- DL manuals
- Yamaha
- Controller
- TS-P
- User Manual
Yamaha TS-P User Manual
Summary of TS-P
Page 1
Ts series userʼs manual ts-s/ts-s2/ts-sh/ts-x/ts-p yamaha single-axis robot controller ver. 2.04 epm0159204 e119.
Page 3: Contents
Contents ts series user’s manual t-1 important information before reading this manual introduction i main functions ii about this manual iii safety alert symbols and signal words iv ce marking v 1. Safety standard v 2. Safety measures v 3. Robot safety measures vi 4. Emc countermeasure example vi sa...
Page 4: Contents
Contents ts series user’s manual t-2 t-3 3.2 power supply connection ts-x ts-p 2-7 3.3 malfunction prevention measures ts-x ts-p 2-10 4. Connecting the robot 2-11 5. Connecting the communication unit 2-13 6. Connecting the regenerative unit ts-x ts-p 2-15 6.1 connecting the rgt ts-x ts-p 2-15 6.2 co...
Page 5: Contents
T-2 contents ts series user’s manual t-3 3. Point data details 3-5 4. Parameter data 3-9 4.1 parameter list 3-9 4.1.1 run parameters 3-9 4.1.2 i/o parameters 3-10 4.1.3 option parameters 3-10 4.1.4 servo parameters 3-11 4.2 parameter details 3-11 4.2.1 run parameters 3-11 4.2.2 i/o parameters 3-14 4...
Page 6: Contents
Contents ts series user’s manual t-4 t-5 2.2 origin point detection method ts-p 5-7 2.3 origin point and coordinates relationship 5-10 2.4 return-to-origin timing chart 5-10 3. Positioning operation 5-11 3.1 basic operation 5-11 3.2 positioning timing chart 5-14 3.3 positioning merge operation 5-16 ...
Page 7: Contents
T-4 contents ts series user’s manual t-5 7.5 stop mode ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh 5-49 7.6 magnetic pole position estimation ts-p 5-49 8. Led status indicators 5-50 9. Ts-monitor (option) ts-x ts-p 5-51 9.1 part names and functions 5-51 9.2 opening or closing the ts-monitor 5-51 9.3 changing the screen 5-52 9...
Page 8: Contents
Contents ts series user’s manual t-6 t-7 4. Regenerative unit specifications 7-12 4.1 dimensional outlines (rgt) 7-12 4.2 dimensional outlines (rgu-2) 7-12 ht1 operation guide introduction a-1 1. What the ht1 does a-2 1.1 ht1 panel layout a-3 1.2 connecting to the external safety circuit (ht1-d) a-5...
Page 9: Contents
T-6 contents ts series user’s manual t-7 7. Monitor functions a-31 7.1 i/o monitor a-31 7.2 status monitor a-32 7.3 run monitor a-33 7.4 alarm display a-34 7.5 warning display a-34 7.6 message display a-35 7.7 alarm record display a-36 7.8 information display a-37 8. Other functions a-38 8.1 operati...
Page 10: Contents
Contents ts series user’s manual t-8 t-9 point data writing 1 (m, p, s, ac, dc, q, zl, zh, n, j, f, t) b-9 point data writing 2 (p_, s_, ac_, dc_, q_) b-10 current position teaching (teach) b-11 point data copying (copy) b-11 point data deleting (del) b-12 parameter data writing (k) b-12 automatic n...
Page 11: Contents
T-8 contents ts series user’s manual t-9 1.1 installation d-2 1.2 wiring d-2 2. Initial setting d-3 2.1 node number setting d-3 2.2 enable setting d-3 3. I/o interface specifications d-4 3.1 configuration d- 4 3.2 cc-link type d-5 3.3 ethernet/ip type d-6 4. Data setting and operation d-7 4.1 restri...
Page 13: Contents
Contents introduction i main functions ii about this manual iii safety alert symbols and signal words iv ce marking v 1. Safety standard v 2. Safety measures v 3. Robot safety measures vi 4. Emc countermeasure example vi safety cautions ix warranty xii important information before reading this manua...
Page 15: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual i introduction thank you for purchasing the ts series robot controller (hereafter referred to simply as "controller"). Please read this manual carefully to ensure correct and safe use of this controller. This manual explains four controller models,...
Page 16: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual ii main functions the following table shows the main functions of the controller. Function explanation reference section positioning operation moves the robot slider to the specified position. There are 4 types of position operation: 1. Positioning...
Page 17: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual iii about this manual this manual is divided into 3 main parts: safety cautions, controller guide, and a supplement (ht1 operation guide, communication command guide, daisy chain guide). In order to use the controller and optional devices in an eff...
Page 18: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual iv safety alert symbols and signal words the following safety alert symbols and signal words are used in this manual to describe safety concerns, handling precautions, prohibited or mandatory action and key points when using this product. Make sure...
Page 19: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual v ce marking 1. Safety standard cautions regarding compliance with ec directives n the yamaha robot (robot and controller) is not, in itself, a robot system. The yamaha robot is just one component that is incorporated into the customer's system (bu...
Page 20: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual vi 3. Robot safety measures electrical shock prevention measures n use the protective ground terminal in order to ensure safety with regard to electrical shocks. For details, refer to the robot's operation manual. 4. Emc countermeasure example rega...
Page 21: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual vii • countermeasure components (1) surge absorber always install an external surge absorber to protect the controller from surge noise that may be generated by lightning. A recommended surge absorber is shown below. • recommended surge absorber ma...
Page 22: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual viii (2) noise filter always install an external noise filter to reduce conduction noise to the power supply line. A recommended noise filter is shown below. • recommended noise filter manufacturer : cosel co., ltd. Type no. : nap-10-472 terminal b...
Page 23: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual ix safety cautions the controller was designed and manufactured with ample consideration given to safety. However, incorrect handling or use may lead to injury, fire, electrical shocks, or other accidents or equipment failures. To prevent possible ...
Page 24: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual x • installation environment provide ample space to ensure that tasks (teaching, inspections, etc.) can be performed safely. Failing to provide adequate space makes tasks difficult to perform, and can cause injuries. Secure the equipment firmly to ...
Page 25: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual xi • operation and handling do not remove the controller or ht1 covers, and do not attempt to disassemble or modify them. Doing so could result in fires or equipment failure. Do not touch or operate the controller or ht1 with wet hands. Doing so co...
Page 26: Important Infor
Important infor mation befor e r eading this manual xii warranty for information on the warranty period and terms, please contact our distributor where you purchased the product. This warranty does not cover any failure caused by: n 1. Installation, wiring, connection to other control devices, opera...
Page 27: Chapter 1
Chapter 1 overview contents 1. Unpacking check 1-1 2. Part names and functions 1-2 3. System configuration 1-5 4. Installation and operation sequence 1-6.
Page 29: Verview
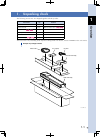
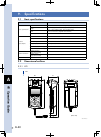
1-1 1 o verview 1. Unpacking check the following accessories are shipped together with this product. Accessories qty remarks controller 1 unit power connector 1 piece with wire-release lever ts-x ts-p ext connector ts-x ts-p 1 piece with wire-release lever dummy connector 1 piece for com1 connector ...
Page 30: Verview
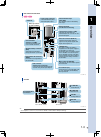
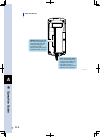
1-2 1 o verview 2. Part names and functions this section explains the part names and functions of the controller. Controller part names and functions ts-s • communication connector 2 (com2) connector for the daisy-chain connection cable. • status indicator lamps (pwr, err) the controller status is i...
Page 31: Verview
1-3 1 o verview part names and functions ts-x ts-p controller • status indicator lamps (pwr, err) the controller status is indicated by led lamps. • ext connector (bottom face of unit body) connector for brake power input and external safety circuit inputs/outputs. • serial no. • power supply connec...
Page 32: Verview
1-4 1 o verview devicenet ts-s, ts-s2, ts-sh ts-x, ts-p ns led green/red when lit. Ms led green/red when lit. Communication connector 23103-m0-00 tip see chapter 7 section 2.4, "devicenet" for details of led indicator lamp meanings. Ns ms ethernet/ip link/activity 1 led green when lit. Link/activity...
Page 33: Verview
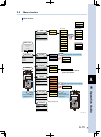
1-5 1 o verview 3. System configuration connect a robot and plc to the controller to configure a desired system. The following shows connection examples. Flip-x series phaser series transervo series p n rgen system configuration diagram • single-axis robot ts-x : flip-x series robot ts-p : phaser se...
Page 34: Verview
1-6 1 o verview 4. Installation and operation sequence the basic sequence from controller installation to actual operation is shown below. Installation and operation sequence · payload setting · soft limit setting chapter 2 ”installation and wiring” chapter 3 "data setting" chapter 4 "i/o signal fun...
Page 35: Chapter 2
Chapter 2 installation and wiring contents 1. Installation method 2-1 1.1 controller main body 2-1 1.1.1 ts-s ts-s2 ts-x ts-p 2-1 1.1.2 ts-sh 2-2 1.1.3 installation screws 2-2 1.2 regenerative unit (rgt) ts-x ts-p 2-3 1.3 regenerative unit (rgu-2) ts-p 2-3 2. Installation conditions 2-4 3. Wiring 2-...
