- DL manuals
- 3Com
- Switch
- Switch 7700
- Configuration Manual
3Com Switch 7700 Configuration Manual
Summary of Switch 7700
Page 1
Http://www.3com.Com/ switch 7700 configuration guide published october 2003.
Page 2
3com corporation 350 campus drive marlborough, ma 01752-3064 copyright © 2003, 3com corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written p...
Page 3: Ontents
C ontents a bout t his g uide conventions 1 s ystem a ccess product overview 3 function features 3 configuring the switch 7700 4 setting terminal parameters 5 configuring through telnet 8 configuring through a dial-up the modem 10 configuring the user interface 12 command line interface 19 command l...
Page 4
Configure ip address 48 displaying and debugging an ip address 49 troubleshooting an ip address configuration 49 arp configuration 50 configure static arp 50 dhcp relay 51 configuring dhcp relay 52 displaying and debugging dhcp relay 53 troubleshooting a dhcp relay configuration 55 ip performance 56...
Page 5
Configure igmp snooping 119 display and debug igmp snooping 120 igmp snooping configuration example 120 troubleshootinigmp snooping 121 common multicast configuration 121 common multicast configuration 122 display and debug common multicast configuration 122 igmp configuration 123 igmp configuration...
Page 6
Configuring the bpdu forwarding mechanism 163 implementing stp on the switch 7700 163 configuring rstp 164 displaying and debugging rstp 173 aaa and radius o peration ieee 802.1x 177 802.1x system architecture 177 configuring 802.1x 179 displaying and debugging 802.1x 183 configuring the aaa and rad...
Page 7
Display the state and information of the system 14 system debugging 14 testing tools for network connection 16 logging function 16 snmp 21 snmp versions and supported mib 21 configure snmp 22 display and debug snmp 26 rmon 28 configure rmon 28 display and debug rmon 30
Page 9: Bout
A bout t his g uide this guide describes the 3com ® switch 7700 and how to configure it. Conventions table 1 and table 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide. Table 1 notice icons table 2 text conventions icon notice type description information note information that describes import...
Page 10
2 a bout t his g uide.
Page 11: Ystem
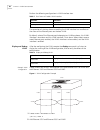
1 s ystem a ccess product overview the 3com switch 7700 is a large capacity, modularized wire speed layer 2/layer 3 ethernet switch. It is designed for ip metropolitan area networks (man), large-sized enterprise network and campus network users. The switch 7700 has an integrated chassis structure. T...
Page 12
4 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess configuring the switch 7700 on the switch 7700, you can set up the configuration environment through the console port. To set up the the local configuration environment: 1 plug the db-9 or db-25 female plug of the console cable into the serial port of the pc or the term...
Page 13
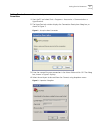
Setting terminal parameters 5 setting terminal parameters to set terminal parameters: 1 start the pc and select start > programs > accessories > communications > hyperterminal . 2 the hyperterminal window displays the connection description dialog box, as shown in figure 2. Figure 2 set up the new c...
Page 14
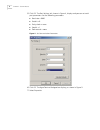
6 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess 5 click ok . The port settings tab, shown in figure 4, displays and you can set serial port parameters. Set the following parameters: ■ baud rate = 9600 ■ databit = 8 ■ parity check = none ■ stopbit = 1 ■ flow control = none figure 4 set communication parameters 6 click...
Page 15
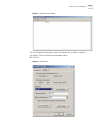
Setting terminal parameters 7 figure 5 hyperterminal window 8 in the properties dialog box, select the settings tab, as shown in figure 6. 9 select vt100 in the emulation dropdown menu. 10 click ok . Figure 6 settings tab.
Page 16
8 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess configuring through telnet after you have correctly configured the ip address of a vlan interface for an ethernet switch through the console port (using the ip address command in vlan interface view), and added the port (that connects to a terminal) to this vlan (using ...
Page 17
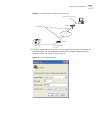
Setting terminal parameters 9 5 on the connect dialog box, enter the ip address of the vlan connected to the pc port and set the terminal type to vt100, as shown in figure 9. Figure 9 connect ethernet switch by telnet the terminal displays user access verification and prompts you for the logon passw...
Page 18
10 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess figure 10 provide telnet client service 1 authenticate the telnet user through the console port on the telnet server (ethernet switch) before login. Note : by default, the password is required for authenticating the telnet user to log in the ethernet switch. If a user ...
Page 19
Setting terminal parameters 11 figure 11 set up remote configuration environment 3 dial for a connection to the switch, using the terminal emulator and modem on the remote end. Dial the telephone number of the modem connected to the ethernet switch. See figure 12 and figure 13. Figure 12 set the dia...
Page 20
12 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess figure 13 dial the remote pc 4 enter the preset login password on the remote terminal emulator and wait for the prompt. 5 use the appropriate commands to configure the switch 7700 or view its running state. Enter ? To get the immediate help. For details on a specific c...
Page 21
Setting terminal parameters 13 to number the user interface by relative number, represented by interface + number assigned to each type of user interface: ■ aux user interface = aux 0. ■ the first vty interface = vty 0, the second one = vty 1, and so on. To configure the user interface: ■ enter the ...
Page 22
14 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess configure the terminal attributes the following commands can be used for configuring the terminal attributes, including enabling/disabling terminal service, disconnection upon timeout, lockable user interface, configuring terminal screen length and history command buff...
Page 23
Setting terminal parameters 15 configure idle-timeout by default, idle-timeout is enabled and set to 10 minutes on all the user interfaces. The idle-timeout command is described in table 5. Lock user interface this command locks the current user interface and prompts the user to enter a password. Th...
Page 24
16 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess configure the authentication method the authentication-mode command configures the user login authentication method that denies access to an unauthorized user. Table 9 describes the authentication-mode command. Perform the following configuration in user interface view...
Page 25
Setting terminal parameters 17 note : by default, the password is required for authenticating the modem and telnet users when they log in. If the password has not been set, when a user logs in, the following message displays, password required, but none set . If the authentication-mode none command ...
Page 26
18 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess perform the following configuration in system view. Configure the attributes of a modem you can use the commands described in table 14 to configure the attributes of a modem when logging in to the switch through the modem. Perform the following configuration in user in...
Page 27
Command line interface 19 perform the following configuration in user interface view. Note the following points: ■ after executing the auto-execute command, the user interface can no longer be used to carry out the routine configurations for the local system. Use this command with caution. ■ make su...
Page 28
20 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess ■ network test commands, such as tracert and ping, for rapid troubleshooting of the network. ■ detailed debugging information to help with network troubleshooting. ■ ability to log in and manage other ethernet switches directly, using the telnet command. ■ ftp service ...
Page 29
Command line interface 21 the command line provides the following views: ■ user view ■ system view ■ ethernet port view ■ vlan view ■ vlan interface view ■ local-user view ■ user interface view ■ ftp client view ■ cluster view ■ pim view ■ rip view ■ ospf view ■ ospf area view ■ route policy view ■ ...
Page 30
22 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess figure 14 relation diagram of the views the table 18 describes the function features of different views and the commands to enter or quit. Table 18 function feature of command view command view function prompt command to enter command to exit user view show the basic i...
Page 31
Command line interface 23 vlan interface view configure ip interface parameters for a vlan or a vlan aggregation [sw7700-vlan- interface1] key in interface vlan-interface 1 in system view quit returns to system view return returns to user view local-user view configure local user parameters [sw7700-...
