- DL manuals
- Wavetronix
- Switch
- SmartSensor Matrix
- User Manual
Wavetronix SmartSensor Matrix User Manual
Summary of SmartSensor Matrix
Page 1
Smartsensor matrix user guide.
Page 2
Smartsensor matrix user guide www.Wavetronix.Com • 78 east 1700 south provo, utah 84606 • 801.734.7200
Page 3
© 2014 wavetronix llc. All rights reserved. Wavetronix, smartsensor, click, command, and all associated product names and logos are trademarks of wavetronix llc. All other products or brand names as they appear are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Protected by us pate...
Page 4: Contents
Contents introduction 5 smartsensor matrix package 6 • selecting a mounting loca- tion 7 part i installing the smartsensor matrix chapter 1 installing the smartsensor matrix 13 sensor mounting guidelines 14 • attaching the mount bracket to the pole 15 • attaching the sensor to the mount bracket 16 •...
Page 5
Part ii using smartsensor manager matrix chapter 4 installing smartsensor manager matrix 45 installing ssmm 46 • microsoft .Net framework 48 chapter 5 communication 49 serial connection 51 • internet connection 53 • virtual con- nection 56 • viewing connection information 58 • upgrading the sensor’s...
Page 6
In this chapter ˽ smartsensor matrix package ˽ selecting a mounting location the wavetronix smartsensor matrix™ is a stop bar presence detector designed for use at signalized intersections (see figure i.1). The smartsensor matrix detects vehicles through the use of a 24.125 ghz (k band) operating ra...
Page 7: Smartsensor Matrix Package
6 introduction • smartsensor matrix user guide ration process is quick and easy. After installation, the sensor will require little or no on-site maintenance and can be remotely configured. This user guide outlines the step-by-step process of installing and configuring the smart- sensor matrix. Any ...
Page 8
Introduction • smartsensor matrix user guide 7 control bridge to rack cards control bridge to sensors configuration toolkit (attach to t-bus) control bridge on t-bus ac power conversion option remote ip connection option (attach to t-bus) figure i.2 – smartsensor matrix system options note smartsens...
Page 9
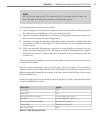
8 introduction • smartsensor matrix user guide 140 ft sensor pole 140 ft figure i.3 – corner radar ˽ line of sight – position the sensor so that it will be able to detect the entire area of interest. Avoid occlusion by installing the sensor away from trees, signs and other road- side structures. ˽ d...
Page 10
Introduction • smartsensor matrix user guide 9 signs or other flat surfaces directly behind it. This will help reduce multiple reflection paths from a single vehicle. ˽ cable length – make sure that you have sufficient homerun and sensor cabling. Cable runs as long as 500 ft. (152.4 m) can be achiev...
Page 12
Part i installing the smartsensor matrix chapter 1 – installing the smartsensor matrix chapter 2 – connecting power and surge protection chapter 3 – contact closure communication.
Page 14
In this chapter ˽ sensor mounting guidelines ˽ attaching the mount bracket to the pole ˽ attaching the sensor to the mount bracket ˽ aligning the sensor to the roadway ˽ applying the silicon dielectric compound ˽ connecting the smartsensor 6-conductor cable ˽ grounding the sensor 1 the installation ...
Page 15: Sensor Mounting Guidelines
14 chapter 1 • installing the smartsensor matrix warning use caution when installing any sensor on or around active roadways. Serious injury can result when installation is performed using methods that are not in accordance with authorized local safety policy and procedures. Always maintain an appro...
Page 16
Chapter 1 • installing the smartsensor matrix 15 ˽ take into consideration the sensor’s field of view, which reaches 140 ft. (42.7 m) from the sensor. Place the sensor so that the field of view covers all the areas of interest. ˽ the mast arm is frequently a good place to mount the sensor. ˽ the mou...
Page 17
16 chapter 1 • installing the smartsensor matrix one swivel joint is used to pan the sensor field of view left or right and the other swivel joint is used to tilt the sensor down towards the roadway. If you are not using the double swivel- mount, make sure the pole straps are adjustable at this poin...
Page 18
Chapter 1 • installing the smartsensor matrix 17 45° 45° edge of first lane of interest stop bar pan sensor towards stop bar figure 1.3 – corner radar field of view position to visualize the extent of the sensor field of view, the 90° field of view is imprinted on the top and bottom of the sensor ca...
