figure 3-24, the calibration panel the composers panels the composers tab provides access to a group of composers that allow generation and editing of arbitrary waveforms, pulse shapes, arbitrary frequency modulation and 3d profiling. Without utilities such as the above, the ...
Page 87
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-35 figure 3-25, the composers panels the wave composer being an arbitrary waveform generator, the 5251 has to be loaded with waveform data before it can start generating waveforms. The waveform generation and editing utility is part of arbconnection and is called...
Page 88
Te5251 user manual 3-36 this program gives you tools to create definitions for arbitrary waveforms. It can also convert coordinates from other products, such as, oscilloscopes and use them directly as waveform data. The program is loaded with many features and options so use the following paragraphs...
Page 89
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-37 *csv (comma delimited text), *prn (space delimited text) and *.0* (lecroy binary format). The open dialog box in figure 3-31 shows the various file extensions that can be opened into the wave composer environment. The file that is opened is automatically conve...
Page 90
Te5251 user manual 3-38 edit commands the edit commands are used for manipulating the waveform that is drawn on the screen. The editing commands are explained in the following paragraphs. Autoline the autoline command lets you draw straight-line segments. To draw a line the left mouse button at the ...
Page 91
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-39 trim right the trim right command lets you trim waveforms to the right of the anchor point. This command is grayed out if the right anchor was not moved from its original right position. The waveform is trimmed and the point at the right anchor point becomes t...
Page 92
Te5251 user manual 3-40 figure 3-28, zooming in on waveform segments wave commands the wave commands let you create waveforms on the screen. The wave command has a library of 8 waveforms: sine, triangle, square, sinc, gaussian, exponent, pulse, noise and dc. Also, from the wave command, you can crea...
Page 93: The Toolbar
3 arbconnection the control panels 3-41 end point – defines where the created waveform will end. Note that as you change the end point the right anchor will automatically adjust itself to the selected end point, 499 shown in the example. Cycles – the cycles parameter defines how many sine cycles wil...
Page 94: The Waveform
Te5251 user manual 3-42 figure 3-30, the toolbar icons the waveform screen waveforms are created and edited on the waveform screen. Figure 3-35 shows an example of a waveform created using the equation editor and the anchors to limit generation of the waveform between points 100 and 900. The various...
Page 95: Generating
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-43 notice on the left top and on the right top there are two triangles pointing to the center of the screen. These are the anchors. The anchors are used as the start and end pointers where your waveform will be created. For example, if...
Page 96
Te5251 user manual 3-44 there are four sub-group parameters in the equation editor plus control buttons and equation field. These parts are described below. Anchor the anchors define start and end point of which the equation will be generated. By default the anchors are placed at the start and the e...
Page 97: Writing Equations
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-45 equation the equation group has four buttons and the equation field. You will be using the equation field for writing your equations. Equation syntax and conventions are discussed in the following paragraphs. The remove button clear...
Page 98: Equation
Te5251 user manual 3-46 equation convention the following paragraphs describe the conventions that are used for writing an equation. To avoid errors, it is extremely important that you make yourself familiar with these conventions before you plan your waveforms. Equations are written in conventional...
Page 99: Typing Equations
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-47 explore your own creativity to generate much more complicated and complex waveforms. Typing equations if you remember from your old high school studies, the simplest curve of y as a function of x is defined by the equation y=ax+b. Y...
Page 100: Equation Samples
Te5251 user manual 3-48 equation samples so far, you have learned how to create two simple waveforms: straight lines and trigonometric functions. Let’s see if we can combine these waveforms to something more interesting. Take the straight line equation and add it to the sinewave equation: amplitude(...
Page 101
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-49 figure 3-34, using the equation editor to modulate sine waveforms. In the following example, as shown in figure 3-40, 20% second harmonic distortion has been added to a standard sinewave. The original waveform had a peak-to-peak val...
Page 102
Te5251 user manual 3-50 figure 3-35, using the equation editor to add second harmonic distortion. In figure 3-41 we created 10 cycles of sinewave made to decay exponentially. The original expression for a standard sinewave is multiplied by the term e^(p/-250). Increasing the value of the divisor (20...
Page 103
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-51 figure 3-36, using the equation editor to generate exponentially decaying sinewave the last example as shown in figure 3-37 is the most complex to be discussed here. Here, 100 cycles of sinewave are amplitude modulated with 10 cycle...
Page 104: Combining
Te5251 user manual 3-52 figure 3-37, using the editor to build amplitude modulated signal with upper and lower sidebands combining waveforms the last but not least powerful feature allows you to combine waveforms which you previously stored on your hard disc. You can write mathematical expressions t...
Page 105
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-53 step 3 – write and compute the original equation: amplitude(p)= c:/sine.Wav*sin(omg*p*5)*c:/noise.Wav/10 if you did not make any mistakes, your waveform screen should look as shown in figure 3-38 figure 3-38, combining waveforms int...
Page 106
Te5251 user manual 3-54 you can check the “force pulse to one segment” option and the 5251 will do some extra “muscle flexing” to fit the pulse as required. To launch the pulse composer point and click on the pulse tab in the panels bar. Figure 3-39 shows an example of the pulse composer. The pulse ...
Page 107
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-55 file commands the file command has 4 command lines that control pulse waveform files. Also use this command to print the active waveform, or exit the pulse composer program. Description of the various commands under file is given be...
Page 108
Te5251 user manual 3-56 insert section the insert section command lets you insert a new section in between sections that were already designed. Only one new section can be inserted at the middle of the train. If an empty section already exists, the insert command will alert for an error. Delete sect...
Page 109
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-57 full train the view full train shows on the pulse screen all sections of the pulse train. Eventually, when all pulse sections have been designed, the entire pulse train as shown when the full train option has been selected will be d...
Page 110
Te5251 user manual 3-58 the pulse composer toolbar the toolbar contains icons for editing the waveform screen, icons for saving and loading waveforms, fields for selecting an active channel and more. The toolbar is shown in figure 3-42. The icons, from left to right operate the following functions: ...
Page 111
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-59 figure 3-43, complete pulse train design figure 3-44, section 5 of the pulse train design.
Page 112
Te5251 user manual 3-60 now that we somewhat understand the terms we use for the pulse design, we start with an example how to design the pulse train as shown in figure 3-43. If you already have some pulses shown on your pulse composer screen, click on new to start from a fresh page. Another step be...
