- DL manuals
- Thecus
- Disk array system
- i Series
- User Manual
Thecus i Series User Manual
Summary of i Series
Page 1
Thecus i series user’s manual.
Page 2: Preface
Preface about this manual this manual is the introduction of i series, and to help user to know the operation of the disk array system easily. Information contained in the manual has been reviewed for accuracy, but not for product warranty because of the various environments/os/settings, information...
Page 3: Table of Contents
Table of contents chapter 1 raid introduction.......................................... 5 1.1 features........................................................................... 5 1.2 terminology ..................................................................... 6 1.3 raid levels ...................
Page 4: Chapter 4
3.7 enclosure management ................................................. 50 3.7.1 ses configuration................................................................................. 51 3.7.2 hardware monitor ................................................................................. 51 3.7.3 ...
Page 5: Chapter 1 Raid Introduction
Chapter 1 raid introduction 1.1 features i series features: • gigabit lan (x2) -to- sata ii (xn bays) raid controller. • raid 6 ready. • sata ii support with sata i backward compatible. • n-way mirror. • on-line volume expansion and raid level migration. • global/dedicated cache configuration by vol...
Page 6: 1.2 Terminology
1.2 terminology the document uses the following terms: raid raid is the abbreviation of “redundant array of independent d isks”. There are different raid levels with different degree of the data protection, data availability, performance to host environment. Pd the physical disk belongs to the membe...
Page 7
Wt w rite-through cache write policy. A caching technique in which the completion of a write request is not signaled until data is safely stored on non-volatile media. Each data is synchronized in both data cache and the accessed physical disks. Wb w rite-back cache write policy. A caching technique...
Page 8: 1.3 Raid Levels
Iscsi i nternet small computer systems interface. Chap c hallenge handshake authentication protocol. An optional security mechanism to control access to an iscsi storage system over the iscsi data ports. Isns i nternet storage name service. 1.3 raid levels raid 0 disk striping. Raid 0 needs at least...
Page 9: Chapter 2 Getting Started
Chapter 2 getting started 2.1 before starting before starting, prepare the following items. 1. Check the “certification list” in appendix a to confirm the hardware setting is fully supported. 2. Read the latest release notes before upgrading. Release notes accompany with release firmware. 3. A serve...
Page 10
The iscsi target is the storage device itself or an appliance which controls and serves volumes or virtual volumes. The target is the device which performs scsi commands or bridges it to an attached storage device. Iscsi targets can be disks, tapes, raid arrays, tape libraries, and etc. Host 2 (init...
Page 11: 2.3 Management Methods
Open-iscsi website: http://www.Open-iscsi.Org/ open-iscsi readme: http://www.Open-iscsi.Org/docs/readme features: http://www.Open-iscsi.Org/cgi-bin/wiki.Pl/roadmap support kernels: http://www.Open-iscsi.Org/cgi-bin/wiki.Pl/supported_kernels google groups: http://groups.Google.Com/group/open-iscsi/th...
Page 12: 2.4 Enclosure
2.3.2 remote control – secure shell ssh (secure shell) is required for i series to remote login. The ssh client software is available at the following web site: sshwinclient www: http://www.Ssh.Com/ putty www: http://www.Chiark.Greenend.Org.Uk/ host name: 192.168.1.100 login name: admin default pass...
Page 13
The following table is function description. Alarm mute mute alarm when error occurs. Reset/shutdown reset or shutdown controller. Quick install quick three steps to create a volume. Please refer to section 3.3 for operation in web ui. View ip setting display current ip address, subnet mask, and gat...
Page 14
Caution before power off, it is better to execute “shutdown” to flush the data from cache to physical disks. 2.4.2 system buzzer the system buzzer features are describing in the following: 1. The system buzzer alarms 1 second when system boots up successfully. 2. The system buzzer alarms continuousl...
Page 15: Chapter 3 Web Gui Guideline
Chapter 3 web gui guideline 3.1 gui hierarchy the below table is the hierarchy of i series gui. Quick install Æ step 1 / step 2 / step 3 / confirm system config system name Æ system name ip address Æ dhcp / static / address / mask / gateway / dns / http port / https port / ssh port language Æ langua...