Page 36
12. Safety circuit construction example 2-29 12.1 performance level 2-29 12.2 circuit configuration examples ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh 2-30 12.2.1 category 3 2-30 12.2.2 overview of circuit operation 2-31 12.3 circuit configuration examples ts-x ts-p 2-32 12.3.1 category 3 2-32 12.3.2 overview of circuit ope...
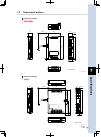
Page 37: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-1 1. Installation method 1.1 controller main body 1.1.1 ts-s ts-s2 ts-x ts-p use the mounting screw holes to install the controller on a vertical wall in the manner shown below. Installation of controller main body ts-s, ts-s2 ts-x, ts-p 23201-m0-00
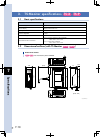
Page 38: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-2 1.1.2 ts-sh use the mounting screw holes to install the controller on a vertical wall in the manner shown below or use the rear groove and claw to install it on a din rail. When using the mounting screw holes, it is necessary to remove the controller top cover before st...
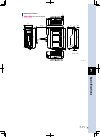
Page 39: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-3 1.2 regenerative unit (rgt) ts-x ts-p use the back plate of the rgt to install it on a vertical wall in the manner shown below. Rgen installation of rgt back plate 23201-m1-00 installation screws n use the following screw type for installation. Mounting area thickness h...
Page 40: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-4 2. Installation conditions this section explains the installation conditions necessary to operate the controller in safe and correct manner. Installation location n install the controller inside the control panel. Installation direction n install the controller on a ver...
Page 41: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-5 3. Wiring 3.1 power supply connection ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh use the power connector supplied with the controller to connect the power supply. Power supply connector terminal names and functions n es1 es2 es- mp24v cp24v 0v power supply connector signal name description es1 e...
Page 42: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-6 considering generated heat amount n use the following tables as a guide to determine the control panel size, controller installation method, and cooling means. Model generated heat amount (w) ts-s, ts-s2 18 ts-sh 25 signal details n • emergency stop ready signal (es-) t...
Page 43: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-7 3.2 power supply connection ts-x ts-p use the power connector supplied with the controller to connect the power supply. Power supply connector terminal names and functions n power supply connector (ts-x 205, 210, 220 ts-p 205, 210, 220 200vac specs.) signal name descrip...
Page 44: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-8 power supply connector wiring procedure n c caution • disconnect the power connector from the controller before wiring. • only one wire can be inserted into one wire hole of the power connector. • when inserting the wire into the terminal, use care to prevent the core w...
Page 45: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-9 c caution 1. Leakage current is measured by a leak tester (hioki electric 3283), with the low-pass filter (100hz) turned on. 2. When using multiple controllers, use the sum of the leakage currents from each controller. 3. Be sure that the controller is securely grounded...
Page 46: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-10 3.3 malfunction prevention measures ts-x ts-p the following precautions must be taken to prevent noise related malfunctions. Installation of noise filter and ferrite core n install a noise filter and ferrite core near the controller. Do not bundle the noise filter's pr...
Page 47: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-11 4. Connecting the robot connect the robot cables to the robot i/o connector on the controller's front face, and to the motor connector. C caution • be sure to use the cable dedicated to the ts controller when connecting the robot. • shut the power off before connecting...
Page 48: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-12 robot i/o connector signal table n ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh pin no. Signal name description 1a ps+ resolver sin input (+) 1b ps- resolver sin input (-) 2a pc+ resolver cos input (+) 2b pc- resolver cos input (-) 3a r+ resolver excitation output (+) 3b r- resolver excitation ou...
Page 49: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-13 5. Connecting the communication unit the controller can be operated from the ht1 (handy terminal) or a communication device with the rs-232c interface, such as a personal computer. • the ht1 is an optional item. • connection with a communication device, such as a perso...
Page 50: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-14 connecting the controller to a communication device n make this connection by using the optional communication cable (dedicated cable) for connection to a communication device, such as a personal computer. C caution • select either the usb or d-sub connection cable for...
Page 51: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-15 6. Connecting the regenerative unit ts-x ts-p the regenerative unit absorbs regenerative current produced during motor speed reduction and radiates it as heat. A regenerative unit is required when operating certain robot models specified by yamaha or when handling larg...
Page 52: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-16 6.2 connecting the rgu-2 ts-p the following explains how to connect the rgu-2. C caution • the power must be off when connecting the regenerative unit. • insert the cable plug into the connector until a clicking sound is heard (fully inserted). • install the regenerati...
Page 53: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-17 7. Absolute battery ts-x ts-sh the absolute battery is used to retain robot position data. 7.1 connecting the absolute battery to install the battery, first connect its cable to the bat connector inside the panel, then install the battery. C caution • plug in and unplu...
Page 54: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-18 7.2 replacing the absolute battery the absolute battery is a consumable item, and should be replaced when data backup problems occur (battery life expired). Although the battery life varies depending on the operating conditions, a general guideline is 8,000 hours (abou...
Page 55: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-19 8. Connecting the i/o signals two types of i/o signal connections (i/o and ext i/o ts-x ts-p ) are provided for connection to external device such as a plc. I/o wiring diagram jog+ jog − manual org / lock start reset servo srv-s / alm end busy out3 out0 +com − com 24v ...
Page 56: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-20 9. Configuring an emergency stop circuit ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh the power supply connector provides functions for configuring safety circuits, including the robot. The following shows a power connector and host unit connection example. Emergency stop circuit external 0v exte...
Page 57: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-21 10. Configuring an emergency stop circuit ts-x ts-p the ext connector provides functions for configuring safety circuits, including the robot. The following shows the ext connector wiring and an example of connection with the host controller. 10.1 ext connector signal ...
Page 58: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-22 • emergency stop contacts 1, 2 (es1, es2) signal name description when using handy terminal without an enable switch when using handy terminal with an enable switch es1 handy terminal's emergency stop contact output 1 connected to handy terminal's safety connector pin ...
Page 59: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-23 10.2 wiring and connecting the ext connector this section explains the ext connector wiring and connecting methods. Ext connector wiring method n c caution • disconnect the ext connector from the controller before wiring. • only one wire can be inserted into one wire p...
Page 60: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-24 10.3 circuit details the following shows an ext connector and host unit connection example. Status safety circuit ts-x ts-p external 0v external "emergency stop" e s + e s 1 e s 2 e s - l1 n1 l n external 24v internal power es ext connector com1 controller no nc mprd y...
Page 61: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-25 11. Connecting the i/o unit when purchasing the controller, a desired i/o unit can be selected from the npn, pnp, cc-link, devicenet and ethernet/ip. The positioning or push operation can be controlled from the host unit, such as plc through the i/o unit. Parallel i/o ...
Page 62: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-26 npn type i/o circuit details n 24vdc +com input -com logic circuit internal circuit 4.7k Ω input circuit 23208-m0-00 type : dc input (plus common type) photo-coupler isolation format load : 24vdc ± 10%, 5.1ma off voltage :19.6vmin (1.0ma) on voltage :4.9vmax (4.0ma) +c...
Page 63: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-27 cc-link n 5 4 3 2 1 terminal arrangement and connector specifications no. Name 1 da 2 db 3 dg 4 nc 5 sld 23212-m0-00 ts-x, ts-p ts-s, ts-s2, ts-sh connection method cc-link connector jump socket 23213-m0-00 manufacturer part name manufacturer name cc-link connector 355...
Page 64: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-28 devicenet n 1 2 3 4 5 terminal array and connector specifications no. Name 1 v- (black) 2 can_l (blue) 3 shield 4 can_h (white) 5 v+ (red) 23214-m0-00 ts-x, ts-p ts-s, ts-s2, ts-sh devicenet connector connection method 23215-m0-00 ethernet/ip n terminal assignments and...
Page 65: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-29 12. Safety circuit construction example this section describes category-specific safety circuit configuration examples using a handy terminal which has an enable switch. Customers should install the appropriate safety measures for their system by referring to the safet...
Page 66: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-30 12.2 circuit configuration examples ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh safety circuit configuration examples are shown below. Customers should install the appropriate safety measures for their system by referring to these safety circuit configuration examples in order to use the robots ...
Page 67: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-31 12.2.2 overview of circuit operation this section describes an overview of the circuit operation for each safety circuit configuration example shown in the previous sections. The safety controller is programmed so that the operation is performed in the table below. Add...
Page 68: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-32 12.3 circuit configuration examples ts-x ts-p safety circuit configuration examples are shown below. Customers should install the appropriate safety measures for their system by referring to these safety circuit configuration examples in order to use the robots more sa...
Page 69: Installation and Wiring
2 installation and wiring 2-33 12.3.2 overview of circuit operation this section describes an overview of the circuit operation for each safety circuit configuration example shown in the previous sections. The safety controller is programmed so that the operation is performed in the table below. Add...
Page 71: Chapter 3
Chapter 3 data setting contents 1. Data overview 3-1 1.1 overview 3-1 1.2 data system-of-units 3-1 2. Point data 3-2 2.1 "standard setting" type 3-3 2.2 "custom setting" type 3-4 3. Point data details 3-5 4. Parameter data 3-9 4.1 parameter list 3-9 4.1.1 run parameters 3-9 4.1.2 i/o parameters 3-10...
Page 73: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-1 1. Data overview 1.1 overview point data and parameter data settings must be specified in order to operate a robot from a ts series controller. Point data n the point data used in positioning operations includes items such as the "run type", "position", and "speed", etc. Up to 255...