Page 113
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-61 the force pulse sections to multiple segments option will place each section of the pulse train into a different memory segment and the generator will automatically be set to operate in sequenced mode. Select this option for the exa...
Page 114
Te5251 user manual 3-62 figure 3-46, using the pulse editor the pulse editor as shown in figure 3-46 has four groups: section structure, pulse train design format, section properties and control buttons. These groups are described below. Pulse train design format there are two methods (or formats) t...
Page 115
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-63 time/level points – programs pulse turning points using level and time markers. This format is a bit more complex to use however, it allows pulse design that require linear transition times. For example, if you want to draw a simple...
Page 116
Te5251 user manual 3-64 repeat – allows multiplication of pulse segments without the need to re-design repetitive parts. After you enter a repeat value, press the apply button to lock in the repeat multiplier. Duration – displays the time that will lapse from the start of the pulse section to the en...
Page 117
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-65 tips 1. Use the tab button to edit the section structure fields. 2. Use append to add an index line at the end of the list. 3. Use insert to add a segment above a focused line. Before we proceed with the design of the next section, ...
Page 118
Te5251 user manual 3-66 pulse example, section 2 the first pulse section is complete. We are ready now to start building the second section of the pulse as shown in figure 3-48. Point and click on the edit command and select the append section option. A new section number will appear but it will sho...
Page 119
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-67 figure 3-49, building section 3 of the pulse example pulse example, section 4 the third pulse section is complete. We are ready now to start building the forth section of the pulse as shown in figure 3-44. Point and click on the edi...
Page 120
Te5251 user manual 3-68 figure 3-50, building section 4 of the pulse example pulse example, section 5 the fourth pulse section is complete. We are ready now to start building the fifth and final section of the pulse as shown in figure 3- 44. Point and click on the edit command and select the append ...
Page 121
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-69 figure 3-51, building section 5 of the pulse example downloading the pulse train congratulations for coming that far. If you followed the above description how to build this pulse example, the screen should look exactly as shown in ...
Page 122
Te5251 user manual 3-70 figure 3-52, the pulse editor download summary interpreting the download summary it is very important for you to understand that when you download a pulse waveform from the pulse composer, parameters and mode of operation may change settings on your generator. The download su...
Page 123
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-71 the fm composer the fm composer looks and feels almost like the waveform composer except there is a major difference in what it does. If you look at the opening screen as shown in figure 4-53, you’ll see that the vertical axis is ma...
Page 124
Te5251 user manual 3-72 figure 3-53, the fm composer opening screen file commands the file command has 4 command lines that control waveform files. Also use this command to exit the fm composer program. Description of the various commands under file is given below. New waveform the new waveform comm...
Page 125
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-73 save waveform as… use the save waveform as… command the first time you save your waveform. It will let you select name, location and format for your waveform file. Print with this command you may print the active waveform window. Th...
Page 126
Te5251 user manual 3-74 figure 3-54, generating sine modulation using the fm composer min. Peak deviation– this parameter defines the backwards peak deviation. Note that the backwards peak deviation cannot exceed the pre-defined deviation parameter as shown on the toolbar. In case you need to exceed...
Page 127
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-75 the 3d composer the 3d composer was specifically designed for simultaneous profiling of amplitude, frequency and phase. Amplitude profiles can be designed separately for channels 1 and 2, but frequency and phase profiles are shared ...
Page 128
Te5251 user manual 3-76 the 3d composer has three main sections: shared horizontal controls, vertical controls and graphical screens. The panels on the left are used for designing the waveform parameters and the screens on the right side depict the shape of the profile. Below find a detailed descrip...
Page 129
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-77 the best idea is to let the 3d composer set up the sample clock and the number of points automatically for you however, in some cases you may fine tune your requirement by pressing the expand button. Figure 3-57 shows the expanded p...
Page 130
Te5251 user manual 3-78 the offset group controls dc offsets of the modulated waveform. Changing offset does not affect other parameters except the location of the waveform along the vertical axis. The clear design button resets the 3d composer and the reduce button closes the dialog box. Vertical c...
Page 131
3 arbconnection generating waveforms using the equation editor 3-79 graphical screens the graphical screens are shown in figure 3-59. You can not change anything on the screens however, anything that you design in the vertical controls fields will automatically be updated and displayed on the graphi...
Page 132: The Command
Te5251 user manual 3-80 figure 3-60, 3d chirp design example the command editor the command editor is an excellent tool for learning low level programming of the 5251. Invoke the command editor from the system menu at the top of the screen. Dialog box, as shown in figure 3-61 will pop up. If you pre...
Page 133: Logging Scpi
3 arbconnection logging scpi commands 3-81 figure 3-61, the command editor low-level scpi commands and queries can be directly sent to the 5251 from the command field and the instrument will respond to queries in the response field. The command editor is very useful while developing your own applica...
Page 134
Te5251 user manual 3-82 figure 3-62, log file example.
Page 135: Chapter 4
4-1 chapter 4 remote programming reference title page what’s in this chapter ...................................................................................................... 4-3 what is required ......................................................................................................
Page 136
Te5251 user manual 4-2 psk modulation programming ...................................................................................... 4-63 run mode commands ........................................................................................................4-66 auxiliary commands ...............
Page 137: What’S In This
4 remote programming reference what’s in this chapter 4-3 what’s in this chapter this chapter lists and describes the set of scpi-compatible (standard commands for programmable instruments) remote commands used to operate the 5251. To provide familiar formatting for users who have previously used th...
Page 138: Command Format
Te5251 user manual 4-4 scpi is an ascii-based instrument command language designed for test and measurement instruments. Scpi commands are based on a hierarchical structure known as a tree system. In this system, associated commands are grouped together under a common node or root, thus forming subs...
Page 139: The Min and Max
4 remote programming reference introduction to scpi 4-5 is the same as sending the following three commands: :trig:slop neg :trig:coun 10 :trig:lev -1 use the colon and semicolon to link commands from different subsystems. For example, in the following command string, an error is generated if both t...
Page 140: Commands
Te5251 user manual 4-6 commands command keyword is separated from the first parameter by a blank space. Use a semicolon ( ; ) to separate multiple commands as shown below: *rst; *stb?; *idn? Scpi parameter type the scpi language defines four different data formats to be used in program messages and ...
Page 141: Scpi Syntax and
4 remote programming reference scpi syntax and styles 4-7 command uses an arbitrary block parameter that is loaded as binary data: trac:data#564000 binary block parameters binary block parameters are used for loading segment and sequence tables into the generator's memory. Information on the binary ...