Page 16: 3.2 Login
Maintenance upgrade Æ browse the firmware to upgrade / export config info Æ system information reset to default Æ sure to reset to factory default? Config import & export Æ import/export / import file shutdown Æ reboot / shutdown logout sure to logout? 3.2 login i series supports graphic user interf...
Page 17: 3.3 Quick Install
1. Raid light: green means raid works well. Red represents raid failure happening. 2. Temperature light: green is normal. Red represents abnormal temperature. 3. Voltage light: green is normal. Red represents abnormal voltage status. 4. Ups light: green is normal. Red represents abnormal ups status....
Page 18
Step 1: select “quick install” then choose the raid level to set. Please refer to figure 3.3.1. After choosing the raid level, click “ ”, which links to another page, user can set up “lun” here. Figure 3.3.1 step 2: please select a lun number. Access control of host would show as a wildcard “*”, whi...
Page 19: 3.4 System Configuration
3.4 system configuration “system config” selection is for the setup of “system name”, “ip address”, “language” , “login config”, “password”, “date”, “mail”, “snmp”, “messenger” , “system log server” and view “event log”. Figure 3.4.1 3.4.1 system name select “system name” to change system name. Defa...
Page 20
3.4.2 ip address select “ip address” to change ip address for remote administration usage. There are 2 selections, dhcp (get ip address from dhcp server) or static ip. The default setting is static ip (192.168.1.100 ) enabled. User can change the http, https, and ssh port number when the default por...
Page 21
3.4.4 login config select “login config” is to set only one admin and set the auto logout timing. The only one admin can prevent multiple users access the same controller in the same time. 1. Auto logout: the options are (1) disable; (2) 5 mins; (3) 30 mins; (4) 1 hour. The system will log out autom...
Page 22
3.4.6 date select “date” to set up the current date, time, and time zone before using or synchronize time from ntp(network time protocol) server. Figure 3.4.6.1 3.4.7 mail select “mail” to enter at most 3 mail addresses for receiving the event notification. Some mail servers would check “mail-from a...
Page 23
Figure 3.4.7.1 3.4.8 snmp select “snmp” to set up snmp trap for alert via snmp. It allows up to 3 snmp trap addresses. Default community setting is “public”. User can choose the event log levels and the default value of snmp is info event log enabled only. Figure 3.4.8.1 there are many snmp tools. T...
Page 24
3.4.9 messenger select “messenger” to set up pop-up message alert via windows messenger (not msn). User must enable the service “messenger” in windows (start Æ control panel Æ administrative tools Æ services Æ messenger), and then event logs can be received. It allows up to 3 messenger addresses. Us...
Page 25
3.4.11 event log select “event log” to view the event messages. Press “filter” button to choose the display. Press “download” button will save the whole event log as text file with file name “log-modelname-serialnumber-date-time.Txt”. Press “clear” button will clear event log. Press “mute” button wi...
Page 26: 3.5 Iscsi Config
3.5 iscsi config “iscsi config” selection is for the setup of “entity property”, “nic”, “node”, “session” , and “chap account”. Figure 3.5.1 3.5.1 entity property select “entity property” to view the view the entity name of the controller, and setup “isns ip” for isns (internet storage name service)...
Page 27
3.5.2 nic select “nic” to change ip addresses of iscsi data ports. Figure 3.5.2.2 (figure 3.5.2.2: there are 2 iscsi data ports.) user can change ip address by clicking the button “ ” in the “dhcp” column. There are 2 selections, dhcp (get ip address from dhcp server) or static ip. Figure 3.5.2.3 de...
Page 28
Chap: chap is the abbreviation of challenge handshake authorization protocol. Chap is a strong authentication method used with point-to-point for user login. It’s a type of authentication in which the authentication server sends the client a key to be used for encrypting the username and password. C...
Page 29
Figure 3.5.4.1 (figure 3.5.4.1: iscsi session.) pressing the button “ “ will display connection(s). Figure 3.5.4.2 (figure 3.5.4.2: iscsi connection.) 3.5.5 chap account enter “chap account” function to create/delete a chap account for authentication. Figure 3.5.5.1 (figure 3.5.5.1: press “create” t...
