- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- Switch 7700
- Configuration Manual
3Com Switch 7700 Configuration Manual
Summary of Switch 7700
Page 1
Http://www.3com.Com/ switch 7700 configuration guide version 3.0 published november 2004 part no.10014298.
Page 2
3com corporation 350 campus drive marlborough, ma 01752-3064 copyright © 2004, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written p...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide conventions 1 s ystem a ccess product overview 3 function features 3 configuring the switch 7700 4 setting terminal parameters 5 configuring through telnet 8 configuring through a dial-up modem 11 configuring the user interface 12 command line interface 20 command line ...
Page 4
N etwork p rotocol o peration configuring ip address 59 subnet and mask 60 configuring an ip address 60 troubleshooting an ip address configuration 62 configuring address resolution protocol (arp) 62 configuring arp 63 dhcp relay 64 configuring dhcp relay 65 troubleshooting a dhcp relay configuratio...
Page 5
Bgp routing 149 bgp peers and peer groups 150 configuring bgp 150 typical bgp configuration examples 168 troubleshooting bgp 174 ip routing policy 174 routing information filters 175 configuring an ip routing policy 176 troubleshooting routing policies 182 route capacity 183 limiting route capacity ...
Page 6
Activating an acl 236 acl configuration examples 237 access control 237 basic acl 238 link acl 239 configuring qos 239 qos concepts 240 configuring qos 243 qos configuration examples 250 configuring acl control 257 configuring acl control for telnet users 258 configuring acl control for snmp users 2...
Page 7
802.1x system architecture 287 configuring 802.1x 289 configuring the aaa and radius protocols 296 configuring aaa 298 configuring the radius protocol 301 troubleshooting aaa and radius 311 r eliability vrrp overview 313 configuring vrrp 314 enable pinging the virtual ip address 314 setting correspo...
Page 8
Configuring rmon 354 ntp 357 configuring ntp 358 ntp configuration examples 364 ssh terminal services 371 configuring the ssh server 373 configuring the ssh client 376 specifying the server ip address 376 displaying and debugging ssh 379 ssh configuration example 380
Page 9: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide describes the 3com ® switch 7700 and how to configure it in version 3.0 of the software. Conventions table 1 lists icon conventions that are used throughout this book. Table 2 lists the text conventions used in this book. Table 1 notice icons icon notice type descripti...
Page 10
2 a bout t his g uide.
Page 11: Ystem
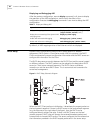
1 s ystem a ccess this chapter covers the following topics: ■ product overview ■ configuring the switch 7700 ■ setting terminal parameters ■ command line interface product overview the 3com switch 7700 is a large capacity, modularized wire speed layer 2/layer 3 switch 7700. It is designed for ip met...
Page 12
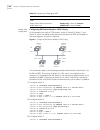
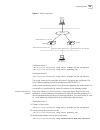
4 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess configuring the switch 7700 on the switch 7700, you can set up the configuration environment through the console port. To set up the local configuration environment: 1 plug the db-9 or db-25 female plug of the console cable into the serial port of the pc or the terminal...
Page 13
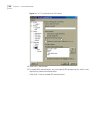
Setting terminal parameters 5 figure 1 setting up the local configuration environment through the console port setting terminal parameters to set terminal parameters: 1 start the pc and select start > programs > accessories > communications > hyperterminal. 2 the hyperterminal window displays the co...
Page 14
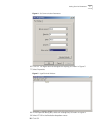
6 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess figure 3 properties dialog box 5 click ok. The port settings tab, shown in figure 4, displays and you can set serial port parameters. Set the following parameters: ■ baud rate = 9600 ■ databit = 8 ■ parity check = none ■ stopbit = 1 ■ flow control = none.
Page 15
Setting terminal parameters 7 figure 4 set communication parameters 6 click ok. The hyperterminal dialogue box displays, as shown in figure 5. 7 select properties. Figure 5 hyperterminal window 8 in the properties dialog box, select the settings tab, as shown in figure 6. 9 select vt100 in the emula...
Page 16
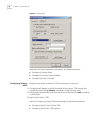
8 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess figure 6 settings tab setting the terminal parameters is described in the following sections: ■ configuring through telnet ■ configuring through a dial-up modem ■ configuring the user interface configuring through telnet before you can telnet to a switch 7700 and config...
Page 17
Setting terminal parameters 9 connecting the pc to the switch 7700 to connect the pc and switch 7700 through telnet: 1 authenticate the telnet user through the console port before the user logs in by telnet. By default, a password is required for authenticating the telnet user to log in the switch 7...
Page 18
10 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess 6 use the appropriate commands to configure the switch 7700 or to monitor the operational state. Enter ? To get immediate help. For details on specific commands, refer to the chapters in this guide. When configuring the switch 7700 by telnet, do not modify the ip addre...
Page 19
Setting terminal parameters 11 configuring through a dial-up modem to configure your router through a dial-up modem: 1 authenticate the modem user through the console port of the switch 7700 before the user logs in to the switch through a dial-up modem. By default, a password is required for authent...
Page 20
12 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess figure 11 set the dialed number figure 12 dial the remote pc 4 enter the preset login password on the remote terminal emulator and wait for the prompt. 5 use the appropriate commands to configure the switch 7700 or view its operational state. Enter ? To get immediate h...
Page 21
Setting terminal parameters 13 ■ remote configuration through a modem through the console port. There are two types of user interfaces: ■ aux user interface is used to log in the switch 7700 through a dial-up modem. A switch 7700 can only have one aux port. ■ vty user interface is used to telnet the...
Page 22
14 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess perform the following configurations in user interface (aux user interface only) view. Configuring the terminal attributes the following commands can be used for configuring the terminal attributes, including enabling/disabling terminal service, disconnection upon time...
Page 23
Setting terminal parameters 15 by default, terminal service is enabled on all the user interfaces. Note the following points: ■ for the sake of security, the undo shell command can only be used on the user interfaces other than the aux user interface. ■ you cannot use this command on the user interf...
Page 24
16 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess managing users the management of users includes, the setting of the user logon authentication method, the level of command a user can use after logging on, the level of command a user can use after logging on from the specific user interface, and the command level. Con...
Page 25
Setting terminal parameters 17 perform username and password authentication when a user logs in through the vty 0 user interface and set the username and password to zbr and 3com respectively: [sw7700-ui-vty0] authentication-mode scheme [sw7700-ui-vty0] quit [sw7700] local-user zbr [sw7700-luser-zbr...
Page 26
18 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess when a user logs in to the switch, the command level that the user can access depends on two points. One is the command level that the user can access, the other is the set command level of the user interface. If the two levels are different, the former is taken. For e...
Page 27
Setting terminal parameters 19 perform the following configuration in user view. The auto-execute command is used to run a command automatically after you log in. The command is automatically executed when you log in again. See table 16. This command is usually used to execute the telnet command aut...
Page 28
20 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess command line interface the switch 7700 provides a series of configuration commands and command line interfaces for configuring and managing the switch 7700. The command line interface has the following features. ■ local configuration through the console port. ■ local o...
Page 29
Command line interface 21 login users are also classified into four levels that correspond to the four command levels. After users of different levels log in, they can only use commands at their own, or lower, levels. To prevent unauthorized users from illegal intrusion, users are identified when sw...
Page 30
22 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess figure 13 relation diagram of the views table 18 describes the function features of different views. For all views, use the quit command to return to system view and use the return command to return to user view. Table 18 function feature of command view command view f...
Page 31
Command line interface 23 features and functions of the command line tasks for configuring the features and functions of the command line are described as follows: ■ online help ■ common command line error messages ■ history command ■ editing features of the command line ■ displaying features of the...
Page 32
24 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess quit exit from current command view super enter the command workspace with specified user priority level telnetestablish one telnet connection tracerttrace route function ■ enter a command with a ? , separated by a space. If this position is for keywords, then all the ...
Page 33
Command line interface 25 common command line error messages all the commands that are entered by users can be correctly executed if they have passed the grammar check. Otherwise, error messages are reported to users. Common error messages are listed in table 19. History command the command line int...
Page 34
26 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess displaying features of the command line if information to be displayed exceeds one screen, the pause function allows users three choices, as described in table 22. Tab press tab after typing the incomplete key word and the system will execute the partial help: if the k...
Page 35: Ort
2 p ort c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ethernet port overview ■ configuring link aggregation ethernet port overview the following features are found in the ethernet ports of the switch 7700: ■ 10base-t/100base-tx gigabit ethernet ports support mdi/mdi-x auto-sensing, and ...
Page 36
28 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration ■ setting cable type for ethernet port ■ setting flow control for ethernet port ■ permitting/forbidding jumbo frames on the ethernet port ■ setting the maximum mac addresses an ethernet port can learn ■ setting the link type for an ethernet port ■ adding the ether...
Page 37
Ethernet port overview 29 setting duplex attribute of the ethernet port set the port to full duplex to send and receive data packets at the same time. Set the port to half-duplex to either send or receive only. If the port has been set to auto-negotiation mode, the local and peer ports will automati...
Page 38
30 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration setting flow control for ethernet port if congestion occurs in the local switch after enabling flow control in both the local and the peer switch, then the switch will inform its peer to pause sending packets. Once the peer switch receives this message, it will pa...
Page 39
Ethernet port overview 31 if the count parameter is set to 0, the port is not permitted to learn mac address. By default, there is no limit to the amount of the mac addresses that an ethernet port can learn. However the number of mac addresses a port can learn is still restricted by the size of the ...
Page 40
32 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration a port on a switch can be configured as an access port, a hybrid port, or a trunk port. However, to reconfigure between hybrid and trunk link types, you must first restore the default, or access link type. The default link type is the access link type. Adding the ...
Page 41
Ethernet port overview 33 ■ a trunk port and isolate-user-vlan cannot be configured simultaneously. A hybrid port and isolate-user-vlan can be configured simultaneously. However, if the default vlan has been mapped in isolate-user-vlan, you cannot modify the default vlan id until the mapping relatio...
Page 42
34 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration ■ qos setting — includes traffic limiting, priority marking, default 802.1p priority, bandwidth assurance, congestion avoidance, traffic redirection, traffic statistics. ■ vlan setting — includes permitted vlan types, default vlan id. ■ port setting — includes por...
Page 43
Configuring link aggregation 35 the following configurations are used for switch a, configure switch b in a similar way: 1 enter the ethernet port view of ethernet1/0/1. [sw7700] interface ethernet1/0/1 2 set the ethernet1/0/1 as a trunk port and allows vlan 2, 6 through 50, and 100 to pass through....
Page 44
36 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration (point-to-point or not), stp priority, path cost, max transmission speed, loop protection, root protection, edge port or not. The qos setting includes traffic limiting, priority marking, default 802.1p priority, bandwidth assurance, congestion avoidance, traffic r...
Page 45
Configuring link aggregation 37 ■ the system sets ports to inactive state if their basic configurations are different from the basic configuration of the active port with the lowest port number. In a static lacp aggregation group, the system sets the ports to active or inactive state based on these ...
Page 46
38 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration compares port priority values and then port numbers and the small port id is considered prior. If system id changes from non-priority to priority, then the selected or standby state is determined by the port priority of the system. You can decide whether the port ...
Page 47
Configuring link aggregation 39 ■ displaying and debugging link aggregation enabling or disabling lacp at a port you should first enable lacp at the ports before performing dynamic aggregation, so that both parties can agree on adding/deleting the ports into/from a dynamic lacp aggregation group. Pe...
