- DL manuals
- Verilink
- Network Hardware
- WANsuite 5165
- Reference Manual
Verilink WANsuite 5165 Reference Manual
Summary of WANsuite 5165
Page 1
I wansuite ® 5165 reference manual october 2002 34-00301.H.
Page 2
Ii w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 copyright notice copyright © 2002 verilink corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in any form by any means without the written permission of ve...
Page 3
Iii 3 the unit has been designed to prevent harm to the network. If the telephone company finds that the equipment is exceeding tolerable parameters, it can temporarily disconnect service. In this case, the telephone company will give you advance notice, if possible. 4 no customer is authorized to r...
Page 4
Iv w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5.
Page 5: Table Of Contents
V table of contents preface scope ..................................................................................................................................................... Xi manual organization ................................................................................................
Page 6
Vi w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 configuring the unit’s ip address ..................................................................................................... 2-2 installation wizard ....................................................................................................................
Page 7
Vii ip gateway details screen ......................................................................................................... 3-58 rip parameters .................................................................................................................... 3-59 ospf parameters .........
Page 8
Viii w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 ds0 status and alarm table ............................................................................................... 4-24 frame relay service details screen .......................................................................................... 4-27 frame relay ...
Page 9: Appendix B Snmp Agent
Ix management interfaces ...................................................................................................................... A-2 10/100 ethernet ........................................................................................................................... A-2 supervis...
Page 10
X w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5.
Page 11: Reface
P r e f a c e xi c hapter 0 p reface this reference guide for the verilink wansuite 5165 intelligent integrated access device (i 2 ad) describes unit features and specifications, configuration, and cabling. It is not a users guide containing step-by-step procedures. This manual is designed to be use...
Page 12: Typographic Conventions
Xii w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 agent. In addition, instructions are provided for loading these mib files into most snmp management stations. Typographic conventions the following table lists the conventions that are used throughout this guide. Related verilink documents the verilink manual as2000, the ...
Page 13
P r e f a c e xiii telephone customer support is available by telephone 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. To speak directly with a verilink customer service representative, you may dial one of the following numbers: • sales and marketing: 800-verilink (837-4546) • technical support : 800 -285-2755 (tol...
Page 14
Xiv w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 the address for you to use when returning a unit to verilink will be provided when the rma is issued. The standard delivery method for return shipments is standard ground for domestic returns and international economy for international returns (unless otherwise specified)...
Page 15: Bout
A b o u t t h e w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 1-1 c h a p t e r 1 c hapter 1 a bout the wan suite 5165 introduction the telecommunications network service market is rapidly changing, where network monitoring, control, and higher performance in packet processing are not only expected, but demanded, at comp...
Page 16
1-2 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 problems (diagnostics) on any permanent virtual circuit (pvc), access line, or physical circuit. Verilink’s framestart™ technology is standard with wansuite 5165 and benefits the initial installation of frame relay circuits by eliminating the requirement for a frame relay...
Page 17: Performance
A b o u t t h e w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 1-3 agreements (slas); isolate performance problems to the lan, local loop or frame relay network; determine appropriate bandwidth needs; and monitor network trends to aid in future capacity planning. Features of the wansuite 5165 performance historically, wan...
Page 18: About Framestart Technology
1-4 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 optional advanced network management as an option for the wansuite 5165, verilink offers a network management system based on redpoint's netvoyant™ software, which was designed to provide it professionals with the information required to make informed, enterprise-wide cap...
Page 19: Features Summary
A b o u t t h e w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 1-5 wansuite 5165 overview and advantages verilink’s wansuite 5165 is an innovative, highly intelligent, software-based wan access device optimized for frame relay access. The wansuite 5165 provides network managers with the tools necessary to monitor and trou...
Page 20
1-6 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 • un-numbered network • address management: nat and dhcp • programmable alarm thresholds • transparent bridging • configurable serial (data) port: • supports v.35, eia-530, and rs-232 • security features • ip host access list • multilevel password access • nat • superviso...
Page 21: Front Panel
A b o u t t h e w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 1-7 • management interfaces: • wansight − an innovative, embedded web-based user interface for remote configuration and real-time reporting via web browser (verilink recommends microsoft internet explorer 5.0 or higher) that decreases installation and configur...
Page 22: Local Supervisory Port
1-8 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 the front panel led status indicators and dip switch are defined in the table below: local supervisory port the supervisory port labeled on the front panel as local is an rj-11 female dce connector configured for 8 bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit. Bit rates are configured...
Page 23: 10/100 Ethernet
A b o u t t h e w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 1-9 notice: for information on pinout assignments for this connector, refer to page a-7. See ordering information on page a-6 for information on cables for this connector. The supervisory port performs several different functions. It serves as the vt100 interf...
Page 24: Serial (Data) Interfaces
1-10 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 ethernet led indicators there are two unlabeled indicator leds on either side of the 10/100 ethernet jack. The led on the left side of the jack pulses amber to indicate data activity (either transmit or receive). The led on the right side of the jack lights green to indi...
Page 25: Power Connection
A b o u t t h e w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 1-11 caution: in accordance with fcc rules, part 68.218(b), you must notify the telephone company prior to disconnecting this product. Power connection no external power supply is required for the wansuite 5165; power is received from its as2000 rack connectio...
Page 26
1-12 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5.
Page 27: Nstallation
I n s t a l l a t i o n 2-1 c h a p t e r 2 c hapter 2 i nstallation this chapter describes the contents of your wansuite 5165 shipment and provides information on connecting and installing the unit. The wansuite 5165 uses an “installation wizard” to help you automatically install the unit quickly a...
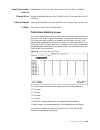
Page 28: Supplied Materials
2-2 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 completeness and the unit has been checked both mechanically and electrically. Supplied materials the wansuite 5165 ships with the following standard items: • wansuite 5165 unit (card and rear module or card without rear module) • t1 network cable • serial (supervisory) c...
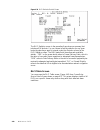
Page 29
I n s t a l l a t i o n 2-3 double-click on this file to launch the program. After the program is fully launched, you will see the following screen: 4 using the tab key to move from field to field, move the cursor to the “com port” field. Using the spacebar, toggle between the available options unti...
Page 30
2-4 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5.
Page 31: Erver
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-1 c h a p t e r 3 c hapter 3 w eb s erver i nterface the wansuite 5165 has an innovative, embedded web-based user interface (wansight) for remote configuration and real-time reporting via microsoft internet explorer 5.0 or higher. Access to the web server interf...
Page 32: Unit Screen
3-2 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 to view the web server interface, use microsoft’s internet explorer 5.0 or higher. To access the web server interface, type the unit’s ip address in the browser’s address (or location) field and press the “enter” key. Layout of interface screens when you first access the ...
Page 33
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-3 figure 3.1 unit screen the unit screen displays the following fields: the unit screen provides the following user-activated buttons: field function object id display-only field used to point an snmp agent to this id. Up time displays the amount of time the uni...
