- DL manuals
- Wavetek
- Transmitter
- 3ST
- Operation Manual
Wavetek 3ST Operation Manual
Wavetek
Wavetek
Wavetek
Wavetek
Wavetek
CATV Division
5808 Churchman Bypass
Indianapolis, IN 46203-6109
(800)851-1198
(317)788-5960
Fax: (317)782-4607
E-Mail: catvsupport@wavetek.com
Internet: http://www.wavetek.com
11/96 Rev. I,
Manual Part No.
6510-00-0273
This document contains information proprietary to
Wavetek. The information in this document
is not to be used or duplicated in any manner without
the prior approval, in writing, of Wavetek.
OPERATION MANUAL
MODEL 3ST
SYSTEM SWEEP TRANSMITTER
Summary of 3ST
Page 1
Wavetek wavetek wavetek wavetek wavetek catv division 5808 churchman bypass indianapolis, in 46203-6109 (800)851-1198 (317)788-5960 fax: (317)782-4607 e-mail: catvsupport@wavetek.Com internet: http://www.Wavetek.Com 11/96 rev. I, manual part no. 6510-00-0273 this document contains information propri...
Page 2: Warranty
Warranty wavetek warrants that all products manufactured or procured by wavetek conform to wavetek’s published specifications and are free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one (1) year from the date of delivery to the original buyer, when used under normal operating conditio...
Page 3: Contents
Contents section 1 - general information 1.1 introduction ................................................................ 1-1 1.2 specifications ............................................................. 1-2 1.2.1 frequency .................................................................... 1-2...
Page 4: Section 3 - User Interface
2.8 worldwide sales offices ..................................... 2-5 section 3 - user interface 3.1 introduction .............................................................. 3-1 3.2 front-panel description ................................... 3-1 3.2.1 soft keys ......................................
Page 5
4.10 spectrum analyzer mode ................................ 4-34 4.11 sweep mode ................................................................. 4-39 4.12 file .................................................................................... 4-40 4.12.1 how to store/view/delete measurement fil...
Page 6: Model 3St
1-1 section 1 general information 1.1 introduction the wavetek sweep system transmitter performs essential cable tv system preventive maintenance tests with accuracy and ease. Signal levels, hum, c/n, and frequency response can be quickly tested without subscriber interference. The sweep system is m...
Page 7
1-2 the 3st transmitter is a full-featured signal analysis meter, with a complete spectrum display and an analog representation of single channel measurement data. When tuned to a specific channel, a comprehensive set of information is provided: tuned channel, video frequency and level, audio freque...
Page 8
1-3 resolution: accuracy: +0.7% 1.2.4 carrier to noise measurement non-scrambled channels only. No preselection required for 78 channels at +10 dbmv input level. Carrier to noise ratio depth of measurement characteristics video carrier level (dbmv) carrier to noise range 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 -10 0 10...
Page 9
1-4 1.2.6 transmitter frequency range: 5 to 1,000 mhz level range: +20 to +50 dbmv (1) ; settable in 2 db increments spectral purity: hars -30 dbc; spurs -35 dbc 1.2.7 spectrum mode spans: 3, 5, 10, 20, and 50 mhz (0.3, 0.5, 1, 2, and 5 mhz/div) sweep rates: 2 seconds (50 & 5 mhz) display scaling an...
Page 10
1-5 *typical specifications range: 60 db maximum resolution: 1 db 1.2.9 depth of modulation assumes presence of white reference on any vits line. Non- scrambled channels only. Range: 80 to 100% resolution: 1.2.10 serial interface serial, rs232; epson, ibm printers 1.2.11 general log linearity: +0.5 ...
Page 11
1-6 fuse 1.25 a, 250v 5x20mm slo-blo (2 required) 1.2.13 standard accessories line cord channel plan transfer cable operations manual 1.2.14 options 16/64 qam digital carrier power measurement - enables stealth to perform accurate level measurements on digital carriers. 1.2.15 optional accessories 1...
