- DL manuals
- Vaz
- Automobile
- VAZ-21213
- Repair Manual
Vaz VAZ-21213 Repair Manual
Summary of VAZ-21213
Page 1
Vaz vehicles vaz-21213, vaz-21214, vaz-21214-20, vaz-21215 repair manual.
Page 2
2 contents section 1. General data..........................................................4 section 2. Engine ..................................................................7 engine - removal and refitting..........................................12 cylinder block .................................
Page 3
About this manual this manual provides information on routine maintenance and servicing and is intended for engineers and mechanics of service outlets, garages and workshops. The manual covers the following models: vaz-21213 model - an off-road vehicle, three-door body of all-steel unitary construct...
Page 4
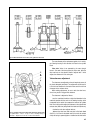
Section 1. General data table 1-1 technical specification features vaz-21213 vaz-21214 vaz-21214-20 vaz-21215 general number of seats 5 5 5 5 kerb weight, kg 1210 1210 1210 1240 payload, kg 400 400 400 400 overall dimensions fig.1-1 maximum braking distance at gvw and 80 km/h on horizontal dry flat ...
Page 5
Features vaz-21213 vaz-21214 vaz-21214-20 vaz-21215 power train clutch single dry plate, diaphragm spring clutch release mechanism hydraulic, servo spring transmission 5-speed, synchro units on all forward gears gear ratio: • first gear 3.67 3.67 3.67 3.67 • second gear 2.10 2.10 2.10 2.10 • third g...
Page 6
Features vaz-21213 vaz-21214 vaz-21214-20 vaz-21215 steering steering mechanism globoidal worm, double-crest roller, steering ratio 16.4 steering linkage three links, relay rod and two steering rods, drop arm, idler arm and swing arms braking system service braking system: • front brakes disc-type, ...
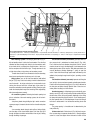
Page 7
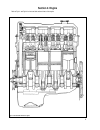
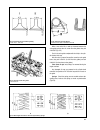
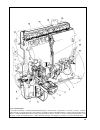
Section 2. Engine refer to fig.2-1 and fig.2-2 for front and side sectional views of the engine. 7 fig.2-1. Side sectional view of the engine.
Page 8
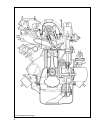
8 fig.2-2. Front sectional view of the engine.
Page 9
Fault diagnosis symptom/fault remedy engine fails to start 1. No fuel to carburettor: - blocked fuel pipes or fuel filter; - clogged carburettor or fuel pump filters; - faulty fuel pump 2. Ignition system fault 3. Carburettor fuel cutoff solenoid fails to open at ignition switch-on: - disconnected, ...
Page 10
Main bearing knocking typical knocking or thumping noticeable at sudden throttle opening at idle which intensifies with higher crankshaft rate. Excessive endfloat of crankshaft causes sharper irregular knocking, especially noticeable during smooth increase or decrease in crankshaft speed. 1. Early i...
Page 11
Excessive oil consumption 1. Oil leaking through engine gaskets 2. Restricted crankcase ventilation system 3. Worn piston rings 4. Broken piston rings 5. Foul windows of oil scraper rings or foul slots in piston grooves due to wrong oil 6. Worn or damaged valve oil caps 7. Badly worn valve stems or ...
Page 12
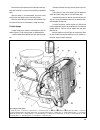
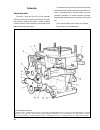
Engine - removal and refitting put the vehicle on a lift or over an inspection pit and apply the handbrake. Take out the spare wheel and its supporting pipe. Disconnect the battery leads and withdraw the battery. Unbolt and remove the bonnet. To remove the air cleaner, disconnect its hoses, remove t...
Page 13
Remove the starter motor heat shield, followed by the starter motor, hot air intake complete with the supply hose. Remove from the cylinder head two side brackets together with the front engine mounting rubbers. Unbolt the clutch and withdraw it. Refitting is a reversal of the removal procedure. Dra...
Page 14
Remove thrust flange 1 (fig.2-8) of the oil pump drive shaft and take the shaft out of the cylinder block. Using picker Ä.40005/1/7 (kit Ä.40005) drive the sprocket off the crankshaft (fig.2-9). Undo the connecting rod bolts, remove the big end cap and carefully lift the pistons with the conrods thr...