Page 32
24 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess feature and functions of the command line online help the command line interface provides full and partial online help modes. You can get the help information through these online help commands, which are described as follows. ■ enter ? In any view to get all the comma...
Page 33
Command line interface 25 -v verbose output. Icmp packets other than echo_response that are received are listed string ip address or hostname of a remote system ip ip protocol ■ enter a command with a ? , separated by a space. If this position is for parameters, all the parameters and their brief de...
Page 34
26 c hapter 1: s ystem a ccess note : cursor keys can be used to retrieve the history commands in windows 3.X terminal and telnet. However, in windows 9x hyperterminal, the cursor keys and do not work, because windows 9x hyperterminal defines the two keys differently. In this case, use the combinati...
Page 35: Ort
2 p ort c onfiguration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ethernet port overview ■ link aggregation configuration ethernet port overview a brief description of switch 7700 i/o modules are listed below: ■ 48-port 10/100base-t auto-sensing fast ethernet card ■ 8-port 1000base-x (gigabit inter...
Page 36
28 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration ■ setting link type for ethernet port ■ adding the ethernet port to a vlan ■ setting the default vlan id for ethernet port entering ethernet port view before configuring the ethernet port, enter ethernet port view first. Perform the following configuration in syst...
Page 37
Ethernet port overview 29 perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. Note: 100m electrical ethernet port can operate in full-duplex, half-duplex or auto-negotiation mode. The gigabit electrical ethernet port can operate in full duplex, half duplex or auto-negotiation mode. When the p...
Page 38
30 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration note: the settings only take effect on 10/100base-t and 10/100/1000base-t ports. The switch 7700 only supports auto (auto-sensing). If you set some other type, you will see the prompt “not support this operation!”. The cable type is auto (auto-recognized) by defau...
Page 39
Ethernet port overview 31 setting the maximum mac addresses an ethernet port can learn use the following command to set an amount limit on mac addresses learned by the ethernet port. If the number of mac address learned by this port exceeds the value set by the user, this port will not learn mac add...
Page 40
32 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration adding the ethernet port to a vlan the following commands are used for adding an ethernet port to a specified vlan. The access port can only be added to one vlan, while the hybrid and trunk ports can be added to multiple vlans. Perform the following configuration ...
Page 41
Ethernet port overview 33 note: ■ the trunk port and isolate-user-vlan cannot be configured simultaneously, while the hybrid port and isolate-user-vlan can be thus configured. However, if the default vlan has been mapped in isolate-user-vlan, you cannot modify the default vlan id until the mapping r...
Page 42
34 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration figure 1 configure the default vlan for a trunk port the following configurations are used for switch a. Configure switch b in the similar way. 1 enter the ethernet port view of ethernet1/0/1. [sw7700] interface ethernet1/0/1 2 set the ethernet1/0/1 as a trunk por...
Page 43
Link aggregation configuration 35 perform the following configuration in system view. Note: the ethernet ports to be aggregated should be configured with the same speed and duplex otherwise, they cannot be aggregated. The switch 7700 does not support ingress aggregation mode. Display and debug link ...
Page 44
36 c hapter 2: p ort c onfiguration mode: both ethernet link aggregation troubleshooting when configuring link aggregation, you might see a message that the configuration has failed. To address this situation: ■ check the input parameter and see whether the starting number of ethernet port is smalle...
Page 45: Vlan C
3 vlan c onfiguration vlan overview a virtual local area network (vlan) groups the devices of a lan logically, but not physically, into segments to implement the virtual workgroups. Using vlan technology, network managers can logically divide the physical lan into different broadcast domains. Every ...
Page 46
38 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration add ethernet ports to a vlan you can use the following command to add ethernet ports to a vlan. Perform the following configuration in vlan view. For the meanings of the parameters related to the ethernet ports and the specific numbering rules of the ports, see “po...
Page 47
Vlan overview 39 set or delete vlan description character string you can use the following command to set or delete vlan description character string. The description character strings, such as workgroup name and department name, are used to distinguish the different vlans. Perform the following con...
Page 48
40 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. The operation of shutting down or enabling the vlan interface has no effect on the status of the ethernet ports on the local vlan. By default, when all the ethernet ports belonging to a vlan are down, this...
Page 49
Garp/gvrp configuration 41 [sw7700-vlan2] port ethernet 1/0/1 ethernet 2/0/1 3 create vlan 3 and enters its view. [sw7700-vlan2] vlan 3 4 add ethernet 1/0/2 and ethernet 2/0/2 to vlan3. [sw7700-vlan3] port ethernet 1/0/2 ethernet 2/0/2 garp/gvrp configuration generic attribute registration protocol ...
Page 50
42 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration setting the garp timer garp timers include the hold, join, leave, and leaveall timers. The garp participant sends join message regularly when join timer times out so that other garp participants can register its attribute values. When the garp participant wants to ...
Page 51
Garp/gvrp configuration 43 configuring gvrp garp vlan registration protocol (gvrp) is a garp application. Based on the garp operating mechanism, gvrp maintains the dynamic vlan registration information in the switch and distributes the information to other switches. All the gvrp-supporting switches ...
Page 52
44 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration perform the following configurations in ethernet port view. Gvrp should be enabled globally before it is enabled on the port. Gvrp can only be enabled or disabled on a trunk port. By default, global gvrp is disabled. Set gvrp registration type the gvrp registration...
Page 53
Garp/gvrp configuration 45 example: gvrp configuration example the network requirement is to dynamically register and update vlan information among switches. Figure 2 gvrp configuration example configure switch a: 1 set ethernet1/0/1 as a trunk port and allows all the vlans to pass through. [sw7700]...
Page 54
46 c hapter 3: vlan c onfiguration.
Page 55: Etwork
4 n etwork p rotocol o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ configure ip address ■ arp configuration ■ dhcp relay ■ ip performance configure ip address ip address is a 32-bit address represented by four octets. Ip addresses are divided into five classes: a, b, c, d and e. The octets ...
Page 56
48 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration with the rapid development of the internet, ip addresses are depleting very fast. The traditional ip address allocation method uses up ip addresses with little efficiency. The concept of mask and subnet was proposed to make full use of the available ip ad...
Page 57
Configure ip address 49 generally, it is sufficient to configure one ip address for an interface. However, you can also configure more than one ip addresses for an interface, so that it can be connected to several subnets. Among these ip addresses, one is the primary ip address and all others are se...
Page 58
50 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration but not receive the arp packets, there are probably errors on the ethernet physical layer. Arp configuration an ip address cannot be directly used for communication between network devices because devices can only identify mac addresses. An ip address is ...
Page 59
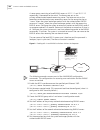
Dhcp relay 51 manually add/delete static arp mapping entries perform the following configuration in system view. Note: static arp mapping entries will not time out, however dynamic arp mapping entries time out after 20 minutes. The arp mapping table is empty and the address mapping is obtained throu...
Page 60
52 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration figure 2 dhcp relay schematic diagram when the dhcp client performs initialization, it broadcasts the request packet on the local network segment. If there is a dhcp server on the local network segment (e.G. The ethernet on the right side of the figure), ...
Page 61
Dhcp relay 53 configure corresponding dhcp server group of the vlan interface perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. When associating a vlan interface to a new dhcp server group, you can configure the association without disassociating it from the previous group. No vlan interfa...