Page 19
18 chapter 1 • installing the smartsensor matrix downstream of the stop bar. 2 tilt the sensor down so it is aimed at the center of the lanes of interest. 3 if necessary, rotate the sensor so that the bottom edge of the sensor is parallel with the roadway. This is necessary where the intersection ap...
Page 20: Grounding The Sensor
Chapter 1 • installing the smartsensor matrix 19 figure 1.6 – sensor 6-conductor cable connector to set up your network in an orderly fashion, it is recommended that labeling be used on the service end of each smartsensor 6-conductor cable. A convenient way to label the cables is to mark the last se...
Page 21
20 chapter 1 • installing the smartsensor matrix caution be careful of electrostatic discharge (esd) when handling the smartsensor matrix device before and during installation. Esd triggered by the sensor handler, particu- larly on the outer grounding lug before being properly grounded, may cause ha...
Page 22
In this chapter ˽ mounting the backplate ˽ connecting ac power ˽ providing system surge protection ˽ terminating smartsensor 6-conductor cables 2 after installation, each smartsensor matrix will need to be integrated into the main traf- fic cabinet for power and surge protection. This chapter contai...
Page 23: Mounting The Backplate
22 chapter 2 • connecting power and surge protection figure 2.1 – intersection preassembled backplate mounting the backplate use the following steps to mount the backplate in the traffic cabinet: 1 locate the area planned for mounting the backplate. The backplate can usually be mounted on the side p...
Page 24
Chapter 2 • connecting power and surge protection 23 warning make sure power to ac mains is disconnected while wiring the ac input. If your in- stallation does not require ac power, you will need to use surplus dc power inside the traffic cabinet. In this case, wavetronix recommends you use the clic...
Page 25
24 chapter 2 • connecting power and surge protection caution an authorized electrical technician should install the preassembled backplate. Per- sons other than authorized and approved electrical technicians should not attempt to connect the backplate to a power supply and/or traffic control cabinet...
Page 26
Chapter 2 • connecting power and surge protection 25 follow the steps below to provide a low impedance protective earth connection: 1 connect one end of a protective earth ground wire to the bottom of the pe terminal block. A 10 awg stranded wire is recommended for protective earth ground connec- ti...
Page 27
26 chapter 2 • connecting power and surge protection ( ) ( ) +24v dc -dc +rs-485 -rs-485 gnd red wire black wire power rs-485 green green gray figure 2.5 – t-bus pinout diagram providing system surge protection the click 222 system surge protector is designed to prevent electrical surges conducted a...
Page 28
Chapter 2 • connecting power and surge protection 27 ˽ td – indicates when data is transmitted over the t-bus or over the control bridge. This led does not indicate data transmitted on the a or b ports. ˽ rd – indicates when data is received over the t-bus or over the control bridge. This led does n...
Page 29
28 chapter 2 • connecting power and surge protection ss m atri x # 2 x x pwr x x drn x x gnd x x 485+ x x 485- x x 485+ x x 485- x out x in x x pwr x x drn x x gnd x x 485+ x x 485- x x 485+ x x 485- x out x in ss m atri x # 3 x x pwr x x drn x x gnd x x 485+ x x 485- x x 485+ x x 485- x out x in ss...
Page 30
Chapter 2 • connecting power and surge protection 29 note do not strip the service end of the cable until after it has been routed through con- duit. The cable should be one continuous run without any splices. Use the steps below to land the sensor cables: 1 after routing your smartsensor 6-conducto...
Page 32
In this chapter ˽ using the click 112/114 dip switches ˽ using the click 104 rotary switch ˽ attaching and programming the click 112/114 ˽ attaching and programming the click 104 ˽ channel mapping 3 each smartsensor matrix communicates with standard traffic cabinets using either the click 104 din ra...
Page 33
32 chapter 3 • contact closure communication note see the click 100–400 series user guide for complete information on how to con- nect and configure the click 104 din rail contact closure module and the click 112/114 detector rack cards. Each smartsensor matrix could potentially use up to 16 channel...
