- DL manuals
- Vento
- Motorcycle
- zipr3i
- Service Manual
Vento zipr3i Service Manual
Summary of zipr3i
Page 2
Chapter 1. General information.........................Page 1 2. Periodic maintance and service.......Page 4 3. Engine..............................................Page 23 4. Fuel and lubrication system...........Page 37 5. Electrical system.............................Page 48 6. Servicing informati...
Page 3: Chapter 1
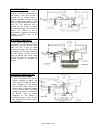
Chapter 1 1-1 general information type & identification frame number frame number is engraving on the steel tube of frame as shown in figure. Engine number engine number is engraving on rear side crankcase shown figure. Both frame nuber and engine number are designed specially for registration your ...
Page 4: 1-2 General Information
1-2 general information precautions and generalinstructions general precautions: warning proper service and repair procedures are important for the safety of the service mechanic and the reliability of the vehicle. When two or more persons are working together, pay attention to the safety of each ot...
Page 5
1-3 general information specifications dimensions and net weight overall length.......................1620mm overall width...........................625mm overall height.......................1010 mm wheelbase.............................1170mm ground clearance......................90mm dead weight....
Page 6: Chapter 2
Rev no.01/ page 6of 128 chapter 2 periodic maintenance and service contents periodic maintenance and service schedule................................5 storage battery.............................................................................7 service and adjustment procedures.........................
Page 7
Rev no.01/ page 7of 128 2-1 periodic maintenance schedule the chart below lists the recommended intervals for all the required periodic service work necessary to keep the motorcycle operating at peak performance and economy. Mileages are expressed in terms of kilometer, miles and time for your conve...
Page 8
Rev no.01/ page 8of 128 2-2 periodic maintenance procedure battery inspection and checking procedure storage battery inspect at initially 1000kms 630 miles 2 months and every 6000 kms 3780 miles 12 months. Open seat, and then remove the battery box cap in themiddle of helmet box. Disconnect negative...
Page 9
Rev no.01/ page 9of 128 battery testing procedure remove the battery from the motorcycle/scooter. Connect the battery on load tester ensuring red lead of tester to (+ve) and black lead to (-ve) terminal of battery. Check the terminal voltage of battery. It should be 12~14.5 volts. Press the push but...
Page 10: Important Tips On Battery
Rev no.01/ page 10of 128 important tips on battery specific gravity the specific gravity of fully charged battery should be 1.220~1.240 use hydrometer to check each cell of battery. Warning remove negative terminal first, then positive terminal. If the battery is corroded by sulfur. Please exchange ...
Page 11: Bolts
Rev no.01/ page 11of 128 2-3 periodic maintenance and adjustment procedure cylinder head nuts and exhaust pipe bolts tighten at initially 1000 km 630 miles or 2 months and every 6000 km 3780 miles or 12 months. If cylinder head nuts are not tightened to the specified torque, may result in leakage of...
Page 12
Rev no.01/ page 12of 128 2-4 periodic maintenance and adjustments procedure spark plug neglecting the spark plug maintenance eventually leads to difficult starting and poor performance. If the spark plug is used for a long time, the electrode gradually burns away and carbon builds up along the insid...
Page 13
Rev no.01/ page 13of 128 2-5 periodic maintenance and adjustment procedur e air cleaner : clean every 3000 kms 1890 miles replace every 12000 kms(1750 miles) if the air cleaner is clogged with dust, air intake resistance will be increased with a result decrease in power output and will be increase i...
Page 14
Rev no.01/ page 14of 128 throttle cable adjust at initially 1000kms 630 miles or after 2 months. And after every 6000 kms 3780 miles or after 12 months. Loosen locknut and adjust throttle cable play by turning adjuster in or out to obtain the following cable play. After adjusting the cable play tigh...
Page 15
Rev no.01/ page 15of 128 2-6 periodic maintenance procedure oil pump: inspect at initially 1000 kms 630 miles 2 months and every 6000 kms 3780 miles or 12 months there after. The oil pump to the engine feeds the engine oil. The amount of oil fed to it is regulated by engine speed and oil pump contro...
Page 16
Rev no.01/ page 16of 128 2-7 periodic maintenance procedure gear oil: inspect at initially 1000 km 600 miles or 2 months and every 6000 km 3780 miles or 12 months thereafter. Inspect gear oil periodically as follows: remove the cover and hose. Remove the kick-start lever. Remove clutch cover remove ...
Page 17
Rev no.01/ page 17of 128 2-8 periodic maintenance procedure brake pads (front brake) observing the limit can check the wear condition of brake pads line marked on the pad. When the wear exceeds the limit mark, replace the pads with new ones. Caution: replace the brake pad as a set, otherwise braking...
