- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Wireless Access Point
- 3CRWEASYA73 / WL-575
- User manual
3Com 3CRWEASYA73 / WL-575 User manual
Summary of 3CRWEASYA73 / WL-575
Page 1
Www.3com.Com user guide 3com outdoor 11a building to building bridge and 11bg access point 3crweasya73 / wl-575 part number 10015232 rev. Aa published august, 2006.
Page 2
3com corporation 350 campus drive marlborough, ma 01752-3064 copyright © 2006 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written pe...
Page 3: Introduction
Iii contents 1 introduction product features 1-1 radio characteristics 1-2 approved channels 1-2 package checklist 1-3 hardware description 1-4 integrated high-gain antenna 1-4 external antenna options 1-4 ethernet port 1-5 power injector module 1-5 grounding point 1-6 water tight test point 1-6 wal...
Page 4: Initial Configuration
Iv using the pole-mounting bracket 3-2 using the wall-mounting bracket 3-4 connect external antennas 3-6 connect cables to the unit 3-7 connect the power injector 3-7 check the led indicators 3-9 align antennas 3-10 4 initial configuration networks with a dhcp server 4-1 networks without a dhcp serv...
Page 5: Command Line Interface
V rssi 5-35 radio interface 5-37 802.11a interface 5-38 configuring radio settings 5-38 configuring common radio settings 5-39 802.11b/g interface 5-43 configuring wi-fi multimedia 5-45 security 5-50 wired equivalent privacy (wep) 5-53 wi-fi protected access (wpa) 5-57 6 command line interface using...
Page 6: Glossary
Vi straight-through wiring b-3 crossover wiring b-4 8-pin din connector pinout b-5 8-pin din to rj-45 cable wiring b-6 glossary index.
Page 7: Erminology
Vii t erminology access point—an internet working device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks. Ad hoc—an ad hoc wireless lan is a group of computers, each with wireless adapters, connected as an independent wireless lan. Backbone—the core infrastructure of a network. The portion of t...
Page 8
Viii rts threshold—transmitters contending for the medium may not be aware of each other (they are “hidden nodes”). The rts/cts mechanism can solve this problem. If the packet size is smaller than the preset rts threshold size, the rts/cts mechanism will not be enabled. Vap—virtual access point. An ...
Page 9: Ntroduction
1-1 1 i ntroduction the 3com outdoor 11a building to building bridge and 11bg access point system provides point-to-point or point-to-multipoint bridge links between remote ethernet lans, and wireless access point services for clients in the local lan area. It includes an integrated high-gain antenn...
Page 10: Adio
1-2 provides access point services for the 5 ghz and 2.4 ghz radios using various external antenna options maximum data rate up to 108 mbps on the 802.11a (5 ghz) radio outdoor weatherproof design ieee 802.11a and 802.11b/g compliant local network connection via 10/100 mbps ethernet port powered thr...
Page 11: Ackage
1-3 p ackage c hecklist the 3com outdoor 11a building to building bridge and 11bg access point package includes: one 3com outdoor 11a building to building bridge and 11bg access point mounting bracket and hardware one weatherproof category 5 network cable one weatherproof console to rs232 cable poe ...
Page 12: Ardware
1-4 h ardware d escription i ntegrated h igh -g ain a ntenna the wl-575 bridge includes an integrated high-gain (17 dbi) flat-panel antenna for 5 ghz operation. With this antenna, in a direct line-of-sight link using a point-to-point deployment, the range can be as long as 15 km (9.3 miles), with a ...
Page 13
1-5 external antennas connect to the n-type rf connectors on the wireless bridge using the optional rf coaxial cables. Using the external antennas in a point-to-multipoint deployment, the maximum range for bridge links are: 802.11b,g: 2.2 km 802.11a: 3 km e thernet p ort the wireless bridge has one ...
Page 14
1-6 network interconnection devices such as a switch or router that provide mdi-x ports. However, when connecting the access point to a workstation or other device that does not have mdi-x ports, you must use crossover twisted-pair cable. The wireless bridge does not have a power switch. It is power...
Page 15: Ystem
1-7 w all - and p ole -m ounting b racket k it the wireless bridge includes a bracket kit that can be used to mount the bridge to a wall, pole, radio mast, or part of a tower structure. S ystem c onfiguration at each location where a unit is installed, it must be connected to the local network using...
Page 16
1-8 the wireless bridge modes connect two or more wired networks, for example networks in different buildings with no wired connections. You will need a 3com outdoor 11a building to building bridge and 11bg access point unit on both sides of the connection. The wireless bridge can connect up to six ...
Page 17
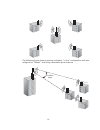
1-9 the following figure shows a point-to-multipoint “in-line” configuration with one bridge set to “master” and using a directional panel antenna. 19° beam angle.
Page 18
1-10
Page 19: Ridge
2-1 2 b ridge l ink p lanning the 3com outdoor 11a building to building bridge and 11bg access point supports fixed point-to-point or point-to-multipoint wireless links. A single link between two points can be used to connect a remote site to larger core network. Multiple bridge links can provide a ...
Page 20: Ata
2-2 d ata r ates using the 5.0 ghz integrated antenna, two wl-575 bridges can operate over a range of up to 15.4 km (9.6 miles) or provide a high-speed connection of 54 mbps (108 mbps in turbo mode). However, the maximum data rate for a link decreases as the operating range increases. A 15.4 km link...
Page 21: Adio
2-3 r adio p ath p lanning although the wireless bridge uses ieee 802.11a radio technology, which is capable of reducing the effect of multipath signals due to obstructions, the wireless bridge link requires a “radio line-of-sight” between the two antennas for optimum performance. The concept of rad...
Page 22
2-4 • be sure there is enough clearance from buildings and that no building construction may eventually block the path. • check the topology of the land between the antennas using topographical maps, aerial photos, or even satellite image data (software packages are available that may include this i...
Page 23
2-5 note that to avoid any obstruction along the path, the height of the object must be added to the minimum clearance required for a clear radio line-of-sight. Consider the following simple example, illustrated in the figure below. A wireless bridge link is deployed to connect building a to a build...
Page 24
2-6 a ntenna p osition and o rientation once the required antenna height has been determined, other factors affecting the precise position of the wireless bridge must be considered: • be sure there are no other radio antennas within 2 m (6 ft) of the wireless bridge • place the wireless bridge away ...
Page 25
2-7 r adio i nterference the avoidance of radio interference is an important part of wireless link planning. Interference is caused by other radio transmissions using the same or an adjacent channel frequency. You should first scan your proposed site using a spectrum analyzer to determine if there a...
Page 26: Thernet
2-8 • snow and ice — falling snow, like rain, has no significant effect on the radio signal. However, a build up of snow or ice on antennas may cause the link to fail. In this case, the snow or ice has to be cleared from the antennas to restore operation of the link. E thernet c abling when a suitab...
Page 27: Ardware
3-1 3 h ardware i nstallation before mounting antennas to set up your wireless bridge links, be sure you have selected appropriate locations for each antenna. Follow the guidance and information in chapter 2, “wireless link planning.” also, before mounting units in their intended locations, you shou...
Page 28: Esting
3-2 t esting b asic l ink o peration set up the units over a very short range (15 to 25 feet), either outdoors or indoors. Connect the units as indicated in this chapter and be sure to perform all the basic configuration tasks outlined in chapter 4, “initial configuration.” when you are satisfied th...
Page 29
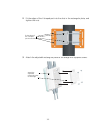
3-3 2 fit the edges of the v-shaped part into the slots in the rectangular plate, and tighten the nuts. 3 attach the adjustable rectangular plate to the bridge with supplied screws. Fit the edges of the v-shaped part into the slots attach the adjustable rectangular plate to the bridge.
Page 30
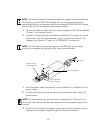
3-4 4 attach the bridge with bracket to the plate already fixed to the pole. 5 use the included nuts to secure the wireless bridge to the pole bracket. Note that the wireless bridge tilt angle may need to be adjusted during the antenna alignment process. Be sure to take account of the antenna polari...