Page 34
3-4 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 maintenance reset use this button to access a screen where you can perform a maintenance reset (figure 3.2). When you click on the arrow in the pull-down menu box on the screen, you will have the option to perform a tdm, packet, packet 2, packet 3, or packet 4 reset. When...
Page 35: Interfaces
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-5 interfaces the wansuite 5165 has the following interfaces: network 1, network 2, serial 1, serial 2, 10/100 ethernet, and supervisory. Each of the interfaces and their associated screens/menus are described below. Network screens the network 1 (shown below in ...
Page 36
3-6 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 function (network 2 only) in the “slaved” function, network 2 is slaved and can only be mapped to network 1. In the network function, network 2 functions as an independent network, but can only be mapped to serial 2. Values: slaved, network default: slaved notice: the “fu...
Page 37
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-7 internal – the unit’s internal frequency standard (t1 1.544 mbps ± 50 bps) is used for all timing. Network 1, network 2 – timing is derived from the network port recovered clock. Serial 1, serial 2 – timing is derived from the serial port recovered clock. Zero...
Page 38
3-8 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 the four columns of the status table are as follows: the table provides error status and alarm threshold information for the following error parameters: es sets the errored seconds (es) threshold. An es is a 1-second period in which at least one logic error occurred. The ...
Page 39
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-9 applicable values range from 000 through 900. A value of “000” means the alarm will never be reset. The network screens provide the user-activated buttons described in the table below. Caution: performance data will be lost upon power cycle or after performing...
Page 40
3-10 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 lofc the loss of frame count (lofc) represents the number of time a loss of frame is declared. A loss of frame is declared after 2.5 seconds of continuous loss of signal or oof. Crces a cyclic redundancy check errored seconds (crces) is a method of confirming the integri...
Page 41
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-11 serial screens notice: all references in this manual to the serial 1 and serial 2 interfaces correspond directly to the wansuite 5165’s data 1 and data 2 ports, respectively. The parameters on all serial screens are the same except for the invert clock parame...
Page 42
3-12 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 notice: dte mode requires the use of an optional dte cable. Refer to optional equipment on page a-6 for ordering information. Packet rate if the port is running in packet mode, the rate must be configured to the desired port speed (in bits per second). In tdm mode, the p...
Page 43
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-13 mode on the serial 2 port. Consequently, this configuration option should remain disabled when configuring services for the serial 1 port. Values: disable, enable default: disable character size selects the number of bits required to make up one asynchronous ...
Page 44
3-14 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 dsr data set ready can be set to “forced true,” “forced false,” or “internal.” the “internal” option sets dsr “on” if the port is enabled and “off” if the port is disabled. Values: forced true, forced false, internal default: forced true dcd the data carrier detect param...
Page 45
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-15 figure 3.10 10/100 ethernet (ip service details) screen unit ip address a unique network address assigned to this unit. Subnet mask defines the network portion of the unit’s ip address. Gateway ip address ip address of the default gateway (router) on the lan ...
Page 46
3-16 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.11 ethernet statistics screen click on the unit access table button on the ethernet (ip details) screen to view the unit access table (figure 3.12), which specifies up to 10 different ip networks that may access the unit’s parameters. If no ip networks are suppl...
Page 47
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-17 figure 3.13 unit access details supervisory screen the supervisory screen (figure 3.14) displays the current speed of the supervisory port interface and other parameters described below. Figure 3.14 supervisory screen speed changes the supervisory port speed ...
Page 48: Services Screen
3-18 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 parity sets the parity bit. Values: none, odd, even default: none stop bit selects the number of bits required to end the character. Values: 1, 2 default: 1 current pin status shows the status of the dte supervisory port pins. Dtr alarm control and status table in additi...
Page 49
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-19 • up − the service is ready to pass data. • idle − the service has nothing to do. The table in the center of the screen displays the available services listed by index number. To view more detailed information about a service, click on the index number associ...
Page 50
3-20 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 about 10 lines of active data, and if a line is selected, the screen will display further decoded data below. Figure 3.17 data line monitor packet table the data line monitor details screen (figure 3.18) is displayed by clicking the appropriate services link on the data ...
Page 51
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-21 service details screen clicking on an index number under the “service index” column on the services screen will display a service details screen such as the one shown below (figure 3.19). (in this example, the selected service type is frame relay.) figure 3.1...
Page 52
3-22 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 interface details button clicking the “interface details” button on the service details screen lets you view interface parameters for the selected service. You will also see the interface parameters for the selected service if you click on the interface under the “interf...
Page 53
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-23 figure 3.21 ds0 monitor details screen number of ds0s number of active ds0s (0 − 24) assigned on a per-service basis. Alarm reset timer (sec) number of seconds that an alarm condition must not be present before an alarm is reset. Zero (0) indicates the alarm ...
Page 54
3-24 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.22 channel table details screen the channel table details screen lets you establish the rate, service, and idle pattern parameters for any available channel. The screen parameters are described below. Rate the unit can operate at any data rate that is a multiple...
Page 55
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-25 figure 3.23 ds0 monitor 24 hour history screen figure 3.24 ds0 monitor 30 day history screen the ds0 monitor 24 hour history and 30 day history screens show the following statistics for the specified period. Period period for which the ds0 monitor history is ...
Page 56
3-26 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.25 frame relay service details screen interface type if this service is connected to a frame relay network, the interface type should be set to “uni” because it is the user side of a user-to-network interface. If it is connected to a frad/router, the interface t...
Page 57
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-27 n2 the n2 counter specifies the total number of link reliability errors and protocol errors that can occur during the sliding event monitor count defined by n3. If this count is exceeded, the port is declared inactive. Values: 1–255 default: 3 n3 this counter...
Page 58
3-28 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 default cir (bps) this is the committed information rate (in bits per second) provided by your frame relay service provider. The unit will apply this value to each dlci learned from the network side to gather statistics and to perform cir enforcement, if required. If a d...
Page 59
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-29 notice: if either side of the frame relay connection goes down, you will be unable to remotely access any connected units. Framestart auto discovery when this parameter is set to “yes,” the unit will send framestart discovery and delay frames to each dlci it ...
Page 60
3-30 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 the frame relay details screen provides the following user-activated buttons: notice: when a “submit” command is executed, the frame relay link will be re-initialized with the new parameters, causing a brief interruption in data transfer. Frame relay port statistics scre...
Page 61
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-31 transmit frames number of frames transmitted by the port. Octets number of octets transmitted by the port. Mgmt frames number of management frames transmitted by the port. Mgmt octets number of management octets transmitted by the port. Stat inquiries number ...
Page 62
3-32 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.27 frame relay port statistics screen buttons scada details screen notice: scada traffic has a higher priority than other types of traffic flowing through the unit. Refer to normal tx queue size on page 3-27 for more details. Click on “scada” under the “type” co...
Page 63
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-33 message size maximum number of characters to buffer before sending a frame. Values: 0 − 1024 default: 256 idle character delay maximum number of idle character time to wait before sending a frame. Values: 0 − 65535 default: 10 input terminator decimal value o...
