- DL manuals
- Yamaha
- Outboard Motor
- F150A
- Service Manual
Yamaha F150A Service Manual
Summary of F150A
Page 1
Service manual 63p-28197-3p-12 f150a fl150a f150b fl150b.
Page 2
Preface this manual has been prepared by yamaha primarily for use by yamaha dealers and their trained mechanics when performing maintenance procedures and repairs to yamaha equipment. It has been written to suit the needs of persons who have the bronze technical certificate of the yta (yamaha techni...
Page 3: Contents
Contents general information 0 specification 1 technical feature and description 2 rigging information 3 troubleshooting 4 electrical system 5 fuel system 6 power unit 7 lower unit 8 bracket unit 9 maintenance 10 index appendix a.
Page 5
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a general information 0 safety while working .................................................... 0-1 rotating part .............................................................................. 0-1 hot part ........................................................................
Page 6
0-1 safety while working safety while working to prevent an accident or injury and to pro- vide quality service, observe the following safety procedures. Rotating part • hands, feet, hair, jewelry, clothing, personal flotation device straps, and so on, can become entangled with internal rotating par...
Page 7
0-2 safety while working 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a self-protection • protect your eyes by wearing safety glasses or safety goggles during all opera- tions involving drilling and grinding, or when using an air compressor. • protect your hands and feet by wearing pro- tective gloves and safety shoes wh...
Page 8
0-3 safety while working handling of sealant • wear protective gloves to protect your skin, when using the sealants. • see the material safety data sheet issued by the manufacturer. Some of the sealants may be harmful to human health. Special service tool use the recommended special service tools to...
Page 9
0-4 how to use this manual 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a how to use this manual manual format the format of this manual has been designed to make service procedures clear and easy to under- stand. Use the following information as a guide for effective and quality service. • parts are shown and detailed i...
Page 10
0-5 how to use this manual abbreviation the following abbreviations are used in this service manual. Abbreviation description abyc american boat and yacht council api american petroleum institute atf automatic transmission fluid awg american wire gauge cca cold cranking ampere dn down side dohc doub...
Page 11
0-6 lubricant, sealant, and thread locking agent 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a lubricant, sealant, and thread locking agent symbol symbols in an exploded diagram or illustration indicate the grade of lubricant and the lubrication points. Symbols in an exploded diagram or illustration indicate the type of...
Page 12
0-7 lubricant, sealant, and thread locking agent threebond 1401 thread locking agent threebond 1530d sealant loctite 271 (red) thread locking agent loctite 242 (blue) thread locking agent loctite 572 (white) sealant silicone sealant sealant symbol name application.
Page 13
0-8 special service tool 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a special service tool for all markets except u.S.A. And canada. Special service tools with part numbers 90890-06883 and fim20000me are distributed by the marine service division. Special service tools with part numbers other than 90890-06883 and fim20...
Page 14
0-9 special service tool test harness (3 pins) 90890-06846 ignition tester (spark gap tester) 90890-06754 test harness (2 pins) 90890-06792 test harness (3 pins) 90890-06791 test harness (2 pins) 90890-06867 fuel pressure gauge 90890-06753 leakage tester 90890-06840 small end bearing installer 90890...
Page 15
0-10 special service tool 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a compression gauge 90890-03160 compression gauge extension 90890-06563 flywheel holder 90890-06522 flywheel stopper 90890-06598 flywheel puller 90890-06521 hydro puller kit 90890-06593 valve spring compressor 90890-04019 valve spring compressor attac...
Page 16
0-11 special service tool valve guide reamer 90890-06804 valve lapper 90890-04101 valve seat cutter holder 90890-06316 valve seat cutter 30° 90890-06327 valve seat cutter 45° 90890-06325 valve seat cutter 60° 90890-06324 valve seat cutter 30° 90890-06326 oil filter wrench 90890-06830 driver rod l3 9...
Page 17
0-12 special service tool 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a bearing separator 90890-06534 gear puller 90890-06540 piston ring compressor 90890-05158 needle bearing attachment 90890-06653 shift rod socket 90890-06681 ring nut wrench extension 90890-06513 ring nut wrench 4 90890-06512 bearing housing puller cl...
Page 18
0-13 special service tool stopper guide stand 90890-06538 bearing puller assembly 90890-06535 driver rod ss 90890-06604 needle bearing attachment 90890-06610 bearing depth plate 90890-06603 bearing inner race attachment 90890-06640 needle bearing attachment 90890-06654 drive shaft holder 6 90890-065...
Page 19
0-14 special service tool 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a ball bearing attachment 90890-06636 driver rod ll 90890-06605 needle bearing attachment 90890-06612 bearing outer race attachment 90890-06628 driver rod ls 90890-06606 bearing outer race attachment 90890-06619 ball bearing attachment 90890-06633 bea...
Page 20
0-15 special service tool dial gauge set 90890-01252 magnet base b 90890-06844 pinion height gauge 90890-06671 slide hammer handle 90890-06531 puller head 90890-06514 needle bearing attachment 90890-06607 ring nut wrench 90890-06578 bearing inner race attachment 90890-06660 ball bearing attachment 9...
Page 21
0-16 special service tool 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a hydraulic pressure gauge 90890-06776/06800 cylinder end screw wrench 90890-06591 trim & tilt wrench 90890-06587 power tilt wrench 90890-06560 ptt piston vice attachment 90890-06572.
Page 22
Specification 1 model feature ..................................................................... 1-1 general feature ......................................................................... 1-1 model name designation ........................................................... 1-2 serial number ....
Page 23
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a specification specified tightening torque ............................................ 1-17 rigging information ................................................................. 1-17 electrical system ..................................................................... 1-17...
Page 24
1-1 model feature model feature general feature f150a, fl150a, f150b, fl150b overall feature • electronic fuel injected, 4-stroke, l4, dohc, 16-valve, 2670.0 cm 3 (162.9 cu. In) engine • low exhaust emissions conform to eu regulations • y-cop (standard for european market and optional for oceanian m...
Page 25
1-2 model feature 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a model name designation 1 model category none: 2-stroke e: enduro f: 4-stroke l: counter rotating propeller t: high thrust (4-stroke) d: twin rotating propeller k: kerosene z: hpdi 2 output horsepower example: 6/9.9/75/150/250/300 3 model generation a/b/c/d/...
Page 26
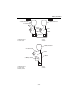
1-3 model feature serial number the outboard motor serial number is indi- cated on a label affixed to the port clamp bracket. 1. Model name 2. Approved model code 3. Transom height 4. Serial number model name approved model code starting serial no. F150aet 63p 1106291– fl150aet 64p 1013389– f150bet ...
Page 27
1-4 model data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a model data dimension and weight overall length 862 mm (33.9 in) overall width 511 mm (20.1 in) overall height l f150aet 1714 mm (67.5 in) fl150aet 1714 mm (67.5 in) overall height x 1842 mm (72.5 in) transom height l f150aet 516 mm (20.3 in) fl150aet 516 mm (2...
Page 28
1-5 model data power unit type 4-stroke, dohc l cylinder quantity 4 total displacement 2670.0 cm 3 (162.9 cu. In) bore × stroke 94.0 × 96.2 mm (3.70 × 3.79 in) compression ratio 9.00 : 1 control system remote control starting system electric starter fuel system fuel injection ignition control system...
Page 29
1-6 model data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a fuel and oil requirement recommended fuel regular unleaded gasoline minimum fuel octane number ron 90 recommended engine oil 4-stroke motor oil engine oil grade *1, *2 api se, sf, sg, sh, sj, sl sae 5w-30, 10w-30, 10w-40 total engine oil quantity (oil pan capa...
Page 30
1-7 electrical technical data electrical technical data ignition timing control system spark plug gap 1.0–1.1 mm (0.039–0.043 in) spark plug wire resistance (#1) 4.6–10.9 k Ω at 20 °c (68 °f) resistance (#2) 3.3–8.0 k Ω at 20 °c (68 °f) resistance (#3) 3.8–9.3 k Ω at 20 °c (68 °f) resistance (#4) 4....
Page 31
1-8 electrical technical data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a shift position switch input voltage 4.75–5.25 v fuel injection control system water detection switch input voltage 4.75–5.25 v fuel injector input voltage 12 v resistance (reference data) 11.50–12.50 Ω at 20 °c (68 °f) high-pressure fuel pump in...
Page 32
1-9 electrical technical data charging system lighting coil output peak voltage (reference data) 11.0 v at cranking (unloaded) 50.0 v at 1500 r/min (unloaded) 110.0 v at 3500 r/min (unloaded) resistance (reference data) 0.2–0.3 Ω at 20 °c (68 °f) fuse 50.0 a rectifier regulator output voltage 13 v a...
Page 33
1-10 electrical technical data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a gauge/sensor water pressure sensor input voltage 4.75–5.25 v output voltage (reference data) 2.5 v at 392.0 kpa (3.92 kgf/cm 2 , 56.8 psi) 4.5 v at 784.0 kpa (7.84 kgf/cm 2 , 113.7 psi) speed sensor input voltage 4.75–5.25 v output voltage (ref...
Page 34
1-11 fuel system technical data fuel system technical data fuel system fuel pressure (reference data) 300.0 kpa (3.00 kgf/cm 2 , 43.5 psi) within 3 sec- onds after engine start switch turned to on 260.0 kpa (2.60 kgf/cm 2 , 37.7 psi) at engine idle speed fuel filter assembly fuel inlet holding press...
Page 35
1-12 power unit technical data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a power unit technical data power unit compression pressure minimum (reference data) *1 880.0 kpa (8.80 kgf/cm 2 , 127.6 psi) engine oil oil pressure *2 320.0 kpa (3.20 kgf/cm 2 , 46.4 psi) at 60 °c (140 °f) with sl 10w-30 engine oil and at 700 r...
Page 36
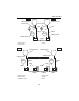
1-13 power unit technical data valve lifter outside diameter 30.970–30.980 mm (1.2193–1.2197 in) valve lifter clearance (reference data) 0.020–0.055 mm (0.0008–0.0022 in) valve spring free length 48.08 mm (1.8929 in) tilt limit 1.7 mm (0.07 in) valve stem diameter (intake) 5.477–5.492 mm (0.2156–0.2...
Page 37
1-14 power unit technical data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a piston ring (oil) dimension height (b) 2.400–2.470 mm (0.0945–0.0972 in) dimension width (t) 2.300–2.700 mm (0.0906–0.1063 in) end gap (reference data) 0.15–0.60 mm (0.0059–0.0236 in) side clearance 0.04–0.13 mm (0.0016–0.0051 in) connecting ro...
Page 38
1-15 lower unit technical data lower unit technical data lower unit assembly (regular rotation model) lower unit holding pressure 69.0 kpa (0.69 kgf/cm 2 , 10.0 psi) gear backlash forward gear backlash *1 f150aet 0.15–0.61 mm (0.0059–0.0240 in) f150bet 0.15–0.68 mm (0.0059–0.0268 in) reverse gear ba...
Page 39
1-16 bracket unit technical data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a bracket unit technical data ptt system hydraulic pressure down 5.85–8.85 mpa (58.5–88.5 kgf/cm 2 , 848.3–1283.3 psi) up 11.2–13.2 mpa (112.0–132.0 kgf/cm 2 , 1624.0–1914.0 psi) motor commutator standard diameter 22.00 mm (0.8661 in) limit 21....
Page 40
1-17 specified tightening torque specified tightening torque specified tightening torques are provided for specific nuts, bolts, and screws. When tightening these fasteners, follow the tightening torque specifications indicated throughout the manual to meet the design aims of the outboard motor. Rig...
Page 41
1-18 specified tightening torque 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a power unit part to be tightened screw size tightening torques n·m kgf·m ft·lb spark plug — 25 2.5 18.4 power unit mounting bolt m8 20 2.0 14.8 m10 42 4.2 31.0 apron screw m6 4 0.4 3.0 ptt motor lead bolt m6 4 0.4 3.0 flywheel magnet nut — 270...
Page 42
1-19 specified tightening torque lower unit (regular rotation model) lower unit (counter rotation model) bracket unit connecting rod bolt 1st m9 13 1.3 9.6 2nd 23 2.3 17.0 3rd 90° main bearing cap bolt 1st m10 30 3.0 22.1 2nd 90° crankcase bolt 1st m8 14 1.4 10.3 2nd 28 2.8 20.7 1st m10 30 3.0 22.1 ...
Page 43
1-20 specified tightening torque 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a ptt unit general tightening torque this chart indicates the tightening torques for standard fasteners with a standard iso thread pitch. Oil pan assembly bolt m8 20 2.0 14.8 m10 42 4.2 31.0 drain bolt — 28 2.8 20.7 oil strainer bolt m6 12 1.2 ...
Page 44
Technical feature and description 2 electronic control system ................................................ 2-1 engine ecm component ........................................................... 2-3 engine speed control ................................................................. 2-5 fail-safe...
Page 45
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a technical feature and description trim ram retraction when there is no load on the tilt ram and trim ram ................................................................................... 2-21 stationary condition ...............................................................
Page 46
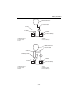
2-1 electronic control system electronic control system this model uses an electronic fuel injection control, digital ignition control, over-revving control, alert control, idle speed control, vapor shut-off valve control, which has been newly added to this model, and fail-safe control. The engine e...
Page 47
2-2 electronic control system 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Pulser coil 2. Tps 3. Air pressure sensor 4. Oil pressure sensor 5. Engine temperature sensor 6. Air temperature sensor 7. Thermoswitch 8. Shift cut-off switch 9. Shift position switch 10. Water detection switch 11. Water pressure sensor (opt...
Page 48
2-3 electronic control system engine ecm component 2 3 4 6 5 1 8 7 10 9 11 12 14 15 16 13 17.
Page 49
2-4 electronic control system 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Engine ecm determines the engine operating conditions according to the input signals from the sensors, and sends output signals to operate the actuators to perform the various control functions. 2. Pulser coil detects the engine speed. Detect...
Page 50
2-5 electronic control system engine speed control the engine ecm decreases the engine speed to protect the engine from damage and to improve the smoothness of gear shifting. Control name criteria description over- revving control when engine speed is more than a predetermined level (f150a, fl150a) ...
Page 51
2-6 electronic control system 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a fail-safe control if the electrical components malfunction, the engine ecm controls the ignition and fuel injection as shown in the table. *1. Control mode when the part malfunctions. Trouble code item trouble conditions to be detected 13 pulser...
Page 52
2-7 additional features additional features y-cop (standard for european market and optional for oceanian market) y-cop consists of a transmitter and a receiver. The receiver transmits an authorization id to the engine ecm. If an authorization id is not received or if the transmitted authorization i...
Page 53
2-8 additional features 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a tilt limiter (f150a, fl150a [optional for european and oceanian markets]) the outboard motors (with applicable serial numbers) covered by this manual can be fitted with an optional tilt limiter that allows the tilt-up action to be halted at a set angl...
Page 54
2-9 ydis ydis overview ydis version 2.00 retains the functionality of former ydis versions, while adding new functionality. The screen has been redesigned, improving ease-of-use. The can-line transmission method, which enables connection to a hub, has been added to the conventional transmission meth...
Page 55
2-10 ydis 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a new functions • by connecting the ydis using can-line, the can bus monitor function can check the names of devices connected to the digital network, the bus load, and the number of error frames. This enables checking of the connection status of the digital network....
Page 56
2-11 ydis logging in version 2.00, it is possible to configure items to be logged, and logging intervals. Configure log- ging, and disconnect the usb cable between the computer and the adapter to start logging. Because the computer is not connected during logging, the adapter can be placed within th...
Page 57
2-12 power unit system 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a power unit system shimless valve lifter newly designed valve lifters “1” have been adopted in place of the valve shims previously used “2”. The valve lifters are available in different thicknesses “a”. Therefore, the valve clearance “b” can be adjusted...
Page 58
2-13 fuel system fuel system fuel diagram 1. Fuel tank 2. Primer pump 3. Fuel filter 4. Low-pressure fuel pump 5. Filter 6. Vapor separator 7. Float chamber 8. Filter 9. High-pressure fuel pump 10. Pressure regulator 11. Fuel rail 12. Fuel injector 13. Intake manifold 14. Combustion chamber 15. Fuel...
Page 59
2-14 fuel system 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a vapor gas diagram tip: when the engine is running, air is drawn from the atmosphere to purge the vapor gas that has accu- mulated in the canister into the combustion chambers. 1. Vapor separator 2. Filter 3. Canister 4. Vapor shut-off valve 5. Intake manifol...
Page 60
2-15 lubrication system lubrication system lubrication diagram 1. Oil pan 2. Oil strainer 3. Oil pump 4. Oil filter 5. Main gallery 6. Oil pressure sensor 7. Crankshaft main journal 8. Crank pin 9. Piston 10. Sleeve 11. Balancer (f150a, fl150a) 12. Crankcase 13. Camshaft journal 14. Camshaft 15. Int...
Page 61
2-16 cooling system 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a cooling system cooling diagram 1. Water 2. Water inlet 3. Water pump 4. Oil pan 5. Exhaust guide 6. Exhaust cover 7. Cylinder block 8. Cylinder head 9. Thermostat 10. Pcv 11. Upper case (muffler) 12. Lower case 13. Propeller boss 14. Trim tab water inlet ...
Page 62
2-17 intake and exhaust system intake and exhaust system intake and exhaust diagram 1. Intake silencer 2. Throttle body 3. Intake manifold 4. Exhaust cover 5. Exhaust guide 6. Exhaust manifold 7. Muffler 8. Propeller boss a. Intake air flow b. Exhaust gas flow 4. Exhaust cover 5. Exhaust guide 6. Ex...
Page 63
2-18 lower unit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a lower unit propeller (sds) the optional shift dampener system (sds) uses a damper “1” to reduce the shock when the out- board motor is shifted into gear, and eliminates the clunk that is sometimes heard. When shifting gears, the protrusions “a” on the dedicat...
Page 64
2-19 ptt unit ptt unit trim-up and tilt-up function pushing the up button on the ptt switch causes the ptt motor “1” to activate the gear pump “2”, generating the ptt fluid pressure. The ptt fluid pressure opens the up-main valve “3” at the same time pushing the shuttle piston “4”, and this opens th...
Page 65
2-20 ptt unit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a trim-down and tilt-down function pushing the dn button on the ptt switch causes the ptt motor “1” to activate the gear pump “2”, generating the ptt fluid pressure. The ptt fluid pressure opens the down-main valve “3” at the same time pushing the shuttle piston ...