Page 15
Fit the centre main bearing shells without an oilway into the bearing recesses. Fit into other cylinder bores the bearing shells with an oilway, while into the relevant main bearing caps - the bearing shells without an oilway. Lower the crankshaft into posi- tion, then stick two thrust washers into ...
Page 16
Locate the flywheel in position so that the marking (a cut-out) near the rim is against the no 4 cylinder crankpin axis. While holding the flywheel stationary with tool Ä.60330/r, bolt it to the crankshaft flange to the specified torque. Using a ring compressor (tool 67.8125.9502), fit the pistons a...
Page 17
Turn the flywheel so that the mark on the crankshaft sprock- et is against the cylinder block mark (fig.2-19). Check to see the camshaft bearing housing centering pins are in position (fig.2-20). Refit the sprocket to the camshaft com- plete with the bearing housing and turn the camshaft so that the...
Page 18
Adjust the clearance between the camshaft lobes and valve levers. Refit the camshaft cover (fig.2-23) complete with the gasket and oil seal to the cylinder block, do not tighten the retaining bolts and nuts fully. Using tool 41.7853.4010 centralize the cover against the crankshaft end, then tighten ...
Page 19
Engine run-in after overhaul after overhaul the engine is bench tested (run-in) at no loads under the following cycle: 750-800 rpm 2 minutes 1000 rpm 3 minutes 1500 rpm 4 minutes 2000 rpm 5 minutes locate the engine on the test bench, start the engine and make checks with respect to the following it...
Page 20
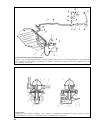
20 fig.2-26. Cylinder size class engraved on the cylinder block fig.2-27. Measuring the cylinder bore with the inside dial gauge: 1 - inside dial gauge; 2 - setting to zero against reference gauge fig.2-25. Basic sizes of the cylinder block.
Page 21
There is practically no wear in the land 1 area of the cylin- ders. Compare the values measured on the first and other cylin- der lands to see the amount of the cylinder wear. When the maximum wear is over 0.15 mm, rebore the cylin- ders to the nearest oversize; provide 0.03 mm honing allowance on t...
Page 22
The connecting rod small-end features a pressed-in steel- bronze bush. As to the diameter of the bush, the connecting rods are divided into three classes in steps of 0.004 mm (similar to the pistons). The class number (5 in fig.2-30) is engraved on the big-end cap. The connecting rod small-end and b...
Page 23
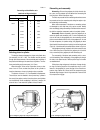
Table 2-1 connecting rod classification as to small-end and big-end weights connecting rod weight, g class paint mark small-end big-end 519±3 Ä white 186±2 525±3 Ç blue 531±3 ë red 519±3 d black 190±2 525±3 e violet 531±3 f green 519±3 g yellow 194±2 525±3 ç brown 531±3 i orange selecting piston to ...
Page 24
Make certain the second compression ring is positioned with the recess facing down (fig.2-30), while the top (or ÇÖêï) mark should face up (the piston crown). Before refitting the oil ring, check to see the joint of the coil expander (spreader ring) is on the side opposite to the ring gap. Inspectio...
Page 25
Crankpins. Regrind when the wear is in excess of 0.03 mm, oval- ity is over 0.03 mm, or when scoring and scuffing is obvious. Regrind the journals and crankpins through reducing the diameter to the nearest undersize (fig.2-36). When regrinding, observe the sizes for the crankshaft fillet as shown in...
Page 26
The nominal design clearance is 0.02-0.07 mm for the crankpins and 0.026-0.073 mm for the main bearing journal. When the running clearance is below the maximum value (0.1 mm for the big-end bearing journals and 0.15 mm for the main bearing journals), the bearing shells can be re-used. When the runni...
Page 27
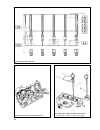
The outer diameter of the replacement guides is 0.2 mm big- ger. Bearing housing 5 with camshaft 6 is fitted to the cylinder head. Valve train. Valves 2 are operated by the cams through levers 4. One end of the lever pushes the valve stem, while the other end rests on the spherical head of adjuster ...
Page 28
Lock nut tightening, until the blade is a firm sliding fit when the lock nut is tightened (fig.2-42); - after the clearance is adjusted at the cylinder no4 exhaust valve and cylinder no3 intake valve, turn the crankshaft progres- sively to the 180° and adjust the clearances, observing the sequence a...