Page 74: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-2 2. Point data the point data includes items such as the "run type", "position", and "speed", etc. Point data item list n p1 to p255 item description 1 run type specifies the positioning operation pattern. 2 position specifies the positioning target position or movement amount. 3 s...
Page 75: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-3 2.1 "standard setting" type the optimum acceleration is automatically set simply by specifying the desired payload. Speed and acceleration concept the optimum acceleration percentage value (%) is specified in accordance with the movement amount and movement speed, based on the max...
Page 76: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-4 2.2 "custom setting" type this setting type allows a more detailed positioning operation. Speed and acceleration concept the acceleration is set in m/s 2 units. The max. Permissible setting value is the max. Accel. For each robot type. Speed "speed" = 600.00 (mm/s) "accel." = 4.00...
Page 77: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-5 3. Point data details this section explains the details of each point data item. Run type 1. Specifies the positioning operation pattern. Tip for details on positioning operation, abs (absolute position movement), and inc (relative position movement), see section 3, "positioning o...
Page 78: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-6 position 2. Specifies the positioning target position or movement amount. • when the "run type" is specified as "abs (absolute position) ..... Target position. • when the "run type" is specified as "inc (relative position) ....... Movement amount from current position. The illustr...
Page 79: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-7 zone (-) 7. Zone (+) 8. "zone (-)" specifies the personal zone output (pzone) range's lower limit (minus-direction limit). "zone (+)" specifies the personal zone output (pzone) range's upper limit (plus-direction limit). The personal zone output can be specified for each point dat...
Page 80: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-8 flag 11. Specifies the following setting items with regard to the positioning operation. Bit setting setting item setting value / setting range bit0 payload select standard setting: selects the payload setting for positioning operations. Custom setting: limits the max. Payload acc...
Page 81: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-9 4. Parameter data the 4 types of parameter data are shown below. Type description run parameter these parameters are required for robot operation, and they include "soft limit" and "zone" settings. I/o parameter these parameters are for terminal assignment and i/o functions. Optio...
Page 82: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-10 • speed switch no. Name setting / setting range units default restart 17 speed switch function 0: disable 1: enable - 0 - 18 switched speed 1 to 100 % 10 - • limitless rotation function no. Name setting / setting range units default restart 19 limitless rotation function 0: disab...
Page 83: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-11 4.1.4 servo parameters • controller setting ts-x ts-sh no. Name setting / setting range units default restart 74 absolute setting 0: disable 1: enable - 1 required • adjustment no. Name setting / setting range units *3 default restart 76 payload 1 0 to max. Payload (k47) kg depen...
Page 84: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-12 settings setting value description 0 push continuation after completion, with no failure judgment. 1 positioning after completion, with no failure judgment. 2 push continuation after completion, with failure judgment. 3 positioning after completion, with failure judgment. K5 push...
Page 85: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-13 • return-to-origin related parameters k13 return-to-origin speed setting range default units restart 0.01 to 100.00 depends on robot type mm/s - function specifies the return-to-origin movement speed. C caution an alarm may occur during return-to-origin operation if the return-to...
Page 86: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-14 n note refer to section 3.8, "speed switch function", in chapter 5 for more details. K18 switched speed setting range default units restart 1 to 100 10 % - function specifies the speed to be used after "speed switch" has been performed. The maximum speed to be used by the speed s...
Page 87: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-15 k25 pout select setting range default units restart 0 to 2 1 - required function specifies the output timing for the pout0 to pout7 point no. Outputs. Settings setting value description 0 no output 1 output at positioning end (after) 2 output at movement start (with) • function s...
Page 88: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-16 4.2.3 servo parameters • controller setting ts-x ts-sh k74 absolute setting setting range default units restart 0 to 1 1 - required function sets the absolute function enabled or disabled. Settings setting value description 0 disable 1 enable • adjustment k76 payload 1 setting ra...
Page 89: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-17 settings setting value description 0 closed mode 1 open mode tip for details regarding the stop mode, see section 7.5, "stop mode", in chapter 5. K124 stop mode switching time setting range default units restart 0 to 5000 200 ms - function specifies the time to wait before shifti...
Page 90: Data Setting
3 data setting 3-18 4.2.6 devicenet k81 devicenet node setting range default units restart 0 to 63 0 - required function specifies the devicenet communication node. K82 devicenet speed setting range default units restart 0 to 2 2 - required function specifies the devicenet baud rate. Settings settin...
Page 91: Chapter 4
Chapter 4 i/o signal functions contents 1. I/o specifications 4-1 1.1 npn and pnp type 4-1 1.2 cc-link type 4-2 1.3 devicenet type 4-4 1.4 ethernet/ip type 4-5 2. I/o signal list 4-6 3. I/o signal details 4-7 3.1 input signal details 4-7 3.2 output signal details 4-9.
Page 93: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-1 1. I/o specifications the ts series allows positioning and push operations to be controlled from a host unit such as a plc, etc., by way of an i/o interface. The i/o specifications for the i/o interface are shown below. (selected at the time of purchase.) i/o specificatio...
Page 94: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-2 1.2 cc-link type operation occurs as a cc-link remote device station, on a one-unit to one-station basis. N note "station no." and "baud rate" settings must be specified in order for the ts series to be recognized as remote station in the cc-link system. These settings ca...
Page 95: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-3 remote registers (word i/o) n remote commands can be executed by using the 4-word input and 4-word output remote registers. Inputs (master remote) output (remote master) address signal name description address signal name description rwwn win0 execution command rwrn wout0...
Page 96: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-4 1.3 devicenet type operate as slave stations, with each unit occupying 6 input and 6 output channels. N note mac id and baud rate settings are required in order for ts series to be properly recognized as a slave station in the devicenet system. These settings can be speci...
Page 97: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-5 1.4 ethernet/ip type operates as slave stations (adapters), with each unit occupying 6 input and 6 output channels. N note ip address setting is required in order for ts series to be properly recognized as a slave station in the ethernet/ip system. This setting can be spe...
Page 98: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-6 2. I/o signal list a list of the i/o signals is given below. For details regarding each signal, refer to section 3 "i/o signal details". Type signal name meaning description inputs pin0 to pin7 point no. Select 0 to 7 • specifies the point no. For the positioning operatio...
Page 99: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-7 3. I/o signal details this section explains the i/o signals in detail. 3.1 input signal details pin0 to pin7 (point no. Select) n these inputs are read as 8-bit binary code point nos. When the start and teach commands are executed. • input example pin7 pin0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 ...
Page 100: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-8 start n this input begins positioning to the point data specified by the pin0 to pin7 point no. Select input. N note this input is enabled only when the manual mode is off. Teach n this input sets (teaches) the current position at the point data position specified by pin0...
Page 101: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-9 3.2 output signal details pout0 to pout7 (point no. Output) n outputs the current positioning operation's point no. As a binary output. When an alarm occurs, these signals output the alarm no. As a binary output. • output example pout7 pout0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 sum at on exam...
Page 102: Signal Functions
4 i/ o signal functions 4-10 pzone n this signal switches on during a positioning operation when the current position enters the point data's "zone+" and "zone-". After positioning ends, this signal remains enabled until the next positioning operation is executed. This signal is enabled only when as...
Page 103: Chapter 5
Chapter 5 operation contents 1. Operation procedure 5-1 1.1 overall operation timing chart 5-1 1.1.1 ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh 5-1 1.1.2 ts-x 5-2 1.1.3 ts-p 5-3 1.1.4 communication check (field network) 5-4 1.2 alarm occurrence and clearing 5-5 2. Origin search (return-to-origin) 5-6 2.1 origin point detecti...
Page 104
5.5 point data writing 5-37 5.6 point data reading 5-38 5.7 parameter data writing 5-39 5.8 parameter data reading 5-40 5.9 continuous query 5-41 5.10 positioning operation 5-42 5.11 special operations 5-44 5.12 special codes 5-45 6. Operation modes 5-46 7. Other functions 5-47 7.1 soft limit functi...
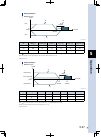
Page 105: Peration
5 o peration 5-1 1. Operation procedure 1.1 overall operation timing chart the operation timing chart from "power on" to the "positioning operation" is shown below. 1.1.1 ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh the ts-s, ts-s2 and ts-sh timing chart is shown below. Alarm (/alm) control power (cp24v) operation-in-progress ...
Page 106: Peration
5 o peration 5-2 1.1.2 ts-x the following shows the timing chart of the ts-x controller. Td ≥ 5ms *3 alarm (/alm) control power (l1, n1) operation-in-progress (busy) main power (l, n) 00h main power ready (mprdy) initial processing operation end (end) emergency stop (e-stop) servo on (servo) servo s...
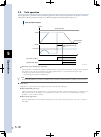
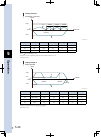
Page 107: Peration
5 o peration 5-3 1.1.3 ts-p the following shows the timing chart of the ts-p controller. Alarm (/alm) control power (l1, n1) operation-in-progress (busy) main power (l, n) main power ready (mprdy) operation end (end) emergency stop (e-stop) servo on (servo) servo status (srv-s) return-to-origin (org...
Page 108: Peration
5 o peration 5-4 1.1.4 communication check (field network) in a field network, always check that the communication state is normal before starting operation. When using the host unit's communication status flag to monitor the communication state, allow a time delay of about 200ms after recognizing a...