Page 12
1-7 (1) specification change - the transmitter output is being changed from +10 to +40 dbmv to +20 to +50 dbmv. To determine which transmitter output range is available on your unit, access the status screen by pressing the fcn key followed by the status second function key. If "enhanced output" is ...
Page 13
2-1 section 2 installation 2.1 introduction this section provides information on how to install the 3st transmit- ter. 2.2 unpacking and inspection the instrument was inspected, and given final operational and quality control tests prior to being carefully packaged for shipment. The unit should oper...
Page 14
2-2 the transmitter output level is variable from +20 to +50 (1) dbmv in 2 db increments. The output level will be attenuated by the tap value of the directional coupler. For example, if a sweep signal level of +16 dbmv is desired on the system and the output of the 3st transmitter is set to +36 dbm...
Page 15: Stealth to Stealth
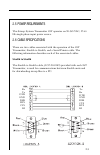
2-3 2.5 power requirements the sweep system transmitter 3st operates on 90-265 vac, 57-63 hz single phase input power source. 2.6 cable specifications there are two cables associated with the operation of the 3st transmitter; stealth to stealth, and a serial printer cable. The following information ...
Page 16: Serial Printer Cable
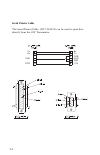
2-4 serial printer cable the serial printer cable, (1217-50-0151) can be used to print data directly from the 3st transmitter. Tx rx gnd dtr rx tx dtr gnd dsr cts.
Page 17
2-5 2.7 technical support although we've worked hard to make the 3st as easy-to-use as possible, the wide range of network architectures available today can make proper configuration a difficult task. If you have a problem using your unit you can contact wavetek's technical support for help. You can...
Page 18
2-6 (1) specification change - the transmitter output is being changed from +10 to +40 dbmv to +20 to +50 dbmv. To determine which transmitter output range is available on your unit, access the status screen by pressing the fcn key followed by the status second function key. If "enhanced output" is ...
Page 19
3-1 section 3 user interface 3.1 introduction this section will help you become familiar with the front-panel controls of the model 3st transmitter. Included are descriptions of the front-panel and notes on the use of features. 3.2 front-panel description the hardware portion of the user interface c...
Page 20
3-2 3.2.2 measurement mode selection keys measurement modes are chosen by pressing the appropriate mea- surement mode selection key. There is a key for each of the eight major measurement functions. These keys are located directly below the display. Level: signal level measurements on individual cha...
Page 21: Sweep:
3-3 scan: use the scan mode to get a good look at absolute carrier levels. In this mode a bar graph showing all carrier levels is displayed. Sweep: this mode injects a low level signal in vacant spectrum areas, and transmits telemetry to any 3sr receivers that are connected to the system. Cable syst...
Page 22: File:
3-4 3.2.3 support mode selection keys support modes are accessed using the support mode selection keys. There is a key for each of the four support functions. These keys are located to the right of the display. File: allows the user to access measurement files. Auto: this function provides automated...
Page 23
3-5 3.2.5 alpha-numeric entry keys the alpha-numeric keys are used to enter data as needed during the operation of the unit. There are three indicators associated with keypad entry. These indicators appear in the title bar to the left of the time. The three are as follows: ab c - alpha entry mode 12...
Page 24: Alpha Entry Mode
3-6 alpha entry mode most numeric keys have alphabetic characters printed on them. These characters can be accessed when the alpha entry indicator appears in the title bar. In the alpha entry mode, a cursor appears below the active position. Repeated pressing of an alphanumeric key sequences through...
Page 25
4-1 section 4 operation - how to use the 3st transmitter 4.1 introduction this section provides detailed operation of the 3st transmitter. Included are detailed descriptions of the various displays of the selected modes of operation. 4.2 stealth sweep start-up procedure the model 3st transmitter is ...
Page 26: Building A Channel Plan
4-2 we recommend that the telemetry be set at 10 db below the video carrier level. Any response irregularities caused by the combining network will be eliminated in the normalization process. After the transmitter is properly connected, the next step is to build a channel plan. This channel plan wil...