Page 48
40 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration to a static one. In the former case, lacp shall be disabled at the member ports automatically, while in the latter case, lacp shall remain enabled. Adding or deleting ethernet ports to or from an aggregation group you can add/delete ports into/from a manual or sta...
Page 49
Configuring link aggregation 41 perform the following configuration in system view. By default, system priority is 32768. Configuring port priority the lacp compares system ids first and then port ids (if system ids are the same) in determining if the member ports are selected or standby ones for a ...
Page 50
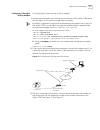
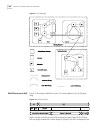
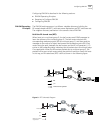
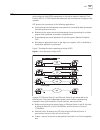
42 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration example: link aggregation configuration switch a connects switch b with three aggregation ports, numbered as ethernet1/0/1 to ethernet1/0/3, so that the incoming and outgoing loads can be balanced among the member ports. Figure 2 networking for link aggregation th...
Page 51
Configuring link aggregation 43 [sw7700-ethernet1/0/1] interface ethernet1/0/2 [sw7700-ethernet1/0/2] port link-aggregation group 1 [sw7700-ethernet1/0/2] interface ethernet1/0/3 [sw7700-ethernet1/0/3] port link-aggregation group 1 3 configure a dynamic lacp aggregation ■ enable lacp at ethernet por...
Page 52
44 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration.
Page 53: Vlan C
3 vlan c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ vlan overview ■ configuring vlans ■ configuring garp/gvrp vlan overview a virtual local area network (vlan) creates logical groups of lan devices into segments to implement virtual workgroups. Using vlan technology, you can logically ...
Page 54
46 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration common vlan configuration tasks the following sections discuss the common tasks for configuring a vlan: ■ creating or deleting a vlan ■ specifying the broadcast suppression ratio for a vlan ■ setting or deleting the vlan description character string ■ specifying or...
Page 55
Configuring vlans 47 setting or deleting the vlan description character string you can use the following command to set or delete the vlan description character string. The description character strings, such as workgroup_name and department_name, are used to distinguish the different vlans. Perform...
Page 56
48 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration status of one or more ethernet ports is up, the status of the vlan interface is up also, so the vlan interface is enabled. Displaying and debugging a vlan after the configuring a vlan, execute the display command in any view to display the vlan configuration, and t...
Page 57
Configuring vlans 49 configuring port-based vlans adding ethernet ports to a vlan use the following command to add ethernet ports to a vlan. Perform the following configuration in vlan view. For the meanings of the parameters related to the ethernet ports and the specific numbering rules of the port...
Page 58
50 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration creating and deleting a vlan protocol type you can use the following command to create or delete a vlan protocol type. Perform the following configuration in vlan view. Creating and deleting the association between a port and a protocol-based vlan perform the follo...
Page 59
Configuring vlans 51 [sw7700-vlan2] vlan 3 4 add ethernet1/0/3 and ethernet1/0/4 to vlan3. [sw7700-vlan3] port ethernet1/0/3 to ethernet1/0/4 example: protocol-based vlan configuration from port g1/0/1, all the traffic with source ip 10.0.0.1 will belong to vlan 2 and any other ip traffic will belon...
Page 60
52 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration 2 configure vlan 2 and vlan 3 as protocol vlans. Set vlan 2 as ip 10.0.0.1 protocol and vlan 3 as ip protocol [sw7700-vlan2]protocol-vlan ? At specify at(appletalk protocol) configuration information ip specify ip(internet protocol) configuration information ipx sp...
Page 61
Configuring garp/gvrp 53 [sw7700-gigabitethernet1/0/1]port hybrid protocol-vlan 2 0 [sw7700-gigabitethernet1/0/1]port hybrid protocol-vlan 3 0 [sw7700-gigabitethernet1/0/1]display th # interface gigabitethernet1/0/1 port link-type hybrid port hybrid vlan 2 to 3 tagged port hybrid vlan 1 untagged por...
Page 62
54 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration messages cooperate to ensure the logout and the re-registration of a message. By exchanging messages, all the attribute information to be registered can be propagated to all the switches in the same switching network. The destination mac addresses of the packets of...
Page 63
Configuring garp/gvrp 55 note that the value of the join timer should be no less than twice the value of the hold timer, and the value of the leave timer should be greater than twice the value of the join timer and smaller than the leaveall timer value. Otherwise, the system displays an error messag...
Page 64
56 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration ■ enabling or disabling port gvrp ■ setting the gvrp registration type when you configure gvrp, you need to enable it globally and for each port participating in gvrp. Similarly, the gvrp registration type can take effect only after you configure port gvrp. In addi...
Page 65
Configuring garp/gvrp 57 ■ when an ethernet port registration type is set to forbidden, all the vlans except vlan1 are logged out and no other vlans can be created or registered on this port. Perform the following configurations in ethernet port view. By default, the gvrp registration type is normal...
Page 66
58 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration [sw7700-ethernet1/0/1] vlan 3 [sw7700-vlan3] vlan 4 3 enable gvrp globally. [sw7700-vlan4] quit [sw7700] gvrp 4 enable gvrp on the trunk port. [sw7700] interface ethernet 1/0/1 [sw7700-ethernet1/0/1] gvrp configure switch b: 1 set gigabit ethernet2/1 as a trunk por...
Page 67: Etwork
4 n etwork p rotocol o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ configuring ip address ■ configuring address resolution protocol (arp) ■ dhcp relay ■ ip performance ■ configuring ipx configuring ip address ip address is a 32-bit address represented by four octets. Ip addresses are divide...
Page 68
60 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration ■ configuring an ip address ■ troubleshooting an ip address configuration subnet and mask ip protocol allocates one ip address for each network interface. Multiple ip addresses can only be allocated to a device which has multiple network interfaces. Ip ad...
Page 69
Configuring ip address 61 perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. The network id of an ip address is identified by the mask. For example, the ip address of a vlan interface is 129.9.30.42 and the mask is 255.255.0.0. After performing the and operation for the ip address and the m...
Page 70
62 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration [sw7700-vlan-interface1] ip address 129.2.2.1 255.255.255.0 troubleshooting an ip address configuration if the ethernet switch cannot ping a certain host on the lan, proceed as follows: 1 determine which vlan includes the port connected to the host. Check...
Page 71
Configuring address resolution protocol (arp) 63 configuring arp the arp mapping table can be maintained dynamically or manually. Addresses that are mapped manually are referred to as static arp. The user can display, add, or delete the entries in the arp mapping table through manual commands. Arp c...
Page 72
64 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration displaying and debugging arp after the previous configuration, execute display command in all views to display the operation of the arp configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute the debugging command in user view to debug the a...
Page 73
Dhcp relay 65 then the server transmits the configuration information to the clients through the dhcp relay, thereby, completing the dynamic configuration of the client. Configuring dhcp is described in the following sections: ■ configuring dhcp relay ■ troubleshooting a dhcp relay configuration con...
Page 74
66 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration configuring the address table entry to check the address of users who have valid and fixed ip addresses in the vlan (with dhcp enabled), it is necessary to add an entry in the static address table. Perform the following configuration in system view. Enabl...
Page 75
Dhcp relay 67 figure 3 networking diagram of configuring dhcp relay 1 configure the dhcp server ip addresses into dhcp server group 1. [sw7700] dhcp-server 1 ip 1.99.255.36 1.99.255.35 2 associate dhcp server group 1 with vlan interface 2. [sw7700-vlan-interface2] dhcp-server 1 3 configure the ip ad...
Page 76
68 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration 8 show the configuration of dhcp server groups in user view. Display dhcp-server 1 9 show the dhcp server group number corresponding to the vlan interface in user view. Display dhcp-server interface vlan-interface 2 display dhcp-server interface vlan-inte...
Page 77
Ip performance 69 finwait timer timeout, the tcp connection will be terminated. Finwait ranges 76 to 3600 seconds and it is 675 seconds by default. ■ the receiving/sending buffer size of connection-oriented socket is in the range from 1 to 32k bytes and is 4k bytes by default. Perform the following ...
Page 78
70 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration if a broadcast packet reaches the destination network after being forwarded by the switch, the switch will receive the broadcast packet; the switch also belongs to the subnet. The vlan of the switch isolates the broadcast domain, it will stop forwarding t...
Page 79
Ipx configuration 71 operations include: terminal debugging debugging tcp packet the tcp packets, received or sent can be checked in real time. Specific packet formats include: tcp output packet: source ip address:202.38.160.1 source port:1024 destination ip address 202.38.160.1 destination port: 42...
Page 80
72 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration next site and if there is any, forwards the packet. The routing information can be configured statically or collected dynamically. This chapter introduces rip in ipx. For the rip configurations on an ip network, refer to the routing protocol section in th...
Page 81
Ipx configuration 73 assigning ipx network numbers to vlan interfaces to enable ipx on a vlan interface after it is enabled globally, you must assign a network number to the vlan interface. One vlan interface can have only one network number. Perform the following configuration in vlan interface vie...
Page 82
74 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration configuring an ipx route limit in ipx, you can configure in the routing table the maximum number of the dynamic routes and equivalent routes to the same destination. These two limit settings are independent. Perform the following configuration in system v...
Page 83
Ipx configuration 75 configuring the update interval of ipx rip the switch broadcasts rip update packets periodically. You can configure the update interval of ipx rip with the following command. Perform the following configuration in system view. By default, ipx rip sends routing updates every 60 s...
Page 84
76 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. By default, the forwarding delay on the vlan interface is one tick. Configuring ipx rip to import static routes by importing static routes, the switch includes the static routes in the ipx rp upd...
Page 85
Ipx configuration 77 configuring the update interval of ipx sap in a huge network, one ipx sap broadcast consumes enormous bandwidth resources. By configuring an appropriate sap update interval, you can reduce the bandwidth waste. Perform the following configuration in system view. By default, ipx s...
Page 86
78 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration ■ respond with the information of the nearest server (the server with the smallest hop count in the service information table on the switch). ■ respond with the information of one server that is picked out from all the known servers through round robin po...
Page 87
Ipx configuration 79 the following table shows some common service types and their values: configuring the maximum length of the service information reserve-queue for one service type ipx supports up to 10240 service entries with 5120 service types and 5120 static service entries at most. You can co...
Page 88
80 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration on the vlan interfaces on the switch. This allows the switch to broadcast update only when route or service information changes, thus avoiding broadcast flooding. Perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. By default, the triggered update...
Page 89
Ipx configuration 81 perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. By default, type 20 broadcast packets are not forwarded. Displaying and debugging ipx after configuration, execute display command in any view to display the operation of the ipx configuration, and to verify the effect ...
Page 90
82 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration the client accesses the file and directory services provided by the server through the ipx network. The node address of the server is 0000-0c91-f61f. Figure 4 illustrates this configuration figure 4 ipx network topology 1 configure switch a enable ipx. [s...
Page 91
Ipx configuration 83 [ sw7700] interface vlan-interface 2 [sw7700-vlan-interface2] ipx network 3 set the ipx packet encapsulation format to ethernet_snap on vlan interface 2. [sw7700-vlan-interface2] ipx encapsulation snap [sw7700-vlan-interface2] quit assign the network number 1001 to vlan interfac...
Page 92
84 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration ■ use the display ipx interface command to check that sap is not disabled on the vlan interface. 4 a type 20 ipx packet cannot be transmitted to other network segments. Do the following: ■ execute the display ipx interface command; check that the forwardi...
Page 93
Ipx configuration 85 ■ check that the vlan interface is up and sap is enabled with the display ipx interface command. ■ check that the hop count of the route to the server is smaller than 16 with the display ipx routing-table command. ■ adequate memory is available for adding the service entry into ...
