- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- 4200G 12-Port
- Configuration Manual
3Com 4200G 12-Port Configuration Manual
Summary of 4200G 12-Port
Page 1
3com ® switch 4200g family configuration guide 4200g 12-port (3cr17660-91) 4200g 24-port (3cr17661-91) 4200g 48-port (3cr17662-91) www.3com.Com part number: 10014915 rev. Ad published: may 2007.
Page 2
3com corporation 350 campus drive marlborough, ma usa 01752-3064 copyright © 2006, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without writt...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide organization of the manual 1 intended readership 2 conventions 2 related manuals 3 1 cli o verview introduction to the cli 1 command level/command view 1 cli features 6 terminal display 7 2 l ogging into an e thernet s witch logging into an ethernet switch 9 introductio...
Page 4
2 c ontents 8 c onfiguration file management introduction to configuration file 41 configuration file-related configuration 41 9 vlan c onfiguration vlan overview 43 vlan configuration 44 displaying a vlan 44 vlan configuration example 45 10 m anagement vlan c onfiguration introduction to management...
Page 5
C ontents 3 port isolation configuration 85 displaying port isolation 85 port isolation configuration example 85 17 p ort s ecurity c onfiguration port security configuration 87 displaying port security 90 port security configuration example 91 18 mac a ddress t able m anagement overview 93 mac addr...
Page 6
4 c ontents habp client configuration 166 displaying and debugging habp 166 23 aaa&radius c onfiguration overview 167 configuration tasks 173 aaa configuration 174 radius configuration 179 displaying aaa&radius information 186 aaa&radius configuration example 187 troubleshooting aaa&radius configura...
Page 7
C ontents 5 28 c onfiguration for m irroring f eatures mirroring features 237 mirroring supported by switch 4200g 239 mirroring configuration 239 displaying and debugging mirroring 248 29 igmp s nooping c onfiguration overview of igmp snooping 249 igmp snooping configuration 252 displaying informati...
Page 8
6 c ontents ntp implementation mode configuration 295 access control permission configuration 297 ntp authentication configuration 297 configuration of optional ntp parameters 299 displaying and debugging ntp 300 configuration example 300 36 ssh t erminal s ervices ssh terminal services 309 sftp ser...
Page 9
C ontents 7 44 d evice m anagement introduction to device management 375 device management configuration 375 displaying the device management configuration 376 remote switch update configuration example 376 45 c onfiguration of n ewly a dded c luster f unctions introduction to the newly added cluste...
Page 10
8 c ontents.
Page 11: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide provides information about configuring your network using the commands supported on the 3com ® switch 4200-g family. The descriptions in this guide applies to the switch 4200-g. Organization of the manual the switch 4200 family configuration guide consists of the follo...
Page 12
2 a bout t his g uide ■ qos—details quality of service. ■ mirroring—details how to configure mirroring. ■ igmp snooping—detailsinternet group management protocol snooping ■ multicast protocol—details how to configure multicast protocols. ■ clustering—details clustering configuration. ■ snmp—details ...
Page 13
Related manuals 3 related manuals the 3com switch 4200 family getting started guide provides information about installation. The 3com switch 4200 family command reference guide provides all the information you need to use the configuration commands. Warning information that alerts you to potential p...
Page 14
4 a bout t his g uide.
Page 15: Cli O
1 cli o verview introduction to the cli a s4200g series ethernet switch provides a command line interface (cli) and commands for you to configure and manage the ethernet switch. The cli is featured by the following: ■ commands are grouped by levels. This prevents unauthorized users from operating th...
Page 16
2 c hapter 1: cli o verview setting a user level switching password table 1 lists the operations to set a user level switching password. Switching to another user level table 2 lists operations to switch to another user level. For security purpose, the password a user enters when switching to a high...
Page 17
Command level/command view 3 ■ system view ■ ethernet port view ■ vlan view ■ vlan interface view ■ loopback interface view ■ local user view ■ user interface view ■ ftp client view ■ sftp client view ■ mst region view ■ cluster view ■ public key view ■ public key editing view ■ basic acl view ■ adv...
Page 18
4 c hapter 1: cli o verview vlan view configure vlan parameters [4200g-vlan1] execute the vlan 1 command in system view. Execute the quit command to return to system view. Execute the return command to return to user view. Vlan interface view configure ip interface parameters for vlans and aggregate...
Page 19
Command level/command view 5 cluster view configure cluster parameters [4200g-cluster] execute the cluster command in system view. Execute the quit command to return to system view. Execute the return command to return to user view. Public key view configure rsa public keys for ssh users [4200g-rsa-...
Page 20
6 c hapter 1: cli o verview cli features online help cli provides two types of online help: complete online help and partial online help. They assist you with your configuration. Complete online help enter a “?” character in any view on your terminal to display all the commands available in the view...
Page 21
Terminal display 7 enter a command, the first several characters of an available keyword which uniquely identifies the keyword, and press , to complete the keyword will be automatically completed. Terminal display cli provides the following display feature: ■ display suspending. That is, the display...
Page 22
8 c hapter 1: cli o verview command edit the cli provides basic command edit functions and supports multi-line editing. The maximum number of characters a command can contain is 256. Table 8 lists the cli edit operations. Table 8 edit operations press… to… a common key insert the character the key r...
Page 23: Ogging
2 l ogging into an e thernet s witch logging into an ethernet switch you can log into an s4200-g series ethernet switch in one of the following ways: ■ logging in locally through the console port ■ telneting locally or remotely to an ethernet port ■ telneting to the console port using a modem ■ logg...
Page 24
10 c hapter 2: l ogging into an e thernet s witch common user interface configuration caution: ■ the auto-execute command command may cause you unable to perform common configuration in the user interface, so use it with caution. ■ before executing the auto-execute command command and save your conf...
Page 25: Ogging
3 l ogging in through the c onsole p ort introduction to log in through the console port is the most common way to log into a switch. It is also the prerequisite to configure other login methods. By default, you can log into an s4200g series ethernet switch through its console port only. To log into...
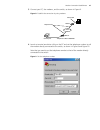
Page 26
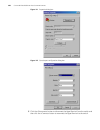
12 c hapter 3: l ogging in through the c onsole p ort figure 2 create a connection figure 3 specify the port used to establish the connection.
Page 27
Console port login configuration 13 figure 4 set port parameters ■ turn on the switch. The user will be prompted to press the enter key if the switch successfully completes post (power-on self test). The prompt (such as ) appears after the user presses the enter key. ■ you can then configure the swi...
Page 28
14 c hapter 3: l ogging in through the c onsole p ort caution: changing of console port configuration terminates the connection to the console port. To establish the connection again, you need to modify the configuration of the termination emulation utility running on your pc accordingly. Refer to “...
Page 29
Console port login configuration with authentication mode being none 15 changes of the authentication mode of console port login will not take effect unless you restart the switch. Console port login configuration with authentication mode being none configuration procedure scheme specify to perform ...
Page 32
18 c hapter 3: l ogging in through the c onsole p ort 3 specify not to authenticate users logging in through the console port. [4200g-ui-aux0] authentication-mode none 4 specify commands of level 2 are available to users logging into the aux user interface. [4200g-ui-aux0] user privilege level 2 5 s...
Page 34
20 c hapter 3: l ogging in through the c onsole p ort ■ the history command buffer can store up to 20 commands. ■ the timeout time of the aux user interface is 6 minutes. Network diagram figure 6 network diagram for aux user interface configuration (with the authentication mode being password) confi...
Page 35
Console port login configuration with authentication mode being scheme 21 console port login configuration with authentication mode being scheme configuration procedure table 18 console port login configuration with authentication mode being scheme operation command description enter system view sys...
Page 38
24 c hapter 3: l ogging in through the c onsole p ort network diagram figure 7 network diagram for aux user interface configuration (with the authentication mode being scheme) configuration procedure 1 enter system view. System-view 2 create a local user named guest and enter local user view. [4200g...
Page 39: Ogging
4 l ogging in u sing m odem introduction the administrator can log into the console port of a remote switch using a modem through pstn (public switched telephone network) if the remote switch is connected to the pstn through a modem to configure and maintain the switch remotely. When a network opera...
Page 40
26 c hapter 4: l ogging in u sing m odem switch configuration after logging into a switch through its console port by using a modem, you will enter the aux user interface. The corresponding configuration on the switch is the same as those when logging into the switch locally through its console port...
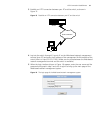
Page 41
Modem connection establishment 27 3 connect your pc, the modems, and the switch, as shown in figure 8. Figure 8 establish the connection by using modems 4 launch a terminal emulation utility on the pc and set the telephone number to call the modem directly connected to the switch, as shown in figure...
Page 42
28 c hapter 4: l ogging in u sing m odem figure 10 call the modem 5 provide the password when prompted. If the password is correct, the prompt (such as ) appears. You can then configure or manage the switch. You can also enter the character ? At anytime for help. If you perform no aux user-related c...
Page 43: Ogging
5 l ogging in through w eb - based n etwork m anagement s ystem introduction an s4200-g series switch has a web server built in. You can log into an s4200-g series switch through a web browser and manage and maintain the switch intuitively by interacting with the built-in web server. To log into an ...
Page 44
30 c hapter 5: l ogging in through w eb - based n etwork m anagement s ystem ■ launch a terminal emulation utility (such as terminal in windows 3.X or hyperterminal in windows 9x) on the pc, with the baud rate set to 9,600 bps, data bits set to 8, parity check set to off, and flow control set to off...
Page 45
Http connection establishment 31 3 establish an http connection between your pc and the switch, as shown in figure 13. Figure 13 establish an http connection between your pc and the switch 4 log into the switch through ie. Launch ie on the web-based network management terminal (your pc) and enter th...
Page 46
32 c hapter 5: l ogging in through w eb - based n etwork m anagement s ystem.
Page 47: Ogging
6 l ogging in through nms introduction you can also log into a switch through an nms (network management station), and then configure and manage the switch through the agent module on the switch. ■ the agent here refers to the software running on network devices (switches) and as the server. ■ snmp ...
Page 48
34 c hapter 6: l ogging in through nms.
Page 49: Ontrolling
7 c ontrolling l ogin u sers introduction a switch provides ways to control different types of login users, as listed in table 24. Controlling telnet users prerequisites the controlling policy against telnet users is determined, including the source and destination ip addresses to be controlled and ...
Page 50
36 c hapter 7: c ontrolling l ogin u sers controlling telnet users by source and destination ip addresses controlling telnet users by source and destination ip addresses is achieved by applying advanced acls, which are numbered from 3000 to 3999. Refer to the acl module for information about definin...
Page 51: Controlling
Controlling network management users by source ip addresses 37 controlling network management users by source ip addresses you can manage a s4200g series ethernet switch through network management software. Network management users can access switches through snmp. You need to perform the following ...
Page 52
38 c hapter 7: c ontrolling l ogin u sers as snmp community name is a feature of snmp v1 and snmp v2, the specified acls in the command that configures snmp community names (the snmp-agent community command) take effect in the network management systems that adopt snmp v1 or snmp v2. Similarly, as s...
Page 53: Controlling Web
Controlling web users by source ip address 39 controlling web users by source ip address you can manage a s4200g series ethernet switch remotely through web. Web users can access a switch through http connections. You need to perform the following two operations to control web users by source ip add...
Page 54
40 c hapter 7: c ontrolling l ogin u sers configuration procedure 1 define a basic acl. System-view [4200g] acl number 2030 match-order config [4200g-acl-basic-2030] rule 1 permit source 10.110.100.46 0 [4200g-acl-basic-2030] rule 2 deny source any 2 apply the acl to only permit the web users source...
Page 55: Onfiguration
8 c onfiguration file management introduction to configuration file configuration file records and stores user configurations performed to a switch. It also enables users to check switch configurations easily. Upon powered on, a switch loads the configuration file known as saved-configuration file, ...
Page 57: Vlan C
9 vlan c onfiguration vlan overview introduction to vlan the virtual local area network (vlan) technology is developed for switches to control broadcast operations in lans. By creating vlans in a physical lan, you can divide the lan into multiple logical lans, each of which has a broadcast domain of...
Page 58
44 c hapter 9: vlan c onfiguration vlan classification you can create port-based and policy-based vlan types a switch 4200g: the port-based vlan members are defined in terms of switch ports. You can add ports to which close-related hosts are connected to the same port-based vlan. This is the simples...