Page 18
Rev no.01/ page 18of 128 2-9 periodic maintenance and adjustment procedure : brakelevr play (rear brake): turn adjusting nut 2 so that the play @ of brake lever is 15-25mm (0.6~0.8) as shown. Brake shoe wear: this vehicle is equipped with the brake lining limit indicator on the rear brake. Inspect b...
Page 19: Tire
Rev no.01/ page 19of 128 tire inspect at initially 1000kms 630 miles 2 months and every 6000km 3780 miles 12 months thereafter tire pressure if the tire pressure is too high, the steering will be adversely affected and tire wear increased. Conversely, if tire pressure is too low, stability will be a...
Page 20
Rev no.01/ page 20of 128 front fork: inspect &adjust at initially 1000 kms 630 miles 2 months and every 6000 km 3780 miles 12 months thereafter. Inspect the front shock absorber for oil leakage or other damage, and replace the defective parts, if necessary. Rear shock absorber: inspect &adjust at in...
Page 21
Rev no.01/ page 21of 128.
Page 22: Lubrication:
Rev no.01/ page 22of 128 lubrication: proper lubrication is important for smooth operation and long life of each working part of the scooter. The major lubrication points are indicated below note lubricate exposed parts, which are subject to rust with a rust preventive spray whenever the motorcycle ...
Page 23: Compression Pressure Check
Rev no.01/ page 23of 128 compression pressure check the compression of the cylinder is a good indicator of its internal condition. The decision to overhaul the cylinder is often based on the results of a compression test. Periodic maintenance records kept at your dealership should include compressio...
Page 24
Rev no.01/ page 24of 128 automatic clutch inspection this vento zip r3i is equipped with an automatic clutch and variable ratio belt drive transmission. The engagement of the clutch is governed by engine rpm and centrifugal mechanism located in the clutch. To ensure proper performance and longer lif...
Page 25
Rev no.01/ page 25of 128 chapter 3 engine contents page engine components removal with the engine in place ............... ...24 engine removal and reinstallation ... .......25 engine components inspection and servicing........................................33 crankshaft ..............................
Page 26
Rev no.01/ page 26of 128 the parts listed below can be removed and reinstalled without removing the engine from the frame. Engine left side kick starter lever clutch cover kick starter shaft kick driven gear fixed drive fan fixed drive gear v-belt movable drive face starter driven gear starter drive...
Page 27
Rev no.01/ page 27of 128 engine removal and reinstallation engine removal remove ignition coil remove muffler remove cylinder cover remove cooling fan cover remove cooling fan remove magneto rotor nut. Remove the magneto rotor. Remove magneto rotor and key. Remove oil pump and retainer..
Page 28
Rev no.01/ page 28of 128 remove oil pump gear. Remove cylinder head and cylinder. Place a cloth stopper below the piston and remove the circlip with pliers. Remove the piston pin and piston. Remove the kick-starter lever. Remove clutch cover remove the kick-starter shaft spring and kick starter shaf...
Page 29
Rev no.01/ page 29of 128 remove the retainer after removing the screws. Remove spring, gasket and kick starter gear. Remove the kick-starter nut with the special a tool. Caution : the nut has counter-clockwise thread. Remove fan and v-belt. Disassemble the movable drive face. Remove the kick-starter...
Page 30
Rev no.01/ page 30of 128 drain gear oil. Remove gear case cover. Remove starter shaft. Remove the circlip and final driven gear. Remove the idle gear shaft assay. Remove the rear axle nut. Remove the rear wheel. Remove brake shoes and rear axle shaft. Remove the rear brake cam lever indicator plate ...
Page 31
Rev no.01/ page 31of 128 disassemble crankcase with a special tool. Remove crankcase. Loosen the clutch shoe nut. Remove the nut while holding down clutch shoe assembly with both hands (as shown)..
Page 32
Rev no.01/ page 32of 128 warning: gradually back off the clutch shoe assembly pressed down by hands to reduce the clutch-sparing load. Releasing your hand suddenly may cause damage to the following parts. Clutch shoe nut clutch shoe assembly springs caution : do not attempt to disassemble the clutch...
Page 33
Rev no.01/ page 33of 128 caution : replace the removed oil seal. Remove the bearing with special tool. Caution : replace the removed bearing with a new one. Removing the bearings with special tools. Remove the bearing retainer. Remove oil seal with the special tools. Caution : replace the removed oi...