Page 29
Disconnect the leads from the spark plugs and coolant tem- perature sender, from carburettor idle switch and fuel cutoff sole- noid. Disconnect the choke cable; disconnect the throttle linkage from the intermediate lever on the valve cover. Loosen the clips and disconnect the carburettor supply / re...
Page 30
Put spring a.94069/5 on tool Ä.94059, fit tapered wheel a.94078 on spindle Ä.94069 for the exhaust valve seats or wheel Ä.94100 for the inlet valve seats, secure the spindle in a grinder and recut the valve seat (fig.2-48). The grinding wheel must be off at the moment the grinding wheel contacts the...
Page 31
When a new valve fails to take up clearance between the valve guide and the valve rim, renew the valve guides using tool Ä.60153/r (fig.2-51). Push in the valve guide complete with the circlip to the cylin- der head to their stop. After the valve is pressed into position, ream the valve guide bores ...
Page 32
For lever springs (fig.2-53) the size Ä (spring unloaded) must be 35 mm, whereas the size Ç (spring loaded 51-73.5 n/ 5.2-7.5 kgf) must be 43 mm. Cylinder head bolts. Multiple use of the cylinder head bolts results in the bolt elongation. Therefore, check the length of the bolt (l) to be 120 mm (les...
Page 33
Drain the cooling water from the radiator and cylinder block, remove the radiator complete with the hoses and thermostat. Undo the retaining nuts and remove the fan. Remove the valve cover and turn the crankshaft to align the tdc mark in the camshaft sprocket against the timing mark in the bearing h...
Page 34
Camshaft bearing housing. Wash and clean the bearing housing, flush clean the oilways. Check the diameters of the holes in the bearings. When the clearance between the camshaft journals and bearing surfaces exceeds 0.2 mm (wear limit), renew the bearing housing. The inner bearing surfaces should be ...
Page 35
When the level in the expansion tank is below the value spec- ified, while its density is in excess of that required, top up distilled water. When the density is as recommended, top up the correct coolant of the same grade as that in the cooling system. When the coolant density is below the value sp...
Page 36
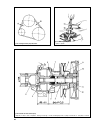
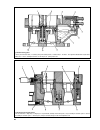
36 fig.2-61. Checking the water pump belt tension fig.2-63. Removing the impeller: 1 - puller; 2 - impeller fig.2-62. Sectional view of the coolant pump: 1 - pulley hub; 2 - shaft; 3 - cover; 4 - impeller; 5 - housing; 6 - thrust ring; 7 - oil seal; 8 - bearing stop screw; 9 - pulley; 10 - blower fa...
Page 37
Water pump drivebelt tension adjustment the belt tension is checked by exerting a hand pressure on the chain between the alternator pulley and pump pulley or between the pump pulley and crankshaft pulley. With proper ten- sion, slack a in the belt (fig.2-61) at 98 n (10 kgf) must be 10-15 ÏÏ, while ...
Page 38
Gradually heat the water from the starting 73-75 °ë in incre- ments of approximately 1 °ë per minute, at constant agitation to ensure homogeneous heating within the container. The value, when the valve travel is 0.1 mm, is deemed as the initial temperature of the main valve opening. The main valve o...
Page 39
39 fig.2-67. Lubrication system: 1 - oil passage to main bearing; 2 - main bearing-to-big-end bearing oil passage; 3 - oil filter relief valve; 4 - paper element; 5 - check valve; 6 - oil pump; 7 - oil pump-to- oil filter oil passage; 8 - oil passage from oil filter to main oil gallery; 9 - oil pass...
Page 40
Removal and refitting. When only the oil pump requires recon- ditioning, remove it from the vehicle (refer to section «engine - removal and refitting»), place it on the turning stand, drain the oil from the sump, turn over the engine and remove the sump. Undo the oil pump bolts and remove the pump c...
Page 41
Oil pump shaft and drive gears check to see there is no denting or scuffing of the shaft bear- ing journals or eccentric cam surfaces. No pitting of the oil pump gears or ignition distributor is per- mitted, if this is the case, renew the gears and shaft. Oil pump shaft bushes. Check the inner diame...
Page 42
Crankcase emission ventilation system flushing the system. For flushing disconnect vent hoses 4 and 5 (fig. 2-75) from the manifolds, remove flame arrester 3 from discharge hose 5, remove cover 6 of oil separator 7 and wash them in petrol or kerosine. Flush and blow dry with compressed air the carbu...