Page 109: Peration
5 o peration 5-5 1.2 alarm occurrence and clearing the operation timing chart from "alarm occurrence" to "alarm clear" is shown below. Operation-in-progress (busy) start (start) operation end (end) 00h point no. Select (pin0 to pin7) setting 00h 00h point no. Output (pout0 to pout7) servo on (servo)...
Page 110: Peration
5 o peration 5-6 2. Origin search (return-to-origin) this controller needs to determine the origin point in order to operate the robot in the single axis coordinate system. This operation is called "origin search" (or "return-to-origin"). Performing the return-to-origin will set the coordinates of t...
Page 111: Peration
5 o peration 5-7 mark method n when the mark method is specified (k66 (return-to-origin method): "mark") as origin point detection method, movement in the return-to-origin direction occurs when a return-to-origin begins, and movement stops at the nearest motor reference position. A return-to-origin ...
Page 112: Peration
5 o peration 5-8 sensor method n movement in the return-to-origin direction occurs when a return-to-origin begins, and movement stops when the sensor detects the origin point dog. A return-to-origin end status is then established. Sensor method return-to-origin direction return-to-origin direction o...
Page 113: Peration
5 o peration 5-9 • when the sensor method is used to detect the origin point and the sensor turns on during absolute search movement when an absolute search (return-to-origin) begins, the robots starts moving toward the origin point. When the origin sensor detects the origin dog, the robot moves in ...
Page 114: Peration
5 o peration 5-10 2.3 origin point and coordinates relationship coordinates are determined in accordance with the return-to-origin direction. The opposite direction from the return-to-origin direction is the "plus" direction. This direction (coordinate) setting can be reversed by changing the k15 ("...
Page 115: Peration
5 o peration 5-11 3. Positioning operation a positioning operation can be performed by creating the required point data ("run type", "position", "speed", "accel.", data, etc.), specifying the desired point nos. At pin0 to pin7 (point no. Select), and then executing the start command input. Positioni...
Page 116: Peration
5 o peration 5-12 setting the "speed", "accel.", and "decel." data n 1.When using the "standard setting" point type the "speed" and "accel." settings are specified as a percentage of the optimal positioning speed and acceleration values for each robot type, based on that robot's maximum speed and ma...
Page 117: Peration
5 o peration 5-13 maximum payload acceleration and the payload n the maximum payload acceleration varies according to the payload setting. The optimum "maximum payload acceleration" is determined based on the robot's registered payload weight. Two "maximum payload acceleration" settings can be selec...
Page 118: Peration
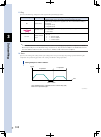
5 o peration 5-14 acceleration s-curve n the ts series features an s-curve function (standard item) to ensure smooth acceleration/deceleration. This results in a maximum acceleration which is 1.4 times that of a trapezoidal acceleration/deceleration format. Acceleration s-curve speed time max. Accel...
Page 119: Peration
5 o peration 5-15 point no. Outputs n an answer-back for the point nos. Used in the positioning operation occurs at the pout0 to pout7 point no. Outputs. This output can be set to occur "with" (at movement start), or "after" (at positioning end) by the k25 (pout select) i/o parameter. (this paramete...
Page 120: Peration
5 o peration 5-16 3.3 positioning merge operation the positioning movement speed can be changed while in progress by performing positioning in the merge operation mode. The figure below shows an example of the following merge operation: "operation 1 (p1 positioning) operation 2 (p2 positioning) oper...
Page 121: Peration
5 o peration 5-17 a period of time required to reach the merge destination speed is insufficient. Positioning merge operation a period of time required to reach the merge destination speed is insufficient. Speed time operation 2 desirable acceleration operation 1 23518-m0-00 c caution in the example...
Page 122: Peration
5 o peration 5-18 3.4 push operation a push operation is performed at the positioning operation. During the push operation, the torque is limited in accordance with the push force being used, allowing workpieces to be grasped and press-fit. Push operation example speed time speed target position pus...
Page 123: Peration
5 o peration 5-19 push judgment time n this setting is used as the reference for "operation end" judgments at push operations. The "operation end judgment" is made when the time during which the torque level is at the push force reaches the k5 (push judgment time) run parameter setting. If a push op...
Page 124: Peration
5 o peration 5-20 3.5 deceleration push operation deceleration ends at the position set as the "near width" value (distance) short of the target position, and the push operation then begins in accordance with the k6 (push speed) run parameter setting. Deceleration push operation deceleration ends wh...
Page 125: Peration
5 o peration 5-21 3.6 continuous operation "continuous operation" refers to consecutive positioning operations which occur in response to an initial start command input. When one positioning operation ends, and the "timer" specified delay (wait) time elapses, the next positioning operation begins fo...
Page 126: Peration
5 o peration 5-22 3.7 output function during positioning operations, individual operation speeds and position information are transmitted to the host unit by the outputs shown below. Output function speed position speed accel. Decel. Target position movement-in-progress output level (k12) movement-i...
Page 127: Peration
5 o peration 5-23 3.8 speed switch function the overall positioning operation speed can be switched between two levels from the host equipment by using the speed switch input (spd). Assigning method n when you set the "speed switch function" (k17) to "enable", the speed switch (spd) will be assigned...
Page 128: Peration
5 o peration 5-24 3.9 limitless rotation function this limitless rotation function achieves the multi-rotation motion in the same direction. Use of the limitless rotation function makes it possible to support the index table using the rotary axis model. The limitless rotation provides three kinds of...
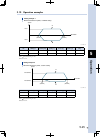
Page 129: Peration
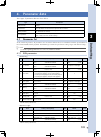
5 o peration 5-25 3.10 operation examples speed position p2 (500mm) p1 (200mm) 100% 100% setting example 1 movement between 2 points, standard setting a b 23525-m0-00 no. Run type position [mm] speed [%] accel. [%] decel. [%] flag p1 abs 200 100 100 100 1 p2 abs 500 100 100 100 0 a: p1 p2 positionin...
Page 130: Peration
5 o peration 5-26 speed position 100mm p1 (0mm) 100% 100% p2 (200mm) 100mm 100mm setting example 3 positioning + pitch feed a b c 23527-m0-00 no. Run type position [mm] speed [%] accel. [%] decel. [%] p1 abs 0 100 100 100 p2 abs 200 100 75 100 p3 inc 100 100 100 100 a: p1 p2 positioning occurs. B: p...
Page 131: Peration
5 o peration 5-27 speed position p1 (0mm) 100% 100% p2 (350mm) p3 (100mm) workpiece setting example 5 workpiece push a b c 23529-m0-00 no. Run type position [mm] speed [%] accel. [%] decel. [%] push force [%] p1 abs 0 100 100 100 100 p2 abs 350 100 100 100 100 p3 inc push 100 10 100 100 70 a: p1 p2 ...
Page 132: Peration
5 o peration 5-28 4. Manual mode in the manual mode, jog movement and position teaching, etc., can be performed from a host unit by using the optional handy terminal (ht1) or the ts-manager support software. This section explains the manual mode functions. 4.1 manual mode timing chart operation-in-p...
Page 133: Peration
5 o peration 5-29 4.2 jog movement when in the manual mode ("manual" on), robot jog movement in the specified direction is possible while the jog+ / jog- input is on. When this input switches off, a deceleration stop occurs. Jog movement can be performed even if a return-to-origin has not been compl...
Page 134: Peration
5 o peration 5-30 4.3 teach (teaching) when in the manual mode ("manual" on) with "/lock" switched off, the current position can be written to the specified point no. At the leading edge of the teach input on. N note the teach function is disabled if a return-to-origin has not yet been completed. Or...
Page 135: Peration
5 o peration 5-31 5. Remote commands 5.1 overview remote commands use the field network's remote register area to read and write various types of information, and perform the positioning operation. Cc-link n inputs (master remote) output (remote master) address signal name description address signal...
Page 136: Peration
5 o peration 5-32 point data writing n name command command option command response win0 win1 win2, win3 wout1 wout2, wout3 operation type write 0200h point no. Operation type point no. - position write 0201h point no. Position data point no. - speed write 0202h point no. Speed data point no. - acce...
Page 137: Peration
5 o peration 5-33 parameter writing n name command command option command response win0 win1 win2, win3 wout1 wout2, wout3 in-position (k3) write 0400h 0003h in-position data - - push mode (k4) write 0400h 0004h push mode - - push judge time (k5) write 0400h 0005h push judge time data - - push speed...
Page 138: Peration
5 o peration 5-34 special codes n name command command option command response win0 win1 win2, win3 wout1 wout2, wout3 status clear (no execution) 0000h - - - - status clear (continuous query continuation) 8000h - - - - command response clear 0f00h - - 0000h 00000000h status n name status descriptio...
Page 139: Peration
5 o peration 5-35 5.3 timing chart this section explains the remote command input/output timing charts using remote command execution flowcharts and examples. When executing a query n status (wout0) 0000h 0000h 0000h 0200h 0200h command option (win1) 0000h 0000h 0000h 0000h 0000h command (win0) 0000...
Page 140: Peration
5 o peration 5-36 5.4 query reads information (current position and speed, etc.) related to the operation. Input command option command win3 win2 win1 win0 - - type 0100h output command response status wout3 wout2 wout1 wout0 data - 0200h n note the "data" is output as 2-word, little endian data. Co...
Page 141: Peration
5 o peration 5-37 5.5 point data writing point data is written. Input command option command win3 win2 win1 win0 data point no. 02xxh output command response status wout3 wout2 wout1 wout0 - point no. (response) 0200h commands and data n command (win0) command option units data write destination poi...