Page 27: Editing A Channel Plan
4-3 editing a channel plan the next step is to edit the channel plan to characterize it for your particular system. Cursor down to edit channel parameters and press enter. A listing of all the channels within the frequency range designated in the build channel plan phase will appear on the screen. N...
Page 28: Storing A Sweep Reference
4-4 the next step is to test the sweep by connecting the model 3sr receiver to a test point and pressing the sweep key (ensure the 3st transmitter is also in the sweep mode). After telemetry is found, the receiver will begin sweeping. If telemetry is not found make sure the 3st transmitter and the 3...
Page 29
4-5 4.3.1 general setup use the up and down soft keys to scroll to additional setup items. When lists are being displayed, the up arrow soft key dims when the first item in the list is reached and the down arrow soft key dims upon reaching the last item..
Page 30: Operator Name
4-6 operator name allows the user to enter the operators name. The name will appear in the header section of the auto test report. Contrast level adjusts the contrast level of the lcd for optimum viewing by the operator. The level is varied on a scale from 1-15. Use the up and down arrow keys to adj...
Page 31: Date Format
4-7 date format use the up and down arrow keys to select the desired date format. When the date format is changed, the new format will appear every- where the date is displayed or printed. The following date formats are available: • mm/dd/yy • dd.Mm.Yy • yy.Mm.Dd printer sets the printer interface t...
Page 32: Beeps
4-8 beeps the 3st transmitter produces beeps to alert you of certain operat- ing conditions. The arrow keys are used to turn beeps on or off as desired. Diagnostics press the enter key to enter the diagnostic mode. The diagnostic mode allows the user to reset the unit to all factory default settings...
Page 33: Signal Level Units
4-9 signal level units use the up and down arrow keys to select the desired level units (dbmv, db µ v, dbm). Test point compensation test point compensation is used to account for loses associated with certain amplifiers. Use the up and down arrow keys or the numeric entry keys to enter the test poi...
Page 34: C/n Calibration
4-10 c/n calibration to increase the accuracy of the c/n measurements, a noise floor calibration is performed. This allows the user to characterize the noise floor of the unit. To perform the calibration, highlight the selection and press the enter key. The unit will provide a prompt to ensure that ...
Page 35: Video Signal Type
4-11 activate the selected channel plan. Channel plans can also be deleted from the list using the delete soft key. An ok and stop soft key is then displayed to confirm or stop the deletion of the channel plan. The currently active channel plan (as indicated in the lower right hand corner of the scr...
Page 36: Sweep Points.
4-12 step 2: select a fixed channel plan to use for building the new plan. Use the up and down arrow keys to select a fixed channel plan to build the new plan from. Press the ok soft key when completed. Step 3: enter the frequency at which to stop searching for channels. Press the enter key followed...
Page 37
4-13 use the up or down arrow keys to select the channel that you wish to edit. Press the edit soft key to view and edit the following parameters:.
Page 38: List.
4-14 note: if the parameter that you wish to edit does not appear on the screen, keep pressing the arrow soft key to scroll through the list. Enabled y/n - if the channel is not enabled it will not be included in any measurement modes. At least one channel must be enabled. If a channel is not enable...
Page 39: Label
4-15 label the label is provided to associate a channel's number with it's programming. Using the alpha keys, label the channel with a desired name (up to four characters). "special" characters can be selected using the up/down arrow keys. The label will appear to the left of the channel number on m...
Page 40: Scrambled
4-16 scrambled y/n - select yes if the channel is scrambled. When a channel is designated as scrambled, the sweep will only look at the video carrier as a sweep reference, instead of both the video and audio carrier. Note: a diamond will appear to the left of the channel type indicator on most scree...
Page 41: Specify Auto Measurements
4-17 if sweep points are entered in the following frequency ranges they will be automatically shifted to avoid measurement inaccuracies. 197.88 to 198.12 lower to 197.87 441.13 to 441.37 lower to 441.12 496.13 to 496.37 lower to 496.12 827.63 to 827.87 lower to 827.62 882.63 to 882.87 lower to 882.6...
