- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- 5500 SI - Switch - Stackable
- Configuration Manual
3Com 5500 SI - Switch - Stackable Configuration Manual
Summary of 5500 SI - Switch - Stackable
Page 1
3com ® switch 5500 family configuration guide switch 5500-si switch 5500-ei switch 5500g-ei www.3com.Com part number: 10014922 rev. Ac published: december 2006.
Page 2
3com corporation 350 campus drive marlborough, ma usa 01752-3064 copyright © 2006, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without writt...
Page 3: Ontents
3 c ontents c ontents a bout t his g uide organization of the manual 21 intended readership 22 conventions 22 related manuals 23 1 g etting s tarted product overview 25 xrn overview 26 major technologies 26 typical networking topology 26 product features 27 logging in to the switch 29 setting up con...
Page 4
4 c hapter : c ontents displaying port configuration information in brief 67 ethernet port configuration example 67 ethernet port troubleshooting 68 link aggregation configuration 68 link aggregation configuration 71 displaying and debugging link aggregation 74 link aggregation configuration example...
Page 5
5 protocol-based vlan configuration 100 configuring protocol-based vlans 100 displaying the information about protocol-based vlans 101 voice vlan configuration 102 voice vlan configuration 102 displaying and debugging of voice vlan 106 voice vlan configuration example 106 creating vlans in batches 1...
Page 6
6 c hapter : c ontents 10 dhcp s erver c onfiguration introduction to dhcp server 125 usage of dhcp server 125 dhcp fundamentals 125 dhcp packet processing modes 127 dhcp address pool 127 global address pool-based dhcp server configuration 128 configuration overview 128 enabling dhcp 128 configuring...
Page 7
7 12 vrrp c onfiguration vrrp overview 151 virtual router overview 152 introduction to backup group 153 vrrp configuration 155 configuring a virtual router ip address 155 configuring backup group-related parameters 156 displaying and clearing vrrp information 157 vrrp configuration example 157 singl...
Page 8
8 c hapter : c ontents introduction to the protection functions 185 prerequisites 186 configuring bpdu protection 187 configuring root protection 187 configuring loop prevention 188 configuring tc-bpdu attack prevention 188 bpdu tunnel configuration 188 introduction to bpdu tunnel 188 configuring bp...
Page 9
9 displaying and debugging rip 233 example: typical rip configuration 233 troubleshooting rip 234 ospf configuration 235 calculating ospf routes 235 basic concepts related to ospf 236 configuring ospf 237 displaying and debugging ospf 253 254 example: configuring dr election based on ospf priority 2...
Page 10
10 c hapter : c ontents option 82 supporting configuration 288 prerequisites 288 enabling option 82 supporting on a dhcp relay 288 option 82 supporting configuration example 289 introduction to dhcp snooping 290 dhcp snooping configuration 291 configuration example 292 introduction to dhcp accountin...
Page 11
11 displaying multicast mac address configuration 324 multicast source deny configuration 325 clearing mfc forwarding entries or statistics information 325 clearing route entries from the core multicast routing table 325 displaying and debugging common multicast configuration 326 internet group mana...
Page 12
12 c hapter : c ontents applying qos profile to the port 374 qos profile configuration example 374 acl control configuration 376 configuring acl for telnet users 376 defining acl 376 importing acl 377 configuration example 377 configuring acl for snmp users 377 configuration example 379 configuring ...
Page 13
13 configuring timers 398 enabling/disabling a quiet-period timer 399 802.1x client version checking configuration 399 enabling the 802.1x client version checking function 399 configuring the maximum number of retires to send version checking request packets 399 configuring the version checking time...
Page 14
14 c hapter : c ontents configuring user re-authentication at reboot 425 configuration example for user re-authentication at reboot 425 setting the radius packet encryption key 425 tag vlan assignment on trunk/hybrid port supported by 802.1x authentication 426 identifier authentication method attrib...
Page 15
15 mac address table management 451 mac address table configuration 452 displaying mac address table 454 mac address table management display example 454 mac address table management configuration example 455 device management 456 device management configuration 456 device management configuration e...
Page 16
16 c hapter : c ontents configure ntp broadcast mode 502 configure ntp multicast mode 504 configure authentication-enabled ntp server mode 505 ssh terminal services 506 configuring ssh server 507 setting system protocol 507 configuring ssh client 510 ssh configuration example 515 file system configu...
Page 17
17 26 rstp c onfiguration stp overview 539 implement stp 539 configuration bpdu forwarding mechanism in stp 543 implement rstp on the switch 543 rstp configuration 544 enable/disable rstp on a switch 547 enable/disable rstp on a port 547 configure rstp operating mode 548 configure the stp-ignore att...
Page 18
18 c hapter : c ontents network management operation logging configuration 569 displaying and debugging snmp 570 snmp configuration example 570 reading usmusr table configuration example 571 29 s ource ip a ddress c onfiguration configuring source ip address for service packets 573 displaying the so...
Page 19
19 32 c lustering clustering overview 601 switch roles 602 introduction to ndp 603 introduction to ntdp 603 introduction to cluster roles 604 management device configuration 605 enabling system and port ndp 605 configuring ndp parameters 605 enabling system and port ntdp 605 configuring ntdp paramet...
Page 20
20 c hapter : c ontents b radius s erver and radius c lient s etup setting up a radius server 627 configuring microsoft ias radius 627 configuring funk radius 652 configuring freeradius 656 setting up the radius client 658 windows 2000 built-in client 658 windows xp built-in client 658 aegis client ...
Page 21: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide provides information about configuring your network using the commands supported on the 3com ® switch 5500 family. The descriptions in this guide apply to the switch 5500-si and switch 5500-ei. Differences between the models are noted in the text. Organization of the m...
Page 22
22 a bout t his g uide ■ acl by radius—details acl by raduis configuration. ■ auto detect—details auto detect configuration. ■ rstp—details spanning tree protocol configuration. ■ poe—details poe profile configuration. ■ snmp—details simple network management protocol configuration. ■ source ip addr...
Page 23
Related manuals 23 related manuals the 3com switch 5500 family getting started guide provides information about installation. The 3com switch 5500 family command reference guide provides all the information you need to use the configuration commands. Variable command text this typeface indicates the...
Page 24
24 a bout t his g uide.
Page 25: Etting
1 g etting s tarted this chapter covers the following topics: ■ product overview ■ xrn overview ■ product features ■ logging in to the switch ■ command line interface ■ user interface configuration product overview the switch 5500 family are layer 3 switching products supporting expandable resilient...
Page 26
26 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted the switch 5500 family supports the following services: ■ internet broadband access ■ man (metropolitan area network), enterprise/campus networking ■ multicast service, multicast routing, and audio and video multicast service. Xrn overview with the xrn (expandable re...
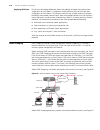
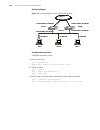
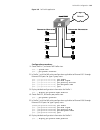
Page 27
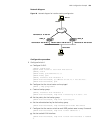
Product features 27 figure 1 networking topology with xrn product features table 4 describes the features: unit 2 unit 1 unit3 unit 4 fabric server core switches workgroup switches desktop pcs table 4 function features features description port 802.1d learning static mac (unicast/multicast) jumbo fr...
Page 28
28 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted multicast internet group management protocol (igmp) snooping multicast vlan registration (mvr) internet group management protocol (igmp) (ei models only) protocol-independent multicast-dense mode (pim-dm) (ei models only) protocol-independent multicast-sparse mode (p...
Page 29
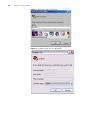
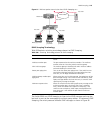
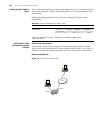
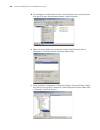
Logging in to the switch 29 logging in to the switch this section describes how to log in to the switch. Setting up configuration environment through the console port perform the following procedure to set up the configuration environment through the console port. 1 to set up the local configuration...
Page 30
30 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted figure 3 setting up a new connection figure 4 configuring the port for connection.
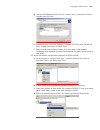
Page 31
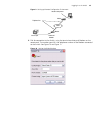
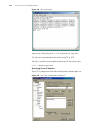
Logging in to the switch 31 figure 5 setting communication parameters 3 the switch is powered on and it displays self-test information. Press to show the command line prompt such as . 4 enter a command to configure the switch or view the operation state. Enter a ? To view online help. For details of...
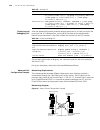
Page 32
32 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted figure 6 setting up the configuration environment through telnet 3 run telnet on the pc and enter the ip address of the vlan connected to the network port on the pc. Figure 7 running telnet 4 the terminal displays login authentication and prompts the user to enter th...
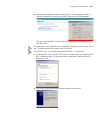
Page 33
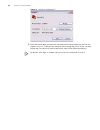
Logging in to the switch 33 figure 8 providing telnet client service 1 authenticate the telnet user through the console port on the telnet server (a switch) before login. By default, the password is required to authenticate telnet users and to enable them to log on to the switch. If a user logs in t...
Page 34
34 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted 2 perform the following configurations on the modem that is directly connected to the switch. (you are not required to configure the modem connected to the terminal.) at&f-------------------reset modem factory settings ats0=1-----------------set auto response (ring o...
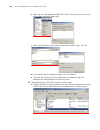
Page 35
Logging in to the switch 35 figure 9 setting up remote configuration environment 4 dial for connection to the switch, using the terminal emulator and modem on the remote end. The number you dial is the telephone number of the modem connected to the switch. See figure 10 and figure 11. Figure 10 sett...
Page 36
36 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted figure 11 dialing on the remote pc 5 enter the preset login password on the remote terminal emulator and wait for the prompt . Then you can configure and manage the switch. Enter ? To view online help. For details of specific commands, refer to the following chapters...
Page 37
Command line interface 37 command line interface the switch 5500 family provide a series of configuration commands and command line interfaces for configuring and managing the switch. The command line interface has the following characteristics: ■ local configuration through the console port. ■ loca...
Page 39
Command line interface 39 vlan interface view configure ip interface parameters for a vlan or a vlan aggregation [sw5500-vlan-interface1] enter interface vlan-interface 1 in system view quit returns to system view return returns to user view local-user view configure local user parameters [sw5500-lu...
Page 40
40 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted features and functions of command line command line help the command line interface provides full and partial online help. You can get help information through the online help commands, which are described below: 1 enter ? In any view to get all the commands in that ...
Page 41
Command line interface 41 displaying characteristics of the command line the command line interface provides a pausing function. If the information to be displayed exceeds one screen, users have three choices, as shown in table 6. History command the command line interface provides a function simila...
Page 42
42 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted editing characteristics of command line the command line interface provides basic command editing and supports the editing of multiple lines. A command cannot be longer than 256 characters. See table 9. User interface configuration user interface configuration is ano...
Page 43
User interface configuration 43 to number the user interface by relative number, represented by interface + number assigned to each type of user interface: ■ aux user interface = aux 0. ■ the first vty interface = vty 0, the second one = vty 1, and so on. User interface configuration tasks for confi...
Page 44
44 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted configuring the attributes of aux (console) port use the speed , flow control , parity , stop bit , and data bit commands to configure these attributes of the aux (console) port. Perform the following configurations in user interface (aux user interface only) view. C...
Page 45
User interface configuration 45 configuring the terminal attributes the following commands can be used for configuring the terminal attributes, including enabling/disabling terminal service, disconnection upon timeout, lockable user interface, configuring terminal screen length, and history command ...
Page 46
46 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted setting the screen length if a command displays more than one screen of information, you can use the following command to set how many lines to be displayed in a screen, so that the information can be separated in different screens and you can view it more convenient...
Page 47
User interface configuration 47 perform the following configuration in user interface view. Configure for password authentication when a user logs in through a vty 0 user interface and set the password to 3com. [sw5500]user-interface vty 0 [sw5500-ui-vty0]authentication-mode password [sw5500-ui-vty0...
Page 48
48 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted by default, the specified logged-in user can access the commands at level 1. Setting the command level used after a user logs in from a user interface you can use the following command to set the command level after a user logs in from a specific user interface, so t...
Page 49
User interface configuration 49 auto-execute command the following command is used to automatically run a command after you log in. After a command is configured to be run automatically, it will be automatically executed when you log in again. This command is usually used to automatically execute th...
Page 50
50 c hapter 1: g etting s tarted.
Page 51: Ddress
2 a ddress m anagement c onfiguration introduction to address management you can easily configure the switch on which the address manage (am) feature is enabled to allow a user with the specified mac address to gain network access through the specified ip address in a small network, such as a campus...
Page 52
52 c hapter 2: a ddress m anagement c onfiguration perform the following operations to bind the mac address and ip address of a legal user to the specified port; no other configuration is required. Address management configuration example this section contains configuration examples. Port-based addr...
Page 53
Address management configuration example 53 to configure an address management ip address pool on gigabitethernet 1/0/1, allowing 20 ip addresses starting from 202.10.20.1 to 202.10.20.20 to access the network, enter the following: [s5500] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 [s5500-gigabitethernet 1/0/1...
Page 54
54 c hapter 2: a ddress m anagement c onfiguration.
Page 55: Ort
3 p ort o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ethernet port configuration introduction ■ link aggregation configuration ■ global broadcast suppression feature ■ configuring vct ■ global broadcast suppression feature ■ displaying port configuration information in brief ■ displaying i...
Page 56
56 c hapter 3: p ort o peration entering ethernet port view before configuring an ethernet port, enter ethernet port view. Perform the following configuration in system view. Enabling/disabling an ethernet port use the following command to disable or enable the port. After configuring the related pa...
Page 57
Ethernet port configuration introduction 57 duplex and can be configured to operate in full (full duplex) or auto (auto-negotiation) mode. The port defaults to auto (auto-negotiation) mode. Setting speed on the ethernet port use the following command to set the speed of the ethernet port. If the spe...
Page 58
58 c hapter 3: p ort o peration permitting/forbidding jumbo frames to pass through an ethernet port an ethernet port may encounter jumbo frames exceeding the standard frame length, when switching large throughput data like transmitting files. This command can forbid or permit jumbo frames to pass th...
Page 59
Ethernet port configuration introduction 59 perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. By default, the port is access port. Note that: ■ you can configure four types of ports concurrently on the same switch, but you cannot switch port type between trunk port, hybrid port and stack po...
Page 60
60 c hapter 3: p ort o peration can configure to tag some vlan packets, based on which the packets can be processed differently. Setting the default vlan id for the ethernet port because the access port can only be included in one vlan, its default vlan is the one to which it belongs. Because a hybr...
Page 61
Ethernet port configuration introduction 61 loopback detection function for a port is enabled only when the loopback-detection enable command is enabled under both system view and port view. When the undo loopback-detection enable command is used under system view, the loopback detection function wi...
Page 62
62 c hapter 3: p ort o peration by default, port loopback detection and the loopback detection control function on trunk and hybrid ports are disabled. The detection interval is 30 seconds, and the system detects the default vlan on the trunk and hybrid ports. Configuring vct you can start the virtu...
Page 63
Ethernet port configuration introduction 63 authenticated devices can obtain data frames from the port so as to prevent illegal devices from filching network data. 2 intrusion protection: by way of checking the source mac addresses of the data frames received on a port, this feature discovers illega...
Page 64
64 c hapter 3: p ort o peration the time set by the port-security timer disableport timer command takes effect when the disableport-temporarily mode is set by the port-security intrusion-mode command. To avoid confliction, the following limitation on the 802.1x and the mac address authentication wil...
Page 65
Ethernet port configuration introduction 65 network diagram figure 14 network diagram for port security configuration configuration procedure configure switch a as follows: 1 enter the system view. System-view 2 enable port security. [s5500] port-security enable 3 enter ethernet1/0/1 port view. [s55...
Page 66
66 c hapter 3: p ort o peration statistics. The vlan setting includes permitted vlan types, and default vlan id. The port setting includes port link type, port speed, and duplex mode. Lacp setting includes lacp enabling/disabling. Perform the following configuration in system view. Note that if the ...
Page 67
Ethernet port configuration introduction 67 displaying port configuration information in brief this s5500 version has a new command, display brief interface for you to display the port configuration information in brief, including the port type, link state, link rate, duplex attribute, link type and...
Page 68
68 c hapter 3: p ort o peration ethernet port troubleshooting fault: default vlan id configuration failed. Troubleshooting: take the following steps. 1 use the display interface or display port command to check if the port is a trunk port or a hybrid port. If it is neither, configure it as a trunk p...
Page 69
Link aggregation configuration 69 types of link aggregation the types of link aggregation are described in the following sections: ■ manual aggregation and static lacp aggregation ■ dynamic lacp aggregation manual aggregation and static lacp aggregation both manual aggregation and static lacp aggreg...
Page 70
70 c hapter 3: p ort o peration ■ the system sets to inactive state the ports with basic configurations different from that of the active port with minimum port number. Because only a defined number of ports can be supported in an aggregation group, if the active ports in an aggregation group exceed...
Page 71
Link aggregation configuration 71 ■ aggregation groups with the minimum master port numbers if they reach the equal rate with other groups after the resources are allocated to them when aggregation groups of higher priority levels appear, the aggregation groups of lower priority levels release their...
Page 72
72 c hapter 3: p ort o peration creating/deleting an aggregation group use the following command to create a manual aggregation group or static lacp aggregation group, but the dynamic lacp aggregation group is established by the system when lacp is enabled on the ports. You can also delete an existi...
Page 73
Link aggregation configuration 73 ■ port with static arp configured ■ port with 802.1x enabled. ■ you must delete the aggregation group, instead of the port, if the manual or static lacp aggregation group contains only one port. Setting/deleting the aggregation group descriptor perform the following...
Page 74
74 c hapter 3: p ort o peration perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. By default, port priority is 32768. Displaying and debugging link aggregation after the above configuration, enter the display command in any view to display the running of the link aggregation configuration, ...
Page 75
Link aggregation configuration 75 link aggregation configuration example networking requirement switch a connects switch b with three aggregation ports, numbered as ethernet1/0/1 to ethernet1/0/3, so that incoming/outgoing load can be balanced among the member ports. Networking diagram figure 16 net...
Page 76
76 c hapter 3: p ort o peration only when the three ports are configured with identical basic configuration, rate and duplex mode, can they be added into a same dynamic aggregation group after lacp is enabled on them, for load sharing. Global broadcast suppression feature this section describes how ...
Page 77
Displaying information about a specified optical port 77 displaying information about a specified optical port you can use the display transceiver-information interface command to display the following information about a specified optical port: ■ hardware type ■ interface type ■ wavelength ■ vender...
Page 78
78 c hapter 3: p ort o peration.
Page 79: Xrn C
4 xrn c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: n introduction to xrn n configuring an xrn fabric n fabric configuration example introduction to xrn several xrn switches of the same model can be interconnected to create a “fabric”, in which each switch is a unit. The ports used to int...
Page 80
80 c hapter 4: xrn c onfiguration table 60 configuring ftm the switch 5500 series: the si units supports basic xrn, that is, distributed device management (ddm) and distributed link aggregation (dla); the ei units support enhanced xrn, that is ddm, distributed resilient routing (drr). Specifying the...
Page 81
Configuring an xrn fabric 81 n if the modified unit id is an existing one, the switch prompts you to confirm if you really want to change the unit id. If you choose to change, the existing unit id is replaced and the priority is set to 5. Then you can use the fabric save-unit-id command to save the ...
Page 82
82 c hapter 4: xrn c onfiguration table 66 setting a fabric name for switches by default, the fabric name is “5500-ei”. Setting an xrn authentication mode for switches only the switches with the same fabric name and xrn authentication mode can constitute a fabric. You can use the commands in the fol...
Page 83
Rmon on xrn 83 networking diagram figure 18 networking diagram of a fabric configuration procedure configure switch a: [sw5500]change unit-id 1 to 1 [sw5500]fabric-port gigabitethernet1/0/51 enable [sw5500]fabric-port gigabitethernet1/0/52 enable [sw5500]sysname hello [hello]xrn-fabric authenticatio...
Page 84
84 c hapter 4: xrn c onfiguration if you configure the same entry in the same rom group for devices of a fabric to be different values, the entry values of all the conflicting devices will adopt that of the conflicting device with the smallest unit id when you synchronize the devices. Such a mechani...