Page 66
2-21 ptt unit trim ram retraction when tilting the outboard motor up when tilting the outboard motor up, applying the tilt lock lever and pushing the dn button on the ptt switch applies fluid pressure to the tilt cylinder “1” upper chamber, in the same way as when tilting the outboard motor down. Be...
Page 67
2-22 ptt unit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a stationary condition when the ptt switch is not pushed, the gear pump assembly will not pump the ptt fluid, the up- main valve and down-main valve will remain closed, and the ptt fluid in the system will remain at a constant pressure. As a result, the tilt ram ...
Page 68
Rigging information 3 important reminder on rigging ......................................... 3-1 outboard motor mounting instructions ...................................... 3-1 crate handling ................................................................... 3-2 crate top cover pictograph descript...
Page 69
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a rigging information battery wiring with house (accessory) battery ......................... 3-25 system diagram .............................................................. 3-29 single outboard motor application (6y8 multifunction meter) ......................................
Page 70
3-1 important reminder on rigging important reminder on rigging outboard motor mounting instructions • overpowering a boat could cause severe instability. Do not install an outboard motor with more horsepower than the maximum rating on the capacity plate of the boat. If the boat does not have a capa...
Page 71
3-2 crate handling 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a crate handling crate top cover pictograph description the following pictographs are important when handling the crate. Read the notice and understand what each pictograph means to prevent damage to the outboard motor when handling, transporting, and storin...
Page 72
3-3 uncrating uncrating uncrating procedure wear gloves to avoid injury by sharp steel edges while uncrating. 1. Check the crate for shipping damage. 2. Remove the top cover. 3. Remove all of the bolts from the bottom plate, and then remove the frame. Be careful not to damage the outboard motor. 4. ...
Page 73
3-4 uncrating 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 11. Remove the steering retainer, and then install a hydraulic steering cylinder or steering cable following the recommen- dation of the manufacturer. 1.
Page 74
3-5 external dimensions external dimensions f150a, fl150a, f150b, fl150b tip: the dimension values may include reference values. *1. Minimum distance between the outboard motors in twin or triple installation *2. Transom height 660 (26.0) t1 256 (10.1) 433 (17.0) 629 (24.8) l:1032 (40.6) x:1148 (45....
Page 75
3-6 external dimensions 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a clamp bracket tip: the dimension values may include reference values. 82 (3.2) 13 (0.5) 180 (7.1) 163.5 (6.4) 254 (10.0) 55.5 (2.2) 367 (14.4) 52 (2.0) 163.5 (6.4) 125.4 (4.9) 125.4 (4.9) 102 (4.9) 102 (4.9) 180 (7.1) 13 (0.5) 50.8 (2.0) 18.5 (0.7) mm...
Page 76
3-7 outboard motor mounting outboard motor mounting installing the outboard motor proper mounting of the outboard motor pro- vides better performance, maximum reliabil- ity, and the highest customer satisfaction. This chapter contains the specifications nec- essary to mount the outboard motor, and m...
Page 77
3-8 outboard motor mounting 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a a. Single outboard motor b. Twin outboard motor 3. Install the special service tool “1”. 4. Adjust the height of the scale “2” to the transom height (h), and place it on the special service tool “1”. Secure the spe- cial service tool “1” to the bo...
Page 78
3-9 rigging grommet mounting 7. Install the mounting bolts, and then tighten the nuts firmly. Make sure that the clamp brackets do not bite into the boat transom. 8. Tighten the locknuts firmly. Rigging grommet mounting rigging grommet description 1. Main wiring harness 2. Water temperature lead (op...
Page 79
3-10 rigging grommet mounting 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 5. Install the shift cable “1” to the shift cable holder “2” and fasten it using the holder “3”. 6. Align the mark “a” on the bushing “1” with the mark “b” on the plate “2”. 7. Adjust the shift cable joint “1”, and then install the shift cable j...
Page 80
3-11 rigging grommet mounting installing the throttle cable 1. Fully screw in the throttle cable joint “1” to the throttle cable “2”. 2. Disengage the holder “1” from the throttle cable holder “2”. Tip: throttle cable position can be adjusted using the throttle cable holder “2”. 3. Install the throt...
Page 81
3-12 rigging grommet mounting 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 6. Install the clip “1”, and then tighten the throttle cable locknut “2” to the specified torque. 7. Check the throttle cable for proper opera- tion. Installing the 6y8 multifunction meter harness 1. Remove the cap “1”. 2. Connect the 6y8 multif...
Page 82
3-13 rigging grommet mounting 4. Install the gauge harness coupler “a” to the bracket “1”. Installing the main wiring harness 1. Route the main wiring harness “1” through the bracket “2”. 2. Connect the main wiring harness coupler “a”, and then secure the main wiring har- ness coupler “a” using the ...
Page 83
3-14 optional equipment 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 6. Install the rigging tube retainer “1”, and then fasten it using the plastic tie “2”. Optional equipment installing the isolator lead 1. Remove the cap “1” from the isolator coupler. 2. Connect the isolator lead coupler “a”. 3. Route the isolator le...
Page 84
3-15 optional equipment installing the speed sensor see 6y8 multifunction meter set up manual for details of the components. 1. Remove the speedometer hose “1” from the rigging grommet “2”, and then cut off the tip “a” of the nipple “3”. 2. Cut the extension hose “1” to 300.0 mm (11.8 in). 3. Instal...
Page 85
3-16 optional equipment 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 10. Remove the bracket “1” and cap “2” from the speed sensor coupler “a”. 11. Connect the speed sensor coupler “a” to the speed sensor “1”. 12. Install the rubber seal in the area “a” of the rigging grommet. Installing the tilt limiter the models with...
Page 86
3-17 optional equipment 7. Remove the junction box cover. 8. Disconnect the battery cables “1” and ptt motor leads “2”. Tip: to pass the tilt limiter lead through the hole in the grommet, remove the ptt motor lead temporarily. 9. Remove the ptt motor lead “1” from the holders “2” and “3”. 10. Remove...
Page 87
3-18 optional equipment 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 14. Route the tilt limiter lead “1” in the same manner as the trim sensor lead “2”, and then fasten them using new plastic ties “3” at the positions where original plastic ties were installed. 15. Route the tilt limiter lead “1” and ptt motor lead “2”...
Page 88
3-19 optional equipment make sure to keep the clearance of 50.8mm (2.0 in) or more between the out- board motor and the motor well. 1. Check that there is no interference between the steering system and the tilt limiter when the outboard motor is steered. 2. Connect the battery cables. 3. Decide the...
Page 89
3-20 y-cop (standard for european market and optional for oceanian market) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a deactivating the tilt limiter to fully tilt the outboard motor up, deactivate the tilt limiter according to the following pro- cedure. 1. Disconnect the tilt limiter couplers “a” and “b”. 2. Connect t...
Page 90
3-21 y-cop (standard for european market and optional for oceanian market) 4. Turn the engine start switch to off. Initial registration is complete. Y-cop is unlocked. 5. Push the lock button “1” of the transmit- ter. Check that the buzzer of the receiver will sound 1 short beep. 6. Turn the engine ...
Page 91
3-22 battery installation 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a battery installation • make sure to connect the battery properly and select the proper cable sizes. Otherwise, a fire could result. • when installing an isolator lead to the positive battery terminal or battery switch, over-cur- rent protection in c...
Page 92
3-23 battery installation 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 3. Red 4. Black 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 3. Battery switch 4. Red 5. Black 3. Red 4. Black 2. Isolator lead stbd port 1. Outboard motor 1. Outboard motor 3. Red 4. Black 4. Black on/off 3. Battery switch 4. Red 5. Black 2. Isolat...
Page 93
3-24 battery installation 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 3. Battery switch 4. Red 5. Black 1. Outboard motor 2. Battery switch 3. Navigation system 4. Boat system 5. Black 6. Red on/off on/off stbd port 3. Battery switch 5. Black 2. Isolator lead 2. Isolator lead 1. Outb...
Page 94
3-25 battery installation battery wiring with house (accessory) battery • when only one battery is used for one engine, connect the positive battery cable and isola- tor lead to the positive battery terminal. If the isolator lead is left unconnected, accidental contact of the isolator lead with the ...
Page 95
3-26 battery installation 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 3. Red 4. Black 5. House battery 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 3. Black 4. Red 5. Battery switch 6. House battery 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 5. House battery 4. Black 3. Red 4. Black 1 2 2. Isolator le...
Page 96
3-27 battery installation 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 3. Black 4. Battery switch 5. Red 6. House battery 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 3. Black 4. Battery switch 5. Red 6. House battery on/off 1 2 on/off stbd port 5. Red 4. Battery switch 1. Outboard motor 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator l...
Page 97
3-28 battery installation 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 3. Black 4. Battery switch 5. Red 6. House battery 1. Outboard motor 2. Isolator lead 3. Battery switch 4. Red 5. Black 6. House battery 1 2 1 2 stbd port 2. Isolator lead 6. House battery 5. Red 4. Battery switch ...
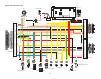
Page 98
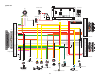
3-29 system diagram system diagram single outboard motor application (6y8 multifunction meter) g b y y y r *1 *2 b p p 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 8 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 a b c c c b 4.
Page 99
3-30 system diagram 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Engine ecm 2. Speed sensor 3. Trim sensor 4. Main wiring harness 5. Remote control box 6. Fuse (10 a) 7. Power wire 8. Pigtail bus wire 9. Single hub 10. Main bus wire 11. Hub 12. Terminal resistor 13. Tachometer unit 14. Speedometer unit 15. Receiver ...
Page 100
3-31 system diagram single outboard motor application (conventional gauge) in up out w(+) *1 gy p/b p/b pu gy p/w g/r gy pu/w pu/w g/w o/b pu pu w/r w/r g/r g/w g/r g y r r r b b w w w r p p o o b w g p p w r b b o o o b b r y l b g *1 y 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 r b g y l y l y 12.
Page 101
3-32 system diagram 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Remote control box 2. Fuel management meter unit 3. Speedometer unit 4. Tachometer unit 5. Fuel tank (fuel level sensor) 6. Fuel flow sensor 7. Gps 8. Speedometer hose 9. Gauge harness 10. Main wiring harness 11. Fuel hose 12. Lamp switch *1. When a gp...
Page 102
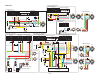
3-33 system diagram twin outboard motor application (6y8 multifunction meter) b p b p/b w l y y y b b r r r r *1 p p 4 4 3 p p 3 2 1 1 6 7 8 9 9 10 11 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 9 11 13 13 14 14 15 16 16 17 18 19 19 20 21 22 23 a b c c c b a b c c c b a b c c c b a b 5.
Page 103
3-34 system diagram 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Engine ecm 2. Speed sensor 3. Water pressure sensor 4. Trim sensor 5. Main wiring harness 6. Remote control box 7. Engine start switch (with engine shut-off switch) 8. Fuse (10 a) 9. Hub 10. Power wire 11. Terminal resistor 12. Pigtail bus wire 13. Mai...
Page 104
3-35 system diagram twin outboard motor application (conventional gauge) trip time batt km/ h knot mph km mile speed yamaha set mode fuel management yamaha set mode 1/h gph km/ l mpg ttl econ sync 1 2 3 4 5 tach x 100 r/min set mode h 1 2 3 4 5 tach x 100 r/min set mode h pu pu b b br br b b o o o y...
Page 105
3-36 system diagram 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Remote control box 2. Switch panel 3. Tachometer unit 4. Fuel management meter unit 5. Speedometer unit 6. Fuel tank (fuel level sensor) 7. Fuel flow sensor 8. Gps 9. Speedometer hose 10. Gauge harness 11. Main wiring harness 12. Fuel hose 13. Lamp swi...
Page 106
3-37 rigging recommendation rigging recommendation extension length recommendation for battery cable do not exceed the recommended extension length for the battery cable. Otherwise, the elec- trical system could be damaged or operate improperly. To extend the length of battery cables, follow the req...
Page 107
3-38 propeller selection 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a propeller selection the size and type of propeller that is used will affect the performance of a boat and outboard motor critically. Propellers greatly affect boat speed, acceleration, engine life, fuel economy, and even boating and steering capabili...
Page 108
3-39 propeller selection *1. These propellers cannot be installed using the spacer “1”. Use the spacer “2” instead. Counter rotation model 3 13 3/8 25 m stainless steel 6g5-45930-00 3 14 1/4 17 m stainless steel 68f-45972-00 3 14 1/4 18 m stainless steel 68f-45978-00 3 13 3/4 19 m stainless steel 68...
Page 109
3-40 propeller selection 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a *1. These propellers cannot be installed using the spacer “1”. Use the spacer “2” instead. 3 14 1/4 17 ml stainless steel 68g-45972-00 3 14 1/4 18 ml stainless steel 68g-45978-00 3 13 3/4 19 ml stainless steel 68g-45974-00 3 13 3/4 21 ml stainless st...
Page 110: — Memo —
3-41 propeller selection — memo —.
Page 111
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a troubleshooting 4 ydis .................................................................................... 4-1 basic components ..................................................................... 4-1 function ..................................................................
Page 112
4-1 ydis 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a ydis the yamaha diagnostic system uses precision fault diagnosis to offer better serviceability at a time when there is increasing demand for service tools for electronically controlled products. It provides quick, reliable, safe, and reasonable service, and is inte...
Page 113
4-2 ydis function ydis version 2.00 comprises the following items. Items in grey do not apply to the models covered by this manual. 10. Graph display 9. Digital display 11. Input setting 2. Engine 3. Diagnosis 6. Engine record 7. Engine operating hours by rpm 8. Engine monitor 12. Component test 15....
Page 114
4-3 ydis 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Start 2. Engine 3. Diagnosis 4. Diagnosis 5. Diagnosis record 6. Engine record 7. Engine operating hours by rpm 8. Engine monitor 9. Digital display 10. Graph display 11. Input setting 12. Component test 13. Stationary test 14. Active test 15. Data logger 16. Log...
Page 115
4-4 ydis 14. Active test while the engine is running and the shift is in the n position, operate the parts to check, and per- form tests to check operating conditions and the engine condition. 16. Logger graph displays in graph form engine operation data stored in the ecm for the last 13 minutes in ...
Page 116
4-5 ydis 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a connecting the communication cable can-line 1. Can-line harness 2. Adapter cap 3. Adapter 4. Usb cable 5. Hub k-line 1. Adapter 2. Adapter cap 3. Usb cable 4. K-line harness a. Ydis coupler (gray) 3. Adapter 4. Usb cable 5. Hub 5. Hub 2. Adapter cap 1. Can-line harn...
Page 117
4-6 outboard motor troubleshooting outboard motor troubleshooting troubleshooting procedure 1. Before troubleshooting the outboard motor, check that fresh fuel of the specified type has been used. 2. Check that all electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion, and that the battery is fu...
Page 118
4-7 outboard motor troubleshooting 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a trouble code table u : indicate —: not applicable *1. When displayed on the ydis screen, “*****” or “immobilizer” represents y-cop. Code no. Item diagnostic flash indicator ydis diagnosis ydis diagno- sis record 1 no trouble (functioning pr...
Page 119
4-8 outboard motor troubleshooting trouble code and checking step —: not applicable trouble code item (condition) symptom checking steps see page 13 pulser coil (irregular signal) “check engine” is displayed. Engine stall measure the pulser coil output peak voltage. 5-22 measure the pulser coil resi...
Page 120
4-9 outboard motor troubleshooting 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a *1. When displayed on the ydis screen, “*****” or “immobilizer” represents y-cop. 37 intake air passage (air leakage) “check engine” is displayed. Engine operates normally except at idle. Check the o-rings and gaskets of the intake manifold...
Page 121
4-10 outboard motor troubleshooting troubleshooting the power unit using the diagnostic flash indicator 1. Connect the special service tool “1”. Tip: before performing this diagnosis, make sure to connect all of the electrical wires properly. A. Diagnostic test lead (blue/white) 2. Start the engine ...
Page 122
4-11 outboard motor troubleshooting 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a troubleshooting the power unit (trouble code not detected) troubleshooting consists of the following 3 items: symptom 1: specific trouble conditions symptom 2: trouble conditions of an area or individual part cause: trouble causes of sympt...
Page 123
4-12 outboard motor troubleshooting symptom 1: unstable engine idle speed, poor acceleration, poor performance, or limited engine speed. Fuel not supplied (all cylinders) — measure the fuel pressure. 6-5 clogged filter check the fuel filter for dirt and obstruc- tions. 6-9 fuel leakage check the fue...
Page 124
4-13 outboard motor troubleshooting 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a spark plug does not pro- duce a spark (some cylinders) spark plug malfunction check the ignition spark. 5-21 check the spark plugs. 7-25 short, open, or loose connec- tion in ignition coil circuit measure the spark plug wire resistance. 5-...
Page 125
4-14 outboard motor troubleshooting symptom 1: high engine idle speed symptom 1: limited engine speed symptom 2 cause checking steps see page — air leakage (throttle valve–cyl- inder head) check the gaskets of the intake manifold and throttle body. 6-34 check the intake manifold for cracks. 6-38 thr...
Page 126
4-15 outboard motor troubleshooting 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a symptom 1: discharged battery symptom 1: y-cop lock and unlock do not function. Symptom 1: y-cop lock and unlock function, but there is no answer-back (beep). Symptom 2 cause checking steps see page — battery performance decrease check the...
Page 127
4-16 outboard motor troubleshooting troubleshooting the ptt unit troubleshooting consists of the following 3 items: symptom 1: specific trouble conditions symptom 2: trouble conditions of an area or individual part cause: trouble causes of symptom 2 — : not applicable symptom 1: ptt unit does not op...
Page 128
4-17 outboard motor troubleshooting 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a symptom 1: ptt unit does not hold the outboard motor up. Troubleshooting the lower unit troubleshooting consists of the following 3 items: symptom 1: specific trouble conditions symptom 2: trouble conditions of an area or individual part c...
Page 129: — Memo —
4-18 outboard motor troubleshooting — memo —.
Page 130
Electrical system 5 electrical component and wiring harness routing ......... 5-1 port ........................................................................................... 5-1 junction box assembly .............................................................. 5-3 rear ..........................
Page 131
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a electrical system checking the thermoswitch ..................................................... 5-25 checking the shift cut-off switch .............................................. 5-26 checking the shift position switch ........................................... 5-26 ch...
Page 132
5-1 electrical component and wiring harness routing electrical component and wiring harness routing port 1. Engine ecm 2. Starter motor 3. Thermoswitch 4. Rectifier regulator 5. Ignition coil 6. Vapor shut-off valve 7. Speed sensor coupler 8. Water pressure sensor coupler 9. Oil pressure sensor 10. ...
