Summary of G-Major
Page 1
G•major guitar effects processor u us se er r’’s s m ma an nu ua al l.
Page 3
A important safety instructions 1 read these instructions. 2 keep these instructions. 3 heed all warnings. 4 follow all instructions. 5 do not use this apparatus near water. 6 clean only with dry cloth. 7 do not block any ventilation openings. Install in accordance with the manufacturer's instructio...
Page 4
Important safety instructions certificate of conformity tc electronic a/s, sindalsvej 34, 8240 risskov, denmark, hereby declares on own responsibility that following products: g•major - guitar effects processor - that is covered by this certificate and marked with ce-label conforms with following st...
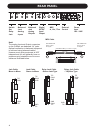
Page 5: Table of Contents
3 table of contents introduction important safety instructions . . . . . .A-b table of contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5 front panel overview . . . . . . . . . . . . .6 rear panel overview . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 signal flow diagram ...
Page 6: Introduction
Introduction congratulations on the purchase of your g•major effects processor. If you have never used a multi-effects processor with your guitar rig, you might be wondering at this point whether you have placed yourself in a position where you have days of work ahead of you, until your g•major beha...
Page 7: Introduction
5 quality with the g•major, tc electronic introduces a guitar effects processor in the “affordable” price range. You should however not be deceived by the price as the g•major delivers true top quality processing with no unwanted coloring of your beloved guitar-tone. As one of the leading companies ...
Page 8: Front Panel Overview
6 front panel overview power key on/off switch for the unit. Input level knob adjusts the input level. Range: 24db output level knob adjusts the output level. Range: 24db input meters peak meter showing input level. The meter range is: 0, -3, -6 , -12, -18, -24, -40db. Input overload leds the overlo...
Page 9: Front Panel Overview
7 front panel overview front panel keys general information a single click will activate/ deactivate the effect. Double clicking on the key will enter the edit menu of the effect algorithm. Lit key led indicates active effect block. Noise gate key on/off key for the noise gate block. Levels all/ rel...
Page 10: Rear Panel
8 rear panel balanced jack analog inputs balanced jack analog outputs external control midi in, out, thru switch out relay jack digital s/pdif input/ output power input 100 - 240v relay jack cable - y-splitter type jack cable stereo to mono jack cable mono to mono tip ring gnd gnd tip gnd tip midi c...
Page 11: Signal Flow
9 signal flow.
Page 12: Basic Setups
10 basic setups connecting and setting up the g•major there are numerous ways of hooking up guitar rigs. On these pages we have listed some of the most commonly used setups. We recommend using serial setups where the entire signal passes through the g•major. This will give you the maximum benefit fr...
Page 13: Basic Setups
11 basic setups connecting and setting up the g•major parallel setup using a line mixer • connect the output of your preamp to the input of the line mixer. • to be able to switch preamp channels with the g•major connect the relay jack connection on the g•major to the channel switching jacks on the p...
Page 14: The Display
12 the display input meter overload leds input type indicator matrix - indication of currently used routing block levels - in/out and mix damp compression/ noise gate preset number indicators of: received midi factory/user preset bank edit indication tuner detected input pitch input meters peak mete...
Page 15: The Display
13 the display preset handling mix meter: indicates the parameter position of the mix level in the block currently being edited. Damp if both the noise gate and the compressor is in use the damp indicator will indicate the noise gate attenuation when no input signal is present and the applied compre...
Page 16: Store
14 store to store a preset with the same name: • press store. If the preset you are about to store is a factory preset the g•major suggests the first available user location but you can select any of the 100 locations using the edit wheel. If the preset you are about to store is a user preset, the g...
Page 17: I/o Setup
15 please note that when using internal clock with external digital audio, the incoming digital audio must be in sync with the g•major internal clock in order to avoid slip-samples. "***rate mismatch****" this error message will occur in the display if the g•major detects slip-samples. Typically thi...
Page 18: Midi/util
16 midi/util the pedal is pressed. Alternating pedal types “stays connected” when pressed, and must be pressed again to be deactivated. Default setting is expression. Pedal calibrate for the g•major to respond correctly to the actions performed by a connected expression pedal, the g•major must be ca...
Page 19: Midi/util
17 midi/util fx mute range: hard/soft this parameter determines how delay and reverb effects should be handled at preset changes. Hard : effects are muted at preset change. Soft : delays will “spill over” and reverbs are smoothly glided to the setting in the preset you access. View angle adjusts the...