Page 94
86 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration ■ the switch receives the gns packets with the debugging ipx packet sap command. ■ sap is enabled on the vlan interface where the gns requests are received. ■ the vlan interface is enabled to respond to gns requests with the display ipx interface command....
Page 95: Ip R
5 ip r outing p rotocol o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ip routing protocol overview ■ static routes ■ rip ■ ospf ■ is-is ■ bgp ■ ip routing policy ■ route capacity ip routing protocol overview routers select an appropriate path through a network for an ip packet according to ...
Page 96
88 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration figure 1 about hops networks can have different sizes, so, the segment lengths connected between two different pairs of routers are also different. If a router in a network is regarded as a node and a route segment in the internet is regarded as a link...
Page 97
Ip routing protocol overview 89 ■ the output interface — indicates an interface through which an ip packet should be forwarded. ■ the next hop address — indicates the next router that an ip packet will pass through. ■ the priority added to the ip routing table for a route — indicates the type of rou...
Page 98
90 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration the user are managed together with the dynamic routes as detected by the routing protocol. The static routes and the routes learned or configured by routing protocols can be shared with each other. Routing protocols (as well as the static configuration...
Page 99
Static routes 91 in a relatively simple network, you only need to configure static routes to make the router work normally. The proper configuration and usage of the static route can improve network performance and ensure bandwidth for important applications. The following routes are static routes: ...
Page 100
92 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring a static route perform the following configurations in system view. The parameters are explained as follows: ■ ip address and mask the ip address and mask use a decimal format. Because the 1s in the 32-bit mask must be consecutive, the dott...
Page 101
Static routes 93 parameters for default route are the same as for static route. Deleting all static routes you can use the undo ip route-static command to delete one static route. The switch 7700 also provides the delete static-route all command for you to delete all static routes at one time, inclu...
Page 102
94 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration figure 3 static route configuration 1 configure the static route for ethernet switch a: [switch a]ip route-static 1.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.2.2 [switch a]ip route-static 1.1.4.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.2.2 [switch a]ip route-static 1.1.5.0 255.255.255.0 1.1....
Page 103
Rip 95 rip routing information protocol (rip) is a simple, dynamic routing protocol, that is distance-vector (d-v) algorithm-based. It uses hop counts to measure the distance to the destination host, which is called routing cost. In rip, the hop count from a router to its directly connected network ...
Page 104
96 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration validity of the routes. With these mechanisms, rip, an interior routing protocol, enables the router to learn the routing information of the entire network. Rip has become one of the most popular standards of transmitting router and host routes. It can...
Page 105
Rip 97 by default, rip is not enabled. Enabling the rip interface for flexible control of rip operation, you can specify the interface and configure the network where it is located in the rip network, so that these interfaces can send and receive rip packets. Perform the following configurations in ...
Page 106
98 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration default multicast address is 224.0.0.9. The advantage of transmitting packets in the multicast mode is that the hosts in the same network that do not run rip, do not receive rip broadcast packets. In addition, this mode prevents the hosts that are runn...
Page 107
Rip 99 before rip completely deletes an unreachable route from the routing table, it advertises the route by sending four update packets with route metric of 16, to let all the neighbors knows that the route is unreachable. Routes do not always become unreachable when a new period starts so the actu...
Page 108
100 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration disabling host route in some cases, the router can receive many host routes from the same segment, and these routes are of little help in route addressing but consume a lot of network resources. Routers can be configured to reject host routes by using...
Page 109
Rip 101 perform the following configuration in vlan interface view the usual packet format follows rfc1723 and nonstandard follows rfc2082. Configuring split horizon split horizon means that the route received through an interface will not be sent through this interface again. The split horizon algo...
Page 110
102 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring the default cost for the imported route when you use the import-route command to import the routes of other protocols, you can specify their cost. If you do not specify the cost of the imported route, rip will set the cost to the default c...
Page 111
Rip 103 configuring route filtering the router provides the route filtering function. You can configure the filter policy rules by specifying the acl and ip-prefix for route redistribution and distribution. To import a route, the rip packet of a specific router can also be received by designating a ...
Page 112
104 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration figure 4 rip configuration the following configuration only shows the operations related to rip. Before performing the following configuration, verify that the ethernet link layer works normally. 1 configure rip on switch a: [switch a] rip [switch a-r...
Page 113
Ospf 105 ■ fast convergence — transmits the update packets instantly after the network topology changes so the change is synchronized in the as ■ loop-free — calculates routes using the shortest path tree algorithm, according to the collected link states so that no loop routes are generated from the...
Page 114
106 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration the hello packet is the most common packet sent by the ospf protocol. A router periodically sends it to its neighbor. It contains the values of some timers, dr, bdr and the known neighbor. ■ database description (dd) packet when two routers synchroniz...
Page 115
Ospf 107 ■ area if all routers on a large network are running ospf, the large number of routers results in an enormous lsd, which consumes storage space, complicates the spf algorithm, and adds cpu load. Furthermore, as a network grows larger, the topology becomes more likely to change. Hence, the n...
Page 116
108 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration ■ setting a shortest path first (spf) calculation interval for ospf ■ configuring the ospf stub area ■ configuring nssa of ospf ■ configuring the route summarization of ospf area ■ configuring ospf virtual link ■ configuring summarization of imported ...
Page 117
Ospf 109 the neighboring routers from transmitting information, and lead to congestion or self-loop of the routing information. Perform the following configuration in ospf area view. You must specify the segment to which the ospf will be applied after enabling the ospf tasks. Configuring router id a...
Page 118
110 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration as you configure the network type, consider the following points: ■ nbma means that a network is non-broadcast and multi-accessible. Atm is a typical example. You can configure the polling interval for hello packets before the adjacency of neighboring...
Page 119
Ospf 111 setting the interface priority for dr election the priority of the router interface determines the qualification of the interface for dr election. A router of higher priority is considered first if there is a collision in the election. Dr is not designated manually, instead, it is elected b...
Page 120
112 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration adjacent router of the interface, and whether the adjacent router is eligible for election. This can be done by configuring the peer ip-address command. If dr-priority-number is not specified, the adjacent router will be regarded as ineligible. Perfor...
Page 121
Ospf 113 by default, the dead interval for the neighboring routers of p2p or broadcast interfaces is 40 seconds and for the neighboring routers of p2mp or nbma interfaces is 120 seconds. Both hello and dead timers restore the default values if you modify the network type. Configuring an interval req...
Page 122
114 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration setting a shortest path first (spf) calculation interval for ospf whenever the ospf lsdb changes, the shortest path requires recalculation. Calculating the shortest path after a change consumes enormous resources and affects the operating efficiency o...
Page 123
Ospf 115 by default, the stub area is not configured, and the cost of the default route to a stub area is 1. Configuring nssa of ospf an nssa is similar to a stub area. However, nssa does not allow importing as-external-lsas (type-5 lsas) although it does allow importing nssa-external-lsas (type-7 l...
Page 124
116 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration type-7 lsa route can be generated only if the default route 0.0.0.0 is in the routing table. Executing the no-import-route command on the asbr prevents the external routes that ospf imported through the import-route command from advertising to the nss...
Page 125
Ospf 117 have a direct physical link with the backbone area 0.0.0.0, a virtual link must be created. If physical connectivity cannot be made due to network topology restrictions, a virtual link can be used to meet the requirements of rfc 2328. The virtual link refers to a logic channel set up throug...
Page 126
118 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration by default, summarization of imported routes is disabled. After the summarization of imported routes is configured, if the local router is an autonomous system border router (asbr), this command summarizes the imported type-5 lsas in the summary addre...
Page 127
Ospf 119 you can specify the route cost type, cost value and tag to overwrite the default route receipt parameters (see “configuring parameters for ospf to import external routes”). The ospf uses the following four types of routes (in priority): ■ intra-area route ■ inter-area route ■ external route...
Page 128
120 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in ospf view. No default cost and tag are available when importing external routes, and the type of the imported route is type-2. The interval for importing the external route is 1 second. The upper limit to the ext...
Page 129
Ospf 121 perform the following configuration in ospf view. By default, the ospf preference is 10, and the imported external routing protocol is 150. Configuring ospf route filtering perform the following configuration in ospf view. By default, ospf does not filter the imported and distributed routin...
Page 130
122 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in ospf view. By default, all the interfaces are allowed to transmit and receive ospf packets. After an ospf interface is set to silent status, the interface can still advertise its direct route. However, the ospf c...
Page 131
Ospf 123 by default, the ospf trap function is disabled so the switch does not send trap packets when any ospf process is abnormal. The configuration is valid for all ospf processes if you do not specify a process id. For detailed configuration of snmp trap, “system management” on page 323. Resettin...
Page 132
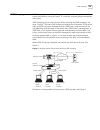
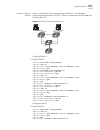
124 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration example: ospf configuration configuring dr election based on ospf priority in this example, four switch 7700 routers, switch a, switch b, switch c, and switch d, which can perform the router functions and run ospf, are located on the same segment, as ...
Page 133
Ospf 125 [switch c-vlan-interface1] ip address 196.1.1.3 255.255.255.0 [switch c-vlan-interface1] ospf dr-priority 2 [switch c] router id 3.3.3.3 [switch c] ospf [switch c-ospf-1] area 0 [switch c-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 196.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 4 configure switch d: [switch d] interface vlan-interf...
Page 134
126 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration figure 7 ospf virtual link configuration the commands listed below implement this configuration. 1 configure switch a: [switch a] interface vlan-interface 1 [switch a-vlan-interface1] ip address 196.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 [switch a] router id 1.1.1.1 [sw...
Page 135
Ospf 127 [switch c-ospf-area-0.0.0.2] network 152.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 troubleshooting ospf 1 ospf has been configured according to the previous procedures, but ospf on the router does not run normally. ■ troubleshoot locally check whether the protocol between two directly connected routers is operating ...
Page 136
128 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration as shown in figure 8, rta and rtd are each configured to belong to only one area, whereas rtb and rtc are both configured to belong to two areas. Rtb belongs to area0, which complies with the backbone area membership requirement. However, rtc does not...
Page 137
Is-is 129 ■ network service access point (nsap) is the iso network layer address. It identifies an abstract network service access point and describes the network address for iso model routing. Configuring is-is is described in the following sections: ■ two-level structure of is-is ■ nsap structure ...
Page 138
130 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration figure 9 is-is topology nsap structure of is-is figure 10 illustrates the nsap structure. The whole address is of 8 to 20 bytes long. Figure 10 nsap structure nsap includes initial domain part (idp) and domain specific part (dsp). Idp and dsp are leng...
Page 139
Is-is 131 authority and format identifier (afi) and initial domain identifier (idi). The afi defines the format of the idi. The dsp has several bytes. The area address is composed of routing field and area identifier. The routing field includes the afi and the idi and may also include the first byte...
Page 140
132 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring integrated is-is integrated is-is is designed to function as a routing protocol for ip. Therefore, the network must be set up with ip addresses and vlans in the same way that is required for rip or ospf. This set up is not discussed in thi...
Page 141
Is-is 133 ■ setting is-is authentication ■ setting the mesh group of the interface ■ setting the router type ■ setting default route generation ■ setting a summary route ■ setting the overload flag bit ■ setting to ignore the lsp checksum errors ■ setting peer change logging ■ setting the lsp refres...
Page 142
134 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in is-is view. The format of parameter net is x…x.Xxxxxxxxxxxx.Xx, among which the first “x…x” is the area address, the twelve xs in the middle is the system id of the router. The last xx should be 00. Caution: a ro...