Page 34
Chapter 3 • contact closure communication 33 note an advantage of using the dip switches for configuration is that if you ever need to replace a click 112/114, you can simply set the dip switches on the new card to match the pattern of the dip switches on the card you are replacing, then slide the n...
Page 35
34 chapter 3 • contact closure communication 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 on off channel group bus 1 bus 2 s4 s5 input mapping switches baud rate switches click 112 –selects channels 1 & 2 figure 3.4 – click 112 dip switches for channels 1 and 2 figure 3.5 shows how to set the dip switches on the...
Page 36
Chapter 3 • contact closure communication 35 as shown in the table below, the outputs are mapped sequentially—that is, they can only be mapped in numerically ordered groups of four (1–4, 5–8, etc.). If you set the switch to 3, for 9–12, then sensor channel 9 would be mapped to output 1, sensor chann...
Page 37
36 chapter 3 • contact closure communication 4 connect a 6-ft. (1.8-m) patch cord from the click 222 rs-485 b port to a bus 1 port on another rack card. 5 if you are using click 112 cards, use an 6-in. (15-cm) patch cord to share bus 1 between cards dedicated to the same sensor. Also, configure one ...
Page 38
Chapter 3 • contact closure communication 37 detection channel menu level 2 menu level 1 mode switch figure 3.7 – click 112/114 menu normally, a smartsensor matrix sensor will send 10 contact closure messages each second. If a rack card does not receive communications from a sensor within 10 seconds...
Page 39
38 chapter 3 • contact closure communication 3 if needed, daisy-chain multiple click 104 devices together by utilizing both rj-11 jacks on each device’s faceplate. Click 104 leds the front panel of the device features a push-button and three banks of leds for on-device configuration and monitoring. ...
Page 40: Channel Mapping
Chapter 3 • contact closure communication 39 menu option. 4 press and hold the mode switch to cycle through the submenu. The level 2 leds will light to indicate that the device is cycling though all configuration options. 5 release the mode switch once the desired configuration option is reached. 6 ...
Page 41
40 chapter 3 • contact closure communication nema ts2, 2070 and other advanced traffic cabinet systems usually allow software pro- gramming of the detector card channel outputs to traffic phases via a channel-to-phase mapping grid in the controller menu. Figure 3.12 illustrates how the detector chan...
Page 44
Part ii using smartsensor manager matrix chapter 4 – installing smartsensor manager matrix chapter 5 – communication chapter 6 – sensor settings chapter 7 – lanes & stop bars chapter 8 – zones & channels chapter 9 – verification chapter 10 – tools.
Page 46
In this chapter ˽ installing ssmm ˽ microsoft .Net framework 4 the smartsensor manager matrix (ssmm) software enables you to configure and interact with the smartsensor matrix. Ssmm can be run on any windows-capable device up to and including windows 8. Note windows rt, found on many new windows tab...
Page 47: Installing Ssmm
46 chapter 4 • installing smartsensor manager matrix wireless link. Follow the steps below to use the click 421 to communicate with the smartsensor matrix: 1 rock the click 421 device onto the green t-bus to the left of the gray t-bus connector on the second din rail on the backplate. 2 make a wired...
Page 48
Chapter 4 • installing smartsensor manager matrix 47 figure 4.1 – ssmm setup wizard 4 select an installation location. The default location provided is normally “c:\program files\wavetronix.” if desired, click browse to choose another location (see figure 4.2). Figure 4.2 – location to be installed ...
Page 49: Microsoft .Net Framework
48 chapter 4 • installing smartsensor manager matrix ssmm software. A pdf reader program (i.E. Adobe acrobat reader) is required to view the release notes. 8 click finish to complete the setup process. Note ssmm is designed for the 96 dpi display setting. The application may not display text properl...
Page 50
In this chapter ˽ serial connection ˽ internet connection ˽ virtual connection ˽ viewing connection info ˽ upgrading the sensor’s embedded software 5 once the sensors are installed, use the ssmm software to change settings, view data and configure the sensors to the roadway. Launch ssmm by either cl...
Page 51
50 chapter 5 • communication figure 5.1 – ssmm splash screen (left) and main screen (right) you can always view the version of ssmm you are using by right-clicking on the main screen and then clicking ssm matrix version . To see the version, date and timestamp of the individual components that make ...