Page 42: Edit Limits
4-18 use the up and down arrow soft keys to cursor to a channel. Use the c/n, hum, and mod soft keys to select the desired auto test measurements. Note: c/n, hum, and modulation cannot be measured on a scrambled channel or a sweep point. Hum and modulation cannot be measured on a digital type carrie...
Page 43: Copy Remote Plan
4-19 copy remote plan this selection allows you to copy a channel plan from one unit to another. Connect a cable between the serial ports of two units. Ensure that the baud rate is set the same for each unit (general setup screen). A baud rate of 19.2k is recommended for uploading plans. Select copy...
Page 44: Forward Telemetry Frequency
4-20 4.3.5 sweep transmitter forward telemetry frequency use the up and down arrow keys or the numeric keypad to enter the telemetry frequency. Note: for successful stealth mode operation, the rx telemetry frequency must match the tx telemetry frequency setting of the model 3st transmitter. Caution:...
Page 45: Include Audio Carriers
4-21 use the up and down arrow keys or the numeric keypad to enter the telemetry level (20-50 (1) dbmv). Forward sweep insertion level this is the level at which the 3st inserts (transmits) sweep points. All sweep points are inserted at the same level. Use the edit box to set the sweep insertion lev...
Page 46: Access Reverse Sweep Plans
4-22 important: the frequency the reverse telemetry carrier should be carefully selected such that it will not interfere with any existing carriers on the reverse plant. Access reverse sweep plans reverse sweep plans are used to define the frequencies at which sweep points will be inserted by 3sr un...
Page 47
4-23 label (up to four characters) • channel number or frequency • channel label • video carrier frequency and level (numerical) • audio carrier frequency and level (numerical) • analog meter of carrier levels • delta between audio and video levels • selected channel plan • test point compensation (...
Page 48: Scale Adjustment
4-24 scale adjustment the up and down arrow keys can be used to adjust the reference level on the analog meter. This is helpful when the audio and video levels differ by large amounts. To automatically scale the analog meter, press the fcn key followed by the scale second function key. When in the t...
Page 49: Level Adjustments
4-25 information displayed in the tilt mode is as follows: • high and low carrier frequencies • high and low carrier levels • tilt measurement • reference level and scale • selected channel plan • test point compensation (appears only if a nonzero value is programmed during setup) when the tilt key ...
Page 50
4-26 to adjust the ref level, press the ref level soft key. Now the ref level can be changed by using the up and down arrow keys or by entering a numeric value followed by the enter key. The refer- ence level is at the top of the graph. Note: the reference value is limited by unit and the scale sett...
Page 51: Level Adjustments
4-27 • audio carrier frequency and level (numerical) • histogram graph of carrier levels • delta between audio and video levels • selected channel plan • test point compensation (appears only if a nonzero value is programmed during setup) • limits annunciators when the scan key is pressed a graph sh...
Page 52: Tilt Compensation
4-28 press the tilt soft key to turn tilt compensation on or off. Tilt channels must be programmed in the channel plan edit mode, before this function can be implemented. The tilt is based on the levels of the highest and lowest channels configured for tilt. When turned on, the compensation value ca...
Page 53
4-29 • adjacent channel error • video level too high/low • ∆ va too high/low the limit annunciators are updated with each scan update. An "aggregate" result summary can be accessed by pressing the lim soft key. This performs a limit check of all channels contained within the scan and reports an over...
Page 54
4-30 4.7 how to measure c/n it is a good engineering practice to use a bandpass filter on the input of the receiver when making c/n measurements. This is to ensure accuracy and extend measurement range. If a preamplifier is used to boost test point levels prior to measurement, it should be placed be...
Page 55: Bandwidth Adjustments
4-31 information displayed in the c/n mode is as follows: • channel number • channel label • carrier frequency • noise offset frequency • noise frequency • bandwidth • c/n ratio • channel plan to make a carrier to noise measurement, press the c/n key. The c/n ratio of the tuned channel or frequency ...