Page 143
Is-is 135 perform the following configuration in vlan interface view.. If the level is not specified, the default setting is, level-1 routing cost. The value parameter is configured according to the link state of the interface. By default, the routing cost of is-is on an interface is 10. Setting the...
Page 144
136 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration if the level is not specified, it defaults to setting the csnp packet broadcast interval for level-1. By default, the csnp packet is transmitted by an interface every 10 seconds. Setting the lsp packet interval lsp carries the link state records for p...
Page 145
Is-is 137 by default, the hello failure interval is 30 seconds. If the level is not specified, it defaults to setting the hello packet failure interval level-1. Setting the priority for dis election in the broadcast network, the is-is needs to elect a dis from all the routers. In is-is, both a level...
Page 146
138 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration setting interface authentication the authentication password set on the interface is mainly used in the hello packet to confirm the validity and correctness of its peers. The authentication passwords at the same level for all the connected interfaces ...
Page 147
Is-is 139 setting the is-is to use the md5 algorithm that is compatible with other vendors’ you must configure this command when the switch needs to authenticate the devices of other vendors using md5 algorithm in is-is. Perform the following configurations in is-is view. By default, the system uses...
Page 148
140 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration setting default route generation in an is-is route domain, a level-1 router only has the lsdb for the local area, so it can only generate routes for the local areas. The level-2 router has the backbone lsdb for the is-is route domain and generates bac...
Page 149
Is-is 141 perform the following configurations in is-is view. By default, no overload bit is set. Setting to ignore the lsp checksum errors after receiving an lsp packet, the local is-is calculates its checksum and compares the result with the checksum in the lsp packet. By default, if the checksum ...
Page 150
142 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration by default, an lsp is refreshed every 900 seconds (15 minutes). Setting the lifetime of lsp when a router generates an lsp, it sets the maximum lifetime of the lsp. When other routers receive this lsp, they reduce its lifetime continuously as time pas...
Page 151
Is-is 143 perform the following configurations in is-is view.. By default, the cpu is released after 5000 routes are processed by the spf of is-is. Setting the spf computing interval when the is-is lsdb changes, the router will compute the shortest path again. However, an immediate calculation upon ...
Page 152
144 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring is-is to import routes of other protocols for is-is, the routes discovered by other routing protocols are processed as routes outside the routing domain. When importing the routes of other protocols, you can specify their default cost. Whe...
Page 153
Is-is 145 protocol specifies the routing protocol sources for distributing routes, which can be direct, static, rip, bgp, ospf, or ospf-ase. For more information, see “configuring for filtering received routes” and “configuring for filtering distributed routes ”. Setting the preference of the is-is ...
Page 154
146 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration execute the display command in all views to display the is-is configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute the debugging command in user view to debug the is-is module. Integrated is-is configuration example as is shown in fig...
Page 155
Is-is 147 figure 11 is-is configuration example 1 configure switch a [switch a] isis [switch a-isis] network-entity 86.0001.0000.0000.0005.00 [switch a] interface vlan-interface 100 [switch a-vlan-interface100] isis enable [switch a] interface vlan-interface 101 [switch a-vlan-interface101] isis ena...
Page 156
148 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration [switch c-vlan-interface101] isis enable [switch c] interface vlan-interface 100 [switch c-vlan-interface100] isis enable 4 configure switch d [switch d] isis [switch d-isis] network-entity 86.0001.0000.0000.0008.00 [switch d] interface vlan-interface...
Page 157
Bgp 149 bgp runs on a router in any of the following modes: ■ internal bgp (ibgp) ■ external bgp (ebgp) bgp is called ibgp when it runs within an as and ebgp when it runs among different ass. Configuring bgp is described in the following sections: ■ bgp messages ■ bgp routing ■ bgp peers and peer gr...
Page 158
150 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration route advertisement policy in the switch 7700, bgp uses the following policies when it advertises routes: ■ if there are multiple routes available, a bgp speaker only selects the optimum one. ■ a bgp speaker only advertises its own route to its peers....
Page 159
Bgp 151 ■ configuring application features of bgp peer (group) ■ configuring the route filtering of a peer (group) ■ configuring networks for bgp distribution ■ configuring interaction between bgp and igp ■ configuring bgp route summarization ■ configuring bgp route filtering ■ configuring bgp route...
Page 160
152 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configurations in bgp view. Use the undo command to delete the application configuration. See “multicast protocol” on page 87 for mbgp configuration commands. Configuring basic features for a bgp peer in configuring a mbgp peer (...
Page 161
Bgp 153 a bgp peer must belong to a peer group. If you want to configure a bgp peer, you need to first create a peer group and then add a peer to the group. If a peer is added to an ibgp peer group, the as number cannot be specified in the command. When a peer group is defined with an as number, all...
Page 162
154 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration this command is higher than the timer command, which is used to configure timers for the whole bgp peers. By default, the keep-alive message is sent every 60 seconds and the value of the hold timer is 180 seconds. Configuring the route update interval...
Page 163
Bgp 155 for detailed information on the route reflector, see “configuring a bgp route reflector” on page 163. Configuring transmission of a default route to a peer group . By default, a local router does not send a default route to any peer group. However, if you use the peer default-route-advertise...
Page 164
156 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring the transmission of community attributes to a peer group configuring the repeating time of a local as using the peer allow-as-loop command, the repeating time of local as can be configured. Perform the following configurations in bgp view....
Page 165
Bgp 157 in bgp, no authentication is performed in setting up tcp connections, by default. The multicast extension configured in bgp view is also available in mbgp, because they use the same tcp link. Configuring the route filtering of a peer (group) the switch 7700 supports filtering imported and ad...
Page 166
158 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration by default, route filtering based on an as path list for a peer or peer group is disabled. Configuring a route filtering policy based on address prefix list for a peer (group) by default, route filtering based on address prefix list for a peer or peer...
Page 167
Bgp 159 perform the following configurations in bgp view.. By default, bgp does not import the route information of other protocols. The specified and imported source route protocols can be direct, static, rip, isis, ospf, ospf-ase, and ospf-nssa. After the import-route command is used in a certain ...
Page 168
160 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configurations in bgp view. The routes received by the bgp can be filtered, and only those routes that meet certain conditions will be received by the bgp. For details, see “configuring bgp route dampening” on page 159. Configuri...
Page 169
Bgp 161 by default, route dampening is disabled. The parameters in the command are dependent on one another. If one parameter is configured, other parameters must be specified. Configuring bgp preferences three types of routes may be involved in bgp: ■ routes learned from external peers ■ routes lea...
Page 170
162 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring local preferences different local preferences can be configured to affect bgp routing. When a router running bgp gets routes with the same destination address but different next hops through different internal peers, it will select the rou...
Page 171
Bgp 163 by default, med comparison is not allowed among routes from neighbors in different ass. You should not use this configuration unless you can make sure that the ass adopt the same igp routing method. Configuring bgp community community attributes are optional and transitive. Some community at...
Page 172
164 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration can have multiple clients. Each client, in turn, can be a route reflector with multiple clients. In the following figure, router a receives an update packet from the external peer and transmits it to router c. Router c is a route reflector with two pe...
Page 173
Bgp 165 by default, the router id of the route reflector is used as the cluster id. Two measures to avoid looping inside an as as route reflector is imported, it is possible that path looping will be generated in as. Path update packets that already left the cluster may attempt to return to the clus...
Page 174
166 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configurations in bgp view.. By default, no autonomous systems are configured as a member of the confederation. Configure the as confederation nonstandard i f it is necessary to perform the interconnection with devices whose bgp ...
Page 175
Bgp 167 one piece of this group of lists, it means that the routing information has been filtered by this group of as-path lists identified with this list number. Defining route-policy see “defining route-policy” on page 167. Defining match principle see “defining if-match clauses for a route policy...
Page 176
168 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration typical bgp configuration examples typical bgp configuration examples are described as follows: ■ configuring the bgp as confederation attribute ■ configuring bgp route reflector ■ configuring bgp routing display the routing information of the specifi...
Page 177
Bgp 169 configuring the bgp as confederation attribute divide the following as 100 into three sub-as: 1001, 1002, and 1003, and configure ebgp, confederation ebgp, and ibgp. Figure 13 as confederation configuration to configure the as confederation: 1 configure switch a: [switch a] bgp 1001 [switch ...
Page 178
170 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configuring bgp route reflector switch b receives an update packet passing ebgp and transmits it to switch c. Switch c is a reflector with two clients: switch b and switch d. When switch c receives a route update from switch b, it will transmit such i...
Page 179
Bgp 171 [switch c] interface vlan-interface 4 [switch c-vlan-interface4] ip address 194.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 c configure bgp peers and route reflector. [switch c] bgp 200 [switch c-bgp] group rr internal [switch c-bgp] peer rr reflect-client [switch c-bgp] peer 193.1.1.2 group rr [switch c-bgp] peer ...
Page 180
172 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration a enable bgp [switch a] bgp 100 b specify the network that bgp sends to [switch a-bgp] network 1.0.0.0 c configure the peers [switch a-bgp] group ex192 external [switch a-bgp] peer 192.1.1.2 group ex192 as-number 200 [switch a-bgp] group ex193 externa...
Page 181
Bgp 173 [switch c] interface vlan-interface 5 [switch c-vlan-interface5] ip address 195.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 [switch c] ospf [switch c-ospf-1] area 0 [switch c-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 193.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [switch c-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 195.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [switch c] bgp 200 [switch c-bgp]...
Page 182
174 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration configured with local preference attribute, 100 by default), switch d will also first select the route 1.0.0.0 from switch c. Troubleshooting bgp the neighborhood cannot be established (the established state cannot be entered). The establishment of a ...
Page 183
Ip routing policy 175 configuring ip routing policy is described in the following sections: ■ routing information filters ■ configuring an ip routing policy ■ troubleshooting routing policies ■ limiting route capacity ■ configuring route capacity routing information filters the switch 7700 supports ...
Page 184
176 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration specify the gateway options and require it to receive only the routing information distributed by certain routers. An ip-prefix is identified by the ip-prefix name. Each ip-prefix can include multiple list items, and each list item can specify the mat...
Page 185
Ip routing policy 177 the deny argument specifies that the apply clauses are not executed. If a route satisfies all the if-match clauses of the node, the node denies the route and the route does not take the test of the next node. If a route does not satisfy all the if-match clauses of the node, how...
Page 186
178 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration by default, no matching is performed. The if-match clauses for a node in the route policy require that the route satisfy all the clauses to match the node before the actions specified by the apply clauses can be executed. If no if-match clauses are sp...
Page 187
Ip routing policy 179 by default, no apply clauses are defined. If the routing information meets the match conditions specified in the route policy and also notifies the med value configured with apply cost-type internal when notifying the igp route to the ebgp peers, then this value is regarded as ...
Page 188
180 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration during the matching, the router checks list items identified by the index-number in the ascending order. If only one list item meets the condition, it means that it has passed the ip-prefix filtering (and does not enter the testing of the next list it...
Page 189
Ip routing policy 181 the route policy supports importing the routes discovered by the following protocols into the routing table: ■ direct: the hop (or host) to which the local interface is directly connected. ■ static: static route configuration ■ rip: route discovered by rip ■ ospf: route discove...
Page 190
182 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration [switch a] ip route-static 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 12.0.0.1 [switch a] ip route-static 30.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 12.0.0.1 [switch a] ip route-static 40.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 12.0.0.1 3 enable ospf protocol and specifies the number of the area to which...