Page 143
4 remote programming reference scpi syntax and styles 4-9 table 4-1, model 5251 scpi commands list summary (continued) keyword parameter form default :ramp :delay 0 to 99.99 0 :transition [:leading] 0 to 99.99 60 :trailing 0 to 99.99 30 :sinc :ncycle 4 to 100 10 :gaussian :exponent 10 to 200 20 :exp...
Page 145
4 remote programming reference scpi syntax and styles 4-11 table 4-1, model 5251 scpi commands list summary (continued) keyword parameter form default modulated waveforms commands (continued) :fsk :frequency :shifted 10 to 100e6 100e3 :baud 1 to 10e6 10e3 :marker 1 to 4000 1 :data :ask [:amplitude] ...
Page 148: Instrument
Te5251 user manual 4-14 instrument control commands this group is used to control output channels and their respective state, amplitude and offset settings, as well as the waveform mode. You can also set the phase offset between channels and select filters to re-structure the shape of your waveform....
Page 149
4 remote programming reference instrument control commands 4-15 output:load description this command will specify the load impedance that will be applied to the 5251 output. Parameters name type default description numeric (integer only) 50 will specify the load impedance that will be applied to the...
Page 150
Te5251 user manual 4-16 description this command will program the 5251 sync position. This command is active in arbitrary (user) mode only. Parameters name range type default description 0 to 2e6-1 numeric (integer only) 0 will set the sync position in waveform points. The sync position can be progr...
Page 151
4 remote programming reference instrument control commands 4-17 parameters name type default description internal discrete int selects an internal source. The internal source could be either the standard 100ppm oscillator, or the optional 1ppm tcxo external discrete activates the external reference ...
Page 154
Te5251 user manual 4-20 parameters name type default description fixed discrete fix selects the standard waveform shapes. There is an array of waveforms that is built into the program. You can find these waveform shapes in the standard waveforms section. User discrete selects the arbitrary waveform ...
Page 155: Standard
4 remote programming reference standard waveforms control commands 4-21 standard waveforms control commands this group is used to control the standard waveforms and their respective parameters. There is an array of standard waveforms that could be used without the need to download waveform coordinat...
Page 157
4 remote programming reference standard waveforms control commands 4-23 triangle:phase(?) description this command programs start phase of the standard triangular waveform. This command has no affect on arbitrary waveforms. Parameters name range type default description 0 to 360 numeric 0 programs t...
Page 158
Te5251 user manual 4-24 pulse:width(?) description this command programs pulse high portion of the standard pulse waveform. This command has no affect on arbitrary waveforms. Parameters name range type default description 0 to 99.999 numeric 10 programs the pulse width parameter in units of percent ...
Page 159
4 remote programming reference standard waveforms control commands 4-25 ramp:delay(?) description this command programs delay of the standard ramp waveform. This command has no affect on arbitrary waveforms. Parameters name range type default description 0 to 99.99 numeric 10 programs the ramp delay...
Page 160
Te5251 user manual 4-26 sinc:ncyclen_cycles>(?) description this command programs the number of “0-crossings” of the standard sinc pulse waveform. This command has no affect on arbitrary waveforms. Parameters name range type default description 4 to 100 numeric (integer only) 10 programs the number ...
Page 161
4 remote programming reference standard waveforms control commands 4-27 dc(?) description this command programs the exponent for the standard exponential waveform. This command has no affect on arbitrary waveforms. Parameters name range type default description -5 to 5 numeric 5 programs the dc ampl...
Page 162: Arbitrary
Te5251 user manual 4-28 arbitrary waveforms control commands this group is used to control the arbitrary waveforms and their respective parameters. This will allow you to create segments and download waveforms. Using these commands you can also define segment size and delete some or all unwanted wav...
Page 163
4 remote programming reference arbitrary waveforms control commands 4-29 keyword parameter range default :trace [:data] :define , (,) 1,16 :delete [:name] 1 to 10k :all :select 1 to 10k 1 :segment [:data] trace# description this command will download waveform data to the 5251 memory. Waveform data i...
Page 164
Te5251 user manual 4-30 figure chapter 4 -1, definite length arbitrary block data format transfer of definite length arbitrary block data must terminate with the eoi bit set. This way, carriage-return (cr – 0dh) and line feed (lf – 0ah) characters can be used as waveform data points and will not cau...
Page 165
4 remote programming reference arbitrary waveforms control commands 4-31 name type description discrete contains information on the size of the binary block that contains waveform coordinates. Binary block of binary data that contains information on the waveform coordinates. Trace:define, descriptio...
Page 166
Te5251 user manual 4-32 number> 1 to 10k numeric (integer only) 1 selects the segment number of which will be deleted trace:delete:all description this command will delete all segments and will clear the entire waveform memory. This command is particularly important in case you want to de-fragment t...
Page 167
4 remote programming reference arbitrary waveforms control commands 4-33 define and download waveforms to individual segments. Using this command, segment table data is loaded to the 5251 using high-speed binary transfer in a similar way to downloading waveform data with the trace command. High-spee...
Page 168: Sequenced
Te5251 user manual 4-34 sequenced waveforms control commands this group is used to control the sequenced waveforms and their respective parameters. This will allow you to create multiple sequence table and modify segment loops and links. Also use these commands to add or delete sequences from your i...
Page 170
Te5251 user manual 4-36 1. Each channel has its own sequence table buffer. Therefore, make sure you selected the correct active channel (with the inst:sel command) before you download sequence table data to the generator 2. Minimum number of sequencer steps is 1; maximum number is 4096 3. The number...
Page 172
Te5251 user manual 4-38 and only a valid trigger signal will advance this step to the next step. Response the 5251 will return the auto, step, sing, or mix depending on the present sequence advance mode setting. Sequence:select(?) description this command will select an active sequence to be generat...
Page 173
4 remote programming reference sequenced waveforms control commands 4-39 sequence:define,,,, bit>(?) description this command builds a step in a sequence table. It defines all of the parameters that are associated with the sequence step such as segment number, link, loop, advance mode and sync mode....
Page 174
Te5251 user manual 4-40 sequence:delete description this command will delete a step in a specific sequence table. Before you use this step make sure your sequence number is setup correctly for this operation. Parameters name range type default description number> 1 to 4096 numeric (integer only) 1 s...