Page 64
3-34 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.30 scada device details screen ppp service details screen click on “ppp” under the “type” column on the services screen to view the ppp service details screen (figure 3.31). This menu gives you access to the configuration parameters described in the paragraphs b...
Page 65
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-35 mru this configuration option may be set to inform the peer that the implementation can receive larger packets, or to request that the peer send smaller packets. Values: 128–4096 default: 1500 port ip address the ip address of the port. For unnumbered ppp lin...
Page 66
3-36 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 chap secret enter the secret (i.E., password) necessary to challenge the peer. Values: user established default: secret parameters to negotiate the table displayed near the bottom of the ppp service details screen shows which parameters are set to be negotiated. You can ...
Page 67
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-37 figure 3.32 ppp statistics screen transmit frames number of frames transmitted by the port. Octets number of octets transmitted by the port. Mgmt frames number of management frames transmitted by the port. Mgmt octets number of management octets transmitted b...
Page 68
3-38 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 the ppp statistics screen provides the following user-activated buttons: pap table at the bottom of the ppp services details screen are buttons that display tables for pap and chap details. The pap table (figure 3.33) displays the usernames and passwords for 10 entries. ...
Page 69
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-39 to delete the username and password for a selected pap index, delete the character string displayed in both fields (leaving them blank) and click the “submit” button. The “type details” button returns you to the ppp type details screen. Chap table from the pp...
Page 70: Applications
3-40 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 applications the applications screens describe configuration tables and statistics for layer 3 and above that do not map to a specific service or interface. Endpoint table screen the endpoint table (figure 3.37) describes all endpoints terminating in the unit; links are ...
Page 71
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-41 figure 3.38 endpoint details screen name when the unit learns a new dlci, it creates an endpoint entry and a dlci entry if they are not already configured. The endpoint’s name will automatically be assigned as “dynamic”; however, this name can (and most likel...
Page 72
3-42 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 backup endpoint if this dlci has an alternative endpoint to which this dlci can be switched if it becomes inactive, the endpoint index of this alternative endpoint would be configured here. For most applications, you will not need to set this parameter. Values: 0–256 def...
Page 73
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-43 the endpoint details screen provides the following user-activated buttons: endpoint service details screen clicking the “service details” button at the bottom of the endpoint table screen displays the typical service details screen. Refer to the service detai...
Page 74
3-44 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 protocol encapsulation the type of encapsulation used by the frad/router connected to the unit. Values: rfc 1490, proprietary default: rfc 1490 proprietary traffic type when protocol encapsulation is set for “proprietary,” the proprietary traffic type parameter defines w...
Page 75
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-45 the status of the remote unit. The status is “active” if both the local and remote dlcis are active and the remote unit answers to the discovery frames sent by this unit. The status is “sos” if the remote unit is active but the frad/router connected to it is ...
Page 76
3-46 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 bits over be threshold sets the tx over be alarm threshold. This threshold is the number of bits per second in excess of cir + be during a 15-minute interval. Setting this field to “0” (zero) disables the alarm. Bits over be alarm reports if the tx over be threshold has ...
Page 77
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-47 figure 3.40 dlci statistics screen there are ninety-six 15-minute buckets (sampled every second) available for dlci statistics. If the unit is powered on at 01:00 pm, the first interval will be completed at 01:15 pm; subsequent intervals would be completed at...
Page 78
3-48 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.41 dlci table screen notice: the dlci table and dlci details screens are available from both the endpoint table and the frame relay service details screens. Service aware screen the service aware function recognizes ip traffic and counts the number of frames and...
Page 79
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-49 notice: if you change a service parameter, you must click on submit to see the appropriate dlcis. The service aware screen provides a “clear alarms” user-activated button at the bottom of the screen. Rule details screen use the rule details screen (figure 3.4...
Page 80
3-50 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 notice: to use this filter, you must specify both the service and dlci parameters on the rule details screen. Ip address establishes the ip address by which the rule will filter ip traffic (if enabled). Ip mask represents a range of ip addresses defined so that only mach...
Page 81
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-51 figure 3.44 traffic meter statistics screen the traffic meter statistics screen reports on the following parameters: • tx frames • tx octets • rx frames • rx octets • rate peak – the peak data rate for the viewed period (see below) • rate average – the averag...
Page 82
3-52 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 each non-zero trap ip address. The snmp details screen (figure 3.45) lets you configure the snmp parameters described in the paragraphs below. Figure 3.45 snmp details screen read community accepts a character string identifying the group authorized to perform read opera...
Page 83
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-53 description describes the type of interface selected for testing. Loop type describes the type of loop test (if any) performed on the selected interface. Setting displays the bandwidth on which you wish to perform the bert. Pattern specifies the pattern to be...
Page 84
3-54 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 bert table on the network interface test details screen the bert table provided on the test details screen lets you set the test parameters listed below. Setting displays the bandwidth on which you wish to perform the bert. The available values for this parameter depend ...
Page 85
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-55 %efs displays the percentage of time that the test ran error-free. This ratio is derived from the number of error free seconds divided by the number of seconds accumulated in elapsed time. Loop table on the network interface test details screen the loop table...
Page 86
3-56 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 you can also view the following read-only parameters from this screen: pattern sync displays the state of pattern sync during a test. If no test is in progress, “no test” is displayed. If a test is active, but the receiver is not in pattern sync, “no sync” is displayed. ...
Page 87
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-57 figure 3.49 trap log screen top talkers screen clicking on the “top talkers” link in the navigation tree displays a screen (figure 3.50), where you can set the parameters for and initiate the generation of a list of ip addresses ranked in terms of the number ...
Page 88
3-58 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 as soon as the specified duration for the report has elapsed, the screen will refresh itself and the resulting report-specific information will be displayed in the outlined box at the bottom of the screen. This report comprises elements as defined in the following paragr...
Page 89
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-59 figure 3.51 ip gateway details screen rip parameters rip enable globally enables rip1, rip2, or no rip. Values: disable, enable rip1, enable rip2 default: enable rip2 rip trust neighbors globally enables the trusted neighbors feature. If there is a list of tr...
Page 90
3-60 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 the ip gateway details screen provides the following user-activated buttons: circuit table screen access this menu by clicking on the “circuit table” button at the bottom of the ip gateway menu. This screen shows the configured circuit. To configure a new circuit, click ...
Page 91
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-61 figure 3.53 circuit details screen. Endpoint endpoint name. By default, the first circuit is always the lan circuit. All other circuits are associated with endpoint names as defined in the endpoint table as shown in figure 3.37. Ip address ip address of the c...
Page 92
3-62 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 ospf area represents the area that this circuit is part of. Ospf lsa timer determines how often the link state acknowledgment (lsa) packet is sent. Values: 1 − 3600 default: 1 ospf lsu delay the estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link state update (lsu) p...
Page 93
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-63 the static route table (figure 3.54) is always associated with a circuit. Access this screen by selecting the static route table from the rip parameters table on the ip gateway details screen. Figure 3.54 static route table screen endpoint endpoint name (or i...
