- DL manuals
- Yamaha
- Music Mixer
- PM 5000
- Owner's Manual
Yamaha PM 5000 Owner's Manual
Summary of PM 5000
Page 1
Owner's manual e.
Page 2
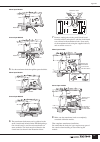
The above warning is located on the rear of the unit. Explanation of graphical symbols the lightning flash with arrowhead symbol within an equilateral triangle is intended to alert the user to the presence of uninsulated “dangerous voltage” within the product’s enclosure that may be of sufficient magn...
Page 3: Precautions
Precautions please read carefully before proceeding * please keep this manual in a safe place for future reference. Warning always follow the basic precautions listed below to avoid the possibility of serious injury or even death from electrical shock, short-circuiting, damages, fire or other hazard...
Page 4
• before connecting the device to other devices, turn off the power for all devices. Before turning the power on or off for all devices, set all volume levels to minimum. • do not insert your fingers or hand in any gaps or openings on the device (vents, etc.). • avoid inserting or dropping foreign o...
Page 5: Fcc Information (U.S.A.)
* this applies only to products distributed by yamaha corporation of america. (class b) advarsel! Lithiumbatteri—eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering. Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri af samme fabrikat og type. Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandoren. Varning explosionsfara vid felak...
Page 6: Foreword
Foreword 6 foreword thank you for choosing a yamaha pm5000 mixing console. The pm5000 is the proud successor to the highly acclaimed yamaha pm4000, which became the definitive sound reinforcement console of the preceding decade in terms of both performance and features. The pm5000 carries on the pm-s...
Page 7: About This Manual
About this manual 7 about this manual general approach most of this manual is devoted to describing the features and functions of the various pm5000 modules. Since the operational design of the pm5000 is based on familiar analog console principles, anyone who is familiar with the pm4000 or similar c...
Page 8: Contents
8 contents foreword 6 about this manual 7 general approach ....................................... 7 the pm5000 models .................................... 7 pm5000 overview 10 panel layout .............................................. 10 top panel .....................................................
Page 9
9 monitor control section 40 monitor source........................................... 40 the monitor outputs.................................. 41 cue signal monitoring............................... 41 solo mode................................................... 44 cue and solo .......................
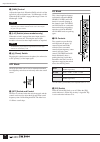
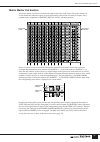
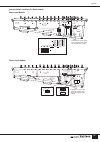
Page 10: Panel Layout
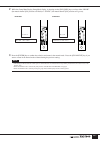
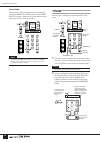
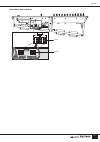
Pm5000 overview 10 panel layout the layout of the pm5000’s functional sections in the basic configuration is shown below. In the pm5000- 52c the master output section is located in the center of the console, while in all other models it is located to the right of the console. Top panel pm5000 overvie...
Page 11
11 pm5000 overview 1 input channel section (page 15) two types of input channels are provided – mono and stereo – but the basic block structure of each is the same. After going through phantom power, input gain, phase reversal, and high-pass filter stages, the audio signal passes through a 4-band equ...
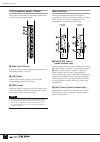
Page 12: Rear Panel
12 pm5000 overview 7 mute master section (page 21) the 8 [mute master] switches can be used to mute specified input channel groups, or as [direct recall] switches for the scene memory. Whether these switches function in the mute master or direct recall mode is specified via a utility mode function. 8 ...
Page 13
13 pm5000 overview ! Mono (stereo) inputs xlr-type input connectors, direct out connectors, and insert in and out connectors are provided on each input channel. Stereo modules feature separate connectors for the l and r channels, but do not have direct out connectors. @ sub inputs each stereo aux ma...
Page 14
14 pm5000 overview expansion:connecting to external equipment the pm5000 is entirely self-contained and can be used effectively on its own, but it does provide some versatile expansion capabilities. In this section we’ll describe how the pm5000 can be synchronized with external gear and cascaded wit...