Page 175: Modulated
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-41 modulated waveforms control commands this group is used to control the modulated waveforms and their respective parameters. Note that the modulation can be turned off to create continuous carrier waveform (cw). The following mo...
Page 176
Te5251 user manual 4-42 table 4 4-6, modulated waveforms commands (continued) keyword parameter form default [:source] frequency shift keying modulation commands :fsk :frequency :shifted 10 to 100e6 100e3 :baud 1 to 10e6 10e3 :marker 1 to 4000 1 :data amplitude shift keying modulation commands :ask ...
Page 178
Te5251 user manual 4-44 description this command programs the cw frequency. Note that the cw waveform is sine only and its frequency setting is separate to the standard sine waveform. The cw frequency setting is valid for all modulation types. Parameters name range type default description 10 to 100...
Page 179: Fm Modulation
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-45 fm modulation programming use the following command for programming the fm parameters. Fm control is internal. There are two types of waveforms that can be used as the modulating waveforms: standard and arbitrary. The standard ...
Page 180
Te5251 user manual 4-46 fm:frequency(?) description this command will set the modulating wave frequency for the built-in standard modulating waveform library. Parameters name range type default description 10e-3 to 100e3 numeric 10e3 programs the frequency of the modulating waveform in units of hz. ...
Page 181
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-47 fm:marker(?) description this function programs marker frequency position. Fm marker can be placed inside the following range: (carrier frequency ± deviation frequency / 2). The marker pulse is output from the sync output conne...
Page 182
Te5251 user manual 4-48 4-8 shows how to prepare the 32-bit word for the fm modulating waveform. There are a number of points you should be aware of before you start preparing the data: 1. The fm function is shared by both channels 2. The number of bytes in a complete fm modulating waveform data mus...
Page 183: Am Modulation
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-49 am modulation programming use the following command for programming the am parameters. Am control is internal. The commands for programming the amplitude modulation function are described below. Note that the carrier waveform f...
Page 184
Te5251 user manual 4-50 am:depth(?) description this command will set the modulating wave frequency for the built-in standard modulating waveform library. Parameters name range type default description 0 to 100 numeric 50 programs the depth of the modulating waveform in units of percent. Response th...
Page 185: Sweep Modulation
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-51 sweep modulation programming use the following command for programming the sweep parameters. Sweep control is internal. The frequency will sweep from start to stop frequencies at an interval determined by the sweep time value a...
Page 186
Te5251 user manual 4-52 sweep:time(?) description this specifies the time that will take the 5251 to sweep from start to stop frequencies. The time does not depend on the sweep boundaries as it is automatically adjusted by the software to the required interval. At the end of the sweep cycle the outp...
Page 187
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-53 the 5251 will return lin, or log depending on the selected spacing setting. Sweep:marker(?) description this function programs marker frequency position. Sweep marker can be placed in between the start and the stop frequencies....
Page 188: Fsk Modulation
Te5251 user manual 4-54 fsk modulation programming use the following command for programming the fsk parameters. Fsk control is internal. The frequency will shift from carrier to shifted frequency setting at a rate determined by the baud value and controlled by a sequence of bits in the fsk data tab...
Page 189
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-55 fsk:frequency:marker(?) description programs where on the data stream the 5251 will generate a pulse, designated as fsk marker, or index point. The marker pulse is generated at the sync output connector. Note that if you intend...
Page 190: Ask Modulation
Te5251 user manual 4-56 ask modulation programming use the following command for programming the ask parameters. Ask control is internal. The amplitude will toggle between two amplitude settings at a rate determined by the baud value and controlled by a sequence of bits in the ask data table. The co...
Page 191: Frequency
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-57 the 5251 will return the present baud value. The returned value will be in standard scientific format (for example: 100khz would be returned as 100e3 – positive numbers are unsigned). Ask:frequency:marker(?) description program...
Page 192: Hopping
Te5251 user manual 4-58 hopping modulation programming parameters. Hop control is internal. The frequency will hop from frequency to frequency at a rate determined by the dwell time value and controlled by a sequence of frequencies in the hop data table. There are two hop modes: fixed dwell, where t...
Page 193
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-59 description this command will download the data array that will cause the instrument to hop through the frequency list. The dwell time for each frequency list item is fixed and can be programmed using the hop:dwel command. Note...
Page 194
Te5251 user manual 4-60 description programs where on the frequency list the 5251 will generate a pulse, designated as hop marker, or index point. The marker pulse is generated at the sync output connector. Parameters name range type default description 1 to 1000 numeric (integer only) 1 programs a ...
Page 195: 3D Modulation
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-61 3d modulation programming use the following command for programming the 3d modulation parameters. 3d modulation requires an external utility to download the modulation coordinates into the 3d memory location. In case you intend...
Page 196
Te5251 user manual 4-62 response the 5251 will return the present marker position. 3d:raster(?) description this command will set the sample clock frequency for the 3d modulation profiler. The 3d waveforms must be created using an external utility and downloaded to the 3d memory before this function...
Page 197: Psk Modulation
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-63 psk modulation programming use the following command for programming the psk parameters. The psk function can shift from start to shifted phase setting, within the range of 0 to 360 °, at a frequency determined by the rate valu...
Page 198
Te5251 user manual 4-64 below you can see how an psk data table and a 16psk data table are constructed. The psk data table sample below shows a list of 10 shifts. The 5251 will step through this list, outputting either start or shifted phases, depending on the data list: zero will generate start pha...
Page 199
4 remote programming reference modulated waveforms control commands 4-65 the 5251 will return the present baud value. The returned value will be in standard scientific format (for example: 100mhz would be returned as 100e-3 – positive numbers are unsigned)..
Page 200: Run Mode
Te5251 user manual 4-66 run mode commands the run mode commands group is used to synchronize device actions with external events. These commands control the trigger modes of the model 5251. The generator can be placed in triggered, gated or burst mode. Trigger source is selectable from an external s...
Page 203
4 remote programming reference run mode commands 4-69 trigger:level(?) description the trigger level command sets the threshold level at the trigger input connector. The trigger level command will affect the generator only after it has been programmed to operate in interrupted run mode. Modify the 5...
Page 206: Auxiliary
Te5251 user manual 4-72 auxiliary commands the auxiliary commands control auxiliary functions that are not directly related to the main function of the arbitrary waveform generator however, constitute an important part of operating the 5251. These commands can transform the 5251 into a stand-alone p...