Page 52: Serial Connection
Chapter 5 • communication 51 the first step is to make a connection to the sensor. The following three types of connections can be made: ˽ serial connection – connect using bluetooth, rs-232, or rs-485 communication. ˽ internet connection – connect using an ip address and a serial to ethernet conver...
Page 53
52 chapter 5 • communication figure 5.3 – serial connection after you have connected to a sensor, the next time you would like to connect you can simply click the magnifying glass icon in the upper right corner of the screen. This will take you to the last connection settings you used to connect to ...
Page 54: Internet Connection
Chapter 5 • communication 53 figure 5.4 – sensor info screen the sensor info screen lists the following sensor settings and version information: ˽ sensor id – the last seven digits of the sensor serial number. This field is not editable. ˽ description – used to describe the application (e.G. Stop ba...
Page 55
54 chapter 5 • communication 420 serial to 802.11b converter. The click 420 provides serial devices with an ip ad- dress on a wireless 802.11b network. ˽ internet service providers – the smartsensor matrix can be equipped with optional external modems (cdma, gms or gprs) and assigned an internet add...
Page 56
Chapter 5 • communication 55 figure 5.6 – internet connection screen 9 click the connect button. When a connection is established you will be directed back to the home page. If you have problems connecting: 1 make sure that all power and communication wiring is correct. 2 check the address and port ...
Page 57: Virtual Connection
56 chapter 5 • communication deletes an address book imports an address book exports an address book edits the selected device adds a device to the address book deletes a device from the address book figure 5.7 – address book virtual connection a virtual connection allows you to use the ssmm softwar...
Page 58
Chapter 5 • communication 57 figure 5.8 – virtual connection screen 3 select or create a virtual sensor file (.Vsf) by clicking the magnifying glass icon. 4 click the search button. This may take up to 30 seconds while the sensors on your vir- tual control bus are discovered and listed. (you can cli...
Page 59
58 chapter 5 • communication note to configure channels for a future installation, connect using a virtual connection, create a virtual sensor file and then back up the configuration settings that you cre- ated. After the file is successfully backed up, the virtual sensor file will change to a senso...
Page 60
Chapter 5 • communication 59 below is a list of the information available on the connection info screen: ˽ status – shows that you are connected. ˽ sensor – shows the subnet and sensor id. ˽ type – shows the type of connection. ˽ duration – shows how long you have been connected. ˽ failures – shows ...
Page 61
60 chapter 5 • communication sion control screen may appear asking you to install firmware upgrades (see figure 5.13). If you think you have reached this screen in error, clicking the recheck button will have the software retry and ensure that there has not been a communication issue. Clicking the d...
Page 62
Chapter 5 • communication 61 ssmm firmware version date is more recent than the sensor firmware version date, the newer firmware will need to be installed; if the sensor’s firmware date is more recent than the ssmm firmware version date, a warning will appear notifying you that older firmware will b...
Page 64: General Sensor Settings
In this chapter ˽ general sensor settings ˽ comm sensor settings ˽ advanced sensor settings 6 click the sensor settings link on the main menu to change and save settings on the sensor. General sensor settings the general tab of the sensor settings screen allows you to change the sensor description, ...
Page 65: Comm Sensor Settings
64 chapter 6 • sensor settings figure 6.1 – serial settings window the general tab contains the following fields: ˽ serial number – contains the sensor serial number and cannot be edited. ˽ sensor id – contains the id used to uniquely identify all sensors on a multi-drop bus. This id is the last sev...
Page 66
Chapter 6 • sensor settings 65 figure 6.2 – comm tab ˽ response delay – used to configure how long the sensor will wait before responding to a message received. This is useful for some communications devices that are unable to quickly change transmission direction. The default value is 10 millisecon...
Page 67: Advanced Tab
66 chapter 6 • sensor settings ˽ source – in normal use, the source is always the radar antenna. However, in some cases, other sources may be used for demonstrations or evaluations. When the source is switched to diagnostic , the antenna is no longer used. Instead, a predetermined sequence of traffi...
Page 68
In this chapter ˽ display options ˽ menu bar ˽ automatic configuration ˽ manual configuration 7 after sensor settings, the next option available from the main menu is sensor setup . When you click this option, the first screen that appears is lanes & stop bars. The lanes & stop bars screen shows the...