Page 133
5-2 electrical component and wiring harness routing 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a d. Install the ignition coil lead, water pres- sure sensor lead, vapor shut-off valve lead, and speed sensor lead to the holder. E. Install the ignition coil lead, vapor shut-off valve lead, and speed sensor lead to the hol...
Page 134
5-3 electrical component and wiring harness routing junction box assembly 1. Engine ecm 2. Ptt relay 3. Starter relay 4. Diode (connect to the ptt relay) 5. Flash indicator connector 6. Fuse (30 a) (starter relay) 7. Main relay 8. Fuse (30 a) (20 a) (spare) 9. Fuse (20 a) (engine start switch, ptt s...
Page 135
5-4 electrical component and wiring harness routing 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 14. Ydis coupler a. Route the starter motor lead and the power supply lead to the left side of the part “a”. B. Do not fasten the starter motor lead using a plastic tie. D. Fasten the wiring harness, rectifier reg- ulator l...
Page 136
5-5 electrical component and wiring harness routing rear 1. Spark plug wire 2. High-pressure fuel pump coupler 3. Fuel injector 4. Shift cut-off switch coupler 5. Shift position switch coupler a. Route the fuel injector lead behind the fuel rail. B. Fasten the spark plug wires #1 and #2 using the ho...
Page 137
5-6 electrical component and wiring harness routing 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a top 1. Air pressure sensor 2. Isc valve 3. Lighting coil (stator assembly) 4. Pulser coil 5. Engine temperature sensor 6. Tps a. F150a, fl150a b. F150b, fl150b d. Install the pulser coil coupler to the junc- tion box. E. Be...
Page 138
5-7 electrical component and wiring harness routing bottom cowling 1. Shift cut-off switch 2. Shift position switch 3. Ptt switch 4. 6y8 multifunction meter communication coupler 5. Gauge harness coupler 6. Isolator coupler 7. 6y8 multifunction meter communication lead 8. Trim meter lead 9. Isolator...
Page 139
5-8 electrical component and wiring harness routing 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a a. Regular rotation model b. Counter rotation model d. Route the wiring harness along the groove in the bottom cowling. E. Install the ptt motor lead and isolator lead to the holder. F. Align the white paint mark on the flu...
Page 140
5-9 ecm circuit ecm circuit circuit diagram tip: the circled numbers in the illustration indicate the engine ecm terminal numbers. 21. Engine ecm 14 15 10 34 33 12 8 35 7 9 4 37 36 5 31 40 39 41 17 22 44 24 28 27 3 2 43 1 23 30 p bz 32 42 26 13 20 18 21 19 16 t 1. Pulser coil #1 2. Pulser coil #2 29...
Page 141
5-10 ecm circuit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 1. Pulser coil #1 2. Pulser coil #2 3. Tps 4. Air pressure sensor 5. Oil pressure sensor 6. Water pressure sensor 7. Speed sensor 8. Ground 9. Engine temperature sensor 10. Air temperature sensor 11. Shift cut-off switch 12. Engine shut-off switch 13. Thermo...
Page 142
5-11 ecm circuit ecm coupler layout 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10111213141516171819202122 23242526272829303132333435363738394041424344 no. Connecting part color 1 6y8 multifunction meter white 2 tachometer green 3 alert buzzer pink 4 engine shut-off switch white 5 water detection switch blue/white 6 vaper sh...
Page 143
5-12 checking the electrical component 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a checking the electrical component using the ydis when checking the tps, isc valve, high- pressure fuel pump, fuel injector, or each sensor, use the ydis. Tip: • when deleting the diagnosis record in the ydis, make sure to check the time...
Page 144
5-13 engine control unit and component using the digital tester the electrical technical data applies to the measurements taken using the yamaha rec- ommended tester. The resistance values shown are the values taken before the engine is started. The actual resistance may vary depending on the envi- ...
Page 145
5-14 engine control unit and component 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 5. Turn the engine start switch to off, and then install the main relay. Checking the engine ecm circuit 1. Disconnect the engine ecm coupler “a”. 2. Check for continuity between the engine ecm coupler terminals and ground. 3. Measure t...
Page 146
5-15 engine control unit and component 5. Turn the engine start switch to off. 6. Connect the engine ecm coupler. Checking the tps 1. Connect the ydis to display “tps”. 2. Start the engine and warm it up for 5–10 minutes, and then stop it. 3. Turn the engine start switch to on, and then measure the ...
Page 147
5-16 fuel control unit and component 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 5. Turn the engine start switch to off. 6. Connect the isc valve coupler. Checking the oil pressure sensor 1. Disconnect the oil pressure sensor cou- pler “a”. 2. Turn the engine start switch to on, and then measure the input voltage at t...
Page 148
5-17 fuel control unit and component 3. Turn the engine start switch to off, and then remove the fuel cup assembly. 4. Check that the float “1” moves smoothly. 5. Check the water detection switch for con- tinuity when the float “1” is in positions “a” and “b”. Do not remove the clip and float. 6. In...
Page 149
5-18 fuel control unit and component 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 6. Connect the fuel injector couplers. Checking the high-pressure fuel pump 1. Check the operation of the high-pressure fuel pump using the ydis “stationary test” and check the operating sound. 2. Disconnect the high-pressure fuel pump co...
Page 150
5-19 charging unit and component 5. Check that the vapor shut-off valve opens and the negative pressure is released when the battery leads are connected to the vapor shut-off valve terminals. Connect the battery leads to the vapor shut-off valve terminals for only a few sec- onds. 6. Remove the spec...
Page 151
5-20 charging unit and component 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Connect the special service tool “1”, and then measure the rectifier regulator output voltage. Tip: do not use peak voltage adapter b when measuring the rectifier regulator output volt- age. 3. Disconnect the special service tool “1” and l...
Page 152
5-21 ignition unit and component ol: indicates overload 5. Connect the rectifier regulator coupler and lighting coil coupler. Ignition unit and component checking the ignition spark 1. Disconnect the spark plug wire from the spark plug. 2. Connect the spark plug wire to the spe- cial service tool “1...
Page 153
5-22 ignition unit and component 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Turn the engine start switch to on, and then measure the input voltage at the ignition coil coupler terminal and ground. 3. Turn the engine start switch to off. 4. Connect the ignition coil coupler “a”. 5. Connect the special service tool ...
Page 154
5-23 ignition unit and component 3. Measure the pulser coil output peak volt- age. Tip: • when measuring the pulser coil output peak voltage under the cranking (unloaded) condition, disconnect the coupler “a” to pre- vent the engine from starting. • when measuring the pulser coil output peak voltage...
Page 155
5-24 ignition unit and component 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 9. Install the air temperature sensor, and then connect the air temperature sensor coupler. Checking the air pressure sensor 1. Disconnect the air pressure sensor cou- pler “a”. 2. Turn the engine start switch to on, and then measure the inpu...
Page 156
5-25 ignition unit and component 3. Turn the engine start switch to off. 4. Remove the engine temperature sensor. 5. Place the engine temperature sensor in a container of water and heat the water slowly. 6. Measure the engine temperature sensor resistance. 7. Install the engine temperature sensor. S...
Page 157
5-26 ignition unit and component 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a c. No continuity d. Continuity 7. Install the thermoswitch. 8. Connect the thermoswitch connectors. Checking the shift cut-off switch 1. Disconnect the shift cut-off switch cou- pler “a”. 2. Turn the engine start switch to on, and then measur...
Page 158
5-27 starting unit and component 6. Install the shift position switch. See “shift rod and shift bracket” (9-1). 7. Connect the shift position switch coupler. Checking the engine shut-off switch 1. Disconnect the 10-pin coupler or engine start switch coupler. 2. Turn the engine start switch to on, an...
Page 159
5-28 starting unit and component 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 4. Install the starter relay, and then connect the starter relay leads. Checking the engine start switch 1. Disconnect the 10-pin coupler or engine start switch coupler. 2. Check the engine start switch for continu- ity. 1. Off 2. On 3. Start...
Page 160
5-29 y-cop (standard for european market and optional for oceanian market) y-cop (standard for european market and optional for oceanian market) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 cover 1 2 control unit assembly 1 3 transmitter 2 4 screw 2 m6 15 mm 5 buzzer 1 6 bracket 1 7 screw 1 ø6 19 mm 8 main wiring h...
Page 161
5-30 y-cop (standard for european market and optional for oceanian market) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a checking y-cop 1. Disconnect the y-cop coupler “a”, and then measure the y-cop input voltage. 2. Connect the y-cop coupler. Checking the buzzer 1. Remove the y-cop buzzer “1”. 2. Connect the battery l...
Page 162
5-31 y-cop (standard for european market and optional for oceanian market) 2. Check the wiring harness for continuity. 3. Install the y-cop main wiring harness “1”, o-ring “2”, and control unit “3”, and then tighten the control unit screws “4” to the specified torque. Do not connect the connectors “...
Page 163
5-32 y-cop (standard for european market and optional for oceanian market) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 3. Measure the button cell battery voltage. Tip: when disposing of button cell battery, make sure to follow local disposal regulations. 4. Install the button cell battery “1” so that the positive side...
Page 164
5-33 starter motor starter motor no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 brush spring 4 2 brush assembly 1 3 brush holder assembly 1 4 starting motor gear assembly 1 5 washer set 1 6 bracket 1 7 bolt 2 m6 117 mm 8 screw 2 m4 16 mm 9 planetary gear 3 10 plate 1 11 stator 1 12 armature 1 13 clutch assembly 1 14 ...
Page 165
5-34 starter motor 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 pinion shaft 1 19 pinion 1 20 pinion stopper set 1 21 bolt 2 m6 37 mm 22 cover 1 23 lever assembly 1 24 seal set 1 not reusable 25 magnet switch 1 26 washer 1 27 nut 1 17 18 12 7 8 6 5 14 3 1 1 1 1 2 9 9 10 11 14 25 26 27 24 2...
Page 166
5-35 starter motor removing the starter motor before removing the starter motor, make sure to disconnect the negative battery terminal. 1. Remove the starter motor from the power unit. See “removing the starter motor” (7-21). Checking the starter motor pinion 1. Check the pinion teeth. Replace the p...
Page 167
5-36 starter motor 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 7. Remove the e-clip “1”, and then remove the clutch assembly “2”. Tip: push the clutch assembly “2” down com- pletely onto the pinion shaft “3” in direction “a”, turn it one spline in direction “b”, and then remove it in direction “c”. 8. Remove the shim ...
Page 168
5-37 starter motor checking the armature (starter motor) 1. Check the commutator. Clean using 600-grit sandpaper and compressed air if dirty. 2. Measure the commutator diameter “a”. Replace the armature if below specifica- tion. 3. Measure the commutator undercut “a”. 4. Check the armature for conti...
Page 169
5-38 starter motor 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Measure the length “a” of each brush. Replace the brush assembly if below specification. Assembling the starter motor do not apply grease or oil to the commu- tator of the armature. 1. Push the brushes “1” into the holders, and then install the armature...
Page 170
5-39 starter motor tip: make sure that the clutch assembly “1” does not come out from the pinion shaft “2”. 7. Install the pinion shaft assembly “1”, the lever “2”, a new rubber seal “3”, the plan- etary gears “4”, the outer gear “5”, and the plate “6”. 8. Align the protrusion “a” on the stator “1” ...
Page 171
5-40 6y8 multifunction meter sensor 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 6y8 multifunction meter sensor checking the water pressure sensor (optional) 1. Disconnect the water pressure sensor coupler “a”. 2. Turn the engine start switch to on, and then measure the input voltage at the water pressure sensor couple...
Page 172
5-41 ptt system 5. Turn the engine start switch to off, and then disconnect the special service tool and pressure pump. 6. Install the speed sensor, and then con- nect the speed sensor coupler. See “installing the speed sensor” (3-15). Ptt system checking the ptt relay 1. Remove the junction box cov...
Page 173
5-42 ptt system 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 7. Connect the positive battery lead to the terminal “a”, and the negative battery lead to the terminal “b”, and then check the ptt relay for continuity. Replace the ptt relay if out of specification. 8. Connect the ptt relay coupler, battery power source, gr...
Page 174
5-43 ptt system 2. Measure the trim sensor resistance. 3. Turn the trim sensor lever “1” from the position “a” to the position “b”, and then measure the resistance as it gradually changes. 4. Connect the trim sensor coupler. Checking the tilt limiter (optional) 1. Disconnect the tilt limiter coupler...
Page 175: — Memo —
5-44 ptt system 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a — memo —.
Page 176
Fuel system 6 hose routing ...................................................................... 6-1 fuel hose ................................................................................... 6-1 air hose, pressure regulator hose, and vapor gas hose ............ 6-2 blowby hose and cooling water...
Page 177
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a fuel system installing the throttle link .......................................................... 6-23 throttle body ................................................................... 6-25 removing the throttle body assembly ..................................... 6-26 chec...
Page 178
6-1 hose routing hose routing fuel hose 1. Fuel hose (primer pump to joint) 2. Fuel hose (joint to fuel filter assembly) 3. Fuel hose (fuel filter assembly to joint) 4. Fuel hose (joint to fuel pump) 5. Fuel hose (joint to fuel pump) 6. Fuel hose (fuel pump to joint) 7. Fuel hose (fuel pump to joint...
Page 179
6-2 hose routing 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a air hose, pressure regulator hose, and vapor gas hose 1. Vapor gas hose (vapor separator to joint) 2. Vapor gas hose (vapor separator to joint) 3. Vapor gas hose (joint to filter) 4. Vapor gas hose (filter to canister tank port) 5. Vapor gas hose (canister p...
Page 180
6-3 hose routing f. Joint g. Joint h. Filter k. Joint m. Pressure regulator a b 3 6 a 8 c 4 7 f m d 5 a c 7 1 g 8 2 12 b 3 k c b 10 m 4 5 d 9 h 6 e 11 7 3 3 b 1 2.
Page 181
6-4 hose routing 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a blowby hose and cooling water hose 1. Blowby hose (cylinder head cover to intake silencer) 2. Blowby hose (cylinder head cover to cyl- inder block) 3. Cooling water hose (exhaust cover to fuel cooler) 4. Cooling water pilot hose (fuel cooler to cooling water...
Page 182
6-5 fuel line fuel line reducing the fuel pressure before servicing the high-pressure fuel line or vapor separator, make sure to reduce the fuel pressure in the fuel line. Otherwise, pressurized fuel could spray out. 1. Remove the cap “1”. 2. Cover the pressure check valve “a” of the fuel rail using...
Page 183
6-6 fuel line 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 3. Disconnect the pressure regulator hose “1”, and then connect the special service tool “2” to the pressure regulator “3”. 4. Block the end of the pressure regulator hose “1” using a rubber plug “4”. 5. Start the engine and let it idle. 6. Check that the fuel ...
Page 184
6-7 fuel filter fuel filter no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 joint 2 2 plastic tie 5 3 hose 1 joint to joint 4 hose 1 joint to fuel filter assembly 5 bolt 2 m6 × 30 mm 6 bolt 2 m6 × 14 mm 7 collar 2 8 grommet 2 9 bracket 1 10 hose 1 fuel filter assembly to joint 11 fuel filter assembly 1 12 o-ring 1 not...
Page 185
6-8 fuel filter 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the fuel filter assembly cover the fuel components using a rag to prevent fuel from spilling out. 1. Disconnect the fuel hoses “1” and “2”. 2. Disconnect the water detection switch coupler “a”. 3. Remove the fuel filter assembly “1”. 4. Remove the br...
Page 186
6-9 fuel filter disassembling the fuel filter assembly 1. Remove the fuel cup assembly “1”, o- ring “2”, and fuel filter element “3”. Checking the fuel filter element 1. Check the fuel filter element. Replace if there is dirt or residue. Checking the fuel cup assembly 1. Check the fuel cup assembly....
Page 187
6-10 fuel filter 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a installing the fuel filter assembly 1. Install the bracket “1”. 2. Install the fuel filter assembly “2”. 3. Route the fuel hose “1” through the bot- tom cowling. 4. Route the fuel hose “2” through the proper holes in the rigging grommet. See “rigging grommet...
Page 188
6-11 fuel pump fuel pump no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 screw 6 m6 × 35 mm 2 cover 2 3 fuel pump body 2 2 4 diaphragm 2 5 spring 2 6 fuel pump body 1 2 7 nut 6 8 spring 2 9 plunger 2 10 pin 2 11 fuel pump assembly 2 12 hose 1 fuel pump to joint 13 joint 2 14 plastic tie 10 15 hose 1 fuel pump to joint...
Page 189
6-12 fuel pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 o-ring 2 not reusable 19 hose 1 joint to fuel pump 20 hose 1 joint to fuel pump 10 n·m (1.0 kgf·m, 7.4 ft·lb) 10 n·m (1.0 kgf·m, 7.4 ft·lb) 1 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 5 4 n·m (0.4 kgf·m, 3.0 ft·lb) 4 n·m (0.4 kgf·m, 3.0 ft·lb) 6 7 7 8 9 ...
Page 190
6-13 fuel pump removing the fuel pump assembly cover the fuel components using a rag to prevent fuel from spilling out. 1. Disconnect the fuel hoses “1”, “2”, “3”, “4”, and “5”. 2. Remove the fuel pump assemblies “1”. Checking the fuel pump assembly 1. Connect the special service tool “1” to the fue...
Page 191
6-14 fuel pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a disassembling the fuel pump assembly 1. Remove the cover “1”, diaphragm “2”, and fuel pump body 2 “3”. 2. Hold fuel pump body 1 “1”. 3. While holding fuel pump body 1 “1” in place, insert a flathead screwdriver into the hole “a” in the plunger “2” and turn it ...
Page 192
6-15 fuel pump 2. Hold fuel pump body 1 “1”. 3. Align the hole “a” in the plunger “1” with the hole “b” in the diaphragm “2”. 4. Install the pin “1”. 5. While holding fuel pump body 1 “1” in place, insert a flathead screwdriver into the hole “a” in the plunger “2” and turn it 90° until the tab “b” o...
Page 193
6-16 fuel pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Connect the fuel hoses “1”, “2”, “3”, “4”, and “5”, and then fasten them using the plastic ties “6”. Fuel pump bolt “3”: 10 n·m (1.0 kgf·m, 7.4 ft·lb) 2 3 3 3 1 1 2 1 6 3 5 4 6 6 6.
Page 194
6-17 canister and vapor shut-off valve canister and vapor shut-off valve no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 nut 1 2 hose 1 filter to joint 3 plastic tie 8 4 joint 1 5 hose 1 joint to bottom cowling 6 clamp 1 7 filter 1 8 vapor shut-off valve 1 9 hose 1 canister to filter 10 canister 1 11 bolt 1 m6 × 16 mm...