Page 30: 3.6 Volume Configuration
Figure 3.5.5.2 (figure 3.5.5.2: create a chap account named “chap1”.) 3.6 volume configuration “volume config” selection is for the setup of volume configurations including “physical disk” , “volume group”, “user data volume”, “cache volume”, and “logical unit” functions. Figure 3.6.1 3.6.1 volume r...
Page 31
Vg pd 2 pd 3 ds pd 1 udv 1 udv 2 udv 3 lun 1 lun 2 lun 3 ram global cv dedicated cv + + + - 31 -.
Page 32
The above diagram describes the relationship of raid components. One vg (volume group) consists of a set of udvs (user data volume) and owns one raid level attribute. Each vg can be divided into several udvs. The udvs from one vg share the same raid level, but may have different volume capacity. Eac...
Page 33
• pd column description: slot the position of hard drives. The number of slot begins from left to right at the front side. The button next to the number of slot is “more information” indication. It shows the details of the hard drive. Wwn w orld wide name. Size (gb) capacity of hard drive. Vg name r...
Page 34
Command, and the speed can achieve serial ata gen-1 signaling speed (1.5gbps). Unknown Æ the disk doesn’t support above command, so the speed is defined as unknown. • pd operations description: free disks make the selected hard drive to be free for use. Global spares set the selected hard drive(s) t...
Page 35
Enter “volume group” to view the status of each volume group. • vg column description: figure 3.6.3.1 (figure 3.6.3.1: there is a raid 0 with 2 physical disks, named “vg-r0”, total size is 148gb, related to 2 udv. Another is a raid 5 with 3 physical disks, named “vg-r5”.) no. Number of volume group....
Page 36
Status 2 “r” Æ rebuild. This volume group is doing rebuilding. Status 3 “m” Æ migration. This volume group is doing migration. Raid the raid level of the volume group. The button next to the raid level is “migrate” function. Click “migrate” can add disk(s) to do expansion or change the raid level of...
Page 37
No. Number of this user data volume. The button in below to the udv no. Is “more information” indication. It shows the details of the user data volume. Name name of this user data volume. The button in below to the udv name is “rename” function. Size(gb) total capacity of this user data volume. The ...
Page 38
• udv operations description: attach attach to a lun. Create create a user data volume function. Delete delete a user data volume function. 3.6.5 cache volume enter “cache volume” function to view the status of cache volume. The global cache volume is a default cache volume, which is created after p...
Page 39
• cv operations description: create create a cache volume function. Delete delete a cache volume function. If there is no free space for creating a new dedicated cache volume, cut down the global cache size first. After resized, then dedicated cache volume can be created. Tips the minimum size of gl...
Page 40
Figure 3.6.6.1 figure 3.6.6.2 (figure 3.6.6.2: udv-01 is attached to lun 0 with every host can access. Udv-02 is attached to lun 1 with only initiator note named “iqn.1991-05.Com.Microsoft:s1300n” can access.) • lun operations description: attach attach a logical unit number to a user data volume. D...
Page 41
Example 2 is to create two udvs. One shares global cache volume, the other uses dedicated cache volume. Set a dedicated spare disk. • example 1 example 1 is to create two udvs in one vg, each udv uses global cache volume. Global cache volume is created after system boots up automatically. So, no act...
Page 42
Figure 3.6.7.2 (figure 3.6.7.2: creating a raid 0 with 2 physical disks, named “vg-r0”. The total size is 148gb. Because of no related udv there, free size still remains 148gb.) step 2: create udv (user data volume). To create a data user volume, please follow the procedures. Figure 3.6.7.3 1. Selec...
Page 43
Figure 3.6.7.4 (figure 3.6.7.4: create udvs named “udv-1” and “udv-2”, related to “vg-r0”, the size of “udv-1” is 50gb, the size of “udv-2” is 98gb. The status of these udvs are online, write back, high priority with cache volume 383mb. There is no lun attached.) step 3: attach lun to udv. There are...