Page 15: Input Channel Section
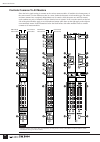
15 input channel section mono and stereo input modules mono and stereo input modules make up the console’s input channel section. In essence each stereo module contains two parallel mono signal paths, and the panel controls control both channels simultaneously. Head amp block initial adjustment of t...
Page 16
16 input channel section 3 [gain] control adjusts the input level. When the [pad] switch is off the input level can be adjusted from –10 db through –60 db. When the [pad] switch is engaged the range is from +16 db through –34 db. 4 [l+r] switch (stereo modules only) when this switch is engaged the s...
Page 17
17 input channel section insert block these switches are used to determine whether and where external processing gear connected to the rear-panel insert in and out connectors will be inserted into the channel signal path. 9 insert [on] switch turns channel insert on or off. When the [on] switch is e...
Page 18
18 input channel section g/a (group/aux) send 1~8 block these controls determine how the channel signal is sent to the console’s 8 group/aux buses. $ send level controls adjust send level to the corresponding group/aux bus (0 db at approximately 2 o’clock). % [on] switch when an [on] switch is engag...
Page 19
19 input channel section ( main out switches determine where the post-fader channel signal will be sent. To assign the channel signal to the stereo bus engage the [st] switch and use the [pan] & or [bal] * control to adjust the stereo image. To send the signal to the mono bus engage the [mono] switc...
Page 20
20 input channel section channel fader block the channel faders determine the level of the channel signal sent to the console’s master buses, and are of primary importance in setting up the balance between the various channels in the mix. The channel faders can also be assigned to specific vca and mu...
Page 21: Channel Grouping
21 input channel section channel grouping this section will describe how channels can be assigned to vca and mute groups. Vca grouping the pm5000 provides two methods of “grouping” input channels so that they can be controlled via a single master fader while maintaining the level relationship betwee...
Page 22
Input channel section 22 vca group assignment procedure 1 press the assign mode [vca] key to initiate the assignment procedure (the indicator will flash). 2 engage a vca master [cue] switch to specify the vca master to which a channel or multiple channels are to be assigned. The [cue] switch will flas...
Page 23
Input channel section 23 mute group assignment procedure 1 press the assign mode [mute] key to initiate the assignment procedure (the indicator will flash). 2 engage a mute master ([1] ~ [8]) switch to specify the muter master to which a channel or multiple channels are to be assigned. The mute maste...
Page 24
Input channel section 24 vca master and master mute switch group control if a number of input channels are assigned to vca masters or mute master switches as described in the preceding section, those channels can be controlled as a group from a single fader or mute switch. Vca section vca master fad...
Page 25
Input channel section 25 the vca 1 ~ vca 12 [cue] switches function as group cue switches for all assigned input channels. When a vca master [cue] switch is engaged it will light, while the [cue] switches of all assigned channels will flash, and the signals from those channels will be routed to the c...
Page 26
25 -1 group mute channel [on] switch indication mode when the channels assigned to a mute master ([1] ~ [8]) switch are muted, the [on] switches of the muted channels can be set to either flash or go out entirely. Flashing is the initial default setting. 1 enter the group mute display setup mode by t...
Page 27
25 -2 2 while the group mute display setup mode display is showing use the [inc]/[dec] keys to select either “blink” (the muted channel [on] switches will flash) or “static” (the muted channel [on] switches will go out). 3 press the [enter] key to confirm the selection and restart in the normal mode. ...
Page 28: Multiple Masters In
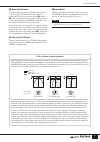
26 master out section multiple masters in single modules the master output section is made up of modules housing the masters for 12 stereo aux buses, 8 g/a (group/aux) buses, a stereo bus, and a mono bus. Both the stereo aux and g/a master modules combine pairs of adjacent masters – odd and even num...
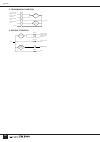
Page 29: Basic Signal Routing
Master out section 27 basic signal routing in the same was as the input channel modules, the only real difference between the stereo aux, g/a, stereo, and mono masters is whether they are mono or stereo. The basic routing is the same for all signals, as summarized in the diagrams below. Each master ...