Page 85
Peer fabric port detection 85 n if the switch can receive disc packets sent by the peer, the ftm module determines whether peer sending ports correspond to local receiving ports according to information in the packet. That is, if a disc packet received by the left port of the switch is sent by the r...
Page 86
86 c hapter 4: xrn c onfiguration reached max units analysis: the "reached max units" message indicates that the maximum number of units allowed by the current fabric is reached. You will fail to add new devices to the fabric in this case. Solution: remove the new device or existing devices in the f...
Page 87
Multiple fabric port candidates 87 a port cannot be a fabric port if the jumboframe function is enabled on the port. So make sure the jumboframe function is disabled on a port if you want to configure the port to be a fabric port. With a port group of a switch being the current fabric port group, yo...
Page 88
88 c hapter 4: xrn c onfiguration.
Page 89: Dldp C
5 dldp c onfiguration this chapter contains dldp overview, fundamentals, precautions during configuration, and configuration information. Dldp overview you may have encountered unidirectional links in networking. When a unidirectional link occurs, the local device can receive packets from the peer d...
Page 90
90 c hapter 5: dldp c onfiguration dldp provides the following features: n as a link layer protocol, it works together with the physical layer protocol to monitor the link status of a device. N while the auto-negotiation mechanism on the physical layer detects physical signals and faults; dldp ident...
Page 91
Dldp overview 91 dldp operating mode dldp can operate in two modes: normal and enhanced. Dldp implementation 1 if the link is up after dldp is enabled on the port, dldp sends dldp packets to the peer device, and analyses and processes dldp packets received from the peer device. Dldp in different sta...
Page 92
92 c hapter 5: dldp c onfiguration 2 dldp analyzes and processes received packets as follows: n in authentication mode, dldp authenticates the packets on the port, and discards those do not pass the authentication. N dldp processes the received dldp packets as follows: 3 if no echo packet is receive...
Page 93
Dldp configuration 93 precautions during dldp configuration it is recommended that the following precautions be taken during dldp configuration: n dldp works only when the link is up. N to ensure unidirectional links can be detected, you should make sure: dldp is enabled on both ends, and the time i...
Page 94
94 c hapter 5: dldp c onfiguration when you use the dldp enable/dldp disable command in system view to enable/disable dldp globally on all optical ports of the switch, this command is only valid for existing optical ports on the device, it is not valid for those added subsequently. Dldp can operate ...
Page 95
Dldp configuration example 95 network diagram figure 21 fiber cross-connection figure 22 correct connection/disconnection in one direction configuration procedure 1 1configure switcha a configure the ports to work in mandatory full duplex mode system-view [s5500a] interface gigabitethernet 2/0/3 [s5...
Page 96
96 c hapter 5: dldp c onfiguration e set the dldp handling mode for unidirectional links to auto [s5500a] dldp unidirectional-shutdown auto f display the dldp status on switch a [s5500a] display dldp 2 if the fibers are correctly connected between the two switches, the system displays the connection...
Page 97: Vlan O
6 vlan o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ vlan configuration ■ voice vlan configuration vlan configuration this chapter describes how to configure a vlan vlan overview a virtual local area network (vlan) creates logical groups of lan devices into segments to implement virtual wor...
Page 98
98 c hapter 6: vlan o peration adding ethernet ports to a vlan use the following command to add ethernet ports to a vlan. Perform the following configuration in vlan view. By default, the system adds all the ports to a default vlan, whose id is 1. Note that you can add/delete a trunk port or a hybri...
Page 99
Vlan configuration 99 shutting down/enabling the vlan interface use the following command to shut down/enable a vlan interface. Perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. The operation of shutting down or enabling the vlan interface has no effect on the up/down status of the etherne...
Page 100
100 c hapter 6: vlan o peration configuration procedure 1 create vlan 2 and enter its view. [sw5500]vlan 2 2 add ethernet1/0/1 and ethernet1/0/2 to vlan2. [sw5500-vlan2]port ethernet1/0/1 to ethernet1/0/2 3 create vlan 3 and enter its view. [sw5500-vlan2]vlan 3 4 add ethernet1/0/3 and ethernet1/0/4 ...
Page 101
Protocol-based vlan configuration 101 i. Creating a vlan protocol type table 85 lists the operations to create a vlan protocol type. As the mode llc dsap ff ssap ff and ipx raw keywords result in the same packet format, the ipx raw keyword takes precedence over the mode llc dsap ff ssap ff keyword, ...
Page 102
102 c hapter 6: vlan o peration voice vlan configuration voice vlan is specially designed for users’ voice flow, and it distributes different port precedence in different cases. The system uses the source mac of the traffic travelling through the port to identify the ip phone data flow. You can eith...
Page 103
Voice vlan configuration 103 enabling/disabling voice vlan features enable/disable the voice vlan in system view. The vlanmust already exist before you can enable voice vlan features. You cannot delete a specified vlan that has enabled voice vlan features and only one vlan can enable voice vlan at o...
Page 104
104 c hapter 6: vlan o peration enabling/disabling voice vlan security mode in security mode, the system can filter out the traffic whose source mac is not oui within the voice vlan, while the other vlans are not influenced. If security mode is disabled, the system cannot filter anything. Perform th...
Page 105
Voice vlan configuration 105 configuring a voice vlan to operate in manual mode refer to table 96 to configure a vlan in manual mode. You can enable voice vlan feature for only one vlan at a moment. A port operating in the automatic mode cannot be added to/removed from a voice vlan. When a voice vla...
Page 106
106 c hapter 6: vlan o peration displaying and debugging of voice vlan after completing the above configuration, enter the display command in any view to view the configuration and running state of voice vlan. Voice vlan configuration example networking requirements create vlan 2 as the voice vlan i...
Page 107
Creating vlans in batches 107 creating vlans in batches to improve efficiency, you can create vlans in batches by performing the operations listed in table 98. Voice vlan configuration voice vlans are vlans configured specially for voice data stream. By adding the ports with voice devices attached t...
Page 108
108 c hapter 6: vlan o peration as multiple types of ip phones exist, you need to match port mode with types of voice stream sent by ip phones, as listed in table 99t configuring the voice vlan function configuration prerequisites ■ create the corresponding vlan before configuring a voice vlan. ■ vl...
Page 109
Voice vlan configuration 109 configuring a voice vlan to operate in automatic mode voice vlan displaying and debugging refer to table 101 to display or debug a voice vlan. Voice vlan configuration example network requirements ■ create vlan 3 as a voice vlan. ■ add/remove ethernet1/0/3 port to/from t...
Page 110
110 c hapter 6: vlan o peration 3 enable the voice vlan function for the port and configure the port to operate in manual mode. [s5500-vlan3] quit [s5500] interface ethernet1/0/3 [s5500-ethernet1/0/3] voice vlan enable [s5500-ethernet1/0/3] undo voice vlan mode auto [s5500-ethernet1/0/3] quit 4 spec...
Page 111: Gvrp C
7 gvrp c onfiguration this chapter contains gvrp configuration information. Introduction to gvrp gvrp (garp vlan registration protocol) is an application of garp (generic attribute registration protocol). Gvrp is based on the work scheme of garp; it maintains dynamic vlan registration information an...
Page 112
112 c hapter 7: gvrp c onfiguration ■ leave: when a garp entity expects to unregister a piece of attribute information, it sends out a leave message. Any garp entity receives this message starts its leave timer, and unregister the attribute information after the timer times out if it does not receiv...
Page 113
Introduction to gvrp 113 gvrp packet format the gvrp packets are in the following format: figure 26 format of gvrp packets table 102 describes the packet fields in figure 26. Protocol specifications gvrp is defined in ieee 802.1q standard. Table 102 description of the packet fields field description...
Page 114
114 c hapter 7: gvrp c onfiguration gvrp configuration the gvrp configuration tasks include configuring the timers, enabling gvrp, and configuring the gvrp port registration mode. Configuration prerequisite the port on which gvrp will be enabled must be configured to the trunk port. Configuration pr...
Page 115
Gvrp configuration 115 table 104 describes the relations between the timers: configuration example network requirements you should enable gvrp on the switches to implement the dynamic registration and update of vlan information between the switches. Network diagram figure 27 network diagram for gvrp...
Page 116
116 c hapter 7: gvrp c onfiguration b configure the port ethernet1/0/2 to the trunk port, and allow all vlan packets to pass [s5500] interface ethernet1/0/2 [s5500-ethernet1/0/2] port link-type trunk [s5500-ethernet1/0/2] port trunk permit vlan all c enable gvrp on the trunk port. [s5500-ethernet1/0...
Page 117: Vlan-Vpn C
8 vlan-vpn c onfiguration this chapter contains configuration information to create vlan-vpns. Vlan-vpn overview the vlan-vpn function enables packets to be transmitted across the operators' backbone networks with vlan tags of private networks nested in those of public networks. In public networks, ...
Page 118
118 c hapter 8: vlan-vpn c onfiguration adjusting the tpid values of vlan-vpn packet tag protocol identifier (tpid) is a portion of the vlan tag field. Ieee 802.1q specifies the value of tpid to be 0x8100. Figure 30 illustrates the structure of the tag field of an ethernet frame defined by ieee 802....
Page 119
Inner vlan tag priority replication configuration 119 the vlan-vpn function is unavailable if the port has any of the protocols among gvrp, gmrp, xrn, ntdp, stp and 802.1x enabled. Inner vlan tag priority replication configuration you can configure to replicate the tag priority of the inner vlan tag...
Page 120
120 c hapter 8: vlan-vpn c onfiguration you can execute the vlan-vpn enable or vlan-vpn uplink enable command for a port, but do not execute both of the two commands for a port. When the tpid field is set to the default value (that is, 0x8100), a port can serve as an uplink port no matter whether or...
Page 121
Vlan-vpn configuration example 121 configuration procedure perform the following procedure to configure switches a and c. 1 configure switch a and switch c. As the configuration performed on switch a and switch c is the same, configuration on switch c is omitted. A configure ethernet1/0/2 port of sw...
Page 122
122 c hapter 8: vlan-vpn c onfiguration.
Page 123: Dhcp O
9 dhcp o verview introduction to dhcp with networks getting larger in size and more complicated in structure, lack of available ip addresses becomes the common situation the network administrators have to face, and network configuration becomes a tough task for the network administrators. With the e...
Page 124
124 c hapter 9: dhcp o verview dhcp ip address assignment this section contains information on dhcp ip address assignments. Ip address assignment policy currently, dhcp provides the following three ip address assignment policies to meet the requirements of different clients: ■ manual assignment. The...
Page 125: Dhcp S
10 dhcp s erver c onfiguration introduction to dhcp server this section contains configuration introduction on dhcp server. Usage of dhcp server generally, dhcp servers are used in the following networks to assign ip addresses: ■ large-sized networks, where manual configuration method bears heavy lo...
Page 126
126 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration ip address lease update after a dhcp server dynamically assigns an ip address to a dhcp client, the ip address keeps valid only within a specified lease time and will be reclaimed by the dhcp server when the lease expires. If the dhcp client wants to use ...
Page 127
Introduction to dhcp server 127 dhcp packet processing modes ■ global address pool: in response to the dhcp packets received from dhcp clients, the dhcp server picks ip addresses from its global address pools and assigns them to the dhcp clients. ■ interface address pool: in response to the dhcp pac...
Page 128
128 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration (such as domain name), you just need to configure them on the network segment or the corresponding subnets. The following is the details of configuration inheritance. ■ a newly created child address pool inherits the configurations of its parent address p...
Page 129
Global address pool-based dhcp server configuration 129 configuring global address pool mode on interface(s) you can configure the global address pool mode on the specified or all interfaces of a dhcp server. After that, when the dhcp server receives dhcp packets from dhcp clients through these inte...
Page 130
130 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration the static-bind ip-address command and the static-bind mac-address command can be executed repeatedly. In this case, the new configuration overwrites the previous one. Configuring to assign ip addresses dynamically ip addresses dynamically assigned to dhc...
Page 131
Global address pool-based dhcp server configuration 131 you can configure domain names to be used by dhcp clients for address pools. After you do this, the dhcp server provides the domain names to the dhcp clients as well while the former assigns ip addresses to the dhcp clients. Configuring netbios...
Page 132
132 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration customizing dhcp service with the evolution of dhcp, new options are constantly coming into being. You can add the new options as the properties of dhcp servers by performing the following configuration. Configuring gateway addresses for dhcp clients gate...
Page 133
Interface address pool-based dhcp server configuration 133 interfaces eases configuration work load and makes you to configure in a more convenient way. Enabling dhcp you need to enable dhcp before performing dhcp configurations. Dhcp-related configurations are valid only when dhcp is enabled. Confi...
Page 134
134 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration bound to a dhcp client to come from a special dhcp address pool that contains only the ip address. Configuring to assign ip addresses by static binding some dhcp clients, such as www servers, need to be assigned fixed ip addresses. This is achieved by bin...
Page 135
Interface address pool-based dhcp server configuration 135 the dhcp server forbidden-ip command can be executed repeatedly. That is, you can repeatedly configure ip addresses that are not dynamically assigned to dhcp clients. Configuring dns services for dhcp clients if a host accesses the internet ...
Page 136
136 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration configuring netbios services for dhcp clients for microsoft windows-based dhcp clients that communicate through netbios protocol, the host name-to-ip address translation is carried out by wins servers. So you need to perform wins-related configuration for...
Page 137
Dhcp security configuration 137 customizing dhcp service with the evolution of dhcp, new options are constantly coming into being. You can add the new options as the properties of dhcp servers by performing the following configuration. Dhcp security configuration dhcp security configuration is neede...
Page 138
138 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration receives a response or the number of the sent icmp packets reaches the specified maximum number. The dhcp server assigns the ip address to the dhcp client only when no response is received during the whole course. Such a mechanism ensures an ip address is...
Page 139
Option 184 supporting configuration 139 the sub-option 3 of option 184 comprises two parts, which carry the previously mentioned two items respectively. A flag value of 0 indicates that the voice vlan identification function is not enabled, in which case the information carried by the vlan id part w...
Page 140
140 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration configuring the option 184 supporting function in system view perform the operations listed in table 129 if you specify to assign ip addresses of an interface-based address pool to dhcp clients. This method allows you to configure the option 184 supportin...
Page 141
Option 184 supporting configuration 141 configuring the option 184 supporting function in interface view perform the operations listed in table 130 if you specify to assign ip addresses of an interface-based address pool to dhcp clients. This method allows you to configure the option 184 supporting ...
Page 142
142 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration configuring the option 184 supporting function in global dhcp address pool view perform the operations listed in table 131 if you specify to assign ip addresses of a global dhcp address pool to dhcp clients. Configuration example network requirements a 3c...
Page 143
Option 184 supporting configuration 143 network diagram figure 33 network diagram for option 184 supporting configuration configuration procedure 1 configure the dhcp client configure the 3com vcx device to operate as a dhcp client and to request for all sub-options of option 184. (omitted) 2 config...
Page 144
144 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration dhcp server displaying and debugging you can verify your dhcp-related configuration by executing the display command in any view. To clear the information about dhcp servers, execute the reset command in user view. Executing the save command will not save...
Page 145
Dhcp server configuration example 145 the dhcp settings of the 10.1.1.0/25 network segment are as follows: ■ lease time: 10 days plus 12 hours ■ domain name: aabbcc.Com ■ dns server: 10.1.1.2 ■ netbios server: none ■ gateway: 10.1.1.126 the dhcp settings of the 10.1.1.128/25 network segment are as f...
Page 146
146 c hapter 10: dhcp s erver c onfiguration 5 return to system view. [s5500-dhcp-pool-1] quit 6 configure dhcp address pool 2, including address range, domain name, dns server address, lease time, netbios server address, and gateway address. [s5500] dhcp server ip-pool 2 [s5500-dhcp-pool-2] network...
Page 147: Dhcp R
11 dhcp r elay c onfiguration introduction to dhcp relay this section contains an introduction to dhcp relay usage of dhcp relay early dhcp implementations assumes that dhcp clients and dhcp servers are on the same network segment, that is, you need to deploy at least one dhcp server for each networ...
Page 148
148 c hapter 11: dhcp r elay c onfiguration actually, a dhcp relay enables dhcp clients and dhcp servers on different networks to communicate with each other by forwarding the dhcp broadcasting packets transparently between them. Dhcp relay configuration if a switch belongs to a fabric, you need to ...
Page 149
Dhcp relay displaying 149 the group number referenced in the dhcp-server groupno command must has already been configured by using the dhcp-server groupno ip ipaddress1 [ ipaddress-list ] command. Dhcp relay displaying you can verify your dhcp relay-related configuration by executing the following d...
Page 150
150 c hapter 11: dhcp r elay c onfiguration 5 configure an ip address for vlan 2 interface, so that this interface is on the same network segment with the dhcp clients.) [s5500-vlan-interface2] ip address 10.110.1.1 255.255.0.0 you need to perform corresponding configurations on the dhcp server to e...
Page 151: Vrrp C
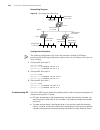
12 vrrp c onfiguration vrrp overview virtual router redundancy protocol (vrrp) is a fault-tolerant protocol. As shown in figure 37, in general, ■ a default route (for example, the next hop address of the default route is 10.100.10.1, as shown in figure 37) is configured for every host on a network. ...
Page 152
152 c hapter 12: vrrp c onfiguration figure 38 virtual router the switches in the backup group have the following features: ■ this virtual router has its own ip address: 10.100.10.1 (which can be the interface address of a switch within the backup group). ■ the switches within the backup group have ...
Page 153
Vrrp overview 153 ■ the virtual router ip addresses and the real ip addresses used by the member switches in the backup group must belong to the same network segment. If they are not in the same network segment, the backup group will be in initial state. ■ a backup group is removed if its last virtu...
Page 154
154 c hapter 12: vrrp c onfiguration configuring switch priority the status of each switch in a backup group is determined by its priority. The master switch in a backup group is the one currently with the highest priority. Switch priority ranges from 0 to 255 (a larger number indicates a higher swi...
Page 155
Vrrp configuration 155 configuring vrrp timer the master switch advertises its normal operation state to the switches within the vrrp backup group by sending vrrp packets once in each specified interval (determined by the adver-interval argument). If the backup switches do not receive vrrp packets f...
Page 156
156 c hapter 12: vrrp c onfiguration configuring backup group-related parameters table 138 lists the operations to configure a switch in a backup group. Configure a virtual router ip address vrrp vrid virtual-router-id virtual-ip virtual-address optional virtual-router-id: vrrp backup group id. Virt...
Page 157
Displaying and clearing vrrp information 157 displaying and clearing vrrp information you can execute the display command in any view to view vrrp configuration. Vrrp configuration example this section contains examples of vrrp configurations. Single-vrrp backup group configuration example network r...
Page 158
158 c hapter 12: vrrp c onfiguration configuration procedure 1 configure switch a. A configure vlan 2. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [lsw-a] vlan 2 [lsw-a-vlan2] port ethernet 1/0/6 [lsw-a-vlan2] quit [lsw-a] interface vlan-interface 2 [lsw-a-vlan-interface2] ip address 2...
Page 159
Vrrp configuration example 159 network diagram figure 40 network diagram for interface tracking configuration configuration procedure 1 configure switch a. A configure vlan 2. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [lsw-a] vlan 2 [lsw-a-vlan2] port ethernet 1/0/6 [lsw-a-vlan2] qui...
Page 160
160 c hapter 12: vrrp c onfiguration 2 configure switch b. A configure vlan 2. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [lsw-b] vlan 2 [lsw-b-vlan2] port ethernet 1/0/5 [lsw-b-vlan2] quit [lsw-b] interface vlan-interface 2 [lsw-b-vlan-interface2] ip address 202.38.160.2 255.255.255....
Page 161
Vrrp configuration example 161 network diagram figure 41 network diagram for multiple-vrrp backup group configuration configuration procedure 1 configure switch a. A configure vlan 2. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [lsw-a] vlan 2 [lsw-a-vlan2] port ethernet 1/0/6 [lsw-a-vl...
Page 162
162 c hapter 12: vrrp c onfiguration b create backup group 1. [lsw-b-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 202.38.160.111 c create backup group 2. [lsw-b-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 202.38.160.112 d set the priority for backup group 2. [lsw-b-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 2 priority 110 n...
Page 163: Mstp C
13 mstp c onfiguration mstp overview spanning tree protocol (stp) cannot enable ethernet ports to transit their states rapidly. It costs two times of the forward delay for a port to transit to the forwarding state even if the port is on a point-to-point link or is an edge port. Rapid spanning tree p...