Page 195
6-18 canister and vapor shut-off valve 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the canister 1. Disconnect the vapor gas hoses “1” and “2”. 2. Remove the spark plug wires from the holders. 3. Remove the vapor gas hose “3” from the holders “4”. 4. Disconnect the vapor gas hoses “1” and “2”. 5. Remove the br...
Page 196
6-19 canister and vapor shut-off valve 4. Apply the specified positive pressure and check that there is no air leakage. Replace the canister if there is air leak- age. Checking the vapor shut-off valve 1. Check the vapor shut-off valve exterior. Replace if cracked. 2. Check the electrical performanc...
Page 197
6-20 canister and vapor shut-off valve 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Connect the vapor gas hoses “3” and “4”, and then fasten them using the plastic ties “5”. 3. Install the vaper gas hose “4” to the holder “6”. 4. Connect the vapor gas hoses “1”, “2”, and “3”, and then fasten them using the plastic t...
Page 198
6-21 intake silencer intake silencer no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 intake silencer assembly 1 2 o-ring 4 not reusable 3 collar 6 4 collar 2 5 grommet 4 6 bolt 6 m6 × 20 mm 7 clamp 1 8 bolt 2 m6 × 45 mm 1 2 2 3 4 5 7 8 2 3 3 8 5 4 5 5 6 6 6 3 3 6 6 6 6 n·m (0.6 kgf·m, 4.4 ft·lb) 6 n·m (0.6 kgf·m, 4.4 ...
Page 199
6-22 throttle link 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a throttle link no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 bolt 1 m6 × 35 mm 2 collar 1 3 wave washer 3 4 throttle cam 1 5 roller 1 6 bolt 2 m6 × 25 mm 7 collar 2 8 throttle lever 1 1 9 washer 3 10 spring 1 11 throttle link rod 1 12 throttle lever 2 1 1 2 3 3 3 4 5 6 6 7 ...
Page 200
6-23 throttle link removing the throttle link 1. Remove the clip “1” and throttle cable joint “2”. 2. Remove the throttle link rod “1” from the throttle cam “2”. 3. Remove the collar “1”, wave washer “2”, throttle cam “3”, spring “4”, and washer “5”. 4. Remove the collar “1”, wave washer “2”, thrott...
Page 201
6-24 throttle link 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Install throttle lever 1 “5” to cylinder block. 3. Install the spring “1” so that the spring end “a” fits into the groove “b” in the throt- tle cam “2”, and then install the washer “3”, wave washer “4”, and collar “5”. 4. Hook the end “a” of the spring ...
Page 202
6-25 throttle body throttle body no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 throttle link joint 1 1 2 nut 1 3 throttle link joint 2 1 4 bracket 2 5 bolt 4 m6 × 16 mm 6 bolt 2 m8 × 20 mm 7 bolt 6 m8 × 70 mm 8 throttle body assembly 1 9 screw 2 m4 × 12 mm 10 tps 1 11 o-ring 1 not reusable 12 synchronizing screw 1 1...
Page 203
6-26 throttle body 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the throttle body assembly 1. Disconnect the tps coupler “a”. 2. Remove the brackets “1”. 3. Remove the throttle body assembly “1”. Checking the tps 1. Check the tps exterior. Replace if cracked. 2. Check the electrical performance of the tps. See...
Page 204
6-27 throttle body and throttle link adjustment throttle body and throttle link adjustment adjusting the throttle link 1. Turn throttle lever 2 “1” until it contacts the stopper “a” of the cylinder block. 2. Adjust the specified clearance “b” so that the mark “c” on the throttle cam “2” and the roll...
Page 205
6-28 throttle body and throttle link adjustment 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 4. Loosen the tps screws “1” and adjust the position of the tps “2” to get the specified output voltage. Tip: • to increase the output voltage, turn the tps “2” in direction “a”. • to decrease the output voltage, turn the tps “...
Page 206
6-29 throttle body and throttle link adjustment tip: • to increase the output voltage, turn the tps “2” in direction “a”. • to decrease the output voltage, turn the tps “2” in direction “b”. 14. Tighten the tps screws. 15. Start the engine and move the shift lever from the n position to the f positi...
Page 207
6-30 fuel injector 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a fuel injector no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 holder 1 2 cap 1 3 bolt 2 m8 × 18 mm 4 fuel rail 1 5 clamp 3 6 o-ring set 1 not reusable 7 fuel injector 4 8 rubber seal 4 not reusable 9 bolt 2 m6 × 25 mm 10 fuel cooler 1 11 clamp 1 1 2 3 3 4 5 6 7 7 7 7 8 8 8 8...
Page 208
6-31 fuel injector removing the fuel injector cover the fuel components using a rag to prevent fuel from spilling out. 1. Reduce the fuel pressure. See “reducing the fuel pressure” (6-4). 2. Disconnect the fuel injector couplers “a” and fuel pump coupler “b”. 3. Remove the holder “1”. 4. Disconnect ...
Page 209
6-32 fuel injector 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 4. Remove the fuel cooler “1”. Checking the fuel rail and fuel injector 1. Check the fuel rail. Replace if cracked or deformed. 2. Check the electric performance of the fuel injector see “checking the fuel injec- tor” (5-17). 3. Measure the volume injected...
Page 210
6-33 fuel injector installing the fuel injector 1. Install a new o-ring “1” and a new rubber seal “2” to the fuel injector “3”. 2. Install the fuel injectors “1” onto the fuel rail “2”. 3. Install the fuel rail “1” onto the intake manifold. 4. Tighten the fuel rail bolts “2” equally and gradually to...
Page 211
6-34 intake manifold and vapor separator 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a intake manifold and vapor separator no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 dowel 2 2 gasket 4 not reusable 3 hose with filter 1 hose to joint 4 holder 1 5 plastic tie 2 6 hose 1 joint to joint 7 joint 2 8 hose 1 vapor separator to fuel rail 9 h...
Page 212
6-35 intake manifold and vapor separator no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 filter 1 19 hose 1 filter to vapor separator 20 wiring harness 1 21 screw 2 m5 × 15 mm 22 air pressure sensor 1 23 filter 1 24 cap 1 25 o-ring 1 not reusable 26 screw 3 m4 × 15 mm 27 isc valve 1 28 grommet 3 29 collar 6 30 bolt 3...
Page 213
6-36 intake manifold and vapor separator 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 35 intake manifold 1 36 hose 1 fuel cooler to vapor separator 37 hose 1 pressure regulator to fuel cooler 3 4 5 34 11 11 37 20 6 9 8 7 10 11 7 13 12 14 15 36 32 33 33 32 32 30 35 23 24 25 31 22 21 26 27 17 2...
Page 214
6-37 intake manifold and vapor separator draining the fuel 1. Loosen the vapor separator drain screw “1”, and then remove the cap “2”. 2. Push the air valve “3” inward. 3. Tighten the vapor separator drain screw to the specified torque. Removing the intake manifold 1. Disconnect the isc valve couple...
Page 215
6-38 intake manifold and vapor separator 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 6. Remove the drain hose “1” and fuel hose “2”. 7. Disconnect the fuel hoses “1”, “2”, and “3”, and remove the fuel filter “4”. 8. Remove the fuel hose “1” and pressure regulator hose “2”. 9. Disconnect the fuel pump coupler “a”. 10. ...
Page 216
6-39 intake manifold and vapor separator installing the vapor separator 1. Connect the vapor gas hoses “1” and “2” and vapor gas hose with filter “3” to the joint “4”. 2. Connect the vapor gas hoses “1” and “2” to the vapor separator. 3. Connect the fuel pump coupler “a”. 4. Connect the fuel hose “1...
Page 217
6-40 intake manifold and vapor separator 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 13. Route the fuel hose “2” through the gap “c” in the intake manifold. 14. Fit the fuel hose “1” into the groove “a” in the intake manifold. 15. Fit the vapor gas hose with filter “2” into the groove “b” in the intake manifold. 16. C...
Page 218
6-41 intake manifold and vapor separator 5. Connect the isc valve coupler “a” and air pressure sensor coupler “b”. 6. Install the holder “1” to the intake mani- fold. 2 1 a b 1 1.
Page 219
6-42 vapor separator and high-pressure fuel pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a vapor separator and high-pressure fuel pump no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 screw 2 m6 × 12 mm 2 pressure regulator 1 3 screw 7 m4 × 16 mm 4 cover assembly 1 5 gasket 1 not reusable 6 pin 1 7 cap 1 8 grommet 1 9 plate 1 10 plate ...
Page 220
6-43 vapor separator and high-pressure fuel pump disassembling the vapor separator 1. Remove the pressure regulator “1”. 2. Remove the cover “1”, gasket “2”, and fil- ter holder “3”. 3. Disconnect the lead coupler “a”, and then remove the high-pressure fuel pump “1”, filter “2”, and grommet “3”. 4. ...
Page 221
6-44 vapor separator and high-pressure fuel pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Check the float. Replace if deteriorated. 3. Check the filter. Clean if there is dirt or residue. 4. Place the cover assembly upside down, and then measure the float height “a”. Tip: when measuring the float height, the flo...
Page 222
6-45 vapor separator and high-pressure fuel pump 9. Install a new gasket “1”, the filter holder “2”, and the cover “3”, and then tighten the float chamber cover screws “4” to the specified torque. 10. Install the pressure regulator “1”, and then tighten the pressure regulator screw “2” to the specif...
Page 223
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a power unit 7 power unit (check and adjustment) ................................. 7-1 checking the compression pressure ......................................... 7-1 checking the oil pressure .......................................................... 7-1 checking the valve cl...
Page 224
Power unit camshaft .......................................................................... 7-33 removing the driven sprocket and camshaft .......................... 7-35 checking the driven sprocket .................................................. 7-35 checking the camshaft ......................
Page 225
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a power unit removing the oil filter bracket ................................................. 7-60 removing the crankcase cover ............................................... 7-60 disassembling the oil pump .................................................... 7-60 checking t...
Page 226
7-1 power unit (check and adjustment) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a power unit (check and adjustment) checking the compression pressure 1. Start the engine, warm it up for 5 min- utes, and then stop it. 2. Remove the clip from the engine shut-off switch. 3. Disconnect the spark plug wires. 4. Remove all ...
Page 227
7-2 power unit (check and adjustment) 4. Remove the canister. See “removing the canister” (6-18). 5. Disconnect the spark plug wires “1”, and then remove the blowby hoses “2” and “3”, all of the spark plugs, and cylinder head cover “4”. 6. Turn the flywheel magnet clockwise to align the “tdc” mark “...
Page 228
7-3 power unit (check and adjustment) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 10. Measure the intake and exhaust valve clearances of the specified cylinders. Adjust if out of specification. See “adjust- ing the valve clearance” (7-3). —: not applicable ✔: specified cylinder 11. Install a new gasket “1” and the cyl...
Page 229
7-4 power unit (check and adjustment) 4. Remove the driven sprockets, camshaft caps, and camshafts. See “removing the driven sprocket and camshaft” (7-35). 5. Remove the valve lifters. See step 1 in “removing the cylinder head” (7-40). 6. Measure the valve lifter thickness “a”, and then write down t...
Page 230
7-5 power unit assembly 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a power unit assembly no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 grommet 3 2 cover 1 3 cover 1 4 apron 1 5 nut 2 6 screw 2 m6 × 40 mm 7 bolt 3 m8 × 35 mm 8 bolt 8 m10 × 140 mm 9 bolt 4 m10 × 35 mm 10 bolt 4 m6 × 16 mm 11 rigging grommet 1 12 plastic tie 1 13 retainin...
Page 231
7-6 power unit assembly no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 dipstick guide 1 19 bolt 1 m6 × 16 mm 20 dipstick 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 10 10 10 11 12 13 14 15 15 16 17 18 19 20 8 8 4 n·m (0.4 kgf·m, 3.0 ft·lb) 42 n·m (4.2 kgf·m, 31.0 ft·lb) 42 n·m (4.2 kgf·m, 31.0 ft·lb) 20 n·m (2.0 kgf·m, 14.8 ft·lb).
Page 232
7-7 power unit assembly 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the power unit 1. Remove the clip “1” and throttle cable “2”. 2. Disconnect the battery cables “1”. 3. Remove the junction box cover “2”. 4. Disconnect the ptt motor leads “1”. 5. Disconnect the 10-pin coupler “a”. 6. Disconnect the fuel hose...
Page 233
7-8 power unit assembly 10. Remove the 6y8 multifunction meter har- ness coupler “a” and gauge harness cou- pler “b” from the bracket “1”. 11. Disconnect the 6y8 multifunction meter harness coupler “a” or gauge coupler “b”. A. 6y8 multifunction meter b. Conventional gauge 12. Disconnect the shift cu...
Page 234
7-9 power unit assembly 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 16. Install the lifting harnesses to the engine hangers “1”. 17. Suspend the power unit. 18. Remove the power unit mounting bolts “2”, “3”, and “4”, and then remove the power unit. Installing the power unit 1. Clean the power unit mating surface, and ...
Page 235
7-10 power unit assembly 5. Connect the cooling water pilot hose “1”. 6. Connect the shift cut-off switch coupler “a” and shift position switch coupler “b”. 7. Connect the 6y8 multifunction meter har- ness coupler “a” or gauge coupler “b”. A. 6y8 multifunction meter b. Conventional gauge harness 8. ...
Page 236
7-11 power unit assembly 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 11. Connect the vapor gas hose “1”, and then fasten it using the clamp “2”. 12. Connect the fuel hose “1”, and then fas- ten it using the plastic tie “2”. 13. Connect the 10-pin coupler “a”. 14. Connect the ptt motor leads “1”, and then tighten the p...
Page 237
7-12 flywheel magnet flywheel magnet no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 nut 1 width across flats: 36 mm 2 washer 1 apply oil on both sides of the washer. 3 base assembly 1 4 screw 4 m6 × 30 mm 5 stator assembly 1 6 pulser coil 1 7 holder 1 8 bracket 2 9 bolt 4 m6 × 35 mm 10 holder 1 11 dowel 2 12 flywheel...
Page 238
7-13 flywheel magnet 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the flywheel magnet 1. Loosen the flywheel magnet nut. Apply force in the direction of the arrow to prevent the flywheel holder “1” from slip- ping off easily. A. Conventional special service tool b. New special service tool 2. Remove the flywhe...
Page 239
7-14 flywheel magnet 3. Remove the holders “1” and “2” and blowby hose “3”. 4. Remove the wiring harness “1” from the holders “2”. 5. Remove the stator assembly “1” and pulser coil “2”. Installing the stator assembly 1. Install the dowels “1”, pulser coil “2”, and stator assembly “3”. 2. Install the...
Page 240
7-15 flywheel magnet 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 5. Connect the pulser coil coupler “a”, and then install the pulser coil coupler “a” to the bracket “1”. Installing the flywheel magnet 1. Install the woodruff key “1”, and then install the flywheel magnet “2” and fly- wheel magnet nut “3”. Tip: make sur...
Page 241
7-16 timing belt timing belt no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 timing belt 1 2 timing belt tensioner 1 3 plate 1 4 dowel 1 5 screw 1 m6 × 10 mm 6 plate 1 7 drive sprocket 1 8 bolt 4 m5 × 40 mm 7 n·m (0.7 kgf·m, 5.2 ft·lb) 39 n·m (3.9 kgf·m, 28.8 ft·lb) 1 2 8 7 6 5 3 4.
Page 242
7-17 timing belt 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the timing belt when the timing belt is not installed, do not turn the crankshaft or driven sprocket. Otherwise, the pistons and valves could collide with each other and be damaged. 1. Turn the crankshaft clockwise to align the mark “a” in the drive...
Page 243
7-18 timing belt installing the timing belt when the timing belt is not installed, do not turn the crankshaft or driven sprocket. Otherwise, the pistons and valves could collide with each other and be damaged. 1. Check that the mark “a” in the drive sprocket and the protrusion “b” on the cylinder bl...
Page 244
7-19 timing belt 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 5. Turn the crankshaft clockwise 2 full turns, and then check that the mark “a” in the drive sprocket and the protrusion “b” on the cylinder block are aligned. Also, check that the “i” marks “c” and “d” on the driven sprockets are aligned. A b d c.
Page 245
7-20 starter motor starter motor no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 cap 1 2 nut 1 3 terminal 1 4 starter motor 1 5 bolt 3 m8 × 45 mm 6 cap 1 7 bolt 1 m6 × 10 mm 8 battery cable 1 9 bolt 1 m8 × 16 mm 10 spring washer 1 11 nut 1 7 10 9 5 4 9 n·m (0.9 kgf·m, 6.6 ft·lb) 3 2 1 6 9 n·m (0.9 kgf·m, 6.6 ft·lb) 8 ...
Page 246
7-21 starter motor 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the starter motor 1. Remove the cap “1” and terminal “2”, and then disconnect the positive lead “3”. 2. Remove the starter motor lead “1” from the holder “2”. 3. Disconnect the starter motor lead “1”. 4. Remove the starter motor “1”. Installing th...
Page 247
7-22 starter motor terminal nut “3”: 9 n·m (0.9 kgf·m, 6.6 ft·lb).
Page 248
7-23 rectifier regulator and ignition coil 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a rectifier regulator and ignition coil no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 rectifier regulator 1 2 gasket 1 not reusable 3 bolt 6 m6 × 30 mm 4 bolt 1 m6 × 16 mm 5 spark plug wire #1 1 6 spark plug wire #2 1 7 spark plug wire #3 1 8 spark pl...
Page 249
7-24 rectifier regulator and ignition coil no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 hose 1 exhaust cover to fuel cooler 19 spark plug 4 18 19 9 13 9 19 19 11 10 12 12 17 10 11 17 14 15 15 16 16 14 3 3 3 1 2 4 8 7 6 5 7 n·m (0.7 kgf·m, 5.2 ft·lb) 25 n·m (2.5 kgf·m, 18.4 ft·lb).
Page 250
7-25 rectifier regulator and ignition coil 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the rectifier regulator 1. Disconnect the rectifier regulator cou- pler “a”, and then remove the ground lead “1”. 2. Remove the rectifier regulator “1”. Removing the ignition coil 1. Remove the spark plug wires “1”, “2”, “3...
Page 251
7-26 rectifier regulator and ignition coil installing the ignition coil 1. Install the ignition coils “1”, and then tighten the ignition coil bolts “2” to the specified torque. 2. Install the wiring harness “3” to the hold- ers “4”, and then connect the ignition coil couplers “a”. 3. Install the spa...