Page 30
Master out section 28 controls common to all masters since the basic signal routing is common to the various master modules, all modules also feature many of the same controls. It is the differences that, in a sense, define the character of each module type. The stereo and mono masters have completel...
Page 31
29 master out section 1 [to matrix] switch when this switch is engaged the signal from the corresponding master is sent to the stereo and mono matrix. The matrix send is derived after the master fader and master [on] switch. Because of this the master [on] switch must be engaged in order to send the...
Page 32: Stereo Aux Master Module
30 master out section stereo aux master module refer to the preceding “controls common to all masters” section for descriptions of the stereo aux master controls not included in this section. 5 [l+r] switch engaging this switch sums the corresponding premixed stereo signal to a mono signal which is ...
Page 33
31 master out section g/a (group/aux) master module refer to the preceding “controls common to all masters” section for descriptions of the g/a master controls not included in this section. ) [to st] switch ! [pan] control @ [to mono] switch when the [to st] switch is engaged the post-fader is sent ...
Page 34
Master out section 32 group/aux switching the g/a modules are all dual types that can be set for group post pan (stereo master), group pre pan (dual mono master), or aux (dual mono master) operation. The current mode of each g/a module is shown by the g/a bus mode indicators. When the g/a bus mode i...
Page 35
33 master out section cue operation differences in the g/a bus modes the way the g/a master signal is sent to the cue buses varies according to the selected g/a bus mode. When the group pre pan or aux mode is selected adjacent g/a master channels function independently and the same signal is sent to...
Page 36
Master out section 34 stereo and mono master modules refer to the preceding “controls common to all masters” section for descriptions of the stereo and mono master controls not included in this section. Compared to the stereo aux and g/a master modules just described, the stereo and mono masters are...
Page 37: Matrix Send Section
Matrix send and master out section 35 matrix send section the matrix send section is located at the top of the console’s master out section. From the hardware standpoint it is a “matrix send block” fed by the outputs of the various master modules, but from an operational perspective it is a separate...
Page 38
Matrix send and master out section 36 the level and balance of signals sent from the mono masters (group/ aux, mono) a stereo matrix can be adjusted via the inner and outer controls, respectively. Stereo signals from stereo masters (stereo aux, stereo) sent to a mono matrix are internally mixed to m...
Page 39: Matrix Master Out Section
Matrix send and master out section 37 matrix master out section the matrix master out section is located to the right of the matrix send section. The matrix master out section determines where the signals received at the matrix send section will finally be output, with a comprehensive complement of [...
Page 40
Oscillator and talkback section 38 the oscillator and talkback sections, located to the right of the master section, are independent. The oscillator section is capable of generating pink noise or sine-wave signals for testing and system setup via the tb bus, while the talkback section can be used to...
Page 41
39 oscillator and talkback section oscillator/talkback signal output the oscillator is capable of producing continuous or burst-output pink noise, or sine wave signals from 20 hz through 20 khz. Engage the oscillator section [pink] switch to generate pink noise. If the [sweep/burst] switch is off th...
Page 42: Monitor Source
40 monitor control section monitor source the monitor out section controls output to the consoles two monitor outputs (monitor a & b out) as well as to the headphone jacks. Three sources can be selected for monitoring: the stereo master signal, input from the 2-track inputs (2tr in 1 & 2), and cue. ...
Page 43: The Monitor Outputs
41 monitor control section the monitor outputs the two monitor outputs can be used independently or simultaneously. When using monitor a and b at the same time, the [lcr] switch can be engaged to allow the monitor b l channel to function as the c (center) channel for lcr monitoring in conjunction wi...
Page 44
Monitor control section 42 when a channel [cue] switch is operated directly the channel’s pre-fader signal will be sent to the monitor outs regardless of whether the channel [on] switch is engaged or disengaged. In contrast to this situation, cue monitoring of input channels via the vca section is a...
Page 45
43 monitor control section the cue points for all masters can be switched at once. To monitor the pre-master-fader signals engage the [master pfl] switch, or disengage it to monitor the post-monitor-fader signals. In the latter case if the “pre on” cue point is selected (before the master [on] switc...