Page 94
3-64 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.55 route details screen endpoint endpoint name (or interface) through which to send the ip packet to reach the target ip address. Target ip address represents the target network that you want this router to reach. Values: 0.0.0.0 − 255.255.255.255 default: 0.0.0...
Page 95
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-65 route table.” this table shows all known dynamic and static routes. Please note that not all parameters are necessarily defined, depending on whether or not the routes were learned dynamically. Primarily, the most useful information is included in "destinatio...
Page 96
3-66 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.57 arp table screen endpoint endpoint name (or interface) through which to send the ip packet to reach the defined ip address. The default is the lan. Ip address the ip address of the unit for which you want to define the mac address. Mac address the mac address...
Page 97
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-67 mac address mac address of the host to be reached. Values: a 6-byte value default: 00-00-00-00-00-00 arp status displays whether this arp is enabled or disabled. Values: enable, disable default: enable the arp details screen provides the following user-activa...
Page 98
3-68 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 the neighbor details screen provides the following user-activated buttons: area table screen an area allows growth and makes the networks at a site easier to manage. An area is self-contained; knowledge of an area’s topology remains hidden from other areas. Thus, multipl...
Page 99
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-69 figure 3.62 area details screen area id this parameter has the same format as the ip address of the mask address. Values: 0.0.0.0 − 255.255.255.255 default: 0.0.0.0 enable displays whether or not the area is enabled. Values: enable, disable default: enable au...
Page 100
3-70 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 throughout the routing domain. The collected link state advertisements of all routers and networks form the protocol's topological database. Values: yes, no default: no the area details screen provides the following user-activated buttons: virtual link table screen to pe...
Page 101
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-71 enable enables this definition of a virtual link. Transmit area id the non-backbone area that the virtual link goes through. Area border router id the router id of the virtual link’s other endpoint. The “add new” button lets you define a new virtual link. Vir...
Page 102
3-72 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.65 tcp server details screen select the tcp connection details screen (figure 3.66) by clicking on the appropriate number under the “connection” column on the above screen. The tcp connection details screen lists the index number, the endpoint name, the tcp loca...
Page 103
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-73 figure 3.68 tcp host access table screen you can access the host access details (figure 3.69) for a specific index number by clicking on the appropriate numbered link under the “index” column. Figure 3.69 tcp host access details network address translation (n...
Page 104
3-74 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 nat details screen the nat details screen (figure 3.70) lets the user configure the nat global parameters described below. Figure 3.70 nat details screen enable enables or disables nat. Default is “disable.” mode selects the network address port translation (napt) mode o...
Page 105
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-75 ip entry timer the maximum time (in seconds) nat will use resources when not using tcp, udp, or icmp. Values: 0 − 65535 default: 120 tcp connection timer the maximum time (in seconds) nat will use resources when attempting to establish a tcp connection. Value...
Page 106
3-76 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 static tcp translation table screen the static tcp translation table screen (figure 3.71) allows static mapping of global tcp server ports to a local host ip address/port combination. The parameters described below enable access to tcp servers on the private/ corporate n...
Page 107
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-77 static udp translation table screen the static udp translation table screen (figure 3.74) allows static mapping of global udp server ports to a local host ip address/port combination. The parameters described below enable access to udp servers on the private/...
Page 108
3-78 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 details screen by clicking on the index number of the desired port on the nat port table screen. Figure 3.75 nat port table screen endpoint the endpoint name of the circuit associated with the lan or wan port. Default is lan for the first port. Enable enables or disables...
Page 109
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-79 figure 3.76 nat port details screen the nat port details screen provides the following user-activated buttons: the nat port status table (figure 3.77) displays for each port the processed packets from specific ip addresses. Figure 3.77 nat port status table s...
Page 110
3-80 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 assigned to any other computer on that network. If a computer moves to a new network, it must be assigned a new ip address for that new network. Dhcp can be used to manage these assignments automatically. Dhcp has other important configuration parameters also, such as th...
Page 111
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-81 lease time tells the dhcp client the number of seconds it can retain this ip address. The client should make a new dhcp request within the specified amount of time to ensure the ip address is not given to another pc. Default is 600 seconds. Primary dns ip add...
Page 112
3-82 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 host name the name of the dhcp server. Default is none. The dhcp host table screen provides the following user-activated buttons: notice: you must save and restart for the new server name to become active. Figure 3.80 dhcp host details screen the dhcp host details screen...
Page 113
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-83 mask mask associated with the ip address shown on the screen. Host name name given to the dhcp client. The static entry table screen provides the following user-activated buttons: figure 3.82 static entry details screen the static entry details screen provide...
Page 114
3-84 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 subnet mask subnet mask associated with the defined range. Exclude start beginning of “excluded” range. Exclude end end of “excluded” range. The ip address list screen provides the following user-activated buttons: figure 3.84 ip address details screen the ip address det...
Page 115
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-85 ip address ip address given to this dhcp client if that client has the mac address defined on this screen. Status provides ip address status. Bridge a bridge operates at the physical network layer, connecting two or more networks and forwarding packets betwee...
Page 116
3-86 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 hello timer specifies the bpdu broadcasting interval. Values: 1 − 65535 s default: 10 s max age timer specifies the length of time a bridge will consider the network topology held in memory as valid. Values: 1 − 65535 s default: 60 s forward delay specifies the length of...
Page 117
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-87 figure 3.88 bridge port details enable enables or disables bridging on this port. Endpoint endpoint name. Bpdu option shows if bpdu packet will be sent and received on this port. Filter by multicast addr dest filters multicast messages received on this port, ...
Page 118
3-88 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 forward transmissions number of times this port has changed from any other state to a “forwarding” state. Input frame number of frames received. Output frame number of frames transmitted. Input discards number of frames discarded. Figure 3.89 bridge lookup table address ...
Page 119
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-89 figure 3.90 smtp details screen mail server ip address ip address of the mail server to which notifications will be sent. Domain name name of domain where the device resides (i.E., verilink.Com) mail from e-mail address of the device (wansuite). While the dev...
Page 120: Utilities
3-90 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 3.91 encryption details screen utilities the options available beneath the utilities branch of the navigation tree serve as utilities for upgrading the software in your wansuite 5165, managing access with passwords, and logging off the system. Notice: make sure yo...
Page 121
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-91 figure 3.92 upload/save screen password the password screen (figure 3.93) is used to modify the password that restricts access to the web server interface. Acceptable characters for use in a password are digits 0–9 and letters a–z and a–z, for a total of 62 d...
Page 122
3-92 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 notice: remember that passwords are case-sensitive and are limited to no more than 10 characters. When logging on, password must be entered exactly as it was programmed. Log out the log out screen (figure 3.94) is used to log the current user off of the web server. The l...
Page 123
W e b s e r v e r i n t e r f a c e 3-93 the local router (router a) for each remote wansuite 5165 to manage. If router a becomes unavailable, there is no way to reach the remote wansuite 5165s. Use of local wansuite 5165 as a gateway if you choose this method, the wansuite 5165s are totally indepen...
Page 124
3-94 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5.