Page 164
164 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration basic mstp terminologies figure 42 illustrates primary mstp terms (assuming that each switch in it has mstp employed). Figure 42 basic mstp terminologies mst region a multiple spanning tree (mst) region comprises multiple switches and the connected network segmen...
Page 165
Mstp overview 165 ist an internal spanning tree (ist) is a spanning tree in an mst region. Ists, along with the common spanning tree (cst), form the common and internal spanning tree (cist) of the entire switched network. An ist is a branch of cist and is a special msti. In figure 42, cist has a bra...
Page 166
166 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration the role of a region edge port is consistent with that of the port in the cist. For example, port 1 on switch a shown in figure 43 is a region edge port, and it is a master port in the cist. Therefore, it is a master port in all mstis in the region. Figure 43 por...
Page 167
Mstp overview 167 determining an msti in an mst region, mstp generates different mstis for different vlans according to vlan-to-spanning tree mappings. Mstp calculates each spanning tree independently in the same way as stp/rstp does. Implementation of stp algorithm in the beginning, each of the por...
Page 168
168 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration mstp implementation on switches mstp is compatible with both stp and rstp. That is, switches running mstp can recognize stp and rstp packets and use them to calculate spanning trees. In addition to the basic mstp functions, a s5500 series switch also provides man...
Page 169
Root bridge configuration 169 prerequisites before configuration, determine what roles the switches will play in the spanning trees, that is, whether a switch will be the root, a branch, or a leaf in a spanning tree. Configuring an mst region configuration procedure changes of mst region parameters,...
Page 170
170 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration configuration example 1 configure an mst region, with the name being info, the mstp revision level being level 1, vlan 2 through vlan 10 being mapped to msti 1, and vlan 20 through vlan 30 being mapped to msti 2. System-view system view: return to user view with ...
Page 171
Root bridge configuration 171 a secondary root bridge becomes a root bridge if the original root bridge fails or is turned off. A secondary root bridge remains unchanged if a new root bridge is configured. If you configure multiple secondary root bridges for a spanning tree instance, the one with th...
Page 172
172 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration configuration example configure the bridge priority of the current switch to be 4,096 in spanning tree instance 1. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s5500] stp instance 1 priority 4096 configuring mstp operation mode a switch running mstp...
Page 173
Root bridge configuration 173 configuration procedure note that only the maximum hop count setting configured on a switch acting as the region root limits the size of the mst region. Configuration example set the maximum hop count of the mst region to 30 on the future region root. System-view system...
Page 174
174 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration to solve this problem, mstp adopts the state transition mechanism. With this mechanism, new root ports and designated ports must go through an intermediate state to the forwarding state, so that the new bpdus can be advertised throughout the network. The introduc...
Page 175
Root bridge configuration 175 it is recommended that you specify the network diameter and the hello time by using the stp root primary or stp root secondary command. Mstp will then automatically calculate the optimal values of the three parameters. Configuration example set the forward delay to 1,60...
Page 176
176 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration configuration procedure in system view configuration procedure in ethernet port view you can configure the maximum transmission speed of ports with either of the above two methods. A too high maximum transmission speed can cause too many mstp bpdus transmitted in...
Page 177
Root bridge configuration 177 configuration procedure in system view configuration procedure in ethernet port view on a switch with bpdu protection not enabled, an edge port becomes a non-edge port again once it receives a bpdu from another port. It is recommended that you configure ethernet ports w...
Page 178
178 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration configuration procedure in system view configuration procedure in ethernet port view only the master ports of aggregation ports can be configured to connect to point-to-point link. You can configure a port to connect to point-to-point link if the port operates in...
Page 179
Root bridge configuration 179 configuration example configure ethernet1/0/1 port to connect to point-to-point link. 1 configure in system view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s5500] stp interface ethernet1/0/1 point-to-point force-true 2 configure in ethernet port view. S...
Page 180
180 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration configuration example enable mstp on the switch and disable mstp on port ethernet1/0/1. 1 configure in system view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s5500] stp enable [s5500] stp interface ethernet1/0/1 disable 2 configure in ethernet po...
Page 181
Leaf node configuration 181 configuring mstp operation mode refer to “configuring mstp operation mode”. Configuring the timeout time factor refer to “configuring the timeout time factor”. Configuring the maximum transmission speed of a port refer to “configuring the maximum transmission speed of a p...
Page 182
182 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration normally, the path cost of a port in full-duplex mode is slightly less than that of the port in half-duplex mode. When calculating the path cost of an aggregate link, the 802.1d-1998 standard does not take the number of the aggregated links into account, whereas ...
Page 183
Leaf node configuration 183 configuration example (a) configure the path cost of port ethernet1/0/1 in spanning tree instance 1 to be 2,000. 1 configure in system view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s5500] stp interface ethernet1/0/1 instance 1 cost 2000 2 configure in e...
Page 184
184 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration configuring the priority of a port in ethernet port view changes of port priorities can cause mstp to redetermine the roles of ports, resulting in state transition of ports. A lower port priority value indicates a higher port priority. If all ports of a switch ha...
Page 185
Protection functions configuration 185 configuration procedure you can perform the mcheck operation in the following two ways. Performing the mcheck operation in system view performing the mcheck operation in ethernet port view caution: execute the stp mcheck command on switches configured to operat...
Page 186
186 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration automatically shut it down and notifies the network administrator of the situation. Only the administrator can restore edge ports that are shut down. Root protection a root bridge and its secondary root bridges must reside in the same region. Particularly, a cist...
Page 187
Protection functions configuration 187 configuring bpdu protection configuration procedure configuration example enable the bpdu protection function. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s5500] stp bpdu-protection as 1000 mbps ports of an switch 5500 cannot be shut down, the bp...
Page 188
188 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration configuring loop prevention configuration procedure configuration example enable the loop prevention function on port ethernet1/0/1. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s5500] interface ethernet1/0/1 [s5500-ethernet1/0/1] stp loop-protectio...
Page 189
Bpdu tunnel configuration 189 figure 44 bpdu tunnel network hierarchy configuring bpdu tunnel notes: ■ you must enable stp on a device before enabling the bpdu tunnel function on it. ■ the bpdu tunnel function is only available to access ports. ■ to implement the bpdu tunnel function, the links betw...
Page 190
190 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration displaying and debugging mstp after completing the above configurations, you can display mstp operation and verify your configuration by executing the display command in any view. You can also clear mstp-related statistics by executing the reset command in user v...
Page 191
Mstp configuration example 191 configuration procedure 1 configure switch a. A enter mst region view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s5500] stp region-configuration b configure the mst region. [s5500-mst-region] region-name example [s5500-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [s...
Page 192
192 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration 4 configure switch d. A enter mst region view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s5500] stp region-configuration b configure the mst region. [s5500-mst-region] region-name example [s5500-mst-region] instance 1 vlan 10 [s5500-mst-region] i...
Page 193
Bpdu tunnel configuration example 193 2 configure switch b. A enable rstp. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. [s5500] stp enable b add ethernet0/1 port to vlan 10. [s5500] vlan 10 [s5500-vlan10] port ethernet 0/1 3 configure switch c. A enable mstp. System-view system view: re...
Page 194
194 c hapter 13: mstp c onfiguration f add the trunk port to all vlans. [s5500-ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan all notes: ■ you must enable stp on a device before enabling the bpdu tunnel function on it. ■ the bpdu tunnel function is only available to access ports. ■ to implement the bpdu tunn...
Page 195: Entralized
14 c entralized mac a ddress a uthentication c onfiguration introduction to centralized mac address authentication centralized mac address authentication controls accesses to a network through ports and mac addresses. This kind of authentication requires no client software. When operating in central...
Page 196
196 c hapter 14: c entralized mac a ddress a uthentication c onfiguration centralized mac address authentication configuration the following sections describe centralized mac address authentication configuration tasks: ■ enabling global/port-based centralized mac address authentication ■ setting cen...
Page 197
Centralized mac address authentication configuration 197 ■ server-timeout timer. If the connection between a switch and a radius server times out when the switch authenticates a user on one of its ports, the switch turns down the user. You can use the server-timeout timer to set the time out time. ■...
Page 198
198 c hapter 14: c entralized mac a ddress a uthentication c onfiguration 4 enable global centralized mac address authentication. [s5500] mac-authentication 5 configure the domain name for centralized mac address authentication user to be aabbcc163.Net. [s5500] mac-authentication domain aabbcc163.Ne...
Page 199: Ssh T
15 ssh t erminal s ervices ssh terminal services this section contains information for ssh terminal services. I ntroduction to ssh secure shell (ssh) can provide information security and powerful authentication to prevent such assaults as ip address spoofing, plain-text password interception when us...
Page 200
200 c hapter 15: ssh t erminal s ervices figure 48 establish ssh channels through wan the communication process between the server and client includes these five stages: 1 version negotiation stage. These operations are completed at this stage: ■ the client sends tcp connection requirement to the se...
Page 201
Ssh terminal services 201 ■ the client authenticates information from the user at the server till the authentication succeeds or the connection is turned off due to authentication timeout. Ssh supports two authentication types: password authentication and rsa authentication. 1 password authenticatio...
Page 202
202 c hapter 15: ssh t erminal s ervices configuring supported protocols when ssh protocol is specified, to ensure a successful login, you must configure the aaa authentication using the authentication-mode scheme command. The protocol inbound ssh configuration fails if you configured authentication...
Page 203
Ssh terminal services 203 configuring authentication type new users must specify authentication type. Otherwise, they cannot access the switch. If rsa authentication type is defined, then the rsa public key of the client user must be configured on the switch. By default, no authentication type is sp...
Page 204
204 c hapter 15: ssh t erminal s ervices the manual mode is rather complex since it requires format conversation with the specific software first and then manual configuration. 2 automatic mode with the command operations on the client include: ■ ssh1.5/2.0-supported client software generates random...
Page 205
Ssh terminal services 205 ssh client configuration table 186 describes ssh configuration tasks. In the initial authentication, if the ssh client does not have the public key for the server which it accesses for the first time, the client continues to access the server and save locally the public key...
Page 206
206 c hapter 15: ssh t erminal s ervices ssh server configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 49, configure a local connection from the ssh client to the switch. The pc runs the ssh 2.0-supported client software. Network diagram figure 49 network diagram for ssh server configurat...
Page 207
Ssh terminal services 207 rsa public key authentication 1 set aaa authentication on the user interfaces. [s5500] user-interface vty 0 4 [s5500-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode scheme 2 set the user interfaces to support ssh. [s5500-ui-vty0-4] protocol inbound ssh 3 configure the login protocol for the...
Page 208
208 c hapter 15: ssh t erminal s ervices network diagram figure 50 network diagram for ssh client configuration configuration procedure 1 configure the client to run the initial authentication. [s5500] ssh client first-time enable 2 configure server public keys on the client. [s5500] rsa peer-public...
Page 209
Ssh terminal services 209 b start the client and use the rsa public key authentication according to the encryption algorithm defined. [s5500] ssh2 10.165.87.136 22 perfer_kex dh_group1 perfer_ctos_cipher des perfer_ctos_hmac md5 perfer_stoc_hmac md5 username: client003 trying 10.165.87.136... Press ...
Page 210
210 c hapter 15: ssh t erminal s ervices both the private and public key must be in /home/user/ for openssh to work. Result: [root@localhost openssh-4.2p1]# ./ssh -2 -l 1 -i /home/user/ssh_rsa_key 192.168.0.131 sftp service the following sections describe sftp service. Sftp overview secure ftp (sftp...
Page 211
Sftp service 211 sftp client configuration the following sections describe sftp client configuration tasks: ■ configuring sftp client ■ enabling the sftp client ■ disabling the sftp client ■ operating with sftp directories ■ operating with sftp files configuring sftp client enabling the sftp client ...
Page 212
212 c hapter 15: ssh t erminal s ervices disabling the sftp client operating with sftp directories sftp directory-related operations include: changing or displaying the current directory, creating or deleting a directory, displaying files or information of a specific directory. Operating with sftp f...
Page 213
Sftp service 213 displaying help information you can display help information about a command, such as syntax and parameters. Sftp configuration example network requirements as shown in figure 51, ■ an ssh connection is present between switch a and switch b. ■ switch b serves as an sftp server, with...
Page 214
214 c hapter 15: ssh t erminal s ervices 2 configure switch a (sftp client) a establish a connection to the remote sftp server and enter sftp client view. [s5500] sftp 10.111.27.91 b display the current directory on the sftp server, delete file z and verify the operation. Sftp-client> dir -rwxrwxrwx...
Page 215
Sftp service 215 f upload file pu to the sftp server and rename it to puk. Verify the operations. Sftp-client> put pu puk local file: pu ---> remote file: flash:/puk uploading file successfully ended sftp-client> dir -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup 1759 aug 23 06:52 vrpcfg.Cfg -rwxrwxrwx 1 noone nogroup ...
Page 216
216 c hapter 15: ssh t erminal s ervices.
Page 217: Ip R
16 ip r outing p rotocol o peration ip routing protocol overview routers select an appropriate path through a network for an ip packet according to the destination address of the packet. Each router on the path receives the packet and forwards it to the next router. The last router in the path submi...
Page 218
218 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring the ip routing protocol is described in the following sections: ■ selecting routes through the routing table ■ routing management policy selecting routes through the routing table for a router, the routing table is the key to forwarding p...
Page 219
Ip routing protocol overview 219 figure 53 the routing table routing management policy the switch 5500 supports the configuration of a series of dynamic routing protocols such as rip and ospf, as well as static routes. The static routes configured by the user are managed together with the dynamic ro...
Page 220
220 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration supporting load sharing and route backup i. Load sharing supports multi-route mode, allowing the user to configure multiple routes that reach the same destination and use the same precedence. The same destination can be reached using multiple differe...
Page 221
Static routes 221 the following routes are static routes: ■ reachable route—the ip packet is sent to the next hop towards the destination. This is a common type of static route. ■ unreachable route—when a static route to a destination has the reject attribute, all the ip packets to this destination ...
Page 222
222 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration the parameters are explained as follows: ■ ip address and mask the ip address and mask use a decimal format. Because the 1s in the 32-bit mask must be consecutive, the dotted decimal mask can also be replaced by the mask-length which refers to the di...
Page 223
Static routes 223 displaying and debugging static routes after you configure static and default routes, execute the display command in any view to display the static route configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Example: typical static route configuration networking requirement...
Page 224
224 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration 2 configure the static route for ethernet switch b [switch b]ip route-static 1.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.3.1 [switch b]ip route-static 1.1.5.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.3.1 [switch b]ip route-static 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.3.1 3 configure the static route fo...
Page 225
Rip 225 ■ cost—the cost for the router to reach the destination, which should be an integer in the range of 0 to 16. ■ timer—the length of time from the last time that the routing entry was modified until now. The timer is reset to 0 whenever a routing entry is modified. ■ route tag—the indication w...
Page 226
226 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration ■ enabling rip to import routes of other protocols ■ configuring the default cost for the imported route ■ setting the rip preference ■ setting additional routing metrics ■ configuring route filtering enabling rip and entering the rip view perform th...
Page 227
Rip 227 3com does not recommend the use of this command, because the destination address does not need to receive two copies of the same message at the same time. Note that peer should be restricted using the following commands: rip work , rip output , rip input and network . Specifying the rip vers...
Page 228
228 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration by default, the values of the period update and timeout timers are 30 seconds and 180 seconds respectively. The value of the garbage-collection timer is four times of that of period update timer: 120 seconds. In fact, you may find that the timeout ti...
Page 229
Rip 229 in addition, the rip work command is functionally equivalent to both the rip input and rip output commands. By default, all interfaces except loopback interfaces both receive and transmit rip update packets. Disabling host route in some cases, the router can receive many host routes from the...
Page 230
230 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in interface view: the usual packet format follows rfc1723 and nonstandard follows rfc2082. Configuring split horizon split horizon means that the route received through an interface will not be sent through this i...
Page 231
Rip 231 perform the following configurations in rip view. By default, the cost value for the rip imported route is 1. Setting the rip preference each routing protocol has its own preference by which the routing policy selects the optimal route from the routes of different protocols. The greater the ...
Page 232
232 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configurations in rip view. Configuring rip to filter the received routes configuring rip to filter the distributed routes by default, rip will not filter the received and distributed routing information. ■ the filter-policy imp...
Page 233
Rip 233 traffic sharing across rip interfaces equal-cost routes are routes with the same destination but different next hop addresses in a routing table. After traffic sharing across rip interfaces is enabled, the system averagely distributes the traffic to its rip interfaces through equal-cost rout...
Page 234
234 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration networking diagram figure 55 rip configuration networking configuration procedure the following configuration only shows the operations related to rip. Before performing the following configuration, please make sure the ethernet link layer can work n...
Page 235
Ospf configuration 235 ospf configuration open shortest path first (ospf) is an interior gateway protocol based on the link state developed by ietf. Only the switch 5500-ei supports the ospf protocol. The switch 5500 uses ospf version 2 (rfc2328), which has the following features: ■ scope—supports n...
Page 236
236 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration ospf packets ospf uses five types of packets: ■ hello packet. The hello packet is the most common packet sent by the ospf protocol. A router periodically sends it to its neighbor. It contains the values of some timers, dr, bdr and the known neighbor....
Page 237
Ospf configuration 237 ■ backup designated router (bdr) if the dr fails, a new dr must be elected and synchronized with the other routers on the segment. This process will take a relatively long time, during which the route calculation is incorrect. To shorten the process, ospf creates a bdr as back...
Page 238
238 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration ■ setting the interface priority for dr election ■ configuring the peer ■ setting the interval of hello packet transmission ■ setting a dead timer for the neighboring routers ■ configuring an interval required for sending lsu packets ■ setting an int...
Page 239
Ospf configuration 239 entering ospf area view perform the following configurations in ospf view. Area_id is the id of the ospf area, which can be a decimal integer or in ip address format. Specifying the interface ospf divides the as into different areas. You must configure each ospf interface to b...
Page 240
240 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring the network type on the ospf interface the route calculation of ospf is based upon the topology of the adjacent network of the local router. Each router describes the topology of its adjacent network and transmits it to all the other rout...
Page 241
Ospf configuration 241 configuring the cost for sending packets on an interface you can control network traffic by configuring different message sending costs for different interfaces. Otherwise, ospf automatically calculates the cost according to the baud rate on the current interface. Perform the ...
Page 242
242 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in interface view: by default, the priority of the interface is 1 in the dr election. The value can be taken from 0 to 255. Configuring the peer in an nbma network, some special configurations are required. Since a...
Page 243
Ospf configuration 243 setting a dead timer for the neighboring routers if hello packets are not received from a neighboring router, that router is considered dead. The dead timer of neighboring routers refers to the interval after which a router considers a neighboring router dead. You can set a de...
Page 244
244 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration the value of interval should be bigger than the interval in which a packet can be transmitted and returned between two routers. An lsa retransmission interval that is too small will cause unnecessary retransmission. Setting a shortest path first (spf...
Page 245
Ospf configuration 245 by default, the stub area is not configured, and the cost of the default route to the stub area is 1. Configuring the nssa of ospf to keep the advantages of stub areas and simultaneously improve the networking flexibility, rfc1587 (ospf nssa option) defines a new type of area,...
Page 246
246 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration generated on the abr, even though the default route 0.0.0.0 is not in the routing table. On an asbr, however, the default type-7 lsa route can be generated only if the default route 0.0.0.0 is in the routing table. Executing the no-import-route comma...
Page 247
Ospf configuration 247 after the summarization of imported routes is configured, if the local router is an autonomous system border router (asbr), this command summarizes the imported type-5 lsas in the summary address range. When nssa is configured, this command will also summarize the imported typ...
Page 248
248 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring the ospf area to support packet authentication all the routers in an area must use the same authentication mode. In addition, all routers on the same segment must use the same authentication key password. Use the authentication-mode simpl...
Page 249
Ospf configuration 249 intra-area and inter-area routes describe the internal as topology whereas the external routes describes how to select the route to the destinations beyond the as. The external type-1 routes refer to imported igp routes (such as static route and rip). Since these routes are mo...
Page 250
250 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration by default, when importing external routes, the type of imported route is type-2, the cost is 1 and the tag is 1. The interval of importing the external route is 1 second. The upper limit to the external routes imported is 1000 per second. Configurin...
