- DL manuals
- Yamaha
- Music Mixer
- M3000-24
- Owner's Manual
Yamaha M3000-24 Owner's Manual
Summary of M3000-24
Page 1
Owner’s manual mode d’emploi bedienungsanleitung m mixing console.
Page 2: Introduction
2 introduction thank you for purchasing the yamaha m3000 mixing console. The m3000 is based on yamaha’s experience with the pm series, and features superb sound quality with a full range of functionality such as vca faders, scene memory, and ga diversity. In order to take full advantage of the m3000...
Page 3: Contents
3 contents features of the system...............................5 control panel............................................6 input channel section................................................ 6 variable/fixed select section.................................... 13 mix section .........................
Page 4: Precautions
4 precautions • connect the mixer power cord only to the power supply unit, and connect the power supply unit to an ac outlet of the type stated in this owner’s manual or as marked on the power supply unit. Failure to do so is a fire and electrical shock hazard. • do not locate the mixer in a place ...
Page 5: Features of The System
5 features of the system • the m3000-40c provides a generous number of input modules; 40 monaural and 4 stereo (the m3000-24 provides 24 monaural and 4 stereo). Stereo output, 16 mix outputs, and 8 matrix outputs are provided in addition. The m3000 is suitable for use in a wide range of applications...
Page 6: Control Panel
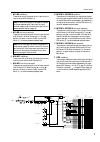
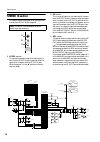
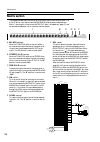
6 control panel input channel section mono input channels the m3000-24 provides 24 input channels, and the m3000-40c provides 40 input channels. All input channels have the same specifications. A phantom power switch/ +48 v indicator this switch turns the +48 v phantom power on/off for each channel....
Page 7
Control panel 7 i m1–m8 switches these switch on/off the signal which is sent from the input channel to mix buses 1–8. J m1–m8 mix level controls these controls send the signal from the input channel to mix buses 1–8. When the control is in the “ ▲ ” position, the level is nominal (0 db). Use the pr...
Page 8
Control panel 8 q st (stereo) switch when this switch is on, the signal of the input channel will be sent to the (st) stereo bus. R pan control this sets the panning of the signal that is sent from the input channel to the st bus. S on/edit switch/ on , check indicators the function of this switch a...
Page 9
Control panel 9 u vca group select switches these switches select the vca master fader(s) which will control the signal output level of this channel. When you select a vca group 1–8, the indicator located at the left of each switch will light, and the corresponding vca master fader (vca master secti...
Page 10: Stereo Input Channels
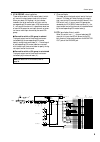
Control panel 10 stereo input channels the m3000 provides four stereo input channels. Ste- reo sound sources such as sub-mixers, effect proces- sor, or cd players can be input to the input a jacks (xlr connectors) or input b jacks (rca phono connectors) located on the rear panel. A gain a control th...
Page 11
Control panel 11 g m1–m8 mix level controls these controls combine the stereo signal from the ste- reo input channel into a mono signal, and send it to mix buses 1–8. When the control is in the “▲” posi- tion, the level is nominal (0 db). Use the pre switch (m) to switch between pre/post fader. H m9...
Page 12
Control panel 12 n st (stereo) switch when this switch is on, the signal of the input channel will be sent to the (st) stereo bus. O bal (balance) control this sets the left/right balance of the signal that is sent from the input channel to the st bus. P on/edit switch/on, check indicators the funct...
Page 13
Control panel 13 variable/fixed select section the m3000’s ga (group/aux) diversity function allows mix buses 1–8 to function either as group buses or as aux buses. In this section, you can switch each pair of mix buses (1/2, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8) between functioning as group buses or as aux buses. A varia...
Page 14: Mix Section
Control panel 14 mix section these output channels control the signals of mix buses 1–16. Mix buses 13/14 and 15/16 are controlled as stereo pairs respectively. The signal that passes through these output channels is output individually from the mix out 1–16 jacks (page 27), and can also be sent to ...
Page 15
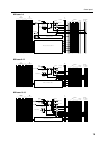
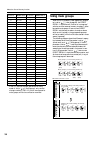
Control panel 15 mix buses 1–8 mix buses 9–12 mix buses 13–16 (sub)(st) from input mix 3-4, 5-6, 7-8: same as mix 1-2 mix 2: same as mix 1 to meter variable fix afl pfl l r on mas afl mas (mix) to matrix control on check on/edit mix out 1 afl to stereo pan to matrix mix insert i/o st r l l r mix (fi...
Page 16: Vca Master Fader Section
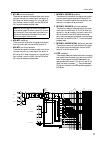
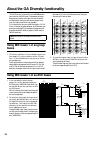
Control panel 16 vca master fader section the vca master fader section allows the gain of input channels assigned to a vca group to be controlled as a whole by the corresponding vca fader. The vca group(s) to which each input channel is assigned is specified by the vca group select switches (mono in...