Page 20: Midi/util
18 midi/util midi mapping what is midi mapping? With the g•major it is possible to map an incoming program change from 1 to 128 to recall any factory or user preset. Example: you send program change no. 1 to both your g•major and you midi preamp (or other midi device). However, you would like the g•...
Page 21: Levels All & Relay 1+2
19 levels all & relay 1+2 basic operation • press the levels all key to enter this menu. • use the parameter/edit wheels in the control section to select and edit parameters and values. • the level parameters described below can all be remote controlled. See explanation on pages 22-23. Preset out le...
Page 22: Tap Menu
20 channel switching & tap tempo • connect the stereo jack to the switch out connection on the g•major rear panel. • connect the two mono jacks (or the stereo jack depending on the used cable) to the channel switching connectors on the combo or preamp. • recall the preset on the g•major to which you...
Page 23: Routings
21 routings routing menu the g•major holds three different effects routings. The routings can be stored with the preset. However you can also choose to fixate your favorite routing by utilizing the "routing lock" function. Consider the routing as how you would connect your stomp boxes on a regular p...
Page 24: Controlling The G•major
22 controlling the g•major introduction if you have played around and listened to the g•major and maybe programmed a few presets you are probably anxious to get control of the unit from your midi board, expression pedals or maybe via the optional g•minor midi foot switch. If you are new to the 19 in...
Page 25: Controlling The G•major
23 controlling the g•major cc value or pedal connected to the pedal input. A midi cc value above 64 will set the current preset to 0db. A midi cc value below 64 will set the current preset back to the preset level. When a new preset is recalled, the presetboost controller is reset (a value below 64 ...
Page 26: Controlling The G•major
Controlling the g•major • “learning” will now no longer blink and the g•major has recognized which external controller you want to control the modifier with and which midi cc value the device is sending if any. Off off means: no external control of the modifier. Pedal when “pedal” is selected it is ...
Page 27: How to
25 how to how to get started • connect the g•major according to your setup as described on pages 10/11 and power on. • find the “loudest” sound from your preamp or effect pedals with the most dynamics and set the input level so peaks are at approx. -3db. The sound with the most dynamics is most like...
Page 28: How to
26 how to matching the speed of a rhythmic tremolo or vibrato to a midi sequence • connect the midi output of your sequencer or other device sending out the midi clock you wish the g•major to sync up to, to the midi input of the g•major. • press tap once to enter the tap menu and use the parameter w...
Page 29: Effect Blocks
27 effect blocks noise gate introduction basic operation of the effect menus the six (or seven including noise gate) effect keys on the front panel, all work as follows: • single click: toggles the current effect on/off. • double click: accesses the edit page of the current effect. The navigation in...
Page 30: Noise Gate & Eq
28 noise gate & eq eq active activate/deactivates the eq. Please note that though the eq is accessed via the noise gate key, the on/off state of the eq is completely independent from the indication on this key. - it is controlled only by the eq active parameter. Freq range: 40hz to 20khz sets the op...
Page 31: Compressor
29 compressor illustration threshold range: -30db to 0db when the signal is above the set threshold point the compressor is activated and the gain of any signal above the threshold point is processed according to the ratio, attack and release settings. Ratio range: off to infinite: 1 the ratio setti...
Page 32: Chorus
30 chorus introduction a chorus/flanger is basically a short delay that is modulated by an lfo (low frequency oscillator). The difference between chorus and flanging is the applied delay time and the feedback parameter in the flanger. The modulation of the short delay gives very small variations in ...
Page 33: Chorus
31 chorus advanced chorus - cho/fla block speed range: 0.050hz to 19.95hz the speed of the chorus, also known as rate. The speed of this effect block is either defined by this parameter or by the tempo parameter which sets the speed according to the globally tapped tempo. This speed parameter is onl...
Page 34: Flanger
32 flanger classic flanger - cho/fla block speed range: 0.050hz to 19.95hz the speed of the flanger, also known as rate. The speed of this effect block is either defined by this parameter or by the tempo parameter which sets the speed according to the globally tapped tempo. This speed parameter is o...
Page 35: Flanger
Flanger vibrato 33 feedback range: -100 to 100 controls the amount of feedback/resonance of the short modulated delay that causes the flange effect. A too high feedback setting (above approx. 90-95%) might introduce an actual internal feedback resulting in a squealing noise that in most cases is unw...
Page 36: Resonance Filter
34 resonance filter resonance filter - filter/mod block the g•major resonance filter is basically a hi cut filter with adjustable q-factor (resonance). With increased resonance value, the filter peak at the cutoff frequency gets very narrow and steep. This phenomenon is the very core of the characte...