Page 59
Vlan configuration example 45 vlan configuration example port-based vlan configuration example network requirements ■ create vlan 2 and vlan 3, with the name of vlan 2 being v2, and the description string being home. ■ add gigabitethernet1/0/1 and gigabitethernet1/0/2 ports to vlan 2; add gigabiteth...
Page 60
46 c hapter 9: vlan c onfiguration.
Page 61: Anagement
10 m anagement vlan c onfiguration introduction to management vlan management vlan to manage an ethernet switch remotely through telnet or network management, the switch need to be assigned an ip address. As for a s4200g series layer 2 ethernet switch, only the management vlan interface can be assig...
Page 62
48 c hapter 10: m anagement vlan c onfiguration configuring the management vlan ■ to configure the management vlan of a switch operating as a cluster management device to be a cluster management vlan (using the management-vlan vlan-id command) successfully, make sure the vlan-id argument provided in...
Page 63
Displaying and debugging management vlan 49 configuration procedure 1 enter system view. System-view 2 create vlan 10 and configure vlan 10 to be the management vlan. [4200ga] vlan 10 [4200ga-vlan10] quit [4200ga] management-vlan 10 3 create the vlan 10 interface and enter vlan interface view. [4200...
Page 64
50 c hapter 10: m anagement vlan c onfiguration.
Page 65: Dhcp/bootp C
11 dhcp/bootp c lient c onfiguration introduction to dhcp client as the network scale expands and the network complexity increases, the network configurations become more and more complex accordingly. It is usually the case that the computer locations change (such as the portable computers or wirele...
Page 66
52 c hapter 11: dhcp/bootp c lient c onfiguration figure 22 interaction between a dhcp client and a dhcp server to obtain valid dynamic ip addresses, a dhcp client exchanges different information with the dhcp server in different phases. Usually, the following three modes are involved: 1 the dhcp cl...
Page 67
Introduction to bootp client 53 2 the dhcp client accesses the network for the second time in this case, the dhcp client establishes connections with the dhcp server through the following steps. A after accessing the network successfully for the first time, the dhcp client can access the network aga...
Page 68
54 c hapter 11: dhcp/bootp c lient c onfiguration configuring a dhcp/bootp client configuration example network requirements to manage the switch s4200ga remotely, which operates as a dhcp client, through telnet, the following are required: ■ s4200ga has an ip address that is obtained through dhcp ■...
Page 69: Oice
12 v oice vlan c onfiguration voice vlan configuration introduction to voice vlan voice vlans are vlans configured specially for voice data stream. By adding the ports with voice devices attached to voice vlans, you can perform qos-related configuration for voice data, ensuring the transmission prio...
Page 70
56 c hapter 12: v oice vlan c onfiguration as multiple types of ip phones exist, you need to match port mode with types of voice stream sent by ip phones, as listed in table 37. Caution: if the voice stream transmitted by an ip phone is tagged and the port which the ip phone is attached to is 802.1x...
Page 71
Voice vlan configuration 57 voice vlan configuration configuration prerequisites ■ create the corresponding vlan before configuring a voice vlan. ■ vlan 1 is the default vlan and do not need to be created. But vlan 1 does not support the voice vlan function. Configuring a voice vlan to operate in au...
Page 72
58 c hapter 12: v oice vlan c onfiguration caution: ■ you can enable voice vlan feature for only one vlan at a moment. ■ if the vlan for whom the voice vlan function is enabled is a dynamic vlan, the vlan becomes a static vlan after you enable the voice vlan function. ■ a port operating in the autom...
Page 73
Voice vlan displaying and debugging 59 voice vlan displaying and debugging voice vlan configuration example voice vlan configuration example (automatic mode) network requirements ■ create vlan 2 and configure it as a voice vlan. ■ configure gigabitethernet1/0/1 port as a trunk port, with vlan 6 as t...
Page 74
60 c hapter 12: v oice vlan c onfiguration configuration procedure 1 create vlan 3. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] vlan 3 2 configure gigabitethernet1/0/3 port to be a trunk port and add it to vlan 3. [4200g] interface gigabitethernet1/0/3 [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0...
Page 75: Gvrp C
13 gvrp c onfiguration introduction to gvrp gvrp (garp vlan registration protocol) is an application of garp (generic attribute registration protocol). Gvrp is based on the mechanism of garp; it maintains dynamic vlan registration information and propagates the information to other switches. Garp is...
Page 76
62 c hapter 13: gvrp c onfiguration leave timer, and unregisters the attribute information if it does not receives a join message again before the timer times out. ■ leaveall: once a garp entity starts up, it starts the leaveall timer, and sends out a leaveall message after the timer times out, so t...
Page 77
Gvrp configuration 63 table 41describes the packet fields figure 23. Protocol specifications gvrp is defined in ieee 802.1q standard. Gvrp configuration the gvrp configuration tasks include configuring the timers, enabling gvrp, and configuring the gvrp port registration mode. Configuration prerequi...
Page 78
64 c hapter 13: gvrp c onfiguration in a network that contains switches with both gvrp and mstp employed, gvrp packets are forwarded along the cist. If you want to broadcast packets of a specific vlan through gvrp, be sure to map the vlan to the cist when configuring the mstp vlan mapping table (the...
Page 79
Displaying and maintaining gvrp 65 network diagram figure 24 network diagram for gvrp configuration configuration procedure 1 configure switch a: a enable gvrp globally. System-view [4200g] gvrp b set the port gigabitethernet1/0/1 to a trunk port, and allow all vlan packets to pass through the port....
Page 80
66 c hapter 13: gvrp c onfiguration.
Page 81: Asic
14 b asic p ort c onfiguration ethernet port overview types and numbers of ethernet ports table 45 lists the types and numbers of the ethernet ports available on the s4200g series ethernet switches. The ethernet ports of the s4200g series switches have the following characteristics: ■ the 10/100/100...
Page 82
68 c hapter 14: b asic p ort c onfiguration configuring the default vlan id for an ethernet port an access port can belong to only one vlan. Therefore, the vlan an access port belongs to is also the default vlan of the access port. A hybrid/trunk port can belong to several vlans, and so a default vl...
Page 83
Configuring ethernet ports 69 configuring ethernet ports making basic port configuration to use the optical interface on a combo port, install the sfp and issue the undo shutdown command in the interface. The corresponding 10/100/1000base-t port will automatically be shutdown. The speed and mdi comm...
Page 84
70 c hapter 14: b asic p ort c onfiguration ■ if you execute the command in ethernet port view, the command takes effect only on current port. Enabling flow control on a port after flow control is enabled on both the local and the peer switches, if congestion occurs on the local switch, the switch w...
Page 85
Configuring ethernet ports 71 configuring trunk port attribute copying port configuration to other ports to keep the configuration of some other ports consistent with a specified port, you can copy the configuration of the specified port to these ports. The configuration may include: ■ vlan settings...
Page 86
72 c hapter 14: b asic p ort c onfiguration setting loopback detection for an ethernet port loopback detection is used to monitor if loopback occurs on a switch port. After you enable loopback detection on ethernet ports, the switch can monitor if external loopback occurs on them. If there is a loop...
Page 87
Ethernet port configuration example 73 after you use the shutdown command on a port, the port cannot run loopback test. You cannot use the speed, duplex, mdi and shutdown commands on the ports running loopback test. Some ports do not support loopback test, and corresponding prompts will be given whe...
Page 88
74 c hapter 14: b asic p ort c onfiguration network diagram figure 25 network diagram for default vlan id configuration configuration procedure the following configuration is used for switch a. Configure switch b in a similar way. 1 enter port view of gigabitethernet1/0/1. [4200g] interface gigabite...
Page 89: Ink
15 l ink a ggregation c onfiguration overview introduction to link aggregation link aggregation means aggregating several ports together to form an aggregation group, so as to implement outgoing/incoming load sharing among the member ports in the group and to enhance the connection reliability. Depe...
Page 90
76 c hapter 15: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration 4 the member ports in a dynamic aggregation group must have the same operation key. Manual aggregation group introduction to manual aggregation group a manual aggregation group is manually created. All its member ports are manually added and can be m...
Page 91
Overview 77 static lacp aggregation group introduction to static lacp aggregation a static lacp aggregation group is also manually created. All its member ports are manually added and can be manually removed (it inhibits the system from automatically adding/removing ports to/from it). Each static ag...
Page 92
78 c hapter 15: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration besides multiple-port aggregation groups, the system is also able to create single-port aggregation groups, each of which contains only one port. Lacp is enabled on the member ports of dynamic aggregation groups. Port status of dynamic aggregation gr...
Page 93
Link aggregation configuration 79 aggregation group categories depending on whether or not load sharing is implemented, aggregation groups can be load-sharing or non-load-sharing aggregation groups. In general, the system only provides limited load-sharing aggregation resources (currently 64 load-sh...
Page 94
80 c hapter 15: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration when creating an aggregation group: ■ if the aggregation group you are creating already exists but contains no port, its type will change to the type you set. ■ if the aggregation group you are creating already exists and contains ports, the possible...
Page 95
Displaying and maintaining link aggregation information 81 configuring a dynamic lacp aggregation group a dynamic lacp aggregation group is automatically created by the system based on lacp-enabled ports. The adding and removing of ports to/from a dynamic aggregation group are automatically accompli...
Page 96
82 c hapter 15: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration you can also execute the reset command in user view to clear statistics on lacp ports. Link aggregation configuration example network requirements ■ switch a connects to switch b with three ports gigabitethernet1/0/1 to gigabitethernet1/0/3. It is re...
Page 97
Link aggregation configuration example 83 2 adopting static lacp aggregation mode a create static aggregation group 1. System-view [4200g] link-aggregation group 1 mode static b add ports gigabitethernet1/0/1 through gigabitethernet1/0/3 to aggregation group 1. [4200g] interface gigabitethernet1/0/1...
Page 98
84 c hapter 15: l ink a ggregation c onfiguration.
Page 99: Ort
16 p ort i solation c onfiguration port isolation overview introduction to port isolation the port isolation function enables you to isolate the ports to be controlled on layer 2 by adding the ports to an isolation group, through which you can improve network security and network in a more flexible ...
Page 100
86 c hapter 16: p ort i solation c onfiguration network diagram figure 27 network diagram for port isolation configuration configuration procedure 1 add gigabitethernet1/0/2, gigabitethernet1/0/3, and gigabitethernet1/0/4 ports to the isolation group. System-view system view: return to user view wit...
Page 101: Ort
17 p ort s ecurity c onfiguration port security configuration introduction to port security port security is a security mechanism that controls network access. It is an expansion to the current 802.1x and mac address authentication. This scheme controls the incoming/outgoing packets on port by check...
Page 102
88 c hapter 17: p ort s ecurity c onfiguration configuring port security userlogin- secure the port opens only after the access user passes the 802.1x authentication. Even after the port opens, only the packets of the successfully authenticated user can pass through the port. In this mode, only one ...
Page 103
Port security configuration 89 the time set by the port-security timer disableport timer command is the same as the time set for temporarily disabling a port while executing the port-security intrusion-mode command under disableport-temporarily mode. With the port security enabled, a device has the ...
Page 104
90 c hapter 17: p ort s ecurity c onfiguration security mac can be learned by the autolearn function of port-security feature, and can be configured by the command or mib manually. Before adding security mac, you may configure the port security mode to autolearn and then the mac address learning met...
Page 105
Port security configuration example 91 port security configuration example network requirements ■ enable port security on port gigabitethernet1/0/1 of switch a, and set the maximum number of the mac addresses accommodated by the port to 80. ■ the ntk packet transmission mode of on the port is ntk-wi...
Page 106
92 c hapter 17: p ort s ecurity c onfiguration 9 enable the sending of intrusion trap messages. [4200g] port-security trap intrusion 10 bind the mac and ip addresses of pc1 to gigabitethernet1/0/1 port. [4200g] am user-bind mac-address 00e0-fc00-4200g ip-address 10.153.1.1 interface gigabitethernet1...
Page 107: Mac A
18 mac a ddress t able m anagement this chapter describes the management of static, dynamic, and blackhole mac address entries. For information about the management of multicast mac address entries, refer to chapter 29. Overview introduction to mac address table a mac address table is a port-based l...