Page 34
Rev no.01/ page 34of 128 remove the right crankshaft oil seal with special tool. Caution : the removed oil seal should be replaced with a new one. Remove the right crankshaft bearing with the special tool. Caution : the removed bearing should be replace with a new one. Remove the left crankshaft bea...
Page 35
Rev no.01/ page 35of 140 bearing: clear bearing with solvent and lubricate with engine oil before inspection. Rotate the bearing inner race by finger to inspect for abnormal play, noise and smooth rotation while the bearings are in the crankcase. Replace the bearing if there is anything unusual. Dam...
Page 36
Rev 01/ page89 of 143 conrod deflection and conrod big end side clearance turn the crankshaft with the connecting rod to feel the smoothness of rotary motion in the big end. Move the rod up and down while holding the crankshaft rigidly to be sure that there is no rattle in the big end. Wear on the b...
Page 37
Rev 01/ page90 of 143 clutch housing inspection: inspect visually the condition of the inner surface of clutch housing, for deep scratches or uneven wear or discoloration caused by burning. Measure the clutch housing inside diameter with inside calipers. Measure the diameter at several points to che...
Page 38
Rev 01/ page91 of 143 driving face spring inspection: measure the free distance of the driven face spring. If the length is shorter than the service limit, replace the spring with a new one. Service limit: 104.5mm (4.11 in) driven face pin and oil seal inspection: turn the driven face and check to s...
Page 39: Section 1.01
Rev 01/ page92 of 143 chapter 4 section 1.01 section 1.02 fuel and lubrication system contents fuel switch 38 carburetor ...39 oil pump ....41.
Page 40
Rev 01/ page93 of 143 fuel switch when turning the starter motor, a negative pressure is generated in the combustion chamber. This negative pressure draws on the fuel tap diaphragm, (through a passage way in the carburetor intake pipe) and vacuum hose. Due to this, the negative pressure increases be...
Page 41: Carburetor
Rev 01/ page94 of 143 carburetor carburetion proper carburetion is determined according to the results of various tests, mainly concerning engine power, fuel consumption and cooling effect of fuel on engine, and jet settings are made so as to satisfy and balance all of these conditions. Therefore, t...
Page 42
Rev 01/ page95 of 143.
Page 43: Air Fuel System
Rev 01/ page96 of 143 air fuel system air-fuel flow circuit fuel is being supplied to the carburetor from fuel tank by controlled fuel cock assy. Air filter box is fitted on the left side of the motorcycle. Fuel gets atomized and mixes with clean air in right proportion in the carburetor and then ai...
Page 44: Carburettor Circuits:
Rev 01/ page97 of 143 air fuel mixture ratio 1. Starting ----------------------------------------------7~8: 1 2. Idling speed------------------------------------------10~12: 1 3. Slow speed ------------------------------------------12~14: 1 4. Medium speed---------------------------------------15~17...
Page 45
Rev 01/ page98 of 143 carburettor circuits 1. Fuel intake circuit: from fuel tank fuel comes into float chamber of carburetor by controlled fuel cock assy . Separate vent is provided at lh side of carburetor body to maintain inside atmospheric pressure. When fuel starts filling the float chamber, fl...
Page 46
Rev 01/ page99 of 143 3 . Idling circuit: after starting operation choke is released, more air starts flowing thru the venturi. From slow jet fuel is sucked due to venturi effect. A separate passage from the air filter side is coming at the diffuser of the slow jet for the atomization of fuel in slo...
Page 47
Rev 01/ page100 of 143 1. High speed circuit during acceleration the throttle valve (piston) is fully raised, more air is being supplied due to higher velocity. Hence pressure drops at the opening of throttle jet needle. Where as more fuel is sucked from the main jet due to tapperness of jet needle....
Page 48: Carburettor Assembly
Rev 01/ page101 of 143 carburettor assembly disassembly procedure for carburettor cleaning: remove the throttle valve from the accelerator cable by compressing the spring up from the seat in long slit. Remove the tip of the cable from the slot of the valve. Remove the jet needle from the throttle va...
Page 49: Warning
Rev 01/ page102 of 143 carburettor tuning or adjustment procedure after installation the carburetor in the engine as per above said procedure, follow the following steps: warming up the engine to the normal running temperature. Adjust idling speed to 1800±100 rpm by throttle stop (idle) screw. Turn ...
Page 50: Ignition System
Rev 01/ page103 of 143 article ii. Chapter 5 article iii. Electrical system contetns ignition system ...49 charging and lighting system ...51 starter system 54 fuel gauge ..57 oil level check light and turn signal indicator .57 switchs .. 59 battery. ...60
Page 51: Ignition System
Rev 01/ page104 of 143 ignition system the ignition system consists of a flywheel magneto, a cdi&ignition coil unit and a spark plug . 1 as the rotor generates, an ac current is induced in the coil. Then current induced in the a direction charges up the capacitor. 2 as the rotor rotates further, the...