Page 207: Digital Pulse
4 remote programming reference auxiliary commands 4-73 digital pulse programming use the following command for programming the pulse parameters. The pulse is created digitally however, it closely simulates an analog pulse generator so pulse parameters are programmed just as they would be programmed ...
Page 208
Te5251 user manual 4-74 auxiliary:pulse:double:delay(?) description this command will program the delay between two adjacent pulses when the double mode is selected. Otherwise, the double pulse delay has no effect on the pulse structure. Parameters name range type default description 0 to 1e3 numeri...
Page 209
4 remote programming reference auxiliary commands 4-75 name range type default description -4.950 to 5 numeric 5 will set the pulse high level in units of volts. Note that the high level setting must be higher than the low level setting. Also note that high to low level value must be equal or larger...
Page 211
4 remote programming reference auxiliary commands 4-77 response the 5251 will return the present rise time value in units of seconds. Auxiliary:pulse:transition:trailing(?) description this command will program the interval it will take the pulse to transition from its high to low level settings. Th...
Page 212: Counter/timer
Te5251 user manual 4-78 counter/timer programming use the following command for programming the counter/timer measuring function and other parameters. The counter/timer function is created digitally however, it closely simulates a stand- alone counter/timer so its functions are programmed just as th...
Page 213
4 remote programming reference auxiliary commands 4-79 proportional to the gating time, the number of displayed digits decreases proportionally to the pulse width of the signal. The best resolution in period measurements is 10 ns. Gtotalize discrete will select the gated totalize measurement functio...
Page 214
Te5251 user manual 4-80 description this command will program the gate time interval for frequency, period averaged and totalize in gated mode. Measurements will be taken only after the input has been armed and valid signal available at the input connector. Notice however, that the gate time interna...
Page 215: Half Cycle
4 remote programming reference auxiliary commands 4-81 half cycle programming use the following command for programming the half cycle functions and their associated parameters. There are three half cycle functions: sine, triangle and square. The specifications and limitations of the half cycle func...
Page 216
Te5251 user manual 4-82 name range type default description 10e-3 to 1e6 numeric 1e6 will set the frequency of the half cycle waveform in units of hz. This parameter does not affect the frequency of other waveform functions. Response the 5251 will return the present half cycle frequency value. The r...
Page 217: System Commands
4 remote programming reference auxiliary commands 4-83 system commands the system-related commands are not related directly to waveform generation but are an important part of operating the 5251. These commands can reset or test the instrument, or query the instrument for system information. Table 4...
Page 218
Te5251 user manual 4-84 system:information:model? Description query only. This query will interrogate the instrument for its model number in a format similar to the following: 5251. The model number is programmed to a secure location in the flash memory and cannot be modified by the user. Response t...
Page 219: Ieee-Std-488.2
4 remote programming reference ieee-std-488.2 common commands and queries 4-85 ieee-std-488.2 common commands and queries since most instruments and devices in an ate system use similar commands that perform similar functions, the ieee-std-488.2 document has specified a common set of commands and qu...
Page 220
Te5251 user manual 4-86 clear the error queue. Use the following command to read the error queue: system:error? Errors have the following format (the error string may contain up to 80 characters): -102,"syntax error" a complete listing of the errors that can be detected by the generator is given bel...
Page 221
4 remote programming reference error messages 4-87 waveform, or activating the built-in sine waveform when one of the 5251 filters is turned on. Corrective action: if in sine, select another function and activate the filter(s). 4. Activating burst mode when the 5251 is set to sequence mode, or activ...
Page 222
Te5251 user manual 4-88 this page was left intentionally blank.
Page 223: Chapter 5
5-1 chapter 5 performance checks title page what’s in this chapter ........................................................................................................... 5-3 performance checks .........................................................................................................
Page 224
Te5251 user manual 5-2 sequence operation ......................................................................................................... 5-17 automatic advance ....................................................................................................... 5-17 step advance ..........
Page 225: What’S In This
5 performance checks what’s in this chapter 5-3 what’s in this chapter this chapter provides performance tests necessary to troubleshoot the model 5251 pxibus universal waveform generator. Warning the procedures described in this section are for use only by qualified service personnel. Many of the s...
Page 226: Warm-Up Period
Te5251 user manual 5-4 warm-up period most equipment is subject to a small amount of drift when it is first turned on. To ensure accuracy, turn on the power to the model 5251 and allow it to warm-up for at least 30 minutes before beginning the performance test procedure. Initial instrument setting t...
Page 227: Frequency
5 performance checks test procedures 5-5 frequency accuracy frequency accuracy checks tests the accuracy of the internal oscillator. The internal oscillator determines the accuracy and stability of the entire generator. Frequency accuracy, internal reference equipment: counter preparation: 1. Config...
Page 228: Amplitude
Te5251 user manual 5-6 table chapter 5-3, frequency accuracy using external 10 mhz reference 5251 setting error limits counter reading pass fail 10.000000000 mhz ±1 hz 50.000000000 mhz ±5 hz amplitude accuracy amplitude accuracy checks tests the accuracy of the output amplifier and attenuators. Each...
Page 229: Offset Accuracy
5 performance checks test procedures 5-7 waveform: modulated modulation: off cw frequency: 1 khz output: on amplitude: as specified in table 5 test procedure: 1. Perform amplitude accuracy tests using table 5 table chapter 5-5, amplitude accuracy, dds output 5251 amplitude setting error limits dmm r...
Page 230
Te5251 user manual 5-8 table chapter 5-6, offset accuracy, dac output 5251 offset setting error limits dmm reading pass fail +4.000 v 4.000 v ±45 mv +1.500 v 1.500 v ±20 mv 0.000 v 0 v ±20 mv -1.500 v -1.500 v ±20 mv -4.000 v -4.000 v ±45 mv 1. Modify 5251 amplitude setting to 6 v and offset setting...
Page 231: Squarewave
5 performance checks test procedures 5-9 squarewave characteristics this tests the characteristics of the square waveform. It includes transition times, ringing and overshoot. Squarewave checks equipment: oscilloscope, 50 Ω, 20 db attenuator feed through preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope fo...
Page 232
Te5251 user manual 5-10 2. Using arbconnection prepare and download the following waveform: wavelength: as required by the test waveform: sinewave test procedure: 1. Perform sinewave distortion tests using table 10 table chapter 5-10, sinewave distortion, dac output tests 5251 sclk sinewave 5251 rea...