Page 31
3-5 1 always attach the bracket to a wall with flat side flush against the wall (see following figure). 2 position the bracket in the intended location and mark the position of the four mounting screw holes. 3 drill four holes in the wall that match the screws and wall plugs included in the bracket ...
Page 32: Onnect
3-6 c onnect e xternal a ntennas the bridge’s primary antenna is it’s built-in internal antenna. For some applications when deploying an wl-575 unit for a bridge link or access point operation, you may need to mount external antennas and connect them to the bridge. Typically, a bridge link requires ...
Page 33: Onnect
3-7 c onnect c ables to the u nit 1 attach the ethernet cable to the ethernet port on the wireless bridge. 2 for extra protection against rain or moisture, apply weatherproofing tape (not included) around the ethernet connector. 3 be sure to ground the unit with an appropriate grounding wire (not in...
Page 34
3-8 1 connect the ethernet cable from the wireless bridge to the rj-45 port labeled “output” on the power injector. 2 connect a straight-through unshielded twisted-pair (utp) cable from a local lan switch to the rj-45 port labeled “input” on the power injector. Use category 5e or better utp cable fo...
Page 35: Heck
3-9 c heck the led i ndicators the bridge’s 11a and 11b/g leds operate in two display modes, which are configurable through the software. The default ap mode indicates data traffic rates. The rssi mode indicates the received signal power and is for use when aligning antennas in a bridge link. When t...
Page 36: Lign
3-10 a lign a ntennas after wireless bridge units have been mounted, connected, and their radios are operating, bridge link antennas must be accurately aligned to ensure optimum performance. This alignment process is particularly important for long-range point-to-point links. In a point-to-multipoin...
Page 37
3-11 when you move the antenna during alignment, the radio signal from the remote antenna can be seen to have a strong central main lobe and smaller side lobes. The object of the alignment process is to set the antenna so that it is receiving the strongest signal from the central main lobe. To align...
Page 38
3-12 1 pan the antenna horizontally back and forth while checking the leds. If using the pole-mounting bracket with the unit, you must rotate the mounting bracket around the pole. Other external antenna brackets may require a different horizontal adjustment. 2 find the point where the signal is stro...
Page 39: Nitial
4-1 4 i nitial c onfiguration the 3com outdoor 11a building to building bridge and 11bg access point offers a variety of management options, including a web-based interface. The initial configuration steps can be made through the web browser interface. The access point requests an ip address via dhc...
Page 40: 3Com W
4-2 c hapter 4: i nitial c onfiguration 1 connect a computer directly to the access point using the supplied standard category 5 utp ethernet cable. 2 enter the access point’s default ip address (169.254.2.1) into the computer’s web browser. If the configuration management system starts, the access ...
Page 41
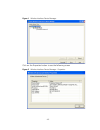
4-3 figure 1 wireless interface device manager click on the properties button to see the following screen figure 2 wireless interface device manager - properties.
Page 42: Sing
4-4 c hapter 4: i nitial c onfiguration directly connect to the device through its ethernet port or console port. Follow the instructions below to login into the ap configuration screen: 1 load a web browser and enter . 2 the logon screen appears. To log on to the web interface: 1 username, type adm...
Page 43
4-5 using the setup wizard logging in – enter the username “admin,” and password “password,” then click login. For information on configuring a user name and password, see page 23. Figure 3 login page note: if you changed the default ip address via the command line interface above, use that address ...
Page 44
4-6 c hapter 4: i nitial c onfiguration the home page displays the main menu. Figure 4 home page launching the setup wizard – to perform initial configuration, click setup wizard on the home page, select the vap you wish to configure, then click on the [next] button to start the process. Figure 5 se...
Page 45
4-7 using the setup wizard figure 6 setup wizard - step 1 2 radio channel – you must enable radio communications for 802.11a and 802.11b/g, and set the operating radio channel. Figure 7 setup wizard - step 2 note: available channel settings are limited by local regulations, which determine the chann...
Page 46
4-8 c hapter 4: i nitial c onfiguration 802.11a turbo mode – if you select enable, the access point will operate in turbo mode with a data rate of up to 108 mbps. Normal mode support 13 channels, turbo mode supports only 5 channels. (default: disabled) 802.11a radio channel – set the operating radio...
Page 47
4-9 using the setup wizard 4 security – set the authentication type to “open” to allow open access without authentication, or “shared” to require authentication based on a shared key. Enable encryption to encrypt data transmissions. To configure other security features use the advanced setup menu as...
Page 48
4-10 c hapter 4: i nitial c onfiguration 5 click finish. 6 click the ok button to complete the wizard. Figure 10 setup wizard - completed note: all wireless devices must be configured with the same key id values to communicate with the access point..
Page 49: Ystem
5-1 5 s ystem c onfiguration before continuing with advanced configuration, first complete the initial configuration steps described in chapter 4 to set up an ip address for the access point. The access point can be managed by any computer using a web browser (such as internet explorer 5.0 or above)...
Page 50: Dvanced
5-2 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration figure 11 advanced setup the information in this chapter is organized to reflect the structure of the web screens for easy reference. However, it is recommended that you configure a user name and password as the first step under administration to control manage...
Page 51
5-3 advanced setup snmp configures snmp settings 5-19 administration configures user name and password for management access; upgrades software from local file, ftp or tftp server; resets configuration settings to factory defaults; and resets the access point 5-23 wds/stp settings configures wds bri...
Page 52: Ystem
5-4 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration s ystem i dentification the system name for the access point can be left at its default setting. However, modifying this parameter can help you to more easily distinguish different devices in your network. Figure 12 system identification system name – an alias ...
Page 53: Tcp / Ip S
5-5 tcp / ip settings tcp / ip s ettings configuring the access point with an ip address expands your ability to manage the access point. A number of access point features depend on ip addressing to operate. By default, the access point will be automatically configured with ip settings from a dynami...
Page 54
5-6 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration dhcp client (enable) – select this option to obtain the ip settings for the access point from a dhcp (dynamic host configuration protocol) server. The ip address, subnet mask, default gateway, and domain name server (dns) address are dynamically assigned to the...
Page 55
5-7 tcp / ip settings figure 14 smart monitor by enabling smart monitor (known as link integrity in the cli) and setting a target ip address, the ap will periodically (set by the ping interval) check to see if the target address responds to pings. If it fails to respond to a ping after the configure...
Page 56: Radius
5-8 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration radius remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) is an authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to radius-aware devices on the network. An authentication server contains a database of user credentials fo...
Page 57
5-9 radius figure 15 radius authentication primary radius server setup – configure the following settings to use radius authentication on the access point. Ip address: specifies the ip address or host name of the radius server. Port: the udp port number used by the radius server for authentication m...
Page 58: Uthentication
5-10 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration secondary radius server setup – configure a secondary radius server to provide a backup in case the primary server fails. The access point uses the secondary server if the primary server fails or becomes inaccessible. Once the access point switches over to the...
Page 59
5-11 authentication the access point can also operate in a 802.1x supplicant mode. This enables the access point itself to be authenticated with a radius server using a configured md5 user name and password. This prevents rogue access points from gaining access to the network. Take note of the follo...
Page 60
5-12 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration figure 16 authentication mac authentication – you can configure a list of the mac addresses for wireless clients that are authorized to access the network. This provides a basic level of authentication for wireless clients attempting to gain access to the netw...
Page 61
5-13 authentication authentication section of this web page to set up the local database, and configure all access points in the wireless network service area with the same mac address database. Radius mac: the mac address of the associating station is sent to a configured radius server for authenti...
Page 62
5-14 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration session key refresh rate: the interval at which the access point refreshes unicast session keys for associated clients. (range: 0-1440 minutes; default: 0 means disabled) 802.1x reauthentication refresh rate: the time period after which a connected client must...
Page 63: Ilter
5-15 filter control f ilter c ontrol the access point can employ network traffic frame filtering to control access to network resources and increase security. You can prevent communications between wireless clients and prevent access point management from wireless clients. Also, you can block specif...
Page 64
5-16 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration prevent intra vap client communication: when enabled, clients associated with a specific vap interface cannot establish wireless communications with each other. Clients can communicate with clients associated to other vap interfaces. Prevent inter and intra va...