Page 191
Route capacity 183 route capacity in practical networking applications, there is always a large number of routes in the routing table, especially ospf routes and bgp routes. The routing information is usually stored in the memory of the ethernet switch. When the size of the routing table increases, ...
Page 192
184 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration setting the safety value for switch memory when the amount of free memory is reduced to the safety value but has not reached the lower limit, you can use the display memory limit command to see how much free memory remains. If automatic memory restora...
Page 193
Route capacity 185 perform the following configurations in system view. By default, memory automatic restoration function of a ethernet switch is enabled. Enabling automatic recovery of disconnected routing protocols perform the following configurations in system view. By default, memory automatic r...
Page 194
186 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration.
Page 195
Route capacity 187.
Page 196
188 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration.
Page 197
Route capacity 189.
Page 198
190 c hapter 5: ip r outing p rotocol o peration.
Page 199: Ulticast
6 m ulticast p rotocol this chapter includes information on the following: ■ ip multicast overview ■ configuring common multicast ■ configuring igmp ■ igmp snooping ■ configuring pim-dm ■ configuring pim-sm ■ gmrp ip multicast overview many transmission methods can be used when the destination (incl...
Page 200
192 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol figure 1 comparison between the unicast and multicast transmission a multicast source does not necessarily belong to a multicast group. It only sends data to the multicast group and it is not necessarily a receiver. Multiple sources can send packets to a multicas...
Page 201
Ip multicast overview 193 a multicast group can be either permanent or temporary. Part of addresses in the multicast group are reserved by the iana and are known as the permanent multicast group. Ip addresses of a permanent group are unchanged, but the members in the group can change. The number of ...
Page 202
194 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol transmitted, the destination is no longer a specific receiver but a group with unspecific members. Therefore, the multicast mac address should be used. Multicast mac addresses correspond to multicast ip addresses. Iana (internet assigned number authority) stipula...
Page 203
Ip multicast overview 195 possible for multicast. The multicast application sends the packets to a group of receivers (as with multicast addresses) who are ready to receive the data but not only to one receiver (as with unicast address). The multicast routing creates a loop-free data transmission pa...
Page 204
196 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol table independently provided for multicast (such as the mbgp multicast routing table). This check mechanism is the basis for most multicast routing protocols , which is known as a rpf (reverse path forwarding) check. A multicast router uses the source address fro...
Page 205
Configuring common multicast 197 by default, multicast routing is disabled. Only when multicast is enabled can another multicast configuration be used. Configuring the multicast route limit if the existing route entries exceed the capacity value you configured when using this command, the system wil...
Page 206
198 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol displaying and debugging common multicast configuration after the previous configurations, execute the display command to view the multicast configuration, and to verify the configuration. Execute debugging command in user view for the debugging of multicast. Con...
Page 207
Configuring igmp 199 igmp version 2 boasts the following improvements over igmp version 1: ■ election mechanism of multicast routers on the shared network segment a shared network segment means that there are multiple multicast routers on a network segment. In this case, all routers running igmp on ...
Page 208
200 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol ■ configuring the igmp querier present timer ■ configuring the maximum query response time ■ deleting igmp groups joined on an interface ■ displaying and debugging igmp enabling multicast after multicast is enabled, igmp will automatically run on all interfaces. ...
Page 209
Configuring igmp 201 if other hosts, which are interested in the specified group, receive the igmp query message from the igmp query router, they send back the igmp membership report message within the specified maximum response time interval. If the igmp query router receives the igmp membership re...
Page 210
202 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol by default, the robust-value is 2. This command is only available on an igmp query router running igmp v2. For a host running igmp v1, this command cannot take effect, because the host may not send the igmp leave message when it leaves a group. Configuring the li...
Page 211
Configuring igmp 203 perform the following configuration in vlan-interface view. By default, no filters are configured. All multicast groups are allowed on the interface. Configuring the igmp query message interval multicast routers send igmp query messages to find present multicast groups on other ...
Page 212
204 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol setting the maximum response time allows the host to respond to query messages quickly. In this case, the router can master the existing status of the members of the multicast group. Perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. The smaller the maxi...
Page 213
Igmp snooping 205 igmp snooping igmp snooping (internet group management protocol snooping) is a multicast control mechanism running on layer 2. It is used for multicast group management and control. Igmp snooping runs on the link layer. When receiving the igmp messages, the layer 2 switch 7700 uses...
Page 214
206 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol figure 4 multicast packet transmission with igmp snooping implement igmp snooping this section introduces related switch concepts of igmp snooping: ■ router port: the port directly connected to the multicast router. ■ multicast member port: the port connected to ...
Page 215
Igmp snooping 207 figure 5 implementing igmp snooping 1 igmp general query message: transmitted by the multicast router to query which multicast group contains member. When a router port receives an igmp general query message, the switch 7700 will reset the aging timer of the port. When a port other...
Page 216
208 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol not have any member, the switch will notify the multicast router to remove it from the multicast tree. Configuring igmp snooping is described in the following sections: ■ configuring igmp snooping ■ igmp snooping configuration example ■ troubleshooting igmp snoop...
Page 217
Igmp snooping 209 by default, the port aging time is 260 seconds. Configuring maximum response time this task sets the maximum response time. If the switch 7700 receives no report message from a port in the maximum response time, it will remove the port from the multicast group. Perform the followin...
Page 218
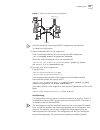
210 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol igmp snooping configuration example to implement igmp snooping on the switch, first enable it. The switch is connected with the router through the router port, and with user pc through the non-router ports. Figure 6 igmp snooping configuration network 1 display t...
Page 219
Configuring pim-dm 211 ■ if they are not consistent, contact the maintenance personnel for help. Configuring pim-dm pim-dm (protocol independent multicast, dense mode) belongs to dense mode multicast routing protocols. Pim-dm is suitable for small networks. Members of multicast groups are relatively...
Page 220
212 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol figure 7 assert mechanism diagram when they detect such a case, routers need to select a unique sender by using the assert mechanism. Routers send assert packets to select the best path. If two or more have the same priority and metric, the path with a higher ip ...
Page 221
Configuring pim-dm 213 after pim-dm is enabled on an interface, it will send pim hello messages periodically, and process protocol packets sent by pim neighbors. Perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. 3com recommends that you configure pim-dm on all interfaces. This configuratio...
Page 222
214 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol configuring the filtering of multicast source/group you can set to filter the source (and group) address of multicast data packets via this command. When this feature is configured, the router filters not only multicast data, but the multicast data encapsulated i...
Page 223
Configuring pim-dm 215 if the existing pim neighbors exceed the configured value during configuration, they are not deleted. Displaying and debugging pim-dm execute the display command in all views to display the running of pim-dm configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute...
Page 224
216 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol configuration procedure this section only provides the configuration for switch a because the configuration procedures for switch b and switch c are similar. 1 enable the multicast routing protocol. [sw7700] multicast routing-enable 2 enable pim-dm. [sw7700] vlan...
Page 225
Configuring pim-sm 217 configuring pim-sm is described in the following sections: ■ pim-sm operating principles ■ preparing to configure pim-sm ■ configuring pim-sm pim-sm operating principles the pim-sm working process is as follows: neighbor discovery, building the rp-rooted shared tree (rpt), mul...
Page 226
218 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol multicast source registration when multicast source s sends a multicast packet to group g, the pim-sm multicast router is responsible for encapsulating the packet into a registration packet upon receipt. It then sends the packet to the corresponding rp in unicast...
Page 227
Configuring pim-sm 219 ■ configuring candidate-bsrs ■ configuring candidate-rps ■ configuring static rp advanced pim-sm configuration includes: ■ configuring the interface hello message interval ■ configuring the filtering of multicast source/group ■ configuring the filtering of pim neighbor ■ confi...
Page 228
220 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. By default, no domain border is set. After this configuration is performed, a bootstrap message cannot cross the border, but other pim packets can. This configuration can effectively divide a network int...
Page 229
Configuring pim-sm 221 candidate-bsrs should be configured on the routers in the network backbone. By default, no bsr is set. The default priority is 0. Only one router can be configured with one candidate-bsr. When a candidate-bsr is configured on another interface, it will replace the previous con...
Page 230
222 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol configuring the interface hello message interval generally, pim-sm advertises hello messages periodically on the interface enabled with it to detect pim neighbors and discover which router is the designated router (dr). Perform the following configuration in vlan...
Page 231
Configuring pim-sm 223 information in the network once it wins in the contention. To prevent malicious bsr proofing in the network, the following two measures need to be taken: ■ prevent the router from being spoofed by hosts though faking legal bsr messages to modify rp mapping. Bsr messages are of...
Page 232
224 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol clearing multicast route entries from pim routing table perform the following configuration in user view. If in this command, the group-address is 224.0.0.0/24 and source-address is the rp address (where group address can have a mask, but the resulting ip address...
Page 233
Configuring pim-sm 225 example: configuring pim-sim host a is the receiver of the multicast group at 225.0.0.1. Host b begins transmitting data destined to 225.0.0.1. Switch a receives the multicast data from host b by switch b. Figure 10 pim-sm configuration networking configure switch a 1 enable p...
Page 234
226 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol [sw7700-vlan-interface10] pim sm [sw7700-vlan-interface10] quit [sw7700] vlan 11 [sw7700-vlan11] port ethernet 1/0/4 to ethernet 1/0/5 [sw7700-vlan11] quit [sw7700] pim [sw7700-pim] interface vlan-interface 11 [sw7700-vlan-interface11] pim sm [sw7700-vlan-interfa...
Page 235
Gmrp 227 [sw7700-vlan-interface12] pim sm [sw7700-vlan-interface12] quit gmrp gmrp (garp multicast registration protocol), based on garp, is used for maintaining dynamic multicast registration information. All the switches supporting gmrp can receive multicast registration information from other swi...
Page 236
228 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol enabling/disabling gmrp on the port perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. Gmrp should be enabled globally before being enabled on a port. By default, gmrp is disabled on the port. Displaying and debugging gmrp after the previous configuration...
Page 237
Gmrp 229 [sw7700-ethernet1/0/1] gmrp.
Page 238
230 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol.
Page 239: S/ O
7 q o s/ o peration ■ acl overview ■ configuring acls ■ displaying and debugging an acl ■ configuring qos ■ configuring acl control acl overview the access control list (acl) classifies the data packets with a series of matching rules, including source address, destination address and port number. T...
Page 240
232 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration this type of filtering includes acls that are used with the qos function, acls used to filter the packet transmitted by the hardware, and so on. Filtering or classifying data transmitted by the software an acl can be used to filter or classify the data transmitted b...
Page 241
Configuring acls 233 configuring acls acl configuration includes the tasks described in the following sections: ■ configuring the time range ■ selecting the acl mode ■ defining an acl ■ activating an acl configure the time range first, then define the acl (using the defined time range in the definit...
Page 242
234 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration defining an acl the switch 7700 supports several kinds of acls. To define the acl: 1 enter the corresponding acl view 2 add a rule to the acl you can add multiple rules to one acl. If a specific time range is not defined, the acl functions after it is activated. Dur...
Page 243
Configuring acls 235 the analyses of three kinds of packet priorities, tos (type of service), ip, and dscp priorities. Perform the following configuration in designated view. An advanced acl is identified with numbers ranging from 3000 to 3999. Note that port1 and port2 in this command specify the t...
Page 244
236 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration perform the following configuration in the designated view. A layer-2 acl can be identified with numbers ranging from 4000 to 4999. If you assign an acl to an interface and then make changes to the acl, you must reassign the acl to the interface before the changes t...