Page 52
Rev 01/ page105 of 143 note: the spark in the spark gap window should be strong and continuous, not intermittent, across a preset 8mm(0.32in) gap. Allow the spark to jump the test gap for at least five minutes continuously. To insure proper operation under the temperature of actual riding. Magneto e...
Page 53
Rev 01/ page106 of 143 charging and lighting system the charging system uses the flywheel magneto shown in the figure. The charging and lighting coils are mounted on the magneto stator and generate ac as the flywheel rotor turns. Ac generated in the charging coil flows to the regulator/rectifier, wh...
Page 54: Charging Output
Rev 01/ page107 of 143 charging output checking: start the engine and keep it running at 5000 rpm with light switch turned on condition. Note: when making the test, be sure that the battery is fully charged condition. Digital tachometer: for measuring engine rpm specified charging output voltage 12~...
Page 55
Rev 01/ page108 of 143 no-load performance disconnect the magneto lead wire coupler. Start the engine and keep it running at 5000 rpm. Using a multimeter, measure the ac voltage between the white and red tracer lead wire and ground. If the tester reading is as follows, magneto is in good condition. ...
Page 56
Rev 01/ page109 of 143 starter system description the starter system is shown in the diagram below namely, the starter motor, relay, starter switch and battery. Depressing the starter button while squeezing the front or rear brake lever energizes the relay, causing the contact points to close, which...
Page 57
Rev 01/ page110 of 143 starter motor inspecition carbon brushes when the brushes are worn, the motor will be unable to produce sufficient torque, and the engine will be difficult to turn over. To prevent the, periodically inspect the length of the brushes and replace them when they are too short or ...
Page 58
Rev 01/ page111 of 143 armature coil using the multimeter, check the coil for open and ground by placing probe pins on each commutator segment and rotor core and on any two segments at various places. With the brushes lifted off the commutator surface. If the coil is found open-circuited or grounded...
Page 59
Rev 01/ page112 of 143 fuel level gauge inspection of fuel level gauge the two different checks to be used for inspection of fuel level gauge. The first and simplest test will tell if the meter is operating but will not indicate the meters accuracy throughout the range. To perform the test, lift the...
Page 60: Signal System:
Rev 01/ page113 of 143 signal system: the same bulb is used for both oil levels check light and turn signal indicator light. The circuit diagram is shown below. When the oil level has fallen to a certain level (the remaining amount of oil has become approximately 160 ml, the oil level check light tu...
Page 61: Battery
Rev 01/ page114 of 143 switches battery a) b) c) d) specifications type designation yuasa/yb4l-b capacity 12v-4ah specific gravity (fully charged) needs charging 1.24~1.28 at 27 0 c below 1.220 initial charging fillng electrolyte remove the aluminum tape sealing the battery electrolyte filler holes..
Page 62
Rev 01/ page115 of 143 battery open the battery cap 1 remove the electrolyte cap . Note after filling the electrolyte completely, use the removed cap as the sealed caps of battery-filler holes. Do not remove or pierce the sealed areas of the electrolyte container. Insert the nozzles of the electroly...
Page 63
Rev 01/ page116 of 143 after confirming that the electrolyte has entered into the battery completely, remove the electrolyte containers from the battery, wait for around 25 minuets. Insert the caps into the filler holes, pressing in firmly so that the top of the caps does not protrude above the uppe...
Page 64
Rev 01/ page117 of 143 chapter 6 servicing inforamtion contents troubleshooting ....................................................................63 wiring diagram.......................................................................65 battery.........................................................
Page 65
Rev 01/ page118 of 143 trouble shooting engine complaint symptom and possible causes remedy engine does not start, or is hard to start. Compression too low 1. Excessively worn cylinder or piston rings. 2. Stiff piston ring in place. 3. Gas leaks from the joint in crankcase, cylinder or cylinder head...
Page 66
Rev 01/ page119 of 143 engine idles poorly. 1. Excessively worn cylinder or piston rings. 2. Stiff piston ring in place. 3. Gas leaks from crankshaft oil seal. 4. Spark plug gaps too wide. 5. Defective cdi & ignition coil unit. 6. Defective magneto stator coil. 7. Float-chamber fuel level out of adj...