Page 251
Ospf configuration 251 configuring ospf route filtering perform the following configuration in ospf view. Configuring ospf to filter the received routes configuring ospf to filter the distributed routes by default, ospf will not filter the imported and distributed routing information. ■ the filter-p...
Page 252
252 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration disabling the interface to send ospf packets use the silent-interface command to prevent the interface from transmitting ospf packets. Perform the following configuration in ospf view. By default, all the interfaces are allowed to transmit and receiv...
Page 253
Ospf configuration 253 perform the following configuration in system view. By default, ospf trap function is disabled, so the switch does not send trap packets when any ospf process is abnormal. The configuration is valid to all ospf processes if you do not specify a process id. For detailed configu...
Page 254
254 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration display command for ospf neighbor information use the command display ospf peer statistics, which has the same display output as that of display ospf peer brief command. The display ospf peer brief command has the following fields in its display outp...
Page 255
Ospf configuration 255 the commands listed in the following examples enable switch a and switch c to be dr and bdr, respectively. The priority of switch a is 100, which is the highest on the network, so it is elected as the dr. Switch c has the second highest priority, so it is elected as the bdr. T...
Page 256
256 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration only when the current dr is offline does the dr change. Shut down switch a, and run display ospf peer command on switch d to display its neighbors. Note that the original bdr (switch c) becomes the dr, and switch b is the new bdr. If all ethernet swi...
Page 257
Ospf configuration 257 [switch b-ospf-1]area 1 [switch b-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]network 197.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [switch b-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]vlink-peer 3.3.3.3 3 configure switch c: [switch c]interface vlan-interface 1 [switch c-vlan-interface1]ip address 152.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [switch c]interface vlan-i...
Page 258
258 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration ■ ensure the backbone area connects with all other areas. ■ the virtual links cannot pass through the stub area. Troubleshooting globally: if ospf cannot discover the remote routes and you have checked all troubleshooting items listed above, check th...
Page 259
Ip routing policy 259 and the matching objects are attributes of routing information. The relationship of if-match clauses for a node uses a series of boolean “and” statements. As a result, a match is found unless all the matching conditions specified by the if-match clauses are satisfied. The apply...
Page 260
260 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration defining a route policy a route policy can include multiple nodes. Each node is a unit for the matching operation. The nodes are tested against the node_number . Perform the following configurations in system view. The permit parameter specifies that...
Page 261
Ip routing policy 261 by default, no matching is performed. The if-match clauses for a node in the route policy require that the route satisfy all the clauses to match the node before the actions specified by the apply clauses can be executed. If no if-match clauses are specified, all the routes wil...
Page 262
262 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in routing protocol view. By default, the routes discovered by other protocols will not be distributed. In different routing protocol views, the parameter options are different. For details, refer to the descriptio...
Page 263
Ip routing policy 263 by default, the filtering of received routes is not performed. Configuring the filtering of distributed routes define a policy concerning route distribution that filters the routing information that does not satisfy the conditions, and distributes routes with the help of an acl...
Page 264
264 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration stop forwarding the packet to the network. Using the following configuration tasks, you can choose to forward the broadcast packet to the network for broadcast. Perform the following configuration in system view. Displaying and debugging the routing ...
Page 265
Route capacity configuration 265 c enable ospf protocol and specifies the number of the area to which the interface belongs. [switch a]router id 1.1.1.1 [switch a]ospf [switch a-ospf-1]area 0 [switch a-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 d import the static routes [switch a-ospf-1]imp...
Page 266
266 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration to add new routes to the routing table and whether or not to keep connection with a routing protocol. The default value normally meets the network requirements. You must be careful when modifying the configuration to avoid reducing the stability of t...
Page 267
Route capacity configuration 267 displaying and debugging route capacity enter the display command in any view to display the operation of the route capacity configuration. Table 264 displaying and debugging route capacity operation command display the route capacity memory information display memor...
Page 268
268 c hapter 16: ip r outing p rotocol o peration.
Page 269: Etwork
17 n etwork p rotocol o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ip address configuration ■ arp configuration ■ resilient arp configuration ■ bootp client configuration ■ dhcp configuration ■ access management configuration ■ udp helper configuration ■ ip performance configuration ip add...
Page 270
270 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration when using ip addresses, note that some of them are reserved for special uses, and are seldom used. The ip addresses you can use are listed in table 265. Subnet and mask with the rapid development of the internet, available ip addresses are depleting ve...
Page 271
Ip address configuration 271 address. If there is no subnet division, then its subnet mask is the default value and the length of "1" indicates the net-id length. Therefore, for ip addresses of classes a, b and c, the default values of corresponding subnet mask are 255.0.0.0, 255.255.0.0 and 255.255...
Page 272
272 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in system view. By default, there is no host name associated to any host ip address. For further information on ip address configuration, please refer to the getting started guide that accompanies your switch. Configu...
Page 273
Arp configuration 273 ip address configuration example networking requirements configure the ip address as 129.2.2.1 and subnet mask as 255.255.255.0 for vlan interface 1 of the switch. Networking diagram figure 63 ip address configuration networking configuration procedure 1 enter vlan interface 1....
Page 274
274 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration suppose there are two hosts on the same network segment: host a and host b. The ip address of host a is ip_a and the ip address of host b is ip_b. Host a will transmit messages to host b. Host a checks its own arp mapping table first to make sure whethe...
Page 275
Introduction to gratuitous arp 275 note that: ■ static arp map entry will be always valid as long as the switch works normally. But if the vlan corresponding to the arp mapping entry is deleted, the arp mapping entry will be also deleted. The valid period of dynamic arp map entries will last only 20...
Page 276
276 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration by sending gratuitous arp packets, a network device can: ■ determine whether or not ip address conflicts exist between it and other network devices. ■ trigger other network devices to update its hardware address stored in their caches. When the gratuito...
Page 277
Introduction to gratuitous arp 277 resilient arp configuration this section contains configuration information for resilient arp. Overview of resilient arp to support resilient networking in xrn applications, redundant links are required between the xrn fabric and other devices. But if intra-fabric ...
Page 278
278 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration you can use the following command to configure through which vlan interface the resilient arp packet is sent. The system provides a default vlan interface to send resilient arp packets. Perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the...
Page 279
Bootp client configuration 279 networking diagram figure 64 networking for resilient arp configuration configuration procedure 1 enable resilient arp function. [sw5500]resilient-arp enable 2 set vlan interface 2 to send resilient arp packets. [sw5500]resilient-arp interface vlan-interface 2 bootp cl...
Page 280
280 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration bootp client configuration bootp client is described in the following section. Configuring a vlan interface to obtain the ip address using bootp perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. By default, the vlan interface cannot use bootp ...
Page 281
Dhcp configuration 281 figure 65 typical dhcp application. To obtain valid dynamic ip addresses, the dhcp client exchanges different types of information with the server at different stages. One of the following three situations may occur: ■ a dhcp client logs into the network for the first time whe...
Page 282
282 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration ■ a dhcp client extends its ip lease period there is a time limit for the ip addresses leased to dhcp clients. The dhcp server shall withdraw the ip addresses when their lease period expires. If the dhcp client wants to continue use of the old ip addres...
Page 283
Dhcp configuration 283 option 82 supporting introduction to option 82 supporting option 82 is a relay agent information option in dhcp packets. When a request packet from a dhcp client travels through a dhcp relay on its way to the dhcp server, the dhcp relay adds option 82 into the request packet. ...
Page 284
284 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration ■ len: specifies the length of the agent information field. ■ agent information field: specifies the sub-options used. 2 sub-option format figure 68 illustrates the sub-option format. Figure 68 sub-option format ■ subopt: sub-option number. Currently, t...
Page 285
Dhcp configuration 285 mechanism of option 82 supporting on dhcp relay the procedure for a dhcp client to obtain an ip address from a dhcp server through a dhcp relay is exactly the same as that for the client to obtain an ip address from a dhcp server directly. The following are the mechanism of op...
Page 286
286 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration dhcp relay configuration dhcp relay configuration is described in the following sections: ■ enabling dhcp ■ enabling dhcp ■ configuring the dhcp server group for the vlan interfaces ■ configuring the user address entry for the dhcp server group ■ enabli...
Page 287
Dhcp configuration 287 configuring the user address entry for the dhcp server group to ensure that a valid user with a fixed ip address in a vlan configured with dhcp relay passes the address validity check of the dhcp security feature, you must add a static address entry which indicates the corresp...
Page 288
288 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration to dhcp servers by dhcp clients through unicast when the dhcp clients release ip addresses, the user address entries maintained by the dhcp cannot be updated in time. The dynamic user address entry updating function is developed to resolve this problem....
Page 289
Dhcp configuration 289 option 82 supporting configuration example network requirements two dhcp clients are on the network segment 10.110.0.0 (255.255.0.0). They obtain ip addresses from a dhcp server through a switch acting as dhcp relay. Option 82 supporting is enabled on the dhcp relay. Network d...
Page 290
290 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration 6 return to system view. [s5500-vlan-interface 100] quit 7 enable option 82 supporting on the dhcp relay, with the keep keyword specified. [s5500] dhcp relay information enable [s5500] dhcp relay information strategy keep introduction to dhcp snooping f...
Page 291
Dhcp configuration 291 figure 71 interaction between a dhcp client and a dhcp server . ■ dhcp snooping listens the following two types of packets to retrieve the ip addresses the dhcp clients obtain from dhcp servers and the mac addresses of the dhcp clients: ■ dhcp-ack packet ■ dhcp-request packet ...
Page 292
292 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration configuration example i. Network requirements as shown in figure 71, the ethernet1/0/1 port of switch a (an s5500 series switch) is connected to switch b (acting as a dhcp relay). A network segment containing some dhcp clients is connect to the ethernet...
Page 293
Introduction to dhcp accounting 293 ■ length: two bytes, identifying the total length of the accounting packet. ■ authenticator: 16 bytes, identifying the information between the radius server and client. The attributes field contains multiple sub-fields. The content of the attributes field is sligh...
Page 294
294 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration dhcp accounting fundamentals after you complete aaa and radius configuration on a switch with the dhcp server function enabled, the dhcp server acts as a radius client. For the authentication process of the dhcp server acting as a radius client. The fol...
Page 295
Introduction to dhcp accounting 295 ■ dhcp accounting is enabled on the dhcp server. ■ the ip addresses of the global dhcp address pool belongs to the network segment 10.1.1.0/24. The dhcp server operates as a radius client and adopts aaa for authentication. Network diagram figure 73 network diagram...
Page 296
296 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration 11 enter vlan 3 interface view and assign the ip address 10.1.2.1/24 to the vlan interface. [s5500] interface vlan-interface 3 [s5500-vlan-interface3] ip address 10.1.2.1 24 12 return to system view. [s5500-vlan-interface3] quit 13 create a domain and a...
Page 297
Introduction to dhcp accounting 297 dhcp relay displaying you can verify your dhcp relay-related configuration by executing the following display commands in any view. Dhcp snooping displaying after the above configuration, you can display ip addresses and the corresponding mac addresses tracked by ...
Page 298
298 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration configuration procedure 1 create a dhcp server group that will use two dhcp servers (a master and an optional backup) and assign it the ip addresses of the two dhcp servers (the first ip address is the master). [sw5500]dhcp-server 0 ip 192.168.1.1 192.1...
Page 299
Access management configuration 299 troubleshooting dhcp relay configuration perform the following procedure if a user cannot apply for an ip address dynamically: 1 use the display dhcp-server groupno command to check if the ip address of the corresponding dhcp server has been configured. 2 use the ...
Page 300
300 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration by default, the system disables the access management function. Configuring the access management ip address pool based on the port you can use the following command to set the ip address pool for access management on a port. The packet whose source ip ...
Page 301
Access management configuration 301 ■ in the same aggregation group, the port isolation feature on one unit is consistent. ■ if a port is removed from an aggregation group, its port isolation configuration will not change. ■ if a port of an aggregation group is isolated on unit 1, then you can achie...
Page 302
302 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration access management configuration example networking requirements organization 1 is connected to port 1 of the switch, and organization 2 to port 2. Ports 1 and 2 belong to the same vlan. The ip addresses range 202.10.20.1 to 202.10.20.20 can be accessed ...
Page 303
Udp helper configuration 303 to delete this feature, enter: system-view [sw5500]acl number 2500 [sw5500-acl-basic-2500]undo rule 0 udp helper configuration this section contains udp helper configuration information. Overview of udp helper the major function of the udp helper is to relay-forward udp ...
Page 304
304 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in system view. Note that: ■ you must first enable the udp helper function and then configure the udp port with the relay function. Otherwise, error information will appear. ■ the parameters dns , netbios-ds, netbios-...
Page 305
Ip performance configuration 305 displaying and debugging udp helper configuration after the above configuration, enter the display command in any view to display the running of the udp helper destination server, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Enter the debugging command in user view...
Page 306
306 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration be terminated. The timeout of synwait timer range is 2 to 600 seconds and it is 75 seconds by default. ■ finwait timer: when the tcp connection state turns from fin_wait_1 to fin_wait_2, finwait timer will be started. If fin packets are not received bef...
Page 307
Ip performance configuration 307 troubleshooting ip performance fault: ip layer protocol works normally but tcp and udp cannot work normally. In the event of such a fault, you can enable the corresponding debugging information output to view the debugging information. ■ use the terminal debugging co...
Page 308
308 c hapter 17: n etwork p rotocol o peration.
Page 309: Ulticast
18 m ulticast p rotocol this chapter includes information on the following: ■ ip multicast overview ■ igmp snooping ■ common multicast configuration ■ internet group management protocol (igmp) ■ pim-dm overview ■ pim-sm overview ip multicast overview the switch 5500-ei supports all of the multicast ...
Page 310
310 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol figure 78 comparison between the unicast and multicast transmission a multicast source does not necessarily belong to a multicast group. It only sends data to the multicast group and it is not necessarily a receiver. Multiple sources can send packets to a multic...
Page 311
Ip multicast overview 311 ranges and meanings of class d addresses are shown in table 306 reserved multicast addresses that are commonly used are shown in table 307. Ethernet multicast mac addresses when unicast ip packets are transmitted in ethernet, the destination mac address is the mac address o...
Page 312
312 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol figure 79 mapping between the multicast ip address and the ethernet mac address only 23 bits of the last 28 bits in the ip multicast address are mapped to the mac address. Therefore, the 32 ip multicast addresses are mapped to the same mac address. Ip multicast ...
Page 313
Ip multicast overview 313 pim-dm (protocol-independent multicast dense mode, pim-dm) pim dense mode is suitable for small networks. It assumes that each subnet in the network contains at least one receiver interested in the multicast source. As a result, multicast packets are flooded to all points o...
Page 314
314 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol applying multicast ip multicast technology effectively solves the problem of packet forwarding from single-point to multi-point. It implements highly-efficient data transmission from single-point to multi-point in ip networks and can save a large amount of netwo...
Page 315
Igmp snooping 315 figure 81 multicast packet transmission when igmp snooping runs igmp snooping terminology table 308 explains switching terminology relevant to igmp snooping. The switch 5500 runs igmp snooping to listen to the igmp messages and map the host and its ports to the corresponding multic...
Page 316
316 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol figure 82 implementing igmp snooping table 309 explains igmp snooping terminology. Table 309 igmp snooping terminology term meaning igmp general query message transmitted by the multicast router to query which multicast group contains member. When a router port ...
Page 317
Igmp snooping 317 configuring igmp snooping igmp snooping configuration includes: ■ enabling/disabling igmp snooping ■ configuring router port aging time ■ configuring maximum response time ■ configuring aging time of multicast group member of the above configuration tasks, enabling igmp snooping is...
Page 318
318 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the port aging time is 105 seconds. Configuring maximum response time use the commands in table 312 to manually configure the maximum response time. If the switch 5500 receives no report message fro...
Page 319
Igmp snooping 319 if igmp fast leave processing is enabled, when receiving an igmp leave message, igmp snooping immediately removes the port from the multicast group. When a port has only one user, enabling igmp fast leave processing on the port can save bandwidth. Configuring igmp snooping filter a...
Page 320
320 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol configuring multicast vlan in old multicast mode, when users in different vlans order the same multicast group, the multicast stream is copied to each of the vlans. This mode wastes a lot of bandwidth. By configuring a multicast vlan, adding switch ports to the ...
Page 321
Igmp snooping 321 note that: ■ you cannot set the isolate vlan as a multicast vlan. ■ one user port can belong to only one multicast vlan. ■ the port connected to a user end can only be set as a hybrid port. ■ a multicast member port must belong to the same multicast vlan with the router port. Or el...
Page 322
322 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol configuration example—enable igmp snooping networking requirements to implement igmp snooping on the switch, first enable it. The switch is connected to the router via the router port, and with user pcs through the non-router ports on vlan 10. Networking diagram...
Page 323
Common multicast configuration 323 diagnosis 3: multicast forwarding table set up on the bottom layer is wrong. 1 enable igmp snooping group in user view and then input the command display igmp-snooping group to check if mac multicast forwarding table in the bottom layer and that created by igmp sno...
Page 324
324 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol multicast mac address entry configuration in layer 2 multicast, the system can add multicast forwarding entries dynamically through layer 2 multicast protocol. However, you can also manually create a static multicast address entry to bind a port to a multicast a...
Page 325
Common multicast configuration 325 multicast source deny configuration the purpose of the multicast source deny feature is to filter out multicast packets on an unauthorized multicast source port to prevent the user connected to the port from setting up a multicast server without permission. Enablin...
Page 326
326 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol the forwarding entries in mfc are deleted along with the routing entries in the multicast kernel routing table. Displaying and debugging common multicast configuration execute display command in any view to display the running of the multicast configuration, and...
Page 327
Internet group management protocol (igmp) 327 igmp is not symmetric on hosts and routers. Hosts need to respond to igmp query messages from the multicast router, —, report the group membership to the router. The router needs to send membership query messages periodically to discover whether hosts jo...
Page 328
328 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol configuring igmp basic igmp configuration includes: ■ enabling multicast ■ enabling igmp on an interface advanced igmp configuration includes: ■ configuring the igmp version ■ configuring the interval and the number of igmp query packets ■ configuring the limit ...
Page 329
Internet group management protocol (igmp) 329 configuring the interval for querying igmp packets the router finds out which multicast groups on its connected network segment have members by sending igmp query messages periodically. Upon the reception of a response message, the router refreshes the m...
Page 330
330 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol configuring the limit of igmp groups on an interface if there is no limit to the number of igmp groups added on a router interface or a router, the router memory may be exhausted, which may cause router failure. You can set number limit for the igmp groups added...
Page 331
Internet group management protocol (igmp) 331 by default, a router joins no multicast group. Limiting multicast groups an interface can access a multicast router learns whether there are members of a multicast group on the network via the received igmp membership message. A filter can be set on an i...
Page 332
332 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol configuring the present time of igmp querier the igmp querier present timer defines the period of time before the router takes over as the querier sending query messages, after the previous querier has stopped doing so. Perform the following configuration in int...
Page 333
Pim-dm overview 333 displaying and debugging igmp after the above configuration, execute display command in any view to display the running of igmp configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute debugging command in user view for the debugging of igmp. Pim-dm overview pim-dm (...
Page 334
334 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol this process is called “flood & prune” process. In addition, nodes that are pruned provide timeout mechanism. Each router re-starts the “flood & prune” process upon pruning timeout. The consistent “flood & prune” process of pim-dm is performed periodically. Duri...
Page 335
Pim-dm overview 335 configuring pim-dm pim-dm basic configuration includes: ■ enabling multicast ■ enabling pim-dm pim-dm advanced configuration includes: ■ entering the pim view ■ configuring sending interval for the hello packets ■ configuring the filtering of multicast source/group ■ configuring ...
Page 336
336 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol using undo pim command, you can clear the configuration in pim view, and back to system view. Configuring sending interval for the hello packets after pim is enabled on an interface, it will send hello messages periodically on the interface. The interval at whic...
Page 337
Pim-dm overview 337 only the routers that match the filtering rule in the acl can serve as a pim neighbor of the current interface. Configuring the maximum number of pim neighbor on an interface the maximum number of pim neighbors of a router interface can be configured to avoid exhausting the memor...