Page 17
Control panel 17 a to matrix switch when this switch is on ( ), the st out a post- fader signal is sent to the matrix. B on/edit switch the function of this switch and indicator will depend on the mode of the m3000. ● in normal mode the on/edit switch will turn st out a on/off. When on, the on indic...
Page 18: Stereo B Section
Control panel 18 stereo b section this section controls the signal which is output from the rear panel st out b jacks (page 28) a level control this controls the output level of the signal which is sent from the st out b jacks. It does not affect the signal which is output from the st out a jacks. W...
Page 19: Monitor Section
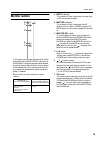
Control panel 19 monitor section in this section you can select the signal which will be monitored from the monitor out jacks and the phones jack. The following signals can be selected as monitor sources. Signal sources in priority group 1 can be selected at any time, and signal sources in pri- orit...
Page 20
Control panel 20 g level control this control adjusts the level of the signal which is output from the monitor out jacks. It does not affect the phones jack. H on switch this is an on/off switch for the signal which is output from the monitor out jacks. When this is on, the indicator located above t...
Page 21: Talkback Section
Control panel 21 talkback section a m1–m2 switch b m3–m4 switch c m5–m6 switch d m7–m8 switch e m9–m12 switch f m13–m16 switch g st switch these switches send the talkback or test tone oscillator signal to mix buses 1–2, mix buses 3–4, mix buses 5–6, mix buses 7–8, mix buses 9–12, mix buses 13– 16, ...
Page 22: Meter Select Section
Control panel 22 meter select section in this section you can select the source whose level will be shown in the meter bridge section. Only one of the sources 1–3 can be selected. A m1–m8 switch when this switch is turned on, the m1/m9/ matrix1–m8/m16/matrix8 meters (page 25) will show the output le...
Page 23
Control panel 23 a utility switch press this switch to enter utility mode, where you can make settings for scene memories and midi, etc. When you are in utility mode, the indicator located above the switch will light. B recall switch use this switch to recall scenes from scene memory. If you select ...
Page 24: Matrix Section
Control panel 24 matrix section the m3000 provides eight matrices which allow output signals from the mix buses 1–16 or the st bus, or input signals from matrix sub in to be mixed at the desired level. Matrix 1–8 are output in mono from matrix out jacks 1-8 respectively (page 27), and can be used as...
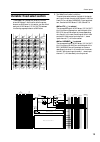
Page 25: Meter Bridge
Control panel 25 meter bridge a m1/m9/matrix1–m8/m16/matrix8 level meters as selected by the switch settings of the meter sel section (page 22), these meters indicate the output levels of mix out 1–8/mix out 9–16/matrix out 1–8. Each meter has a peak indicator which lights 3 db before peak level. B ...
Page 26: Rear Panel
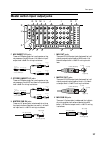
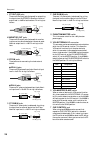
26 rear panel mono input channel input/out- put jacks a input jacks these are xlr-3-31 type input jacks (balanced). Nominal input level is –16 db ~ –60 db when the 26 db pad switch (page 6) is off, or +10 db ~ –34 db when the pad switch is on. When the rear panel phantom master switch and the phanto...
Page 27
Rear panel 27 master section input/output jacks f mix insert i/o jacks these are trs phone jacks for inserting external sig- nal processors into mix buses 1–16. Nominal input/ output level is 0 db. Pin wiring is as follows. G stereo insert i/o jacks these are trs phone jacks for inserting external s...
Page 28
Rear panel 28 l st out a/b jacks these are xlr output jacks (balanced) for outputting the signals from the stereo a/b sections. Nominal output level is +4 db for both sections. Pin wiring is as follows. M monitor out jacks these are xlr output jacks (balanced) for monitor- ing the monitor source sel...
Page 29: Tion Power Supply
Rear panel 29 u midi in/out/thru connectors these are standard five-pin midi connectors. By con- necting a sequencer or personal computer to these con- nectors, you can select scenes remotely, or backup scene memories. If two or more m3000 consoles are con- nected via midi, a scene selection on one ...
Page 30: Buses
30 about the ga diversity functionality the ga diversity functionality of the m3000 allows you to switch the mix buses 1–8 between acting as group buses (output level from the input channels will be fixed) or acting as aux buses (output level from the input channels will be variable). This functiona...
Page 31: What Is Scene Memory?
31 about the scene memory function what is scene memory? Scene memory is a function which stores the on/off status of the mono/stereo input channels and of mix buses 1–12, 13/14, 15/16 and st a as one of 128 “scenes.” a scene that has been stored can be recalled instantly at a touch of a switch. It ...