Page 142: Peration
5 o peration 5-38 5.6 point data reading point data is read. Input command option command win3 win2 win1 win0 - point no. 03xxh output command response status wout3 wout2 wout1 wout0 data point no. (response) 0200h n note the "data" is output as 2-word, little endian data. Commands and data n comman...
Page 143: Peration
5 o peration 5-39 5.7 parameter data writing parameter data is written. Input command option command win3 win2 win1 win0 data parameter no. 0400h output command response status wout3 wout2 wout1 wout0 - - 0200h command type and data n command (win0) command option unit parameter no. (win1) data (win...
Page 144: Peration
5 o peration 5-40 5.8 parameter data reading parameter data is read. Input command option command win3 win2 win1 win0 - parameter no. 0500h output command response status wout3 wout2 wout1 wout0 data - 0200h command type and response data n command (win0) command option command response unit paramet...
Page 145: Peration
5 o peration 5-41 5.9 continuous query this function outputs operation information such as the current position and speed, etc., in a continuous manner. Input command option command win3 win2 win1 win0 - - type 8100h output command response status wout3 wout2 wout1 wout0 data - 0200h c caution outpu...
Page 146: Peration
5 o peration 5-42 5.10 positioning operation there are two kinds of positioning operations available, "data designation type 1" that performs the operation by specifying the position data and "data designation type 2" that performs the operation by specifying the position and speed data. So, it is n...
Page 147: Peration
5 o peration 5-43 status n name status description wout0 command ready 0000h shows the command executable status. Positioning operation in-progress (0100 + n) h receives the command to show that the positioning operation is in progress. The point number that is registered when entering the data is o...
Page 148: Peration
5 o peration 5-44 5.11 special operations special operations are explained below. Brake release 1. Releases the brake. Input command option command win3 win2 win1 win0 - - 0e00h output command response status wout3 wout2 wout1 wout0 - - 0200h brake on 2. Turns the brake on. Input command option comm...
Page 149: Peration
5 o peration 5-45 5.12 special codes this section explains the special codes. Status clear (no execution) 1. The status is changed to the command ready (command executable status). Input command option command win3 win2 win1 win0 - - 0000h output command response status wout3 wout2 wout1 wout0 - - 0...
Page 150: Peration
5 o peration 5-46 6. Operation modes in addition to i/o control from a host unit (plc, etc.), the ts series also offers communication control from a personal computer (running the ts-manager support software) and from handy terminal (ht1). In order to use these tools in a safe manner, the desired op...
Page 151: Peration
5 o peration 5-47 7. Other functions 7.1 soft limit function software imposed limits can be applied to the robot's range of motion in order to prevent interference with peripheral equipment. Robot movement is then restricted to target positions which are within the range specified by the soft limit ...
Page 152: Peration
5 o peration 5-48 7.3 alarm no. Output function when an error alarm occurs, the alarm no. Is output to the pout0 to pout7 point no. Outputs. If multiple alarms have occurred, the highest priority alarm no. Is output. The alarm no. Output function can be enabled/ disabled by the k30 (alarm no. Output...
Page 153: Peration
5 o peration 5-49 7.5 stop mode ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh this switches the control during stop state after positioning operations. Use "flag" for each point to switch the stop mode. Item setting value description stop mode select flag bit1=0 closed mode flag bit1=1 open mode closed mode n this controller de...
Page 154: Peration
5 o peration 5-50 8. Led status indicators operation statuses are indicated by 2 types of leds located on the front face of the controller. The following table shows the led statuses and their meanings. Led name color status meaning pwr blue off control power shutoff blinking (at 0.5sec intervals) s...
Page 155: Peration
5 o peration 5-51 9. Ts-monitor (option) ts-x ts-p this ts-monitor is a lcd panel option prepared as an option of the controller. The ts monitor displays various information on the screen, allowing you to check such information. Screen contents information screen displays the controller, robot model...
Page 156: Peration
5 o peration 5-52 9.3 changing the screen press the ▲ button or ▼ button on the ts-monitor to change the ts-monitor screen as follows. Changing the screen after normal startup startup screen information screen transits after a certain period of time has elapsed. Main screen i/o screen check screen r...
Page 157: Peration
5 o peration 5-53 9.4 screen configuration and meaning startup screen n when starting up the ts-monitor, the following screen will appear. Startup screen software version ts-monitor ver. 1.00 booting up... 24501-m1-00 information screen n "information" is displayed in the page name area at the upper...
Page 158: Peration
5 o peration 5-54 simple status display display meaning description s servo status displays the servo status. On: servo on status, off: servo off status e emergency stop displays the emergency stop status. On: emergency stop status p main power failure displays the main power voltage drop. On: main ...
Page 159: Peration
5 o peration 5-55 status screen n "status" is displayed in the page name area at the uppermost portion on the status screen. Status srv-s e-stop orgsen p-blk tlm-s org-s move warn status screen on off status display : on, : off 24506-m1-00 status display display meaning description srv-s servo statu...
Page 160: Peration
5 o peration 5-56 run type display meaning hold servo is off or robot is stopping. Abs abs inc inc abs merge abs merge operation inc merge inc merge operation abs push abs push operation inc push inc push operation abs->push abs deceleration push operation inc->push inc deceleration push operation o...
Page 161: Peration
5 o peration 5-57 9.5 screen color in case of alarm the screen color of the ts-monitor changes according to the alarm occurrence status. The screen status and its meaning are descried in the table below. Status meaning blinks in blue (at intervals of 0.5 sec.). Servo is off and no error alarm occurs...
Page 162: Peration
5 o peration 5-58 9.6 setup screen you can set the lcd contrast and backlight on time on the setup screen. To set these items, follow the steps below. 1 start up the setup screen. Turn on the power while holding down the ▼ button. 2 display the set contents of the lcd. When the setup screen is displ...
Page 163: Chapter 6
Chapter 6 troubleshooting contents 1. Alarm groups 6-1 2. Alarm recording function 6-2 3. Alarm list 6-3 4. Alarms: possible causes and actions 6-4.
Page 165: Troubleshooting
6 troubleshooting 6-1 1. Alarm groups alarms on this controller are one of the following 5 groups. Group description message alarm error messages involving data editing or operation commands sent as data. Operation alarm alarm that appears when operation ends due to an error. Error alarm (internal c...
Page 166: Troubleshooting
6 troubleshooting 6-2 2. Alarm recording function this function records and stores the error alarms (internal cause) as they occur, along with their alarm number and alarm conditions at that time. Up to 50 alarms can be stored. * this function does not store the "81: ac power down" error alarm. Alar...
Page 167: Troubleshooting
6 troubleshooting 6-3 3. Alarm list the following table shows alarm numbers, messages, and reset methods. Alarm no. Alarm message reset *1 origin position *2 02 data error - - 03 data range over - - 04 monitor mode - - 05 running - - 06 manual mode - - 41 servo off - - 42 origin incomplete - - 43 no...
Page 168: Troubleshooting
6 troubleshooting 6-4 4. Alarms: possible causes and actions message alarms n no. Message meaning possible cause action 02 data error data setting error attempt was made to enter data that exceeded the specified range. Enter data within the specified range. 03 data range over data setting range exce...
Page 169: Troubleshooting
6 troubleshooting 6-5 error alarms (internal causes) n no. Message meaning possible cause action 81 ac power down drop in control power supply voltage. Power supply voltage too low. Check the power supply. Momentary power outage (below 50% of specified input voltage) occurred for more than 40ms. Ts-...
Page 170: Troubleshooting
6 troubleshooting 6-6 no. Message meaning possible cause action 8a abs. Battery err. Ts-x ts-sh absolute battery voltage dropped below the low error detection level (2.5v). Absolute battery is disconnected. Connect the absolute battery correctly. Absolute battery has worn out or failed. Replace the ...
Page 171: Troubleshooting
6 troubleshooting 6-7 error alarms (external causes) n no. Message meaning possible cause action c1 emergency stop emergency stop was activated. External safety circuit functioned and emergency stop was activated. Ensure safety and then cancel the safety circuit. Emergency stop wiring is incomplete....
Page 173: Chapter 7
Chapter 7 specifications contents 1. Controller basic specifications 7-1 1.1 basic specifications 7-1 1.1.1 ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh 7-1 1.1.2 ts-x ts-p 7-2 1.2 list of controlled robots 7-3 1.3 dimensional outlines 7-5 2. I/o interface specifications 7-7 2.1 npn 7-7 2.2 pnp 7-7 2.3 cc-link 7-7 2.4 devicene...
Page 175: Specifications
7 specifications 7-1 1. Controller basic specifications 1.1 basic specifications 1.1.1 ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh item ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh controllable robot *1 transervo series current consumption 2.5a (max. 4.5a) 3.5a (max. 6.5a) dimensions w30×h162×d82mm w30×h162×d123mm weight approx. 0.2kg approx. 0.3kg cont...
Page 176: Specifications
7 specifications 7-2 1.1.2 ts-x ts-p item 100v ac input 200v ac input ts-x105 ts-p105 ts-x110 ts-p110 ts-x205 ts-p205 ts-x210 ts-p210 ts-x220 ts-p220 controllable robot *1 ts-x: flip-x series ts-p: phaser series power capacity 400va 600va 400va 600va 1400va dimensions w58×h162×d131mm w70×h162×d131mm...