Page 108
94 c hapter 18: mac a ddress t able m anagement mac address learning mechanism the mac address learning mechanism enables a switch to acquire the mac addresses of the network devices on the segments connected to the ports of the switch. A packet can be directly forwarded if its destination mac addre...
Page 109
Mac address table management 95 by setting the maximum numbers of mac addresses that can be learnt from individual ports, you can control the number of the mac address entries the mac address table can dynamically maintains. When the number of the mac address entries learnt from a port reaches the s...
Page 110
96 c hapter 18: mac a ddress t able m anagement disabling mac address learning for a vlan you can disable a switch from learning mac addresses in specific vlans to improve stability and security for the users belong to these vlans and prevent unauthorized accesses. Displaying and maintaining a mac a...
Page 111
Configuration example 97 configuration procedure 1 enter system view. System-view 2 add a static mac address entry. [4200g] mac-address static 00e0-fc35-dc71 interface gigabitethernet1/0/2 vlan 1 3 set the aging time to 500 seconds. [4200g] mac-address timer aging 500 4 display the information about...
Page 112
98 c hapter 18: mac a ddress t able m anagement.
Page 113: Ogging
19 l ogging in through t elnet introduction you can telnet to a remote switch to manage and maintain the switch. To achieve this, you need to configure both the switch and the telnet terminal properly. Common configuration table 75 lists the common telnet configuration. Telnet configurations for dif...
Page 114
100 c hapter 19: l ogging in through t elnet telnet configuration with authentication mode being none configuration procedure scheme specify to perform local authentication or radius authentication aaa configuration specifies whether to perform local authentication or radius authentication optional ...
Page 116
102 c hapter 19: l ogging in through t elnet network diagram figure 30 network diagram for telnet configuration (with the authentication mode being none) configuration procedure 1 enter system view. System-view 2 enter vty 0 user interface view. [4200g] user-interface vty 0 3 configure not to authen...
Page 118
104 c hapter 19: l ogging in through t elnet configuration example network requirements assume that you are a level 3 aux user and want to perform the following configuration for telnet users logging into vty 0: ■ authenticate users logging into vty 0 using the local password. ■ set the local passwo...
Page 119
Telnet configuration with authentication mode being scheme 105 telnet configuration with authentication mode being scheme configuration procedure table 81 telnet configuration with the authentication mode being scheme operation command description enter system view system-view — configure the authen...
Page 120
106 c hapter 19: l ogging in through t elnet set the maximum number of lines the screen can contain screen-length screen-length optional by default, the screen can contain up to 24 lines. You can use the screen-length 0 command to disable the function to display information in pages. Set history com...
Page 122
108 c hapter 19: l ogging in through t elnet refer to the corresponding modules in this manual for information about aaa, radius, and ssh. Configuration example network requirements assume that you are a level 3 aux user and want to perform the following configuration for telnet users logging into v...
Page 123
Telnet connection establishment 109 [4200g-ui-vty0] user privilege level 2 8 configure telnet protocol is supported. [4200g-ui-vty0] protocol inbound telnet 9 set the maximum number of lines the screen can contain to 30. [4200g-ui-vty0] screen-length 30 10 set the maximum number of commands the hist...
Page 124
110 c hapter 19: l ogging in through t elnet figure 34 launch telnet 4 enter the password when the telnet window displays “login authentication” and prompts for login password. The cli prompt (such as ) appears if the password is correct. If all vty user interfaces of the switch are in use, you will...
Page 125
Telnet connection establishment 111 where xxxx is the ip address or the host name of the switch operating as the telnet server. You can use the ip host to assign a host name to a switch. 4 enter the password. If the password is correct, the cli prompt (such as ) appears. If all vty user interfaces o...
Page 126
112 c hapter 19: l ogging in through t elnet.
Page 127: Mstp C
20 mstp c onfiguration mstp overview spanning tree protocol (stp) cannot enable ethernet ports to transit their states rapidly. It costs two times of the forward delay for a port to transit to the forwarding state even if the port is on a point-to-point link or the port is an edge port. This slows d...
Page 128
114 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration figure 36 basic mstp terminologies mst region an mst region (multiple spanning tree region) comprises multiple physically-interconnected mstp-enabled switches and the corresponding network segments connected to these switches. These switches have the same region ...
Page 129
Mstp overview 115 ist an internal spanning tree (ist) is a spanning tree in an mst region. Ists together with the common spanning tree (cst) form the common and internal spanning tree (cist) of the entire switched network. An ist is a special msti; it belongs to an mst region and is a branch of cist...
Page 130
116 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration in figure 37, switch a, b, c, and d form an mst region. Port 1 and port 2 on switch a connect upstream to the common root. Port 5 and port 6 on switch c form a loop. Port 3 and port 4 on switch d connect downstream to other mst regions. Figure 37 shows the roles ...
Page 131
Mstp overview 117 implementation of mstp mstp divides a network into multiple mst regions at layer 2. The cst is generated between these mst regions, and multiple spanning trees (or, mstis) can be generated in each mst region. As well as rstp, mstp uses configuration bpdus to generate spanning trees...
Page 132
118 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration first, the switch generates a designated port configuration bpdu for each of its port using the root port configuration bpdu and the root port path cost, with the root id being replaced with that of the root port configuration bpdu, root path cost being replaced ...
Page 133
Root bridge configuration 119 in a network that contains switches with both gvrp and mstp employed, gvrp packets are forwarded along the cist. If you want to broadcast packets of a specific vlan through gvrp, be sure to map the vlan to the cist when configuring the mstp vlan mapping table (the cist ...
Page 134
120 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration mst region configuration configuration procedure configuring mst region-related parameters (especially the vlan mapping table) results in spanning trees being regenerated. To reduce network topology jitter caused by the configuration, mstp does not regenerate spa...
Page 135
Root bridge configuration 121 admin configuration format selector :0 region name :info revision level :1 instance vlans mapped 0 11 to 19, 31 to 4094 1 1 to 10 2 20 to 30 root bridge/secondary root bridge configuration mstp can automatically choose a switch as a root bridge. You can also manually sp...
Page 136
122 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration you can configure a switch as the root bridges of multiple spanning tree instances. But you cannot configure two or more root bridges for one spanning tree instance. So, do not configure root bridges for the same spanning tree instance on two or more switches usi...
Page 137
Root bridge configuration 123 ■ rstp mode: in this mode, the protocol packets sent out of the ports of the switch are rstp packets. If the switched network contains rstp-enabled switches, you can configure the current mstp-enabled switch to operate in this mode by using the stp mode rstp command. ■ ...
Page 138
124 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration configuration example 1 configure the maximum hops of the mst region to be 30 (assuming that the current switch operates as the region root). System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] stp max-hops 30 network diameter configuration in a swi...
Page 139
Root bridge configuration 125 ■ the max age parameter is used to judge whether or not a configuration bpdu is obsolete. Obsolete configuration bpdus will be discarded. Configuration procedure all switches in a switched network adopt the three time-related parameters configured on the cist root bridg...
Page 140
126 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration configuration example 1 configure the forward delay parameter to be 1,600 centiseconds, the hello time parameter to be 300 centiseconds, and the max age parameter to be 2,100 centiseconds (assuming that the current switch operates as the cist root bridge). System...
Page 141
Root bridge configuration 127 configuration procedure (in system view) configuration procedure (in ethernet port view) as the maximum transmitting speed parameter determines the number of the configuration bpdus transmitted in each hello time, set it to a proper value to avoid mstp from occupying to...
Page 142
128 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration configuration procedure (in system view) configuration procedure (in ethernet port view) on a switch with bpdu protection not enabled, an edge port becomes a non-edge port again once it receives a bpdu from another port. You are recommended to configure the ether...
Page 143
Root bridge configuration 129 configuration procedure (in system view) configuration procedure (in ethernet port view) among aggregated ports, you can only configure the links of master ports as point-to-point links. If an autonegotiating port operates in full duplex mode after negotiation, you can ...
Page 144
130 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] stp interface gigabitethernet1/0/1 point-to-point force-true ■ configure in ethernet port view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] b [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0/1] stp point-to-poi...
Page 145
Leaf node configuration 131 ■ configure in ethernet port view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] stp enable [4200g] interface gigabitethernet1/0/1 [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0/1] stp disable leaf node configuration table 102 lists mstp-related configurations about leaf n...
Page 146
132 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration maximum transmitting speed configuration refer to “maximum transmitting speed configuration”. Edge port configuration refer to “edge port configuration”. Path cost configuration the path cost parameters reflects the link rates on ports. For a port on an mstp-enab...
Page 147
Leaf node configuration 133 normally, the path cost of a port operating in full-duplex mode is slightly less than that of the port operating in half-duplex mode. When calculating the path cost of an aggregated link, the 802.1d-1998 standard does not take the number of the ports on the aggregated lin...
Page 148
134 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration ■ configure in ethernet port view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] interface gigabitethernet1/0/1 [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0/1] stp instance 1 cost 2000 configuration example (b) 1 change the path cost of gigabitethernet1/0/1 port...
Page 149
The mcheck configuration 135 a lower port priority value indicates a higher port priority. If all the ports of a switch have the same port priority value, the port priorities are determined by the port indexes. Changing the priority of a port will cause spanning tree regeneration. You can configure ...
Page 150
136 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration performing the mcheck operation in system view performing the mcheck operation in ethernet port view caution: the stp mcheck command takes effect only when the switch operate in mstp mode, and does not take effect when the switch operates in stp/rstp mode.) confi...
Page 151
Protection function configuration 137 root protection a root bridge and its secondary root bridges must reside in the same region. A cist and its secondary root bridges are usually located in the high-bandwidth core region. Configuration errors or attacks may result in configuration bpdus with their...
Page 152
138 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration bpdu protection configuration configuration procedure configuration example enable the bpdu protection function. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] stp bpdu-protection root protection configuration enabling the root protection funct...
Page 153
Bpdu tunnel configuration 139 enabling the loop prevention function on specified ports in system view enabling the loop prevention function on a port in ethernet port view configuration example enable loop prevention function on gigabitethernet1/0/1 port. System-view system view: return to user view...
Page 154
140 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration as shown in figure 38, the upper part is the operator’s network, and the lower part is the user network. The operator’s network comprises packet ingress/egress devices, and the user network has networks a and b. On the operator’s network, configure the arriving b...
Page 155
Digest snooping configuration 141 digest snooping configuration introduction according to ieee 802.1s, two interconnected mstp switches can interwork with each other through mstis in an mst region only when the two switches have the same mst region-related configuration. Interconnected mstp switches...
Page 156
142 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration ■ to enable the digest snooping feature, the interconnected switches must be configured with exactly the same mst region-related configuration. ■ the digest snooping feature must be enabled on all the ports of your s4200g switch that are connected to partners' pr...
Page 157
Rapid transition configuration 143 figure 40 the mstp rapid transition mechanism limitation on the combination of rstp and mstp exists to implement rapid transition. For example, when the upstream switch adopts rstp, the downstream switch adopts mstp and does not support rstp mode, the root port on ...
Page 158
144 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration figure 41 network diagram for rapid transition configuration configuration procedure ■ configure in ethernet port view. Enable the rapid transition feature on root ports or alternate ports only. Table 119 configure the rapid transition feature in system view oper...
Page 159
Mstp displaying and debugging 145 mstp displaying and debugging you can verify the above configurations by executing the display commands in any view. Execute the reset command in user view to clear mstp statistics. Execute the debugging command in user view to debug the mstp module. Mstp implementa...
Page 160
146 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration b configure the mst region. [4200g-mst-region] region-name example [4200g-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [4200g-mst-region] instance 3 vlan 30 [4200g-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 40 [4200g-mst-region] revision-level 0 c activate the settings of the mst region. [42...
Page 161
Mstp implementation example 147 b configure the mst region. [4200g-mst-region] region-name example [4200g-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [4200g-mst-region] instance 3 vlan 30 [4200g-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 40 [4200g-mst-region] revision-level 0 c activate the settings of the mst region. [4200g-m...
Page 162
148 c hapter 20: mstp c onfiguration.
Page 163: 802.1
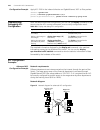
21 802.1 x c onfiguration introduction to 802.1x the 802.1x protocol (802.1x for short) was developed by ieee802 lan/wan committee to address security issues of wireless lans. It was then used in ethernet as a common access control mechanism for lan ports to address mainly authentication and securit...