Page 62
54 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration example: configuring dhcp relay configure the vlan interface corresponding to the user and the related dhcp server so as to use dhcp relay. Figure 3 networking diagram of configuring dhcp relay 1 configure the ip address corresponding to dhcp server group...
Page 63
Dhcp relay 55 end in different vlans. The corresponding interface vlan of the dhcp server group 1 is configured as 4000, and that of the group 2 is configured as 3001. [3com] vlan 4000 [3com-vlan4000] port ethernet 1/0/4 [3com] interface vlan 4000 [3com-vlan-interface4000] ip address 1.99.255.1 255....
Page 64
56 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration ip performance tcp attributes to be configured include: ■ synwait timer : when sending the syn packets, tcp starts the synwait timer. If response packets are not received before synwait timeout, the tcp connection will be terminated. The timeout of synwai...
Page 65
Ip performance 57 troubleshooting ip performance if the ip layer protocol works normally but tcp and udp do work normally, you can enable the corresponding debugging information output to view the debugging information. ■ use the terminal debugging command to output the debugging information to the ...
Page 66
58 c hapter 4: n etwork p rotocol o peration.
Page 67: Outing
5 r outing p rotocol o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ip routing protocol overview ■ static routes ■ rip ■ ospf ■ ip routing policy ip routing protocol overview routers select an appropriate path through a network for an ip packet according to the destination address of the pac...
Page 68
60 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration figure 1 about hops networks can have different sizes so the segment lengths connected between two different pairs of routers are also different. If a router in a network is regarded as a node and a route segment in the internet is regarded as a link, mes...
Page 69
Ip routing protocol overview 61 ■ the priority added to the ip routing table for a route — indicates the type of route that is selected. There may be multiple routes with different next hops to the same destination. These routes can be discovered by different routing protocols, or they can be the st...
Page 70
62 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration routing protocols (as well as the static configuration) can generate different routes to the same destination, but not all these routes are optimal. In fact, at a certain moment, only one routing protocol can determine a current route to a single destinat...
Page 71
Static routes 63 the following routes are static routes: ■ reachable route — the normal route in which the ip packet is sent to the next hop by the route marked by the destination. It is a common type of static route. ■ unreachable route — when a static route to a destination has the reject attribut...
Page 72
64 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration the ip address and mask use a decimal format. Because the 1s in the 32-bit mask must be consecutive, the dotted decimal mask can also be replaced by the mask-length which refers to the digits of the consecutive 1s in the mask. ■ transmitting interface or ...
Page 73
Static routes 65 example: typical static route configuration as shown in the figure 3, the masks of all the ip addresses in the figure are 255.255.255.0. All the hosts or switches must be interconnected in pairs by configuring static routes. Figure 3 static route configuration 1 configure the static...
Page 74
66 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration 4 configure the default gateway of the host a to be 1.1.1.2 5 configure the default gateway of the host b to be 1.1.5.2 6 configure the default gateway of the host c to be 1.1.4.1 using this procedure, all the hosts or switches in figure 3 can be intercon...
Page 75
Rip 67 ■ route tag — the indication whether the route is generated by an interior routing protocol or by an exterior routing protocol. The whole process of rip startup and operation can be described as follows: 1 if rip is enabled on a router for the first time, the router broadcasts a request packe...
Page 76
68 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration enable rip and enter the rip view perform the following configurations in system view. By default, rip is not enabled. Enable the rip interface for flexible control of rip operation, you can specify the interface and configure the network where it is loca...
Page 77
Rip 69 usually, this command is not recommended because the opposite side does not need to receive two of the same messages at a time. It should be noted that the peer command should also be restricted by rip work , rip output , rip input and network commands. Specify the rip version rip has two ver...
Page 78
70 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. The rip work command is functionally equivalent to both rip input and rip output commands. By default, all interfaces except loopback interfaces both receive and transmit rip update packets. Disa...
Page 79
Rip 71 perform the following configurations in rip view. Rip-2 uses the route aggregation function by default. Set rip-2 packet authentication rip-1 does not support packet authentication. However, you can configure packet authentication on rip-2 interfaces. Rip-2 supports two authentication modes: ...
Page 80
72 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. By default, split horizon of the interface is enabled. Configure rip to import routes of other protocols rip allows users to import the route information of other protocols into the routing table...
Page 81
Rip 73 perform the following configurations in rip view. By default, the preference of rip is 100. Set additional routing metric the additional routing metric is the input or output routing metric added to an rip route. It does not change the metric value of the route in the routing table, but adds ...
Page 82
74 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration by default, rip does not filter received and distributed routing information. Display and debug rip after configuring rip, execute the display command in all views to display the rip configuration, and to verify the effect of the configuration. Execute th...
Page 83
Ospf 75 figure 4 rip configuration note : the following configuration only shows the operations related to rip. Before performing the following configuration, verify that the ethernet link layer works normally. 1 configure rip on switch a: [switch a] rip [switch a-rip] network 110.11.2.0 [switch a-r...
Page 84
76 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration ■ scope — supports networks in various sizes and can support several hundred routers ■ fast convergence — transmits the update packets instantly after the network topology changes so the change is synchronized in the as ■ loop-free — calculates routes wit...
Page 85
Ospf 77 when two routers synchronize their databases, they use the dd packets to describe their own link state databases (lsds), including the digest of each lsa. The digest refers to the head of an lsa, which can be used to uniquely identify the lsa. Synchronizing databases with dd packets reduces ...
Page 86
78 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration topology becomes more likely to change. Hence, the network is always in “turbulence”, and a large number of osfp packets are generated and transmitted in the network. This shrinks network bandwidth. In addition, each change causes all the routers on the n...
Page 87
Ospf 79 ■ configure nssa of ospf ■ configure the route summarization of ospf area ■ configure ospf virtual link ■ configure route summarization imported into ospf ■ configure the ospf area to support packet authentication ■ configure ospf packet authentication ■ configure ospf to import the routes o...
Page 88
80 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in ospf area view. You must specify the segment to which the ospf will be applied after enabling the ospf tasks. Configure router id a router id is a 32-bit unsigned integer that uniquely identifies a router within an a...
Page 89
Ospf 81 the sending polling hello packets before the adjacency of the neighboring routers is formed. ■ configure the interface type to nonbroadcast on a broadcast network without multi-access capability. ■ configure the interface type to p2mp if not all the routers are directly accessible on an nbma...
Page 90
82 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration set the interface priority for dr election the priority of the router interface determines the qualification of the interface for dr election, a router of higher priority is considered first if there is a collision in the election. Dr is not designated ma...
Page 91
Ospf 83 broadcasting the hello packets, you must manually specify an ip address for the adjacent router for the interface, and whether the adjacent router is eligible for election. This can be done by configuring the peer ip-address command. If dr-priority-number is not specified, the adjacent route...
Page 92
84 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration by default, the dead interval for the neighboring routers of p2p or broadcast interfaces is 40 seconds and for the neighboring routers of p2mp or nbma interfaces is 120 seconds. Note that both hello and dead timers restore the default values if you modify...
Page 93
Ospf 85 note that a lsa retransmission interval that is too small will cause unnecessary retransmission. Set a shortest path first (spf) calculation interval for ospf whenever the ospf lsdb changes, the shortest path requires recalculation. Calculating the shortest path after a change consumes enorm...
Page 94
86 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration by default, the stub area is not configured, and the cost of the default route to a stub area is 1. Configure nssa of ospf nssa and nssa lsa (also called type-7 lsa) are transformations of the stub area and are highly similar to a stub area. Nssa does not...