Page 32: Operations In Normal Mode
About the scene memory function 32 operations in normal mode storing a scene (normal mode) 1. Make sure that the m3000 is in normal mode, and use the on/edit switches of the mono/ste- reo input channels, the mix section and the ste- reo a section to make the desired on/off settings. 2. Use the scene...
Page 33: Operations In Check Mode
About the scene memory function 33 operations in check mode in check mode you can verify the settings of a scene before recalling it, or edit the on/off status of the on/ edit keys without affecting the internal audio sig- nals. To move from normal mode to check mode, press the check switch in the s...
Page 34: Operations In Utility Mode
About the scene memory function 34 operations in utility mode in utility mode you can modify various settings related to scene memory operations. Operations such as bulk out and bulk dump request are also per- formed in this mode. Basic operation in utility mode 1. When the m3000 is in normal mode, ...
Page 35: Control Change Table
About the scene memory function 35 responding program change message will be transmit- ted. If this is set to “ ” (local), the corresponding program change will be transmitted even when you select a scene for which data has not been saved, thus allowing you to select programs on an external device. ...
Page 36: Using Mute Groups
About the scene memory function 36 • if the cc (control change) parameter of utility mode is set to “ ” (mute group), only control change numbers (105–112) which correspond to mute groups will be transmitted or received. Using mute groups when the utility mode op (recall operation) parame- ter is se...
Page 37: Adding/defeating Mute Groups
About the scene memory function 37 adding/defeating mute groups 1. Store the channel or bus mute settings that you wish to use as a mute group in a memory num- ber 1–8. 2. In utility mode, select the op (recall operation) item, and switch the display to “ .” (for details refer to page 34.) 3. Either...
Page 38: About The Vca Functionality
38 about the vca functionality the vca master section of the m3000 contains eight vca master faders. These vca master faders 1–8 can be used to control the overall input level of input channels assigned to the corresponding vca groups 1–8. If you wish to use the vca functionality, set the rear panel...
Page 39: To Control A Single Channel
About the vca functionality 39 using two or more vca master faders to control a single channel as the opposite of the example on the previous page, it is also possible to assign a channel to two or more vca groups. The following diagram shows an exam- ple of signal flow when channel 1 is assigned to...
Page 40
About the vca functionality 40 • if the vca mute switch of a vca master fader is turned on (the indicator beside the switch will light), the post-fader signal of all input channels assigned to that vca group will be muted. This is convenient when you wish to simultaneously mute or un-mute multiple c...
Page 41: Error Messages
41 error messages one of the following error messages may appear in the memory display while operating the m3000 or when the power is turned on. If this occurs, refer to the following explanations and take the appropriate action. (* is an error number) an error occurred while receiving midi data. If...
Page 42: Specifications
42 specifications general specifications 0 db is referenced to 0.775 vrms. Total harmonic distortion less than 0.1% (thd+n) (master output) 20 hz–20 khz @ +14 db 600 Ω less than 0.05%(2nd-10th) 20 hz–20 khz @ +14 db 600 Ω frequency response 0+1, –3 db (master output) 20 hz–20 khz @ +4 db 600 Ω hum &...
Page 43: Input/output Characteristics
Specifications 43 input/output characteristics input specifications • 0 db=0.775 vrms. *1 xlr connectors are balanced. *2 xlr connector is unbalanced. *3 phono jacks are unbalanced. *4 sub in phone jacks(trs) are unbalanced(t=signal, r=gnd, s=gnd). *5 insert phone jacks(trs) are unbalanced(t=output,...
Page 44: Other
Specifications 44 other connector wiring dc power input vca external i/o included items power supply connection cable (3 m, 10 pin) pin no. Signal name 1 power supply remote 2 +15 v 3 ± 15 v gnd 4 +48 v gnd 5 –15 v 6 +12 v 7 +12v gnd/ power supply remote 8 power supply remote 9 +48 v 10 frame gnd pi...
Page 45: Dimensions
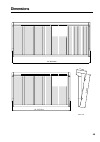
45 d: 874 h: 265 w: 2043/40ch w: 1515/24ch units: mm dimensions.
Page 46: Midi Data Format
46 midi data format 1. Midi channel the same channel is used for transmission and recep- tion. Select from channel numbers 1–16. 2. Midi program change program change numbers 0–127 correspond to scene memory numbers 1–128. This correspondence can- not be changed. However when mute group is selected,...
Page 47: Idi Implementation
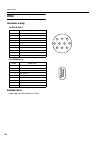
47 idi implementation chart m yamaha [mixing console] date:apl/08, 1998 model : m3000 midi implementation chart version : 1.0 function... Transmitted recognized remarks basic default 1 - 16 1 - 16 memorized channel changed 1 - 16 1 - 16 default x omni off/omni on memorized mode messages x x altered ...
Page 48
V302330 r2 1 ap 148 np printed in taiwan yamaha corporation pro audio division, #18/3 p.O. Box 3, hamamatsu, 430-8651, japan.