Page 252
7-27 fuse box 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a fuse box no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 fuse box assembly 1 2 fuse 2 50 a 3 screw 4 m5 × 10 mm 4 fuse 2 20 a 5 relay 1 6 fuse 1 30 a 7 screw 3 m5 × 20 mm 8 cover 1 9 gasket 1 10 fuse puller 1 11 fuse 1 20 a, spare 12 fuse 1 30 a, spare 10 1 9 8 7 6 4 11 5 3 3 2 2...
Page 253
7-28 wiring harness wiring harness no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 wiring harness 1 2 cover 1 3 screw 3 ø6 × 19 mm 4 wiring harness 1 5 bolt 4 m6 × 16 mm 6 plastic tie 2 7 bolt 2 m6 × 20 mm 8 bolt 2 m6 × 10 mm 9 ptt relay 1 10 cap 1 11 bolt 1 m6 × 10 mm 12 screw 1 ø6 × 19 mm 13 bracket 1 14 starter rel...
Page 254
7-29 wiring harness 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 grommet 3 19 collar 3 20 grommet 1 21 junction box 1 22 bolt 1 m6 × 16 mm 23 screw 1 ø6 × 19 mm 24 holder 1 25 screw 1 ø6 × 19 mm 26 bracket 1 27 grommet 1 28 air temperature sensor 1 4 n·m (0.4 kgf·m, 3.0 ft·lb) 4 n·m (0.4 k...
Page 255
7-30 wiring harness removing the wiring harness 1. Disconnect the thermoswitch connectors “a”. 2. Remove the bracket “1”. 3. Disconnect the oil pressure sensor cou- pler “a”. 4. Remove the ground leads “1”. 5. Disconnect the engine temperature sen- sor coupler “a”. 6. Remove the 10-pin wiring harnes...
Page 256
7-31 wiring harness 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 12. Disconnect the air temperature sensor coupler “c”, and then remove the ydis coupler “d”. 13. Remove the holder “5” and plastic ties “6” and “7”. Installing the wiring harness see “electrical component and wiring har- ness routing” (5-1). 1. Install th...
Page 257
7-32 wiring harness 7. Install the joint connectors “a”. 8. Install the 10-pin wiring harness coupler “b” to the holder “1”. 9. Connect the engine temperature sensor coupler “a”. 10. Install the ground leads “1”. 11. Connect the oil pressure sensor coupler “a”. 12. Install the bracket “1”. 13. Conne...
Page 258
7-33 camshaft 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a camshaft no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 bolt 2 m6 × 42 mm 2 bracket 1 3 grommet 3 4 collar 3 5 bolt 13 m6 × 30 mm 6 holder 2 7 bracket 2 8 grommet 5 9 cylinder head cover 1 10 screw 8 m4 × 8 mm 11 plate 1 12 clamp 2 13 hose 1 cylinder head cover to cylinder block...
Page 259
7-34 camshaft no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 camshaft 1 ex 19 oil seal 2 not reusable 20 dowel 2 21 camshaft 1 in 22 driven sprocket 2 23 bolt 2 m10 × 35 mm 24 dowel 4 25 gasket 1 not reusable 11 9 8 10 5 5 7 5 25 23 23 22 24 22 19 19 20 20 17 16 15 14 18 21 12 12 13 8 8 8 4 4 3 3 2 1 3 24 24 6 7 6 6...
Page 260
7-35 camshaft 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the driven sprocket and camshaft when the timing belt is not installed, do not turn the crankshaft or driven sprock- ets. Otherwise, the pistons and valves could collide with each other and be dam- aged. 1. Remove the cylinder head cover. 2. Secure the...
Page 261
7-36 camshaft installing the driven sprocket and camshaft when the timing belt is not installed, do not turn the crankshaft or driven sprock- ets. Otherwise, the pistons and valves could collide with each other and be dam- aged. 1. Install new oil seals “1” and the dowels “2” onto the camshafts “3” ...
Page 262
7-37 camshaft 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 5. Tighten the camshaft cap bolts “1” and “2” gradually to the specified torques in 2 stages and in the order [1], [2], and so on. 6. Install the driven sprockets “1”. 7. Secure the camshaft using a wrench, and then tighten the driven sprocket bolts “2” to the ...
Page 263
7-38 cylinder head cylinder head no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 valve lifter 16 2 valve cotter 32 3 valve spring retainer 16 4 valve spring 16 5 valve spring seat 16 6 valve seal 16 not reusable 7 valve guide 16 not reusable 8 intake valve 8 9 exhaust valve 8 10 anode assembly 2 11 bolt 2 m8 × 40 mm 1...
Page 264
7-39 cylinder head 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 bolt 10 m8 × 55 mm 19 plug 1 20 gasket 1 not reusable 21 cylinder head 1 22 gasket 1 not reusable 23 screw 3 m6 × 16 mm 24 anode 1 25 dowel 2 26 anode 1 27 anode 1 5 6 a b c 28 n·m (2.8 kgf·m, 20.7 ft·lb) 56 n·m (5.6 kgf·m, 41...
Page 265
7-40 cylinder head removing the cylinder head 1. Remove the valve lifters “1”. Tip: make sure to keep the parts in the order of removal. 2. Remove the cylinder head “1”. Do not scratch or damage the mating sur- faces of the cylinder head and cylinder block. Disassembling the cylinder head 1. Remove ...
Page 266
7-41 cylinder head 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a checking the cylinder head 1. Remove carbon deposits from the com- bustion chambers, and then check the cylinder head for damage and scratches. 2. Check the cylinder head warpage using a straightedge “1” and a thickness gauge “2” in 7 directions. Replace t...
Page 267
7-42 cylinder head 4. Measure the valve stem runout. Checking the valve guide before checking the valve guides, make sure that the valve stem diameter is within specifi- cation. 1. Measure the valve guide inside diameter “a”. 2. Calculate the valve guide clearance. Replacing the valve guide after re...
Page 268
7-43 cylinder head 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a tip: • to ream the valve guide, turn the valve guide reamer clockwise. • when removing the valve guide reamer, do not turn it counterclockwise. • after reaming the valve guide, make sure to clean it. 4. Measure the valve guide inside diameter. Checking the...
Page 269
7-44 cylinder head 2. Cut the surface of the valve seat using a 45° cutter by turning the cutter clockwise until the valve seat face has become smooth. Do not overcut the valve seat. To prevent chatter marks, make sure to turn the cut- ter evenly using a downward force of 40–50 n (4.0–5.0 kgf, 8.8–1...
Page 270
7-45 cylinder head 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a example: • if the valve seat contact area is too wide and situated in the center of the valve face, cut the top edge of the valve seat using a 30° cutter. Cut the bottom edge using a 60° cutter to center the area and set its width. A. Previous contact widt...
Page 271
7-46 cylinder head 2. Install the valve “1”, valve spring seat “2”, valve spring “3”, and valve spring retainer “4” in this order, and then install the spe- cial service tools “5” and “6”. 3. Compress the valve spring, and then install the valve cotters “1”. 4. Tap the valve spring retainer lightly ...
Page 272
7-47 cylinder head 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 4. Tighten the cylinder head bolts “2” to the specified torques in 2 stages and in the order [11], [12], and so on. 5. Install the valve lifters “1”. Cylinder head bolt “1” [1]–[10] (m10): 1st: 28 n·m (2.8 kgf·m, 20.7 ft·lb) 2nd: 56 n·m (5.6 kgf·m, 41.3 ft...
Page 273
7-48 exhaust cover exhaust cover no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 bolt 1 m6 × 16 mm 2 holder 1 3 thermoswitch 1 4 bolt 3 m6 × 30 mm 5 cover 1 6 gasket 1 not reusable 7 thermostat 1 8 gasket 1 not reusable 9 anode assembly 1 10 bolt 1 m6 × 20 mm 11 gasket 1 not reusable 12 cover 1 13 grommet 1 14 anode 1...
Page 274
7-49 exhaust cover 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 spring 1 19 pcv 1 20 grommet 1 21 gasket 1 not reusable 22 bolt 19 m6 × 30 mm 23 bracket 1 24 plug 1 m18 × 17 mm 25 gasket 1 not reusable 26 bolt 1 m6 × 12 mm 27 holder 1 28 plug 1 m14 × 12 mm 29 gasket 1 not reusable 30 exhau...
Page 275
7-50 exhaust cover removing the exhaust cover 1. Remove the thermoswitch “1”, thermo- stat “2”, and pcv “3”. 2. Remove the exhaust cover “1”. Checking the pcv 1. Check the pcv “1”. Replace if damaged or worn. 2. Check the grommet “2”. Replace if deformed. 3. Check the spring “3”. Replace if deformed...
Page 276
7-51 exhaust cover 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a do not apply grease, oil, or paint to the anodes. Installing the exhaust cover 1. Install a new gasket “1” and the exhaust cover “2”, and then tighten the exhaust cover bolts “3” to the specified torques in 2 stages and in the order [1], [2], and so on. 2....
Page 277
7-52 cylinder block (f150a, fl150a) cylinder block (f150a, fl150a) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 bolt 10 m8 × 55 mm 2 bolt 2 m6 × 40 mm 3 balancer assembly 1 4 seal 2 not reusable 5 bracket 1 6 engine hanger 1 7 bolt 5 m6 × 20 mm 8 bolt 2 m6 × 45 mm 9 oil filler neck 1 10 gasket 1 not reusable 11 o-r...
Page 278
7-53 cylinder block (f150a, fl150a) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 plug 1 m14 × 12 mm 19 engine hanger 1 20 oil pressure sensor 1 21 o-ring 1 not reusable 22 oil filter 1 23 union bolt 1 24 o-ring 2 not reusable 25 relief valve 1 26 oil filter bracket 1 27 bolt 4 m6 × 40 mm 2...
Page 279
7-54 cylinder block (f150a, fl150a) removing the oil pump assembly 1. Remove the oil pump assembly “1”. Removing the oil filter bracket 1. Remove the oil filter “1”. 2. Remove the oil filter bracket “1”. Removing the balancer assembly 1. Remove the balancer assembly “1”. Disassembling the oil pump 1...
Page 280
7-55 cylinder block (f150a, fl150a) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Install a new oil seal “1” into the oil pump housing “2”. 3. Install the outer rotor “1”, the inner rotor “2”, a new gasket “3”, and the oil pump cover “4”, and then tighten the oil pump cover screws “5” to the specified torque. 4. Inst...
Page 281
7-56 cylinder block (f150a, fl150a) 2. Apply a thin, even layer of sealant onto the mating surface of the balancer assembly. 3. Align the marks “a” on the balancer shafts with the marks “b”. 4. Install the balancer assembly “1”, and then tighten the balancer assembly bolts “2” and “3” to the specifi...
Page 282
7-57 cylinder block (f150a, fl150a) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a oil filter wrench “2”: 90890-06830 oil filter “1”: 18 n·m (1.8 kgf·m, 13.3 ft·lb) 1 2 1.
Page 283
7-58 cylinder block (f150b, fl150b) cylinder block (f150b, fl150b) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 bolt 10 m8 × 35 mm 2 bolt 2 m6 × 25 mm 3 crankcase cover 1 4 bracket 1 5 engine hanger 1 6 bolt 5 m6 × 20 mm 7 bolt 2 m6 × 45 mm 8 oil filler neck 1 9 gasket 1 not reusable 10 o-ring 1 not reusable 11 oil...
Page 284
7-59 cylinder block (f150b, fl150b) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 engine hanger 1 19 oil pressure sensor 1 20 o-ring 1 not reusable 21 oil filter 1 22 joint 1 23 o-ring 2 not reusable 24 relief valve 1 25 oil filter bracket 1 26 bolt 4 m6 × 40 mm 27 bolt 4 m6 × 40 mm 28 oil ...
Page 285
7-60 cylinder block (f150b, fl150b) removing the oil pump assembly see “removing the oil pump assembly” (7- 54). Removing the oil filter bracket see “removing the oil filter bracket” (7-54). Removing the crankcase cover 1. Remove the crankcase cover “1”. Disassembling the oil pump see “disassembling...
Page 286
7-61 crankcase 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a crankcase no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 crankcase 1 2 bolt 10 m10 × 85 mm 3 bolt 10 m8 × 55 mm 4 main bearing cap 1 5 dowel 10 6 crankshaft journal bearing 5 7 oil seal 1 not reusable 8 crankshaft 1 9 crankshaft journal bearing 4 10 thrust bearing 1 11 o-ring 1...
Page 287
7-62 crankcase no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 piston pin 4 19 piston 4 20 piston ring set 4 2 2 3 1 5 4 12 7 9 10 6 8 11 6 6 6 6 9 13 16 15 20 14 14 16 17 18 17 19 a b c 13 n·m (1.3 kgf·m, 9.6 ft·lb) 23 n·m (2.3 kgf·m, 17.0 ft·lb) 90 ° a b 30 n·m (3.0 kgf·m, 22.1 ft·lb) 90 q a b 14 n·m (1.4 kgf·m, 10...
Page 288
7-63 crankcase 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a disassembling the cylinder block 1. Remove the crankcase “1”. 2. Remove the main bearing cap “1”. 3. Remove the connecting rod bolts “1” and connecting rod caps “2”, and then remove the piston and connecting rod assemblies “3”. Tip: • to prevent mixing the pis...
Page 289
7-64 crankcase 6. Remove the clips “1” and piston pin “2”, and then remove the connecting rod “3”. Tip: make sure to keep the parts in the order of removal. Checking the piston diameter 1. Measure the piston outside diameter “a” at the specified measuring point “b”. Checking the cylinder bore 1. Mea...
Page 290
7-65 crankcase 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a checking the piston ring end gap 1. Level the piston ring “1” in the cylinder using a piston crown at the specified measuring point “a”. 2. Measure the piston ring end gap “b”. Checking the piston ring groove 1. Measure the piston ring grooves. Checking the pi...
Page 291
7-66 crankcase checking the piston pin diameter 1. Measure the piston pin diameter “a”. Checking the connecting rod small end inside diameter and big end inside diameter 1. Tighten the connecting rod bolts “1” to the specified torques in 3 stages. Tip: • when checking the oil clearance, reuse the re...
Page 292
7-67 crankcase 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Measure the crankshaft runout. Checking the big end oil clearance 1. Clean the crankpin bearings, connecting rod, connecting rod cap, and crankpin. 2. Install the crankpin bearings “1” into the connecting rod “2” and connecting rod cap “3”. Tip: install the...
Page 293
7-68 crankcase tip: in the third tightening stage for the connect- ing rod bolts “1”, mark the connecting rod bolts and the connecting rod cap with identifi- cation marks “a”, and then tighten the bolts 90° from the marks on the connecting rod cap. 6. Remove the connecting rod cap, and then measure ...
Page 294
7-69 crankcase 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a example: if the connecting rod big end inside diameter is “35” and the crankpin mark is “81”, select the bearing colors in “d”. The upper bearing color is blue and the lower bearing color is red. Upper bearing color lower bearing color “a” green green “b” gree...
Page 295
7-70 crankcase crankpin bearing selection table a. Connecting rod big end inside diameter b. Crankpin mark 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 a b a b c d e.
Page 296
7-71 crankcase 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a checking the journal oil clearance 1. Clean the crankshaft journal bearings, crankshaft journals, and bearing portions of the crankcase and cylinder block. 2. Place the cylinder block upside down. 3. Install the crankshaft journal bearings “1” and crankshaft “...
Page 297
7-72 crankcase 7. Install the crankcase “1”, and then tighten the crankcase bolts “2” and “3” to the specified torques in 2 stages and in the order [1], [2], and so on. Tip: • do not turn the crankshaft until the journal oil clearance measurement has been com- pleted. • in the second tightening stag...
Page 298
7-73 crankcase 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Select the suitable colors “1” for the crankshaft journal bearing from the “crankshaft journal bearing selection table”. Example: if the crankshaft journal mark is “81” and the cylinder block mark is “30”, select the bearing colors in “e”. J1/j2/ j4/j5 uppe...
Page 299
7-74 crankcase crankshaft journal bearing selection table a. Cylinder block mark b. Crankshaft journal mark 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 a a b b c d e f.
Page 300
7-75 crankcase 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a assembling the cylinder block 1. Install a new collar “1” by striking it using a plastic hammer. 2. Assemble the piston “1”, the connecting rod “2”, the piston pin “3”, and new clips “4”. Tip: • face the mark “a” on the connecting rod “2” in the same direction...
Page 301
7-76 crankcase 7. Install the crankshaft journal bearings “1” and thrust bearing “2” into the cylinder block “3”. Tip: • install the crankshaft journal bearings “1” in the original positions. • install the thrust bearing “2” at the position “a”. 8. Install new oil seal “1” onto the crankshaft “2”, a...
Page 302
7-77 crankcase 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 10. Install the crankshaft journal bearings “1” into the main bearing cap. 11. Install the main bearing cap “1”, and then tighten the main bearing cap bolts “2” to the specified torques in 2 stages and in the order [1], [2], and so on. Tip: in the second tight...
Page 303
7-78 crankcase tip: in the second tightening stage for the m10 bolts “3”, mark the m10 bolts and the crank- case with identification marks “a”, and then tighten the bolts 90° from the marks on the crankcase. Crankcase bolts “3” [1]–[4] (m10): 1st: 30 n·m (3.0 kgf·m, 22.1 ft·lb) 2nd: 90° crankcase bo...
Page 304
Lower unit 8 lower unit (regular rotation model, l-transom model) ..................... 8-1 removing the lower unit ............................................................ 8-3 disassembling the propeller (sds propeller) ............................ 8-3 checking the propeller ......................
Page 305
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a lower unit checking the lower case ......................................................... 8-23 assembling the forward gear ................................................... 8-23 assembling the drive shaft housing ......................................... 8-23 assembling...
Page 306
Lower unit water pump and shift rod (counter rotation model) .... 8-51 removing the water pump and shift rod .................................. 8-53 disassembling the water pump housing .................................. 8-53 checking the water pump and shift rod ................................... ...
Page 307
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a lower unit shimming check sheet ............................................................ 8-67 measuring the forward gear backlash and reverse gear backlash before disassembly ............................. 8-69 shimming procedure .............................................
Page 308
8-1 lower unit (regular rotation model, l-transom model) lower unit (regular rotation model, l-transom model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 hose nipple 1 2 o-ring 1 not reusable 3 check screw 1 4 gasket 2 not reusable 5 dowel 2 6 grommet 1 7 bolt 1 m10 × 45 mm 8 lower unit 1 9 spacer 1 10 propeller 1...