Page 56
4-32 4.8 how to measure hum hum is undesirable modulation of the television video carrier by power line frequencies and harmonics (e.G., 60 or 120 hz), or other low frequency disturbances (fcc limit: simply press the hum key when tuned to any non-scrambled chan- nel. In the hum mode the hum modulati...
Page 57: Note: The
4-33 note: the includes 50 to 1000hz. Information displayed in the hum mode is as follows: note: hum measurements taken while the desktop charger is in use will affect the hum reading. For the most accurate reading disconnect the charger prior to taking hum measurements. 4.9 modulation this function...
Page 58
4-34 4.10 spectrum analyzer mode the spectrum analyzer display provides a view of the system spectrum with variable spans from 50 mhz to 3 mhz and a dynamic range of better than 60 db. When the spectrum key is pressed, the following screen is displayed..
Page 59: Level Adjustments
4-35 level adjustments a lvl (level) soft key is used to adjust the vertical parameters of the graph. These parameters include max hold, ref level and scale. The max hold function ensures that the highest signal over multiple sweeps is displayed. When the max hold soft key is pressed, as indicated i...
Page 60: Receiver.
4-36 how to make fcc in-channel response measurements (fcc limit: , + 2 db) the frequency response of any channel can be measured using the spectrum analyzer mode. A flat signal source must be inserted at the input of the modulator or processor. In testing a modulator this source may be a full field...
Page 61
4-37 press the ok soft key once the carrier has been turned off. The cso/ctb measurement is now displayed..
Page 62
4-38 the light trace represents the carrier prior to it being turned off. The dark trace represents the distortion products. The measurement value is computed by a ratio of the peak level of the video carrier to the peak of the distortion products of the second and third order beats. The "worst case...
Page 63
4-39 4.11 sweep mode the transmitter sweep mode operates the same as the scan mode with the following exceptions: • sweep telemetry is transmitted • sweep points are injected • sweep point levels are displayed in the graph note: sweep telemetry will cease when another mode is selected..
Page 64
4-40 4.12 file the file menu consists of two file submenus; store measurement, and measurement files. 4.12.1 how to store/view/delete measurement files the store measurement feature allows the user to store sweep, spectrum and scan measurements. To store a measurement, press the file key while takin...
Page 65
4-41 to view measurement files, press the measurement files soft key. A listing of all currently stored measurement files is displayed. Use the up and down arrow keys to select the file to be viewed. Once selected, press the view soft key. Scan measurements can be stored, but can only be viewed/prin...
Page 66
4-42 4.13 auto the auto menu consists of three file submenus; test locations, perform auto test, and auto test results. 4.13.1 how to create/edit/delete test locations test locations allow the user to create specific test point location parameters used in the auto test report. The test locations can...
Page 67
4-43 press the new soft key to create a new test location file. The unit will then prompt for a file name. Once a name is entered, press the ok soft key to execute the operation..
Page 68
4-44 each location in the list has an associated type and values for the descriptive parameters. The parameters are shown in the following table. Parameter min max default units 1 area 15 column alpha numeric field 2 amp id 15 column alpha numeric field 3 power configuration in / out / through 4 fee...
Page 69
4-45 characteristic trunk head extender fiber field 1 area yes yes yes yes 2 amp id yes yes yes 3 power configuration yes yes yes 4 feeder maker config yes yes yes 5 trunk termination yes yes yes 6 voltage setting yes yes yes 7 rev pad yes yes yes 8 rev equalizer yes yes yes 9 fwd pad yes yes 10 fwd...
Page 70: Auto Test Location
4-46 auto test location using the up and down arrow keys, select an auto test location. Select none if location information is not desired. Press the ok soft key when completed. To create a new auto test location, press the new soft key. Auto test characteristics.
Page 71: Ok Soft Key When Completed.
