Thank you for choosing
WARRIOR BOATS
For your boating and fishing enjoyment
Please read the Owner’s Manual completely
before operating your new Warrior Boat.
It will aid you in understanding the operation
and maintenance of the many unique features
of your boat. If you need further assistance
with any special applications or problems,
please contact your Warrior Dealer or Warrior
Boats. We wish you many happy hours of boating
and fishing fun in your new Warrior Boat.
2012
Summary of Boats
Page 1
Thank you for choosing warrior boats for your boating and fishing enjoyment please read the owner’s manual completely before operating your new warrior boat. It will aid you in understanding the operation and maintenance of the many unique features of your boat. If you need further assistance with a...
Page 2: Outboard Engine:
Certifications and specifications boat model:_________________________ side console dual console backtroller serial #:_____________________________ color:_______________________________ outboard engine: brand:_____________horsepower:___________ outboard 2 stroke 4 stroke serial #:___________________...
Page 3
1 introduction/warranty 2 safety 3 navigation 4 livewell's 5 wiring 6 steering 7 maintenance 8 trailers table of contents.
Page 4: Introduction
Introduction this manual has been compiled to help you operate your craft with safety and pleasure. It contains details of the craft; typical equipment supplied or fitted in its systems and information on its operation and maintenance. Please read it carefully, and familiarize yourself with the craf...
Page 5: Education
Education learn how to operate your boat safely. This book is not intended to teach everything you need to know. We strongly urge you to get training in proper boat handling and navigation before taking command. Some agencies which offer boating courses are: u.S. Coast guard auxiliary united states ...
Page 6: Nautical Terms
Owner/operator responsibilities the law requires the owner/operator to assist any person or boat in distress as long as he does not endanger his boat. The owner/operator is also responsible for understanding and complying with the following procedures and operational requirements: state registration...
Page 7: Fenders
Fenders rope or plastic pieces hung over the side to protect the hull from chafing. Freeboard height of exposed hull from water line to deck. Ground tackle general term referring to anchor, anchor lines, etc. Gunwale (pronounced gun’l) meeting juncture of hull and deck hatch an opening in deck to pr...
Page 8: Safety
Safety the freedom of boating is a magnificent feeling. However, fun can be overtaken by disaster if you ignore safety precautions. This book presents basic guidelines, but it cannot describe every possible risk you may encounter. You are strongly urged to: take a boating safety course and get hands...
Page 9: Fire Suppression Equipment
Fire suppression equipment general fire suppression equipment can be either fixed or portable. Fixed systems are located in the machinery compartments, and should be supplemented by portable extinguishers mounted at key sites, for example, near the engine compartment, galley and helm. Coast guard or...
Page 10: Remember:
Remember: certification plate states maximum weight/number of persons the boat will handle safely under normal conditions. Give yourself an extra margin in rough water. Install drain plugs before launching. Ensure proper bilge pump operation. Anchor from bow if using only one anchor. Match speed to ...
Page 11
When purchasing pfds, look for a tag saying they are approved by the national boating law enforcement agency. Children and non-swimmers must wear pfds at all times when aboard. All passengers and crew should wear them, since an unworn pfd is often useless in an emergency. The law requires that pfds ...
Page 12: Impaired Operation
Impaired operation give special attention to the effects of alcohol and drugs while boating. No other single factor causes so many marine accidents and deaths. Wind, waves and sun heighten the effects of alcohol and drugs, so your reactions may be quickly impaired. Load capacity the u.S. Coast guard...
Page 13: Propulsion
Propulsion propulsion system consists of an engine turning a shaft, which transfers power to a propeller. Mounting may be outboard, stern drive (inboard engine/outboard propeller), or inboard. `` stability loose fluids or weight within the hull substantially reduces stability. Keep bilge area as dry...
Page 14: Weather
Weather learn to understand weather patterns and signs of change. Bad weather and sea conditions can cause an uncomfortable and unsafe situation. Here are a few basic weather-related rules: check the forecast and sea conditions before leaving and while underway. A sudden change in wind direction or ...
Page 15: Recommended Equipment
Recommended equipment a wise boater will include many of the following items: visual distress signals for day and night use (required in some areas; consult local regulations) marine radio compass depth sounder charts spare keys portable radio with weather band waterproof flashlight batteries moorin...