Page 43
Fuel system air cleaner and temperature regulator removal and refitting. To remove the air cleaner, release spring retainers 14 (fig. 2-76) and undo nut 7 securing air clean- er cover 8. Remove the cover and lift out filter element 10. Undo the nuts holding housing 13 to the carburettor. Disconnect ...
Page 44
44 fig.2-78. Fuel tank and fuel pipeline associated components 1 - fuel tank; 2 - hoses, fuel vapour separator and fuel tank; 3 - fuel vapour separator; 4 - filler pipe; 5 - cap; 6 - hose, fuel tank and filler pipe; 7 - hose, fuel vapour sepa- rator and fuel tank cover; 8 - fuel level sender; 9 - co...
Page 45
Check and renew any worn components. Always fit new pump gaskets, remember to lubricate the gaskets with a thin layer of grease before refitting them to the pump. Refitting pump to engine. For correct fitting, use two out of three gaskets as stated below: «Ä» gasket of 0.27-0.33 mm; «Ç» gasket of 0....
Page 46
Carburettor general description the engine is fitted with the 21073-1107010 carburettor (fig.2-81) of emulsion, twin progressive throttle type. The carbu- rettor features a balanced float barrel, a system of drawing crankcase emission on the throttle body, a part throttle channel heater and secondar...
Page 47
Table 2-2 21073-1107010 carburettor parameters primary barrel secondary barrel barrel diameter, mm 32 32 venturi diameter,mm 24 24 main jet system: • fuel jet marking* 107.5 117.5 • air jet marking 150 135 emulsion tube, type zd zc idling and air correction systems, primary barrel: • fuel jet markin...
Page 48
48 fig.2-82. Main metering system: 1 - main air jets and emulsion tubes; 2 - atomizers, primary and secondary barrels; 3 - balance orifice; 4 - fuel filter; 5 - return pipe with calibrated orifice to petrol tank; 6 - needle valve; 7 - float; 8 - secondary throttle valve; 9 - main fuel jets; 10 - pri...
Page 49
Main metering system. Fuel through gauze filter 4 (fig. 2- 82) and needle valve 6 is fed to the float chamber. From the float chamber fuel flows through main fuel jets 9 to the emulsion wells to be mixed with air, escaping from emulsion tubes 1 which are built as one piece with the main air jets. Th...
Page 50
Engine speed. Inner profiles 4.1 and 4.2 operate choke lever 6 allowing choke opening to a certain amount at intermediate posi- tions of lever 4. Rotation of choke lever 4 anticlockwise causes the wider slot to release choke lever 6 stud; the choke is held in a fully closed position by return spring...
Page 51
When the crankshaft speed goes down as low as 1900 rpm on the overrun, the control unit re-triggers the fuel cutoff solenoid to feed fuel through the idle jet, and the engine gradually shifts to idling. Secondary barrel locking. The secondary throttle can open only with the open choke when lever 5 e...
Page 52
Undo shaft 19, extract ball 17 with the spring, remove choke lever 18, detach the choke lever spring. When applicable, undo choke retaining screws, withdraw plate 14 and spindle 16. Dismantle the diaphragm-type choke control unit, having removed cover 8 complete with adjusting screw 7. Lift out spri...
Page 53
Float components. Wash the components in petrol and examine them. The floats must have no damages. Check to see there are no damages on the needle valve sealing face and seat which can result in the valve leakage. The valve must easily oper- ate in its socket, the ball should not stick. The float we...
Page 54
Part throttle enrichment unit (economizer). The diaphragm must be integral and have no damages. Renew the diaphragm complete with the pushrod when the pushrod length (the head included) is less than 6.0 mm. Carburettor - reassembly reassembly of the carburettor is a reverse of the dismantling proced...
Page 55
Throttle must be fully closed. If not, adjust the pedal and throttle by means of end piece 10 at front rod 1 end. Secure the end of throttle linkage cable 3 so that with knob 5 pulled, the choke is fully closed, while with knob 5 pushed in - fully open. Engine idle adjustment. This is to be done via...
Page 56
Exhaust system exhaust gases escape from the engine through the exhaust manifold, front exhaust pipe (downpipe) 2 (fig.2-93), centre (front) silencer 7 and main (rear) silencer 6. Gasket 1 is fitted between the exhaust manifold and down- pipe. The silencer pipes are connected through their flared en...