4-47 use up and down arrow keys to scroll through the location character- istics for the test being performed. Press the enter key after each parameter is entered to update the display. If changes are made and you want them updated in the location file, press the save soft key. If changes are made a...
Page 72: Voltage Measurements
4-48 voltage measurements use the numeric entry keys to enter the following system voltage measurements: • ac voltage • dc voltage (regulated) • dc voltage (unregulated) the voltage measurements are printed in the auto test report. Press the ok soft key when completed..
Page 73: Test Point Compensation
4-49 test point compensation test point compensation is used to account for loses associated with certain amplifiers. Use the up and down arrow keys or the numeric entry keys to enter the test point compensation. (-100.0 to +100.0 db in 0.1 db steps). Press the ok soft key when the desired value has...
Page 74: Results File
4-50 results file enter a file name for the auto test results to be stored. If an existing file name is used, a warning message will appear prompting the user to overwrite the existing file or create a new one. When the desired file name has been entered, press the ok soft key to proceed with the au...
Page 75: Scheduled
4-51 while the auto test is in progress, the measurement currently being performed (i.E. Level, c/n, hum, or modulation) is indicated on the screen. A bar graph showing the percentage of completion is dis- played. Scheduled if the scheduled mode is selected, the start, stop, and interval information...
Page 76
4-52 using the numeric entry keys, enter the start and stop information for the date and time as well as the interval amount. Press the enter key after each parameter is entered to update the display. Use the up and down arrow soft keys to select the parameter to be entered. Press the ok soft key to...
Page 77
4-53 4.13.3 viewing/printing auto test files upon completion of the auto test, the unit will enter the auto test results mode to display the auto test files. This allows the user to view or print the auto test results. Use the up and down arrow soft keys to select a file, then press the view soft ke...
Page 78
4-54 information provided on each interval includes: • interval number • date measurement was made • time measurement was made • temperature • pass/fail test results an "x" in the pass/fail column indicates an overall failure of the measurements taken during that interval. A check mark indicates tha...
Page 79
4-55 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- wavetek stealth 24 hour test report model: 3st serial no: 1234567 cal date: 06/21/95 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- operator: john file: proof1 ----------------------------------...
Page 80
4-56 the channels with the asterisks indicate those channels that ex- ceeded the max delta adjacent channels limit. The limits that the readings were compared to, are printed at the bottom of the report. To the right of the limits, the report displays each interval that failed the specific limit. If...
Page 81
4-57 use the more soft key to toggle between level measurements, c/n, hum, and modulation measurements. When viewing the list of c/n, hum, and modulation measurements, the following symbols will replace the measurement value if an error occurred: • under - under range • over over range • error - syn...
Page 82
4-58 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- wavetek stealth auto test report model: 3st serial no: 1234567 cal date: 06/21/95 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- operator: john file: proof1 inverval: 1 date: 07/20/95 time: 15:1...
Page 83
4-59 4.14 status to view the status screen, press the fcn key followed by the status second function key. The status screen provides unit information to the user. An important feature is the amount of memory currently being used. This allows the user to decide if unwanted files should to be deleted ...
Page 84
5-1 section 5 reverse sweep option 5.1 introduction this section provides detailed operation of the model 3st reverse sweep option. Included are detailed descriptions of how to perform reverse sweeping as well as the various displays. 5.1.1 wavetek stealth reverse sweep concept with the reverse swee...
Page 85
5-2 this is why it is best to transmit the sweep from the amplifier test point and measure it in the headend. This ensures that the system is properly aligned to carry signals in the reverse path. 5.1.3 interfacing with different network architectures single cable - split band network the model 3st ...
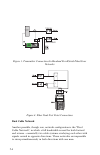
Page 86
5-3 systems with directional test points are set up as shown in figure 2. In this configuration the ddc-20 is used to provide a sample of the reverse sweep output to the input of the 3sr receiver. Figure 2. Single cable - split band network reverse sweep configuration with directional test points. A...