Page 338
338 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol displaying and debugging pim-dm after the above configuration, execute the display command in any view to display the running of pim-dm configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute the debugging command in user view for the debugging of ...
Page 339
Pim-sm overview 339 configuration procedure this section only describes the configuration procedure for switch_a. Follow a similar configuration procedure for switch_b and switch_c. 1 enable the multicast routing protocol. [sw5500]multicast routing-enable 2 enable igmp and pim-dm. [sw5500]vlan 10 [s...
Page 340
340 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol pim-sm operating principle the working procedures for pim-sm include: neighbor discovery, building the rp-rooted shared tree (rpt), multicast source registration and switch over to the spt. Neighbor discovery the pim-sm router uses hello messages to perform neig...
Page 341
Pim-sm overview 341 preparations before configuring pim-sm configuring candidate rps in a pim-sm network, multiple rps (candidate-rps) can be configured. Each candidate-rp (c-rp) is responsible for forwarding multicast packets with the destination addresses in a certain range. Configuring multiple c...
Page 342
342 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol ■ clearing pim neighbors it should be noted that at least one router in an entire pim-sm domain should be configured with candidate-rps and candidate-bsrs. Enabling multicast refer to “common multicast configuration” on page 323. Enabling pim-sm this configurati...
Page 343
Pim-sm overview 343 configuring candidate-bsrs in a pim domain, one or more candidate bsrs should be configured. A bsr (bootstrap router) is elected among candidate bsrs. The bsr takes charge of collecting and advertising rp information. The automatic election among candidate bsrs operates as follow...
Page 344
344 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol configuring static rp static rp serves as the backup of dynamic rp, so as to improve network robusticity. Perform the following configuration in pim view. Basic acl can control the range of multicast group served by static rp. If static rp is in use, all routers...
Page 345
Pim-sm overview 345 perform the following configuration in pim view. If an entry of a source group is denied by the acl, or the acl does not define operation to it, or there is no acl defined, the rp will send registerstop messages to the dr to prevent the register process of the multicast data stre...
Page 346
346 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol in bsr mechanism, a c-rp router unicasts c-rp messages to the bsr, which then propagates the c-rp messages among the network by bsr message. To prevent c-rp spoofing, you need to configure crp-policy on the bsr to limit legal c-rp range and their service group r...
Page 347
Pim-sm overview 347 networking diagram figure 87 pim-sm configuration networking configuration procedure 1 on switch_a: a enable pim-sm. [sw5500]multicast routing-enable [sw5500]vlan 10 [sw5500-vlan10]port ethernet 1/0/2 to ethernet 1/0/3 [sw5500-vlan10]quit [sw5500]interface vlan-interface 10 [sw55...
Page 348
348 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol [sw5500]vlan 11 [sw5500-vlan11]port ethernet 1/0/4 to ethernet 1/0/5 [sw5500-vlan11]quit [sw5500]interface vlan-interface 11 [sw5500-vlan-interface11]igmp enable [sw5500-vlan-interface11]pim sm [sw5500-vlan-interface11]quit [sw5500]vlan 12 [sw5500-vlan12]port et...
Page 349
349.
Page 350
350 c hapter 18: m ulticast p rotocol.
Page 351: Acl C
19 acl c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ brief introduction to acl ■ qos configuration ■ qos profile configuration ■ acl control configuration ■ acl control configuration brief introduction to acl a series of matching rules are required for the network devices to identify th...
Page 352
352 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration the depth-first principle is to put the statement specifying the smallest range of packets on the top of the list. This can be implemented through comparing the wildcards of the addresses. The smaller the wildcard is, the less hosts it can specify. For example, 12...
Page 353
Brief introduction to acl 353 table 362 set the absolute time range when the start-time and end-time are not configured, it will be all the time for one day. The end time shall be later than the start time. When end-time end-date is not configured, it will be all the time from now to the date which ...
Page 354
354 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration table 363 define basic acl define advanced acl the rules of the classification for advanced acl are defined on the basis of the attributes such as source and destination ip address, the tcp or udp port number in use and packet priority to process the data packets....
Page 355
Brief introduction to acl 355 table 365 define layer-2 acl defining the user-defined acl the user-defined acl matches any bytes in the first 80 bytes of the layer-2 data frame with the character string defined by the user and then processes them accordingly. To correctly use the user-defined acl, yo...
Page 356
356 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration table 367 activate acl displaying and debugging acl after the above configuration, execute display command in all views to display the running of the acl configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute reset command in user view to clear the ...
Page 357
Brief introduction to acl 357 configuration procedure in the following configurations, only the commands related to acl configurations are listed. 1 define the work time range define time range from 8:00 to 18:00. [sw5500]time-range 3com 8:00 to 18:00 working-day 2 define the acl to access the payme...
Page 358
358 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration [sw5500]acl number 2000 b define the rules for packet which source ip is 10.1.1.1. [sw5500-acl-basic-2000]rule 1 deny source 10.1.1.1 0 time-range 3com 3 activate acl. Activate the acl 2000. [sw5500-gigabitethernet1/0/50]packet-filter inbound ip-group 2000 link ac...
Page 359
Qos configuration 359 qos configuration traffic traffic refers to all packets passing through a switch. Traffic classification traffic classification means identifying the packets with certain characteristics, using the matching rule called classification rule, set by the configuration administrator...
Page 360
360 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration figure 91 sp the sp is designed for the key service application. A significant feature of the key service is the need for priority to enjoy the service to reduce the responding delay when congestion occurs. Take 8 egress queues for each port as an example, sp divi...
Page 361
Qos configuration 361 qos configuration the process of qos based traffic: 1 identify the traffic by acl 2 perform the qos operation to the traffic. The configuration steps of qos based traffic: 1 define the acl 2 configure the qos operation if qos is not based on traffic, you need not define acl fir...
Page 362
362 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration configuration example for setting priority of a protocol packet 1 change ospf protocol packets’ ip priority to be 3.Enter system view. System-view [s5500] 2 set ospf protocol packets’ ip priority to be 3. [s5500] protocol-priority protocol-type ospf ip-precedence ...
Page 363
Qos configuration 363 configure traffic mirroring 1 configure monitor port perform the following configuration in the ethernet port view. Table 375 configure monitor port only one monitor port can be configured on one switch. If a group of switches form a fabric, only one monitor port can be configu...
Page 364
364 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration configuring the mapping relationship between cos and local precedence using the following commands, you can configure the maps. Perform the following configuration in system view. Table 380 map configuration by default, the switch uses the default mapping relation...
Page 365
Qos configuration 365 you should first define an acl before this configuration task. The granularity of traffic limit is 64kbps. If the target-rate user input is in ( n*64, (n+1)*64], in which n is a natural number, switch automaticaly sets (n+1)*64 as the parameter value. This configuration achieve...
Page 366
366 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration table 385 configuring traffic statistics for details about the command, refer to the command reference manual. Configuring wred operation the function of wred operation is to avoid congestion in advance. Perform the following configuration in the ethernet port vie...
Page 368
368 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration controlling telnet using source mac this configuration can be implemented by means of layer 2 acl, which ranges from 4000 to 4999. For the definition of acl, refer to acl part. Configuration example network requirements only telnet users from 10.110.100.52 and 10....
Page 369
Qos configuration 369 displaying and debugging qos configuration you can use the display command in any view to see the qos operation and to check the status of the configuration. You can also clear the statistic information using the reset command in the ethernet interface view. Qos configuration e...
Page 370
370 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration networking diagram figure 93 qos configuration example configuration procedure only the commands concerning qos/acl configuration are listed here. 1 define outbound traffic for the wage server. A enter numbered advanced acl view. [sw5500]acl number 3000 b define t...
Page 371
Qos configuration 371 networking diagram figure 94 qos configuration example configuration procedure define port mirroring, with monitoring port being ethernet3/0/8. [sw5500-ethernet3/0/8]monitor-port [sw5500-ethernet3/0/1]mirroring-port both priority relabeling configuration example networking requ...
Page 372
372 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration qos profile configuration when used together with the 802.1x authentication function, the qos profile function can offer preconfigured qos settings for a qualified user in authentication (or a group of users). When the user passes the 802.1x authentication, the sw...
Page 373
Qos profile configuration 373 perform the following configuration in system view. Table 393 entering qos profile view you cannot delete the specific qos profile which has been applied to the port. Adding/removing traffic action to a qos profile from the qos profile view, you can configure the qos ac...
Page 374
374 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration ■ port-based mode: the switch delivers the traffic actions in the qos profile directly to the user port. Perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. Table 395 configuring profile application mode by default, port-based mode is enabled on the port. A...
Page 375
Qos profile configuration 375 the user (with user name someone and authentication password hello ) is accessed from the ethernet1/0/1 port into the switch. The user is assigned into the 3com163.Net domain. The qos profile example references the acl with bandwidth limited to 128 kbps and new dscp pre...
Page 376
376 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration g configure the qos profile [sw5500]qos-profile example [sw5500-qos-profile-example]traffic-limit inbound ip-group 3000 128 exceed drop [sw5500-qos-profile-example]traffic-priority inbound ip-group 3000 dscp 46 [sw5500-qos-profile-example]quit h set user based mod...
Page 377
Acl control configuration 377 importing acl you can import a defined acl in user interface view to achieve acl control. Perform the following configurations respectively in system view and user interface view. Table 400 importing acl see the command reference manual for details about these commands....
Page 378
378 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration importing acl import the defined acl into the commands with snmp community, username and group name configured, to achieve acl control over snmp users. Perform the following configurations in system view. Table 401 importing acl snmp community is one of the featur...
Page 379
Acl control configuration 379 configuration example networking requirement only snmp users from 10.110.100.52 and 10.110.100.46 can access the switch. Networking diagram figure 99 acl configuration for snmp users configuration procedure 1 define a basic acl. [sw5500]acl number 2000 match-order confi...
Page 380
380 c hapter 19: acl c onfiguration for more about the commands, refer to the command reference manual. Only the numbered basic acl can be called for web nm user control. Configuration example networking requirements only permit web nm user from 10.110.100.46 access switch. Networking diagram figure...
Page 381: Onfiguration
20 c onfiguration for q o s f eatures rspan features remote switched port analyzer (rspan) refers to remote port mirroring. It breaks through the limitation that the mirrored port and the mirroring port have to be located in the same switch, and makes it possible that the mirrored and mirroring port...
Page 382
382 c hapter 20: c onfiguration for q o s f eatures to implement the remote port management, a special vlan, called remote-probe vlan, needs to be defined in all three types of switches. All the mirrored packets will be forwarded to destination switch from the source switch using this vlan, and ther...
Page 383
Rspan features 383 configuration procedures in the source switch configuration procedures in the intermediate switch table 404 configuration procedures in the source switch operation command description enter system view system-view — establish remote-probe vlan, and enter vlan view vlan vlan-id the...
Page 384
384 c hapter 20: c onfiguration for q o s f eatures configuration procedures in the source switch configuration example network diagram requirements the network description is as follows: ■ switch a is connected to the data monitoring device using ethernet1/0/2. ■ ethernet1/0/1, the trunk port of sw...
Page 385
Rspan features 385 ■ configure switch c to be the source switch, ethernet1/0/2 to be the source port of remote mirroring, and ethernet1/0/5 to be the reflector port. Set ethernet1/0/5 to be access port, with stp disabled. Network diagram figure 102 network diagram for rspan configuration procedure 1...
Page 386
386 c hapter 20: c onfiguration for q o s f eatures [s5500-ethernet1/0/1] port trunk permit vlan 10 [s5500-ethernet1/0/1] quit [s5500] mirroring-group 1 remote-destination [s5500] mirroring-group 1 monitor-port ethernet1/0/2 [s5500] mirroring-group 1 remote-probe vlan 10 [s5500] display mirroring-gr...
Page 387
Displaying information of the display acl command 387 ■ a fixed weighting value is deducted from the weighting value of each element of the rule. The rule with the smallest weighting value left has the highest priority. ■ if the number and type of elements are the same for all rules, then the rule w...
Page 388
388 c hapter 20: c onfiguration for q o s f eatures the synchronization feature of queue scheduling for aggregation ports this feature provides the synchronization function of queue scheduling on each individual port of the aggregation port group, as illustrated as follows: 1 the new feature support...
Page 389
Configuring control over telnet 389 controlling telnet using source ip this configuration can be implemented by means of basic acl, which ranges from 2000 to 2999. Controlling telnet using source ip and destination ip this configuration can be implemented by means of advanced acl, which ranges from ...
Page 390
390 c hapter 20: c onfiguration for q o s f eatures controlling telnet using source mac this configuration can be implemented by means of layer 2 acl, which ranges from 4000 to 4999. For the definition of acl, refer to acl part. Configuration example network requirements only telnet users from 10.11...
Page 391: 802.1
21 802.1 x c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ieee 802.1x overview ■ configuring 802.1x ■ centralized mac address authentication ■ aaa and radius protocol configuration for information on setting up a radius server and radius client refer to appendix b. For details on how to ...
Page 392
392 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration authenticator and authentication server exchange information through eap (extensible authentication protocol) frames. The user and the authenticator exchange information through the eapol (extensible authentication protocol over lans) frame defined by ieee 802...
Page 393
Configuring 802.1x 393 implementing 802.1x on the switch the switch 5500 family not only supports the port access authentication method regulated by 802.1x, but also extends and optimizes it in the following way: ■ support to connect several end stations in the downstream using a physical port. ■ th...
Page 394
394 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration setting the port access control mode the following commands can be used for setting 802.1x access control mode on the specified port. When no port is specified, the access control mode of all ports is configured. Perform the following configurations in system ...
Page 395
Configuring 802.1x 395 setting the user number on a port the following commands are used for setting the number of users allowed by 802.1x on a specified port. When no port is specified, all the ports accept the same number of users. Perform the following configurations in system view or ethernet po...
Page 396
396 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration the eap-tls mode authenticates supplicant systems by authenticating licenses of both authentication servers and supplicant systems on both sides. In this mode, supplicant systems are authenticated by their licenses only, which are applied for from authenticati...
Page 397
Configuring 802.1x 397 network diagram figure 105 network diagram for 802.1x peap configuration configuration procedure the following configurations assume that peap is selected on 802.1x clients and the radius server to authenticate 802.1x supplicant systems. Configure the switch. 1 enter system vi...
Page 398
398 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration configuring timers the following commands are used for configuring the 802.1x timers. Perform the following configurations in system view. Table 421 configuring timers handshake-period: this timer begins after the user has passed the authentication. After sett...
Page 399
802.1x client version checking configuration 399 enabling/disabling a quiet-period timer you can use the following commands to enable/disable a quiet-period timer of an authenticator (which can be a switch 5500). If an 802.1x user has not passed the authentication, the authenticator will keep quiet ...
Page 400
400 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration the supplicant system. Such a process goes on and on until the maximum number of retries is reached. If the maximum number of retries is reached and the supplicant system still does not respond, the switch ceases checking the client version of the supplicant s...
Page 401
802.1x client version checking configuration 401 when the guest vlan function is enabled: ■ the switch broadcasts active authentication packets to all 802.1x-enabled ports. ■ the switch adds the ports that do not return response packets to guest vlan when the maximum number of authentication retries...
Page 402
402 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration configuration procedure 1 enter system view. System-view 2 create vlan 2. [s5500] vlan 2 3 enter ethernet1/0/1 port view. [s5500] interface ethernet1/0/1 4 configure the port to operate in port-based authentication mode. [s5500-ethernet1/0/1] dot1x port-method...
Page 403
802.1x client version checking configuration 403 ■ cams is configured to disable use of multiple network adapters, proxies, or ie proxies. By default, an 802.1x client allows the use of multiple network adapters, proxies, and ie proxies. If cams is configured to disable the use of multiple network a...
Page 404
404 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration a server group, consisting of two radius servers at 10.11.1.1 and 10.11.1.2 respectively, is connected to the switch. The former one acts as the primary-authentication/second-accounting server. The latter one acts as the secondary-authentication/primary-accoun...
Page 405
Centralized mac address authentication 405 6 set the encryption key when the system exchanges packets with the authentication radius server. [sw5500-radius-radius1]key authentication name 7 set the encryption key when the system exchanges packets with the accounting radius server. [sw5500-radius-rad...
Page 406
406 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration centralized mac address authentication configuration centralized mac address authentication configuration includes: ■ enabling mac address authentication both globally and on the port ■ configuring domain name used by the mac address authentication user ■ conf...
Page 407
Centralized mac address authentication 407 configuring the user name and password for fixed mode if you configure the centralized mac address authentication mode to be fixed mode, you need to configure the user name and password for fixed mode. Configuring domain name used by the mac address authent...
Page 408
408 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration displaying and debugging centralized mac address authentication after the above configuration, perform the display command in any view, you can view the centralized mac address authentication running state and check the configuration result. Perform the debugg...
Page 409
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 409 2 add local access user. A set the user name and password. [sw5500]local-user 00e0fc010101 [sw5500-luser-00e0fc010101]password simple 00e0fc010101 b set the service type of the user to lan-access. [sw5500-luser-00e0fc010101]service-type lan-access 3 enable t...
Page 410
410 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration returns the configuration information and accounting data to nas. Here, nas controls users and corresponding connections, while the radius protocol regulates how to transmit configuration and accounting information between nas and radius. Nas and radius exchan...
Page 411
Aaa and radius protocol configuration 411 among the above configuration tasks, creating isp domain is compulsory, otherwise the user attributes cannot be distinguished. The other tasks are optional. You can configure them at requirements. Creating/deleting an isp domain what is internet service prov...
Page 412
412 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration ■ none—no authentication and accounting. Table 438 configuring aaa scheme adopted by the isp domain by default, after an isp domain is created, the default aaa scheme is local . You cannot use a radius scheme together with the local or none scheme. You can use...
Page 413
Aaa separation 413 enabling the selection of the radius accounting option if no radius server is available or if the radius accounting server fails when the accounting optional is configured, the user can still use the network resource, otherwise, the user will be disconnected. The user configured w...
Page 414
414 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration configuring separate aaa schemes if a bound aaa scheme (that is, the authentication, authorization and accounting are bound in one scheme) is configured as well as the separate authentication, authorization and accounting schemes, the separate ones will be ado...
Page 415
Aaa separation 415 network diagram figure 108 network diagram for separate aaa schemes configuration procedure 1 enter system view. System-view 2 create an isp domain named cams. [s5500] domain cams 3 return to system view. [s5500-isp-cams] quit 4 configure a radius scheme named radius. [s5500] radi...
Page 416
416 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration ■ if the threshold is reached, the switch sends messages containing the user's remaining online time to the client at the interval you configured. ■ the client keeps the user informed of the updated remaining online time through a dialog box. Perform the follo...
Page 417
Dynamic vlan assignment 417 dynamic vlan assignment through dynamic vlan assignment, the ethernet switch dynamically adds the ports of the successfully authenticated users to different vlans depending on the attribute values assigned by radius server, so as to control the network resources the users...
Page 418
418 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration network diagram figure 109 network diagram for dynamic vlan assignment configuration procedure 1 create a radius scheme. [s5500] radius scheme ias [s5500-radius-ias] primary authentication 1.11.1.1 [s5500-radius-ias] primary accounting 1.11.1.1 [s5500-radius-i...
Page 419
Dynamic vlan assignment 419 setting attributes of the local user the attributes of a local user include its password display mode, state, service type and some other settings. Setting the password display mode perform the following configurations in system view. Table 447 setting the password displa...
Page 420
420 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration however, the user-privilege level is a global value for all service types. Entering the following two commands will result in the user having a level of 3 for all service types. In this case both telnet and ssh: [5500-si-luser-adminpwd]service-type telnet leve...
Page 421
Dynamic vlan assignment 421 among the above tasks, creating the radius scheme and setting the ip address of the radius server are required, while other tasks are optional and can be performed as per your requirements. Creating/deleting a radius scheme as mentioned above, radius protocol configuratio...
Page 422
422 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration the authorization information from the radius server is sent to radius clients in authentication response packets, so you do not need to specify a separate authorization server. In real networking environments, you may specify two radius servers as primary and...
Page 423
Dynamic vlan assignment 423 setting the maximum times of real-time accounting request failing to be responded to a radius server usually checks if a user is online with a timeout timer. If the radius server has not received the real-time accounting packet from nas for a while, it will consider that ...