Page 125: Vt100 I
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-1 c h a p t e r 4 c hapter 4 vt100 i nterface introduction this chapter describes the menus and options associated with the wansuite 5165’s vt100 interface. The screens displayed throughout this chapter were accessed through a telnet session. Notice: the material presen...
Page 126
4-2 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.1 vt100 terminal screen components cursor controls the vt100 interface uses a blinking cursor to select various menus and then to select sub-menus and/or fields within those menus. You can navigate using this cursor in different ways, depending on the program you...
Page 127
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-3 menu after changing the parameters. In some cases, you will press the “enter” key to save new parameters. Fields enclosed in brackets [ ] offer a list of selections from which to choose. The selections may be made by pressing your spacebar to “toggle” between choices....
Page 128: System Screen
4-4 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 caution: if you do not enter a keystroke for 10 minutes, the terminal interface logs you off automatically. System screen the first option on the main menu screen is the system screen (figure 4.3). This screen lets you view and set specific information about the unit in s...
Page 129
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-5 notice: remember that passwords are case-sensitive and are limited to no more than 10 characters. When logging on, password must be entered exactly as it was programmed. The system screen displays the user-selectable prompts listed below. Maintenance reset select this...
Page 130: Interfaces Screen
4-6 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.5 confirmation screen notice: performing a “maintenance reset” or a “save and restart” will terminate communications with the unit. Refresh (by pressing “ctrl+u”) after approximately 10 seconds to restore communications. Save and restart selecting “save and resta...
Page 131
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-7 from the interfaces screen, you may choose from the following: network 1, network 2, serial 1, serial 2, 10/100 ethernet, or supervisory. Network configuration screens the wansuite 5165 network screens let you view and make changes to the network interface's configura...
Page 132
4-8 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 “enable” instructs the unit to use ansi t1.403, which sends a prm once every second. Setting this field to “disable” instructs the unit to use at&t tr54016, which provides performance reporting on request only. Values: disable, enable default: disable learn ds0s on boot d...
Page 133
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-9 line build-out (long haul) sets the transmit line build out (lbo) for the long-haul network interface. Values: 0, − 7.5, − 15.0, − 22.5 db default: 0 db dsx level (short haul) specifies the dte dsx-1 interface output level. Values: 0 − 110, 111 − 220, 221 − 330, 331 −...
Page 134
4-10 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 loss sets the loss of signal seconds (loss) threshold. A loss is 1-second period in which the e1 received signal is interrupted. The default value is 5 seconds. Uas sets the unavailable seconds (uas) threshold. A uas is a 1-second period in which consecutive severely err...
Page 135
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-11 performance screens the performance prompt near the bottom of the network screens displays a performance 24 hour screen (figure 4.8), which provides a summary of the error events that have occurred during each interval of the past 24 hours. In addition to the paramet...
Page 136
4-12 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.9 performance 30 day screen caution: performance data will be lost upon power cycle or after performing a maintenance reset/restart. Serial screens notice: all references in this manual to the serial 1 and serial 2 interfaces correspond directly to the wansuite ...
Page 137
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-13 figure 4.10 serial 2 screen type this parameter selects the type of interface (based on its electrical signal characteristics) used by the equipment connected to the serial port. Values: v.35, rs-232, eia-530 default: v.35 notice: v.35 requires the use of an optional...
Page 138
4-14 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 bundling selects whether the dte channel assignment is made as a “contiguous” group or as “alternate” channels. Selecting “alternate” ensures ones density. Because the unit allows individual channels to be configured for a service, a value of “arbitrary” will be returned...
Page 139
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-15 ll the local loopback (ll) parameter can be set to “enable” or “disable.” selecting “enable” allows the unit to go into local loop when the ll pin on the serial port goes high. The unit exits the loop when the ll pin goes low. If you select “disable,” the unit ignore...
Page 140
4-16 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 dsr data set ready can be set to “forced true,” “forced false,” or “internal.” the “internal” option sets dsr “on” if the port is enabled and “off” if the port is disabled. Values: forced true, forced false, internal default: forced true dcd the data carrier detect param...
Page 141
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-17 unit ip address a unique network address assigned to this unit. Subnet mask defines the network portion of the unit’s ip address. Gateway ip address ip address of the default gateway (router) on the lan side of the unit. Dhcp client if dhcp client is enabled at power...
Page 142
4-18 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.13 unit access details supervisory configuration screen the supervisory configuration screen (figure 4.14) displays the current speed of the supervisory port interface and other asynchronous parameters as described below. The supervisory port supports only async...
Page 143: Service Table Screen
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-19 parity sets the parity bit. Values: none, odd, even default: none stop bit selects the number of bits required to end the character. Values: 1, 2 default: 1 dtr alarm control choices for dtr alarm control are “enable” and “disable”; the default setting is “disable.” ...
Page 144
4-20 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.15 service table screen the status for a particular service will display as one of the following: • dead − the service is not functional because required resources are not available. • changed − the service parameter was changed and a save and restart is require...
Page 145
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-21 figure 4.16 data line monitor config table service enable and disable displays whether capture is enabled or disabled. Tx/rx filter displays the direction of the captured data. Pattern filter enable displays the filter for the pattern being searched and captured. Pat...
Page 146
4-22 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.17 data monitor packet table screen mode the two modes available are “analyze” and “live.” the live mode lets you capture data and create a usable text file of the captured data. In analyze mode, the packet switch will return the data via the data line monitor p...
Page 147
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-23 service details screen from the service details screen, you can access and change the parameters listed below. The new parameters are saved when you press the “esc” key and return to the previous screen. Figure 4.19 service details screen interface selecting one of t...
Page 148
4-24 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 ds0 monitor details screen to access the ds0 monitor details screen, select “tdm” in the column on the service table screen. This screen lets you configure what are considered high and low ds0 utilization parameters, and will report alarms if the monitored statistics ris...
Page 149
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-25 statistics. This table also gives the status of the alarms (ok, alarmed) related to ds0s. The user-activated prompts listed below are at the bottom of the ds0 monitor details screen. Figure 4.21 channel table details screen the channel table details screen lets you e...
Page 150
4-26 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.22 ds0 monitor 24 hour history screen figure 4.23 ds0 monitor 30 day history screen the ds0 monitor 24 hour history and 30 day history screens show the following statistics for the specified period. Period period for which the ds0 monitor history is displayed. T...
Page 151
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-27 frame relay service details screen access the frame relay service details screen (figure 4.24) by selecting “frame relay” under the column on the service table screen. Figure 4.24 frame relay service details screen the frame relay service details screen displays serv...
Page 152
4-28 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 once it discovers the link management type, the unit should be set to the discovered value so that subsequent unit or network re-initialization will be faster. Values: auto, ccitt, ansi, lmi, none default: ansi max frame size if auto diagnostic is set to “yes,” the unit ...
Page 153
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-29 rx threshold number of bits per second sent during a 15-minute interval after which an rx alarm will be triggered. Default of 0 disables this alarm. Values: 0–4294967295 default: 0 rx alarm status of this alarm (ok, alarmed). Default cir (bps) this is the committed i...