Page 309
8-2 lower unit (regular rotation model, l-transom model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 bolt 1 m10 × 70 mm 19 drain screw 1 20 bolt 6 m10 × 45 mm 17 9 8 12 11 13 14 10 5 5 3 4 20 20 7 6 19 4 18 2 1 15 16 43 n·m (4.3 kgf·m, 31.7 ft·lb) 48 n·m (4.8 kgf·m, 35.4 ft·lb) 48 n·m (4....
Page 310
8-3 lower unit (regular rotation model, l-transom model) removing the lower unit • make sure to disconnect the battery cables from the battery, and remove the clip from the engine shut-off switch. • when removing the lower unit with the power unit installed, make sure to sus- pend the outboard motor...
Page 311
8-4 lower unit (regular rotation model, l-transom model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a do not apply grease, oil, or paint to the trim tab. Assembling the propeller (sds propeller) 1. Place a new damper “1” in the propeller “2”. Tip: align the mark “a” on the damper “1” with the mark “b” on the propeller ...
Page 312
8-5 lower unit (regular rotation model, l-transom model) a. Before tightening the propeller nut “3” to the specified torque. B. After tightening the propeller nut “3” to the specified torque. Installation depth “a” (reference data): 9.4 mm (0.37 in) a b 1 1 2 2 3 3.
Page 313
8-6 lower unit (regular rotation model, x-transom model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a lower unit (regular rotation model, x-transom model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 hose nipple 2 2 o-ring 2 not reusable 3 check screw 1 4 gasket 2 not reusable 5 bolt 12 m10 × 45 mm 6 extension 1 7 dowel 4 8 cover 2 9 ...
Page 314
8-7 lower unit (regular rotation model, x-transom model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 washer 1 19 cotter pin 1 not reusable 20 propeller nut 1 21 spacer 1 sds propeller 22 damper 1 sds propeller 23 trim tab 1 24 bolt 1 m10 × 200 mm 25 drain screw 1 23 15 14 18 17 19 20 16 7 7 3 4 5 5 13 12 7 10 11 ...
Page 315
8-8 lower unit (regular rotation model, x-transom model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the lower unit • make sure to disconnect the battery cables from the battery, and remove the clip from the engine shut-off switch. • when removing the lower unit with the power unit installed, make sure to sus...
Page 316
8-9 water pump and shift rod (regular rotation model) water pump and shift rod (regular rotation model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 shift rod 1 2 e-clip 1 3 o-ring 1 not reusable 4 plate 1 5 bolt 3 m6 × 20 mm 6 oil seal 1 not reusable 7 collar 1 8 spacer 1 9 washer 2 10 wave washer 1 11 impeller 1 ...
Page 317
8-10 water pump and shift rod (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 o-ring 1 not reusable 19 insert cartridge 1 20 o-ring 1 not reusable 21 water pump housing 1 22 bolt 4 m8 × 45 mm 23 seal 1 24 cover 1 2 15 14 15 3 4 5 5 6 5 7 8 9 10 9 11 22 22 22 12 13 16 ...
Page 318
8-11 water pump and shift rod (regular rotation model) removing the water pump and shift rod 1. Remove the water pump housing “1”, o-ring “2”, dowels “3”, collar “4”, spacer “5”, washers “6”, wave washer “7”, and impeller “8”. 2. Remove the woodruff key “9”, outer plate cartridge “10”, and gasket “1...
Page 319
8-12 water pump and shift rod (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a tip: if the engine overheats, the inside of the water pump housing may be deformed. Therefore, make sure to remove the insert cartridge when checking the water pump housing. 2. Check the impeller, insert cartridge, and o...
Page 320
8-13 propeller shaft housing (regular rotation model) propeller shaft housing (regular rotation model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 slider 1 2 ball 2 5.54 mm (0.22 in) (reference data) 3 ball 2 4.74 mm (0.19 in) (reference data) 4 ball 2 8.72 mm (0.34 in) (reference data) 5 spring 1 6 dog clutch 1 f...
Page 321
8-14 propeller shaft housing (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 key 1 19 needle bearing 1 not reusable 20 oil seal 2 not reusable 21 claw washer 1 22 ring nut 1 1 2 2 3 5 3 4 6 8 9 10 11 13 14 15 16 17 20 21 22 1 2 2 5 4 3 8 10 3 9 4 18 12 19 7 145 n·m (1...
Page 322
8-15 propeller shaft housing (regular rotation model) removing the propeller shaft housing assembly 1. Straighten the bent tab “1” on the claw washer. 2. Loosen the ring nut. 3. Remove the ring nut “1” and claw washer “2”. 4. Remove the propeller shaft housing assembly and key. 5. Remove the washer ...
Page 323
8-16 propeller shaft housing (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a disassembling the propeller shaft housing assembly 1. Remove the reverse gear “1” and thrust washer “2”. 2. Remove the ball bearing “1”. 3. Remove the oil seals “1” along with the needle bearing “2”. Checking the propelle...
Page 324
8-17 propeller shaft housing (regular rotation model) assembling the propeller shaft assembly 1. Install the spring “1”, balls “2”, “3”, and “4”, and slider “5”. Tip: when installing the slider “5”, make sure that the balls do not fall out of position. 2. Install the dog clutch “1” so that the hole ...
Page 325
8-18 propeller shaft housing (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a tip: install an oil seal halfway into the propeller shaft housing, and then install the other oil seal. 3. Install the thrust washer “1” and a new ball bearing “2” onto the reverse gear “3”. Tip: face the bearing identifi...
Page 326
8-19 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 thrust bearing 1 2 pinion shim (t3) — 3 o-ring 1 not reusable 4 needle bearing 1 not reusable 5 drive shaft housing 1 6 bolt 4 m8 × 25 mm 7 oil seal 2 not reusabl...
Page 327
8-20 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 water inlet cover (port) 1 19 screw 1 m5 × 45 mm 20 needle bearing 1 not reusable 21 pinion 1 22 pinion nut 1 9 10 18 19 1 n·m (0.1 kgf·m, 0.7 ft·lb) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 6 12 95 n·m (9.5 kgf·m...
Page 328
8-21 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) removing the drive shaft 1. Remove the cover “1”, drive shaft hous- ing “2”, pinion shims “3”, and thrust bear- ing “4”. 2. Loosen the pinion nut, and then remove the pinion “1”, drive shaft “2”, and sleeve. 3. Remove the forward gear assembly...
Page 329
8-22 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Remove the needle bearings from the forward gear. Disassembling the lower case • use heat-resistant gloves. Otherwise, burns could result. • to prevent fires, remove any flammable substances, such as gasoline and oi...
Page 330
8-23 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) checking the lower case 1. Check the lower case. Replace if cracked or damaged. Assembling the forward gear 1. Install new needle bearings “1” and “2” at the specified installation depth “a” and “b”. Tip: • face the bearing identification mark...
Page 331
8-24 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 3. Install a new o-ring “1”. Assembling the lower case • use heat-resistant gloves. Otherwise, burns could result. • to prevent fires, remove any flammable substances, such as gasoline and oil, around the working area....
Page 332
8-25 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) 4. Install a new needle bearing “1” in the lower case. Tip: • make sure to face the bearing identification mark “a” on the needle bearing toward the pinion. • the needle bearing contains 18 rollers. 5. Install the water inlet covers “1” and “2...
Page 333
8-26 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 5. Tighten the pinion nut “1” to the specified torque. 6. Check that the drive shaft turns smoothly. Installing the propeller shaft housing assembly 1. Install the washer “1” and propeller shaft housing assembly “2”. 2...
Page 334
8-27 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) 5. Bend one of the 4 tabs on the claw washer outward, and then bend the other 3 tabs inward. Installing the shift rod 1. Install a new o-ring “1” and a new oil seal “2” to the plate “3”. 2. Install the e-clip “1” and plate “2” to the shift rod...
Page 335
8-28 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 4. Align the slot “a” in the impeller “2” with the woodruff key “1”, and then install the impeller “2”. 5. Install the washers “1”, wave washer “2”, spacer “3”, and collar “4”. Tip: the spacer “3” and collar “4” should...
Page 336
8-29 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) installing the lower unit (l-transom model) • make sure to disconnect the battery cables from the battery, and remove the clip from the engine shut-off switch. • when installing the lower unit with the power unit installed, make sure to sus- p...
Page 337
8-30 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 9. Place a block of wood between the anti- cavitation plate and the propeller to pre- vent the propeller from turning, and then tighten the propeller nut to the specified torque. 10. Install a new cotter pin “1”. Tip: ...
Page 338
8-31 drive shaft and lower case (regular rotation model) 7. Install the trim tab and propeller. See steps 6–9 in “installing the lower unit (l- transom model)” (8-29). 8. Fill the lower unit with gear oil up to the proper level. See steps 5–9 in “changing the gear oil” (10-11). Lower case mounting b...
Page 339
8-32 shimming (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a shimming (regular rotation model) shimming workflow 1. Remove the water pump assembly. 2. Measure the backlash before disassem- bly. 3. Within specification? 4. Yes 5. Shimming is not required. 6. No 7. Disassemble the lower unit. 8. Se...
Page 340
8-33 shimming (regular rotation model) shimming check sheet lower case deviation pinion height (mm) forward gear backlash (mm) reverse gear backlash (mm) serial number p f r remarks measurements measuring point #1 measuring point #2 measuring point #3 measuring point #4 average round-down average (m...
Page 341
8-34 shimming (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a forward gear shim (t1) thickness adjustment in 2 places (mm) reverse gear shim (t2) thickness adjustment in 2 places (mm) number of shim(s) subtotal 0.10 0.12 0.15 0.18 0.30 0.40 0.50 total number of shim(s) subtotal 0.10 0.12 0.15 0.18...
Page 342
8-35 shimming (regular rotation model) measuring the forward gear backlash and reverse gear backlash before disassembly 1. Install the lower unit onto a repair stand. 2. Remove the water pump assembly. 3. Set the gear shift to the n position. 4. Set up the special service tools “1”, “2”, and “3”, an...
Page 343
8-36 shimming (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a tip: • after installing the handle holder, pull the drive shaft upward to remove any free play. • do not press the spring more than 5.0 mm (0.197 in). Otherwise, too much torque will be required to turn the drive shaft, making it diffic...
Page 344
8-37 shimming (regular rotation model) 14. Determine the backlash average, and then round down the average to 2 decimal places. Example: 15. Check that the forward gear backlash average is within specification. Tip: adjust the shim thicknesses if the forward gear backlash is out of specification. 16...
Page 345
8-38 shimming (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a shimming procedure • before selecting the forward gear shim (t1) and reverse gear shims (t2), make sure to select the pinion shims (t3). • when assembling the lower unit to measure the backlash after selecting the pinion shims (t3), do ...
Page 346
8-39 shimming (regular rotation model) selecting the pinion shim (t3) • spray anti-rust lubricant on the bearing before installation. Do not apply gear oil to the parts. Otherwise, correct measure- ments cannot be obtained. • keep the parts free of foreign material, such as dirt and lint. Be careful...
Page 347
8-40 shimming (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 5. Install the special service tool “1” to the drive shaft spline and hold the special service tool “1”. 6. Tighten the pinion nut “2” to the specified torque. 7. Hold the special service tool “1” so that the pinion is facing up. 8. Tur...
Page 348
8-41 shimming (regular rotation model) example: 11. Determine the pinion shim (t3) thickness adjustment using the “pinion shim (t3) selection table” according to the rounded average (m) and the deviation (p) stamped on the lower case. See “pinion shim (t3) selection table” (a-12). Tip: the (p) mark ...
Page 349
8-42 shimming (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Measure the thickness of original forward gear shim (t1) in 2 places. Tip: do not reuse a shim if deformed or scratched. 3. Determine the forward gear shim (t1) thickness adjustment using the “forward gear shim (t1) selection chart” ...
Page 350
8-43 shimming (regular rotation model) 5. Install the determined forward gear shims (t1) and taper roller bearing outer race. Measuring the reverse gear backlash • spray anti-rust lubricant on the gears and bearings before installation. Do not apply gear oil to the parts. Otherwise, correct measurem...
Page 351
8-44 shimming (regular rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a a. Backlash measurement (bl2) b. Shim thickness adjustment 4. Calculate the new reverse gear shim (t2) thickness. Tip: • use the lowest number of shims to obtain the required shim thickness. • if the calculated shim thickness cannot be ...
Page 352
8-45 lower unit (counter rotation model, l-transom model) lower unit (counter rotation model, l-transom model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 hose nipple 1 2 o-ring 1 not reusable 3 check screw 1 4 gasket 2 not reusable 5 dowel 2 6 grommet 1 7 bolt 1 m10 × 45 mm 8 lower unit 1 9 spacer 1 10 propeller ...
Page 353
8-46 lower unit (counter rotation model, l-transom model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 bolt 1 m10 × 70 mm 19 drain screw 1 20 bolt 6 m10 × 45 mm 12 11 13 14 55 n·m (5.5 kgf·m, 40.6 ft·lb) 17 9 8 10 5 5 3 4 20 20 7 6 19 4 18 2 1 15 16 43 n·m (4.3 kgf·m, 31.7 ft·lb) 48 n·m (4...
Page 354
8-47 lower unit (counter rotation model, l-transom model) removing the lower unit 1. Drain the gear oil. 2. Remove the propeller, trim tab, and lower unit. See steps 2–7 in “removing the lower unit” (8-3). Tip: when disassembling the lower unit, measure the backlash before disassembly. See “mea- sur...
Page 355
8-48 lower unit (counter rotation model, x-transom model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a lower unit (counter rotation model, x-transom model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 hose nipple 2 2 o-ring 2 not reusable 3 check screw 1 4 gasket 2 not reusable 5 bolt 12 m10 × 45 mm 6 extension 1 7 dowel 4 8 cover 2 9...
Page 356
8-49 lower unit (counter rotation model, x-transom model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 washer 1 19 cotter pin 1 not reusable 20 propeller nut 1 21 spacer 1 sds propeller 22 damper 1 sds propeller 23 trim tab 1 24 bolt 1 m10 × 200 mm 25 drain screw 1 16 23 15 14 18 17 19 20 7 7 3 4 5 5 13 12 7 10 11...
Page 357
8-50 lower unit (counter rotation model, x-transom model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the lower unit 1. Drain the gear oil. 2. Remove the propeller and trim tab. See steps 2–6 in “removing the lower unit” (8-3). 3. Remove the lower unit and extension. See step 3 in “removing the lower unit” (8...
Page 358
8-51 water pump and shift rod (counter rotation model) water pump and shift rod (counter rotation model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 shift rod 1 2 e-clip 1 3 o-ring 1 not reusable 4 plate 1 5 bolt 3 m6 × 20 mm 6 oil seal 1 not reusable 7 collar 1 8 spacer 1 9 washer 2 10 wave washer 1 11 impeller 1...
Page 359
8-52 water pump and shift rod (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 o-ring 1 not reusable 19 insert cartridge 1 20 o-ring 1 not reusable 21 water pump housing 1 22 bolt 4 m8 × 45 mm 23 seal 1 24 cover 1 2 15 14 15 3 4 5 5 6 5 7 8 9 10 9 11 22 22 22 12 13 16 ...
Page 360
8-53 water pump and shift rod (counter rotation model) removing the water pump and shift rod 1. Remove the water pump. See steps 1–4 in “removing the water pump and shift rod” (8-11). 2. Remove the shift rod “1”. Disassembling the water pump housing see “disassembling the water pump hous- ing” (8-11...
Page 361
8-54 propeller shaft housing (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a propeller shaft housing (counter rotation model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 slider 1 2 ball 2 5.54 mm (0.22 in) (reference data) 3 ball 2 4.74 mm (0.19 in) (reference data) 4 ball 2 8.72 mm (0.34 in) (reference data) 5 ...
Page 362
8-55 propeller shaft housing (counter rotation model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 propeller shaft housing 1 19 key 1 20 needle bearing 1 not reusable 21 oil seal 2 not reusable 22 claw washer 1 23 ring nut 1 9 15 11 12 13 14 18 16 17 21 22 23 1 2 2 5 4 3 8 15 3 9 19 10 20 1 2 2 3 5 3 4 6 8 7 145 n...
Page 363
8-56 propeller shaft housing (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the propeller shaft housing assembly 1. Remove the ring nut and claw washer. See steps 1–3 in “removing the propel- ler shaft housing assembly” (8-15). 2. Remove the propeller shaft housing assembly, key, and for...
Page 364
8-57 propeller shaft housing (counter rotation model) checking the propeller shaft 1. Check the propeller shaft. Replace if damaged or worn. 2. Measure the propeller shaft runout. Checking the dog clutch see “checking the dog clutch” (8-16). Checking the propeller shaft housing see “checking the pro...
Page 365
8-58 propeller shaft housing (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a when heating the propeller shaft housing, heat the entire installation area evenly. Otherwise, the propeller shaft housing could be damaged. 5. While holding the special service tool “1”, strike the tool to check that the...
Page 366
8-59 propeller shaft housing (counter rotation model) 9. Install the cross pin “1”, and then install the spring “2”. 10. Install a new o-ring “1”. 1 1 a a b b c 2 d 1 2 1 2 1.
Page 367
8-60 drive shaft and lower case (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a drive shaft and lower case (counter rotation model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 thrust bearing 1 2 pinion shim (t3) — 3 o-ring 1 not reusable 4 needle bearing 1 not reusable 5 drive shaft housing 1 6 bolt 4 m8 × 25 mm...
Page 368
8-61 drive shaft and lower case (counter rotation model) no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 reverse gear 1 19 water inlet cover (port) 1 20 screw 1 m5 × 45 mm 21 needle bearing 1 not reusable 22 pinion 1 23 pinion nut 1 14 16 15 9 10 19 20 1 n·m (0.1 kgf·m, 0.7 ft·lb) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 6 12 11 13 18 21 22 ...
Page 369
8-62 drive shaft and lower case (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the drive shaft see steps 1 and 2 in “removing the drive shaft” (8-21). Removing the reverse gear 1. Remove the reverse gear “1” and thrust bearing “2”. Disassembling the drive shaft housing see “disassembling...
Page 370
8-63 drive shaft and lower case (counter rotation model) 3. Remove the needle bearing. See step 3 in “disassembling the lower case” (8-22). Checking the pinion see “checking the pinion” (8-22). Checking the reverse gear 1. Check the teeth and dogs of the reverse gear. Replace if cracked or worn. Che...
Page 371
8-64 drive shaft and lower case (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 4. Install the needle bearing and water inlet covers. See steps 4 and 5 in “assembling the lower case” (8-24). Assembling the drive shaft housing see “assembling the drive shaft housing” (8- 23). Installing the reverse...