Page 67
Rev 01/ page120 of 143 section 3.03 carburetor complaint symptom and possible causes remedy trouble with starting. 1. Starter jet is clogged. 2. Air leaking from a joint between starter body and carburetor. 3. Air leaking from carburetor s joint s or vacuumed hose joint. 4. Starter plunger is not op...
Page 68: (B)
Rev 01/ page121 of 143 spark plug electrodes overheat or burn. 1. Spark plug too hot. 2. The engine overheats. 3. Spark plug loose. 4. Mixture too lean. 5. Not enough engine oil. Replace by cold type plug, tune up. Retighten. Adjust carburetor. Check oil pump. Magneto does not charge. 1. Open or sho...
Page 69
Rev 01/ page122 of 143 battery complaint (c) symptom and possible causes (i) remedy battery runs down quickly. 1. The charging method is not correct. 2. Cell plates have lost much of their active material as a result of over-charging. 3. A short-circuit condition exists within the battery due to exc...
Page 70
Rev 01/ page123 of 143 handling feels too heavy. 1. Steering stem nut over tightened. 2. Broken bearing/race in steering stem. 3. Distorted steering stem. 4. Not enough pressure in tires. Adjust. Replace. Replace. Adjust. Wobbly handle. 1. Loss of balance between right and left front suspension. 2. ...
Page 71
Rev 01/ page124 of 143 noisy front suspension. 1. Not enough grease. 2. Loose nuts on suspension. Refill. Retighten. Wobbly rear wheel. 1. Distorted wheel rim. 2. Defective or incorrect tire. 3. Loose nuts on the rear shock absorber. 4. Worn engine mounting bushing. 5. Loose nuts or bolts for engine...
Page 72
Rev 01/ page125 of 143 leakage of brake fluid. 1. Insufficient tightening of connection joints. 2. Cracked hose. 3. Worn piston seal. Replace or repair replace. Replace. Brake drags. 1. Rusty moving parts. Replace.
Page 73
Rev 01/ page126 of 143 wire, cable and brake hose routing.
Page 74
Rev 01/ page127 of 143 carburetor.
Page 75: (E)
Rev 01/ page128 of 143 (e).
Page 76
Rev 01/ page129 of 143 ignition coil starting relay cdi horn.
Page 77
Rev 01/ page130 of 143.
Page 78
Rev 01/ page131 of 143 special tools listed below for removal and reinstallation no. Tool number description 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 t01 t02 t03 t04 t05 t06 t07 t08 t10 t 11 t shape of sleeve sleeve tools 7mm,8mm,10mm,12mm,13mm flywheel remover sleeve (18mm,24mm) screw remover cylinder pressure gauge p...
Page 79
Rev 01/ page132 of 143 10
Page 80
Rev 01/ page133 of 143 tightenting torque o f screw thread parts engineitem n m cylinder guide cover tapping screw 1-4 fan guide cover lock bolt 10-12 cylinder cover locknut 15-18 spark plug 15-18 inlet pipe lock bolt 10-12 cooling fan impeller lock screw 10-12 flywheel lock bolt 45-50 magneto stato...
Page 81
Rev 01/ page134 of 143 servicing data cylinder+piston+piston ring description standard tolerance mm( in) piston to cylinder clearance 0.06-0.07 (0.0024-0.0028) 0.120 (0.0047) cylinder bore 40.005-40.020 (1.5750-1.5756) 40.075 (1.5778) piston diameter 39.94-39.955 (1.5724-1.5746) 39.885 (1.5703) cyli...
Page 82
Rev 01/ page135 of 143 conrod web to web width 38-38.1(1.496-1.500) crankshaft runout 0.05(0.002) oil pump description specification pump reduction ratio 30.000(30/1) cci pump discharge ratio(full open) 1.1-1.3ml/5min(working pressure is 0.06mpa and rotating speed 118r/min) clutch description standa...
Page 83
Rev 01/ page136 of 143 type ngk/r/br8hsa spark plug gap 0.6~0.8mm 0.020~0.028 ignition coil resistance primary /secondary 0.2 ~0.3 /7k ~10k plug cap-ground description specification note lighting green/red ground charging white ground magneto coil resistance exciting 200±20 at 20 blue white or green...
Page 84
Rev 01/ page137 of 143 tire pressure front tire air pressure 175kpa rear tire air pressure 196kpa fuel +engine oil description specification remark fuel type unleaded gasoline 90 or high octane number is recommended. Fuel tank capacity 5.2l gear oil sae85/90 gear oil capacity 0.10 ±0.01l gear oil ch...
Page 85
This document was created with win2pdf available at http://www.Daneprairie.Com. The unregistered version of win2pdf is for evaluation or non-commercial use only..