Page 69: Display Options
68 chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars vehicle detections are represented by tracks (a series of dots) along the sensor’s view. The vehicle tracks show where the sensor is detecting traffic and will later help you configure lanes. Vehicle track history can be cleared from the screen by clicking the clear ...
Page 70
Chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars 69 the edit area also contains the approach name in a small window outside of the sensor’s view (see figure 7.3) if needed, click on the name box to see the entire approach name. This allows you to always know which approach is being configured. The approach name can be...
Page 71
70 chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars figure 7.5 – automatic configuration overlay smartsensor matrix is constantly running the auto-configuration process in order to find undiscovered lanes and stop bars. During this process, lanes will appear in the auto cfg overlay. You will need to select and capture...
Page 72: Menu Bar
Chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars 71 figure 7.6 – capture window note if a stop bar is found for a lane during the auto-configuration process, it will be cap- tured with the lane. Menu bar the menu bar at the bottom of the screen allows you to perform a variety of operations during sensor configuration....
Page 73
72 chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars saving the configuration after automatic and manual configuration is complete, click the save config button to save the changes to the sensor. If you attempt to leave the lanes & stop bar view before saving your changes, the following prompt will appear (see figure 7...
Page 74
Chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars 73 figure 7.9 – restart or reboot window note after you have mounted and aligned the sensor, you should always reboot the sensor so that thresholds can adjust to the current view. Editing thresholds warning changing matrix thresholds can have an adverse effect on matrix...
Page 75: Automatic Configuration
74 chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars figure 7.11 – zoom in feature after you click on adjust bins or adjust all , the sensitivity slider window will appear (see figure 7.12). Click on the up/down buttons to change the sensitivity (in decibels). Negative values will lower the rejection threshold in order...
Page 76: Manual Configuration
Chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars 75 manual configuration after the automatic configuration process is complete, manual adjustments can be made to fine-tune the sensor configuration. In some cases, it will be easier to configure the sensor manually than to use the auto-configured lanes and stop bars. Th...
Page 77
76 chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars figure 7.15 – moving lane outside edit area inserting/deleting/moving a stop bar to insert a lane stop bar: 1 select a lane in the edit area. 2 click on the selected lane again to bring up the edit lane window (see figure 7.14). 3 click on the insert stop bar option ...
Page 78
Chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars 77 to delete a lane node: 1 select a lane in the edit area. 2 click on the selected lane in the vicinity of the desired node to bring up the node ad- justment window (see figure 7.17). 3 click on the delete node option. Figure 7.17 – node adjustment window moving a lane...
Page 79
78 chapter 7 • lanes & stop bars adjusting the width of a lane node adjusting the width of a lane node will adjust the width of the lane. 1 select a lane in the edit area. 2 click on the selected lane and then click again on the node that will be adjusted and the edit node window will appear. 3 chan...
Page 80
In this chapter ˽ menu bar ˽ placing zones ˽ measuring zones 8 after you have configured the lanes and stop bars, click on tab 2 to configure the zones and channels. The zones & channels screen allows you to place zones and configure detection channels (see figure 8.1). Figure 8.1 – zones & channels...
Page 81: Menu Bar
80 chapter 8 • zones & channels when you enter the zones & channels tab and you haven’t yet configured any zones, you will be prompted to add auto zones (see figure 8.2). If you click yes , a zone will be placed in each configured lane. Lanes and stop bars must be defined before you can add auto zon...
Page 82: Placing Zones
Chapter 8 • zones & channels 81 figure 8.3 – zones & channels menu bar the zones & channels menu bar contains the following options: ˽ to main menu – returns you to the main menu. ˽ save config – saves the zones and channel mapping to the sensor. ˽ undo changes – undoes changes made to the zones and...
Page 83: Channel Type
82 chapter 8 • zones & channels editing zones click the edit zone button to adjust the currently selected zone. An entire zone can be moved by clicking and dragging or by using the arrow buttons on the edit zone window (see figure 8.5). Zones can overlap each other. This window can also be used to a...
Page 84
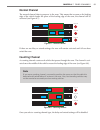
Chapter 8 • zones & channels 83 normal channel the normal channel detects presence in the zone. This means that as soon as the leading edge of the vehicle breaks the plane of the leading edge of the zone, the channel will be activated (see figure 8.7). Channel led pulse channel led channel led figur...