Page 95
Ospf 87 all routers connected to the nssa must use the nssa command to configure the area with the nssa attribute. The default-route-advertise parameter is used to generate the default type-7 lsas. The default type-7 lsa route is generated on the abr, even though the default route 0.0.0.0 is not in ...
Page 96
88 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in ospf area view. By default, the inter-area routes are not summarized. Configure ospf virtual link according to rfc2328, after the area division of ospf, the backbone are is established with an area-id of 0.0.0.0. The...
Page 97
Ospf 89 the area-id and router-id variables have no default value. By default, the hello timer is 10 seconds, retransmit is 5 seconds, trans-delay is 1 second, and the dead timer is 40 seconds. Configure route summarization imported into ospf the ospf implementation in the switch 7700 supports route...
Page 98
90 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. By default, the interface is not configured with either simple authentication or md5 authentication. Configure ospf to import the routes of other protocols the dynamic routing protocols on the ro...
Page 99
Ospf 91 perform the following configuration in ospf view. By default, ospf does not import the routing information of other protocols. The protocol variable specifies a source routing protocol that can be imported, such as direct, static, rip, or bgp. Configure parameters for ospf to import external...
Page 100
92 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration configure ospf to import the default route the import-route command cannot be used to import the default route. Using the default-route-advertise command, you can import the default route into the routing table. Perform the following configuration in ospf...
Page 101
Ospf 93 by default, ospf does not filter the imported and distributed routing information. For detailed description, see “ip routing policy”. Configure filling the mtu field when an interface transmits dd packets ospf-running routers use the dd (database description) packets to describe their own ls...
Page 102
94 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configuration in user view. Resetting the ospf process can immediately clear the invalid lsas, make the modified router id effective or re-elect the dr and bdr. Display and debug ospf after configurating ospf, execute the display com...
Page 103
Ospf 95 figure 6 configuring dr election based on ospf priority the commands listed in the following examples enable switch a and switch c to be dr and bdr respectively. The priority of switch a is 100, which is the highest on the network, so it is elected as the dr. Switch c has the second highest ...
Page 104
96 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration on switch a, execute the display ospf peer command to display the ospf neighbors. Note that switch a has three neighbors. The state of each neighbor is full, which means that adjacency is set up between switch a and each neighbor. Switch a and switch c sh...
Page 105
Ospf 97 [switch a] ospf [switch a-ospf] area 0 [switch a-ospf-area-0.0.0.0] network 196.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 2 configure switch b: [switch b] interface vlan-interface 7 [switch b-vlan-interface7] ip address 196.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 [switch b] interface vlan-interface 8 [switch b-vlan-interface8] ip addres...
Page 106
98 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration ■ if the physical link and the lower layer protocol are normal, check the ospf parameters configured on the interface. The parameters should be the same parameters configured on the router adjacent to the interface. The same area id should be used, and th...
Page 107
Ip routing policy 99 to enrich its routing knowledge. While importing the routing information, it must import only the information that meets its conditions. To implement the routing policy, you must define a set of rules by specifying the characteristics of the routing information to be filtered. Y...
Page 108
100 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration gateway options and require it to receive only the routing information distributed by certain routers. An ip-prefix is identified by the ip-prefix name. Each ip-prefix can include multiple list items, and each list item can independently specify the matc...
Page 109
Ip routing policy 101 the deny argument specifies that the apply clauses are not executed. If a route satisfies all the if-match clauses of the node, the node denies the route and the route does not take the test of the next node. If a route does not satisfy all the if-match clauses of the node, how...
Page 110
102 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration by default, no matching is performed. Note that: ■ the if-match clauses for a node in the route policy require that the route satisfy all the clauses to match the node before the actions specified by the apply clauses can be executed. ■ if no if-match cl...
Page 111
Ip routing policy 103 by default, no apply clauses are defined. Note that if the routing information meets the match conditions specified in the route policy and also notifies the med value configured with apply cost-type internal when notifying the igp route to the ebgp peers, then this value is re...
Page 112
104 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration perform the following configurations in system view. During the matching, the router checks list items identified by the index-number in the ascending order. If only one list item meets the condition, it means that it has passed the ip-prefix filtering (...
Page 113
Ip routing policy 105 perform the following configuration in routing protocol view. By far, the route policy supports importing the routes discovered by the following protocols into the routing table: ■ direct: the hop (or host) to which the local interface is directly connected. ■ static: static ro...
Page 114
106 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration figure 9 filtering received routing information configure switch a: 1 configure the ip address of vlan interface. [switch a] interface vlan-interface 100 [switch a-vlan-interface100] ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0 [switch a] interface vlan-interface 200 [...
Page 115
Ip routing policy 107 ■ the if-match mode of at least one node of the route policy should be the permit mode. When a route-policy is used for the routing information filtering, if a piece of routing information does not pass the filtering of any node, then it means that the route information does no...
Page 116
108 c hapter 5: r outing p rotocol o peration.
Page 117: Ulticast
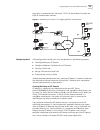
6 m ulticast p rotocol this chapter includes information on the following: ■ ip multicast overview ■ gmrp ■ igmp snooping ■ common multicast configuration ■ igmp configuration ■ pim-dm configuration ■ pim-sm configuration ip multicast overview many transmission methods can be used when the destinati...
Page 118
110 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol figure 1 comparison between the unicast and multicast transmission note: a multicast source does not necessarily belong to a multicast group. It only sends data to the multicast group and it is not necessarily a receiver. Multiple sources can send packets to a mu...
Page 119
Ip multicast overview 111 ranges and meanings of class d addresses are shown in table 1. Reserved multicast addresses that are commonly used are shown table 2: ethernet multicast mac addresses when unicast ip packets are transmitted in ethernet, the destination mac address is the mac address of the ...
Page 120
112 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol figure 2 mapping between the multicast ip address and the ethernet mac address only 23 bits of the last 28 bits in the ip multicast address are mapped to the mac address. Therefore the 32 ip multicast addresses are mapped to the same mac address. Ip multicast pro...
Page 121
Ip multicast overview 113 resources related (such as bandwidth and cpu of routers) are consumed. In order to decrease the consumption of these precious network resources, branches that do not have members send prune messages toward the source to reduce the unwanted/unnecessary traffic. To enable the...
Page 122
114 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol application of multicast ip multicast technology effectively solves the problem of packet forwarding from single-point to multi-point. It implements high-efficient data transmission from single-point to multi-point in ip networks and can save a large amount of ne...
Page 123
Gmrp 115 by default, gmrp is disabled. Enabling/disabling gmrp on the port perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. Gmrp should be enabled globally before being enabled on a port. By default, gmrp is disabled on the port. Displaying and debugging gmrp after the previous configurati...
Page 124
116 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol [sw7700-ethernet1/0/1] gmrp igmp snooping igmp snooping (internet group management protocol snooping) is a multicast control mechanism running on layer 2. It is used for multicast group management and control. Igmp snooping runs on the link layer. When receiving ...
Page 125
Igmp snooping 117 figure 5 multicast packet transmission with igmp snooping implement igmp snooping this section introduces related switch concepts of igmp snooping: ■ router port: the port directly connected to the multicast router. ■ multicast member port: the port connected to the multicast membe...
Page 126
118 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol figure 6 implementing igmp snooping 1 igmp general query message: transmitted by the multicast router to query which multicast group contains member. When a router port receives an igmp general query message, the switch 7700 will reset the aging timer of the port...