Page 65: Vlan
5-17 filter control vlan the access point can employ vlan tagging support to control access to network resources and increase security. Vlans separate traffic passing between the access point, associated clients, and the wired network. There can be a vlan assigned to each associated client, a defaul...
Page 66
5-18 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration a vlan id (1-4094) can be assigned to a client after successful ieee 802.1x authentication. The client vlan ids must be configured on the radius server for each user authorized to access the network. If a client does not have a configured vlan id on the radius...
Page 67: Snmp
5-19 snmp snmp simple network management protocol (snmp) is a communication protocol designed specifically for managing devices on a network. Equipment commonly managed with snmp includes switches, routers and host computers. Snmp is typically used to configure these devices for proper operation in ...
Page 68
5-20 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration figure 19 snmp snmp – enables or disables snmp management access and also enables the access point to send snmp traps (notifications). (default: disable) location – a text string that describes the system location. (maximum length: 255 characters) contact – a ...
Page 69
5-21 snmp trap destination community name – the community string sent with the notification operation. (maximum length: 23 characters, case sensitive; default: public) engine id – sets the engine identifier for the snmpv3 agent that resides on the access point. This engine protects against message r...
Page 70: Snmp
5-22 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration dot1xmacaddrauthsuccess - a client station has successfully authenticated its mac address with the radius server. Dot1xmacaddrauthfail - a client station has failed mac address authentication with the radius server. Dot1xauthnotinitiated - a client station did...
Page 71: Dministration
5-23 administration auth type – the authentication type used for the snmp user; either md5 or none. When md5 is selected, enter a password in the corresponding passphrase field. Priv type – the data encryption type used for the snmp user; either des or none. When des is selected, enter a key in the ...
Page 72: Ssh S
5-24 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration figure 22 administration username – the name of the user. The default name is “admin.” (length: 3-16 characters, case sensitive) new password – the password for management access. (length: 3-16 characters, case sensitive) confirm new password – enter the passw...
Page 73
5-25 administration telnet server status: enables or disables the telnet server. (default: enabled) ssh server status: enables or disables the ssh server. (default: enabled) ssh server port: sets the udp port for the ssh server. (range: 1-65535; default: 22) u pgrading f irmware you can upgrade new ...
Page 74
5-26 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration figure 24 firmware upgrade before upgrading new software, verify that the access point is connected to the network and has been configured with a compatible ip address and subnet mask. If you need to download from an ftp or tftp server, take the following addi...
Page 75
5-27 administration if upgrading from an ftp server, be sure that you have an account configured on the server with a user name and password. If vlans are configured on the access point, determine the vlan id with which the ftp or tftp server is associated, and then configure the management station,...
Page 76: Wds
5-28 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration restore factory settings – click the restore button in the user interface to reset the configuration settings for the access point to the factory defaults and reboot the system. Note that all user configured information will be lost. You will have to re-enter ...
Page 77
5-29 wds and spanning tree settings figure 25 wds and spanning tree settings wds bridge – up to six wds bridge or repeater links (mac addresses) per radio interface can be specified for each unit in the wireless bridge network. One unit only must be configured as the “root bridge” in the wireless ne...
Page 78
5-30 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration • root bridge: operates as the root bridge in the wireless bridge network. Up to six ”child” links are available to other bridges in the network. Master/slave mode – selects between master and slave mode. A single master enables up to five slave links, whereas...
Page 79
5-31 wds and spanning tree settings figure 27 spanning tree protocol spanning tree protocol – stp uses a distributed algorithm to select a bridging device (stp-compliant switch, bridge or router) that serves as the root of the spanning tree network. It selects a root port on each bridging device (ex...
Page 80
5-32 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration • range: 0-65535 • default: 32768 bridge max age – the maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without receiving a configuration message before attempting to reconfigure. All device ports (except for designated ports) should receive configuration messages ...
Page 81: Ystem
5-33 system log the spanning tree protocol is detecting network loops. Where more than one port is assigned the highest priority, the port with lowest numeric identifier will be enabled. • default: 128 • range: 0-240, in steps of 16 s ystem l og the access point can be configured to send event and e...
Page 82: Sntp
5-34 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration logging host – enables the sending of log messages to a syslog server host. Up to four syslog servers are supported on the access point. (default: disable) server name / ip – specifies a syslog server name or ip address. (default: 0.0.0.0) sntp server – enable...
Page 83: Rssi
5-35 rssi the access point acts as an sntp client, periodically sending time synchronization requests to specific time servers. You can configure up to two time server ip addresses. The access point will attempt to poll each server in the configured sequence. Sntp server – configures the access poin...
Page 84
5-36 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration figure 29 rssi rssi: auto refresh – enables or disables the refreshing of rssi information. Rssi value – the displayed rssi value for a selected port. Port number – selects a specific wds port for which to display the rssi output value. Ports 1-6 are available...
Page 85: Adio
5-37 radio interface led status: mode – selects ap mode or bridge mode. Bridge port – allows the user to select the bridge port for the led display. (default:1; range: 1~6) there are currently no equivalent cli commands for the rssi controls. R adio i nterface the ieee 802.11a and 802.11g interfaces...
Page 86: 802.11
5-38 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration 802.11 a i nterface the ieee 802.11a interface operates within the 5 ghz band, at up to 54 mbps in normal mode or up to 108 mbps in turbo mode. First configure the radio settings that apply to the individual vaps (virtual access point) and the common radio set...
Page 87
5-39 radio interface closed system – when enabled, the vap interface does not include its ssid in beacon messages. Nor does it respond to probe requests from clients that do not include a fixed ssid. (default: disable) maximum associations – this command configures the maximum number of clients that...
Page 88
5-40 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration description – adds a comment or description to the wireless interface. (range: 1-80 characters) turbo mode – the normal 802.11a wireless operation mode provides connections up to 54 mbps. Turbo mode is an enhanced mode (not regulated in ieee 802.11a) that prov...
Page 89
5-41 radio interface radio channel – the radio channel that the access point uses to communicate with wireless clients. When multiple access points are deployed in the same area, set the channel on neighboring access points at least four channels apart to avoid interference with each other. For exam...
Page 90
5-42 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration maximum transmit data rate – the maximum data rate at which the access point transmits unicast packets on the wireless interface. The maximum transmission distance is affected by the data rate. The lower the data rate, the longer the transmission distance. (op...
Page 91: 802.11
5-43 radio interface negotiate the sending of a data frame. After receiving an rts frame, the station sends a cts (clear to send) frame to notify the sending station that it can start sending data. If the rts threshold is set to 0, the access point always sends rts signals. If set to 2347, the acces...
Page 92
5-44 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration figure 32 radio settings b/g client access mode– selects the operating mode for the 802.11g wireless interface. (default: 802.11b+g) 802.11b+g: both 802.11b and 802.11g clients can communicate with the access point (up to 54 mbps). 802.11b only: both 802.11b a...
Page 93
5-45 radio interface super mode – the atheros proprietary super g performance enhancements are supported by the access point. These enhancements include bursting, compression, fast frames and dynamic turbo. Maximum throughput ranges between 40 to 60 mbps for connections to atheros-compatible clients...
Page 94
5-46 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration the access point implements qos using the wi-fi multimedia (wmm) standard. Using wmm, the access point is able to prioritize traffic and optimize performance when multiple applications compete for wireless network bandwidth at the same time. Wmm employs techni...
Page 95
5-47 radio interface resolution mechanism first selects data with the highest priority to be granted a transmit opportunity. Then the same collision resolution mechanism is used externally to determine which device has access to the wireless medium. For each ac queue, the collision resolution mechan...
Page 96
5-48 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration figure 34 wmm configuration wmm– sets the wmm operational mode on the access point. When enabled, the parameters for each ac queue will be employed on the access point and qos capabilities are advertised to wmm-enabled clients. (default: support) disable: wmm ...
Page 97
5-49 radio interface initial wait time is a random value between zero and the cwmin value. Specify the cwmin value in the range 0-15 microseconds. Note that the cwmin value must be equal or less than the cwmax value. Logcwmax (maximum contention window)– the maximum upper limit of the random backoff...