Page 164
150 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration pae a pae (port access entity) is responsible for the implementation of algorithm and protocol-related operations in the authentication mechanism. The authenticator system pae authenticates the supplicant systems when they log into the lan and controls the aut...
Page 165
Introduction to 802.1x 151 ■ eap protocol packets transmitted between the supplicant system and the authenticator system are encapsulated as eapol packets. ■ eap protocol packets transmitted between the supplicant system pae and the radius server can either be encapsulated as eapor (eap over radius)...
Page 166
152 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration note that eapol-start, eapol-logoff, and eapol-key packets are only transmitted between the supplicant system and the authenticator system. Eap-packets are encapsulated by radius protocol to allow them successfully reach the authentication servers. Network man...
Page 167
Introduction to 802.1x 153 figure 48 the format of an eap-message field the message-authenticator field, as shown in figure 49, is used to prevent unauthorized interception of access requesting packets during authentications using chap, eap, and so on. A packet with the eap-message field must also h...
Page 168
154 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration figure 50 802.1x authentication procedure (in eap relay mode) the detailed procedure is as follows. ■ a supplicant system launches an 802.1x client to initiate an access request through the sending of an eapol-start packet to the switch, with its user name and...
Page 169
Introduction to 802.1x 155 ■ the radius server compares the received encrypted password (contained in a radius access-request packet) with the locally-encrypted password. If the two match, it will then send feedbacks (through a radius access-accept packet and an eap-success packet) to the switch to ...
Page 170
156 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration figure 51 802.1x authentication procedure (in eap terminating mode) the authentication procedure in eap terminating mode is the same as that in the eap relay mode except that the randomly-generated key in the eap terminating mode is generated by the switch, an...
Page 171
Introduction to 802.1x 157 ■ handshake timer (handshake-period): this timer sets the handshake-period and is triggered after a supplicant system passes the authentication. It sets the interval to for a switch to send handshake request packets to online users. If you set the number of retries to n by...
Page 172
158 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration ■ after the maximum number of authentication retries have been made and there are still ports that have not sent any response back, the switch will then add these ports into the guest vlan. ■ when the maximum number of authentication retries is reached, the sw...
Page 173
Timer and maximum user number configuration 159 configuring basic 802.1x functions caution: 802.1x-related configurations can all be performed in system view. Port access control mode and port access method can also be configured in port view. If you perform a configuration in system view and do not...
Page 174
160 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration as for the dot1x max-user command, if you execute it in system view without specifying the interface-list argument, the command applies to all ports. You can also use this command in port view. In this case, this command applies to the current port only and th...
Page 175
Advanced 802.1x configuration 161 the proxy checking function needs the support of 3com's 802.1x client program. The configuration listed in table 124 takes effect only when it is performed on cams as well as on the switch and the client version checking function is enabled on the switch (by the dot...
Page 176
162 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration supplicant systems that are not authenticated, fail to pass the authentication, or are offline belong to guest vlans. Displaying and debugging 802.1x you can verify the 802.1x-related configuration by executing the display command in any view. You can clear 80...
Page 177
Configuration example 163 and the authenticating radius server to be name, and money for interaction between the switch and the counting radius. Configure the waiting period for the switch to resend packets to the radius server to be 5 seconds, that is, if after 5 seconds the radius still has not se...
Page 178
164 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration 6 assign ip addresses to the secondary authentication and accounting radius server. [4200g-radius-radius1] secondary authentication 10.11.1.2 [4200g-radius-radius1] secondary accounting 10.11.1.1 7 set the password for the switch and the authentication radius ...
Page 179: Habp C
22 habp c onfiguration introduction to habp with 802.1x enabled, a switch authenticates and then authorizes 802.1x-enabled ports. Packets can be forwarded only by authorized ports. If ports connected to the switch are not authenticated and authorized by 802.1x, their received packets will be filtere...
Page 180
166 c hapter 22: habp c onfiguration habp client configuration habp clients reside on switches attached to habp servers. After you enable habp for a switch, the switch operates as an habp client by default. So you only need to enable habp on a switch to make it an habp client. Displaying and debuggi...
Page 181: Aaa&radius C
23 aaa&radius c onfiguration overview introduction to aaa aaa is shortened from the three security functions: authentication, authorization and accounting. It provides a uniform framework for you to configure the three security functions to implement the network security management. The network secu...
Page 182
168 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration generally, aaa adopts the client/server structure, where the client acts as the managed resource and the server stores user information. This structure has good scalability and facilitates the centralized management of user information. Introduction to isp ...
Page 183
Overview 169 figure 54 databases in radius server in addition, the radius server can act as the client of some other aaa server to provide the authentication or accounting proxy service. Basic message exchange procedure of radius the messages exchanged between a radius client (a switch, for example)...
Page 184
170 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration 3 the radius server compares the received user information with that in the users database to authenticate the user. If the authentication succeeds, it sends back an authentication response (access-accept), which contains the information of user’s rights, t...
Page 185
Overview 171 2 the identifier field (one byte) identifies the request and response packets. It is subject to the attribute field and varies with the received valid responses, but keeps unchanged during retransmission. 3 the length field (two bytes) specifies the total length of the packet (including...
Page 186
172 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration the radius protocol takes well scalability. Attribute 26 (vender-specific) defined in this protocol allows a device vendor to extend radius to implement functions that are not defined in standard radius. Figure 57 depicts the structure of attribute 26. The ...
Page 187
Configuration tasks 173 configuration tasks table 134 configuration tasks configuration task description related section aaa configuration create an isp domain required creating an isp domain configure the attributes of the isp domain optional configuring the attributes of an isp domain configure an...
Page 188
174 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration aaa configuration the goal of aaa configuration is to protect network devices against unauthorized access and at the same time provide network access services to legal users. If you need to use isp domains to implement aaa management on access users, you ca...
Page 189
Aaa configuration 175 caution: ■ on an s4200g series switch, each access user belongs to an isp domain. You can configure up to 16 isp domains on the switch. When a user logs in, if no isp domain name is carried in the user name, the switch assumes that the user belongs to the default isp domain. ■ ...
Page 190
176 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration ■ if you execute the scheme local command, the local scheme is adopted as the primary scheme. In this case, only local authentication is performed, no radius authentication is performed. ■ if you execute the scheme none command, no authentication is perform...
Page 191
Aaa configuration 177 configuring dynamic vlan assignment the dynamic vlan assignment feature enables a switch to dynamically add the switch ports of successfully authenticated users to different vlans according to the attributes assigned by the radius server, so as to control the network resources ...
Page 192
178 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration configuring the attributes of a local user when local scheme is chosen as the aaa scheme, you should create local users on the switch and configure the relevant attributes. The local users are users set on the switch, with each user uniquely identified by a...
Page 193
Radius configuration 179 ■ if the configured authentication method is none or requires a password, the command level that a user can access after login is determined by the level of the user interface cutting down user connections forcibly radius configuration the radius protocol configuration is pe...
Page 194
180 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration configuring radius authentication/auth orization servers caution: ■ the authentication response sent from the radius server to the radius client carries the authorization information. Therefore, no separate authorization server can be specified. ■ in an act...
Page 195
Radius configuration 181 caution: ■ in an actual network environment, you can either specify two radius servers as the primary and secondary accounting servers respectively, or specify only one server as both the primary and secondary accounting servers. In addition, because radius adopts different ...
Page 196
182 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration caution: you must set the share keys separately for the authentication/authorization packets and the accounting packets if the authentication/authorization server and the accounting server are different devices and the shared keys on the two servers are als...
Page 197
Radius configuration 183 when both the primary and secondary servers are in active or block state, the switch sends packets only to the primary server. Configuring the attributes for data to be sent to radius servers caution: ■ generally, the access users are named in the userid@isp-name format. Whe...
Page 198
184 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration ■ for a radius scheme, if you have specified that no isp domain names are carried in the user names, you should not adopt this radius scheme in more than one isp domain. Otherwise, such errors may occur: the radius server regards two different users having ...
Page 199
Radius configuration 185 to charge the users in real time, you should set the interval of real-time accounting. After the setting, the switch sends the accounting information of online users to the radius server at regular intervals. Configuring whether or not to send trap message when radius server...
Page 200
186 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration the user re-authentication upon device restart function is designed to resolve the above problem. After this function is enabled, every time the switch restarts: 1 the switch generates an accounting-on packet, which mainly contains the following information...
Page 201
Aaa&radius configuration example 187 aaa&radius configuration example remote radius authentication of telnet/ssh user s the configuration procedure for the remote authentication of ssh users through radius server is similar to that of telnet users. The following description only takes the remote aut...
Page 202
188 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration network diagram figure 58 remote radius authentication of telnet users configuration procedure 1 enter system view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] 2 adopt aaa authentication for telnet users [4200g] user-interface vty 0 4 ...
Page 203
Troubleshooting aaa&radius configuration 189 network requirements in the network environment shown in figure 59, you are required to configure the switch so that the telnet users logging into the switch are authenticated locally. Network diagram figure 59 local authentication of telnet users configu...
Page 204
190 c hapter 23: aaa&radius c onfiguration possible reasons and solutions: ■ the user name is not in the userid@isp-name format, or no default isp domain is specified on the switch—use the correct user name format, or set a default isp domain on the switch. ■ the user is not configured in the databa...
Page 205: Entralized
24 c entralized mac a ddress a uthentication c onfiguration centralized mac address authentication overview centralized mac address authentication is port-/mac address-based authentication used to control user permissions to access a network. Centralized mac address authentication can be performed w...
Page 206
192 c hapter 24: c entralized mac a ddress a uthentication c onfiguration ■ configuring the isp domain for mac address authentication users ■ configuring the timers used in centralized mac address authentication the configuration of the maximum number of learned mac addresses (refer to the mac-addre...
Page 207
Displaying and debugging centralized mac address authentication 193 configuring the isp domain for mac address authentication users table 159 lists the operations to configure the isp domain for centralized mac address authentication users. Configuring the timers used in centralized mac address auth...
Page 208
194 c hapter 24: c entralized mac a ddress a uthentication c onfiguration centralized mac address authentication configuration example centralized mac address authentication configuration is similar to 802.1x. In this example, the differences between the two lie in the following: centralized mac add...
Page 209: Arp C
25 arp c onfiguration introduction to arp address resolution protocol (arp) is used to resolve ip addresses into mac addresses. Necessity of the address resolution ip address is used on the network layer and cannot be used directly for communication, because network devices can only identify mac add...
Page 210
196 c hapter 25: arp c onfiguration arp table in an ethernet, the mac addresses of two hosts must be available for the two hosts to communicate with each other. Each host in an ethernet maintains an ip address-to-mac address mapping table known as arp mapping table, as illustrated in figure 60. An e...
Page 211
Introduction to gratuitous arp 197 table 165 describes the apr mapping table fields. Arp implementation procedure the arp mapping table of a host is empty when the host is just started up. And when a dynamic arp mapping entry is not in use for a specified period of time, it is removed from the arp m...
Page 212
198 c hapter 25: arp c onfiguration by sending gratuitous arp packets, a network device can: ■ determine whether or not ip address conflicts exist between it and other network devices. ■ trigger other network devices to update its hardware address stored in their caches. When the gratuitous arp pack...
Page 213
Gratuitous arp packet learning configuration 199 enabling the arp entry checking function when multiple hosts share one multicast mac address, you can specify whether or not to create multicast mac address arp entries for mac addresses learned by performing the operations listed in table 169. Gratui...
Page 215: Acl C
26 acl c onfiguration acl overview an access control list (acl) is used primarily to identify traffic flows. In order to filter data packets, a series of match rules must be configured on the network device to identify the packets to be filtered. After the specific packets are identified, and based ...
Page 216
202 c hapter 26: acl c onfiguration acl match order an acl may contain a number of rules, and each rule specifies a different packet range. This brings about the issue of match order when packets are matched. An acl supports the following four types of match orders: ■ configured order: acl rules are...
Page 217
Defining basic acls 203 configuration procedure if only a periodic time section is defined in a time range, the time range is active only within the defined periodic time section. If only an absolute time section is defined in a time, the time range is active only within the defined absolute time se...