Page 424
424 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration table 455 setting the maximum retransmitting times of stopping accounting reques t by default, the stopping accounting request can be retransmitted up to 500 times. Enabling the selection of the radius accounting option perform the following configurations in ...
Page 425
User re-authentication at reboot 425 the switch can automatically generate the main attributes (nas-id, nas-ip and session id) of the accounting-on packets. However, you can also manually configure the nas-ip attribute with the nas-ip command. When doing this, be sure to configure a correct and vali...
Page 426
426 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration by default, the keys of radius authentication/authorization and accounting packets are all “3com”. Tag vlan assignment on trunk/hybrid port supported by 802.1x authentication currently, the 802.1x authentication module supports tag vlan assignment only on acce...
Page 427
User re-authentication at reboot 427 by default, the newly created radius scheme supports the server type standard , while the "system" radius scheme created by the system supports the server type 3com . Setting the radius server state for the primary and secondary servers (no matter if they are an ...
Page 428
428 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration setting the unit of data flow that transmitted to the radius server the following command defines the unit of the data flow sent to radius server. Perform the following configurations in radius scheme view table 463 setting the unit of data flow transmitted to...
Page 429
User re-authentication at reboot 429 setting the timers of the radius server setting the response timeout timer of the radius server after radius (authentication/authorization or accounting) request packet has been transmitted for a period of time, if nas has not received the response from the radiu...
Page 430
430 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration configure the radius server response timer if the nas receives no response from the radius server after sending a radius request (authentication/authorization or accounting request) for a period of time, the nas resends the request, thus ensuring the user can ...
Page 431
User re-authentication at reboot 431 aaa and radius protocol configuration example for the hybrid configuration example of aaa/radius protocol and 802.1x protocol, refer to “802.1x configuration example” on page 403. Configuring the ftp/telnet user authentication at a remote radius server configurin...
Page 432
432 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration configuration procedure 1 add a telnet user. For details about configuring ftp and telnet users, refer to user interface configuration in the getting started chapter. 2 configure remote authentication mode for the telnet user, that is, scheme mode. [sw5500-ui-...
Page 433
User re-authentication at reboot 433 2 method 2: using local radius authentication server. Local server method is similar to remote radius authentication. But you should modify the server ip address to 127.0.0.1, authentication password to 3com, the udp port number of the authentication server to 16...
Page 434
434 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration and that completes the configuration of the new radius server and associating it with a domain. Network login network login must first be enabled globally by issuing the command dot1x: [5500-xx]dot1x 802.1x is enabled globally (where xx is either ei or si) onc...
Page 435
User re-authentication at reboot 435 once the radius scheme and domain have been set up, see domain and radius scheme creation, then switch login is enabled. By default, when you use the username admin to login, you are actually logging in as "admin@local". If no domain is given, the "@local" is aut...
Page 436
436 c hapter 21: 802.1 x c onfiguration fault three: after being authenticated and authorized, the user cannot send charging bill to the radius server. Troubleshooting: ■ the accounting port number may be set improperly. Please set a proper number. ■ the accounting service and authentication/authori...
Page 437: Ile
22 f ile s ystem m anagement this chapter covers the following topics: ■ file system overview ■ file attribute configuration ■ configuring file management ■ configuration file backup and restoration ■ ftp overview ■ tftp overview ■ mac address table management ■ device management ■ system maintenanc...
Page 438
438 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement based on the operated objects, the file system can be divided as follows: ■ directory operation ■ file operation ■ storage device operation ■ set the prompt mode of the file system directory operation you can use the file system to create or delete a direct...
Page 439
File attribute configuration 439 file attribute configuration you can assign the main/backup attribute to a file so as to use this file as the main/backup startup file upon next startup of switch, check the main and backup files, and toggle between the main and backup attributes of file. You can use...
Page 440
440 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement file operation the file system can be used to delete or undelete a file and permanently delete a file. Also, it can be used to display file contents, rename, copy and move a file and display the information about a specified file. Using the delete file-url ...
Page 441
Configuring file management 441 setting the prompt mode of the file system the following command can be used for setting the prompt mode of the current file system. Perform the following configuration in system view. Table 477 file system operation configuring file management the management module o...
Page 442
442 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement the configuration files are displayed in their corresponding saving formats. Saving the current-configuration use the save command to save the current-configuration in the flash memory, and the configurations will become the saved-configuration when the sys...
Page 443
Configuration file backup and restoration 443 configuration file backup and restoration the configuration file backup and restoration feature enables you to perform the following tasks: 1 copy the current configurations on switch to a file on a tftp server as a backup. 2 download the configuration f...
Page 444
444 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement table 484 configuration of the switch as ftp client table 485 configuration of the switch as ftp server the prerequisite for normal ftp function is that the switch and pc are reachable. Enabling/disabling ftp server you can use the following commands to ena...
Page 445
Ftp overview 445 if the ip-addr in the command is not an address of the device, your configuration fails. If you specify a non-existent interface in the command, your configuration fails. Configuring the ftp server authentication and authorization you can use the following commands to configure ftp ...
Page 446
446 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement displaying and debugging ftp server after the above configuration, execute display command in all views to display the running of the ftp server configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Table 490 display and debug ftp server the display...
Page 447
Ftp overview 447 displaying the source ip address of the ftp client use the display command in any view to display the source ip address of the ftp client for service packets. Ftp client configuration example networking requirement the switch serves as the ftp client and the remote pc as the ftp ser...
Page 448
448 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement password:***** 230 logged in successfully [ftp] 3 type in the authorized directory of the ftp server. [ftp]cd switch 4 use the put command to upload the config.Cfg to the ftp server. [ftp]put config.Cfg 5 use the get command to download the switch.App from ...
Page 449
Tftp overview 449 3 run ftp client on the pc and establish ftp connection. Upload the switch.App to the switch under the flash directory and download the config.Cfg from the switch. Ftp client is not shipped with the switch, so you need to buy it separately. If the flash memory of the switch is not ...
Page 450
450 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement downloading files by means of tftp to download a file, the client sends a request to the tftp server and then receives data from it and sends acknowledgement to it. You can use the following commands to download files by means of tftp. Perform the following...
Page 451
Mac address table management 451 3 enter system view and download the switch.App from the tftp server to the flash memory of the switch. System-view [sw5500] 4 configure ip address 1.1.1.1 for the vlan interface, ensure the port connecting the pc is also in this valn (vlan 1 in this example). [sw550...
Page 452
452 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement figure 117 the switch forwards packets with mac address table the switch also provides the function of mac address aging. If the switch receives no packet for a period of time, it will delete the related entry from the mac address table. However, this funct...
Page 453
Mac address table management 453 setting mac address aging time setting an appropriate aging time implements mac address aging. Too long or too short an aging time set by subscribers will cause the ethernet switch to flood a large amount of data packets. This affects the switch operation performance...
Page 454
454 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement displaying mac address table after the above configuration, execute the display command in all views to display the running of the mac address table configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute the debugging command in user view to ...
Page 455
Mac address table management 455 configuration procedure the display command shows a stack wide view of the mac address table. [sw5500]display mac-address mac addr vlan id state port index aging time(s) 00e0-fc00-3943 1 learned ethernet1/0/11 300 0000-0000-5100 1 learned ethernet2/0/22 300 0020-9c08...
Page 456
456 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement device management with the device management function, the switch can display the current running state and event debugging information about the unit, thereby implementing the maintenance and management of the state and communication of the physical device...
Page 457
Device management 457 upgrading bootrom you can use this command to upgrade the bootrom with the bootrom program in the flash memory. This configuration task facilitates the remote upgrade. You can upload the bootrom program file from a remote end to the switch using ftp and then use this command to...
Page 458
458 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement networking diagram figure 120 networking for ftp configuration configuration procedure 1 configure ftp server parameters on the pc. Define a user named as switch , password hello , read and write authority over the switch directory on the pc. 2 configure th...
Page 459
System maintenance and debugging 459 8 use the boot boot-loader command to specify the downloaded program as the application at the next login and reboot the switch. Boot boot-loader switch.App display boot-loader the app to boot at the next time is: flash:/switch.App the app to boot of board 0 at t...
Page 460
460 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement basic system configuration setting the system name for the switch perform the operationof sysname command in the system view. Table 508 set the name for the switch setting the system clock perform the operationof clock datetime command in the user view. Tab...
Page 461
Terminating the ftp connection of a specified user 461 terminating the ftp connection of a specified user by using the following command, the network administrator can forcibly terminate the ftp connection of a specified user on the ftp server, in order to secure the operation of the network. Restar...
Page 462
462 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement system debugging enable/disable the terminal debugging the switch provides various ways for debugging most of the supported protocols and functions, which can help you diagnose and address the errors. The following switches can control the outputs of the de...
Page 463
Displaying the state and information of the system 463 table 515 enable/disable the debugging for more about the usage and format of the debugging commands, refer to the relevant chapters. Since the debugging output will affect the system operating efficiency, do not enable the debugging without nec...
Page 464
464 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement testing tools for network connection this section contains the tools necessary to test network connections. Ping the ping command can be used to check the network connection and if the host is reachable. Perform the following operation in all views. Table 5...
Page 465
Introduction to remote-ping 465 the execution process of tracert is described as follows: send a packet with ttl value as 1 and the first hop sends back an icmp error message indicating that the packet cannot be sent, for the ttl is timeout. Re-send the packet with ttl value as 2 and the second hop ...
Page 466
466 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement remote-ping configuration this section contains information on remote-ping. Introduction to remote-ping configuration the configuration tasks for remote-ping include: ■ enabling remote-ping client ■ creating test group ■ configuring test parameters the test...
Page 467
Remote-ping configuration 467 the remote-ping test does not display test results. You can use the display remote-ping command to view the test results. You can use the display remote-ping command to check the test history as well as the latest test results. Configuration example network requirement ...
Page 468
468 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement 5 display the test results. [s5500-remote-ping-administrator-icmp] display remote-ping results administrator icmp [s5500-remote-ping-administrator-icmp] display remote-ping history administrator icmp logging function this section contains information on the...
Page 469
Logging function 469 " yyyy " is the year field. If changed to boot format, it represents the milliseconds from system booting. Generally, the data are so large that two 32 bits integers are used, and separated with a dot '.'. For example: 0.166970 sw5500 ifnet/6/updown:line protocol on interface et...
Page 470
470 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement note that there is a slash ('/') between module name and severity. 5 severity switch information falls into three categories: log information, debugging information and trap information. The info-center classifies every kind of information into 8 severity o...
Page 471
Logging function 471 table 521 info-center-defined severity note that there is a slash between severity and digest. 6 digest the digest is abbreviation, it represent the abstract of contents. Note that there is a colon between digest and content. 7 content it is the contents of logging information. ...
Page 472
472 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement 1 sending the information to loghost. Table 523 sending the information to loghos t 2 sending the information to the control terminal. Table 524 sending the information to the control terminal . Device configuration default value configuration description s...
Page 473
Logging function 473 3 sending the information to monitor terminal 4 sending the information to log buffer. Table 526 sending the information to log buffer 5 sending the information to trap buffer. Table 527 sending the information to trap buffer table 525 sending the information to monitor terminal...
Page 474
474 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement 6 sending the information to snmp table 528 sending the information to snmp 7 turn on/off the information synchronization switch in fabric figure 124 turn on/off the information synchronization switch in fabric sending the information to loghost to send inf...
Page 475
Logging function 475 table 530 configuring to output information to loghost ensure to enter the correct ip address using the info-center loghost command to configure loghost ip address. If you enter a loopback address, the system prompts of invalid address appears. 3 configuring the information sour...
Page 476
476 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement 4 configuring loghost the configuration on the loghost must be the same with that on the switch. For related configuration, see the configuration examples in the latter part of this chapter. Setting format of time stamps due to be sent to log host table 532...
Page 477
Logging function 477 table 534 configuring to output information to control termina l 3 configuring the information source on the switch. With this configuration, you can define the information sent to the control terminal that is generated by which modules, information type, information level, and ...
Page 478
478 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement perform the following operation in user view: table 537 enabling terminal display function sending the information to telnet terminal or dumb termina l to send information to a telnet terminal or dumb terminal, follow the steps below: 1 enabling info-center...
Page 479
Logging function 479 modu-name specifies the module name; default represents all the modules; level refers to the severity levels; severity specifies the severity level of information. The information with the level below it will not be output. Channel-number specifies the channel number and channel...
Page 480
480 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement sending the information to the log buffer to send information to the log buffer, follow the steps below: 1 enabling info-center perform the following operation in system view. Table 543 enabling/disabling info-center info-center is enabled by default. After...
Page 481
Logging function 481 if you want to view the debugging information of some modules on the switch, you must select debugging as the information type when configuring the information source, meantime using the debugging command to turn on the debugging switch of those modules. You can use the followin...
Page 482
482 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement modu-name specifies the module name; default represents all the modules; level refers to the severity levels; severity specifies the severity level of information. The information with the level below it will not be output. Channel-number specifies the chan...
Page 483
Logging function 483 3 configuring the information source on the switch. With this configuration, you can define the information that is sent to snmp nm: generated by which modules, information type, information level, and so on. Perform the following operation in system view. Table 553 defining inf...
Page 484
484 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement the switch provides a command to turn on/off the synchronization switch in every switch. If the synchronization switch of a switch is turned off, it does not send information to other switches but still receives information from others. 1 enable info-center...
Page 485
Logging function 485 configuring synchronous information output function synchronous information output function works to prevent users’ input from being interrupted by system output. While enabled, this function allows users to view their input so far after each system output; thus avoids displayin...
Page 486
486 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement 2 configuration on the loghost this configuration is performed on the loghost. The following example is performed on sunos 4.0 and the operation on unix operation system produced by other manufactures is generally the same to the operation on sunos 4.0. A p...
Page 487
Logging function 487 networking diagram figure 128 schematic diagram of configuration configuration procedure 1 enabling info-center [sw5500]info-center enable set the host with the ip address of 202.38.1.10 as the loghost; set the severitylevel threshold value as informational, set the output langu...
Page 489
Rmon configuration 489 rmon configuration remote network monitoring (rmon) is a type of ietf-defined mib. It is the most important enhancement to the mib ii standard. It is mainly used for monitoring the data traffic on a segment and even on a whole network. It is one of the most widely used network...
Page 490
490 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement you can use the following commands to add/delete an entry to/from the alarm table. Perform the following configuration in system view. Table 558 add/delete an entry to/from the alarm table adding/deleting an entry to/from the event table rmon event manageme...
Page 491
Rmon configuration 491 table 561 add/delete an entry to/from the extended rmon alarm table adding/deleting an entry to/from the statistics table the rmon statistics management concerns the port usage monitoring and error statistics when using the ports. The statistics include collision, crc and queu...
Page 492
492 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement rmon configuration example networking requirements set an entry in rmon ethernet statistics table for the ethernet port performance, which is convenient for network administrators’ query. Networking diagram figure 130 rmon configuration networking configura...
Page 493
Ntp overview 493 ■ record for an application when a user logs in to a system, a file is modified, or basic operating principle of ntp figure 131 illustrates the basic operating principle of ntp: figure 131 basic operating principle of ntp in figure 131, switch a and switch b are connected using the ...
Page 494
494 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement in this way, switch a uses the above information to set the local clock and synchronize it with the clock on switch b. The operating principle of ntp is briefly introduced above. For more information, refer to rfc1305. Ntp configuration ntp is used for time...
Page 495
Ntp configuration 495 table 563 configure ntp time server ntp version number number ranges from 1 to 3 and defaults to 3; the authentication key id keyid ranges from 0 to 4294967295; interface-name or interface-type interface-number specifies the ip address of an interface, from which the source ip ...
Page 496
496 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement configuring ntp broadcast client mode designate an interface on the local switch to receive ntp broadcast messages and operate in broadcast client mode. The local switch listens to the broadcast from the server. When it receives the first broadcast packets,...
Page 497
Ntp configuration 497 multicast ip address ip-address defaults to 224.0.1.1. This command can only be configured on the interface where the ntp multicast packets will be received. Configuring ntp id authentication enable ntp authentication, set md5 authentication key, and specify the reliable key. A...
Page 498
498 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement an interface is specified by interface-name or interface-type interface-number . The source address of the packets will be taken from the ip address of the interface. If the ntp-service unicast-server or ntp-service unicast-peer command also designates a tr...
Page 499
Typical ntp configuration examples 499 setting maximum local sessions this configuration task is to set the maximum local sessions. Perform the following configurations in system view. Table 575 set the maximum local sessions number specifies the maximum number of local sessions, ranges from 0 to 10...
Page 500
500 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement networking diagram figure 132 typical ntp configuration networking diagram configuration procedure configure switch 1: 1 enter system view. System-view 2 set the local clock as the ntp master clock at stratum 2. [switch1]ntp-service refclock-master 2 config...
Page 501
Typical ntp configuration examples 501 after the synchronization, switch 2 turns into the following status: [switch2]display ntp-service status clock status: synchronized clock stratum: 8 reference clock id: 1.0.1.11 nominal frequency: 100.0000 hz actual frequency: 100.0000 hz clock precision: 2^17 ...
Page 502
502 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement 3 configure switch 5: (switch 4 has been synchronized by switch 3) a enter system view. System-view b after performing local synchronization, set switch 4 as a peer. [switch5]ntp-service unicast-peer 3.0.1.32 the above examples configure switch 4 and switch...
Page 503
Typical ntp configuration examples 503 c enter vlan-interface2 view. [switch3]interface vlan-interface 2 d set it as broadcast server. [switch3-vlan-interface2]ntp-service broadcast-server 2 configure switch 4: a enter system view. System-view b enter vlan-interface2 view. [switch4]interface vlan-in...
Page 504
504 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement configure ntp multicast mode network requirements switch 3 sets the local clock as the master clock at stratum 2 and multicast packets from vlan-interface2. Set switch 4 and switch 1 to receive multicast messages from their respective vlan-interface2. (note...
Page 505
Typical ntp configuration examples 505 configure authentication-enabled ntp server mode network requirements switch 1 sets the local clock as the ntp master clock at stratum 2. Switch 2 sets switch 1 as its time server in server mode and itself in client mode and enables authentication. (note that s...
Page 506
506 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement ssh terminal services secure shell (ssh) can provide information security and powerful authentication to prevent such assaults as ip address spoofing, plain-text password interception when users log on to the switch remotely from an insecure network environ...
Page 507
Ssh terminal services 507 way: the rsa public key of the client user is configured at the server. The client first sends the member modules of its rsa public key to the server, which checks its validity. If it is valid, the server generates a random number, which is sent to the client after being en...
Page 508
508 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement configuring and canceling local rsa key pair in executing this command, if you have configured rsa host key pair, the system gives an alarm after using this command and prompts that the existing one will be replaced. The server key pair is created dynamical...
Page 509
Ssh terminal services 509 defining ssh authentication retry value setting ssh authentication retry value can effectively prevent malicious registration attempt. Perform the following configurations in system view. Table 582 defining ssh authentication retry value by default, the retry value is 3. En...
Page 510
510 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement configuring ssh client there are several types of ssh client software, such as putty and freebsd. You should first configure the client’s connection with the server. The basic configuration tasks on the client include: ■ specifying server ip address. ■ sele...
Page 511
Ssh terminal services 511 figure 137 ssh key convert. Use the save button to save this converted key to a file. Open the public key file in notepad and the following lines of text before the existing text: rsa peer-public-key mykey public-key-code begin where mykey is a name used to identify the key...
Page 512
512 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement figure 138 text file of mykey save this to a file ending with a ".Bat" extension e.G "keys.Bat". This file can be transferred to the switch using ftp or tftp. The key is installed using the execute command in the system view [sw5500]execute keys.Bat specify...
Page 513
Ssh terminal services 513 in the host name (or ip address) text box key in the ip address of the switch, for example, 10.110.28.10. You can also input the ip address of an interface in up state, but its route to ssh client pc must be reachable. Selecting ssh protocol select ssh for the protocol item...
Page 514
514 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement figure 141 ssh client configuration interface (3) click browse to enter the file select interface. Choose a desired file and click ok. Opening ssh connection click open to enter ssh client interface. If it runs normally, you are prompted to enter username a...
Page 515
Ssh terminal services 515 displaying and debugging ssh run the display command in any view to view the running of ssh and further to check configuration result. Run the debugging command to debug the ssh. Perform the following configurations in any view. Table 584 display ssh information ssh configu...