Page 127
Igmp snooping 119 any member, the switch will notify the multicast router to remove it from the multicast tree. Configure igmp snooping the main igmp snooping configuration includes: ■ enabling/disabling igmp snooping ■ configuring the aging time of router port ■ configuring maximum response time ■ ...
Page 128
120 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the maximum response time is 10 seconds. Configure aging time of multicast group member this task sets the aging time of the multicast group member port. If the switch receives no multicast group rep...
Page 129
Common multicast configuration 121 figure 7 igmp snooping configuration network 1 display the status of gmrp. Display gmrp status 2 display the current status of igmp snooping when gmrp is disabled. Display igmp-snooping configuration 3 enable igmp snooping if it is disabled. [sw7700] igmp-snooping ...
Page 130
122 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol common multicast configuration common multicast configuration includes: ■ enabling multicast enabling multicast enable multicast first before enabling the multicast routing protocol. Enabling multicast will automatically enable igmp operation on all interfaces. P...
Page 131
Igmp configuration 123 igmp configuration igmp (internet group management protocol) is a protocol in the tcp/ip suite responsible for management of ip multicast members. It is used to establish and maintain multicast membership among ip hosts and their connected neighboring routers. Igmp excludes tr...
Page 132
124 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol multicast group. This prevents the hosts of members of other multicast groups from sending response messages. ■ max response time the max response time is added in igmp version 2. It is used to dynamically adjust the allowed maximum time for a host to response to...
Page 133
Igmp configuration 125 limit ing access to ip multicast groups a multicast router learns whether there are members of a multicast group on the network via the received igmp membership message. A filter can be set on an interface to limit the range of allowed multicast groups. Perform the following c...
Page 134
126 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol configuring the igmp querier present timer the igmp querier present timer defines the period of time before the router takes over as the querier. Perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. By default, the value is 120 seconds. If the router has r...
Page 135
Pim-dm configuration 127 pim-dm configuration pim-dm (protocol independent multicast, dense mode) belongs to dense mode multicast routing protocols. Pim-dm is suitable for small networks. Members of multicast groups are relatively dense in such network environments. The working procedures of pim-dm ...
Page 136
128 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol independent of any specified unicast routing protocol such as the routing information learned by rip and ospf ■ assert mechanism as shown in the following figure, both routers a and b on the lan have their own receiving paths to multicast source s. In this case, ...
Page 137
Pim-dm configuration 129 perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. It’s recommended you configure pim-dm on all interfaces in non-special cases. This configuration is effective only after the multicast routing is enabled in system view. Once enabled pim-dm on an interface, pim-sm c...
Page 138
130 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol pim-dm configuration example ls_a has a port carrying vlan 10 to connect multicast source, a port carrying vlan11 to connect ls_b and a port carrying vlan12 to connect ls_c. Configure to implement multicast between multicast source and receiver 1 and receiver 2. ...
Page 139
Pim-sm configuration 131 [sw7700-vlan-interface11] ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.0.0 [sw7700-vlan-interface11] pim dm [sw7700-vlan-interface11] quit [sw7700] interface vlan-interface 12 [sw7700-vlan-interface12] ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.0.0 [sw7700-vlan-interface12] pim dm pim-sm configuration pim-sm...
Page 140
132 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol figure 10 rpt schematic diagram multicast source registration when multicast source s sends a multicast packet to the group g, the pim-sm multicast router is responsible for encapsulating the packet into a registration packet upon receipt. It then sends the packe...
Page 141
Pim-sm configuration 133 calculate the rps corresponding to multicast groups according to the same algorithm after receiving the c-rp messages that the bsr advertises. It should be noted that one rp can serve multiple multicast groups or all multicast groups. Each multicast group can only be uniquel...
Page 142
134 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol once enabled , pim-dm cannot be enabled on the same interface. Configure the interface hello message interval generally, pim-sm advertises hello messages periodically on the interface enabled with it to detect pim neighbors and discover which router is the design...
Page 143
Pim-sm configuration 135 using undo pim command, you can clear the configuration in pim view, and back to system view. Configure candidate-bsrs in a pim domain, one or more candidate bsrs should be configured. A bsr (bootstrap router) is elected among candidate bsrs. The bsr takes charge of collecti...
Page 144
136 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol multicast group in the specified range. It is suggested to configure candidate rp on the backbone router. Configure rp to filter the register messages sent by dr in the pim-sm network, the register message filtering mechanism can control which sources to send mes...
Page 145
Pim-sm configuration 137 example: configuring pim-sim in actual network, we assume that the switches can intercommunicate. Suppose that host a is the receiver of the multicast group at 225.0.0.1. Host b begins transmitting data destined to 225.0.0.1. Ls_a receives the multicast data from host b via ...
Page 146
138 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol [sw7700] vlan 12 [sw7700-vlan12] port ethernet 1/0/6 to ethernet 1/0/7 [sw7700-vlan12] quit [sw7700] pim [sw7700-pim] interface vlan-interface 12 [sw7700-vlan-interface12] pim sm [sw7700-vlan-interface12] quit 2 configure the threshold for multicast group to swit...
Page 147
Pim-sm configuration 139 configure ls_c: 1 enable pim-sm. [sw7700] multicast routing-enable [sw7700] vlan 10 [sw7700-vlan10] port ethernet 1/0/2 to ethernet 1/0/3 [sw7700-vlan10] quit [sw7700] pim [sw7700-pim] interface vlan-interface 10 [sw7700-vlan-interface10] pim sm [sw7700-vlan-interface10] qui...
Page 148
140 c hapter 6: m ulticast p rotocol.
Page 149: S/acl O
7 q o s/acl o peration acl overview a series of matching rules are required for the network devices to identify the packets to be filtered. After identifying the packets, the switch can permit or deny them to pass through according to the defined policy. The access control list (acl) is used to impl...
Page 150
142 c hapter 7: q o s/acl o peration ■ for basic acl statements, source address wildcards are compared directly. If the wildcards are the same, the configuration sequence is used. ■ for the acl based on the interface filter, the rule that is configured with any is listed at the end, while others fol...
Page 151
Configuring acl 143 ■ activating acl these steps must be done in sequence. Configure the time range first, then select the acl mode and define the acl (using the defined time range in the definition), followed by activating the acl to validate it. Configuring the time range the process of configurin...
Page 152
144 c hapter 7: q o s/acl o peration note : if a specific time range is not defined, the acl always functions after it is activated. During the process of defining the acl, you can use the rule command several times to define multiple rules for an acl. If acl is used to filter or classify the data t...
Page 153
Configuring acl 145 the advanced acl is identified with numbers ranging from 100 to 199. Note that port1 and port2 in this command specify the tcp or udp ports used by various high-layer applications. For some common port numbers, you can use the mnemonic symbols as shortcut. For example, “bgp” can ...
Page 154
146 c hapter 7: q o s/acl o peration perform the following configuration in the designated view. Layer-2 acl can be identified with numbers ranging from 200 to 299. Activating acl perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. Displaying and debugging acl after you configure acl, execute...
Page 155
Qos overview 147 server of the financial dept. Is accessed through ethernet1/0/1 (at 129.110.1.2). The acl must be properly configured to prevent departments other than the office of president from having access to the payment query server between 8:00 am and 6:00 pm. The office of president (at 129...
Page 156
148 c hapter 7: q o s/acl o peration out (fifo) policy. Switches and routers make their best effort to transmit the packets to the destination, not making any commitment or guarantee of the transmission reliability, delay, or to satisfy other performance requirements. Ethernet technology is currentl...