Page 44
Figure 3.6.7.6 (figure 3.6.7.6: udv1 is attached to lun 0 with any hosts can access. Udv2 is attached to lun 1 with only initiator note named “iqn.1991-05.Com.Microsoft:s1300n” can access.) tips the matching rules of access control are from top to down by sequence. Please refer 3.6.6 for details. St...
Page 45
(figure 3.6.7.7: slot 5 is set as global spare disk.) step 5: done. They can be used as iscsi disks. Delete udvs, vg, please follow the steps. Step 6: detach lun from udv. In “/ volume config / logical unit”, figure 3.6.7.8 1. Select luns by clicking the checkbox of the row, then click “ ”. There wi...
Page 46
1. Select “/ volume config / volume group”. 2. Select a vg by clicking the checkbox of the row, make sure that there is no udv on this vg, or the udv(s) on this vg must be deleted first. 3. Click “ “. There will pop up a confirmation page. 4. Choose “ok” 5. Done. The vg has been deleted. Tips the ac...
Page 47
Figure 3.6.7.9 1. Select “/ volume config / cache volume”. 2. If there is no free space for creating a new dedicated cache volume, cut down the global cache size first by clicking the button “ ” in the size column. After resized, click “ ” to return to cache volume page. 3. Click “ “ to enter the se...
Page 48
Figure 3.6.7.10 1. Select “/ volume config / user data volume”. 2. Click “ ”. 3. Input a udv name, choose a vg name, select dedicated cache which is created at step 1, and input the size for the udv; decide the stripe height, block size, read/write mode and set priority, finally click “ “. 4. Done. ...
Page 49
Step 4: attach lun to udv. Please refer to step 3 of example 1 to attach lun. Step 5: set dedicated spare disk. To set dedicated spare disks, please follow the procedures: 1. Select “/ volume config / physical disk”. 2. Select a vg from the list box, then select the free disk(s), click “ ” to set as...
Page 50: 3.7 Enclosure Management
To free dedicated spare disks, please follow the procedures: 1. Select “/ volume config / physical disk”. 2. Select the dedicated spare disk by clicking the checkbox of the row, then click “ “ to free disk. Step 11: delete dedicated cache volume. To delete the cache volume, please follow the procedu...
Page 51
5. Led status: 10 seconds. Figure 3.7.1 3.7.1 ses configuration ses represents scsi enclosure services, one of the enclosure management standards. Enter “ses config” function can enable or disable the management of ses. Figure 3.7.1.1 (figure 3.7.1.1: enable ses in lun 0, and can be accessed from ev...
Page 52
Figure 3.7.2.1 if “auto shutdown” has been checked, the system will shutdown automatically when voltage or temperature is out of the normal range. For better data protection, please check “auto shutdown”. For better protection and to avoid single short period of high temperature triggering auto shut...
Page 53
Figure 3.7.3.1 3.7.4 ups enter “ups” function will set ups (uninterruptible power supply). Figure 3.7.4.1 currently, the system only support and communicate with smart-ups function of apc (american power conversion corp.) ups. Please check detail from http://www.Apc.Com/ . First, connect the system ...
Page 54: 3.8 System Maintenance
(%) function. Shutdown delay (s) if power failure occurred, and the system can not return back to the setting value period, the system will shutdown. Setting delay to “0” will disable the function. Shutdown ups select on, when power is gone, ups will shutdown by itself after the system shutdown succ...
Page 55
Figure 3.8.1 3.8.1 upgrade enter “upgrade” function to upgrade firmware. Please prepare new firmware file named “xxxx.Bin” in local hard drive, then press “ ” to select the file. Click “ ”, it will pop up a message “upgrade system now? If you want to downgrade to the previous fw later, please export...
Page 56
3.8.3 reset to default enter “reset to default” function, it allows user to reset controller to the factory default setting. Figure 3.8.3.1 reset to default sets password to default: admin, and set ip address to default as static ip. Default ip address: 192.168.1.100 (static ip) default subnet mask:...
Page 57: 3.9 Logout
3.8.5 shutdown enter “shutdown” function; it will display “reboot” and “shutdown” buttons. Before power off, it’s better to press “shutdown” to flush the data from cache to physical disks. The step is better for the data protection. Figure 3.8.5.1 3.9 logout for security reason, “logout” function wi...