Page 177: Specifications
7 specifications 7-3 1.2 list of controlled robots list n robot ts-s ts-s2 ts-sh ts-x ts-p 105 205 110 210 220 105 205 110 210 220 type model transer vo series ss ss04 ss05 ss05h ssc ssc04 ssc05 ssc05h sg sg07 sr sr03 sr04 sr05 srd srd03 srd04 srd05 sth sth04 sth06 rf rf02 rf03 rf04 bd bd04 bd05 bd0...
Page 178: Specifications
7 specifications 7-4 robot i/o setting and transervo series controllable robot n ts-s2 ts-sh the robot i/o setting at shipment may vary depending on the robot model. Robot robot i/o setting return-to-origin method model detailed type bk sensor ss04, ss05, ss05h s, l, r stroke-end method sb, lb, rb s...
Page 179: Specifications
7 specifications 7-5 1.3 dimensional outlines r 152 5 82 (70) 30 5 5 25 φ 4.5 4.5 162 152 (units : mm) ts-s dimensional outlines ts-s2 23701-m3-00 (units : mm) dimensional outlines ts-sh (70) 123 152 5 25 φ 4.5 4.5 30 r 4 (12) 162 35.2: din rail width is 35mm. 4 80.7: center position of din rail 237...
Page 180: Specifications
7 specifications 7-6 131 (90) 167 58 152 φ 5.4 5 5.4 4 (8) ext connector 53 162 r (units : mm) ts-x ts-p (105/110/205/210) dimensional outlines 23701-m1-00 (units : mm) 131 167 (90) 162 58 70 4 53 5.4 5 152 (8) ext connector r φ 5.4 ts-x ts-p (220) dimensional outlines 23702-m1-00
Page 181: Specifications
7 specifications 7-7 2. I/o interface specifications 2.1 npn input 16 points, 24v dc ±10%, 5.1ma per point, positive common output 16 points, 24v dc ±10%, 50ma per point, total 0.4a or less per 8 points, sink type 2.2 pnp input 16 points, 24v dc ±10%, 5.5ma per point, negative common output 16 point...
Page 182: Specifications
7 specifications 7-8 2.4 devicenet devicenet specifications n item description compatible devicenet specs. Volume1 release2.0 volume2 release2.0 vendor name yamaha motor co.,ltd. (id=636) device type generic device (device no.0) product code 11 product revision 1.1 max. Network current consumption 4...
Page 183: Specifications
7 specifications 7-9 2.5 ethernet/ip ethernet/ip specifications n item description compatible ethernet/ip specs. Volume1 : common industrial protocol(cip tm ) edition 3.8 volume2 : ethernet/ip adaptation edition 1.9 vendor name yamaha motor co.,ltd. (id=636) device type generic device product code 1...
Page 184: Specifications
7 specifications 7-10 3. Ts-monitor specifications ts-x ts-p 3.1 basic specifications item specifications effective display dimensions w40.546 × h25.63mm screen display graphic monochrome lcd backlight blue and red, 2-color lcd contrast adjustment 5 steps number of display dots 128 × 64 dots outside...
Page 185: Specifications
7 specifications 7-11 162 167 58 152 φ 5.4 5 (83.5) 137.5 (8) ext connector 53 70 5.4 4 (units : mm) r dimensional outlines ts-x ts-p (220) with ts-monitor 23704-m1-00
Page 186: Specifications
7 specifications 7-12 4. Regenerative unit specifications 4.1 dimensional outlines (rgt) rgen 2 120 30 15 142 152 162 φ 5.5 r2.75 (units : mm) rgt 23705-m1-00 4.2 dimensional outlines (rgu-2) p n rgen 250 290 40 157 265 5.5 16 250 (units : mm) rgu-2 23701-m2-00
Page 187: Ht1 Operation Guide
Ht1 operation guide contents introduction a-1 1. What the ht1 does a-2 1.1 ht1 panel layout a-3 1.2 connecting to the external safety circuit (ht1-d) a-5 2. Connecting or disconnecting the ht1 a-6 2.1 connecting to the controller a-6 2.2 disconnecting from the controller a-7 3. Basic operations a-8 ...
Page 188
7. Monitor functions a-31 7.1 i/o monitor a-31 7.2 status monitor a-32 7.3 run monitor a-33 7.4 alarm display a-34 7.5 warning display a-34 7.6 message display a-35 7.7 alarm record display a-36 7.8 information display a-37 8. Other functions a-38 8.1 operation mode a-38 8.2 setting mode a-39 8.2.1 ...
Page 189: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-1 introduction this "ht1 operation guide" explains how to use the ht1 and ht1-d (with enable switch) handy terminals that come with the ts series robot controller as an option. Before reading this section, read the precautions and descriptions stated in the "controller guid...
Page 190: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-2 1. What the ht1 does the ht1 handy terminal is provided as an option for the ts series controller. When connected to the controller, the ht1 allows you to perform the following operations and checks. Ht1 tasks with the ht1 you can: refer to: point data editing data editin...
Page 191: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-3 1.1 ht1 panel layout the ht1 consists of a lcd screen, data edit keys, run/stop keys, and emergency stop button as shown below. • lcd screen this is a liquid crystal display (lcd) screen with 32 characters × 10 lines (pixel display), showing the operation menus and variou...
Page 192: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-4 • enable switch (ht1-d only) this switch is used along with an external safety circuit. This switch turns off (opens) the circuit when pressed or released. Pressing this switch to mid-position enables the circuit. • safety connector (ht1-d only) use this connector along w...
Page 193: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-5 1.2 connecting to the external safety circuit (ht1-d) using the safety connector on the ht1-d allows configuring an external safety circuit with the ht1-d emergency stop button or enable switch. Ht1-d wiring diagram n external safety circuit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 14 15 emergenc...
Page 194: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-6 2. Connecting or disconnecting the ht1 the ht1 can be connected or disconnected from the controller as needed regardless of whether controller power is on or off. C caution • do not modify the ht1 cable. Modified cables might cause communication errors or malfunctions. • ...
Page 195: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-7 2.2 disconnecting from the controller the ht1 can be disconnected from the controller, regardless of whether the controller power is on or off. Pull the ht1 cable connector straight outwards from the com1 connector on the controller. Controller grip the connector body and...
Page 196: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-8 3. Basic operations the ht1 operation keys are only a minimum number of necessary keys, so ht1 operating procedures can easily be mastered even by first-time users. The ht1 operation keys are divided into two groups: data edit keys and run/stop keys. 3.1 operation key lay...
Page 197: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-9 3.2 screen configuration tip for position and zone parameters, a two decimal place number can be displayed and input in the ts-s, ts-s2, ts-sh and ts-x controllers. A three decimal place number can be input and displayed in the ts-p controller. Main menu screen n on the m...
Page 198: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-10 "run mode" display n the currently selected "run mode" is displayed as an abbreviation on the right of the status area. The meaning of each abbreviation is described below. P 1 1. Run type 2. Position 3. Speed 4. Accel. 5. Decel. 6. Push abs 100.00 100 100 100 100 - mm %...
Page 199: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-11 3.3 starting to use the keys you can operate the ht1 while selecting the displayed menus (refer to section 3.5, "menu structure"). The following steps explain a basic ht1 key operation, showing the procedure for setting point data. C caution before editing data, always m...
Page 200: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-12 tip • the point number can also be selected from the point number list that appears when you select "point list" from the "function" menu. (refer to section 4.4, "displaying a list of point data".) • for instructions on how to enter numbers such as point numbers, refer t...
Page 201: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-13 8 set the other point data items. Follow steps 5 to 7 to set the necessary data items. N note repeat steps 3 to 7 when setting data items for other point numbers. 9 after editing the data, press clr . The cursor returns to the point number row. Pressing clr returns to th...
Page 202: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-14 3.4 how to enter numbers the ht1 has no number keys. Use and to enter numbers. 2 3 . 4 5 2 3 . 4 6 2 3 . 4 4 2 3 . 4 6 2 3 . 4 6 0 2 3 . 4 6 func func 1 2 3 . 4 6 - - + func 1. When in number edit mode, the edit cursor appears at the rightmost digit of the number. 2. To ...
Page 203: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-15 3.5 menu structure menu func clr run stop menu point operation parameter monitor run mode connection terminal nrm [01] menu point operation parameter monitor run mode connection terminal nrm [01] menu point operation parameter monitor run mode connection terminal nrm [01...
Page 204: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-16 4. Editing the point data the procedure for editing point data is described in the previous section 3.3, "starting to use the keys", so please read it again. This section describes how to set the position for point data using point teaching, as well as how to copy or del...
Page 205: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-17 4 specify the speed to move the robot. Specify the speed as described below, on the "function" menu that appears when you press func . 1. Select "change speed" and press . The edit cursor then appears on the speed value. 2. Set the speed and press . To set the speed, use...
Page 206: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-18 4.1.2 direct teaching direct teaching is basically the same as teaching playback, except that you move the robot by hand to a desired position in emergency stop. 1 open the "point teaching" screen and select the point number. Follow the instructions described in steps 1 ...
Page 207: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-19 4.2 copying point data this section describes how to copy created point data to another point data number. 1 on the main menu screen, select "point". The "point" menu screen appears. 2 move the cursor to "point teaching" and press . The "point teaching" screen appears, s...