Page 157
Qos overview 149 bandwidth assurance through the traffic reservation, a minimum bandwidth is reserved for specified traffic flow. Even when the network congestion occurs, the qos requirements such as packet dropping ratio, delay, and jitter can also be satisfied. Port rate limit the port rate limit ...
Page 158
150 c hapter 7: q o s/acl o peration traffic mirroring the traffic mirroring function copies the specified data packets to the monitoring port for network diagnosis and troubleshooting. Traffic counting with flow-based traffic counting, you can request a traffic count to count and analyze the packet...
Page 159
Qos overview 151 perform the following configuration in ethernet port view. You have to define the corresponding acl before performing this configuration task. The purpose of this configuration task is to implement traffic policing over the data flow matching the acl. The traffic beyond the limit wi...
Page 160
152 c hapter 7: q o s/acl o peration configure which priority is used for queue scheduling you can use the following command to configure which priority is used for queue scheduling. Perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the switch chooses the local preference as the basic ...
Page 161
Qos overview 153 for more information about the commands, refer to the “ 3com command reference guide” . Configure traffic statistics the traffic statistics function counts the transmitted data that matches the acl rules. After the traffic statistics function is configured, you can use the display q...
Page 162
154 c hapter 7: q o s/acl o peration for output and description of the related commands, refer to the “ 3com command reference guide” . Example: qos configuration the interconnection between different departments on a company network is implemented through the 100m ports of the ethernet switch. The ...
Page 163
User logonacl control configuration 155 at the first level, the user connection is controlled with an acl filter and only legal users can be connected to the switch. At the second level, a connected user can log on to the device only if the user can pass the password authentication. This chapter int...
Page 164
156 c hapter 7: q o s/acl o peration for more information about the command, refer to the “ 3com command reference guide” . Note : only the numbered basic acl can be called for telnet user control. Example: controlling telnet users with acl figure 4 illustrates a configuration that controls telnet u...
Page 165
User logonacl control configuration 157 perform the following configuration in system view. The snmp community-name attribute is a feature of snmp v1. Therefore, calling an acl for snmp community name configuration can filter the access to snmp v1 network management system. The snmp group-name and u...
Page 166
158 c hapter 7: q o s/acl o peration [sw7700-acl-basic-21] quit [sw7700] acl number 22 match-order config [sw7700-acl-basic-22] rule 1 permit source 10.110.100.55 0 [sw7700-acl-basic-22] quit 2 call the basic acls. [sw7700] snmp-agent community public read acl 20 [sw7700] snmp-agent group v2c 3comgr...
Page 167: Stp O
8 stp o peration stp overview spanning tree protocol (stp) is applied in a loop network to block some undesirable redundant paths with certain algorithms and prune the network into a loop-free tree, thereby avoiding the proliferation and infinite cycling of a packet in the loop network. Implementing...
Page 168
160 c hapter 8: stp o peration figure 1 designated switch and designated port calculating the stp algorithm the following example illustrates the calculation process of stp. The figure1-2 below illustrates the network. Figure 2 switch 7700 networking to facilitate the descriptions, only the first fo...
Page 169
Implementing stp 161 configuration bpdu of ethernet 1/0/7: {1, 0, 1, e1/0/7} configuration bpdu of ethernet 1/0/4: {1, 0, 1, e1/0/4} ■ switch c configuration bpdu of ethernet 1/0/1: {2, 0, 2, e1/0/1} configuration bpdu of ethernet 1/0/5: {2, 0, 2, e1/0/5} selecting the optimum configuration bpdu eve...
Page 170
162 c hapter 8: stp o peration configuration bpdu of ethernet 1/0/1: {0, 0, 0, e1/0/1} configuration bpdu of ethernet 1/0/2: {0, 0, 0, e1/0/2} ■ switch b ethernet 1/0/7 receives the configuration bpdu from switch a and finds that the received bpdu has a higher priority than the local one, so it upda...
Page 171
Implementing stp on the switch 7700 163 receive the data forwarded from switch a until spanning tree calculation is triggered again by changes, for example, the link from switch b to c is down. Thus the spanning tree is stabilized. The tree with the root switch a is illustrated in figure 3. Figure 3...
Page 172
164 c hapter 8: stp o peration to achieve the rapid transition of the root port state, the following requirement should be met: the old root port on this switch has stopped data forwarding and the designated port in the upstream has begun forwarding data. The conditions for rapid state transition of...
Page 173
Implementing stp on the switch 7700 165 among the above-mentioned tasks, only the steps of enabling stp on the switch and enabling stp on the port are required. For other tasks, if you do not configure them, the system will use the default settings. Before enabling spanning tree, relative parameters...
Page 174
166 c hapter 8: stp o peration perform the following configurations in system view. The diameter of the switching network should not exceed 7. Users can configure this parameter according to the actual networking. By default, the parameter is configured to 7. Configuring rstp operating mode rstp is ...
Page 175
Implementing stp on the switch 7700 167 is enabled, an assignment of a priority to the bridge will lead to recalculation of the spanning tree. By default, the priority of the bridge is 32768. Specifying the switch as a primary or secondary root switch rstp can determine the spanning tree root throug...
Page 176
168 c hapter 8: stp o peration state and resume data frame forwarding. This delay ensures that the new configuration bpdu has been propagated throughout the network before the data frame forwarding is resumed. Perform the following configurations in system view. The forward delay of the bridge is re...
Page 177
Implementing stp on the switch 7700 169 if the max age is too short, it results in frequent calculation of spanning tree or misjudging the network congestion as a link fault. On the other hand, a max age that is too long may make the bridge unable to find link failure in time and weaken the network ...
Page 178
170 c hapter 8: stp o peration bridge is configured as an edge port, rstp will automatically detect and reconfigure it as a non-edgeport. After the network topology changes, if a configured non-edgeport changes to an edgeport and is not connected to any other port, you should configure it as an edge...
Page 179
Implementing stp on the switch 7700 171 tree. If all the ethernet ports of the bridge adopt the same priority parameter value, then the priority of these ports depends on the ethernet port index number. Note that changing the priority of an ethernet port causes recalculation of the spanning tree. Yo...
Page 180
172 c hapter 8: stp o peration perform the following configurations in ethernet port view. This command can be used when the bridge runs rstp in rstp mode, but it cannot be used when the bridge runs rstp in stp-compatible mode. Configuring the switch security function an rstp switch provides bpdu pr...
Page 181
Implementing stp on the switch 7700 173 after being configured with bpdu protection, the switch disables the edge port through rstp, which receives a bpdu, and notifies the network manager at same time. Only the network manager can resume these. The port configured with root protection only plays a ...
Page 182
174 c hapter 8: stp o peration figure 4 rstp configuration example only the configurations related to rstp are listed in the following procedure. Switch a serves as the root. Switch d through switch f are configured in basically the same way so only the rstp configuration on switch d is introduced. ...
Page 183
Implementing stp on the switch 7700 175 and do not disable those involved. (the following configuration takes ethernet 0/4 as an example.) [sw7700] interface ethernet 0/4 [sw7700-ethernet0/4] stp disable 3 configure switch c and switch b to serve as standby of each other and sets the bridge priority...
Page 184
176 c hapter 8: stp o peration 3 configure the ports (ethernet 0/1 through ethernet 0/24) directly connected to users as edge ports and enable bpdu protection function. (take ethernet 0/1 as an example.) [sw7700] interface ethernet 0/1 [sw7700-ethernet0/1] stp edged-port enable [sw7700] stp bpdu-pro...