Page 98: Ecurity
5-50 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration s ecurity the access point is configured by default as an “open system,” which broadcasts a beacon signal including the configured ssid. Wireless clients with an ssid setting of “any” can read the ssid from the beacon and automatically set their ssid to allow ...
Page 99
5-51 security the access point can simultaneously support clients using various different security mechanisms. The configuration for these security combinations are outlined in the following table. Note that mac address authentication can be configured independently to work with all security mechani...
Page 100
5-52 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration dynamic wep (802.1x) only authentication: open system encryption: enable 802.1x: required set 802.1x key refresh and re authentication rates local, radius, or disabled yes c 802.1x wpa only authentication: wpa encryption: enable wpa configuration: required cip...
Page 101
5-53 security w ired e quivalent p rivacy (wep) wep provides a basic level of security, preventing unauthorized access to the network, and encrypting data transmitted between wireless clients and the access point. Wep uses static shared keys (fixed-length hexadecimal or alphanumeric strings) that ar...
Page 102
5-54 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration note that all clients share the same keys, which are used for user authentication and data encryption. Up to four keys can be specified. These four keys are used for all vap interfaces on the same radio. To set up wep shared keys, click radio settings under 80...
Page 103
5-55 security encryption – enable or disable the access point to use data encryption (wep, tkip, or aes). If this option is selected when using static wep keys, you must configure at least one key on the access point and all clients. (default: disabled) cipher modes – selects an encryption method fo...
Page 104
5-56 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration hexadecimal: enter keys as 10 hexadecimal digits (0-9 and a-f) for 64 bit keys, 26 hexadecimal digits for 128 bit keys, or 32 hexadecimal digits for 152 bit keys (802.11a radio only). This is the default setting. Alphanumeric: enter keys as 5 alphanumeric char...
Page 105
5-57 security key type – select the preferred method of entering wep encryption keys on the access point and enter up to four keys: • hexadecimal: enter keys as 10 hexadecimal digits (0-9 and a-f) for 64 bit keys, 26 hexadecimal digits for 128 bit keys, or 32 hexadecimal digits for 152 bit keys (802...
Page 106
5-58 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration temporal key integrity protocol (tkip): wpa specifies tkip as the data encryption method to replace wep. Tkip avoids the problems of wep static keys by dynamically changing data encryption keys. Basically, tkip starts with a master (temporal) key for each user...
Page 107
5-59 security for wpa2. However, the computational intensive operations of aes-ccmp requires hardware support on client devices. Therefore to implement wpa2 in the network, wireless clients must be upgraded to wpa2-compliant hardware. Wpa2 mixed-mode: wpa2 defines a transitional mode of operation fo...
Page 108: Status Information
5-60 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration status information the status page includes information on the following items: access point status the ap status window displays basic system configuration settings, as well as the settings for the wireless interface. Figure 38 ap status ap system configurati...
Page 109
5-61 security http server: shows if management access via http is enabled. Http server port: shows the tcp port used by the http interface. Version: shows the software version number. 802.1x: shows if ieee 802.1x access control for wireless clients is enabled. Ap wireless configuration – the ap wire...
Page 110
5-62 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration system” and “shared key.” open-system authentication accepts any client attempting to connect to the access point without verifying its identity. The shared-key approach uses wired equivalent privacy (wep) to verify client identity by distributing a shared key...
Page 111
5-63 security access point was set to “open authentication”, but a client sent an authentication request frame with a “shared key.” access point was set to “shared key authentication,” but a client sent an authentication frame for “open system.” wep keys do not match: when the access point uses “sha...
Page 112
5-64 c hapter 5: s ystem c onfiguration.
Page 113: Ommand
6-1 6 c ommand l ine i nterface u sing the c ommand l ine i nterface a ccessing the cli when accessing the management interface for the over a direct connection to the console port, or via a telnet connection, the access point can be managed by entering command keywords and parameters at the prompt....
Page 114
6-2 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface telnet connection telnet operates over the ip transport protocol. In this environment, your management station and any network device you want to manage over the network must have a valid ip address. Valid ip addresses consist of four numbers, 0 to 255, sepa...
Page 115
6-3 using the command line interface e ntering c ommands this section describes how to enter cli commands. Keywords and arguments a cli command is a series of keywords and arguments. Keywords identify a command, and arguments specify configuration parameters. For example, in the command “show interf...
Page 116
6-4 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface showing commands if you enter a “?” at the command prompt, the system will display the first level of keywords for the current configuration mode (exec, global configuration, or interface). You can also display a list of valid keywords for a specific command...
Page 117
6-5 using the command line interface negating the effect of commands for many configuration commands you can enter the prefix keyword “no” to cancel the effect of a command or reset the configuration to the default value. For example, the logging command will log system messages to a host server. To...
Page 118
6-6 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface configuration commands configuration commands are used to modify access point settings. These commands modify the running configuration and are saved in memory. The configuration commands are organized into four different modes: • global configuration (gc) -...
Page 119
6-7 using the command line interface table 8 keystroke commands c ommand g roups the system commands can be broken down into the functional groups shown below. Table 9 command groups keystroke function ctrl-a shifts cursor to start of command line. Ctrl-b shifts cursor to the left one character. Ctr...
Page 120: General Commands
6-8 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface the access mode shown in the following tables is indicated by these abbreviations: exec (executive mode), gc (global configuration), ic-e (interface-ethernet configuration), ic-w (interface-wireless configuration), and ic-w-vap (interface-wireless vap config...
Page 121
6-9 using the command line interface default setting none command mode exec example related commands end (6-9) end this command returns to the previous configuration mode. Default setting none command mode global configuration, interface configuration example this example shows how to return to the ...
Page 122
6-10 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface exit this command returns to the exec mode or exits the configuration program. Default setting none command mode any example this example shows how to return to the exec mode from the interface configuration mode, and then quit the cli session: ping this co...
Page 123
6-11 using the command line interface - destination unreachable - the gateway for this destination indicates that the destination is unreachable. - network or host unreachable - the gateway found no corresponding entry in the route table. • press to stop pinging. Example reset this command restarts ...
Page 124
6-12 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface show history this command shows the contents of the command history buffer. Default setting none command mode exec command usage • the history buffer size is fixed at 10 commands. • use the up or down arrow keys to scroll through the commands in the history...
Page 125: System Management Commands
6-13 using the command line interface system management commands these commands are used to configure the user name, password, system logs, browser management options, clock settings, and a variety of other system information. Table 11 system management commands country this command configures the a...
Page 126
6-14 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface syntax country country_code> country_code - a two character code that identifies the country of operation. See the following table for a full list of codes. Table 12 country codes country code country code country code country code albania al dominican repu...
Page 127
6-15 using the command line interface default setting us - for units sold in the united states 99 (no country set) - for units sold in other countries command mode exec command usage • if you purchased an access point outside of the united states, the country code must be set before radio functions ...
Page 128
6-16 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default setting outdoor 11a building to building command mode global configuration example system name this command specifies or modifies the system name for this device. Use the no form to restore the default system name. Syntax system name name> no system...
Page 129
6-17 using the command line interface default setting admin command mode global configuration example password after initially logging onto the system, you should set the password. Remember to record it in a safe place. Use the no form to reset the default password. Syntax password password> no pass...
Page 130
6-18 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage • the access point supports secure shell version 2.0 only. • after boot up, the ssh server needs about two minutes to generate host encryption keys. The ssh server is disabled while the keys are ...
Page 131
6-19 using the command line interface command mode interface configuration (ethernet) example ip http port this command specifies the tcp port number used by the web browser interface. Use the no form to use the default port. Syntax ip http port port-number> no ip http port port-number - the tcp por...
Page 132
6-20 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface command mode global configuration example related commands ip http port (6-19) ip https port use this command to specify the udp port number used for https/ssl connection to the access point’s web interface. Use the no form to restore the default port. Synt...
Page 133
6-21 using the command line interface example ip https server use this command to enable the secure hypertext transfer protocol (https) over the secure socket layer (ssl), providing secure access (i.E., an encrypted connection) to the access point’s web interface. Use the no form to disable this fun...