Page 154
4-30 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 received between the network and the serial port regardless of the number of dlcis or frame size. Framestart auto diagnostic mode should be left set to “yes” unless the frame relay connection has more that 128 dlcis, or if there is a very high traffic rate on a constant ...
Page 155
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-31 changes state, provided at least one destination ip address for trap is configured in the snmp configuration. Values: disable, enable default: disable rx invalid threshold number of invalid frames received during a 15-minute interval after which an rx invalid alarm w...
Page 156
4-32 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.25 frame relay statistics screen. To view the port statistics (figure 4.26) for a specific interval, select that interval from the frame relay statistics column. Figure 4.26 frame relay port statistics screen transmit frames number of frames transmitted by the p...
Page 157
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-33 receive frames number of frames received by the port. Octets number of octets received by the port. Mgmt frames number of management frames received by the port. Mgmt octets number of management octets received by the port. Fecn number of forward explicit congestion ...
Page 158
4-34 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 accm the asynchronous control character map (accm) configuration option provides a method to negotiate the use of control character transparency on asynchronous links. Values: 0–ffffffff (hex) default: ffffffff mru the maximum receive units (mru) configuration option may...
Page 159
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-35 chap secret enter the secret (i.E., password) necessary to challenge the peer. Values: user established default: secret initiate negotiation determines whether the port actively negotiates with the peer site or passively waits for negotiation requests. Values: yes, n...
Page 160
4-36 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.28 ppp statistics screen period selects the interval (current, summary, or numbered interval) to be viewed on the ppp statistics screen. Tx frames number of frames transmitted by the port. Tx octets number of octets transmitted by the port. Rx frames number of f...
Page 161
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-37 figure 4.29 pap table screen to change the username and password for a selected pap index, access the pap details screen (figure 4.22) by selecting the applicable index number in the pap table. Enter the new information in the appropriate field(s) and press the “esc”...
Page 162
4-38 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 to change the username and secret for a selected chap index, enter the new information in the appropriate field(s) and press the “esc” key. Scada service details screen notice: scada traffic has a higher priority than other types of traffic flowing through the unit. Refe...
Page 163
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-39 scada loopback determines if and where scada will loopback received data. Values: none, loopback to network, loopback to port default: none the table below these parameters displays the scada statistics. You can clear all scada statistics by selecting the “scada clea...
Page 164: Applications
4-40 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 ip service details screen the ip service details screen (figure 4.11), accessed by selecting “ip” from the column in the ip service screen, lets you configure the ip parameters described on page 4-16. To change any of the available parameters, you must enter new values i...
Page 165
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-41 page 4-42. When in ip gateway, if you decide to use a “discovered” endpoint, you must rename it. A discovered endpoint cannot be used elsewhere (i.E., ip gateway) until it has been renamed. Also, it will not be saved in the configuration database. Notice: endpoint na...
Page 166
4-42 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.36 endpoint details screen name when the unit learns a new dlci, it creates an endpoint entry and a dlci entry if they are not already configured. The endpoint’s name will automatically be assigned as “dynamic”; however, this name can (and most likely should) be...
Page 167
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-43 backup endpoint if this dlci has an alternative endpoint to switch to in case this dlci becomes inactive, you would configure the endpoint index of this alternate endpoint here. For most applications, you will not need to set this parameter. Values: 0–256 default: 0 ...
Page 168
4-44 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 some cases change, parameters including index, interface, type, and pair. A delete service prompt is also included on this screen. Dlci details screen the dlci details screen (figure 4.37) lets you access the configuration parameters described in the following paragraphs...
Page 169
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-45 be (bps) if an excess burst rate is configured here, its value will be used instead of the default excess burst of the frame relay service. Values: 0–1536000 default: 0 bc (bps) if cir enforcement is configured to “yes,” the unit will throttle the committed burst dow...
Page 170
4-46 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 remote unit if the remote unit is a verilink unit with framestart technology, and framestart auto discovery is enabled, this field displays the first three digits of the unit id configured on the remote end of this dlci. Values: 000 − 999 default: 000 remote ip address d...
Page 171
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-47 uas threshold sets the unavailable seconds (uas) alarm threshold. This threshold is the number of seconds after which the dlci is unavailable. Setting this field to “0” (zero) disables the alarm. Uas alarm reports if the uas threshold has been exceeded. Dlci statisti...
Page 172
4-48 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.39 dlci statistics details screen the dlci statistics screen in the preceding figure shows a summary that includes all 96 buckets. You can choose to see the statistics for any given bucket by selecting a specific interval under the column on the dlci statistics ...
Page 173
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-49 figure 4.40 dlci table screen service aware screen the service aware function recognizes ip traffic and counts the number of frames and bytes passed for a specific service based on filters by dlci, by ip address, and by ip port. Each row of the service aware table re...
Page 174
4-50 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 rule configuration screen select from the column to bring up the rule config screen (figure 4.42) to establish service aware parameters. To establish a rule, select the desired rule configuration options, provide the appropriate filter information where required, and pre...
Page 175
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-51 enter ip port or select from list establishes the ip port by which the rule will filter ip traffic (if enabled). Filter by ip port enables or disables filtering of the ip traffic by the ip port specified in the ip port field. Tx alarm threshold specifies the threshol...
Page 176
4-52 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 summary represents the past 24 hours; reports the additive number of frames/octets, the highest peak encountered for 24 hours, and the average for 24 hours. Current reports on the current 15-minute interval. Interval 1, interval 2,..., interval 96 reports on intervals 1-...
Page 177
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-53 diagnostics screen the diagnostics screen (figure 4.45) provides a table for viewing the current settings for the test and maintenance functions performed on the available interfaces. This screen shows an upper-level view of all the interfaces so you can see if any p...
Page 178
4-54 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.46 network interface test details screen bert table on network interface test details screen the bert table lets you set the test parameters listed below. Setting displays the bandwidth on which you wish to perform the bert. The available values for this paramet...
Page 179
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-55 “no sync” is displayed. If the receiver is in pattern sync, “in sync” is displayed. Elapsed time displays the time elapsed since a timed test began or, if completed, the total test time. Bit errors displays the total number of bit errors detected since the test began...
Page 180
4-56 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 bert pattern specifies the pattern to be transmitted during a test for the selected port. Values: marks, qrss, 511, 2047, 2^15, spaces default: qrss notice: the 2^15 pattern is the itu (european) version, not the ansi version. Test duration specifies the length of time f...
Page 181
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-57 trap log screen a trap is a mechanism that permits a device to send an alarm for certain network events to an snmp management station. The trap log screen (figure 4.48) shows a collection of all the traps that have been generated. The table shown in this screen lists...
Page 182
4-58 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 to generate a top talkers report, enter the duration parameters and desired report size in the available fields as described below, and then press the “enter” key or select the “start” prompt on the screen. Duration establishes the amount of time (in seconds) for which t...