Page 85: Mapping Zones to Channels
84 chapter 8 • zones & channels pulse channel a pulse activates the channel for a very short period of time once the front edge of the ve- hicle crosses the leading edge of the zone (see figure 8.9). You can configure how long you would like the pulse to be by changing the pulse channel width settin...
Page 86
Chapter 8 • zones & channels 85 figure 8.10 – zone/channel map window each channel column contains channel number and channel type (n=normal, c=count, p=pulse). Click on the individual zones in the zone column to highlight the zones in the edit area. Editing channels the edit channel button will all...
Page 87
86 chapter 8 • zones & channels figure 8.12 – output settings (normal, counting, pulse) ˽ detector input – the detector input number provides a way for you to map inputs to the intersection phase in the controller. By default, the detector input will be set to “00;” if the input is left at “00,” the...
Page 88: Measuring Zones
Chapter 8 • zones & channels 87 figure 8.13 – output settings pop-up the dashes in the table mean that those particular settings are disabled due to the selected channel type. Double click on any channel row to change the output settings for that channel. Measuring zones the ssmm software contains a...
Page 89
88 chapter 8 • zones & channels where on the edit area and used to measure anything in the sensor’s view (see figure 8.15). These flags will not be saved to the sensor. Figure 8.15 – using flags.
Page 90
In this chapter ˽ channel indicators ˽ verification menu bar 9 after the configuration is complete, you will need to verify that the sensor was configured correctly. To verify lane configuration and channel mapping, click on tab 3. This will bring up the verification window (see figure 9.1). Figure ...
Page 91: Channel Indicators
90 chapter 9 • verification vehicle detections in a stopped queue are represented by a stationary light blue rectangle. Channel indicators when detections enter a zone, they will cause the indicators for the channel mapped to that zone to turn red. To see the zones mapped to a particular channel, se...
Page 92: Verification Menu Bar
Chapter 9 • verification 91 figure 9.3 – delay and extend zone settings when vehicles stop before and after a zone, the stopped vehicle queue is extended to fill the space between the two vehicles. This ensures that a queue of vehicles that extends in front and behind a zone will always activate the...
Page 93
92 chapter 9 • verification undo your last edit, edit thresholds and pause/play traffic (see figure 9.6). Click the but- ton at the right side of the menu bar to see a window with menu descriptions. Figure 9.6 – verification view menu bar the verification menu bar contains the following options: ˽ t...
Page 94
In this chapter ˽ backup/restore ˽ rack cards tools ˽ tracker logging ˽ sensor self tests 10 the tools screen allows you to back up or restore your sensor configuration, log vehicle detec- tions, and perform several other functions (see figure 10.1). When connected to a sensor, all the options will ...
Page 95: Backup/restore
94 chapter 10 • tools backup/restore to back up or restore the sensor settings that you have changed, click the backup/restore button on the tools screen (see figure 10.2). Figure 10.2 – backup/restore to create a backup, click on the magnifying glass icon in the back-up file section. Choose a desti...
Page 96: Rack Cards Tools
Chapter 10 • tools 95 rack cards tools access tools for working with rack cards and other contact closure devices by clicking the rack card tools button on the tools screen when a sensor connection is not active (see figure 10.3). Figure 10.3 – rack card tools the rack card tools screen allows you t...
Page 97
96 chapter 10 • tools figure 10.4 – rack card tool serial settings 2 after you have entered the correct settings, close the serial settings window and click the search button. 3 once a list of devices appears, click on the desired row. You can identify a device by its id, device, description or loca...
Page 98
Chapter 10 • tools 97 channel outputs switch the channel outputs toggle switch and 1–16 checkboxes are used to help assist in testing of the rack card outputs. If the channel outputs switch is on, all the selected channel outputs on the click 112/114 rack card or click 104 contact closure device wil...
Page 99
98 chapter 10 • tools this tool records vehicle detections as shown on the verification page. Recorded vehicle detections can be used later for playback using a virtual connection. Click on the open folder icon to select a log file. The select tracker log file screen allows you to specify the name o...