Page 58: 4.1 Rebuild
Chapter 4 advanced operation 4.1 rebuild if one physical disk of the vg which is set as protected raid level (e.G.: raid 3 , raid 5, or raid 6) is failed or has been unplugged/removed, then, the vg status is changed to degraded mode, the system will search/detect spare disk to rebuild the degraded v...
Page 59
When rebuilding, the status of pd/vg/udv is “r”; and “r%” in udv will display the ratio in percentage. After complete rebuilding, “r” and “dg” will disappear. Vg will become complete one. Tips the list box doesn’t exist if there is no vg or only vg of raid 0, jbod. Because user cannot set dedicated ...
Page 60
4.2 vg migration and expansion to migrate the raid level, please follow the below procedures. If the vg migrates to the same raid level of the original vg, it is expansion. 1. Select “/ volume config / volume group”. 2. Decide which vg to be migrated, click the button “ ” in the raid column next the...
Page 61: 4.3 Udv Extension
Figure 4.2.3 (figure 4.2.3: a raid 0 migrates to raid 5, complete percentage is 2%.) to do migration/expansion, the total size of vg must be larger or equal to the original vg. It does not allow expanding the same raid level with the same hard disks of original vg. During setting migration, if user ...
Page 62: 4.4 Disk Roaming
4. Extension starts. If udv needs initialization, it will display an “i” in “status 3” and complete percentage of initialization in “r%”. Figure 4.3.1 (figure 4.3.1: extend udv-r0 from 80gb to 90gb.) tips the size of udv extension must be larger than original. Caution udv extension cannot be execute...
Page 63: Appendix
Appendix a. Certification list • ram i series ram spec: 184pins, ddr333(pc2700), reg.(register) or ub(unbufferred), ecc or non-ecc, from 64mb to 1gb, 32-bit or 64-bit data bus width, x8 or x16 devices, 9 to 11 bits column address. Vendor model atp ag64l72t8sqc4s, 512mb ddr-400 (ecc) with samsung atp...
Page 64
Os software/release number microsoft windows microsoft iscsi software initiator version 2.04 system requirements: 1. Windows xp professional with sp2 2. Windows 2000 server with sp4 3. Windows server 2003 with sp1 4. Windows server 2003 r2 linux the iscsi initiators are different for different linux...
Page 65: B. Event Notifications
Dell powerconnect 5324 dell powerconnect 2724 dell powerconnect 2708 hp procurve 1800-24g d-link dgs-3024 • hard drive i series support sata i, ii disks. Vendor model hitachi deskstar 7k250, hds722580vlsa80, 80gb, 7200rpm, sata, 8m hitachi deskstar 7k80, hds728080pla380, 80gb, 7200rpm, sata-ii, 8m h...
Page 66
• pd/s.M.A.R.T. Events level type description info disk inserted info: disk is inserted. Info disk removed info: disk is removed. Warning s.M.A.R.T. Threshold exceed condition warning: disk s.M.A.R.T. Threshold exceed condition occurred for attribute of 1. Read error rate 2. Spin up time 3. Realloca...
Page 67
Info ses load conf. Ok info: ses configuration has been loaded. Warning ses load conf. Failure error: failed to load ses configuration. The ses device is disabled. Info ses is disabled info: the ses device is disabled. Info ses is enabled info: the ses device is enabled • environmental events level ...
Page 68
Warning rtc access failed warning: fail to access rtc device info reset password info: reset admin password to default. Info reset ip info: reset network settings set to default. • system config events level type description info sys config. Defaults restored info: default system configurations rest...
Page 69
Warning vg created fail warning: fail to create vg . Info vg deleted info: vg has been deleted. Info udv created ok info: udv has been created. Warning udv created fail warning: fail to create udv . Info udv deleted info: udv has been deleted. Info udv attached ok info: udv has been lun-attached. Wa...
Page 70
Read/write error failed. Error pd read/write error error: pd lba length error. Error udv recoverable read/write error error: udv stripe pd lba length recoverable error udv unrecoverable read/write error error: udv stripe pd lba length unrecoverable info udv stripe rewrite start/fail/succeed info: ud...