Page 46: Solo Mode
Monitor control section 44 solo mode cue and solo the terms “solo” and “cue” monitoring are often used interchangeably, and in some cases they are actually the same thing. In the pm5000 and most other sound-reinforcement consoles, however, “cue” is a signal sent to the operator’s monitor speakers wh...
Page 47
45 monitor control section basic operation the solo mode can be activated by holding the [solo mode] switch on the meter bridge for more than two seconds – the [solo mode] switch will flash. For reasons why you might not be able to switch to the solo mode, see page 66. No change in the output signal ...
Page 48
46 monitor control section master solo select with complex, large-scale setups, the basic method of using individual [cue] switches to check the sends to the main house speakers, sub-speakers, on-stage monitors, recording equipment and other gear can be confusing and tedious. The master solo functio...
Page 49: Meter Bridge
Monitor control section 47 meter bridge the pm5000 meter bridge features precise bar-graph meters that display the signal levels at the master outs (stereo aux, group/aux, stereo, mono), matrix outs (stereo, mono), cue (l/c/r), and the talkback/ oscillator bus, from –39 db to peak level in 3-db incr...
Page 50
48 monitor control section the meter bridge also features independent dimmer controls for the meters, panel switch illumination, and gooseneck lamps, as well as a [lamp off] switch for the gooseneck lamps. Confirmation leds are also provided for the phantom power supply and other power-supply voltage...
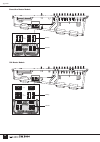
Page 51: Control Functions
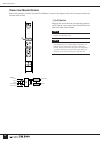
49 digital control section control functions the digital control section includes the majority of functions used for digital control of the pm5000 scene memory and utility features. Digital control section 1 5 2 4 3 8 9 6 7 @ ! # $ % 9 ).
Page 52
50 digital control section 1 scene display (3 digits + 3 dots) when the pm5000 scene memory function is active the current (last recalled) scene memory number – 000 ~ 999 – is shown on this display. The three display dots indicate the status of the current scene as follows: left dot: the scene conta...
Page 53: Scene Memory Functions
51 digital control section scene memory functions overview a “scene” is a set of panel settings stored in one of the pm5000’s 1,000 internal scene memories (000 ~ 999). Any stored scene can be instantly recalled at any time for fast efficient changes. The first 10 scene memories (000 ~ 009) contain pr...
Page 54
52 digital control section fade time fade time settings can be used to create smooth transitions between recalled scenes. The fade time specified for a scene is common to all channel and vca faders, but you can individually specify the faders to which the fade time will apply. The procedure for setti...
Page 55
53 digital control section scene store the following procedure stores the panel settings along with the current fade time settings (set as described in the preceding section). 1 specify the scene memory number to which the scene is to be stored (010 ~ 999). The desired scene number can be directly e...
Page 56
54 digital control section recall undo the previous scene recall operation can be undone by pressing the [recall undo] switch. If the [undo recall] switch is then pressed a second time the pre- undo state will once more be recalled. Title edit titles of up to 12 characters can be entered for each sc...
Page 57
55 digital control section 3 when the [enter] key is pressed to confirm and enter the title, the [title] switch indicator will go out and the scene number will revert to that of the current scene (if the title of the current scene was edited after the scene was stored, the scene number will not chang...
Page 58: Utility Functions
56 digital control section 3 press the [enter] key to confirm the selected scene number and the scene number will light continuously. At the same time the scene settings will be reproduced by the panel controls but no change will occur in the console’s audio output. 4 if necessary, change the fader a...
Page 59
57 digital control section common operations all utility functions are accessed and edited by using the alpha-numeric keypad, [clear/exit] key, [enter] key, and [inc] and [dec] keys while checking functions and values on the scene display, message display, and parameter display. 1 press the [utility...
Page 60
58 digital control section 4 when a parameter that can be edited is selected, the first editable parameter will appear flashing on the display. Use the [inc] and [dec] keys or the alpha- numeric keypad to edit the value as required, and then press [enter]. When available, the next editable value will ...