Page 185: Aaa
9 aaa and radius o peration this chapter covers the following topics: ■ ieee 802.1x ■ configuring the aaa and radius protocols ieee 802.1x ieee 802.1x (hereinafter simplified as 802.1x) is a port-based network access control protocol that is used as the standard for lan user access authentication. I...
Page 186
178 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration there are two types of ports for the authenticator. One is the uncontrolled port, and the other is the controlled port. The uncontrolled port is always in a bi-directional connection state. The user can access and share the network resources any time through...
Page 187
Ieee 802.1x 179 implement 802.1x on ethernet switch the 3com switch 7700 not only supports the port access authentication method regulated by 802.1x, but also extends and optimizes it in the following way: ■ support to connect several end stations in the downstream via a physical port. ■ the access ...
Page 188
180 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration by default, 802.1x authentication has not been enabled globally and on any port. Setting the port access control mode the following commands can be used for setting 802.1x access control mode on the specified port. When no port is specified, the access contr...
Page 189
Ieee 802.1x 181 setting number of users on a port the following commands are used for setting number of users allowed by 802.1x on specified port. When no port is specified, all the ports accept the same number of users. Perform the following configurations in system view or ethernet port view. By d...
Page 190
182 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration perform the following configurations in system view. By default, the max-retry-value is 3. That is, the switch can retransmit the authentication request frame to a supplicant for 3 times at most. Configuring timers the following commands are used for configu...
Page 191
Ieee 802.1x 183 by default, the quiet-period-value is 60 seconds, the tx-period-value is 30 seconds, the supp-timeout-value is 30 seconds, the server-timeout-value is 100 seconds. Enabling/disabling quiet-period timer you can use the following commands to enable/disable a quiet-period timer of the s...
Page 192
184 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration a server group, consisting of two radius servers at 10.11.1.1 and 10.11.1.2 respectively, is connected to the switch. The former one acts as the primary-authentication/second-accounting server. The latter one acts as the secondary-authentication/primary-acco...
Page 193
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 185 [sw7700-radius-radius1] key authentication name 7 set the encryption key when the system exchanges packets with the accounting radius server. [sw7700-radius-radius1] key accounting money 8 set the timeouts and times for the system to retransmit packets to...
Page 194
186 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration ■ authorizes the user with specified services. ■ accounts for network resources that are consumed by the user. Generally, by applying client/server architecture, aaa framework boasts the following advantages: ■ good scalability. ■ able to use standard authen...
Page 195
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 187 client-end is implemented on the switch 7700. The figure below illustrates the radius authentication network. Figure 3 networking with switch 7700 applying radius authentication configuring aaa aaa configuration includes tasks that are described in the fo...
Page 196
188 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration for the switch 7700, each supplicant belongs to an isp domain. Up to 16 domains can be configured in the system. If a user has not reported its isp domain name, the system will put it into the default domain. Perform the following configurations in system vi...
Page 197
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 189 creating a local user a local user is a group of users set on nas. The username is the unique identifier of a user. A supplicant requesting network service may use local authentication only if its corresponding local user has been added onto nas. Perform ...
Page 198
190 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration disconnecting a user by force sometimes it is necessary to disconnect a user or a category of users by force. The system provides the following command to serve for this purpose. Perform the following configurations in system view. By default, no online user...
Page 199
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 191 ■ setting username format transmitted to radius server ■ setting the unit of data flow that transmitted to radius server ■ configuring a local radius server group among the above tasks, creating radius server group and setting ip address of radius server ...
Page 200
192 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration in real networking environments, the above parameters should be set according to the specific requirements. For example, you may specify 4 groups of different data to map 4 radius servers, or specify one of the two servers as primary authentication/authoriza...
Page 201
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 193 encryption key. Only when the keys are identical can both ends to accept the packets from each other end and give response. Perform the following configurations in radius server group view. Setting the response timeout timer of radius server radius (authe...
Page 202
194 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration setting a real-time accounting interval to implement this feature, it is necessary to set a real-time accounting interval. After the attribute is set, nas will transmit the accounting information of online users to the radius server regularly. Perform the fo...
Page 203
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 195 how to calculate the value of retry-times ? Suppose that radius server connection will timeout in t and the real-time accounting interval of nas is t, then the integer part of the result from dividing t by t is the value of count . Therefore, when applied...
Page 204
196 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration setting the supported type of radius server the switch 7700 supports the standard radius protocol and the extended radius service platforms, such as ip hotel, and portal. Perform the following configurations in radius server group view. By default, radius se...
Page 205
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 197 if a radius server group is configured not to allow usernames including isp domain names, the radius server group shall not be simultaneously used in more than one isp domain. Otherwise, the radius server will regard two users in different isp domains as ...
Page 206
198 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration configuration. Execute the debugging command in user view to debug aaa and radius. Example: aaa and radius protocol configuration aaa/radius protocol configuration commands are generally used together with 802.1x configuration commands. Refer to the typical ...
Page 207
Configuring the aaa and radius protocols 199 5 there might be some communication fault between nas and radius server, which can be discovered through pinging radius from nas. Ensure the normal communication between nas and radius. Radius packet cannot be transmitted to radius server. 1 the communica...
Page 208
200 c hapter 9: aaa and radius o peration.
Page 209: Eliability
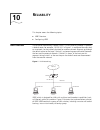
10 r eliability this chapter covers the following topics: ■ vrrp overview ■ configuring vrrp vrrp overview virtual router redundancy protocol (vrrp) is a fault-tolerant protocol. In general, a default route, for example, 10.100.10.1 in figure 1, is configured for every host on a network, so that pac...
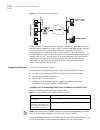
Page 210
202 c hapter 10: r eliability figure 2 virtual router this virtual router has its own ip address: 10.100.10.1, which can be the interface address of a switch within the virtual router. The switches within the virtual router have their own ip addresses, such as 10.100.10.2 for the master switch and 1...
Page 211
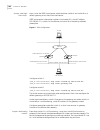
Configuring vrrp 203 the following command is used for assigning an ip address of the local segment to a virtual router or removing an assigned virtual ip address of a virtual router from the virtual address list. Perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. Configuring the priority o...
Page 212
204 c hapter 10: r eliability perform the following configuration in vlan interface view. The delay ranges from 0 to 255, measured in seconds. The default mode is preemption with a delay of 0 second. Note : if the preemption mode is cancelled, the delay time automatically becomes 0 seconds. Configur...
Page 213
Configuring vrrp 205 backup switch’s master-down-interval is three times the duration of the adver-interval . Excessive network traffic or the differences between different switch timers results in master-down-interval timing out and state changing abnormally. Such problems can be solved through pro...
Page 214
206 c hapter 10: r eliability example: vrrp single virtual router host a uses the vrrp virtual router which combines switch a and switch b as its default gateway to visit host b on the internet. Vrrp virtual router information includes virtual router id1, virtual ip address 202.38.160.111, switch a ...
Page 215
Configuring vrrp 207 configure switch a 1 create a virtual router. [lsw_a-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 202.38.160.111 2 set the priority for the virtual router. [lsw_a-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 priority 110 3 set the authentication key for the virtual router. [lsw_a-vlan-interface2] vr...