Page 245
Acl configuration examples 237 the matched information of the display acl config command specifies the rules treated by the switch’s cpu. The matched information of the transmitted data by the switch can be displayed with the display qos-info traffic-statistic command. For a description of the synta...
Page 246
238 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration in the following configuration steps, only the commands related to acl configurations are listed. Define the work time range: 1 set the time range 8:00 to 18:00. [sw7700] time-range 3com 8:00 to 18:00 working day define the acl to access the payment server: 1 enter ...
Page 247
Configuring qos 239 [sw7700]acl name traffic-of-host basic define the rules for packet with source ip address 10.1.1.1. [sw7700-acl-basic-traffic-of-host]rule 1 deny ip source 10.1.1.1 0 time-range 3com 4 activate acl. Activate the acl traffic-of-host . [sw7700-ethernet2/0/1]qos [qsw7700-qoss-ethern...
Page 248
240 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration (fifo) policy. Switches and routers make their best effort to transmit the packets to the destination, not making any commitment or guarantee of the transmission reliability, delay, or to satisfy other performance requirements. Ethernet technology is currently the m...
Page 249
Configuring qos 241 the classification standards are encapsulated in the header of the packets. The packet content is seldom used as the classification standard. Packet filter packet filters filter network traffic. For example, the deny operation discards the traffic that is matched with a traffic c...
Page 250
242 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration figure 3 sp sp is designed for the key service application. A significant feature of the key service is required, for priority to enjoy the service, to reduce the response delay when congestion occurs. Take 4 egress queues for each port as example, sp divides the qu...
Page 251
Configuring qos 243 this random number is compared with the discarding probability for the current queue. Any packet whose random number is greater than the probability is discarded. The longer the queue, the higher the discarding probability . However, there is a maximum discarding probability. Thr...
Page 252
244 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration perform the following two configuration tasks in system view. Setting port mirroring port mirroring means duplicating data on the monitored port to the designated monitor port, for purpose of data analysis and supervision. The switch supports many-to-one mirroring, ...
Page 253
Configuring qos 245 configuring the mapping list for 802.1p priority you cannot modify the mapping between local priority levels and outbound queues, but you can change the mapping between 802.1p and local priority levels. Then the mapping between 802.1p priority levels and outbound queues change. P...
Page 254
246 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration configuring the priority for queue scheduling you can use the following command to configure which priority is used for queue scheduling. Perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the switch chooses the local preference as the basic priority. E...
Page 255
Configuring qos 247 setting line limit line limit refers to limiting the total rate at the port. The adjustment step for the line rate of the switch 7700 is 1mbps. Perform the following configurations in qos view. You can set line limit at a single port. Setting traffic bandwidth you can set desired...
Page 256
248 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration only the 20-port 10/100/1000base-t and 20-port 1000base-x-sfp i/o modules support this configuration. Relabeling the priority level relabeling the priority level creates a policy to tag the priority of the packets so they match the acl. The new priority can be fille...
Page 257
Configuring qos 249 configuring traffic statistics the traffic statistics function counts the transmitted data that matches the acl rules. After the traffic statistics function is configured, you can use the display qos-info traffic-statistic command to display the statistics information. Perform th...
Page 258
250 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration for output and description of the related commands, see the switch 7700 command reference guide. Qos configuration examples this section provides the following configuration examples: ■ traffic limit and line rate ■ port mirroring ■ priority relabeling configuration...
Page 259
Configuring qos 251 figure 4 traffic limit and line rate configuration only the commands concerning qos/acl configuration are listed here. To create this configuration: 1 define outbound traffic for the wage server. Enter name-based advanced acl view using the traffic-of-payserver. [sw7700]aclname t...
Page 260
252 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration for a 48-port module, the monitoring port and the monitored port must all be at the ports 1-24 or ports 25-48, on which only one mirroring group can be configured in one direction. Figure 5 port mirroring configuration to create this configuration: define a mirrorin...
Page 261
Configuring qos 253 [sw7700-acl-basic-2000]rule 0 permit ip source 1.0.0.2 0 time-range 3com 3 relabel ef priority for pc1 packets. Enter qos view. [sw7700-gigabitethernet7/0/1]qos [sw7700-qosb-gigabitethernet7/0/1] relabel ef priority for pc1 packets. [sw7700-qosb-gigabitethernet7/0/1]traffic-prior...
Page 262
254 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration [sw7700-qosb-gigabitethernet7/0/1]traffic-redirect inbound ip-group 1 rule 0 interface gigabitetherent7/0/8 queue scheduling modify the correspondence between 802.1p priority levels and local priority levels to change the mapping between 802.1p priority levels and q...
Page 263
Configuring qos 255 red run the red operation for the packets sent between 8:00 and 18:00 every day from ip address 1.0.0.1 to the port e3/0/8. Red operation is set so that the queue length that triggers random discarding ranges from 64 kbytes to 128 kbytes. The probability for random discarding is ...
Page 264
256 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration the 20-port 10/100/1000base-t and 20-port 1000base-x-sfp i/o modules do not support this configuration. Figure 10 traffic bandwidth to create this configuration: 1 define the time range 8:00 to 18:00. [sw7700]time-range 3com 8:00 to 18:00 daily 2 define traffic rule...
Page 265
Configuring acl control 257 figure 11 traffic statistics to create this configuration: 1 define the time range 8:00 to 18:00. [sw7700]time-range 3com 8:00 to 18:00 daily 2 define traffic rules for pc1 packets. [sw7700]acl number 2000 [sw7700-acl-basic-2000]rule 0 permit ip source 1.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 tim...
Page 266
258 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration configuring acl control for telnet users by configuring acl control over telnet, users can filter the malicious and illegal connection requests before password authentication, and ensure device security. The steps to control telnet users with acl are described in th...
Page 267
Configuring acl control 259 figure 12 control telnet user with acl use the following commands to control telnet users with acl. 1 define the basic acls. [sw7700]acl number 2000 match-order config [sw7700-acl-basic-2000]rule 1 permit source 10.110.100.52 0 [sw7700-acl-basic-2000]rule 2 permit source ...
Page 268
260 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration the privacy-mod priv-password parameters are supported only in the extended version of the software. Snmp community is one of the features of snmp v1 and snmp v2, so with these versions of snmp, you can import the acl into the commands with snmp community already co...
Page 269
Configuring acl control 261 2 import the basic acls. [sw7700]snmp-agent community read 3com acl 2000 [sw7700]snmp-agent group v2c 3comgroup acl 2001 [sw7700]snmp-agent usm-user v2c 3comuser 3comgroup acl 2002.
Page 270
262 c hapter 7: q o s/ o peration.
Page 271: Stp O
8 stp o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ stp overview ■ configuring stp ■ mstp overview ■ configuring mstp stp overview spanning tree protocol (stp) is applied in a loop network to block undesirable redundant paths. Using stp avoids the proliferation and infinite cycling of a pac...
Page 272
264 c hapter 8: stp o peration designating switches and ports a designated switch is a switch in charge of forwarding packets to the local switch by a port called the designated port. For a lan, the designated switch is a switch that forwards packets to the network segment by the designated port. As...
Page 273
Configuring stp 265 generating the configuration bpdu when initialized, each port of the switches will generate the configuration bpdu taking itself as the root, root path cost as 0, designated switch ids as their own switch ids, and the designated ports as their ports. ■ switch a configuration bpdu...
Page 274
266 c hapter 8: stp o peration the comparison process of each switch is: ■ switch a ethernet 1/0/1 receives the configuration bpdu from switch b and finds out that the local configuration bpdu priority is higher than that of the received one, so it discards the received configuration bpdu. The confi...
Page 275
Configuring stp 267 calculation is launched again by new events, for example, the link from switch b to c is down or the port receives a better configuration bpdu. Ethernet 1/0/1 receives the updated configuration bpdu, {0, 5, 1, e1/0/4}, from switch b. Since this configuration bpdu is better then t...
Page 276
268 c hapter 8: stp o peration a transitional state mechanism is then adopted to ensure the new configuration bpdu has been propagated throughout the network before the root port and designated port begin to send data again. That is, the root port and designated port should undergo a transitional st...
Page 277
Mstp overview 269 figure 4 mstp concepts mst region a multiple spanning tree region contains several physically and directly connected mstp-capable switches sharing the same region name, vlan-spanning tree mapping configuration and mstp revision level configuration, and the network segments between ...
Page 278
270 c hapter 8: stp o peration multiple spanning tree instance (msti) multiple spanning trees can be generated in an mst region and are independent of one another. Each of these spanning trees is called an msti. Msti region root the msti region root refers to the root of the msti in an mst region. E...
Page 279
Configuring mstp 271 figure 5 port roles mstp principles mstp divides the entire layer 2 network into several mst regions, and calculates and generates cst for them. Multiple spanning trees are generated in a region and each of them is called an msti. The instance 0 is called ist, and others are cal...
Page 280
272 c hapter 8: stp o peration ■ configuring the path cost of a port ■ configuring the priority of a port ■ configuring the port connection with the point-to-point link ■ configuring the mcheck variable of a port ■ configuring the switch security function ■ enabling mstp on the device ■ enabling or ...
Page 281
Configuring mstp 273 configuring the mst region perform the following configuration in mst region view. An mst region can contain up to 16 spanning tree instances, among which instance 0 is an ist and instances 1 through 16 are mstis. Upon the completion of these configurations, the current switch i...
Page 282
274 c hapter 8: stp o peration you can use the following commands to specify the current switch as the primary or secondary root of the spanning tree. Perform the following configuration in system view. After a switch is configured as primary root switch or secondary root switch, you cannot modify t...
Page 283
Configuring mstp 275 region itself. In mstp mode, the switch ports send mstp or stp packets (when connected to the stp switch) and the switch provides the multiple spanning tree function. You can use the following command to configure mstp running mode. Mstp can intercommunicate with stp. If there i...
Page 284
276 c hapter 8: stp o peration each time it is forwarded by a switch, the max hop is reduced by 1. The switch discards the configuration bpdu with 0 hops left. This makes it impossible for the switch beyond the max hops to take part in the spanning tree calculation, thereby limiting the scale of the...
Page 285
Configuring mstp 277 configuring the time parameters of a switch the switch has three time parameters: ■ forward delay, ■ hello time, ■ and max age. Forward delay is the switch state transition mechanism. The spanning tree will be recalculated upon link faults and its structure will change according...
Page 286
278 c hapter 8: stp o peration a max age that is too short, can cause the network device to calculate the spanning tree frequently and mistake the congestion as a link fault. If the max age is too long, the network device may not be able to discover the link fault and recalculate the spanning tree i...
Page 287
Configuring mstp 279 by default, the max transmission speed on every ethernet port of the switch is 3. Configuring a port as an edge port an edge port refers to the port not directly connected to any switch, or indirectly connected to a switch over the connected network. You can configure a port as ...
Page 288
280 c hapter 8: stp o peration the traffic from different vlans can run over different physical links, thereby implementing the vlan-based load-balancing..
Page 289
Configuring mstp 281 you can configure the path cost of a port in the following ways. Configuring in system view perform the following configuration in system view. Configuring in ethernet port view perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. For more about the commands, see the switc...
Page 290
282 c hapter 8: stp o peration configuring in ethernet port view perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. For more about the commands, see the switch 7700 command reference guide. After the change of port priority, mstp will recalculate the port role and transit the state. A smalle...
Page 291
Configuring mstp 283 for more about the commands, see the switch 7700 command reference guide. The ports connected with the point-to-point link, upon some port role conditions being met, can transit to forwarding state rapidly through transmitting synchronization packet, thus, reducing the unnecessa...