Page 372
8-65 drive shaft and lower case (counter rotation model) installing the lower unit (x-transom model) 1. Check that the shift rod is in the n posi- tion. See steps 1 and 2 in “installing the lower unit (l-transom model)” (8-29). 2. Install the extension and lower unit. See steps 2–6 in “installing th...
Page 373
8-66 shimming (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a shimming (counter rotation model) shimming workflow 1. Remove the water pump assembly. 2. Measure the backlash before disassem- bly. 3. Within specification? 4. Yes 5. Shimming is not required. 6. No 7. Disassemble the lower unit. 8. Se...
Page 374
8-67 shimming (counter rotation model) shimming check sheet lower case deviation pinion height (mm) forward gear backlash (mm) reverse gear backlash (mm) serial number p f r remarks measurements measuring point #1 measuring point #2 measuring point #3 measuring point #4 average round-down average (m...
Page 375
8-68 shimming (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a forward gear shim (t2) thickness adjustment in 2 places (mm) reverse gear shim (t1) thickness adjustment in 2 places (mm) number of shim(s) subtotal 0.10 0.12 0.15 0.18 0.30 0.40 0.50 total number of shim(s) subtotal 0.10 0.12 0.15 0.18...
Page 376
8-69 shimming (counter rotation model) measuring the forward gear backlash and reverse gear backlash before disassembly two washers (90201-26m00) are required for the reverse gear backlash measurement in the counter rotation model. Prepare the washers before starting the shimming proce- dure. 1. Ins...
Page 377
8-70 shimming (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a tip: • after installing the handle holder, pull the drive shaft upward to remove any free play. • do not press the spring more than 5.0 mm (0.197 in). Otherwise, too much torque will be required to turn the drive shaft, making it diffic...
Page 378
8-71 shimming (counter rotation model) 13. Determine the backlash average, and then round down the average to 2 decimal places. Example: 14. Check that the forward gear backlash average is within specification. Tip: adjust the shim thicknesses if the forward gear backlash is out of specification. 15...
Page 379
8-72 shimming (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a shimming procedure • before selecting the forward gear shims (t2) and reverse gear shims (t1), make sure to select the pinion shims (t3). • when assembling the lower unit to measure the backlash after selecting the pinion shims (t3), do...
Page 380
8-73 shimming (counter rotation model) selecting the pinion shim (t3) see “selecting the pinion shim (t3)” (8-39). Selecting the propeller shaft shim (t4) 1. Install the original propeller shaft shims (t4). Tip: • if the original shims are missing, measure the free play without any shims. • do not r...
Page 381
8-74 shimming (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 8. Calculate the new propeller shaft shim (t4) thickness. Tip: use up to 3 shims to obtain the required shim thickness. Calculation formula: new propeller shaft shim (t4) thickness = current propeller shaft shim thickness + shim thickne...
Page 382
8-75 shimming (counter rotation model) 3. Determine the forward gear shim (t2) thickness adjustment using the “forward gear shim (t2) selection chart” according to the backlash measurement (bl2) from “measuring the forward gear backlash”. See “reverse gear shim (t1) selection chart (fl150a)” (a-16) ...
Page 383
8-76 shimming (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a measuring the reverse gear backlash • spray anti-rust lubricant on the gear and bearings before installation. Do not apply gear oil to the parts. Otherwise, correct measurements cannot be obtained. • keep the parts free of foreign mater...
Page 384
8-77 shimming (counter rotation model) a. Backlash measurement (bl1) b. Shim thickness adjustment 4. Calculate the new reverse gear shim (t1) thickness. Tip: • use the lowest number of shims to obtain the required shim thickness. • if the calculated shim thickness cannot be obtained with a combinati...
Page 385: — Memo —
8-78 shimming (counter rotation model) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a — memo —.
Page 386
Bracket unit 9 shift rod and shift bracket ................................................ 9-1 removing the shift rod and shift bracket ................................... 9-3 disassembling the shift bracket ................................................. 9-3 assembling the shift bracket ...........
Page 387
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a bracket unit ptt unit ............................................................................ 9-33 removing the ptt unit ............................................................ 9-34 checking the hydraulic pressure ............................................. 9-35 ...
Page 388
9-1 shift rod and shift bracket shift rod and shift bracket no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 shift position switch 1 2 screw 4 m4 × 16 mm 3 plate 2 4 clip 2 5 bushing 1 6 bracket 1 7 washer 1 8 shift lever 1 9 shift cut-off switch 1 10 spring 1 11 bushing 2 12 bolt 2 m6 × 50 mm 13 bracket 1 14 grease ni...
Page 389
9-2 shift rod and shift bracket 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 washer 2 19 bracket 1 20 ball 1 6.34 mm (0.25 in) (reference data) 21 spring 1 22 shift rod detent bolt 1 23 dowel 1 24 grease nipple 1 25 bushing 1 26 o-ring 1 not reusable 27 bolt 1 m6 × 35 mm 28 shift rod 1 29 ...
Page 390
9-3 shift rod and shift bracket removing the shift rod and shift bracket 1. Remove the shift bracket assembly “1”. 2. Remove the shift lever “1” and shift rod assembly “2”. 3. Remove the shift rod detent bolt “1”, spring “2”, and ball “3”. 4. Remove the circlip “4” and bushing “5”. Disassembling the...
Page 391
9-4 shift rod and shift bracket 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 2. Install the shift position switch “1” and plate “2”, and then tighten the shift posi- tion switch screws “3” to the specified torque. 3. Install the bushing “1” to the bracket “2”. 4. Fit the spring end “a” into the cutout “b” in the bracke...
Page 392
9-5 shift rod and shift bracket 3. Install a new o-ring “1” to the shift rod assembly “2”. 4. Install the grommet “3” to the upper case. 5. Install the shift lever “4” to the set pin “a” of the shift rod assembly “2”. 6. Install the dowel “5” and shift rod assem- bly “2”, and then align the center o...
Page 393
9-6 ptt switch and cowling lock lever 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a ptt switch and cowling lock lever no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 gasket 2 regular rotation model 2 ptt switch 1 regular rotation model 3 bolt 4 m6 × 20 mm 4 holder 2 5 cover 1 regular rotation model 6 cowling lock lever (rear) 1 7 cowling ...
Page 394
9-7 ptt switch and cowling lock lever no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 hook 2 19 grommet 1 20 hose 1 hose joint to exhaust cover 21 plastic tie 3 22 hose joint 1 23 hose joint 1 24 gasket 1 25 adapter 1 26 screw 2 ø6 × 19 mm 27 clamp 1 28 ptt switch 1 counter rotation model 29 cover 1 counter rotation ...
Page 395
9-8 ptt switch and cowling lock lever 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the ptt switch 1. Remove the holder “1”, and then remove the ptt switch “2”. A. Regular rotation model b. Counter rotation model removing the cowling lock lever 1. Remove the spring “1”. 2. Remove the lever “1” and cowling lock ...
Page 396
9-9 ptt switch and cowling lock lever 2. Pass the flushing hose “2”, trim sensor lead “3”, and ptt motor leads “4” through the grommet “1”, and then fasten them using the plastic ties “5” around the grommet “1”. Tip: align the white paint mark “a” on the flushing hose “2” with the outer end of the g...
Page 397
9-10 ptt switch and cowling lock lever 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a a. Regular rotation model b. Counter rotation model stbd 1 2 3 a port 1 2 3 b.
Page 398
9-11 bottom cowling bottom cowling no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 bolt 5 m6 × 20 mm 2 pin 2 3 holder 2 4 bracket 1 5 bracket 1 6 bracket 1 7 clamp 1 8 holder 1 9 grommet 4 10 collar 4 11 rubber seal 1 12 water outlet 1 13 grommet 2 14 bolt 4 m8 × 35 mm 15 grommet 8 16 collar 4 17 rubber seal 1 6 4 1 3...
Page 399
9-12 bottom cowling 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 bottom cowling 1 19 grommet 1 6 4 1 3 3 2 2 5 1 1 1 8 10 9 14 15 15 16 13 11 13 7 12 17 18 19 14 15 14 15 15 16 14 15 15 16 15 16.
Page 400
9-13 upper case and mounts upper case and mounts no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 self-locking nut 2 2 nut 2 3 washer 4 4 bolt 4 m10 × 40 mm 5 cover 1 6 cover 1 7 washer 2 8 lower mount 2 9 washer 2 10 washer 2 11 washer 2 12 bolt 2 m14 × 225 mm 13 cap 2 14 collar 2 15 washer 4 16 upper mount 2 17 brack...
Page 401
9-14 upper case and mounts 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 bolt 3 m10 × 45 mm 19 washer 2 20 bolt 2 m14 × 203 mm 21 bolt 1 m6 × 10 mm 22 nipple 1 23 plastic tie 2 24 speedometer hose 1 adapter to nipple 25 adapter 1 26 bolt 1 m6 × 20 mm 1 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 5 6 7 7 7 8 8 8 9 9 9 10...
Page 402
9-15 upper case and mounts removing the upper case 1. Drain the remaining engine oil. 2. Disconnect the ground lead “1”. 3. Remove the adapter “2”, and then dis- connect the speedometer hose “3”. 4. Loosen the upper mount bracket bolts “4” and lower mount cover bolts (port and stbd) “5”. 5. Remove t...
Page 403
9-16 upper case and mounts 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 6. Install the ground lead (stbd) “2”, wash- ers “3”, upper mounting nuts “4”, and lower mounting nuts “5”, and then tighten the upper mounting nuts “4” and lower mounting nuts “5” to the specified torque. Tip: fit the ground lead “2” into the groo...
Page 404
9-17 upper case upper case no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 upper case 1 2 circlip 1 3 bushing 1 4 rubber seal 1 5 dowel 2 6 screw 2 m6 × 15 mm 7 baffle plate 1 8 bolt 2 m8 × 30 mm 9 bolt 4 m10 × 45 mm 10 grommet 2 11 gasket 1 not reusable 12 drain bolt 1 13 damper 1 14 rubber seal 1 15 rubber seal 1 no...
Page 405
9-18 upper case 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a disassembling the upper case 1. Remove the drain bolt “1”. 2. Remove the upper case bolts “1” and “2”, and then remove the oil pan assembly “3”. 3. Remove the circlip “1”, and then remove the bushing “2”. Checking the drive shaft bushing 1. Check the bushing....
Page 406
9-19 upper case 7. Install a new gasket “1” and the drain bolt “2”, and then tighten the drain bolt “2” to the specified torque. Baffle plate screw “3”: 4 n·m (0.4 kgf·m, 3.0 ft·lb) oil pan assembly bolt (m8) “10”: 20 n·m (2.0 kgf·m, 14.8 ft·lb) oil pan assembly bolt (m10) “11”: 42 n·m (4.2 kgf·m, 3...
Page 407
9-20 oil pan and exhaust manifold 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a oil pan and exhaust manifold no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 exhaust guide 1 2 gasket 1 not reusable 3 gasket 1 not reusable 4 collar 3 5 oil strainer 1 6 bolt 3 m6 × 25 mm 7 dowel 2 8 oil pan 1 9 bolt 10 m8 × 35 mm 10 bolt 4 m8 × 60 mm 11 gask...
Page 408
9-21 oil pan and exhaust manifold no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 dowel 2 19 muffler 1 20 bolt 8 m8 × 35 mm 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 12 n·m (1.2 kgf·m, 8.9 ft·lb) 20 n·m (2.0 kgf·m, 14.8 ft·lb) 20 n·m (2.0 kgf·m, 14.8 ft·lb) 20 n·m (2.0 kgf·m, 14.8 ft·lb).
Page 409
9-22 oil pan and exhaust manifold 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a disassembling the oil pan and exhaust manifold 1. Remove the muffler “1”, plate “2”, and exhaust manifold “3”. 2. Remove the oil pan “1” and oil strainer “2”. Checking the oil pan and exhaust manifold 1. Clean the removed parts. 2. Check the...
Page 410
9-23 oil pan and exhaust manifold 3. Install a new gasket “1”, the exhaust manifold “2”, the rubber seal “3”, and then tighten the exhaust manifold bolts “4” temporarily. Tip: make sure that the sealant “a” side of the gasket “1” is facing toward the exhaust mani- fold. 4. Tighten the exhaust manifo...
Page 411
9-24 steering arm 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a steering arm no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 steering arm 1 2 washer 2 3 bushing 2 4 o-ring 1 not reusable 5 bushing 1 6 steering yoke 1 7 circlip 1 8 grommet 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 5 6 7 8.
Page 412
9-25 steering arm removing the steering arm 1. Remove the circlip “1”, and then remove the steering yoke “2” by striking it using a copper hammer. 2. Remove the washer “1”, bushing “2”, o-ring “3”, and bushing “4”. 3. Remove the steering arm from the swivel bracket. Installing the steering arm 1. In...
Page 413
9-26 steering arm 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 4. Hold the steering arm “1”, and then strike the steering yoke “2” using a copper hammer until the groove “a” for installing the circlip is visible. 5. Install the circlip “3”. 6. Inject grease into the grease nipple “1” until grease comes out from both th...
Page 414
9-27 clamp bracket and swivel bracket clamp bracket and swivel bracket no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 self-locking nut 1 2 clamp bracket (stbd) 1 3 grease nipple 6 4 ground lead 1 5 screw 1 m6 × 10 mm 6 ground lead 1 7 tilt stop lever 1 8 bushing 2 9 tilt stop lever 1 10 bushing 2 11 washer 2 12 clamp...
Page 415
9-28 clamp bracket and swivel bracket 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 washer 2 19 nut 2 20 anode 1 21 plate 2 22 bolt 4 m6 × 30 mm 23 ground lead 1 24 bushing 2 25 collar 1 26 pin 2 27 distance collar 2 28 pin 1 29 spring 1 30 hook 1 31 bolt 1 m6 × 10 mm 32 screw 1 m5 × 35 mm ...
Page 416
9-29 clamp bracket and swivel bracket no. Part name q’ty remarks 35 screw 2 m6 × 15 mm 36 trim sensor 1 1 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 5 6 8 7 8 9 10 10 11 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 21 22 22 23 24 25 26 27 27 28 26 26 26 27 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 3 n·m (0.3 kgf·m, 2.2 ft·lb) 15 n·m (1.5 kgf·m, 11.1...
Page 417
9-30 clamp bracket and swivel bracket 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the clamp bracket 1. Remove the ptt unit. See “removing the ptt unit” (9-34). 2. Remove the plastic tie “1”. 3. Remove the anode “1” and ground lead “2”. 4. Remove the trim sensor cam “3”. 5. Remove the ground leads “4” and “5”....
Page 418
9-31 clamp bracket and swivel bracket 2. Install the bushings “1” and “2”, collar “3”, distance collar assembly “4”, and tilt stop levers “5” and “6”. 3. Install the pins “1”, hook “2”, and spring “3”. 4. Install the trim sensor “1”, and then tighten the trim sensor screw “2” to the specified torque...
Page 419
9-32 clamp bracket and swivel bracket 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 11. Inject grease into the grease nipples until grease comes out from the bushings “a”. 12. Install the ptt unit. See “installing the ptt unit” (9-39). Adjusting the trim sensor cam 1. Fully tilt the swivel bracket down. 2. Loosen the tr...
Page 420
9-33 ptt unit ptt unit no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 upper mounting shaft 1 2 circlip 1 3 bushing 6 4 ptt unit 1 5 ground lead 1 6 bolt 1 m6 × 10 mm 7 bolt 2 m10 × 30 mm 8 washer 2 9 lower mounting shaft 1 10 plastic tie 3 1 2 3 3 3 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 7 8 39 n·m (3.9 kgf·m, 28.8 ft·lb).
Page 421
9-34 ptt unit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the ptt unit when removing the ptt unit with the power unit installed, make sure to sus- pend the outboard motor. 1. Fully tilt the swivel bracket up, and then support it using the tilt stop lever “1”. 2. Remove the plastic ties “1”, and then pull out ...
Page 422
9-35 ptt unit checking the hydraulic pressure check the hydraulic pressure. Check the internal parts if out of specification. 1. Place the ptt unit in an upright position. 2. Connect the battery jumper leads to the ptt motor lead “1” to fully extend the ptt rams. 3. Remove the reservoir cap “1”, and...
Page 423
9-36 ptt unit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 8. Connect the battery jumper leads to the ptt motor lead “1” to fully retract the ptt rams. 9. Reverse the connection between battery jumper leads and the ptt motor lead “1” to fully extend the ptt rams, and then measure the hydraulic pressure when the reading...
Page 424
9-37 ptt unit 14. Repeat steps 2–4 to check the fluid level. 15. Connect the battery jumper leads to the ptt motor lead “1” to fully retract the ptt rams, and then measure the hydrau- lic pressure when the reading on the pressure gauge stabilizes. 16. Reverse the connection between battery jumper le...
Page 425
9-38 ptt unit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 3. Check the fluid level. See steps 2–4 in “checking the hydraulic pressure” (9-35). 4. Connect the battery jumper leads to the ptt motor lead “1” to fully retract the ptt rams. Tip: if the ptt rams do not move down easily, push on the ptt rams to assist operat...
Page 426
9-39 ptt unit installing the ptt unit • after tilting the swivel bracket up, make sure to support it using the tilt stop lever. • when installing the ptt unit with the power unit installed, make sure to sus- pend the outboard motor. 1. Connect the battery jumper leads to the ptt motor lead “1” to re...
Page 427
9-40 ptt unit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 7. Install the ground lead “1”. 8. Fasten the ptt motor lead and trim sen- sor lead using the plastic ties “1”. 2 1 1 1 1 1.
Page 428
9-41 ptt cylinder ptt cylinder no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 tilt ram 1 2 dust seal 1 not reusable 3 o-ring 1 not reusable 4 tilt cylinder end screw 1 5 o-ring 1 not reusable 6 ball 1 3.96 mm (0.16 in) (reference data) 7 pin 1 8 ball 4 3.94 mm (0.15 in) (reference data) 9 washer 1 10 o-ring 1 not reu...
Page 429
9-42 ptt cylinder 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 dust seal 2 not reusable 19 circlip 2 20 free piston 1 21 o-ring 1 not reusable 65 n·m (6.5 kgf·m, 47.9 ft·lb) 2 5 11 10 8 12 20 21 19 18 17 16 14 15 13 1 9 8 8 7 6 8 4 3 7 n·m (0.7 kgf·m, 5.2 ft·lb) 160 n·m (16.0 kgf·m, 118.0 ...