Page 183
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-59 a single autonomous system (as). Ospf chooses the least cost path as the best path. While rip is ideal for small- to medium-sized networks, ospf is more suitable for complex networks with a large number of routers. Ospf provides equal cost multipath routing where pac...
Page 184
4-60 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 distributes routing information between routers in a single autonomous system. This protocol is suitable for complex networks with a large number of routers. If a large network is involved, ospf may be the solution for the user. Values: disable, enable default: disable o...
Page 185
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-61 circuit details screen access this menu by selecting “circuit details” from the preceding menu. This screen is used to establish the configuration parameters of a given circuit. The screen’s parameters are described in the paragraphs below. Figure 4.52 circuit detail...
Page 186
4-62 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 ospf lsa timer determines how often the link state acknowledgment (lsa) packet is sent. Ospf lsu delay the estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link state update (lsu) packet over this circuit interface. Values: 1 − 3600 default: 1 ospf router priority this...
Page 187
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-63 figure 4.53 static route table screen the fields on this screen are described in the table below. Route details screen the route details screen (figure 4.54) displays the details associated with a specific route. Use this screen to establish the configuration paramet...
Page 188
4-64 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 endpoint endpoint name (or interface) through which to send the ip packet to reach the target ip address. Target ip address represents the target network that you want this router to reach. Target ip mask mask of the target ip or network. Next hop ip address: ip address ...
Page 189
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-65 static arp table screen arp (address resolution protocol) is used by the router to dynamically associate a high-level ip address to a low-level physical hardware address. Arp packets are only sent across a single physical network. There are some cases when an ip-comp...
Page 190
4-66 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.57 arp details screen endpoint endpoint name (or interface) through which to send the ip packet to reach the defined ip address. Currently, this is always the lan. Ip address ip address of the circuit. Values: 0.0.0.0 − 255.255.255.255 default: 0.0.0.0 mac addre...
Page 191
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-67 figure 4.58 trusted neighbors screen add new adds a trusted neighbors ip address. Neighbor details screen access this screen (figure 4.59) by selecting a number under the column. This screen lists all ip addresses of trusted neighbors. Figure 4.59 neighbor details sc...
Page 192
4-68 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.60 area table screen the fields displayed on the area table screen are described below. Area details screen this screen (figure 4.61) displays the details associated with a defined area. Figure 4.61 area details screen field description area id displays the id o...
Page 193
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-69 area id this parameter has the same format as the ip address of the mask address. Values: 0.0.0.0 − 255.255.255.255 default: 0.0.0.0 enable displays whether or not this area is enabled. Values: enable, disable default: enable auth type indicates type of authenticatio...
Page 194
4-70 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 backbone, virtual links can be configured through non-backbone areas. Basically, virtual links are used to connect components that are otherwise not connected to the backbone. A virtual link is treated by ospf as a point-to-point unnumbered network joining two area borde...
Page 195
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-71 figure 4.63 virtual link details screen tcp server notice: tcp server traffic has a higher priority than other types of traffic flowing through the unit. Refer to normal tx queue size on page 4-30 for more details. The tcp server is a general-purpose application that...
Page 196
4-72 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 access the tcp connection details screen (figure 4.65) by selecting the appropriate number under the column. The tcp connection details screen lists the index number, endpoint name, tcp local port number, and whether or not this entry is enabled. Figure 4.65 tcp connecti...
Page 197
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-73 figure 4.67 tcp host access screen you can access the host access details (figure 4.68) for a specific number by selecting the appropriate number under the column. Figure 4.68 tcp host access details screen network address translation (nat) nat is a method of connect...
Page 198
4-74 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 notice: you must save and restart for any changes in nat configuration parameters to take effect. Nat details screen the nat details screen (figure 4.69) lets the user configure the nat global parameters described below. Figure 4.69 nat details screen enable enables or d...
Page 199
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-75 applications. The timers’ values minimize nat resources. Generally, when a timer has expired, the resources used are no longer needed. Those resources will then be available for other connection resources. Ip entry timer the maximum time (in seconds) nat will use res...
Page 200
4-76 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 static tcp trans table screen the static tcp trans table screen (figure 4.70) allows static mapping of global tcp server ports to a local host ip address/port combination. The parameters described below enable access to tcp servers on the private/ corporate network “behi...
Page 201
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-77 figure 4.71 static tcp trans details screen nat ports screen the parameters on the nat ports screen (figure 4.72) define the nat global/internet and local/corporate ports. These parameters are configured in the nat ports details screen shown in figure 4.73. Access th...
Page 202
4-78 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 “disable” will override an “enable” parameter set under “filter non local address” on the nat details menu. Type defines whether this port is local or global. Default is lan global. All others are local. Ip address ip address of this port. Default is the value defined in...
Page 203
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-79 figure 4.74 nat port status screen ip address original ip address of the host. Nat ip address translated ip address of the host. Processed packets number of packets processed by nat for this address. Static udp trans table screen the static udp trans table screen (fi...
Page 204
4-80 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 server address ip address of the local udp server. Default is 0.0.0.0. The “add new” prompt lets the user add additional addresses. You can configure or change the above-listed parameters on the static udp trans details screen (figure 4.76), which is accessed by selectin...
Page 205
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-81 dhcp server details screen the dhcp server details screen (figure 4.77) lets you configure the parameters described below. Figure 4.77 dhcp server details screen enable enables or disables the dhcp server. Default is “disable.” number of ports defines the number of d...
Page 206
4-82 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 the dhcp server details screen provides the following user-activated prompts: dhcp hosts screen in some cases, it may be necessary to provide an ip station with a specific dhcp server name, which may be used by the ip station when making a dhcp request. That name is incl...
Page 207
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-83 figure 4.79 static entries screen mac address mac address you want to associate with an ip address. Ip address ip address given to the dhcp client if that client has the mac address defined on this screen. Mask mask associated with the ip address shown on the screen....
Page 208
4-84 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 ip start starting ip address of the dhcp client pool. Ip end ending ip address of the dhcp client pool. Ip exclude start beginning of “excluded” range. Ip exclude end end of “excluded” range. Select “add new” to add an ip address. Ip address status screen the ip address ...
Page 209
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-85 the bridge details screen shown in figure 4.82 lets you access and configure the parameters described below. Figure 4.82 bridge details screen from this screen, you may view the parameters described below. Enable enables or disables bridging capability. Values: enabl...
Page 210
4-86 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 filter aging timer specifies the length of time an entry in the lookup table will be held if no traffic is received from the specified mac address. Values: 1 − 65535 s default: 300 s the bridge details screen provides the following user-activated prompts: figure 4.83 bri...
Page 211
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-87 figure 4.84 bridge port details enable enables or disables bridging on this port. Endpoint endpoint name. Bpdu option shows if bpdu packet will be sent and received on this port. Filter by multicast addr dest filters multicast messages received on this port, which re...
Page 212
4-88 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 designated bridge designated bridge mac address. Forward transmissions number of times this port has changed from any other state to a “forwarding” state. Input frame number of frames received. Output frame number of frames transmitted. Input discards number of frames di...