Page 61
59 digital control section date/time (parameter no. U02) this is the date and time maintained by the pm5000’s internal clock. The date and time parameters are used to time-stamp scene memory and other data saved to external compactflash memory cards. 1 press [enter] after selecting the above display...
Page 62
60 digital control section ● format 2 if you selected fmt and pressed [enter] in step 1, above, the following confirmation message should appear. 3 press the alpha-numeric [1] key to begin formatting the card, or [3] to abort the operation. Never remove a memory card from the card slot during a forma...
Page 63
61 digital control section 4 press the alpha-numeric [1] key to begin loading the file, or [3] to abort the operation. Never remove a memory card from the card slot during a load operation. The following display will appear while the data is being loaded. ● data delete 2 after selecting del and press...
Page 64
62 digital control section memory protect (parameter no. U05) this function can be used to temporarily protect the scene memory from being overwritten (only the recall operation is available). 1 press [enter] after selecting the above display and one of the displays shown below will appear: either o...
Page 65
63 digital control section copy scene: the contents of the target (“trg”) scene memory are copied to the destination (“dst”) scene number. This is similar to a copy-and paste operation on a personal computer. Insert scene: inserts a “no data” scene immediately before the specified target (“trg”) scen...
Page 66
64 digital control section 2 use the [inc] and [dec] keys to select grp post (group stereo), grp pre (group mono) or aux, and the press the [enter] key. The following confirmation message will appear on the parameter display. 3 press the alpha-numeric [1] key to execute the selected operation, or [3]...
Page 67
65 digital control section safety and protection functions this category includes a number of “recall safe” functions that can be set to protect specific parameters when a scene is recalled, thus maintaining the settings of the protected parameters. There’s also a solo safe function that can prevent ...
Page 68
66 digital control section recall safe select (parameter no. U11) each input, vca master, master out, and matrix out channel on the pm5000 features [recall safe] and [fader safe] switches that can be used to protect all of the corresponding channel’s settings or just the fader setting from scene rec...
Page 69
67 digital control section input solo safe (parameter no. U13) the pm5000 allows independent solo monitoring for the input channel, vca and master sections: when the solo mode is active only channels on which the [cue] switch is engaged are output while all other channels are muted. The input solo s...
Page 70
68 digital control section monitor delay (parameter no. U15) when the monitor speakers are located a significant distance from the main house speakers the resulting delay between the two sources can severely reduce the intelligibility of the sound. In such situations the pm5000’s internal digital del...
Page 71
69 digital control section master cue afl position (parameter no. U16) the cue signal from each master section can be switched to pre- or –post-fader via the [master pfl] switch in the monitor control section (page 43). This function determines whether the cue signal is taken from before or after th...
Page 72
70 digital control section fader mode (parameter no. U18) normally the console’s motor fader system will physically move the faders to recalled settings when a scene recall or preview operation occurs. This function makes it possible to defeat the motor-drive system so that the faders do not move wh...
Page 73
71 digital control section direct recall/ mute master (parameter no. U20) in addition to their normal function as mute master switches, the console’s 8 mute master switches can also be used as direct recall switches for scene recall. In this case the scene numbers to be recalled by each direct recal...
Page 74
72 digital control section gpi the pm5000’s rear-panel gpi port provides 3 input and 8 output channels for gpi pulse communication with external equipment. One of the input channels controls talkback on/off (same function as the tb [on] switch). One of the functions in this section determines whethe...
Page 75
73 digital control section ● fader start 1 after selecting fader start and pressing the [enter] key a display like the one shown below will appear. The example display indicates that the input channel 34 fader (“ch34”) will produce a signal at gpi output number 3 (“gp3”) when fader is raised above –...
Page 76
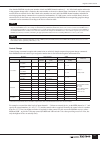
Digital control section 74 cascade the pm5000 allows cascade connection to other consoles for master-slave operation. Two types of cascade connection are possible: type “a” for cascade connection of two pm5000 consoles, and type “b” for connection to pm4000/3500 series consoles (in the latter case t...