Page 218
204 c hapter 26: acl c onfiguration configuration procedure in the case that you specify the rule id when defining a rule: ■ if the rule corresponding to the specified rule id already exists, you will edit the rule, and the modified part in the rule will replace the original content, while other par...
Page 219
Defining advanced acls 205 configuration preparation before configuring an acl rule containing time range arguments, you need to configure define the corresponding time ranges. For the configuration of time ranges, refer to ?Advanced acl. The values of source and destination ip addresses, the type o...
Page 221
Defining layer 2 acls 207 if the protocol type is icmp, you can also directly input the icmp message name after the icmp-type argument. Table 178 describes some common icmp messages. Configuration example configure acl 3000 to permit icmp packets to pass. System-view [4200g] acl number 3000 [4200g-a...
Page 222
208 c hapter 26: acl c onfiguration configuration tasks in the case that you specify the rule id when defining a rule: ■ if the rule corresponding to the specified rule id already exists, you will edit the rule, and the modified part in the rule will replace the original content, while other parts r...
Page 223
Applying acls on ports 209 configuration example configure acl 4000 to deny packets whose 802.1p priority is 3. System-view [4200g] acl number 4000 [4200g-acl-ethernetframe-4000] rule deny cos 3 [4200g-acl-ethernetframe-4000] display acl 4000 ethernet frame acl 4000, 1 rule acl's step is 1 rule 0 de...
Page 224
210 c hapter 26: acl c onfiguration configuration example apply acl 2100 in the inbound direction on gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to filter packets. System-view [4200g] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0/1] packet-filter inbound ip-group 2100 displaying and debugging acl configuratio...
Page 225
Acl configuration examples 211 configuration procedure only the commands related to the acl configuration are listed below. 1 define a time range that contain a periodic time section from 8:00 to 18:00. System-view [4200g] time-range test 8:00 to 18:00 working-day 2 define an acl on traffic to the w...
Page 226
212 c hapter 26: acl c onfiguration layer 2 acl configuration example network requirements through layer 2 acl configuration, packets with the source mac address of 00e0-fc01-0101 and destination mac address of 00e0-fc01-0303 are to be filtered within the time range from 8:00 to 18:00 everyday. Netw...
Page 227: S C
27 q o s c onfiguration introduction to qos qos (quality of service) is a concept generally existing in occasions with service supply and demand. It evaluates the ability to meet the need of the customers in service. Generally, the evaluation is not to grade precisely. Its purpose is to analyze the ...
Page 228
214 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration ■ rfc2474 re-defines the tos field in the ip packet header, which is called the ds field. The first six (bit 0-bit 5) bits of the ds field indicate dscp precedence in the range of 0 to 63.The first three bits in dscp precedence are class selector codepoints, bit...
Page 229
Introduction to qos 215 2 802.1p priority 802.1p priority lies in layer 2 packet headers and is applicable to occasions where the layer 3 packet header does not need analysis but qos must be assured in layer 2. Figure 65 an ethernet frame with a 802.1q tag header as shown in figure 65, each host sup...
Page 230
216 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration the precedence is called 802.1p priority because the related applications of this precedence are defined in detail in the 802.1p specification. Priority remark the priority remark function is to use acl rules in traffic identifying and remark the priority for th...
Page 231
Introduction to qos 217 figure 67 evaluate the traffic with the token bucket 1 evaluate the traffic with the token bucket the evaluation for the traffic specification is based on whether the number of tokens in the bucket can meet the need of packet forwarding. If the number of tokens in the bucket ...
Page 232
218 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration two token buckets are used in this evaluation. Their rates of putting tokens into the buckets are cir and pir respectively, and their sizes are cbs and ebs respectively (the two buckets are called c bucket and e bucket respectively for short), representing diffe...
Page 233
Introduction to qos 219 for example, if the device a sends packets to the device b. The device b will perform tp on packets from the device a to drop the packets beyond the specification. In order to avoid meaningless packet loss, you can perform ts on the packets on the egress of the device a and c...
Page 234
220 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration the disadvantage of sp queue is that: if there are packets in the queues with higher priority for a long time in congestion, the packets in the queues with lower priority will be “starved to death” because they are not served. 2 wrr queue figure 70 diagram for w...
Page 235
Priority mapping 221 traffic-based traffic statistics the function of traffic-based traffic statistics is to use acl rules in traffic identifying and perform traffic statistics on the packets matching with the acl rules. You can get the statistics of the packets you are interested in through this fu...
Page 236
222 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration you can select the priority trust mode of the port as you require. In the mode of trusting the packet precedence, the switch can trust the following priorities as you configure: ■ trust the 802.1p priority of the packets ■ trust the dscp precedence of the packet...
Page 237
Qos supported by switch 4200g 223 figure 73 the mapping process of trusting the dscp precedence in the default mode and automap mode figure 74 the mapping process of trusting the dscp precedence in the remap mode qos supported by switch 4200g packets packets 7 0 6 62 7 0 7 63 . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Page 238
224 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration configuring priority mapping refer to priority mapping for introduction to priority mapping. Setting to trust the port precedence in the mode of trusting the port precedence, the switch will replace the 802.1p priority carried in the packet with the precedence o...
Page 239
Configuring priority mapping 225 configuration prerequisites ■ the priority trust mode is specified to trusting the 802.1p priority of the packets ■ the value of the “cos-->other precedence” mapping table is specified table 190 the “cos-->other precedence” mapping table and its default value 802.1p ...
Page 240
226 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration configuration procedure configuration example set to trust the 802.1p priority of the packets and adopt the default value in the “cos->other precedence” mapping table. Specify the precedence of gigabitethernet1/0/1 to 7. System-view system view: return to user v...
Page 241
Configuring priority mapping 227 setting to trust the dscp precedence of the packets refer to trusting the dscp precedence of the packets for the description on trusting the dscp precedence of the packets. You can modify the “dscp-->other precedence” mapping relationship as required. The switch also...
Page 242
228 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration configuration procedure configuration example set to trust the dscp precedence of the packets in the default mode and the dscp->other priority mapping mode adopts the default value. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] interface giga...
Page 243
Configuring tp 229 configuring tp refer to t for the introduction to tp. Configuration prerequisites ■ acl rules used for traffic identifying are defined. Refer to the acl module in the book for defining acl rules ■ the limit rate for tp, the actions for the packets within the specified traffic and ...
Page 244
230 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration configuration example ■ the gigabitethernet1/0/1 of the switch is accessed into the 10.1.1.1/24 network segment ■ perform tp on the packets from the 10.1.1.1/24 network segment and the rate of tp is set to100kbps ■ the packets within the specified traffic are fo...
Page 245
Configuring queue-scheduling 231 configuration example perform ts on all the traffic on the gigabitethernet1/0/1. Set the max rate to 650kbps and the burst size to 12kbytes. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [4200g] interface gigabitethernet1/0/1 [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0/1] ...
Page 246
232 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration configuration procedure of the sdwrr queue scheduling configuration example ■ set the queue-scheduling mode of queue0 to queue5 to the sdwrr queue scheduling, and that of queue6 and queue7 to the default sp queue scheduling ■ queue3, queue4, and queue5 join in t...
Page 247
Setting the precedence of protocol packet 233 acl-rule: issued acl rules which can be the combination of various acl rules. The way of combination is described table 202 . Clearing the traffic statistics configuration example ■ the gigabitethernet1/0/1 of the switch is accessed into the 10.1.1.1/24 ...
Page 248
234 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration configuration example set the ip precedence of the icmp protocol packet to 3. The configuration procedure is as follows: system-view [4200g] protocol-priority protocol-type icmp ip-precedence 3 [4200g] display protocol-priority displaying and maintaining qos aft...
Page 249
Qos configuration example 235 qos configuration example configuration example of tp and limiting rate on the port i.Network requirement the enterprise network interworks all the departments through the ports of the ethernet switch. The salary query server is accessed through the gigabitethernet1/0/1...
Page 250
236 c hapter 27: q o s c onfiguration [4200g-acl-adv-3000] quit 2 limit the outbound traffic of the salary query server a limit the average rate of outbound traffic within 640kbps and set the precedence of packets exceeding the specification to 4. [4200g] interface gigabitethernet1/0/1 [4200g-gigabi...
Page 251: Onfiguration
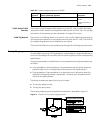
28 c onfiguration for m irroring f eatures mirroring features mirroring refers to the process of copying packets that meet the specified rules to a destination port. Generally, a destination port is connected to a data detect device, which users can use to analyze the mirrored packets for monitoring...
Page 252
238 c hapter 28: c onfiguration for m irroring f eatures ■ intermediate switch: the switch between the source and the destination switch on the network. ■ destination switch: the switch to which the destination port for remote mirroring belongs. Table 206 describes how the ports on various switches ...
Page 253
Mirroring supported by switch 4200g 239 mac-based mirroring in mac-based mirroring, the device mirrors the following packets to the destination port. ■ packets whose source mac addresses match the specified mac addresses ■ packets whose destination mac addresses match the specified mac addresses vla...
Page 254
240 c hapter 28: c onfiguration for m irroring f eatures configuration procedure acl-rule: applied acl rules, which can be the combination of different types of acl rules. Table 209 describes the acl combinations. Configuration example ■ gigabitethernet1/0/1 on the switch is connected to the 10.1.1....
Page 255
Mirroring configuration 241 configuring port mirroring configuration prerequisites ■ the source port is specified and whether the packets to be mirrored are inbound or outbound is specified: inbound: only mirrors the packets received using the port; outbound:onlymirrors the packets sent by the port;...
Page 256
242 c hapter 28: c onfiguration for m irroring f eatures configuring port mirroring in system view configuration example ■ the source port is gigabitethernet1/0/1. Mirror all packets received and sent using this port. ■ the destination port is gigabitethernet1/0/7. Configuration procedure: system-vi...
Page 257
Mirroring configuration 243 configuration procedure configuration example ■ configure mac-based mirroring to mirror the packets matching the mac address 00e0-fc01-0101 to the destination port. ■ the destination port is gigabitethernet1/0/2. Configuration procedure: system-view system view: return to...
Page 258
244 c hapter 28: c onfiguration for m irroring f eatures configuration procedure configuration example ■ configure vlan-based mirroring to mirror the packets received by all ports in vlan 2. ■ the destination port is gigabitethernet1/0/2. Configuration procedure: system-view system view: return to u...
Page 259
Mirroring configuration 245 configuring rspan on the source switch configuring rspan on the intermediate switch table 215 configure rspan on the source switch operation command description enter system view system-view - create a remote-probe vlan and enter vlan view vlan vlan-id vlan-id is the id o...
Page 260
246 c hapter 28: c onfiguration for m irroring f eatures configuring rspan on the destination switch configuration example ■ switch a is connected to the data detect device using gigabitethernet1/0/2. ■ gigabitethernet1/0/1, the trunk port of switch a, is connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/1, the trun...
Page 261
Mirroring configuration 247 to meet the requirement above by using the rspan function, perform the following configuration: ■ define vlan10 as remote-probe vlan. ■ define switch a as the destination switch; configure ethernet1/0/2, the port that is connected to the data detect device, as the destina...
Page 262
248 c hapter 28: c onfiguration for m irroring f eatures [4200g] interface gigabitethernet1/0/1 [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 10 [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [4200g] interface gigabitethernet1/0/2 [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan 10 3 configure switch a....
Page 263: Igmp S
29 igmp s nooping c onfiguration overview of igmp snooping igmp snooping fundamentals igmp snooping (internet group management protocol snooping) is a multicast control mechanism running on layer 2 switch. It is used to manage and control multicast groups. When the igmp messages transferred from the...
Page 264
250 c hapter 29: igmp s nooping c onfiguration igmp snooping fundamentals igmp snooping terminologies before going on, we first describe the following terms involved in igmp snooping: ■ router port: the switch port directly connected to the multicast router. ■ multicast member port: a switch port co...
Page 265
Overview of igmp snooping 251 to implement layer 2 multicast, the switch processes four different types of igmp messages it received, as shown in table 221. Table 221 igmp snooping messages message sender receiver purpose switch action igmp general query message multicast router and multicast switch...
Page 266
252 c hapter 29: igmp s nooping c onfiguration igmp snooping configuration the following sections describe the igmp snooping configuration tasks. ■ enabling igmp snooping ■ configuring timers ■ enabling igmp fast leave processing ■ configuring igmp snooping filtering acl ■ configuring to limit port ...
Page 267
Igmp snooping configuration 253 configuring timers this configuration task is to manually configure the aging time of the router port, the aging time of the multicast member ports, and the query response timeout time. ■ if the switch receives no general query message from a router within the aging t...
Page 268
254 c hapter 29: igmp s nooping c onfiguration in practice, when a user orders a multicast program, an igmp report message is generated. When the message arrives at the switch, the switch examines the multicast filtering acl configured on the access port to determine if the port can join the corresp...
Page 269
Igmp snooping configuration 255 multicast vlan is mainly used in layer 2 switching, but you must make corresponding configuration on the layer 3 switch. Table 227 configure multicast vlan on layer 3 switch operation command description enter system view system-view — create a vlan and enter the vlan...
Page 270
256 c hapter 29: igmp s nooping c onfiguration ■ you cannot set the isolate vlan as a multicast vlan. ■ one port can belong to only one multicast vlan. ■ the port connected to a user end can only be as set as a hybrid port. Displaying information about igmp snooping you can execute the following dis...
Page 271
Igmp snooping configuration example 257 2 enable igmp snooping on vlan 10 where no layer 3 multicast protocol is enabled. [4200g] vlan 10 [4200g-vlan10] igmp-snooping enable example 2 configure multicast vlan on layer 2 and layer 3 switches. Network requirements table 230 describes the network devic...
Page 272
258 c hapter 29: igmp s nooping c onfiguration configuration procedure the following configuration is based on the prerequisite that the devices are properly connected and all the required ip addresses are already configured. 1 configure switch a: a set the interface ip address of vlan 20 to 168.10....
Page 273
Troubleshooting igmp snooping 259 [ switch b-gigabitethernet 1/0/1] quit e define the gigabitethernet 1/0/2 port as a hybrid port, add the port to vlan 3 and vlan 10, and configure the port to exclude vlan tags in its outbound packets for vlan 3 and vlan 10, and set vlan 3 as the default vlan of the...
Page 274
260 c hapter 29: igmp s nooping c onfiguration.
Page 275: Outing
30 r outing p ort j oin to m ulticast g roup c onfiguration routing port join to multicast group configuration introduction normally, an igmp host responds to igmp query messages of the multicast router. In case of response failure, the multicast router may consider that there is no multicast member...
Page 276
262 c hapter 30: r outing p ort j oin to m ulticast g roup c onfiguration.
Page 277: Ulticast
31 m ulticast mac a ddress e ntry c onfiguration introduction in layer 2 multicast, the system can add multicast forwarding entries dynamically through layer 2 multicast protocol. However, you can also statically bind a port to a multicast address entry by configuring a multicast mac address manuall...
Page 278
264 c hapter 31: m ulticast mac a ddress e ntry c onfiguration ■ you cannot enable port aggregation on a port where you have configured a multicast mac address; and you cannot configure a multicast mac address on an aggregation port. Displaying multicast mac address configuration you can use the fol...
Page 279: Luster
32 c luster c onfiguration cluster overview introduction to cluster a cluster is implemented through hgmp v2. By employing hgmp v2, a network administrator can manage multiple switches using the public ip address of a switch known as a management device. The switches under the management of the mana...
Page 280
266 c hapter 32: c luster c onfiguration hgmp v2 provides the following functions: ■ topology discovery: hgmp v2 implements ndp (neighbor discovery protocol) to discover the information about the directly connected neighbor devices, including device type, software/hardware version, connecting port a...
Page 281
Cluster overview 267 figure 84 role changing rule ■ each cluster has one (and only one) management device. A management device collects ndp/ntdp information to discover and determine candidate devices, which can be then added into the cluster through manual configurations. ■ a candidate device becom...
Page 282
268 c hapter 32: c luster c onfiguration upon detecting a change occurred on a neighbor, a member device informs the management device of the change through handshake packets. The management device then collects the specified topology information through ntdp. Such a mechanism enables topology chang...
Page 283
Management device configuration 269 enabling ndp globally and for specific ports configuring ndp-related parameters enabling ntdp globally and for specific ports configuring ntdp-related parameters table 235 enable ndp globally and for a specific port operation command description enter system view ...
Page 284
270 c hapter 32: c luster c onfiguration enabling the cluster function configuring cluster parameters configuring cluster parameters manually configuring a cluster automatically table 239 enable the cluster function operation command description enter system view system-view — enable the cluster fun...
Page 285
Member device configuration 271 configuring internal-external interaction member device configuration member device configuration involves: ■ enabling ndp globally and for specific ports ■ enabling ntdp globally and for specific ports ■ enabling the cluster function ■ specifying the cluster ftp/tftp...
Page 286
272 c hapter 32: c luster c onfiguration specifying the cluster ftp/tftp server intra-cluster configuration displaying and maintaining a cluster you can view the configuration of a cluster using the display commands, which can be executed in any view. Table 245 specify the cluster ftp/tftp server op...
Page 287
Hgmp v2 configuration example 273 hgmp v2 configuration example network requirements three switches form a cluster, in which: ■ the management device is an s4200g series switch. ■ the rest are member devices. The s4200g series switch operates as the management device of the cluster. Other detailed i...
Page 288
274 c hapter 32: c luster c onfiguration network diagram figure 85 network diagram for hgmp cluster configuration configuration procedure 1 configure the management device. A enable ndp globally and for gigabitethernet1/0/2 and gigabitethernet1/0/3 ports. [4200g] ndp enable [4200g] interface gigabit...
Page 289
Hgmp v2 configuration example 275 f configure the delay time for topology-collection request packets to be forwarded on member devices to be 150 ms. [4200g] ntdp timer hop-delay 150 g configure the delay time for topology-collection request packets to be forwarded through the ports of member devices...
Page 290
276 c hapter 32: c luster c onfiguration d establish a connection with the cluster ftp server. Ftp cluster e download the file named aaa.Txt from the cluster tftp server. Tftp cluster get aaa.Txt f upload the file named bbb.Txt to the cluster tftp server. Tftp cluster put bbb.Txt upon the completion...
Page 291: Snmp C
33 snmp c onfiguration snmp overview by far, the simple network management protocol (snmp) has gained the most extensive application in the computer networks. Snmp has been put into use and widely accepted as an industry standard in practice. It is used for ensuring the transmission of the managemen...
Page 292
278 c hapter 33: snmp c onfiguration mibs supported by the device the management variable in the snmp packet describes management objects of a device. To uniquely identify the management objects of the device in snmp messages, snmp adopts the hierarchical naming scheme to identify the managed object...
Page 293
Configuring snmp basic functions 279 configuring snmp basic functions the configuration of snmp v3 configuration is different from that of snmp v1 and snmp v2c, therefore snmp basic function configurations for different versions are introduced respectively. For specific configurations, refer to tabl...
Page 295
Configuring trap 281 configuring trap trap is the information that the managed device initially sends to the nms without request. Trap is used to report some urgent and important events (for example, the managed device is rebooted). Configuration prerequisites complete snmp basic configuration. Conf...
Page 296
282 c hapter 33: snmp c onfiguration setting the logging function for network management you can use the display logbuffer command to display logging information for the get and set operations sent from nms. Displaying snmp after the above configuration is completed, execute the display command in a...
Page 297
Snmp configuration example 283 network diagram figure 87 network diagram for snmp network procedure 1 set the community name, group name and user. System-view [4200g] snmp-agent sys-info version all [4200g] snmp-agent community write public [4200g] snmp-agent mib-view include internet 1.3.6.1 [4200g...
Page 298
284 c hapter 33: snmp c onfiguration.
Page 299: Rmon C
34 rmon c onfiguration introduction to rmon remote monitoring (rmon) is a kind of management information base (mib) defined by internet engineering task force (ietf) and is a most important enhancement made to mib ii standards. Rmon is mainly used to monitor the data traffic across a network segment...
Page 300
286 c hapter 34: rmon c onfiguration you can specify a network device to act in one of the following ways in response to an event: ■ logging the event ■ sending trap messages to the nms ■ logging the event and sending trap messages to the nms alarm group rmon alarm management enables monitors on spe...
Page 301
Rmon configuration 287 with the rmon statistics management function, you can monitor the usage of a port and make statistics on the errors occurred when the ports are being used. Rmon configuration prerequisites before performing rmon configuration, make sure the snmp agents are correctly configured...
Page 302
288 c hapter 34: rmon c onfiguration displaying and debugging rmon after the above configuration, you can execute the display command in any view to display the rmon running status, and verify the effect of the configuration. Rmon configuration example network requirements ■ ensure that the snmp age...
Page 303
Rmon configuration example 289 2 display rmon configuration. [4200g-gigabitethernet1/0/1] display rmon statistics gigabitethernet1/0/1 statistics entry 1 owned by user1-rmon is valid. Interface : gagabitethernet1/0/1 etherstatsoctets : 0 , etherstatspkts : 0 etherstatsbroadcastpkts : 0 , etherstatsm...
Page 304
290 c hapter 34: rmon c onfiguration.
Page 305: Ntp C
35 ntp c onfiguration introduction to ntp network time protocol (ntp) is a time synchronization protocol defined by rfc1305. It is used for time synchronization among a set of distributed time servers and clients. Ntp is based on user datagram protocol (udp). Ntp is intended for time synchronization...
Page 306
292 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration working principle of ntp the working principle of ntp is shown in figure 89. In figure 89, the ethernet switch a (ls_a) is connected to the ethernet switch b (ls_b) through their ethernet ports. Both of them have system clocks of their own, and they need to synchr...
Page 307
Introduction to ntp 293 at this time, ls_a has enough information to calculate the following two parameters: ■ the delay for an ntp packet to make a round trip between ls_a and ls_b: delay = (t 4 -t 1 )-(t 3 -t 2 ). ■ the time offset of ls_a with regard to ls_b: offset = ((t 2 -t 1 ) + (t 3 -t 4 ))/...
Page 308
294 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration broadcast mode figure 92 ntp implementation mode: broadcast mode multicast mode figure 93 ntp implementation mode: multicast mode table 256 describes how the above mentioned ntp modes are implemented on an s4200g series switch. Table 256 ntp implementation modes o...
Page 309
Ntp implementation mode configuration 295 caution: an s4200g series switch can operate in ntp peer mode, ntp broadcast server mode or ntp multicast server mode only after it is synchronized. Ntp implementation mode configuration a switch can operate in the following ntp modes: ■ ntp server mode ■ nt...
Page 310
296 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration ntp server mode when an s4200g series switch operates in ntp server mode, ■ the remote server identified by the remote-ip argument operates as the ntp time server. The s4200g series switch operates as the client, whose clock is synchronized to the ntp server. (in ...
Page 311
Access control permission configuration 297 ■ the total number of the servers and peers configured for a switch can be up to 128. ■ after the configuration, the s4200g series switch does not establish connections with the peer if it operates in ntp server mode. Whereas if it operates in any of the o...
Page 312
298 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration configuring ntp authentication configuring ntp authentication on the client ■ ntp authentication requires that the authentication keys configured for the server and the client are the same. Besides, the authentication keys must be trusted keys. Otherwise, the clie...
Page 313
Configuration of optional ntp parameters 299 configuring ntp authentication on the server the procedures for configuring ntp authentication on the server are the same as that on the client. Besides, the client and the server must be configured with the same authentication key. Configuration of optio...
Page 314
300 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration caution: ■ the source ip address in an ntp packet is the address of the sending interface specified by the ntp-service unicast-server command or the ntp-service unicast-peer command if you provide the address of the sending interface in these two commands. ■ dynam...
Page 315
Configuration example 301 network diagram figure 94 network diagram for the ntp server mode configuration configuration procedures the following configurations are for the s4200g 1 switch. 1 display the ntp status of the s4200g 1 switch before synchronization. Display ntp-service status clock status...
Page 316
302 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration note: 1 source(master),2 source(peer),3 selected,4 candidate,5 configured ntp peer mode configuration network requirements s4200g 2 sets the local clock to be the ntp master clock, with the clock stratum being 2. Configure an s4200g 1 series switch to operate as a...
Page 317
Configuration example 303 display the status of the s4200g switch after the synchronization. [s4200g] display ntp-service status clock status: synchronized clock stratum: 2 reference clock id: 3.0.1.32 nominal frequency: 250.0000 hz actual frequency: 249.9992 hz clock precision: 2^19 clock offset: 0...
Page 318
304 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration configuration procedures 1 configure s4200g 3. A enter system view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s4200g] b enter vlan interface 2 view. [s4200g] interface vlan-interface 2 [s4200g-vlan-interface2] c configure s4200g 3 to be the broadc...
Page 319
Configuration example 305 root delay: 27.47 ms root dispersion: 208.39 ms peer dispersion: 9.63 ms reference time: 17:03:32.022 utc thu sep 6 2001 (bf422ae4.05aea86c) the output information indicates that s4200g 1 is synchronized to s4200g 3, with the clock stratum of 3, one stratum higher than s420...
Page 320
306 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration 2 configure s4200g 1. A enter system view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s4200g] b enter vlan interface 2 view. [[s4200g] interface vlan-interface 2 c configure s4200g 4 to be a multicast client. [s4200g-vlan-interface2] ntp-service mu...
Page 321
Configuration example 307 ntp server mode with authentication configuration network requirements the local clock of s4200g1 operates as the master ntp clock, with the clock stratum set to 2. A s4200g 2 series switch operates in client mode with s4200g 1 as the time server. S4200g 1 operates in the s...
Page 322
308 c hapter 35: ntp c onfiguration after the above configuration, the s4200g 2 series switch can be synchronized to s4200g 1. You can display the status of s4200g 2 after the synchronization. [s4200g] display ntp-service status clock status: synchronized clock stratum: 3 reference clock id: 1.0.1.1...
Page 323: Ssh T
36 ssh t erminal s ervices ssh terminal services introduction to ssh secure shell (ssh) can provide information security and powerful authentication to prevent such assaults as ip address spoofing, plain-text password interception when users log on to the switch remotely using an insecure network en...
Page 324
310 c hapter 36: ssh t erminal s ervices figure 100 establish ssh channels through wan the communication process between the server and client includes these five stages: 1 version negotiation stage. These operations are completed at this stage: ■ the client sends tcp connection requirement to the s...
Page 325
Ssh terminal services 311 ssh supports two authentication types: password authentication and rsa authentication. (1) password authentication works as follows: ■ the client sends its username and password to the server. ■ the server compares the username and password received with those configured lo...
Page 326
312 c hapter 36: ssh t erminal s ervices configuring supported protocols caution: when ssh protocol is specified, to ensure a successful login, you must configure the aaa authentication using the authentication-mode scheme command. The protocol inbound ssh configuration fails if you configured authe...
Page 327
Ssh terminal services 313 configuring authentication type new users must specify authentication type. Otherwise, they cannot access the switch. Caution: ■ if rsa authentication type is defined, then the rsa public key of the client user must be configured on the switch. ■ by default, no authenticati...
Page 328
314 c hapter 36: ssh t erminal s ervices ssh client configuration table 269 describes ssh configuration tasks. In the initial authentication, if the ssh client does not have the public key for the server which it accesses for the first time, the client continues to access the server and save locally...
Page 329
Ssh terminal services 315 ssh server configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 101, configure a local connection from the ssh client to the switch. The pc runs the ssh2.0-supported client software. Network diagram figure 101 network diagram for ssh server configuration configurat...
Page 330
316 c hapter 36: ssh t erminal s ervices configure the login protocol for the client002 user as ssh and authentication type as rsa public key. [4200g] ssh user client002 authentication-type rsa generate randomly rsa key pairs on the ssh2.0 client and send the corresponding public keys to the server....
Page 331
Sftp service 317 [4200g-rsa-key-code] 1991c164b0df178c55fa833591c7d47d5381d09ce82913 [4200g-rsa-key-code] d7edf9c08511d83ca4ed2b30b809808eb0d1f52d045de4 [4200g-rsa-key-code] 0861b74a0e135523ccd74cac61f8e58c452b2f3f2da0dc [4200g-rsa-key-code] c48e3306367fe187bdd944018b3b69f3cbb0a573202c16 [4200g-rsa-...
Page 332
318 c hapter 36: ssh t erminal s ervices sftp server configuration the following sections describe sftp server configuration tasks: ■ configuring service type for an ssh user ■ enabling the sftp server ■ setting connection timeout time configuring service type for an ssh user enabling the sftp serve...
Page 333
Sftp service 319 sftp client configuration the following sections describe sftp client configuration tasks: enabling the sftp client you can enable the sftp client, establish a connection to the remote sftp server and enter stp client view. Table 274 configuring sftp client serial no operation comma...
Page 334
320 c hapter 36: ssh t erminal s ervices disabling the sftp client operating with sftp directories sftp directory-related operations include: changing or displaying the current directory, creating or deleting a directory, displaying files or information of a specific directory. Operating with sftp f...
Page 335
Sftp service 321 displaying help information you can display help information about a command, such as syntax and parameters. Sftp configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 103, ■ an ssh connection is present between switch a and switch b. ■ switch b serves as an sftp server, wit...
Page 336
322 c hapter 36: ssh t erminal s ervices b display the current directory on the sftp server, delete file z and verify the operation. Sftp-client> dir -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 1759 aug 23 06:52 vrpcfg.Cfg -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 225 aug 24 08:01 pubkey2 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 aug 24 07:3...
Page 337
Sftp service 323 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 sep 02 06:35 pub -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 sep 02 06:36 puk sftp-client> g exit from sftp. Sftp-client> quit bye [4200g].
Page 338
324 c hapter 36: ssh t erminal s ervices.
Page 339: Ile
37 f ile s ystem m anagement file attribute configuration introduction to file attributes an app file, a configuration file, or a web file can be of one of these three attributes: main, backup and none, as described in table 280. An app file is an executable file, with .App as the extension. A confi...
Page 340
326 c hapter 37: f ile s ystem m anagement perform the following configuration in user view. Caution: before configuring the main or backup attribute for a file, make sure the file already exists. For example, to configure the main or backup attribute for a web file, you need to make sure the file e...
Page 341
File system configuration 327 according to the operation objects, the operations on the file system fall into the following categories: ■ directory operation ■ file operation ■ storage device operation ■ prompt mode configuration file path and file name can be represented in one of the following way...
Page 342
328 c hapter 37: f ile s ystem m anagement ■ managing a configuration file ■ renaming a file ■ copying a file ■ moving a file ■ displaying the content of a file ■ displaying the information about a file ■ checking file system table 283 describes the file-related operations. Perform the following con...
Page 343
File system configuration 329 as for the save command listed in table 283 the safely keyword determines the ways to save the current configuration, as described in the following. ■ if you execute this command with the safely keyword not specified, the system saves the current configuration in the fa...
Page 344
330 c hapter 37: f ile s ystem m anagement 7 -rw- 296368 apr 02 2000 00:34:16 s3u01_00.Btm 8 -rw- 951305 apr 02 2000 00:34:25 s3v01_00.Web 9 -rw- 8451 apr 01 2000 23:56:53 3comoscfgdef.Old 10 -rw- 3114 apr 02 2000 23:21:44 l3config.Old 11(*) -rw- 3628 apr 09 2000 00:11:00 updt.Cfg 12 -rwh 716 apr 05...
Page 345
Testing tools for network connection 331 display the file information after the copy operation. Dir flash:/test directory of unit1>flash:/ 1 drw- - apr 16 2000 01:22:48 test 15367 kb total (623 kb free) (*) -with main attribute (b) -with backup attribute (*b) -with both main and backup attribute tes...
Page 346
332 c hapter 37: f ile s ystem m anagement you can configure up to 50 ip addresses by using the command repeatedly. Tracert the tracert is used for testing the gateways passed by the packets from the source host to the destination one. It is mainly used for checking if the network is connected and a...
Page 347: Ftp
38 ftp and tftp c onfiguration ftp configuration introduction to ftp ftp (file transfer protocol) is commonly used in ip-based networks to transmit files. Before world wide web comes into being, files are transferred through command lines, and the most popular application is ftp. At present, althoug...
Page 348
334 c hapter 38: ftp and tftp c onfiguration table 289 describes the operations needed when a switch operates as an ftp server. Caution: the ftp-related functions require that the route between a ftp client and the ftp server is reachable. Ftp configuration: a switch operating as an ftp server prere...
Page 349
Ftp configuration 335 ftp services are implemented in this way: an ftp client sends ftp requests to the ftp server. The ftp server receives the requests, perform operations accordingly, and return the results to the ftp client. To prevent unauthorized accesses, an ftp server disconnects a ftp connec...
Page 350
336 c hapter 38: ftp and tftp c onfiguration configuration example: a switch operating as an ftp client network requirements a switch and a remote pc operate as an ftp client and an ftp server. ■ create a user account on the ftp server, with the user name being switch, password being hello, and the ...
Page 351
Ftp configuration 337 network diagram figure 106 network diagram for ftp configuration (a) configuration procedure 1 perform ftp server-related configurations on the pc, that is, create a user account on the ftp server, with the user name being switch, password being hello, and the permission to acc...
Page 352
338 c hapter 38: ftp and tftp c onfiguration 6 specify the downloaded file (the file named switch.Bin) to be the startup file used when the switch starts the next time and restart the switch. Thus the switch application is upgraded. Boot boot-loader switch.Bin reboot configuration example: a switch ...
Page 353
Tftp configuration 339 3 after uploading the application, you can update the application on the switch. Specify the downloaded file (the file named switch.Bin) to be the startup file used when the switch starts the next time and restart the switch. Thus the switch application is upgraded. Boot boot-...
Page 354
340 c hapter 38: ftp and tftp c onfiguration table 293 describes the operations needed when a switch operates as an tftp client. Tftp configuration prerequisites a switch operates as a tftp client. A pc operates as the tftp server. The network operates properly, as shown in figure 108 4. Configurati...
Page 355
Tftp configuration 341 network diagram figure 109 network diagram for tftp configuration configuration procedure 1 start the tftp server and configure the work directory on the pc. 2 configure the switch. A log into the switch. (you can log into a switch through the console port or by telneting to t...
Page 356
342 c hapter 38: ftp and tftp c onfiguration.
Page 357: Nformation
39 i nformation c enter information center overview information center is an indispensable part of ethernet switches and exists as an information hub of system software modules. The information center manages most information outputs; it sorts information carefully, and hence can screen information ...
Page 358
344 c hapter 39: i nformation c enter 4 module name it indicates the modules that generate the information. Table 295 gives some examples of the modules. Note that a slash (/) separates the module name and severity level. 5 level switch information falls into three categories: log information, debug...
Page 359
Information center configuration 345 information center configuration the switch supports information output to six directions. By far, each output direction is assigned with an information channel, as shown in table 297. Settings for the six output directions are independent. However, for any outpu...
Page 360
346 c hapter 39: i nformation c enter enabling information output to a log host table 299 lists the related configurations on the switch. To view the debug information of specific modules, you need to set the information type as debug in the info-center source command, and enable the debugging funct...
Page 361
Information center configuration 347 enabling information output to a monitor terminal table 302 lists the related configurations on the switch. When there are multiple telnet users or dumb terminal users, some configuration parameters (including module filter, language and severity level threshold ...
Page 362
348 c hapter 39: i nformation c enter perform the following configuration in user view. Enabling information output to the log buffer table 304 lists the related configurations on the switch. To view debug information of specific modules, you need to set the information type as debugin the info-cent...
Page 363
Information center configuration 349 to view debug information of specific modules, you need to set the information type as debug in the info-center source command, and enable debugging on corresponding modules with the debugging command as well. Enabling information output to the snmp table 306 lis...
Page 364
350 c hapter 39: i nformation c enter displaying and debugging information center after the performing the above configurations, you can execute the display command in any view to display the running status of the information center, and thus validate your configurations. You can also execute the re...
Page 365
Information center configuration example 351 terminal logging.
Page 366
352 c hapter 39: i nformation c enter.
Page 367: Oot
40 b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading traditionally, the loading of switch software is accomplished through a serial port. This approach is slow, inconvenient, and cannot be used for remote loading. To resolve these problems, the tftp and ftp modules are introduced into the switch. With these mo...
Page 368
354 c hapter 40: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading cpu type : bcm4704 cpu clock speed : 200mhz bus clock speed : 33mhz memory size : 64mb mac address : 00e0fc005104 press ctrl-b to enter boot menu… 5 press . The system displays: password : to enter the boot menu, you should press within five se...
Page 369
Local software loading 355 loading bootrom software follow these steps to load the bootrom software: 1 at the prompt "enter your choice(0-9):" in the boot menu, press or , and then press to enter the bootrom update menu shown below: bootrom update menu: 1. Set tftp protocol parameter 2. Set ftp prot...
Page 370
356 c hapter 40: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading figure 111 properties dialog box figure 112 console port configuration dialog box 5 click the button to disconnect the hyperterminal from the switch and then click the button to reconnect the hyperterminal to the switch..
Page 371
Local software loading 357 figure 113 connect and disconnect buttons the new baud rate takes effect only after you disconnect and reconnect the terminal emulation program. 6 press to start downloading the program. The system displays the following information: now please start transfer file with xmo...
Page 372
358 c hapter 40: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading figure 115 sending file page after the download completes, the system displays the following information: loading …cccccccccc done! You need not reset the hyperterminal’s baud rate and can skip the last step if you have chosen 9600 bps. In this...
Page 373
Local software loading 359 loading software using tftp through ethernet port introduction to tftp tftp, one protocol in tcp/ip protocol suite, is used for trivial file transfer between client and server. It uses udp to provide unreliable data stream transfer service. Loading bootrom software figure ...
Page 374
360 c hapter 40: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading loading host software follow these steps to load the host software. 1 select in boot menu. The system displays the following information: 1. Set tftp protocol parameter 2. Set ftp protocol parameter 3. Set xmodem protocol parameter 0. Return to...
Page 375
Remote software loading 361 4 enter 2 in the above menu to download the bootrom software using ftp. Then set the following ftp-related parameters as required: load file name :s4200g.Btm switch ip address :10.1.1.2 server ip address :10.1.1.1 ftp user name :4200g ftp user password :abc 5 press . The ...
Page 376
362 c hapter 40: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading figure 118 remote loading using ftp 1 download the software to the switch using ftp commands. Ftp 10.1.1.1 trying … press ctrl+k to abort connected. 220 wftpd 2.0 service (by texas imperial software) ready for new user user(none):abc 331 give m...
Page 377
Remote software loading 363 after the above operations, the bootrom and host software loading is completed. Pay attention to the following: ■ the loading of host software takes effect only after you restart the switch with the reboot command. ■ if the space of the flash memory is not enough, you can...
Page 378
364 c hapter 40: b oot rom and h ost s oftware l oading.
Page 379
41 basic system configuration and debugging basic system configuration the following sections describe the basic system configuration and management tasks: ■ setting the system name of the switch ■ setting the date and time of the system ■ setting the local time zone ■ setting the summer time ■ sett...
Page 380
366 c hapter 41: basic system configuration and debugging perform the following configuration in user view. Setting the summer time this configuration task is to set the name, time range (start time and end time), and time offset of the summer timer. The operation here saves you from manually adjust...
Page 381
Displaying the system status 367 entering system view from user view perform the following configuration in user view. Displaying the system status you can use the following display commands to check the status and configuration information about the system. For information about protocols and ports...
Page 382
368 c hapter 41: basic system configuration and debugging the relation between the two switches is as follows: figure 119 debugging information output you can use the following commands to operate the two kinds of switches. Perform the following operations in user view. Displaying debugging status t...
Page 383
System debugging 369 displaying operating information about modules in system when your ethernet switch is in trouble, you may need to view a lot of operating information to locate the problem. Each functional module has its own operating information display command(s). You can use the command here ...
Page 384
370 c hapter 41: basic system configuration and debugging.
Page 385: Ip P
42 ip p erformance c onfiguration ip performance configuration introduction to tcp attributes you can configure the following tcp attributes of the ethernet switch: ■ synwait timer: when a syn packet is sent, tcp starts the synwait timer. If no response packet is received before the synwait timer ti...
Page 386
372 c hapter 42: ip p erformance c onfiguration you can execute the reset commands in user view to clear the ip, tcp and udp traffic statistics. You can also execute the debugging commands to enable different ip performance debugging. Troubleshooting the ip performance configuration symptom: ip pack...
Page 387: Etwork
43 n etwork c onnectivity t est network connectivity test ping you can use the ping command to check the network connectivity and the reachability of a host. This command can output the following results: ■ response status for each ping packet. If no response packet is received within the timeout ti...
Page 388
374 c hapter 43: n etwork c onnectivity t est.
Page 389: Evice
44 d evice m anagement introduction to device management the device management function of the ethernet switch can report the current status and event-debugging information of the boards to you. Through this function, you can maintain and manage your physical device, and restart the system when some...
Page 390
376 c hapter 44: d evice m anagement specifying the app to be adopted at reboot app is the host software of the switch. If multiple apps exist in the flash memory, you can use the command here to specify the one that will be adopted when the switch reboots. Perform the following configuration in use...
Page 391
Remote switch update configuration example 377 perform the following configuration on the ftp server. ■ configure an ftp user, whose name and password are switch and hello respectively. Authorize the user with the read-write right of the switch directory on the pc. ■ make appropriate configuration s...
Page 392
378 c hapter 44: d evice m anagement d enter the authorized path on the ftp server. [ ftp] cd switch e execute the get command to download the switch.Bin and boot.Btm files on the ftp server to the flash memory of the switch. [ ftp] get switch.Bin [ ftp] get boot.Btm f execute the quit command to te...
Page 393: Onfiguration
45 c onfiguration of n ewly a dded c luster f unctions introduction to the newly added cluster functions the newly added cluster functions aim to improve switch performance. They extend switch functionality. With the cluster function employed, you can manage and maintain all the member switches in a...
Page 394
380 c hapter 45: c onfiguration of n ewly a dded c luster f unctions configuration of the newly added cluster functions configuring the tftp server and snmp host for a cluster you can perform the operations listed in table 329 on the master device of a cluster to configure the tftp server and snmp h...
Page 395
Introduction to the newly added cluster functions 381 notes perform the operations listed in table 330 in cluster view on the master device. The configuration can only be synchronized to the member devices in the white list only. The configuration remains valid on a member device even if it quits th...
Page 396
382 c hapter 45: c onfiguration of n ewly a dded c luster f unctions # display the current topology. [chwn_0.S4200g-cluster]display cluster current-topology -------------------------------------------------------------------- (peerport) connectflag (nativeport) [sysname:devicemac] ------------------...
Page 397
Introduction to the newly added cluster functions 383 finish to synchronize the command. # configure the group name to be ggg. [chwn_0.S4200g-cluster] cluster-snmp-agent group v3 ggg member 2 succeeded in the group configuration. Member 1 succeeded in the group configuration. Finish to synchronize t...
Page 398
384 c hapter 45: c onfiguration of n ewly a dded c luster f unctions # radius scheme system # domain system # vlan 1 # snmp-agent snmp-agent local-engineid 800007db000fe224055f6877 snmp-agent community read aaa@cm2 snmp-agent community write bbb@cm2 snmp-agent sys-info version all snmp-agent group v...
Page 399
Introduction to the newly added cluster functions 385 ■ configuring topology management topology management is performed based on white list and blacklist. The meanings of white list and blacklist are as follows: ■ white list: correct network topology confirmed by the network administrator. You can ...
Page 400
386 c hapter 45: c onfiguration of n ewly a dded c luster f unctions configuring cluster interoperation after creating a cluster, you can universally configure servers, nms hosts and logging hosts for the cluster on the management device. Member devices can access the configured servers through the ...
Page 401
Introduction to the newly added cluster functions 387 synchronizing user name and password user name and password synchronization of web users simplifies user configuration. With this function employed, the configuration performed on the master device is synchronized to all the member devices in the...
Page 402
388 c hapter 45: c onfiguration of n ewly a dded c luster f unctions # user-interface aux 0 user-interface vty 0 4 # return configuring topology authentication you can save a reference topology file that serves as the basis of the current network topology. It can be used to locate problems in subseq...
Page 403
Displaying and debugging a cluster 389 configuration procedure displaying and debugging a cluster after the above-mentioned configuration, you can use the display command or the tracemac command in any view to view the cluster operating information, so as to verify configuration result. Use the rese...
Page 404
390 c hapter 45: c onfiguration of n ewly a dded c luster f unctions configuration example for newly added cluster functions network requirements in a cluster formed by switch a, switch b, switch c, and switch d, switch a is the master switch. Ndp and ntdp configurations are performed on the related...
Page 405
Configuration example for newly added cluster functions 391 configuration procedure perform the following configurations on the master device (switch a). # configure a tftp server and snmp host for the cluster. [s4200g] cluster [s4200g-cluster]tftp-server 10.1.1.15 [s4200g-cluster] snmp-host 10.1.1....
Page 406
392 c hapter 45: c onfiguration of n ewly a dded c luster f unctions.
Page 407: Dhcp R
46 dhcp r elay c onfiguration introduction to dhcp relay usage of dhcp relay early dhcp implementations assumes that dhcp clients and dhcp servers are on the same network segment, that is, you need to deploy at least one dhcp server for each network segment, which is far from economical. Dhcp relay ...
Page 408
394 c hapter 46: dhcp r elay c onfiguration note that such an interacting process may be repeated several times for a dhcp client to be successfully configured. Actually, a dhcp relay enables dhcp clients and dhcp servers on different networks to communicate with each other by forwarding the dhcp br...
Page 409
Dhcp relay configuration 395 3 if the packet contains option 82, the dhcp relay processes the packet depending on the configured policy (that is, discards the packet, replaces the original option 82 in the packet with its own, or leaves the original option 82 unchanged in the packet), and forwards t...
Page 410
396 c hapter 46: dhcp r elay c onfiguration you can configure an interface to forward dhcp packets received from dhcp clients to a group of external dhcp server(s), so that the dhcp server(s) in this group can assign ip addresses to the dhcp clients under this interface. You can configure up to eigh...
Page 411
Option 82 supporting configuration 397 configuring the dynamic user address entry updating function when a dhcp client obtains an ip address from a dhcp server with the help of a dhcp relay, the dhcp relay creates an entry (dynamic entry) in the user address table to track the binding information ab...
Page 412
398 c hapter 46: dhcp r elay c onfiguration option 82 supporting configuration example network requirements two dhcp clients are on the network segment 10.110.0.0 (255.255.0.0). They obtain ip addresses from a dhcp server through a switch acting as dhcp relay. Option 82 supporting is enabled on the ...
Page 413
Dhcp relay displaying 399 dhcp relay displaying you can verify your dhcp relay-related configuration by executing the following display commands in any view. Dhcp relay configuration example network requirements the dhcp clients on the network segment 10.110.0.0 (255.255.255.0) are connected to a po...
Page 414
400 c hapter 46: dhcp r elay c onfiguration you need to perform corresponding configurations on the dhcp server to enable the dhcp clients to obtain ip addresses from the dhcp server. The dhcp server configurations differ depending on different dhcp server devices and are thus omitted. Troubleshooti...
Page 415: Tatic
47 s tatic r oute c onfiguration introduction to static route attributes and functions of static route a static route is a special route. You can set up an interconnecting network with the static route configuration. The problem for such configuration is when a fault occurs to the network, the stati...
Page 416
402 c hapter 47: s tatic r oute c onfiguration static route configuration static route configuration includes: ■ configuring a static route ■ configuring a default route ■ deleting all the static routes configuring a static route perform the following configurations in system view. The parameters ar...
Page 417
Displaying and debugging static route 403 configuring a default route perform the following configurations in system view. The meanings of parameters in the command are the same as those of the static route. Deleting all the static routes you can use the undo ip route-static command to delete one st...
Page 418
404 c hapter 47: s tatic r oute c onfiguration networking diagram figure 126 networking diagram of the static route configuration example configuration procedure 1 configure the static route for ethernet switch a [ switch a] ip route-static 1.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.2.2 [ switch a] ip route-static 1...
Page 419: Udp H
48 udp h elper c onfiguration overview of udp helper the major function of udp helper is to relay-forward udp broadcast packets, that is, it can convert udp broadcast packets into unicast packets and send to the designated server, as a relay. When udp helper starts, the switch can judge if to forwar...
Page 421
Overview of udp helper 407 udp helper configuration example networking requirement the ip address of vlan interface 2 on the switch is 10.110.1.1, which is connected with network segment 10.110.0.0. Set to relay-forward the broadcast packets with destination ip of all 1s and destination udp port 55 ...
Page 422
408 c hapter 48: udp h elper c onfiguration.