Page 100: Sensor Self Tests
Chapter 10 • tools 99 sensor self tests the sensor self tests screen allows you to check the sensor to verify it is working properly (see figure 10.8). To run the sensor self test, click the run sensor self tests button. Figure 10.8 – sensor diagnostics the test results will appear as either “succes...
Page 102
In this chapter ˽ appendix a –cable connector definitions ˽ appendix b –cable lengths ˽ appendix c – click 221 user reference guide ˽ appendix d – click 600 installation ˽ appendix e - matrix extended range 11 appendix a – cable connector definitions the connector end of the smartsensor 6-conductor ...
Page 103
102 appendix a b c d e f g h figure a.1 – smartsensor matrix connector the smartsensor 6-conductor cable has seven wires. Table a.1 details the pinout of the cable connector and the corresponding wire in the cable. The sensor itself also contains internal wires that connect to the protective earth l...
Page 104
Appendix 103 3 strip each of the seven smartsensor cable wires back about 1/4 in. (0.6 cm). 4 insert the wires into the contacts and verify the wire is visible through the contact inspection hole. 5 crimp the wires by following the crimping tool instructions. Daniels manufacturing company provides p...
Page 105
104 appendix note contact wavetronix technical services if you have a need for a cabled connection over 500 ft. (152.4 m). Appendix c – click 221 user reference guide the click 221 is a dc 8 a surge protector (8 a is the maximum rating of a t-bus connec- tor). The dc source voltage and pe (protectiv...
Page 106
Appendix 105 (reverse polarity), the device is not powered or the surge protection circuitry is no longer operational. If the led flickers on an then off when power is applied, this means that the device is conducting power, but the surge is no longer fully functional. When the surge is no longer fu...
Page 107
106 appendix during normal operation, be sure that all appropriate switches are turned on. Caution an authorized electrical technician should install the preassembled backplate. Per- sons other than authorized and approved electrical technicians should not attempt to connect the backplate to a power...
Page 108
Appendix 107 configure the sensor, and lets the sensor send its detection data back to the cabinet. Before you can plug in the cables, you’ll need to terminate each one into the terminal blocks included with your click 600. The method for doing this is identical to the method used with the preassemb...
Page 109
108 appendix note you don’t have to do anything special to tell the device to push data on any port; all data received on any port is automatically pushed on all other ports. The data bus portion of the faceplate also has the following features: next to each rj-11 jack is a switch that turns power o...
Page 110
Appendix 109 3 insert the other end of each wire into a second 5-position connector. 4 plug one connector into the t-bus port on the click 600; plug the other into the end of your t-bus. Lastly, there are four leds on the faceplate. These leds have the following functions: ˽ red led (pw) – illuminat...
Page 111
110 appendix 200 ft 140 ft 100 ft 26' 15' 18' 11' 13' 8' figure e.1 – matrix beam footprints in an installation where the smartsensor matrix is installed in its preferred stop bar loca- tion, angular resolution will likely not be a problem. This is because as the vehicles approach the stop bar they ...
Page 112
Appendix 111 200 ft 140 ft 100 ft figure e.2 – dual approach monitoring signal-to-noise ratio and the stop bar effect the smartsensor matrix collects data beyond its advertised range. However, the signal-to- noise ratio, or the signal-to-clutter ratio, is not large enough at the far ranges to consis...
Page 113
112 appendix example a semi truck is is situated in a left turn lane and its far edge is 30 feet from the sensor. If the sensor is mounted 20 feet above the roadway and a 13-foot tall semi is in the lane closest to the sensor, then a vehicle that is 5 feet tall would be fully occluded within a 34 fo...
Page 114
Appendix 113 2 perform a batch upgrade of sensors to a new version of firmware. As a simple example, a microsoft windows batch file can be used to sequentially upgrade all the sensors listed in the file. Note the auto upgrade command line feature will connect to one sensor at a time and upgrade if n...
Page 115
114 appendix “c:\program files\wavetronix\smartsensor manager matrix v1.4.2\bin\ssm matrix v1.4.2.Exe” internet or it is possible to specify all of the connection options as in the following example: “c:\program files\wavetronix\smartsensor manager matrix v1.4.2\bin\ssm matrix v1.4.2.Exe” internet u...
Page 116
Www.Wavetronix.Com.