Page 77
Digital control section 75 linked functions when two pm5000 consoles are cascaded for channel expansion complete functional linking can be achieved as well (you can specify which functions are to be linked as described below). It is advisable only to link the functions you intend to use, however, to...
Page 78
76 digital control section cascade (parameter no. U23) to allow fuss-free type a connection of pm5000 consoles, the pm5000 is shipped from the factory with all of the function links listed in the above chart on. If you want to turn some of these off, use the following parameter on the slave pm5000. ...
Page 79
77 digital control section midi the midi in, out, and thru connectors provided on the rear panel allow pm5000 operation to be linked to external midi devices. If the pm5000 midi out connector is connected to the midi in connector of an external device, the external device can be controlled by operat...
Page 80
78 digital control section program change the pm5000 employs a number of “strategies” to ensure full functionality with the standard midi implementation. For example, in order to be able to handle recall of all 1,000 pm5000 scenes via midi program change commands, bank select commands (a type of con...
Page 81
Digital control section 79 note that the pm5000 uses the same number of bank and midi channel numbers (1 ~ 16). If the bank number referred to in the program change table is limited to the same number as the receive channel, then a maximum of 128 scenes can be recalled from an external device. But i...
Page 82
80 digital control section ● nrpn control in the pm5000 nrpn (non-registered parameter number) data can be used for the same control functions as control change commands. Nrpn is actually a subset of the midi control change numbers (cc#99, 98), and is commonly employed to allow system exclusive data...
Page 83
81 digital control section midi control change (program no. U25) the functions in this section determine whether the pm5000 sends and receives control change commands, as well as whether nrpn will be enabled. 1 press [enter] after selecting the above display and a display like the one shown below wi...
Page 84
82 digital control section 2 use the [inc] and [dec] keys to set the selected parameter as required. 3 set the other functions as required. Midi echo back (parameter no. 27) independently determines whether program change and control change commands internally generated by the pm5000 will be mixed w...
Page 85
83 digital control section midi program change table (parameter no. 28) the program change table determines the correspondence between the pm5000 scene numbers and the program change numbers that will be received and transmitted. The table itself is a simple combination of midi channel/bank number, ...
Page 86: Appendix
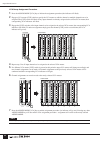
84 appendix installing options and changing internal switch settings please refer module installation and internal setting changes to your yamaha dealer or one of the yamaha service centers. The following optional (sold separately) modules and transformer are available: ● input section modules • mnm...
Page 87
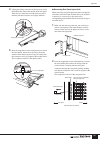
85 appendix 4 unplug the wiring connectors at the top (rear) end of the module that connect the module to the rear panel. There are two connectors on both mono and stereo modules, but their locations are slightly different. 5 press the snap button on the wiring harness to release the wire bundle, th...
Page 88
86 appendix ● module installation the module installation procedure is the reverse of the removal procedure described above. Rear panel input units first pass the wiring through the opening in the rear panel and pull it through to the open module area. Then attach the rear-panel unit with two screws...
Page 89
87 appendix mono input module stereo input module 5 pass the transformer leads through the square lead hole. Mono input module stereo input module 6 the transformer leads must now be soldered to the small circuit board included in the itr5000 package. One circuit board is used for each transformer o...
Page 90
Appendix 88 internal switch settings for each module as you tell from the pm5000 block diagram, each module has a number of internal switch settings. These settings can be changed to “customize” the pm5000 signal flow to most ideally suit your mixing requirements. The chart below lists the switches a...
Page 91
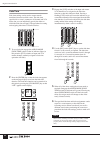
Appendix 89 internal switch locations on each module mono input module stereo input module pre pre pre post post post sw107 jb j sw106 sw105 aux pre post/pre eq direct out pre f ader / post f ader, post on sw direct out pre eq / post eq jb j18 remove these screws and the bracket. Replace after makin...
Page 92
Appendix 90 stereo/aux master module g/a master module staux.Ga (odd) staux.Ga (even) fader on sw to matrix pre post pre post pre post pre post fader on sw printing switches sw106 sw105 sw103 sw102 sw106 sw105 sw103 sw102 ga (odd) staux.Ga (odd) staux.Ga (even) to st to matrix ga (even) on sw post p...