Page 292
284 c hapter 8: stp o peration the command can be used only if the switch runs mstp. The command does not make any sense when the switch runs in stp-compatible mode. Configuring the switch security function an mstp switch provides bpdu protection, root protection, and loop-protection functions. For ...
Page 293
Configuring mstp 285 after configured with bpdu protection, the switch will disable the edge port through mstp, which receives a bpdu, and notifies the network manager at the same time. These ports can be resumed by the network manager only. The port configured with root protection only plays the ro...
Page 294
286 c hapter 8: stp o peration configuring in system view perform the following configuration in system view. Configuring in ethernet port view perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. For more information about the commands, see the switch 7700 command reference guide. A redundant...
Page 295: Aaa
9 aaa and radius o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ieee 802.1x ■ configuring the aaa and radius protocols ieee 802.1x ieee 802.1x (hereinafter simplified as 802.1x) is a port-based network access control protocol that is used as the standard for lan user access authentication. I...
Page 296
288 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration lans) frame defined by ieee 802.1x. Authentication data are encapsulated in the eap frame, which is encapsulated in packets of other aaa upper layer protocols (e.G. Radius). This provides a channel through the complicated network to the authentication server...
Page 297
Ieee 802.1x 289 the eapol-encapsulated-asf-alert is related to the network management information and terminated by the authenticator. 802.1x provides an implementation solution of user id authentication. However, 802.1x itself is not enough to implement the scheme. The administrator of the access d...
Page 298
290 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration perform the following configurations in system view or ethernet port view. User can configure 802.1x on an individual port. The configuration will take effect right after 802.1x is enabled globally. By default, 802.1x authentication has not been enabled glob...
Page 299
Ieee 802.1x 291 checking the users that log on the switch by proxy the following commands are used for checking the users that log on by proxy. Perform the following configurations in system view or ethernet port view. Setting number of users on a port the following commands are used for setting the...
Page 300
292 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration ■ eap relay — the switch sends authentication information to the radius server in the form of eap packets, directly, so that the radius server never supports eap authentication perform the following configurations in system view. Setting the maximum retransm...
Page 301
Ieee 802.1x 293 perform the following configurations in system view. Quiet-period: specify the quiet timer. If an 802.1x user has not passed the authentication, the authenticator will keep quiet for a while (which is specified by quiet-period timer) before launching the authentication again. During ...
Page 302
294 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration perform the following configuration in system view. Displaying and debugging 802.1x execute the display command in all views to display the vlan configuration, and to verify the configuration. Execute the reset command in user view to reset 802.1x statistics...
Page 303
Ieee 802.1x 295 the user name of the local 802.1x access user is localuser and the password is localpass (input in plain text). The idle cut function is enabled. Figure 2 enabling 802.1x and radius to perform aaa on the requester the following examples concern most of the aaa/radius configuration co...
Page 304
296 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration [sw7700-radius-radius1] timer realtime-accounting 15 10 configure the system to transmit the user name to the radius server after removing the domain name. [sw7700-radius-radius1] user-name-format without-domain [sw7700-radius-radius1] quit 11 create the use...
Page 305
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 297 as mentioned above, aaa is a management framework, so it can be implemented by some protocols. Radius is frequently used. Remote authentication dial-in user service, radius for short, is distributed information switching protocol in client/server architec...
Page 306
298 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration figure 3 networking with switch 7700 applying radius authentication configuring the aaa and radius protocols is described in the following sections: ■ configuring aaa ■ configuring the radius protocol ■ troubleshooting aaa and radius configuring aaa aaa conf...
Page 307
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 299 complete set of exclusive isp domain attributes on a per-isp domain basis, which includes aaa policy (radius server group applied etc.) for the switch 7700, each supplicant belongs to an isp domain. Up to 16 domains can be configured in the system. If a u...
Page 308
300 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration creating a local user a local user is a group of users set on nas. The username is the unique identifier of a user. A supplicant requesting network service may use local authentication only if its corresponding local user has been added onto nas. Perform the...
Page 309
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 301 disconnecting a user by force sometimes it is necessary to disconnect a user or a category of users by force. The system provides the following command to serve this purpose. Perform the following configurations in system view. By default, no online user ...
Page 310
302 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration ■ setting the maximum retransmitting times of the stop accounting request ■ setting the supported type of radius server ■ setting radius server state ■ setting username format transmitted to radius server ■ setting the unit of data flow that transmitted to r...
Page 311
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 303 perform the following configurations in radius server group view. In real networking environments, the above parameters should be set according to the specific requirements. For example, you may specify 4 groups of different data to map 4 radius servers, ...
Page 312
304 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration setting the radius packet encryption key radius client (switch system) and radius server use md5 algorithm to encrypt the exchanged packets. The two ends verify the packet by setting the encryption key. Only when the keys are identical can both ends accept t...
Page 313
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 305 by default, radius request packet will be retransmitted up to three times. Enabling the selection of the radius accounting option if no radius server is available or if radius accounting server fails when the accounting optional is configured, the user ca...
Page 314
306 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration setting maximum times of real-time accounting request the radius server usually verifies that a user is online with timeout timer. If the radius server has not received the real-time accounting packet from nas for a specified period, it stops accounting. The...
Page 315
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 307 the server responds or discards the messages. Use this command to set the maximum retransmission times. Perform the following configurations in radius server group view. By default, the stop accounting request can be retransmitted for up to 500 times. Set...
Page 316
308 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration setting username format transmitted to radius server as mentioned before, clients are generally named in userid@isp-name format. The part following “@” is the isp domain name. The switch 7700 will put users into different isp domains according to their domai...
Page 317
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 309 when using the local radius server function of the switch 7700, remember the number of the udp port used for authentication is 1812 and the number for accounting is 1813. Displaying and debugging the aaa and radius protocols after you configure radius, ex...
Page 318
310 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration between the switch and the authentication server is "expert". The switch cuts off domain name from username and sends the left part to the radius server. Figure 4 configuring remote radius authentication for telnet users 1 add a telnet user. For details abou...
Page 319
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 311 troubleshooting aaa and radius the radius protocol of tcp/ip protocol suite is located on the application layer. It basically specifies how to exchange user information between nas and radius server of isp. So it is likely to be invalid. Tasks for trouble...
Page 320
312 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration.
Page 321: Eliability
10 r eliability this chapter covers the following topics: ■ vrrp overview ■ configuring vrrp vrrp overview virtual router redundancy protocol (vrrp) is a fault-tolerant protocol. In general, a default route, for example, 10.100.10.1 in figure 1, is configured for every host on a network, so that pac...
Page 322
314 c hapter 10: r eliability figure 2 virtual router this virtual router has its own ip address: 10.100.10.1, which can be the actual interface address of a switch within the virtual router. The switches within the virtual router have their own ip addresses, such as 10.100.10.2 for the master switc...
Page 323
Configuring vrrp 315 perform the following commands in system view. By default, ping response for the virtual ip address is disabled. Setting correspondence between virtual ip and mac addresses this operation sets the virtual ip address to correspond to either the real or the virtual mac address. In...
Page 324
316 c hapter 10: r eliability perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. Configuring the priority of switches the status of each switch in the virtual router group is determined by its priority in vrrp. The switch with the highest priority becomes the master. The priority ranges fro...
Page 325
Configuring vrrp 317 the delay ranges from 0 to 255, measured in seconds. The default mode is preemption with a delay of 0 second. Configuring authentication type and authentication key to prevent unauthorized routes from joining the virtual router, a key can be configured that is used in one of the...
Page 326
318 c hapter 10: r eliability by default, adver-interval is 1. Configuring a switch to track an interface the vrrp track interface function expands the backup function by including other switch interfaces of participating routers. Backup is provided not only to the interface where the virtual router...
Page 327
Configuring vrrp 319 figure 3 vrrp configuration configure switch a: [sw7700_a-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 202.38.160.111 [sw7700_a-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 priority 110 configure switch b: [sw7700_b-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 202.38.160.111 the virtual router can be use...
Page 328
320 c hapter 10: r eliability 4 set master to send vrrp packets every 5 seconds. [sw7700_a-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 timer advertise 5 5 track an interface. [sw7700_a-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 track vlan-interface 3 reduced 30 configure switch b 1 create a virtual router. [sw7700_b-vlan-interf...
Page 329
Configuring vrrp 321 [sw7700_b-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 2 priority 110 troubleshooting vrrp the configuration of vrrp is simple so almost all troubleshooting can be done by viewing the configuration and debugging information. Here are some possible failures you might experience and the correspondi...
Page 330
322 c hapter 10: r eliability.
Page 331: Ystem
11 s ystem m anagement this chapter covers the following topics: ■ file system ■ managing the mac address table ■ managing devices ■ maintaining and debugging the system ■ snmp ■ rmon ■ ntp ■ ssh terminal services file system the switch 7700 provides a file system module for efficient management wit...
Page 332
324 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following operations in user view. Managing files you can use the file system to delete, undelete, or permanently delete a file. It can also be used to display file contents; rename, copy, and move a file; and display the information about a specified...
Page 333
File system 325 example: file system operation 1 format the flash. Format flash: all sectors will be erased, proceed? [confirm] y format flash: completed 2 display the working directory in the flash. Cd flash:/ pwd flash:/ 3 create a directory named test. Mkdir test 4 display the flash directory inf...
Page 334
326 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following configuration in all views. The configuration files are displayed in their corresponding saving formats. Saving the current configuration use the save command to retain the current-configuration in the flash memory. The configurations are sa...
Page 335
File system 327 ftp server configuration includes tasks described in the following sections: ■ enabling and disabling the ftp server ■ configuring the ftp server authentication and authorization ■ configuring ftp server parameters ■ displaying and debugging the ftp server ■ introduction to ftp clien...
Page 336
328 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement configuring ftp server parameters you can use the following commands to configure the connection timeout of the ftp server. If the ftp server does not receive a service request from the ftp client for a period of time, it will cut the connection to it, thereby av...
Page 337
Managing the mac address table 329 ■ downloading files with tftp configuring the file transmission mode tftp transmits files in two modes; binary mode for program files and ascii mode for text files. Use the following commands to configure the file transmission mode. Perform the following configurat...
Page 338
330 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement destined for the same mac address can be forwarded directly. If the mac address cannot be found after broadcasting the packet, the switch will drop it and notify the transmitter that the packet did not arrive at the destination. Figure 1 the switch 7700 forwards ...
Page 339
Managing the mac address table 331 perform the following configuration in system view. Disabling or enabling global mac address learning with the address learning function, an ethernet switch can learn new mac addresses. When it receives a packet destined for a mac address it has already learned, th...
Page 340
332 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement setting mac address aging time setting an appropriate aging time implements mac address aging. Too long or too short an aging time set by subscribers will cause the ethernet switch to flood a large amount of data packets. This affects the switch operation perform...
Page 341
Managing the mac address table 333 execute the debugging command in user view to debug mac address table configuration. Example: configuring mac address table management the user logs in to the switch through the console port to configure the address table management. Set the address aging time to 5...
Page 342
334 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement 00-e0-fc-17-a7-d6 1 learnedethernet1/0/2 300 00-e0-fc-5e-b1-fb 1 learned ethernet1/0/2 300 00-e0-fc-55-f1-16 1 learned ethernet1/0/2 300 managing devices with device management, the switch 7700 displays the current state and event debugging information about the ...
Page 343
Managing devices 335 resetting a slot the switch 7700 allows the administrator to reset a slot in the system. Perform the following configuration in user view. The parameter slot-num ranges from 0 to 6. Setting the parameter to 0 resets the fabric module, taking the same effect as resetting the enti...