Page 134
6-22 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface web-redirect use this command to enable web-based authentication of clients. Use the no form to disable this function. Syntax [no] web-redirect default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage • the web redirect feature is used to su...
Page 137
6-25 using the command line interface show apmanagement this command shows the ap management configuration, including the ip addresses of management stations allowed to access the access point, as well as the interface protocols which are open to management access. Command mode exec example outdoor ...
Page 138
6-26 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface show system this command displays basic system configuration settings. Default setting none command mode exec example outdoor 11a building to building #show system system information ========================================================== serial number :...
Page 139
6-27 using the command line interface show version this command displays the software version for the system. Command mode exec example show config this command displays detailed configuration information for the system. Command mode exec example outdoor 11a building to building #show version versio...
Page 140
6-28 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface protocol filter information =========================================================== local bridge :disabled ap management :enabled ethernet type filter :disabled enabled protocol filters ----------------------------------------------------------- no prot...
Page 141
6-29 using the command line interface ----------------security----------------------------------- closed system : disabled multicast cipher : wep unicast cipher : tkip and aes wpa clients : required wpa key mgmt mode : pre shared key wpa psk key type : alphanumeric encryption : disabled default tran...
Page 142
6-30 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface radius secondary server information ======================================== ip : 0.0.0.0 port : 1812 key : ***** retransmit : 3 timeout : 5 radius mac format : no-delimiter radius vlan format : hex ======================================== snmp information ...
Page 143
6-31 using the command line interface sntp information =========================================================== service state : disabled sntp (server 1) ip : 137.92.140.80 sntp (server 2) ip : 192.43.244.18 current time : 00 : 14, jan 1st, 1970 time zone : -5 (bogota, eastern, indiana) daylight s...
Page 144: System Logging Commands
6-32 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface show hardware this command displays the hardware version of the system. Command mode exec example system logging commands these commands are used to configure system logging on the access point. Table 13 system loggign commands ssh server : enabled ssh serv...
Page 145
6-33 using the command line interface logging on this command controls logging of error messages; i.E., sending debug or error messages to memory. The no form disables the logging process. Syntax [no] logging on default setting disabled command mode global configuration command usage the logging pro...
Page 146
6-34 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default setting none command mode global configuration example logging console this command initiates logging of error messages to the console. Use the no form to disable logging to the console. Syntax [no] logging console default setting disabled command m...
Page 147
6-35 using the command line interface command usage messages sent include the selected level down to emergency level. Example logging facility-type this command sets the facility type for remote logging of syslog messages. Syntax logging facility-type type> type - a number that indicates the facilit...
Page 148
6-36 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example logging clear this command clears all log messages stored in the access point’s memory. Syntax logging clear command mode global configuration example show logging this command displays the logging configuration. Syntax show logging command mode exe...
Page 149: System Clock Commands
6-37 using the command line interface show event-log this command displays log messages stored in the access point’s memory. Syntax show event-log command mode exec example system clock commands these commands are used to configure sntp and system clock settings on the access point. Table 14 system ...
Page 151
6-39 using the command line interface default setting enabled command mode global configuration command usage the time acquired from time servers is used to record accurate dates and times for log events. Without sntp, the access point only records the time starting from the factory default set at t...
Page 152
6-40 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface related commands sntp-server enable (6-38) sntp-server daylight-saving this command sets the start and end dates for daylight savings time. Use the no form to disable daylight savings time. Syntax [no] sntp-server daylight-saving default setting disabled co...
Page 153
6-41 using the command line interface command mode global configuration command usage this command sets the local time zone relative to the coordinated universal time (utc, formerly greenwich mean time or gmt), based on the earth’s prime meridian, zero degrees longitude. To display a time correspond...
Page 154: Dhcp Relay Commands
6-42 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface dhcp relay commands dynamic host configuration protocol (dhcp) can dynamically allocate an ip address and other configuration information to network clients that broadcast a request. To receive the broadcast request, the dhcp server would normally have to b...
Page 156: Snmp Commands
6-44 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface command mode exec example snmp commands controls access to this access point from management stations using the simple network management protocol (snmp), as well as the hosts that will receive trap messages. Table 16 snmp commands outdoor 11a building to b...
Page 157
6-45 using the command line interface show snmp filter displays the snmp v3 notification filters exec 6-58 show snmp filter-assignments displays the snmp v3 notification filter assignments exec 6-59 show snmp displays the status of snmp communications exec 6-60 command function mode page.
Page 159
6-47 using the command line interface default setting none command mode global configuration example related commands snmp-server location (6-47) snmp-server location this command sets the system location string. Use the no form to remove the location string. Syntax snmp-server location text> no snm...
Page 160
6-48 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface snmp-server enable server this command enables snmp management access and also enables this device to send snmp traps (i.E., notifications). Use the no form to disable snmp service and trap messages. Syntax snmp-server enable server no snmp-server enable se...
Page 161
6-49 using the command line interface • host_name - name of the host. (range: 1-63 characters) • community-string - password-like community string sent with the notification operation. Although you can set this string using the snmp-server host command by itself, we recommend that you define this st...
Page 162
6-50 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface re-associated with the access point. - dot11stationrequestfail - a client station has failed association, re-association, or authentication. - dot1xauthfail - a 802.1x client station has failed radius authentication. - dot1xauthnotinitiated - a client stati...
Page 163
6-51 using the command line interface default setting all traps enabled command mode global configuration command usage this command is used in conjunction with the snmp-server host and snmp-server enable server commands to enable snmp notifications. Example snmp-server engine-id this command is use...
Page 164
6-52 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example snmp-server user this command configures the snmp v3 users that are allowed to manage the access point. Use the no form to delete an snmp v3 user. Syntax snmp-server user user-name> user-name - a user-defined string for the snmp user. (32 characters...
Page 165
6-53 using the command line interface • the command prompts for the following information to configure an snmp v3 user: - user-name - a user-defined string for the snmp user. (32 characters maximum) - group-name - the name of the snmp group to which the user is assigned (32 characters maximum). Ther...
Page 166
6-54 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface syntax snmp-server targets target-id> ip-addr> sec-name> [version {3}] [udp-port {port-number}] [notification-type {trap}] no snmp-server targets target-id> • target-id - a user-defined name that identifies a receiver of snmp notifications. (maximum length:...
Page 168
6-56 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example snmp-server filter-assignments this command assigns snmp v3 notification filters to targets. Use the no form to remove an snmp v3 filter assignment. Syntax snmp-server filter-assignments target-id> filter-id> no snmp-server filter-assignments target...
Page 169
6-57 using the command line interface syntax show snmp groups command mode exec example show snmp users this command displays the snmp v3 users and settings. Syntax show snmp users command mode exec example show snmp group-assignments this command displays the snmp v3 user group assignments. Outdoor...
Page 170
6-58 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface syntax show snmp group-assignments command mode exec example show snmp target this command displays the snmp v3 notification target settings. Syntax show snmp target command mode exec example show snmp filter this command displays the snmp v3 notification f...
Page 171
6-59 using the command line interface command mode exec example show snmp filter-assignments this command displays the snmp v3 notification filter assignments. Syntax show snmp filter-assignments command mode exec example outdoor 11a building to building#show snmp filter filter: trapfilter type: inc...
Page 172
6-60 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface show snmp this command displays the snmp configuration settings. Command mode exec example outdoor 11a building to building #show snmp snmp information ============================================== service state : enable community (ro) : ***** community (r...
Page 173: Flash/file Commands
6-61 using the command line interface flash/file commands these commands are used to manage the system code or configuration files. Table 17 flash/file commands bootfile this command specifies the image used to start up the system. Syntax bootfile filename> filename - name of the image file. Default...
Page 174
6-62 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example copy this command copies a boot file, code image, or configuration file between the access point’s flash memory and a ftp/tftp server. When you save the configuration settings to a file on a ftp/tftp server, that file can later be downloaded to the ...
Page 175
6-63 using the command line interface example the following example shows how to upload the configuration settings to a file on the tftp server: the following example shows how to download a configuration file: delete this command deletes a file or image. Syntax delete filename> filename - name of t...