Page 93
Appendix 91 stereo/mono master module fader on sw mono master st master to matrix pre post pre post pre post pre post fader on sw sw102 sw103 sw105 sw106 sw102 sw103 sw105 sw106 printing switches.
Page 94: Connector Pin Assignments
92 appendix connector pin assignments the connector diagrams refer to the console connectors. Cascade connector these are the cascade connector pin assignments for the pm5000 as well as the pm4000/3500 series consoles that can be cascade-connected to the pm5000. Pm5000 cascade type b pin assignments...
Page 95
93 appendix pm5000 self-diagnostic function the pm5000 automatically performs a battery of internal tests when the power is turned on. If no problems are encountered the scene number will appear on the display and normal operation will be possible. If a system or other internal error is found consol...
Page 96: Error Messages
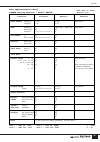
Appendix 94 error messages any of the following messages appearing on the 4-character message display indicate that an error has occurred. Refer to the information listed below in combination with the “troubleshooting” section on next page. Error message meaning action startup error [h.Er] fatal har...
Page 97: Troubleshooting
Appendix 95 troubleshooting symptom possible cause & solution power won’t turn on. Panel displays and illumination won’t light. • is the dedicated pw5000 properly connected via the supplied power cable? • is the pw5000 [power on/off] switch in the on position? • is the [panel led dimmer] control on ...
Page 98: Specifications
Appendix 96 specifications 1. General specifications 0dbu is referenced to 0.775 vrms. Total harmonic distortion (master output) less than 0.1% (thd+n) 20hz-20khz @ +14dbu 600 Ω (input gain control at maximum) frequency response (master output) 0+1,-3db 20hz-20khz @ +4dbu 600 Ω (input gain control a...
Page 99
Appendix 97 *1 hum & noise are measured with a 6db/octave filter @ 12.7khz; equivalent to a 20khz filter with infinite db/octave attenuation. Temperature condition @+10 - +25°c *2 pan/bal: the left or the right turning around. *3 turn over /roll-off frequency of shelving: 3db below maximum variable lev...
Page 100
98 appendix 2.2 output characteristics *1 24ch, 32ch, 48ch *2 all xlr connectors are balanced, phone jacks (trs) are balanced (t=+, r=-, s=gnd). Phone jacks (stereo) are unbalanced. *3 0dbu is referenced to 0.775vrms. 2.3 others 3. Others 3.1 included accessories power supply connection cable (3.6m)...
Page 101: Midi Data Format
99 appendix midi data format 1. Transmit/receive data 1.1 channel message 1.1.1 control change (bn) bank select in single mode when bank is on, this message can be received if the rx ch matches. This will specify the bank for a subsequently received program change. In single mode when bank is on and...
Page 102
100 appendix 2. Transmission condition 3. Receive condition midi tx ch? Control change bank select $bnh control change $bnh control change nrpn $bnh midi in bank on nrpn on assign on echo on midi out program change $cnh pgm on midi tx ch? Or multi on midi rx ch? Control change bank select $bnh contr...
Page 103
Appendix 101 transmit function receive remarks basic channel note number velocity after touch pitch bend control change program change system exclusive system common system real time aux messages notes mode default changed note on note off key’s ch’s clock commands local on/off all notes off active ...
Page 104: Index
102 index index symbols [+48v] switch ...................................................................... 15 +48v master switch ............................................................. 13 ∑·peak indicators ............................................................... 29 [ø] (phase) switch ...
Page 105
103 index midi ...............................................................................14 , 77 midi channel ....................................................................... 78 midi control change .......................................................... 81 midi echo back ................
Page 106
For details of products, please contact your nearest yamaha representative or the authorized distributor listed below. Pour plus de détails sur les produits, veuillez-vous adresser à yamaha ou au distributeur le plus proche de vous figurant dans la liste suivante. Die einzelheiten zu produkten sind b...