Page 208: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-20 4.3 deleting point data this section describes how to delete created point data. C caution deleted data cannot be restored, so be careful. 1 on the main menu screen, select "point". The "point" menu screen appears. 2 move the cursor to "point teaching" and press . The "p...
Page 209: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-21 4.4 displaying a list of point data you can display a list of point data. You can also make entries on the data edit screen by selecting a point number from the displayed list. 1 on the main menu screen, select "point". The "point" menu screen appears. 2 move the cursor ...
Page 210: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-22 5. Parameter setting the ht1 allows you to set parameters needed for robot operation. For detailed information and the setting range of each parameter, refer to the "controller guide", chapter 3, section 4, "parameter data". C caution before editing data, always make sur...
Page 211: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-23 5.2 setting i/o parameters this section describes how to set an i/o parameter using "out0 select" (terminal assignment) as an example. Basically, other i/o parameters can also be set in the same manner. N note power must be turned off and then back on to enable changes m...
Page 212: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-24 5.3 setting option parameters the following example shows the option parameters setting method when using cc-link. The same setting method is used for devicenet. N note power must be turned off and then back on to enable changes made to option parameters. 1 on the main m...
Page 213: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-25 5.4 setting servo parameters this section describes how to set a servo parameter using "payload" as an example. 1 on the main menu screen, select "parameter". The "parameter" menu screen opens showing selectable parameter groups. 2 move the cursor to "servo parameter" an...
Page 214: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-26 6. Operating the robot 6.1 turning the servo on or off this section describes how to check the servo status or how to turn the servo on or off. If the robot has a brake, the brake can also be engaged or released. 1 on the main menu screen, select "operation" the "operati...
Page 215: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-27 6.2 origin search (return-to-origin) to find the robot origin position, use the following procedure after making sure that the servo is on. N note origin search cannot be performed unless the servo is on. W warning the robot will now move, so use caution. 1 on the main m...
Page 216: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-28 6.3 operating the robot this section describes how to position the robot using the ht1. W warning the robot will now move, so use caution. 1 on the main menu screen, select "operation". The "operation" menu screen appears showing selectable menu items. 2 move the cursor ...
Page 217: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-29 5 press run to start operation. The robot starts moving to the position specified by the point data. The message "running…" appears during operation. If you want to stop the operation, press stop . - mm % % % % run:positioning start current pos. 180.00 mm p 1 1. Run type...
Page 218: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-30 6.4 resetting an alarm if an alarm occurs during operation, the robot will immediately stop. After removing the cause of the alarm, the operation can be resumed by reset. 1 on the "operation" menu screen, move the cursor to "reset" and press . The "reset" screen opens sh...
Page 219: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-31 7. Monitor functions the ht1 has the following monitor functions that display various types of information for checking operation and status. Monitor function description i/o monitor displays the status of i/o signals exchanged with the host device. Status monitor displa...
Page 220: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-32 7.2 status monitor 1 on the main menu screen, select "monitor". The "monitor" menu screen opens showing selectable menu items. 2 move the cursor to "status monitor" and press . The "status monitor" screen opens. The meaning of each item is as follows: = off, = on srv-s :...
Page 221: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-33 7.3 run monitor 1 on the main menu screen, select "monitor". The "monitor" menu screen opens showing selectable menu items. 2 move the cursor to "run monitor" and press . The "run monitor" screen opens. Pressing displays the second page. Pressing returns to the first pag...
Page 222: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-34 7.4 alarm display 1 on the main menu screen, select "monitor". The "monitor" menu screen opens showing selectable menu items. 2 move the cursor to "alarm" and press . The "alarm" screen opens showing up to 8 alarms that have occurred most recently. If 9 or more alarms ha...
Page 223: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-35 7.6 message display 1 on the main menu screen, select "monitor". The "monitor" menu screen opens showing selectable menu items. 2 move the cursor to "message" and press . The "message" screen opens showing 1 cause (alarm) of the operation stop that occurred most recently...
Page 224: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-36 7.7 alarm record display 1 on the main menu screen, select "monitor". The "monitor" menu screen opens showing selectable menu items. 2 move the cursor to "alarm records" and press . The "alarm records" screen opens showing up to 50 past alarms that occurred. Pressing or ...
Page 225: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-37 7.8 information display the model names and specifications of the controller and robot being used can be displayed. 1 on the main menu screen, select "monitor". The "monitor" menu screen opens showing selectable menu items. Pressing displays the second page. (pressing re...
Page 226: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-38 8. Other functions 8.1 operation mode when using the ht1, the operation mode can be set to any of the followings modes. The default setting is "normal mode". Run mode ht1 operation i/o control from host device description normal mode permitted permitted all ht1 operation...
Page 227: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-39 8.2 setting mode when you start the ht1 while holding down func , the "settings" screen appears as shown below. From this screen, you can change the lcd display language (japanese/english) if needed. Serial port language back light brightness b brightness gc brightness g...
Page 228: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-40 9. Specifications 9.1 basic specifications item specifications basic specifications outer dimensions w88 × h191 × d45 mm (not including emergency stop button) weight ht1 : 260kg (without cable), 400g (including cable) ht1-d : 300kg (without cable), 440g (including cable)...
Page 229: Peration Guide
A ht 1 o peration guide a-41 9.2.2 ht1-d 88 191 safety connector 63 3-position enable switch 20 45 53 (units: mm) ht1-d 23a14-m0-00
Page 231: Contents
Communication command guide contents introduction b-1 1. Communication specifications b-2 1.1 communication parameter specifications b-2 1.2 communication command specifications b-2 2. Communication command lists b-3 3. Communication command description b-5 3.1 robot operation commands b-5 positioni...
Page 233: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-1 introduction the ts series robot controller allows you to write the point data or operate the robot using a communication device, such as a personal computer through the rs-232c communication. This "communication command guide" explains how to set the communication ...
Page 234: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-2 1. Communication specifications 1.1 communication parameter specifications the communication parameters on the mating unit, such as personal computer must be set as follows. Refer to the relevant unit's operation manual for the setting procedure. Communication param...
Page 235: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-3 2. Communication command lists robot operation commands n command format command description start @start[.] positioning operation stop @stop[.] operation stop org @org[.] return-to-origin jog+ @jog+[.] jog movement (+ direction) jog- @jog-[.] jog movement (- direct...
Page 236: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-4 query commands n command format command description ?M @?M[.] point data reading operation type ?P @?P[.] position ?S @?S[.] speed ?Ac @?Ac[.] acceleration ?Dc @?Dc[.] deceleration ?Q @?Q[.] push ?Zl @?Zl[.] zone (-) ?Zh @?Zh[.] zone (+) ?N @?N[.] near width ?J @?J[...
Page 237: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-5 3. Communication command description 3.1 robot operation commands the robot operation commands are intended to operate or stop the robot. Positioning operation (start) format @start[.] c/r l/f @start[#p][.] c/r l/f meaning starts the positioning operation of specifi...
Page 238: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-6 return-to-origin (org) format @org[.] c/r l/f meaning performs the return-to-origin. Function this command has the same function as the return-to-origin (org) input. Setting : 1 to 16 (this setting can be omitted when the same command is sent to all the controllers ...
Page 239: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-7 inching movement (inch+, inch-) format @inch+[.] c/r l/f @inch-[.] c/r l/f meaning performs the inching movement in the + or - direction. Function performs the inching movement of the robot in a specified direction (+/-). N note • the inching width (amount) is set u...
Page 240: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-8 3.2 status change commands the status change commands are intended to change the servo or brake status. Servo status change (srvo) format @srvo[.] c/r l/f meaning changes the servo status. Function this command has the same function as the servo on (servo) input. Se...
Page 241: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-9 3.3 edit commands the edit commands are intended to write data, such as parameter or point. Point data writing 1 (m, p, s, ac, dc, q, zl, zh, n, j, f, t) format @m[.]= c/r l/f @p[.]= c/r l/f @s[.]= c/r l/f @ac[.]= c/r l/f @dc[.]= c/r l/f @q[.]= c/r l/f @zl[.]= c/r l...
Page 242: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-10 setting : 1 to 255 : 1 to 16 (this setting can be omitted when the same command is sent to all the controllers connected with the host device, as by daisy chain connection.) communication example transmission response @p1.1=30000 c/r l/f writes "30000" to "position...
Page 243: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-11 setting : 1 to 255 : 1 to 16 (this setting can be omitted when the same command is sent to all the controllers connected with the host device, as by daisy chain connection.) communication example transmission response @p_1.1=30000 c/r l/f writes "30000" to "positio...
Page 244: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-12 point data deleting (del) format @del[-][.] c/r l/f meaning deletes specified point data. Function deletes the point data between point no.1 and point no.2. N note if the number specified for point no.1 is larger than that of point no.2, the point data between poin...
Page 245: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-13 automatic node number setting (setid) format @setid meaning sets node numbers for daisy-chained controllers. Function sets the node numbers to the daisy-chained controllers from "1" in order of distance starting from the controller nearest to the host communication...
Page 246: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-14 3.4 query commands the query commands are intended to read the data or robot status. Point data reading (?M, ?P, ?S, ?Ac, ?Dc, ?Q, ?Zl, ?Zh, ?N, ?J, ?F, ?T) format @?M[.] c/r l/f @?P[.] c/r l/f @?S[.] c/r l/f @?Ac[.] c/r l/f @?Dc[.] c/r l/f @?Q[.] c/r l/f @?Zl[.] c...