Page 430
9-43 ptt cylinder removing the tilt ram and trim ram before removing the tilt cylinder end screw, make sure that the ptt rams are fully extended. Otherwise, fluid could be expelled forcefully from the ptt unit due to internal pressure. 1. Connect the battery jumper leads to the ptt motor lead “1” to...
Page 431
9-44 ptt cylinder 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a disassembling the tilt ram 1. Remove the tilt piston absorber valves “1” and o-ring “2”. 2. Remove the tilt piston “1”. Disassembling the trim ram 1. Remove the o-ring “1” and backup ring “2”. Checking the tilt cylinder and trim cylinder 1. Check the ptt bo...
Page 432
9-45 ptt cylinder 2. Install the tilt cylinder end screw “1” and tilt piston “2”. 3. Tighten the tilt ram “1” to the specified torque. 4. Install a new o-ring “1”. 5. Install the absorber valves “2”. 6. Install the plate “3”, washer “4”, and tilt piston screw “5”, and then tighten the tilt piston sc...
Page 433
9-46 ptt cylinder 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a installing the trim ram 1. Install a new o-ring “1” to the free piston “2”. 2. Install the free piston “1” and push it down until it bottoms out. 3. Fill the trim cylinders with the recom- mended fluid up to the proper level “a”. 4. Install the trim ram ass...
Page 434
9-47 ptt cylinder cylinder end screw wrench “2”: 90890-06591 tilt cylinder end screw “1”: 150 n·m (15.0 kgf·m, 110.6 ft·lb) 1 2.
Page 435
9-48 ptt motor 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a ptt motor no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 armature 1 2 stator 1 3 screw 3 m5 × 20 mm 4 bolt 6 m6 × 25 mm 5 screw 2 m4 × 16 mm 6 circuit breaker 1 7 brush holder 1 8 brush 1 9 spring 2 10 o-ring 1 not reusable 11 motor base assembly 1 12 oil seal 1 not reusable 13...
Page 436
9-49 ptt motor no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 circlip 1 19 filter 1 20 o-ring 1 not reusable 4 5 5 6 7 8 9 10 3 2 3 4 15 4 4 16 17 14 1 12 11 18 19 20 7 n·m (0.7 kgf·m, 5.2 ft·lb) 7 n·m (0.7 kgf·m, 5.2 ft·lb) 4 4 13.
Page 437
9-50 ptt motor 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a removing the reservoir 1. Remove the reservoir “1” and o-ring “2”. Tip: place a container under the ptt unit to catch the fluid. 2. Remove the circlip “1”, filter “2”, and o-ring “3”. Removing the ptt motor 1. Remove the ptt motor assembly “1”, o-ring “2”, and...
Page 438
9-51 ptt motor checking the armature (ptt motor) 1. Check the commutator. Clean using 600- grit sandpaper and compressed air if dirty. 2. Measure the commutator diameter “a”. Replace the armature if below specifica- tion. 3. Measure the commutator undercut “a”. Replace the armature if below specific...
Page 439
9-52 ptt motor 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 3. Check the ptt motor base. Replace the ptt motor assembly if the base is cracked or damaged. Checking the reservoir 1. Check the reservoir. Replace if cracked or damaged. Assembling the ptt motor do not apply grease or oil to the commu- tator of the armature...
Page 440
9-53 ptt motor installing the ptt motor when assembling the ptt unit, do not use a rag. Otherwise, dust and particles could get on the ptt unit components, causing poor performance. 1. Install the joint “1”. Make sure that the deeper end of the groove “a” is facing the ptt motor when installing the ...
Page 441
9-54 ptt gear pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a ptt gear pump no. Part name q’ty remarks 1 bolt 4 m5 × 25 mm 2 plate 1 3 wave washer 1 4 valve lock screw 2 5 spring 1 6 valve support pin 1 7 o-ring 1 not reusable 8 ball 1 3.15 mm (0.12 in) (reference data) 9 spring 1 10 valve pin 1 11 valve seal 1 not r...
Page 442
9-55 ptt gear pump no. Part name q’ty remarks 18 spring 1 19 ball 2 3.15 mm (0.12 in) (reference data) 20 spring 1 21 o-ring 4 not reusable 22 o-ring 4 not reusable 23 bracket 1 24 bolt 1 m4 × 25 mm 25 bolt 1 m5 × 25 mm 26 plug 1 27 ball 1 3.94 mm(0.16 in) (reference data) 28 port plug 2 29 spacer 1...
Page 443
9-56 ptt gear pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a no. Part name q’ty remarks 35 o-ring 2 not reusable 36 manual valve seat 2 37 spring 1 38 adapter 1 39 spring 1 40 o-ring 1 not reusable 41 o-ring 1 not reusable 42 manual valve 1 43 circlip 1 44 main valve 2 1 7 n·m (0.7 kgf·m, 5.2 ft·lb) 2 3 4 5 6 4 9 10...
Page 444
9-57 ptt gear pump removing the gear pump assembly 1. Remove the plate “1”, filter “2”, backup ring “3”, wave washer “4”, protection valves “5” and “6”, and gear pump assembly “7”. Disassembling the gear pump housing 1. Remove the o-rings “1” and “2”, spacers “3” and “4”, and port plugs “5”. 2. Remo...
Page 445
9-58 ptt gear pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a a. Up-relief valve b. Down-relief valve 2. Remove the bracket “1” and o-rings “2” and “3”. 3. Remove the gear housing “1”, and then remove the drive gear “2”, driven gear “3”, balls “4”, and pins “5”. 4. Remove the valve seat “1” and o-ring “2”. Checking t...
Page 446
9-59 ptt gear pump assembling the gear pump lubricate the parts using atf dexron ii dur- ing assembly. When assembling the ptt unit, do not use a rag. Otherwise, dust and particles could get on the ptt unit components, causing poor performance. 1. Install a new o-ring “1” and the valve seat “2”. 2. ...
Page 447
9-60 ptt gear pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a a. Up-relief valve b. Down-relief valve assembling the gear pump housing lubricate the parts using atf dexron ii dur- ing assembly. When assembling the ptt unit, do not use a rag. Otherwise, dust and particles could get on the ptt unit components, causing ...
Page 448
9-61 ptt gear pump 8. Install the spacers “1” and “2”, the port plugs “3”, and new o-rings “4” and “5”. Installing the gear pump assembly lubricate the parts using atf dexron ii dur- ing assembly. When assembling the ptt unit, do not use a rag. Otherwise, dust and particles could get on the ptt unit...
Page 449: — Memo —
9-62 ptt gear pump 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a — memo —.
Page 450
Maintenance 10 outline .............................................................................. 10-1 maintenance interval chart 1 ................................................... 10-1 maintenance interval chart 2 ................................................... 10-3 predelivery check ......
Page 451
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a maintenance adjusting the shift link/shift cable .......................................... 10-15 checking the spark plug ........................................................ 10-15 checking the timing belt ........................................................ 10-15 re...
Page 452
10-1 outline outline • to obtain long product life, yamaha strongly recommends that the specified periodic checks and maintenance be performed according to the maintenance interval charts. • if replacement parts are necessary, use only genuine yamaha parts of equivalent design and qual- ity. Any par...
Page 453
10-2 outline 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a engine oil replacement f/u f/u engine oil filter (cartridge) replacement f/u fuel filter (can be disassembled) inspection or replacement as necessary f/u f/u fuel line (high pressure) inspection f f fuel line (high pressure) inspection or replacement as necessar...
Page 454
10-3 outline maintenance interval chart 2 main switch/stop switch/ choke switch inspection or replacement as necessary u u wire harness connections/wire coupler connections inspection or replacement as necessary u u (yamaha) meter/gauge inspection u u item actions every 1000 hours exhaust guide/exha...
Page 455
10-4 predelivery check 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a predelivery check to make the delivery process smooth and efficient, complete the predelivery checks as explained in the following procedures. Checking the battery battery electrolyte is dangerous; it con- tains sulfuric acid, which is poisonous and hi...
Page 456
10-5 predelivery check checking the cooling water pilot hole 1. Start the engine, and then check that cooling water is discharged from the cooling water pilot hole. Checking the engine oil level 1. Place the outboard motor in an upright position. If the outboard motor is not level, the oil level ind...
Page 457
10-6 predelivery check 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a a. 703 remote control model b. 704 remote control model checking the fuel line 1. Check that the fuel hoses are connected securely. See “fuel hose” (6-1). This outboard motor is equipped with a 4- stroke engine. Never use premixed fuel or 2-stroke outb...
Page 458
10-7 predelivery check tip: the appropriate mounting height depends on the combination of the boat and outboard motor. To determine the appropriate mount- ing height, test run the outboard motor at dif- ferent heights. 2. Check that the clamp brackets are secured using the clamp bolts. Checking the ...
Page 459
10-8 general periodic maintenance 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a break-in operate the engine under load (in gear with a propeller installed) for 10 hours as follows: 1. For the first hour “a” of operation: operate the engine at varying speeds up to 2000 r/min or approximately 1/2 throt- tle. 2. For the se...
Page 460
10-9 general periodic maintenance 4. Install the water inlet covers and trim tab, and then tighten the water inlet cover screw and trim tab bolt to the specified torque. Tip: after installing the water inlet covers, make sure that there is no rattling. Checking the cooling water pilot hole 1. Place ...
Page 461
10-10 general periodic maintenance 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 5. Remove the dipstick “1” and extract the engine oil using the oil changer “2”. 6. Fill the engine with the specified amount of the recommended engine oil through the oil filler hole. Install the oil filler cap and dipstick. Do not overfil...
Page 462
10-11 general periodic maintenance 3. Install a new oil filter “1”, and then tighten it to the specified torque. 4. Fill the engine with the specified amount of the recommended engine oil through the oil filler hole. 5. Install the oil filler cap and dipstick, and then start the engine and warm it u...
Page 463
10-12 general periodic maintenance 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a 4. Remove the check screw “4” and gasket “5” and let the oil drain completely. After the gear oil has been drained, check the used oil. If the oil is milky, water is get- ting into the lower case, which can cause gear damage. 5. Place the o...
Page 464
10-13 general periodic maintenance tip: make sure to set the gear shift to the r posi- tion before injecting grease into the grease nipple on the shift rod. 2. Apply low temperature resistant grease to the specified lubrication point. 3. Apply corrosion resistant grease to the specified lubrication ...
Page 465
10-14 general periodic maintenance 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 a checking the pcv 1. Check the pcv. See “checking the pcv” (7-50). Checking the propeller/propeller nut/ cotter pin 1. Check the propeller. See “checking the propeller” (8-3). 2. Check the propeller nut and cotter pin. See “installing the lo...
Page 466
10-15 general periodic maintenance 3. Check the ptt unit for fluid leakage. Adjusting the shift link/shift cable 1. Disconnect the shift cable, and then adjust it. See “installing the shift cable” (3-9). Checking the spark plug 1. Check the spark plugs. See “checking the spark plug” (7-25). Checking...
Page 467
I-1 index a. Abbreviation ................................................0-5 adjusting the forward gear shim thickness (t1) .........................................8-41 adjusting the forward gear shim thickness (t2) .........................................8-74 adjusting the reverse gear shim thic...
Page 468
I-2 index 0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 a checking the cylinder head.......................7-41 checking the cylinder head and cylinder block anode ......................................................7-45 checking the diaphragm and valve...........6-14 checking the dog clutch...................8-16, 8-5...
Page 469
I-3 index checking the tilt cylinder and trim cylinder.............................................9-44 checking the tilt limiter (optional)..............5-43 checking the timing belt.................7-17, 10-15 checking the tps ............................5-15, 6-26 checking the trim sensor ..........
Page 470
I-4 index 0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 a forward gear shim (t2) selection chart (fl150a) ................................................ A-16 forward gear shim (t2) selection chart (fl150b) ................................................ A-17 fuel control unit and component...............5-16 fuel diag...
Page 471
I-5 index l. Logging .....................................................2-12 lower unit .................................................2-19 lower unit (counter rotation model)..........................1-19 lower unit (counter rotation model, l-transom model) ........................................
Page 472
I-6 index 0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 a removing the fuel injector and vapor shut-off valve........................................................6-18 removing the fuel pump assembly...........6-13 removing the gear pump assembly .........9-57 removing the ignition coil .........................7-25 re...
Page 473
I-7 index troubleshooting the power unit using the ydis....................................................4-6 troubleshooting the ptt unit...........4-16, 4-17 twin outboard motor application (conventional gauge).....................................................3-35 twin outboard motor applicati...
Page 474: — Memo —
I-8 index 0 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 a — memo —.
Page 476
Oct. 2011 – ** × 2 abe (e).
Page 477
A-1 appendix a wiring diagram ..................................................................A-1 how to use the wiring diagram .................................................. A-1 engine control unit and fuel unit ................................................ A-2 ignition unit .................
Page 478
A-2 engine control unit and fuel unit 1. Engine ecm 2. Oil pressure sensor 3. Isc valve 4. Speed sensor 5. Water pressure sensor 6. High-pressure fuel pump 7. Fuel injector 8. Vapor shut-off valve 9. Water detection switch 10. Joint connector 1 11. Joint connector 2 12. Fuse box 13. Battery 14. Star...
Page 479
A-3 1 23 22 44 1 1 11 10 23 1 12 13 24 g b b r w p y b r r w p y l l g g o o o o b b b b y/g p /w p/w l /w l/w r /y r /y r/y g /r g/r g /b g/b g /y g/y r r r r g /y r r /y g /b b b pu /g pu /r pu /b pu /y r /y r /y r /y r /y #1 #3 #2 #4 b l /w l r /y l/w g/b pu/b pu/r pu/y l a b c d e f a 3 5 6 4 2 ...
Page 480
A-4 ignition unit 1. Engine ecm 2. Pulser coil 3. Thermoswitch 4. Ignition coil 5. Air pressure sensor 6. Tps 7. Engine temperature sensor 8. Shift position switch 9. Shift cut-off switch 10. Air temperature sensor 11. Joint connector 1 12. Joint connector 2 13. Fuse box 14. Battery 15. Starter moto...
Page 481
A-5 6. Tps 1 23 22 44 a a b c d e f 1 11 10 23 g b r w p y b r r w p p p p p g y o o o b b b b b b b b b b y/g p /g p/g w /r w/r w /b w/b l /g l/g l /y l/y b/o b /w b/w b /y b/y b/y r /y r /y r/y r b /o r r r /y r /y r /y g /y r 3 4 2 7 8 9 10 13 14 15 16 22 30 31 32 33 34 35 37 42 44 1 r 8 6 7 19 1...
Page 482
A-6 charging unit and starting unit (f150a, fl150a for european and oceanian markets) 1. Engine ecm 2. Ptt relay 3. Ptt motor 4. Starter relay 5. Starter motor 6. Ptt switch 7. Trim sensor 8. Tilt limiter 9. Joint connector 1 10. Joint connector 2 11. Fuse box 12. Stator assembly 13. Rectifier regul...
Page 483
A-7 1 23 22 44 a b c d e f w p y b y/g r/y r r r r /y g /y b b w l b d e b w /b r /y l /w l/w f g h r ac 1 ac 1 ac 1 + 1 1 11 10 23 14. Battery + 2 r r r r g g g b r r r br br g b b b b b b b/w l r r r lg p p p p p /b p /b p /w p b sb l b l g g r w p y b sb lg a 3 1 4 2 8 13 16 23 24 26 27 28 30 32 ...
Page 484
A-8 charging unit and starting unit (f150a, fl150a [except for european and oceanian markets] and f150b, fl150b) 1. Engine ecm 2. Ptt relay 3. Ptt motor 4. Starter relay 5. Starter motor 6. Ptt switch 7. Trim sensor 8. Joint connector 1 9. Joint connector 2 10. Fuse box 11. Stator assembly 12. Recti...
Page 485
A-9 1 11 10 23 r r 2 1 a d b e g r w p y b r r r r /y g /y w l b w /b r /y l /w r lg ac 1 ac 1 ac 1 + 1 + 2 r r g g g b sb lg r r r br br g l b b b b b b b/w r r r p p p p/b p/b p/b p /b p /b p /w f g p b a b d e f c g 1 23 22 44 3 1 4 2 8 13 16 23 24 26 27 28 30 32 36 42 w p y b y/g r/y b b l/w p g...
Page 486
A-10 control unit 1. 703 remote control 2. Engine start switch 3. Engine shut-off switch 4. Ptt switch 5. On 6. Off 7. Start 8. Clip removed 9. Clip installed 10. Up 11. Free 12. Dn 13. Neutral switch 14. Switch panel (6r5-82570-05) 15. 704 remote control 16. Main wiring harness 17. Twin switch pane...
Page 487
A-11 y y r b r y g b r y b g b l lg sb b br br p w w w w y sb sb r r r lg lg w b w b r y br sb r lg b bz r w y g p br b y r w br b b r y g b w b w b r y br sb r lg sb r lg a b b 6. Off 7. Start 5. On 8. Clip removed 9. Clip installed 10. Up 12. Dn 11. Free 6. Off 7. Start 5. On 8. Clip removed 9. Cl...
Page 488
A-12 shim selection table and chart (regular rotation model) pinion shim (t3) selection table (mm) a. Pinion height measurement (m) b. Stamped value on the lower case (p) a 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.17 0.18 0.19 0.20 0.21 0.22 0.23 0.24 0.25 0....
Page 489
A-13 forward gear shim (t1) selection chart (f150a) a. Backlash measurement (bl1) b. Shim thickness adjustment reverse gear shim (t2) selection chart (f150a) a. Backlash measurement (bl2) b. Shim thickness adjustment 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125 1...
Page 490
A-14 forward gear shim (t1) selection chart (f150b) a. Backlash measurement (bl1) b. Shim thickness adjustment reverse gear shim (t2) selection chart (f150b) a. Backlash measurement (bl2) b. Shim thickness adjustment 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125 1...
Page 491
A-15 shim selection table and chart (counter rotation model) pinion shim (t3) selection table see “pinion shim (t3) selection table” (a-12) propeller shaft shim (t4) selection table the shim thickness does not have to be adjusted for the gray-colored cell. (mm) a. Free play measurement b. Shim thick...
Page 492
A-16 forward gear shim (t2) selection chart (fl150a) a. Backlash measurement (bl2) b. Shim thickness adjustment reverse gear shim (t1) selection chart (fl150a) a. Backlash measurement (bl1) b. Shim thickness adjustment 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125...
Page 493
A-17 forward gear shim (t2) selection chart (fl150b) a. Backlash measurement (bl2) b. Shim thickness adjustment reverse gear shim (t1) selection chart (fl150b) a. Backlash measurement (bl1) b. Shim thickness adjustment 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125...