Page 16: Explosion
` explosion if explosion is imminent, put on pfds, grab distress signals and survival gear, and immediately abandon ship. Fire turn off engines, generators, stoves and blowers. Extinguish smoking materials. Have portable fire extinguishers ready. Do not breathe fumes or vapors caused by fire or exti...
Page 17: Collision
Flooding, swamping or capsizing stay with the boat! A boat will usually float even if there is major hull damage. Rescuers can spot a boat much easier than a head bobbing in the water. Signal for help. Collision account for everyone on board. Check for injuries. Inspect structural damage. Reduce flo...
Page 18: Drowning
Drowning swim to rescue a drowning victim only as a last resort. Immediate resuscitation is critical! At least two people on board should be certified in cpr. Keep the victim warm. Use care in handling. Spinal injury may exist if the victim fell overboard. Signal for help. Medical emergency in an em...
Page 19: Before Departure:
If you hear a distress call, stop all radio transmissions. If you can directly assist, respond on the emergency frequency. If you cannot assist, do not transmit on that frequency. However, continue to monitor until it is obvious that help is being provided. Seaworthiness / operational inspection upd...
Page 20: Trailering (If Applicable):
Trailering (if applicable): boat position – secure on trailer tiedowns – tight winch – locked trailer hitch – connected engine clearance – in trailering position safety chains – attached electrical – lights, brake lights, turn signals working mirrors – adjusted for trailering after return pfds and o...
Page 21: Operation Fueling:
Operation fueling: fuel system – no leaks bilge pump – operating properly bilge – clean, no leaks float plan – notify person with whom you filed plan general fuel during daylight. Check fill plate label to ensure fuel is placed only in fuel tank. Avoid spills. Know your fuel capacity and consumption...
Page 22
Starting engine – general checklist: fuel – supply adequate, including reserve oil – level adequate battery (s) – power adequate drain plugs – installed gear – neutral bilge blower – run at least 4 minutes before starting “sniff test” – no leaks or fumes emergency stop switch – attached to operator ...
Page 23: Navigation
Navigation rules of the road navigational rules are commonly called rules of the road. There are two types: inland rules apply to vessels on unites states inland waters; international rules apply to vessels on the high seas. Basic principles agree, but some differences exist. Learn and follow the ru...
Page 24: Warning
3-2 warning stability hazard load boat properly. The manufacturer’s load rating is the maximum under normal conditions. Adjust downward if weather, water or other conditions are adverse. Allow passengers to ride only in areas that do not pose a hazard to themselves or the boat. Do not allow passenge...
Page 25: Boarding (Wear A Pfd)
Boarding (wear a pfd) board only one person at a time. Step or climb into the cockpit. Never jump into a boat. Load gear after you are aboard. Carrying gear while boarding can cause you to lose balance. Distribute weight evenly. Instruct passengers where to sit during on-plane operation to reduce po...
Page 26: Starting, Stopping
Starting, stopping see the engine operator’s manual for detailed instructions. Do not ignore any alarm! Correct problem before casting off. 3-4 warning control hazard the operator must be in correct position – seated, facing forward, hands on controls – when engine is running. Ensure all items are s...
Page 27: Basic Rules
Basic rules power-driven vessels must keep out of the way of: a vessel unable to maneuver a vessel whose maneuverability is restricted a vessel engaged in commercial fishing a sailing vessel sailing vessels must keep out of the way of: a vessel unable to maneuver a vessel whose maneuverability is re...
Page 28: Boat Navigational Lights
Boat navigational lights boats must display navigational lights when operating between sunset and sunrise and during periods of reduced visibility, e.G., fog or rain, to alert other boats to their presence and course. Although boat manufacturers usually provide lights to comply with these rules, it ...
Page 29
Special use vessels such a public safety, pilot, dive boats and dredges have other light requirements. International and inland rules differ slightly on navigational light placement. Understand the basics and learn the boat lights in your area. Avoid lights you do not recognize. 3-7.
Page 30
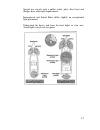
Charts & aids to navigation a vast expanse of open water off your bow might appear to be a go anywhere playground or a place to become hopelessly lost. It is neither. How do you know where to go? Just as maps and signs guide you on land, nautical charts and buoys guide you afloat. Nautical charts pr...
Page 31
3-9.
Page 32: Live Well Control Center
Live well control center livewell system a. Filling a livewell eagle/falcon models a. Depress “aerator” switch b. Depress either “auto” or “manual” switch auto mode – when “auto” is depressed, the aerator pump will run on the adjustable timer. The more the timer is turned up, the longer the run time...
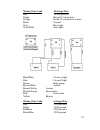
Page 33: Air Locking
V1783/v1890 side console falcon aerator switch on dash panel fills stern livewells. Recirculator switch on dash panel recirculates stern livewell on port side. Aerator switch on bow panel fills bow livewell. Recirculator switch on bow panel recirculates bow livewell. V1800 side console & dual consol...
Page 34: 4-Wire Boat Wiring Devices
4-wire boat wiring devices the marinco system provides a convenient way of connecting a trolling motor or a battery charger to your boat’s batteries. The marinco 4-wire 12v battery charger plug (red) is used to charge two (2) 12v batteries from a single 12v-battery charger. It can also be used to co...
Page 35: 12 Volt Trolling Motor
Plugs and receptacles – 12/24v locking charge plug (red) connects to a 12v-battery charger to allow simultaneous charging of two (2) 12v batteries when plugged into receptacle. Trolling motor plug connects to the trolling motor. Jumpered internally to supply 12v or 24v power to the trolling motor wh...
Page 36: 24 Volt Trolling Motor
24 volt trolling motor on the 12/24v trolling motor plug, connect the positive 24v wire to the terminal marked “24”, and the negative wire to the terminal marked “-“. Tighten all terminal screws to 14-20 in.-lb torque. Attach the body of the plug to the housing by the two assembly screws. Tighten th...
Page 37: Emergency Power Supply
On board battery “maintainer” plug power charge jumper into “start” and “troll” ports. Start outboard. As the outboard runs, it will charge the cranking battery and the trolling motor batteries simultaneously. Important: do not leave jumper plugged into power charge panel when boat is not being used...
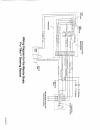
Page 38: Wiring Color Code
Wiring color code 14 gauge wire red 12 volt positive purple keyed 12 volt positive orange fused 12 volt positive or horn black ground gray bow light gray/white stern light blue/white courtesy light blue livewell light brown bilge pump brown/white aerator brown/yellow aerator brown/orange recirculato...
Page 39: Tilt Harness
Battery energy gauge – bow panel depress “test” – monitor will display battery status battery energy gauge – stern panel (backtroller models) depress “test” – monitor will display battery status trolling motor circuit protection the two trolling motor wire harnesses (one from the bow, one from the s...
Page 40: Fuel Tank Id Tag
*****************caution***************** disconnecting the battery(s) while the engine is running by either removing the battery cable(s) from the battery post(s) or by inadvertently turning a battery switch to the “off” position will cause extremely high voltage to be produced on the 12 volt line ...
Page 41: Drain Plugs
Drain plugs one plug is located in the transom to allow water to drain before trailering or storing. Hull drain plug the screw-type drain plug is constructed of black nylon and features an “o” ring for positive sealing. Fine threads maintain sealing under high vibration conditions. The plug is retai...
Page 42: Seat Pedestals
Seat pedestals the abyc (american boat and yacht council) has recommended seating standards for the marine industry. Warrior boats use two types of class a pedestals. They are: ad driver pedestal – seat mount must incorporate a “mechanical interference lock” and resist 150 foot pounds of torque. The...
Page 43: 36 Volt Trolling Motor
36 volt trolling motor wiring: red plug – the red plug is connected to the red wire from the trolling motor. Insert the wire into the opening marked “+”. Make sure that all terminals are tight. Install plug body onto plug base. Black plug – the black plug is connected to the black wire from the trol...
Page 48: Controls
Controls steering in a hydraulic system, steering wheel movement pumps hydraulic fluid through lines to a cylinder, which transfers movement to the outboard. A reservoir holds extra fluid; a valve protects against overpressure. In a mechanical system, the steering wheel connects to a cable, which tr...
Page 49: Steering
Steering boat steering differs from automobile steering in several important ways: turn the boat steering wheel in the direction you want the bow to go, but remember that the boast actually turns at the stern. Boat steering is not self-centering. Boat steering is affected by engine and propeller tor...
Page 50: Gear Shift & Throttle
Gear shift & throttle 6-3 warning control hazard tiller steering avoid serious injury or death from loss of boat control due to excessive steering forces. Always maintain a firm grip on the tiller handle. Adjust engine trim and trim tab per instructions in the installation guide. Warning personal in...
Page 51: Ignition
With common single lever control, gear shift/throttle lever controls engine thrust direction and speed. Moving the lever forward engages the forward gear and then the throttle advance. To reverse propeller direction, bring the lever back to the neutral (middle) position, then move it further back to...
Page 52: Warning
Emergency engine stop switch with lanyard an emergency engine stop switch turns off the engine when the operator leaves the helm a sufficient distance in an unsafe situation, for example by falling. Familiarize yourself with its operation and always use it. Before operating boats, attach one end of ...
Page 53: Power Trim & Tilt
Power trim & tilt power trim and tilt adjust a stern drive or outboard propeller’s angle to the hull. The switch is on the gear shift/throttle lever. Trim generally refers to an approximate 20 degree range used for normal in-water operation. Tilt refers to more extreme angles of adjustment. 6-6 caut...
Page 54: Trimming
Trimming most stern drive and outboard engines have a power trim, which enables you to change the angle of your drive unit by pressing a button. See your engine operator’s manual for a complete discussion of characteristics resulting from different trim settings. Power trim is designed to give quick...
Page 55: Visibility
In most cases, best performance is obtained with the unit positioned so that the boat runs at a 3 to 5 degree angle to the water (front of hull just slightly out of the water). Outboard engines may have a trim tab to compensate for steering torque, which causes the boat to pull to one side. Torque i...
Page 56: General Considerations
Post a lookout to watch for obstacles when visibility from the helm is limited due to operating conditions. General considerations you are responsible for passengers’ actions. If they place themselves or the boat in danger, immediately correct them. Know how your boat handles under different conditi...
Page 57
Some procedures apply in all situations: move slowly. Plan maneuvers ahead of time. Use wind and current whenever possible to move or slow the boat. If there is more than one way to approach a berth, use the most conservative maneuver: high wind/current – approach against the wind or current mild wi...
Page 58: Warning
6-11 warning caution if stern drive is equipped with power tilt for trailering, use it only for that purpose. Tilting drive unit into the trailering zone while underway may damage the drive unit or engine. Speed hazard operate boat at speeds within the operator’s ability to maintain control and reac...
Page 59: Operating In Shallow Water
Operating in shallow water shallow water presents obvious hazards. In addition to insufficient draft, shallow means sand bars, stumps, or other unmarked obstructions in deep water. Other hazards in shallow water include mud, sand, weeds and debris, which can foul your engine’s cooling water intakes....
Page 60: Abyc Requirements:
Meets all the requirements as set forth by the american boat and yacht council as published in “standards and recommended practices for small craft”. Abyc requirements: abyc e-9 dc electrical systems under 50 volts abyc h-30 hydraulic systems abyc p-17 steering systems for outboard, inboard/outboard...
Page 61: Operation Instructions
Operation instructions warning! The boat owner/operator is responsible to make passengers aware of basic operations of the boat so passengers can operate, maneuver the boat in the event of an emergency. The operator should make passengers aware of the location of emergency equipment, such as throwab...
Page 62: Warning!
On mode in the “on mode”, the engine is steered hydraulically and controlled with the steering switch on the feather trim grip. The steering torque in the “on mode” is eliminated giving the driver push button steering control. To operate the “on mode”, turn the on/off switch to the “on” position. Th...
Page 63: Service Schedule
Service schedule the manufacturer of each system in your boat should provide a recommended service schedule, listing items requiring routine attention, type of maintenance, and frequency. The schedule is a guide based on average operating conditions. Under severe operating conditions, shorten servic...
Page 64: Maintaining Hull & Deck
Maintaining hull & deck fiberglass/gelcoat the hull and deck consist of a molded shell and exterior gelcoat. Gelcoat is the outer surface with the shiny appearance associated with fiberglass. Wash fiberglass regularly with clean, fresh water. Wax gelcoated surfaces to maintain luster. In northern cl...
Page 65: Upholstery And Seating
Upholstery and seating clean all vinyl with a good grade of vinyl protective cleaner. Avoid harsh detergents. Please consult these cleaning recommendations: steps 1 2 3 betadine b a chewing gum d a b eye shadow b motor oil b spray paint b e mildew or wet leaves* c a b shoe polish* d b e yellow musta...
Page 66: Windshields
*suntan lotion, shoe polish, wet leaves, and some other products contain dyes that stain permanently. Certain household cleaners, powdered abrasives, steel wool and industrial cleaners can cause damage and discoloration and are not recommended. Dry cleaning fluids and lacquer solvents should not be ...
Page 67: Batteries
Batteries the manufacturer selects batteries for their ability to furnish power for starting and operating the dc system. Refer to the manufacturer’s specification when replacing a battery. Disconnecting battery: a. Turn off items drawing power. B. Turn off battery switch, if equipped. C. Remove neg...
Page 68: Breakers And/or Fuses
Breakers and/or fuses breakers and/or fuses are usually located under or near the dash panel. If a breaker trips, determine and correct the fault, then reset by pushing the breaker button. If a fuse blows, determine and correct the fault, then replace the fuse. 7-6 warning shock/fire hazard disconne...
Page 69: Alarms & Monitors
Alarms & monitors some boats have alarms to indicate problems with high engine water temperature, low oil pressure, carbon monoxide, flooding, or explosive fumes. The manufacturer will provide information on those features, if available, as well as on monitors or gauges not provided as standard equi...
Page 70: Navigational Equipment
Navigational equipment compass a marine compass is optional on some boats. However, a compass is invaluable in determining position and course. A qualified technician must adjust the compass for errors caused by nearby iron, steel, magnets, or electric wires. Since a compass seldom can be corrected ...
Page 71: Winterizing/storing
Winterizing/storing storing boat on land/trailer – checklist boat: a. Hull drain plugs – remove b. Bow – store higher than stern c. Cover – support to prevent pooling of water d. Ventilation – allow air flow to prevent mildew e. Tiedowns – slack off to reduce hull strain f. Inspection – regularly du...
Page 72: Fuel System:
Fuel system: a gasoline: a. Fuel tank – filled with gasoline and a gasoline stabilizer and conditioner b. Engine – run for 10 minutes to ensure that gasoline in carburetor and fuel lines is treated trailer (if used): a. Security – protect against theft; install a lock on the trailer coupling b. Supp...
Page 73: Recommissioning
Recommissioning boat stored on land/trailer – checklist boat: a. Components – inspect and clean b. Hull drain plugs – install engine: a. Refer to engine operator’s manual for detailed information on fitting out after winter storage batteries: a. Terminal posts – clean with wire brush or steel wool b...
Page 74: Trailering
Securing outboard when trailering place outboard in vertical operating position if ground clearance is adequate. If additional ground clearance is needed, use an outboard support bar to secure motor. Do not rely on tilt support lever for trailering. Shift outboard to forward gear to prevent propelle...
Page 75: Securing Boat To Trailer
Securing boat to trailer attach bow to trailer with safety chain or u-bolt. Winch line should be tight, but do not rely on winch line to fasten bow to trailer. Use at least two nylon web tiedowns to secure transom to trailer. Add tiedowns on side of boat if load or road conditions require. Place sid...
Page 76: Pre-Trip Checklist:
Pre-trip checklist: trailer wheel bearings – greased trailer and tow vehicle tires – correct pressure trailer and tow vehicle lights and brakes – operating spare tires, jacks, parts – usable boat steering mechanism – lubricated boat connections and linkages – tight tiedowns – secured winch line – ta...
Page 77: Pre-Launch Checklist:
Pre-launch checklist: drain plugs – installed boat cover – removed equipment – loaded for proper trim bow and stern lines – fastened fenders – rigged tiedowns – removed fuel and water tanks – filled outboard or stern drive – tilted up electrical connection to tow vehicle – unplugged trailer wheel be...
Page 78: Warning
Keep clear as boat is cranked onto trailer open drain plugs while boat is tilted inspect propeller for nicks or other damage wipe hardware, including canvas snaps, with clean, soft cloth and spray with demoisturant. Complete tiedown and secure gear for road 8-5 warning personal injury hazard – sever...
Page 79: Maneuvering With Trailer
Maneuvering with trailer start with basics – accelerating, slowing, stopping smoothly and steadily increase distance from vehicle ahead do not pass other vehicles until you feel comfortable pulling trailer maintain steady control in the wake of large trucks and buses when turning, signal your intent...
Page 80
8-7.