Page 516
516 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement [sw5500-luser-client002]service-type ssh 4 specify aaa authentication on the user interface. [sw5500]user-interface vty 0 4 [sw5500-ui-vty0-4]authentication-mode scheme 5 select ssh protocol on the switch. [sw5500-ui-vty0-4]protocol inbound ssh 6 specify rs...
Page 517
File system configuration 517 file system configuration perform the following file system configuration in user view. If you delete a file and then another file with the same name under the same directory, the recycle bin only reserves the last deleted file. The files which are deleted by using the ...
Page 518
518 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement to ensure that the switch can use the current configurations after it restarts, you are recommended to save the current configurations by using the save command before restarting the switch. If multiple switches compose one fabric, executing the save comman...
Page 519
Ftp lighting configuration 519 enabling ftp server on switch after ftp server is enabled on an switch 5500 switch, the seven-segment digital led on the front panel of the switch will rotate clockwise when an ftp client is uploading file to the ftp server (the switch 5500 switch), and will stop rotat...
Page 520
520 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement enabling ftp client on the switch after ftp client is enabled on an switch 5500 switch, the seven-segment digital led on the front panel of the switch will rotate clockwise when the ftp client (the switch 5500 switch) is downloading file from a ftp server, ...
Page 521
Tftp lighting configuration 521 the switch can only act as a tftp client. Figure 146 network diagram for tftp configuration tftp lighting procedure the tftp server and the tftp client must be reachable to each other for the tftp function operates normally. After tftp client is enabled on an switch 5...
Page 522
522 c hapter 22: f ile s ystem m anagement.
Page 523: Ort
23 p ort t racking c onfiguration introduction to the port tracking function with the port tracking function enabled, you can specify to track the link state of the master’s uplink port and decrease the priority of the switch when the port fails. This in turn triggers the new master to be determined...
Page 524
524 c hapter 23: p ort t racking c onfiguration network diagram figure 147 network diagram for port tracking configuration configuration procedure configure the master switch. 1 enter system view. System-view system view: return to user view with ctrl+z. 2 create vlan 2. [s5500] vlan 2 [s5500-vlan2]...
Page 525: Ynamically
24 d ynamically a pply acl by radius s erver c onfiguration introduction to dynamically apply acl by radius server the switch can dynamically provide pre-defined acl rules for one or one group of authenticated user(s) through the combination of dynamically apply acl by radius server function and 802...
Page 526
526 c hapter 24: d ynamically a pply acl by radius s erver c onfiguration configuration example this section contains a configuration example. Network requirements the switch implements the dynamically apply acl by radius server function for the access users. The ip address of the vlan interface, wh...
Page 527
Configuration example 527 configuration procedure configuration on the radius server 1 click user/manage users. See figure 150. Figure 150 the first step 2 create a new user, and then on the general attributes page input the password of the user, meanwhile set the "account expiration date" as dec-31...
Page 528
528 c hapter 24: d ynamically a pply acl by radius s erver c onfiguration figure 152 the third step 4 click options/encryption keys, set the encryption key. See figure 153. Figure 153 the fourth step 5 input the nas ip and the encryption key. See figure 154..
Page 529
Configuration example 529 figure 154 the fifth step configuration on the switch 1 enable 802.1x. System-view [s5500] dot1x [s5500] dot1x interface ethernet 1/0/1 2 configure the ip address information for the radius server. [s5500] radius scheme radius1 [s5500-radius-radius1] primary authentication ...
Page 530
530 c hapter 24: d ynamically a pply acl by radius s erver c onfiguration on unit 1:total 1 connections matched, 1 listed. Total 1 connections matched, 1 listed. [s5500] display connection ucibindex 28 ------------------------unit 1------------------------ index=28 , username=test@test163.Net mac=00...
Page 531: Uto
25 a uto d etect c onfiguration introduction to the auto detect function the auto detect function uses icmp request/reply packets to test the connectivity of a network regularly. The auto detect function is carried out through detecting groups. A detecting group comprises of a group of the ip addres...
Page 532
532 c hapter 25: a uto d etect c onfiguration network diagram figure 155 network diagram for auto detect configuration configuration procedure 1 enter system view. System-view 2 create detecting group 10. [s5500] detect-group 10 3 specify to detect the ip address of 10.1.1.4, taking the ip address o...
Page 533
Auto detect implementation in static routing 533 you can utilize a single detecting group simultaneously in multiple implementations mentioned above. Refer to the routing protocol part in switch 5500 series switch operation manual for information about static routing. Refer to the reliability part i...
Page 534
534 c hapter 25: a uto d etect c onfiguration configuration procedure configure switch a. System-view [s5500 a] detect-group 8 [s5500 a-detect-group-8] detect-list 1 ip address 10.1.1.4 nexthop 192.168.1.2 [s5500 a] ip route-static 10.1.1.4 24 192.168.1.2 detect-group 8 auto detect implementation in...
Page 535
Auto detect implementation in vrrp 535 network diagram figure 157 network diagram for vrrp configuration procedure 1 configure switch b. A create detecting group 9. System-view [s5500 b] detect-group 9 b specify to detect the reachability of the ip address 10.1.1.4, setting the detect number to 1. [...
Page 536
536 c hapter 25: a uto d etect c onfiguration c set the backup group preference value of switch d to 100. [s5500 d-vlan-interface1] vrrp vrid 1 priority 100 auto detect implementation in vlan interface backup the interface backup function is used to back up vlan interfaces by using the auto detect f...
Page 537
Auto detect implementation in vlan interface backup 537 network diagram figure 158 network diagram for vlan interface backup configuration procedure 1 configure switch c. A enter system view. System-view b configure a static route to vlan interface 1 on switch a as the primary route, with the ip add...
Page 538
538 c hapter 25: a uto d etect c onfiguration g add the ip address of 10.1.1.4 to detecting group 10 to detect the reachability of the ip address, with the ip address of 192.168.1.2 as the next hop, and set the detecting number to 1. [s5500 a-detect-group-10] detect-list 1 ip address 10.1.1.4 nextho...
Page 539: Rstp C
26 rstp c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ stp overview ■ rstp configuration ■ rstp configuration example stp overview spanning tree protocol (stp) is applied in loop networks to block some undesirable redundant paths with certain algorithms and prune the network into a loop-...
Page 540
540 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration for a switch, the designated bridge is a switch in charge of forwarding bpdu to the local switch using a port called the designated port. For a lan, the designated bridge is a switch that is in charge of forwarding bpdu to the network segment using a port called ...
Page 541
Stp overview 541 2 select the optimum configuration bpdu every switch transmits its configuration bpdu to others. When a port receives a configuration bpdu with a lower priority than that of its own, it will discard the message and keep the local bpdu unchanged. When a higher-priority configuration ...
Page 542
542 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration switch b compares the configuration bpdus of the ports and selects the bp1 bpdu as the optimum one. Thus bp1 is elected as the root port and the configuration bpdus of switch b ports are updated as follows. The configuration bpdu of the root port bp1 retains as {...
Page 543
Stp overview 543 to facilitate the descriptions, the description of the example is simplified. For example, the root id and the designated bridge id in actual calculation should comprise both switch priority and switch mac address. Designated port id should comprise port priority and port mac addres...
Page 544
544 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration in a switch equipped with the xrn feature, rstp has the following characteristics: 1) processing the whole fabric as a node; 2) participation of all ports except those used as fabric ports in role selection; 3) a single root port and bridge id for the whole fabri...
Page 545
Rstp configuration 545 specify a switch as the root or backup root bridge the role of the current switch as the root or backup root bridge depends on the stp calculation. A switch can be made the root bridge by specifying its bridge preference to 0. Configure the bridge preference of a switch the br...
Page 546
546 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration configure the timeout time factor of a switch the switch, if has not received any hello packet from the upstream switch for thrice the hello time, will consider the upstream switch failed and recalculate the spanning tree. In a stable network, it is recommended t...
Page 547
Rstp configuration 547 after the stp protocol is enabled, the modification of any parameter will result in the re-calculation of the spanning tree on the switch. It is therefore recommended to configure all the rstp parameters before enabling the stp feature on the switch and the port. Enable/disabl...
Page 548
548 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration perform the following configurations in ethernet port view. Table 597 enable/disable rstp on a port note that the redundancy route may be generated after rstp is disabled on the ethernet port. By default, rstp on all the ports will be enabled after it is enabled ...
Page 549
Rstp configuration 549 set priority of a specified bridge whether a bridge can be selected as the “root” of the spanning tree depends on its priority. By assigning a lower priority, a bridge can be artificially specified as the root of the spanning tree. You can use the following command to configur...
Page 550
550 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration by default, a switch is neither the primary root nor the secondary root of the spanning tree. Set forward delay of a specified bridge link failure will cause recalculation of the spanning tree and change its structure. However, the newly calculated configuration ...
Page 551
Rstp configuration 551 table 604 set max age of the specified bridge if the max age is too short, it will result in frequent calculation of spanning tree or misjudge the network congestion as a link fault. On the other hand, too long max age may make the bridge unable to find link failure in time an...
Page 552
552 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration by default, an ethernet port can transmit at most 3 stp packets within one hello time. Set specified port to be an edgeport edgeport is not connected to any switch directly or indirectly using the connected network. You can use the following command to set a spec...
Page 553
Rstp configuration 553 specify the standard to be followed in path cost calculation the following two standards are currently available on the switch: ■ dot1d-1998: the switch calculates the default path cost of a port by the ieee 802.1d-1998 standard. ■ dot1t: the switch calculates the default path...
Page 554
554 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration table 611 configure a specified port to be connected to a point-to-point link the two ports connected using the point-to-point link can enter the forwarding state rapidly by transmitting synchronous packets, so that the unnecessary forwarding delay can be reduced...
Page 555
Rstp configuration 555 causes the network topology to reconfigure and may cause links to switch state. In normal cases, these ports will not receive stp bpdu. If someone forges a bpdu to attack the switch, the network topology to reconfigure. Bpdu protection function is used against such network att...
Page 556
556 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration for detailed information about the configuration commands, refer to the command manual. Display and debug rstp after the above configuration, execute display command in all views to display the running of the rstp configuration, and to verify the effect of the co...
Page 557
Rstp configuration example 557 configuration procedure 1 configure switch a a enable rstp globally. [sw5500]stp enable b the port rstp defaults are enabled after global rstp is enabled. You can disable rstp on those ports that are not involved in the rstp calculation, however, be careful and do not ...
Page 558
558 c hapter 26: rstp c onfiguration b the port rstp defaults are enabled after global rstp is enabled. You can disable rstp on those ports that are not involved in rstp calculation, however, be careful and do not disable those involved. (the following configuration takes ethernet 1/0/4 as an exampl...
Page 559: E P
27 p o e p rofile c onfiguration i ntroduction to poe profile on a large-sized network or a network with mobile users, to help network administrators to monitor the poe features of the switch, 3com switch 5500 family have provided poe profile features. Features of poe profile: ■ various poe profiles...
Page 560
560 c hapter 27: p o e p rofile c onfiguration various poe features can be configured within one poe profile. The following holds while using the apply poe-profile command to apply a poe profile to a group of ports: ■ the display current-configuration command can be used to indicate that the poe pro...
Page 561
Poe profile configuration 561 figure 164 poe profile application configuration procedures 1 create profile 1, and enter poe profile view. System-view [s5500] poe-profile profile1 2 in profile 1, add the poe policy configuration applicable to ethernet1/0/1 through ethernet1/0/5 ports for type a group...
Page 562
562 c hapter 27: p o e p rofile c onfiguration 7 apply the configured profile 1 to ethernet1/0/1 through ethernet1/0/5 ports. [s5500] apply poe-profile profile1 interface ethernet1/0/1 to ethernet1/0/5 8 apply the configured profile 2 to ethernet1/0/6 through ethernet1/0/10 ports. [s5500] apply poe-...
Page 563: Snmp C
28 snmp c onfiguration snmp configuration introduction the simple network management protocol (snmp) has gained the most extensive application in the computer networks. Snmp has been put into use and widely accepted as an industry standard in practice. It is used for ensuring the transmission of the...
Page 564
564 c hapter 28: snmp c onfiguration the current snmp agent of the switch supports snmp v1, v2c and v3. The mibs supported are listed in table 616. Table 616 mibs supported by the switch (sheet 1 of 2) mib attribute mib content references public mib mib ii based on tcp/ip network device rfc1213 ospf...
Page 565
Snmp configuration introduction 565 configure snmp the main configuration of snmp includes: ■ set community name ■ set the method of identifying and contacting the administrator ■ enable/disable snmp agent to send trap ■ set the destination address of trap ■ set snmp system information ■ set the eng...
Page 566
566 c hapter 28: snmp c onfiguration setting community name snmp v1 and snmpv2c adopt the community name authentication scheme. The snmp message incompliant with the community name accepted by the device will be discarded. Snmp community is named with a character string, which is called community na...
Page 567
Snmp configuration introduction 567 setting lifetime of trap message you can use the following command to set the lifetime of a trap message. A trap message that exists longer than the set lifetime will be dropped. Perform the following configuration in system view. Table 620 set the lifetime of tra...
Page 568
568 c hapter 28: snmp c onfiguration table 623 set/delete an snmp group setting the source address of trap you can use the following commands to set or remove the source address of the trap. Perform the following configuration in system view. Table 624 set the source address of trap adding/deleting ...
Page 569
Snmp configuration introduction 569 table 627 set the size of snmp packet sent/received by an agent the agent can receive/send the snmp packets of the sizes ranging from 484 to 17940, measured in bytes. By default, the size of snmp packet is 1500 bytes. Enabling/disabling a port transmitting trap in...
Page 570
570 c hapter 28: snmp c onfiguration displaying and debugging snmp after the above configuration, execute the display command in all views to display the running of the snmp configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute the debugging command in user view to debug snmp configu...
Page 571
Snmp configuration introduction 571 configuration procedure 1 enter the system view. System-view 2 set the community name , group name and user. [sw5500]snmp-agent sys-info version all [sw5500]snmp-agent community write public [sw5500]snmp-agent mib include internet 1.3.6.1 [sw5500]snmp-agent group ...
Page 572
572 c hapter 28: snmp c onfiguration networking diagram figure 167 snmp configuration example configuration procedure [sw5500]snmp-agent community read public [sw5500]snmp-agent community write private [sw5500]snmp-agent sys-info version all [sw5500]snmp-agent group v3 sdsdsd [sw5500]snmp-agent usm-...
Page 573: Ource
29 s ource ip a ddress c onfiguration configuring source ip address for service packets you can configure source ip address or source interface for the ftp server, ftp client, tftp client, telnet server, telnet client, ssh server, ssh2 client and sftp client to enhance service manageability. Table 6...
Page 574
574 c hapter 29: s ource ip a ddress c onfiguration if the ip-addr in the command is not an address of the device, your configuration fails. If you specify a non-existent interface in the command, your configuration fails. Displaying the source ip address configuration use the display commands in an...
Page 575: Assword
30 p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations introduction to password control configuration the password control feature is designed to manage the following passwords: ■ telnet passwords: passwords for logging into the switch through telnet. ■ ssh passwords: passwords for logging into the switch...
Page 576
576 c hapter 30: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations password control configuration this section contains configuration information on password control. Configuration prerequisites a user pc is connected to the switch to be configured; both devices are operating normally. Configuration tas...
Page 577
Password control configuration 577 length limitation, the configured minimum password length (if available); the enable/disable state of history password recording, the maximum number of history password records, the time when the password history was last cleared; the timeout time for password auth...
Page 578
578 c hapter 30: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations after password aging is enabled, the device will decide whether the user password ages out when a user logging into the system is undergoing the password authentication. This has three cases: 1 the password has not expired. The user logs...
Page 579
Password control configuration 579 configuring history password recording with this function enabled, when a login password expires, the system requires the user to input a new password and save the old password automatically. You can configure the maximum number of history records allowed for each ...
Page 580
580 c hapter 30: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations configuring a user login password in encryption mode configuring login attempts limitation and failure processing mode when the maximum number of attempts is exceeded, the system operates in one of the following processing mode: ■ lockti...
Page 581
Displaying password control 581 the system administrator can perform the following operations to manually remove one or all user entries in the blacklist. Configuring the timeout time for users to be authenticated when the local/remote server receives the user name, the authentication starts; when t...
Page 582
582 c hapter 30: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations password control configuration example network requirements a pc is connected to the switch to be configured. You can configure the password control parameters as required. Network diagram figure 168 network diagram for password control ...
Page 583
Password control configuration example 583 7 display the information about the password control for all users. S5500[s5500] display password-control global password settings for all users: password aging: enabled (90 days) password length: enabled (10 characters) password history: enabled (max histo...
Page 584
584 c hapter 30: p assword c ontrol c onfiguration o perations.
Page 585: Msdp C
31 msdp c onfiguration among switch 5500 series ethernet switches, only switch 5500-ei series ethernet switches support the configurations described in this chapter. Routers and router icons in this chapter represent routers in the common sense and ethernet switches running routing protocols. Introd...
Page 586
586 c hapter 31: msdp c onfiguration msdp peers are interconnected over tcp connections (using port 639). A tcp connection can be established between rps in different pim-sm domains, between rps in the same pim-sm domain, between an rp and a common router, or between common routers. Figure 169 shows...
Page 587
Introduction to msdp 587 figure 170 typical networking of anycast rp . Typically, a multicast source s registers to the nearest rp to create an spt, and receivers also send join messages to the nearest rp to construct an rpt, so it is likely that the rp to which the multicast source has registered i...
Page 588
588 c hapter 31: msdp c onfiguration figure 171 identifying the multicast source and receiving multicast data the complete interoperation process between a multicast source s in the pim-sm1 domain and receivers in the pim-sm1 and pim-sm4 domains is as follows: 1 the multicast source s in the pim-sm1...
Page 589
Introduction to msdp 589 figure 172 forwarding sa messages between msdp peers as shown above, rp1 belongs to as1. Rp2, rp3 and rp4 belong to as2. Rp5 and rp6 belong to as3. An msdp peering relationship exists among these rps. Rp2, rp3, and rp4 form a mesh group. These msdp peers perform rpf check an...
Page 590
590 c hapter 31: msdp c onfiguration configuring msdp basic functions to enable exchange of information from the multicast source s between two pim-sm domains, you need to establish msdp peering relationships between rps in these pim-sm domains, so that the information from the multicast source can ...
Page 591
Configuring connection between msdp peers 591 configuring msdp basic functions configuring connection between msdp peers an as may contain multiple msdp peers. To avoid sa flooding between the msdp peers, you can use the msdp mesh mechanism to improve traffic. When multiple msdp peers are fully conn...
Page 592
592 c hapter 31: msdp c onfiguration configuring description information for msdp peers you can configure description information for each msdp peer to manage and memorize the msdp peers. Configuring anycast rp application if you configure rps that have the same address on two routers in the same pi...
Page 593
Configuring sa message transmission 593 configuring msdp peer connection control the connection between msdp peers can be flexibly controlled. You can disable the msdp peering relationships temporarily by shutting down the msdp peers. As a result, sa messages cannot be transmitted between such two p...
Page 594
594 c hapter 31: msdp c onfiguration configuring the transmission and filtering of sa request messages after you enable sending sa request messages to msdp peers, when a router receives a join message, it sends an sa request message to the specified remote msdp peer, which responds with an sa messag...
Page 595
Configuring sa message transmission 595 configuring a rule for filtering received and forwarded sa messages besides the creation of source information, controlling multicast source information allows you to control the forwarding and reception of source information. You can control the reception of ...
Page 596
596 c hapter 31: msdp c onfiguration displaying and debugging msdp configuration after the above-mentioned configuration, you can use the display command in any view to view the msdp running information, so as to verify configuration result. In the user view, you can execute the reset command to res...
Page 597
Msdp configuration example 597 the pim-sm network implements ospf to provide unicast routes and establish msdp peers between switchc and switchd. Meanwhile, the loopback10 interfaces of switchc and switchd play the roles of c-bsr and c-rp. Network diagram figure 173 network diagram for anycast rp co...
Page 598
598 c hapter 31: msdp c onfiguration c when the multicast source s1 in the pim-sm domain sends multicast information, the receivers attached to switchd can receive the multicast information and can view the pim routing information on the switch by using the display pim routing-table command. For exa...