Page 233
5 performance checks test procedures 5-11 sinewave spectral purity, dds output equipment: spectrum analyzer preparation: 1. Connect 5251 output to the spectrum analyzer input. Use 50 Ω and 20 db feedthrough termination at the spectrum analyzer input 2. Configure the 5251 as follows: waveform: modula...
Page 234: Trigger Operation
Te5251 user manual 5-12 table chapter 5-13, sinewave flatness, dac output test 5251 sine frequency error limits oscilloscope reading pass fail 1 mhz 6 divisions reference x x 10 mhz 6 ±0.2 divisions 50 mhz 6 ±0.3 divisions 100 mhz 6 ±0.5 divisions sinewave flatness, dds output equipment: oscilloscop...
Page 235
5 performance checks test procedures 5-13 trigger, gate, and burst characteristics equipment: oscilloscope, function generator, counter preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope as follows: termination: 50 Ω, 20d b feedthrough attenuator at the oscilloscope input setup: as required for the test 2. ...
Page 236
Te5251 user manual 5-14 wave: ttl square from the main output. 4. Connect the function generator output to the 5251 trig in connector 5. Configure the 5251 as follows: frequency: 25 mhz waveform: sinewave run mode: burst burst count: 5 counts trigger delay: on delay: 5 s amplitude: 5 v trigger sourc...
Page 237
5 performance checks test procedures 5-15 6. Configure the 5251, channel 1 only, as follows: sclk: 200 ms/s waveform: arbitrary run mode: triggered trigger level 0 v trigger delay: on delay: as required for the test amplitude: 5 v trigger source: external output: on test procedure: 1. Perform trigge...
Page 238
Te5251 user manual 5-16 table chapter 5-17, re-trigger delay tests 5251 re-trigger setting error limits counter reading pass fail 1 μs 1 μs ±150 ns 1 ms 1 ms ±50 ns 1 s 1 s ±50 ms trigger slope equipment: oscilloscope, function generator preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope follows: terminatio...
Page 239: Sequence
5 performance checks test procedures 5-17 frequency 10 khz run mode: continuous waveform: squarewave. Amplitude: 1 v 4. Connect the function generator output to the 5251 trig in connector 5. Configure the 5251 as follows: frequency: 1 mhz waveform: sine wave run mode: triggered trigger level: 0 v ch...
Page 240
Te5251 user manual 5-18 wavelength: 128 points waveform: 1 cycle square 5. Using arbconnection, build and download the following sequence table: step 1: segment 1, loop 100,000 step 2: segment 2, loop 100,000 step 3: segment 3, loop 100,000 step 4: segment 4, loop 100,000 step 5: segment 5, loop 100...
Page 241: Sync Output
5 performance checks test procedures 5-19 8. Using arbconnection, build and download the following sequence table: step 1: segment 1, loop 1 step 2: segment 2, loop 1 step 3: segment 3, loop 1 step 4: segment 4, loop 1 step 5: segment 5, loop 1 test procedure: 1. From arbconnection, click on the man...
Page 242
Te5251 user manual 5-20 sync qualifier - bit equipment: oscilloscope preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope as follows: time base: as required by the test amplitude: 2 v/div 2. Connect 5251 sync output to the oscilloscope input 3. Configure model 5251 as follows: waveform: sine output: on sync: ...
Page 243: Arbitrary Waveform
5 performance checks test procedures 5-21 arbitrary waveform memory operation this tests the integrity of the waveform memory. The waveform memory stores the waveforms that are being generated at the output connector and therefore, flaws in the memory can cause distortions and impurity of the output...
Page 244
Te5251 user manual 5-22 4. Configure model 5251 controls as follows: waveform: modulated modulation: fm carrier freq: 1 mhz mod frequency: 10 khz deviation: 500 khz sync: on output: on test procedure: 1. Verify fm operation on the oscilloscope as follows: waveform: sine frequency: 10 khz max a: 1.25...
Page 245
5 performance checks test procedures 5-23 run mode: continuous waveform: squarewave. Amplitude: 2 v offset: 1 v 5. Connect the function generator output connector to the 5251 trig in connector 6. Configure model 5251 controls as follows: waveform: modulated modulation: fm mod run mode: triggered car...
Page 246
Te5251 user manual 5-24 waveform: modulated modulation: fm modulation run mode: burst burst: 5 carrier freq: 1 mhz mod frequency: 10 khz deviation: 500 khz sync: on output: on test procedure: 1. Verify burst fm – standard waveforms operation on the oscilloscope as follows: waveform: burst of 5 sine ...
Page 247
5 performance checks test procedures 5-25 sync: on output: on test procedure: 1. Verify gated fm – standard waveforms operation on the oscilloscope as follows: waveform: gated sine waveforms sine frequency: 10 khz gated period: 1 ms max a: 1.25 mhz min a: 750 khz test results pass fail re-triggered ...
Page 248
Te5251 user manual 5-26 test results pass fail fm - arbitrary waveforms equipment: oscilloscope preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope as follows: time base: 0.2 ms sampling rate: 50 ms/s at least. Trace a view: jitter, type: freq, clk. Trigger source: channel 2, positive slope amplitude: 1 v/di...
Page 249
5 performance checks test procedures 5-27 4. Configure model 5251 controls as follows: waveform: modulated modulation: am carrier freq: 1 mhz mod frequency: 1 khz mod depth: 50 % mod wave ch1 sine mod wave ch2 triangle sync: on output: on test procedure: 1. Verify am operation on the oscilloscope as...
Page 250
Te5251 user manual 5-28 test results pass fail psk equipment: oscilloscope preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope as follows: time base: 50 μs amplitude: 1 v/div. 2. Connect the 5251 output to the oscilloscope input, channel 1 3. Connect the 5251 sync to the oscilloscope input, channel 2 4. Conf...
Page 251
5 performance checks test procedures 5-29 shift amplitude: 2 v baud rate: 10 khz sync: on output: on 5. Using arbconnection, prepare and download 10-step ask list with alternating “0” and “1” test procedure: 1. Verify ask operation on the oscilloscope as follows: waveform: sinewave period: 0.1 ms am...
Page 252
Te5251 user manual 5-30 test procedure: 1. Verify hop operation on the oscilloscope as follows: waveform: frequency steps, increasing dwell time from 50 μs to 500 μs max a: 2.8 mhz min a: 1.0 mhz period: 2750 μs test results pass fail fix dwell time frequency hops equipment: oscilloscope preparation...