Page 344
336 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement the default setting is 1 (8g to slots 1 and 2, 4g to slots 3-6) displaying devices execute the display command in all views to display the device management configuration, and to verify the configuration. Maintaining and debugging the system this section includes...
Page 345
Maintaining and debugging the system 337 setting the time zone you can configure the name of the local time zone, and the time difference between the local time and the standard universal time coordinated (utc). Perform the following commands in user view. By default, the utc time zone is set. Setti...
Page 346
338 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement enabling and disabling terminal debugging the switch 7700 provides various ways for debugging most of the supported protocols and functions. The following switches control the outputs of debugging information: ■ the protocol debugging switch controls debugging ou...
Page 347
Maintaining and debugging the system 339 for more about the usage and format of the debugging commands, refer to the appropriate chapters. Since the debugging output will affect the system operating efficiency, do not enable the debugging command unnecessarily. Use the debugging all command, especia...
Page 348
340 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement tracert command tracert is used for testing the gateways from the source host to the destination. It is used for checking if the network is connected and analyzing where faults occur in the network. The following list provides the tracert execution process: 1 tra...
Page 349
Maintaining and debugging the system 341 for the above configuration, the log host is not configured on the switch. All other configurations will take effect after enabling the logging function. Enabling and disabling the logging function you can use the following commands to enable or disable the l...
Page 350
342 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement the system assigns a channel in each output direction by default. See table 39. The six settings are independent from each other. The settings will take effect only after enabling the information center. Defining the log filtering rules the syslog classifies the ...
Page 351
Maintaining and debugging the system 343 use the following commands to define the filtering rules of the channels. Perform the following operation in system view. Modu-name specifies the module name. Level refers to the severity levels and severity specifies the severity level of information. The in...
Page 352
344 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement local4.Crit /var/log/sw7700/config sw7700 security messages: local5.Notice /var/log/sw7700/security pay attention to the following points when editing the file “/etc/syslog.Conf”: ■ the description must start from a fresh line and begin with a pound key #. ■ use ...
Page 353
Snmp 345 displaying and debugging the syslog function after performing the syslog configuration, execute the display command in all views to display the configuration and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute the reset command in user view to clear the statistics of the syslog module. E...
Page 354
346 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement snmp versions and supported mib to uniquely identify the management variables of a device in snmp messages, snmp adopts the hierarchical naming scheme to identify the managed objects. It is like a tree. A tree node represents a managed object, as shown in the fig...
Page 355
Snmp 347 ■ setting the community name ■ enabling and disabling the snmp agent to send a trap ■ setting the destination address of a trap ■ setting the lifetime of the trap message ■ setting snmp information ■ setting the engine id of a local or remote device ■ setting and deleting an snmp group ■ se...
Page 356
348 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following configuration in system view. Setting the destination address of a trap you can use the following commands to set or delete the destination address of the trap. Perform the following configuration in system view. The authentication parameter...
Page 357
Snmp 349 perform the following configuration in system view. By default, syslocation is specified as “marlborough ma”. Setting the engine id of a local or remote device use the following commands to set the engine id of a local or remote device. Perform the following configuration in system view. By...
Page 358
350 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement setting the source address of the trap use the following commands to set or remove the source address of the trap. Perform the following configuration in system view. Adding and deleting a user to or from an snmp group use the following commands to add or delete ...
Page 359
Snmp 351 the agent can receive or send the snmp packets ranging from 484 bytes to 17940 bytes. By default, the size of an snmp packet is 1500 bytes. Perform the following configuration in system view. Enabling and disabling transmission of trap information to enable or disable transmission of trap i...
Page 360
352 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement example: snmp configuration a network management station (nms) and the ethernet switch are connected by the ethernet. The ip address of nms is 129.102.149.23 and the ip address of the vlan interface on the switch is 129.102.0.1. Perform the following configuratio...
Page 361
Rmon 353 [sw7700-vlan2] port ethernet 2/0/3 [sw7700-vlan2] interface vlan 2 [sw7700-vlan-interface2] ip address 129.102.0.1 255.255.255.0 5 set the administrator id, contact and the physical location of the ethernet switch. [sw7700] snmp-agent sys-info contact mr.Smith-tel:3306 [sw7700] snmp-agent s...
Page 362
354 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement configuring rmon rmon configuration includes tasks described in the following sections: ■ adding and deleting an entry to or from the alarm table ■ adding and deleting an entry to or from the event table ■ adding and deleting an entry to or from the history contr...
Page 363
Rmon 355 use the following commands to add or delete an entry to or from the history control table. Perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. Adding and deleting an entry to or from the extended rmon alarm table you can use the command to add or delete an entry to or from the extend...
Page 364
356 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement displaying the rmon configuration execute the display command in all views to display the rmon configuration, and to verify the configuration. Example: rmon configuration set an entry in the rmon ethernet statistics table for ethernet port performance, which is c...
Page 365
Ntp 357 ntp as the network topology gets more and more complex, it becomes important to synchronize the clocks of the equipment on the entire network. Network time protocol (ntp) is a tcp/ip feature that advertises the accurate time throughout the network. Ntp ensures the consistency of the followin...
Page 366
358 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement the system clocks are synchronized as follows: ■ ethernet switch a sends an ntp packet to ethernet switch b. The packet carries the timestamp 10:00:00am (t1) that tells when it left ethernet switch a. ■ when the ntp packet arrives at ethernet switch b, ethernet s...
Page 367
Ntp 359 local switch will operate in broadcast mode. If you configure an interface on the local switch to receive ntp broadcast packets, the local switch will operate in broadcast client mode. If you configure an interface on the local switch to transmit ntp multicast packets, the local switch will ...
Page 368
360 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following configurations in system view. Ntp version number number ranges from 1 to 3 and defaults to 3; the authentication key id keyid ranges from 1 to 4294967295; interface-name or interface-type interface-number specifies the ip address of an inte...
Page 369
Ntp 361 this command can only be configured on the interface where the ntp broadcast packets are received. Configuring ntp multicast server mode designate an interface on the local switch to transmit ntp multicast packets. In this case, the local equipment operates in multicast mode and serves as a ...
Page 370
362 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following configurations in system view. Setting the ntp authentication key this configuration task sets the ntp authentication key. Perform the following configurations in system view. Key number number ranges from 1 to 4294967295; the key value cont...
Page 371
Ntp 363 an interface is specified by interface-name or interface-type interface-number. The source address of the packets will be taken from the ip address of the interface. If the ntp-service unicast-server or ntp-service unicast-peer command also designates a transmitting interface, use the one de...
Page 372
364 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement ip address acl number is specified through the acl-number parameter and ranges from 2000 to 2999. The meanings of other authority levels are as follows: ■ query: allow control query for the local ntp service only. ■ synchronization: allow request for local ntp ti...
Page 373
Ntp 365 ■ configuring ntp multicast mode ■ configuring authentication-enabled ntp server mode configuring ntp servers on sw77001, set the local clock as the ntp master clock at stratum 2. On sw77002, configure sw77001 as the time server in server mode and set the local equipment as in client mode. F...
Page 374
366 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement root delay: 0.00 ms root dispersion: 0.00 ms peer dispersion: 0.00 ms reference time: 00:00:00.000 utc jan 1 1900(00000000.00000000) after the synchronization, sw77002 turns into the following status: [sw77002] display ntp-service status clock status: synchronize...
Page 375
Ntp 367 note: 1 source(master),2 source(peer),3 selected,4 candidate,5 configured configuring ntp peers on sw77003, set local clock as the ntp master clock at stratum 2. On sw77002, configure sw77001 as the time server in server mode and set the local equipment as in client mode. At the same time, s...
Page 376
368 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement clock precision: 2^17 clock offset: 0.0000 ms root delay: 0.00 ms root dispersion: 10.94 ms peer dispersion: 10.00 ms reference time: 20:54:25.156 utc mar 7 2002(c0325201.2811a112) by this time, sw77004 has been synchronized by sw77005 and it is at stratum 2, or ...
Page 377
Ntp 369 configure ethernet switch sw77004: 1 enter system view. System-view 2 enter vlan-interface2 view. [sw77004] interface vlan-interface 2 [sw77004-vlan-interface2] ntp-service broadcast-client configure ethernet switch sw77001: 1 enter system view. System-view 2 enter vlan-interface2 view. [sw7...
Page 378
370 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement ******************************************************************** ****** [12345]127.127.1.0 local(0) 7 377 64 57 0.0 0.0 1.0 [5]1.0.1.11 0.0.0.0 16 0 64 - 0.0 0.0 0.0 [5]128.108.22.44 0.0.0.0 16 0 64 - 0.0 0.0 0.0 note: 1 source(master),2 source(peer),3 select...
Page 379
Ssh terminal services 371 segments, sw77001 cannot receive the multicast packets from sw77003, while sw77004 is synchronized by sw77003 after receiving the multicast packet. Configuring authentication-enabled ntp server mode sw77001 sets the local clock as the ntp master clock at stratum 2. Sw77002 ...
Page 380
372 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement figure 9 setting up ssh channels in lan 1 switch running ssh server 2 pc running ssh client 3 ethernet lan in figure 9, the vlan for the ethernet port must be configured with vlan interfaces and ip address. The communication process between the server and client ...
Page 381
Ssh terminal services 373 which compares it with the local authentication data. If the data match, the user is allowed to access the switch. Otherwise, the authentication process fails. ■ session request: the client sends session request messages to the server which processes the request messages. ■...
Page 382
374 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement configuring and cancelling a local rsa key pair in executing this command, if you have configured an rsa host key pair, the system gives an alarm after using this command and prompts that the existing one will be replaced. The server key pair is created dynamical...
Page 383
Ssh terminal services 375 defining the ssh authentication timeout value perform the following configurations in system view . By default, the timeout value for ssh authentication is 60 seconds. Defining the ssh authentication retry value setting the ssh authentication retry value can effectively pre...
Page 384
376 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following configurations in the public key view . Associating a public key with an ssh user perform the following configurations in system view . Configuring the ssh client there are several types of ssh client software, such as putty and freebsd. You...
Page 385
Ssh terminal services 377 figure 10 figure 8-2 putty configuration for basic options 1 enter the ip address of the switch in the host name (or ip address) text box. You can also input the ip address of an interface in up state, but its route to ssh client pc must be reachable. 2 select the ssh proto...
Page 386
378 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement figure 11 putty configuration for ssh version 4 select the 1 radio button. 5 to enable rsa authentication, you must specify rsa private key file, which is not required for password authentication. Select ssh > auth to enable rsa authentication..
Page 387
Ssh terminal services 379 figure 12 putty configuration for rsa authentication 6 click browse to select the rsa private key file. Click ok. 7 click open to enter the ssh client interface. If it runs normally, you are prompted to enter the username and password. 8 enter the username and password and ...
Page 388
380 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement ssh configuration example see figure 13 for an illustration of the local connection configuration from the ssh client to the switch. The client uses the ssh protocol to access the switch. Figure 13 networking for ssh local configuration 1 ssh client 2 switch to c...
Page 389
Ssh terminal services 381 [sw7700-key-code]c48e3306367fe187bdd944018b3b69f3cbb0a573202c16 [sw7700-key-code]bb2fc1acf3ec8f828d55a36f1cddc4bb45504f020125 [sw7700-key-code]public-key-code end [sw7700-rsa-public]peer-public-key end [sw7700]ssh user client002 assign rsa-key key002 you need to specify the...
Page 390
382 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement.