- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- 4200G 12-Port
- Configuration Manual
3Com 4200G 12-Port Configuration Manual
Summary of 4200G 12-Port
Page 1
3com switch 4200g family configuration guide switch 4200g 12-port switch 4200g 24-port switch 4200g 48-port switch 4200g pwr 24-port product version: v3.02.00 manual version: 6pw100-20081201 www.3com.Com 3com corporation 350 campus drive, marlborough, ma, usa 01752 3064.
Page 2
Copyright © 2006-2008, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written permission from 3com corporation. 3com corporation reserv...
Page 3: About This Manual
About this manual organization 3com switch 4200g family configuration guide is organized as follows: part contents 1 login introduces the ways to log into an ethernet switch and cli related configuration. 2 configuration file management introduces configuration file and the related configuration. 3 ...
Page 4
Part contents 28 file system management introduces basic configuration for file system management. 29 ftp-sftp-tftp introduces basic configuration for ftp, sftp and tftp, and the applications. 30 information center introduces information center configuration. 31 system maintenance and debugging intr...
Page 5
Gui conventions convention description button names are inside angle brackets. For example, click . [ ] window names, menu items, data table and field names are inside square brackets. For example, pop up the [new user] window. / multi-level menus are separated by forward slashes. For example, [file...
Page 6: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 logging in to an ethernet switch ············································································································1-1 logging in to an ethernet switch ····································································································...
Page 7
Ii switch configuration························································································································4-2 modem connection establishment ·········································································································4-2 5 cli configu...
Page 8
1-1 1 logging in to an ethernet switch go to these sections for information you are interested in: z logging in to an ethernet switch z introduction to the user interface logging in to an ethernet switch to manage or configure a switch 4200g, you can log in to it in one of the following three method...
Page 9
1-2 table 1-1 description on user interface user interface applicable user port used remarks aux users logging in through the console port console port each switch can accommodate one aux user. Vty telnet users and ssh users ethernet port each switch can accommodate up to five vty users. One user in...
Page 11: Introduction
2-1 2 logging in through the console port go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z setting up a login environment for login through the console port z console port login configuration z console port login configuration with authentication mode being none z console...
Page 12
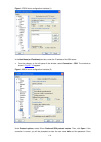
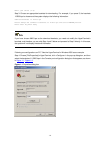
2-2 2) if you use a pc to connect to the console port, launch a terminal emulation utility (such as terminal in windows 3.X or hyperterminal in windows 9x/windows 2000/windows xp. The following assumes that you are running windows xp) and perform the configuration shown in figure 2-2 through figure ...
Page 13
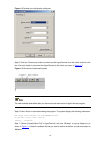
2-3 figure 2-4 set port parameters 3) turn on the switch. You will be prompted to press the enter key if the switch successfully completes post (power-on self test). The prompt appears after you press the enter key. 4) you can then configure the switch or check the information about the switch by ex...
Page 14
2-4 configuration remarks set the maximum number of lines the screen can contain optional by default, the screen can contain up to 24 lines. Set history command buffer size optional by default, the history command buffer can contain up to 10 commands. Set the timeout time of a user interface optiona...
Page 15: Modes
2-5 to do… use the command… remarks set the maximum number of lines the screen can contain screen-length screen-length optional by default, the screen can contain up to 24 lines. You can use the screen-length 0 command to disable the function to display information in pages. Set the history command ...
Page 16: None
2-6 changes made to the authentication mode for console port login takes effect after you quit the command-line interface and then log in again. Console port login configuration with authentication mode being none configuration procedure follow these steps to configure console port login with the au...
Page 17: Password
2-7 network diagram figure 2-5 network diagram for aux user interface configuration (with the authentication mode being none) configuration pc running telnet ethernet ge1/0/1 configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # enter aux user interface view. [sysname] user-interface aux 0 # sp...
Page 18
2-8 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter aux user interface view user-interface aux 0 — configure to authenticate users using the local password authentication-mode password required by default, users logging in to a switch through the console port are not authentica...
Page 19: Scheme
2-9 system-view # enter aux user interface view. [sysname] user-interface aux 0 # specify to authenticate users logging in through the console port using the local password. [sysname-ui-aux0] authentication-mode password # set the local password to 123456 (in plain text). [sysname-ui-aux0] set authe...
Page 21
2-11 z set the authentication password of the local user to 123456 (in plain text). Z set the service type of the local user to terminal and the command level to 2. Z configure to authenticate the users in the scheme mode. Z the baud rate of the console port is 19,200 bps. Z the screen can contain u...
Page 22
2-12 # set the maximum number of commands the history command buffer can store to 20. [sysname-ui-aux0] history-command max-size 20 # set the timeout time of the aux user interface to 6 minutes. [sysname-ui-aux0] idle-timeout 6 after the above configuration, you need to modify the configuration of t...
Page 23: Logging In Through Telnet
3-1 3 logging in through telnet go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z telnet configuration with authentication mode being none z telnet configuration with authentication mode being password introduction switch 4200g supports telnet. You can manage and maintain ...
Page 24
3-2 configuration description configure the protocols the user interface supports optional by default, telnet and ssh protocol are supported. Set the commands to be executed automatically after a user log in to the user interface successfully optional by default, no command is executed automatically...
Page 25
3-3 to do… use the command… remarks set the history command buffer size history-command max-size value optional the default history command buffer size is 10, that is, the history command buffer of a user can store up to 10 commands by default. Set the timeout time of the vty user interface idle-tim...
Page 26
3-4 to improve security and prevent attacks to the unused sockets, tcp 23 and tcp 22, ports for telnet and ssh services respectively, will be enabled or disabled after corresponding configurations. Z if the authentication mode is none, tcp 23 will be enabled, and tcp 22 will be disabled. Z if the au...
Page 27
3-5 network diagram figure 3-1 network diagram for telnet configuration (with the authentication mode being none) configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # enter vty 0 user interface view. [sysname] user-interface vty 0 # configure not to authenticate telnet users logging in to vty ...
Page 28
3-6 when the authentication mode is password, the command level available to users logging in to the user interface is determined by the user privilege level command. Configuration example network requirements assume current user logins through the console port and the current user level is set to t...
Page 29
3-7 telnet configuration with authentication mode being scheme configuration procedure follow these steps to configure telnet with the authentication mode being scheme: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter one or more vty user interface views user-interface vty first...
Page 30
3-8 refer to the aaa part of this manual for information about aaa, radius, and hwtacacs. Configuration example network requirements assume current user logins through the console port and the user level is set to the administrator level (level 3). Perform the following configurations for users logg...
Page 31: Telnetting to A Switch
3-9 # set the maximum number of lines the screen can contain to 30. [sysname-ui-vty0] screen-length 30 # set the maximum number of commands the history command buffer can store to 20. [sysname-ui-vty0] history-command max-size 20 # set the timeout time to 6 minutes. [sysname-ui-vty0] idle-timeout 6 ...
Page 32
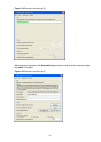
3-10 figure 3-5 network diagram for telnet connection establishment configuration pc running telnet ethernet workstation server workstation ethernet port ethernet switch 4) launch telnet on your pc, with the ip address of vlan-interface 1 of the switch as the parameter, as shown in figure 3-6 . Figu...
Page 33
3-11 telnetting to another switch from the current switch you can telnet to another switch from the current switch. In this case, the current switch operates as the client, and the other operates as the server. If the interconnected ethernet ports of the two switches are in the same lan segment, mak...
Page 34: Logging In Using A Modem
4-1 4 logging in using a modem go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z configuration on the switch side z modem connection establishment introduction the administrator can log in to the console port of a remote switch using a modem through public switched telepho...
Page 35
4-2 you can verify your configuration by executing the at&v command. The configuration commands and the output of different modems may differ. Refer to the user manual of the modem when performing the above configuration. Switch configuration after logging in to a switch through its console port by ...
Page 36
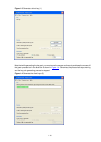
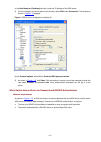
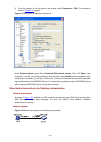
4-3 figure 4-1 establish the connection by using modems console port pstn telephone line modem serial cable telephone number of the romote end: 82882285 modem modem 4) launch a terminal emulation utility on the pc and set the telephone number to call the modem directly connected to the switch, as sh...
Page 37
4-4 figure 4-3 set the telephone number figure 4-4 call the modem 5) if the password authentication mode is specified, enter the password when prompted. If the password is correct, the prompt (such as ) appears. You can then configure or manage the switch. You can also enter the character ? At anyti...
Page 38: Cli Configuration
5-1 5 cli configuration when configuring cli, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to the cli z command hierarchy z cli views z cli features introduction to the cli a command line interface (cli) is a user interface to interact with a switch. Through the cli on ...
Page 39
5-2 z monitor level (level 1): commands at this level are mainly used to maintain the system and diagnose service faults, and they cannot be saved in configuration file. Such commands include debugging and terminal. Z system level (level 2): commands at this level are mainly used to configure servic...
Page 40
5-3 to do… use the command… remarks configure the level of a command in a specific view command-privilege level level view view command required z you are recommended to use the default command level or modify the command level under the guidance of professional staff; otherwise, the change of comma...
Page 41
5-4 can switch to a higher level temporarily; when the administrators need to leave for a while or ask someone else to manage the device temporarily, they can switch to a lower privilege level before they leave to restrict the operation by others. The high-to-low user level switching is unlimited. H...
Page 42
5-5 when both the super password authentication and the hwtacacs authentication are specified, the device adopts the preferred authentication mode first. If the preferred authentication mode cannot be implemented (for example, the super password is not configured or the hwtacacs authentication serve...
Page 43
5-6 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter isp domain view domain domain-name — set the hwtacacs authentication scheme for user level switching authenticationsuper hwtacacs-scheme hwtacacs-scheme-name required by default, the hwtacacs authentication scheme for user lev...
Page 44: Cli Views
5-7 # set the password used by the current user to switch to level 3. [sysname] super password level 3 simple 123 z a vty 0 user switches its level to level 3 after logging in. # a vty 0 user telnets to the switch, and then uses the set password to switch to user level 3. Super 3 password: user priv...
Page 45
5-8 table 5-1 lists the cli views provided by the 3com switch 4200g, operations that can be performed in different cli views and the commands used to enter specific cli views. Table 5-1 cli views view available operation prompt example enter method quit method user view display operation status and ...
Page 46
5-9 view available operation prompt example enter method quit method user interface view configure user interface parameters [sysname-ui-aux 0] execute the user-interface command in system view. Ftp client view configure ftp client parameters [ftp] execute the ftp command in user view. Sftp client v...
Page 47: Cli Features
5-10 view available operation prompt example enter method quit method remote-ping test group view configure remote-ping test group parameters [sysname-remot e-ping-a123-a12 3] execute the remote-ping command in system view. Hwtacacs view configure hwtacacs parameters [sysname-hwtac acs-a123] execute...
Page 48
5-11 2) enter a command, a space, and a question mark (?). If the question mark “?” is at a keyword position in the command, all available keywords at the position and their descriptions will be displayed on your terminal. Clock ? Datetime specify the time and date summer-time configure summer time ...
Page 49
5-12 operation function press get to the next line. Command history the cli provides the command history function. You can use the display history-command command to view a specific number of latest executed commands and execute them again in a convenient way. By default, the cli can store up to 10 ...
Page 50
5-13 error message remarks wrong parameter a parameter entered is wrong. Found at '^' position an error is found at the '^' position. Command edit the cli provides basic command edit functions and supports multi-line editing. The maximum number of characters a command can contain is 254. Table 5-4 l...
Page 51: Management Interface
6-1 6 logging in through the web-based network management interface go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z establishing an http connection z configuring the login banner z enabling/disabling the web server introduction switch 4200g has a web server built in. It ...
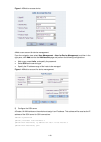
Page 52: Configuring The Login Banner
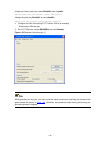
6-2 3) establish an http connection between your pc and the switch, as shown in figure 6-1 . Figure 6-1 establish an http connection between your pc and the switch 4) log in to the switch through ie. Launch ie on the web-based network management terminal (your pc) and enter the ip address of the man...
Page 53
6-3 configuration example network requirements z a user logs in to the switch through web. Z the banner page is desired when a user logs into the switch. Network diagram figure 6-3 network diagram for login banner configuration configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # configure the...
Page 54
6-4 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the web server ip http shutdown required by default, the web server is enabled. Disable the web server undo ip http shutdown required to improve security and prevent attack to the unused sockets, tcp 80 port (which is for htt...
Page 55: Logging In Through Nms
7-1 7 logging in through nms go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z connection establishment using nms introduction you can also log in to a switch through a network management station (nms), and then configure and manage the switch through the agent software on...
Page 56: Packets
8-1 8 configuring source ip address for telnet service packets go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z configuring source ip address for telnet service packets z displaying source ip address configuration overview you can configure source ip address or source interfa...
Page 57
8-2 operation command description specify a source interface for telnet server telnet-server source-interface interface-type interface-number optional specify source ip address for telnet client telnet source-ip ip-address optional specify a source interface for telnet client telnet source-interface...
Page 58: User Control
9-1 9 user control go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction z controlling telnet users z controlling network management users by source ip addresses z controlling web users by source ip address refer to the acl part for information about acl. Introduction you can co...
Page 59
9-2 z if no acl is configured on the vty user interface, users are not controlled when establishing a telnet connection using this user interface. Z if an acl is configured on the vty user interface, there will be two possibilities: if the packets for establishing a telnet connection match the acl r...
Page 61
9-4 z defining an acl z applying the acl to control users accessing the switch through snmp to control whether an nms can manage the switch, you can use this function. Prerequisites the controlling policy against network management users is determined, including the source ip addresses to be control...
Page 62
9-5 network diagram figure 9-2 network diagram for controlling snmp users using acls switch 10.110.100.46 host a ip network host b 10.110.100.52 configuration procedure # define a basic acl. System-view [sysname] acl number 2000 [sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule 1 permit source 10.110.100.52 0 [sysname-...
Page 64
9-7 [sysname-acl-basic-2030] quit # apply acl 2030 to only permit the web users sourced from the ip address of 10.110.100.52 to access the switch. [sysname] ip http acl 2030
Page 65: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 configuration file management···············································································································1-1 introduction to configuration file ···································································································...
Page 66
1-1 1 configuration file management when configuring configuration file management, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to configuration file z configuration task list introduction to configuration file a configuration file records and stores user configuration...
Page 67: Configuration Task List
1-2 z when saving the current configuration, you can specify the file to be a main or backup or normal configuration file. Z when removing a configuration file from a switch, you can specify to remove the main or backup configuration file. Or, if it is a file having both main and backup attribute, y...
Page 68
1-3 when you use the save safely command to save the configuration file, if the switch reboots or the power fails during the saving process, the switch initializes itself in the following two conditions when it starts up next time: z if a configuration file with the extension .Cfg exists in the flas...
Page 70
1-5 the configuration file must use .Cfg as its extension name and the startup configuration file must be saved at the root directory of the switch. Displaying switch configuration to do… use the command… remarks display the initial configuration file saved in the flash of a switch display saved-con...
Page 71: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 vlan overview ··········································································································································1-1 vlan overview·············································································································...
Page 72: Vlan Overview
1-1 1 vlan overview this chapter covers these topics: z vlan overview z port-based vlan vlan overview introduction to vlan the traditional ethernet is a broadcast network, where all hosts are in the same broadcast domain and connected with each other through hubs or switches. Hubs and switches, whic...
Page 73
1-2 figure 1-1 a vlan implementation advantages of vlans compared with traditional ethernet technology, vlan technology delivers the following benefits: z confining broadcast traffic within individual vlans. This saves bandwidth and improves network performance. Z improving lan security. By assignin...
Page 74
1-3 figure 1-3 format of vlan tag a vlan tag comprises four fields: tag protocol identifier (tpid), priority, canonical format indicator (cfi), and vlan id. Z the 16-bit tpid field with a value of 0x8100 indicates that the frame is vlan tagged. On the switch 4200g series ethernet switches, the defau...
Page 75: Port-Based Vlan
1-4 z independent vlan learning (ivl), where the switch maintains an independent mac address forwarding table for each vlan. The source mac address of a packet received in a vlan on a port is recorded to the mac address forwarding table of this vlan only, and packets received in a vlan are forwarded...
Page 76
1-5 z an access port can belong to only one vlan. Usually, ports directly connected to pcs are configured as access ports. Z a trunk port can carry multiple vlans to receive and send traffic for them. Except traffic of the default vlan, traffic passes through a trunk port will be vlan tagged. Usuall...
Page 77
1-6 table 1-1 packet processing of an access port processing of an incoming packet for an untagged packet for a tagged packet processing of an outgoing packet receive the packet and tag the packet with the default vlan tag. Z if the vlan id is just the default vlan id, receive the packet. Z if the v...
Page 78: Vlan Configuration
2-1 2 vlan configuration when configuring a vlan, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z vlan configuration z configuring a port-based vlan vlan configuration vlan configuration task list complete the following tasks to configure vlan: task remarks basic vlan configuration req...
Page 79
2-2 z vlan 1 is the system default vlan, which needs not to be created and cannot be removed, either. Z the vlan you created in the way described above is a static vlan. On the switch, there are dynamic vlans which are registered through gvrp. For details, refer to “gvrp” part of this manual. Z when...
Page 80
2-3 to do... Use the command... Remarks disable the vlan interface shutdown enable the vlan interface undo shutdown optional by default, the vlan interface is enabled. In this case, the vlan interface’s status is determined by the status of the ports in the vlan, that is, if all ports of the vlan ar...
Page 82
2-5 to do… use the command… remarks assign the specified access port or ports to the current vlan port interface-list required by default, all ports belong to vlan 1. Configuring the default vlan for a port because an access port can belong to its default vlan only, there is no need for you to confi...
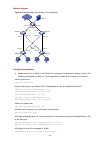
Page 83
2-6 z the devices within each vlan can communicate with each other but that in different vlans cannot communicate with each other directly. Network diagram figure 2-1 network diagram for vlan configuration configuration procedure z configure switch a. # create vlan 101, specify its descriptive strin...
Page 84
2-7 # configure gigabitethernet1/0/3 of switch a. [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port link-type trunk [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 101 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/3] port trunk permit vlan 201 # configure gigabitethernet1/0/10 of swi...
Page 85: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 static routing configuration····················································································································1-1 introduction ·····················································································································...
Page 86: Static Routing Configuration
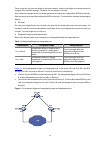
1-1 1 static routing configuration introduction routing table routing table routing tables play a key role in routing. Each router maintains a routing table, and each entry in the table specifies which physical interface a packet destined for a certain destination should go out to reach the next hop...
Page 87
1-2 figure 1-1 a sample routing table switch a switch b switch h switch e 16.0.0.2 17.0.0.3 15.0.0.0 12.0.0.0 17.0.0.0 11.0.0.0 16.0.0.0 13.0.0.0 14.0.0.0 switch c switch d switch f switch g 11.0.0.1 12.0.0.1 12.0.0.2 15.0.0.1 15.0.0.2 17.0.0.1 16.0.0.1 13.0.0.1 13.0.0.2 14.0.0.1 14.0.0.2 14.0.0.3 1...
Page 88: Configuring A Static Route
1-3 z if there is no default route and the destination address of the packet fails to match any entry in the routing table, the packet will be discarded and an icmp packet will be sent to the source to report that the destination or the network is unreachable. The network administrator can configure...
Page 90
1-5 the default gateways for the three hosts a, b and c are 1.1.2.3, 1.1.6.1 and 1.1.3.1 respectively. The configuration procedure is omitted. 4) display the configuration. # display the ip routing table of switch a. [switcha] display ip routing-table routing table: public net destination/mask proto...
Page 91: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 voice vlan configuration························································································································1-1 voice vlan overview···············································································································...
Page 92: Voice Vlan Configuration
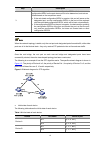
1-1 1 voice vlan configuration when configuring voice vlan, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z voice vlan overview z voice vlan configuration z displaying and maintaining voice vlan z voice vlan configuration example voice vlan overview voice vlans are vlans configured spe...
Page 93
1-2 figure 1-1 network diagram for ip phones as shown in figure 1-1 , the ip phone needs to work in conjunction with the dhcp server and the ncp to establish a path for voice data transmission. An ip phone goes through the following three phases to become capable of transmitting voice data. 2) after...
Page 94
1-3 z an untagged packet carries no vlan tag. Z a tagged packet carries the tag of a vlan. To set an ip address and a voice vlan for an ip phone manually, just make sure that the voice vlan id to be set is consistent with that of the switch and the ncp is reachable to the ip address to be set. How s...
Page 95
1-4 for more information about cos and dscp precedence values, refer to the qos part of the manual. Configuring voice vlan assignment mode of a port a port can work in automatic voice vlan assignment mode or manual voice vlan assignment mode. You can configure the voice vlan assignment mode for a po...
Page 96
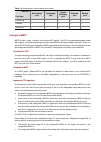
1-5 table 1-2 matching relationship between port types and voice devices capable of acquiring ip address and voice vlan automatically voice vlan assignment mode voice traffic type port type supported or not access not supported trunk supported make sure the default vlan of the port exists and is not...
Page 97
1-6 table 1-3 matching relationship between port types and voice devices acquiring voice vlan through manual configuration voice vlan assignment mode port type supported or not access not supported trunk supported make sure the default vlan of the port exists and is not a voice vlan, and the access ...
Page 98: Voice Vlan Configuration
1-7 the following table presents how a packet is handled when the voice vlan is operating in security mode and normal mode. Table 1-4 how a packet is handled when the voice vlan is operating in different modes voice vlan mode packet type processing method untagged packet packet carrying the voice vl...
Page 99
1-8 to do… use the command… remarks set the voice vlan aging timer voice vlan aging minutes optional the default aging timer is 1440 minutes. Enable the voice vlan function globally voice vlan vlan-id enable required enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number required enable ...
Page 100
1-9 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — set an oui address that can be identified by the voice vlan voice vlan mac-address oui mask oui-mask [ description text] optional without this address, the default oui address is used. Enable the voice vlan security mode voice vlan ...
Page 101
1-10 z the voice vlan function can be enabled for only one vlan at one time. Z if the link aggregation control protocol (lacp) is enabled on a port, voice vlan feature cannot be enabled on it. Z voice vlan function can be enabled only for the static vlan. A dynamic vlan cannot be configured as a voi...
Page 102
1-11 voice vlan configuration example voice vlan configuration example (automatic mode) network requirements as shown in figure 1-2 , z the mac address of ip phone a is 0011-1100-0001. The phone connects to a downstream device named pc a whose mac address is 0022-1100-0002 and to gigabitethernet 1/0...
Page 103
1-12 # configure the allowed oui addresses as mac addresses prefixed by 0011-1100-0000 or 0011-2200-0000. In this way, device a identifies packets whose mac addresses match any of the configured oui addresses as voice packets. [devicea] voice vlan mac-address 0011-1100-0001 mask ffff-ff00-0000 descr...
Page 104
1-13 voice vlan configuration example (manual mode) network requirements create a voice vlan and configure it to operate in manual mode. Add the port to which an ip phone is connected to the voice vlan to enable voice traffic to be transmitted within the voice vlan. Z create vlan 2 and configure it ...
Page 105
1-14 # enable the voice vlan function on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. [devicea-gigabitethernet1/0/1] voice vlan enable verification # display the oui addresses, the corresponding oui address masks and the corresponding description strings that the system supports. Display voice vlan oui oui address mask d...
Page 106: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 gvrp configuration ··································································································································1-1 introduction to gvrp ········································································································...
Page 107: Gvrp Configuration
1-1 1 gvrp configuration when configuring gvrp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to gvrp z gvrp configuration z displaying and maintaining gvrp z gvrp configuration example introduction to gvrp garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) is an implementation of g...
Page 108
1-2 2) garp timers timers determine the intervals of sending different types of garp messages. Garp defines four timers to control the period of sending garp messages. Z hold: when a garp entity receives a piece of registration information, it does not send out a join message immediately. Instead, t...
Page 109
1-3 figure 1-1 format of garp packets the following table describes the fields of a garp packet. Table 1-1 description of garp packet fields field description value protocol id protocol id 1 message each message consists of two parts: attribute type and attribute list. — attribute type defined by th...
Page 110: Gvrp Configuration
1-4 gvrp as an implementation of garp, garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) maintains dynamic vlan registration information and propagates the information to the other switches through garp. With gvrp enabled on a device, the vlan registration information received by the device from other devices ...
Page 111
1-5 to do ... Use the command ... Remarks enter system view system-view — enable gvrp globally gvrp required by default, gvrp is disabled globally. Enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — enable gvrp on the port gvrp required by default, gvrp is disabled on the port. S z...
Page 112
1-6 table 1-2 relations between the timers timer lower threshold upper threshold hold 10 centiseconds this upper threshold is less than or equal to one-half of the timeout time of the join timer. You can change the threshold by changing the timeout time of the join timer. Join this lower threshold i...
Page 113: Gvrp Configuration Example
1-7 displaying and maintaining gvrp to do … use the command … remarks display garp statistics display garp statistics [ interface interface-list ] display the settings of the garp timers display garp timer [ interface interface-list ] display gvrp statistics display gvrp statistics [interface interf...
Page 114
1-8 [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all # enable gvrp on gigabitethernet1/0/1. [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] gvrp [switcha-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # configure gigabitethernet1/0/2 to be a trunk port and to permit the packets of all the vlans. [switcha] interface gigabitethe...
Page 115
1-9 5, 7, 8, # display the vlan information dynamically registered on switch b. [switchb] display vlan dynamic total 3 dynamic vlan exist(s). The following dynamic vlans exist: 5, 7, 8, # display the vlan information dynamically registered on switch e. [switche] display vlan dynamic total 1 dynamic ...
Page 116
1-10 5, 8, # display the vlan information dynamically registered on switch e. [switche] display vlan dynamic no dynamic vlans exist!.
Page 117: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 port basic configuration ··························································································································1-1 ethernet port configuration ···································································································...
Page 118: Port Basic Configuration
1-1 1 port basic configuration ethernet port configuration combo port configuration a combo port can operate as either an optical port or an electrical port. Inside the device there is only one forwarding interface. For a combo port, the electrical port and the corresponding optical port are tx-sfp ...
Page 120
1-3 z only ports on the front panel of the device support the auto-negotiation speed configuration feature. And ports on the extended interface card do not support this feature currently. Z after you configure auto-negotiation speed(s) for a port, if you execute the undo speed command or the speed a...
Page 121
1-4 to do... Use the command... Remarks enable flow control on the ethernet port flow-control by default, flow control is not enabled on the port. Duplicating the configuration of a port to other ports to make other ports have the same configuration as that of a specific port, you can duplicate the ...
Page 122
1-5 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enable loopback detection globally loopback-detection enable required by default, loopback detection is disabled globally. Set the interval for performing port loopback detection loopback-detection interval-time time optional th...
Page 124
1-7 configuring the interval to perform statistical analysis on port traffic by performing the following configuration, you can set the interval to perform statistical analysis on the traffic of a port. When you use the display interface interface-type interface-number command to display the informa...
Page 125
1-8 configuration examples # in the default conditions, where up/down log output is enabled, execute the shutdown command or the undo shutdown command on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. The up/down log information for gigabitethernet 1/0/1 is generated and displayed on the terminal. System-view system view: ...
Page 127: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 link aggregation configuration ··············································································································1-1 overview ····························································································································...
Page 128: Overview
1-1 1 link aggregation configuration when configuring link aggregation, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z link aggregation classification z aggregation group categories z link aggregation configuration z displaying and maintaining link aggregation configuration...
Page 129
1-2 table 1-1 consistency considerations for ports in an aggregation category considerations stp state of port-level stp (enabled or disabled) attribute of the link (point-to-point or otherwise) connected to the port port path cost stp priority stp packet format loop protection root protection port ...
Page 130
1-3 z there is a limit on the number of selected ports in an aggregation group. Therefore, if the number of the selected ports in an aggregation group exceeds the maximum number supported by the device, those with lower port numbers operate as the selected ports, and others as unselected ports. Amon...
Page 131: Aggregation Group Categories
1-4 are connected to the same peer device and have the same speed, duplex mode, and basic configurations, and their peer ports have the same configurations. Besides multiple-port aggregation groups, the system is also able to create single-port aggregation groups, each of which contains only one por...
Page 132
1-5 in general, the system only provides limited load-sharing aggregation resources, so the system needs to reasonably allocate the resources among different aggregation groups. The system always allocates hardware aggregation resources to the aggregation groups with higher priorities. When load-sha...
Page 133
1-6 link aggregation configuration z the commands of link aggregation cannot be configured with the commands of port loopback detection feature at the same time. Z the ports where the mac-address max-mac-count command is configured cannot be added to an aggregation group. Contrarily, the mac-address...
Page 134
1-7 z if the aggregation group you are creating already exists and contains ports, the possible type changes may be: changing from dynamic or static to manual, and changing from dynamic to static; and no other kinds of type change can occur. Z when you change a dynamic/static group to a manual group...
Page 135
1-8 configuring a dynamic lacp aggregation group a dynamic lacp aggregation group is automatically created by the system based on lacp-enabled ports. The adding and removing of ports to/from a dynamic aggregation group are automatically accomplished by lacp. You need to enable lacp on the ports whic...
Page 136
1-9 if you have saved the current configuration with the save command, after system reboot, the configuration concerning manual and static aggregation groups and their descriptions still exists, but that of dynamic aggregation groups and their descriptions gets lost. Displaying and maintaining link ...
Page 137
1-10 configuration procedure the following only lists the configuration on switch a; you must perform the similar configuration on switch b to implement link aggregation. 1) adopting manual aggregation mode # create manual aggregation group 1. System-view [sysname] link-aggregation group 1 mode manu...
Page 138
1-11 [sysname] interface gigabitethernet1/0/3 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/3] lacp enable the three lacp-enabled ports can be aggregated into one dynamic aggregation group to implement load sharing only when they have the same basic configuration (such as rate, duplex mode, and so on)..
Page 139: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 port isolation configuration ·····················································································································1-1 port isolation overview ········································································································...
Page 140: Port Isolation Configuration
1-1 1 port isolation configuration when configuring port isolation, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z port isolation overview z port isolation configuration z displaying and maintaining port isolation configuration z port isolation configuration example port isolation ove...
Page 141
1-2 z when a member port of an aggregation group joins/leaves an isolation group, the other ports in the same aggregation group will join/leave the isolation group at the same time. Z for ports that belong to an aggregation group and an isolation group simultaneously, removing a port from the aggreg...
Page 142
1-3 configuration procedure # add gigabitethernet1/0/2, gigabitethernet1/0/3, and gigabitethernet1/0/4 to the isolation group. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [sysname] interface gigabitethernet1/0/2 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port isolate [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/2]...
Page 143: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 port security configuration······················································································································1-1 port security overview···········································································································...
Page 144: Port Security Configuration
1-1 1 port security configuration when configuring port security, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z port security overview z port security configuration task list z displaying and maintaining port security configuration z port security configuration example port security ...
Page 145
1-2 table 1-1 description of port security modes security mode description feature norestriction in this mode, access to the port is not restricted. In this mode, neither the ntk nor the intrusion protection feature is triggered. Autolearn in this mode, the port automatically learns mac addresses an...
Page 146
1-3 security mode description feature userlogin in this mode, port-based 802.1x authentication is performed for access users. In this mode, neither ntk nor intrusion protection will be triggered. Userloginsecure mac-based 802.1x authentication is performed on the access user. The port is enabled onl...
Page 147
1-4 security mode description feature macaddresselseus erloginsecure in this mode, a port performs mac authentication of an access user first. If the authentication succeeds, the user is authenticated. Otherwise, the port performs 802.1x authentication of the user. In this mode, there can be only on...
Page 148
1-5 task remarks ignoring the authorization information from the radius server optional configuring security mac addresses optional enabling port security configuration prerequisites before enabling port security, you need to disable 802.1x and mac authentication globally. Enabling port security fol...
Page 149
1-6 this configuration is different from that of the maximum number of mac addresses that can be leaned by a port in mac address management. Follow these steps to set the maximum number of mac addresses allowed on a port: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethe...
Page 150
1-7 z before setting the port security mode to autolearn, you need to set the maximum number of mac addresses allowed on the port with the port-security max-mac-count command. Z when the port operates in the autolearn mode, you cannot change the maximum number of mac addresses allowed on the port. Z...
Page 151
1-8 configuring intrusion protection follow these steps to configure the intrusion protection feature: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — set the corresponding action to be taken by the switch when ...
Page 152
1-9 follow these steps to configure a port to ignore the authorization information from the radius server: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — ignore the authorization information from the radius ser...
Page 153
1-10 to do... Use the command... Remarks in system view mac-address security mac-address interface interface-type interface-number vlan vlan-id interface interface-type interface-number add a security mac address in ethernet port view mac-address security mac-address vlan vlan-id either is required....
Page 154
1-11 [switch] port-security enable # enter gigabitethernet1/0/1 port view. [switch] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 # set the maximum number of mac addresses allowed on the port to 80. [switch-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port-security max-mac-count 80 # set the port security mode to autolearn. [switch-gig...
Page 155: Port Binding Configuration
2-1 2 port binding configuration when configuring port binding, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z port binding overview z displaying and maintaining port binding configuration z port binding configuration example port binding overview introduction port binding enables the...
Page 156
2-2 port binding configuration example port binding configuration example network requirements it is required to bind the mac and ip addresses of host a to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 on switch a, so as to prevent malicious users from using the ip address they steal from host a to access the network. Netw...
Page 157: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 mac address table management············································································································1-1 overview ·································································································································...
Page 158: Mac Address Table Management
1-1 1 mac address table management this chapter describes the management of static, dynamic, and blackhole mac address entries. For information about the management of multicast mac address entries, refer to the part related to multicast protocol. Overview introduction to mac address table an ethern...
Page 159
1-2 figure 1-1 mac address learning diagram (1) figure 1-2 mac address table entry of the switch (1) 2) after learning the mac address of user a, the switch starts to forward the packet. Because there is no mac address and port information of user b in the existing mac address table, the switch forw...
Page 160
1-3 figure 1-4 mac address learning diagram (3) 4) at this time, the mac address table of the switch includes two forwarding entries shown in figure 1-5 . When forwarding the response packet, the switch unicasts the packet instead of broadcasting it to user a through gigabitethernet 1/0/1, because m...
Page 161
1-4 aging timer only takes effect on dynamic mac address entries. Entries in a mac address table entries in a mac address table fall into the following categories according to their characteristics and configuration methods: z static mac address entry: also known as permanent mac address entry. This...
Page 162
1-5 configuring a mac address entry you can add, modify, or remove a mac address entry, remove all mac address entries concerning a specific port, or remove specific type of mac address entries (dynamic or static mac address entries). You can add a mac address entry in either system view or ethernet...
Page 163
1-6 setting the aging time of mac address entries setting aging time properly helps effective utilization of mac address aging. The aging time that is too long or too short affects the performance of the switch. Z if the aging time is too long, excessive invalid mac address entries maintained by the...
Page 164: Configuration Example
1-7 operation command description set the maximum number of mac addresses the port can learn mac-address max-mac-count count required by default, the number of the mac addresses a port can learn is not limited. Displaying mac address table information to verify your configuration, you can display in...
Page 165
1-8 --- 4 mac address(es) found on port gigabitethernet1/0/2 ---.
Page 166: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 mstp configuration ··································································································································1-1 stp overview ················································································································...
Page 167
Ii configuring loop guard ················································································································1-37 configuring tc-bpdu attack guard ·····························································································1-37 configuring digest snoopin...
Page 168: Mstp Configuration
1-1 1 mstp configuration go to these sections for information you are interested in: z mstp overview z configuring root bridge z configuring leaf nodes z performing mcheck operation z configuring guard functions z configuring digest snooping z configuring rapid transition z stp maintenance configura...
Page 169
1-2 there is one and only one root bridge in the entire network, and the root bridge can change alone with changes of the network topology. Therefore, the root bridge is not fixed. Upon network convergence, the root bridge generates and sends out configuration bpdus periodically. Other devices just ...
Page 170
1-3 all the ports on the root bridge are designated ports. 4) path cost path cost is a value used for measuring link capacity. By comparing the path costs of different links, stp selects the most robust links and blocks the other links to prune the network into a tree. How stp works stp identifies t...
Page 171
1-4 table 1-2 selection of the optimum configuration bpdu step description 1 upon receiving a configuration bpdu on a port, the device performs the following processing: z if the received configuration bpdu has a lower priority than that of the configuration bpdu generated by the port, the device wi...
Page 172
1-5 step description 3 the device compares the calculated configuration bpdu with the configuration bpdu on the port whose role is to be determined, and acts as follows based on the comparison result: z if the calculated configuration bpdu is superior, this port will serve as the designated port, an...
Page 173
1-6 device port name bpdu of port cp1 {2, 0, 2, cp1} device c cp2 {2, 0, 2, cp2} z comparison process and result on each device the following table shows the comparison process and result on each device. Table 1-5 comparison process and result on each device device comparison process bpdu of port af...
Page 174
1-7 device comparison process bpdu of port after comparison by comparison: z the configuration bpdus of cp1 is elected as the optimum configuration bpdu, so cp1 is identified as the root port, the configuration bpdus of which will not be changed. Z device c compares the calculated designated port co...
Page 175
1-8 to facilitate description, the spanning tree calculation process in this example is simplified, while the actual process is more complicated. 2) the bpdu forwarding mechanism in stp z upon network initiation, every switch regards itself as the root bridge, generates configuration bpdus with itse...
Page 176: Mstp Overview
1-9 mstp overview background of mstp disadvantages of stp and rstp stp does not support rapid state transition of ports. A newly elected root port or designated port must wait twice the forward delay time before transiting to the forwarding state, even if it is a port on a point-to-point link or it ...
Page 177
1-10 basic mstp terminologies figure 1-4 illustrates basic mstp terms (assuming that mstp is enabled on each switch in this figure). Figure 1-4 basic mstp terminologies cst bpdu region a0: vlan 1 mapped to msti 1 vlan 2 mapped to msti 2 other vlans mapped to cist bpdu bpdu a d c b region b0: vlan 1 ...
Page 178
1-11 region a0 contains these mappings: vlan 1 to msti 1; vlan 2 to msti 2, and other vlans to cist. In an mst region, load balancing is implemented according to the vlan-to-msti mapping table. Ist an internal spanning tree (ist) is a spanning tree in an mst region. Ists together with the common spa...
Page 179
1-12 switch blocks one of the two ports to eliminate the loop that occurs. The blocked port is the backup port. In figure 1-5 , switch a, switch b, switch c, and switch d form an mst region. Port 1 and port 2 on switch a connect upstream to the common root. Port 5 and port 6 on switch c form a loop....
Page 180
1-13 table 1-6 combinations of port states and port roles port role port state root/master port designated port region boundary port alternate port backup port forwarding √ √ √ — — learning √ √ √ — — discarding √ √ √ √ √ principle of mstp mstp divides a layer 2 network into multiple mst regions. The...
Page 181
1-14 z for configuration bpdus with both the same root bridge id and the same external path costs, master bridge id, internal path cost, designated bridge id,id of sending port,id of receiving port are compared in turn. For mstp, msti configuration information is generally expressed as follows: (ins...
Page 182: Configuring Root Bridge
1-15 stp-related standards stp-related standards include the following. Z ieee 802.1d: spanning tree protocol z ieee 802.1w: rapid spanning tree protocol z ieee 802.1s: multiple spanning tree protocol configuring root bridge complete the following tasks to configure the root bridge: task remarks ena...
Page 183
1-16 in a network containing switches with both gvrp and mstp enabled, gvrp messages travel along the cist. If you want to advertise a vlan through gvrp, be sure to map the vlan to the cist (msti 0) when configuring the vlan-to-msti mapping table. Configuration prerequisites the role (root, branch, ...
Page 184
1-17 configuration, mstp does not recalculate spanning trees immediately after the configuration; it does this only after you perform one of the following operations, and then the configuration can really takes effect: z activate the new mst region-related settings by using the active region-configu...
Page 185
1-18 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — specify the current switch as the root bridge of a spanning tree stp [ instance instance-id ] root primary [ bridge-diameter bridgenumber [ hello-time centi-seconds ] ] required specify the current switch as the secondary root ...
Page 186
1-19 configuration example # configure the current switch as the root bridge of msti 1 and a secondary root bridge of msti 2. System-view [sysname] stp instance 1 root primary [sysname] stp instance 2 root secondary configuring the bridge priority of the current switch root bridges are selected acco...
Page 187
1-20 z the port automatically determines the format (legacy or dot1s) of received mstp packets and then determines the format of the packets to be sent accordingly, thus communicating with the peer devices. Z if the format of the received packets changes repeatedly, mstp will shut down the correspon...
Page 188
1-21 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp compliance configuring the mstp operation mode to make an mstp-enabled switch compatible with stp/rstp, mstp provides the following three operation modes: z stp-compatible mode, where the ports of a switch send stp bpdus to neighboring devices. If stp-ena...
Page 189
1-22 configuration procedure follow these steps to configure the maximum hop count for an mst region: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — configure the maximum hop count of the mst region stp max-hops hops required by default, the maximum hop count of an mst region is...
Page 190
1-23 configuring the mstp time-related parameters three mstp time-related parameters exist: forward delay, hello time, and max age. You can configure the three parameters to control the process of spanning tree calculation. Configuration procedure follow these steps to configure mstp time-related pa...
Page 191
1-24 you are recommended to specify the network diameter of the switched network and the hello time by using the stp root primary or stp root secondary command. After that, the three proper time-related parameters are determined automatically. Configuration example # configure the forward delay para...
Page 192
1-25 configure the maximum transmitting rate for specified ports in system view follow these steps to configure the maximum transmitting rate for specified ports in system view: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — configure the maximum transmitting rate for specified ...
Page 193
1-26 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — configure the specified ports as edge ports stp interface interface-list edged-port enable required by default, all the ethernet ports of a switch are non-edge ports. Configure a port as an edge port in ethernet port view follo...
Page 194
1-27 you can determine whether or not the link connected to a port is a point-to-point link in one of the following two ways. Specify whether the link connected to a port is point-to-point link in system view follow these steps to specify whether the link connected to a port is point-to-point link i...
Page 195: Configuring Leaf Nodes
1-28 enabling mstp configuration procedure follow these steps to enable mstp in system view: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enable mstp stp enable required mstp is enabled by default. Disable mstp on specified ports stp interface interface-list disable optional b...
Page 196
1-29 task remarks enabling mstp required to prevent network topology jitter caused by other related configurations, you are recommended to enable mstp after performing other configurations. Configuring an mst region required configuring how a port recognizes and sends mstp packets optional configuri...
Page 197
1-30 configuring the path cost for a port the path cost parameter reflects the rate of the link connected to the port. For a port on an mstp-enabled switch, the path cost may be different in different mstis. You can enable flows of different vlans to travel along different physical links by configur...
Page 198
1-31 when calculating the path cost of an aggregated link, the 802.1d-1998 standard does not take the number of the ports on the aggregated link into account, whereas the 802.1t standard does. The following formula is used to calculate the path cost of an aggregated link: path cost = 200,000,000 / l...
Page 199
1-32 [sysname] stp pathcost-standard dot1d-1998 2) perform this configuration in ethernet port view system-view [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] undo stp instance 1 cost [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit [sysname] stp pathcost-standard dot1d-1998 configuring...
Page 200: Performing McHeck Operation
1-33 [sysname] stp interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 instance 1 port priority 16 2) perform this configuration in ethernet port view system-view [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] stp instance 1 port priority 16 specifying whether the link connected to a port is a...
Page 201: Configuring Guard Functions
1-34 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — perform the mcheck operation stp mcheck required configuration example # perform the mcheck operation on gigabitethernet 1/0/1. 1) perform this configuration ...
Page 202
1-35 loop guard a switch maintains the states of the root port and other blocked ports by receiving and processing bpdus from the upstream switch. These bpdus may get lost because of network congestions or unidirectional link failures. If a switch does not receive bpdus from the upstream switch for ...
Page 203
1-36 configuration prerequisites mstp runs normally on the switch. Configuring bpdu guard configuration procedure follow these steps to configure bpdu guard: to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enable the bpdu guard function stp bpdu-protection required the bpdu guard...
Page 204
1-37 [sysname] stp interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 root-protection 2) perform this configuration in ethernet port view system-view [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] stp root-protection configuring loop guard configuration procedure follow these steps to configu...
Page 205: Configuring Digest Snooping
1-38 system-view [sysname] stp tc-protection enable # set the maximum times for the switch to remove the mac address table and arp entries within 10 seconds to 5. System-view [sysname] stp tc-protection threshold 5 configuring digest snooping introduction according to ieee 802.1s, two interconnected...
Page 206: Configuring Rapid Transition
1-39 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — enable the digest snooping feature stp config-digest-snooping required the digest snooping feature is disabled on a port by default. Return to system view qui...
Page 207
1-40 z proposal packets: packets sent by designated ports to request rapid transition z agreement packets: packets used to acknowledge rapid transition requests both rstp and mstp specify that the upstream switch can perform rapid transition operation on the designated port only when the port receiv...
Page 208
1-41 some other manufacturers' switches adopt proprietary spanning tree protocols that are similar to rstp in the way to implement rapid transition on designated ports. When a switch of this kind operating as the upstream switch connects with a 3com switch running mstp, the upstream designated port ...
Page 209
1-42 to do... Use the command... Remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — enable the rapid transition feature stp no-agreement-check required by default, the rapid transition feature is disabled on a port. Z the rapid transition fea...
Page 210: Mstp Configuration Example
1-43 enabling trap messages conforming to 802.1d standard a switch sends trap messages conforming to 802.1d standard to the network management device in the following two cases: z the switch becomes the root bridge of an instance. Z network topology changes are detected. Configuration procedure foll...
Page 211
1-44 z all switches in the network belong to the same mst region. Z packets of vlan 10, vlan 30, vlan 40, and vlan 20 are forwarded along msti 1, msti 3, msti 4, and msti 0 respectively. In this network, switch a and switch b operate on the convergence layer; switch c and switch d operate on the acc...
Page 212
1-45 [sysname] stp region-configuration # configure the region name, vlan-to-msti mapping table, and revision level for the mst region. [sysname-mst-region] region-name example [sysname-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [sysname-mst-region] instance 3 vlan 30 [sysname-mst-region] instance 4 vlan 40 [sy...
Page 213: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 802.1x configuration ·································································································································1-1 introduction to 802.1x······································································································...
Page 214
Ii displaying and maintaining system-guard·····························································································4-1.
Page 215: 802.1X Configuration
1-1 1 802.1x configuration when configuring 802.1x, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to 802.1x z introduction to 802.1x configuration z basic 802.1x configuration z advanced 802.1x configuration z displaying and maintaining 802.1x configuration z configurati...
Page 216
1-2 figure 1-1 architecture of 802.1x authentication z the supplicant system is the entity seeking access to the lan. It resides at one end of a lan segment and is authenticated by the authenticator system at the other end of the lan segment. The supplicant system is usually a user terminal device. ...
Page 217
1-3 z the controlled port can be used to pass service packets when it is in authorized state. It is blocked when not in authorized state. In this case, no packets can pass through it. Z controlled port and uncontrolled port are two properties of a port. Packets reaching a port are visible to both th...
Page 218
1-4 figure 1-3 the format of an eapol packet in an eapol packet: z the pae ethernet type field holds the protocol identifier. The identifier for 802.1x is 0x888e. Z the protocol version field holds the version of the protocol supported by the sender of the eapol packet. Z the type field can be one o...
Page 219
1-5 z the length field indicates the size of an eap packet, which includes the code, identifier, length, and data fields. Z the data field carries the eap packet, whose format differs with the code field. A success or failure packet does not contain the data field, so the length field of it is 4. Fi...
Page 220
1-6 eap relay mode this mode is defined in 802.1x. In this mode, eap packets are encapsulated in higher level protocol (such as eapor) packets to enable them to successfully reach the authentication server. Normally, this mode requires that the radius server support the two newly-added fields: the e...
Page 221
1-7 figure 1-8 802.1x authentication procedure (in eap relay mode) supplicant system pae raduis server eapol eapor eapol-start eap- request / identity eap- response / identity eap- request / md5 challenge eap-success eap- response / md5 challenge radius access - request (eap- response / identity) ra...
Page 222
1-8 feedbacks (through a radius access-accept packet and an eap-success packet) to the switch to indicate that the supplicant system is authenticated. Z the switch changes the state of the corresponding port to accepted state to allow the supplicant system to access the network. Z the supplicant sys...
Page 223
1-9 figure 1-9 802.1x authentication procedure (in eap terminating mode) supplicant system pae authenticator system pae radius server eapol radius eapol- start eap- request /identity eap- response/identity eap- request/ md5 challenge eap- success eap- response/md5 challenge radius access-request ( c...
Page 224
1-10 z re-authentication timer (reauth-period). The switch initiates 802.1x re-authentication at the interval set by the re-authentication timer. Z radius server timer (server-timeout). This timer sets the server-timeout period. After sending an authentication request packet to the radius server, th...
Page 225
1-11 z only disconnects the supplicant system but sends no trap packets. Z sends trap packets without disconnecting the supplicant system. This function needs the cooperation of 802.1x client and a cams server. Z the 802.1x client needs to be capable of detecting multiple network adapters, proxies, ...
Page 226
1-12 z after the maximum number retries have been made and there are still ports that have not sent any response back, the switch will then add these ports to the guest vlan. Z users belonging to the guest vlan can access the resources of the guest vlan without being authenticated. But they need to ...
Page 227
1-13 z the radius server has the switch perform 802.1x re-authentication of users. The radius server sends the switch an access-accept packet with the termination-action attribute field of 1. Upon receiving the packet, the switch re-authenticates the user periodically. Z you enable 802.1x re-authent...
Page 228: Basic 802.1X Configuration
1-14 basic 802.1x configuration configuration prerequisites z configure isp domain and the aaa scheme to be adopted. You can specify a radius scheme or a local scheme. Z ensure that the service type is configured as lan-access (by using the service-type command) if local authentication scheme is ado...
Page 229
1-15 to do… use the command… remarks enable online user handshaking dot1x handshake enable optional by default, online user handshaking is enabled. Enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — z 802.1x configurations take effect only after you enable 802.1x both globally and ...
Page 232
1-18 as for the dot1x version-user command, if you execute it in system view without specifying the interface-list argument, the command applies to all ports. You can also execute this command in port view. In this case, this command applies to the current port only and the interface-list argument i...
Page 233
1-19 z the guest vlan function is available only when the switch operates in the port-based access control mode. Z only one guest vlan can be configured for each switch. Z the guest vlan function cannot be implemented if you configure the dot1x dhcp-launch command on the switch to enable dhcp-trigge...
Page 234: Configuration Example
1-20 during re-authentication, the switch always uses the latest re-authentication interval configured, no matter which of the above-mentioned two ways is used to determine the re-authentication interval. For example, if you configure a re-authentication interval on the switch and the switch receive...
Page 235
1-21 a real-time accounting packet to the radius servers once in every 15 minutes. A user name is sent to the radius servers with the domain name truncated. Z the user name and password for local 802.1x authentication are “localuser” and “localpass” (in plain text) respectively. The idle disconnecti...
Page 236
1-22 [sysname-radius-radius1] secondary authentication 10.11.1.2 [sysname-radius-radius1] secondary accounting 10.11.1.1 # set the password for the switch and the authentication radius servers to exchange messages. [sysname-radius-radius1] key authentication name # set the password for the switch an...
Page 237
2-1 2 quick ead deployment configuration when configuring quick ead deployment, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to quick ead deployment z configuring quick ead deployment z displaying and maintaining quick ead deployment z quick ead deployment configuration...
Page 238
2-2 configuring quick ead deployment configuration prerequisites z enable 802.1x on the switch. Z set the port authorization mode to auto for 802.1x-enabled ports using the dot1x port-control command. Configuration procedure configuring a free ip range a free ip range is an ip range that users can a...
Page 239
2-3 large number of users log in but cannot pass authentication, the switch may run out of acl resources, preventing other users from logging in. A timer called acl timer is designed to solve this problem. You can control the usage of acl resources by setting the acl timer. The acl timer starts once...
Page 240
2-4 network diagram figure 2-1 network diagram for quick ead deployment host switch web server ip network 192.168.0.110/24 192.168.0.111/24 192.168.0.109/24 ge1/0/1 configuration procedure before enabling quick ead deployment, make sure sure that: z the web server is configured properly. Z the defau...
Page 241: Troubleshooting
2-5 troubleshooting symptom: a user cannot be redirected to the specified url server, no matter what url the user enters in the ie address bar. Solution: z if a user enters an ip address in a format other than the dotted decimal notation, the user may not be redirected. This is related with the oper...
Page 242: Habp Configuration
3-1 3 habp configuration when configuring habp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to habp z habp server configuration z habp client configuration z displaying and maintaining habp configuration introduction to habp when a switch is configured with the 802.1x ...
Page 243: Habp Client Configuration
3-2 to do... Use the command... Remarks configure the current switch to be an habp server habp server vlan vlan-id required by default, a switch operates as an habp client after you enable habp on the switch. If you want to use the switch as a management switch, you need to configure the switch to b...
Page 244: System Guard Configuration
4-1 4 system guard configuration system-guard overview at first, you must determine whether the cpu is under attack to implement system guard for the cpu. You should not determine whether the cpu is under attack just according to whether congestion occurs in a queue. Instead, you must do that in the...
Page 245
4-2 table 4-2 display and maintain system-guard operation command display the record of detected attacks display system-guard attack-record display the state of the system-guard feature display system-guard state.
Page 246: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 aaa overview ············································································································································1-1 introduction to aaa ·····································································································...
Page 247
Ii local authentication of ftp/telnet users·····················································································2-28 hwtacacs authentication and authorization of telnet users ···················································2-30 troubleshooting aaa ·································...
Page 248: Aaa Overview
1-1 1 aaa overview introduction to aaa aaa is the acronym for the three security functions: authentication, authorization and accounting. It provides a uniform framework for you to configure these three functions to implement network security management. Z authentication: defines what users can acce...
Page 249: Introduction to Aaa Services
1-2 z none accounting: no accounting is performed for users. Z remote accounting: user accounting is performed on a remote radius or tacacs server. Introduction to isp domain an internet service provider (isp) domain is a group of users who belong to the same isp. For a username in the format of use...
Page 250
1-3 figure 1-1 databases in a radius server in addition, a radius server can act as a client of some other aaa server to provide authentication or accounting proxy service. Basic message exchange procedure in radius the messages exchanged between a radius client (a switch, for example) and a radius ...
Page 251
1-4 5) the radius client accepts or denies the user depending on the received authentication result. If it accepts the user, the radius client sends a start-accounting request (accounting-request, with the status-type attribute value = start) to the radius server. 6) the radius server returns a star...
Page 252
1-5 code message type message description 4 accounting-request direction: client->server. The client transmits this message to the server to request the server to start or end the accounting (whether to start or to end the accounting is determined by the acct-status-type attribute in the message). T...
Page 253
1-6 type field value attribute type type field value attribute type 10 framed-routing 32 nas-identifier 11 filter-id 33 proxy-state 12 framed-mtu 34 login-lat-service 13 framed-compression 35 login-lat-node 14 login-ip-host 36 login-lat-group 15 login-service 37 framed-appletalk-link 16 login-tcp-po...
Page 254
1-7 compared with radius, hwtacacs provides more reliable transmission and encryption, and therefore is more suitable for security control. Table 1-3 lists the primary differences between hwtacacs and radius. Table 1-3 differences between hwtacacs and radius hwtacacs radius adopts tcp, providing mor...
Page 255
1-8 figure 1-6 aaa implementation procedure for a telnet user the basic message exchange procedure is as follows: 1) a user sends a login request to the switch acting as a tacacs client, which then sends an authentication start request to the tacacs server. 2) the tacacs server returns an authentica...
Page 256
1-9 9) after receiving the response indicating an authorization success, the tacacs client pushes the configuration interface of the switch to the user. 10) the tacacs client sends an accounting start request to the tacacs server. 11) the tacacs server returns an accounting response, indicating that...
Page 257: Aaa Configuration
2-1 2 aaa configuration aaa configuration task list you need to configure aaa to provide network access services for legal users while protecting network devices and preventing unauthorized access and repudiation behavior. Complete the following tasks to configure aaa (configuring a combined aaa sch...
Page 258
2-2 task remarks creating an isp domain and configuring its attributes required configuring separate aaa schemes required configuring an aaa scheme for an isp domain required with separate aaa schemes, you can specify authentication, authorization and accounting schemes respectively. You need to con...
Page 260
2-4 z you can execute the scheme radius-scheme radius-scheme-name command to adopt an already configured radius scheme to implement all the three aaa functions. If you adopt the local scheme, only the authentication and authorization functions are implemented, the accounting function cannot be imple...
Page 262
2-6 for authentication, it also does so for authorization and accounting, even if authorization and accounting fail. Configuring dynamic vlan assignment the dynamic vlan assignment feature enables a switch to dynamically add the switch ports of successfully authenticated users to different vlans acc...
Page 263
2-7 z in string mode, if the vlan id assigned by the radius server is a character string containing only digits (for example, 1024), the switch first regards it as an integer vlan id: the switch transforms the string to an integer value and judges if the value is in the valid vlan id range; if it is...
Page 265
2-9 z the following characters are not allowed in the user-name string: /:*?. And you cannot input more than one “@” in the string. Z after the local-user password-display-mode cipher-force command is executed, any password will be displayed in cipher mode even though you specify to display a user p...
Page 266
2-10 task remarks creating a radius scheme required configuring radius authentication/authorization servers required configuring radius accounting servers required configuring shared keys for radius messages optional configuring the maximum number of radius request transmission attempts optional con...
Page 267
2-11 creating a new radius scheme, you should configure the ip address and udp port number of each radius server you want to use in this scheme. These radius servers fall into two types: authentication/authorization, and accounting. And for each type of server, you can configure two servers in a rad...
Page 268
2-12 to do… use the command… remarks create a radius scheme and enter its view radius scheme radius-scheme-name required by default, a radius scheme named "system" has already been created in the system. Set the ip address and port number of the primary radius authentication/authorization server pri...
Page 269
2-13 to do… use the command… remarks set the ip address and port number of the secondary radius accounting server secondary accounting ip-address [ port-number ] optional by default, the ip address and udp port number of the secondary accounting server are 0.0.0.0 and 1813 for a newly created radius...
Page 270
2-14 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — create a radius scheme and enter its view radius scheme radius-scheme-name required by default, a radius scheme named "system" has already been created in the system. Set a shared key for radius authentication/authorization message...
Page 273
2-17 z generally, the access users are named in the userid@isp-name or userid.Isp-name format. Here, isp-name after the “@” or “.” character represents the isp domain name, by which the device determines which isp domain a user belongs to. However, some old radius servers cannot accept the usernames...
Page 274
2-18 z if you adopt the local radius server function, the udp port number of the authentication/authorization server must be 1645, the udp port number of the accounting server must be 1646, and the ip addresses of the servers must be set to the addresses of this switch. Z the message encryption key ...
Page 275
2-19 to do… use the command… remarks set the response timeout time of radius servers timer response-timeout seconds optional by default, the response timeout time of radius servers is three seconds. Set the time that the switch waits before it try to re-communicate with primary server and restore th...
Page 276
2-20 online when the user re-logs into the network before the cams performs online user detection, and the user cannot get authenticated. In this case, the user can access the network again only when the cams administrator manually removes the user's online information. The user re-authentication at...
Page 277
2-21 hwtacacs configuration task list complete the following tasks to configure hwtacacs: task remarks creating a hwtacacs scheme required configuring tacacs authentication servers required configuring tacacs authorization servers required configuring tacacs accounting servers optional configuring s...
Page 278
2-22 to do… use the command… remarks set the ip address and port number of the primary tacacs authentication server primary authentication ip-address [ port ] required by default, the ip address of the primary authentication server is 0.0.0.0, and the port number is 0. Set the ip address and port nu...
Page 279
2-23 z you are not allowed to configure the same ip address for both primary and secondary authorization servers. If you do this, the system will prompt that the configuration fails. Z you can remove a server only when it is not used by any active tcp connection for sending authorization messages. C...
Page 280
2-24 the tacacs client and server adopt md5 algorithm to encrypt hwtacacs messages before they are exchanged between the two parties. The two parties verify the validity of the hwtacacs messages received from each other by using the shared keys that have been set on them, and can accept and respond ...
Page 281
2-25 generally, the access users are named in the userid@isp-name or userid.Isp-name format. Where, isp-name after the “@” or “.” character represents the isp domain name. If the tacacs server does not accept the usernames that carry isp domain names, it is necessary to remove domain names from user...
Page 282
2-26 displaying and maintaining aaa configuration displaying and maintaining aaa configuration to do… use the command… remarks display configuration information about one specific or all isp domains display domain [ isp-name ] display information about user connections display connection [ access-ty...
Page 284
2-28 network diagram figure 2-1 remote radius authentication of telnet users internet telnet user radius server 10.110.91.164/16 configuration procedure # enter system view. System-view # adopt aaa authentication for telnet users. [sysname] user-interface vty 0 4 [sysname-ui-vty0-4] authentication-m...
Page 285
2-29 the configuration procedure for local authentication of ftp users is similar to that for telnet users. The following text only takes telnet users as example to describe the configuration procedure for local authentication. Network requirements in the network environment shown in figure 2-2 , yo...
Page 286
2-30 z enable the local radius server function, set the ip address and shared key for the network access server to 127.0.0.1 and aabbcc, respectively. Z configure local users. Hwtacacs authentication and authorization of telnet users network requirements you are required to configure the switch so t...
Page 287: Troubleshooting Aaa
2-31 troubleshooting aaa troubleshooting radius configuration the radius protocol operates at the application layer in the tcp/ip protocol suite. This protocol prescribes how the switch and the radius server of the isp exchange user information with each other. Symptom 1: user authentication/authori...
Page 288: Ead Configuration
3-1 3 ead configuration introduction to ead endpoint admission defense (ead) is an attack defense solution. Using this solution, you can enhance the active defense capability of network endpoints, prevents viruses and worms from spreading on the network, and protects the entire network by limiting t...
Page 289: Ead Configuration Example
3-2 z configuring the ip address of the security policy server. Z associating the isp domain with the radius scheme. Ead is commonly used in radius authentication environment. This section mainly describes the configuration of security policy server ip address. For other related configuration, refer...
Page 290
3-3 network diagram figure 3-2 ead configuration configuration procedure # configure 802.1x on the switch. Refer to “configuring 802.1x” in 802.1x and system guard configuration. # configure a domain. System-view [sysname] domain system [sysname-isp-system] quit # configure a radius scheme. [sysname...
Page 291: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 mac address authentication configuration ··························································································1-1 mac address authentication overview ··································································································1-1 perfo...
Page 292
1-1 1 mac address authentication configuration when configuring mac address authentication, go to these sections for information you are interested: z mac address authentication overview z related concepts z configuring basic mac address authentication functions z mac address authentication enhanced...
Page 293: Related Concepts
1-2 format configured with the mac-authentication authmode usernameasmacaddress usernameformat command; otherwise, the authentication will fail. Z in fixed mode, all users’ mac addresses are automatically mapped to the configured local passwords and usernames. Z the service type of a local user need...
Page 295
1-4 task remarks configuring a guest vlan optional configuring the maximum number of mac address authentication users allowed to access a port optional configuring a guest vlan different from guest vlans described in the 802.1x and system-guard manual, guest vlans mentioned in this section refer to ...
Page 296
1-5 after a port is added to a guest vlan, the switch will re-authenticate the first access user of this port (namely, the first user whose unicast mac address is learned by the switch) periodically. If this user passes the re-authentication, this port will exit the guest vlan, and thus the user can...
Page 297
1-6 z if more than one client are connected to a port, you cannot configure a guest vlan for this port. Z when a guest vlan is configured for a port, only one mac address authentication user can access the port. Even if you set the limit on the number of mac address authentication users to more than...
Page 298: Configuration
1-7 z if both the limit on the number of mac address authentication users and the limit on the number of users configured in the port security function are configured for a port, the smaller value of the two configured limits is adopted as the maximum number of mac address authentication users allow...
Page 299
1-8 # set the user name in mac address mode for mac address authentication, requiring hyphened lowercase mac addresses as the usernames and passwords. [sysname] mac-authentication authmode usernameasmacaddress usernameformat with-hyphen lowercase # add a local user. Z specify the user name and passw...
Page 300: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ip addressing configuration····················································································································1-1 ip addressing overview·············································································································...
Page 301: Ip Addressing Configuration
1-1 1 ip addressing configuration the term ip address used throughout this chapter refers to ipv4 address. For details about ipv6 address, refer to ipv6 management. When configuring ip addressing, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ip addressing overview z configuring ip a...
Page 302
1-2 table 1-1 ip address classes and ranges class address range remarks a 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 the ip address 0.0.0.0 is used by a host at bootstrap for temporary communication. This address is never a valid destination address. Addresses starting with 127 are reserved for loopback test. Packe...
Page 303: Configuring Ip Addresses
1-3 subnetting. When designing your network, you should note that subnetting is somewhat a tradeoff between subnets and accommodated hosts. For example, a class b network can accommodate 65,534 (2 16 – 2. Of the two deducted class b addresses, one with an all-ones host id is the broadcast address an...
Page 304
1-4 for saving ip address resources, the ip address of a loopback interface is automatically configured with a 32-bit mask. Displaying ip addressing configuration to do… use the command… remarks display information about a specified or all layer 3 interfaces display ip interface [ interface-type int...
Page 305: Ip Performance Overview
2-1 2 ip performance optimization configuration when optimizing ip performance, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ip performance overview z configuring ip performance optimization z displaying and maintaining ip performance optimization configuration ip performance overvi...
Page 306
2-2 z synwait timer: when sending a syn packet, tcp starts the synwait timer. If no response packet is received within the synwait timer interval, the tcp connection cannot be created. Z finwait timer: when a tcp connection is changed into fin_wait_2 state, the finwait timer is started. If no fin pa...
Page 307: Configuration
2-3 z if the destination of a packet is local while the transport layer protocol of the packet is not supported by the local device, the device sends a “protocol unreachable” icmp error packet to the source. Z when receiving a packet with the destination being local and transport layer protocol bein...
Page 309: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 arp configuration ····································································································································1-1 introduction to arp ········································································································...
Page 310: Arp Configuration
1-1 1 arp configuration when configuring arp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to arp z configuring arp z configuring gratuitous arp z displaying and debugging arp z arp configuration examples introduction to arp arp function address resolution protocol (arp...
Page 311
1-2 figure 1-1 arp message format hardware type (16 bits) protocol type (16 bits) length of hardware address length of protocol address operator (16 bits) hardware address of the sender ip address of the sender hardware address of the receiver ip address of the receiver hardware type (16 bits) hardw...
Page 312
1-3 value description 5 chaos 6 ieee802.X 7 arc network arp table in an ethernet, the mac addresses of two hosts must be available for the two hosts to communicate with each other. Each host in an ethernet maintains an arp table, where the latest used ip address-to-mac address mapping entries are st...
Page 313: Configuring Arp
1-4 mode, all hosts on this subnet can receive the request, but only the requested host (namely, host b) will process the request. 3) host b compares its own ip address with the destination ip address in the arp request. If they are the same, host b saves the source ip address and source mac address...
Page 314: Configuring Gratuitous Arp
1-5 z static arp entries are valid as long as the ethernet switch operates normally. But some operations, such as removing a vlan, or removing a port from a vlan, will make the corresponding arp entries invalid and therefore removed automatically. Z as for the arp static command, the value of the vl...
Page 316: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 dhcp overview··········································································································································1-1 introduction to dhcp ······································································································...
Page 317: Dhcp Overview
1-1 1 dhcp overview when configuring dhcp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to dhcp z dhcp ip address assignment z dhcp packet format z protocol specification introduction to dhcp with networks getting larger in size and more complicated in structure, lack o...
Page 318
1-2 z manual assignment. The administrator configures static ip-to-mac bindings for some special clients, such as a www server. Then the dhcp server assigns these fixed ip addresses to the clients. Z automatic assignment. The dhcp server assigns ip addresses to dhcp clients. The ip addresses will be...
Page 319: Dhcp Packet Format
1-3 updating ip address lease after a dhcp server dynamically assigns an ip address to a dhcp client, the ip address keeps valid only within a specified lease time and will be reclaimed by the dhcp server when the lease expires. If the dhcp client wants to use the ip address for a longer time, it mu...
Page 320: Protocol Specification
1-4 z siaddr: ip address of the dhcp server. Z giaddr: ip address of the first dhcp relay agent that the dhcp client passes after it sent the request packet. Z chaddr: hardware address of the dhcp client. Z sname: name of the dhcp server. Z file: path and name of the boot configuration file that the...
Page 321
2-1 2 dhcp relay agent configuration when configuring the dhcp relay agent, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to dhcp relay agent z configuring the dhcp relay agent z displaying and maintaining dhcp relay agent configurationdhcp relay agent configuration exam...
Page 322
2-2 figure 2-1 typical dhcp relay agent application in the process of dynamic ip address assignment through the dhcp relay agent, the dhcp client and dhcp server interoperate with each other in a similar way as they do without the dhcp relay agent. The following sections only describe the forwarding...
Page 323
2-3 figure 2-2 padding contents for sub-option 1 of option 82 figure 2-3 padding contents for sub-option 2 of option 82 mechanism of option 82 supported on dhcp relay agent the procedure for a dhcp client to obtain an ip address from a dhcp server through a dhcp relay agent is similar to that for th...
Page 324
2-4 task remarks correlating a dhcp server group with a relay agent interface required configuring dhcp relay agent security functions optional configuring the dhcp relay agent to support option 82 optional correlating a dhcp server group with a relay agent interface to enhance reliability, you can ...
Page 325
2-5 z you can configure up to eight dhcp server ip addresses in a dhcp server group. Z you can map multiple vlan interfaces to one dhcp server group. But one vlan interface can be mapped to only one dhcp server group. Z if you execute the dhcp-server groupno command repeatedly, the new configuration...
Page 326
2-6 z the address-check enable command is independent of other commands of the dhcp relay agent. That is, the invalid address check takes effect when this command is executed, regardless of whether other commands (such as the command to enable dhcp) are used. Z before executing the address-check ena...
Page 327
2-7 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable option 82 support on the dhcp relay agent dhcp relay information enable required disabled by default. Configure the strategy for the dhcp relay agent to process request packets containing option 82 dhcp relay information stra...
Page 328
2-8 network diagram figure 2-4 network diagram for dhcp relay agent switch b dhcp server switch a dhcp relay dhcp client dhcp client dhcp client dhcp client vlan-int2 10.1.1.2/24 vlan-int1 10.10.1.1/24 vlan-int2 10.1.1.1/24 configuration procedure # create dhcp server group 1 and configure an ip add...
Page 329
2-9 z check if an address pool that is on the same network segment with the dhcp clients is configured on the dhcp server. Z check if a reachable route is configured between the dhcp relay agent and the dhcp server. Z check the dhcp relay agent. Check if the correct dhcp server group is configured o...
Page 330: Introduction to Dhcp Client
3-1 3 dhcp/bootp client configuration when configuring the dhcp/bootp client, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to dhcp client z introduction to bootp client z configuring a dhcp/bootp client z displaying dhcp/bootp client configuration introduction to dhcp c...
Page 332
3-3 network diagram figure 3-1 a dhcp network wins server client switch a client dns server dhcp server vlan-int1 configuration procedure the following describes only the configuration on switch a serving as a dhcp client. # configure vlan-interface 1 to dynamically obtain an ip address by using dhc...
Page 333: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 dns configuration·····································································································································1-1 dns overview················································································································...
Page 334: Dns Configuration
1-1 1 dns configuration when configuring dns, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z dns overview z configuring domain name resolution z displaying and maintaining dns z dns configuration examples z troubleshooting dns this chapter covers only ipv4 dns configuration. For detai...
Page 335
1-2 2) the dns resolver looks up the local domain name cache for a match. If a match is found, it sends the corresponding ip address back. If not, it sends the query to the dns server. 3) the dns server looks up its dns database for a match. If no match is found, it sends a query to a higher-level d...
Page 336
1-3 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure a mapping between a host name and an ip address ip host hostname ip-address required no ip address is assigned to a host name by default. The ip address you assign to a host name last time will overwrite the previous one i...
Page 338
1-5 dynamic domain name resolution configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 1-3 , the switch serving as a dns client uses dynamic domain name resolution to access the host at 3.1.1.1/16 through its domain name host. The dns server has the ip address 2.1.1.2/16. The dns suffix is...
Page 339: Troubleshooting Dns
1-6 reply from 3.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=1 ttl=125 time=4 ms reply from 3.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=2 ttl=125 time=4 ms reply from 3.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=3 ttl=125 time=4 ms reply from 3.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=4 ttl=125 time=4 ms reply from 3.1.1.1: bytes=56 sequence=5 ttl=125 time=5 ms --- ho...
Page 340: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 acl configuration·····································································································································1-1 acl overview ···············································································································...
Page 341: Acl Configuration
1-1 1 acl configuration acl overview as the network scale and network traffic are increasingly growing, security control and bandwidth assignment play a more and more important role in network management. Filtering data packets can prevent a network from being accessed by unauthorized users efficien...
Page 342
1-2 depth-first match order for rules of an advanced acl 1) protocol range: a rule which has specified the types of the protocols carried by ip is prior to others. 2) range of source ip address: the smaller the source ip address range (that is, the more the number of zeros in the wildcard mask), the...
Page 343: Acl Configuration
1-3 z when an acl is directly applied to hardware for packet filtering, the switch will permit packets if the packets do not match the acl. Z when an acl is referenced by upper-layer software to control telnet, snmp and web login users, the switch will deny packets if the packets do not match the ac...
Page 344
1-4 z if only a periodic time section is defined in a time range, the time range is active only when the system time is within the defined periodic time section. If multiple periodic time sections are defined in a time range, the time range is active only when the system time is within one of the pe...
Page 346
1-6 advanced acls support analysis and processing of three packet priority levels: type of service (tos) priority, ip priority and differentiated services codepoint (dscp) priority. Using advanced acls, you can define classification rules that are more accurate, more abundant, and more flexible than...
Page 347
1-7 [sysname] acl number 3000 [sysname-acl-adv-3000] rule permit tcp source 129.9.0.0 0.0.255.255 destination 202.38.160.0 0.0.0.255 destination-port eq 80 # display the configuration information of acl 3000. [sysname-acl-adv-3000] display acl 3000 advanced acl 3000, 1 rule acl's step is 1 rule 0 pe...
Page 348: Acl Assignment
1-8 z the content of a modified or created rule cannot be identical with the content of any existing rules; otherwise the rule modification or creation will fail, and the system prompts that the rule already exists. Configuration example # configure acl 4000 to deny packets sourced from the mac addr...
Page 349
1-9 assigning an acl globally configuration prerequisites before applying acl rules to a vlan, you need to define the related acls. For information about defining an acl, refer to section configuring basic acl , section configuring advanced acl , section configuring layer 2 acl . Configure procedure...
Page 350
1-10 configuration example # apply acl 2000 to vlan 10 to filter the inbound packets of vlan 10 on all the ports. System-view [sysname] packet-filter vlan 10 inbound ip-group 2000 assigning an acl to a port group configuration prerequisites before applying acl rules to a vlan, you need to define the...
Page 351: Displaying Acl Configuration
1-11 configuration procedure table 1-8 apply an acl to a port operation command description enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — apply an acl to the port packet-filter inbound acl-rule required for description on the acl-rule argument, ...
Page 352
1-12 example for upper-layer software referencing acls example for controlling telnet login users by source ip network requirements apply an acl to permit users with the source ip address of 10.110.100.52 to telnet to the switch. Network diagram figure 1-1 network diagram for controlling telnet logi...
Page 353
1-13 configuration procedure # define acl 2001. System-view [sysname] acl number 2001 [sysname-acl-basic-2001] rule 1 permit source 10.110.100.46 0 [sysname-acl-basic-2001] quit # reference acl 2001 to control users logging in to the web server. [sysname] ip http acl 2001 example for applying acls t...
Page 354
1-14 advanced acl configuration example network requirements different departments of an enterprise are interconnected through a switch. The ip address of the wage query server is 192.168.1.2. The r&d department is connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of the switch. Apply an acl to deny requests from ...
Page 355
1-15 network diagram figure 1-5 network diagram for layer 2 acl configuration procedure # define a periodic time range that is active from 8:00 to 18:00 everyday. System-view [sysname] time-range test 8:00 to 18:00 daily # define acl 4000 to filter packets with the source mac address of 0011-0011-00...
Page 356
1-16 network diagram figure 1-6 network diagram for applying an acl to a vlan ge1/0/1 pc 1 pc 3 database server pc 2 vlan 10 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 192.168.1.2 configuration procedure # define a periodic time range that is active from 8:00 to 18:00 in working days. System-view [sysname] time-range test 8:0...
Page 357: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 qos configuration·····································································································································1-1 overview ···················································································································...
Page 358: Qos Configuration
1-1 1 qos configuration when configuring qos, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z overview z qos features supported by the switch 4200g series z introduction to qos features z qos configuration z qos configuration examples overview introduction to qos quality of service (qo...
Page 359
1-2 and jitter. As for mission-critical applications, such as transactions and telnet, they may not require high bandwidth but do require low delay and preferential service during congestion. The emerging applications demand higher service performance of ip networks. Better network services during p...
Page 360: Introduction to Qos Features
1-3 table 1-1 qos features supported by the switch 4200g series qos feature description reference traffic classification classify incoming traffic based on acls. The switch 4200g series support the following types of acls: z basic acls z advanced acls z layer 2 acls z for information about acls, ref...
Page 361
1-4 priority trust mode introduction to precedence types 1) ip precedence, tos precedence, and dscp figure 1-2 ds field and tos byte as shown in figure 1-2 , the tos field of the ip header contains eight bits: the first three bits (0 to 2) represent ip precedence from 0 to 7 and the subsequent four ...
Page 362
1-5 z best effort (be) class: this class is a special cs class that does not provide any assurance. Af traffic exceeding the limit is degraded to the be class. Currently, all ip network traffic belongs to this class by default. Table 1-3 description on dscp values dscp value (decimal) dscp value (bi...
Page 363
1-6 the 4-byte 802.1q tag header consists of a two-byte tag protocol identifier (tpid) field, whose value is 0x8100, and a two-byte tag control information (tci) field. Figure 1-4 presents the format of the 802.1q tag header. Figure 1-4 802.1q tag header 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 priority vlan i...
Page 364
1-7 when a packet carrying no 802.1q tag reaches a port, the switch uses the port priority as the 802.1p precedence value of the received packet, searches for the set of precedence values corresponding to the port priority of the receiving port in the 802.1p-precedence-to-other-precedence mapping ta...
Page 365
1-8 table 1-6 the default cos-precedence-to-other-precedence mapping table of switch 4200g series 802.1p precedence value target local precedence value target drop precedence value 0 2 0 1 0 0 2 1 0 3 3 0 4 4 0 5 5 0 6 6 0 7 7 0 table 1-7 the default dscp -to-other-precedence mapping table of switch...
Page 366
1-9 token bucket a token bucket can be considered as a container holding a certain number of tokens. The system puts tokens into the bucket at a set rate. When the token bucket is full, the extra tokens will overflow. Figure 1-6 evaluate the traffic with the token bucket token bucket drop packet cla...
Page 367
1-10 traffic policing is widely used for policing traffic entering the network of internet service providers (isps). It can classify the policed traffic and perform pre-defined policing actions based on different evaluation results. These actions include: z dropping the nonconforming packets. Z forw...
Page 368
1-11 figure 1-8 diagram for sp queuing sp queuing is specially designed for mission-critical applications. The key feature of mission-critical applications is that they require preferential service to reduce the response delay when congestion occurs. Assume that there are eight output queues on the ...
Page 369
1-12 wrr queuing schedules all the queues in turn and ensure that all of them can be served for a certain time by assigning each queue a weight representing a certain amount of resources. Assume there are eight output queues on the port. Wrr assigns queues 7 through 0 the weights w7, w6, w5, w4, w3,...
Page 370: Qos Configuration
1-13 by enabling the burst function on your device, you can improve the processing performance of the device operating in the above scenarios and thus reduce packet loss rate. Because the burst function may affect the qos performance of your device, you must make sure that you are fully aware of the...
Page 371
1-14 follow these steps to configure a port to trust 802.1p precedence: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — configure to trust 802.1p precedence priority-trust cos required by default, port priority is t...
Page 372
1-15 configuration procedures 1) configuring the cos-precedence-to-other-precedence mapping table follow these steps to configure the cos-precedence-to-other-precedence mapping table: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure the cos-precedence-to-local-p recedence ma...
Page 373
1-16 [sysname] qos dscp-local-precedence-map 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 : 3 [sysname] qos dscp-local-precedence-map 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 : 4 [sysname] qos dscp-local-precedence-map 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 : 1 [sysname] qos dscp-local-precedence-map 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 : 7 [sysname] qos dscp-local-...
Page 374
1-17 36 : 7 37 : 7 38 : 7 39 : 7 40 : 0 41 : 0 42 : 0 43 : 0 44 : 0 45 : 0 46 : 0 47 : 0 48 : 5 49 : 5 50 : 5 51 : 5 52 : 5 53 : 5 54 : 5 55 : 5 56 : 6 57 : 6 58 : 6 59 : 6 60 : 6 61 : 6 62 : 6 63 : 6 setting the priority of protocol packets refer to protocol priority for information about priority ...
Page 375
1-18 configuration examples # set the ip precedence value of icmp packets to 3. System-view [sysname] protocol-priority protocol-type icmp ip-precedence 3 # after completing the above configuration, display the list of protocol priorities manually specified. [sysname] display protocol-priority proto...
Page 376
1-19 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter port group view port-group group-id — configure traffic policing traffic-limit inbound acl-rule target-rate required disabled by default. 4) configuring traffic policing for a port follow these steps to configure traffic poli...
Page 377
1-20 configuring traffic shaping refer to traffic policing and traffic shaping for information about traffic shaping. Configuration prerequisites z the queue for which traffic shaping is to be performed has been determined. Z the maximum traffic rate and the burst size have been determined. Z the po...
Page 378
1-21 to do… use the command… remarks configure sp queuing undo queue-scheduler [ queue-id ] & optional by default, sp queuing is used on all the output queues of a port. 2) configuring sdwrr queuing follow these steps to configure sdwrr queuing: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view syst...
Page 379
1-22 qid: scheduling-group weight ----------------------------------- 0 : wrr , group2 20 1 : wrr , group2 20 2 : wrr , group2 40 3 : wrr , group1 20 4 : wrr , group1 20 5 : wrr , group1 30 6 : sp 0 7 : sp 0 configuring traffic accounting refer to flow-based traffic accounting for information about ...
Page 380
1-23 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter port group view port-group group-id — collect statistics about acl matching packets traffic-statistic inbound acl-rule required by default, traffic accounting is disabled. Clear statistics about acl matching packets reset tra...
Page 381
1-24 system-view [sysname] acl number 2000 [sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule permit source 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [sysname-acl-basic-2000] quit [sysname] traffic-statistic vlan 2 inbound ip-group 2000 [sysname] reset traffic-statistic vlan 2 inbound ip-group 2000 enabling the burst function refer to burst f...
Page 383
1-26 figure 1-10 network diagram for traffic policing configuration configuration procedure 1) define an acl for traffic classification # create acl 2000 and enter basic acl view to match packets sourced from network segment 192.168.1.0/24. System-view [sysname] acl number 2000 [sysname-acl-basic-20...
Page 384: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 mirroring configuration································································································ 1-1 mirroring overview······································································································ 1-1 1.1.1 local port mirroring ··...
Page 385: Mirroring Configuration
1-1 1 mirroring configuration when configuring mirroring, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z mirroring overview z mirroring configuration z displaying port mirroring z mirroring configuration examples mirroring overview mirroring is to duplicate packets from a port to anot...
Page 386
1-2 remote port mirroring remote port mirroring does not require the source and destination ports to be on the same device. The source and destination ports can be located on multiple devices across the network. This allows an administrator to monitor traffic on remote devices conveniently. To imple...
Page 387: Mirroring Configuration
1-3 table 1-1 ports involved in the mirroring operation switch ports involved function source port port monitored. It copies packets to the reflector port through local port mirroring. There can be more than one source port. Reflector port receives packets from the source port and broadcasts the pac...
Page 388
1-4 task remarks configuring local port mirroring optional configuring remote port mirroring optional on a switch 4200g, only one destination port for local port mirroring or one reflector port for remote port mirroring can be configured, and the two kinds of ports cannot both exist. 1.1.2 configuri...
Page 389
1-5 when configuring local port mirroring, note that: z you need to configure the source and destination ports for the local port mirroring to take effect. Z the source port and the destination port cannot be a member port of an existing mirroring group; besides, the destination port cannot be a mem...
Page 391
1-7 to do… use the command… remarks return to system view quit — enter the view of the ethernet port connecting to the source switch, destination switch or other intermediate switch interface interface-type interface-number — configure the current port as trunk port port link-type trunk required by ...
Page 392: Displaying Port Mirroring
1-8 to do… use the command… remarks configure the destination port for the remote destination mirroring group mirroring-group group-id monitor-port monitor-port required configure the remote-probe vlan for the remote destination mirroring group mirroring-group group-id remote-probe vlan remote-probe...
Page 393
1-9 network diagram figure 1-3 network diagram for local port mirroring configuration procedure configure switch c: # create a local mirroring group. System-view [sysname] mirroring-group 1 local # configure the source ports and destination port for the local mirroring group. [sysname] mirroring-gro...
Page 394
1-10 z department 1 is connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of switch a. Z department 2 is connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/2 of switch a. Z gigabitethernet 1/0/3 of switch a connects to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of switch b. Z gigabitethernet 1/0/2 of switch b connects to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of switch ...
Page 395
1-11 [sysname] vlan 10 [sysname-vlan10] remote-probe vlan enable [sysname-vlan10] quit # configure the source ports, reflector port, and remote-probe vlan for the remote source mirroring group. [sysname] mirroring-group 1 mirroring-port gigabitethernet 1/0/1 gigabitethernet 1/0/2 inbound [sysname] m...
Page 396
1-12 system-view [sysname] mirroring-group 1 remote-destination # configure vlan 10 as the remote-probe vlan. [sysname] vlan 10 [sysname-vlan10] remote-probe vlan enable [sysname-vlan10] quit # configure the destination port and remote-probe vlan for the remote destination mirroring group. [sysname]...
Page 397: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 stack ···························································································································································1-1 stack function overview ·························································································...
Page 398: Stack
1-1 1 stack among switch 4200g series switches, switch 4200g 24-port, switch 4200g pwr 24-port, and switch 4200g 48-port switches support stacks formed by 10ge stack boards. Stack function overview a stack is a management domain formed by a group of ethernet switches interconnected through their sta...
Page 399: Main Switch Configuration
1-2 z connect the intended main switch and slave switches through stack modules and dedicated stack cables. (refer to 3com switch 4200g 10g interface module installation guide for the information about stack modules and stack cables.) z configure the ip address pool for the stack and enable the stac...
Page 400: Slave Switch Configuration
1-3 z to add a switch to a stack successfully, make sure the ip address pool contains at least one unoccupied ip address. Z make sure the ip addresses in the ip address pool of a stack are successive so that they can be assigned successively. For example, the ip addresses in an ip address pool with ...
Page 401: Stack Configuration Example
1-4 displaying and debugging a stack use the display command to display the information about a stack. The display command can be executed in any view. Table 1-4 display and maintain stack configurations operation command description display the stack status information on the main switch display st...
Page 402
1-5 network diagram figure 1-1 network diagram for stack configuration configuration procedure # configure the ip address pool for the stack on switch a. System-view [sysname] stacking ip-pool 129.10.1.15 3 # create the stack on switch a. [sysname] stacking enable [stack_0.Sysname] quit # display th...
Page 403
1-6 ip: 129.10.1.16/16 member number: 2 name:stack_2.Sysname device: 4200g 24-port mac address: 000f-e200-3135 member status:up ip: 129.10.1.17/16 # switch to switch b (a slave switch). Stacking 1 # display the information about the stack on switch b. Display stacking slave device for stack. Member ...
Page 404: Cluster
2-1 2 cluster cluster overview introduction to hgmp a cluster contains a group of switches. Through cluster management, you can manage multiple geographically dispersed in a centralized way. Cluster management is implemented through huawei group management protocol (hgmp). Hgmp version 2 (hgmpv2) is...
Page 405
2-2 you can configure and manage all the member devices through the management device without the need to log onto them one by one. Z it provides the topology discovery and display function, which assists in monitoring and maintaining the network. Z it allows you to configure and upgrade multiple sw...
Page 406
2-3 figure 2-2 state machine of cluster role z a candidate device becomes a management device when you create a cluster on it. Note that a cluster must have one (and only one) management device. On becoming a management device, the device collects network topology information and tries to discover a...
Page 407
2-4 z the management device adds the candidate devices to the cluster or removes member devices from the cluster according to the candidate device information collected through ntdp. Introduction to ndp ndp is a protocol used to discover adjacent devices and provide information about them. Ndp opera...
Page 408
2-5 device busy processing of the ntdp topology collection responses. To avoid such cases, the following methods can be used to control the ntdp topology collection request advertisement speed. Z configuring the devices not to forward the ntdp topology collection request immediately after they recei...
Page 409
2-6 to create a cluster, you need to determine the device to operate as the management device first. The management device discovers and determines candidate devices through ndp and ntdp, and adds them to the cluster. You can also add candidate devices to a cluster manually. After a candidate device...
Page 410
2-7 additionally, on the management device, you can configure the ftp server, tftp server, logging host and snmp host to be shared by the whole cluster. When a member device in the cluster communicates with an external server, the member device first transmits data to the management device, which th...
Page 411: Cluster Configuration Tasks
2-8 1) determine whether the destination mac address or destination ip address is used to trace a device in the cluster z if you use the tracemac command to trace the device by its mac address, the switch will query its mac address table according to the mac address and vlan id in the command to fin...
Page 412
2-9 configuration task remarks configuring the cluster synchronization function optional configuring the management device management device configuration tasks table 2-3 management device configuration tasks operation description enabling ndp globally and on specific ports required configuring ntdp...
Page 413
2-10 operation command description in system view ndp enable interface port-list enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number enable ndp on specified ethernet ports in ethernet port view enable ndp on the port ndp enable use either approach. By default, ndp is enabled on a port...
Page 414
2-11 operation command description configure the device forward delay of topology collection requests ntdp timer hop-delay time optional by default, the device forward delay is 200 ms. Configure the port forward delay of topology collection requests ntdp timer port-delay time optional by default, th...
Page 415
2-12 operation command description configure a multicast mac address for the cluster cluster-mac h-h-h required by default, the cluster multicast mac address is 0180-c200-000a. Set the interval for the management device to send multicast packets cluster-mac syn-interval time-interval optional by def...
Page 416
2-13 operation command description configure a shared ftp server for the cluster ftp-server ip-address optional by default, the management device acts as the shared ftp server. Configure a shared tftp server for the cluster tftp-server ip-address optional by default, no shared tftp server is configu...
Page 417
2-14 to reduce the risk of being attacked by malicious users against opened socket and enhance switch security, the switch 4200g series ethernet switches provide the following functions, so that a cluster socket is opened only when it is needed: z opening udp port 40000 (used for cluster) only when ...
Page 418
2-15 operation command description enable ntdp globally ntdp enable required enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — enable ntdp on the port ntdp enable required enabling the cluster function table 2-15 enable the cluster function operation command description enter syst...
Page 420
2-17 connected to the current cluster, this device cannot join the cluster and participate in the unified management and configuration of the cluster. Configure the enhanced cluster features table 2-18 the enhanced cluster feature configuration tasks operation description configure cluster topology ...
Page 421
2-18 operation command description display the information about all the devices in the base cluster topology display cluster base-members configure cluster device blacklist perform the following configuration on the management device. Table 2-20 configure the cluster device blacklist operation comm...
Page 422
2-19 z ndp and ntdp have been enabled on the management device and member devices, and ndp- and ntdp-related parameters have been configured. Z a cluster is established, and you can manage the member devices through the management device. 2) configuration procedure perform the following operations o...
Page 423
2-20 z the mib view name is mib_a, which includes all objects of the subtree org z the snmpv3 user is user_a, which belongs to the group group_a. # create a community with the name of read_a, allowing read-only access right using this community name. System-view [test_0.Sysname] cluster [test_0.Sysn...
Page 424
2-21 snmp-agent snmp-agent local-engineid 800007db000fe22405626877 snmp-agent community read read_a@cm0 snmp-agent community write write_a@cm0 snmp-agent sys-info version all snmp-agent group v3 group_a snmp-agent mib-view included mib_a org snmp-agent usm-user v3 user_a group_a undo snmp-agent trap...
Page 425
2-22 z perform the above operations on the management device of the cluster. Z creating a public local user is equal to executing these configurations on both the management device and the member devices (refer to the aaa operation part in this manual), and these configurations will be saved to the ...
Page 426
2-23 cluster configuration example basic cluster configuration example network requirements three switches compose a cluster, where: z an switch 4200g series switch serves as the management device. Z the rest are member devices. Serving as the management device, the switch 4200g switch manages the t...
Page 427
2-24 [sysname-ethernet1/0/1] ntdp enable [sysname-ethernet1/1] quit # enable the cluster function. [sysname] cluster enable 2) configure the management device # enable ndp globally and on gigabitethernet 1/0/2 and gigabitethernet 1/0/3. System-view [sysname] ndp enable [sysname] interface gigabiteth...
Page 428
2-25 [sysname-cluster] ip-pool 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.248 # name and build the cluster. [sysname-cluster] build aaa [aaa_0.Sysname-cluster] # add the attached two switches to the cluster. [aaa_0.Sysname-cluster] add-member 1 mac-address 000f-e20f-0011 [aaa_0.Sysname-cluster] add-member 17 mac-addres...
Page 429
2-26 enhanced cluster feature configuration example network requirements z the cluster operates properly. Z add the device with the mac address 0001-2034-a0e5 to the cluster blacklist, that is, prevent the device from being managed and maintained by the cluster. Z save the current cluster topology a...
Page 430: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 snmp configuration··································································································································1-1 snmp overview·················································································································...
Page 431: Snmp Configuration
1-1 1 snmp configuration when configuring snmp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z snmp overview z configuring basic snmp functions z configuring trap-related functions z enabling logging for network management z displaying snmp z snmp configuration example snmp overview t...
Page 432
1-2 z set the permission for a community to access an mib object to be read-only or read-write. Communities with read-only permissions can only query the switch information, while those with read-write permission can configure the switch as well. Z set the basic acl specified by the community name. ...
Page 435
1-5 configuring trap-related functions configuring basic trap functions traps refer to those sent by managed devices to the nms without request. They are used to report some urgent and important events (for example, the rebooting of managed devices). Note that basic snmp configuration is performed b...
Page 436: Displaying Snmp
1-6 follow these steps to configure extended trap function: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — configure the extended trap function snmp-agent trap ifmib link extended optional by default, the linkup/linkdown trap adopts the standard format defined in if-mib. For details...
Page 438
1-8 [sysname] snmp-agent usm-user v3 managev3user managev3group authentication-mode md5 passmd5 privacy-mode des56 cfb128cfb128 # set the vlan-interface 2 as the interface used by nms. Add port gigabitethernet 1/0/2, which is to be used for network management, to vlan 2. Set the ip address of vlan-i...
Page 439: Rmon Configuration
2-1 2 rmon configuration when configuring rmon, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to rmon z rmon configuration z displaying rmon z rmon configuration example introduction to rmon remote monitoring (rmon) is a kind of mib defined by internet engineering task f...
Page 440
2-2 error statistics and performance statistics of the network segments to which the ports of the managed network devices are connected. Thus, the nms can further manage the networks. Commonly used rmon groups event group event group is used to define the indexes of events and the processing methods...
Page 441: Rmon Configuration
2-3 statistics group statistics group contains the statistics of each monitored port on a switch. An entry in a statistics group is an accumulated value counting from the time when the statistics group is created. The statistics include the number of the following items: collisions, packets with cyc...
Page 442: Displaying Rmon
2-4 z the rmon alarm and rmon prialarm commands take effect on existing nodes only. Z for each port, only one rmon statistics entry can be created. That is, if an rmon statistics entry is already created for a given port, you will fail to create another statistics entry with a different index for th...
Page 443
2-5 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # add the event entries numbered 1 and 2 to the event table, which will be triggered by the following extended alarm. [sysname] rmon event 1 log [sysname] rmon event 2 trap 10.21.30.55 # add an entry numbered 2 to the extended alarm table to allow the system t...
Page 444: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 multicast overview ····································································································································1-1 multicast overview ········································································································...
Page 445
Ii.
Page 446: Multicast Overview
1-1 1 multicast overview multicast overview with development of networks on the internet, more and more interaction services such as data, voice, and video services are running on the networks. In addition, highly bandwidth- and time-critical services, such as e-commerce, web conference, online auct...
Page 447
1-2 information transmission in the broadcast mode when you adopt broadcast, the system transmits information to all users on a network. Any user on the network can receive the information, no matter the information is needed or not. 0 shows information transmission in broadcast mode. Figure 1-2 inf...
Page 448
1-3 figure 1-3 information transmission in the multicast mode source server receiver receiver receiver host a host b host c host d host e packets for the multicast group assume that hosts b, d and e need the information. To transmit the information to the right users, it is necessary to group hosts ...
Page 449: Multicast Models
1-4 table 1-1 an analogy between tv transmission and multicast transmission step tv transmission multicast transmission 1 a tv station transmits a tv program through a television channel. A multicast source sends multicast data to a multicast group. 2 a user tunes the tv set to the channel. A receiv...
Page 450: Multicast Architecture
1-5 asm model in the asm model, any sender can become a multicast source and send information to a multicast group; numbers of receivers can join a multicast group identified by a group address and obtain multicast information addressed to that multicast group. In this model, receivers are not aware...
Page 451
1-6 as receivers are multiple hosts in a multicast group, you should be concerned about the following questions: z what destination should the information source send the information to in the multicast mode? Z how to select the destination address? These questions are about multicast addressing. To...
Page 452
1-7 class d address range description 239.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 administratively scoped multicast addresses, which are for specific local use only. As specified by iana, the ip addresses ranging from 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 are reserved for network protocols on local networks. The following tabl...
Page 453
1-8 ethernet multicast mac address when a unicast ip packet is transported in an ethernet network, the destination mac address is the mac address of the receiver. When a multicast packet is transported in an ethernet network, a multicast mac address is used as the destination address because the des...
Page 454
1-9 figure 1-5 positions of layer 3 multicast protocols as 1 as 2 source receiver receiver receiver pim pim msdp igmp igmp igmp 1) multicast management protocols typically, the internet group management protocol (igmp) is used between hosts and layer 3 multicast devices directly connected with the h...
Page 455
1-10 figure 1-6 positions of layer 2 multicast protocols source receiver receiver multicast packets igmp snooping 1) igmp snooping running on layer 2 devices, internet group management protocol snooping (igmp snooping) are multicast constraining mechanisms that manage and control multicast groups by...
Page 456
1-11 2) if the corresponding (s, g) entry exists, but the interface on which the packet actually arrived is not the incoming interface in the multicast forwarding table, the multicast packet is subject to an rpf check. Z if the result of the rpf check shows that the rpf interface is the incoming int...
Page 457
1-12 z a multicast packet from source arrives to vlan-interface 1 of switch c, and the corresponding forwarding entry does not exist in the multicast forwarding table of switch c. Switch c performs an rpf check, and finds in its unicast routing table that the outgoing interface to 192.168.0.0/24 is ...
Page 458: Igmp Snooping Configuration
2-1 2 igmp snooping configuration igmp snooping overview internet group management protocol snooping (igmp snooping) is a multicast constraining mechanism that runs on layer 2 devices to manage and control multicast groups. Principle of igmp snooping by analyzing received igmp messages, a layer 2 de...
Page 459
2-2 figure 2-2 igmp snooping related ports router a switch a switch b eth1/0/1 eth1/0/2 eth1/0/3 eth1/0/1 eth1/0/2 receiver receiver host a host b host c host d source multicast packets router port member port ports involved in igmp snooping, as shown in figure 2-2 , are described as follows: z rout...
Page 460
2-3 when receiving a general query the igmp querier periodically sends igmp general queries to all hosts and routers on the local subnet to find out whether active multicast group members exist on the subnet. Upon receiving an igmp general query, the switch forwards it through all ports in the vlan ...
Page 461: Igmp Snooping Configuration
2-4 immediately delete the forwarding entry corresponding to that port from the forwarding table; instead, it resets the aging timer of the member port. Upon receiving the igmp leave message from a host, the igmp querier resolves from the message the address of the multicast group that the host just...
Page 462
2-5 1.1.1 enabling igmp snooping table 2-3 enable igmp snooping operation command remarks enter system view system-view — enable igmp snooping globally igmp-snooping enable required by default, igmp snooping is disabled globally. Enter vlan view vlan vlan-id — enable igmp snooping on the vlan igmp-s...
Page 463
2-6 z before configuring related igmp snooping functions, you must enable igmp snooping in the specified vlan. Z different multicast group addresses should be configured for different multicast sources because igmpv3 snooping cannot distinguish multicast data from different sources to the same multi...
Page 464
2-7 enabling fast leave processing in ethernet port view table 2-7 enable fast leave processing in ethernet view operation command remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — enable fast leave processing for specific vlans igmp-snoopin...
Page 465
2-8 operation command remarks configure a multicast group filter igmp-snooping group-policy acl-number [vlan vlan-list ] required no group filter is configured by default, namely hosts can join any multicast group. Configuring a multicast group filter in ethernet port view table 2-9 configure a mult...
Page 466
2-9 operation command remarks limit the number of multicast groups on a port igmp-snooping group-limit limit [ vlan vlan-list [ overflow-replace ] ] required the system default for switch 4200g series is 256. Z to prevent bursting traffic in the network or performance deterioration of the device cau...
Page 467
2-10 operation command remarks configure the interval of sending general queries igmp-snooping query-interval seconds optional by default, the interval of sending general queries is 60 seconds. Configure the source ip address of general queries igmp-snooping general-query source-ip { current-interfa...
Page 468
2-11 operation command remarks configure the current port as a static member port for a multicast group in a vlan multicast static-group group-address vlan vlan-id required by default, no port is configured as a static multicast group member port. In vlan interface view table 2-14 configure a static...
Page 469
2-12 configuring a port as a simulated group member generally, hosts running igmp respond to the igmp query messages of the multicast switch. If hosts fail to respond for some reason, the multicast switch may consider that there is no member of the multicast group on the local subnet and remove the ...
Page 470
2-13 configuring a vlan tag for query messages by configuring the vlan tag carried in igmp general and group-specific queries forwarded and sent by igmp snooping switches, you can enable multicast packet forwarding between different vlans in a layer-2 multicast network environment. Follow these step...
Page 471
2-14 operation command remarks enable igmp igmp enable required by default, the igmp feature is disabled. Return to system view quit — enter ethernet port view for the layer 2 switch to be configured interface interface-type interface-number — define the port as a trunk or hybrid port port link-type...
Page 472
2-15 z one port can belong to only one multicast vlan. Z the port connected to a user terminal must be a hybrid port. Z the multicast member ports must be in the same vlan with the router port. Otherwise, the multicast member port cannot receive multicast packets. Z if a router port is in a multicas...
Page 473
2-16 network diagram figure 2-3 network diagram for igmp snooping configuration multicast packets source router a switch a receiver receiver host b host a host c 1.1.1.1/24 ge1/0/4 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 igmp querier ge1/0/1 ge1/0/1 10.1.1.1/24 ge1/0/2 1.1.1.2/24 vlan100 configuration procedure 1) configur...
Page 474
2-17 # view the detailed information of the multicast group in vlan 100 on switch a. Display igmp-snooping group vlan100 total 1 ip group(s). Total 1 mac group(s). Vlan(id):100. Total 1 ip group(s). Total 1 mac group(s). Static router port(s): dynamic router port(s): gigabitethernet1/0/1 ip group(s)...
Page 475
2-18 device device description networking description switch b layer 2 switch z vlan 2 contains gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and vlan 3 contains gigabitethernet 1/0/2. Z the default vlans of gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 are vlan 2 and vlan 3 respectively. Z vlan 10 contains gigabitethern...
Page 476
2-19 [switcha-vlan-interface20] ip address 168.10.1.1 255.255.255.0 [switcha-vlan-interface20] pim dm [switcha-vlan-interface20] quit # configure vlan 10. [switcha] vlan 10 [switcha-vlan10] quit # define gigabitethernet 1/0/10 as a hybrid port, add the port to vlan 10, and configure the port to forw...
Page 477
2-20 [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] port hybrid pvid vlan 3 [switchb-gigabitethernet1/0/2] quit troubleshooting igmp snooping symptom: multicast function does not work on the switch. Solution: possible reasons are: 1) igmp snooping is not enabled. Z use the display current-configuration command to c...
Page 478
3-1 3 common multicast configuration common multicast configuration configuring a multicast mac address entry in layer 2 multicast, the system can add multicast forwarding entries dynamically through a layer 2 multicast protocol. Alternatively, you can statically bind a port to a multicast mac addre...
Page 479
3-2 z if the multicast mac address entry to be created already exists, the system gives you a prompt. Z if you want to add a port to a multicast mac address entry created through the mac-address multicast command, you need to remove the entry first, create this entry again, and then add the specifie...
Page 480: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ntp configuration ·····································································································································1-1 introduction to ntp ·······································································································...
Page 481: Ntp Configuration
1-1 1 ntp configuration when configuring ntp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to ntp z ntp configuration task list z configuring ntp implementation modes z configuring access control right z configuring ntp authentication z configuring optional ntp paramete...
Page 482
1-2 z defining the accuracy of clocks by stratum to synchronize the clocks of all devices in a network quickly z supporting access control and md5 encrypted authentication z sending protocol packets in unicast, multicast, or broadcast mode z the clock stratum determines the accuracy, which ranges fr...
Page 483
1-3 figure 1-1 implementation principle of ntp ip network ip network ip network ip network device b device a device b device a device b device a device b device a 10:00:00 am 11:00:01 am 10:00:00 am ntp message 10:00:00 am 11:00:01 am 11:00:02 am ntp message ntp message ntp message received at 10:00...
Page 484
1-4 ntp implementation modes according to the network structure and the position of the local ethernet switch in the network, the local ethernet switch can work in multiple ntp modes to synchronize the clock. Server/client mode figure 1-2 server/client mode symmetric peer mode figure 1-3 symmetric p...
Page 485
1-5 broadcast mode figure 1-4 broadcast mode multicast mode figure 1-5 multicast mode table 1-1 describes how the above mentioned ntp modes are implemented on 3com s4200g series ethernet switches. Table 1-1 ntp implementation modes on 3com s4200g series ethernet switches ntp implementation mode conf...
Page 486: Ntp Configuration Task List
1-6 ntp implementation mode configuration on s4200g series switches multicast mode z configure the local s4200g ethernet switch to work in ntp multicast server mode. In this mode, the local switch sends multicast ntp messages through the vlan interface configured on the switch. Z configure the local...
Page 487
1-7 z udp port 123 is opened only when the ntp feature is enabled. Z udp port 123 is closed as the ntp feature is disabled. These functions are implemented as follows: z execution of one of the ntp-service unicast-server, ntp-service unicast-peer, ntp-service broadcast-client, ntp-service broadcast-...
Page 490
1-10 configuring a switch to work in the multicast client mode follow these steps to configure a switch to work in the ntp multicast client mode: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan interface view interface vlan-interface vlan-id — configure the switch to work ...
Page 492
1-12 z in addition, for the server/client mode and the symmetric peer mode, you need to associate a specific key on the client (the symmetric-active peer in the symmetric peer mode) with the corresponding ntp server (the symmetric-passive peer in the symmetric peer mode); for the ntp broadcast/multi...
Page 493
1-13 to do… use the command… remarks enable ntp authentication ntp-service authentication enable required disabled by default. Configure an ntp authentication key ntp-service authentication-keyid key-id authentication-mode md5 value required by default, no ntp authentication key is configured. Confi...
Page 494
1-14 task remarks configuring an interface on the local switch to send ntp messages optional configuring the number of dynamic sessions allowed on the local switch optional disabling an interface from receiving ntp messages optional configuring an interface on the local switch to send ntp messages f...
Page 495: Displaying Ntp Configuration
1-15 disabling an interface from receiving ntp messages follow these steps to disable an interface from receiving ntp messages: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan interface view interface vlan-interface vlan-id — disable an interface from receiving ntp message...
Page 496
1-16 reference clock id: none nominal frequency: 60.0002 hz actual frequency: 60.0002 hz clock precision: 2^18 clock offset: 0.0000 ms root delay: 0.00 ms root dispersion: 0.00 ms peer dispersion: 0.00 ms reference time: 00:00:00.000 utc jan 1 1900 (00000000.00000000) # set device a as the ntp serve...
Page 497
1-17 network diagram figure 1-7 network diagram for ntp peer mode configuration device a device b device c 3.0.1.31/24 3.0.1.32/24 3.0.1.33/24 configuration procedure 1) configure device c. # set device a as the ntp server. System-view [devicec] ntp-service unicast-server 3.0.1.31 2) configure devic...
Page 498
1-18 # view the information about the ntp sessions of device c (you can see that a connection is established between device c and device b). [devicec] display ntp-service sessions source reference stra reach poll now offset delay disper ***************************************************************...
Page 499
1-19 # set device a as a broadcast client. [devicea] interface vlan-interface 2 [devicea-vlan-interface2] ntp-service broadcast-client after the above configurations, device a and device d will listen to broadcast messages through their own vlan-interface 2, and device c will send broadcast messages...
Page 500
1-20 network diagram figure 1-9 network diagram for ntp multicast mode configuration vlan-int2 1.0.1.31/24 vlan-int2 3.0.1.31/24 vlan-int2 3.0.1.32/24 device a device b device c device d configuration procedure 1) configure device c. # enter system view. System-view # set device c as a multicast ser...
Page 501
1-21 root dispersion: 208.39 ms peer dispersion: 9.63 ms reference time: 17:03:32.022 utc apr 2 2007 (bf422ae4.05aea86c) the output information indicates that device d is synchronized to device c, with a clock stratum level of 3, one stratum level lower than that device c. # view the information abo...
Page 502
1-22 after the above configurations, device b is ready to synchronize with device a. Because the ntp authentication function is not enabled on device a, the clock of device b will fail to be synchronized to that of device a. 2) to synchronize device b, you need to perform the following configuration...
Page 503: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ssh configuration·····································································································································1-1 ssh overview················································································································...
Page 504: Ssh Configuration
1-1 1 ssh configuration when configuring ssh, go to these sections for information you are interested: z ssh overview z ssh server and client z displaying and maintaining ssh configuration z comparison of ssh commands with the same functions z ssh configuration examples ssh overview introduction to ...
Page 505
1-2 the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. Supported symmetric key algorithms include des, 3des, and aes, which can effectively prevent data eavesdropping. Z asymmetric key algorithm asymmetric key algorithm is also called public key algorithm. Both ends have their own key pair, co...
Page 506
1-3 z currently, the switch that serves as an ssh server supports two ssh versions: ssh2 and ssh1, and the switch that serves as an ssh client supports only ssh2. Z unless otherwise noted, ssh refers to ssh2 throughout this document. Version negotiation z the server opens port 22 to listen to connec...
Page 507: Ssh Server and Client
1-4 z the server starts to authenticate the user. If authentication fails, the server sends an authentication failure message to the client, which contains the list of methods used for a new authentication process. Z the client selects an authentication type from the method list to perform authentic...
Page 508: Configuring The Ssh Server
1-5 figure 1-2 network diagram for ssh connections configure the devices accordingly this document describes two cases: z the 3com switch acts as the ssh server to cooperate with software that supports the ssh client functions. Z the 3com switch acts as the ssh server to cooperate with another 3com ...
Page 509
1-6 task remarks configuring the user interfaces for ssh clients required preparation configuring the ssh management functions optional version configuring the ssh server to be compatible with ssh1 clients optional this task determines which ssh versions the server should support. By default, the ss...
Page 511
1-8 to do... Use the command... Remarks specify a source ip address for the ssh server ssh-server source-ip ip-address optional by default, no source ip address is configured. Specify a source interface for the ssh server ssh-server source-interface interface-type interface-number optional by defaul...
Page 512
1-9 to do... Use the command... Remarks generate an rsa key pairs public-key local create rsa generate key pair(s) generate a dsa key pair public-key local create dsa required by default, no key pairs are generated. Z the command for generating a key pair can survive a reboot. You only need to confi...
Page 513
1-10 ssh uses the authentication function of aaa to authenticate the password of the user that is logging in. Based on the aaa authentication scheme, password authentication can be done locally or remotely. For local authentication, the ssh server saves the user information and implements the authen...
Page 514
1-11 z for password authentication type, the username argument must be consistent with the valid user name defined in aaa; for publickey authentication, the username argument is the ssh local user name, so that there is no need to configure a local user in aaa. Z if the default authentication type f...
Page 515
1-12 configuring the public key of a client on the server this configuration is not necessary if the password authentication mode is configured for ssh users. With the publickey authentication mode configured for an ssh client, you must configure the client’s rsa or dsa host public key(s) on the ser...
Page 516
1-13 this configuration task is unnecessary if the ssh user’s authentication mode is password. For the publickey authentication mode, you must specify the client’s public key on the server for authentication. Follow these steps to assign a public key for an ssh user: to do... Use the command... Rema...
Page 517: Configuring The Ssh Client
1-14 z with the filename argument specified, you can export the rsa or dsa host public key to a file so that you can configure the key at a remote end by importing the file. If the filename argument is not specified, this command displays the host public key information on the screen in a specified ...
Page 518
1-15 task remarks opening an ssh connection with password authentication required for password authentication; unnecessary for publickey authentication opening an ssh connection with publickey authentication required for publickey authentication; unnecessary for password authentication z for putty, ...
Page 519
1-16 figure 1-3 generate a client key (1) note that while generating the key pair, you must move the mouse continuously and keep the mouse off the green process bar in the blue box of shown in figure 1-4 . Otherwise, the process bar stops moving and the key pair generating process is stopped. Figure...
Page 520
1-17 after the key pair is generated, click save public key and enter the name of the file for saving the public key (public in this case) to save the public key. Figure 1-5 generate the client keys (3) likewise, to save the private key, click save private key. A warning window pops up to prompt you...
Page 521
1-18 figure 1-7 generate the client keys (5) specifying the ip address of the server launch putty.Exe. The following window appears. Figure 1-8 ssh client configuration interface 1.
Page 522
1-19 in the host name (or ip address) text box, enter the ip address of the server. Note that there must be a route available between the ip address of the server and the client. Selecting a protocol for remote connection as shown in figure 1-8 , select ssh under protocol. Selecting an ssh version f...
Page 523
1-20 opening an ssh connection with publickey authentication if a user needs to be authenticated with a public key, the corresponding private key file must be specified. A private key file is not required for password-only authentication. From the category on the left of the window, select connectio...
Page 524
1-21 configuring the ssh client for publickey authentication when the authentication mode is publickey, you need to configure the rsa or dsa public key of the client on the server: z to generate a key pair on the client, refer to configuring key pairs. Z to export the rsa or dsa public key of the cl...
Page 525
1-22 with first-time authentication enabled, an ssh client that is not configured with the ssh server's host public key saves the host public key sent by the server without authenticating the server. Attackers may exploit the vulnerability to initiate man-in-middle attacks by acting as an ssh server...
Page 527
1-24 to do... Use the command... Remarks display the mappings between host public keys and ssh servers saved on a client display ssh server-info display the current source ip address or the ip address of the source interface specified for the ssh client. Display ssh2 source-ip comparison of ssh comm...
Page 528: Ssh Configuration Examples
1-25 z after rsa key pairs are generated, the display rsa local-key-pair public command displays two public keys (the host public key and server public key) when the switch is working in ssh1-compatible mode, but only one public key (the host public key) when the switch is working in ssh2 mode. Z th...
Page 529
1-26 # generate rsa and dsa key pairs. [switch] public-key local create rsa [switch] public-key local create dsa # set the authentication mode for the user interfaces to aaa. [switch] user-interface vty 0 4 [switch-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode scheme # enable the user interfaces to support ssh. [s...
Page 530
1-27 in the host name (or ip address) text box, enter the ip address of the ssh server. 2) from the category on the left pane of the window, select ssh under connection. The window as shown in figure 1-13 appears. Figure 1-13 ssh client configuration interface (2) under protocol options, select 2 fr...
Page 531
1-28 network diagram figure 1-14 switch acts as server for password and radius authentication configuration procedure 4) configure the radius server this document takes cams version 2.10 as an example to show the basic radius server configurations required. # add an access device. Log in to the cams...
Page 532
1-29 figure 1-15 add an access device # add a user account for device management. From the navigation tree, select user management > user for device management, and then in the right pane, click add to enter the add account page and perform the following configurations: z add a user named hello, and...
Page 533
1-30 generating the rsa and dsa key pairs on the server is prerequisite to ssh login. # generate rsa and dsa key pairs. [switch] public-key local create rsa [switch] public-key local create dsa # set the authentication mode for the user interfaces to aaa. [switch] user-interface vty 0 4 [switch-ui-v...
Page 534
1-31 figure 1-17 ssh client configuration interface (1) in the host name (or ip address) text box, enter the ip address of the ssh server. Z from the category on the left pane of the window, select connection > ssh. The window as shown in figure 1-18 appears. Figure 1-18 ssh client configuration int...
Page 535
1-32 authentication succeeds, you will log in to the server. The level of commands that you can access after login is authorized by the cams server. You can specify the level by setting the exec privilege level argument in the add account window shown in figure 1-16 . When switch acts as server for ...
Page 536
1-33 # enable the user interfaces to support ssh. [switch-ui-vty0-4] protocol inbound ssh [switch-ui-vty0-4] quit # configure the hwtacacs scheme. [switch] hwtacacs scheme hwtac [switch-hwtacacs-hwtac] primary authentication 10.1.1.1 49 [switch-hwtacacs-hwtac] primary authorization 10.1.1.1 49 [swit...
Page 537
1-34 2) from the category on the left pane of the window, select connection > ssh. The window as shown in figure 1-21 appears. Figure 1-21 ssh client configuration interface (2) under protocol options, select 2 from preferred ssh protocol version. Then, click open. If the connection is normal, you w...
Page 538
1-35 configuration procedure under the publickey authentication mode, either the rsa or dsa public key can be generated for the server to authenticate the client. Here takes the rsa public key as an example. Z configure the ssh server # create a vlan interface on the switch and assign an ip address,...
Page 539
1-36 # import the client’s public key named switch001 from file public. [switch] public-key peer switch001 import sshkey public # assign the public key switch001 to client client001. [switch] ssh user client001 assign publickey switch001 z configure the ssh client (taking putty version 0.58 as an ex...
Page 540
1-37 figure 1-24 generate a client key pair (2) after the key pair is generated, click save public key and enter the name of the file for saving the public key (public in this case). Figure 1-25 generate a client key pair (3).
Page 541
1-38 likewise, to save the private key, click save private key. A warning window pops up to prompt you whether to save the private key without any protection. Click yes and enter the name of the file for saving the private key (private.Ppk in this case). Figure 1-26 generate a client key pair (4) af...
Page 542
1-39 figure 1-28 ssh client configuration interface (2) under protocol options, select 2 from preferred ssh protocol version. 4) select connection/ssh/auth.The following window appears. Figure 1-29 ssh client configuration interface (3).
Page 543
1-40 click browse to bring up the file selection window, navigate to the private key file and click ok. 5) from the window shown in figure 1-29 , click open. If the connection is normal, you will be prompted to enter the username. When switch acts as client for password authentication network requir...
Page 544
1-41 [switchb] local-user client001 [switchb-luser-client001] password simple abc [switchb-luser-client001] service-type ssh level 3 [switchb-luser-client001] quit # configure the authentication type of user client001 as password. [switchb] ssh user client001 authentication-type password z configure...
Page 545
1-42 configuration procedure in public key authentication, you can use either rsa or dsa public key. Here takes the dsa public key as an example. Z configure switch b # create a vlan interface on the switch and assign an ip address, which the ssh client will use as the destination for ssh connection...
Page 546
1-43 # import the client public key pair named switch001 from the file switch001. [switchb] public-key peer switch001 import sshkey switch001 # assign the public key switch001 to user client001. [switchb] ssh user client001 assign publickey switch001 z configure switch a # create a vlan interface on...
Page 547
1-44 when switch acts as client and first-time authentication is not supported network requirements as shown in figure 1-32 , establish an ssh connection between switch a (ssh client) and switch b (ssh server) for secure data exchange. The user name is client001 and the ssh server’s ip address is 10...
Page 548
1-45 before doing the following steps, you must first generate a dsa key pair on the client and save the key pair in a file named switch001, and then upload the file to the ssh server through ftp or tftp. For details, refer to the following “configure switch a”. # import the client’s public key file...
Page 549
1-46 when first-time authentication is not supported, you must first generate a dsa key pair on the server and save the key pair in a file named switch002, and then upload the file to the ssh client through ftp or tftp. For details, refer to the above part “configure switch b”. # import the public k...
Page 550: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 file system management configuration ·································································································1-1 file system configuration ··················································································································...
Page 551: File System Configuration
1-1 1 file system management configuration file system configuration introduction to file system to facilitate management on the switch memory, 3com switches 4200g provide the file system function, allowing you to access and manage the files and directories. You can create, remove, copy or delete a ...
Page 552
1-2 table 1-2 directory operations to do… use the command… remarks create a directory mkdir directory optional delete a directory rmdir directory optional display the current work directory pwd optional display the information about specific directories and files dir [ /all ] [ file-url ] optional e...
Page 553
1-3 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — execute the specified batch file execute filename optional this command should be executed in system view. Z for deleted files whose names are the same, only the latest deleted file is kept in the recycle bin and can be restored. Z ...
Page 555: File Attribute Configuration
1-5 1 -rw- 1235 apr 05 2000 01:51:34 test.Cfg 2 -rw- 1235 apr 05 2000 01:56:44 1.Cfg 15367 kb total (3585 kb free) (*) -with main attribute (b) -with backup attribute (*b) -with both main and backup attribute file attribute configuration introduction to file attributes the following three startup fi...
Page 556
1-6 attribute. If you download a valid file with the same name as the deleted file to the flash memory, the file will possess the main attribute. After the boot rom of a switch is upgraded, the original default app file has the main attribute. Booting with the startup file the device selects the mai...
Page 557
1-7 to do… use the command… remarks display the information about the app file used as the startup file display boot-loader [ unit unit-id ] display information about the web file used by the device display web package optional available in any view z before configuring the main or backup attribute ...
Page 558: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ftp and sftp configuration····················································································································1-1 introduction to ftp and sftp ·······································································································...
Page 559: Ftp and Sftp Configuration
1-1 1 ftp and sftp configuration when configuring ftp and sftp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to ftp and sftp z ftp configuration z sftp configuration introduction to ftp and sftp introduction to ftp file transfer protocol (ftp) is commonly used in ip-bas...
Page 560: Ftp Configuration
1-2 ftp configuration complete the following tasks to configure ftp: task remarks creating an ftp user required enabling an ftp server required configuring connection idle time optional specifying the source interface and source ip address for an ftp server optional disconnecting a specified user op...
Page 561
1-3 z only one user can access a 3com switch 4200g at a given time when the latter operates as an ftp server. Z operating as an ftp server, a 3com switch 4200g cannot receive a file whose size exceeds its storage space. The clients that attempt to upload such a file will be disconnected with the ftp...
Page 562
1-4 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — specify the source interface for an ftp server ftp-server source-interface interface-type interface-number specifying the source ip address for an ftp server ftp-server source-ip ip-address use either command not specified by defaul...
Page 563
1-5 z login banner: after the connection between an ftp client and an ftp server is established, the ftp server outputs the configured login banner to the ftp client terminal. Figure 1-1 process of displaying a login banner z shell banner: after the connection between an ftp client and an ftp server...
Page 564
1-6 displaying ftp server information to do… use the command… remarks display the information about ftp server configurations on a switch display ftp-server display the source ip address set for an ftp server display ftp-server source-ip display the login ftp client on an ftp server display ftp-user...
Page 565
1-7 to do… use the command… remarks dir [ remotefile ] [ localfile ] query a specified file on the ftp server ls [ remotefile ] [ localfile ] optional if no file name is specified, all the files in the current directory are displayed. The difference between these two commands is that the dir command...
Page 566
1-8 to do… use the command… remarks specify an interface as the source interface the ftp client uses every time it connects to an ftp server ftp source-interface interface-type interface-number specify an ip address as the source ip address the ftp client uses every time it connects to an ftp server...
Page 567
1-9 network diagram figure 1-3 network diagram for ftp configurations: a switch operating as an ftp server configuration procedure 1) configure switch a (the ftp server) # log in to the switch and enable the ftp server function on the switch. Configure the user name and password used to access ftp s...
Page 568
1-10 # download file config.Cfg. Ftp> get config.Cfg 200 port command okay. 150 opening ascii mode data connection for config.Cfg. 226 transfer complete. Ftp: 3980 bytes received in 8.277 seconds 0.48kbytes/sec. This example uses the command line window tool provided by windows. When you log in to t...
Page 569
1-11 z configure the login banner of the switch as “login banner appears” and the shell banner as “shell banner appears”. Network diagram figure 1-4 network diagram for ftp banner display configuration configuration procedure 1) configure the switch (ftp server) # configure the login banner of the s...
Page 570
1-12 network diagram figure 1-5 network diagram for ftp configurations: a switch operating as an ftp client configuration procedure 1) configure the pc (ftp server) perform ftp server–related configurations on the pc, that is, create a user account on the ftp server with username switch and password...
Page 571: Sftp Configuration
1-13 [ftp] get switch.Bin # execute the quit command to terminate the ftp connection and return to user view. [ftp] quit # after downloading the file, use the boot boot-loader command to specify the downloaded file (switch.Bin) to be the application for next startup, and then restart the switch. Thu...
Page 572
1-14 to do… use the command… remarks enable an sftp server sftp server enable required disabled by default. Configuring connection idle time after the idle time is configured, if the server does not receive service requests from a client within a specified time period, it terminates the connection w...
Page 575
1-17 configuration procedure 1) configure the sftp server (switch b) # create key pairs. System-view [sysname] public-key local create rsa [sysname] public-key local create dsa # create a vlan interface on the switch and assign to it an ip address, which is used as the destination address for the cl...
Page 576
1-18 connected to 192.168.0.1 ... The server is not authenticated. Do you continue to access it?(y/n):y do you want to save the server's public key?(y/n):n enter password: sftp-client> # display the current directory of the server. Delete the file z and verify the result. Sftp-client> dir -rwxrwxrwx...
Page 577
1-19 sftp-client> rename new1 new2 file successfully renamed sftp-client> dir -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 1759 aug 23 06:52 config.Cfg -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 225 aug 24 08:01 pubkey2 -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 283 aug 24 07:39 pubkey1 drwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 0 sep 01 06:22 new -rwxrwxrwx 1 noo...
Page 578: Tftp Configuration
2-1 2 tftp configuration when configuring tftp, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to tftp z tftp configuration introduction to tftp compared with ftp, trivial file transfer protocol (tftp) features simple interactive access interface and no authentication con...
Page 579
2-2 task remarks basic configurations on a tftp client — tftp configuration: a switch operating as a tftp client specifying the source interface or source ip address for an ftp client optional tftp server configuration for details, see the corresponding manual — tftp configuration: a switch operatin...
Page 580
2-3 to do… use the command… remarks specify an interface as the source interface a tftp client uses every time it connects to a tftp server tftp source-interface interface-type interface-number specify an ip address as the source ip address a tftp client uses every time it connects to a tftp server ...
Page 581
2-4 network diagram figure 2-1 network diagram for tftp configurations configuration procedure 1) configure the tftp server (pc) start the tftp server and configure the working directory on the pc. 2) configure the tftp client (switch). # log in to the switch. (you can log in to a switch through the...
Page 582
2-5 for information about the boot boot-loader command and how to specify the startup file for a switch, refer to the system maintenance and debugging module of this manual..
Page 583: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 information center·····································································································································1-1 information center overview ·······························································································...
Page 584: Information Center
1-1 1 information center when configuring information center, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z information center overview z information center configuration z displaying and maintaining information center z information center configuration examples information center ov...
Page 585
1-2 information filtering by severity works this way: information with the severity value greater than the configured threshold is not output during the filtering. Z if the threshold is set to 1, only information with the severity being emergencies will be output; z if the threshold is set to 8, inf...
Page 586
1-3 outputting system information by source module the system information can be classified by source module and then filtered. Some module names and description are shown in table 1-3 . Table 1-3 source module name list module name description 8021x 802.1x module acl access control list module adbm...
Page 587
1-4 module name description sysmib system mib module tac hwtacacs module telnet telnet module tftpc tftp client module vlan virtual local area network module vty virtual type terminal module xm xmodem module default default settings for all the modules to sum up, the major task of the information ce...
Page 588
1-5 z if the address of the log host is specified in the information center of the switch, when logs are generated, the switch sends the logs to the log host in the above format. For detailed information, refer to setting to output system information to a log host . Z there is the syslog process on ...
Page 589
1-6 locate and solve problems globally. In this case, you can configure the information center to add utc time zone to the time stamp of the output information, so that you can know the standard time when the information center processing each piece of information. That is, you can know the greenwic...
Page 590
1-7 source this field indicates the source of the information, such as the source ip address of the log sender. This field is optional and is displayed only when the output destination is the log host. Context this field provides the content of the system information. Information center configuratio...
Page 591
1-8 z if the system information is output before you input any information following the current command line prompt, the system does not echo any command line prompt after the system information output. Z in the interaction mode, you are prompted for some information input. If the input is interrup...
Page 593
1-10 follow these steps to enable the system information display on the console: to do… use the command… remarks enable the debugging/log/trap information terminal display function terminal monitor optional enabled by default. Enable debugging information terminal display function terminal debugging...
Page 598
1-15 information center configuration examples log output to a unix log host network requirements the switch sends the following log information to the unix log host whose ip address is 202.38.1.10: the log information of the two modules arp and ip, with severity higher than “informational”. Network...
Page 599
1-16 when you edit the file “/etc/syslog.Conf”, note that: z a note must start in a new line, starting with a “#” sign. Z in each pair, a tab should be used as a separator instead of a space. Z no space is allowed at the end of a file name. Z the device name (facility) and received log information s...
Page 600
1-17 system-view [switch] info-center enable # configure the host whose ip address is 202.38.1.10 as the log host. Permit all modules to output log information with severity level higher than error to the log host. [switch] info-center loghost 202.38.1.10 facility local7 [switch] info-center source ...
Page 601
1-18 through combined configuration of the device name (facility), information severity level threshold (severity), module name (filter) and the file “syslog.Conf”, you can sort information precisely for filtering. Log output to the console network requirements the switch sends the following informa...
Page 602
1-19 network diagram figure 1-4 network diagram configuration procedure # name the local time zone z8 and configure it to be eight hours ahead of utc time. Clock timezone z8 add 08:00:00 # set the time stamp format of the log information to be output to the log host to date. System-view system view:...
Page 603: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 boot rom and host software loading ···································································································1-1 introduction to loading approaches ·······································································································1-...
Page 604
1-1 1 boot rom and host software loading traditionally, switch software is loaded through a serial port. This approach is slow, time-consuming and cannot be used for remote loading. To resolve these problems, the tftp and ftp modules are introduced into the switch. With these modules, you can load/d...
Page 605
1-2 the loading process of the boot rom software is the same as that of the host software, except that during the former process, you should press “6” or and after entering the boot menu and the system gives different prompts. The following text mainly describes the boot rom loading process. Boot me...
Page 606
1-3 2. Select application file to boot 3. Display all files in flash 4. Delete file from flash 5. Modify bootrom password 6. Enter bootrom upgrade menu 7. Skip current configuration file 8. Set bootrom password recovery 9. Set switch startup mode 0. Reboot enter your choice(0-9): loading by xmodem t...
Page 607
1-4 enter your choice (0-5): step 3: choose an appropriate baudrate for downloading. For example, if you press 5, the baudrate 115200 bps is chosen and the system displays the following information: download baudrate is 115200 bps please change the terminal's baudrate to 115200 bps and select xmodem...
Page 608
1-5 figure 1-2 console port configuration dialog box step 5: click the button to disconnect the hyperterminal from the switch and then click the button to reconnect the hyperterminal to the switch, as shown in figure 1-3 . Figure 1-3 connect and disconnect buttons the new baudrate takes effect after...
Page 609
1-6 figure 1-4 send file dialog box step 8: click . The system displays the page, as shown in figure 1-5 . Figure 1-5 sending file page step 9: after the sending process completes, the system displays the following information: loading ...Cccccccccc done! Step 10: reset hyperterminal’s baudrate to 9...
Page 610
1-7 loading host software follow these steps to load the host software: step 1: select in boot menu and press . The system displays the following information: 1. Set tftp protocol parameter 2. Set ftp protocol parameter 3. Set xmodem protocol parameter 0. Return to boot menu enter your choice(0-3): ...
Page 611
1-8 you can use one pc as both the configuration device and the tftp server. Step 2: run the tftp server program on the tftp server, and specify the path of the program to be downloaded. Tftp server program is not provided with the 3com series ethernet switches. Step 3: run the hyperterminal program...
Page 612
1-9 0. Return to boot menu enter your choice(0-3): step 2: enter 1 in the above menu to download the host software using tftp. The subsequent steps are the same as those for loading the boot rom, except that the system gives the prompt for host software loading instead of boot rom loading. When load...
Page 613
1-10 at the prompt "enter your choice(0-9):" in the boot menu, press or , and then press to enter the boot rom update menu shown below: bootrom update menu: 1. Set tftp protocol parameter 2. Set ftp protocol parameter 3. Set xmodem protocol parameter 0. Return to boot menu enter your choice(0-3): st...
Page 614
1-11 remote boot rom and software loading if your terminal is not directly connected to the switch, you can telnet to the switch, and use ftp or tftp to load the boot rom and host software remotely. Remote loading using ftp loading procedure using ftp client 1) loading the boot rom as shown in figur...
Page 615
1-12 reboot before restarting the switch, make sure you have saved all other configurations that you want, so as to avoid losing configuration information. 2) loading host software loading the host software is the same as loading the boot rom program, except that the file to be downloaded is the hos...
Page 616
1-13 you can configure the ip address for any vlan on the switch for ftp transmission. However, before configuring the ip address for a vlan interface, you have to make sure whether the ip addresses of this vlan and pc are routable. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [sysname]...
Page 617
1-14 figure 1-11 enter boot rom directory step 6: enter ftp 192.168.0.28 and enter the user name test, password pass, as shown in figure 1-12 , to log on to the ftp server. Figure 1-12 log on to the ftp server step 7: use the put command to upload the file switch.Btm to the switch, as shown in figur...
Page 618
1-15 figure 1-13 upload file switch.Btm to the switch step 8: configure switch.Btm to be the boot rom at next startup, and then restart the switch. Boot bootrom switch.Btm this will update bootrom on unit 1. Continue? [y/n] y upgrading bootrom, please wait... Upgrade bootrom succeeded! Reboot after ...
Page 619: Basic System Configuration
2-1 2 basic system configuration and debugging when configuring basic system configuration and debugging, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z basic system configuration z displaying the system status z debugging the system basic system configuration perform the following ba...
Page 620: Displaying The System Status
2-2 to do… use the command… remarks return from current view to user view return optional the composite key has the same effect with the return command. Displaying the system status to do… use the command… remarks display the current date and time of the system display clock display the version of t...
Page 621
2-3 displaying debugging information on the terminal is the most commonly used way to output debugging information. You can also output debugging information to other directions. For details, refer to information center operation. You can use the following commands to enable the two switches. Follow...
Page 622: Network Connectivity Test
3-1 3 network connectivity test when configuring network connectivity test, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ping z tracert network connectivity test ping you can use the ping command to check the network connectivity and the reachability of a host. To do… use the comman...
Page 623: Device Management
4-1 4 device management when configuring device management, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to device management z device management configuration z displaying the device management configuration z remote switch app upgrade configuration example introductio...
Page 624
4-2 before rebooting, the system checks whether there is any configuration change. If yes, it prompts whether or not to proceed. This prevents the system from losing the configurations in case of shutting down the system without saving the configurations use the following command to reboot the ether...
Page 625
4-3 enabling of this function consumes some amounts of cpu resources. Therefore, if your network has a high cpu usage requirement, you can disable this function to release your cpu resources. Specifying the app to be used at reboot app is the host software of the switch. If multiple apps exist in th...
Page 626
4-4 transceiver type applied environment whether can be an optical transceiver whether can be an electrical transceiver xfp (10-gigabit small form-factor pluggable) generally used for 10g ethernet interfaces yes no xenpak (10 gigabit ethernet transceiver package) generally used for 10g ethernet inte...
Page 627
4-5 to do… use the command… remarks display the currently measured value of the digital diagnosis parameters of the anti-spoofing optical transceiver(s) customized by h3c display transceiver diagnosis interface [ interface-type interface-number ] available for anti-spoofing pluggable optical transce...
Page 628
4-6 the host software switch.App and the boot rom file boot.Btm of the switch are stored in the directory switch on the pc. Use ftp to download the switch.App and boot.Btm files from the ftp server to the switch. Network diagram figure 4-1 network diagram for ftp configuration configuration procedur...
Page 629
4-7 [ftp] 5) enter the authorized path on the ftp server. [ftp] cd switch 6) execute the get command to download the switch.App and boot.Btm files on the ftp server to the flash memory of the switch. [ftp] get switch.App [ftp] get boot.Btm 7) execute the quit command to terminate the ftp connection ...
Page 630: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 remote-ping configuration ·······················································································································1-1 remote-ping overview ············································································································...
Page 631: Remote-Ping Configuration
1-1 1 remote-ping configuration when configuring remote-ping, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z remote-ping overview z remote-ping configuration z remote-ping configuration examples remote-ping overview introduction to remote-ping remote-ping is a network diagnostic tool....
Page 632
1-2 test types supported by remote-ping table 1-1 test types supported by remote-ping supported test types description icmp test dhcp test ftp test http test dns test snmp test for these types of tests, you need to configure the remote-ping client and corresponding servers. Jitter test tcppublic tes...
Page 633
1-3 test parameter description test type (test-type) z you can use remote-ping to test a variety of protocols, see table 1-1 for details. Z to perform a type of test, you must first create a test group of this type. One test group can be of only one remote-ping test type. Z if you modify the test ty...
Page 634: Remote-Ping Configuration
1-4 test parameter description trap z a remote-ping test will generate a trap message no matter whether the test successes or not. You can use the trap switch to enable or disable the output of trap messages. Z you can set the number of consecutive failed remote-ping tests before trap output. You ca...
Page 635
1-5 follow these steps to configure icmp test on remote-ping client: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the remote-ping client function remote-ping-agent enable required by default, the remote-ping client function is disabled. Create a remote-ping test group and e...
Page 636
1-6 to do… use the command… remarks enable the remote-ping client function remote-ping-agent enable required by default, the remote-ping client function is disabled. Create a remote-ping test group and enter its view remote-ping administrator-name operation-tag required by default, no test group is ...
Page 637
1-7 to do… use the command… remarks configure the test type test-typeftp required by default, the test type is icmp. Configure the number of probes per test count times optional by default, each test makes one probe. Configure the maximum number of history records that can be saved history-records n...
Page 638
1-8 to do… use the command… remarks configure the destination ip address destination-ip ip-address required you can configure an ip address or a host name. By default, no destination address is configured. Configure dns-server dns-server ip-address required when you use the destination-ip command to...
Page 639
1-9 follow these steps to configure jitter test on remote-ping client: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the remote-ping client function remote-ping-agent enable required by default, the remote-ping client function is disabled. Create a remote-ping test group and...
Page 640
1-10 to do… use the command… remarks configure the type of service tos value optional by default, the service type is zero. Configure the number of test packets that will be sent in each jitter probe jitter-packetnum number optional by default, each jitter probe will send 10 packets. Configure the i...
Page 641
1-11 to do… use the command… remarks configure the automatic test interval frequency interval optional by default, the automatic test interval is zero seconds, indicating no automatic test will be made. Configure the probe timeout time timeout time optional by default, a probe times out in three sec...
Page 643
1-13 to do… use the command… remarks configure the destination port destination-port port-number z required in a udpprivate test z a udppublic test is a udp connection test on port 7. Use the remote-ping-server udpecho ip-address 7 command on the server to configure the listening service port; other...
Page 644
1-14 to do… use the command… remarks enable the remote-ping client function remote-ping-agent enable required by default, the remote-ping client function is disabled. Create a remote-ping test group and enter its view remote-ping administrator-name operation- tag required by default, no test group i...
Page 645
1-15 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the remote-ping client function remote-ping-agent enable required by default, the remote-ping client function is disabled. Create a remote-ping test group and enter its view remote-ping administrator-name operation- tag requ...
Page 646
1-16 configuration procedure z configure remote-ping client (switch a): # enable the remote-ping client. System-view [sysname] remote-ping-agent enable # create a remote-ping test group, setting the administrator name to administrator and test tag to icmp. [sysname] remote-ping administrator icmp # ...
Page 647
1-17 5 3 1 0 2000-04-02 20:55:12.2 for detailed output description, see the corresponding command manual. Dhcp test network requirements both the remote-ping client and the dhcp server are 4200g ethernet switches. Perform a remote-ping dhcp test between the two switches to test the time required for...
Page 648
1-18 remote-ping entry(admin administrator, tag dhcp) test result: send operation times: 10 receive response times: 10 min/max/average round trip time: 1018/1037/1023 square-sum of round trip time: 10465630 last complete test time: 2000-4-3 9:51:30.9 extend result: sd maximal delay: 0 ds maximal del...
Page 649
1-19 network diagram figure 1-4 network diagram for the ftp test configuration procedure z configure ftp server (switch b): configure ftp server on switch b. For specific configuration of ftp server, refer to the ftp-sftp-tftp part of the manual. Z configure remote-ping client (switch a): # enable t...
Page 650
1-20 [sysname-remote-ping-administrator-ftp] display remote-ping results administrator ftp remote-ping entry(admin administrator, tag ftp) test result: destination ip address:10.2.2.2 send operation times: 10 receive response times: 10 min/max/average round trip time: 3245/15891/12157 square-sum of ...
Page 651
1-21 network diagram figure 1-5 network diagram for the http test configuration procedure z configure http server: use windows 2003 server as the http server. For http server configuration, refer to the related instruction on windows 2003 server configuration. Z configure remote-ping client (switch ...
Page 652
1-22 system busy operation number: 0 connection fail number: 0 operation sequence errors: 0 drop operation number: 0 other operation errors: 0 http result: dns resolve time: 0 http operation time: 675 dns resolve min time: 0 http test total time: 748 dns resolve max time: 0 http transmission success...
Page 653
1-23 network diagram figure 1-6 network diagram for the jitter test configuration procedure z configure remote-ping server (switch b): # enable the remote-ping server and configure the ip address and port to listen on. System-view [sysname] remote-ping-server enable [sysname] remote-ping-server udpe...
Page 654
1-24 last complete test time: 2000-4-2 8:14:58.2 extend result: sd maximal delay: 10 ds maximal delay: 10 packet lost in test: 0% disconnect operation number: 0 operation timeout number: 0 system busy operation number: 0 connection fail number: 0 operation sequence errors: 0 drop operation number: 0...
Page 655
1-25 network diagram figure 1-7 network diagram for the snmp test configuration procedure z configure snmp agent (switch b): # start snmp agent and set snmp version to v2c, read-only community name to public, and read-write community name to private. System-view [sysname] snmp-agent [sysname] snmp-a...
Page 656
1-26 # start the test. [sysname-remote-ping-administrator-snmp] test-enable # display test results [sysname-remote-ping-administrator-snmp] display remote-ping results administrator snmp remote-ping entry(admin administrator, tag snmp) test result: destination ip address:10.2.2.2 send operation time...
Page 657
1-27 configuration procedure z configure remote-ping server (switch b): # enable the remote-ping server and configure the ip address and port to listen on. System-view [sysname] remote-ping-server enable [sysname] remote-ping-server tcpconnect 10.2.2.2 8000 z configure remote-ping client (switch a):...
Page 658
1-28 [sysname-remote-ping-administrator-tcpprivate] display remote-ping history administrator tcpprivate remote-ping entry(admin administrator, tag tcpprivate) history record: index response status lastrc time 1 4 1 0 2000-04-02 08:26:02.9 2 5 1 0 2000-04-02 08:26:02.8 3 4 1 0 2000-04-02 08:26:02.8 ...
Page 659
1-29 [sysname-remote-ping-administrator-udpprivate] test-type udpprivate # configure the ip address of the remote-ping server as 10.2.2.2. [sysname-remote-ping-administrator-udpprivate] destination-ip 10.2.2.2 # configure the destination port on the remote-ping server. [sysname-remote-ping-administr...
Page 660
1-30 dns test network requirements an switch 4200g serves as the remote-ping client, and a pc serves as the dns server. Perform a remote-ping dns test between the switch and the dns server to test the time required from the client sends a dns request to it receives a resolution result from the dns s...
Page 661
1-31 min/max/average round trip time: 6/10/8 square-sum of round trip time: 756 last complete test time: 2006-11-28 11:50:40.9 extend result: sd maximal delay: 0 ds maximal delay: 0 packet lost in test: 0% disconnect operation number: 0 operation timeout number: 0 system busy operation number: 0 con...
Page 662: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 poe configuration ·····································································································································1-1 poe overview ··············································································································...
Page 663: Poe Configuration
1-1 1 poe configuration when configuring poe, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z poe overview z poe configuration z poe configuration example poe overview introduction to poe power over ethernet (poe)-enabled devices use twisted pairs through electrical ports to supply pow...
Page 664: Poe Configuration
1-2 z each ethernet electrical port can supply at most a power of 15,400 mw to a pd. Z when ac power input is adopted for the switch, the maximum total power that can be provided is 300 w. The switch can determine whether to supply power to the next remote pd it detects depending on its available po...
Page 665
1-3 enabling the poe feature on a port follow these steps to enable the poe feature on a port: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter ethernet port view interface interface-type interface-number — enable the poe feature on a port poe enable required z by default, the p...
Page 666
1-4 more than one port has the same lowest priority, the switch will power down the pd connected to the port with larger port number. Z manual : when the switch is close to its full load in supplying power, it will not make change to its original power supply status based on its priority when a new ...
Page 667
1-5 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the pd compatibility detection function poe legacy enable required disabled by default. Configuring a pd disconnection detection mode to detect the pd connection with pse, poe provides two detection modes: ac detection and dc...
Page 668
1-6 z when the internal temperature of the switch decreases from x (x>65°c, or x>149°f) to y (60°c≤y ports. Z when the internal temperature of the switch increases from x (x (60°c ports. Upgrading the pse processing software online the online upgrading of pse processing software can update the proce...
Page 669: Poe Configuration Example
1-7 displaying poe configuration to do… use the command… remarks display the current pd disconnection detection mode of the switch display poe disconnect display the poe status of a specific port or all ports of the switch display poe interface [ interface-type interface-number ] display the poe pow...
Page 670
1-8 configuration procedure # upgrade the pse processing software online. System-view [switcha] poe update refresh 0290_021.S19 # enable the poe feature on gigabitethernet 1/0/1, and set the poe maximum output power of gigabitethernet 1/0/1 to 12,000 mw. [switcha] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [sw...
Page 671: Poe Profile Configuration
2-1 2 poe profile configuration when configuring poe profile, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to poe profile z poe profile configuration z displaying poe profile configuration z poe profile configuration example introduction to poe profile on a large-sized ...
Page 673
2-3 poe profile configuration example poe profile application example network requirements switch a is a switch 4200g supporting poe. Gigabitethernet 1/0/1 through gigabitethernet 1/0/10 of switch a are used by users of group a, who have the following requirements: z the poe function can be enabled ...
Page 674
2-4 # in profile 1, add the poe policy configuration applicable to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 through gigabitethernet 1/0/5 ports for users of group a. [switcha-poe-profile-profile1] poe enable [switcha-poe-profile-profile1] poe mode signal [switcha-poe-profile-profile1] poe priority critical [switcha-po...
Page 675: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 smart link configuration ·························································································································1-1 smart link overview ············································································································...
Page 676: Smart Link Configuration
1-1 1 smart link configuration when configuring smart link, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z smart link overview z configuring smart link z displaying and maintaining smart link z smart link configuration example smart link overview as shown in figure 1-1 , dual-uplink n...
Page 677
1-2 slave port the slave port can be either an ethernet port or a manually-configured or static lacp aggregation group. For example, you can configure gigabitethernet 1/0/2 of switch a in figure 1-1 as the slave port through the command line. Flush message when a forwarding link fails, the device wi...
Page 678: Configuring Smart Link
1-3 operating mechanism of smart link figure 1-2 network diagram of smart link operating mechanism as shown in figure 1-2 , gigabitethernet 1/0/1 on switch a is active and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 on switch a is blocked. When the link connected to gigabitethernet 1/0/1 fails, gigabitethernet 1/0/1 is b...
Page 679
1-4 task remarks create a smart link group add member ports to the smart link group configuring a smart link device enable the function of sending flush messages in the specified control vlan required configuring associated devices enable the function of processing flush messages received from the s...
Page 680
1-5 to do… use the command… remarks enable the function of sending flush messages in the specified control vlan flush enable control-vlan vlan-id optional by default, no control vlan for sending flush messages is specified. Configuring associated devices an associated device mentioned in this docume...
Page 681
1-6 6) when you copy a port, the smart link/monitor link group member information configured on the port will not be copied to other ports. 7) if a single port is specified as a member of a smart link/monitor link group, you cannot execute the lacp enable command on this port or add this port into o...
Page 682
1-7 network diagram figure 1-3 network diagram for smart link configuration configuration procedure 1) configure a smart link group on switch a and configure member ports for it. Enable the function of sending flush messages in control vlan 1. # enter system view. System-view # enter ethernet port v...
Page 683
1-8 # enter system view. System-view # enable the function of processing flush messages received from vlan 1 on gigabitethernet 1/0/2. Smart-link flush enable control-vlan 1 port gigabitethernet 1/0/2 3) enable the function of processing flush messages received from vlan 1 on switch d. # enter syste...
Page 684: Monitor Link Configuration
2-1 2 monitor link configuration when configuring monitor link, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to monitor link z configuring monitor link z displaying monitor link configuration z monitor link configuration example introduction to monitor link monitor link...
Page 685
2-2 how monitor link works figure 2-2 network diagram for a monitor link group implementation as shown in figure 2-2 , the devices switch c and switch d are connected to the uplink device switch e. Switch c is configured with a monitor link group, where gigabitethernet 1/0/1 is the uplink port, whil...
Page 686: Configuring Monitor Link
2-3 configuring monitor link before configuring a monitor link group, you must create a monitor link group and configure member ports for it. A monitor link group consists of an uplink port and one or multiple downlink ports. The uplink port can be a manually-configured or static lacp link aggregati...
Page 687
2-4 to do… use the command… remarks monitor link group view port interface-type interface-number uplink quit interface interface-type interface-number configure the specified ethernet port as the uplink port of the monitor link group ethernet port view port monitor-link group group-id uplink configu...
Page 688
2-5 z a smart link/monitor link group with members cannot be deleted. A smart link group as a monitor link group member cannot be deleted. Z the smart link/monitor link function and the remote port mirroring function are incompatible with each other. Z if a single port is specified as a smart link/m...
Page 689
2-6 network diagram figure 2-3 network diagram for monitor link configuration block switch a switch b ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 switch c switch d switch e ge1/0/1 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/3 server ge1/0/2 ge1/0/2 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/1 ge1/0/3 ge1/0/11 ge1/0/10 pc 1 pc 4 pc 3 pc 2 configuration procedure 1) enable smart link o...
Page 690
2-7 2) enable monitor link on switch c and switch d and enable the function of processing flush messages received from vlan 1. Perform the following configuration on switch c. The operation procedure on switch d is the same as that performed on switch c. # enter system view. System-view # create mon...
Page 691: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 ipv6 configuration·····································································································································1-1 ipv6 overview ·············································································································...
Page 692: Ipv6 Configuration
1-1 1 ipv6 configuration when configuring ipv6, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z ipv6 overview z ipv6 configuration task list z ipv6 configuration example z the term “router” in this document refers to a router in a generic sense or an ethernet switch running a routing p...
Page 693
1-2 figure 1-1 comparison between ipv4 header format and ipv6 header format adequate address space the source ipv6 address and the destination ipv6 address are both 128 bits (16 bytes) long. Ipv6 can provide 3.4 x 10 38 addresses to completely meet the requirements of hierarchical address division a...
Page 694
1-3 enhanced neighbor discovery mechanism the ipv6 neighbor discovery protocol is implemented by a group of internet control message protocol version 6 (icmpv6) messages. The ipv6 neighbor discovery protocol manages message exchange between neighbor nodes (nodes on the same link). The group of icmpv...
Page 695
1-4 z multicast address: an identifier for a set of interfaces (typically belonging to different nodes), similar to an ipv4 multicast address. A packet sent to a multicast address is delivered to all interfaces identified by that address. Z anycast address: an identifier for a set of interfaces (typ...
Page 696
1-5 z unassigned address: the unicast address :: is called the unassigned address and may not be assigned to any node. Before acquiring a valid ipv6 address, a node may fill this address in the source address field of an ipv6 packet, but may not use it as a destination ipv6 address. Multicast addres...
Page 697
1-6 introduction to ipv6 neighbor discovery protocol the ipv6 neighbor discovery protocol (ndp) uses five types of icmpv6 messages to implement the following functions: z address resolution z neighbor unreachability detection z duplicate address detection z router/prefix discovery z address autoconf...
Page 698
1-7 address resolution similar to the arp function in ipv4, a node acquires the link-layer address of neighbor nodes on the same link through ns and na messages. Figure 1-3 shows how node a acquires the link-layer address of node b. Figure 1-3 address resolution the address resolution procedure is a...
Page 699
1-8 figure 1-4 duplicate address detection the duplicate address detection procedure is as follows: 1) node a sends an ns message whose source address is the unassigned address :: and the destination address is the corresponding solicited-node multicast address of the ipv6 address to be detected. Th...
Page 700: Ipv6 Configuration Task List
1-9 z rfc 3513: internet protocol version 6 (ipv6) addressing architecture z rfc 3596: dns extensions to support ip version 6 ipv6 configuration task list complete the following tasks to configure ipv6: task remarks configuring an ipv6 unicast address required configuring ipv6 ndp optional configuri...
Page 702
1-11 configuring ipv6 ndp configuring a static neighbor entry the ipv6 address of a neighbor node can be resolved into a link-layer address dynamically through ns and na messages or statically through manual configuration. You can configure a static neighbor entry in two ways: z mapping a vlan inter...
Page 703
1-12 follow these steps to configure the attempts to send an ns message for duplicate address detection: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enter vlan interface view interface interface-type interface-number — configure the attempts to send an ns message for duplicate ad...
Page 704
1-13 to do… use the command… remarks configure a static ipv6 route ipv6 route-static ipv6-address prefix-length [ interface-type interface-number] nexthop-address required by default, no static ipv6 route is configured. Configuring ipv6 tcp properties the ipv6 tcp properties you can configure includ...
Page 706
1-15 to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable the dynamic domain name resolution function dns resolve required disabled by default. Configure an ipv6 dns server dns server ipv6 ipv6-address [ interface-type interface-number ] required if the ipv6 address of the dns serv...
Page 707: Ipv6 Configuration Example
1-16 to do… use the command… remarks display the statistics of ipv6 packets and ipv6 icmp packets display ipv6 statistics display the statistics of ipv6 tcp packets display tcp ipv6 statistics display the ipv6 tcp connection status display tcp ipv6 status display the statistics of ipv6 udp packets d...
Page 708
1-17 configuration procedure 1) configure switch a. # configure an automatically generated link-local address for the interface vlan-interface 2. System-view [switcha] interface vlan-interface 2 [switcha-vlan-interface2] ipv6 address auto link-local # configure an eui-64 address for the interface vl...
Page 709
1-18 2001::20f:e2ff:fe00:1, subnet is 2001::/64 3001::2, subnet is 3001::/64 joined group address(es): ff02::1:ff00:2 ff02::1:ff00:1 ff02::1 mtu is 1500 bytes nd dad is enabled, number of dad attempts: 1 nd reachable time is 30000 milliseconds nd retransmit interval is 1000 milliseconds hosts use st...
Page 710
1-19 bytes=56 sequence=3 hop limit=255 time = 60 ms reply from 2001::20f:e2ff:fe00:1 bytes=56 sequence=4 hop limit=255 time = 60 ms reply from 2001::20f:e2ff:fe00:1 bytes=56 sequence=5 hop limit=255 time = 60 ms --- 2001::20f:e2ff:fe00:1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) receiv...
Page 711: Configuring Ipv6 Application
2-1 2 ipv6 application configuration when configuring ipv6 application, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introduction to ipv6 application z configuring ipv6 application z ipv6 application configuration example z troubleshooting ipv6 application introduction to ipv6 appli...
Page 712
2-2 ipv6 traceroute the traceroute ipv6 command is used to record the route of ipv6 packets from source to destination, so as to check whether the link is available and determine the point of failure. Figure 2-1 traceroute process as figure 2-1 shows, the traceroute process is as follows: z the sour...
Page 714
2-4 displaying and maintaining ipv6 telnet to do… use the command… remarks display the use information of the users who have logged in display users [ all ] available in any view ipv6 application configuration example ipv6 applications network requirements in figure 2-3 , swa, swb, and swc are three...
Page 715
2-5 bytes=56 sequence=2 hop limit=64 time = 31 ms reply from 3003::1 bytes=56 sequence=3 hop limit=64 time = 31 ms reply from 3003::1 bytes=56 sequence=4 hop limit=64 time = 31 ms reply from 3003::1 bytes=56 sequence=5 hop limit=64 time = 31 ms --- 3003::1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted...
Page 716
2-6 z use the display ipv6 interface command to determine the interfaces of the source and the destination and the link-layer protocol between them are up. Z use the display ipv6 route-table command to verify that the destination is reachable. Z use the ping ipv6 -t timeout { destination-ipv6-addres...
Page 717: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 udp helper configuration ························································································································1-1 introduction to udp helper ······································································································...
Page 718: Udp Helper Configuration
1-1 1 udp helper configuration when configuring udp helper, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z introductiontoudphelper z configuring udp helper z displaying and maintaining udp helper z udp helper configuration example introduction to udp helper sometimes, a host needs to ...
Page 719: Configuring Udp Helper
1-2 protocol udp port number tftp (trivial file transfer protocol) 69 time service 37 configuring udp helper follow these steps to configure udp helper: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable udp helper udp-helper enable required disabled by default. Specify a udp por...
Page 720
1-3 to do… use the command… remarks clear statistics about packets forwarded by udp helper reset udp-helper packet available in user view udp helper configuration example cross-network computer search through udp helper network requirements pc a resides on network segment 192.168.1.0/24 and pc b on ...
Page 721: Table of Contents
I table of contents 1 access management configuration ········································································································1-1 access management overview ··············································································································1...
Page 722: Access Management Overview
1-1 1 access management configuration when configuring access management, go to these sections for information you are interested in: z access management overview z configuring access management z access management configuration examples access management overview normally, client pcs in a network a...
Page 723
1-2 configuring access management follow these steps to configure access management: to do… use the command… remarks enter system view system-view — enable access management function am enable required by default, the system disables the access management function. Enable access management trap am t...
Page 724
1-3 z allow the pcs of organization 1 to access the external network through gigabitethernet 1/0/1 on switch a. The port belongs to vlan 1, and the ip address of vlan-interface 1 is 202.10.20.200/24. Z disable the pcs that are not of organization 1 (pc 2 and pc 3) from accessing the external network...
Page 725
1-4 z allow the pcs of organization 1 to access the external network through gigabitethernet 1/0/1 of switch a. Z allow the pcs of organization 2 to access the external network through gigabitethernet 1/0/2 of switch a. Z gigabitethernet 1/0/1 and gigabitethernet 1/0/2 belong to vlan 1. The ip addre...
Page 726
1-5 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] port isolate [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/1] quit # configure the access management ip address pool on gigabitethernet 1/0/2. [sysname] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [sysname-gigabitethernet1/0/2] am ip-pool 202.10.20.25 26 202.10.20.55 11 # add gigabitethernet 1/...
Page 727: Table of Contents
I table of contents appendix a acronyms ································································································································ a-1.
Page 728: Appendix A Acronyms
A-1 appendix a acronyms a aaa authentication, authorization and accounting abr area border router acl access control list arp address resolution protocol as autonomous system asbr autonomous system border router b bdr backup designated router c car committed access rate cli command line interface co...
Page 729
A-2 l lsa link state advertisement lsdb link state database m mac medium access control mib management information base n nbma non broadcast multiaccess nic network information center nms network management system nvram nonvolatile ram o ospf open shortest path first p pim protocol independent multi...
Page 730
A-3 vod video on demand w wrr weighted round robin x xid exchange identification xrn expandable resilient networking.