Page 247: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-15 communication example transmission response @?P1.1 c/r l/f reads "position" of point data 1. P1.1=30000 c/r l/f receives the data. Ok.1 c/r l/f normal end @?S2.1 c/r l/f reads "speed" of point data 2. S2.1=100 c/r l/f receives the data. Ok.1 normal end parameter da...
Page 248: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-16 status data reading (?D) format @?D[.] c/r l/f meaning reads specified status information. Function reads the status information, such as current position or speed. Setting : 0 to 20 (see the table below.) : 1 to 16 (this setting can be omitted when the same comman...
Page 249: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-17 input/output information reading (?In, ?Inb, ?Out, ?Outb) format input information @?In[.] c/r l/f @?Inb[.] c/r l/f output information @?Out[.] c/r l/f @?Outb[.] c/r l/f meaning reads specified input/output information. Function reads the information on specified i...
Page 250: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-18 word input/output information reading (?Win, ?Wout) format input information @?Win[.]c/r l/f output information @?Wout[.]c/r l/f meaning reads specified word input/output information. Function reads the word input/output information. The read-out results of the wor...
Page 251: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-19 option information reading (?Opt, ?Optb) format @?Opt[.] c/r l/f @?Optb[.] c/r l/f meaning reads specified option information. Function reads the option information, such as zone output or emergency stop status. The read-out results of the option information in dec...
Page 252: Communication Command Guide
B communication command guide b-20 alarm/warning information reading (?Alm, ?Warn) format @?Alm[.] c/r l/f @?Warn[.] c/r l/f meaning reads the alarm/warning information currently occurring. Function reads the alarm/warning information currently occurring. Tip for details regarding the alarm and warn...
Page 253: Daisy Chain Guide
Daisy chain guide contents introduction c-1 1. Installation and wiring c-2 1.1 installation c-2 1.2 wiring c-3 2. Node number setting c-5 2.1 automatic node number assignment function c-5 2.1.1 when using the ts-manager c- 5 2.1.2 when using the ht1 c- 7 2.2 when controllers with same node number ex...
Page 255: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-1 introduction the daisy chain function of the ts series controllers allows connection of up to 16 controllers in a daisy chain. Data settings such as point data and parameter data for any desired controller in the daisy chain can be set and the controller status monitored with...
Page 256: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-2 1. Installation and wiring 1.1 installation w warning • to use the daisy chain connection, be sure to install an external emergency stop circuit. • be sure to be ready to perform external emergency stop before you operate a daisy-chained controller from the handy terminal or ...
Page 257: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-3 1.2 wiring to connect controllers in a daisy chain, the yamaha-specified daisy chain connection cables must be used. The number of connection cables required is the number of controllers to be connected minus one. Also a computer with the ts-manager software installed and one...
Page 258: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-4 c caution • select either the usb or d-sub connection cable for the communication cable. To perform the communication through the usb port of a communication device, such as a personal computer, use the usb communication cable. If the d-sub communication cable is connected to...
Page 259: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-5 2. Node number setting 2.1 automatic node number assignment function daisy-chained controllers can be distinguished from each other by being assigned a different "node number". Node numbers can be set with the "automatic node number assignment function" of the support softwar...
Page 260: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-6 3 select the com port. Select the com port to which the communication cable is connected, and click the [ok] button. A confirmation message appears asking whether to start automatic node number assignment. "automatic node number assignment" screen click. 24c03-m0-00 4 start a...
Page 261: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-7 2.1.2 when using the ht1 to perform automatic node number assignment using the ht1, follow the steps below. 1 select "connection". On the ht1 menu screen, select "connection". The connection screen appears. 24c29-m0-00 menu point operation parameter monitor run mode connectio...
Page 262: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-8 2.2 when controllers with same node number exist on network 2.2.1 when using the ts-manager if controllers having the same node number are connected in a daisy chain, a warning message appears when you try to connect a computer with the controllers. (see below.) in this case,...
Page 263: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-9 2.2.2 when using the ht1 if controllers having the same node number are connected in a daisy chain, an error message appears on the ht1 screen stating that there exist controllers with the same node number. In this case, perform automatic node number assignment as described b...
Page 264: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-10 2.3 switching the controllers you can check and edit the information of the daisy-chained controllers from the ts-manager or from the ht1. 2.3.1 when using the ts-manager 1 from the "file" menu, select "new" – "connection...". The "new connection" dialog box then appears. Ti...
Page 265: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-11 4 select the controller. Select the controller you want to connect and then click the [ok] button. If not all controllers are displayed, click the [research] button. N note if controllers having the same node number are found when "research" is performed, a message screen ap...
Page 266: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-12 2.3.2 switching the controllers using the ht1 to switch the controllers using the ht1, follow the steps below. 1 select "connection". On the ht1 menu screen, select "connection". A list of daisy-chained controllers is then displayed. 24c40-m0-00 menu point operation paramete...
Page 267: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-13 3. Writing and transferring saved and newly made data this section describes how to write or transfer data from the computer to a daisy-chained controller. C caution the daisy chain function cannot be used concurrently with the ts-monitor (lcd monitor option) ts-x ts-p . If ...
Page 268: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-14 3 select the controller where you want to transfer data. In the "node select" window, select the controller where you want to transfer data and click the [ok] button. If not all controllers are displayed, click the [research] button. "node select" window select controller (n...
Page 269: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-15 4 write the data. When a confirmation message appears asking whether to write the data to the selected controller, check the data name and the target controller, and click the [ok] button to start writing the data. If you want to cancel writing the data, click the [cancel] b...
Page 270: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-16 3.2 transferring data to controller 1 select the "pc to controller…" command. Transferring data to controller select. 24c19-m0-00 2 select the file you want to transfer. When the "data transfer [pc to controller]" window appears, click the […] button next to the "file name" ...
Page 271: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-17 3 select the com port to connect to the controller. To transfer data to a currently connected controller, select the "com port (in use)" (see below.). When you want to transfer data to a controller other than the currently connected one, either disconnect the connection or c...
Page 272: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-18 if the robot name set in the data to be transferred to the controller does not match the robot name currently set in the controller, a confirmation message appears asking whether to continue data transfer. If you want to continue data transfer, click the [yes] button. Transf...
Page 273: Daisy Chain Guide
C daisy chain guide c-19 another message appears asking whether to start data transfer. Check the data name and target controller, and click the [ok] button to start data transfer. To cancel data transfer, click the [cancel] button. "data transfer confirmation" message click. 24c27-m0-00 6 check tha...
Page 275: Gateway Function Guide
Gateway function guide contents introduction d-1 1. Installation and wiring d-2 1.1 installation d-2 1.2 wiring d-2 2. Initial setting d-3 2.1 node number setting d-3 2.2 enable setting d-3 3. I/o interface specifications d-4 3.1 configuration d-4 3.2 cc-link type d-5 3.3 ethernet/ip type d-6 4. Dat...
Page 277: Gateway
D gateway function guide d-1 introduction the gateway function of the ts series controller is that one controller incorporating the field network option plays a role of the gateway to collectively control multiple controllers through the daisy chain connection. Up to four controllers can be connecte...
Page 278: Gateway
D gateway function guide d-2 1. Installation and wiring 1.1 installation system configuration diagram controller #1 (gateway) controller #2 daisy chain connection (up to four controllers) controller # 3 controller # 4 daisy chain connection cable daisy chain connection cable daisy chain connection c...
Page 279: Gateway
D gateway function guide d-3 2. Initial setting this section describes the initial setting to enable the gateway function. 2.1 node number setting when connecting the gateway, set node numbers for the controllers to be connected. Set node number “1” for the controller that becomes the top of the gat...
Page 280: Gateway
D gateway function guide d-4 3. I/o interface specifications this section describes the i/o interface specifications of the gateway function. 3.1 configuration in the gateway connections, the first controller (gateway) with the field network option installed has i/o interfaces for this controller an...
Page 281: Gateway
D gateway function guide d-5 3.2 cc-link type this cc-link type operates as a remote device station of the cc-link and occupies four stations. C caution even when the number of connection units is less than 4, the number of stations to be occupied remains unchanged. The area without connection desti...
Page 282: Gateway
D gateway function guide d-6 3.3 ethernet/ip type this ethernet/ip type operates as an ethernet ip adapter, and both the input and output occupy 24 channels. C caution even when the number of connection units is less than 4, the number of channels to be occupied remains unchanged. The area without c...
Page 283: Gateway
D gateway function guide d-7 4. Data setting and operation this section describes the data setting, operation, and restrictions about the gateway function. 4.1 restrictions on gateway function to use the gateway function, there are restrictions shown below. • continuous query when the gateway functi...
Page 284
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without the permission of yamaha motor co., ltd. Information furnished by yamaha in this manual is believed to be reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed for possible inaccuracies or omissions. If you find any par...
Page 285
Http://global.Yamaha-motor.Com/business/robot/ robot manuals can be downloaded from our company website. Please use the following for more detailed information. Yamaha motor co., ltd. Im operations 882 soude, nakaku, hamamatsu, shizuoka, 435-0054, japan tel. 81-53-460-6103 fax. 81-53-460-6811.
Page 286
Http://global.Yamaha-motor.Com/business/robot/ robot manuals can be downloaded from our company website. Please use the following for more detailed information. Yamaha motor co., ltd. Im operations 882 soude, nakaku, hamamatsu, shizuoka, 435-0054, japan tel. 81-53-460-6103 fax. 81-53-460-6811.