Page 87: Dual Cable Network
5-4 combining network file auto setup tilt scan level c/n hum mod sweep spect print system sweep transmitter 3st figure 3. Transmitter connections in headend for hybrid fiber/coax networks figure 4. Fiber node test point connections dual cable network another possible, though rare, network configura...
Page 88
5-5 the problem is that the two systems use the same spectrum, making it impossible to distinguish between the two with one instrument. The recommended method for these systems is to first sweep the forward portion of the network, then move the transmitter out to the furthest extremity and sweep the...
Page 89
5-6 important: reverse sweep should be disabled when there are no 3sr units being used with the reverse sweep option. This will optimize the update rate of the forward sweep. It should also be disabled if you are using the 3hrv for reverse sweeping. 5.2.2 select the frequency of the reverse telemetr...
Page 90: Creating.
5-7 5.2.5 creating a new reverse sweep plan press the new soft key to create a new reverse sweep plan. You will be asked to enter a name for the plan that you are creating. Use the alphanumeric keys followed by the enter key. Then press the ok soft key to continue. Note: a warning message will appea...
Page 91
5-8 next, enter the start frequency. This will be the frequency of the first sweep point in the plan. Use the numeric keys followed by the enter key. Then press the ok soft key to continue. The interval is entered next. This interval determines the spacing between sweep points. Use the numeric keys ...
Page 92
5-9 finally, you are asked to enter the stop frequency. There will be no sweep points generated beyond the stop frequency. Use the numeric keys followed by the enter key. Then press the ok soft key to continue..
Page 93
5-10 sweep points are generated beginning at the start frequency and continuing until the stop frequency is reached. The frequency of each point is calculated by adding the step interval to the frequency of the previous point. After it has been created, the new plan will appear in the reverse sweep ...
Page 94
5-11 note that the frequency of the selected sweep point also appears in the edit box below the list. You can change the frequency by using the numeric keys followed by the enter key. The list will be updated when the enter key is pressed. To remove a sweep point, use the up or down arrow to select ...
Page 95
A-1 appendix a status indicators/icons introduction there are numerous status indicators/icons displayed on the stealth 3st. The following is a list of all status indicators/icons and an explanation of each. The status indicators are displayed in the title bar as shown in the example below. - video ...
Page 96: Message
B-1 appendix b user messages introduction there are numerous user messages that will appear on the unit. Some messages can be caused by improper operation or unit malfunc- tion. The following list provides an explanation of the condition that caused the message to appear, followed by the suggested r...
Page 97: Message
B-2 message error... Insufficient signal level to perform the measurement! Condition a minimum carrier level is required for c/n and hum measurements. Response choose another channel or frequency with greater than the minimum level. Message sorry... This is an illegal name and cannot be used. Condit...
Page 98: Message
B-3 message error... The selected reference has been corrupted! Condition the reference cannot be used because of a non-volatile memory failure. Response delete the corrupted reference and select another. Message sorry... Not enough sweeps have occurred to store an accurate reference. Please allow m...
Page 99: Message
B-4 message sorry... There is not enough memory to store a new file! Condition memory is currently at maximum capacity. Response delete unwanted files to make more memory available. Message warning... The selected sweep file will be deleted! Condition a sweep file is about to be deleted. Response pr...
Page 100: Message
B-5 cancel. Message sorry... The active plan cannot be deleted! Condition an attempt to delete the active channel plan. Response select a different plan as the active plan, then delete the desired plan. Message error... This plan is corrupted and cannot be used! Condition the plan cannot be used bec...
Page 101: Message
B-6 response press ok to delete, stop to cancel. Message sorry... The last channel cannot be deleted! Condition an attemp was made to delete the last channel of a plan. Response a channel plan must contain at least one channel. If desired, delete the entire plan. Message warning... This operation ca...
Page 102: Message
B-7 response press ok to reset settings, stop to cancel. Message error... C/n cannot be measured on a scrambled channel! Condition a channel that has been programmed as scrambled in setup has been selected in c/n mode. Response select a channel that is not scrambled. C/n measurements are not possibl...