Page 216
208 c hapter 10: r eliability configure switch b: 1 create virtual router 1. [lsw_b-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 1 virtual-ip 202.38.160.111 2 create virtual router 2. [lsw_b-vlan-interface2] vrrp vrid 2 virtual-ip 202.38.160.112 3 set the priority for the virtual router. [lsw_b-vlan-interface2] vrrp ...
Page 217: Ystem
11 s ystem m anagement this chapter includes the following information: ■ file system management ■ mac address table management ■ device management ■ system maintenance and debugging ■ snmp ■ rmon file system management the ethernet switch provides a file system module for efficient management with ...
Page 218
2 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement file operation the file system can be used to delete or undelete a file or permanently delete a file. It can also be used to display file contents, rename, copy and move a file and display the information about a specified file. You can use the commands in table 2 ...
Page 219
File system management 3 2 display the working directory in the flash. Cd flash:/ pwd flash:/ 3 create a directory named test. Mkdir test 4 display the flash directory information after creating the test directory. Dir directory of * 0 drw- 0 mar 09 2002 12:01:44 test 523776 bytes total (476160 byte...
Page 220
4 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following configuration in all views. The configuration files are displayed in their corresponding saving formats. Save the current-configuration use the save command to retain the current-configuration in the flash memory. The configurations are saved ...
Page 221
File system management 5 the ethernet switch provides the following ftp services: ■ ftp server: you can run ftp client program to log in the server and access the files on it. ■ ftp client: after connected to the server through running the terminal emulator or telnet on a pc, you can access the file...
Page 222
6 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following configuration in system view. By default, the ftp server connection timeout is 30 minutes. Display and debug ftp server after the above configuration, execute display command in all views to display the ftp server configuration, and to verify ...
Page 223
Mac address table management 7 configure the file transmission mode tftp transmits files in two modes; binary mode for program files and ascii mode for text files. You can use the following commands to configure the file transmission mode. Perform the following configuration in system view. By defau...
Page 224
8 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement mac address of the device, which will then be learned and added into the mac address table by the ethernet switch. The consequent packets destined for the same mac address can be forwarded directly thereafter. If the mac address cannot be found after broadcasting t...
Page 225
Mac address table management 9 perform the following configuration in system view. When deleting the dynamic address table entries, the learned entries will be deleted simultaneously. Disable/enable global mac address learning with the address learning function, an ethernet switch can learn new mac ...
Page 226
10 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement set mac address aging time setting an appropriate aging time implements mac address aging. Too long or too short an aging time set by subscribers will cause the ethernet switch to broadcast a large amount of data packets without mac addresses. This affects the swi...
Page 227
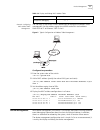
Device management 11 example: configuring mac address table management the user logs in the switch via the console port to configure the address table management. Set the address aging time to 500s and add a static address 00e0-fc35-dc71 to ethernet 1/0/2 in vlan1. Figure 2 typical configuration of ...
Page 228
12 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement reboot ethernet switch perform the following configuration in user view. Designate the app adopted when booting the ethernet switch next time in the case that there are several operational images in the flash memory, you can use this command to designate the opera...
Page 229
System maintenance and debugging 13 perform the following configuration in user view. Set backboard view the backboard view command determines the backplane bandwidth allocated to each slot in the switch 7700. Currently, the switch fabric has the capability of 32gbpos full duplex yet the chassis has...
Page 230
14 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement you can use the following commands to perform the basic system configurations. Use the sysname command in system view, use the clock command in user view and use the display clock command in all views. Display the state and information of the system the display co...
Page 231
System maintenance and debugging 15 figure 3 debug output you can use the following commands to control the above-mentioned debugging. Perform the following operations in user view. For more about the usage and format of the debugging commands, refer to the relevant chapters. Since the debugging out...
Page 232
16 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement you can perform the following operations in all views. Testing tools for network connection ping the ping command can be used to check the network connection and to verify if the host is reachable. Perform the following operation in user view. The output of the co...
Page 233
System maintenance and debugging 17 the information efficiently. Coupled with the debugging program, the syslog provides powerful support for the network administrators and the r&d personnel to monitor the operating state of networks and diagnose network failures. The syslog of the switch 7700 has t...
Page 234
18 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following configuration in system view. The system assigns a channel in each output direction by default. See table 35. The settings in the six directions are independent from each other. The settings will take effect only after enabling the informatio...
Page 235
System maintenance and debugging 19 you can use the following commands to define the filtering rules of the channels. Perform the following operation in system view. Modu-name specifies the module name. Level refers to the severity levels and severity specifies the severity level of information. The...
Page 236
20 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement local4.Crit /var/log/sw7700/config sw7700 security messages: local5.Notice /var/log/sw7700/security pay attention to the following points when editing the file “/etc/syslog.Conf”: ■ the description must start from a fresh line and begin with a pound key #. ■ use t...
Page 237
Snmp 21 snmp the simple network management protocol (snmp) has gained the most extensive application in the computer networks. Snmp has been put into use and widely accepted as the industry standard. It is used for transmitting management information between any two nodes. In this way, network admin...
Page 238
22 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement the current snmp agent of ethernet switch supports snmp v1, v2c and v3. The mibs supported are listed in the following table. Configure snmp the main configuration of snmp includes: ■ set community name ■ set the method of identifying and contacting the administra...
Page 239
Snmp 23 you can use the following commands to set the community name. Perform the following configuration in system view. Set the method of identifying and contacting the administrator the syscontact is a management viable of the system group in mib ii. The content is the method of identifying and c...
Page 240
24 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement perform the following configuration in system view. Set lifetime of the trap message you can use the following command to set lifetime of trap message. Trap message that exists longer than the set lifetime will be droped. Perform the following configuration in sys...
Page 241
Snmp 25 by default, the engine id is expressed as enterprise no. + device information. The device information can be ip address, mac address, or user-defined text. Set/delete an snmp group you can use the following commands to set or delete an snmp group. Perform the following configuration in syste...
Page 242
26 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement create/update view information or deleting a view you can use the following commands to create, update the information of views or delete a view. Perform the following configuration in system view. Set the size of snmp packet sent/received by an agent you can use ...
Page 243
Snmp 27 example: snmp configuration network management station (nms) and the ethernet switch are connected via the ethernet. The ip address of nms is 129.102.149.23 and that of the vlan interface on the switch is 129.102.0.1. Perform the following configurations on the switch: setting the community ...
Page 244
28 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement rmon remote network monitoring (rmon) is a type of ietf-defined mib. It is the most important enhancement to the mib ii standard. It is used for monitoring the data traffic on a segment and even on a whole network. It is one of the widely used network management s...
Page 245
Rmon 29 defined in event management. The alarm management includes browsing, adding and deleting alarm entries. You can use the following commands to add/delete an entry to/from the alarm table. Perform the following configuration in system view. Add/delete an entry to/from the event table rmon even...
Page 246
30 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement add/delete an entry to/from the extended rmon alarm table you can use the command to add/delete an entry to/from the extended rmon alarm table. Perform the following configuration in system view. Add/delete an entry to/from the statistics table the rmon statistics...
Page 247
Rmon 31 figure 6 rmon configuration networking 1 configure rmon. [sw7700-ethernet2/0/1] rmon statistics 1 owner 3com-rmon 2 view the configurations in user view. Display rmon statistics ethernet2/0/1 statistics entry 1 owned by 3com-rmon is valid. Gathers statistics of interface ethernet2/0/1. Recei...
Page 248
32 c hapter 11: s ystem m anagement.