Page 253
5 performance checks test procedures 5-31 test results pass fail sweep equipment: oscilloscope preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope as follows: time base: 0.2 ms sampling rate: 50 ms/s at least. Trace a view: jitter, type: freq, clk. Trigger source: channel 2, positive slope amplitude: 1 v/div...
Page 254: Auxiliary
Te5251 user manual 5-32 test results pass fail 4. Change sweep step to logarithmic and verify oscilloscope exponential down waveform with properties as in 3 above test results pass fail auxiliary counter/timer operation this tests the operation of the auxiliary counter/timer function. Note that when...
Page 255
5 performance checks test procedures 5-33 table chapter 5-18, frequency measurement accuracy function generator setting error limits 5251 counter reading pass fail 1.000000 mhz ±2 hz 100.0000 mhz ±100 hz 120.0000 mhz ±200 hz 2. Change the display time to hold 3. Press the reset/arm button and verify...
Page 256
Te5251 user manual 5-34 pulse width equipment: function generator with at least 1 ppm accuracy preparation: 1. Configure the function generator as follows: frequency: as required by the test wave: square duty cycle: as required by the test amplitude 500 mv 2. Connect the function generator to the 52...
Page 257
5 performance checks test procedures 5-35 test procedure: 1. Manually reset the 5251 to reset and arm the totalize function 2. Manually trigger the function generator and verify that the 5251 counter reading is 100 ±1 test results pass fail totalize, infinite equipment: function generator with at le...
Page 258
Te5251 user manual 5-36 this page was intentionally left blank.
Page 259: Chapter 6
6-1 chapter 6 adjustments and firmware update title page what’s in this chapter ........................................................................................................... 6-3 performance checks ............................................................................................
Page 260
Te5251 user manual 6-2 setup 20 ........................................................................................................................... 6-16 amplitude adjustments-modulation ..................................................................................... 6-16 setup 21 .........
Page 261: What’S In This
6 adjustments and firmware update what’s in this chapter 6-3 what’s in this chapter this chapter provides adjustment information for the 5251 single channel pxibus waveform generator. Warning the procedures described in this section are for use only by qualified service personnel. Many of the steps ...
Page 262: Recommended
Te5251 user manual 6-4 recommended test equipment recommended equipment for adjustments is listed in table 6-1. Instruments other than those listed may be used only if their specifications equal or exceed the required minimal characteristics. Also listed below are accessories required for calibratio...
Page 263
6 adjustments and firmware update adjustment procedures 6-5 figure 6-1, calibration password 4. Type your user name password and click on ok. The calibration panel as shown in figure 6-2 will appear. Figure 6-2, calibration panel note initial factory adjustments require that the covers be removed fr...
Page 264
Te5251 user manual 6-6 calibrations are marked with numbers from 1 to 47 and, except the (50m) and tcxo adjustments in the osc (oscillators) group, should be carried out exactly in the order as numbered on the panel. The numbers that are associated with each adjustment are identified as setup number...
Page 265: Reference
6 adjustments and firmware update reference oscillators adjustments 6-7 reference oscillators adjustments use this procedure to adjust the reference oscillators. The reference oscillators determine the accuracy of the output frequency so if you suspect that there is an accuracy issue, proceed with t...
Page 266: Base Line Offset
Te5251 user manual 6-8 amplitude 2 v wave: square adjustment: 1. Adjust cal:setup57 for counter reading of 10 mhz, ±2 hz base line offset adjustments the base line offset adjustments assure that the ac signal is symmetrical around the 0v line. Use this procedure if you suspect that there is a base l...
Page 267: Setup 3
6 adjustments and firmware update base line offset adjustments 6-9 setup 3 base line offset, amplifier in – modulation equipment:dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feedthrough termination, dual banana to bnc adapter preparation: 1. Configure the dmm as follows: function: dcv range: 100 mv 2. Connect the 52...
Page 268: Setup 6
Te5251 user manual 6-10 output: on amplitude: 6 v adjustment: 1. Adjust cal:setup 5 for dmm reading of 0 v, ±20 mv setup 6 base line offset, amplifier out - arbitrary equipment: dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feed through termination, dual banana to bnc adapter preparation: 1. Configure the dmm as foll...
Page 269: Setup 8
6 adjustments and firmware update offset adjustments 6-11 setup 8 offset (+3 v) output amplifier in equipment: dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feed through termination, dual banana to bnc adapter preparation: 1. Configure the dmm as follows: function: dcv range: 10 v 2. Connect the 5251 output to the dm...
Page 270: Setup 11
Te5251 user manual 6-12 termination 3. Configure the 5251as follows: amplitude: 20 mv offset -1 v output: on adjustment: 1. Cal: setup 10 for dmm reading of -1 v, ± 5 mv setup 11 -3 v offset output amplifier in equipment: dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feed through termination, dual banana to bnc adapt...
Page 271: Setup 13
6 adjustments and firmware update offset adjustments 6-13 setup 13 (+) offset, output amplifier out equipment: dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feed through termination, dual banana to bnc adapter preparation: 1. Configure the dmm as follows: function: dcv range: 1 v 2. Connect the 5251 output to the dmm...
Page 272: Amplitude
Te5251 user manual 6-14 amplitude adjustments the amplitude adjustments assure that the ac levels are within the specified range. Use this procedure if you suspect that the amplitude accuracy is an issue. Setup 15 9 v amplitude - arbitrary equipment: dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feed through terminat...
Page 273: Setup 17
6 adjustments and firmware update amplitude adjustments 6-15 setup 17 5 v amplitude - arbitrary equipment: dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feed through termination, dual banana to bnc adapter preparation: 1. Configure the dmm as follows: function: acv range: 1 v 2. Connect the 5251 output to the dmm inp...
Page 274: Setup 20
Te5251 user manual 6-16 3. Configure the 5251as follows: frequency: 1 khz output: on amplitude: 1.1 v adjustment: 1. Adjust cal:setup19 for dmm reading of 389 mv ±3 mv setup 20 1 v amplitude – arbitrary, amp-out equipment: dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feed through termination, dual banana to bnc adap...
Page 275: Setup 22
6 adjustments and firmware update amplitude adjustments-modulation 6-17 amplitude: 9 v mode: modulation adjustment: 1. Adjust cal:setup21 for dmm reading of 3.182 v ±30 mv setup 22 7 v amplitude - modulation equipment: dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feed through termination, dual banana to bnc adapter ...