Page 176
6-64 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example this example shows how to delete the test.Cfg configuration file from flash memory. Related commands bootfile (6-61) dir (6-64) dir this command displays a list of files in flash memory. Command mode exec command usage file information is shown belo...
Page 177: Radius Client
6-65 using the command line interface show bootfile this command displays the name of the current operation code file that booted the system. Syntax show snmp filter-assignments command mode exec example radius client remote authentication dial-in user service (radius) is a logon authentication prot...
Page 179
6-67 using the command line interface example radius-server key this command sets the radius encryption key. Syntax radius-server [secondary] key key_string> • secondary - secondary server. • key_string - encryption key used to authenticate logon access for client. Do not use blank spaces in the str...
Page 180
6-68 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default setting 3 command mode global configuration example radius-server timeout this command sets the interval between transmitting authentication requests to the radius server. Syntax radius-server [secondary] timeout number_of_seconds • secondary - seco...
Page 181
6-69 using the command line interface default setting 0 (disabled) command mode global configuration command usage • when the radius accounting server udp port is specified, a radius accounting session is automatically started for each user that is successfully authenticated to the access point. Exa...
Page 183: 802.1X Authentication
6-71 using the command line interface default setting none command mode exec example 802.1x authentication the access point supports ieee 802.1x access control for wireless clients. This control feature prevents unauthorized access to the network by requiring an 802.1x client application to submit u...
Page 185
6-73 using the command line interface stations initiating 802.1x, only those stations successfully authenticated are allowed to access the network. For those stations not initiating 802.1x, access to the network is allowed after successful 802.11 association..
Page 186
6-74 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface • when 802.1x is required, the access point enforces 802.1x authentication for all 802.11 associated stations. If 802.1x authentication is not initiated by the station, the access point will initiate authentication. Only those stations successfully authenti...
Page 187
6-75 using the command line interface example 802.1x session-key-refresh-rate this command sets the interval at which unicast session keys are refreshed for associated stations using dynamic keying. Syntax 802.1x session-key-refresh-rate rate> rate - the interval at which the access point refreshes ...
Page 188
6-76 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default 0 (disabled) command mode global configuration example 802.1x-supplicant enable this command enables the access point to operate as an 802.1x supplicant for authentication. Use the no form to disable 802.1x authentication of the access point. Syntax...
Page 189
6-77 using the command line interface syntax 802.1x-supplicant user username> no 802.1x-supplicant user • username - the access point name used for authentication to the network. (range: 1-32 alphanumeric characters) • password - the md5 password used for access point authentication. (range: 1-32 al...
Page 190: Mac Address Authentication
6-78 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface command mode exec example mac address authentication use these commands to define mac authentication on the access point. For local mac authentication, first define the default filtering policy using the address filter default command. Then enter the mac ad...
Page 192
6-80 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default none command mode global configuration command mode • the access point supports up to 1024 mac addresses. • an entry in the address table may be allowed or denied access depending on the global setting configured for the address entry default comman...
Page 193
6-81 using the command line interface address filter delete this command deletes a mac address from the filter table. Syntax address filter delete mac-address> mac-address - physical address of client. (enter six pairs of hexadecimal digits separated by hyphens.) default none command mode global con...
Page 194: Filtering Commands
6-82 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default disabled command mode global configuration example related commands address filter entry (6-79) radius-server address (6-66) 802.1x-supplicant user (6-76) mac-authentication session-timeout this command sets the interval at which associated clients ...
Page 196
6-84 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default disabled command mode global configuration command usage this command can disable wireless-to-wireless communications between clients via the access point. However, it does not affect communications between wireless clients and the wired network. Ex...
Page 197
6-85 using the command line interface filter ap-manage this command prevents wireless clients from accessing the management interface on the access point. Use the no form to disable this filtering. Syntax [no] filter ap-manage default enabled command mode global configuration example filter uplink e...
Page 198
6-86 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default disabled command mode global configuration example filter ethernet-type enable this command checks the ethernet type on all incoming and outgoing ethernet packets against the protocol filtering table. Use the no form to disable this feature. Syntax ...
Page 199
6-87 using the command line interface filter ethernet-type protocol this command sets a filter for a specific ethernet type. Use the no form to disable filtering for a specific ethernet type. Syntax filter ethernet-type protocol protocol> no filter ethernet-type protocol protocol> protocol - an ethe...
Page 200: Wds Bridge Commands
6-88 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example wds bridge commands the commands described in this section are used to set the operation mode for each access point interface and configure wireless distribution system (wds) forwarding table settings. Table 22 wds bridge commands outdoor 11a buildi...
Page 202
6-90 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface when the access point is operating in this mode, traffic is not forwarded to the ethernet port from the radio interface. • up to four wds bridge links (mac addresses) per radio interface can be specified for each unit in the wireless bridge network. One uni...
Page 203
6-91 using the command line interface bridge-link parent this command configures the mac address of the parent bridge node. Syntax bridge-link parent mac-address> mac-address - the wireless mac address of the parent bridge unit. (12 hexadecimal digits in the form “xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx”). Default settin...
Page 204
6-92 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default setting none command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage • in root bridge mode, up to six child bridge links can be specified using link index numbers 1 to 6. • in bridge mode, up to five child links can be specified using link ind...
Page 205
6-93 using the command line interface default setting 300 seconds command mode global configuration command usage if the mac address of an entry in the address table is not seen on the associated interface for longer than the aging time, the entry is discarded. Example outdoor 11a building to buildi...
Page 206
6-94 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface show bridge aging-time this command displays the current wds forwarding table aging time setting..
Page 207
6-95 using the command line interface command mode exec example show bridge filter-entry this command displays current entries in the wds forwarding table. Command mode exec outdoor 11a building to building#show bridge aging-time aging time: 300 outdoor 11a building to building#.
Page 208
6-96 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example outdoor 11a building to building#show bridge filter-entry max entry numbers =512 current entry nums =13 **************************************************************** *********************** bridge mac addr table *********** **********************...
Page 210
6-98 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface command mode exec example outdoor 11a building to building#show bridge link wireless a interface wireless a wds information ==================================== ap role: bridge parent: 00-12-34-56-78-9a child: child 2: 00-08-12-34-56-de child 3: 00-00-00-00...
Page 211: Spanning Tree Commands
6-99 using the command line interface spanning tree commands the commands described in this section are used to set the mac address table aging time and spanning tree parameters for both the ethernet and wireless interfaces. Table 23 bridge commands bridge stp enable this command enables the spannin...
Page 212
6-100 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface syntax [no] bridge stp enable default setting enabled command mode global configuration example this example globally enables the spanning tree protocol. Bridge stp forwarding-delay use this command to configure the spanning tree bridge forward time global...
Page 213
6-101 using the command line interface changes before it starts to forward frames. In addition, each port needs time to listen for conflicting information that would make it return to the discarding state; otherwise, temporary data loops might result. Example bridge stp hello-time use this command t...
Page 214
6-102 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface syntax bridge stp max-age seconds> no bridge stp max-age seconds - time in seconds. (range: 6-40 seconds) the minimum value is the higher of 6 or [2 x (hello-time + 1)]. The maximum value is the lower of 40 or [2 x (forward-time - 1)]. Default setting 20 s...
Page 215
6-103 using the command line interface default setting 32768 command mode global configuration command usage bridge priority is used in selecting the root device, root port, and designated port. The device with the highest priority becomes the stp root device. However, if all devices have the same p...
Page 216
6-104 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example bridge-link port-priority use this command to configure the priority for the specified port. Syntax bridge-link port-priority index> priority> • index - specifies the bridge link number on the wireless bridge. (range: 1-6 required on wireless inter...
Page 217: Ethernet Interface Commands
6-105 using the command line interface syntax show bridge stp command mode exec example ethernet interface commands the commands described in this section configure connection parameters for the ethernet port and wireless interface. Table 24 ehternet interface commands outdoor 11a building to buildi...
Page 218
6-106 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface interface ethernet this command enters ethernet interface configuration mode. Default setting none command mode global configuration example to specify the 10/100base-tx network interface, enter the following command: dns server this command specifies the ...