Page 37: Phaser
35 phaser vintage phaser/smooth phaser - filter (mod block) two effective good phaser types. The vintage phaser will give you the phasing effect similar to the one found in old stomp boxes. The smooth phaser is a more subtle type. Excellent for a less dominant effect. The vintage phaser utilizes fou...
Page 38: Tremolo
Tremolo panner 36 panner - filter/mod block the panner simply pans the signal from left channel to the right. Speed range: 0.050hz to 19.95hz sets the speed of the panning. Width range: 0 to 100% a 100% setting will sweep the signal completely from the left to right. Very often a more subtle setting...
Page 39: Delay
37 delay introduction the g•major holds 3 different delay modes that cover not only your basic needs, but also delay effects you until now maybe thought of as unachievable unless hooked up with expensive studio equipment. Once you get the grasp of what the three modes are used for, setting up a dela...
Page 40: Delay
38 delay out level range: -100 to 0db sets the overall output level of this block. Dynamic delay the dynamic delay initially introduced in the well-recognized tc 2290, is a function that allows the delay output level to be actively altered by the dynamics of the input level. A function that can be u...
Page 41: Delay
39 delay dlytime 2 range: 0 to 1800ms sets the delay time of the second delay line. Tempo range: 1/32t to 1 bar or ignored the tempo parameter sets the relationship to the global tempo. When set to anything else than ignored the tempo defined by the speed parameter is ignored. Fb 1 range: 0 to 100% ...
Page 42: Pitch
40 pitch detune a detune effect has a sound that to some extend can be associated with a chorus effect. The source signal is split and a specified amount of the signal is detuned by an amount of cents specified by you. (100 cents is 1 semitone). The main difference between the detune effect and the ...
Page 43: Pitch
41 pitch pitch shifter with the g•major pitch shifter you are able to add 2 voices, each with a fixed pitch within +/- one octave from the input note. The processing of the g•major is at a speed where you will never notice any “searching” for the notes as with many older octaver units or octaver sto...
Page 44: Reverb
42 reverb spring the spring algorithm is designed to reproduce the sound of the old spring reverbs, such as the ones used in vintage guitar amps. Decay range: 0.1 to 20s the decay parameter determines the length of the reverb tail. The length is defined as the time it takes for the reverb tail to de...
Page 45: Reverb
43 reverb hall decay range: 0.1 to 20s the decay parameter determines the length of the reverb tail. The length is defined as the time it takes for the reverb tail to decay approximately 60db. Pre delay range: 0 to 100ms a short delay placed between the direct signal and the reverb tail. By using pr...
Page 46: Reverb
44 reverb room decay range: 0.1 to 20s the decay parameter determines the length of the reverb diffuse field. The length is defined as the time it takes for the reverb diffuse field to decay approximately 60db. Pre delay range: 0 to 100ms a short delay placed between the direct signal and the reverb...
Page 47: Reverb
45 reverb plate decay range: 0.1 to 20s the decay parameter determines the length of the reverb diffuse field. The length is defined as the time it takes for the reverb diffuse field to decay approximately 60db. Pre delay range: 0 to 100ms a short delay placed between the direct signal and the rever...
Page 48: Appendix -
46 appendix - midi implementation chart guitar effects processor g•major - february 2002 function transmitted recognized remarks basic channel default 1 1 changed 1-16 1-16 mode default messages x x altered note number x x true voice x x velocity note on x x note off x x after touch keys x x ch’s x ...
Page 49: Appendix
47 appendix - technical specifications digital inputs and outputs connectors: formats: output dither: sample rates: processing delay: frequency response dio: analog inputs connectors: impedance, bal / unbal: max. Input level: min. Input level for 0 dbfs: sensitivity: a to d conversion: a to d delay:...
Page 50: Preset List
48 preset list g-major verb & slap clean reverb sheryls sound tremolo pedal speed so scho scotty's blues straight lead funky thang right on the edge bluebox echoes sparkle pan chorus clean cowboy cowboy slap the good, bad & ugly rockabilly slap all that lee a bit of chet a shadows of h. Marvin filte...
Page 51
49 frequently asked questions this section give answers to some of the most frequently asked questions regarding the g•major. More information can be found via tc support interactive, which can be accessed via www.Tcelectronic.Com which midi foot controller is the most suitable for the g•major? Ther...
Page 52
50 frequently asked questions have a variable mix knob, so that you can control how much of the effect you want mixed in with the dry signal. In a parallel loop situation you wish to avoid direct signal to pass the unit. Therefore use the kill dry parameter in the g•major levels all menu and control...