Page 276: Setup 24
Te5251 user manual 6-18 setup 24 3 v amplitude - modulation equipment: dmm, bnc to bnc cable, 50 Ω feed through termination, dual banana to bnc adapter preparation: 1. Configure the dmm as follows: function: acv range: 1 v 2. Connect the 5251 output to the dmm input. Terminate the 5251output at the ...
Page 277: Pulse Response
6 adjustments and firmware update pulse response adjustments 6-19 2. Connect the 5251 output to the dmm input. Terminate the 5251output at the dmm input with the, 50 Ω feed through termination 3. Configure the 5251as follows: frequency: 1 khz output: on amplitude: 1 v mode: modulation adjustment: 1....
Page 278: Flatness
Te5251 user manual 6-20 3. Set oscilloscope input impedance to 50 Ω 4. Set oscilloscope vertical sensitivity to 0.1 v adjustment: 1. Adjust vertical trace to 6 divisions 2. Adjust c25 for best pulse response (4 ns type, 5 % aberrations) flatness adjustments the flatness adjustments assure that the f...
Page 279: Setup 31
6 adjustments and firmware update flatness adjustments 6-21 setup 31 20 mhz amplitude equipment: 50 Ω, 20 db feed through termination, oscilloscope preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope as follows: input impedance: 50 Ω range: 100 mv 2. Connect the 5251 output to the oscilloscope input. Termina...
Page 280: Setup 34
Te5251 user manual 6-22 frequency: 37.3333333 mhz output: on adjustment: 1. Adjust cal:setup33 to get the signal of 6 divisions on the screen. Setup 34 56 mhz amplitude equipment: 50 Ω, 20db feed through termination, oscilloscope preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope as follows: input impedance...
Page 281: Setup 37
6 adjustments and firmware update flatness adjustments 6-23 range: 100 mv 2. Connect the 5251 output to the oscilloscope input. Terminate the 5251output at the oscilloscope input with the, 50 Ω, 20 db feed through termination 3. Configure the 5251as follows: frequency: 80 mhz output: on adjustment: ...
Page 282: Setup 39
Te5251 user manual 6-24 setup 39 10 mhz amplitude, amplifier out equipment: 50 Ω, 20 db feed through termination, oscilloscope preparation: 1. Configure the oscilloscope as follows: input impedance: 50 Ω range: 100 mv 2. Connect the 5251 output to the oscilloscope input. Terminate the 5251output at ...
Page 283: Setup 42
6 adjustments and firmware update flatness adjustments 6-25 frequency: 30 mhz output: on adjustment: 1. Adjust cal:setup41 to get the signal of 6 divisions on the screen. Setup 42 37.3333333 mhz amplitude, amplifier out equipment: 50 Ω, 20 db feed through termination, oscilloscope preparation: 1. Co...
Page 284: Setup 45
Te5251 user manual 6-26 input impedance: 50 Ω range: 100 mv 2. Connect the 5251 output to the oscilloscope input. Terminate the 5251output at the oscilloscope input with the, 50 Ω, 20 db feed through termination 3. Configure the 5251as follows: frequency: 56.0000001 mhz output: on adjustment: 1. Adj...
Page 285: Setup 47
6 adjustments and firmware update flatness adjustments 6-27 setup 47 frequency flatness – modulation equipment: oscilloscope, bnc to bnc cable, 20 db feedthrough attenuator preparation: 1. Configure the 5251as follows: function: modulation on modulation: sweep start freq: 1 mhz stop freq: 100 mhz sw...
Page 286: Updating The 5251
Te5251 user manual 6-28 updating the 5251 firmware warning only qualified persons may perform firmware updates. Do not even attempt to perform this operation unless you were trained and certified by tabor as you may inflict damage to the operation of the instrument. Always verify with the factory th...
Page 287
6 adjustments and firmware update updating the 5251 firmware 6-29 2) using a scpi command from an external utility, you can read the firmware version by sending the following query: syst:info:firm:vers? The response is a string showing the firmware version, similar to 1.0. 3) using arbconnection, se...
Page 288
Te5251 user manual 6-30 this page was intentionally left blank.
Page 289: Appendices
1 appendices appendix title page a specifications .................................................................................................................. A-1.
Page 290
Te5251 user manual 2.
Page 291: Appendix A
A-1 appendix a specifications operating modes description the 5251 can source multiple waveform shapes and functions. It can be programmed to operate as one of the following modes: function generator, arbitrary waveform generator, sequence generator, pulse generator, modulation generator, and half c...
Page 292
Te5251 user manual a-2 filters description filters can be switch in and out freely except in standard waveform shape where the filters are automatically used by the instrument to reconstruct the sine shape. Type 25 mhz, bessel; 50 mhz bessel; 60 mhz elliptic; 120 mhz elliptic general run modes descr...
Page 293
A appendices specifications a-3 frequency/time accuracy internal 10 mhz reference 0.0001% (1 ppm tcxo) initial tolerance from 19 c to 29 c; 1ppm/ c below 19 c and above 29 c; 1 ppm/year aging rate external 10 mhz reference connector front panel smb frequency 10 mhz impedance and level 10 k Ω 5%, ttl...
Page 294
Te5251 user manual a-4 start phase resolution 0.01 square duty cycle range 0% to 99.9% pulse delay, rise/fall time, high time ranges 0%-99.99% of period (each independently) ramp delay, rise/fall time, high time ranges 0%-99.9% of period (each independently) gaussian pulse time constant range 10-200...
Page 295
A appendices specifications a-5 single sequence advance current segment is sampled the specified number of repetitions and then idles at the end of the segment. Next trigger samples the next segment the specified repeat count, and so on. Mixed sequence advance each step of a sequence can be programm...
Page 296
Te5251 user manual a-6 modulating frequency range 10 mhz to 100 khz peak deviation up to 50 mhz arbitrary fm description operated from an external utility only such as arbconnection. The modulating waveform can be designed as an arbitrary waveform modulated waveform sine wave carrier frequency range...
Page 297
A appendices specifications a-7 carrier frequency range 10 hz to 100 mhz modulating sampling clock 1 s/s to 2.5 ms/s number of profile indexes 2 to 30000 pulse generator waveforms characteristics operation the 5251 has a special mode where the instrument type is transformed to operate as a digital p...
Page 298
Te5251 user manual a-8 counter/timer characteristics operation the 5251 has a special mode where the instrument type is transformed to operate as a counter/timer. When this mode is selected, the operation of the arbitrary waveform and its outputs are disabled measurement functions frequency, period,...