Page 599
Troubleshooting msdp configuration 599 troubleshooting msdp configuration the following sections provide troubleshooting guidelines for msdp configuration. Msdp peer always in the down state symptom an msdp peer is configured, but it is always in the down state. Analysis an msdp peer relationship be...
Page 600
600 c hapter 31: msdp c onfiguration.
Page 601: Lustering
32 c lustering clustering overview clustering enables the network to manage multiple switches through the public ip address of a switch named the management device. Managed switches in a cluster are member devices, and often may not have an assigned public ip address. Management and maintenance on m...
Page 602
602 c hapter 32: c lustering ■ topology collection: clustering implements ntdp (neighbor topology discovery protocol) to collect information on device connections and candidate devices within a specified hop range. ■ member recognition: members in the cluster can be located, thus the management devi...
Page 603
Clustering overview 603 figure 175 role changing rule ■ a cluster can have only one management device, which is necessary to the cluster. The management device collects ndp/ntdp information to discover and confirm candidate devices, which can be then added into the cluster through manual configurati...
Page 604
604 c hapter 32: c lustering when the ndp on the member device finds changes of neighbors, it will advertise the changes to the management device by handshake packets. The management device can run ntdp to collect the specified topology information and show the network topology changes in time. On a...
Page 605
Management device configuration 605 management device configuration management device configuration involves: ■ enable system and port ndp ■ configure ndp parameters ■ enable system and port ntdp ■ configure ntdp parameters ■ enable the cluster function ■ configure cluster parameters ■ configuring i...
Page 606
606 c hapter 32: c lustering enabling the cluster function configuring cluster parameters configuring cluster parameters manually configure the time that collected devices wait before forwarding the topology-collection request ntdp timer hop-delay time optional argument time is the delay time. Confi...
Page 607
Management device configuration 607 configuring a cluster automatically configuring internal-external interaction nm interface for cluster management configuration configuration preparation ■ the cluster switches are properly connected. ■ the internal server is properly connected with the management...
Page 608
608 c hapter 32: c lustering member device configuration member device configuration involves: ■ enable system and port ndp ■ enable system and port ntdp ■ specifying the cluster ftp/tftp server enabling system and port ndp enabling system and port ntdp specifying the cluster ftp/tftp server table 6...
Page 609
Configuring cluster parameters 609 configuring cluster parameters displaying and maintaining cluster configurations you can view the configuration information of a cluster with the display commands, which can be executed in any view. Table 668 configure cluster parameters operation command remark en...
Page 610
610 c hapter 32: c lustering clustering configuration example network requirements three switches form a cluster, in which: ■ switch 5500 acts as the management device. ■ other two switches act as member devices. As the management device, switch 5500 manages the member devices and is configured as f...
Page 611
Clustering configuration example 611 b configure holdtime of ndp information as 200 seconds. [s5500] ndp timer aging 200 c configure interval of ndp packets as 70 seconds. [s5500] ndp timer hello 70 d enable system ntdp and port ntdp on e1/0/2 and e1/0/3. [s5500] ntdp enable [s5500] interface ethern...
Page 612
612 c hapter 32: c lustering 2 configure member devices (take one member as example) a enable system ndp and port ndp on port ethernet1/1. [s5500] ndp enable [s5500] interface ethernet 1/1 [s5500-ethernet1/1] ndp enable b enable system ntdp and port ntdp on port ethernet1/1. [s5500] ntdp enable [s55...
Page 613
Clustering configuration example 613 network diagram figure 176 network diagram for the interfaces of cluster management network configuration procedure configuring the switch 5500 switch 1 enter system view. Specify vlan 3 as the management vlan. System-view system view: return to user view with ct...
Page 614
614 c hapter 32: c lustering.
Page 615: Hwtacacs C
33 hwtacacs c onfiguration configuring hwtacacs this chapter contains information on hwtacacs configuration. Hwtacacs configuration tasks refer to the tasks in table 671 to configure hwtacacs. Table 671 hwtacacs configuration section task command view description creating a hwtacas scheme creating a...
Page 616
616 c hapter 33: hwtacacs c onfiguration pay attention to the following when configuring a tacacs server: ■ hwtacacs server does not check whether a scheme is being used by users when changing most of hwtacacs attributes, unless you delete the scheme. ■ by default, the tacacs server has no key. In t...
Page 617
Configuring hwtacacs 617 configuring hwtacacs authentication servers perform the following configuration in hwtacacs view. The primary and secondary authentication servers cannot use the same ip address. The default port number is 49. If you execute this command repeatedly, the new settings will rep...
Page 618
618 c hapter 33: hwtacacs c onfiguration configuring source address for hwtacacs packets sent by nas perform the following configuration in the corresponding view. The hwtacacs view takes precedence over the system view when configuring the source address for hwtacacs packets sent from the nas. By d...
Page 619
Configuring hwtacacs 619 setting the unit of data flows destined for the tacacs server perform the following configuration in hwtacacs view. The default data flow unit is byte. Setting timers regarding tacacs server setting the response timeout timer since hwtacacs is implemented on the basis of tcp...
Page 620
620 c hapter 33: hwtacacs c onfiguration the setting of real-time accounting interval somewhat depends on the performance of the nas and the tacacs server: a shorter interval requires higher device performance. You are therefore recommended to adopt a longer interval when there are a large number of...
Page 621
Hwtacacs protocol configuration example 621 hwtacacs protocol configuration example for the hybrid configuration example of aaa/radius protocol and 802.1x protocol, refer to configuration example in 802.1x configuration. It will not be detailed here. Configuring the ftp/telnet user authentication at...
Page 622
622 c hapter 33: hwtacacs c onfiguration configuration procedure 1 configure a hwtacacs scheme. [s5500] hwtacacs scheme hwtac [s5500-hwtacacs-hwtac] primary authentication 10.110.91.164 49 [s5500-hwtacacs-hwtac] primary authorization 10.110.91.164 49 [s5500-hwtacacs-hwtac] key authentication expert ...
Page 623: Assword
A p assword r ecovery p rocess introduction the switch 5500 has two separate password systems: n passwords which are used by the web user interface and the cli and are stored in the 3comoscfg.Cfg file. For more information on this, refer to the getting started guide which accompanies your switch. N ...
Page 624
624 c hapter a: p assword r ecovery p rocess bootrom interface during the initial boot phase of the switch (when directly connected using the console), various messages are displayed and the following prompt is shown with a five second countdown timer: press ctrl-b to enter boot menu... 4 before the...
Page 625
Bootrom interface 625 skipping the current configuration file enter boot menu option 7 to enable the switch to boot from the factory default configuration file 3comoscfg.Def . When the switch has booted from the factory default it can be configured with an ip address and default gateway if needed. T...
Page 626
626 c hapter a: p assword r ecovery p rocess if the user configured bootrom password is lost, a fixed, unit unique password can be provided by 3com technical support to bypass the lost password. Please ensure that the switch is registered with 3com promptly as the unit unique password will only be s...
Page 627: Radius S
B radius s erver and radius c lient s etup this appendix covers the following topics: n setting up a radius server n setting up the radius client setting up a radius server there are many third party applications available to configure a radius server. 3com has successfully installed and tested the ...
Page 628
628 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup b the server will need to run in native mode in order to support eap-tls which is not available in mixed mode. To change mode go to the active directory users and computers window, right-click domain and choose properties, select change mode. ...
Page 629
Setting up a radius server 629 d follow the wizard to create a user, enter the required information at each stage e the password for the user must be set to be stored in reversible encryption. Right-click the user account and select properties. Select the account tab, check the box labelled store pa...
Page 630
630 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup a go to control panel > add/remove programs > add/remove windows components. The certificate services component should be checked. B select next and continue through the wizard. In the certificate authority type window select enterprise root c...
Page 631
Setting up a radius server 631 4 install the internet authentication service (ias) program. A go to control panel > add/remove programs > add/remove windows components. Enable networking services and ensure internet authentication service component is checked. B select ok to end the wizard. 5 config...
Page 632
632 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup d go to programs > administrative tools > active directory users and computers and right-click your active directory domain. Select properties e select the group policy tab, and ensure that the default domain policy is highlighted. Click edit ...
Page 633
Setting up a radius server 633 g the certificate request wizard will start. Select next > computer certificate template and click next. H ensure that your certificate authority is checked, then click next. Review the policy change information and click finish. I open up a command prompt (start > run...
Page 634
634 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup e give the policy a name, for example eap-tls, and select next. F click add... G set the conditions for using the policy to access the network. Select day-and-time-restrictions, and click add... Click permitted, then ok. Select next. H select ...
Page 635
Setting up a radius server 635 k select the appropriate certificate and click ok. There should be at least one certificate. This is the certificate that has been created during the installation of the certification authority service. Windows may ask if you wish to view the help topic for eap. Select...
Page 636
636 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup b when you are prompted for a login, enter the user account name and password that you will be using for the certificate. C select request a certificate and click next > there are two ways to request a certificate: the advanced request or the ...
Page 637
Setting up a radius server 637 f either copy the settings from the screenshot below or choose different key options. Click save to save the pkcs #10 file. The pkcs #10 file is used to generate a certificate. G you will receive this warning messages, select yes followed by this warning message, selec...
Page 638
638 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup j select the second option as shown in the screenshot below, and click next > k open the previously saved pkcs #10 certificate file in notepad, select all (control + a) and copy (control + c), as shown below l paste the copied information into...
Page 639
Setting up a radius server 639 m download the certificate and certification path. Click on the download ca certificate hyperlink to save the certificate. Save the file as der encoded. Click on the download ca certification path hyperlink to save the pkcs #7, and select save the certificate is also i...
Page 640
640 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup p leave the settings on the next screen as is, click next > followed by finish and ok. This will install the certificate, q launch the certification authority management tool on the server and expand the issued certificates folder. You should ...
Page 641
Setting up a radius server 641 save the certificate using der x.509 encoding, select der encoded binary followed by next. Provide a name for the certificate and save it to a specified location. Click finish and followed by ok. T exit the certification authority management tool and launch the active ...
Page 642
642 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup u select the user that becomes the ieee 802.1x client. Right-click on the user and select name mappings. Select add v select the certificate that you have just exported and click open. Click ok w in the security identity mapping screen, click ...
Page 643
Setting up a radius server 643 b create a new remote access policy under ias and name it switch login. Select next> c specify switch login to match the users in the switch access group, select next > d allow switch login to grant access to these users, select next >.
Page 644
644 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup e use the edit button to change the service-type to administrative. F add a vendor specific attribute to indicate the access level that should be provided:.
Page 645
Setting up a radius server 645 the value 010600000003 indicates admin privileges for the switch. 01 at the end indicates monitor and 02 indicates manager access. On the switch 5500, 00 indicates visitor level. 11 configure the radius client. Refer to “setting up the radius client” for information on...
Page 646
646 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup follow these steps to set up auto vlan and qos for use by microsoft ias: 1 define the vlan groups on the active directory server and assign the user accounts to each vlan group. Go to programs > administrative tools > active directory users an...
Page 647
Setting up a radius server 647 d go to programs > administrative tools > internet authentication service. And select remote access policies. Select the policy that you configured earlier, right-click and select properties. E click add to add policy membership. F select the windows-groups attribute t...
Page 648
648 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup g select the vlan group that you have just created and click add and then ok to confirm. H click ok again to return you to the security policy properties..
Page 649
Setting up a radius server 649 i click edit profile... And select the advanced tab. Click add. Refer to table 686 and table 687 for the radius attributes to add to the profile. J select tunnel-medium-type and click add. K ensure that the attribute value is set to 802 and click ok. L click ok again o...
Page 650
650 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup m select the tunnel-pvt-group-id entry and click add. N click add, ensure that the attribute value is set to 4 (attribute value in string format), and click ok. This value represents the vlan id. O click ok again on the multivalued attribute i...
Page 651
Setting up a radius server 651 p click add again. In the pull down menu, select virtual lans and click ok. Q click ok again and to return to the add attributes screen. Click close. You will now see the added attributes r click ok to close the profile screen and ok again to close the policy screen. T...
Page 652
652 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup configuring funk radius 3com has successfully installed and tested funk radius running on a windows server in a network with switch 5500 deployed. Download the funk steel-belted radius server application from www.Funk.Com and install the appli...
Page 653
Setting up a radius server 653 3 either re-boot the server or stop then restart the radius service. To stop and restart the steel-belted radius service, go to control panel > administrative tools > services. Scroll down to the steel-belted service, stop and restart it. Funk radius is now ready to ru...
Page 654
654 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup passwords are case sensitive. 6 enter the shared secret to encrypt the authentication data. The shared secret must be identical on the switch 5500 and the radius server a select ras clients from the left hand list, enter a client name , the ip...
Page 655
Setting up a radius server 655 configuring auto vlan and qos for funk radius to set up auto vlan and qos using funk radius, follow these steps: 1 edit the dictionary file radius.Dct so that return list attributes from the funk radius server are returned to the switch 5500. The changes to make are: a...
Page 656
656 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup the following example shows the user name homer with the correct return list attributes inserted, the vlans and qos profiles must also be created on the 3com switch 5500. Configuring freeradius 3com has successfully installed and tested freera...
Page 657
Setting up a radius server 657 2 update the dictionary for switch login a in /usr/local/etc/raddb create a new file called dictionary.3com containing the following information: vendor 3com 43 attribute 3com-user-access-level 1 integer 3com value 3com-user-access-level monitor 1 value 3com-user-acces...
Page 658
658 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup in the example above, tunnel-medium-type has been set to tmt802, to force freeradius to treat 802 as a string requiring to be looked up in the dictionary and return integer 6, rather than return integer 802 which would be the case if tunnel-me...
Page 659
Setting up the radius client 659 generate an eapol-logoff message when the user logs-off, which leaves the port authorized. To reduce the impact of this issue, decrease the "session-timeout" return list attribute to force re-authentication of the port more often. Alternatively, use a radius client w...
Page 660
660 c hapter b: radius s erver and radius c lient s etup b this screen will appear: c leave the profile as default. The identity is an account created on the radius server with the password. D click ok to finish the configuration. E restart the client either by rebooting, or stopping and re-starting...
Page 661: Uthenticating
C a uthenticating the s witch 5500 with c isco s ecure acs this appendix covers the following topics: n cisco secure acs (tacacs+) and the 3com switch 5500 n setting up the cisco secure acs (tacacs+) server cisco secure acs (tacacs+) and the 3com switch 5500 cisco secure acs and tacacs+ are propriet...
Page 662
662 c hapter c: a uthenticating the s witch 5500 with c isco s ecure acs adding a 3com switch 5500 as a radius client once logged into the cisco secure acs interface, follow these steps: 1 select network configuration from the left hand side 2 select add entry from under aaa clients. 3 enter the det...
Page 663
Setting up the cisco secure acs (tacacs+) server 663 5 select interface configuration from the left hand side. 6 select radius (ietf) from the list under interface configuration. 7 check the radius attributes that you wish to install. If you want to use auto vlan and qos, ensure that you have the fo...
Page 664
664 c hapter c: a uthenticating the s witch 5500 with c isco s ecure acs 8 select submit. 9 repeat step 1 through step 8 for each switch 5500 on your network. When all of the switch 5500s have been added as clients to the cisco secure acs server, restart the secure acs server by selecting system con...
Page 665
Setting up the cisco secure acs (tacacs+) server 665 the screen below shows specific radius attributes having been selected for the user. The user has the student profile selected and is assigned to vlan 10 untagged. The radius attributes need to have already been selected, see step 7 in adding a 3c...
Page 666
666 c hapter c: a uthenticating the s witch 5500 with c isco s ecure acs 1=monitor 2=manager 3=administrator b locate the application csutil.Exe . In the utils directory of the install path (eg. C:\program files\cisco secure acs\utils\). C copy the 3com.Ini file into the utils directory d at the com...
Page 667
Setting up the cisco secure acs (tacacs+) server 667 2 to use the new radius attributes, a client needs to be a user of radius (3com) attributes. Select network configuration from the left hand side and select an existing device or add a new device. In the aaa client setup window select radius (3com...
Page 668
668 c hapter c: a uthenticating the s witch 5500 with c isco s ecure acs 5 ensure that the 3com-user-access-level option is selected for both user and group setup, as shown below 6 select user setup and either modify the attributes of an existing user (select find to display the user list in the rig...
Page 669
Setting up the cisco secure acs (tacacs+) server 669 7 in the radius (3com) attribute box , check 3com-user-access-level and select administrator from the pull down list, see below: 8 select submit. The switch 5500 can now be managed by the network administrator through the cisco secure acs server..
Page 670
670 c hapter c: a uthenticating the s witch 5500 with c isco s ecure acs.
Page 671: Xrn
D 3c om xrn this section explains what 3com xrn™ (expandable resilient networking) is and how you can use it to benefit your network. It also explains how to implement xrn on your network. This chapter contains the following sections: n what is xrn? N xrn terminology n benefits of xrn n xrn features...
Page 672
672 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn what is xrn? Xrn (expandable resilient network) is a 3com lan technology built into the software and hardware of your switch that offers high availability, scalability, and connectivity. Supported switches xrn is supported by the 3com operating system on the following swit...
Page 673
Benefits of xrn 673 benefits of xrn the benefits of xrn include: n increased environmental resilience provided by: n hardware and software redundancy per unit or across the distributed fabric. N distributed management across the distributed fabric. N distributed link aggregation across the distribut...
Page 674
674 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn switch units within the distributed fabric provide the same router interfaces and mirror each other’s routing tables. This allows each unit to keep the routing local to the unit for locally connected hosts and devices. In the example shown in figure 178, there is a single ...
Page 675
Xrn features 675 table 691 aggregated links and member links supported within a fabric distributed link aggregation example you can also use dla to create highly resilient network backbones, supporting multihomed links to the wiring closets as shown in figure 179. Intelligent local forwarding ensure...
Page 676
676 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn how to implement xrn—overview this section provides an overview on how to implement xrn in your network. Following the steps below will ensure that your xrn network operates correctly. 1 design your network using xrn distributed fabrics, taking into account all the importa...
Page 677
Important considerations and recommendations 677 n when you create a distributed fabric the relevant port-based tables do not double in size, they remain as they were. N when switch 5500 units are in an xrn distributed fabric their unit ids are user configurable. N the maximum number of switch units...
Page 678
678 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn n all multihomed links and alternate paths must carry all vlans, and packets must be tagged. N the distributed fabric is the stp root bridge. N individual port members of each aggregated link must have vlan membership manually configured before the aggregated link is set u...
Page 679
Network example using xrn 679 figure 180 a dual xrn distributed fabric network how to set up this network this section provides information on how to configure an xrn network as shown in figure 180. It assumes you have carried out step 1 to step 4 as detailed in “how to implement xrn—overview” on pa...
Page 680
680 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn recovering your xrn network in the event of a failure within your xrn network, 3com recommends that you follow the recommendations below. Unit failure the steps below outline the procedure to recover your xrn network in the event of a unit failure within your distributed f...
Page 681
How xrn interacts with other features 681 how xrn interacts with other features this section provides supplementary information on how xrn interacts with other software features supported by your switch. Vlans figure 181 shows a single aggregated link, created automatically using lacp, connecting th...
Page 682
682 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn figure 182 how xrn interacts with vlans—example 2 legacy aggregated links legacy aggregated links, will react in the normal way if a unit within the distributed fabric fails, that is, all traffic will be redirected down the link(s) to the unit that is still operating. Howe...
Page 683
How xrn interacts with other features 683 stp/rstp stp/rstp should be used for multihomed links if you are not able to use aggregated links. Figure 184 shows how stp will prevent a loop occurring on a multihomed link. Stp/rstp should always be enabled if your multihomed links are aggregated links. F...
Page 684
684 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn how a failure affects the distributed fabric this section provides supplementary information on how the distributed fabric and traffic flow is affected by failure of an fabric interconnect and of a unit in the distributed fabric. Loss of a switch within the xrn distributed...
Page 685
How a failure affects the distributed fabric 685 router switch b will continue to do all the routing. As it was routing prior to switch a’s failure there will be no change of the router identity, that is, the router interface ip addresses will not change. The router interface mac addresses may chang...
Page 686
686 a ppendix d: 3c om xrn ieee802.1d (legacy stp) and rstp the switch 4200 is using legacy stp. Stp (and rstp) will reconfigure the network to open the previously blocked link to switch b. The stp reconfiguration will cause all switch forwarding databases (mac address tables) to be fast aged (if us...