Page 71
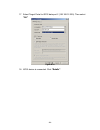
Figure c.2 4. Click “ok”. Please see figure c.3. Figure c.3 5. Click “targets”. Please see figure c.4. - 71 -.
Page 72
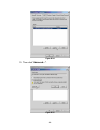
Figure c.4 6. Click “log on”. Please see figure c.5. Check “enable multi-path” if running mpio. Figure c.5 7. Click “advance…” if chap information is needed. Please see figure c.6. - 72 -.
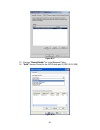
Page 73
Figure c.6 8. Click “ok”. The status would be “connected”. Please see figure c.7 9. Done, it can connect to an iscsi disk. - 73 -.
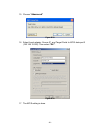
Page 74
Figure c.7 the following procedure is to log off iscsi device. - 74 -.
Page 75
1. Click “details”. Please see figure c.8. Figure c.8 2. Check the identifier, which will be deleted. 3. Click “log off”. 4. Done, the iscsi device log off successfully. D. Mpio and mc/s setup instructions here is the step by step to setup mpio. There are 2 kinds of scenarios for mpio. Please see fi...
Page 76
Figure d.1 the setup instructions are in the following figures. 1. Create a vg . Figure d.2 2. Create a udv. - 76 -.
Page 77
Figure d.3 3. Run microsoft iscsi initiator and check the initiator node name. Figure d.4 4. Attaching lun to udv_1 udv. Input the initiator node name in host field. Figure d.5 5. The volume config setting is done. - 77 -.
Page 78
Figure d.6 6. Check iscsi settings. The ip address of iscsi data port 1 is 192.168.11.229, port 2 is 192.168.12.229 for example. Figure d.7 7. Add target portals on microsoft iscsi initiator. Figure d.8 8. Input the ip address of iscsi data port 1 (192.168.11.229 as mentioned in previous page). - 78...
Page 79
Figure d.9 9. Add second target portals on microsoft iscsi initiator. Figure d.10 - 79 -.
Page 80
10. Input the ip address of iscsi data port 2 (192.168.12.229 as mentioned in previous page). Figure d.11 11. The initiator setting is done. - 80 -.
Page 81
Figure d.12 12. Log on. Figure d.13 - 81 -.
Page 82
13. Enable “enable multi-path” checkbox. Then click “advanced”. Figure d.14 14. Select target portal to iscsi data port 1 (192.168.11.229). Then click “ok” - 82 -.
Page 83
Figure d.15 15. Log on “enable multi-path” again. Figure d.16 16. Enable “enable multi-path” checkbox. Then click “advanced…”. Figure d.17 - 83 -.
Page 84
17. Select target portal to iscsi data port 2 (192.168.12.229). Then select “ok” figure d.18 18. Iscsi device is connected. Click “details”. - 84 -.
Page 85
Figure d.19 19. Click “device” tab, then click “advanced”. Figure d.20 - 85 -.
Page 86
20. Click “mpio” tab, select “load balance policy” to “round robin”. Figure d.21 21. Click “apply”. Figure d.22 - 86 -.
Page 87
22. Run “device manage” in windows. Make sure mpio device is available. Then the disk can be tested performance by iometer. The mc/s setup instructions are very similar to mpio, detail steps are in the following figures. For the target side setting, the steps are exactly the same as mpio. Please ref...
Page 88
Figure d.24 10. Then click “advanced…”. Figure d.25 - 88 -.
Page 89
11. Select set local adapter, source ip, and target portal to iscsi data port 1 (192.168.11.229). Then click “ok”. Figure d.26 12. After connected, click “details”, then in the “session” tab, click “connections” . - 89 -.
Page 90
- 90 - figure d.27 13. Choose “round robin” for load balance policy. 14. “add” source portal for the iscsi data port 2(192.168.12.229) figure d.28.
Page 91
- 91 - 15. Choose “adavanced” figure d.29 16. Select local adapter, source ip, and target portal to iscsi data port 2 (192.168.12.229). Then select “ok”. Figure d.30 17. The mc/s setting is done..