Page 219
6-107 using the command line interface related commands show interface ethernet (6-110) ip address this command sets the ip address for the access point. Use the no form to restore the default ip address. Syntax ip address ip-address> netmask> gateway> no ip address • ip-address - ip address • netma...
Page 220
6-108 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface ip dhcp this command enables the access point to obtain an ip address from a dhcp server. Use the no form to restore the default ip address. Syntax [no] ip dhcp default setting enabled command mode interface configuration (ethernet) command usage • you mus...
Page 222
6-110 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface command usage this command allows you to disable the ethernet port due to abnormal behavior (e.G., excessive collisions), and reenable it after the problem has been resolved. You may also want to disable the ethernet port for security reasons. Example the ...
Page 223: Wireless Interface Commands
6-111 using the command line interface wireless interface commands the commands described in this section configure connection parameters for the wireless interfaces. Table 25 wireless interface commands command function mode page interface wireless enters wireless interface configuration mode gc 6-...
Page 225
6-113 using the command line interface vap this command provides access to the vap (virtual access point) interface configuration mode. Syntax vap vap-id> vap-id - the number that identifies the vap interface. (options: 0-3) default setting none command mode interface configuration (wireless) exampl...
Page 226
6-114 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface (e.G., setting the speed to 54 mbps limits the effective maximum speed to 108 mbps). Example turbo this command sets the access point to an enhanced proprietary modulation mode (not regulated in ieee 802.11a) that provides a higher data rate of up to 108 m...
Page 227
6-115 using the command line interface rate. However, this reduces the number of channels supported (e.G., 5 channels for the united states). Example multicast-data-rate this command configures the maximum data rate at which the access point transmits multicast and management packets (excluding beac...
Page 229
6-117 using the command line interface transmit-power this command adjusts the power of the radio signals transmitted from the access point. Syntax transmit-power signal-strength> signal-strength - signal strength transmitted from the access point. (options: full, half, quarter, eighth, min) default...
Page 230
6-118 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default setting b+g mode command mode interface configuration (wireless - 802.11g) command usage • for japan, only 13 channels are available when set to g or b+g modes. When set to b mode, 14 channels are available. • both the 802.11g and 802.11b standards...
Page 232
6-120 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface antenna id this command specifies the antenna type connected to the access point represented by a four-digit hexadecimal id number, either the integrated diversity antennas (the "default antenna") or an optional external antenna. Syntax antenna id antenna-...
Page 233
6-121 using the command line interface default setting indoor command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage • when an external antenna is selected, the antenna control must be set to “right.” • selecting the correct location ensures that the access point only uses radio channels that...
Page 234
6-122 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface dtim-period this command configures the rate at which stations in sleep mode must wake up to receive broadcast/multicast transmissions. Syntax dtim-period interval> interval - interval between the beacon frames that transmit broadcast or multicast traffic....
Page 235
6-123 using the command line interface fragmentation-length this command configures the minimum packet size that can be fragmented when passing through the access point. Syntax fragmentation-length length> length - minimum packet size for which fragmentation is allowed. (range: 256-2346 bytes) defau...
Page 236
6-124 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default setting 2347 command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage • if the threshold is set to 0, the access point always sends rts signals. If set to 2347, the access point never sends rts signals. If set to any other value, and the packe...
Page 237
6-125 using the command line interface example super-g this command enables atheros proprietary super g performance enhancements. Use the no form to disable this function. Syntax [no] super-g default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (wireless - 802.11g) command usage these enhan...
Page 238
6-126 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example ssid this command configures the service set identifier (ssid). Syntax ssid string> string - the name of a basic service set supported by the access point. (range: 1 - 32 characters) default setting 802.11a radio: vap_test_11a (0 to 3) 802.11g radi...
Page 239
6-127 using the command line interface command mode interface configuration (wireless-vap) command usage when closed system is enabled, the access point will not include its ssid in beacon messages. Nor will it respond to probe requests from clients that do not include a fixed ssid. Example max-asso...
Page 240
6-128 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default setting 30 command mode interface configuration (wireless-vap) example auth-timeout-value this command configures the time interval within which clients must complete authentication to the vap interface. Syntax auth-timeout-value minutes> minutes -...
Page 241
6-129 using the command line interface command mode interface configuration (wireless-vap) command usage you must first enable vap interface 0 before you can enable vap interfaces 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, or 7. Example show interface wireless this command displays the status for the wireless interface. Syn...
Page 242
6-130 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface command mode exec example outdoor 11a building to building #show interface wireless g 0 wireless interface information ========================================================================= ----------------identification---------------------------------...
Page 243
6-131 using the command line interface ----------------security------------------------------------------------- closed system : disabled multicast cipher : wep unicast cipher : tkip and aes wpa clients : disabled wpa key mgmt mode : pre shared key wpa psk key type : passphrase wpa psk key : empty p...
Page 244
6-132 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface wmm ap parameters ac0(best effort) : logcwmin: 4 logcwmax: 6 aifsn: 3 admission control: no txop limit: 0.000 ms ac1(background) : logcwmin: 4 logcwmax: 10 aifsn: 7 admission control: no txop limit: 0.000 ms ac2(video) : logcwmin: 3 logcwmax: 4 aifsn: 1 ad...
Page 245: Rogue Ap Detection Commands
6-133 using the command line interface show station this command shows the wireless clients associated with the access point. Command mode exec example rogue ap detection commands a “rogue ap” is either an access point that is not authorized to participate in the wireless network, or an access point...
Page 246
6-134 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface the access point can be configured to periodically scan all radio channels and find other access points within range. A database of nearby access points is maintained where any rogue aps can be identified. Table 26 rogue ap commands rogue-ap enable this co...
Page 247
6-135 using the command line interface the rogue ap database can be viewed using the show rogue-ap command. • the access point sends syslog messages for each detected access point during a rogue ap scan. Example rogue-ap authenticate this command forces the unit to authenticate all access points on ...
Page 248
6-136 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface access points are allowed or are rogues. If you enable authentication, you should also configure a radius server for this access point (see “radius” on page 8). Example rogue-ap duration this command sets the scan duration for detecting access points. Synt...
Page 249
6-137 using the command line interface syntax rogue-ap interval minutes - the interval between consecutive scans. (range: 30-10080 minutes) default setting 720 minutes command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage this command sets the interval at which scans occur. Frequent scanning...
Page 250
6-138 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface default setting disabled command mode interface configuration (wireless) command usage while the access point scans a channel for rogue aps, wireless clients will not be able to connect to the access point. Therefore, avoid frequent scanning or scans of a ...
Page 251: Wireless Security Commands
6-139 using the command line interface show rogue-ap this command displays the current rogue ap database. Command mode exec example wireless security commands the commands described in this section configure parameters for wireless security on the 802.11a and 802.11g interfaces. Table 27 wireless se...
Page 253
6-141 using the command line interface • to use wep shared-key authentication, set the authentication type to “shared-key” and define at least one static wep key with the key command. Encryption is automatically enabled by the command. • to use wep encryption only (no authentication), set the authen...
Page 254
6-142 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface wep). To place the vap into aes only mode, use “required” and then select the “cipher-ccmp” option for the cipher-suite command. Example related commands encryption (6-142) key (6-143) encryption this command enables data encryption for wireless communicat...
Page 255
6-143 using the command line interface example related commands key (6-143) key this command sets the keys used for wep encryption. Use the no form to delete a configured key. Syntax key index> size> type> value> no key index • index - key index. (range: 1-4) • size - key size. (options: 64, 128, or...
Page 256
6-144 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example related commands key (6-143) encryption (6-142) transmit-key (6-144) transmit-key this command sets the index of the key to be used for encrypting data frames for broadcast or multicast traffic transmitted from the vap to wireless clients. Syntax t...
Page 257
6-145 using the command line interface • in a mixed-mode environment with clients using static and dynamic keys, select transmit key index 2, 3, or 4. The access point uses transmit key index 1 for the generation of dynamic keys. Example cipher-suite this command defines the cipher algorithm used to...