Page 213
V t 1 0 0 i n t e r f a c e 4-89 reporting the following event: oofs threshold exceeded, ifindex 3, count 5 the parameters associated with the smtp details screen are described below. Figure 4.86 smtp screen mail server ip address ip address of the mail server to which notifications will be sent. Do...
Page 214
4-90 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 figure 4.87 encryption details screen.
Page 215: Pecifications
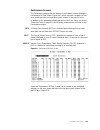
S p e c i f i c a t i o n s a-1 a p p e n d i x a a ppendix a s pecifications network 1 interface line rate: 1.544 mbps ( ± 50 bps) line framing: d4 or esf line code: ami or b8zs input signal: ds1, +1 to − 27 db (albo) connection: rj-48c jack, 100 Ω ( ± 5%) output signal: 3.0 v ( ± 10%) base - peak ...
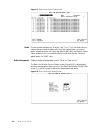
Page 216: Management Interfaces
A-2 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 line build out: 0, − 7.5, − 15, − 22.5 db attenuation transient voltage: 1000 v protection, fused input / output jitter control: per tr 62411 and t1.403 timing source: with “function” parameter in slave mode, timing parameter is ignored with “function” parameter in networ...
Page 217
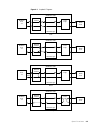
S p e c i f i c a t i o n s a-3 figure a.1 loopback diagrams wansuite 5165 internal logic network port t1 network framer port logic nx64 port llb wansuite 5165 internal logic network port t1 network framer port logic nx64 port plb wansuite 5165 internal logic network port t1 network framer port logi...
Page 218: Alarms
A-4 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 alarms activation: programmable thresholds on all interfaces reporting: snmp traps, e-mail notification power 5.5 vac: 120 ma, 7 w maximum, 24 btu maximum (power received from rack connection) mechanical mounting: rack-mount in as2000 dimensions: width 0.94 inches (2.39 c...
Page 219: Industry Listings
S p e c i f i c a t i o n s a-5 tx/rx mgmt octets peak/average throughput peak/average round-trip delay round-trip delay time-outs uas (unavailable seconds) ppp statistics collected in 96 15-minute intervals per port tx/rx frames tx/rx octets tx/rx mgmt frames tx/rx mgmt octets rx invalid frames pea...
Page 220: Ordering Information
A-6 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 ordering information the following is standard equipment: optional equipment the following optional equipment is available for the wansuite 5165: contact technical support (page xii) for further information. Description wansuite 5165 front module (card) /dim 5165 rear mod...
Page 221: Connector Pin Assignments
S p e c i f i c a t i o n s a-7 connector pin assignments the serial interface is a standard db-25 jack. Serial interface pin assignments for dte mode (packet use only) *this refers to the db-25 serial interface connector on the back of the unit. Function abbrev. Direction pin # db-25* rs-232 v.35 e...
Page 222
A-8 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 serial interface pin assignments for dce mode *this refers to the db-25 serial interface connector on the back of the unit. Ethernet connection pin assignments the 10/100 ethernet interface is an 8-pin modular jack that complies with standard twisted-pair, 10/100base-t re...
Page 223
S p e c i f i c a t i o n s a-9 network 1 interface pin assignments the net 1 physical interface is a standard rj-48c, 8 -pin modular jack. The table below displays the pinout assignments. Network 2 interface pin assignments the net 2 physical interface is a standard rj-48c, 8 -pin modular jack. The...
Page 224
A-10 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5.
Page 225: Snmp A
S n m p a g e n t b-1 a p p e n d i x b a ppendix b snmp a gent introduction this chapter provides specific information for configuring and using the snmp agent within the wansuite 5165. The wansuite 5165 incorporates an ethernet port that provides connectivity for lan-based management stations. The...
Page 226: Snmp Trap Configuration
B-2 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 • rfc2863.Mib − describes generic objects for network interface sub-layers (this mib is an updated version of mib-ii's iftable, and incorporates the extensions defined in rfc 1229.) • rfc2493.Mib − provides textual conventions to be used by systems supporting 15-minute ba...
Page 227: Generic Traps
S n m p a g e n t b-3 generic traps trap no. Description varbinds coldstart snmptraps 1 a coldstart trap signifies that the snmpv2 entity, acting in an agent role, is reinitializing itself and that its configuration may have been altered. Warmstart snmptraps 2 a warmstart trap signifies that the snm...
Page 228: Standard Traps
B-4 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 standard traps trap no. Description varbinds dsx1linestatuschange ds1traps 0 1 a dsx1linestatuschange trap is sent when the value of an instance dsx1linestatus changes. It can be utilized by an nms to trigger polls. When the line status change results from a higher level ...
Page 229: Soon-to-Be-Standard Traps
S n m p a g e n t b-5 soon-to-be-standard traps the hdsl2 mib is on the verge of becoming an rfc. Hdsl2shdsltraps object identifier ::= { hdsl2shdsllinemib 2 } hdsl2shdsltrapsprefix object identifier ::= { hdsl2shdsltraps 0 } trap no. Description varbinds hdsl2shdslloopattencrossing trap 1 this trap...
Page 230
B-6 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 hdsl2shdslperfloswsthresh trap 6 this trap indicates that the losw seconds threshold (as per the hdsl2shdslendpointthreshlosws value) has been reached/exceeded for the hdsl2/shdsl segment endpoint identified by the ifindex, hdsl2shdslinvindex, hdsl2shdslendpointside, and ...
Page 231
S n m p a g e n t b-7 hdsl2shdslnoneighborpresent 15 this trap indicates that the bit setting for noneighborpresent in the hdsl2shdslendpointcurrstatus object for this endpoint has changed. Ifindex, hdsl2shdslinvindex, hdsl2shdslendpointside, hdsl2shdslendpointwirepair hdsl2shdsllocalpowerloss 16 th...
Page 232: Enterprise-Specific Traps
B-8 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 enterprise-specific traps ipadtrapsprefix trap no. Description varbinds ipadfrportrxinvalidframesexceeded 25000 this trap is sent out when an ipad frame relay port receive invalid frames alarm threshold has been exceeded. Ipadfrportrxinvalmalarm ipadfrportrxthroughputexce...
Page 233
S n m p a g e n t b-9 ipadt1e1lossalarmdeclared 25012 this trap is sent out when a loss of signal seconds alarm is declared. T1e1losscount ipadt1e1uasalarmdeclared 25013 this trap is sent out when an unavailable seconds alarm is declared. T1e1uascount ipadt1e1cssalarmdeclared 25014 this trap is sent...
Page 234
B-10 w a n s u i t e 5 1 6 5 generic mib loading instructions the mibs were written using the standard asn.1 notation. Any standard snmp manager should be able to compile the mibs. Although the exact procedure for loading mibs may vary from one platform to another, the following basic steps are the ...
Page 235
Five-year hardware limited warranty i. Limited warranty. Subject to the limitations and disclaimers set forth in this hardware limited warranty, verilink warrants to the original pur- chaser (“buyer”) that the verilink equipment and component parts (“goods”) purchased by buyer shall be free from def...