Page 258
6-146 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface and a re-keying mechanism. Select tkip if there are clients in the network that are not wpa2 compliant. • tkip defends against attacks on wep in which the unencrypted initialization vector in encrypted packets is used to calculate the wep key. Tkip changes...
Page 259
6-147 using the command line interface the mic calculation is performed in the access point for each transmitted packet and this can impact throughput and performance. The access point supports a choice of hardware or software for mic calculation. The performance of the access point can be improved ...
Page 260
6-148 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example related commands auth (6-140) pmksa-lifetime this command sets the time for aging out cached wpa2 pairwise master key security association (pmksa) information for fast roaming. Syntax pmksa-lifetime minutes> minutes - the time for aging out pmksa i...
Page 262: Link Integrity Commands
6-150 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface link integrity commands the access point provides a link integrity feature that can be used to ensure that wireless clients are connected to resources on the wired network. The access point does this by periodically sending ping messages to a host device i...
Page 263
6-151 using the command line interface host does not respond or is unreachable) exceeds the limit set by the link-integrity ping-fail-retry command, the link is determined as lost. Example link-integrity ping-host this command configures the link host name or ip address. Use the no form to remove th...
Page 264
6-152 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface example link-integrity ping-fail-retry this command configures the number of consecutive failed ping counts before the link is determined as lost. Syntax link-integrity ping-fail-retry counts> counts - the number of failed ping counts before the link is de...
Page 265: Iapp Commands
6-153 using the command line interface syntax [no] link-integrity ethernet-detect default setting disabled command mode global configuration example show link-integrity this command displays the current link integrity configuration. Command mode exec example iapp commands the command described in th...
Page 266: Vlan Commands
6-154 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface iapp this command enables the protocol signaling required to hand over wireless clients roaming between different 802.11f-compliant access points. Use the no form to disable 802.11f signaling. Syntax [no] iapp default enabled command mode global configurat...
Page 267
6-155 using the command line interface the vlan commands supported by the access point are listed below. Table 29 vlan commands note: when vlans are enabled, the access point’s ethernet port drops all received traffic that does not include a vlan tag. To maintain network connectivity to the access p...
Page 268
6-156 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface vlan this command enables vlans for all traffic. Use the no form to disable vlans. Syntax [no] vlan enable default disabled command mode global configuration command description • when vlans are enabled, the access point tags frames received from wireless ...
Page 269
6-157 using the command line interface default setting 1 command mode global configuration command usage the management vlan is for managing the access point. For example, the access point allows traffic that is tagged with the specified vlan to manage the access point via remote management, ssh, sn...
Page 270: Wmm Commands
6-158 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface • if the vlan id has not been configured for a client on the radius server, then the frames are tagged with the default vlan id of the vap interface. Example wmm commands the access point implements qos using the wi-fi multimedia (wmm) standard. Using wmm,...
Page 273
6-161 using the command line interface default command mode interface configuration (wireless) example ap parameters wmm parameters ac0 (best effort) ac1 (background) ac2 (video) ac3 (voice) logcwmin 4 4 3 2 logcwmax 10 10 4 3 aifs 3 7 2 2 txop limit 0 0 94 47 admission control disabled disabled dis...
Page 274
6-162 c hapter 6: c ommand l ine i nterface.
Page 275: Roubleshooting
A-1 a t roubleshooting check the following items before you contact local technical support. 1 if wireless bridge units do not associate with each other, check the following: check the power injector led for each bridge unit to be sure that power is being supplied. Be sure that antennas in the link ...
Page 276
A-2 if authentication is being performed through ieee 802.1x, be sure the wireless users have installed and properly configured 802.1x client software. If mac address filtering is enabled, be sure the client’s address is included in the local filtering database or on the radius server database. If t...
Page 277
A-3 reset the bridge’s hardware using the console interface, web interface, or through a power reset..
Page 278
A-4.
Page 279: Ables
B-1 b c ables and p inouts t wisted -p air c able a ssignments for 10/100base-tx connections, a twisted-pair cable must have two pairs of wires. Each wire pair is identified by two different colors. For example, one wire might be green and the other, green with white stripes. Also, an rj-45 connecto...
Page 280: 10/100Base-Tx P
B-2 10/100base-tx p in a ssignments use unshielded twisted-pair (utp) or shielded twisted-pair (stp) cable for rj-45 connections: 100-ohm category 3 or better cable for 10 mbps connections, or 100-ohm category 5 or better cable for 100 mbps connections. Also be sure that the length of any twisted-pa...
Page 281
B-3 s traight -t hrough w iring because the 10/100 mbps input port on the power injector uses an mdi pin configuration, you must use “straight-through” cable for network connections to hubs or switches that only have mdi-x ports. However, if the device to which you are connecting supports automatic ...
Page 282
B-4 c rossover w iring because the 10/100 mbps port on the power injector uses an mdi pin configuration, you must use “crossover” cable for network connections to pcs, servers or other end nodes that only have mdi ports. However, if the device to which you are connecting supports automatic mdi/mdi-x...
Page 283: 8-P
B-5 8-p in din c onnector p inout the ethernet cable from the power injector connects to an 8-pin din connector on the wireless bridge. This connector is described in the following figure and table. 8-pin din ethernet port pinout pin signal name 1 transmit data plus (td+) 2 transmit data minus (td-)...
Page 284: 8-P
B-6 8-p in din to rj-45 c able w iring to construct an extended ethernet cable to connect from the power injector’s rj-45 output port to the wireless bridge’s 8-pin din connector, follow the wiring diagram below. Use category 5 or better utp or stp cable, maximum length 100 m (328 ft), and be sure t...
Page 285: Lossary
Glossary-1 g lossary 10base-t ieee 802.3 specification for 10 mbps ethernet over two pairs of category 3 or better utp cable. 100base-tx ieee 802.3u specification for 100 mbps fast ethernet over two pairs of category 5 or better utp cable. Access point an internetworking device that seamlessly conne...
Page 286
Glossary-2 broadcast key broadcast keys are sent to stations using 802.1x dynamic keying. Dynamic broadcast key rotation is often used to allow the access point to generate a random group key and periodically update all key-management capable wireless clients. Csma/ca carrier sense multiple access w...
Page 287
Glossary-3 ieee 802.11b a wireless standard that supports wireless communications in the 2.4 ghz band using direct sequence spread spectrum (dsss). The standard provides for data rates of 1, 2, 5.5, and 11 mbps. Ieee 802.11g a wireless standard that supports wireless communications in the 2.4 ghz ba...
Page 288
Glossary-4 radius a logon authentication protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to the network. Roaming a wireless lan mobile user moves around an ess and maintains a continuous connection to the infrastructure network. Rts threshold transmitters contending for the...
Page 289
Glossary-5 network services. All the services are delivered using a single radio channel, enabling virtual ap technology to optimize the use of limited wlan radio spectrum. Virtual lan (vlan) a virtual lan is a collection of network nodes that share the same collision domain regardless of their phys...
Page 290
Glossary-6.
Page 291: Ndex
Index-7 i ndex numbers 802.11g 6-112 a aes 5-58 authentication 5-10 cipher suite 6-141 closed system 6-127 configuring 5-10 mac address 5-12, 6-79 type 4-9, 5-50, 6-127 web redirect 5-14, 6-22 b beacon interval 5-42, 6-121 rate 5-42, 6-122 bootp 6-107, 6-108 bpdu 5-31 c cable assignments b-1 crossov...
Page 292
Index-8 h hardware version, displaying 6-27 http, secure server 6-21 https 6-21 i iapp 6-153 ieee 802.11a 1-2, 5-37, 6-112 configuring interface 5-38, 6-112 maximum data rate 6-115 radio channel 6-116 ieee 802.11b 5-37 ieee 802.11f 6-153 ieee 802.11g 5-37 configuring interface 5-43, 6-112 maximum da...
Page 293
Index-9 configuring 4-6 ssl 6-21 sta interface settings 6-103 to ?? Path cost 6-103 port priority 6-104 startup files, setting 6-61 station status 5-61, 6-133 status displaying device status 5-60, 6-26 displaying station status 5-61, 6-133 straight-through cable b-3 system clock, setting 5-35, 6-39 ...